| [1] |
于红, 敬思群. 油莎豆化学成分及应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2015,36(6):242−245.
|
| [2] |
阳振乐. 油莎豆的特性及其研究进展[J]. 北方园艺,2017,17(392):199−208.
|
| [3] |
Rahul V Manek, Philip F Builders, William M Kolling, et al. Physicochemical and binder properties of starch obtained from Cyperus esculentus[J]. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech,2012,13(2):379−388. doi: 10.1208/s12249-012-9761-z
|
| [4] |
Moonjung Kim, Siwon No, Suk Hoo Yoon. Stereospecific analysis of fatty acid composition of Chufa ( Cyperus esculentus L.) tuber oil[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society,2007,84(11):1079−1080. doi: 10.1007/s11746-007-1131-8
|
| [5] |
陈星, 陈滴, 刘蕾. 油莎豆全成分分析[J]. 食品科技,2009,34(3):165−168.
|
| [6] |
杨帆, 朱文学. 油莎豆研究现状及展望[J]. 粮食与油脂,2020,33(7):4−6.
|
| [7] |
Hankins C N, Shannon L M. Physical and enzymatic properties of a phytohemagglutinin from mung beans[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,1978,253(21):7791−7797. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)34439-3
|
| [8] |
Wei-Liang W, Guo-Jie W, Dao-Shuang L, et al. The physiological function and research progress of angiotensin-i-converting enzyme inhibitory petides[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2006,22(3):251−254.
|
| [9] |
孙宁玲. 高血压领域的热点及思考[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2015,23(3):203−205.
|
| [10] |
罗鹏. 葵花籽ACE抑制肽的分离纯化、结构分析与稳态化研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018.
|
| [11] |
Martin M, Deussen A. Effects of natural peptides from food proteins on angiotensin converting enzyme activity and hypertension[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2019,59(8):1264−1283. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1402750
|
| [12] |
Fagyas M, Úri K, Siket I M, et al. New perspectives in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) I: Endogenous angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e87843.
|
| [13] |
Ceren D D, Aysun Y, Funda K G, et al. Angiotensin-i-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from plants[J]. Nutrients,2017,9(4):316. doi: 10.3390/nu9040316
|
| [14] |
Wei L W, Guo J W, Dao S L, et al. The physiological function and research progress of angiotensin-i-converting enzyme inhibitory petides[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2006(3):251−254.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
胡炜东, 蔡永敏, 鲁富宽. 响应面法优化油莎豆粕蛋白抗氧化肽制备工艺[J]. 食品工业,2014,35(2):105−108.
|
| [17] |
胡炜东, 蔡永敏, 鲁富宽, 等. 响应面分析法优化油莎豆粕蛋白提取工艺[J]. 食品科技,2013,38(6):171−175, 184.
|
| [18] |
Cushman D W, Cheung H S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung[J]. Elsevier,1971,20(7):1637−1648.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
安传相. 核桃源蛋白ACE抑制肽制备及分离纯化的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
周洁静, 侯银臣, 刘旺旺, 等. 羊胎盘提取残余物免疫肽制备工艺的优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(3):129−134.
|
| [23] |
韩扬. 超声辅助酶法制备燕麦ACE抑制肽的研究[D]. 北京: 北京工商大学, 2010.
|
| [24] |
麻成金, 黄伟, 黄群, 等. 复合酶法提取仿栗籽蛋白的工艺优化[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(20):27−32.
|






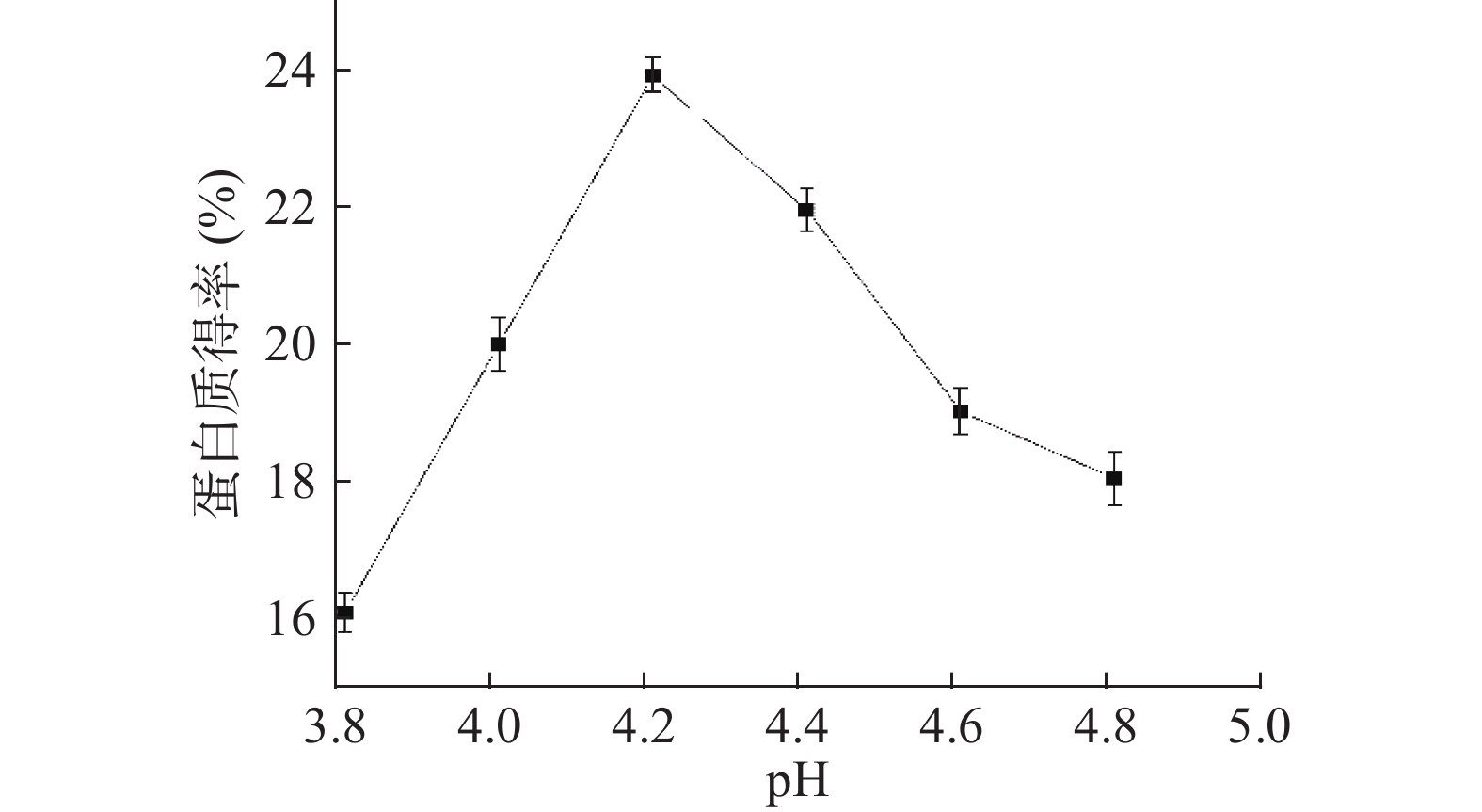




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: