Analysis of Nutritional Components and Volatile Flavor Compounds in Common Edible Fungi
-
摘要: 食用菌营养丰富,是优质蛋白质的潜在来源。本研究以18个常见食用菌品种为研究对象,分析了食用菌中的水分、灰分、蛋白、总糖和L-麦角硫因等营养成分,并采用顶空固相微萃取结合气相色谱-质谱联用法(HS-SPME-GC-MS)分析了其中6种食用菌子实体、菌丝体及发酵液的风味物质。结果表明,18种食用菌水分含量为6.7~13.77 g/100 g、灰分含量为2.24~10.9 g/100 g、脂肪含量为0.3~2.92 g/100 g、总糖含量为2.11~10.5 g/100 g。粗蛋白含量在7.88~35.87 g/100 g之间,其中双孢菇的蛋白质含量高达35.87 g/100 g。氨基酸种类齐全、含量丰富且含有人体必需的8种必需氨基酸。主成分分析表明香菇、黑木耳、灰树花、草菇和金针菇等食用菌的氨基酸组成比例与鸡蛋最相似,但与肉类、大豆和小麦等氨基酸组成相差较大。高效液相色谱结果表明香菇中富含麦角硫因,含量高达336 mg/kg,且灰树花、羊肚菌、双孢菇和鸡腿菇的麦角硫因含量也高于100 mg/kg。HS-SPME-GC-MS在6种食用菌中共鉴定出34种主要挥发性化合物,包括醛类、酮类、酯类、醇类、酚类、醚类、烷烃类和杂环化合物。灵芝菌丝体富含己醛、甲基壬基甲酮、反-2-辛烯醛、2-正戊基呋喃、2,4-壬二烯醛等成分,与其他17种样品有明显差异;6种食用菌发酵液的风味物质相似,均具有庚酸乙酯、18-冠醚-6等特有风味物质;而灵芝、鸡腿菇子实体以及杏鲍菇菌丝具有2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚、苯甲酸甲酯等特有风味。本研究通过分析常见食用菌的营养成分及风味物质,为食用菌的高值化开发提供了数据基础。Abstract: Edible fungi were rich in nutrients and were potential sources of high-quality protein. In this study, nutritional components such as moisture, ash, protein, total sugar and L-ergothione in 18 kinds of edible fungi were analyzed, and headspace solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) were used to analyze the fruit-body, mycelium and fermentation broth of 6 edible fungi (Lentinula edodes, Agaricus bisporus, Coprinus comatus, Pleurotus eryngii, Auricularia heimuer and Ganoderma lucidum). The results showed that the water content of 18 edible fungi ranged from 6.7 to 13.77 g/100 g, ash content from 2.24 to 10.9 g/100 g, fat content from 0.3 to 2.92 g/100 g and total sugar content from 2.11 to 10.5 g/100 g. The crude protein content of 18 edible fungi ranged from 7.88 to 35.87 g/100 g, among which the protein content of Agaricus bisporus was as high as 35.87 g/100 g. There was no significant difference in the content of other nutrients. The amino acids were rich and contained 8 kinds of essential amino acids necessary for human body. Principal component analysis showed that the amino acid composition ratio of Lentinula edodes, Auricularia heimuer, Grifola frondosa, Volvariella volvacea, and Flammulina velutipes was most similar to that of egg, but significantly different from that of meat, soybeans and wheat. The results of high performance liquid chromatography showed that Lentinula edodes was rich in ergothioneine, and the content was up to 336 mg/kg. The ergothioneine content of edible fungi such as Grifola frondosa, Morchella, Agaricus bisporus and Coprinus comatus were also higher than 100 mg/kg. A total of 34 volatile compounds, including aldehydes, ketones, esters, alcohols, phenols, ethers, alkanes and heterocyclic compounds, were identified by HS-SPME-GC-MS in 6 edible fungi. Ganoderma lucidum mycelium was rich in hexal, methylnonylketone, trans-2-octenal, 2-n-amylfuran, 2,4-nononadienal and other volatile compounds, which were significantly different from the other 17 samples. The flavor substances of the fermentation broth of the six edible fungi were similar, and all of them had special flavor substances such as ethyl heptanate and 18-crown-6. Pleurotus eryngii mycelium and the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lucidum and Coprinus comatus contained butylated hydroxytoluene, methyl benzoate and other unique substances. This study provides data basis for the development of high value edible fungi by analyzing the nutritional components and flavor substances of common edible fungi.
-
Keywords:
- edible fungi /
- nutrient content /
- amino acid composition /
- volatile flavor compounds
-
食用菌是一类子实体硕大、可食用的“蕈菌”类真菌的总称,品种多样。我国是世界上认识和利用食用菌最早的国家,也是世界上最早栽培食用菌的国家。我国食用菌资源十分丰富,年产量占世界总产量的70%左右[1]。食用菌含有丰富的蛋白质、膳食纤维、维生素和矿物质等营养物质,热量和脂肪含量较低[2-4],具有极高的营养价值和药用价值,此外,其味道鲜美、风味独特,备受广大消费者的关注和青睐。
食用菌蛋白质含量丰富,通常在20%~45%(干重),远高于小麦、玉米、大米等粮食作物,且含有完整的必需氨基酸,是优质蛋白的良好来源[5]。研究表明食用菌带来的饱腹感比肉更大[6],因此被素食主义者广泛用作蛋白质的补充剂。食用菌含有天冬氨酸和谷氨酸两种鲜味氨基酸,这是其味道鲜美的主要原因,并且核苷酸和谷氨酸的协同作用也大大提高了食用菌的鲜味[7]。食用菌中不饱和脂肪酸含量很高,其中亚油酸占主导地位,亚油酸对维持机体健康不可缺少,但不能直接在机体中合成,因此食用菌是必需脂肪酸的主要摄入来源[8]。据报道,食用菌还含有凝集素、三萜、β-葡聚糖、酚类、类黄酮、香菇多糖、核苷、核苷酸和麦角硫因等多种生物活性物质[9-11],具有提高免疫力、抗疲劳、抗肿瘤、降血脂、抗炎症等多种生理功能[12-13];潜在的促进健康和预防疾病的作用使其在保健食品与医药等领域展现出广阔的研究前景[14]。此外,食用菌独特的香味来自于挥发性风味物质,主要包括八碳化合物和含硫化合物,同时醛、酮、酸和酯类化合物也对食用菌的香气起到修饰调和的作用[15]。
目前,对食用菌营养成分的研究大多集中在个别常见食用菌的检测分析上,缺少不同品种之间的比较。而且大众对于市面上逐渐丰富的食用菌种类,如竹荪、滑子菇和灰树花等品种的营养成分缺乏了解。由于风味是评价食用菌品质的重要指标之一,风味成分的研究对食用菌产品的品质控制、产品分级、改良和新产品的开发具有辅助作用[16]。殷朝敏等[17]采用HS-SPME-GC-MS结合HPLC分析研究了平菇、香菇、双孢菇、杏鲍菇和金针菇5种食用菌鲜品的风味成分,但近年来国内外关于各种食用菌菌丝体和发酵液的风味物质分析较少,很多市面上的食用菌的挥发性风味物质还未被研究。
本研究分析了香菇、金针菇、平菇、草菇、双孢菇、茶树菇、猴头菇、滑子菇、鸡腿菇、杏鲍菇、竹荪、赤灵芝、蛹虫草、灰树花、黑木耳、银耳、羊肚菌和姬松茸共18种常见食用菌的水分、灰分、蛋白质、脂肪和总糖等营养物质;分析了食用菌的氨基酸组成比例并测定了食用菌中特殊氨基酸L-麦角硫因的含量。进一步采用液体发酵法培养其中6种食用菌(香菇、双孢菇、鸡腿菇、杏鲍菇、黑木耳和灵芝)的菌丝,对6种食用菌的子实体及对应菌丝体、发酵液中挥发性物质进行聚类分析。本研究为食用菌资源的挖掘、高值化开发利用提供科学依据,为食用菌蛋白质产业开发提供一定参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
食用菌干样:香菇、金针菇、平菇、草菇、双孢菇、茶树菇、猴头菇、滑子菇、鸡腿菇、杏鲍菇、竹荪、赤灵芝、蛹虫草、灰树花、黑木耳、银耳、羊肚菌和姬松茸等子实体 西安超市或农贸市场,产地标称见表1。香菇714、双孢菇、鸡腿菇451、杏鲍菇634、灵芝453和黑木耳等菌株 陕西微生物研究所;乙腈(色谱纯)、甲醇(色谱纯)、甲酸(色谱纯)、L-麦角硫因(纯度≥98%) 上海麦克林生化有限公司,其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
表 1 18种食用菌子实体样品信息Table 1. Information of fruiting body samples of 18 edible fungi编号 名称 产地 编号 名称 产地 1 香菇 河南南阳 10 杏鲍菇 福建古田 2 金针菇 福建古田 11 竹荪 福建古田 3 平菇 河南南阳 12 赤灵芝 吉林长白山 4 草菇 福建宁德 13 蛹虫草 吉林长白山 5 双孢菇 河南商丘 14 灰树花 福建宁德 6 茶树菇 福建宁德 15 黑木耳 陕西商洛 7 猴头菇 福建古田 16 银耳 河北廊坊 8 滑子菇 吉林长白山 17 羊肚菌 陕西渭南 9 鸡腿菇 福建宁德 18 姬松茸 云南昆明 RS-FS1811粉碎机 合肥荣事达电子;SX-8-10箱式马弗炉 北京永光明;氨基酸自动分析仪 日本HITACHI公司;KQ5200DE超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器;离心机 赛默飞世尔科技;DFCNW-5LB氮气吹干仪 杭州德克尔;电子分析天平 江苏电子分析仪器厂;全自动凯氏定氮仪 瑞典Foss;电烘箱 顺德莱基;真空冷冻干燥机 北京四环;7200可见分光光度计 上海尤尼克。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 营养成分测定
按照国家标准测定水分、灰分、蛋白质、脂肪、总糖和麦角硫因的含量。采用GB 5009.3-2016方法检测水分,采用GB 5009.4-2016方法测定灰分,采用GB 5009.5-2016方法测定蛋白质,采用GB 5009.6-2016方法测定脂肪,多糖含量采用NY/T 1676-2008中方法测定。氨基酸的测定采用盐酸水解处理样品后,利用氨基酸自动分析仪进行分析。采用NY/T 3872-2021方法检测食用菌中L-麦角硫因的含量。
1.2.2 子实体、菌丝体及发酵液风味物质测定
将食用菌菌株接种至PDB培养基35 ℃培养,过滤后分别收集菌丝体和发酵液。菌丝体与发酵液真空冷冻干燥后置于−80 ℃暂存。采用顶空固相微萃取结合气相色谱-质谱联用对6种食用菌的子实体、菌丝体和发酵液中的风味物质进行分析[18]。
色谱条件:采用HP-INNOWAX(30 m×25 mm×25 µm)毛细管柱,程序升温:进样口250 ℃,柱初温40 ℃,停留3 min,以5 ℃/min升至150 ℃,停留1 min,然后以10 ℃/min升至220 ℃,最后保留2 min;载气为He,流速1.0 mL/min;进样口为不分流模式。
质谱条件:离子化方式为电子轰击电离,质谱接口温度为280 ℃,离子源温度为230 ℃,四级杆温度150 ℃,质量扫描范围m/z 50~550。
1.3 数据处理
利用SPSS Statistics 23和R语言软件对数据进行分析处理。使用热图和主成分分析进行样本聚类分析,热图和主成分分析分别采用R软件包pheatmap和factoextra绘制[19]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 食用菌营养成分分析
分别测定香菇、金针菇、平菇、草菇、双孢菇、茶树菇、猴头菇、滑子菇、鸡腿菇、杏鲍菇、竹荪、赤灵芝、蛹虫草、灰树花、黑木耳、银耳、羊肚菌和姬松茸共18种食用菌的水分、灰分、蛋白质、脂肪和总糖的含量,发现食用菌整体表现均呈现出高蛋白、低脂肪,富含矿物质的特点,但在营养成分上存在一定差异。新鲜食用菌含水率高,约为80%~92%。干燥后食用菌含水量通常在9%~13%[3-5]。
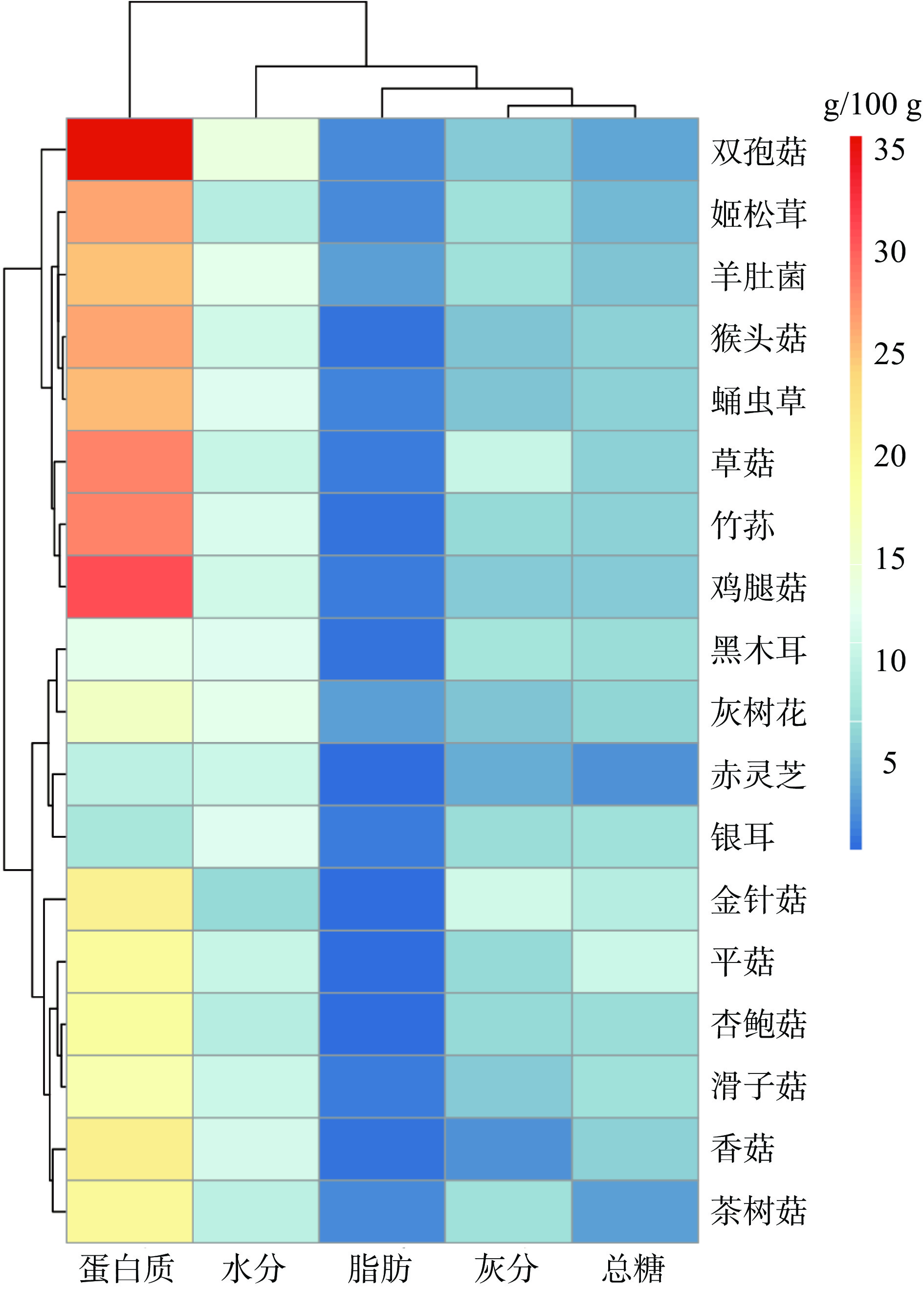
通过热图聚类分析以直观地比较不同化合物之间的差异性和相似性。聚类分析结果如图1所示,双孢菇、姬松茸、羊肚菌、猴头菇、蛹虫草、草菇、竹荪、鸡腿菇营养成分组成上总体较相似,金针菇、平菇、杏鲍菇、滑子菇、香菇、茶树菇聚在一类。其中,双孢菇、鸡腿菇、竹荪、草菇、姬松茸、猴头菇、蛹虫草、羊肚菌蛋白质含量较高,分别为35.87、30.9、28.25、28.1、26.6、26.55、25.47 g/100 g,银耳蛋白质含量最低为7.88 g/100 g,表明不同食用菌品种的蛋白质含量存在明显差异。平菇、金针菇、银耳、滑子菇等总糖含量较高,分别为10.5、9、7.24、7.07 g/100 g。而18种食用菌脂肪含量均比较低,特别是平菇脂肪含量在0.3 g/100 g,羊肚菌、灰树花脂肪含量相对较高,分别达到了2.92和2.91 g/100 g。
2.2 食用菌氨基酸组成分析
食用菌不仅蛋白质含量高,氨基酸组成也较全面,含有人体必需的8种必需氨基酸。此外,食用菌含有大多数谷物所缺乏的赖氨酸和亮氨酸,能满足人们对氨基酸的需求,是一种较理想的蛋白质来源。食用菌氨基酸聚类分析结果如图2所示,总体上看姬松茸、猴头菇、草菇、鸡腿菇、竹荪、双孢菇氨基酸组成接近。鲜味氨基酸中的特征性氨基酸天冬氨酸和谷氨酸含量较高,例如双孢菇天冬氨酸含量高达38.4 g/kg,鸡腿菇、猴头菇、姬松茸谷氨酸含量分别为42.84、43.56、50.05 g/kg。滑子菇、灰树花、黑木耳、银耳、赤灵芝氨基酸组成接近,茶树菇、平菇、金针菇、蛹虫草、羊肚菌、香菇、杏鲍菇聚在一类。
氨基酸尤其是必需氨基酸的组成与比例是评价蛋白质营养价值的重要指标。FAO/WHO提出理想蛋白质必需氨基酸/总氨基酸比值在0.4左右,由表2可知,平菇、茶树菇、赤灵芝、双孢菇、杏鲍菇、竹荪、鸡腿菇、金针菇、银耳、灰树花、香菇和黑木耳等食用菌必需氨基酸占比均在0.4左右,分别为48.32%、47.45%、47.19%、42.37%、42.18%、41.32%、39.70%、39.49%、39.39%、39.16%、37.20%和37.06%。由于富含谷氨酸与天冬氨酸,食用菌常被用于烹调提鲜。18种食用菌中的呈味氨基酸(谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、苯丙氨酸、丙氨酸、甘氨酸和酪氨酸)占比达38.12%~56.02%,含量丰富。尤其是滑子菇、草菇、姬松茸、猴头菇和香菇的呈味氨基酸占比均高于50%。18种食用菌中的酸味类氨基酸(天冬氨酸和谷氨酸)占比为17.78%~30.60%,其中含量最高的为猴头菇,最低的为赤灵芝。甜味类氨基酸(丝氨酸、甘氨酸、苏氨酸、丙氨酸和脯氨酸)占比为23.14%~36.53%,其中含量最高的为滑子菇,最低的为平菇。苦味类氨基酸(苯丙氨酸、异亮氨酸、组氨酸、亮氨酸、蛋氨酸和缬氨酸)占比为28.41%~43.68%,含量最高的为茶树菇,最低的为滑子菇。草菇、滑子菇、姬松茸、猴头菇的甜味和酸味氨基酸总含量较高,分别为60.45%、60.2%、58.57%、58.05%,而平菇甜味和酸味氨基酸总含量最低(42%)。滑子菇甜味和酸味氨基酸总含量与苦味氨基酸比值高达2.12倍,茶树菇甜味和酸味氨基酸总含量与苦味氨基酸比值最低(1.07%)。
表 2 18种食用菌样品中必需氨基酸和呈味氨基酸组成Table 2. Analysis of essential amino acids and tasting amino acids in 18 kinds of edible fungi samples编号 食用菌种类 必需氨基酸(%) 呈味氨基酸(%) 甜味氨基酸(%) 苦味氨基酸(%) 酸性氨基酸(%) 1 香菇 37.20 51.42 28.85 32.53 26.91 2 平菇 48.32 38.12 23.14 37.51 18.86 3 金针菇 39.49 44.51 27.19 36.54 21.96 4 双孢菇 42.37 46.60 24.88 37.89 24.71 5 杏鲍菇 42.18 44.40 25.13 40.85 22.74 6 茶树菇 47.45 41.80 25.14 43.68 21.62 7 黑木耳 37.06 47.83 31.23 36.17 21.44 8 赤灵芝 47.19 39.85 28.43 42.26 17.78 9 竹荪 41.32 45.28 28.37 38.73 22.79 10 滑子菇 25.48 56.02 36.53 28.41 23.67 11 鸡腿菇 39.70 46.27 24.39 35.14 27.22 12 猴头菇 35.81 53.02 27.45 31.96 30.60 13 银耳 39.39 48.48 33.33 33.94 20.61 14 蛹虫草 36.23 47.84 27.28 34.47 26.07 15 姬松茸 35.70 53.53 29.54 32.84 29.03 16 草菇 34.20 55.46 30.64 30.29 29.81 17 灰树花 39.16 47.29 25.86 36.06 26.74 18 羊肚菌 36.12 48.30 28.87 35.44 25.17 为进一步评估食用菌蛋白质的营养价值,采集鸡蛋、小麦、大豆、鸡肉、牛肉、猪肉、羊肉等常规蛋白质来源氨基酸组成数据[20-25],通过PCA分析(图3),发现多数食用菌(黑木耳、香菇、灰树花、竹荪、金针菇、银耳、鸡腿菇、草菇、羊肚菌、蛹虫草等)氨基酸组成与鸡蛋表现出高度的相似性,双孢菇、平菇、赤灵芝三种食用菌氨基酸组成接近,进一步说明食用菌蛋白质作为优质蛋白质来源开发潜力巨大。
2.3 食用菌样品麦角硫因含量分析
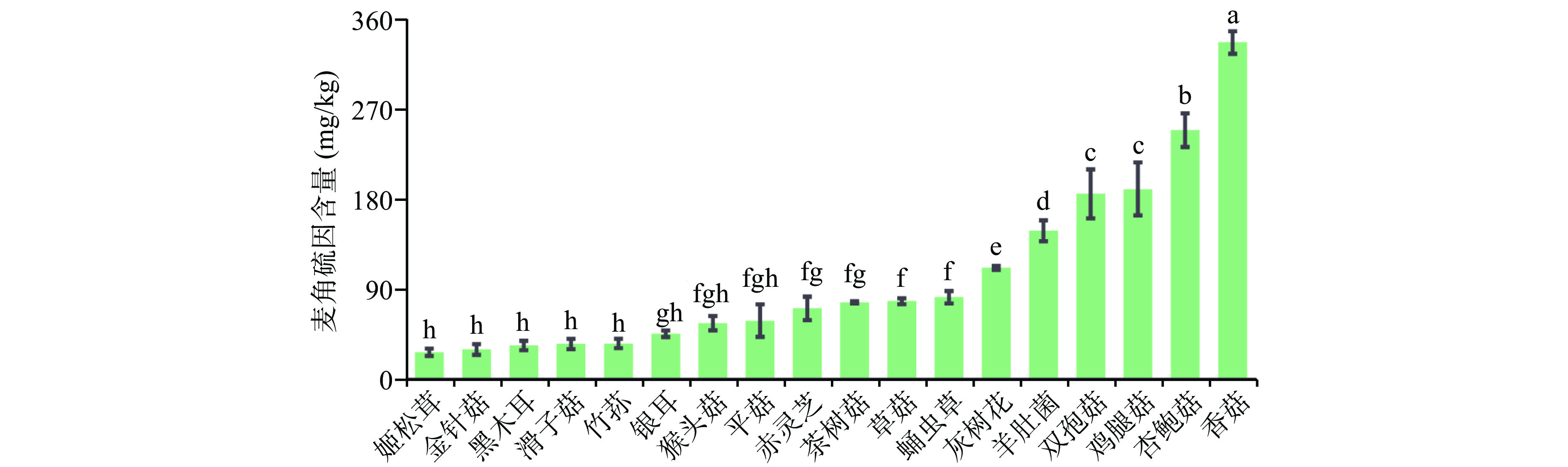
研究表明,食用菌是麦角硫因(EGT)的重要来源[11],具有保护皮肤、抗氧化、抗炎和抗抑郁等多种生理活性[26]。对18种食用菌的EGT含量进行测定,结果见图4,其中,香菇、杏鲍菇、鸡腿菇、双孢菇、羊肚菌、灰树花中麦角硫因含量显著较高(P<0.05) ,分别为:345.07、259.74、170.52、161.07、139.37、110.42 mg/kg。平菇、银耳、竹荪、滑子菇、黑木耳、金针菇、姬松茸等食用菌中麦角硫因含量显著较低,均在50 mg/kg以下。
2.4 食用菌挥发性风味物质分析
食用菌不仅具有较高的营养和保健价值,而且风味独特。挥发性风味成分是影响食用菌品质的重要指标之一,也是影响消费的重要因素。考虑到未来采用工业发酵生产的方式其主要产物为菌丝体和发酵液两部分,鉴于实验室液体发酵培养香菇714(目前市场生产主要使用的菌株编号之一)、双孢菇、鸡腿菇451、杏鲍菇634、灵芝453和黑木耳这6类常见食用菌菌丝相对成熟,本研究通过分析各部分之间的风味差异,为工业发酵生产替代提供一定参考。以香菇714、双孢菇、鸡腿菇451、杏鲍菇634、灵芝453和黑木耳等6种常见食用菌的干燥子实体及相应生物发酵培养的菌丝体和发酵液为主要研究对象,主要风味物质信息见表3。主要鉴定出34种挥发性化合物,包括醛类、酮类、酯类、醇类、酚类、醚类、烷烃类和杂环化合物。黑木耳中含量最高的挥发物有苯乙醛、异戊醛;鸡腿菇中含量最高的挥发物有苯甲醛、苯乙醛;香菇中含量最高的挥发性化合物为1-辛烯-3-醇、阿托醛;双孢菇中含量最高的挥发物有苯甲醛、苯甲醇;而灵芝中含量最高的挥发物主要有六甲基环三硅氧烷、甲氧基苯肟、己醛、2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚。
表 3 6种食用菌样品中主要风味物质信息Table 3. Major volatile compounds in 6 kinds of edible fungi species编号 保留时间
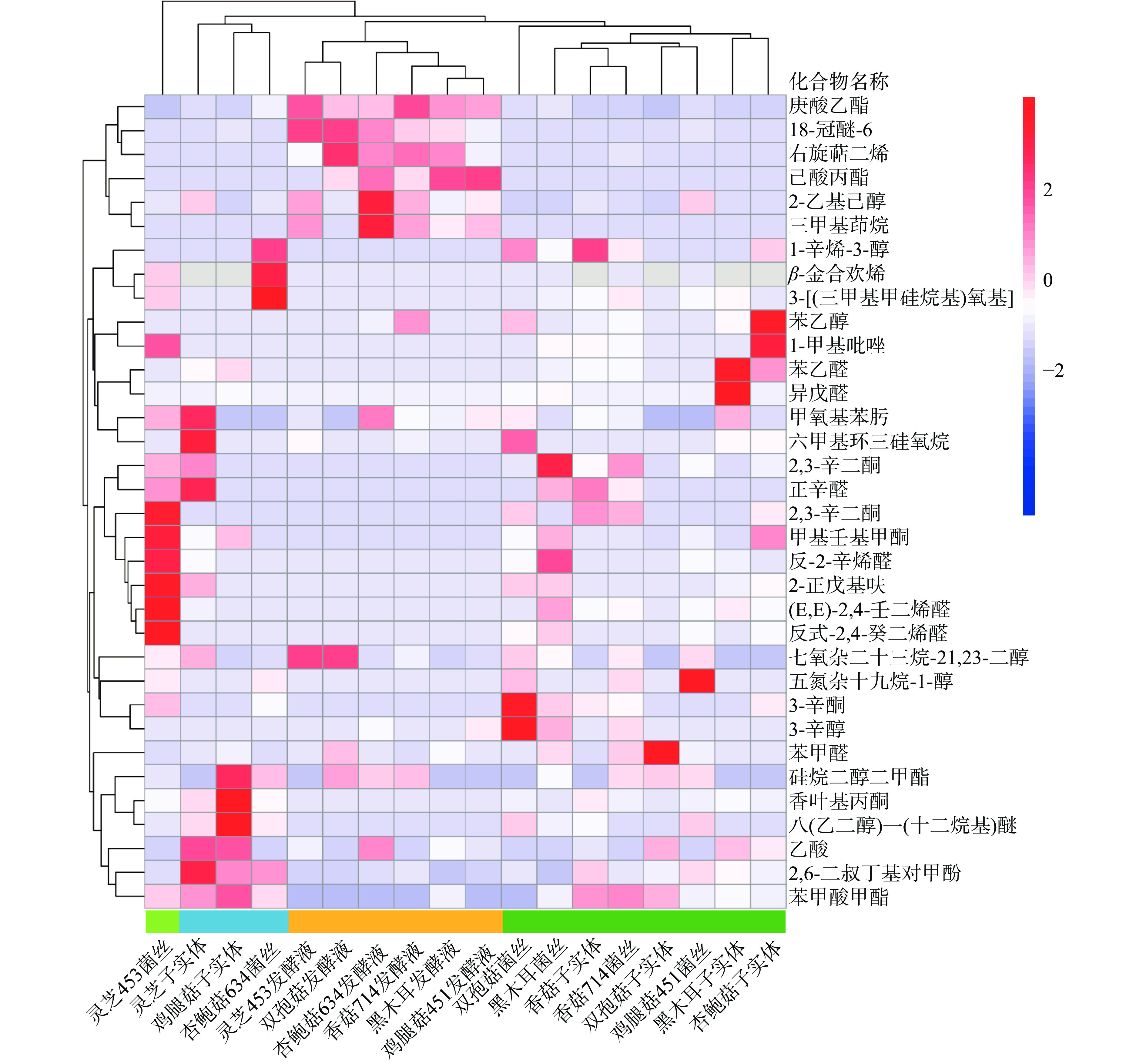
(RT)(min)CAS 化合物名称 1 6.4119 590-86-3 异戊醛 2 10.3995 66-25-1 己醛 3 13.1419 5989-27-5 右旋萜二烯 4 14.1634 3777-69-3 2-正戊基呋喃 5 15.3107 106-68-3 3-辛酮 6 16.2202 124-13-0 正辛醛 7 16.8219 626-77-7 己酸丙酯 8 17.0177 585-25-1 2,3-辛二酮 9 17.4235 106-30-9 庚酸乙酯 10 19.3124 69688-22-8 3-[(三甲基甲硅烷基)氧基] 11 19.4803 589-98-0 3-辛醇 12 19.6342 5920-29-6 1-甲基吡唑 13 20.2498 2548-87-0 反-2-辛烯醛 14 20.8933 3391-86-4 1-辛烯-3-醇 15 21.2573 64-19-7 乙酸 16 22.0129 104-76-7 2-乙基己醇 17 22.8243 100-52-7 苯甲醛 18 24.5873 112-12-9 甲基壬基甲酮 19 25.0910 93-58-3 苯甲酸甲酯 20 25.6227 122-78-1 苯乙醛 21 25.7766 18794-84-8 (E)-β-金合欢烯 22 25.8606 1066-42-8 硅烷二醇二甲酯 23 26.8680 5910-87-2 (E,E)-2,4-壬二烯醛 24 27.0639 2613-76-5 1,1,3-三甲基茚烷 25 27.8614 1000222-86-6 甲氧基苯肟 26 28.5891 541-05-9 六甲基环三硅氧烷 27 28.9108 25152-84-5 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 28 29.5404 3796-70-1 香叶基丙酮 29 30.3519 128-37-0 2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚 30 30.7857 60-12-8 苯乙醇 31 33.3043 17455-13-9 18-冠醚-6 32 34.0178 5117-19-1 3,6,9,12,15,18,21-七氧杂二十三烷-21,23-二醇 33 37.0960 3055-98-9 八(乙二醇)一(十二烷基)醚 34 37.7535 1786-94-3 3,6,9,12,15-五氮杂十九烷-1-醇 通过挥发性有机化合物的聚类分析以直观地比较不同化合物之间的差异性和相似性。结果如图5所示,将6个食用菌子实体、对应的食用菌菌丝体和相应的发酵液等18个样品组按照风味物质组成分为4组:杏鲍菇、黑木耳、双孢菇、香菇等子实体与鸡腿菇菌丝体、香菇菌丝、黑木耳菌丝、双孢菇菌丝一组;杏鲍菇菌丝与鸡腿菇、灵芝子实体一组;各食用菌发酵液聚在一组,与子实体和菌丝体风味差异较大。此外,灵芝菌丝体风味组成较为独特,单独一组。食用菌生物发酵可以快速工业化生产,食用菌蛋白质工业化开发可以使用生物发酵法制备。风味分析发现,杏鲍菇、黑木耳、双孢菇、香菇等子实体与鸡腿菇菌丝体、香菇菌丝、黑木耳菌丝、双孢菇菌丝风味组成接近,可以开发鸡腿菇体、香菇、黑木耳、双孢菇菌丝生物发酵法替代工艺,以适应大规模工业化生产的需求。食用菌发酵液中庚酸乙酯、18-冠醚-6、右旋萜二烯、己酸丙酯、2-乙基己醇含量较高。与其他食用菌及菌丝体不同,灵芝菌丝体中己醛、甲基壬基甲酮、反-2-辛烯醛、2-正戊基呋喃、2,4-壬二烯醛和反式-2,4-癸二烯醛含量较高。
3. 结论
本文对18种常见食用菌的基本营养成分进行了分析检测,结果表明食用菌的蛋白质含量高,含脂量低,氨基酸组成平衡合理,可作为优质蛋白质的重要来源。采用液体发酵法培养食用菌菌丝,通过分析香菇、双孢菇、鸡腿菇、杏鲍菇、黑木耳和灵芝的子实体、菌丝体和发酵液中的挥发性风味物质,发现香菇和鸡腿菇的菌丝体和子实体风味物质相近。未来研究需对更多种类的食用菌生物发酵菌丝体和发酵液中蛋白质含量等营养成分、风味物质进行进一步分析,通过深加工技术以提高菌丝体和发酵液的食用价值和经济价值。同时,食用菌发酵工厂化生产具有产量高、成本低、周期短等优势,生物发酵替代食用菌子实体栽培具有深远的发展潜力,其可能性有待探索。本研究将为食用菌的深加工和科学消费提供参考,为大食物观背景下食用菌价值的挖掘提供理论依据。
-
表 1 18种食用菌子实体样品信息
Table 1 Information of fruiting body samples of 18 edible fungi
编号 名称 产地 编号 名称 产地 1 香菇 河南南阳 10 杏鲍菇 福建古田 2 金针菇 福建古田 11 竹荪 福建古田 3 平菇 河南南阳 12 赤灵芝 吉林长白山 4 草菇 福建宁德 13 蛹虫草 吉林长白山 5 双孢菇 河南商丘 14 灰树花 福建宁德 6 茶树菇 福建宁德 15 黑木耳 陕西商洛 7 猴头菇 福建古田 16 银耳 河北廊坊 8 滑子菇 吉林长白山 17 羊肚菌 陕西渭南 9 鸡腿菇 福建宁德 18 姬松茸 云南昆明 表 2 18种食用菌样品中必需氨基酸和呈味氨基酸组成
Table 2 Analysis of essential amino acids and tasting amino acids in 18 kinds of edible fungi samples
编号 食用菌种类 必需氨基酸(%) 呈味氨基酸(%) 甜味氨基酸(%) 苦味氨基酸(%) 酸性氨基酸(%) 1 香菇 37.20 51.42 28.85 32.53 26.91 2 平菇 48.32 38.12 23.14 37.51 18.86 3 金针菇 39.49 44.51 27.19 36.54 21.96 4 双孢菇 42.37 46.60 24.88 37.89 24.71 5 杏鲍菇 42.18 44.40 25.13 40.85 22.74 6 茶树菇 47.45 41.80 25.14 43.68 21.62 7 黑木耳 37.06 47.83 31.23 36.17 21.44 8 赤灵芝 47.19 39.85 28.43 42.26 17.78 9 竹荪 41.32 45.28 28.37 38.73 22.79 10 滑子菇 25.48 56.02 36.53 28.41 23.67 11 鸡腿菇 39.70 46.27 24.39 35.14 27.22 12 猴头菇 35.81 53.02 27.45 31.96 30.60 13 银耳 39.39 48.48 33.33 33.94 20.61 14 蛹虫草 36.23 47.84 27.28 34.47 26.07 15 姬松茸 35.70 53.53 29.54 32.84 29.03 16 草菇 34.20 55.46 30.64 30.29 29.81 17 灰树花 39.16 47.29 25.86 36.06 26.74 18 羊肚菌 36.12 48.30 28.87 35.44 25.17 表 3 6种食用菌样品中主要风味物质信息
Table 3 Major volatile compounds in 6 kinds of edible fungi species
编号 保留时间
(RT)(min)CAS 化合物名称 1 6.4119 590-86-3 异戊醛 2 10.3995 66-25-1 己醛 3 13.1419 5989-27-5 右旋萜二烯 4 14.1634 3777-69-3 2-正戊基呋喃 5 15.3107 106-68-3 3-辛酮 6 16.2202 124-13-0 正辛醛 7 16.8219 626-77-7 己酸丙酯 8 17.0177 585-25-1 2,3-辛二酮 9 17.4235 106-30-9 庚酸乙酯 10 19.3124 69688-22-8 3-[(三甲基甲硅烷基)氧基] 11 19.4803 589-98-0 3-辛醇 12 19.6342 5920-29-6 1-甲基吡唑 13 20.2498 2548-87-0 反-2-辛烯醛 14 20.8933 3391-86-4 1-辛烯-3-醇 15 21.2573 64-19-7 乙酸 16 22.0129 104-76-7 2-乙基己醇 17 22.8243 100-52-7 苯甲醛 18 24.5873 112-12-9 甲基壬基甲酮 19 25.0910 93-58-3 苯甲酸甲酯 20 25.6227 122-78-1 苯乙醛 21 25.7766 18794-84-8 (E)-β-金合欢烯 22 25.8606 1066-42-8 硅烷二醇二甲酯 23 26.8680 5910-87-2 (E,E)-2,4-壬二烯醛 24 27.0639 2613-76-5 1,1,3-三甲基茚烷 25 27.8614 1000222-86-6 甲氧基苯肟 26 28.5891 541-05-9 六甲基环三硅氧烷 27 28.9108 25152-84-5 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 28 29.5404 3796-70-1 香叶基丙酮 29 30.3519 128-37-0 2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚 30 30.7857 60-12-8 苯乙醇 31 33.3043 17455-13-9 18-冠醚-6 32 34.0178 5117-19-1 3,6,9,12,15,18,21-七氧杂二十三烷-21,23-二醇 33 37.0960 3055-98-9 八(乙二醇)一(十二烷基)醚 34 37.7535 1786-94-3 3,6,9,12,15-五氮杂十九烷-1-醇 -
[1] 李玉. 中国食用菌产业发展现状, 机遇和挑战——走中国特色菇业发展之路, 实现食用菌产业强国之梦[J]. 菌物研究,2018,16(3):5−11. [LI Y. The status, opportunities and challenges of edible fungi industry in China: Develop with Chinese characteristics, realize the dream of powerful mushroom industrial country[J]. Journal of Fungal Research,2018,16(3):5−11. LI Y. The status, opportunities and challenges of edible fungi industry in China: Develop with Chinese characteristics, realize the dream of powerful mushroom industrial country[J]. Journal of Fungal Research, 2018, 16(3): 5-11.
[2] LAKHANPAL T N, RANA M. Medicinal and nutraceutical genetic resources of mushrooms[J]. Plant Genetic Resources,2005,3(2):288−303. doi: 10.1079/PGR200581
[3] CHANG S T. The world mushroom industry: Trends and technological development[J]. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms,2006,8(4).
[4] YU Q, GUO M, ZHANG B, et al. Analysis of nutritional composition in 23 kinds of edible fungi[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2020,2020:1−9.
[5] KAKON A J, CHOUDHURY M B K, SAHA S. Mushroom is an ideal food supplement[J]. Journal of Dhaka National Medical College & Hospital,2012,18(1):58−62.
[6] HESS J M, WANG Q, KRAFT C, et al. Impact of Agaricus bisporus mushroom consumption on satiety and food intake[J]. Appetite,2017,117:179−185. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.06.021
[7] MAU J. The umami taste of edible and medicinal mushrooms[J]. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms,2005,7(1):119−126.
[8] CHATURVEDI V K, AGARWAL S, GUPTA K K, et al. Medicinal mushroom: boon for therapeutic applications[J]. 3 Biotech,2018,8:1−20.
[9] PATEL S, GOYAL A. Recent developments in mushrooms as anti-cancer therapeutics: A review[J]. 3 Biotech,2012,2:1−15.
[10] EL ENSHASY H A, HATTI-KAUL R. Mushroom immunomodulators: Unique molecules with unlimited applications[J]. Trends in biotechnology,2013,31(12):668−677. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.09.003
[11] KALARAS M D, RICHIE J P, CALCAGNOTTO A, et al. Mushrooms: A rich source of the antioxidants ergothioneine and glutathione[J]. Food chemistry,2017,233:429−433. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.109
[12] MA G, YANG W, ZHAO L, et al. A critical review on the health promoting effects of mushrooms nutraceuticals[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2018,7(2):125−133. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2018.05.002
[13] KUMAR K, MEHRA R, GUINÉ R P F, et al. Edible mushrooms: A comprehensive review on bioactive compounds with health benefits and processing aspects[J]. Foods,2021,10(12):2996. doi: 10.3390/foods10122996
[14] 闫文杰, 段昊, 吕燕妮, 等. 食用菌在我国保健食品中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(21):296−302. [YAN W J, DUAN H, LÜ Y N, et al. Recent development in the application of edible fungi in health foods in china[J]. Food Science,2020,41(21):296−302. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200416-208 YAN W J, DUAN H, LÜ Y N, et al. Recent development in the application of edible fungi in health foods in china[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(21): 296-302. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200416-208
[15] 冯涛, 水梦竹, 李雪, 等. 食用菌风味物质的研究进展[J]. 食用菌学报,2018,25(4):97−104. [FENG T, SHUI M Z, LI X, et al. Advances in flavor substances research in edible mushrooms[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2018,25(4):97−104. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2018.04.015 FENG T, SHUI M Z, LI X, et al. Advances in flavor substances research in edible mushrooms[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2018, 25(4): 97-104. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2018.04.015
[16] 李润, 杨焱, 刘晓风, 等. 食用菌风味影响因素及其评价研究进展[J]. 食用菌学报,2020,27(4):202−214. [LI R, YANG Y, LIU X F, et al. Research progress on influential factors and evaluation of edible fungi flavor[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2020,27(4):202−214. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2020.04.024 LI R, YANG Y, LIU X F, et al. Research progress on influential factors and evaluation of edible fungi flavor[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2020, 27(4): 202-214. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2020.04.024
[17] 殷朝敏, 范秀芝, 史德芳, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合HPLC分析5种食用菌鲜品中的风味成分[J]. 食品工业科技,2019(3):254−260. [YIN C M, FAN X Z, SHI D F, et al. Flavor compounds analysis of 5 fresh mushrooms using HS-SPME-GC-MS and HPLC[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019(3):254−260. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.03.040 YIN C M, FAN X Z, SHI D F, et al. Flavor compounds analysis of 5 fresh mushrooms using HS-SPME-GC-MS and HPLC[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019 (3): 254-260. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.03.040
[18] LI H, LV S, FENG L, et al. Smartphone-based image analysis for rapid evaluation of kiwifruit quality during cold storage[J]. Foods,2022,11(14):2113.
[19] LI H, KANG X, WANG S, et al. Early detection and monitoring for Aspergillus flavus contamination in maize kernels[J]. Food Control,2021,121:107636.
[20] ATTIA YA, AL-HARTHI MA, KORISH MA, et al. Protein and amino acid content in four brands of commercial table eggs in retail markets in relation to human requirements[J]. Animals (Basel),2020,10(3):406.
[21] ZHANG P, MA G, WANG C, et al. Effect of irrigation and nitrogen application on grain amino acid composition and protein quality in winter wheat[J]. PLoS One,2017,12(6):e0178494.
[22] 朱怡霖, 张海生, 杨淑芳, 等. 18种大豆种子蛋白质、氨基酸和脂肪酸的组成成分分析[J]. 中国油脂,2017,42(01):144−148. [ZHU Y, ZHANG H, YANG S, et al. Analysis of protein content, compositions of amino acid and fatty acid in 18 kinds of soybean seeds[J]. China Oils and Fats,2017,42(01):144−148. ZHU Y, ZHANG H, YANG S, et al. Analysis of protein content, compositions of amino acid and fatty acid in 18 kinds of soybean seeds[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2017, 42(01):144-148.
[23] HE W, LI P, WU G, et al. Amino acid nutrition and metabolism in chickens[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol,2021,1285:109−131.
[24] GAN M, SHEN L, CHEN L, et al. Meat quality, amino acid, and fatty acid composition of liangshan pigs at different weights[J]. Animals (Basel),2020,10(5):822.
[25] MAZHANGARA IR, CHIVANDI E, MUPANGWA JF, et al. The potential of goat meat in the red meat industry[J]. Sustainability,2019,11(13):3671.
[26] HALLIWELL B, CHEAH I K, TANG R M Y. Ergothioneine–a diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential[J]. FEBS letters,2018,592(20):3357−3366. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13123
-
期刊类型引用(21)
1. 岳诗博,崔航,沈琴,曹冬梅. 基于液相色谱-质谱代谢组学技术的硒化黑木耳代谢产物及通路分析. 食品科学. 2025(03): 162-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘梦晨,张琳,黄橙紫,张皓越,彭源德,谢纯良,周映君,朱作华,龚文兵,胡颂平. 不同食用菌水提物与醇提物活性成分含量及抗氧化活性分析. 食品研究与开发. 2025(02): 40-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 田义明,徐纯,杨桥,张馨方,常松林,任佳丽. 干燥方式对食用菌中二氧化硫含量的影响及内源性转化因素初探. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 248-254 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨林雷,沈真辉,罗祥英,李荣平,李荣春. 食用菌麦角硫因的研究进展. 生物工程学报. 2025(02): 574-587 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙丹丹,姜琳琳,杨啸吟,毛衍伟,张一敏,郝剑刚,梁荣蓉. 食用菌营养价值、功能特性及其在肉制品加工中的应用研究进展. 肉类研究. 2025(02): 67-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王红,岑宇晴,刘俊杰,刘岩岩,李红,黄竹青. 斑玉蕈生物学特性及子实体农艺性状分析. 北方园艺. 2024(05): 112-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王小平,刘忠莹,钟洋,张定秋,陆阳,朱敏敏,郑红毅,何叶馨,王鑫,黄韬睿,江祖彬. 基于离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析木耳、香菇、松茸和茶树菇中砷形态分布. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 李家敏,俞珊,胡文康,曾雪峰. 云芝发酵红薯浆水代谢产物对酸奶风味的影响. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(07): 28-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王文倩,高雅,王子强,章慧莺,陈海涛,王书奇. 干制双孢蘑菇香气化合物分析及其对咸味感知的增强作用. 中国食品学报. 2024(04): 315-326 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈建胜,杨正友,王延圣,弓志青,王文亮,贾凤娟,崔文甲,张剑,侯福荣,李永生,宋莎莎. 食用菌营养组成、功能活性及加工现状研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(12): 358-366 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 松桂花,王怡文,周志磊,曹旭珍,罗桑江才,德央,毛健. 亚东黑木耳特征香气物质研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(15): 306-314 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 康茂约,隋玉洁,倪赞,陈芳芳,张崇生. 瓜子等不同食品中二氧化硫假阳性的快速验证及实际应用分析. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(15): 308-315 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 何丰翼,张璐璐,杨娟,于文斌. 基于ICP-MS的食用菌微量元素和重金属的定量分析方法研究. 中外食品工业. 2024(06): 29-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 曹燕妮,华蓉,刘韵然,游金坤,王娟,杨璐敏,孙达锋. 石墨消解仪-分光光度法测定金顶侧耳中的总糖含量. 中国食用菌. 2024(04): 70-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李惠琳,李珏,李宝通,艾则麦提·图尔洪,赵雷,黄中杰,何庆峰. 杏鲍菇多糖对小鼠急性化学性肝损伤的抗炎及抗氧化作用. 食品研究与开发. 2024(21): 68-74+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 刘芹,闻诗歌,刘阳,孔维丽,崔筱,张亚南,王昱峰. 15种常见食用菌营养成分分析及评价. 中国瓜菜. 2024(11): 67-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 陈诗杰,宋昀程,陈静,钱正祥,李金鑫. 灰树花工厂化瓶栽菌株筛选试验. 食用菌. 2023(06): 22-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 张勇,李青,李云霞,萧晋川,杨杰,张泽轩. 暖棚栽培羊肚菌的营养及土壤环境分析. 中国食用菌. 2023(06): 74-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 袁梦晗,张夜路,丁慧敏,黄馨阅,陶明煊. 红须腹菌酸多糖及其羧甲基酸多糖对免疫抑制型小鼠脏器抗氧化作用的影响. 南京师范大学学报(工程技术版). 2023(04): 57-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 周凯,李乔智,胡新,周辉,徐宝才. 真菌蛋白模拟肉研究现状及未来展望. 中国食品学报. 2023(12): 323-336 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 孙翠焕,陈丽媛,陈杰,赵博伦,郭玲玲. 食用菌菌种现状及退化防控措施. 微生物学杂志. 2023(06): 124-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



