Metabolomics Analysis of Five Types of Wangdu Chili Peppers Based on HPLC and GC-MS
-
摘要: 为了分析望都辣椒的代谢差异,本研究采用高效液相色谱(High-Performance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC)和气相色谱-质谱技术(Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry,GC-MS),对艳椒(YJ)、辣研(LY)、国塔(GT)、研椒110(YJA)、热辣(RL)等五种不同品种的望都辣椒进行化学成分检测与非靶向代谢组学分析,并利用机器学习方法对筛选的差异代谢产物进行分类识别。首先利用HPLC对五个品种辣椒中辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱和VC的含量进行测量,然后利用GC-MS对五种辣椒进行非靶向代谢物分析,对筛选出的代谢产物采用主成分分析(PCA)与正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA),得到差异代谢产物及差异代谢通路,并根据差异代谢产物来进行机器学习识别。在五种辣椒中,热辣中辣椒碱与二氢辣椒碱含量最高,分别为533.897±62.187 μg/g和264.526±28.532 μg/g,VC在艳椒中含量最高,为146.9±0.029 mg/100 g。由OPLS-DA筛选出16种差异代谢物,其中,奎宁酸和乌头酸等有机酸在艳椒中含量较高;D-山梨醇在辣研中含量最高;国塔当中柠檬酸、D-果糖、D-甘露糖和乳酸富集程度最高;研椒110中D-塔格糖与氨基酸含量最高;而热辣中葡萄糖和肌醇含量在所有品种中占优势。基于京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)通路富集分析结果表明,差异代谢通路主要为半乳糖代谢、果糖和甘露糖代谢、柠檬酸循环、淀粉和蔗糖代谢、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢等。最后,利用三种机器学习方法随机森林(Random Forest,RF)、XGBoost和BP神经网络对五种辣椒筛选的差异代谢物进行分类验证,建立的分类识别模型正确率分别为100%、92.9%和78.6%,可以用于识别辣椒品种。该研究结果可为望都辣椒的品质评价、品种改良及综合利用提供基础数据。Abstract: To analyze the metabolic differences in Wangdu peppers, this study employed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to detect chemical components and perform non-targeted metabolomics analysis on five different varieties of Wangdu peppers: Yan Jiao (YJ), La Yan (LY), Guo Ta (GT), Yan Jiao 110 (YJA), and Re La (RL). Machine learning was used to classify and identify the differential metabolites screened. First, HPLC was used to measure the content of capsaicin, dihydrocapsaicin, and Vitamin C (VC) in the five pepper varieties. Then, GC-MS was used for non-targeted metabolite analysis of the five peppers. Principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) were employed to identify differential metabolites and metabolic pathways. Machine learning methods were used to identify the different pepper varieties based on the differential metabolites. In the five pepper varieties, Re La had the highest content of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin, at 533.897±62.187 μg/g and 264.526±28.532 μg/g, respectively. Yan Jiao had the highest VC content at 146.9±0.029 mg/100 g. OPLS-DA identified 16 differential metabolites, including organic acids such as quinic acid and aconitic acid, which were higher in Yan Jiao, D-sorbitol, which was highest in La Yan, citric acid, D-fructose, D-mannose, and lactic acid, which were most enriched in Guo Ta, D-tagatose and amino acids, which were highest in Yan Jiao 110, and glucose and inositol, which were most abundant in Re La. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that the differential metabolic pathways mainly included galactose metabolism, fructose and mannose metabolism, the citric acid cycle, starch and sucrose metabolism, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, and pyruvate metabolism. Finally, three machine learning methods—random forest (RF), XGBoost, and backpropagation (BP) neural networks were used to classify and validate the differential metabolites of the five pepper varieties. The established classification models achieved accuracies of 100%, 92.9%, and 78.6%, respectively, demonstrating their utility in identifying pepper varieties. These results would provide fundamental data for the quality evaluation, variety improvement, and comprehensive utilization of Wangdu peppers.
-
Keywords:
- chili pepper /
- varieties /
- GC-MS /
- metabolomics /
- machine learning
-
辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)隶属茄科辣椒属,是一种一年生或多年生草本植物,原产于中南美洲,约于16世纪后期传入中国,是一种重要的蔬菜作物[1]。我国辣椒产量居世界第一[2],贵州、四川、湖南、云南、河南和河北等省份是重要的辣椒生产区[3],其中望都辣椒是我国国家地理标志产品,拥有几十种辣椒制品。辣椒中富含胡萝卜素、柠檬酸、蛋白质、VC等营养成分[4]以及钙、磷、铁等微量元素[5],其中辣椒的VC含量在蔬菜中占首位,但由于VC是一种水溶性代谢物,在高温下易分解;辣椒碱是辣椒中的一种生物活性成分,赋予辣椒特有的辛辣味,是影响辣椒品质的另一项重要指标。辣椒的果实和根茎有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、减肥等药理作用[6],具有较高的药用价值。然而,辣椒的营养组分、功效作用与其品种密切相关,此外辣椒的深加工产品制备工艺也受产品品种的影响。因此,建立辣椒品种识别模型对于辣椒品种选育和深加工具有重要意义。
基于液相色谱-质谱(LC-MS)、气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)等的非靶向代谢组学技术(Untargeted Metabolomics)可用于筛选样品中已知和未知代谢物的定量信息,近年来,也被广泛应用于食品、药材等的代谢物组分变化识别,从而实现产品品种和产地来源的鉴别[7]。辣椒代谢物主要是挥发性化合物,例如挥发性有机酸、酯类、醛类等,使用GC-MS更为合适,并且GC-MS的运行成本通常比LC-MS低,分析速度快,这对于大量样品的高通量分析是非常重要的。杨创创等[8]对13份干辣椒的挥发性代谢物进行了检测,得到主要代谢物是柠檬烯、香橙烯、乙酸乙酯。Elvia等[9]基于核磁共振(NMR)的代谢指纹图谱确定对两个不同地区种植的辣椒的代谢物水平,发现两者的差异代谢物为氨基酸、有机酸和糖。以上研究分析了不同品种辣椒的代谢差异,但并未对辣椒的品种进行识别验证,因此,本研究对辣椒的品种进行了识别验证。目前,机器学习与代谢组学的联用,为差异代谢物识别和预测模型建立提供了新的思路。
河北省望都辣椒作为我国国家地理标志产品,因色泽纯正、肉质肥厚、辣香浓郁而负盛名,但长期以来没有专业的育种技术,使传统望都辣椒在纯度和品质上受到一定影响,因此比较不同品种辣椒品质与差异代谢物可以为辣椒品种改良、品种选育奠定基础。本研究以望都县的艳椒、辣研、热辣、研椒110和国塔五种外形相近的辣椒为研究对象,利用HPLC测定样品中VC和辣椒碱类物质的含量,采用GC-MS非靶向代谢组学方法,对辣椒进行代谢物的差异分析,并结合机器学习来进行品种鉴别,探究品种差异对辣椒代谢物形成的影响,以期为辣椒种类识别和产品加工提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
红辣椒:艳椒(YJ)、辣研(LY)、国塔(GT)、研椒110(YJA)、热辣(RL) 产自河北望都(图1);甲醇 色谱纯,德国默克公司;N-甲基-N-(三甲基硅烷)三氟乙酰胺(MSTFA)(纯度≥99%)、吡啶(色谱纯)、甲氧胺盐酸盐(纯度≥99%)、抗坏血酸标品(纯度≥99%)、辣椒碱标品(纯度≥99%)、二氢辣椒碱标品(纯度≥99%) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;核糖醇 纯度≥98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
CNWB-15ZK电磁波真空干燥机 杭州三特医药化工设备有限公司;Allegra X-12R冷冻离心机 美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司;JT-DCY-12Y水浴氮吹仪 杭州聚同电子有限公司;CM-5台式分光测色计 日本Konica Minolta公司;CHA-2恒温气浴箱 苏州威尔实验用品有限公司;Agilent 7890-5975C气相色谱串联质谱仪 安捷伦科技有限公司;e2695高效液相色谱仪 美国沃特世公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 色差测定
取五种辣椒样品,使用分光测色计对其色度进行测定,记录L*、a*、b*值。其中,L*表示样品色泽的亮度,a*值表示红度或绿度,b*值表示黄度或蓝度。每组样品平行测定3次[10]。
1.2.2 样品处理
取辣椒样品,40 ℃真空干燥,粉碎过40目筛,干燥保存待用。
1.2.3 辣椒碱与二氢辣椒碱的测定
称取50 mg样品,加入1.5 mL 75%的乙醇,超声处理(400 W、40 kHz、60 ℃、50 min),离心分离10 min(5000 r/min、4 ℃),取上清液,加入1.5 mL 75%的乙醇,混匀,重复操作2次,定容至5.0 mL,过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,待测。
色谱条件:参考刘录等[11]的方法上机,色谱柱为xBridge® C18(5 μm,4.6×250 mm),甲醇:3‰磷酸水溶液梯度洗脱,流速1 mL/min,检测波长280 nm,进样量2 μL,柱温40 ℃。
1.2.4 VC含量的测定
取1.2.2制备的样品1 g,按1:20固液比加入水,15000 r/min均质提取2 min,离心3 min(4000 r/min、4 ℃)后,将上清液移至50 mL容量瓶中并定容,按上述方法重复提取1次。参考蒋侬辉等[12]的上机方法。
色谱条件:色谱柱,Atiantis T3柱(5 μm,4.6×250 mm);检测波长210 nm,流动相为甲醇:0.1%的磷酸=2.5:97.5(V/V)梯度洗脱,流速1 mL/min,柱温:35 ℃。
1.2.5 代谢产物的测定
1.2.5.1 样品预处理
取50 mg辣椒样品到EP管中,每种辣椒取9份,加入1 mL水(含25 μg核糖醇),混匀,室温下500 W超声提取15 min,10000 r/min离心15min。将上清液转移到新的EP管中,取1 mL甲醇对残渣进行同样的处理。将两种上清液混合进行衍生化(胺化)反应,取500 μL的混合上清液于EP管中,用氮吹仪吹干,加入100 μL甲氧胺盐试剂(甲氧胺盐酸盐溶于吡啶20 mg/mL),混匀后,室温下将混合物500 W超声处理5 min,80 ℃孵育30 min;加入100 μL双(三甲基硅基)三氟乙酰胺,70 ℃孵育1.5 h,冷却至室温;过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,上机检测。每个待测样本提取液等体积混合后进行衍生化反应,制成QC样品,在上机时等间隔插入QC样品进样。
1.2.5.2 GC条件
色谱柱:HP-5MS毛细管柱(30 m×250 μm×0.25 μm),载气:氦气;进样模式:不分流;进样量:1 μL;升温程序:起始温度80 ℃,保持2 min,以5 ℃/min的速度升温至300 ℃并保持12 min。
1.2.5.3 MS条件
质谱条件:全扫描方式;离子源温度240 ℃;溶剂延迟5 min;质量扫描范围m/z 50~650。界面温度280 ℃;电压1.2 kV;电子能量70 eV;扫描速度5 scans/s。采用NIST14数据库进行定性分析,最终得到代谢物鉴定结果。
1.3 数据处理
试验结果为3次重复的平均值,以平均值±标准偏差表示,采用Excel 2019进行数据整理、标准偏差计算,采用SPSS 22统计软件进行差异显著性分析,采用Origin 2022软件进行相关分析和绘图。
采用SIMCA14.1软件进行主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)、正交偏最小二乘分析(Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis,OPLS-DA)、多元统计分析。首先通过主成分分析(PCA)对数据进行降维处理,并对整体的分布趋势进行预览,然后采取正交偏最小二乘-判别分析(OPLS-DA),以P<0.05和VIP≥1作为截止标准,筛选差异代谢物,利用Metaboanalyst 6.0(http://www.metaboanalyst.ca)对差异代谢物进行聚类热图分析,用KEGG通路对差异代谢物进行分析,并用显著性分析(P value)确定相关通路,最后利用SPSSPRO中三种机器学习方法(随机森林、XGBoost和BP神经网络)进行建模,通过差异代谢物来对品种分类验证。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同品种辣椒色泽分析
对艳椒(YJ)、辣研(LY)、国塔(GT)、研椒110(YJA)、热辣(RL)等五种不同品种的辣椒进行色差分析。结果如图2所示,不同辣椒样品的亮度、红度,黄度均有差别,其中RL的L*、a*、b*值最大,为37.99、35.81、23.67,且与其余样品间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。辣椒果皮中的辣椒红素、玉米黄质、β–胡萝卜素、叶绿素a、叶绿素b和飞燕草素,是影响果色的主要物质[13],说明RL的辣椒红素等类胡萝卜素累计最多,而其余品种辣椒色差度并不显著,因此不能通过色泽来进行区分识别。
2.2 不同品种辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱含量分析
辣椒碱是一种存在于辣椒中的生物碱,赋予辣椒特有的辛辣味道。辣味是辣椒碱与疼痛感觉神经系统中的瞬时受体电位—香草酸受体1(TRPV1),即辣椒素受体相结合,出现灼烧和疼痛等感觉[14],然后发展为辛辣感。辣椒碱类物质具有抗氧化[15]、抗肿瘤[16]、降脂[17]等活性。此外,人们对辣味的接受程度因人而异,因此辣椒碱类物质的含量是影响辣椒品质的一项重要指标。从图3可以看出,样品RL的辣椒碱与二氢辣椒碱含量最高,分别为533.897±62.187、264.526±28.532 μg/g,说明RL品种辣椒的辣度最辣,与朱志妍等[18]研究相比结果偏高,可能是辣椒的品种不同导致。对于艳椒(YJ)、辣研(LY)、国塔(GT)、研椒110(YJA)、热辣(RL)来说,利用辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱含量仅仅可以区分出热辣辣椒产品。
2.3 不同品种辣椒VC含量分析
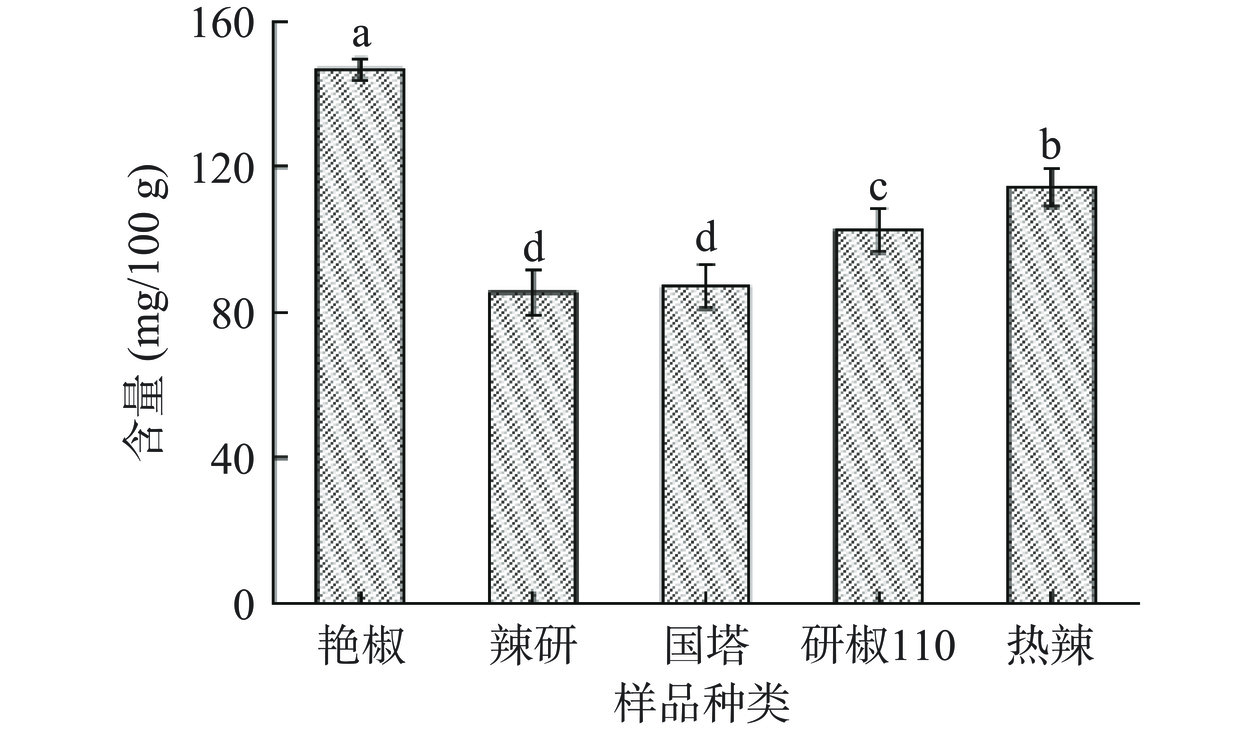
辣椒应用价值丰富,含有丰富的VC,其含量在蔬菜中占首位,是番茄的7倍~15倍[19]。辣椒中含有的VC,作为天然抗氧化剂,可消除有害氧自由基的毒性,可用于抗氧化[20]与抗癌[21]。五种辣椒中VC含量见图4,从图中可以看出,五种辣椒中VC含量范围在85.4~146.9 mg/100 g之间,与王蜜蜜等[22]的研究结果相当。样品YJ中VC的含量最高,为146.9±2.9 mg/100 g,LY中VC含量最低,为85.4±6.3 mg/100 g。利用VC含量,仅可以区分出艳椒(YJ)、研椒110(YJA)和热辣(RL),而辣研(LY)和国塔(GT)不容易区分开来。
2.4 辣椒代谢产物分析
2.4.1 PCA分析
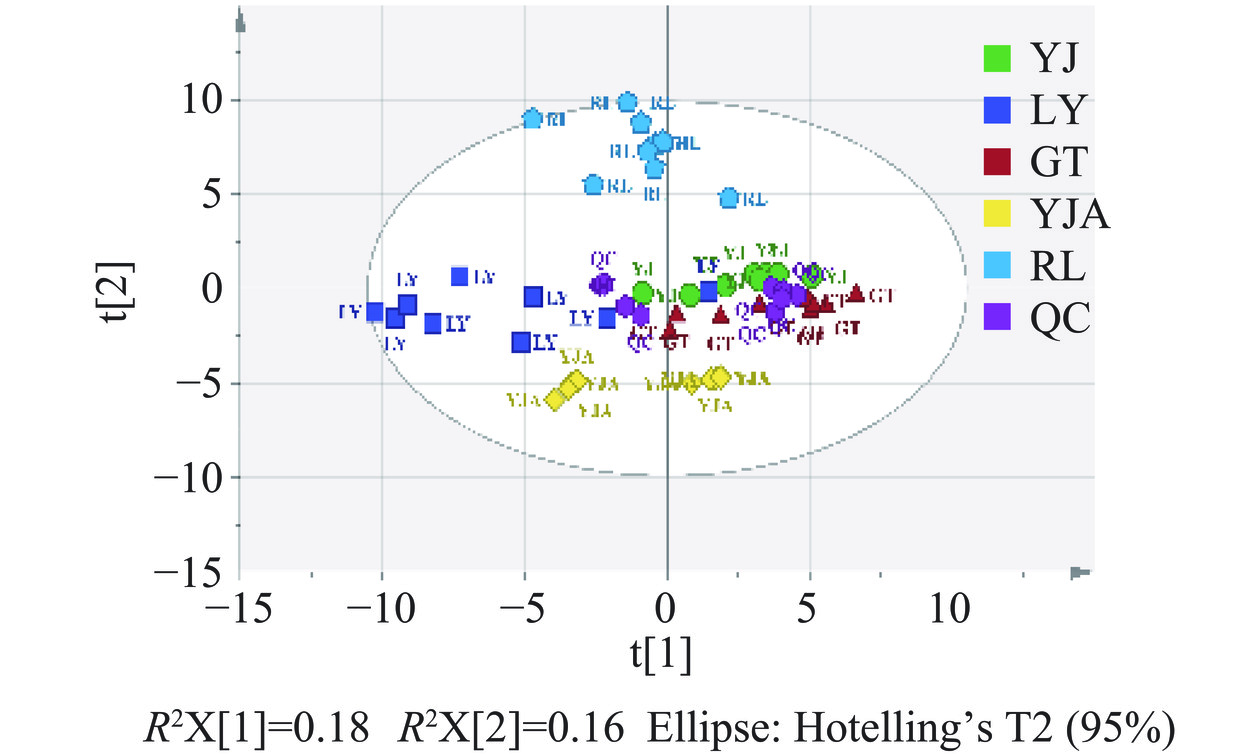
考虑到利用单一理化指标无法对不同品种的辣椒进行识别,进一步利用GC-MS非靶向代谢组学进行差异代谢物筛选。基于GC-MS分析,在五种辣椒样品中共得到95种代谢物,为清晰得出它们之间的代谢物差异,首先利用主成分分析法对五种辣椒代谢物进行降维处理,得到二维图进而判别辣椒之间的差异。在无监督PCA得分图中,每个实心圆代表一个样本,对代谢物进行主成分分析可以总体反映样本组间和组内差异,结果如图5所示。由图可知,得分图的所有样本基本都在95%置信椭圆内,但无法得到有效分离,且PC1与PC2只解释了总方差的34%,因此还需进一步采用有监督的识别模式进行分析。
2.4.2 OPLS-DA分析
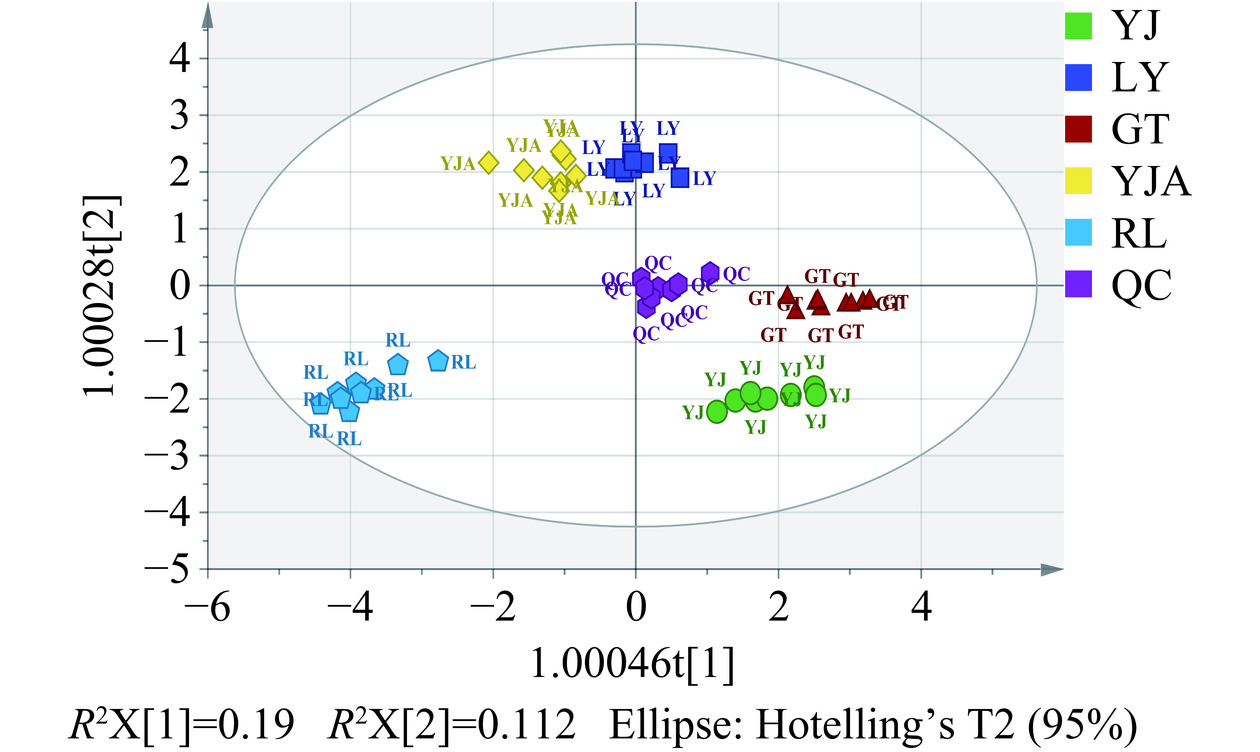
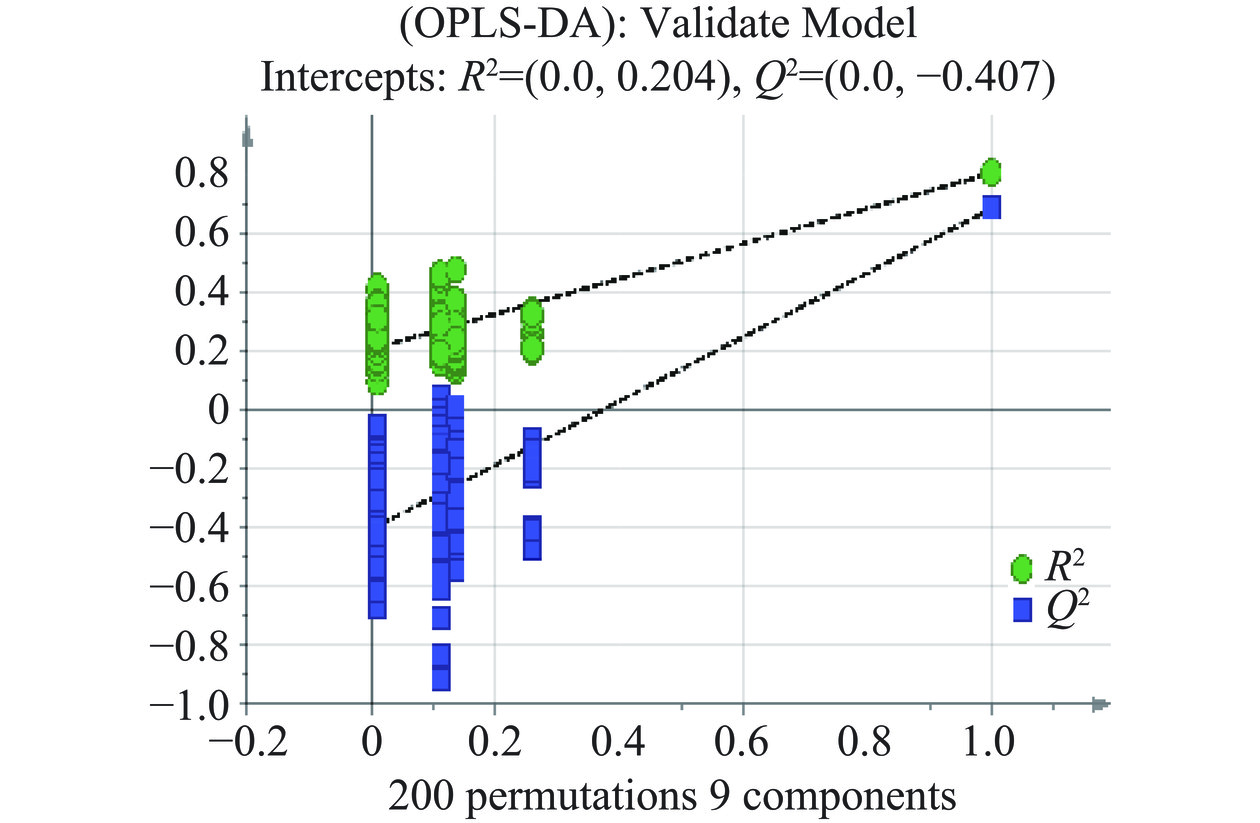
为了更好地实现高水平的组间分离,采用有监督的OPLS-DA进行分析[23]。在OPLS-DA模型中,R2Y和Q2的值常用于判断其稳定性和观察原始数据的可靠性,两者的值越接近1,模型越可靠。如图6所示,R2Y=0.838,Q2=0.716,表明模型能很好地解释样本间的差异。为防止模型过拟合,采用200次响应的置换检验(Response Permutation Testing,RPT检验)对模型进行验证,其中R2、Q2为回归直线与y轴的截距值,R2表示模型能够解释的方差总和,Q2表示模型的预测能力;使用RPT检验时,一般要求Q2<0。由图7可知,R2=0.204,Q2=−0.407,回归线呈向上的趋势,Q2<0,没有出现过拟合的现象,说明OPLS-DA模型可靠,可用于后续的分析。
2.4.3 差异代谢物筛选
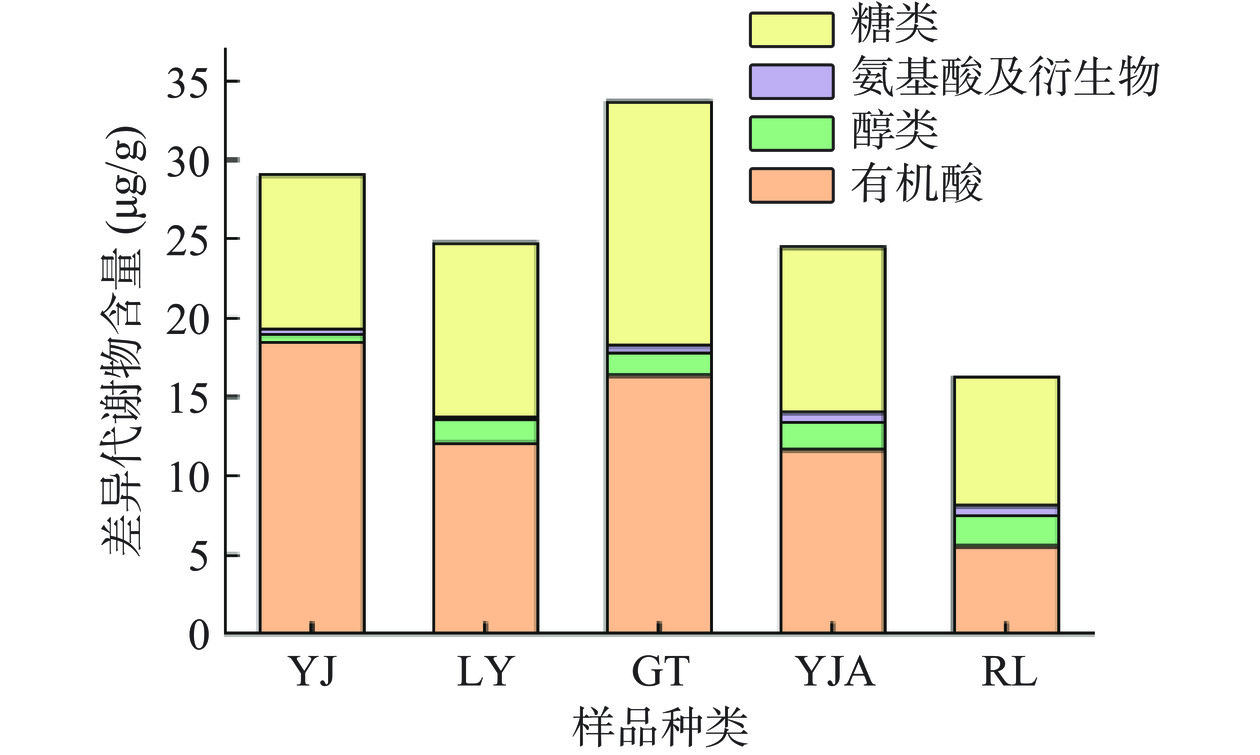
采用多维分析和单维分析相结合的方法,可以进一步筛选组间差异代谢物。根据OPLS-DA模型分析结果,筛选主成分的VIP值不低于1、t检验P<0.05的差异代谢物进行汇总(表1),共筛选出16种差异代谢物,含有糖类、醇类、有机酸、氨基酸及其衍生物等物质,每种辣椒的各类代谢物如图8所示,在YJ、LY、GT和YJA中有机酸的相对含量最高,而RL品种中糖类的相对含量较高,而氨基酸及其衍生物在所有品种的辣椒中相对含量最少,说明可能有机酸、糖是区分5种辣椒的关键差异代谢物。
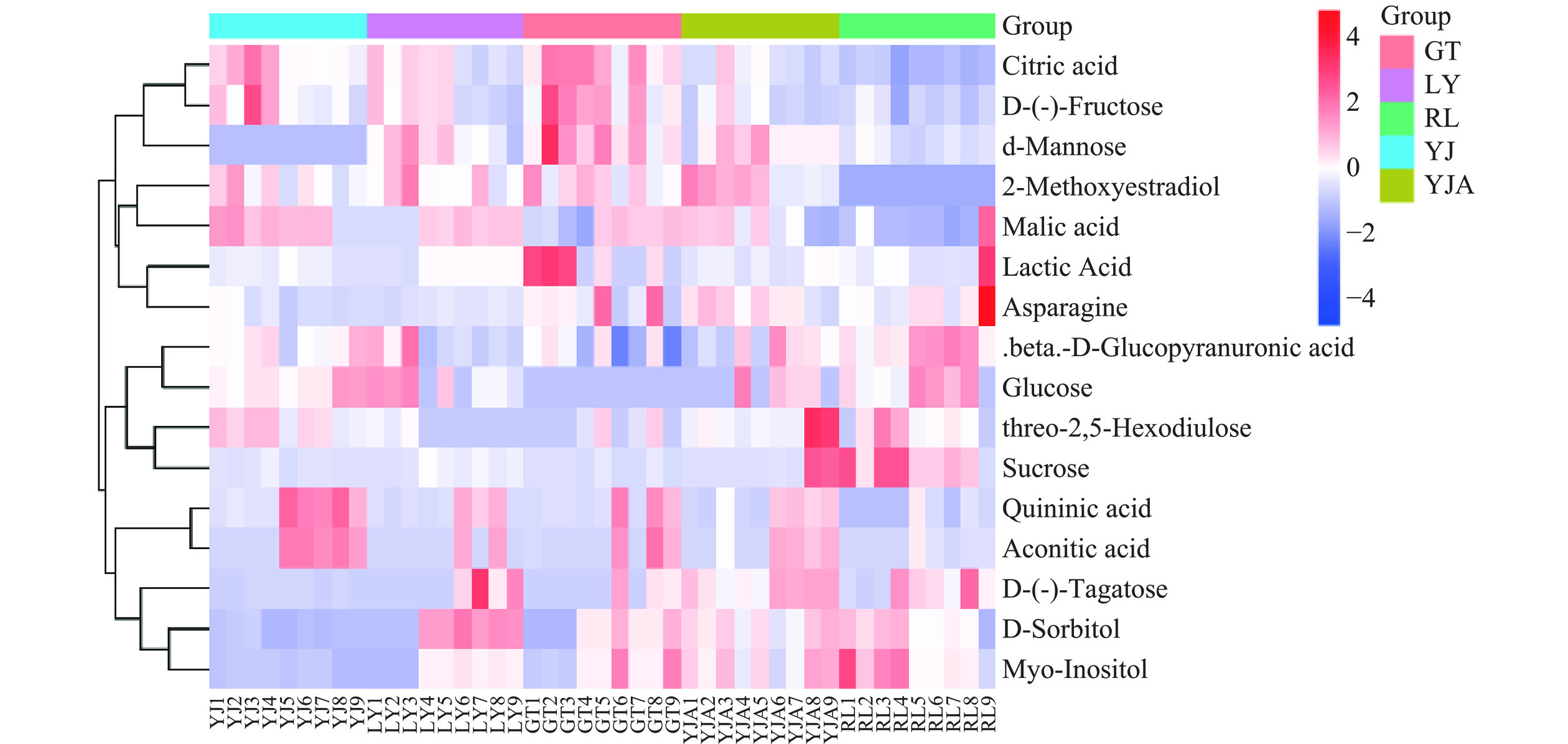
表 1 不同品种辣椒代谢差异物筛选Table 1. Screening of metabolic differences in different varieties of chili peppers代谢物 英文对照 P值 VIP 乳酸 Lactic acid 0.001 1.676 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.001 2.090 苹果酸 Malic acid 0.001 1.533 肌醇 Myo-Inositol 0.001 1.689 山梨醇 D-Sorbitol 0.001 1.784 天门冬氨酸 Asparagine 0.001 1.326 奎宁酸 Quininic acid 0.003 1.580 D-果糖 D-Fructose 0.006 1.035 柠檬酸 Citric acid 0.007 3.143 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.008 1.517 2-甲氧基雌二醇 2-Methoxyestradiol 0.019 1.574 β-D-吡喃葡萄糖醛酸 β-D-Glucopyranuronic acid 0.008 1.026 苏氨酸-2,5-外二脲 threo-2,5-Hexodiulose 0.011 1.144 D-塔格糖 D-Tagatose 0.027 2.606 D-甘露糖 d-Mannose 0.033 2.764 乌头酸 Aconitic acid 0.0422 2.297 为了更直观地观察差异代谢物在五种辣椒间的含量差异,对筛选出的差异化合物进行聚类,绘制所有差异代谢物的层次聚类热图,如图9所示。在五种辣椒中,差异代谢产物有明显不同,以代谢产物类别差异对辣椒进行分析,差异代谢物中有机酸有6种,包含乳酸、柠檬酸、奎宁酸、乌头酸、β-D-吡喃葡萄糖醛酸和苹果酸。乳酸在品种GT中含量明显高于其他品种,其可能由糖酵解生成,也可能由苹果酸脱羧生成[24];品种GT跟LY中富含柠檬酸,它是柠檬酸循环与乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢的中间产物,是辣椒能量代谢和新陈代谢过程中的重要组成部分;奎宁酸、乌头酸和苹果酸在辣椒中分布广泛,其中奎宁酸影响辣椒的生长过程与代谢过程,通常涉及细胞壁合成、酸碱平衡和抗氧化活性等,而乌头酸是一种食用增味剂,可用于中药,这两种有机酸在YJ中含量最高,苹果酸则为水果的重要成分,酸爽可口,在YJ、LY和GT当中比较丰富。
醇类作为广泛分布在植物中的生物标记物之一,差异代谢物中的醇类有三种为D-山梨醇、肌醇和2-甲氧基雌二醇,肌醇是化学上非常稳定的极性小分子,是一种碳环糖多元醇, 具有抗炎、抗氧化和降脂活性[25],其在RL中含量最高;D-山梨醇改善辣椒果实的着色,影响辣椒的糖代谢[26],五种辣椒中,LY的D-山梨醇含量最高;2-甲氧基雌二醇有抗癌抗肿瘤的生物活性,并不是天然存在的,可能是在衍生化的过程中产生。糖类代谢物包含葡萄糖、蔗糖、D-果糖、D-塔格糖和D-甘露糖,其中,D-果糖相对含量高于其它代谢物,参与果糖与甘露糖代谢,影响辣椒生长和发育,同时也可以影响辣椒的口感和风味特性,在GT中,D-果糖与D-甘露糖含量明显高于其它品种,而葡萄糖与蔗糖在RL中含量最高,D-塔格糖在YJA中最丰富。
氨基酸及其衍生物有两种,为天门冬氨酸与苏氨酸-2,5-外二脲,天冬氨酸被称为味氨基酸,呈鲜味,能影响果实风味[27],可以优化根系形态,促进植物对养分的吸收[28],在品种YJA跟GT中含量较高;苏氨酸是人体八种必需氨基酸之一,对于生物体的生长和发育具有重要作用[29],在品种YJA广泛存在。氨基酸在辣椒的代谢通路中也广泛存在,Lozada等[30]揭示了Jalapeño和Serrano两种辣椒差异代谢组分包含有机酸、核苷酸及其衍生物、氨基酸及其衍生物、生物碱等,其中参与了萜类主干生物合成和光合作用。Tilen等[31]对不同辣椒品种果实代谢差异的HPLC/MS分析,分析了包括糖类、有机酸、辣椒素、酚类物质等16种代谢产物。在三个品种中,果糖是最常见糖,其次为葡萄糖和蔗糖,这与本文研究结果相似,有机酸中的柠檬酸、苹果酸、奎宁酸和草酸含量都有所差异,抗坏血酸仅在一个品种中有差异,不同品种间辣椒素总含量无显著差异。Nemesio等[32]对墨西哥的10个新品种辣椒核磁共振代谢组学分析,发现柠檬酸、甲酸、苹果酸、果糖、蔗糖和半乳糖为差异代谢物,对不同品种的辣椒分类有重要作用。
2.4.4 代谢通路分析
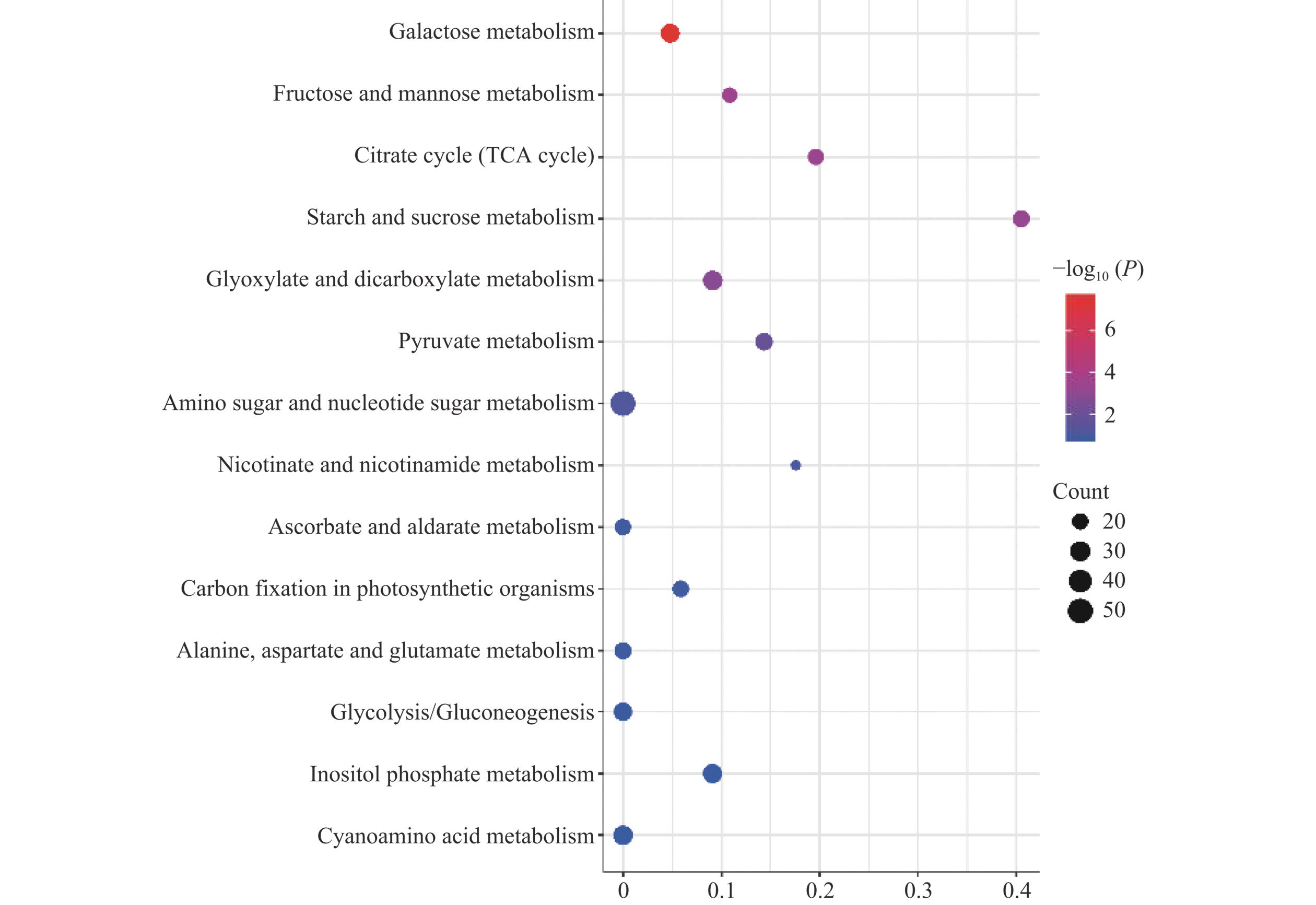
为了进一步了解不同品种辣椒代谢途径差异,运用Metaboanalyst 6.0对五种辣椒进行富集分析。将筛选出的16个差异性代谢物投影至KEGG数据库中的Pathway数据库并与其进行匹配,由P<0.05筛选出6条主要的代谢通路,主要为糖醇代谢与有机酸代谢,分别为半乳糖代谢、果糖和甘露糖代谢、柠檬酸循环、淀粉和蔗糖代谢、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢(图10)。
半乳糖代谢、果糖和甘露糖代谢、淀粉和蔗糖代谢主要作用于辣椒的糖代谢,分解和生成相关糖类物质;柠檬酸循环、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢涉及乌头酸、柠檬酸、苹果酸和乳酸,是碳水化合物、脂肪和氨基酸的最终常见氧化途径,它是身体能量供应最重要的代谢途径,也是连接几乎所有个体代谢途径的最重要的中枢途径,其中一些二羧酸与丙酮酸是一种重要的代谢中间产物,参与到柠檬酸循环中。
2.4.5 机器学习识别
为了对辣椒的品种识别进行验证,采用了三种机器学习方法提高验证结果的可靠性,以16种差异代谢物作为数据集减少运算的复杂度,将数据集随机划分为训练集(70%)和测试集(30%)进行机器学习方法测试,采用XGBoost、随机森林(RF)和BP神经网络三种方法建立分类模型,为了减小过拟合现象,使用十折交叉验证,比较不同品种辣椒的分类准确率。结果由表2可知,在预测准确率上,RF模型与XGBoost模型识别准确率较高,分别为100%和92.9%,能够得到预期结果,说明上述数据可以完成分类识别。
表 2 三种机器学习方法对辣椒的识别准确率(%)Table 2. Recognition accuracy of two machine learning methods for chili peppers (%)模型 RF XGBoost BP神经网络 训练集 100 100 100 测试集 100 92.9 78.6 3. 结论
本研究对五个品种的望都辣椒的色泽、VC、辣椒碱类的含量及代谢产物进行了检测和统计分析,五种辣椒中RL品种辣椒的L*、a*和b*值为最高,而其余品种色泽度区分不明显;辣椒碱类物质中,品种RL含量最高,辣度最辣,其余品种差异并不显著;而利用VC含量,艳椒(YJ)的含量最高,而辣研(LY)和国塔(GT)含量最低,不容易区分。采用GC-MS非靶向代谢组学方法,利用PCA分析与OPLS-DA分析,筛选出16种差异代谢物,包含有机酸、醇类、糖类和氨基酸及其衍生物,其中在艳椒(YJ)、辣研(LY)、国塔(GT)和研椒110(YJA)中有机酸的相对含量最高,而热辣(RL)品种中糖类的相对含量较高,不同品种辣椒所富集的差异代谢物也不同,奎宁酸和乌头酸等有机酸在艳椒(YJ)中含量较高,乌头酸为中药成分,故艳椒(YJ)可以应用于药品开发;D-山梨醇在辣研(LY)中含量最高,国塔(GT)当中柠檬酸、D-果糖、D-甘露糖和乳酸富集程度最高,可应用于功能性食品开发,研椒110(YJA)中D-塔格糖与氨基酸含量最高,故可以应用于香料制作,而热辣(RL)中葡萄糖跟肌醇含量在所有品种中占优势,该结果可以作为区分不同品种辣椒的判断指标。最后利用机器学习对辣椒的差异代谢物进行识别验证,RF模型、XGBoost和BP神经网络模型识别准确率分别为100%、92.9%和78.6%,RF模型、XGBoost能够达到预期结果,而BP神经网络模型准确率较低,还需要进一步训练优化。本研究在为进一步进行品种鉴别提供了参考,对开发品质优良的新品种发挥积极作用。
-
表 1 不同品种辣椒代谢差异物筛选
Table 1 Screening of metabolic differences in different varieties of chili peppers
代谢物 英文对照 P值 VIP 乳酸 Lactic acid 0.001 1.676 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.001 2.090 苹果酸 Malic acid 0.001 1.533 肌醇 Myo-Inositol 0.001 1.689 山梨醇 D-Sorbitol 0.001 1.784 天门冬氨酸 Asparagine 0.001 1.326 奎宁酸 Quininic acid 0.003 1.580 D-果糖 D-Fructose 0.006 1.035 柠檬酸 Citric acid 0.007 3.143 葡萄糖 Glucose 0.008 1.517 2-甲氧基雌二醇 2-Methoxyestradiol 0.019 1.574 β-D-吡喃葡萄糖醛酸 β-D-Glucopyranuronic acid 0.008 1.026 苏氨酸-2,5-外二脲 threo-2,5-Hexodiulose 0.011 1.144 D-塔格糖 D-Tagatose 0.027 2.606 D-甘露糖 d-Mannose 0.033 2.764 乌头酸 Aconitic acid 0.0422 2.297 表 2 三种机器学习方法对辣椒的识别准确率(%)
Table 2 Recognition accuracy of two machine learning methods for chili peppers (%)
模型 RF XGBoost BP神经网络 训练集 100 100 100 测试集 100 92.9 78.6 -
[1] GUO G J, PAN B G, YI X X, et al. Genetic diversity between local landraces and current breeding lines of pepper in China[J]. Scientific Reports,2023,13(1):4058. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29716-4
[2] 邹学校, 杨莎, 朱凡, 等. 中国高口感品质鲜食辣椒产业发展与未来趋势[J]. 园艺学报,2024,51(1):27−38. [ZOU X X, YANG S, ZHU F, et al. The development and future trends of China's high taste and quality fresh chili industry[J]. Journal of Horticulture,2024,51(1):27−38.] ZOU X X, YANG S, ZHU F, et al. The development and future trends of China's high taste and quality fresh chili industry[J]. Journal of Horticulture, 2024, 51(1): 27−38.
[3] 张子峰. 我国辣椒产业发展现状、主要挑战与应对之策[J]. 北方园艺,2023(14):153−158. [ZHANG Z F. The current development status, main challenges, and countermeasures of China's chili industry[J]. Northern Horticulture,2023(14):153−158.] ZHANG Z F. The current development status, main challenges, and countermeasures of China's chili industry[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023(14): 153−158.
[4] TANJA C, JASMINA R, STELA J. Quality of pepper seed by-products:A review[J]. Foods,2022,11(5):748. doi: 10.3390/foods11050748
[5] NACCARATO A, FURIA E, SINDONA G, et al. Multivariate class modeling techniques applied to multielement analysis for the verification of the geographical origin of chili pepper[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,206:217−222. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.072
[6] IVAN I M, POPOVICI V, CHIȚESCU C L, et al. Phytochemical profile, antioxidant and cytotoxic potential of Capsicum annuum(L.) dry hydro-ethanolic extract[J]. Pharmaceutics,2024,16(2):245. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020245
[7] 沈央红, 方金玉, 朱军莉, 等. 代谢组学在食品质量安全领域的应用进展[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(5):282−289. [SHEN Y H, FANG J Y, ZHU J L, et al. The application progress of metabolomics in the field of food quality and safety[J]. Food Science,2023,44(5):282−289. ].] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211129-353 SHEN Y H, FANG J Y, ZHU J L, et al. The application progress of metabolomics in the field of food quality and safety[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(5): 282−289. ]. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211129-353
[8] 杨创创, 何建文, 张正海, 等. 13份干辣椒挥发性风味品质评价[J]. 中国蔬菜,2023(10):37−49. [YANG C C, HE J W, ZHANG Z H, et al. Evaluation of volatile flavor quality of 13 dried chili peppers[J]. Chinese Vegetables,2023(10):37−49.] YANG C C, HE J W, ZHANG Z H, et al. Evaluation of volatile flavor quality of 13 dried chili peppers[J]. Chinese Vegetables, 2023(10): 37−49.
[9] ELVIA B M, ELIDETH F R, NURY P H, et al. 1 H NMR-based metabolomic fingerprinting to determine metabolite levels in serrano peppers (Capsicum annum L.) grown in two different regions[J]. Food Research International,2017,102:163−170. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.10.005
[10] 杨芳, 邓凤琳, 袁海彬, 等. 基于气相色谱-离子迁移谱结合多元统计方法研究辣椒产地对辣椒油理化性质和风味成分的影响[J]. 核农学报,2023,37(7):1393−1402. [YANG F, DENG F L, YUAN H B, et al. Based on gas chromatography ion migration spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical methods, the influence of chili pepper production areas on the physicochemical properties and flavor components of chili oil[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2023,37(7):1393−1402.] doi: 10.11869/j.issn.1000-8551.2023.07.1393 YANG F, DENG F L, YUAN H B, et al. Based on gas chromatography ion migration spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical methods, the influence of chili pepper production areas on the physicochemical properties and flavor components of chili oil[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 2023, 37(7): 1393−1402. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.1000-8551.2023.07.1393
[11] 刘录, 陈海云, 刘菲菲, 等. HPLC法测定云南省不同辣椒品种中辣椒碱及二氢辣椒碱的含量[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(5):299−303. [LIU L, CHEN H Y, LIU F F, et al. HPLC method for determining the content of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin in different pepper varieties in Yunnan Province[J]. Food Industry Technology,2013,34(5):299−303.] LIU L, CHEN H Y, LIU F F, et al. HPLC method for determining the content of capsaicin and dihydrocapsaicin in different pepper varieties in Yunnan Province[J]. Food Industry Technology, 2013, 34(5): 299−303.
[12] 蒋侬辉, 凡超, 刘伟, 等. 运用RP-HPLC同时测定火龙果中7种有机酸和Vc含量的方法研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2015,37(5):798−803. [JIANG N H, FAN C, LIU W, et al. Study on the simultaneous determination of seven organic acids and Vc content in dragon fruit using RP-HPLC[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University,2015,37(5):798−803.] JIANG N H, FAN C, LIU W, et al. Study on the simultaneous determination of seven organic acids and Vc content in dragon fruit using RP-HPLC[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2015, 37(5): 798−803.
[13] 李平平, 张祥, 刘雨婷, 等. 辣椒63份种质果皮颜色与呈色物质的关系[J]. 园艺学报,2022,49(7):1589−1601. [LI P P, ZHANG X, LIU Y T, et al. The relationship between peel color and coloring substances of 63 chili germplasms[J]. Journal of Horticulture,2022,49(7):1589−1601.] LI P P, ZHANG X, LIU Y T, et al. The relationship between peel color and coloring substances of 63 chili germplasms[J]. Journal of Horticulture, 2022, 49(7): 1589−1601.
[14] 程杰, 罗洲, 肖书剑, 等. 辣椒、花椒及其制品辣度和麻度检测研究现状[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(6):209−215. [CHENG J, LUO Z, XIAO S J, et al. Current research status on the detection of spiciness and numbness in chili peppers, Sichuan peppercorns and their products[J]. Chinese Seasoning,2023,48(6):209−215.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.06.036 CHENG J, LUO Z, XIAO S J, et al. Current research status on the detection of spiciness and numbness in chili peppers, Sichuan peppercorns and their products[J]. Chinese Seasoning, 2023, 48(6): 209−215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.06.036
[15] KEITHELLAKPAM S. Antioxidant potential and factors influencing the content of antioxidant compounds of pepper:A review with current knowledge[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2023,22(4):3011−3052. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.13170
[16] WANG W L, HUANG Y L, HU W X, et al. Synthesis, structures and anti-tumor properties of capsaicin analogues[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities-Chinese,2010,31(12):2400−2406.
[17] LEE H, SONG J, CHUNG S, et al. Gochujang elicits anti-obesity effects by increasing capsaicin-independent brown adipogenesis and thermogenesis in high-fat diet induced obese mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2023,111:239.
[18] 朱志妍, 田浩, 潘俊, 等. 云南省主要辣椒品种活性成分及其加工适应性[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(21):7091−7100. [ZHU Z Y, TIAN H, PAN J, et al. The active ingredients and processing adaptability of the main chili pepper varieties in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2022,13(21):7091−7100].] ZHU Z Y, TIAN H, PAN J, et al. The active ingredients and processing adaptability of the main chili pepper varieties in Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing, 2022, 13(21): 7091−7100].
[19] XU Z N, ZHONG D J, WANG J Y, et al. Colour, physicochemical, microbiological and bioactive component quality analysis of peppers in Guizhou[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2022,58(2):665−675.
[20] HUNGERFORD A J, BAKOS H W, AITKEN R J. Addition of vitamin C mitigates the loss of antioxidant capacity, vitality and DNA integrity in cryopreserved human semen samples[J]. Antioxidants,2024,13(2):247. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020247
[21] CHEN D, WEI X Y, YANG K, et al. Piperlongumine combined with vitamin C as a new adjuvant therapy against gastric cancer regulates the ROS-STAT3 pathway[J]. The Journal of International Medical Research, 2022, 50(4):3000605221093308.
[22] 王蜜蜜, 胡能兵, 庞丹丹, 等. 辣椒主要营养品质比较[J]. 安徽科技学院学报,2019,33(6):38−42. [WANG M M, HU N B, PANG D D, et al. Comparison of the main nutritional qualities of chili peppers[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology,2019,33(6):38−42.] WANG M M, HU N B, PANG D D, et al. Comparison of the main nutritional qualities of chili peppers[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2019, 33(6): 38−42.
[23] 李萌, 卢玺丞, 黄云艳, 等. 基于代谢组学技术分析不同纬度山羊乳的差异性[J]. 分析化学,2021,49(11):1864−1875. [LI M, LU X C, HUANG Y Y, et al. Analysis of differences in goat milk at different latitudes based on metabolomics techniques[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2021,49(11):1864−1875.] LI M, LU X C, HUANG Y Y, et al. Analysis of differences in goat milk at different latitudes based on metabolomics techniques[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 49(11): 1864−1875.
[24] CHEN D, LIU S Q. Transformation of chemical constituents of lychee wine by simultaneous alcoholic and malolactic fermentations[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 196.
[25] ROSTAMI S, AREFHOSSEINI S, TUTUNCHI H, et al. Does myo-inositol supplementation influence oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2024,12(2):1279−1289.
[26] 周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 等. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报,2023,50(5):959−971. [ZHOU P, GUO R, YAN S B, et al. A molecular mechanism study on the effect of exogenous sorbitol on sugar metabolism in peach leaves and fruits[J]. Journal of Horticulture,2023,50(5):959−971.] ZHOU P, GUO R, YAN S B, et al. A molecular mechanism study on the effect of exogenous sorbitol on sugar metabolism in peach leaves and fruits[J]. Journal of Horticulture, 2023, 50(5): 959−971.
[27] 彭真汾, 王威, 叶清华, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法定量分析橄榄果实氨基酸组分[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(24):231−238. [PENG Z F, WANG W, YE Q H, et al. Quantitative analysis of amino acid components in olive fruit using high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2018,39(24):231−238.] PENG Z F, WANG W, YE Q H, et al. Quantitative analysis of amino acid components in olive fruit using high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(24): 231−238.
[28] 刘媛, 袁亮, 张水勤, 等. 不同分子量聚天冬氨酸对小麦根系生长和养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(13):2526−2537. [LIU Y, YUAN L, ZHANG S Q, et al. The effects of polyaspartic acid with different molecular weights on the growth and nutrient uptake of wheat roots[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science,2022,55(13):2526−2537].] doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.13.004 LIU Y, YUAN L, ZHANG S Q, et al. The effects of polyaspartic acid with different molecular weights on the growth and nutrient uptake of wheat roots[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science, 2022, 55(13): 2526−2537]. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.13.004
[29] DANIEL P F, DIRLEISE P, EDUARDO K B, et al. L-threonine requirement of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen):Growth performance, body composition, plasma and liver metabolites[J]. Journal of Applied Animal Research,2023,51(1):358−365. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2023.2203746
[30] LOZADA D N, PULICHERLA S R, HOLGUIN F O. Widely targeted metabolomics reveals metabolite diversity in Jalapeno and Serrano chile peppers (Capsicum annuum L.)[J]. Metabolites,2023,13(2):288. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020288
[31] TILEN Z, ALJAŽ M, ROBERT V, et al. Metabolic variation among fruits of different chili cultivars (Capsicum spp.) using HPLC/MS[J]. Plants,2021,11(1):101. doi: 10.3390/plants11010101
[32] NEMESIO V R, MOISÉS R M, REINALDO M A, et al. 1 H NMR-based metabolomics profiling of ten new races from Capsicum annuum cv. serrano produced in Mexico[J]. Food Research International,2019,119:785−792. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.10.061
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 马晓青,孙皓岩,魏宝红,胡淑曼,杨文哲,杨雪. 紫贻贝酶解工艺及抗炎活性研究. 食品科技. 2024(01): 116-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 程钰,胡蓉,李强,蒋蕾,何跃辉,卢静,王淑军. 复合蛋白酶水解菲律宾蛤蜊及产物的生物学活性研究. 食品科技. 2024(06): 134-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 付雪媛,杜芬,孙呈浩,王明丽,王长伟. 蛤蜊肽的制备工艺优化及其增强免疫活性. 食品工业科技. 2023(09): 244-253 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 沈畅华,杨娟,张远红,曾晓房. 双酶酶解鸽胸肉工艺优化及抗氧化性评价. 食品与机械. 2023(04): 163-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴伟东,马诗淳,陈锐,周广平,邓宇. 厌氧角蛋白降解菌KD-1粗酶和商业蛋白酶酶解猪肉的功能与评价. 中国沼气. 2022(02): 47-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李佳芸,王欣之,韦源青,卞慧敏,刘睿,吴皓. 马氏珍珠贝软体酶法制备降糖肽的工艺优化及肽段分析. 食品工业科技. 2021(22): 202-211 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
