Preparation of Carboxymethyl Porous Starch by Mechanical Activation Solid Phase Etherification Method Synthesis and Its Application in Powdered Soy Sauce
-
摘要: 为获得一种绿色高效的羧甲基多孔淀粉制备工艺,本研究以酶解制得的多孔木薯淀粉为原料,氯乙酸钠为醚化剂,氢氧化钠为催化剂,采用机械活化协同固相醚化法制备羧甲基多孔淀粉,通过单因素实验探究各因素对羧甲基多孔淀粉取代度(Degree of substitution,DS)的影响,并探讨羧甲基多孔淀粉在酱油中的应用。结果表明,机械活化协同固相法制备羧甲基多孔淀粉的最佳工艺条件为:多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠的物质的量之比为1:1,氢氧化钠质量分数为18.8%,球磨时间1.5 h,反应温度50 ℃,此条件下制备得到的羧甲基多孔淀粉取代度最高为0.2532。通过红外光谱仪(Infrared spectrometer,FTIR)、X-射线粉末衍射仪(X-ray powder diffractometer,XRD)和扫描电镜(Scanning electron microscope,SEM)等表征,进一步证实多孔淀粉发生了羧甲基化反应。随着羧甲基多孔淀粉DS的增大其冷水溶解度、吸水率和柠檬黄吸附量增大;当DS为0.2532时,羧甲基多孔淀粉的冷水溶解度达到64.94%,吸水率达到180.73%,柠檬黄吸附量达到2.5086 mg·g−1。羧甲基多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油相比于木薯淀粉和多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油溶解性更好,吸潮性更低,氨基酸态氮含量更高,与原酱油最接近。因此,机械活化协同固相醚化法可有效制备羧甲基多孔淀粉,该法操作简单,绿色环保,取代高,为多孔淀粉的开发利用提供了科学依据。Abstract: In order to obtain a green and efficient preparation process for carboxymethyl porous starch, carboxymethyl porous starch was prepared by mechanical activation solid phase etherification method, where enzymatically hydrolyzed porous cassava starch was used as raw material, sodium chloroacetate as etherifying agent, and sodium hydroxide as catalyst. Single-factor experiments were conducted to explore the effects of various factors on the degree of substitution (DS) of carboxymethyl porous starch, and the application of carboxymethyl porous starch in soy sauce was discussed. The results showed that the optimal process conditions for the preparation of carboxymethyl porous starch by mechanical activation and solid phase synthesis method were as follows: The molar ratio of porous starch to sodium chloroacetate was 1:1, the mass fraction of sodium hydroxide was 18.8%, the ball milling time was 1.5 h, and the reaction temperature was 50℃. Under these conditions, the highest DS of carboxymethyl porous starch obtained was up to 0.2532. Furthermore, the carboxymethylation reaction of porous starch was confirmed by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). With the increase of DS of carboxymethyl porous starch, its cold water solubility, water absorption, and adsorption of lemon yellow increased. When DS was 0.2532, the cold water solubility of carboxymethyl porous starch reached 64.94%, the water absorption rate reached 180.73%, and the adsorption amount of lemon yellow reached 2.5086 mg·g−1. The powder soy sauce prepared by carboxymethyl porous starch has better solubility, lower moisture absorption, and higher content of amino acid nitrogen, and is closer to the original soy sauce compared to those prepared by cassava starch and porous starch. Therefore, the mechanical activation and solid phase etherification method can effectively prepare carboxymethyl porous starch, which is simple to operate, environmentally friendly, and highly substitutive, providing a scientific basis for the development and utilization of porous starch.
-
酱油粉是一种可食用的固体粉末,它以新鲜的液体酱油为原料,经过吸附、干燥和粉碎等制备工艺制得[1]。相比于传统液体酱油,酱油粉可以很好地保留酱油原有的香味,并有效克服传统酱油带有的焦糊味和氧化味等问题[2]。其色泽红润、风味鲜香,溶水性好,易于保存和运输,使用也更为方便快捷。目前市场上多用原淀粉和多孔淀粉制备酱油粉,但是原淀粉透明度较低,粘稠度较大,溶解性也较差,无法满足需要[3]。通过酶解、化学或者物理改性更改淀粉的结构或者理化性质,改善淀粉的不足,扩大淀粉的应用范围[4]。多孔淀粉作为一种拥有大量孔洞的新型改性淀粉,增加了淀粉颗粒的比表面积,提高了其吸附性能[5−8],扩大了其应用范围[9−10]。朱弘毅等[11]使用颗粒状冷水可溶性多孔淀粉为载体,成功制得了具有更好吸附性能和更优异溶水性能的粉末酱油。张洪微等[12]使用多孔玉米淀粉制得的粉末酱油,不仅色泽和红色指数接近原酱油,口感也与原酱油无异。
羧甲基多孔淀粉是一种变性淀粉,结合了多孔淀粉和羧甲基淀粉[13]的特性。在不影响吸附性的情况下,对多孔淀粉进行羧甲基反应,在淀粉分子中引入羧甲基基团,同时保留了多孔淀粉疏松多孔的结构,从而使其溶水性和吸水性等性能获得显著提升[14]。在需要同时具有吸附性和良好溶水性的应用领域,羧甲基多孔淀粉可以发挥重要作用,例如在医药领域,可利用其吸附性包埋药物以方便患者吞服,且其相比于不易溶于水的多孔淀粉,羧甲基多孔淀粉能更好地溶解吸收。王宇霞[15]利用羧甲基多孔淀粉吸附黄酮类化合物,成功使黄酮醇分布均匀,并显著提高了其水溶性和生物利用度。孙林皓等[16]以玉米淀粉为原料用酶解的方法制备多孔淀粉,再使用溶剂法制备得到羧甲基多孔淀粉,用来包埋肉桂醛制备得到微胶囊,大大提高了其抑菌活性和保鲜性能。谷绒等[17]以多孔淀粉为原料,在液相中以碱化、醚化等多步法制备粉末酱油用羧甲基多孔淀粉,制得的羧甲基多孔淀粉理化性能有所提高,制备的粉末酱油效果较好。目前,工业上主要采用液相法和固相法制备羧甲基化多孔淀粉,由于液相法存在很多副反应,且醚化剂利用率很低,因此得到的羧甲基多孔淀粉产量低且容易糊化。固相法则是一种能耗低、操作简单、原料利用率高、无废弃物排放的经济高效的生产工艺。一般流程是碱与淀粉混合碱化一定时间后,再加入一定量的一氯乙酸,在高温下或在流化床中反应一定的时间。优点是产物含水量较低、耗能低、烘干速度快、无废水排放。但在目前的干法工艺条件下,淀粉和反应试剂未能充分混合,导致反应效率低且均匀性差。这是由于半结晶淀粉的超分子结构使其难以与各种反应试剂接触,化学试剂分子无法进入淀粉分子的内部空间,从而导致反应不足。此外,传统的加入一级或几级碱处理的方法也无法完全破坏淀粉的内部结构。因此,在这种非均相的反应体系中,淀粉的非晶相区域成为醚化反应的主要区域,醚化剂和结晶区的羟基难以接触,导致反应不充分,取代物大多分布在淀粉的小颗粒表面,平均取代度(Degree of substitution, DS)较低,原料利用率低,导致产品的溶解性能差,不利于工业化生产。
机械活化通过机械力作用使物料的物理化学性质和结构发生变化,提高自由能,降低化学反应活化能,增加物料的反应活性[18]。相比于传统的固相反应,机械活化协同固相法的方法能使反应物反应的均匀性更好,在保质保量的同时还能降低合成温度,减少能耗,能很好地避免反应物和产物在高热下分解,从而实现在较低温度下提高化学反应的速率和原料的利用率[19−20]。主要原因是在机械力强大的剪切力作用下,反应物料会产生晶格畸变和结构局部破坏,反应物得以充分混合,反应接触面积增大,活化能降低,反应活性增强,更有利于进行干法反应。这种方法可进一步提高反应效率,简化工艺,减少环境污染。目前未见采用机械活化协同固相法制备羧甲基多孔淀粉并应用于粉末酱油的报道,本试验在前期研究的基础上,以机械活化协同固相法对多孔淀粉进行羧甲基化,以取代度为指标优化生产工艺,测定羧甲基多孔淀粉的冷水溶解度、吸水率和柠檬黄吸附量等理化特性,并对其微观结构进行表征。将制备的羧甲基多孔淀粉应用于粉末酱油中,探讨粉末酱油性能变化。该研究拓宽了羧甲基多孔淀粉在食品工业上的应用,为实现干法工业化生产羧甲基多孔淀粉提供研究基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
木薯淀粉 食品级,广西合浦县健丰淀粉有限责任公司;氯乙酸钠 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;氢氧化钠 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;淀粉糖化酶(10万U/g)、柠檬黄 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;磷酸氢二钠 分析纯,天津市福晨化学试剂厂;柠檬酸 分析纯,潍坊英轩实业有限公司;盐酸 分析纯,西陇科学股份有限公司;无水乙醇 分析纯,广东光华科技股份有限公司;溴化钾 光谱纯,西陇科学股份有限公司。
SHB-III循环水式多用真空泵 郑州长城科工贸有限公司;DHG-9036A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;DF-101S集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;FW100高速粉碎机 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;SY-2230恒温水浴摇床 广州深华公司;Spectrum Two傅里叶红外光谱仪 美国PerkinElmer公司;D8 Advance X-射线粉末衍射仪 德国Bruker AXS有限公司;S-4800高分辨冷场发射扫描电子显微镜 日本Hitachi公司;机械活化装置 自制[21]。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酶解法制备多孔淀粉
参考文献[22−23]方法稍作修改,在装有50 g木薯淀粉的250 mL锥形瓶中加入pH约为4.0的Na2HPO4-柠檬酸缓冲溶液100 mL,置于磁力搅拌器中,在40 ℃的水温下搅拌10 min,然后加入0.03 g的淀粉糖化酶,在40 ℃的水温下搅拌6 h,随后立刻加入3 mL提前配制好的质量分数为4%的NaOH溶液。将所得溶液装入离心管置于离心机中,在4000 r/min的转速下离心10 min后分离得到多孔淀粉,在55 ℃、常压条件下进行干燥、粉碎,过120目筛,得到多孔淀粉,放入干燥器保存。
1.2.2 多孔淀粉的羧甲基化
参考文献[24]方法制备羧甲基多孔淀粉。准确称量50 g多孔淀粉干基和一定量氢氧化钠固体充分混合,密封1 h,加入定量氯乙酸钠充分搅拌均匀,密封避光静置24 h。将充分混匀的反应物料置于自制的球磨搅拌机中,调节搅拌速率为380 r/min,在一定温度下球磨搅拌一定时间。反应时间结束后将样品和氧化锆球分开,用无水乙醇洗涤至没有氯离子,所得样品在55 ℃下干燥、粉碎,然后过120目筛,装袋,放入干燥器保存。
取代度的测定参考文献[25],称取0.5 g羧甲基多孔淀粉样品,将其放置在小烧杯中,加入2 mol·L−1 HCl(70%乙醇溶液配制而成)溶液30 mL,置于磁力搅拌器上搅拌1 h,然后过滤,用无水乙醇洗涤酸化后的滤饼,直至不含氯离子。将清洗干净的滤饼转移到250 mL锥形瓶中,添加40 mL浓度为0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH标准溶液,将其溶解,添加一滴酚酞指示剂,在微热条件下使溶液变透明状。用0.1 mol·L−1盐酸标准溶液返滴,直到酚酞指示剂的红色刚好退去时,立即停止,记录所用盐酸标准溶液的用量。根据式(1)计算淀粉所消耗的NaOH的物质量(A)。按式(2)计算羧甲基淀粉DS。
(1) (2) 式中:A为中和1 g酸式羧甲基淀粉所消耗的NaOH的物质的量,mmol;VNaOH为加入使淀粉溶解的NaOH标准溶液的体积,mL;VHCl为滴定过量NaOH标准溶液所消耗的HCl标准溶液的体积,mL;CNaOH为使淀粉溶解的NaOH标准溶液的浓度,mol·L−1;CHCl为滴定过量NaOH标准溶液的HCl标准溶液的浓度,mol·L−1;M为用于测定的酸式羧甲基淀粉的质量,g;0.162为淀粉的失水葡萄糖单元的物质的量,mmol;0.058为失水葡萄糖单元中一个羟基被羧甲基取代后,失水葡萄糖单元毫摩尔质量的净增值。
1.2.3 单因素实验
根据前期实验结果,固定多孔淀粉干基用量50 g,多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠物质的量之比为1:1.00、氢氧化钠的质量分数为18.8%、球磨反应温度50 ℃,球磨时间1.5 h,主要考察淀粉与氯乙酸钠物质的量比(1:0.50、1:0.75、1:1.00、1:1.25、1:1.50)、氢氧化钠质量分数(14.8%、16.8%、18.8%、20.8%、22.8%)、球磨时间(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、3.0 h)、反应温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃)因素对淀粉醚化反应的影响,以DS为评价指标进行单因素实验。
1.2.4 羧甲基多孔淀粉的表征和性能测试
1.2.4.1 羧甲基多孔淀粉的表征
利用傅里叶变换红外光谱(Infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)技术,以纯溴化钾作为扫描背景,在4000~500 cm−1的扫描范围内,将2 mg的试样与200 mg溴化钾混合压片,测定其分子结构;利用X射线衍射技术研究木薯粉和其他样品的晶体结构;将测试样品固定在样品台上喷金,利用扫描电镜观察测试样品的形态和结构。
1.2.4.2 羧甲基多孔淀粉吸水率的测定
吸水率的测定参考文献[20]方法,称取10.00 g淀粉样品,置于布氏漏斗中,恒温下与过量的蒸馏水混合搅拌30 min,抽滤,直至没有蒸馏水滴滴下。记录淀粉的前后质量差,计算多孔淀粉的吸水率。按式(3)进行计算:
(3) 式中:m1为吸饱水后的样品质量,g;m0为样品初始质量,g。
1.2.4.3 羧甲基多孔淀粉柠檬黄吸附量的测定
参考文献[26−27]方法测定柠檬黄吸附量,将0.5 g样品与50 mL浓度为0.021 mg·mL−1的柠檬黄溶液充分混匀后盖上玻璃塞,30 ℃恒温振荡2 h,过滤,430 nm条件下测定吸光度。按式(4)进行计算:
(4) 式中:C1为吸附后的柠檬黄滤液浓度,mg·mL−1;C0为原来未吸附前柠檬黄溶液的浓度,mg·mL−1;V为混合溶液体积,mL;m为样品质量,g。
1.2.5 粉末酱油的制备和性能测试
1.2.5.1 粉末酱油的制备
参考文献[28]方法,把酱油直接喷到羧甲基多孔淀粉中,搅拌均匀,使淀粉淀粉充分吸附酱油,此时会呈现非牛顿流体状态,证明淀粉充分吸满了酱油,提前预热好干燥箱调至55 ℃,将其放入干燥箱中,待产品干燥后取出磨碎,过筛,包装,制得粉末酱油。
1.2.5.2 粉末酱油吸潮性的测定
参考文献[17]方法测定粉末酱油的吸潮性。取1.2.5.1制备的粉末酱油5.000 g敞口放置,记录初始质量,直接暴露于空气中,定时测定各个样品的质量,直至其质量几乎没有发生改变。按式(5)进行计算:
(5) 式中:m0为样品的初始质量,g;m1为样品吸潮一段时间后恒重不变的质量,g。
1.2.5.3 粉末酱油氨基酸态氮的测定
氨基酸态氮含量的测定参考文献[17]方法进行。称取1.00 g样品于100 mL容量瓶中,用水稀释至刻度,混匀。吸取此稀释液0.50 mL置于10 mL的比色管中,添加4 mL的乙酸-乙酸钠缓冲液和4 mL的显色剂,以水稀释到刻度,摇晃均匀。再将其放入100 ℃滚烫的水浴缸内,加热15 min后,将其移出冷却到室温。然后用一个10 mm的比色皿,用零管作基准,在400 nm波长处测定样品溶液的吸光度。同时做样本的空白试验,在将样本吸光度扣除样本空白吸光度之后,代入到线性回归方程中,得到稀释液中的氨基酸态氮的含量,最后再按式(6)计算样品的氨基酸态氮含量:
(6) 式中:m1为样品稀释液中氨基酸态氮的含量,g·100 g−1;m为样品的质量,g;V1为吸取稀释液置于比色管中的体积,mL;V2为稀释液的体积,mL。
1.2.5.4 粉末酱油水溶解前后直观图
在室温26.7 ℃下分别称取1.0 g不同粉末酱油溶于99 mL水后置于恒温水浴摇床中振荡0.5 h后拍摄所得。
1.2.5.5 粉末酱油形貌
取适量粉末酱油样品平铺于导电硅胶上,镀金再置于扫描电镜内,1.0 kV 电子束加速电压,分别在 2000、5000、10000放大倍数下观察不同粉末酱油样品表面形貌。
1.3 数据处理
进行3次重复试验,数据取三次重复试验的平均值,用平均值±标准偏差表示,用Origin 7.0软件进行数据处理和作图;利用SPSS 25.0软件进行显著性分析,通过Bonferroni T检验,在95%置信水平下显著(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同因素对羧甲基多孔淀粉制备的影响
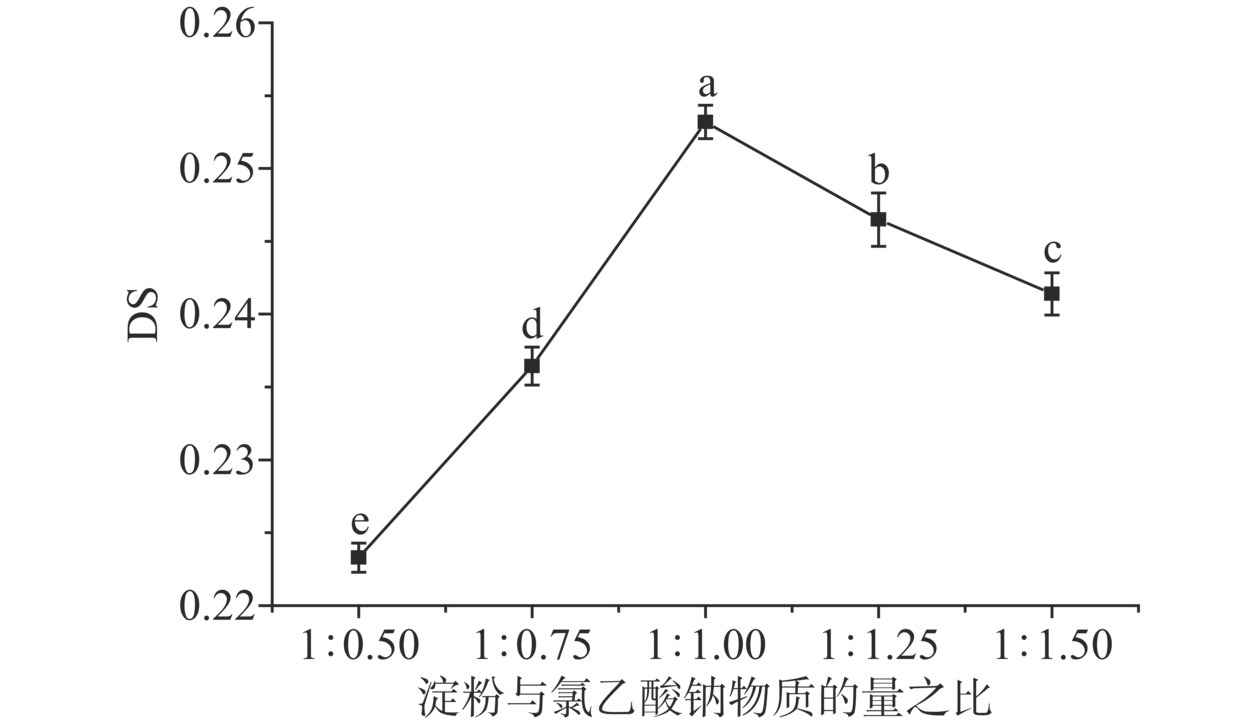
2.1.1 淀粉与氯乙酸钠物质的量之比对取代度的影响
多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠物质的量之比对取代度的影响如图1所示。从图1可以看出,羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS随氯乙酸钠质量分数的增加而增加,在多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠质量分数的比值为1:1时,其DS值为0.2532(P<0.05),而在多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠质量分数的比值大于1:1时,其DS有下降趋势。这可能是由于氯乙酸钠的用量越多,在机械活化时,淀粉与氯乙酸钠发生碰撞的机会越大,使得两者能够更加充分的接触,进而提高了淀粉的醚化反应速率。但随着氯乙酸钠用量的增加,副反应发生的频率也会增加,形成羟基乙酸钠的概率增加[20],从而使得羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS反而降低。
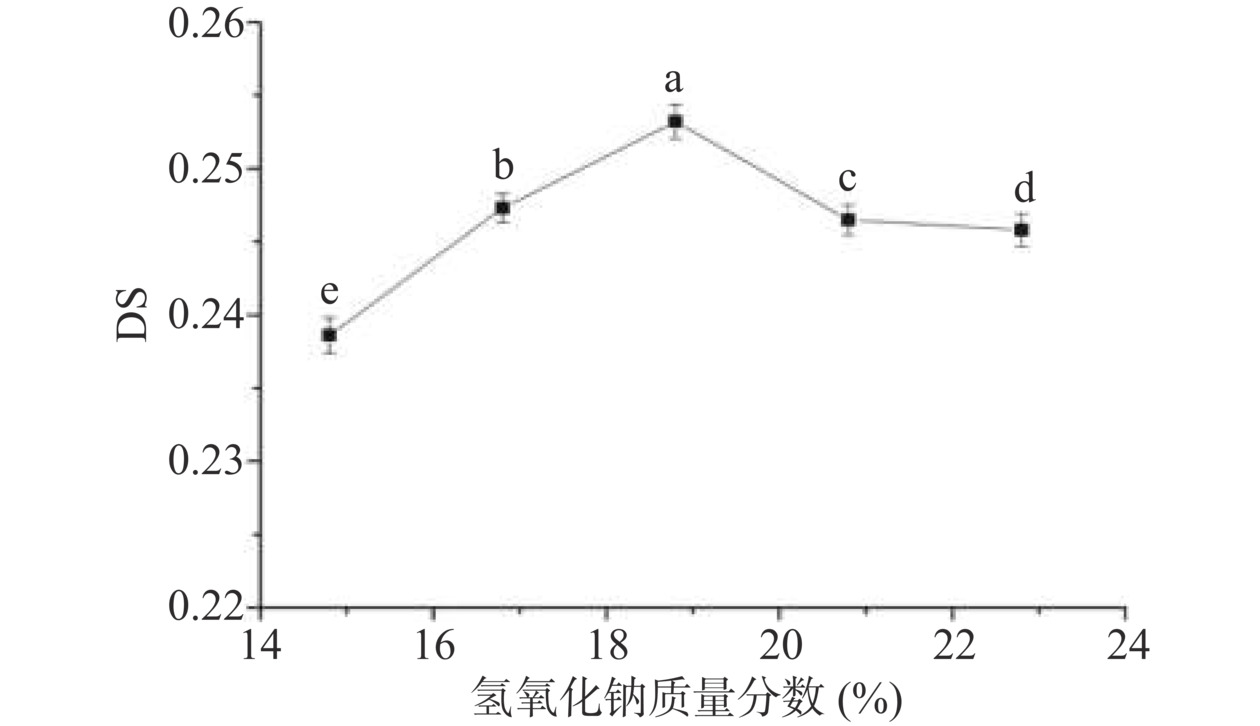
2.1.2 氢氧化钠质量分数对取代度的影响
氢氧化钠质量分数对取代度的影响如图2所示。从图2可以看出,随着NaOH含量的增加,淀粉的DS值呈先升高后降低的趋势。碱能破坏多孔淀粉的结晶结构,并使多孔淀粉上的羟基变成亲核能力较强的负氧离子,进行亲核取代反应[29],但当碱用量超过一定值时,碱会过多中和氯乙酸钠,降低反应效率,从而降低DS。此外,过量的碱还可在其表面生成一层凝胶,将其包覆,阻碍了氯乙酸钠与多孔淀粉有效结合,进而降低了羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS[20]。
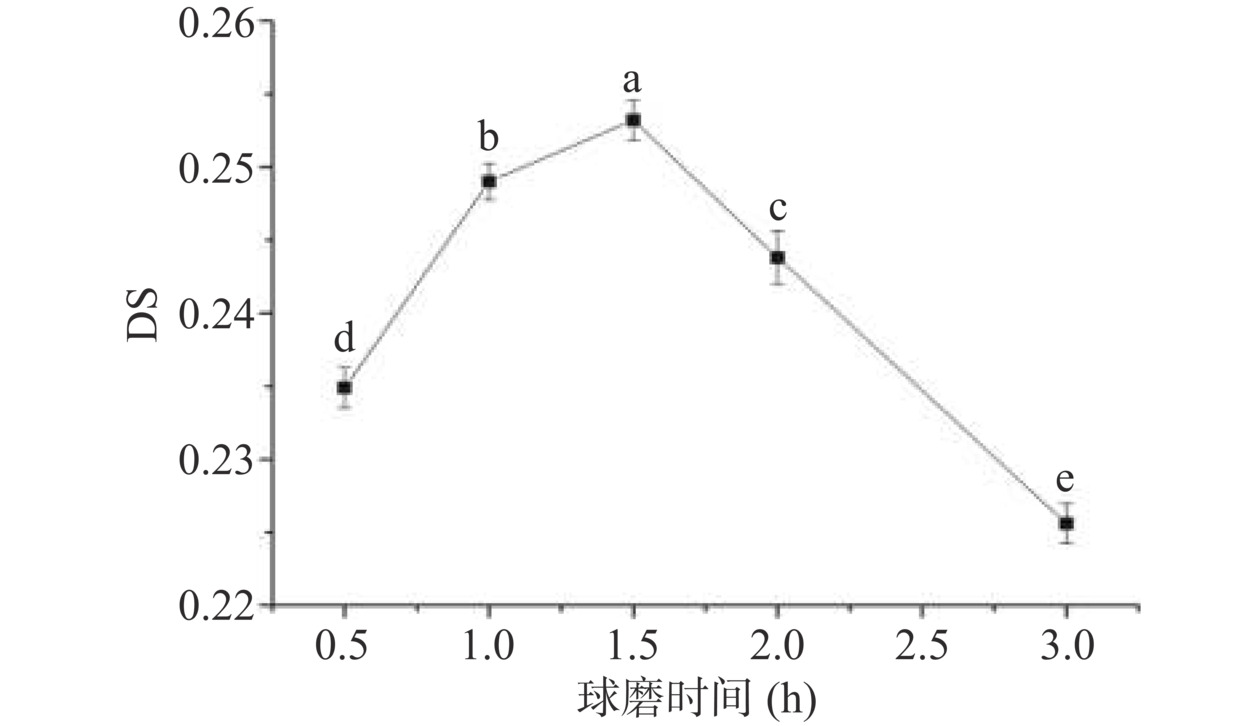
2.1.3 球磨时间对取代度的影响
球磨时间对取代度的影响如图3所示。从图3可以看出,随着球磨时间的增加,羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS表现出了先增加后下降的趋势,由球磨0.5 h时的0.2349增大到球磨时间为1.5 h的0.2532,之后羧甲基多孔淀粉DS随球磨时间的延长出现较大的下降趋势。这可能是球磨时间低于1.5 h,多孔淀粉的晶体结构还没有被机械力充分破坏,多孔淀粉颗粒表面的包裹作用使得醚化剂氯乙酸钠不能渗透到多孔淀粉内部进行反应,导致淀粉DS较低。当反应时间达到1.5 h时,多孔淀粉的致密结晶结构完全被破坏,与氯乙酸钠的接触面增大,有利于醚化试剂的高效渗入。但超过1.5 h,反应时间过长,会使粉碎的淀粉微粒在机械力的作用下再次聚集,这对氯乙酸钠与多孔淀粉微粒的结合不利;此外,随着反应时间的增加,会产生更多的副反应,如氯乙酸钠和氢氧化钠会生成羟乙酸钠等。同时,所得到的羧甲基多孔淀粉在较大的机械压力下,容易发生团聚和变性,导致DS降低[19]。
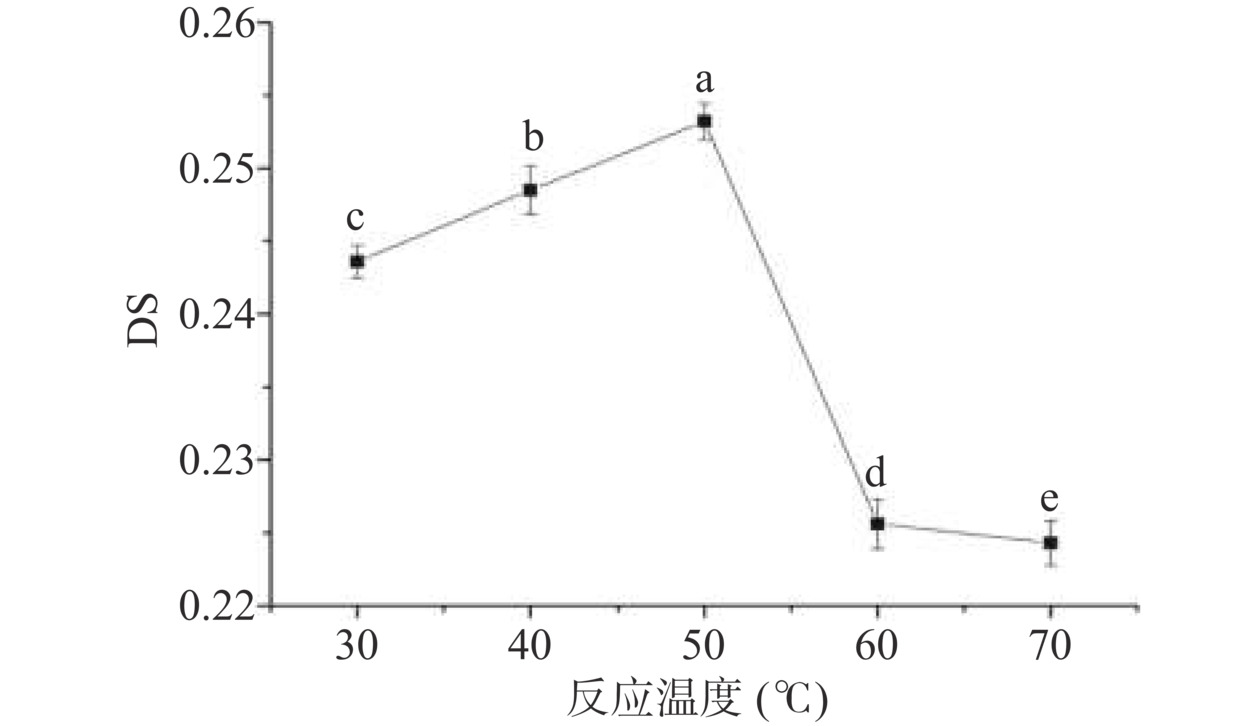
2.1.4 反应温度对取代度的影响
反应温度对取代度的影响如图4所示。从图4可以看出,随着反应温度的升高,羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS先上升后下降。当反应温度为50 ℃时,羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS达到最大值为0.2532;之后随着温度升高,羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS反而大大降低。在一定范围内升高温度,分子热运动速率加快,氢键易于断开,有利于醚化剂与多孔淀粉充分接触,从而可以提升多孔淀粉的反应活性。但温度过高时,多孔淀粉易形成凝胶结块,而较高的温度又会引起副反应,使其DS值降低[30]。
2.2 木薯淀粉、多孔淀粉、羧甲基多孔淀粉的结构表征
2.2.1 SEM分析
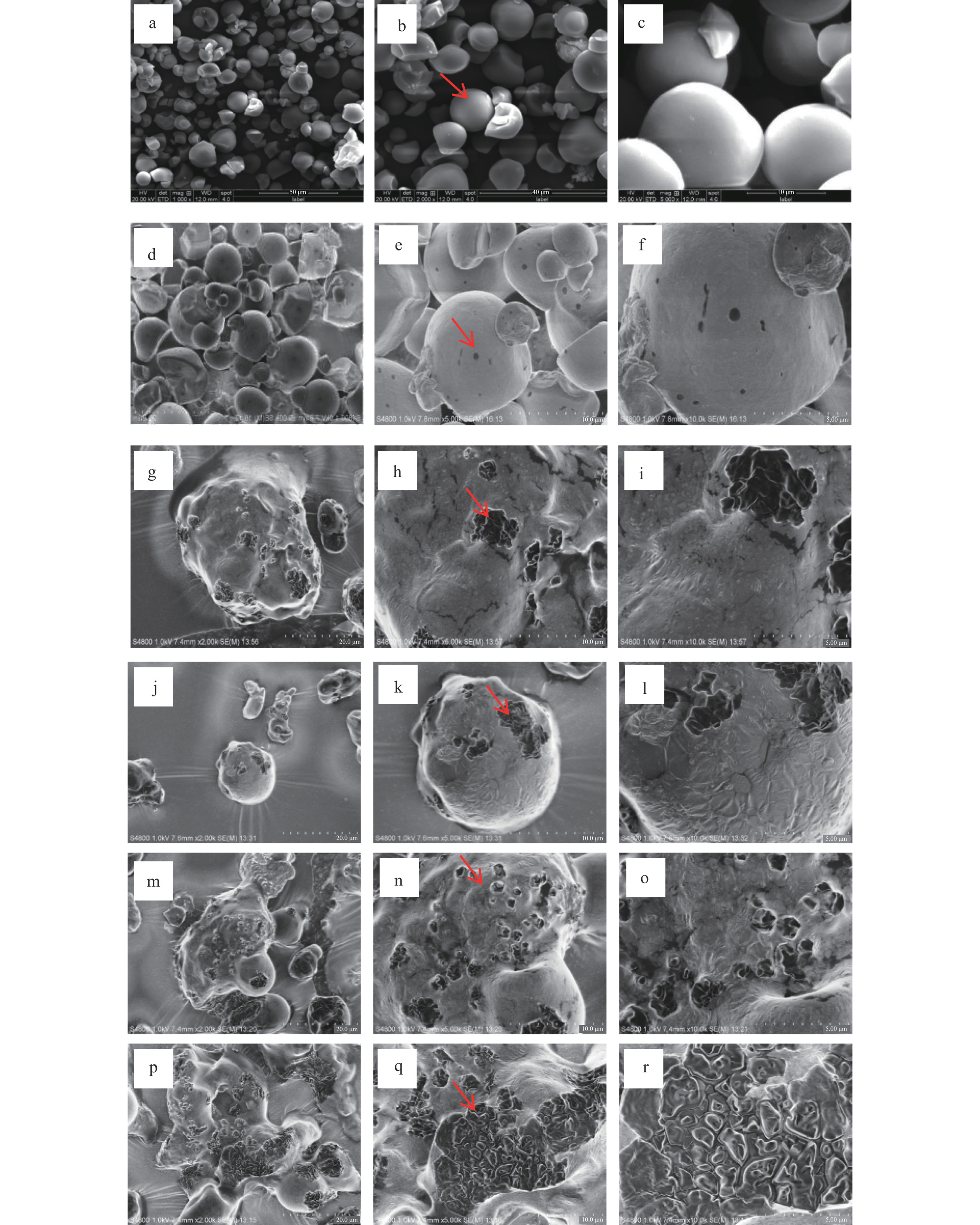
图5为不同淀粉样品的形貌电镜图。从图5a~图5c可以看到,木薯淀粉的颗粒表面光滑圆润,大部分呈球形或椭圆状,少数呈球形不规则裂开的样貌。通过对比图5c、图5f发现,多孔淀粉在木薯淀粉原有的基础上多了零散的圆形孔洞,这说明了酶解法制备多孔淀粉的可行性。对比图5b、图5e、图5h可知,羧甲基多孔淀粉的颗粒形貌与木薯淀粉和多孔淀粉完全不同,在机械球磨的高速搅拌和挤压下,多孔淀粉的球形外表发生形变,孔洞变大数量增多;在机械剪切力的作用下,淀粉分子被分解,分子间氢键被切断,结晶区遭到破坏,表面变粗糙,表明淀粉中存在着醚化现象。对比图5h、图5k、图5n、图5q发现,随着DS的增大,在DS为0.2532时,羧甲基多孔淀粉分子的孔洞数量达到最多,分散的小分子块状随着DS的增大变为不规则的大分子团聚物。这说明醚化反应并不会影响多孔淀粉的孔洞结构,多孔淀粉羧甲基化过程中在机械球磨的作用下受到了挤压,产生了形变。
2.2.2 FTIR分析
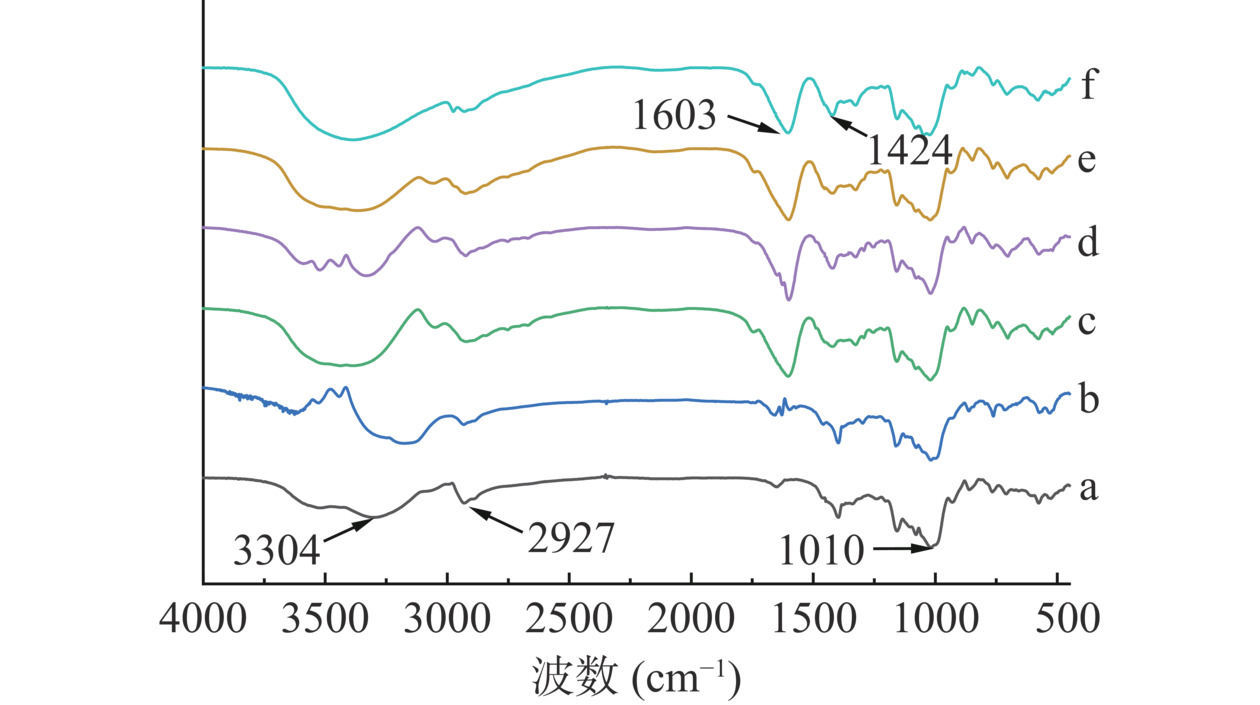
图6为木薯淀粉、多孔淀粉以及通过改变球磨反应时间得到的不同取代度的羧甲基多孔淀粉的红外光谱图。其中a为木薯淀粉(DS=0),b为多孔淀粉(DS=0),c~f是取代度分别为0.2256、0.2349、0.2438、0.2532的羧甲基多孔淀粉。从图6可以看出,经过不同反应时间得到的羧甲基多孔淀粉除了与木薯原淀粉和多孔淀粉的3304、2927、1010 cm−1处波数附近有相同的吸收峰之外,在1603 cm−1处出现了羧酸盐-COO-的不对称伸缩振动强吸收峰,以及在1424 cm−1处出现了羧酸盐-COO-的对称伸缩振动弱吸收峰,表明多孔淀粉成功接上了醚键[19]。
![]() 图 6 不同淀粉的红外光谱图注:a.木薯淀粉;b.多孔淀粉;c.DS=0.2256;d.DS=0.2349;e.DS=0.2438;f.DS=0.2532;图7同。Figure 6. IR spectra of different starch
图 6 不同淀粉的红外光谱图注:a.木薯淀粉;b.多孔淀粉;c.DS=0.2256;d.DS=0.2349;e.DS=0.2438;f.DS=0.2532;图7同。Figure 6. IR spectra of different starch2.2.3 XRD分析
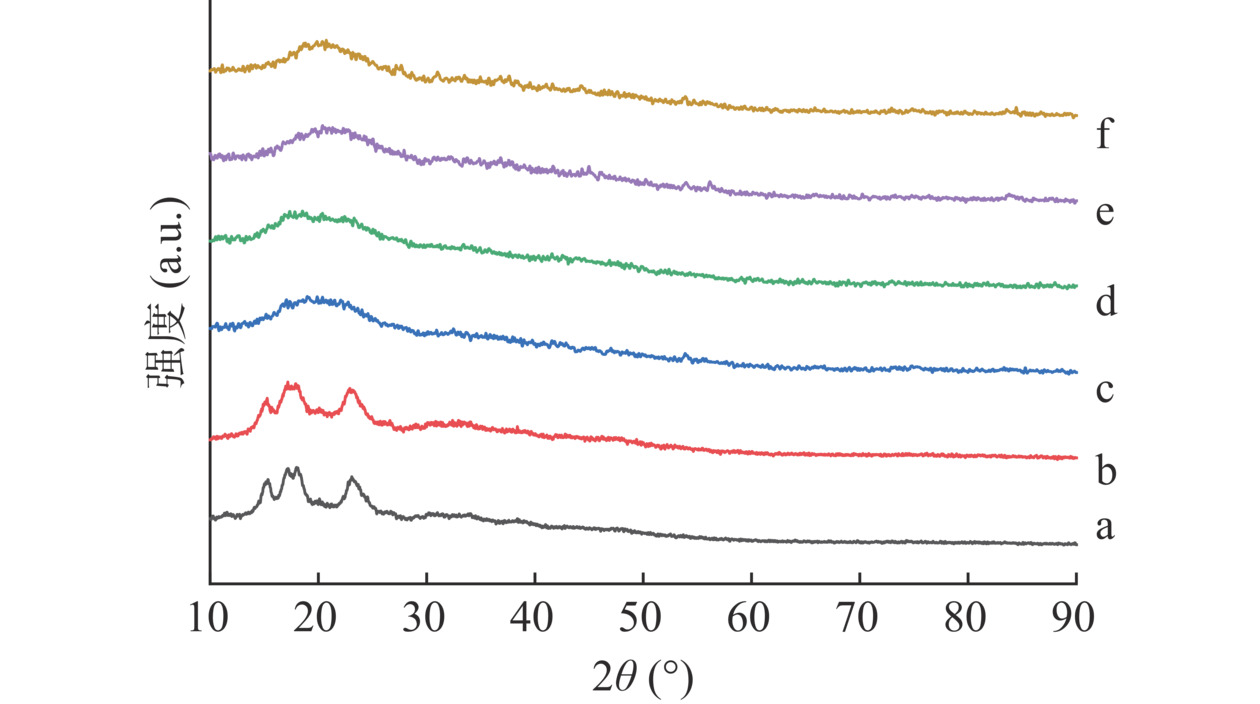
图7为木薯淀粉、多孔淀粉以及通过改变球磨反应时间得到的不同取代度的多孔羧甲基淀粉的XRD图谱。其中a为木薯淀粉(DS=0),b为多孔淀粉(DS=0),c~f是取代度分别为0.2256、0.2349、0.2438、0.2532的羧甲基多孔淀粉。比较图7中的a、b可知,木薯淀粉和多孔淀粉的衍射尖峰的趋势基本一致,证明其仅仅只是物理上的改变实现了多孔,并没有发生化学反应。比较图7中的a、b、c、d、e、f可知,羧甲基多孔淀粉其衍射尖峰样貌与多孔淀粉和木薯淀粉大不相同,由原来的尖峰变为馒头峰,木薯淀粉的尖峰完全消失。这主要是由于机械球磨搅拦过程中的挤压、剪切作用及醚化反应使得多孔淀粉的结晶结构破坏,结晶度大大降低[30]。
2.3 羧甲基多孔淀粉的理化特性分析
表1为木薯淀粉(DS=0)、多孔淀粉(DS=0)以及取代度分别为0.2256、0.2349、0.2438、0.2532的羧甲基多孔淀粉的冷水溶解度、吸水率和柠檬黄吸附量数据。从表1可以看出,羧甲基化处理后,羧甲基多孔淀粉在冷水中的溶解度和吸水率都高于未处理的木薯粉和多孔淀粉,且随取代度的增加呈良好的线性增长趋势。多孔淀粉在经过羧甲基化后其冷水溶解度大大增加,从冷水几乎不溶,到在机械球磨搅拌和羧甲基化的双重作用下冷水溶解度最高能达到64.94%。这是由于在机械球磨的作用下,多孔淀粉的支链结构大部分转变为直链结构,直链淀粉的水溶性要比支链淀粉好很多,并且羧甲基多孔淀粉中的羧甲基基团具有亲水性,是亲水性淀粉,而多孔淀粉疏松多孔的结构也更利于水分子进入淀粉颗粒内部,使得淀粉分子溶出[31]。因此,相比木薯淀粉和多孔淀粉,羧甲基多孔淀粉的溶解度大幅提高。此外,因为多孔淀粉多孔疏松的结构其吸水性能也要比木薯淀粉要好,并且在球磨搅拌活化的作用下改变了多孔淀粉的支链结构,使其更容易吸附水分,再加上羧甲基是一种显负电性的离子基团,它会导致分子之间相互排斥,从而使羧甲基多孔淀粉的分子结构变得松散,增加了接触面积,使羧甲基多孔淀粉的吸水性得到了进一步的提高。表1中还可以看到,淀粉的柠檬黄黄吸附量几乎为零,取代度为0.2532的羧甲基多孔淀粉其柠檬黄吸附性能比多孔淀粉的吸附性能好,对比前面的电镜图可知,这是因为机械球磨活化的过程增加了羧甲基多孔淀粉孔洞的数量和增大了孔洞内径,进一步增强了吸附性能。羧甲基多孔淀粉的溶解度和酒石黄吸附量均优于文献[11]。
表 1 不同DS淀粉样品的冷水溶解度、吸水率和柠檬黄吸附量Table 1. Comparison of cold water solubility, water absorption, and lemon yellow adsorption capacity of different DS starch samples样品 冷水溶解度(%)
(室温26.7 ℃)吸水率(%) 柠檬黄吸附量
(mg·g−1)DS=0(木薯淀粉) 0.56±0.05e 78.46±1.63f 0.0013±0.0004e DS=0(多孔淀粉) 3.23±0.03d 105.34±2.45e 0.5776±0.083d DS=0.2256 42.66±0.11c 162.37±1.38d 1.0420±0.12c DS=0.2349 46.94±0.09c 168.75±4.29c 2.1467±0.35b DS=0.2438 53.46±0.32b 175.46±3.16b 2.3800±0.61b DS=0.2532 64.94±0.13a 180.73±2.18a 2.5086±0.73a 注:所有数值均为三次重复试验的平均值±标准偏差,同一列中不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 2.4 粉末酱油的理化特性分析
表2为木薯淀粉(DS=0)、多孔淀粉(DS=0)以及取代度分别为0.2256、0.2349、0.2438、0.2532的羧甲基多孔淀粉粉末酱油的吸潮率及氨基酸态氮含量数据。从表2可以得知,羧甲基多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油在吸潮性以及氨基酸态氮含量的测定中其性能比木薯淀粉和多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油好。这是因为木薯淀粉分子中的羟基很容易和水分子相互作用生成氢键,从而导致其吸潮性很强,羧甲基多孔淀粉的羧甲基化反应发生的位置则刚好是羟基的位置,发生亲核取代反应将羟基转变为醚键[17],使其吸潮性减弱,更有利于粉末酱油的保存。酱油中的氨基酸态氮的含量多少反映酱油味道的好坏。从表2中可以得知,羧甲基多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油其氨基酸态氮含量比木薯淀粉以及多孔淀粉所制备的粉末酱油高,且随着DS的增大呈现出较为良好的增长趋势。这是因为酱油属于弱酸性溶液,酱油中的氨基酸属于两性物质,在偏酸性环境下表现出带正电荷,而羧甲基多孔淀粉所携带的羧甲基基团表现出带负电荷,阴阳离子基团相互吸引,使得羧甲基多孔淀粉吸附酱油的能力更强。
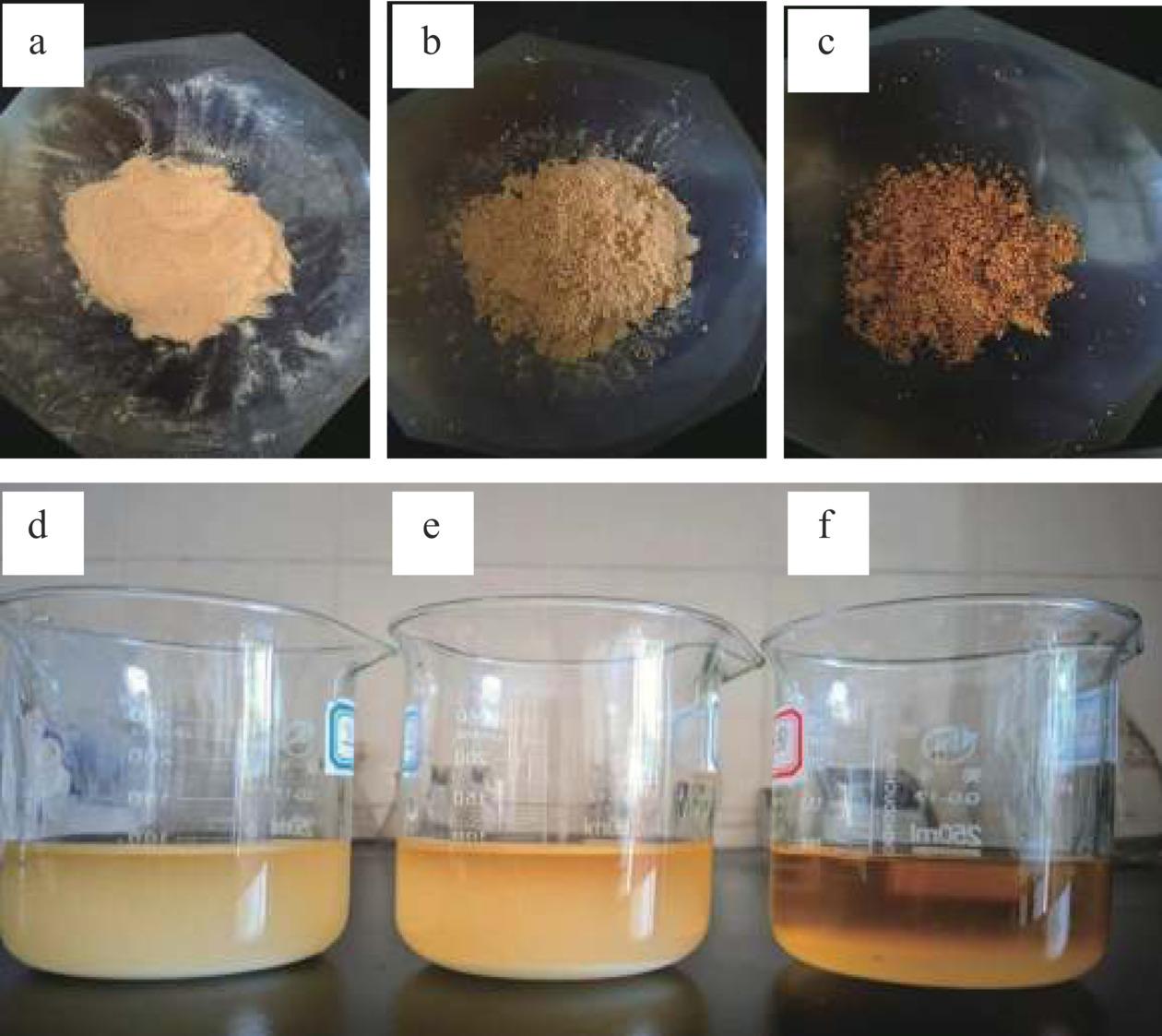
表 2 不同DS样品吸潮率和氨基酸态氮含量Table 2. Moisture absorption and amino acid nitrogen content of different DS samples样品 吸潮率(%) 氨基酸态氮含量(g/100 mL) DS=0(液体酱油) − 0.6248±0.009a DS=0(木薯淀粉酱油) 14.32±0.31a 0.3788±0.013g DS=0(多孔淀粉酱油) 13.76±0.27b 0.4885±0.021f DS=0.2256 10.42±0.82c 0.5133±0.016e DS=0.2349 9.68±0.43d 0.5327±0.032d DS=0.2438 8.54±0.18e 0.5628±0.033c DS=0.2532 7.84±0.92f 0.5876±0.042b 图8为不同淀粉粉末酱油的对比直观图及其溶于水后的直观图。为便于比较,以溶解性最好的羧甲基多孔淀粉粉末酱油(DS=0.2532)进行对比观察。
从图8a~图8c中可以看到,羧甲基多孔淀粉粉末酱油相比于木薯淀粉粉末酱油和多孔淀粉粉末酱油其颜色要更深,说明在同等条件下羧甲基多孔淀粉的吸附酱油的能力更强,所吸附的酱油量更多。观察对比图8d~图8f中烧杯的酱油粉溶液可以看出,羧甲基多孔淀粉粉末酱油相比于其他两者其溶于水后所得的溶液颜色要更加浓郁,更接近酱油的颜色,并且几乎见不到固体颗粒,水溶性更好,这是因为羧甲基多孔淀粉含有带负电荷的官能团(-CH2COO−),从而使其具有更好的水溶性。羧甲基多孔淀粉粉末酱油的氨基酸态氮吸附量和吸潮性均优于文献[2,11],是良好的粉末酱油载体。
2.5 不同粉末酱油的SEM分析
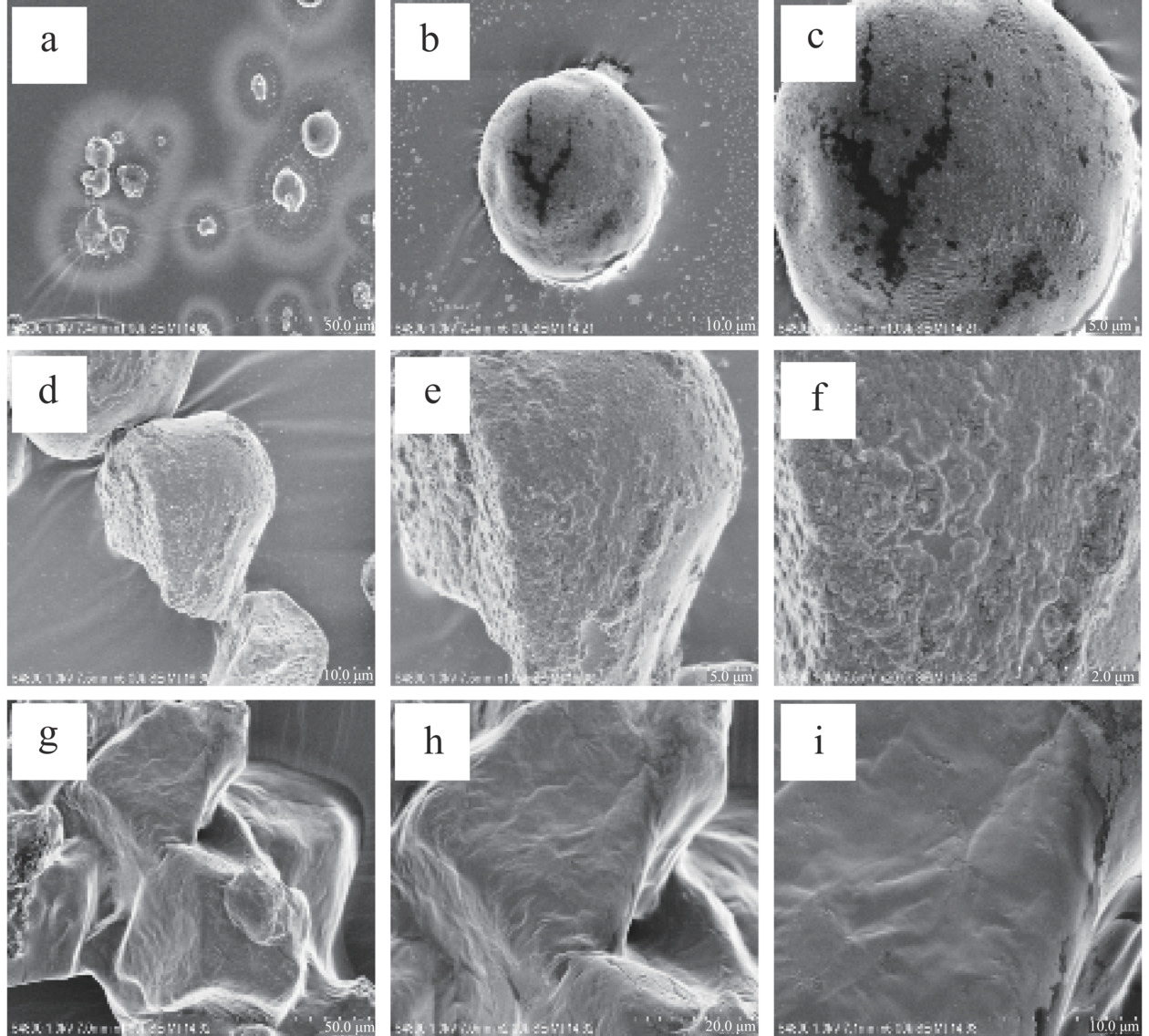
图9为木薯淀粉(DS=0)、多孔淀粉(DS=0)和羧甲基多孔淀粉(DS=0.2532)所制备的粉末酱油样品形貌电镜图。对比图9c、图9f可以看出,多孔淀粉粉末酱油相比于木薯淀粉粉末酱油其吸附在孔中的酱油块更多,这是因为多孔淀粉本身具有的多孔疏松结构,使其具有较好的吸附性,可以吸附更多的酱油。对比图9f、图9i得知,羧甲基多孔淀粉酱油相比于多孔淀粉酱油,其存在的羧甲基亲水基团使其表层能更多地与酱油吸附结合,表面不再粗糙,结合更牢固不易脱落。
3. 结论
本试验采用单因素实验法优化了羧甲基多孔淀粉的工艺参数,最佳制备工艺为:多孔淀粉与氯乙酸钠物质的量之比为1:1、氢氧化钠质量分数为18.8%、球磨时间1.5 h、反应温度50 ℃,在此条件下得到的羧甲基多孔淀粉的DS值为0.2532。随着DS的增加,羧甲基多孔淀粉的冷水溶解度、吸水率和对酒石黄吸附量均有所提高,当DS为0.2532时,冷水溶解度达到64.94%,吸水率达到180.73%,柠檬黄吸附量达到2.5086 mg·g−1。FTIR、XRD、SEM测试结果表明:多孔淀粉经醚化处理后,在1603和1424 cm−1处出现了羧酸盐-COO-的特征吸收峰,结晶度下降,由光滑的球型颗粒变为不规则团聚物。羧甲基多孔淀粉对酱油氨基酸态氮的吸附性增强,吸潮性降低,是粉末酱油的良好载体。后期研究中,需进一步优化羧甲基多孔淀粉生产工艺,提高产品取代度及理化性能,探究结构与性能的构效关系,为羧甲基多孔淀粉的开发应用提供理论基础和数据支持。
-
图 6 不同淀粉的红外光谱图
注:a.木薯淀粉;b.多孔淀粉;c.DS=0.2256;d.DS=0.2349;e.DS=0.2438;f.DS=0.2532;图7同。
Figure 6. IR spectra of different starch
表 1 不同DS淀粉样品的冷水溶解度、吸水率和柠檬黄吸附量
Table 1 Comparison of cold water solubility, water absorption, and lemon yellow adsorption capacity of different DS starch samples
样品 冷水溶解度(%)
(室温26.7 ℃)吸水率(%) 柠檬黄吸附量
(mg·g−1)DS=0(木薯淀粉) 0.56±0.05e 78.46±1.63f 0.0013±0.0004e DS=0(多孔淀粉) 3.23±0.03d 105.34±2.45e 0.5776±0.083d DS=0.2256 42.66±0.11c 162.37±1.38d 1.0420±0.12c DS=0.2349 46.94±0.09c 168.75±4.29c 2.1467±0.35b DS=0.2438 53.46±0.32b 175.46±3.16b 2.3800±0.61b DS=0.2532 64.94±0.13a 180.73±2.18a 2.5086±0.73a 注:所有数值均为三次重复试验的平均值±标准偏差,同一列中不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 不同DS样品吸潮率和氨基酸态氮含量
Table 2 Moisture absorption and amino acid nitrogen content of different DS samples
样品 吸潮率(%) 氨基酸态氮含量(g/100 mL) DS=0(液体酱油) − 0.6248±0.009a DS=0(木薯淀粉酱油) 14.32±0.31a 0.3788±0.013g DS=0(多孔淀粉酱油) 13.76±0.27b 0.4885±0.021f DS=0.2256 10.42±0.82c 0.5133±0.016e DS=0.2349 9.68±0.43d 0.5327±0.032d DS=0.2438 8.54±0.18e 0.5628±0.033c DS=0.2532 7.84±0.92f 0.5876±0.042b -
[1] 陈翠兰, 张本山, 高凌云, 等. 非晶颗粒态淀粉在粉末酱油中的应用[J]. 现代食品科技,2009,25(11):1291−1294. [CHEN C L, ZHANG B S, GAO L Y, et al. Application of non-crystalline gGranular starch (NCGC) in sauce powder production[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2009,25(11):1291−1294.] CHEN C L, ZHANG B S, GAO L Y, et al. Application of non-crystalline gGranular starch (NCGC) in sauce powder production[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2009, 25(11): 1291−1294.
[2] 姚卫蓉, 朱仁宏, 郑书铭, 等. 多孔淀粉在粉末酱油中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2005,36(1):76−78. [YAO W R, ZHU R H, ZHENG S M, et al. Application of porous starch in powder soy sauce[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2005,36(1):76−78.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2005.01.024 YAO W R, ZHU R H, ZHENG S M, et al. Application of porous starch in powder soy sauce[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2005, 36(1): 76−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2005.01.024
[3] ABEDI E, SAYADI M, POURMOHAMMADI K. Effect of freezing-thawing pre-treatment on enzymatic modification of corn and potato starch treated with activated α-amylase:Investigation of functional properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,129:107676−107691. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107676
[4] LATIP D N H, SAMSUDIN H, UTRA U, et al. Modification methods toward the production of porous starch:A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020(3):1−22.
[5] LI D D, TAO Y, SHI Y N, et al. Preparation of porous starch by α-amylase-catalyzed hydrolysis undera moderate electric field[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,137(4):1110449−110456.
[6] LACERDA L D, LEITE D C, SILVEIRA N. Relationships between enzymatic hydrolysis conditions and properties of rice porous starches[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2019,89:102819−102828. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2019.102819
[7] SATHYAN S, NISHA P. Correction:Optimization and characterization of porous starch from corn starch and application studies in emulsion stabilization[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2022,15(9):2100−2101. doi: 10.1007/s11947-022-02875-4
[8] 王宇霞, 马云翔, 苟丽娜, 等. 羧甲基多孔淀粉表征及其对槲皮素吸附研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(20):105−111. [WANG Y X, MA Y X, GOU L N, et al. The characterization of carboxymethyl porous starch and its adsorption on quercetin[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(20):105−111.] WANG Y X, MA Y X, GOU L N, et al. The characterization of carboxymethyl porous starch and its adsorption on quercetin[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(20): 105−111.
[9] CHEN J H, WANG Y X, LIU J, et al. Preparation, characterization, physicochemical property and potential application of porous starch: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,148:1169−1181. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.055
[10] POORESMAEIL M, NAMAZI H. Developments on carboxymethyl starch-based smart systems as promising drug carriers:A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,258:117654−117670. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117654
[11] 朱弘毅, 杜先锋. 三种淀粉载体粉末酱油的性质对比研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(20):284−287. [ZHU H Y, DU X F. Comparison of soy sauce powder produced with three kinds of starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(20):284−287.] ZHU H Y, DU X F. Comparison of soy sauce powder produced with three kinds of starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(20): 284−287.
[12] 张洪微, 崔素萍, 魏文毅, 等. 多孔玉米淀粉制备粉末酱油的研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2009,17(2):54−56. [ZHANG H W, CUI S P, WEI W Y, et al. Study on the preparation of pulverous soy sauce with porous corn starch[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2009,17(2):54−56.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2009.02.019 ZHANG H W, CUI S P, WEI W Y, et al. Study on the preparation of pulverous soy sauce with porous corn starch[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods, 2009, 17(2): 54−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2009.02.019
[13] WANG Y J, XIE Z F, WU Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl starch from cadmium-contaminated rice[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,308:125674−125679. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125674
[14] 王严超. 羧甲基化多孔淀粉乳液凝胶的制备及性质研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2023. [WANG Y C. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated porous starch emulsion gel[D]. Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University, 2023.] WANG Y C. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated porous starch emulsion gel[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2023.
[15] 王宇霞. 羧甲基多孔淀粉的制备、表征及其应用研究[D]. 兰州:甘肃农业大学, 2022. [WANG Y X. Research on preparation, characterization and application of carboxymethyl porous starch[D]. Lanzhou:Gansu Agricultural University, 2022.] WANG Y X. Research on preparation, characterization and application of carboxymethyl porous starch[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2022.
[16] 孙林皓, 曾贞, 周瑶, 等. 一种新型肉桂醛微胶囊的制备及其食品保鲜性能研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2018,37(5):81−88. [SUN L H, ZENG Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Preparation of a novel microcapsule of cinnamaldehyde and its effect on food preservation[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2018,37(5):81−88.] SUN L H, ZENG Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Preparation of a novel microcapsule of cinnamaldehyde and its effect on food preservation[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018, 37(5): 81−88.
[17] 谷绒, 车振明, 马嫄, 等. 羧甲基多孔淀粉的制备及其在粉末酱油中的应用[J]. 粮油加工,2007(11):110−113. [GU R, CHE Z M, MA Y, et al. Preparation of methylated porous starch and its application in powdered soy sauce[J]. Cereals and Oils Processing,2007(11):110−113.] GU R, CHE Z M, MA Y, et al. Preparation of methylated porous starch and its application in powdered soy sauce[J]. Cereals and Oils Processing, 2007(11): 110−113.
[18] 杨家添, 唐金铭, 张亚美, 等. 机械活化辛烯基琥珀酸西米淀粉酯的制备及其乳化性能分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):249−256. [YANG J T, TANG J M, ZHANG Y M, et al. Preparation and emulsification performance analysis of octenyl succnic anhydride modified strach from mechanical activated sago strach[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(13):249−256.] YANG J T, TANG J M, ZHANG Y M, et al. Preparation and emulsification performance analysis of octenyl succnic anhydride modified strach from mechanical activated sago strach[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(13): 249−256.
[19] 陈渊, 廖春萍, 谢秋季, 等. 机械活化固相醚化法制备羧甲基淀粉和羧甲基壳聚糖混合物及其溶解性能[J]. 食品科技,2017,42(9):254−263. [CHEN Y, LIAO C P, XIE Q J, et al. Preparation of the compound of carboxymethyl starch and carboxymethyl chitosan by mechanical activation-strengthened solid phase etherification and its solubility[J]. Food Science and Technology,2017,42(9):254−263.] CHEN Y, LIAO C P, XIE Q J, et al. Preparation of the compound of carboxymethyl starch and carboxymethyl chitosan by mechanical activation-strengthened solid phase etherification and its solubility[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2017, 42(9): 254−263.
[20] 陈渊, 杨家添, 谢秋季, 等. 木薯羧甲基淀粉的机械活化固相化学法制备、表征及其特性[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(2):45−52. [CHEN Y, YANG J T, XIE Q J, et al. Preparation, structural characterization and properties of carboxymethyl cassava starch by mechanical activation-assisted solid-state reaction[J]. Food Science,2018,39(2):45−52.] CHEN Y, YANG J T, XIE Q J, et al. Preparation, structural characterization and properties of carboxymethyl cassava starch by mechanical activation-assisted solid-state reaction[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(2): 45−52.
[21] GAN T, ZHANG Y J, YANG M N, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and application of a multifunctional cellulose derivative as an environmentally friendly corrosion and scale inhibitor in simulated cooling water systems[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(32):10786−10797.
[22] 武赟, 吕真, 杜先锋. 超声波辅助酶解制备多孔淀粉的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2008,34(4):25−30. [WU Y, LÜ Z, DU X F. Ultrasound-assisted technology for producing porous starch by enzyme hydrolysis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2008,34(4):25−30.] WU Y, LÜ Z, DU X F. Ultrasound-assisted technology for producing porous starch by enzyme hydrolysis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2008, 34(4): 25−30.
[23] 朱玉, 郭丽, 杜先锋, 等. 变性多孔淀粉吸附卷烟烟气气相物的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2012,27(8):24−30. [ZHU Y, GUO L, DU X F, et al. Study on modified starches of the adsorption of cigarette smoke vapour phase compounds[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils,2012,27(8):24−30.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2012.08.006 ZHU Y, GUO L, DU X F, et al. Study on modified starches of the adsorption of cigarette smoke vapour phase compounds[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils, 2012, 27(8): 24−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2012.08.006
[24] 谢秋季, 晏全, 杨家添, 等. 机械活化干法制备玉米羧甲基淀粉工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(10):236−241. [XIE Q J, YAN Q, YANG J T, et al. Research on technology of preparing carboxymethyl maize starch by mechanical activation-strengthened dry method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(10):236−241.] XIE Q J, YAN Q, YANG J T, et al. Research on technology of preparing carboxymethyl maize starch by mechanical activation-strengthened dry method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(10): 236−241.
[25] 张友松. 变性淀粉生产与应用手册[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2001:648−655. [ZHANG Y S. Manual of production and application of modified starch[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2001:648−655.] ZHANG Y S. Manual of production and application of modified starch[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2001: 648−655.
[26] 徐阮园. 大米多孔淀粉制备工艺的优化及在卷烟过滤嘴中的应用[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2010. [XU R Y. Garden optimum in process of porous rice starch and its use in cigarette filter tip[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2010.] XU R Y. Garden optimum in process of porous rice starch and its use in cigarette filter tip[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2010.
[27] BELLO-PÉREZ L A, ROMERO-MANILLA R, PAREDES-LÓPEZ O. Preparation and properties of physically modified banana starch prepared by alcoholic-alkaline treatment[J]. Starch/Staerke,2000,52(5):154−159. doi: 10.1002/1521-379X(200006)52:5<154::AID-STAR154>3.0.CO;2-#
[28] 黄金龙. 喷雾干燥制备酱油粉工艺优化及其品质分析研究[D]. 成都:西华大学, 2021. [HUANG J L. Research on process optimization of soy sauce powder using spray drying and its quality analysis[D]. Chengdu:Xihua University, 2021.] HUANG J L. Research on process optimization of soy sauce powder using spray drying and its quality analysis[D]. Chengdu: Xihua University, 2021.
[29] 张春晓, 任洁, 马艳梅, 等. 磁性两性淀粉复合微球的制备及吸附性能研究[J]. 化学工程师,2018,32(10):6−10. [ZHANG C X, REN J, MA Y M, et al. Preparation and adsorption properties of magnetic amphoteric starch composite microspheres[J]. Chemical Engineer,2018,32(10):6−10.] ZHANG C X, REN J, MA Y M, et al. Preparation and adsorption properties of magnetic amphoteric starch composite microspheres[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2018, 32(10): 6−10.
[30] 陈渊, 黎胤宏, 覃峰, 等. 机械活化干法制备新型淀粉基水泥砂浆保水增稠剂[J]. 硅酸盐通,2019,38(4):1237−1244. [CHEN Y, LI Y H, QIN F, et al. Preparation for novel starch-based water-retention and thickening admixture of cement mortar by mechanical activation-strengthened dry method[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2019,38(4):1237−1244.] CHEN Y, LI Y H, QIN F, et al. Preparation for novel starch-based water-retention and thickening admixture of cement mortar by mechanical activation-strengthened dry method[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2019, 38(4): 1237−1244.
[31] CAO F, LU S M, WANG L, et al. Modified porous starch for enhanced properties:Synthesis, characterization and applications[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,415:135765−135775. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135765
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 贾润琪,唐玉杰,何伟炜,宋萧萧,殷军艺. 抗坏血酸在黄原胶体系中的降解动力学. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 151-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



