Anti-obesity Mechanism of Sophora japonica L. through Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
-
摘要: 目的:通过网络药理学结合分子对接对槐花作用于肥胖的机制进行了研究和探讨。方法:使用TCMSP平台对槐花活性成分及靶点进行检索,利用Uniprot数据库对靶点进行校对,收集肥胖疾病相关靶点,使用Venny2.1构建槐花靶点和肥胖靶点交集图。通过String12.0对槐花和肥胖交集靶点进行蛋白质相互作用网络分析(PPI),并采用Cytoscape3.7.2绘制槐花-肥胖靶点PPI网络图。在Metascape平台对槐花关键活性成分和肥胖疾病的靶点进行GO及KEGG通路富集分析,使用AutoDockTools1.5.7和PyMOL2.1.1对筛选出的靶点进行分子对接和可视化处理。结果:槐花具有70个能够作用于肥胖疾病的相关靶点,主要活性成分包括槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素、β-谷甾醇,核心靶点涉及AKT1、IL6、PPARG等。GO富集分析显示,槐花活性成分通过对有机氮化合物、对脂质及脂多糖反应等生物过程发挥抗肥胖作用。KEGG通路分析得到脂质和动脉粥样硬化、AGE-RAGE、HIF-1、IL-17等多条信号通路具有抗肥胖作用。分子对接结果表明槐花核心活性成分和对应靶点对接结果良好。结论:本研究表明槐花通过多靶点、多成分、多通路发挥抗肥胖作用,并为进一步研究槐花有效成分和分子作用机制提供理论依据和方法。Abstract: Objective: The mechanism of action of Sophora japonica L. on obesity was studied and investigated by network pharmacology combined with molecular docking. Methods: The active ingredients and targets of Sophora japonica L. were searched using the TCMSP platform, and the targets were calibrated using the Uniprot database to collect targets related to obesity diseases, and the intersection map of Sophora japonica L. targets and obesity targets was constructed using Venny2.1. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis was performed on the intersection targets of Sophora japonica L. and obesity by String12.0, and the PPI network map of Sophora japonica L.-obesity targets was drawn using Cytoscape3.7.2. GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of key active components of Sophora japonica L. and obesity disease targets were performed on the Metascape platform, and molecular docking and visualisation of the screened targets were performed using AutoDockTools1.5.7 and PyMOL2.1.1. Results: Sophora japonica L. had 70 relevant targets capable of acting on obesity diseases, and the major active components included quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, β-sitosterol, and the core targets included AKT1, IL6, PPARG, and so on. GO enrichment analysis showed that the active components of Sophora japonica have anti-obesity effects on biological processes such as organic nitrogen compounds, and the response to lipids and lipopolysaccharides and so on. KEGG pathway analysis revealed the results of lipid and atherosclerosis, AGE-RAGE, and atherosclerosis. sclerosis, AGE-RAGE, HIF-1, IL-17, and many other signalling pathways with anti-obesity effects. The molecular docking results showed that the core active components of Sophora japonica L. and the corresponding targets docked well. Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that Sophora japonica L. exerted its anti-obesity effects through multiple targets, components, and pathways, which would provide a theoretical basis and methodology for further research on the effective components and molecular mechanisms of Sophora japonica L..
-
Keywords:
- Sophora japonica L. /
- key active ingredients /
- obesity /
- network pharmacology /
- molecular docking
-
肥胖目前是影响人类健康的公共卫生问题,随着饮食结构、生活方式等的改变,全球肥胖患病群体日益庞大,随之诱发的糖尿病、高血压、心脑血管疾病、癌症等多种疾病严重威胁人类健康。2020年中国成年居民超重率和肥胖率分别为34.3%和16.4%,超重肥胖超50%[1]。当前批准使用的减肥药中,如奥利司他通过选择性地抑制胃脂肪酶和胰脂肪酶,从而减少脂肪的吸收。但同时也会产生脂溶性维生素吸收降低和消化道症状(如腹胀、腹泻)的不良反应[2]。芬特明是一种口服药物,可抑制食欲,据报道其副作用为高血压、头晕和烦躁不安[3]。上述治疗方案对于肥胖患者的临床效果收益十分有限。通过天然产物来研究抗肥胖机制已经成为当前的研究热点,有研究发现辣木叶[4]和沙棘[5]具有抗肥胖作用,但目前对于槐花的抗肥胖作用研究甚少。
2021年国家卫健委发布了《按照传统既是食品又是中药材的物质目录管理规定》[6]。在目录中包括了槐花、栀子、砂仁、胖大海、茯苓等87个,既是食品又是药品的物品名单。其中的槐花始载于五代吴越国日华子(大明)所撰的《日华子本草》,是豆科植物槐的花蕾,味苦、性微寒[7]。槐花的成熟果实先前被证明含有抗脂肪作用的化合物[8],并且Park等[9]研究发现给小鼠喂有槐花成分的饲料可以防止高脂肪饮食引起的体重增加,并改善肥胖引起的脂质含量和血糖水平升高。
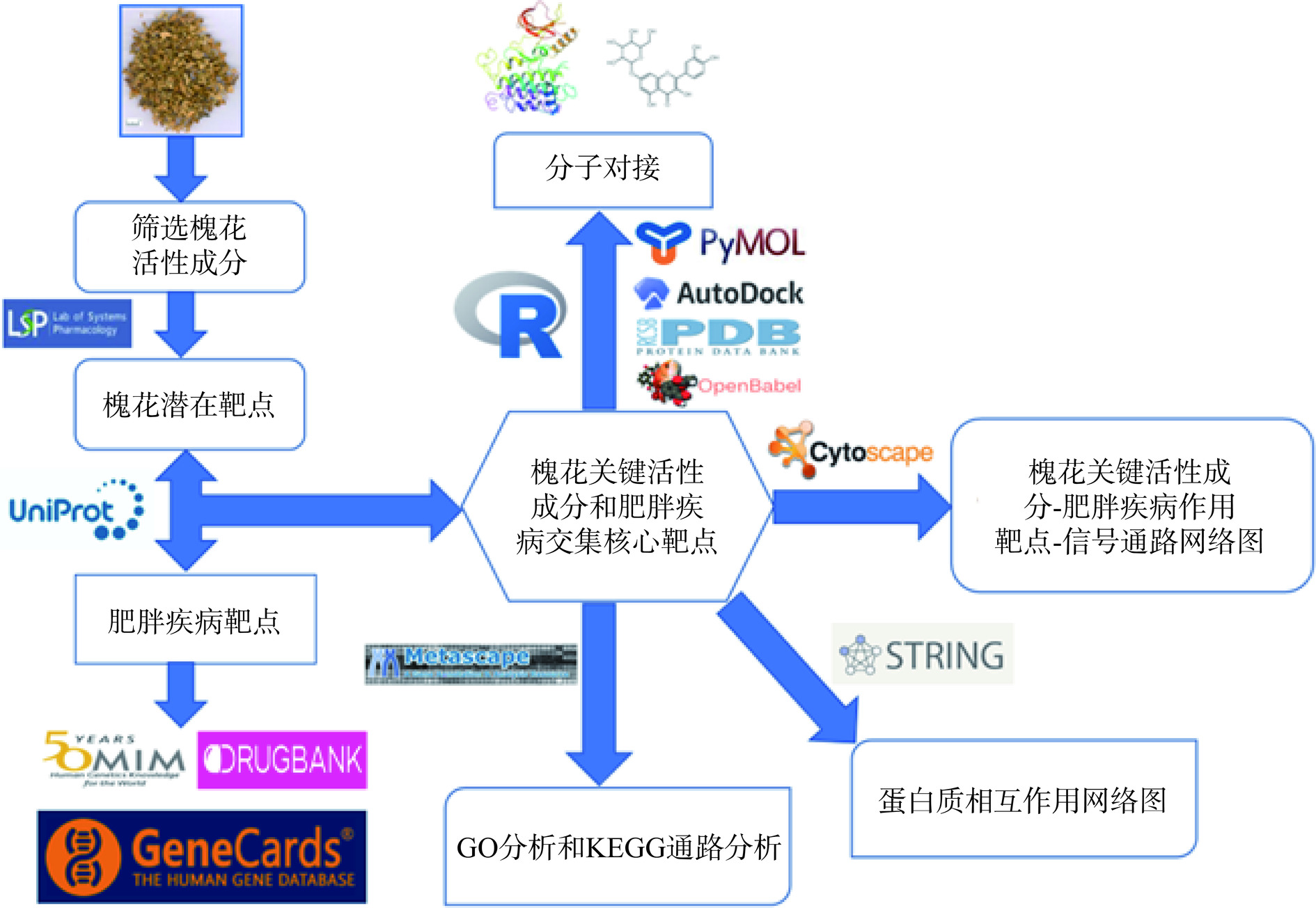
目前研究槐花提取物的主要方法是通过小鼠实验、细胞实验来证明其作用效果与机理。但由于槐花提取物中活性物质成分较多,抵抗肥胖作用途径多样,相关靶点繁杂,致使槐花提取物对肥胖疾病干预作用体内相关研究的实验量较大,因此其机制目前还尚不明确。可见如何较为简便且科学系统地研究槐花发挥抗肥胖作用正是亟待解决的问题。网络药理学是一门在生物网络背景下研究疾病机制和药物作用机制的新技术,目标是在多个层面上以系统的方式解释科学难题[10]。网络药理学集成了医学、系统生物学、计算机科学、生物信息学等多领域的技术,通过广泛应用网络数据库资源,阐释药物如何调控基因表达,对药物的作用靶点进行预测。通过构建多层次的“疾病—靶点—信号通路—药物”互作网络,从微观药理学的角度解释药物多途径、多靶点治疗疾病的机制。本研究通过网络药理学并结合分子对接技术,利用GO功能注释、KEGG通路富集分析等方法对槐花中生物活性物质如何干预肥胖疾病进行探讨。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据库及软件
TCMSP(https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php)、OMIM(https://www.omim.org/)、GeneCard(https://www.genecards.org/)、DrugBank(https://go.drugbank.com/)、Uniprot(https://www.uniprot.org/)、RCSB PDB(https://www.rcsb.org/)、MetaScape(https://metascape.org/gp/index.html#/main/step1)和STRING 12.0(https://cn.string-db.org/);软件有OpenBabel 3.1.1、Cytoscape 3.7.2、AutoDockTools 1.5.7、R 4.3.2和PyMOL 2.1.1。
1.2 槐花主要成分的筛选
从中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)数据库中搜集槐花的所有活性成分,口服生物利用度(Oral bioavailability,OB)是指制剂中药物被吸收进入人体循环的速率与程度。药物相似性(Drug-likeness,DL)指化合物与已知药物的相似性及评估化合物作为药物的潜力。根据Liu等[11]研究,活性成分应以其“OB>30%和DL≥0.18”作为筛选依据,对槐花活性成分进行筛选。然后基于TCMSP数据库,将主要活性成分和潜在靶点配对,在Uniprot数据库中以“homo sapiens”物种为条件筛选出每个活性成分对应的靶点,即为槐花的主要成分预测靶点。
1.3 肥胖相关靶点的筛选
利用肥胖(Obesity)为关键词,在OMIM数据库、GeneCards数据库、DrugBank数据库疾病基因数据库分别进行检索与筛选,将得到的靶点汇总并去除重复值,再根据文献报道补充未预测到的有效成分的已知靶点,最后利用Uniprot数据库将所得靶点进行标准化处理。
1.4 蛋白质相互作用(Protein Protein Interaction,PPI)网络构建及关键靶点筛选
为了解槐花相关靶点与肥胖疾病靶点间的相互作用关系,利用Venny 2.1绘制二者靶点交集图。将得到的交集靶点上传至STRING12.0(Search tool for the retrieval of interaction genes/proteins)数据库中[12],选择生物种类为智人获取蛋白相互作用关系,并下载文件为.TSV的格式,将其导入Cytoscape3.7.2中构建PPI网络图,并且利用Cytoscape3.7.2软件中的CytoNCA插件对PPI网络进一步进行拓扑分析,筛选出PPI网络图中的核心靶点。
1.5 槐花成分与肥胖疾病靶点GO功能分析和KEGG通路分析
利用Metascape平台[13]对作用靶点进行生物信息富集分析,包括基因本体论(GO)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)进行富集分析,其中GO分析包括生物过程(biological process,BP)、分子功能(molecular function,MF)和细胞成分(cellular component,CC)。对GO和KEGG的分析结果分别按照P值从小到大的顺序排列,且把P的临界值设置为0.01,选取符合条件且相关的前20条结果。
1.6 槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路网络图的构建
槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路网络图主要通过软件Cytoscape3.7.2来绘制,其中用“节点”(Node)来表示槐花成分或槐花、肥胖疾病靶点,用“边”(Edge)来表示两个节点之间的关系,使用Cytoscape中Tools的Network Analyzer工具来对整体的网络图进行分析,其中参数包括连接度(Degree)、度中心性(Degree Centrality)、介数中心性(Betweenness Centrality)及接近中心性(Closeness Centrality)等,用来分析槐花中关键活性成分和肥胖疾病靶点之间的作用关系。
1.7 分子对接模拟
在上述构建的槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路网络图中,按照Degree值高低进行排序,筛选出数值排序为前四的活性成分,在PPI网络图中筛选Degree值为前五的靶点。从TCMSP和RCSB PDB数据库中获取活性成分和关键靶点的分子结构,通过Autodock对配体受体进行预处理后开始分子对接,之后取能量最低的结果通过PyMOL对结合位点进行可视化分析和绘图。将槐花主要活性成分和核心靶点的对接结合能结果汇总并使用R语言进行热图的绘制。
1.8 操作流程
本研究的具体分析流程图如图1所示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 槐花活性成分及其靶点筛选
从TCMSP数据库中获取槐花的活性成分见表1。通过设定OB≥30%且DL≥0.18为条件筛选后,最终纳入共活性成分6个。为了方便研究,6个共活性成分标记为“HH1-HH6”。将6种活性成分导入TCMSP中收集对应的靶点,并用UniProt数据库校准靶点名称,去除重复及无效值后得到193个槐花的主要活性成分靶点。
表 1 槐花的关键活性成分信息Table 1. Information of key active ingredients of locust flower编号 MOL ID 英文名 中文名称 OB DL HH1 MOL000354 isorhamnetin 异鼠李素 49.6 0.31 HH2 MOL000358 beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 HH3 MOL000422 kaempferol 山奈酚 41.88 0.24 HH4 MOL005935 N-[6-(acridin-9-ylamino)hexyl]benzamide N-[6-(乙喹啉-9-基)己基]苯甲酰胺 41.7 0.78 HH5 MOL005940 quercetin-3'-methyl ether 槲皮素-3'-甲基醚 46.44 0.3 HH6 MOL000098 quercetin 槲皮素 46.43 0.28 2.2 肥胖疾病相关作用靶点的收集与韦恩图的构建
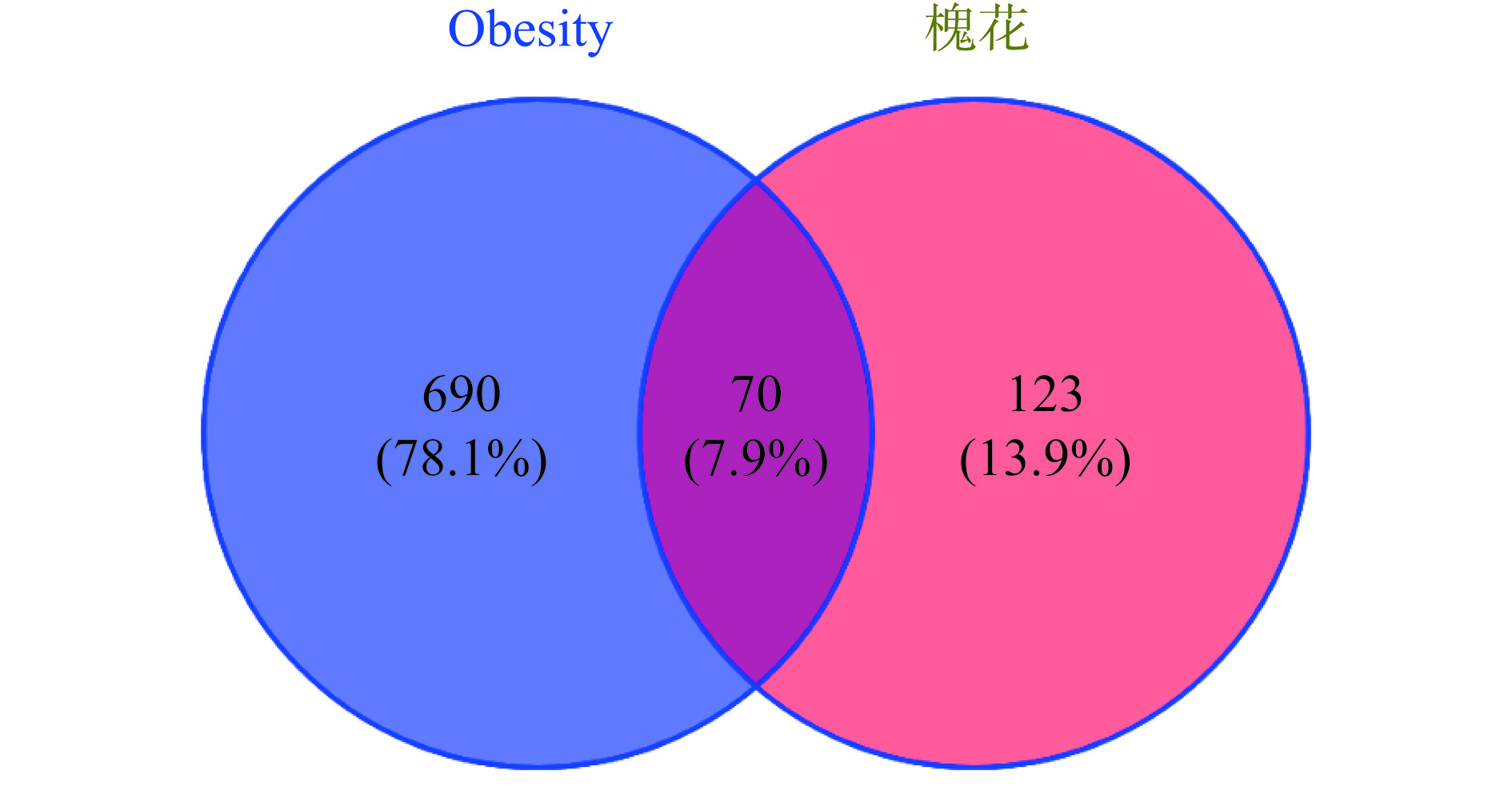
通过OMIM数据库、GeneCards数据库、DrugBank数据库,以肥胖(Obesity)为关键词,分别检索肥胖的靶点,并将三个数据库得到的靶点合并去重后,共得到760个靶点,与2.1中槐花活性成分相关的193个靶点共同导入Venny2.1.0中进行分析绘制韦恩图,共获得70个交集靶点(见图2),即为槐花对肥胖作用的潜在作用靶点。
2.3 槐花关键活性成分和肥胖疾病潜在交集靶点蛋白质相互作用网络(PPI)的构建
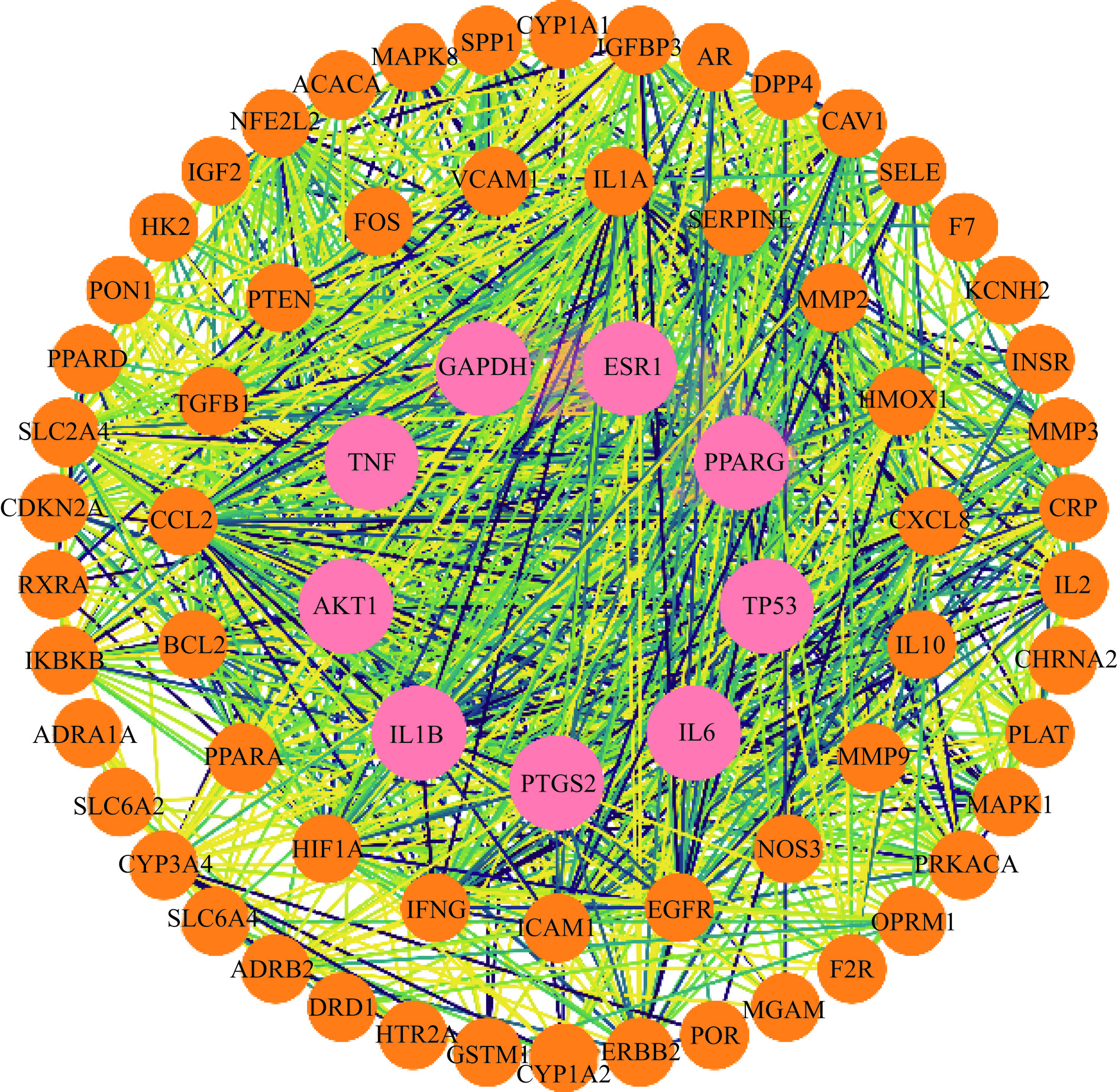
将得到的70个交集靶点数据提交至STRING 12.0数据库并进行PPI网络分析,目的筛选交集靶点中处于关键位置节点的靶点。将分析结果保存为“.TSV”格式文件,将此文件导入Cytoscape 3.7.2中重新构建靶蛋白PPI网络(见图3)。图3中的线代表蛋白之间的相互作用关系,圆形代表靶点,其中有70个节点,拥有1128条相互作用边,平均节点度为32.2。由图3可知,槐花关键活性成分作用于肥胖疾病的绝大多数靶点均具有一至多条的网络互作关系,说明槐花中关键活性成分干预肥胖的途径具有多样性和复杂性且各途径存在一定的关联性,并根据度值(Degree)结果筛选出核心靶点。
2.4 GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析
2.4.1 GO通路富集分析
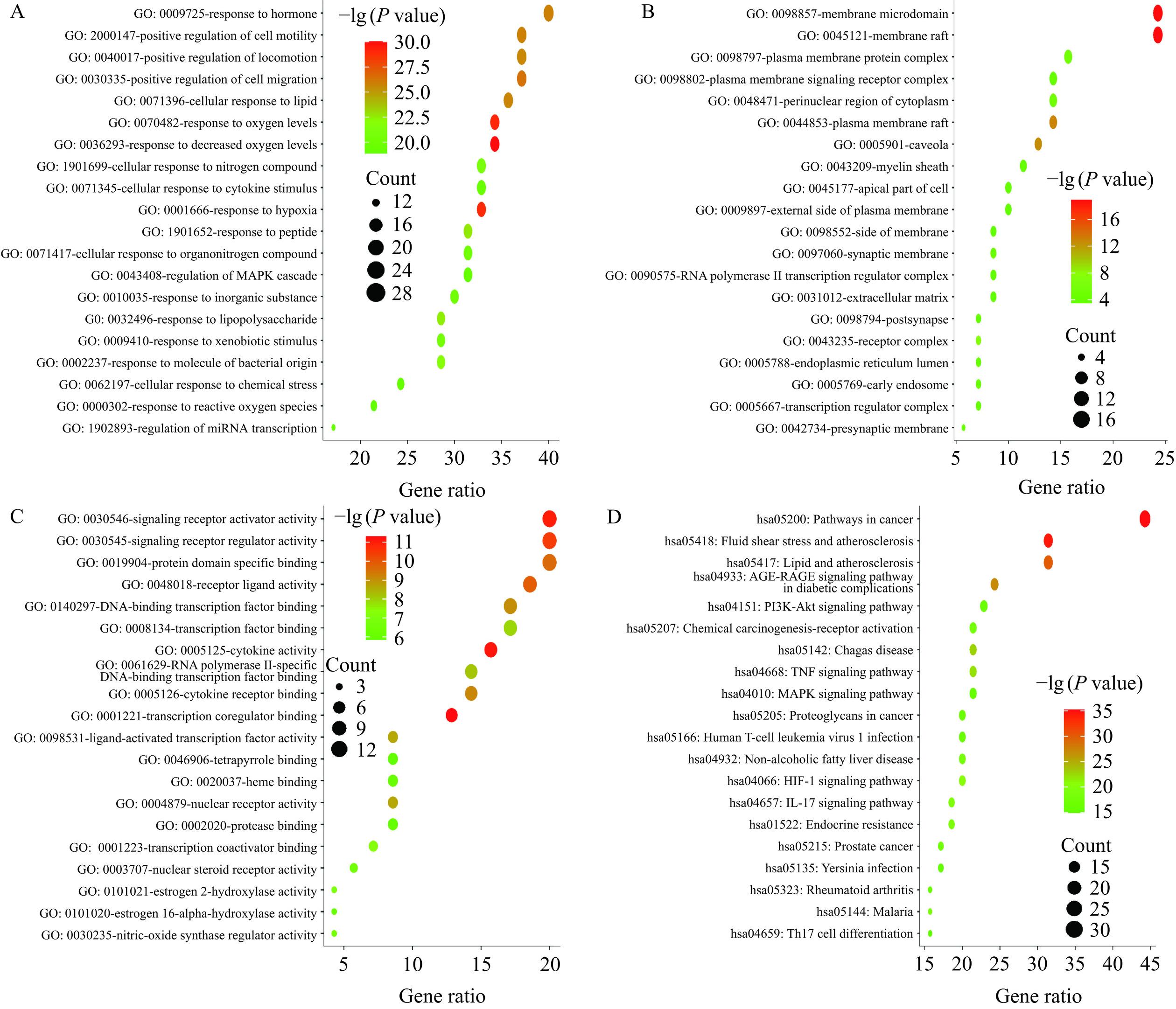
利用Metascape平台,设置P<0.01作为筛选条件,将交集靶点进行GO的生物过程(BP)、分子功能(MF)和细胞组分(CC)分析,总共富集到1437个条目,其中1284项BP,99项MF,54项CC,根据lgP筛选出排名前20的条目,并利用微生信绘制柱状图(见图4A~图4C)。其中,交集靶点主要分布在膜微区(membrane microdomain)、膜筏(membrane raft)、细胞质膜(plasma membrane)等细胞成分中,通过信号受体激活(signaling receptor activator activity)、蛋白质结构域特异性结合(protein domain specific binding)、DNA结合转录因子(DNA-binding transcription factor binding)等方式参与细胞对有机氮化合物(cellular response to organonitrogen compound)、脂质(cellular response to lipid)、脂多糖(response to lipopolysaccharide)及激素的反应(response to hormone)等生物进程,从而起到抗肥胖作用。
2.4.2 KEGG通路富集分析
利用Metascape平台,设置P<0.01作为筛选条件,将交集靶点进行KEGG分析,共得到204条信号通路,根据lgP筛选出排名前20条目,并利用微生信绘气泡图(见图4D)。主要涉及癌症通路(Pathways in cancer)、脂质和动脉粥样硬化(Lipid and atherosclerosis)、糖尿病并发症中的高级糖基化终末产物-受体信号通路(AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications)、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)、HIF-1(HIF-1 signaling pathway)、IL-17(IL-17 signaling pathway)等信号通路。
2.5 槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路网络图的构建
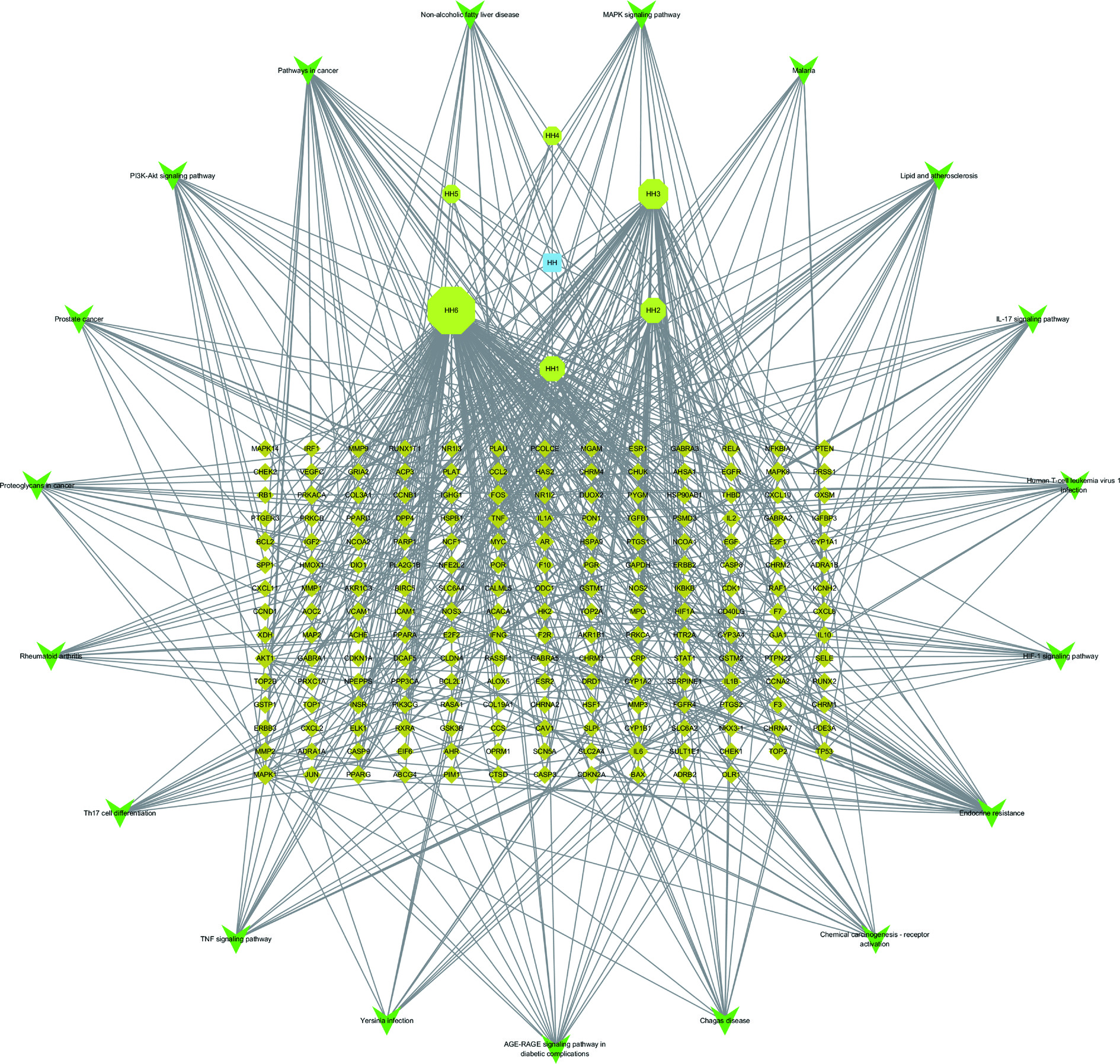
为进一步探究槐花防治肥胖作用机制中活性成分、作用靶点与信号通路之间的相互作用关系,将槐花关键活性成分、肥胖疾病作用靶点和信号通路运用Cytoscape3.7.2软件构建“槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路”网络图(见图5),图5中共有219个节点,610条边。其中结点表示槐花/肥胖疾病靶点或成分,直线表示两个结点的相互作用关系,图中黄色正八边形表示槐花关键活性成分,棕色菱形表示肥胖疾病作用靶点,绿色三角形表示信号通路,利用图中连线密集程度表示各节点之间的互作关系和强度。通过内置的Network Analyzer插件,对网络拓扑学参数进行分析。结果显示,槐花活性成分HH6(槲皮素)度值为155,介度为0.713,紧密度为0.668;HH3(山奈酚)的度值分别为64,介度为0.139,紧密度为0.432;HH2(异鼠李素)度值为39,介度为0.138,紧密度为0.393;HH1(β-谷甾醇)度值为38,介度为0.118,紧密度为0.386。这表明在治疗肥胖的过程中,这四种活性成分发挥了重要作用。20条信号通路富集到53个靶基因,其中AKT1、MAKP1、IL6、FOS、TNF、MAPK8、IKBKB、IL1B、TGFB1等关键靶点与成分之间存在重复多次作用于多条信号通路的情况,因此,槐花活性成分可能通过多靶点调节细胞间信号转导、增殖、分化、代谢及特异性结合等信号表达对防治肥胖发挥重要作用。以上这些数据表明了槐花是通过多成分、多靶点、多通路来充分发挥抗肥胖疾病的作用。
2.6 分子对接分析
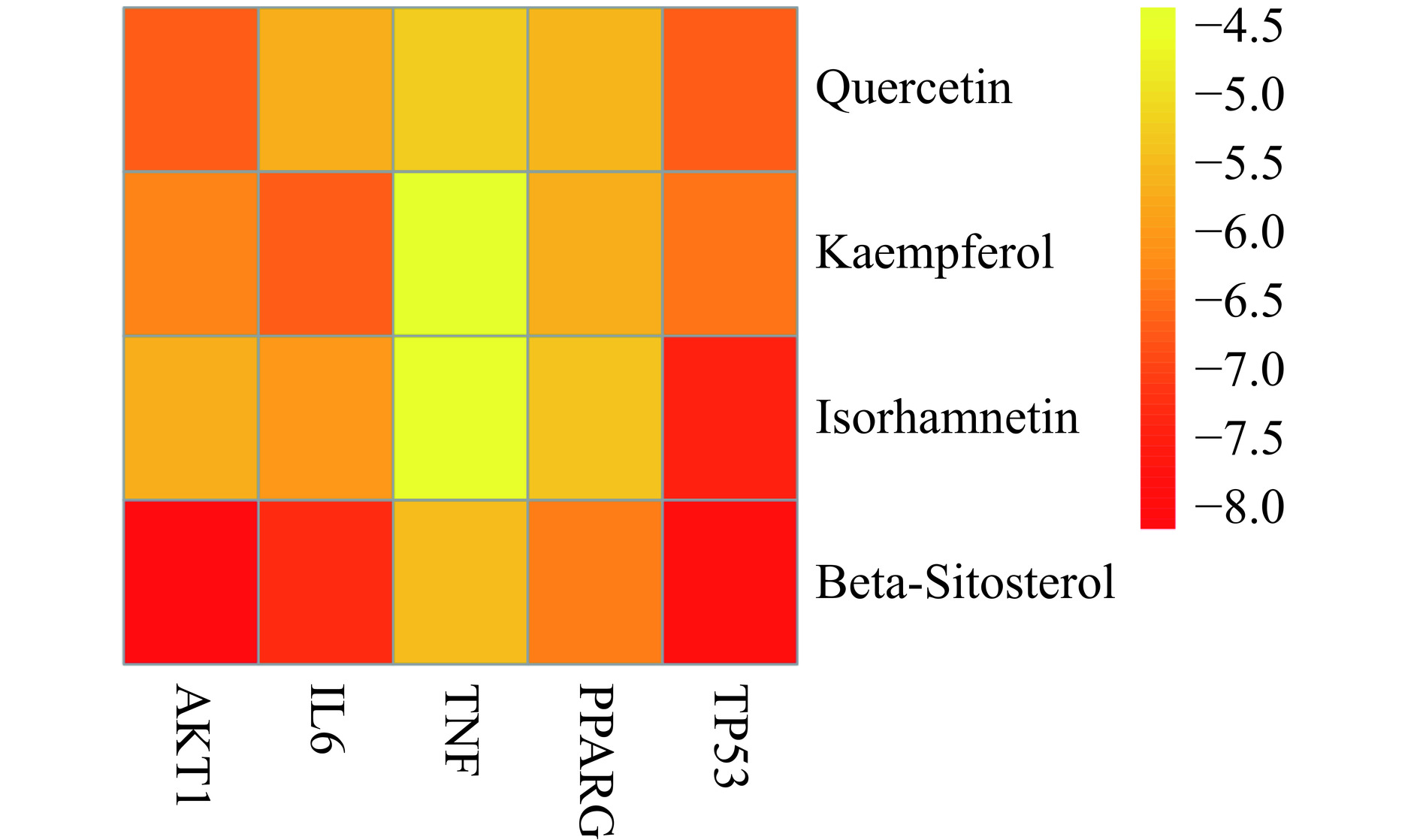
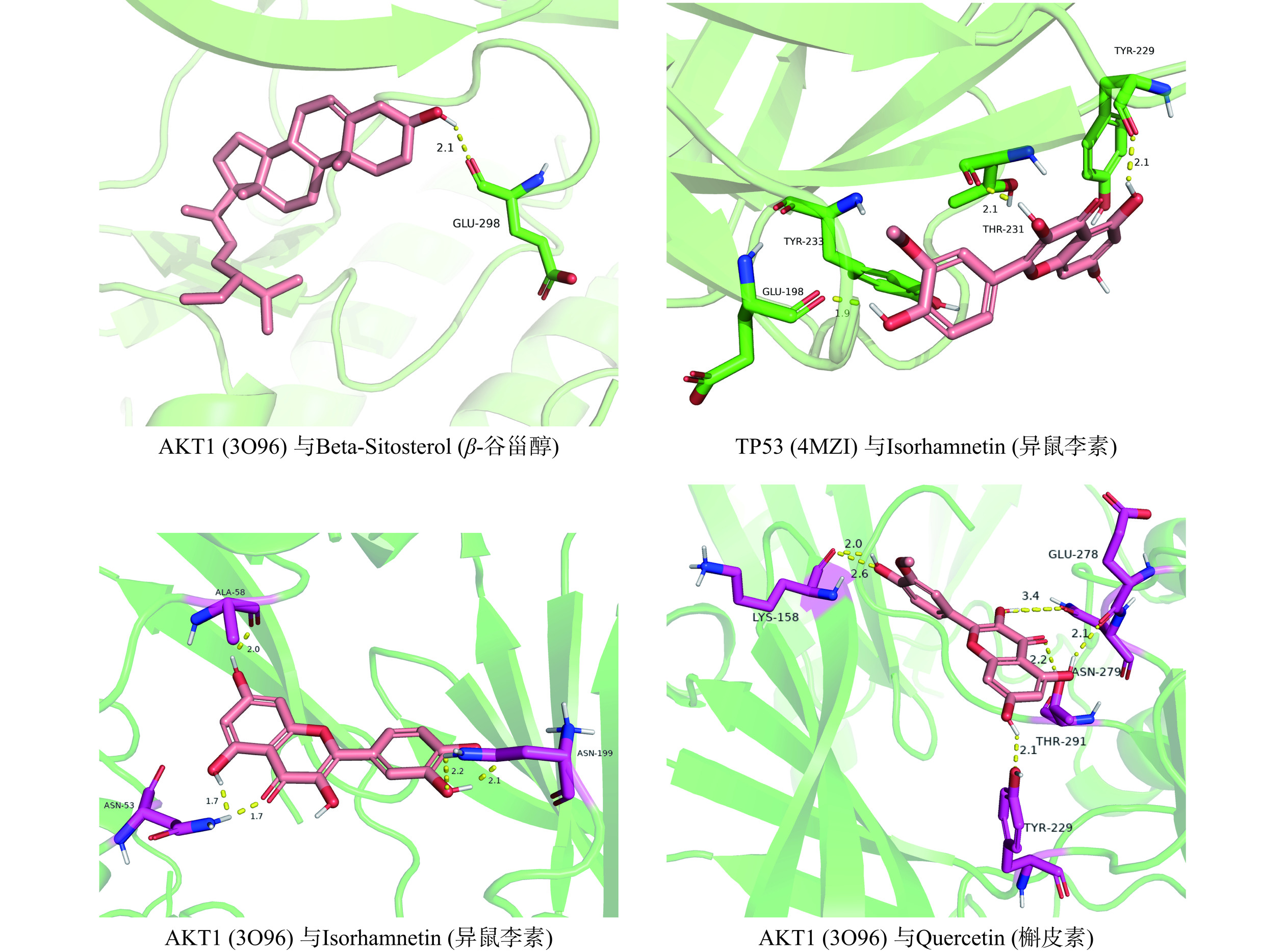
在2.5构建的槐花活性成分-靶点-信号通路网络中,按照Degree值进行排序,筛选出前四的成分,分别为槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素、β-谷甾醇4个活性成分,筛选出的靶点为AKT1、IL6、TNF、PPARG、TP53。分别从TCMSP和RCSB PDB[14]数据库中获取活性成分和关键靶点的分子结构,通过Autodock 4.2.6[15]对配体受体进行预处理后开始分子对接,之后取能量绝对值最大的结果,通常认为结合能小于−5.0 kJ/mol则为对接结果良好,小于0 kJ/mol则认为可以在自然状态下对接。通过PyMOL对结合位点进行可视化分析和绘图(图6)。槐花关键活性成分与关键靶点20次分子对接结果如表2所示。结果显示,槐花中关键活性成分与各核心靶点之间的结合能力较好,四种活性成分与各靶点的结合能均小于−5 kcal/mol,说明对接结果良好并且有较高的结合亲和力。其中β-谷甾醇与ATK1及TP53对接结合能分为−8.2和−7.9 kcal/mol,说明该成分与靶点结合能力较高。分子对接图(见图7)表明槐花关键活性成分能与核心靶点蛋白形成稳定的氢键和结合构象。以上分子对接实验结果证明了网络药理学筛选的准确性。
表 2 槐花关键活性成分与对应核心靶点的分子对接结合能(kcal/mol)Table 2. Molecular docking binding energy between the key active ingredients of Sophora japonica L. and corresponding core targets (kcal/mol)活性成分 AKT1
(3O96)IL6
(1ALU)TNF
(5M2I)PPARG
(6MS7)TP53
(4MZI)槲皮素
(Quercetin)−6.7 −5.7 −5.3 −5.6 −6.7 山奈酚
(Kaempferol)−6.3 −6.7 −4.4 −5.7 −6.5 异鼠李素
(Isorhamnetin)−5.7 −6.0 −4.5 −5.4 −7.5 β-谷甾醇
(β-Sitosterol)−8.2 −7.3 −5.5 −6.4 −7.9 3. 讨论
本文通过网络药理学筛选出槐花中对肥胖具有治疗的潜在的四种化合物,分别为槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素、β-谷甾醇。槲皮素是一种存在于许多水果和蔬菜中的类黄酮,对代谢综合征相关的异常起有益的作用,可以改善肥胖、葡萄糖耐受不良和血液甘油三酯水平[16], 并且槲皮素能通过靶向PPARα/γ调节糖异生,以改善肝脏脂肪堆积,通过减少肥胖介导的氧化应激来限制肥胖[17]。β-谷甾醇是植物甾醇类成分之一,属于四环三帖类化合物[18],具有抗糖尿病、降血脂、抗癌、抗关节炎和保肝作用[19]并改变了参与脂质代谢的基因的表达[20],且有研究表明β-谷甾醇摄入量与肥胖患病率呈负相关[21]。山奈酚是一种在植物中发现的次生代谢产物,是一种天然存在的类黄酮[22]。山奈酚通过对Pnpla2和Lipe mRNA水平的积极作用,促进Cebpa基因表达的下调和减少成熟脂肪细胞中的脂质积累,从而调节3T3-L1细胞的成脂分化[23],也可通过抑制脂肪生成、调节脂质和葡萄糖代谢、改变肠道微生物群和激活自噬来对抗肥胖[24]。异鼠李素是一种类黄酮化合物,具有广泛的药理作用[25]。César等[26]发现,在给小鼠喂养从仙人掌中提取的异鼠李素苷后可减少高脂饮食引起的体重增加,增加胰岛素分泌并增加能量消耗,导致肝脏和脂肪组织脂肪积累减少,防止肝脏脂肪变性和脂肪细胞肥大。因此,通过膳食摄入含有异鼠李素糖苷提取物可以预防肥胖。
结合PPI网络图和“槐花关键活性成分-肥胖疾病作用靶点-信号通路”图得出AKT1、IL6、TNF、PPARG、TP53等靶点可能是作用于肥胖疾病的潜在靶点。ATK1能够改善胰岛素敏感性,并导致脂肪量和血糖浓度降低,在恢复饮食引起的肥胖和年龄相关的脂肪积累以及改善葡萄糖代谢方面发挥作用[27]。IL-6促进脂肪组织中的脂肪分解并抑制脂质的合成,从而降低血脂且IL-6的水平与肥胖人群的肥胖程度呈负相关,表明内源性IL-6具有抗肥胖作用[28]。TNF-α代表一种局部脂肪组织参与肥胖相关的胰岛素抵抗,防止脂肪细胞进一步脂质积累和减少脂肪储存来限制肥胖[29]。PPARG具有调节参与脂质代谢,并直接参与调节大多数脂肪细胞基因[30],在绝对脂肪量储存和肥胖发展中可能具有调节作用。PPARG是脂肪细胞分化所必需的,是脂肪生成过程中脂肪特异性基因表达的关键转录因子,可以调节全身胰岛素抵抗[31]。TP53基因在调节糖酵解、脂肪分解和糖原合成等各种代谢活动中起着重要作用[32]。Kang等[33]研究发现,在人类TP53种系突变的小鼠同源物中同样可以影响脂肪代谢。
将核心靶点进行KEGG和GO分析,进一步探究槐花对肥胖疾病的影响机制。AGE-RAGE信号通路能够通过潜在的机制改善高脂肪饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠的骨骼质量[34]。PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活能改善糖尿病小鼠胰岛素抵抗,发挥抗糖尿病作用[35]。HIF是一种由HIF-1α和HIF-1β两个亚基组成的转录因子,其中HIF-1α已被提出在促进和维持膳食肥胖中发挥关键作用[36]。脂肪生成可受IL-17调节,降低IL-17的水平改善了饮食诱导的小鼠肥胖、脂肪肝、葡萄糖和脂质代谢[37],且肥胖症中IL-17水平的升高可能导致肥胖症的癌症发病率增加[38]。
4. 结论
本研究首次从网络药理学和分子对接技术角度探讨了药食同源性物质槐花对肥胖疾病的潜在作用机制,结果表明槐花中的活性成分通过对有机氮化合物、对脂质及脂多糖反应,并通过脂质和动脉粥样硬化、AGE-RAGE、HIF-1、IL-17等多条信号通路起到抗肥胖疾病的作用。可见槐花可通过“多成分-多靶点-多通路”的方式干预肥胖疾病的发生,本研究不足之处在于缺少实验验证和临床验证,需要在未来进行进一步的研究,但一定程度上为后续对槐花的研究和开发提供了新的思路。
-
表 1 槐花的关键活性成分信息
Table 1 Information of key active ingredients of locust flower
编号 MOL ID 英文名 中文名称 OB DL HH1 MOL000354 isorhamnetin 异鼠李素 49.6 0.31 HH2 MOL000358 beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 HH3 MOL000422 kaempferol 山奈酚 41.88 0.24 HH4 MOL005935 N-[6-(acridin-9-ylamino)hexyl]benzamide N-[6-(乙喹啉-9-基)己基]苯甲酰胺 41.7 0.78 HH5 MOL005940 quercetin-3'-methyl ether 槲皮素-3'-甲基醚 46.44 0.3 HH6 MOL000098 quercetin 槲皮素 46.43 0.28 表 2 槐花关键活性成分与对应核心靶点的分子对接结合能(kcal/mol)
Table 2 Molecular docking binding energy between the key active ingredients of Sophora japonica L. and corresponding core targets (kcal/mol)
活性成分 AKT1
(3O96)IL6
(1ALU)TNF
(5M2I)PPARG
(6MS7)TP53
(4MZI)槲皮素
(Quercetin)−6.7 −5.7 −5.3 −5.6 −6.7 山奈酚
(Kaempferol)−6.3 −6.7 −4.4 −5.7 −6.5 异鼠李素
(Isorhamnetin)−5.7 −6.0 −4.5 −5.4 −7.5 β-谷甾醇
(β-Sitosterol)−8.2 −7.3 −5.5 −6.4 −7.9 -
[1] 郭丽杰, 黄绯绯, 杜文雯, 等. 中国成年居民超重肥胖的代际差异[J]. 卫生研究,2024,53(1):14−20,65. [GUO Lijie, HUANG Feifei, DU Wenwen, et al. Generational differences in overweight and obesity among Chinese adult resident[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research,2024,53(1):14−20,65.] GUO Lijie, HUANG Feifei, DU Wenwen, et al. Generational differences in overweight and obesity among Chinese adult resident[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2024, 53(1): 14−20,65.
[2] 沈焕玲, 张莹. 肥胖的饮食和药物治疗的研究现状[J]. 医学综述,2018,24(10):1998−2003. [SHENG Huanling, ZHANG Ying. Current situation of diet and drug therapy for obesity[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2018,24(10):1998−2003.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2018.10.026 SHENG Huanling, ZHANG Ying. Current situation of diet and drug therapy for obesity[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2018, 24(10): 1998−2003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2018.10.026
[3] KIM K K, CHO H J, KANG H C, et al. Effects on weight reduction and safety of short-term phentermine administration in Korean obese people[J]. Yonsei Medical Journal,2006,47(5):614. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.5.614
[4] 李婷婷, 管亚, 弘子姗, 等. 基于网络药理学及分子对接技术探讨辣木叶抗肥胖的作用机制[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(15):34−45. [LI Tingting, GUAN Ya, HONG Zishan, et al. Study on the anti-obesity mechanism of action of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves by network-based pharmacology and molecular docking techniques[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(15):34−45.] LI Tingting, GUAN Ya, HONG Zishan, et al. Study on the anti-obesity mechanism of action of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves by network-based pharmacology and molecular docking techniques[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(15): 34−45.
[5] 陆梦柯, 王梓琴, 张春. 基于网络药理学与分子对接探讨沙棘抗肥胖作用机制[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):1−11. [LU Mengke, WANG Ziqin, ZHANG Chun. Exploring the mechanism of hippophae fructus anti-obesity through network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(6):1−11.] LU Mengke, WANG Ziqin, ZHANG Chun. Exploring the mechanism of hippophae fructus anti-obesity through network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(6): 1−11.
[6] 严家慧, 申雪, 彭昶, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究青果-槐花药对抗幽门螺杆菌感染的活性成分和作用机制[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2022,39(4):429−436. [YAN Jiahui, SHEN Xue, PENG Chang, et al. Active components and mechanism of canarii fructus-sophorae flos on inhibition of helicobacter pyloriInfection based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2022,39(4):429−436.] YAN Jiahui, SHEN Xue, PENG Chang, et al. Active components and mechanism of canarii fructus-sophorae flos on inhibition of helicobacter pyloriInfection based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2022, 39(4): 429−436.
[7] 陈芝强, 陈怡, 林瑞婷, 等. 基于网络药理学的地榆-槐花药对治疗直肠癌作用机制的研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2019,30(7):837−845. [CHEN Zhiqiang, CHEN Yi, LIN Ruiting, et al. The active mechanism of “sanguisorbae radix-sophorae flos” on rectal cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2019,30(7):837−845.] CHEN Zhiqiang, CHEN Yi, LIN Ruiting, et al. The active mechanism of “sanguisorbae radix-sophorae flos” on rectal cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2019, 30(7): 837−845.
[8] HE X R, BAI Y J, ZHAO Z F, et al. Local and traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Sophora japonica L.:A review[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2016,187:160−182. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.014
[9] PARK K W, LEE J E, PARK K. Diets containing Sophora japonica L. prevent weight gain in high-fat diet-induced obese mice[J]. Nutrition Research,2009,29(11):819−824. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2009.09.014
[10] HOPKINS A L. Network pharmacology:The next paradigm in drug discovery[J]. Nature Chemical Biology,2008,4(11):682−690. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.118
[11] LIU H, WANG J N, ZHOU W, et al. Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines:An example using licorice[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2013,146(3):773−793. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.02.004
[12] SZKLARCZYK D, KIRSCH R, KOUTROULI M, et al. The STRING database in 2023:Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2023,51(D1):D638−D646. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1000
[13] ZHOU Y, ZHOU B, PACHE L, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets[J]. Nature Communications,2019,10(1):1523. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
[14] GOODSELL D S, ZARDECKI C, COSTANZO L D, et al. RCSB protein data bank:Enabling biomedical research and drug discovery[J]. Protein Science,2020,29(1):52−65. doi: 10.1002/pro.3730
[15] MORRIS G M, HUEY R, LINDSTROM W, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4:Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry,2009,30(16):2785−2791. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21256
[16] KÁBELOVÁ A, MALÍNSKÁ H, MARKOVÁ I, et al. Quercetin supplementation alters adipose tissue and hepatic transcriptomes and ameliorates adiposity, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance in adult male rats[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:952065. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.952065
[17] NABAVI S F, RUSSO G L, DAGLIA M, et al. Role of quercetin as an alternative for obesity treatment:You are what you eat![J]. Food Chemistry,2015,179:305−310. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.006
[18] BABU S, JAYARAMAN S. An update on β-sitosterol:A potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,131:110702.
[19] PONNULAKSHMI R, SHYAMALADEVI B, VIJAYALAKSHMI P, et al. Insilico and in vivo analysis to identify the antidiabetic activity of beta sitosterol in adipose tissue of high fat diet and sucrose induced type-2 diabetic experimental rats[J]. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods,2019,29(4):276−290. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2018.1545815
[20] FENG S, DAI Z, LIU A B, et al. Intake of stigmasterol and β-sitosterol alters lipid metabolism and alleviates NAFLD in mice fed a high-fat western-style diet[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids,2018,1863(10):1274−1284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.08.004
[21] GUO P, FENG R, LI Z, et al. Gender differences in the relationships between dietary phytosterols intake and prevalence of obesity in Chinese population[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2023,11(1):569−577.
[22] CHEN J, ZHONG H, HUANG Z, et al. A critical review of kaempferol in intestinal health and diseases[J]. Antioxidants,2023,12(8):1642. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081642
[23] TORRES-VILLARREAL D, CAMACHO A, CASTRO H, et al. Anti-obesity effects of kaempferol by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells[J]. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry,2019,75(1):83−88. doi: 10.1007/s13105-018-0659-4
[24] NEJABATI H R, NIKZAD S, ROSHANGAR L. Kaempferol:A dietary flavonol in alleviating obesity[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design,2023,29(20):1547−1556. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230719121548
[25] GONG G, GUAN Y Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Isorhamnetin:A review of pharmacological effects[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,128:110301.
[26] CÉSAR R R, NIMBE T, JANET A G U, et al. The effect of isorhamnetin glycosides extracted from opuntia ficus-indica in a mouse model of diet induced obesity[J]. Food & Function,2015,6(3):805−815.
[27] CHENG K K, AKASAKI Y, LECOMMANDEUR E, et al. Metabolomic analysis of Akt1-mediated muscle hypertrophy in models of diet-induced obesity and Age-related fat accumulation[J]. Journal of Proteome Research,2015,14(1):342−352. doi: 10.1021/pr500756u
[28] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines:The link between obesity and osteoarthritis[J]. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews,2018,44:38−50.
[29] ZAHORSKA-MARKIEWICZ B, JANOWSKA J, OLSZANECKA-GLINIANOWICZ M, et al. Serum concentrations of TNF-α and soluble TNF-α receptors in obesity[J]. International Journal of Obesity,2000,24(11):1392−1395. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801398
[30] LEFTEROVA M I, HAAKONSSON A K, LAZAR M A, et al. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond[J]. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism,2014,25(6):293−302.
[31] DARWISH N M, GOUDA W, ALMUTAIRI S M, et al. PPARG expression patterns and correlations in obesity[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science,2022,34(6):102116. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102116
[32] SABIR J S M, EL O A, SHAIK N A, et al. The genetic association study of TP53 polymorphisms in Saudi obese patients[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences,2019,26(7):1338−1343. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.04.006
[33] KANG J G, LAGO C U, LEE J E, et al. A mouse homolog of a human TP53 germline mutation reveals a lipolytic activity of p53[J]. Cell Reports,2020,30(3):783−792.
[34] XIA B K, ZHU R Y, ZHANG H, et al. Lycopene improves bone quality and regulates AGE/RAGE/NF-кB signaling pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022:3697067.
[35] YIN X, XU Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Association of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway genetic variants with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2017,128:127−135. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.04.002
[36] GARCÍA-FUENTES E, SANTIAGO-FERNÁNDEZ C, GUTIÉRREZ-REPISO C, et al. Hypoxia is associated with a lower expression of genes involved in lipogenesis in visceral adipose tissue[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine,2015,13(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0732-5
[37] LEE S H, JHUN J Y, BYUN J K, et al. IL-17 axis accelerates the inflammatory progression of obese in mice via TBK1 and IKBKE pathway[J]. Immunology Letters,2017,184:67−75. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.02.004
[38] GISLETTE T, CHEN J. The possible role of IL-17 in obesity-associated cancer[J]. The Scientific World Journal,2010,10:2265−2271. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.212





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



