Optimization of Radio Frequency-assisted Hot Air Drying on Penaeus vannamei and Its Effects on the Quality
-
摘要: 为了研究射频联合热风干燥对南美白对虾品质的影响,本文基于南美白对虾介电特性,优化对虾射频联合热风干燥工艺,并以热风干燥(hot air drying,HAD)为对照,对比分析射频干燥(radio-frequency drying,RFD)和射频联合热风干燥(radio frequency-assisted hot air drying,RFHAD)对虾干的呈味核苷酸和等鲜量的影响。结果显示,对虾的介电常数和损耗因子随着射频温度和水分含量的升高而增加,更有利于水分的迁移和干燥速率提升。射频穿透深度与水分含量、温度和频率呈负相关。此外,随着叠放层数增加和极板间距缩小,对虾的干燥速率显著增加(P<0.05),综合考虑确立最佳射频干燥条件为对虾叠放四层和极板间距9 cm。同时与HAD相比,RFHAD处理显著提高了虾干中呈味核苷酸和等鲜量(P<0.05),其中等鲜量是HAD组的4.86倍。综上,RFHAD可显著提高虾干的干燥速率,同时提高呈味核苷酸含量,提升虾干滋味和鲜度。Abstract: To study the effects of radio frequency-assisted hot air drying (RFHAD) on the quality of South American white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei), the RFHAD process based on the dielectric properties of the shrimp was optimized. The effects of radio frequency drying (RFD) and RFHAD on the flavor nucleotide contents and equivalent umami levels in dried shrimp were compared with those of hot-air drying (HAD). The results showed that as the temperature and moisture content increased, the dielectric constant and loss factor of the shrimp also increased, facilitating moisture migration and enhancing the drying rate. The penetration depth of the RFD was negatively correlated with moisture content, temperature, and frequency. Additionally, increasing the number of stacked layers and reducing the plate spacing significantly increased the drying rate of the shrimp (P<0.05). Considering all these factors, the optimal RFD conditions for shrimp were determined to be the stacking of four layers of shrimp with a plate spacing of 9 cm. Compared with HAD, RFHAD treatment significantly increased the flavor nucleotide contents and equivalent umami levels in dried shrimp (P<0.05), and the equivalent umami levels were 4.86-fold higher than those in the HAD group. In conclusion, RFHAD significantly improved the drying rate of shrimp while increasing the flavor nucleotide content, thereby enhancing the flavor and freshness of dried shrimp.
-
南美白对虾(Penaeus vannamei),又名凡纳滨对虾、白对虾,具有高产量、快生长、强适应性、易养殖等特点,是世界上最重要的经济虾类之一[1]。近几年全国南美白对虾海水养殖产量呈现逐年递增趋势,2019年,中国海洋水产虾产量达114万吨,2022年达134万吨,目前养殖产量居世界首位。南美白对虾具有高蛋白低脂肪的营养特点,其蛋白含量达18.71%、脂肪含量仅为1.07%,富含必需氨基酸、虾青素、维生素、矿物质元素等营养成分,对弥补膳食结构不足和改善人体健康状况均具有显著作用[2−3]。虾具有高水分(60%~70%)和高蛋白质含量,这增加了其在物流过程和贮藏过程中微生物污染的风险,使其相较于其他水产品更易腐败变质,严重影响了其货架期品质[4−5]。干制加工是南美白对虾主要的加工方式之一,不仅可以抑制微生物生长繁殖,提高产品的安全性和延长货架期,同时还能赋予虾独特的香气、鲜甜的滋味以及更加丰富的口感,深受广大消费者的喜爱,市场前景广阔。
目前传统的干燥方式主要是日光晾晒干燥和热风干燥,但前者由于干燥环境不卫生和干燥时间长使得产品的品质难以保证,易导致产品硬度过高、复水性差、质地不理想等;后者由于能耗高、温度高、易对产品造成热损伤和过度氧化等问题使得学者们不得不探索新的干燥方法。近年来,为了满足当前和未来消费者的消费需求,新型干燥技术发展迅速,主要包括微波干燥技术、红外干燥技术、射频干燥技术、真空冷冻干燥技术等[6]。其中,射频干燥技术(Radio frequency drying,RFD)是一种新兴的热技术,通常指用1~100 MHz的电磁波使食品物料中的带电离子不断碰撞、运动,进而达到物料升温脱水的效果[7]。由于RFD加工技术具有渗透性大、加热均匀性强、能效高、体积大等特点,已被广泛应用于大尺寸、散装食品材料的加工[8]。研究发现射频联合热风干燥(Radio frequency-assisted hot air drying,RFHAD)可以显著提高干燥速率,同时其对产品质量的影响最小[7,9]。目前RFHAD技术在果蔬、谷物、坚果、水产等方面均有所研究和应用,其中水产品方面仅有学者研究发现RFHAD罗非鱼鱼片的干燥速率为HAD的1.1~1.4倍,且RFHAD鱼片具有较高的复水率且体积收缩率较低[9]。目前关于射频联合热风干燥南美白对虾或者其他海产品的研究十分有限。
此外,虾在干燥过程中的滋味变化不可忽视,已有研究报道虾中主要的滋味成分为游离氨基酸、核苷酸及其衍生物、无机盐、季胺碱以及小分子肽等,这些物质的相互协同作用赋予虾的鲜甜滋味。国内外对南极磷虾、小龙虾、南美白对虾的滋味成分已有部分研究。贾倩男等[10]采用高效液相色谱、原子吸收光谱、电子舌、滋味重组等方法明确了鹰爪虾的关键滋味活性化合物;姚静玉等[11]利用1H核磁共振技术确定了小龙虾的滋味特征和呈味模式。此外,有学者基于中华管鞭虾虾肉挥发性成分的分析,确定了超高压处理对虾肉风味品质的影响[12]。刁华玉等[13]研究发现解冻后的南极磷虾肉以甜味和苦位为主,且空气解冻的虾肉苦位氨基酸占比增加。因此探究加工技术对虾滋味品质的影响也是食品质量监控的关键环节。
本文以南美白对虾为研究对象,基于对虾在不同温度、水分含量及频率下介电特性与穿透深度的分析,优化干燥叠放层数和极板间距,确立最佳射频联合热风干燥参数,并对比热风干燥、射频干燥和射频联合热风干燥对南美白对虾呈味核苷酸、等鲜量的影响,以期为射频联合热风干燥技术在南美白对虾干产业的应用提供理论指导和技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
南美白对虾、食盐 购于宁波市大润发超市;乙醇、乙腈、乙酸、甲醇、磷酸 色谱纯,阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;磷酸氢二钾(分析纯)、氢氧化钾(分析纯)、GMP、IMP、AMP标准品(色谱纯) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
HGJL-5RFS食品射频加工装备 合肥哈工金浪装备科技有限公司;DHG-9070A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科技有限公司;PNA-L 网络分析仪 美国安捷伦公司;LC-100高效液相色谱仪 上海伍丰科学仪器有限公司;TLG-16低温离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;VSD150-3干式氮吹仪 无锡沃信仪器有限公司;ESH31水分含量测定仪 上海舜宇光学科技有限公司;MS105DU精密天平 梅特勒托利多科技(中国)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 对虾前处理
将体型大小均一的新鲜南美白对虾清洗干净,用6%的食盐水煮制3~5 min 后,捞出沥干,待用。并采用GB 5009.3-2016直接法测定其初始干基含水率为70%±0.85%,即为空白对照组(CK)。
1.2.2 对虾介电特性与穿透深度测定
1.2.2.1 不同水分含量和干燥温度的南美白对虾样品制备
采用热风干燥法制备不同含水率的南美白对虾样品,取预煮后对虾(500 g)于60 ℃的热风干燥箱进行干燥,每隔30 min通过水分含量测定仪测定样品水分含量,当对虾的水分含量达到20%、40%、60%时,留样并冷藏储存。
1.2.2.2 介电特性的测量
采用同轴探针连接网络分析仪测定不同水分含量的南美白对虾的介电特性[14]。测量前仪器预热1 h并进行校准,本试验的测量范围为10~3000 MHz,间隔每1 MHz采集一个数据点,该频率测量范围涵盖了5个可用于微波与射频加热的频率,包括射频段的13.56、27.12和40.68 MHz、微波段的915和2450 MHz。测量时,每个对虾样品依次在40、50和60 ℃下测量介电特性,每组温度测定3次平行。
1.2.2.3 穿透深度计算
穿透深度(Penetration depth,dp)是指射频或微波从物质表面穿透至其能量衰减为初始值1/e(e=2.718)时的穿透距离[15],计算公式如下:
dp=c2πf√2ε'[√1+(ε''ε')2−1] (1) 式中,dp为穿透深度,m;c为光在真空中的速度,3×108 m/s;f为频率,Hz;ε'和ε''分别为样品在不同温度、水分含量下测得的介电常数和介电损耗。
1.2.3 射频干燥参数优化
取预煮后南美白对虾置于带有均匀通气小孔的聚丙烯框(25 cm×15 cm×8 cm),并设计单因素实验优化对虾叠放层数(1~4层)和射频极板间距(8.5、9和9.5 cm)。将盛有南美白对虾样品的容器置于射频腔内两极板间中央位置,并将荧光测温探头垂直插入样品中部、角落等5个具有代表性的位置,记录样品不同位置处的温度变化。每隔一段时间称取重量,计算水分比(moisture ratio,MR)和干燥速率(drying rate,DR),公式如下:
DR=Mt1−Mt2t2−t1 (2) 式中,DR为干燥t时刻的干燥速率,g/kg·min−1;t1和 t2是干燥起始和终止时间,h;Mt1和Mt2分别是干燥起始和终止时的干基含水率,g/g,干基含水率的计算公式如下:
Mt=Wt−WdsWds (3) 式中,Wt是t时刻的样品重量,g;Wds是样品干物质的重量,g。
MR=MtM0 (4) 式中,M0和Mt为初始干基含水率和在任意干燥 t时刻的干基含水率,g/g。
1.2.4 不同干燥方式试验组设计
射频干燥试验组:根据1.2.3中射频干燥参数优化的最佳条件进行射频处理,当水分含量达到15%时,视为干燥结束,所得干燥样品即为射频干燥组(RFD);射频联合热风干燥试验组:根据1.2.3中射频干燥参数优化的最佳条件进行射频处理,并结合射频系统配备的热风系统,温度设为60 ℃,当水分含量达到15%时,视为干燥结束,所得干燥样品即为射频联合热风干燥组(RFHAD);热风干燥组:热风干燥温度为60 ℃,当水分含量达到15%时,视为干燥结束,所得干燥样品即为热风干燥组(HAD)。
1.2.5 指标测定方法
1.2.5.1 呈味核苷酸的测定
样品的预处理与分析方法参考宣晓婷等[16]的方法并作适当修改。取约0.2 g虾干样品进行研磨,并加入1 mL 1 mol/L高氯酸水溶液,8000 r/min离心15 min;取0.5 mL上清液,再加入0.5 mL 2 mol/L氢氧化钾水溶液,8000 r/min离心15 min,离心后取出上清液,通过0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤后待测。
HPLC分析条件:C18反相色谱柱(150 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相A: 100%甲醇; B:1 mol/L磷酸钾水溶液pH7.0,A:B=1:99;进样量10 μL,流速1 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,紫外波长254 nm。利用核苷酸标准品的浓度与峰面积建立标准曲线,从而计算样品中核苷酸的含量,呈味核苷酸标准曲线见表1。
表 1 呈味核苷酸标准曲线Table 1. Flavor nucleotides standard curves呈味核苷酸
种类IMP GMP AMP 标准曲线 y = 22640x−1868.3 y = 7516.3x−713.84 y = 21766x−1939.3 R2 0.9974 0.9976 0.9974 1.2.5.2 等鲜量评价
等鲜量评价参考蔡路昀等[17]的方法,以100 g虾干干物质样品中谷氨酸钠(mono sodium glutamate,MSG)的含量表示呈鲜物质总量,计算公式如下:
Y=∑aibi+1218(∑aibi)(∑ajbj) (5) 式中,Y为等鲜量,g/100 g;ai为呈鲜氨基酸(Asp或Glu)的含量,mg/g,其检测方法参考Xuan等[18]的方法;aj为呈鲜核苷酸的含量,包括5'-GMP、5'-IMP、5'-AMP;bi为呈味氨基酸相对谷氨酸的值(Glu=1、Asp=0.077);bj为呈味核苷酸相对5'-肌苷酸的值(5'-GMP=2.3、5'-IMP=1、5'-AMP=0.18);1218为协同作用常数。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验结果均平行测定3次,测定所得数据均以平均值±标准差的形式表示,数据采用SPSS19.0软件做单因素方差分析(ANOVA),采用Duncan多重比较法进行显著性分析,在P<0.05水平上具有统计学意义。用Origin 8.5软件进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同水分含量和温度对南美白对虾介电特性的影响
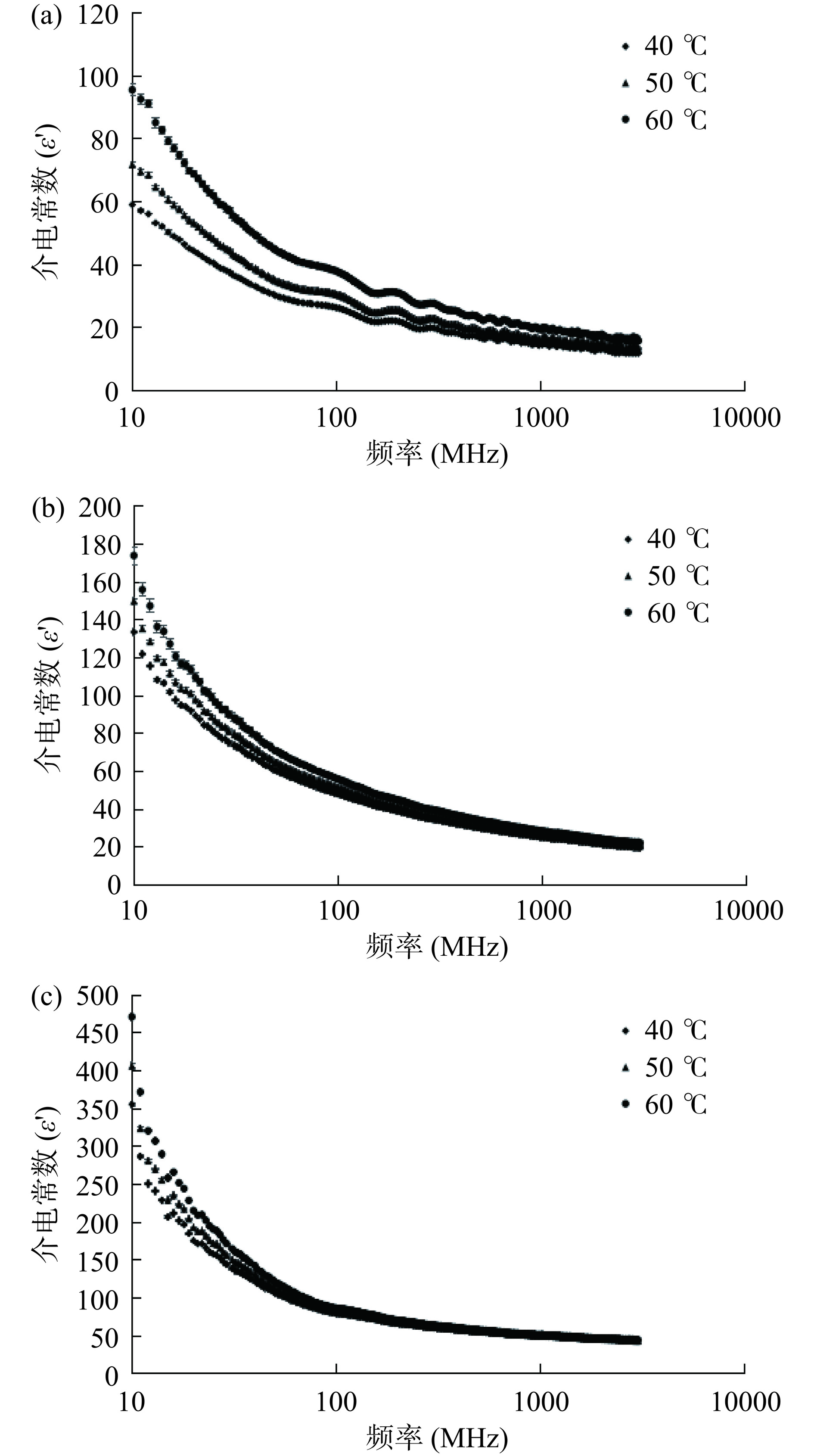
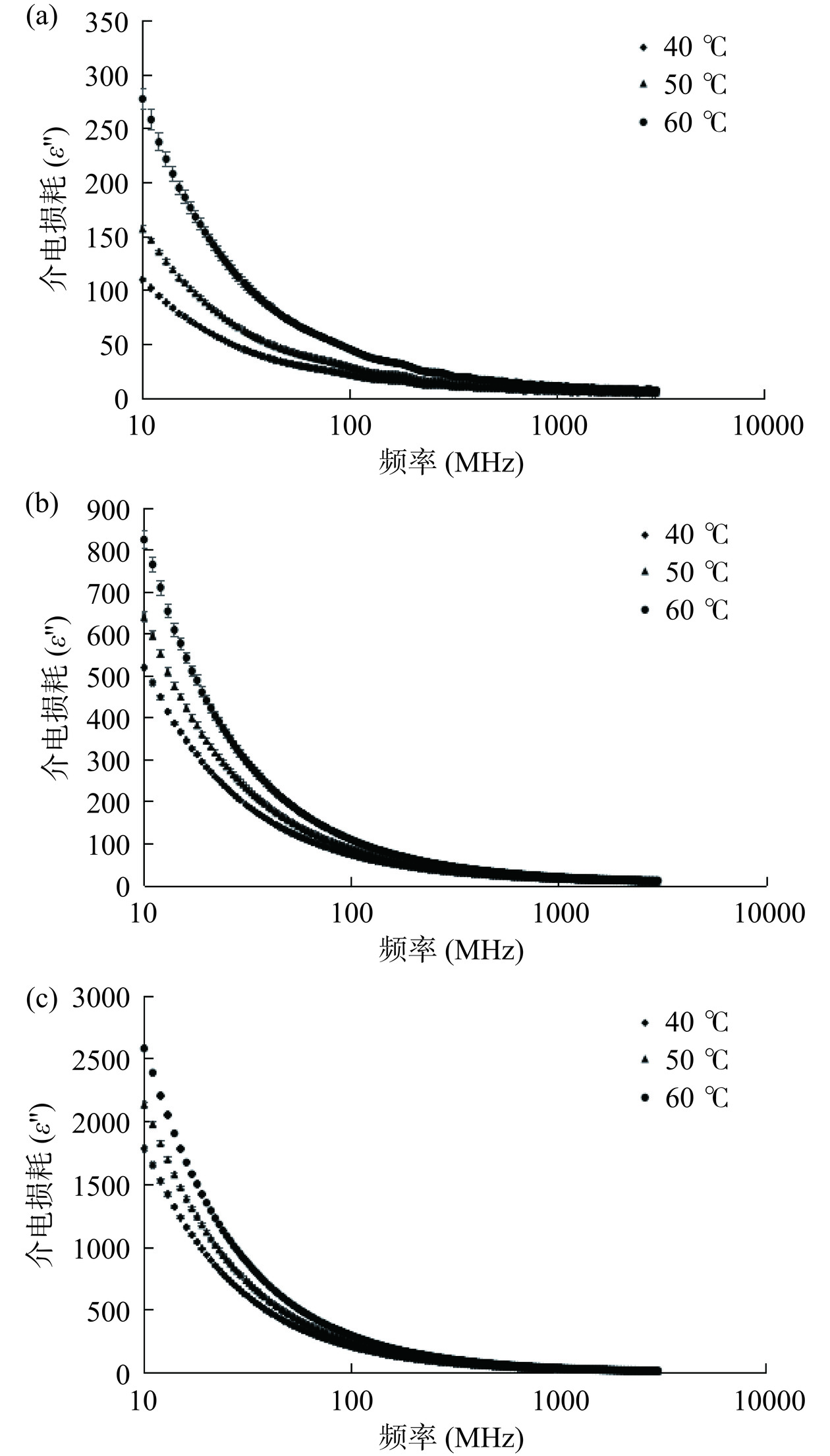
介电特性是影响物料与射频电磁场之间的相互作用的能量,包括介电常数ε'和介电损耗ε'',分别代表了物料存储电场的能力和电磁能转变为热能的能力[19]。图1和图2对比三个温度水平下,水分含量分别为19.71%、39.73%和59.37%南美白对虾的介电常数和介电损耗随频率变化的规律。由图1~图2可知,南美白对虾的介电常数和介电损耗随着频率的增加而减小,其中该下降趋势在低频率范围内更加明显。此外,水分含量越高的南美白对虾的介电常数下降越显著,当温度均为40 ℃时,水分含量为19.71%、39.73%和59.37%的南美白对虾的介电常数分别下降了79.89%、85.28%和87.86%,且这种下降趋势在低频率或更高温度条件下尤为明显。此外,南美白对虾的介电损耗特性有相类似的变化趋势。这可能是由于自由水转变为单层或多层结合水,导致自由水的松弛峰值下降的同时增强了结合水的迁移振荡[20]。相类似的结论在苹果、冬枣等介电特性研究中均有报道[14,21]。周旭[14]在探究猕猴桃切片介电特性时,发现在<100 MHz的频率范围内损耗因子与频率的对数呈负线性相关,因此也验证了射频过程中物料的离子传导是影响介电损耗的关键因素。理论上,介电常数和介电损耗因子越大,物料中的水分子布朗运动更为显著,进而可以缩短物料的干燥进程,因此在射频的频率范围内,更有利于提高南美白对虾的干燥速率。此外,温度和水分含量是影响介电常数和介电损耗因子的关键参数。温度和水分含量越高,介电常数和介电损耗因子越大,物料内部温度上升越明显,更有利于水分的迁移和干燥速率的提升。因此后续研究中结合热风干燥常用温度范围,确定适宜温度为60 ℃。
![]() 图 1 不同水分含量下南美白对虾的介电常数与频率的关系注:(a)19.71%;(b)39.73%;(c)59.37%;图2同。Figure 1. Frequency-dependent dielectric constant (ε') of shrimp with different moisture content
图 1 不同水分含量下南美白对虾的介电常数与频率的关系注:(a)19.71%;(b)39.73%;(c)59.37%;图2同。Figure 1. Frequency-dependent dielectric constant (ε') of shrimp with different moisture content2.2 不同水分含量和温度对射频在南美白对虾中穿透深度的影响
由表2可知,随着水分含量和温度的降低,南美白对虾的穿透深度显著增加(P<0.05)。对虾在射频段频率下(27 MHz和40 MHz)的穿透深度显著高于微波段(915 MHz和2450 MHz)(P<0.05),且该现象在水分含量低的时候更为明显。有研究报道,不同样品介质的能量穿透深度受频率、温度、含水率的影响会存在差异性,这是由于物料内部原子与电磁波相互作用力受到材质影响所导致的差异。在大豆蛋白[22]、蜂蜜[23]、年糕[24]等大多数物料的穿透深度随频率的增加而降低,但温度和水分含量对物料穿透深度的影响存在差异,如土豆泥的穿透深度随水分含量的上升而升高[25],年糕的穿透深度随温度的升高而升高[24],与本文的研究结果正好相反。而Guo等[26]研究发现绿豌豆、扁豆等样品的穿透深度随水分含量的升高而降低,这与本文的研究结果相一致。
表 2 南美白对虾在不同水分含量和温度条件下的穿透深度(cm)Table 2. Penetration depths of shrimp over different temperatures and moisture contents (cm)水分含量(%) 温度(℃) 频率(MHz) 27 40 915 2450 19.71 40 25.29±0.17iD 20.53±0.07iC 2.93±0.01iB 1.35±0.00iA 50 20.38±0.12hD 16.63±0.09hC 2.54±0.01hB 1.20±0.00hA 60 14.54±0.30gD 11.91±0.23gC 2.05±0.03gB 1.03±0.01gA 39.73 40 10.07±0.06fD 8.30±0.05fC 1.63±0.01fB 0.81±0.00fA 50 8.96±0.09eD 7.38±0.08eC 1.49±0.01eB 0.77±0.00eA 60 7.79±0.11dD 6.42±0.09dC 1.34±0.02dB 0.71±0.01dA 59.37 40 5.24±0.03cD 4.33±0.02cC 1.13±0.01cB 0.66±0.00cA 50 4.76±0.02bD 3.92±0.02bC 1.01±0.01bB 0.62±0.00bA 60 4.30±0.01aD 3.54±0.01aC 0.90±0.00aB 0.58±0.00aA 注:同列不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著,同行不同大写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。 2.3 南美白对虾射频干燥参数优化
2.3.1 不同叠放层数对南美白对虾射频干燥特性的影响
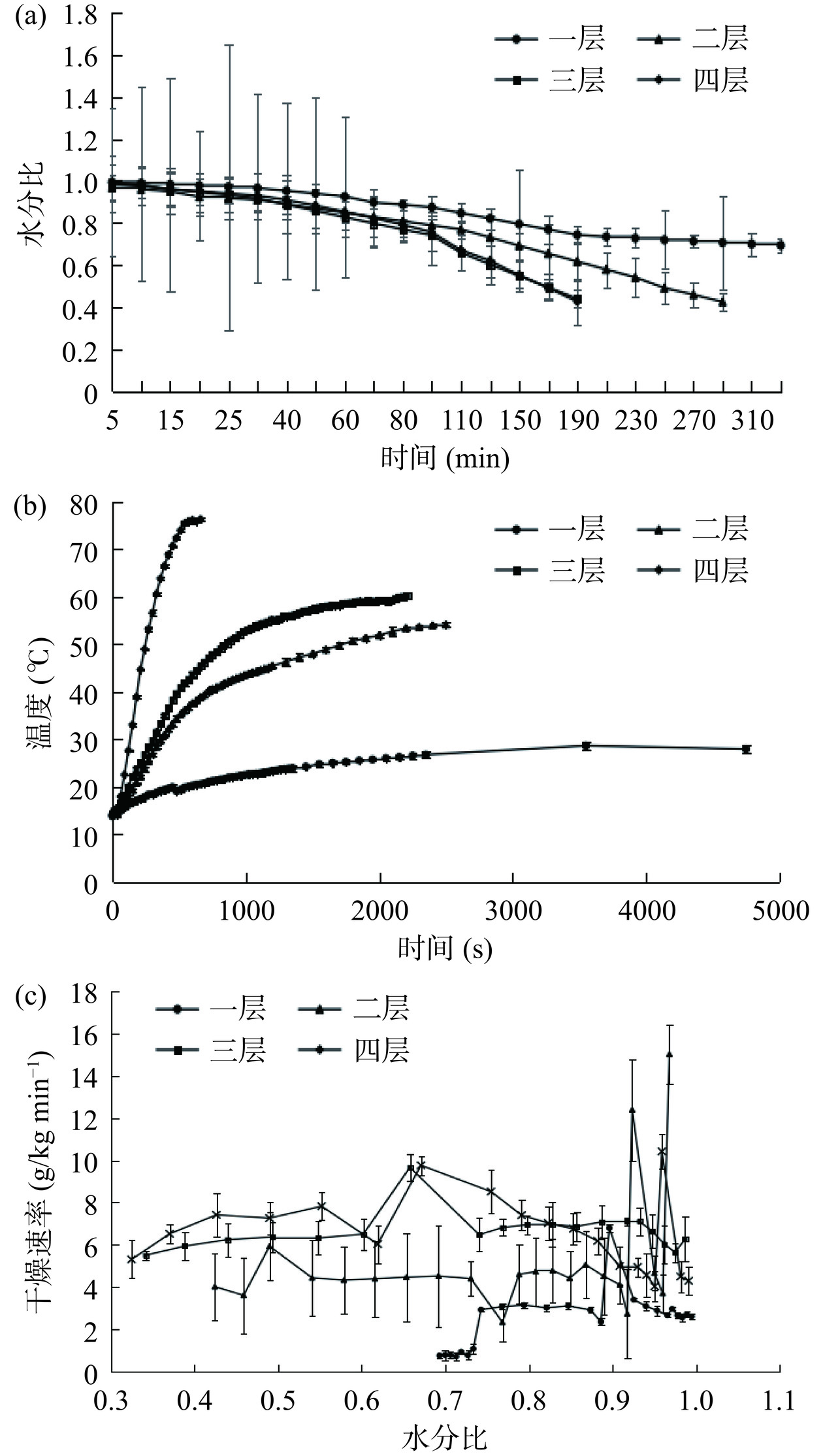
由图3可知,随着叠放层数的增加,对虾样品距离极板的间距越小,射频电场强度增加,因此射频干燥速率随之增加。图3(a)为不同叠放层数对样品干燥过程中水分比的影响,叠放层数为三层以上的样品的水分比下降更为明显。图3(b)对比分析了不同叠放层数对样品中心温度的影响,从图中可知,对虾样品中心温度随着干燥时间的延长呈快速上升后平衡的趋势,其中叠放四层时中心温度上升速率最快,干燥600 s时达到最高值(76.1±0.6)℃,后续中心温度保持相对恒定。由干燥速率与水分比的关系图(图3(c))中可以看出干燥速率在干燥前期波动较大,后期干燥速率呈现随着叠放层数的增加而增大的趋势,这是由于样品叠放层数大,吸收的射频能量大,且所吸收的射频能量主要用于水分的迁移与蒸发[27],因此样品层数越多其升温速率和干燥速率更快。综合考虑,选取叠放层数四层作为后续试验条件。
2.3.2 不同极板间距对南美白对虾射频干燥特性的影响
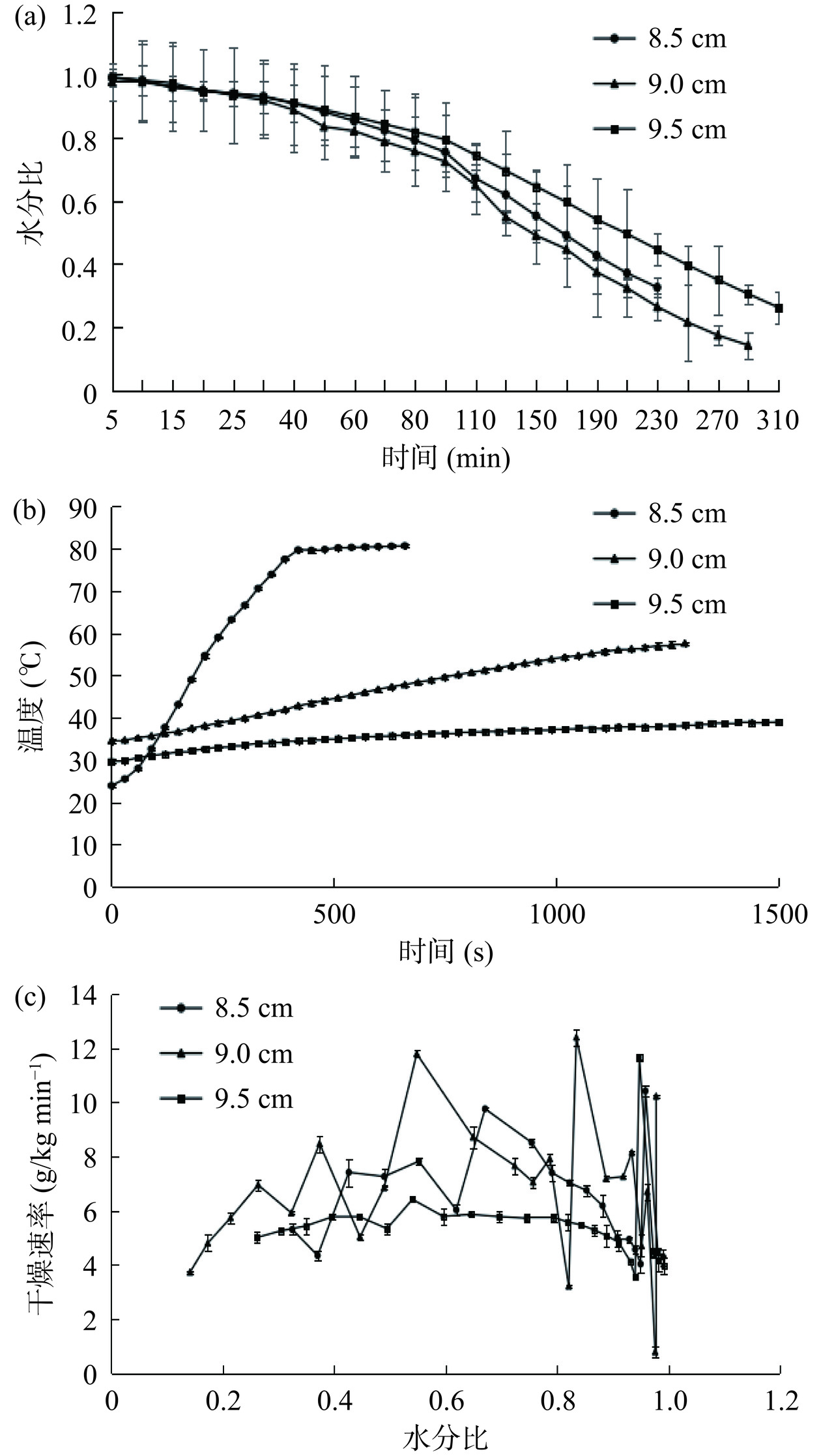
图4为南美白对虾在不同极板间距(8.5~9.5 cm)的射频干燥过程中的水分比、中心温度和干燥速率的变化。当南美白对虾干燥240 min时,不同极板间距(8.5~9.5 cm)的样品水分比分别为0.32±0.03、0.26±0.04和0.45±0.05,说明极板间距为9 cm时,对虾干燥进程更快。通过分析样品温度和时间的关系曲线(图4(a)和图4(b)),发现当极板间距为8.5 cm时样品中心温度呈先快速上升后趋于平缓,而极板间距为9~9.5 cm时样品中心温度呈缓慢上升。这是由于极板间距小,样品所吸收的射频能量越大,中心温度快速上升,但存在过热现象。图4(c)显示了不同极板间距对南美白对虾的射频干燥速率的影响,三个极板间距下的对虾干燥速率呈波动变化,整体来说极板间距越大,对虾的干燥速率越小,但极板间距为9 cm时其平均干燥速率较8.5 cm组更高,这可能是由于极板间距过小会导致射频场的能量过于集中于样品底部影响对虾干燥品质[28],因此综合考虑选取9 cm的极板间距作为后续试验条件。
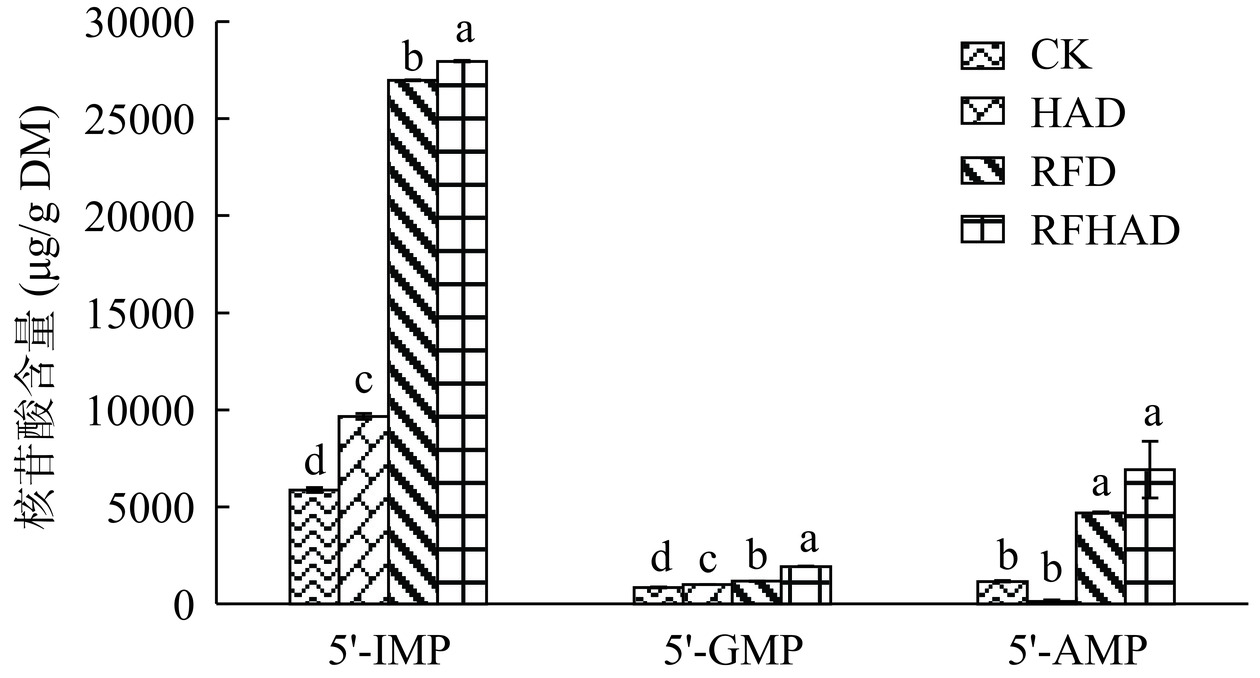
2.4 呈味核苷酸含量分析
由图5可知,南美白对虾干中的呈味核苷酸以5'-肌苷酸二钠(5'-IMP)为主。有研究表明,5'-IMP与甜味氨基酸(如甘氨酸、丙氨酸、丝氨酸等)相互作用有增鲜作用,与鲜味氨基酸互作可增强鲜度和醇厚感,因此其对虾干的滋味具有重要贡献[29]。
传统热风干燥处理的虾干中的5'-IMP和5'-鸟苷酸二钠(5'-GMP)较对照组有一定升高,但5'-腺苷酸二钠(5'-AMP)含量损失较大,这是由于受热不稳定所造成。与传统热风干燥相比,射频干燥处理显著提高了虾干中5'-IMP、5'-GMP和5'-AMP含量(P<0.05)。同时,射频联合热风干燥处理的虾干的呈味核苷酸含量最高,其5'-IMP、5'-AMP、5'-GMP含量分别达到27949.19±35.16、6929.57±1460.79和1938.63±4.22 μg/g DM,分别是热风干燥组各呈味核苷酸含量的2.89、46.55和1.92倍以及射频干燥组各呈味核苷酸含量的1.04、1.47和1.65倍,说明射频联合热风处理的虾干样品滋味和鲜度最佳,这与射频可使物料中心温度快速上升相关。
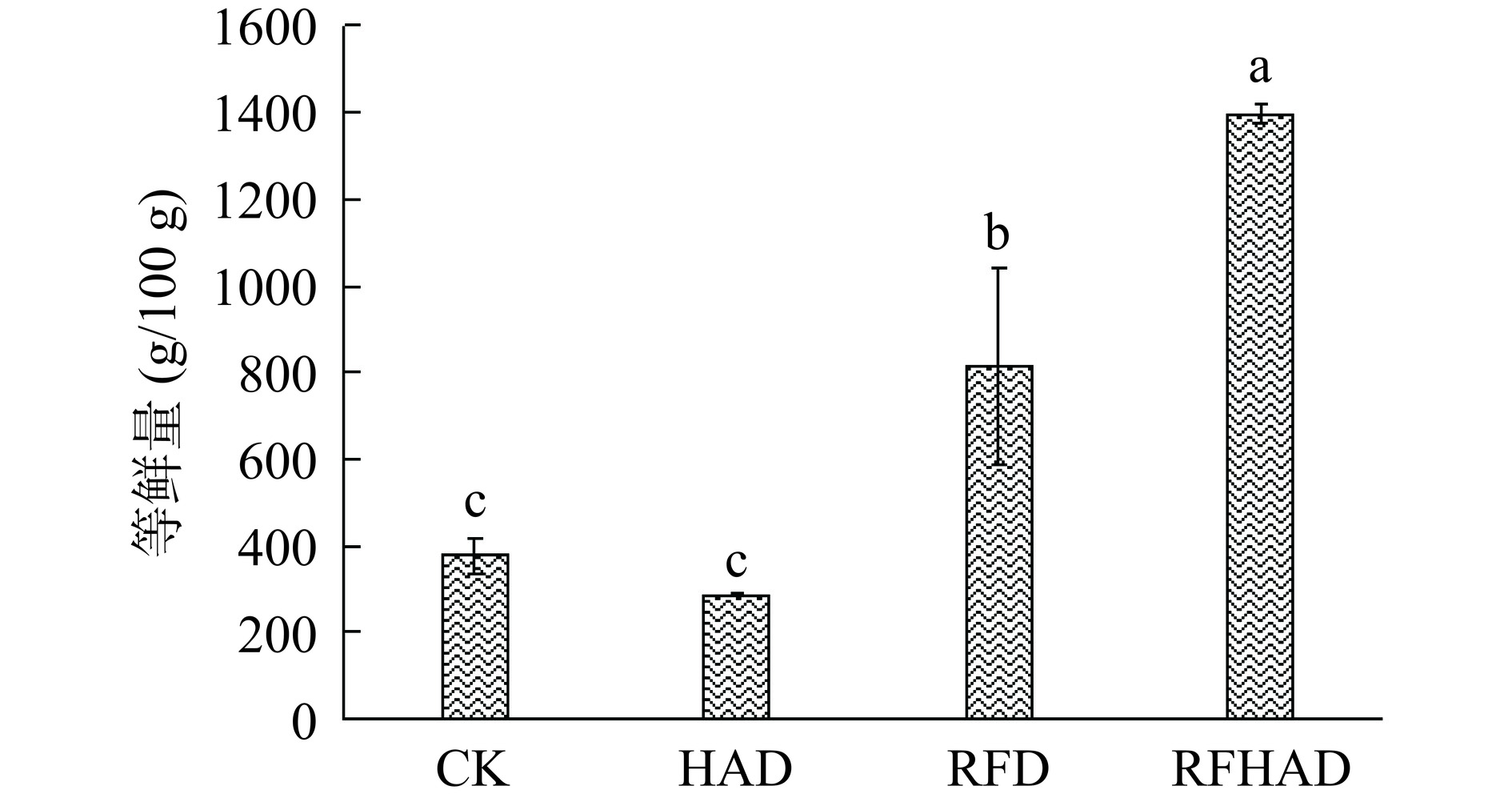
2.5 等鲜量分析
不同干燥方式对南美白对虾等鲜量的影响如图6所示。等鲜量(equivalent umami concentration,EUC)是单一谷氨酸钠产生与呈味核苷酸和鲜味氨基酸互作时所产生的鲜味强度一致时所需的量[30]。由图6可知,与对照组相比,传统热风处理使得对虾虾干的等鲜量下降了23.87%,这是由于过长时间的受热所导致。而射频处理可显著提高虾干的等鲜量(P<0.05),其中RFD组和RFHAD组对虾的等鲜量分别是HAD组的2.83和4.86倍,且RFHAD组的虾干等鲜量值达到最高为1395.85±23.18 g/100 g,这与呈味核苷酸的结果相一致。射频联合热风干燥可显著提高虾干的干燥速率,同时提高呈味核苷酸含量。蔡路昀等[17]同样研究发现热风干燥处理的中国对虾虾干的等鲜量最低,这是由于过度加热或长时间干燥处理会破坏呈鲜物质。同样研究发现热风干燥处理的中国对虾虾干的等鲜量最低,这是由于过度加热或长时间干燥处理会破坏呈鲜物质[17]。
3. 结论
本文基于南美白对虾介电特性研究,探讨了南美白对虾射频联合热风干燥工艺优化。研究结果表明,对虾的介电常数和介电损耗随着频率的增加而减小,而随着温度和水分含量越高而越大,更有利于水分的迁移和干燥速率的提升。此外,随着水分含量和温度的降低,南美白对虾的穿透深度显著增加(P<0.05)。叠放层数和极板间距是影响射频干燥速率的关键因素,随着叠放层数的增加和极板间距的缩小,对虾的干燥速率明显增加,但考虑射频存在过热现象,确立最佳射频干燥条件为对虾叠放四层和极板间距9 cm。此外,研究发现通过对比传统热风干燥,RFHAD处理显著提高了虾干中呈味核苷酸和等鲜量(P<0.05)。综上,射频联合热风干燥可显著提高虾干的干燥速率,同时提高呈味核苷酸含量,提升虾干滋味和鲜度。
-
图 1 不同水分含量下南美白对虾的介电常数与频率的关系
注:(a)19.71%;(b)39.73%;(c)59.37%;图2同。
Figure 1. Frequency-dependent dielectric constant (ε') of shrimp with different moisture content
表 1 呈味核苷酸标准曲线
Table 1 Flavor nucleotides standard curves
呈味核苷酸
种类IMP GMP AMP 标准曲线 y = 22640x−1868.3 y = 7516.3x−713.84 y = 21766x−1939.3 R2 0.9974 0.9976 0.9974 表 2 南美白对虾在不同水分含量和温度条件下的穿透深度(cm)
Table 2 Penetration depths of shrimp over different temperatures and moisture contents (cm)
水分含量(%) 温度(℃) 频率(MHz) 27 40 915 2450 19.71 40 25.29±0.17iD 20.53±0.07iC 2.93±0.01iB 1.35±0.00iA 50 20.38±0.12hD 16.63±0.09hC 2.54±0.01hB 1.20±0.00hA 60 14.54±0.30gD 11.91±0.23gC 2.05±0.03gB 1.03±0.01gA 39.73 40 10.07±0.06fD 8.30±0.05fC 1.63±0.01fB 0.81±0.00fA 50 8.96±0.09eD 7.38±0.08eC 1.49±0.01eB 0.77±0.00eA 60 7.79±0.11dD 6.42±0.09dC 1.34±0.02dB 0.71±0.01dA 59.37 40 5.24±0.03cD 4.33±0.02cC 1.13±0.01cB 0.66±0.00cA 50 4.76±0.02bD 3.92±0.02bC 1.01±0.01bB 0.62±0.00bA 60 4.30±0.01aD 3.54±0.01aC 0.90±0.00aB 0.58±0.00aA 注:同列不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著,同行不同大写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著。 -
[1] 林雅文, 刘佳晨, 李艾靑, 等. 不同干燥方法对南美白对虾理化特性和微观结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(19):74−81. [LIN Y W, LIU J C, LI A Q, et al. Effects of difference drying methods on physicochemical properties and microstructure of Penaeus vannamei[J]. Food Science,2023,44(19):74−81.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221019-189 LIN Y W, LIU J C, LI A Q, et al. Effects of difference drying methods on physicochemical properties and microstructure of Penaeus vannamei[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(19): 74−81. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221019-189
[2] CHEN Y R, HWAN C A, HUANG L H, et al. Kinetic analysis and dynamic prediction of growth of vibrio parahaemolyticus in raw white shrimp at refrigerated and abuse temperatures[J]. Food Control,2019,100:204−211. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.01.013
[3] BECERRA J A H, FLORES A A O, VALERIO-ALFARO G, et al. Cholesterol oxidation and astaxanthin degradation in shrimp during sun drying and storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,145:832−839. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.098
[4] LI X, WANG Y, SUN Y Q, et al. Nutritional evaluation, flavor characteristics and microbial community of shrimp paste made from different materials and variance analysis[J]. Food Chemistry Advances,2023,2:100268. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2023.100268
[5] ZHANG B, CAO H J, LIN H M, et al. Insights into ice-growth inhibition by trehalose and alginate oligosaccharides in peeled pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during frozen storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,278:482−490. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.087
[6] SHEWALE R S, RAJORIYA D, BHAVYA M L, et al. Application of radio frequency heating and low humidity air for sequential drying of apple slices:Process intensification and quality improvement[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,135:109904. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109904
[7] MAHMOOD N, LIU Y H, MUNIR Z S, et al. Effects of hot air assisted radio frequency drying on heating uniformity, drying characteristics and quality of paddy[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,158:113131. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113131
[8] CHEN L, WEI X Y, IRMAK S, et al. Inactivation of Salm-onella enterica and Enterococcus faecium NRRL B-2354 in cumin seeds by radio frequency heating[J]. Food Control,2019,103:59−69. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.04.004
[9] CAO F F, ZHANG R Y, TANG J M, et al. Radio frequency combined hot air (RFD-HA) drying of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) fillets:Drying kinetics and quality analysis[J]. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 2021, 74:102791.
[10] 贾倩男, 侯虎, 王聪, 等. 基于感官组学解析热加工鹰爪虾关键滋味成分的变化[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(20):212−218. [JIA Q N, HOU H, WANG C, et al. Sensomics analysis of the changes in key taste components of trachypenaeus curvirostris during thermal treatment[J]. Food Science,2023,44(20):212−218.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221215-161 JIA Q N, HOU H, WANG C, et al. Sensomics analysis of the changes in key taste components of trachypenaeus curvirostris during thermal treatment[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(20): 212−218. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221215-161
[11] 姚静玉, 刘洁, 柏雪莹, 等. 利用1H NMR分析小龙虾的特征性滋味组成[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(8):170−175. [YAO J Y, LIU J, BAI X Y, et al. Determination of characteristic taste compounds of crayfish by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Food Science,2023,44(8):170−175.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220615-152 YAO J Y, LIU J, BAI X Y, et al. Determination of characteristic taste compounds of crayfish by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(8): 170−175. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220615-152
[12] 王芝妍, 官爱艳, 吕梁玉, 等. 超高压处理对中华管鞭虾虾肉风味的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(18):156−162. [WANG Z Y, GUAN A Y, LÜ L Y, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure (UHP) on the flavor of solenocera melantho meat[J]. Food Science,2017,38(18):156−162.] WANG Z Y, GUAN A Y, LÜ L Y, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure (UHP) on the flavor of solenocera melantho meat[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(18): 156−162.
[13] 刁华玉, 林松毅, 陈冬, 等. 解冻方式对南极磷虾肉理化特性和滋味的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(4):228−238. [DIAO H Y, LIN S Y, CHEN D, et al. Effect of thawing methods on the physico-chemical and taste characteristics of antarctic krill meat[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(4):228−238.] DIAO H Y, LIN S Y, CHEN D, et al. Effect of thawing methods on the physico-chemical and taste characteristics of antarctic krill meat[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(4): 228−238.
[14] 周旭. 猕猴桃切片的射频真空及热风联合干燥研究[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学, 2019. [ZHOU X. Developing radio frequency-vacuum and combined dehydration with hot air drying for kiwifruit slices[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University, 2019.] ZHOU X. Developing radio frequency-vacuum and combined dehydration with hot air drying for kiwifruit slices[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2019.
[15] 昝沛清, 邱伟强, 冯宇辉, 等. 鸭蛋快速腌制过程中蛋清的介电特性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2023,42(5):12−19. [ZAN P Q, QIU W Q, FENG Y H, et al. Study on dielectric properties of duck egg white during quick pickling process[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2023,42(5):12−19.] ZAN P Q, QIU W Q, FENG Y H, et al. Study on dielectric properties of duck egg white during quick pickling process[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2023, 42(5): 12−19.
[16] 宣晓婷, 王瑛, 尚海涛, 等. 超高压辅助中华绒螯蟹脱壳及对其品质的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2023,54(2):149−156. [XUAN X T, WANG Y, SHANG H T, et al. Effects of high pressure processing on the shucking and quality of Chinese mitten crab[J]. Journal of Shenyang Aricultural University,2023,54(2):149−156.] XUAN X T, WANG Y, SHANG H T, et al. Effects of high pressure processing on the shucking and quality of Chinese mitten crab[J]. Journal of Shenyang Aricultural University, 2023, 54(2): 149−156.
[17] 蔡路昀, 年琳玉, 曹爱玲, 等. 不同干燥方式对中国对虾风味组分的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(11):291−298. [CAI L Y, NIAN L Y, CAO A L, et al. Effect of different drying methods on flavor components of Chinese shrimp (Fenneropnaeus chinensis)[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2017,33(11):291−298.] CAI L Y, NIAN L Y, CAO A L, et al. Effect of different drying methods on flavor components of Chinese shrimp (Fenneropnaeus chinensis)[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(11): 291−298.
[18] XUAN X T, YU N, DING T, et al. Radio frequency-assisted hot air drying of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei):Drying Kinetics, product quality, structural and thermal behaviors[J]. CyTA-Journal of Food, 2024, 22(1):2303445.
[19] ZHOU X, LI R, LYNG J G, et al. Dielectric properties of kiwifruit associated with a combined radio frequency vacuum and osmotic drying[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2018,239:72−82. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.07.006
[20] FENG H, YIN Y, TANG J M. Microwave drying of food and agricultural materials:Basics and heat and mass transfer modeling[J]. Food Engineering Reviews,2012,4(2):89−106. doi: 10.1007/s12393-012-9048-x
[21] 刘欢, 王吉强, 牛玉宝, 等. 冬枣片热风干燥过程介电参数变化规律研究[J]. 包装与食品机械,2021,39(5):13−19. [LIU H, WANG J Q, NIU Y B, et al. Study on variation rules of dielectric parameters during hot-air drying process of winter jujube slices[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2021,39(5):13−19.] LIU H, WANG J Q, NIU Y B, et al. Study on variation rules of dielectric parameters during hot-air drying process of winter jujube slices[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2021, 39(5): 13−19.
[22] AHMED J, RAMASWAMY H S, RAGHAVAN G S V. Dielectric properties of soybean protein isolate dispersions as a function of concentration, temperature and pH[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2007,41(1):71−81.
[23] GUO W C, ZHU X H, LIU Y, et al. Sugar and water contents of honey with dielectric property sensing[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2009,97(2):275−281.
[24] 宋春芳, 桑田, 王燕, 等. 基于微波干燥的江南年糕介电特性的研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2015,31(11):177−183. [SONG C F, SANG T, WANG Y, et al. Effect of microwave drying on the dielectric properties of Jiangnan rice cakes[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology,2015,31(11):177−183.] SONG C F, SANG T, WANG Y, et al. Effect of microwave drying on the dielectric properties of Jiangnan rice cakes[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology, 2015, 31(11): 177−183.
[25] UAN G D, CHENG M, WANG Y, et al. Dielectric properties of mashed potatoes relevant to microwave and radio-frequency pasteurization and sterilization processes[J]. Journal of Food Science,2004,69(1):30−37.
[26] GUO W C, WANG S J, TIWARI G, et al. Temperature and moisture dependent dielectric properties of legume flour associated with dielectric heating[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2009,43(2):193−201.
[27] YIN M Y, MATSUOKA R, YANAGISAWA T, et al. Effect of different drying methods on free amino acid and flavor nucleotides of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) adductor muscle[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,396:133620. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133620
[28] EKWZIE F C, CHENG J H, SUN D W. Effects of atmospheric pressure plasma jet on the conformation and physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins from king prawn (Litopenaeus vannamei)[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,276:147−156.
[29] KAWAI M, OKIYAMA A, UEDA Y. Taste enhancements between various amino acids and IMP[J]. Chemical senses,2002,27(8):739−745. doi: 10.1093/chemse/27.8.739
[30] YAMAGUCHI S, YOSHIKAWA T, IKEDA S. Measurement of the relative taste intensity of some L-α-amino acids and 5'-nucleotides[J]. Journal of Food Science,1971,36(6):846−849. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1971.tb15541.x





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



