Effects of Low-carbon and High Protein Bread Diet on Blood Lipid, Immune Index and Intestinal Flora in Mice
-
摘要: 目的:采用高蛋白谷朊粉为主要原料制作面包作为小鼠饮食,观测低碳水高蛋白(low carbohydrate and high protein diet,LC-HP)饮食与高油、高糖饮食对小鼠血脂、免疫指标和肠道菌群的影响。方法:将健康的昆明种小鼠随机分为低碳水高蛋白组(A组,碳水化合物CHO 11.41%,蛋白质Pr 39.18%)、对照组(B组,CHO 47.4%,Pr 9.6%)、高油组(C组,CHO 51.4%,Pr 8.5%)、高糖组(D组,CHO 60.6%,Pr 7.3%),每组10只,雌雄各半,试验期28 d。每7 d称量小鼠体重,试验期末测定脏器系数,检测血清中甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)水平、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)、肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor,TNF-α)、血清白细胞介素6(interleukin 6,IL-6);16S rDNA测序检测小鼠粪便样本中菌群的变化。结果:A组小鼠体重增长率显著低于C组和D组(P<0.05);A组小鼠总TG、TC水平显著低于其它三组(P<0.05),A组小鼠LDL-C水平显著低于C、D组(P<0.05),A组小鼠HDL-C水平显著高于D组(P<0.05);A组免疫器官系数高于其它三组但无显著性;A组小鼠血清TNF-α、IL-6水平显著高于C、D组(P<0.05);A组反映肠道中微生物群落的丰富性和多样性的ACE、Chao1和Shannon指数均高于其他三组,且有益菌相对丰度显著(P<0.05)增加。结论:小鼠进食低碳水面包,与进食普通面包和进食高糖高油面包比较,能够降低体重增长率和血脂水平,调节免疫指标,改善肠道菌群组成,且确证了面包高糖比高油的健康不利影响更大。Abstract: Objective: To observe the effects of low carbohydrate and high protein diet (LC-HP) and high oil and high sugar diet on blood lipid, immune index and intestinal flora in mice. Use of high protein gluten as the main ingredient to make bread as the diet of mice. Methods: Healthy Kunming mice were randomly divided into low-carbon and high-protein group (group A, CHO 11.41%, Pr 39.18%), control group (group B, CHO 47.4%, Pr 9.6%), high-oil group (group C, CHO 51.4%, Pr 8.5%) and high-sugar group (group D, CHO 60.6%, Pr 7.3%). Each group consisted of 10 animals, 50 parts male and 50 parts female, for a 28 d experimental period. The mice were weighed every 7 days, and the organ coefficient was determined at the end of the experiment. The serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (high density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) were detected. 16S rDNA sequencing was used to detect the changes of flora in mouse fecal samples. Results: The weight growth rate of mice in group A was significantly lower than that in groups C and D (P<0.05). The levels of total TG and TC in group A were significantly lower than those in the other three groups (P<0.05), the levels of LDL-C in group A were significantly lower than those in groups C and D (P<0.05), and the levels of HDL-C in group A were significantly higher than those in group D (P<0.05). The immune organ coefficient of group A was higher than that of the other three groups, but there was no significant difference. The serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in group A were significantly higher than those in groups C and D (P<0.05). ACE, Chao1 and Shannon index of group A, which reflected the richness and diversity of intestinal microbial communities, were higher than those of the other three groups, and the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria was significantly increased (P<0.05). Conclusion: Compared with ordinary bread and high-sugar and high-oil bread, eating low-carbon water bread in mice could reduce the weight growth rate and blood lipid level, adjust immune indexes and improve the composition of intestinal flora, and it is confirmed that high-sugar bread had greater adverse health effects than high-oil bread.
-
Keywords:
- low-carbon water and high-protein diet /
- blood lipid /
- immunity /
- flora
-
在营养过剩、遗传和体力活动等因素共同影响下,现代人群较容易出现糖尿病、免疫失调、智力下降等营养相关的现象,消费者越发的倾向于采用饮食调节身体机能和状态。膳食因素伴随终身,改变膳食方式是控制肥胖较直接的切入点之一[1]。膳食减重策略根据其各自所强调内容的不同主要包括:低碳水化合物膳食[2]、高蛋白质膳食[3]、低血糖指数膳食[4]、限制能量膳食[5]、低脂膳食[6]以及地中海膳食[7]等。低碳水化合物膳食,是通过每日减少进食碳水化合物20~60 g来限制热量摄入(即减少每天热量摄入量的20%),增加蛋白质和脂肪的消耗,以替代原有碳水化合物的那部分热量[8],增加蛋白质消耗也即降低了蛋白质的生物价值。高蛋白饮食是一种每日蛋白质摄入量占总能量20%~30%的膳食模式[9]。有研究显示,高蛋白饮食可有效降低体重,改善血脂水平[10],然而,从能量代谢角度,在高蛋白低碳水的膳食中,减少的那部分碳水化合物热量被蛋白质和(或)脂肪替代,现有研究并没有解释在满足蛋白质需要前提下,碳水化合物与蛋白质提供同等能量水平,高蛋白饮食仍然能够减重降脂的原因;也没有阐明在蛋白质摄入充足且总能量水平相当前提下,额外增加蛋白质摄食相对于碳水化合物更具有饱腹感的原因。尽管高蛋白膳食有利于减少食物摄入的作用已众所周知,但人们疑虑的高蛋白饮食导致氮过剩可能带来的血生化和免疫微生物紊乱的忧虑并没有解决。这就需要针对性地设计低碳水高蛋白、高糖和高油饮食比较试验来明确这三个问题。
谷朊粉是从小麦中提取出的高蛋白聚合物,主要包含麦谷蛋白以及一些蛋白质质量分数较高的化合物。谷朊粉作为小麦中面筋性蛋白,具有很高的营养价值和良好的功能性质[11],应用范围广,具有较高的经济价值[12]。在食品加工过程中,谷朊粉可以作为一种重要的食品添加剂与食品改良剂,其氨基酸组成成分较齐全,营养成分较高[13]。在烘焙产品中,谷朊粉可以用来强化蛋白质含量低、质量不理想或不适合制作面包的面粉,添加谷朊粉后能够提高蛋白质含量,改善面包品质[14]。
本研究以谷朊粉为主要原材料,辅以膳食纤维、代糖等原料制备低碳水高蛋白谷朊粉面包,探究低碳水高蛋白饮食对小鼠的血脂、免疫指标以及肠道菌群的影响,以期为低碳水高蛋白食品开发和普通人群消费提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
健康昆明小鼠 3周龄,40只,雌雄各半,购买于北京华阜康生物科技有限公司,动物生产许可证号:SCXK(京)2019-0008,动物实验伦理审批号:2023 03 16 001,动物房温度为26~30 ℃,自由饮水,适应期1周,饲养于吉林农业大学实验动物中心;谷朊粉、熟黑豆粉、菊粉、燕麦麸皮、木糖醇、赤藓糖醇、酵母粉、饮用水 长春市迅驰广场沃尔玛超市;甘油三酯(TG)测试盒、总胆固醇(TC)测试盒、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)测试盒、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)测试盒、小鼠肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)ELISA检测试剂盒、小鼠白细胞介素6(IL-6)ELISA检测试剂盒 上海科兴商贸有限公司。
BSA224S-CW电子天平 北京赛多利斯器械公司;电烤箱 天猫小熊电器官方旗舰店;EL-10A全自动酶标仪 日本岛津公司;Neofuge-23R台式高速冷冻离心机 上海力申公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 低碳水高蛋白与对照饮食准备
制作低碳水高蛋白饮食谷朊粉面包,谷朊粉和熟黑豆粉混粉(9:1)300 g,菊粉和燕麦麸皮(1:1)20 g、木糖醇和赤藓糖醇(1:1)20 g、酵母粉3 g、温水200 mL,烤箱上下火模式180 ℃烘烤25 min,参考戴媛等[14]豌豆蛋白面包的制作,蛋白质的测定参照国标法[15]进行,碳水化合物的计算参考李小彦等[16]的研究,得到低碳水高蛋白饮食谷朊粉面包(CHO 11.41%、Pro 39.18%);对照饮食基础饲料(CHO 47.4%,Pr 9.6%);高油饮食配方:80%基础饲料+20%花生油(CHO 51.4%,Pr 8.5%);高糖饮食配方:80%基础饲料+20%白砂糖(CHO 60.6%,Pr 7.3%)。
1.2.2 小鼠饲养与分组
本试验获得吉林农业大学实验动物保护协会许可,小鼠按照吉林农业大学实验动物保护和使用规则饲养。选取3周龄的健康昆明种小鼠40只,雌雄各半,适应性喂养7 d后随机平分为四组:低碳水高蛋白饮食组(A组)、对照组(B组)、高油组(C组)、高糖组(D组),每组10只,雌雄各半。低碳水高蛋饮食组(A组)饲喂自制低碳水高蛋白谷朊粉面包,对照组(B组)饲喂基础饲料,高油组(C组)饲喂高油饮食,高糖组(D组)饲喂高糖饮食。试验期间自由进食、进水,喂养持续28 d,每7 d对单只小鼠称量一次体重。
1.2.3 样本采集
小鼠试验最后一天,排便量按每3~4只小鼠收集制成混合样,每组3样,装入2 mL无菌冻存管,液氮速冻后转移到−80 ℃冻存用于肠道菌群分析;末次喂食后禁食不禁水12 h,眼球取血后,室温静置1 h后于4 ℃,3500 r/min离心15 min,取上清液;处死后,取小鼠脾脏、胸腺用于称重。
1.2.4 指标的测定
1.2.4.1 小鼠体重增长率
1.2.4.2 小鼠血清生化指标
血液室温静置1 h后于4 ℃,3500 r/min离心15 min[17],取上清液进行生化指标检测,包括甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)。
1.2.4.3 小鼠免疫器官系数
将免疫器官(脾脏和胸腺)用生理盐水漂洗,滤纸吸干水分后进行精密称重,计算免疫器官系数。
1.2.5 小鼠肠道菌群16S rDNA测序
按照上海科兴商贸有限公司提供的取样和试样处理要求对小鼠粪便进行DNA提取,完成基因组DNA抽提后,利用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测抽提的基因组DNA按指定测序区域,合成带有barcode的特异引物。对PCR产物进行纯度检测后进行荧光定量分析。按照IlluminaMiseq平台的标准化操作流程利用纯化后的扩增片段构建Illumina PE250文库,进行 Illumina PE250测序,Illumina PE250测序得到的PE reads首先根据overlap关系进行拼接,同时对序列质量进行质控和过滤,区分样本后进行OTU聚类分析和物种分类学分析,基于OTU聚类分析结果,进行α-多样性分析、物种组成分析。
1.3 数据处理
应用GraphPad Prism 8.0.2、SPSS 17.0软件对数据进处理与统计学分析,采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)试验数据,以均数±标准差表示,以P<0.05为显著性差异水平。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 小鼠体重变化
小鼠体重指数直接反应超重或肥胖现象[18]。由表1和图2数据可知,各组小鼠体重随饲养时间延长均有增加。高油C、高糖D组雄雌小鼠的体重增长率较高,分别达到了23.17%、28.83%和23.42%、30.68%。低碳水高蛋白A组小鼠的体重增长率,雄、雌鼠分别为12.81%、8.99%,显著低于其它三组(P<0.05),表明食用低碳高蛋白饮食能够使小鼠体重增长率减慢,表1中低碳水高蛋白饮食对比对照饮食,雄鼠体重增长率少22.95%,雌鼠体重增长率少115.02%,对雌鼠减慢效应更强,高油、高糖饮食增重率无显著差异。
表 1 低碳水高蛋白饮食与高油、高糖饮食小鼠的体重变化Table 1. Weight changes of mice feed with LC-HP diet and high-oil and high-sugar diet性别 组别 饮食组成 初始体重(g) 7 d(g) 14 d(g) 21 d(g) 28 d(g) 体重增长率(%) 雄 A 低碳水高蛋白 33.34±0.72 34.59±0.82 36.03±0.91 36.93±0.88 37.60±0.57 12.81±2.67de B 对照 33.4±1.40 34.81±1.31 36.42±2.51 37.73±2.77 38.69±2.54 15.75±3.50cd C 高油 34.38±0.81 35.53±1.05 38.05±0.69 40.63±0.64 42.33±0.90 23.17±3.51b D 高糖 36.03±1.63 38.25±1.79 40.01±0.99 42.63±0.97 44.43±0.97 23.42±3.41b 雌 A 低碳水高蛋白 31.02±1.55 31.69±1.89 32.70±1.88 33.47±1.26 33.78±0.91 8.99±2.72d B 对照 30.16±0.68 32.10±0.73 33.67±0.44 35.05±0.59 35.98±0.82 19.33±2.41bc C 高油 31.15±1.34 34.92±1.63 36.16±1.24 38.76±1.95 40.13±1.88 28.83±1.06a D 高糖 31.69±2.01 34.26±2.19 36.83±2.97 39.26±2.46 41.36±2.04 30.68±5.29a 注:同列不同字母表示数据差异显著,P<0.05。 2.2 小鼠血清生化指标变化
血生化指标中的高、低密度脂蛋白直接包含蛋白质成分,是能量与蛋白膳食研究的常见指标,用于辅助分析肥胖或体重效应。图1(A)低碳水高蛋白饮食A组TG水平显著低于(P<0.05)其它三组小鼠血清中的TG水平,高糖饲料D组小鼠血清中TG含量显著高于其它组(P<0.05)。图1(B)中D组小鼠血清中TC水平在所有试验组中最高,显著(P<0.05)高于另外三组。A组TC水平最低,与其他三组相比存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。图1(C)中D组小鼠血清中LDL-C含量水平显著高于A、B、C组(P<0.05)。A组与B组、B组与C组之间均不存在显著性差异(P>0.05),C组小鼠血清的LDL-C水平显著高于A组(P<0.05)。可见,食用高油饲料和高糖饲料导致小鼠血清LDL-C的升高效果明显;其中,食用自制低碳水高蛋白面包和食用基础饲料的小鼠血清LDL-C水平上差异不显著(P>0.05),且食用自制低碳水高蛋白面包对于控制LDL-C的升高有积极作用。图1(D)可知,A、B组小鼠血清中HDL-C含量显著高于D组(P<0.05),A组小鼠血清中HDL-C含量在四组中最高,D组小鼠血清中HDL-C含量在四组中最低。血清生化指标测试表明,低碳水高蛋白饮食处理降低了血清TC、TG、LDL-C水平,HDL-C未受到显著影响;高糖饮食是导致高血脂水平的更重要因素。
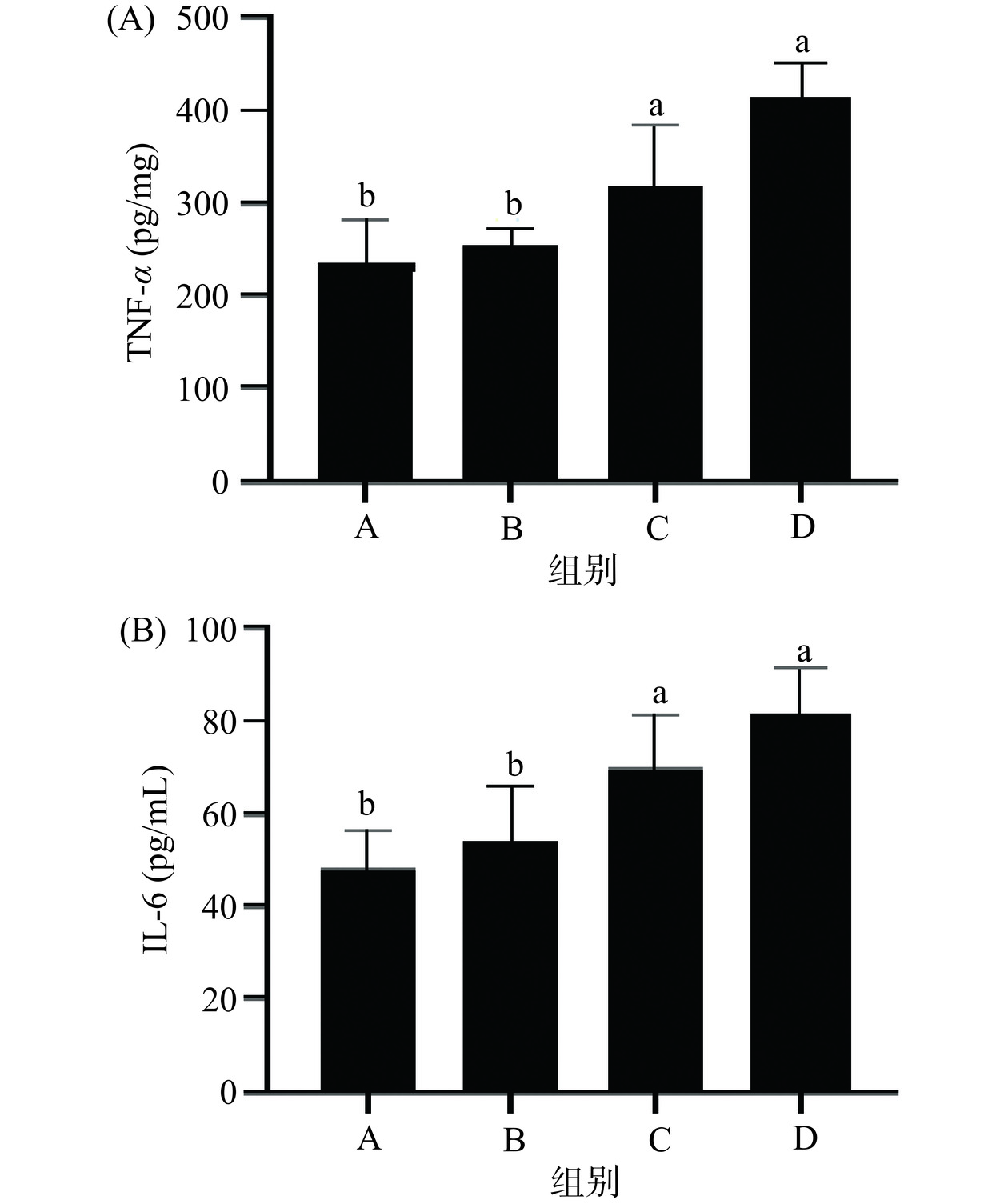
2.3 小鼠血清中TNF-α、IL-6变化
TNF-α介导免疫调节、炎症、生长调节等多方面的效应[19],与本研究的体增重与免疫相关;IL-6具有广泛生物活性,能促进并调节免疫系统炎性反应中多种细胞的增殖与分化[20],IL-6也是营养免疫研究中反映肝脏免疫机能的常用的和代表性的指标。由图2可知,小鼠连续分别喂养28 d后,与食用对照组B比较:食用高油饮食C组和高糖饮食D组的TNF-α、IL-6水平均显著升高(P<0.05),食用低碳水高蛋白饮食A组的TNF-α、IL-6水平与对照B组无显著性差异。结果表明,试验饮食对血清TNF-α、IL-6的增大效果顺序为:高糖>高油>对照>低碳高蛋白。
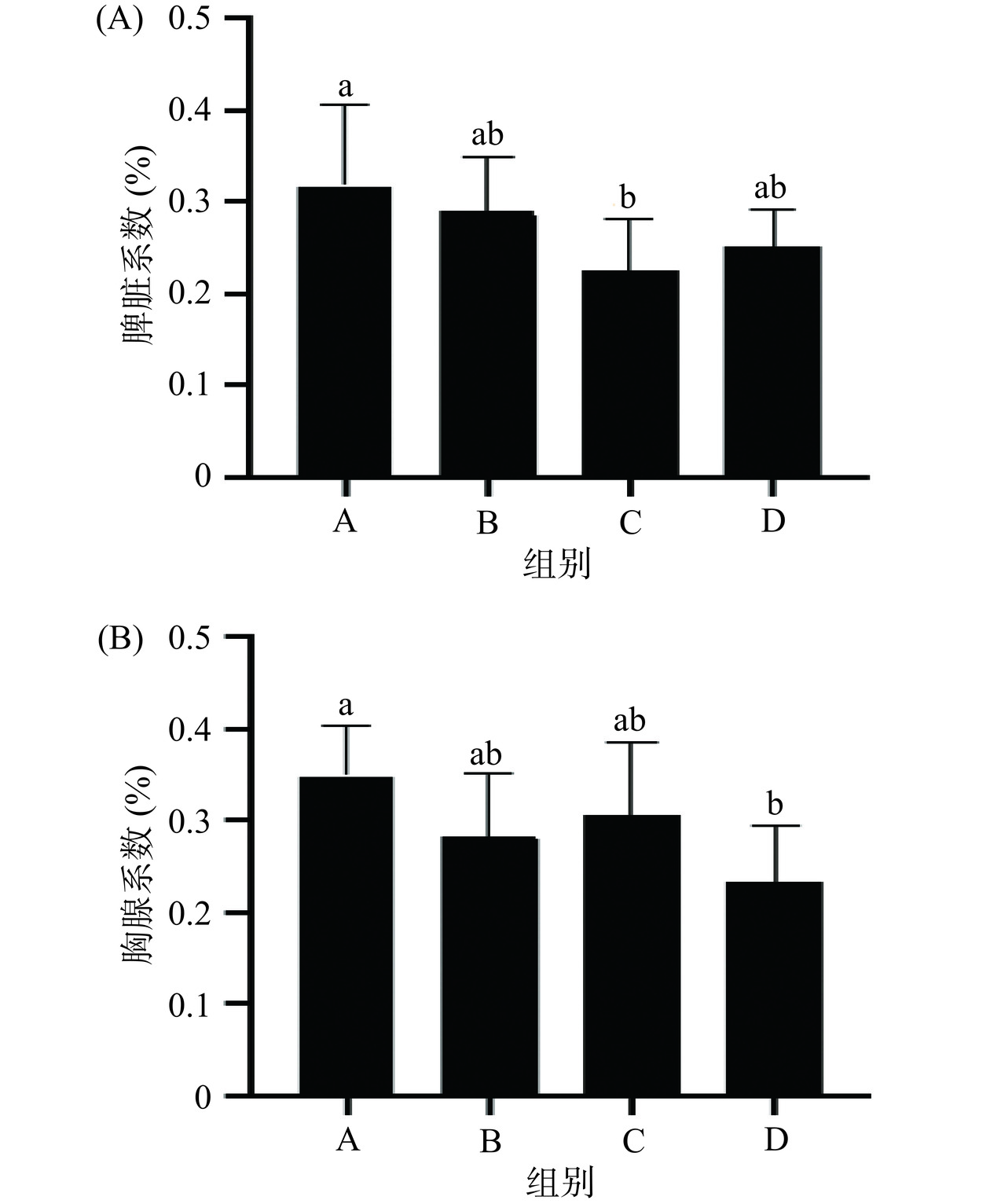
2.4 小鼠脾脏、胸腺系数比较
脾脏、胸腺都属于免疫器官,测定脾脏、胸腺系数对于考察低碳水高蛋白饮食具有参考意义。从图3(A)可知,A组小鼠的脾脏系数显著(P<0.05)高于C组,A、B、D组脾脏系数无显著性差异(P>0.05),但食用低碳水高蛋白饮食组小鼠的脾脏系数高于其它两组。从图3(B)知A组小鼠的胸腺系数显著高于D组(P<0.05),A、B、C组脾脏系数无显著性差异(P>0.05),A组小鼠的脾脏系数高于其它两组。结果表明,食用低碳水高蛋白饮食对脾脏系数和胸腺系数无显著的提高作用,而高油饮食导致血脂升高,由于白细胞的血液储备能力与动员能力比低碳水高蛋白处理组下降,导致脾脏系数显著降低(P<0.05)。蛋白质氨基酸营养素是胸腺T、B淋巴细胞的直接合成原料,在不缺乏能量前提下,高糖饮食挤占蛋白质供应水平,与低碳水高蛋白饮食组小鼠相比,高糖饮食组小鼠胸腺系数显著降低(P<0.05)。
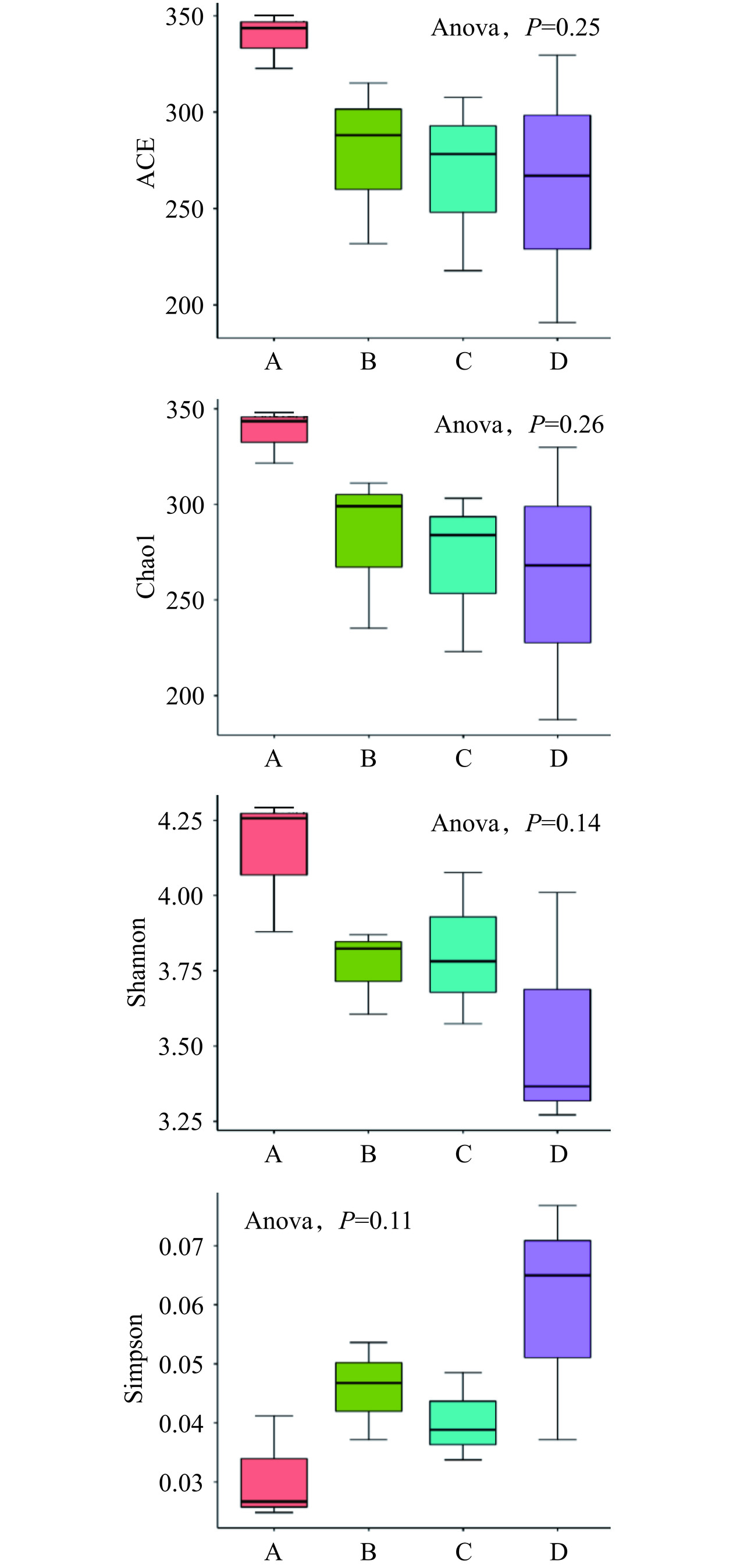
2.5 小鼠肠道菌群Alpha多样性分析
Alpha多样性可以选取ACE、Chao1、Shannon和Simpson 4个常用指数来分析鼠类肠道菌群的多样性[21]。本试验每个试样采用了3~4个平均样本,重复数n=3,由图4可知,A组的衡量菌种多样性ACE、Chao1、Shannon三个指数高于(P<0.11/3~0.26/3)B、C、D组,C、D组的ACE和Chao1指标略低于B组。低碳水高蛋白饮食提高了小鼠肠道菌群丰度和多样性,而高油、高糖饮食对低肠道菌群多样性有不利影响,其中,高糖相比高油不利影响更大。
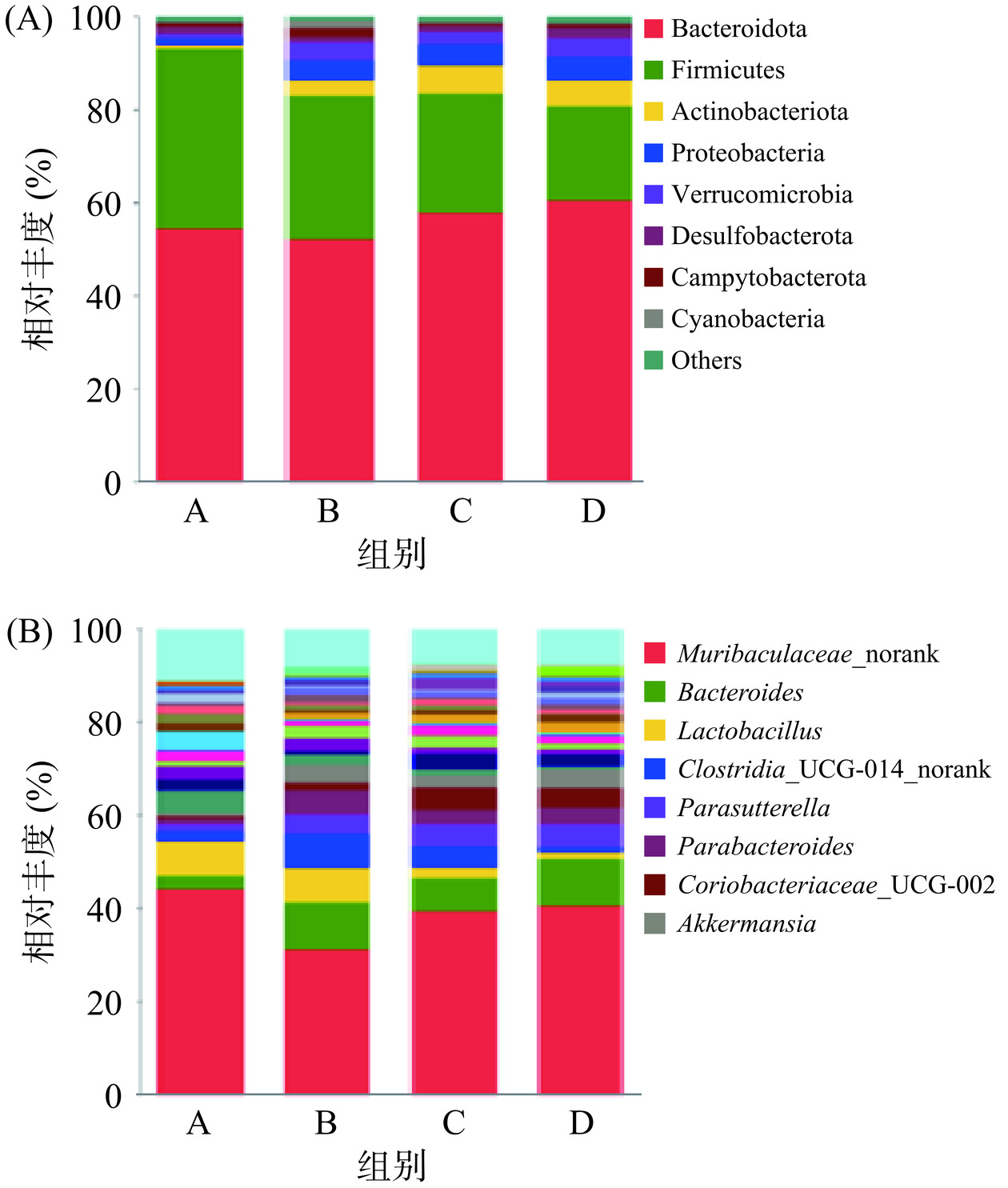
2.6 小鼠肠道菌群物种组成分析
试验小鼠的粪便样本进行16S rDNA测序后,检测不同试验组间肠道菌群在门水平与属水平的菌群变化物种丰度变化。如图5(A)所示,门水平上共检测出了9类优势菌群,其中拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、放线菌门(Actinobacteriota)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobia)为优势菌种。低碳水高蛋白饮食的肠道厚壁菌门相对丰度最高,而高油和高糖饮食的拟杆菌门增加,厚壁菌门减少。
对各试验组小鼠粪便样本菌群在属水平上进行分析结果如图5(B)所示:菌群以Muribaculaceae_norank菌属、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)、乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)、Clostridia_UCG-014_norank菌属、Parasutterella菌属、Parabacteroides菌属、Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002菌属、阿克曼菌(Akkermansia)为主。小鼠肠道乳酸菌在低碳水高蛋白、高油、高糖饮食组比对照组丰度增加;拟杆菌在低碳水高蛋白组减少约3倍;乳杆菌在高油、高糖组丰度降低约3~6倍;Clostridia_UCG-014_norank菌在低碳水高蛋白、高糖组丰度比对照组降低约3~5倍;Parasutterella菌在低碳水高蛋白组丰度比其它组降低约3倍;Parabacteroides菌在低碳水高蛋白组丰度比对照降低约3倍。结果表明,与对照组对比,低碳水高蛋白饮食提高了乳酸菌丰度,降低了Clostridia_UCG-014_norank菌、拟杆菌、Parasutterella菌和Parabacteroide菌的丰度,但高油高糖饮食的乳杆菌丰度降低,对Parasutterella菌和Parabacteroide菌的丰度没有影响。
3. 讨论
本试验所设计的低碳水、高蛋白、高油、高糖饮食指标,已经明显超出了《中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量》[22]规定的及日常人类均衡饮食的相关指标水平。低碳水高蛋白饮食中由菊粉和燕麦麸皮构成膳食纤维主要来源,不仅会直接影响宿主体内肠道菌群组成,同时菊粉也会通过影响宿主的新陈代谢和免疫系统,间接地塑造肠道菌群,改变肠道菌群的多样性;代糖几乎不产生能量[23−24],饮食可消化能量减少;谷朊粉的蛋白质含量较高,蛋白质的营养成分高,通过人体肠道消化吸收所产生的高能量增加机体饱腹感[25]。常见肉、乳、大豆等高蛋白饮食原料的可消化性好,而多数植物性碳水化合物往往与纤维素伴生,影响能量转化利用,导致蛋白质饱腹感强,利于减重,这与本试验的低碳水高蛋白饮食减重结果一致。关于体增重性别差异,本试验的低碳水高蛋白饮食导致小鼠体重增长缓慢,达成了预期的相对理想的减重目的与效果,尤其是对于同化代谢能力较强雌性小鼠,减慢效果更好;同时,依靠消耗蛋白质供应水平增加来提供能量,比碳水化合物直接供能的能量吸收效率下降,脂肪同化减少,会直接导致血清TC、TG、LDL-C水平降低,HDL-C增加;反之,高糖和高油脂饮食处理,直接导致血清TC、TG、LDL-C水平上升,HDL-C水平降低。肥胖和血脂水平与TNF-α、IL-6等免疫因子相关[26−27],本试验水平下,高油饮食降低脾脏系数,高糖饮食降低胸腺系数。同时,高油、高糖饮食激发了TNF-α、IL-6分泌,可能造成免疫失衡或应激状态,进而影响体增重。
肠道菌群的多样性能够反映出肠道内微生物的丰富度和均匀性,肠道菌群的平衡对于维持肠道健康有着重要意义[28],例如,拟杆菌在调节宿主肠道微环境、分泌短链脂肪酸等代谢产物、分解多糖以提高营养利用率、加快肠黏膜血管生成、促进免疫系统发育提高宿主免疫力等方面起重要作用[29],乳杆菌能够抑制肠道致病菌生长,维持肠道菌群平衡,还可以刺激和调节免疫应答[30],肠道菌群的调节也是影响体重增长的间接因素之一。本试验中,TNF-α、IL-6水平的变化可能是通过调节肠道微生物组成,间接影响血清免疫因子水平。至于被人们疑虑的高蛋白饮食导致氮过剩可能带来的尿酸代谢等问题,尚待下一步的长期试验来探明。试验操作实践中,微生物也普遍倾向于高蛋白基质条件,这是低碳水高蛋白饮食提高小鼠肠道菌群丰度和多样性的根本原因。相反,高油、高糖饮食对低肠道菌群丰度和多样性有不利影响,其中,高糖比高油对肠道菌群的不利影响更大。具体在本试验中表现为,低蛋白高碳水饮食提高了乳酸菌丰度,降低了Clostridia_UCG-014_norank菌、拟杆菌、Parasutterella菌和Parabacteroide菌的丰度,而高油、高糖饮食的乳杆菌丰度降低。
4. 结论
通过比较低碳水高蛋白面包饮食、普通饮食、高油饮食和高糖饮食对体增重率、血脂、免疫指标、肠道菌群影响的小鼠试验,发现食用低碳高蛋白饮食能够使小鼠尤其是雌性小鼠体重增长率减慢,同时降低血脂水平,调节免疫指标或使TNF-α、IL-6激发更为温和,且对肠道微生物的丰度和多样性组成有利。试验结果也体现出高糖饮食是导致高血脂水平的更重要因素。
-
表 1 低碳水高蛋白饮食与高油、高糖饮食小鼠的体重变化
Table 1 Weight changes of mice feed with LC-HP diet and high-oil and high-sugar diet
性别 组别 饮食组成 初始体重(g) 7 d(g) 14 d(g) 21 d(g) 28 d(g) 体重增长率(%) 雄 A 低碳水高蛋白 33.34±0.72 34.59±0.82 36.03±0.91 36.93±0.88 37.60±0.57 12.81±2.67de B 对照 33.4±1.40 34.81±1.31 36.42±2.51 37.73±2.77 38.69±2.54 15.75±3.50cd C 高油 34.38±0.81 35.53±1.05 38.05±0.69 40.63±0.64 42.33±0.90 23.17±3.51b D 高糖 36.03±1.63 38.25±1.79 40.01±0.99 42.63±0.97 44.43±0.97 23.42±3.41b 雌 A 低碳水高蛋白 31.02±1.55 31.69±1.89 32.70±1.88 33.47±1.26 33.78±0.91 8.99±2.72d B 对照 30.16±0.68 32.10±0.73 33.67±0.44 35.05±0.59 35.98±0.82 19.33±2.41bc C 高油 31.15±1.34 34.92±1.63 36.16±1.24 38.76±1.95 40.13±1.88 28.83±1.06a D 高糖 31.69±2.01 34.26±2.19 36.83±2.97 39.26±2.46 41.36±2.04 30.68±5.29a 注:同列不同字母表示数据差异显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] 林旭, 刘鑫, 黎怀星, 等. 肥胖的膳食控制策略[J]. 内科理论与实践,2017,12(4):245−255. [LIN Xu, LIU Xin, LI Huaixing, et al. Diet control strategies for obesity[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine Concepts & Practice,2017,12(4):245−255.] LIN Xu, LIU Xin, LI Huaixing, et al. Diet control strategies for obesity[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine Concepts & Practice, 2017, 12(4): 245−255.
[2] KIRKPATRICK C F, BOLICK J P, KRIS-ETHERTON P M, et al. Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors:A scientific statement from the national lipid association nutrition and lifestyle task force[J]. Journal of Clinical Lipidology,2019,13(5):689−711. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.08.003
[3] WOJCIK J L, AUKEMA H M, ZAHRADKA P, et al. Effects of high protein diets on metabolic syndrome parameters[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2016,8:43−49. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2016.02.001
[4] GAESSER G A, MILLER JONES J, ANGADI S S. Perspective:Does glycemic index matter for weight loss and obesity prevention? examination of the evidence on “fast” compared with “slow” carbs[J]. Advances in Nutrition,2021,12(6):2076−2084. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab093
[5] SCHUTTE S, ESSER D, SIEBELINK E, et al. Diverging metabolic effects of 2 energy-restricted diets differing in nutrient quality:A 12-week randomized controlled trial in subjects with abdominal obesity[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2022,116(1):132−150. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac025
[6] BASILE A, RENNER M, SCILLIAN J, et al. Restricting calories on low-carbohydrate vs low-fat diets for weight loss:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Current Developments in Nutrition,2020,4:nzaa063_007. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzaa063_007
[7] MANCINI J G, FILION K B, ATALLAH R, et al. Systematic review of the mediterranean diet for long-term weight loss[J]. The American Journal of Medicine,2016,129(4):407−415. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.11.028
[8] 张明. 低碳水化合物饮食在糖尿病中的应用[J]. 糖尿病天地(临床),2015,9(2):83. [ZHANG Ming. Application of low-carbohydrate diet in diabetes[J]. Clinical Journal of Diabetes World (Clinical),2015,9(2):83.] ZHANG Ming. Application of low-carbohydrate diet in diabetes[J]. Clinical Journal of Diabetes World (Clinical), 2015, 9(2): 83.
[9] 卫星, 孙萍. 高蛋白饮食体重管理模式对超重/肥胖病人代谢指标的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(20):3840−3843. [WEI Xing, SUN Ping. Effect of high-protein diet and weight management model on metabolic indexes of overweight/obese patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease,2023,21(20):3840−3843.] doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.20.032 WEI Xing, SUN Ping. Effect of high-protein diet and weight management model on metabolic indexes of overweight/obese patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, 2023, 21(20): 3840−3843. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.20.032
[10] KOSTOGRYS R B, FRANCZYK-ŻARÓW M, MAŚLAK E, et al. Effect of low carbohydrate high protein (LCHP) diet on lipid metabolism, liver and kidney function in rats[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2015,39(2):713−719. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.01.008
[11] XIN Z, YU Z, TIANYI Z, et al. Potential of hydrolyzed wheat protein in soy-based meat analogues:Rheological, textural and functional properties[J]. Food Chemistry:X, 2023:20100921.
[12] 王泽宇. 谷朊粉应用及深加工技术探讨[J]. 食品安全导刊,2019(36):71. [WANG Zeyu. Discussion on the application and deep processing technology of gluten[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2019(36):71.] WANG Zeyu. Discussion on the application and deep processing technology of gluten[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2019(36): 71.
[13] 吕一鸣, 田潇凌, 王晓曦, 等. 小麦蛋白质研究与开发现状[J]. 粮食加工,2022,47(3):8−13. [LÜ Yiming, TIAN Xiaoling, WANG Xiaoxi, et al. Research and development status of wheat protein[J]. Grain Processing,2022,47(3):8−13.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6395.2022.3.xblykj202203004 LÜ Yiming, TIAN Xiaoling, WANG Xiaoxi, et al. Research and development status of wheat protein[J]. Grain Processing, 2022, 47(3): 8−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6395.2022.3.xblykj202203004
[14] 戴媛, 冷进松, 傅婷婷. 豌豆蛋白面包的制作工艺优化及其品质[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(11):194−199. [DAI Yuan, LENG Jinsong, FU Tingting. Processing optimization and quality of pea protein bread[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(11):194−199.] DAI Yuan, LENG Jinsong, FU Tingting. Processing optimization and quality of pea protein bread[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(11): 194−199.
[15] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社. China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standards. Determination of protein in Food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China. [16] 李小彦, 姜晓燕, 刘美娟. 食品中碳水化合物计算方法探讨[J]. [J]. 现代食品,2020(10):175−176,179. [LI Xiaoyan, JIANG Xiaoyan, LIU Meijuan. Discussion on calculation method of carbohydrate in food[J]. Modern Food,2020(10):175−176,179.] LI Xiaoyan, JIANG Xiaoyan, LIU Meijuan. Discussion on calculation method of carbohydrate in food[J]. Modern Food, 2020(10): 175−176,179.
[17] LIU Y, YE L, CHEN H, et al. Herbicide propisochlor exposure induces intestinal barrier impairment, microbiota dysbiosis and gut pyroptosis[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2023,262:115154. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115154
[18] 李志春, 陈赶林, 郑凤锦, 等. 甘蔗醋对高脂喂养小鼠体质量、脏器系数和血清生化指标的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(1):50−54. [LI Zhichun, CHEN Ganlin, ZHENG Fengjin, et al. Effects of sugarcane vinegar on body weight, organ coefficient and serum biochemical indexes in mice fed with high fat[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(1):50−54.] doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.01.010 LI Zhichun, CHEN Ganlin, ZHENG Fengjin, et al. Effects of sugarcane vinegar on body weight, organ coefficient and serum biochemical indexes in mice fed with high fat[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(1): 50−54. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.01.010
[19] 杨玲, 陈可纯, 罗朵生, 等. 基于肠道菌群-TβMCA-FXR轴探讨田黄方对老年脂代谢紊乱小鼠作用机制[J]. 中药药理与临床,2023,39(1):18−24. [YANG Ling, CHEN Kechun, LUO Duosheng, et al. Based on the intestinal flora -TβMCA-FXR axis, the mechanism of Tianhuangfang in the treatment of senile mice with lipid metabolism disorder[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2023,39(1):18−24.] YANG Ling, CHEN Kechun, LUO Duosheng, et al. Based on the intestinal flora -TβMCA-FXR axis, the mechanism of Tianhuangfang in the treatment of senile mice with lipid metabolism disorder[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2023, 39(1): 18−24.
[20] 杨国平, 叶敏霞, 张荣, 等. 基于高通量测序的鼠类肠道细菌群落多样性分析[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械,2021,27(2):148−153. [YANG Guoping, YE Minxia, ZHANG Rong, et al. Diversity analysis of intestinal bacterial community in rodents based on high-throughput sequencing[J]. Chinese Journal of Hygienic Insecticides & Equipments,2021,27(2):148−153.] YANG Guoping, YE Minxia, ZHANG Rong, et al. Diversity analysis of intestinal bacterial community in rodents based on high-throughput sequencing[J]. Chinese Journal of Hygienic Insecticides & Equipments, 2021, 27(2): 148−153.
[21] 赖碧玉, 洪梦颖, 何永嘉, 等. 基于16S rDNA技术探讨针灸对腹泻型肠易激综合征模型大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2023,43(12):1411−1421. [LAI Biyu, HONG Mengying, HE Yongjia, et al. Based on 16S rDNA technology, this paper discusses the influence of acupuncture on intestinal flora in rats with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion,2023,43(12):1411−1421.] LAI Biyu, HONG Mengying, HE Yongjia, et al. Based on 16S rDNA technology, this paper discusses the influence of acupuncture on intestinal flora in rats with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion, 2023, 43(12): 1411−1421.
[22] 中国营养学会. 中国营养学会发布《2023版中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量》[J]. 营养学报, 2023, 45(5):414. [China Nutrition Society. China Nutrition Society issued the Reference Intake of Dietary Nutrients for China Residents[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2023, 45(5):414.] China Nutrition Society. China Nutrition Society issued the Reference Intake of Dietary Nutrients for China Residents[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2023, 45(5): 414.
[23] 方婷, 徐馨, 曲梦影, 等. 代糖与健康的研究进展[J]. 环境与职业医学,2023,40(7):775−781. [FANG Ting, XU Xin, QU Mengying, et al. Research progress of sugar substitute and health[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine,2023,40(7):775−781.] doi: 10.11836/JEOM22468 FANG Ting, XU Xin, QU Mengying, et al. Research progress of sugar substitute and health[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 2023, 40(7): 775−781. doi: 10.11836/JEOM22468
[24] CARLSON J L, ERICKSON J M, LLOYD B B, et al. Health effects and sources of prebiotic dietary fiber[J]. Current Developments in Nutrition,2018,2(3):nzy005. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzy005
[25] 刘爽, 彭依晴, 杜晨阳, 等. 影响饱腹感的成分及其生理功能的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(22):8827−8833. [LIU Shuang, PENG Yiqing, DU Chenyang, et al. Research progress on components affecting satiety and their physiological functions[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(22):8827−8833.] LIU Shuang, PENG Yiqing, DU Chenyang, et al. Research progress on components affecting satiety and their physiological functions[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2021, 12(22): 8827−8833.
[26] 曾江琴, 孙勤国, 徐鸿婕, 等. 小陷胸汤对高血脂小鼠血脂及免疫功能的影响[J]. 现代免疫学,2021,41(5):374−379. [ZENG Jiangqin, SUN Qinguo, XU Hongjie, et al. Effect of Xiaoxinxiong decoction on blood lipid and immune function in hyperlipidemia mice[J]. Current Immunology,2021,41(5):374−379.] ZENG Jiangqin, SUN Qinguo, XU Hongjie, et al. Effect of Xiaoxinxiong decoction on blood lipid and immune function in hyperlipidemia mice[J]. Current Immunology, 2021, 41(5): 374−379.
[27] LIN S, YU Y, CENTA M, et al. Induction of lipid-lowering immune reactions by apolipoprotein B-specific T-helper cells in hypercholesterolemic mice[J]. Atherosclerosis,2023,379:S11.
[28] 任彩君, 吴黎明, 王凯. 膳食多酚对肠道菌群影响研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(1):400−409. [REN Caijun, WU Liming, WANG Kai. Research progress on the effect of dietary polyphenols on intestinal flora[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):400−409.] REN Caijun, WU Liming, WANG Kai. Research progress on the effect of dietary polyphenols on intestinal flora[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(1): 400−409.
[29] YAO Y, CAI X, FEI W, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in immunity, inflammation and metabolism[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2022,62(1):1−12. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1854675
[30] 汪雪, 陈颖, 崔省委, 等. 乳杆菌属益生菌在家畜疾病防治中的应用[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医,2022,52(6):17−20,29. [WANG Xue, CHEN Ying, CUI Shengwei, et al. Application of Lactobacillus probiotics in prevention and treatment of livestock diseases[J]. Gansu Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2022,52(6):17−20,29.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-799X.2022.06.006 WANG Xue, CHEN Ying, CUI Shengwei, et al. Application of Lactobacillus probiotics in prevention and treatment of livestock diseases[J]. Gansu Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 52(6): 17−20,29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-799X.2022.06.006
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



