Stability Analysis of Pickering Nanoemulsion Covered by Dual-protein Natural Symbiotic Particles
-
摘要: 利用双蛋白天然共生颗粒制备Pickering纳米乳液并对其物化稳定性进行分析,以此拓宽其在食品领域中的应用潜力。本研究采用碱提取-等电点沉淀法(Alkali extraction-isoelectric point precipitation,AE)和盐提取-透析法(Salt extraction-dialysis,SE)从大豆-亚麻籽混合粕中富集大豆蛋白(Soy protein)和亚麻籽蛋白(Flaxseed protein),制备双蛋白天然共生颗粒(Natural particles,SFNPs)。首先,利用外观观察、原子力显微镜(Atomic force microscopy,AFM)、圆二色谱和拉曼光谱对两种双蛋白共生颗粒进行表征;其次,将其作为颗粒稳定剂制备Pickering纳米乳液,并对其物理和化学稳定性进行表征。结果表明AE-SFNPs的尺度更为均一,且具有良好的分散性。与SE-SFNPs相比,AE-SFNPs的二级结构中β-折叠占比更高,达51.25%,具有更加致密有序和良好柔性的结构特性。2种双蛋白天然共生颗粒均可制备出Pickering纳米乳液。在28 d的贮藏期间,AE-SFNPs稳定乳液的粒径仅增加了约14 nm,电位基本稳定在-34 mV左右,而SE-SFNPs稳定乳液的粒径增加了约12倍,电位降低了1.32倍。贮藏至第28 d时,AE-SFNPs的稳定性指数(Turbiscan stability index,TSI,5.83),远小于SE-SFNPs的TSI值(55.13)。尤其是,AE-SFNPs制备的Pickering纳米乳液表现出了比酪蛋白酸钠(食品领域加工常用乳化剂)制备的纳米乳液更佳的物理稳定性和化学稳定性。因此,AE-SFNPs可作为一种天然高效植物蛋白基颗粒稳定剂制备Pickering纳米乳液,为丰富纳米乳液的工业化应用提供了新的解决策略。
-
关键词:
- 植物基双蛋白 /
- 共生提取 /
- 天然颗粒 /
- 界面重构 /
- Pickering纳米乳液
Abstract: Pickering nanoemulsions were prepared using dual-protein natural symbiotic particles and their physicochemical stability was analyzed to broaden their potential application in the food industry. This study employed alkali extraction-isoelectric point precipitation (AE) and salt extraction-dialysis (SE) to enrich soy protein and flaxseed protein from soybean-flaxseed mixed meal for fabricating dual-protein symbiotic natural particles (SFNPs). First, two dual-protein symbiotic particles were characterized using appearance observation, AFM, circular dichroism, and Raman spectroscopy. Then, Pickering nanoemulsions were prepared with them as particle stabilizers and characterized for their physical and chemical stability. Results demonstrated that AE-SFNPs had a higher uniformity of size and better dispersibility. AE-SFNPs also showed a higher proportion (as high as 51.25%) of β-sheet in its secondary structure, endowing it a more tightly ordered and flexible structure compared with SE-SFNPs. Moreover, both AE-SFNPs and SE-SFNPs could be used to generate Pickering nanoemulsion. During 28 days of storage, the particle size of the stabilized emulsion of AE-SFNPs increased only about 14 nm and its ζ-potential was stabilized at about -34 mV. In contrast, the particle size of the stabilized emulsion of SE-SFNPs increased about 12 fold, and its ζ-potential was decreased 1.32 fold. The stability index (TSI, 5.83) of the AE-SFNPs was much smaller than the TSI value (55.13) of the SE-SFNPs when stored until the 28th day. Notably, the Pickering nanoemulsion stabilized by AE-SFNPs exhibited higher physical and chemical stability than that prepared by sodium caseinate (a common emulsifier used in food processing). Therefore, AE-SFNPs can serve as a natural and efficient plant protein-based particle stabilizer to prepare Pickering nanoemulsion. This work provides a new strategy to enhance the industrial application of nanoemulsions. -
纳米乳液是指一种平均液滴大小分布为100~500 nm范围的乳液,因其比传统乳液具备更高的稳定性、溶解性和生物利用率等优势,近年来在食品领域引起了广泛关注[1−3]。选择合适的乳化剂是形成和稳定纳米乳液的关键因素之一,目前,合成表面活性剂因其出色的乳化性能,通常被用于制备纳米乳液[4−5]。然而,考虑到合成表面活性剂潜在的安全问题以及消费者对天然成分的日益青睐,开发更绿色、更健康的食品级成分作为乳化剂来替代合成表面活性剂非常重要[6]。
大豆蛋白因其来源广泛、成本低、具备良好的两亲性等优势,常被用作天然乳化剂[7],但由于其分子量大、柔性较差等结构问题,导致在高能乳化过程中蛋白质易发生变性和聚集,表现出较差的界面特性,进而导致大豆蛋白基纳米乳液稳定性较差[8−10]。如何利用大豆蛋白基天然乳化剂制备粒径小、分散性好、稳定性高的纳米乳液是亟待克服的难题。目前研究报道引入其他蛋白质与大豆蛋白形成复合物颗粒,可以有效调节其在油/水界面上的界面特性,进而改善大豆蛋白的乳化性能[10−12]。本团队前期实现了亚麻籽蛋白与大豆蛋白的共生富集,与单独大豆蛋白相比,共生纳米颗粒的乳化性提高了1.36倍以上,与酪蛋白酸钠乳化性能相当[13],具备代替动物基蛋白在食品加工中的应用潜力,但目前有关双蛋白共生颗粒的应用场景有限,鉴于纳米乳液被越来越多的工业产品所采用,包括食品配料、药品、护理品和包装等[9],探究共生颗粒在制备高稳定性纳米乳液的潜能具有重要意义。
Pickering纳米乳液属于纳米乳液的范畴,其乳滴尺寸为纳米级,油-水界面由颗粒所覆盖,兼具Pickering乳液和纳米乳液的双重优势[14−15],不仅具备高稳定性、低粘度和半透明性的特征优势[16],而且大大减少了表面活性剂的使用,更符合绿色、可持续发展的理念[17]。因此,在之前的研究基础上[13],本工作利用高压微射流对碱提取-等电点沉淀法(Alkali extraction-isoelectric point precipitation,AE)和盐提取-透析法(Salt extraction-dialysis,SE)获得的双蛋白天然颗粒(Natural particles,SFNPs)稳定的Pickering乳液进行处理,试图制备Pickering纳米乳液,并尝试对其物化稳定性和稳定机制进行初步探究。本研究有望为植物基蛋白颗粒稳定的纳米乳液在食品领域中的应用提供新的研究策略。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆(品种:油6019#) 中国农业科学院油料作物研究所;亚麻籽(品种:张亚2#) 中国甘肃省农业科学院;亚麻籽油(食品级) 北京红井源有限公司;酪蛋白酸钠 北京沃凯生物科技有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
M-110E高压微射流纳米均质机 德国Microfluidicsgon公司;T25高速剪切均质机 德国IKA公司;ZetaSizer Nano-ZS纳米粒度及Zeta电位仪 英国马尔文仪器公司;Thermo Fischer DXR拉曼光谱仪、FEI Talos F200C低温冷冻透射电镜 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;J-1500圆二色光谱仪 日本JASCO公司;F7000荧光分光光度计 日本日立公司;Turbiscan Lab多重光散射仪 法国Formulaction仪器公司;Bruker Dimension Icon原子力显微镜 布鲁克(北京)科技有限公司;SU8010低温冷冻扫描电镜 日立科学仪器(北京)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大豆蛋白-亚麻籽蛋白天然共生颗粒的制备
首先,通过将大豆和亚麻籽进行冷榨、粉碎和索氏抽提去残油,获得脱脂豆粕和脱脂亚麻籽粕。然后,在前期实验室工作的基础上,将脱脂豆粕和脱脂亚麻籽粕按照8:2(w/w)的比例进行混合,通过以下两种提取方法获得不同样品[13]:
碱提取-等电点沉淀法:将混合粕按1:10(w/v)的比例分散在超纯水中。在室温下,适度搅拌2 h,并用2 mol/L NaOH调节pH维持在9.0,以8000×g的转速离心30 min,收集上清液。随后,用2 mol/L HCl调节pH至4.0后,在相同条件下再次离心,收集沉淀。将收集的沉淀按照1:5的比例在超纯水中复溶,并调节pH至7.0。最后,进行冷冻干燥,获得大豆蛋白-亚麻籽蛋白天然共生颗粒(AE-SFNPs)(蛋白含量为78.17%,蛋白得率为31.90%)。
盐提取-透析法:将混合粕按1:10(w/v)的比例分散在0.3 mol/L CaCl2溶液中。在室温下,适度搅拌2 h,并用2 mol/L NaOH或HCl调节pH维持在5.6,以8000×g的转速离心30 min,收集上清液。在4 ℃下用超纯水中透析48 h(截留分子量:3 kDa,电导率达到~20 μs/cm)。最后,将透析后的上清液进行冷冻干燥,获得大豆蛋白-亚麻籽蛋白天然共生颗粒(SE-SFNPs)(蛋白含量为83.93%,蛋白得率为28.70%)。上述所得组分均储存在4 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.2 大豆蛋白-亚麻籽蛋白天然共生颗粒的表征
1.2.2.1 外观和原子力显微镜观察
制备1%(w/v)的样品溶液:称取0.1 g样品粉末溶于10 mL超纯水中,适度搅拌并调节pH至7.0。首先,数码相机对外观进行拍照;然后,将5 μL的样品(10 μg/mL)置于云母板上,自然条件下干燥后,通过原子力显微镜观察样品形貌(图片视野选择为5 μm×5 μm)[18]。
1.2.2.2 圆二色谱测定
制备浓度为0.4 mg/mL的样品溶液:首先,称取0.4 g样品粉末溶于100 mL超纯水中,适度搅拌并调节pH至7.0,获得4 mg/mL样品储备液;然后,取适量样品储备液用超纯水将其稀释至0.4 mg/mL。在带宽1.0 nm和光径100 mm条件下利用圆二色光谱仪(CD)获取190~240 nm的远紫外圆二色谱。同时,使用CD Pro软件分析α-螺旋、β-折叠、β-转角和无规卷曲的含量[19]。
1.2.2.3 拉曼光谱的测定
将样品粉末直接平铺在载玻片上进行拉曼光谱测定,激发光波长为785 nm,激光功率150 mW,扫描范围400~2000 cm−1,扫描时间60 s/次,分辨率1 cm−1。以苯丙氨酸(1003±1 cm−1)作为归一化因子。进行了三次平行测定,数据由OMNIC进行基线校正和平滑处理,并使用Peakfit 4.12软件进行蛋白质酰胺I带的峰值拟合。数据以平均值±标准差表示。分析了酪氨酸(I850/I830)和色氨酸(I760)残基微环境和二硫键(500~550 cm−1)构象[20]。
1.2.2.4 荧光光谱的测定
制备0.4 mg/mL的样品溶液:首先,称取0.4 g样品粉末溶于100 mL超纯水中,适度搅拌并调节pH至7.0,获得4 mg/mL样品储备液;然后,取适量样品储备液用超纯水将其稀释至0.4 mg/mL。使用F7000荧光分光光度计进行分析,采用石英比色皿,光程为1 cm。激发波长为290 nm,发射波长为300~400 nm。激发和发射狭缝宽度均设置为2.5 nm,电压为650 V,扫描速度为1200 nm/min[21]。
1.2.3 Pickering纳米乳液的制备
首先,称取适量1.2.1中制备的蛋白质样品溶于超纯水,调节pH至7.0,磁力搅拌2 h,制备浓度为1%(w/v)样品溶液;将组分溶液与亚麻籽油以19:1(v/v)的比例混合,用高速剪切均质机在15000 r/min下分散5 min获得粗乳,再用微射流在10000 psi下均质4次获得亚麻籽油Pickering纳米乳液。为了探究蛋白样品的应用潜力,选用食品领域常用的酪蛋白酸钠,将利用上述相同步骤制备的纳米乳液作为对照组。为防止在储藏实验中微生物污染引起试验数据误差,乳液制备完成之后向乳液中添加0.02%(w/v)叠氮化钠用来抑制微生物的生长。最后将乳液分装于5 mL样品瓶中并用封口膜密封,置于室温25 ℃下避光储藏28 d,分别于第0、3、7、14、21和28 d取样对相关指标进行测定。
1.2.4 Pickering纳米乳液界面微观结构表征
1.2.4.1 低温冷冻透射电镜
利用低温冷冻透射电镜(Cryo-TEM)观察Pickering纳米乳液液滴的微观形态。将5 μL乳液液滴置于多孔碳涂层铜网网格上,用滤纸轻轻吸干以除去多余的液体。然后,将铜网迅速浸入−180 ℃的液态乙烷中,形成一个理想的没有冰晶的玻璃化样品。在成像之前,铜网储存在液氮中。将样品在−180 ℃阶段温度和120~200 kV工作电压下进行扫描[22]。
1.2.4.2 低温冷冻扫描电镜
利用低温冷冻扫描电镜(Cryo-SEM)观察Pickering纳米乳液液滴的界面膜结构。取3.0 μL乳液在液氮中冷冻,转移到冷冻制备室中(−140 ℃)。然后将其切割成横截面,在−60 ℃下升华15 min。在10 mA溅射镀膜1200 s后,用低温冷冻扫描电子显微镜进行观察[23]。
1.2.5 Pickering纳米乳液界面结构形成原因探究
利用ZetaSizer Nano-ZS纳米粒度仪分别测定样品在经过高速剪切(制备粗乳条件:15000 r/min,5 min)以及微射流(制备Pickering纳米乳液条件:10000 psi,4次)后的粒度分布情况,以进一步探究AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs稳定Pickering纳米乳液界面结构形成的原因。
1.2.6 Pickering纳米乳液的稳定性研究
1.2.6.1 外观形貌、粒径和ζ-电势
以超纯水溶液为分散剂,将Pickering纳米乳液以1:200的比例进行稀释,使用纳米粒度及Zeta电位仪测定第0、3、7、14、21和28 d乳液的电位和粒径,并用数码相机拍摄纳米乳液室温下避光贮藏28 d的外观变化。
1.2.6.2 动力学稳定性测定
采用Turbiscan Lab多重光散射仪监测储藏过程中Pickering纳米乳液的动力学稳定性。仪器采用波长为880 nm的脉冲近红外光源进行扫描,将装有20 mL乳液的专用样品瓶轻放至仪器测试槽中,设置测试温度25 ℃,分别在第0、3、7、14、21和28 d对乳液进行一次扫描,记录稳定性指数(Turbiscan stability index,TSI)[24]。
1.2.6.3 纳米乳液储藏过程中氢过氧化物测定
采用紫外分光光度计法对乳液体系中氢过氧化物含量进行测定[25]。具体方法如下:0.3 mL乳液与1.5 mL破乳剂(异辛烷:异丙醇=3:1)混合,涡旋振荡10 s,重复3次,每次间隔20 s进行乳液破乳,5000×g离心10 min获得油相。取200 μmol/L上层有机相于10 mL离心管中,并加入2.8 mL甲醇/丁醇(2:1)混合液,紧接着加入30 μL Fe2+和3.14 mol/L硫氰酸铵(1:1,v/v)混合液,振荡均匀,暗反应20 min后在510 nm波长下使用紫外分光光度计测定吸光度。
1.2.6.4 纳米乳液储藏过程中TBARS测定
采用紫外分光光度计对乳液体系中的丙二醛含量进行测定[26]。具体方法如下:在耐高温螺盖玻璃皂化管中加入1 mL乳液并与2 mL TBA试剂混合,振荡均匀,沸水浴15 min,冷却至室温,5000×g离心15 min,在532 nm波长下使用紫外分光光度计测定吸光度。使用1,1,3,3-四乙氧基丙烷配制标准溶液绘制标准曲线,单位为mmol TEP/kg油。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验均重复3次,数据以“平均值±标准误差”形式表示。利用软件SPSS Statistics 26的单因素方差分析法评估平均值之间的差异,P<0.05表示存在显著性差异。利用软件Origin 2021和软件Visio 2021进行图表绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 大豆蛋白-亚麻籽蛋白天然共生颗粒性质分析
2.1.1 外观观察和原子力显微镜(AFM)分析
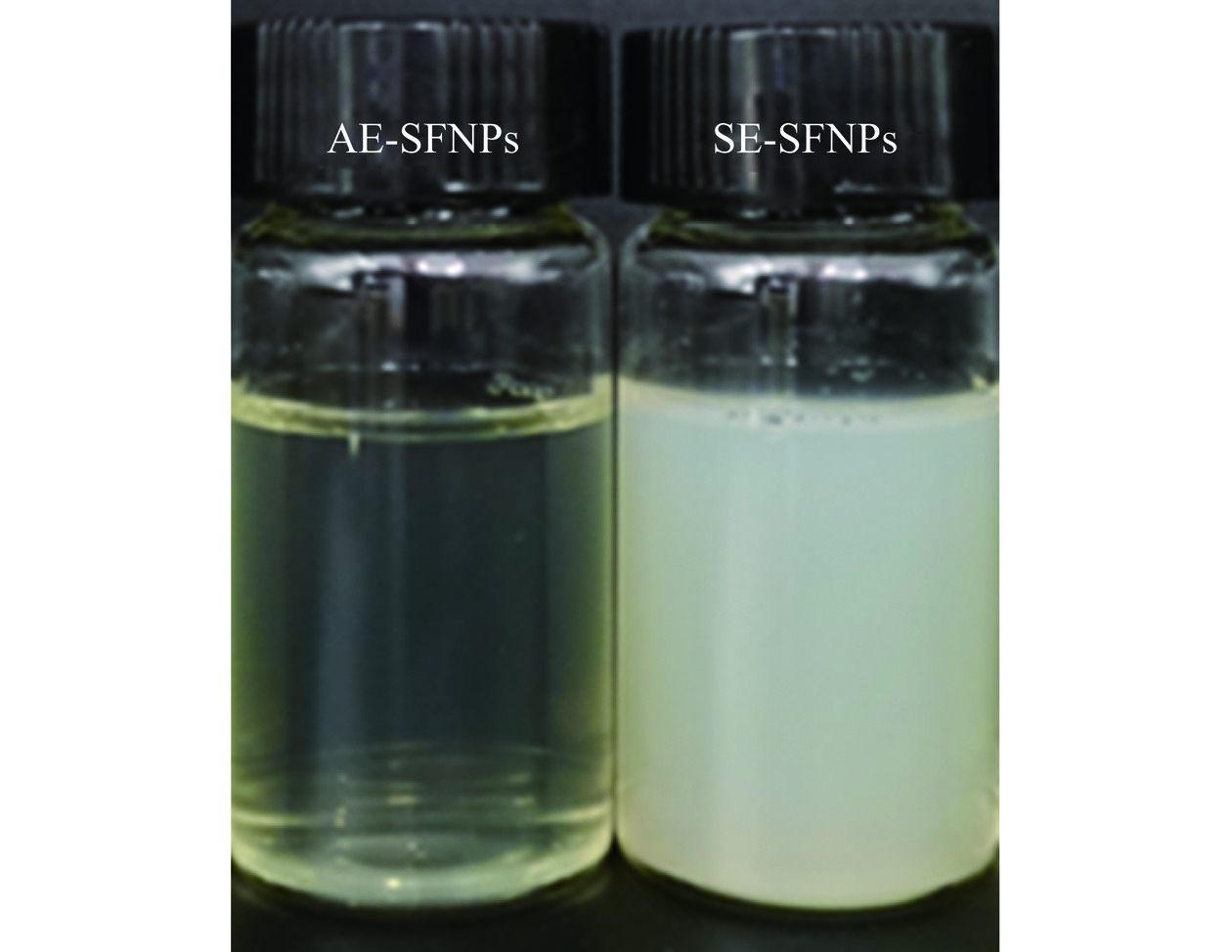
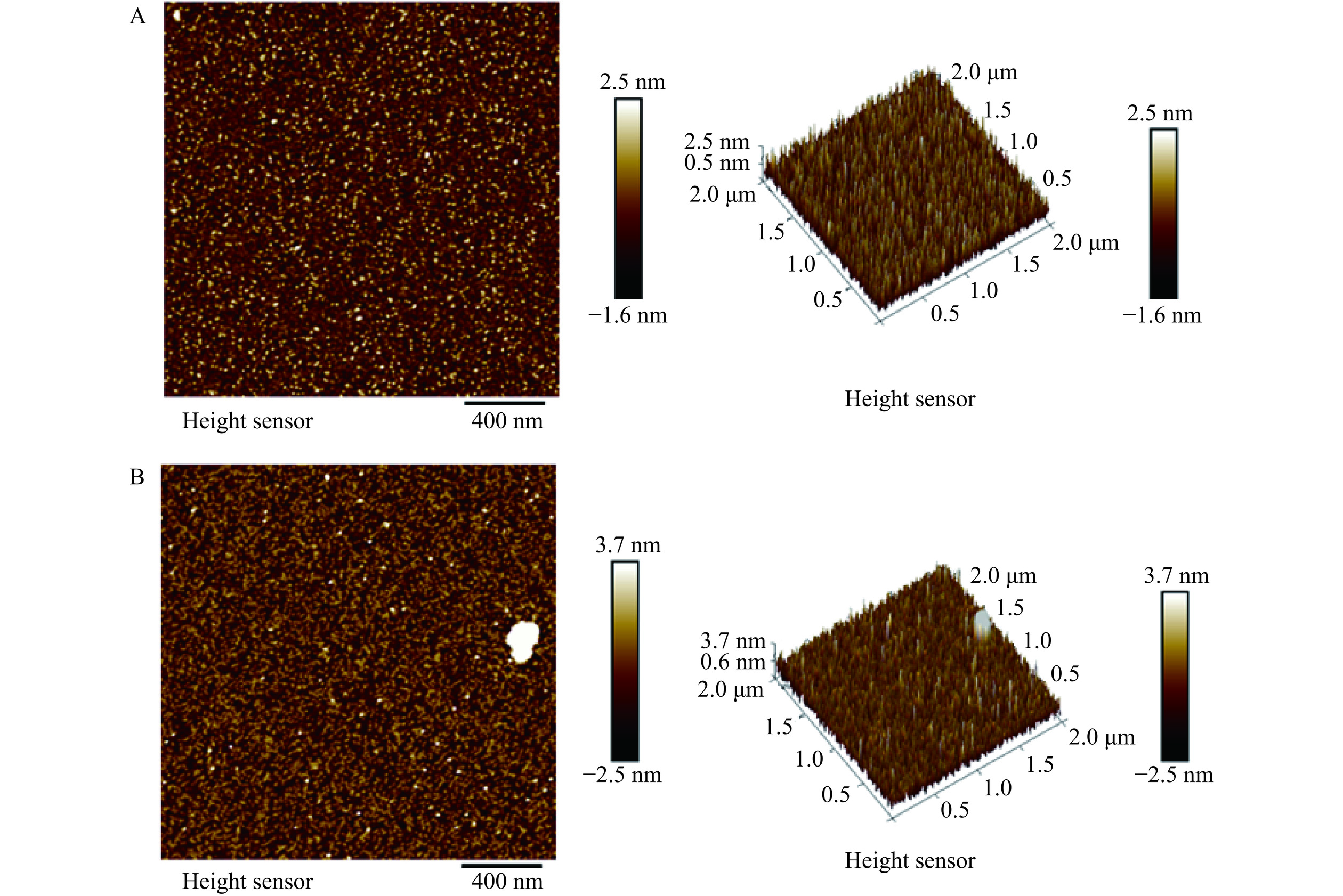
图1显示了浓度为1%(w/v)的AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs在pH7.0条件下溶液的外观状态,AE-SFNPs澄清透亮,说明分散体系较为均一,而SE-SFNPs的外观偏浑浊,表明盐提-透析法得到的AE-SFNPs分散性较差,两种不同提取方法制备得到SFNPs的分散状态明显不同可能与其颗粒尺寸有关。由前期的研究可知,AE法制备的双蛋白天然共生颗粒的平均粒径为160.53 nm,远小于SE法制备的共生颗粒(359.03 nm)[13]。同时,两者的原子力显微镜图像进一步显示AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs均呈现类似球形的颗粒态,AE-SFNPs的尺度小,分散相对均一(图2A),而SE-SFNPs的尺度不均一,且有较大蛋白聚集体产生(图2B),远大于AE-SFNPs的颗粒尺寸,这与两者粒径的测定结果相一致。
2.1.2 圆二色谱(CD)分析
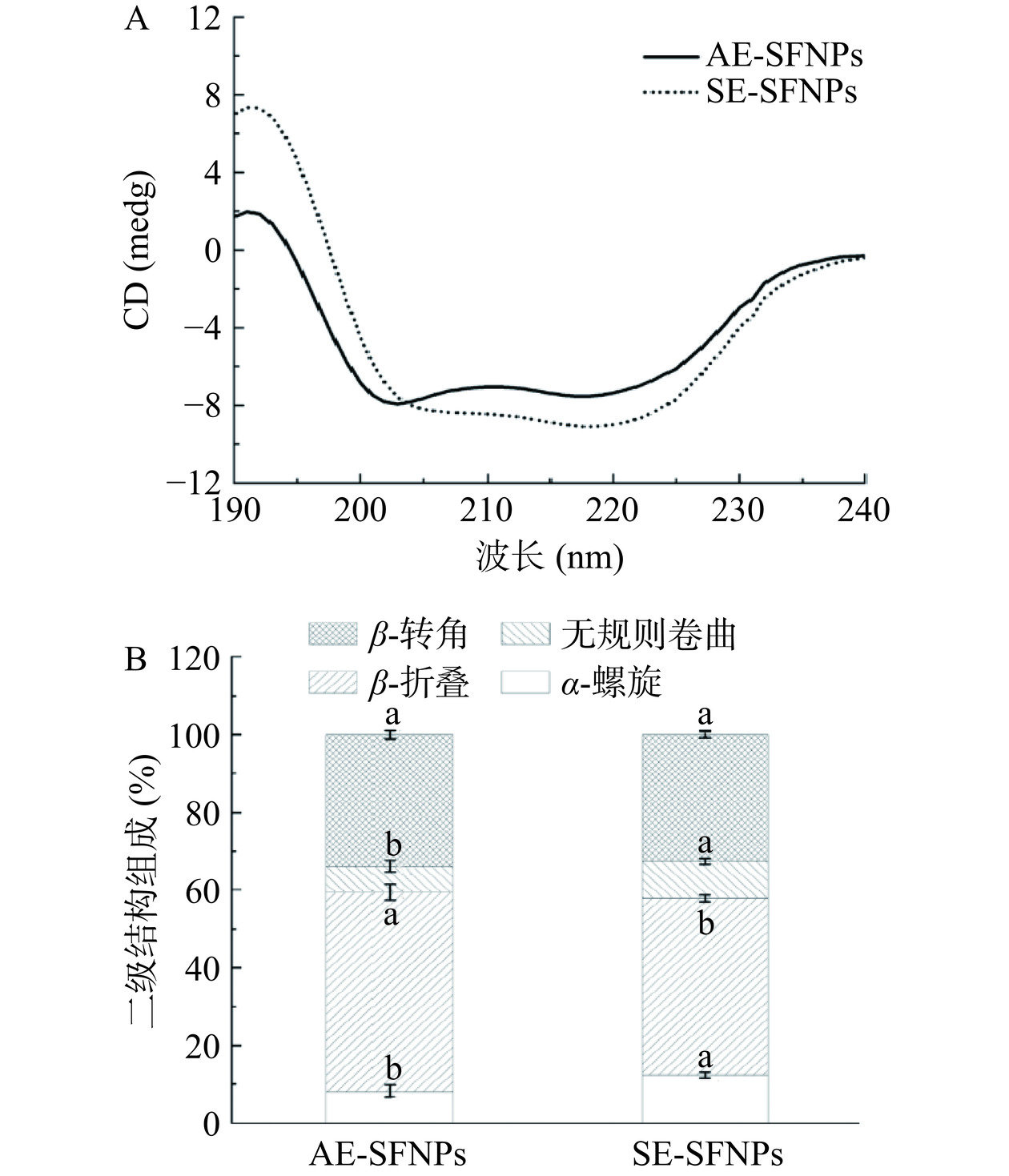
由图3A可以看出,AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的CD光谱图存在明显差异,代表其二级结构的不同。为了得到具体的二级结构含量,利用CD Pro软件进一步计算了α-螺旋、β-折叠、β-转角、无规则卷曲在AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs中的占比,如图3B所示,AE-SFNPs的α-螺旋占比仅8.25%,比SE-SFNPs少4.15%,而其β-折叠占比51.25%,比SE-SFNPs显著多5.75%(P<0.05),这表明β-折叠在AE-SFNPs的二级结构中占比更大,而α-螺旋占比少。据报道,β-折叠比α-螺旋具有更强的灵活性[27],因此,AE-SFNPs的柔性可能更强。
2.1.3 拉曼光谱分析
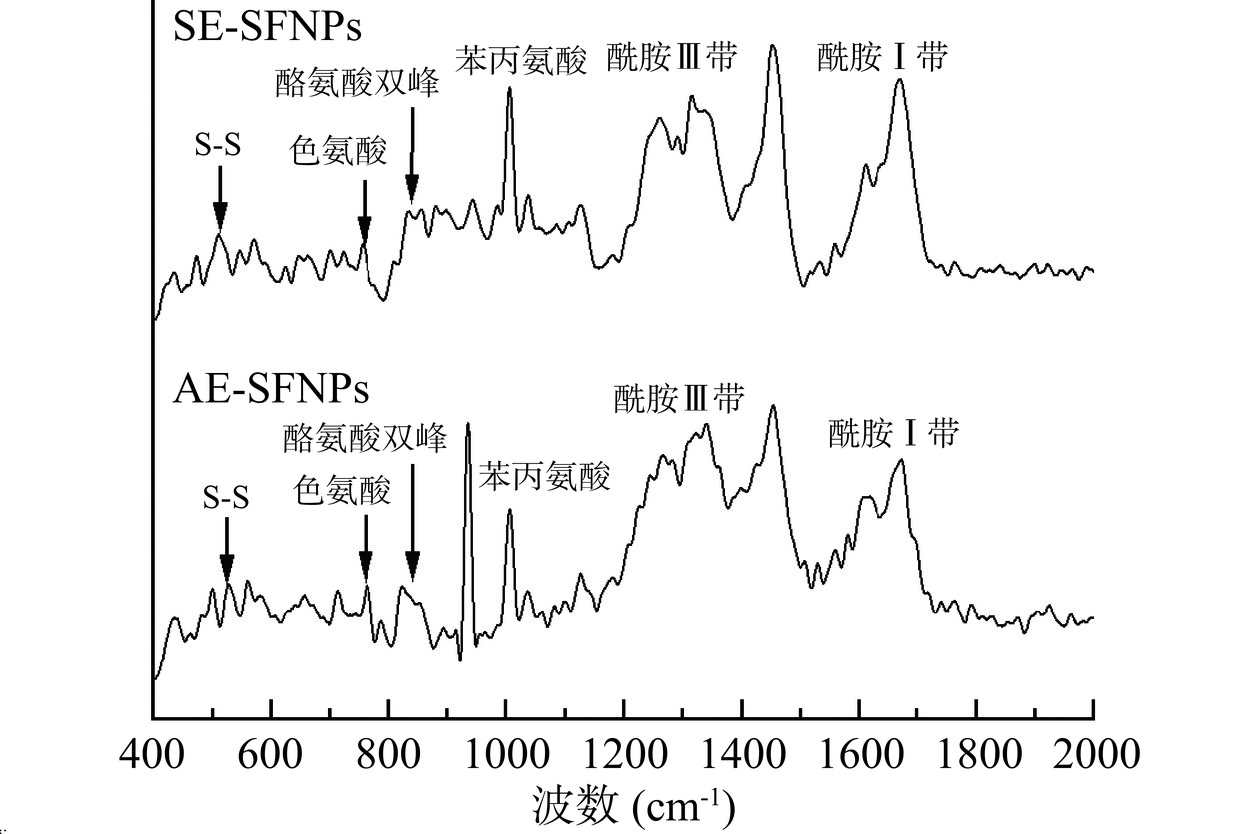
两种提取方法制备得到的SFNPs在波长400~2000 cm-1的拉曼光谱如图4所示,根据已有的相关特征峰的研究[28],在图4中分别标注出了AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的拉曼特征峰,即二硫键伸缩振动S-S、色氨酸、酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸、酰胺Ⅲ带和酰胺Ⅰ带拉曼特征峰。由图4可以看出,与SE-SFNPs相比,AE-SFNPs的色氨酸和酪氨酸的吸收峰较强,而且二硫键伸缩振动S-S的吸收峰强度也有差异,这反映出不同提取方法制备的SFNPs的疏水微环境、二硫键构型存在显著差异性。因此,对上述AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的拉曼光谱进行分析,根据蛋白质分子结构对应吸收峰的相对强度,进一步获得了SFNPs的氨基酸侧链和二硫键的相关信息。
AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的酪氨酸费米共振线(I850/I830)和色氨酸(I760)残基分析结果见表1。通过对比AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的I850/I830比值,发现AE-SFNPs的I850/I830比值(1.090)更接近1.25~1.40的范围,表明其酪氨酸残基更倾向于“暴露态”,而SE-SFNPs的I850/I830的比值(0.840)更接近0.3~0.5的范围,这表明其酪氨酸残基更趋向于“包埋态”[29]。因此,AE-SFNPs结构内部的酪氨酸疏水基团的暴露可以赋予其更高的表面疏水性[30]。此外,研究表明I760越大,色氨酸残基微环境极性就越强,进而导致色氨酸残基由“包埋态”向“暴露态”转变[31]。显然,AE-SFNPs的I760相对较大,表明AE-SFNPs的色氨酸残基的“暴露态”趋向性更大,这可能是由于其蛋白质分子的展开程度较大引起的;而SE-SFNPs的I760较小,可能与其大聚集体的形成有关,导致色氨酸残基大多被包埋在分子内部[30]。
AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的二硫键构型(g-g-g/g-g-t/t-g-t模式)的结果见表2,AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs均以g-g-g构型为主,这与之前g-g-g构型二硫键在大豆蛋白中所占比例最大(~42%)的研究结果一致[30]。但是在本研究中AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs二硫键中g-g-g构型的总占比相对减少约6%,而g-g-t构型/t-g-t构型的总占比表现出不同程度的增加,这也进一步证实了与亚麻籽蛋白的共生富集对大豆蛋白二硫键构型有着显著影响。此外,AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs中二硫键g-g-t和t-g-t构型的相对含量具有显著性差异(P<0.05),结合氨基酸侧链的分析可知,疏水基团“暴露态”的趋向性可能与t-g-t构型占比的相对增加和g-g-t构型占比的相对减少有关。
表 2 AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的二硫键构型的含量(%)Table 2. Content of disulfide bond conformations of AE-SFNPs and SE-SFNPs (%)样品 g-g-g g-g-t t-g-t AE-SFNPs 36.738±3.803a 29.542±4.922a 33.720±1.119b SE-SFNPs 36.003±1.447a 33.409±2.816b 30.587±2.263a 2.1.4 荧光光谱分析
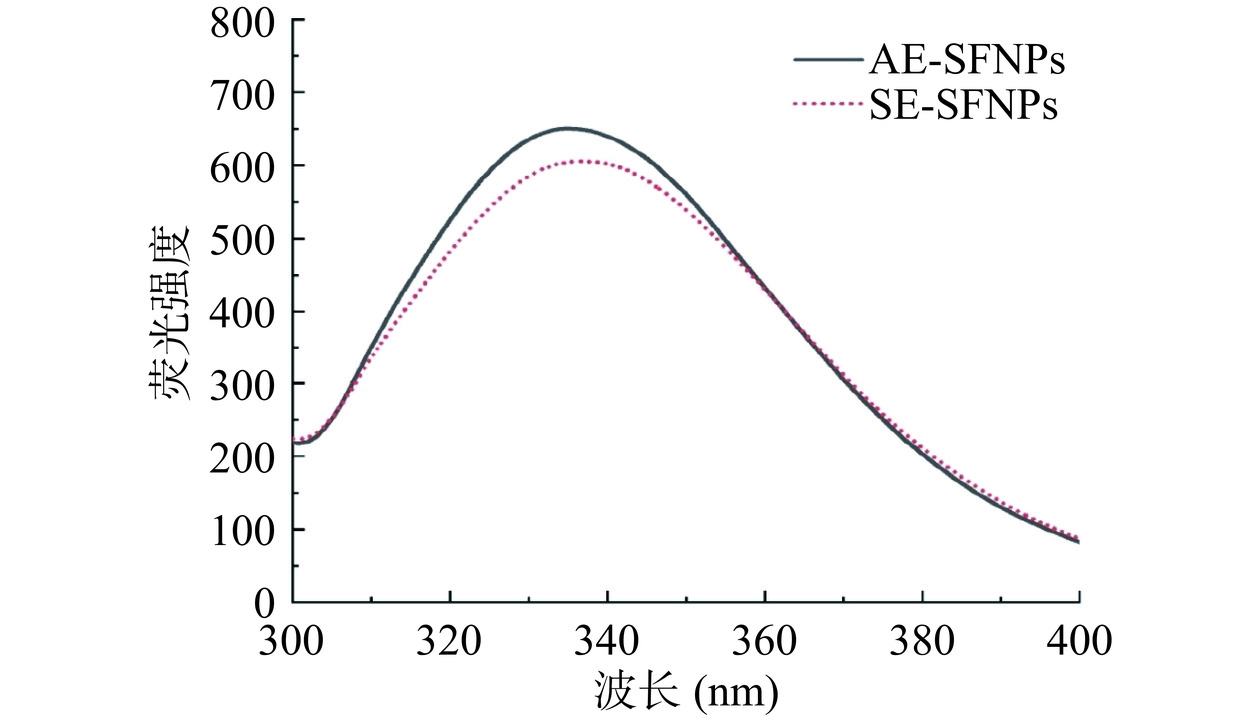
通常,蛋白质的荧光光谱主要来源于色氨酸残基的荧光发射,可以用来表征蛋白质极性和构象的变化[21]。如图5所示,通过比较AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的荧光光谱,发现AE-SFNPs的荧光强度强于SE-SFNPs,这可能与蛋白质之间的相互作用力(氢键、疏水相互作用等)有关,导致蛋白质的结构变得更加伸展,使得更多的色氨酸残基暴露在极性环境中[32]。这一观察结果与氨基酸侧链的分析结果相一致,SE-SFNPs因有较大蛋白聚集体的形成,使蛋白质分子表面的色氨酸残基大多被包埋进结构内部,导致其荧光强度较低。
综上所述,外观状态、颗粒尺度和AFM结果表明AE-SFNPs比SE-SFNPs具有更为均一的颗粒尺度和良好的分散性,结合团队之前的工作基础,猜测一方面可能与两者的氨基酸组成以及亚基组成不同相关[13];另一方面与不同提取过程对蛋白聚集状态的影响有关。CD光谱分析表明,AE-SFNPs二级结构中β-折叠占比更多、α-螺旋占比更少,使其具有更灵活的结构;拉曼光谱和荧光光谱分析表明,AE-SFNPs的酪氨酸残基和色胺酸残基比SE-SFNPs更倾向于“暴露态”,且AE-SFNPs的荧光强度高于SE-SFNPs,从而使得AE-SFNPs的疏水性氨基酸更易于暴露在分子表面,具有更高的表面疏水性。接下来利用AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs作为颗粒乳化剂制备了Pickering纳米乳液,并对其油-水界面形态、乳滴微观结构以及乳液在贮藏期间的物理稳定性和化学稳定性以及稳定机制进行初步表征与阐述。
2.2 Pickering纳米乳液的界面形态
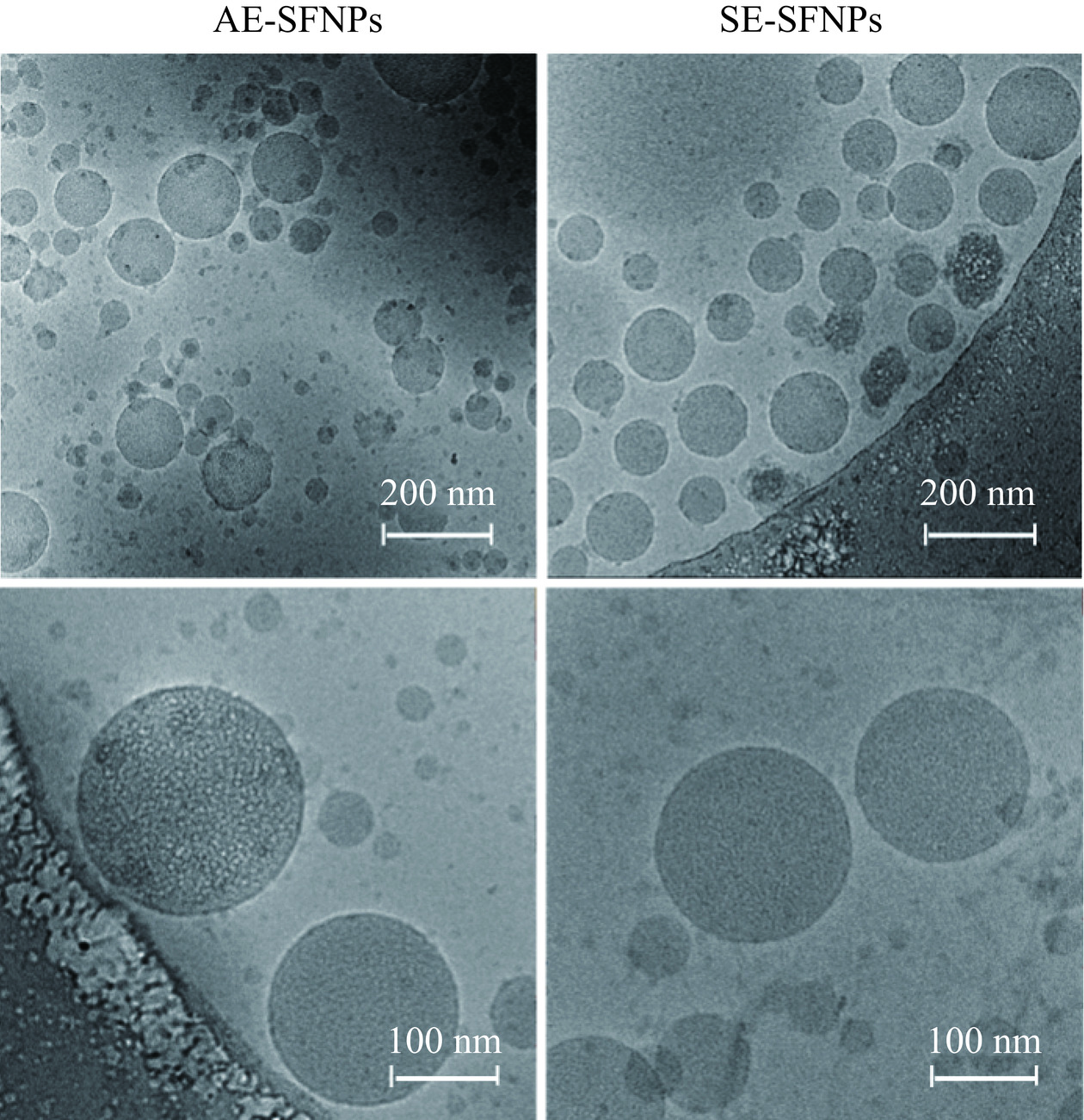
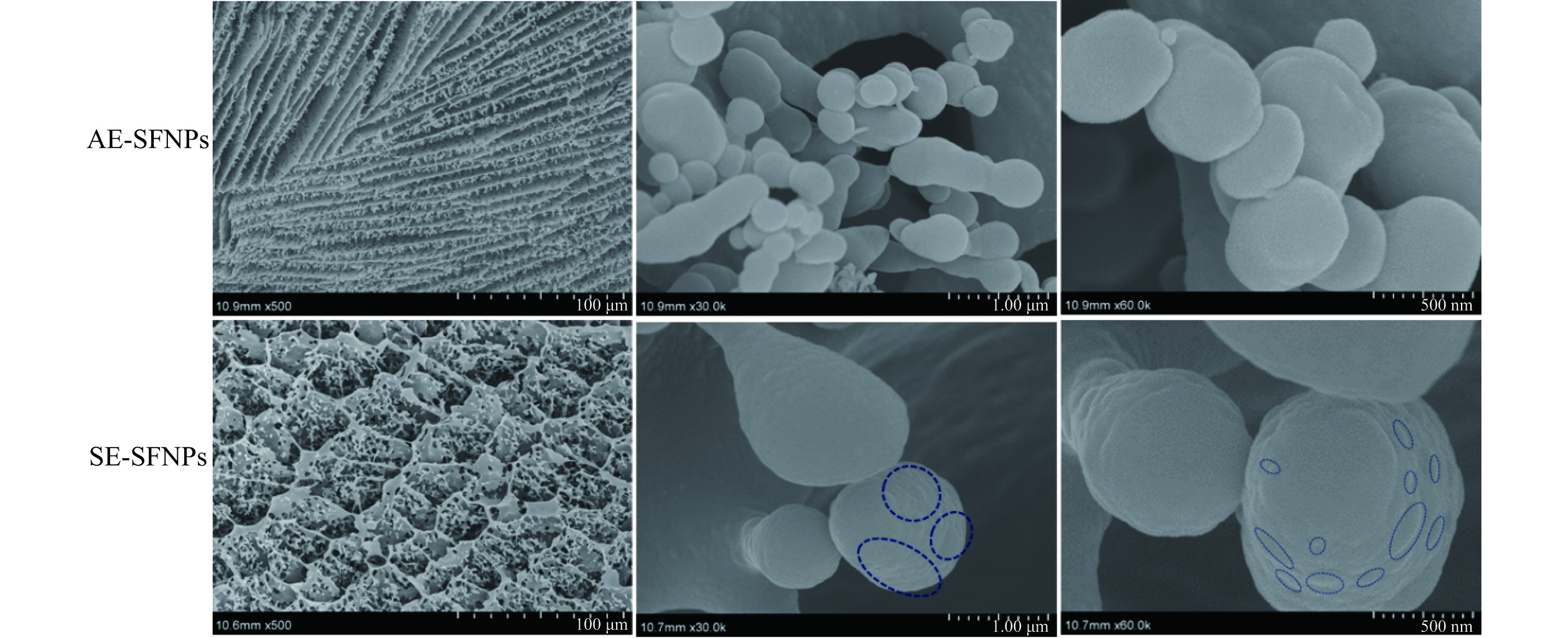
为了揭示AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs在油-水界面上的微观结构和组装行为,利用Cryo-TEM和Cryo-SEM观察了Pickering纳米乳液的界面膜形态。图6和图7分别显示了由两种双蛋白天然共生颗粒 AE-SFNPs 和 SE-SFNPs 稳定的 Pickering 纳米乳液的 Cryo-TEM 和 Cryo-SEM 图像。结果显示,两种颗粒稳定的乳液尺度均为纳米级,乳液界面均被类似球形的颗粒所覆盖,说明两种共生颗粒均可吸附于油-水界面。此处制备的乳液与蛋白稳定的普通型纳米乳液不同,其界面是由纳米尺度的颗粒来稳定,即属于新型乳液:Pickering纳米乳液。这在Persson等[15]和Han等[17]的报道中也发现了相似的研究结果,即纳米乳滴被密集堆积的颗粒稳定。相较于普通纳米乳液而言,吸附于Pickering纳米乳液表面的固体颗粒会在油/水界面处发生不可逆吸附[15],形成刚性较强的油-水界面膜,来进一步增强乳液液滴间的空间排斥,能够有效防止乳液液滴间的聚结与歧化[33]。由图6和图7可知,与SE-SFNPs相比,吸附于乳滴界面的AE-SFNPs的颗粒大小分布较为均匀,排列更加密集有序,进而形成光滑、紧密的界面膜结构,具有更强的阻止乳液聚结和歧化的能力,有利于粒径较小、均一稳定的Pickering纳米乳液的形成[34]。而SE-SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液的界面膜存在着明显的大小不均的颗粒状结构,经Nano Measurer软件计算可得,吸附在界面上的颗粒大至400 nm,小至几十纳米(如图7虚线框选部分所示),这将导致颗粒排列有序性降低,因此,形成的界面膜较为粗糙,致密性较差,其防止乳滴之间聚结和歧化的能力较弱。
从界面结构来看,吸附在界面膜上的AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的颗粒尺度与前文分析的关于天然共生颗粒的颗粒尺度和AFM的结果差异较大,这可能归因于SFNPs在高能乳化制备乳液的过程中,经高速剪切和微射流处理后的颗粒大小和分布的差异化表现。
2.3 Pickering纳米乳液界面结构形成原因探究
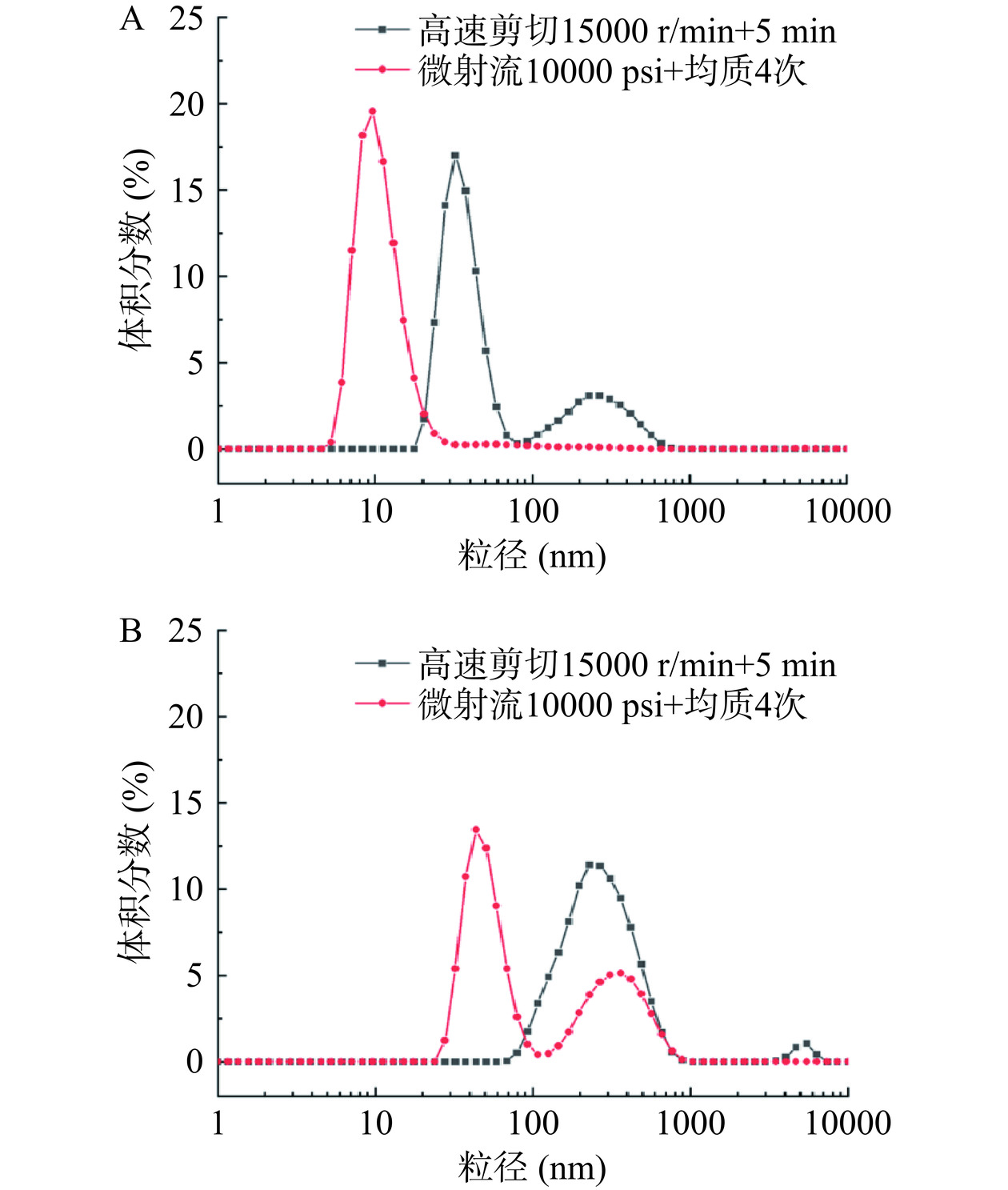
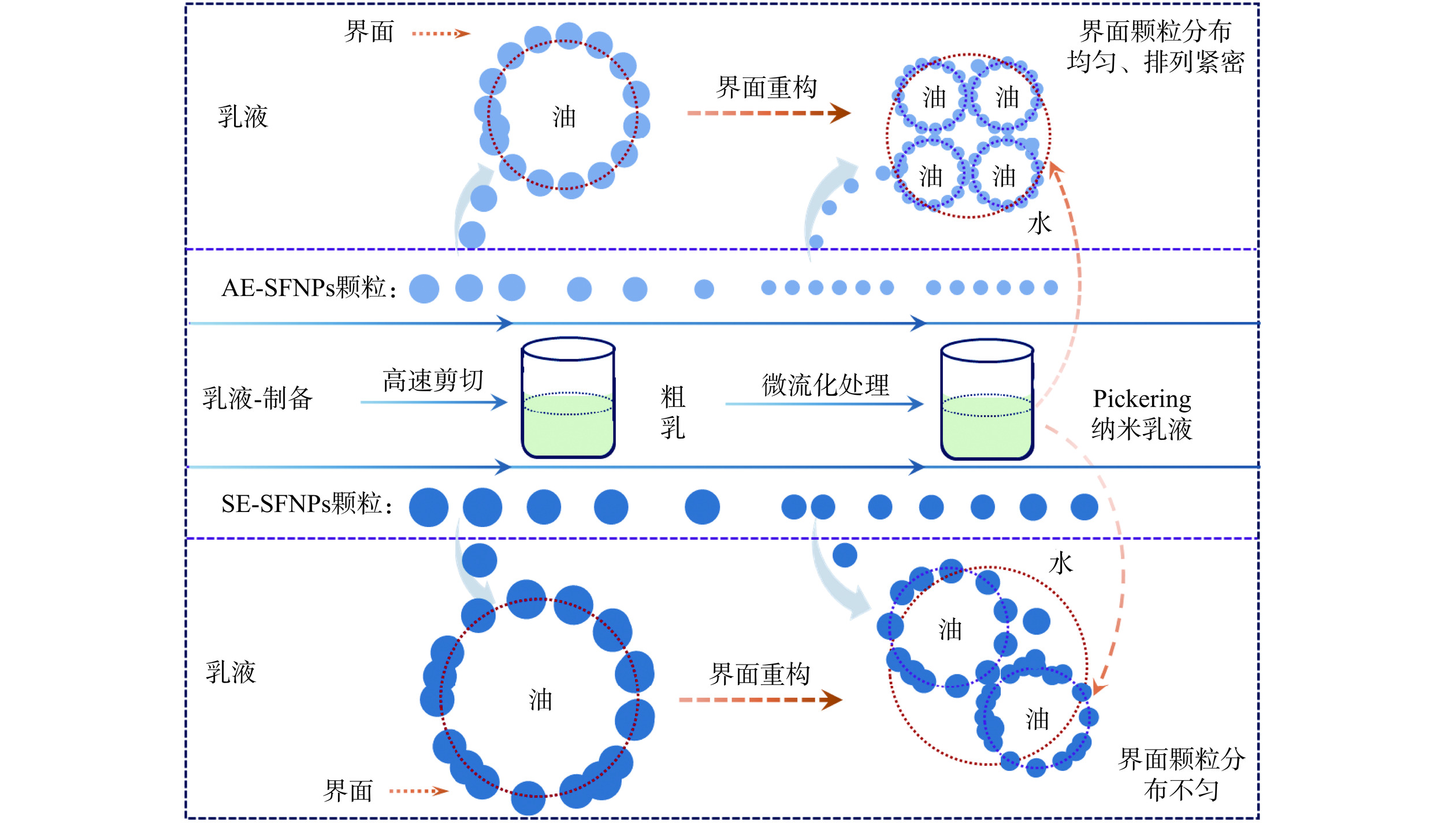
通常,Pickering纳米乳液的形成以高能乳化为主:即先用高速剪切制备粗乳,然后将粗乳通过高压均质或微射流进行处理获得Pickering纳米乳液[14]。为了进一步探究AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs稳定Pickering纳米乳液的形成与稳定机制,测定了AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs经过高速剪切(制备粗乳条件:15000 r/min,5 min)和微射流处理(制备Pickering纳米乳液条件:10000 psi,4次)的粒度分布情况,结果如图8所示。随着外界能量输入的增加,与经高速剪切后的粒度分布相比,经高压微射流处理的AE-SFNPs的粒度分布向粒径小的方向移动且粒径分布范围变窄,双峰转变为单峰(图8A),表明在高速剪切与高压微射流的过程中进一步产生了粒径更小且均一的AE-SFNPs(大部分约10 nm)。粗乳在形成Pickering纳米乳液的过程中,乳滴的比表面积增大,较小的AE-SFNPs吸附于油-水界面,重构乳液界面,进而形成了更加致密、均匀的油-水界面层[34−35],与乳液界面的微观形态结果相一致(图6和图7)。SE-SFNPs的粒度分布也在向较小的方向移动且粒径分布范围变窄,但还是表现为双峰,且其粒度分布主要在30~90 nm以及170~660 nm的范围,表明SE-SFNPs在外加能量的作用下尺度分布仍然不均匀,有较大颗粒聚集体的存在,这种情况可能导致在形成Pickering纳米乳液的界面重构过程中SE-SFNPs颗粒分布不均匀,容易导致多颗粒聚结并堆积在界面层[15],形成的界面膜致密性较差,这与乳液界面的微观形态结果相一致(图6和图7)。
2.4 Pickering纳米乳液的稳定性分析
2.4.1 外观形貌、粒径和ζ-电位分析
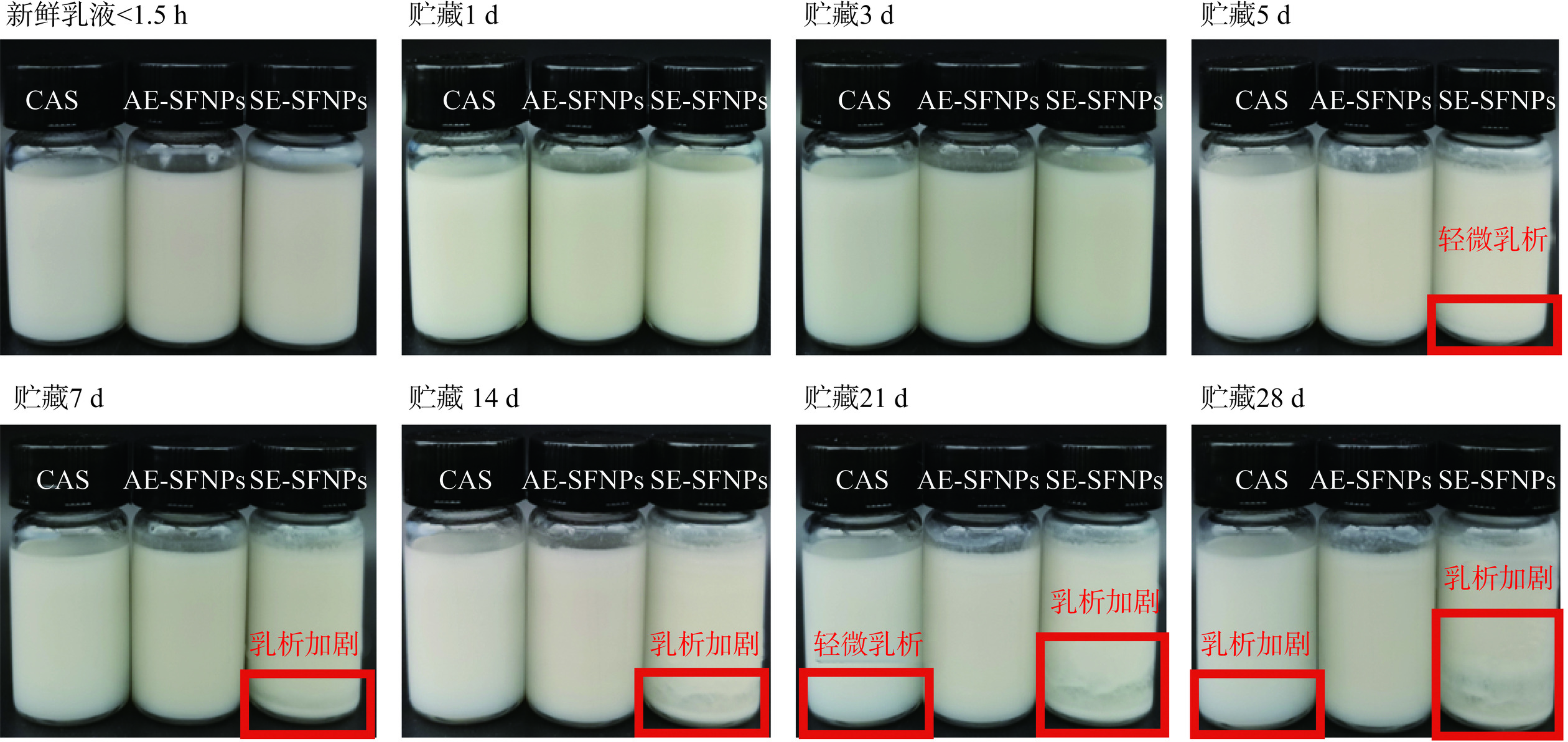
使用AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs作为颗粒乳化剂制备Pickering纳米乳液,为了探究其应用潜力,选用食品领域常用的蛋白类乳化剂,即酪蛋白酸钠稳定的纳米乳液作为对照。3种乳液的长期稳定性在室温下避光贮藏连续监测了28 d,在这期间乳液的外观形貌、粒径和ζ-电位的变化情况如图9和表3所示。在贮藏初期,由AE-SFNPs、SE-SFNPs和酪蛋白酸钠制备的乳液在外观上均呈现为均匀、不透明的乳白色液体,乳液粒径均为纳米级(~200 nm);贮藏7 d时,由SE-SFNPs制备的Pickering纳米乳液发生明显的“乳析”现象(见图9红框),另外两组未发生此现象。SE-SFNPs的乳液粒径也随之表现出了明显的增长趋势,由201.13 nm增大至851.10 nm。SE-SFNPs稳定的乳液随着贮藏时间的延长发生了更加剧烈的乳析,贮藏至第28 d时的乳液粒径比新鲜乳液的增大了约11.9倍,电位的绝对值降低了6.24 mV。此外,由酪蛋白酸钠制备的纳米乳液在贮藏至21 d时也表现出了轻微的“乳析”现象,对应表1中乳液粒径增大和电位降低的变化趋势,即贮藏至第28 d时,乳液粒径增大约1.68倍,电位的绝对值降低了11.63 mV,电位的降低可能是随着贮藏时间的推移,油脂发生了不同程度的氧化,产生的氢过氧化物随之分解的醇、醛等产物可能会中和羟基离子,进而导致乳液的电位绝对值出现了降低趋势[36−37]。尤其是,AE-SFNPs制备的Pickering纳米乳液,在28 d的贮藏过程中,未出现“乳析”现象,粒径基本稳定在230±10 nm,电位稳定在-33±2 mV,表现出比酪蛋白酸钠稳定的纳米乳液更高的抗絮凝和聚结稳定性,这可能主要归因于AE-SFNPs在制备Pickering纳米乳液的过程中表现出良好的界面重构行为,形成了致密、均匀的界面膜结构(图6和图7),有效阻止了乳滴的聚结和歧化[14],显著提高了Pickering纳米乳液的贮藏稳定性。
表 3 SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液与对照组的粒径和ζ-电位变化Table 3. Changes in particle size and ζ-potential of Pickering nanoemulsions stabilized by SFNPs and control group贮藏天数(d) 粒径(nm) ζ−电位(mV) 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 0 181.17±2.06a 227.17±2.53a 201.13±2.51a −46.81±0.85ab −35.28±0.60a −25.74±0.24a 3 180.63±0.84a 224.63±5.88ab 225.43±18.57a −44.65±2.37b −33.40±0.41bc −26.29±0.88a 7 178.70±2.34a 231.53±6.31ab 851.10±61.44b −47.65±1.65ab −33.27±0.14c −26.29±0.88a 14 187.70±2.65b 230.43±2.25ab 1779.33±84.61c −48.65±2.37a −34.42±0.74ab −21.56±1.03b 21 212.30±1.61c 233.13±2.10b 2219.67±114.61d −44.65±2.37b −33.24±0.91c −20.01±1.02c 28 303.53±5.80d 241.07±2.60c 2401.67±74.10e −35.18±0.54c −32.84±0.54c −19.50±0.30c 2.4.2 动力学稳定性
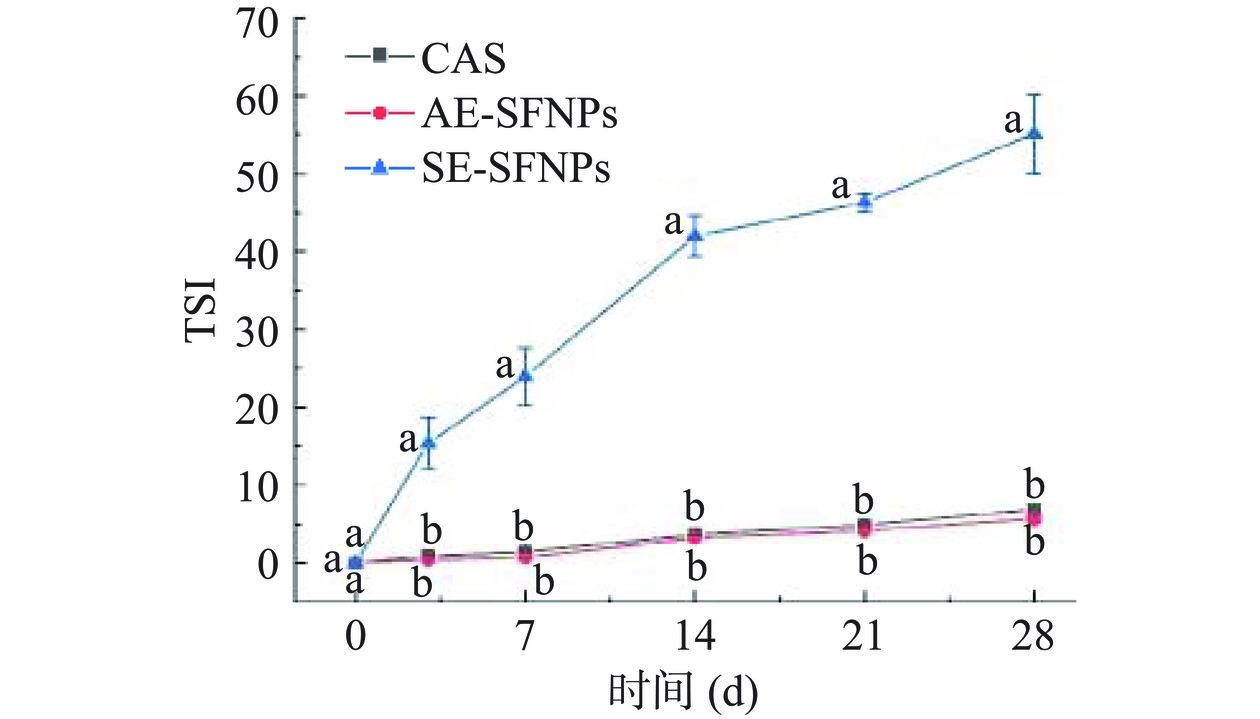
稳定性指数是计算样品两次扫描之间差异的关键参数,可以用于评估样品的不稳定动力学与储存时间的关系[24]。当TSI<0.5时,意味着样品在较长时间内表现出稳定状态,未发生明显变化。在1.0<TSI<3.0时,说明样品没有明显的不稳定发生。但在TSI>3.0时,可以观察到絮凝或沉积物产生的现象[38]。图10显示了AE-SFNPs、SE-SFNPs和对照组酪蛋白酸钠稳定的乳液在贮藏期间(0、3、7、14、21和28 d)的TSI变化,随着贮藏时间的延长,TSI值越大,说明乳液体系中乳液粒径和乳滴聚集的变化越大,进而表明乳液体系的稳定性越差[39]。结果显示,SE-SFNPs的TSI值随时间的延长增幅越来越大,28 d时已高达55.13,说明其稳定性最差,与图9的结果相一致。酪蛋白酸钠和AE-SFNPs稳定的乳液的TSI值在贮藏期间增幅较小,储存至第28 d时,AE-SFNPs的TSI值仅为5.83,小于酪蛋白酸钠的TSI值(6.50),表明AE-SFNPs制备的Pickering纳米乳液的稳定性强于酪蛋白酸钠制备的纳米乳液,具有较好的动力学稳定性。
2.4.3 Pickering纳米乳液的化学稳定性分析
表4显示了AE-SFNPs、SE-SFNPs和酪蛋白酸钠制备的乳液的氢过氧化物(初级氧化产物)和TBARS(次级氧化产物),用于分析乳液的化学稳定性。随着贮藏时间的延长,观察到所有组的氢过氧化物和TBARS水平均发生显著变化(P<0.05)。贮藏至28 d时,乳液中氢过氧化物大小顺序:SE-SFNPs>AE-SFNPs≈酪蛋白酸钠;TBARS含量大小顺序:SE-SFNPs>酪蛋白酸钠>AE-SFNPs,表明AE-SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液的氧化稳定性相对较好,且变化较小,原因可能是由于亚麻籽油与AE-SFNPs经高速剪切和微流化处理后,使得大部分油脂被包埋在乳液液滴内部,界面结构紧实,有效减少了外界氧气或其他促氧物质与油脂的接触位点,从而进一步减缓了氧化速度,提升了化学稳定性[40]。
表 4 SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液与对照组的氢过氧化物和TBARS浓度变化Table 4. Changes in hydroperoxide and TBARS concentrations in SFNPs-stabilized Pickering nanoemulsions and control group贮藏天数(d) 氢过氧化物(mmol/kg Oil) TBARS(mmol/kg) 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 0 0.416±0.001a 0.469±0.076a 0.970±0.007a 0.020±0.006a 0.032±0.003a 0.045±0.004a 3 0.510±0.002b 0.564±0.162a 1.017±0.094ab 0.026±0.003b 0.078±0.001c 0.058±0.002a 7 0.597±0.076c 0.951±0.077b 1.286±0.035bc 0.030±0.001b 0.077±0.001c 0.094±0.001c 14 0.781±0.023d 1.192±0.035c 1.518±0.031c 0.034±0.001c 0.074±0.001c 0.076±0.002b 21 1.971±0.020e 2.586±0.053d 2.538±0.023d 0.051±0.001d 0.068±0.002b 0.140±0.014d 28 2.422±0.035f 2.434±0.120d 5.585±0.263e 0.105±0.001e 0.086±0.002d 0.236±0.002e 基于实验结果,图11总结了双蛋白天然共生颗粒稳定Pickering纳米乳液的潜在作用机制。AE-SFNPs在高速剪切和高压微射流的过程中产生了颗粒尺度更小、分散更均匀的纳米颗粒,粗乳在形成Pickering纳米乳液的过程中,乳滴的比表面积随之粒径的减小而增大,这时颗粒较小的AE-SFNPs快速地吸附于油-水界面,以重构Pickering纳米乳液的界面层结构,进而形成了更加致密、均匀的油-水界面层,有效阻止了乳滴的聚结和歧化,赋予了其更高的稳定性[14,41]。而SE-SFNPs因尺度分布不均匀,在重构Pickering纳米乳液界面时,形成的界面膜致密性较差,导致乳液稳定性较差。
3. 结论
本研究通过碱提取-等电点沉淀法和盐提取-透析法从大豆-亚麻籽混合粕中直接制备双蛋白天然共生颗粒(SFNPs),并将其作为颗粒稳定剂制备Pickering纳米乳液。研究发现,在高能乳化前,AE-SFNPs表现出比SE-SFNPs更小的粒径、更好的分散性和结构柔性。经高能乳化,AE-SFNPs制备的Pickering纳米乳液表现出比SE-SFNPs更小的粒径、更均匀的分散性以及更佳的物理稳定性和化学稳定性,也优于酪蛋白酸钠制备的纳米乳液。因此,AE-SFNPs是一种天然高效的植物蛋白基颗粒稳定剂。本研究为大豆蛋白基纳米乳液的制备提供了新的解决策略。
-
表 1 AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的酪氨酸(I850/I830)和色氨酸(I760)的包埋/暴露情况
Table 1 Encapsulation/exposure of tyrosine (I850/I830) and tryptophan (I760) of AE-SFNPs and SE-SFNPs
表 2 AE-SFNPs和SE-SFNPs的二硫键构型的含量(%)
Table 2 Content of disulfide bond conformations of AE-SFNPs and SE-SFNPs (%)
样品 g-g-g g-g-t t-g-t AE-SFNPs 36.738±3.803a 29.542±4.922a 33.720±1.119b SE-SFNPs 36.003±1.447a 33.409±2.816b 30.587±2.263a 表 3 SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液与对照组的粒径和ζ-电位变化
Table 3 Changes in particle size and ζ-potential of Pickering nanoemulsions stabilized by SFNPs and control group
贮藏天数(d) 粒径(nm) ζ−电位(mV) 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 0 181.17±2.06a 227.17±2.53a 201.13±2.51a −46.81±0.85ab −35.28±0.60a −25.74±0.24a 3 180.63±0.84a 224.63±5.88ab 225.43±18.57a −44.65±2.37b −33.40±0.41bc −26.29±0.88a 7 178.70±2.34a 231.53±6.31ab 851.10±61.44b −47.65±1.65ab −33.27±0.14c −26.29±0.88a 14 187.70±2.65b 230.43±2.25ab 1779.33±84.61c −48.65±2.37a −34.42±0.74ab −21.56±1.03b 21 212.30±1.61c 233.13±2.10b 2219.67±114.61d −44.65±2.37b −33.24±0.91c −20.01±1.02c 28 303.53±5.80d 241.07±2.60c 2401.67±74.10e −35.18±0.54c −32.84±0.54c −19.50±0.30c 表 4 SFNPs稳定的Pickering纳米乳液与对照组的氢过氧化物和TBARS浓度变化
Table 4 Changes in hydroperoxide and TBARS concentrations in SFNPs-stabilized Pickering nanoemulsions and control group
贮藏天数(d) 氢过氧化物(mmol/kg Oil) TBARS(mmol/kg) 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 酪蛋白酸钠 AE-SFNPs SE-SFNPs 0 0.416±0.001a 0.469±0.076a 0.970±0.007a 0.020±0.006a 0.032±0.003a 0.045±0.004a 3 0.510±0.002b 0.564±0.162a 1.017±0.094ab 0.026±0.003b 0.078±0.001c 0.058±0.002a 7 0.597±0.076c 0.951±0.077b 1.286±0.035bc 0.030±0.001b 0.077±0.001c 0.094±0.001c 14 0.781±0.023d 1.192±0.035c 1.518±0.031c 0.034±0.001c 0.074±0.001c 0.076±0.002b 21 1.971±0.020e 2.586±0.053d 2.538±0.023d 0.051±0.001d 0.068±0.002b 0.140±0.014d 28 2.422±0.035f 2.434±0.120d 5.585±0.263e 0.105±0.001e 0.086±0.002d 0.236±0.002e -
[1] WILSON R J, LI Y, YANG G, et al. Nanoemulsions for drug delivery[J]. Particuology,2022,64:85−97. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2021.05.009
[2] PRIMOZIC M, DUCHEK A, NICKERSON M, et al. Formation, stability and in vitro digestibility of nanoemulsions stabilized by high-pressure homogenized lentil proteins isolate[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,77:126−141. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.09.028
[3] MCCLEMENTS D J, RAO J. Food-grade nanoemulsions:Formulation, fabrication, properties, performance, biological fate, and potential toxicity[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2011,51:285−330. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2011.559558
[4] 李季楠, 吴艳, 胡浩, 等. 食品纳米乳液的研究进展[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(2):217−225. [LI Jinan, WU Yan, HU Hao, et al. Research progress of food nanoemulsions[J]. Food and Machinery,2019,35(2):217−225.] LI Jinan, WU Yan, HU Hao, et al. Research progress of food nanoemulsions[J]. Food and Machinery, 2019, 35(2): 217−225.
[5] XIA J, SUN X, JIA P, et al. Multifunctional sustainable films of bacterial cellulose nanocrystal-based, three-phase pickeringnanoemulsions:A promising active food packaging for cheese[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,466:143295. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.143295
[6] JIN W, XU W, LIANG H, et al. 1-Nanoemulsions for food:Properties, production, characterization, and applications[M]. GRUMEZESCU A M. Emulsions. Academic Press, 2016:1−36.
[7] LI Y, LIU B, JIANG L, et al. Interaction of soybean protein isolate and phosphatidylcholine in nanoemulsions:A fluorescence analysis[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,87:814−829. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.09.006
[8] PENG X Q, XU Y T, LIU T, et al. Molecular mechanism for improving emulsification efficiency of soy glycinin by glycation with soy soluble polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(46):12316−12326. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03398
[9] XU J, MUKHERJEE D, CHANG S K C. Physicochemical properties and storage stability of soybean protein nanoemulsions prepared by ultra-high pressure homogenization[J]. Food Chem,2018,240:1005−1013. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.077
[10] CHEN N N, YANG B Y, WANG Y, et al. Improving the colloidal stability and emulsifying property of flaxseed 11S globulin by heat induced complexation with soy 7S globulin[J]. LWT-Food Sci Technol,2022,161:113364. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113364
[11] ZHANG X Y, QI B K, XIE F Y, et al. Emulsion stability and dilatational rheological properties of soy/whey protein isolate complexes at the oil-water interface:Influence of pH[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,113:106391. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106391
[12] XIAO Y Z, REN W, WEI F, et al. Rice glutelins and β-conglycinin or glycinin forming binary structures with different structural and functional properties[J]. Food Biophysics,2021,16(4):532−543. doi: 10.1007/s11483-021-09693-9
[13] SHAO J, YANG J, JIN W, et al. Regulation of interfacial mechanics of soy protein via co-extraction with flaxseed protein for efficient fabrication of foams and emulsions[J]. Food Research International,2024,175:113673. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113673
[14] GAUTHIER G, CAPRON I. Pickering nanoemulsions:An overview of manufacturing processes, formulations, and applications[J]. JCIS Open,2021,4:100036. doi: 10.1016/j.jciso.2021.100036
[15] PERSSON K H, BLUTE I A, MIRA I C, et al. Creation of well-defined particle stabilized oil-in-water nanoemulsions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2014,459:48−57.
[16] MCCLEMENTS D J. Advances in edible nanoemulsions:Digestion, bioavailability, and potential toxicity[J]. Progress in Lipid Research,2021,81:101081. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101081
[17] HAN W, LIU T X, TANG C H. Use of oligomeric globulins to efficiently fabricate nanoemulsions:Importance of enhanced structural stability by introducing trehalose[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2023,141:108695. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108695
[18] LI K Y, ZHANG X R, HUANG G Q, et al. Complexation between ovalbumin and gum arabic in high total biopolymer concentrations and the emulsifying ability of the complexes[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2022,642:128624.
[19] YANG J, DUAN Y, GENG F, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted pH shift-induced interfacial remodeling for enhancing the emulsifying and foaming properties of perilla protein isolate[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2022,89:106108. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106108
[20] ZHANG X, HUANG L X, NIE S Q, et al. FTIR characterization of the secondary structure of insulin encapsulated within liposome[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences,2003,12(1):11−14.
[21] LIAO X, WANG S, LI Y, et al. Effects of "nine steaming nine sun-drying" on proximate composition, protein structure and volatile compounds of black soybeans[J]. Food Research International,2022,155:111070. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111070
[22] MACHADO A H E, LUNDBERG D, RIBEIRO A J, et al. Preparation of calcium alginate nanoparticles using water-in-oil (W/O) nanoemulsions[J]. Langmuir,2012,28(9):4131−4141. doi: 10.1021/la204944j
[23] GUO Y, WU C, DU M, et al. In-situ dispersion of casein to form nanoparticles for Pickering high internal phase emulsions[J]. LWT,2021,139:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110538
[24] WANG L, YU X, GENG F, et al. Effects of tocopherols on the stability of flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by different emulsifiers:Interfacial partitioning and interaction[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131691. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131691
[25] KIRALAN S S, DOĞU-BAYKUT E, KITTIPONGPITTAYA K, et al. Increased antioxidant efficacy of tocopherols by surfactant solubilization in oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(43):10561−10566. doi: 10.1021/jf503115j
[26] CHEN F, LIANG L, ZHANG Z P, et al. Inhibition of lipid oxidation in nanoemulsions and filled microgels fortified with omega-3 fatty acids using casein as a natural antioxidant[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,63:240−248. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.09.001
[27] LIU H, ZHANG H, LIU Q, et al. Solubilization and stable dispersion of myofibrillar proteins in water through the destruction and inhibition of the assembly of filaments using high-intensity ultrasound[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2020,67:105160. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105160
[28] 吕博, 李明达, 张毅方, 等. 用拉曼光谱分析低压均质处理对大豆分离蛋白结构的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(10):58−63. [LÜ Bo, LI Mingda, ZHANG Yifang, et al. Effect of low-pressure homogenization treatment on the structure of soybean isolate proteins analyzed by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2018,34(10):58−63.] LÜ Bo, LI Mingda, ZHANG Yifang, et al. Effect of low-pressure homogenization treatment on the structure of soybean isolate proteins analyzed by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2018, 34(10): 58−63.
[29] WONG H W, CHOI S M, PHILLIPS D L, et al. Raman spectroscopic study of deamidated food proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,113(2):363−370. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.027
[30] 齐宝坤, 赵城彬, 江连洲, 等. 热处理对大豆11S球蛋白表面疏水性的影响及拉曼光谱分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(18):15−20. [QI Baokun, ZHAO Chengbin, JIANG Lianzhou, et al. Effect of heat treatment on surface hydrophobicity of soybean 11S globulin and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Food Science,2018,39(18):15−20.] QI Baokun, ZHAO Chengbin, JIANG Lianzhou, et al. Effect of heat treatment on surface hydrophobicity of soybean 11S globulin and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(18): 15−20.
[31] 王中江, 江连洲. 大豆分离蛋白在不同pH下的拉曼光谱分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(11):63−66. [WANG Zhongjiang, JIANG Lianzhou. Raman spectroscopic analysis of soybean isolates at different pH[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2012,33(11):63−66.] WANG Zhongjiang, JIANG Lianzhou. Raman spectroscopic analysis of soybean isolates at different pH[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2012, 33(11): 63−66.
[32] WANG Y R, YANG Q, FAN J L, et al. The effects of phosphorylation modification on the structure, interactions and rheological properties of rice glutelin during heat treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297:124978. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124978
[33] SIHLER S, SCHRADE A, CAO Z, et al. Inverse pickering emulsions with droplet sizes below 500 nm[J]. Langmuir,2015,31(38):10392−10401. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b02735
[34] YANG J, DUAN Y Q, ZHANG H H, et al. Ultrasound coupled with weak alkali cycling-induced exchange of free sulfhydryl-disulfide bond for remodeling interfacial flexibility of flaxseed protein isolates[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2023,140:108597. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108597
[35] QIAN C, MCCLEMENTS D J. Formation of nanoemulsions stabilized by model food-grade emulsifiers using high-pressure homogenization:Factors affecting particle size[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(5):1000−1008. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.09.017
[36] MCCLEMENTS D J, JAFARI S M. Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers:A review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2018,251:55−79. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.12.001
[37] 程晨, 黄凤洪, 黄庆德, 等. 脂质伴随物对多不饱和脂肪酸乳液稳定性的影响研究进展[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2019,41(5):816−824. [CHENG Chen, HUANG Fenghong, HUANG Qingde, et al. Research progress on the effect of lipid concomitants on the stability of polyunsaturated fatty acid emulsions[J]. Chinese Journal of Oilseed Crops,2019,41(5):816−824.] CHENG Chen, HUANG Fenghong, HUANG Qingde, et al. Research progress on the effect of lipid concomitants on the stability of polyunsaturated fatty acid emulsions[J]. Chinese Journal of Oilseed Crops, 2019, 41(5): 816−824.
[38] JIN W, PAN Y, WU Y, et al. Structural and interfacial characterization of oil bodies extracted from Camellia oleifera under the neutral and alkaline condition[J]. LWT,2021,141:110911. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110911
[39] CHENG C, YU X, MCCLEMENTS D J, et al. Effect of flaxseed polyphenols on physical stability and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil-in-water nanoemulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125207
[40] 闫馨月, 贾亦佳, 孙诗艳, 等. 火麻油复合纳米乳液的制备及稳定性研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2022,41(6):84−90. [YAN Xinyue, JIA Yijia, SUN Shiyan, et al. Preparation and stability of composite nanoemulsions of hemp oil[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology,2022,41(6):84−90.] YAN Xinyue, JIA Yijia, SUN Shiyan, et al. Preparation and stability of composite nanoemulsions of hemp oil[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology, 2022, 41(6): 84−90.
[41] HAN W, LIU T X, TANG C H. Transforming monomeric globulins into pickering particles to stabilize nanoemulsions:Contribution of trehalose[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2023,141:108687. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108687






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



