In Vitro Screening, Domestication and Identification of Lipid-lowering Functional Lactic Acid Bacteria
-
摘要: 目的:本研究以来源传统发酵食品中的310株乳酸菌为菌株资源,筛选出具有降血脂功能的乳酸菌。方法:利用邻苯二甲醛法测定菌株胆固醇去除率,采用梯度增加胆固醇浓度的培养方法对初筛菌株进行驯化,单试剂法测定甘油三酯去除率,检测菌悬液及胞内提取物对胆固醇酯酶和胰脂肪酶活性的抑制能力,采用16S rDNA和pheS基因序列对目标菌株进行鉴定。同时对其模拟胃肠道耐受性、自聚集力和疏水性进行研究。结果:初筛菌株BC17经过高浓度胆固醇驯化后,其胆固醇去除率提高到35.70%;该菌株的甘油三酯去除率为58.87%,其胞内提取物对胰脂肪酶和胆固醇酯酶活性的抑制率分别为34.92%和52.95%,菌悬液对两种酶的抑制率分别为7.01%和42.99%;BC17在模拟胃肠道中培养6 h存活率为53.99%;BC17具有较强的自聚集力,24 h可达到69.04%;在乙酸乙酯、二甲苯和氯仿中的疏水率分别为33.71%、38.36%和51.02%;经形态学观察、16S rDNA和pheS基因序列分析,BC17为植物乳植杆菌。结论:植物乳植杆菌BC17具有良好的体外降血脂功能,且具有优良的益生特性,可为降血脂功能发酵产品和益生菌剂的开发提供潜在的菌株资源,应用前景广阔。Abstract: Objective: In order to screen Lactobacillus species with lipid-lowering function, 310 strains of the lactic acid bacteria were obtained from the source of traditional fermented foods. Methods: The o-phthalaldehyde method was applied to measure the strains’ rate of cholesterol removal. The culture strategy with a gradient rise in cholesterol concentration was utilized to domesticate the original screening strains. The single-reagent approach was used to determine the rate of triglyceride. The inhibitory potential of bacterial suspensions and intracellular extracts on the activities of cholesterol esterase and pancreatic lipase was tested. The 16S rDNA and the pheS gene sequences were utilized to determine the target bacteria. In addition, the self-aggregation force, hydrophobicity, and simulated gastrointestinal system tolerance were examined. Results: After high concentration cholesterol domestication, the cholesterol removal rate of strain BC17 in the initial screening increased to 35.70%. Additionally, the strain's triglyceride removal rate was 58.87%. Intracellular extracts inhibited the activities of pancreatic lipase and cholesterol esterase by 34.92% and 52.95%, respectively, while its suspensions inhibited the activities of the two enzymes by 7.01% and 42.99%, respectively. After being cultivated for 6 h in a simulated gastrointestinal system, BC17 had a 53.99% survival rate. BC17 had a high self-aggregation rate, which reached 69.04% in 24 h. The hydrophobic rates of ethyl acetate, xylene, and chloroform, respectively, were 33.71%, 38.36%, and 51.02%. BC17 was identified as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum based on morphology, 16S rDNA and pheS genes sequence analysis. Conclusion: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17 has a good in vitro lipid-lowering activity and outstanding probiotic qualities, thus making it a prospective strain resource for the development of lipid-lowering functional fermentation products and probiotic agents with a wide range of applications.
-
Keywords:
- lactic acid bacteria /
- lipid-lowering /
- domestication /
- pancreatic lipase /
- cholesterol esterase
-
高脂血症(Hyperlipidemia)是因脂类代谢过程紊乱导致血脂水平变化异常的一种疾病,主要表现为血液中总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇浓度升高、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇浓度降低[1]。近年来,随着生活习惯和饮食习惯的改变等多因素影响,高脂血症发病率有明显增高趋势[2]。大量研究资料表明,血脂过高诱发的动脉粥样硬化、冠心病、心肌梗死等心脑血管疾病已对人类健康造成严重威胁[3−4]。
胰脂肪酶(Pancreatic lipase,PL)和胆固醇酯酶(Cholesterol esterase,CE)是研究降血脂活性和机制的两种重要酶。胆固醇酯酶又称甾醇酯酶,可以催化膳食中的胆固醇酯在小肠中水解为游离胆固醇[5],抑制其活性可以降低血清中胆固醇水平[6],是治疗胆固醇相关疾病的重要靶点[7]。胰脂肪酶是最主要的脂肪水解酶,抑制胰脂肪酶活性可以减少对脂肪的吸收[8],降低血清中甘油三酯水平,有利于改善膳食导致的肥胖和肥胖相关的胰岛素抵抗[9]。奥利司他(Orlistat)作为唯一被美国食品和药物管理局批准的抗肥胖药物,也是胰脂肪酶的抑制剂[10],具有极好的减肥功效。由于奥利司他抑制脂肪的吸收,长期服用可能会导致腹泻、胀气等副作用,严重阻碍了临床的长期使用[11−13],因此寻找更有效且具有良好安全性的治疗血脂异常的药物迫在眉睫。
乳酸菌作为人体肠道里面有益的微生物,已被广泛应用于增强免疫力[14]、改善肠道菌群[15]、降血糖[16]及抗肿瘤[17]等方面。近年来益生菌降血脂作用的研究受到越来越多的关注,国内外研究已经证实一些乳酸菌(如乳杆菌、双歧杆菌等)具有降胆固醇的益生功能[18−20],利用降胆固醇功能优良且稳定的乳酸菌开发具有降血脂作用的功能(保健)食品[21],对高脂血症的人群进行营养干预,减少胆固醇和甘油三酯的摄入量有助于降低血液和组织中的脂质含量,从而减轻肥胖和慢性疾病等症状的发生[22]。
本研究以来源于传统发酵食品乳酸菌为菌株资源,以体外去除胆固醇能力为初筛指标,同时以甘油三酯去除能力、胰脂肪酶和胆固醇酯酶抑制活性为复筛指标,筛选出具有降血脂功能的乳酸菌,并进一步对菌株的模拟胃肠道耐受能力、自聚集力和疏水性进行研究,旨在获得具有优良降血脂功能和自主知识产权的益生菌株资源,为开发具有降血脂功能(保健)食品提供可靠的菌株资源。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
310株乳酸菌 主要来源于新疆酸马奶、新疆酸奶、广东潮州泡菜、南通酸浆、东北酸菜、贵州酸汤/酸鱼、云南酸菜等传统发酵食品,保藏于江苏省农业科学院农产品加工研究所121实验室;胆固醇、邻苯二甲醛、吐温80 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甘油三酯、奥利司他、胆固醇酯酶(10 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;蔗糖脂肪酸酯 柳州爱格副食品科技股份有限公司;牛胆盐 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;甘油三酯试剂盒 南京建成股份有限公司;胰脂肪酶(15-35 U/mg) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;4-硝基苯丁酸酯(PNPB)、牛磺胆酸钠、4-硝基苯磷酸二钠盐(PNPP)、胰蛋白酶(500 U) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;乙酸乙酯、二甲苯 江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司;氯仿 上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司;所用试剂均为分析纯;0.2 mg/mL高胆固醇液体培养基(MRS-CHOL):准确称取2 g牛胆盐,1 g蔗糖脂肪酸酯,加入20 mL吐温80,20 mL胆固醇-无水乙醇溶液(10 mg/mL),混合均匀后,将其加入到1 L MRS液体培养基中;0.2 mg/mL甘油三酯液体培养基:称取0.2 g甘油三酯溶解于20 mL吐温80中(可加热),将其加入到1 L MRS液体培养基中。
LRH-150生化培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;Multiskan skyhigh分光光度计 Thermo Scientific公司;DSX18L-1手提式高压蒸气灭菌器 上海申安医疗机械厂;SW-CJ-1C型双人单面净化工作台 苏州净化设备有限公司;HH-4数字恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司;WH-3型漩涡混合仪 上海跃进医疗器械有限公司;Allegra X-30R Centrifuge冷冻离心机 Beckman Coulter公司;H1650-W/H1650W台式微量高速离心机 长沙湘仪仪器有限公司;XO-1000D超声波细胞破碎仪 南京先欧仪器制造有限公司;UV-1800紫外分光光度计 广州晓分仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌株活化
将从−80 ℃冰箱中取出甘油保藏的乳酸菌按5%(v/v)接种量接种于MRS液体培养基中,37 ℃培养24 h后进行平板划线,平板倒置培养48 h,挑取单菌落于MRS液体培养基中,37 ℃培养24 h后,4 ℃冷藏备用。
1.2.2 胆固醇去除率的测定
分别取0.1 mL质量浓度为0.05、0.1、0.15、0.2、0.25、0.3 mg/mL的胆固醇标准溶液后,再分别依次加入0.1 mL 1 mg/mL邻苯二甲醛溶液、1.3 mL冰醋酸和1 mL浓硫酸,充分振荡、混匀,室温显色10 min,在550 nm测定吸光值并以胆固醇标准浓度为横坐标,波长550 nm处吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线。
按5%(v/v)的接种量将活化好的乳酸菌接种于MRS-CHOL液体培养基中,37 ℃静置培养24 h。取1 mL发酵液,6000 r/min离心10 min取上清液,采用邻苯二甲醛法[23]测定上清液中胆固醇含量,并按以下公式计算胆固醇去除率。
胆固醇去除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 式中:A0为未接菌上清液胆固醇含量;A1为菌株发酵上清液胆固醇含量(mg/mL)。
1.2.3 胆固醇驯化
将初筛得到的菌株依次接种到0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6和0.7 mg/mL的高胆固醇液体培养基中,在37 ℃培养24 h为一代。在每个浓度下测定菌密度,根据其能否生长以及生长状况确定最高的耐胆固醇浓度,并将驯化后的菌液保存在胆固醇浓度相对低的培养基中,4 ℃保存备用。
1.2.4 甘油三酯去除率的测定
按5%(v/v)的接种量将活化好的乳酸菌接种于甘油三酯液体培养基中,37 ℃静置培养24 h。取1 mL发酵液,6000 r/min离心10 min取上清液,根据甘油三酯试剂盒说明书方法测定上清液中甘油三酯含量。按以下公式计算甘油三酯去除率。
甘油三酯去除率(\%)=A0−A1A0×100 式中:A0为未接菌上清液甘油三酯含量(mmol/L);A1为菌株发酵上清液甘油三酯含量(mmol/L)。
1.2.5 乳酸菌对脂代谢相关酶活力的抑制能力
1.2.5.1 菌悬液和胞内提取物的制备
将活化好的菌液在4 ℃,10000 r/min离心10 min后弃掉上清液,加入无菌水洗涤菌体3次后,用无菌水重悬,调整OD600 nm至2.0,得到菌悬液。取出一部分菌悬液置于冰水浴中进行超声破碎(5 s/次,间隔5 s,持续1 h)至光学显微镜下无菌体后,再次4 ℃,5000 r/min离心15 min,收集上清液得到胞内提取物。
1.2.5.2 胰脂肪酶活力的测定
根据Zhao等[24]的方法对乳酸菌抑制胰脂肪酶活性的进行测定。将200 μL样品和200 μL 2 U/mL胰脂肪酶溶液混合均匀,置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中温育15 min后,立即加入400 μL 10 mmol/L pNPP溶液混匀,再次置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中温育15 min。反应结束后,快速放置于100 ℃水浴5 min,以终止反应。终止后的反应液6000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,于405 nm波长下测吸光度,以10 μg/mL奥利司他作为阳性对照。酶活性抑制率公式如下。
抑制率(\%)=(1−As−AnAc−A0)×100 式中:As为样品组吸光度;An为样品对照组吸光度;Ac为空白组吸光度;A0为空白对照组吸光度。
1.2.5.3 胆固醇酯酶活力的测定
参考Li等[25]对胆固醇酯酶活力的测定方法,并稍加改动。在1 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.1 mol/L,pH7.0,含有0.1 mol/L NaCl和5.16 mmol/L牛磺胆酸钠)中加50 μL样品和50 μL胆固醇酯酶溶液(2 U/mL)混合均匀,置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中温育15 min后,立即加入100 μL 4 mmol/L PNPB溶液混匀,再次置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中温育15 min。反应结束后6000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,于405 nm波长下测吸光度。根据1.2.5.2的公式计算乳酸菌对胆固醇酯酶活性的抑制率。
1.2.6 形态学观察
参照《乳酸细菌分离鉴定及实验方法》[26]对筛选到的菌株进行形态学观察,将筛选出的菌株在固体培养基上培养形成单菌落,观察菌落形态。用接种环挑取适量生长良好的分离株菌落,涂片、固定于载玻片上,放置待冷后进行革兰氏染色,采用光学显微镜进一步观察细菌形态,并作初步鉴定。
1.2.7 分子生物学鉴定
由上海生工生物工程技术服务公司对筛选菌株的16S rDNA和pheS基因序列进行测序。将所得序列提交至美国国家生物技术信息中心的GenBank数据中,进行同源性比对分析。选取同源性较高的菌株,采用MEGA 7软件中的邻接法构建系统发育树。
1.2.8 模拟胃肠道环境的耐受性
称取0.35 g胃蛋白酶和0.2 g NaCl溶解于100 mL蒸馏水中,用1 mol/L HCl调整pH至3.0,完成人工模拟胃液的配制。准确称取0.5 g NaCl、0.3 g牛胆盐和0.1 g胰蛋白酶溶解于100 mL蒸馏水中,用0.1 mol/L NaOH调整pH至8.0,配制成人工模拟肠液。人工模拟胃肠液均需用0.22 μm无菌微孔滤膜过滤除菌。
参考Ruiz等[27]的方法进行耐模拟胃肠道能力的测定。取对数期的菌液4 ℃,10000 r/min离心10 min后,用无菌生理盐水清洗两遍,将菌体重悬于模拟胃液中,放入37 ℃,150 r/min摇床培养3 h后,吸取1 mL已经处理3 h的含菌的人工胃液,接种于9 mL模拟人工肠液中,37 ℃,150 r/min继续摇床培养3 h,每隔1 h用平板计数法测定活菌数,并按以下公式计算存活率。
存活率(\%)=NtN0×100 式中:N0表示接种第0 h的活菌数;Nt表示接种第t h的活菌数(lg CFU/mL)。
1.2.9 表面疏水性和自聚集能力的测定
将活化好的菌液离心收集菌体,用无菌生理盐水清洗3次,再重新悬浮于生理盐水中,测定其在600 nm处的吸光度,并调整菌悬液的OD值,使其范围在1.00±0.05。
参考Deng等[28]的方法测定乳酸菌的表面疏水性和自聚集能力。菌液与等体积有机相(二甲苯、乙酸乙酯和氯仿)混合,37 ℃温育10 min后,涡旋振荡2 min,再在37 ℃下静置1 h。取水相测定吸光度,并按以下公式计算疏水性。
疏水率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 式中:A0表示萃取前水相在600 nm处的吸光度;A1表示萃取后水相在600 nm处的吸光度。
按上述方法制备菌悬液,吸取4 mL菌悬液移入EP管中,37 ℃下静置24 h,分别于0、2、4、8、12和24 h取上层菌液测定吸光度。按以下公式计算自聚集能力。
自聚集力(%)=A0−AtA0×100 式中:A0表示第0 h的上层菌液在600 nm处的吸光度;At表示第t h的上层菌液在600 nm处的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据均由3次平行实验计算得出平均值,分别使用SPSS Statistics 26和Origin 2021进行数据分析处理以及绘图,用平均值±标准差(x±s)表示。运用Duncan多重比较法对差异显著性进行比较分析(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 体外筛选具有降血脂功能乳酸菌的筛选及驯化
2.1.1 具有去除胆固醇功能乳酸菌的筛选
本研究采用邻苯二甲醛法对310株乳酸菌发酵上清液胆固醇含量进行测定,其中胆固醇标准曲线方程为:y=4.4185x+0.0665,拟合直线方程的R2=0.9845,有较高的拟合度,说明此方程可以作为标准曲线,用于计算发酵上清液中的胆固醇浓度。结果发现,大部分菌株不能去除MRS-CHOL培养基中的胆固醇,表1筛选出32株具有去除胆固醇能力的菌株,其中胆固醇去除率小于15%有24株,去除率在15%~20%之间有5株,超过20%有3株,分别为nt4-10、4Y和ntl5,去除率分别为24.62%、22.62%和20.59%。不同乳酸菌体外去除胆固醇的能力存在显著差异(P<0.05)。这一结果与大部分学者的研究相符合,Zhang等[29]从贵州省传统发酵食品中分离出86株的乳酸菌,表现出7.29%~25.66%的胆固醇去除率。但本实验菌株胆固醇去除率远远低于Ding等[30]从牦牛发酵乳中筛选得到的L. plantarum Lp3胆固醇(73.3%),乳酸菌去除胆固醇能力的差异可能与从不同样本分离出的乳酸菌产生的个体差异以及不同培养条件等因素有关。
表 1 不同乳酸菌胆固醇去除率Table 1. Cholesterol degradation rate of different lactic acid bacteria菌株 胆固醇去除率(%) 菌株 胆固醇去除率(%) 2-4 14.67±1.13ef BC2 6.72±0.30kl 3-1d 12.68±1.17fghi 22-3Y 11.49±1.60fghij 7-2 11.38±1.42fghij nt2-8 18.65±1.27cd 9-9d 12.46±0.37fghij pc15 5.37±0.96l C-M2 11.45±1.70fghij M3 14.16±1.35efg DY1 12.54±1.76fghij qc2 18.58±2.48cd FD1 10.05±0.02hijk MN3 12.00±2.42fghij G10 12.55±1.47fghij MX 10.81±1.78ghij KM1 8.75±0.88jk AB4X 9.32±1.09ijk M15 9.05±1.89ijk 1-1 11.44±1.49fghij ntl5 20.59±0.51bc 22-4Y 22.62±0.98ab pc12 10.33±0.89hij GJ9 12.28±3.52fghij BC17 19.04±0.99cd SS2-6 18.21±3.02cd qc9 11.69±1.83e P13 12.52±1.62fghij SD8 16.22±1.26de GS7 13.51±3.15efgh TM27 10.76±0.20ghij nt4-10 24.62±2.61a 注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.1.2 具有去除胆固醇功能乳酸菌的驯化
驯化是指在相对较短的时间内,改善乳酸菌的目标表型和生理特征,而不会影响其他优良性状[31]。将8株具有较强胆固醇去除能力的乳酸菌依次接种到不同胆固醇浓度的培养基中,发现当浓度达到0.6和0.7 mg/mL时乳酸菌生长受到抑制,因此最高耐胆固醇浓度为0.5 mg/mL。将乳酸菌在最高耐胆固醇浓度的培养基中连续驯化3代,将驯化后的乳酸菌重新接种至胆固醇浓度为0.2 mg/mL的MRS液体培养基中,利用邻苯二甲醛法测定胆固醇含量,驯化前后胆固醇去除率如表2所示。经过高胆固醇培养基的驯化,8株乳酸菌的胆固醇去除率均有升高,且均高于20%,其中有5株乳酸菌的去除率高于30%,菌株SS2-6、BC17和4Y胆固醇去除率显著高于其他菌株(P<0.05)。菌株SS2-6的胆固醇去除率从18.21%上升至36.86%,提高了0.98倍。菌株BC17胆固醇去除率从19.02%提高到35.70%,提高了0.88倍。结果显示,通过驯化可以有效的提高菌株的功能特性。
表 2 乳酸菌驯化前后胆固醇去除率Table 2. Cholesterol removal rate of before and after lactic acid bacteria domestication菌株 驯化前胆固醇去除率(%) 驯化后胆固醇去除率(%) SS2-6 18.21±3.02cd 36.86±2.48a BC17 19.04±0.99bcd 35.70±1.58a 4Y 22.62±1.76ab 34.79±1.41a nt4-10 24.62±2.61a 31.75±0.59b nt2-8 18.65±1.27bcd 30.85±0.33b qc2 18.58±2.48bcd 29.88±0.12b ntl5 20.59±0.51abc 29.06±0.79b SD8 16.22±1.26d 23.30±0.77c 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.1.3 具有去除甘油三酯功能乳酸菌的筛选
目前大多数研究发现乳酸菌在体内具有降低甘油三酯能力,但很少研究体外降甘油三酯能力[32],甘油三酯是人体内含量最多的脂类,大部分组织均可以利用甘油三酯的分解产物供给能量。人体积累过量的甘油三酯会导致肥胖,是代谢综合症的主要危险因素,严重的甘油三酯积累会引起胰腺炎和脂肪肝。对8株高胆固醇驯化后的乳酸菌的去除甘油三酯能力进行测定,利用单试剂法测定发酵上清液中甘油三酯含量,由表3可知,各菌株对甘油三酯的去除率差异较大,去除率在5.64%~58.87%之间,菌株4Y没有降低甘油三酯的能力。菌株BC17甘油三酯去除率显著高于其他菌株(P<0.05),为58.87%。实验结果与Li等[33]从传统发酵食品开菲尔中筛选得到的Lactobacillus rhamnosus S51甘油三酯去除率(53.72%)相似。
表 3 不同乳酸菌甘油三酯去除率Table 3. Triglyceride removal rate of different lactic acid bacteria菌株 甘油三酯去除率(%) BC17 58.87±1.25a SD8 5.64±1.04e SS2-6 30.32±2.34c nt2-8 23.38±1.00d ntl5 25.21±1.25d nt4-10 41.13±1.04b qc2 32.34±1.00c 4Y − 注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);“−”表示未检出。 2.2 降血脂相关酶活力的测定
胰脂肪酶由胰腺的腺泡细胞分泌,是水解脂肪的关键酶[34],在人体脂肪消化中发挥着重要作用,它能将膳食中的甘油三酯水解成单甘油酯和脂肪酸,然后被重新吸收并最终合成为人体所需的脂肪[35]。因此抑制胰脂肪酶活性作为预防和治疗高脂血症和肥胖症的一个措施和靶点已经被广泛研究,前人的许多研究表明多种化合物(如多酚类、多糖类等)具有较强的胰脂肪酶抑制活性[36−38]。
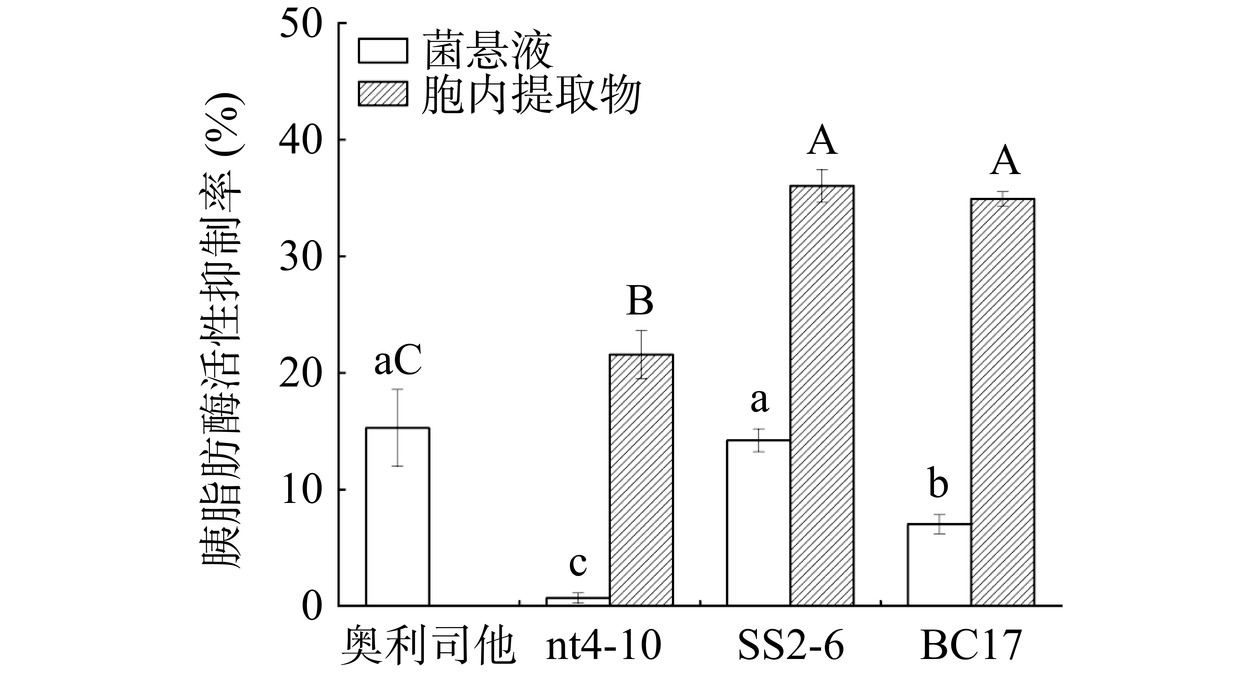
综合选择胆固醇和甘油三酯去除率较高的3株乳酸菌,测定其菌悬液和胞内提取物对胰脂肪酶和胆固酯酶活性的抑制率的影响,结果如图1和图2所示。从图1中可知,3株乳酸菌胞内提取物和菌悬液对胰脂肪酶活力均有不同程度的抑制作用,其中菌株SS2-6和BC17的胞内提取物对酶的抑制率最高,但两者之间无显著差异(P>0.05),分别为36.04%和34.92%。3株乳酸菌胞内提取物对酶的抑制程度均比10 μg/mL奥利司他高,胞内提取物相较于菌悬液,对胰脂肪酶均具有较高的抑制能力。
![]() 图 1 乳酸菌菌悬液和胞内提取物对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制率注:不同小写字母表示不同乳酸菌菌悬液差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同乳酸菌胞内提取物差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity by Lactobacillus suspensions and intracellular extracts
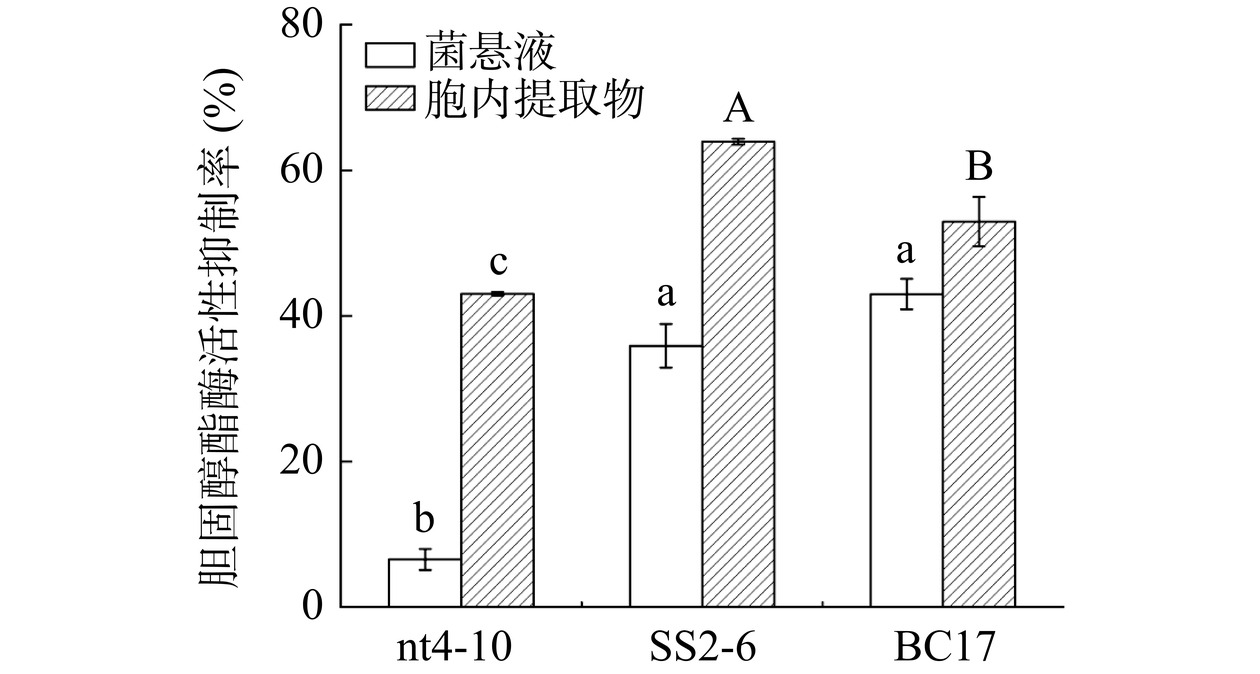
图 1 乳酸菌菌悬液和胞内提取物对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制率注:不同小写字母表示不同乳酸菌菌悬液差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同乳酸菌胞内提取物差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity by Lactobacillus suspensions and intracellular extracts胆固醇酯酶能够催化胆固醇酯分解为胆固醇和对应脂肪酸[39],因此,抑制酶的活性可一定程度地减少人体对胆固醇、脂肪酸吸收,进而降低血清胆固醇含量,调节血脂水平。3株乳酸菌对胆固醇酯酶的活性抑制率如图2所示,菌株SS2-6胞内提取物对胆固醇酯酶的抑制率显著高于其他菌株(P<0.05),抑制率为63.93%。菌株SS2-6和BC17菌悬液对酶的抑制率并无显著差异(P>0.05),分别为35.89%和42.99%。与乳酸菌菌悬液相比,胞内提取物对胆固醇酯酶的抑制能力更高。
综合上述多种实验结果,菌株SS2-6和BC17均具有较强的降血脂功能,两株菌的胆固醇去除率没有显著差异(P>0.05),但甘油三酯去除能力结果显示,菌株BC17去除率是SS2-6的1.94倍,最终选择菌株BC17进行后续实验。
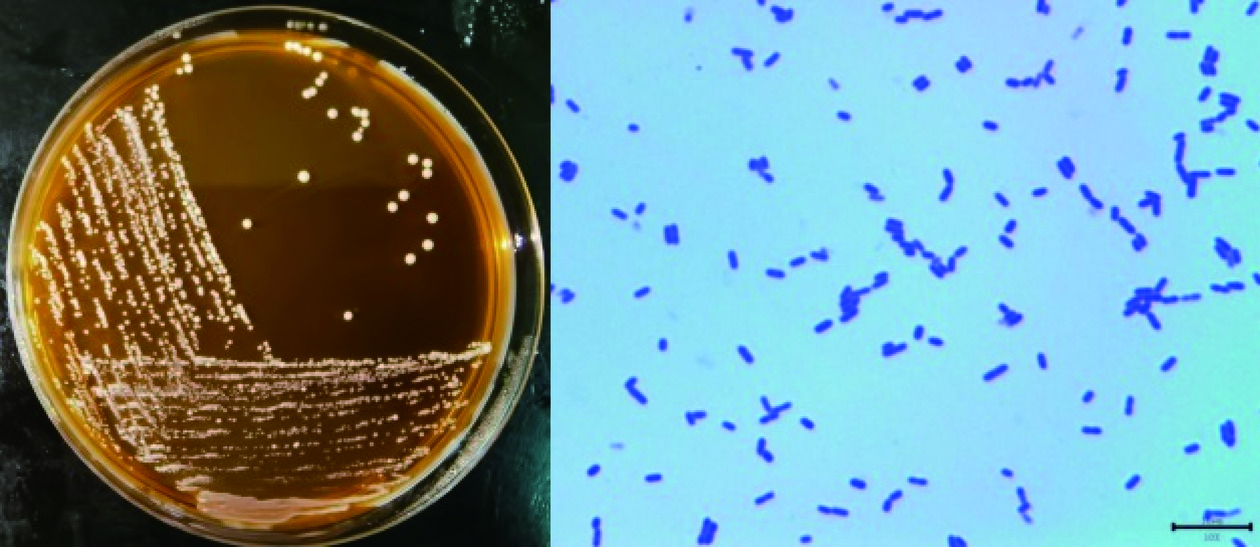
2.3 菌株BC17的形态观察
将菌株BC17接种至MRS琼脂培养基中37℃培养48 h后观察菌落形态,结果见图3(左)。单菌落直径约2~3 mm,圆形凸起,颜色呈白色,菌落表面光滑。挑取单个菌落进行革兰氏染色并在生物显微镜下观察菌体形态,结果如图3(右)所示,菌株为革兰氏阳性菌,细长短杆状,成单或者成对排列,长短不均一。
2.4 菌株BC17的分子生物学鉴定
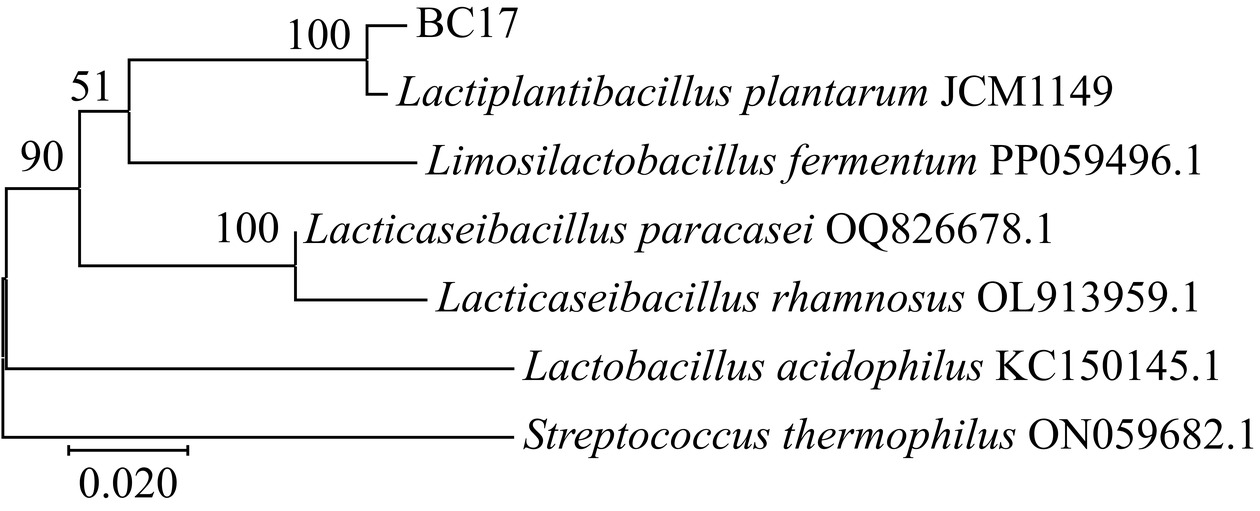
经上海生工生物工程有限公司对扩增、纯化后菌株BC17的16S rDNA产物进行序列测定,其序列长度为1503 bp。使用BLAST软件将菌株BC17的16S rDNA序列与数据库中已提交的核酸序列进行同源性比较,以植物乳植杆菌JCM1149为模式菌株构建系统发育树见图4。从图4中可发现菌株BC17与模式菌株同处一个进化分支,亲缘关系最近,为乳杆菌属。
为了进一步确定菌株BC17,结合持家基因苯丙氨酰-tRNA合成酶α亚基基因(pheS)基因序列进一步鉴定,由上海生工有限公司合成引物pheS-21-F(5’-CAYCCNGCHCGYGAYATGC-3’)和pheS-23-R(5’-GGRTGRACCATVCCNGCHCC-3’),对菌株BC17的phe S基因进行测序,其序列长度为435 bp。经BLAST后发现其pheS基因序列同样与乳杆菌属内菌种的同源性最高。利用MEGA 7软件,以植物乳植杆菌JCM1149为模式菌株,绘制系统发育树。结果如图5所示,菌株BC17与植物乳植杆菌JCM1149处于同一分支,亲缘关系最近。
综合菌落和菌体形态特征以及16S rDNA和pheS基因序列的系统发育分析结果,将菌株BC17初步鉴定为植物乳植杆菌。
2.5 菌株BC17模拟胃肠道耐受性的测定
益生菌经过胃肠道环境时,除受低pH、高浓度胆盐影响,还要承受胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶等多种消化酶的影响[40]。植物乳植杆菌BC17在模拟胃肠液中的活菌数和存活率随时间的变化见表4。由表4可知,植物乳植杆菌BC17在模拟胃液、模拟肠液中连续处理6 h,其存活率和活菌数均呈逐渐下降的趋势,其中经模拟胃液处理3 h后的存活率为79.52%,活菌数为8.81 lg CFU/mL,与0 h相比下降了1.15 lg CFU/mL。在模拟肠液中连续处理3 h后存活率为53.99%,活菌数达到5.63 lg CFU/mL。植物乳植杆菌BC17在模拟胃液和肠液中均具有较高的存活率,说明该菌株具备在宿主肠道定植的基本条件。
表 4 植物乳植杆菌BC17模拟胃肠道耐受性Table 4. Simulated gastrointestinal tolerance of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17指标 模拟胃液 模拟肠液 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h 存活率(%) 89.80±0.03a 88.44±0.90b 79.52±0.51c 58.20±0.29d 56.54±0.29e 53.99±0.87f 活菌数(lg CFU/mL) 9.96±0.01a 8.95±0.00b 8.81±0.09c 7.92±0.05d 5.80±0.03e 5.63±0.03f 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.6 菌株BC17表面疏水性和自聚集能力的测定
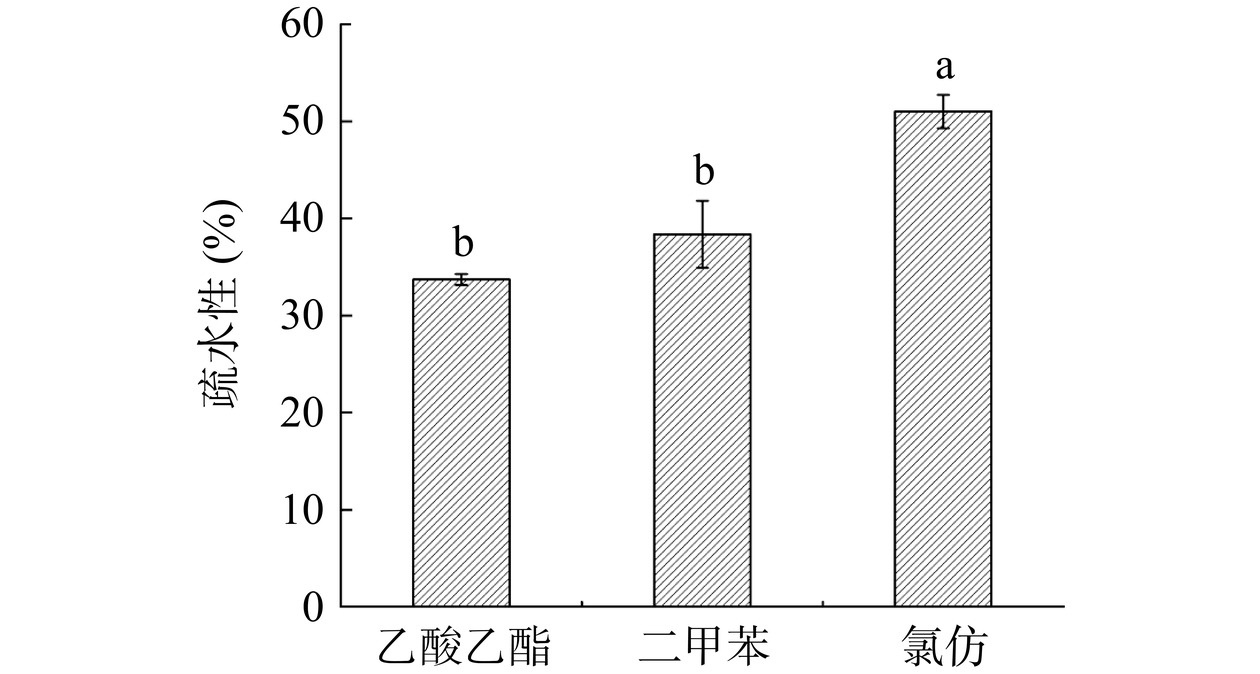
益生菌能否与肠道黏膜表面受体结合取决于菌株的表面性质,具有高度疏水性的菌株通常与粘膜细胞有较强的黏附性[41−42]。由图6可知,植物乳植杆菌BC17在氯仿中的疏水性最高,为51.02%,但在乙酸乙酯和二甲苯中的疏水性并无显著差异(P>0.05),分别为33.71%和38.36%。
![]() 图 6 植物乳植杆菌BC17的疏水性注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。Figure 6. Hydrophobicity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17
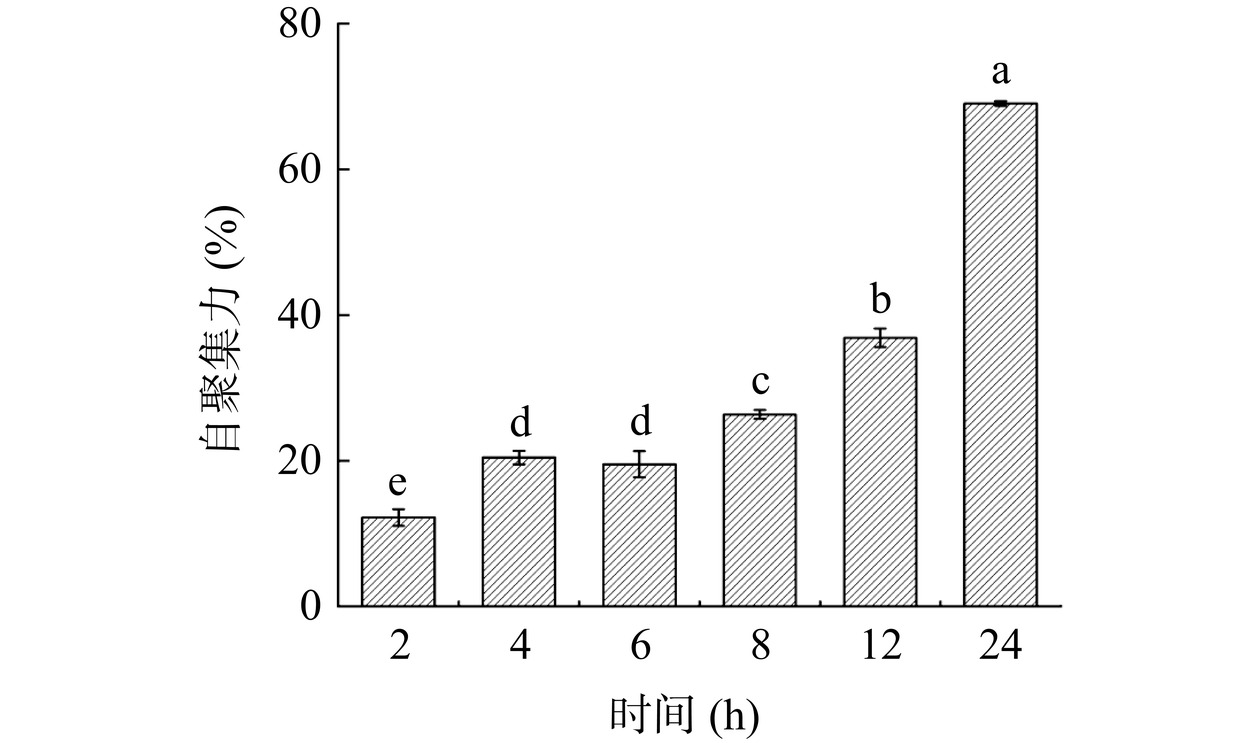
图 6 植物乳植杆菌BC17的疏水性注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。Figure 6. Hydrophobicity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17自聚力是防止病原体表面定植的重要益生特性之一,菌株在大量、快速的增殖过程中会出现自凝聚性,其与菌株黏附能力呈正相关[43−44]。细菌对于自聚集能力的划分标准为:自聚集力在16%~35%为低自聚集能力,36%~50%为中等自聚集能力,51%以上为高自聚集能力[45]。由图7可知,植物乳植杆菌BC17表面自凝聚能力随静置时间增加逐渐增强(P<0.05)。菌株静置24 h后,表现出了较高的自凝聚能力,达到69.04%,属于高自聚集能力。
3. 结论
高血脂诱发的动脉粥样硬化、冠心病、心肌梗死等心脑血管疾病已对人类健康严重威胁,而来源发酵食品的乳酸菌具有降血脂、降血糖、抗炎等多种功效。因此,本研究以来源传统发酵食品中的310株乳酸菌为菌株资源,利用体外检测法测定菌株的去除胆固醇和甘油三酯的能力,筛选具有降血脂功能的菌株资源;采用梯度提高胆固醇浓度的方法驯化初筛菌株,提升菌株的降血脂功能特性。
以去除胆固醇能力为检测指标,初步筛选出32株具有较强去除胆固醇能力的乳酸菌;通过梯度驯化的方法,获得8株胆固醇降解能力显著增强的菌株,其中驯化后菌株BC17胆固醇去除率由19.04%提升至35.86%,提高了0.88倍,可见通过驯化可以提升菌株的功能特性;BC17的甘油三脂去除率最高,达到了58.87%;菌株BC17菌悬液和胞内提取物对两种酶均表现出较强的抑制能力。16S rDNA和pheS基因序列鉴定结果表明,BC17菌株为植物乳植杆菌。菌株益生特性结果表明,BC17对模拟胃肠道具有较好的耐受性,且自聚集力和疏水性均较高。
本研究所获得的植物乳植杆菌BC17具有良好的体外降血脂功能和益生特性,可为降血脂功能发酵产品和益生菌剂的开发提供潜在的菌株资源,应用前景广阔。该菌株的体内降血脂特性及降血脂机理还需进一步研究。
-
图 1 乳酸菌菌悬液和胞内提取物对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制率
注:不同小写字母表示不同乳酸菌菌悬液差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同乳酸菌胞内提取物差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。
Figure 1. Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity by Lactobacillus suspensions and intracellular extracts
图 6 植物乳植杆菌BC17的疏水性
注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图7同。
Figure 6. Hydrophobicity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17
表 1 不同乳酸菌胆固醇去除率
Table 1 Cholesterol degradation rate of different lactic acid bacteria
菌株 胆固醇去除率(%) 菌株 胆固醇去除率(%) 2-4 14.67±1.13ef BC2 6.72±0.30kl 3-1d 12.68±1.17fghi 22-3Y 11.49±1.60fghij 7-2 11.38±1.42fghij nt2-8 18.65±1.27cd 9-9d 12.46±0.37fghij pc15 5.37±0.96l C-M2 11.45±1.70fghij M3 14.16±1.35efg DY1 12.54±1.76fghij qc2 18.58±2.48cd FD1 10.05±0.02hijk MN3 12.00±2.42fghij G10 12.55±1.47fghij MX 10.81±1.78ghij KM1 8.75±0.88jk AB4X 9.32±1.09ijk M15 9.05±1.89ijk 1-1 11.44±1.49fghij ntl5 20.59±0.51bc 22-4Y 22.62±0.98ab pc12 10.33±0.89hij GJ9 12.28±3.52fghij BC17 19.04±0.99cd SS2-6 18.21±3.02cd qc9 11.69±1.83e P13 12.52±1.62fghij SD8 16.22±1.26de GS7 13.51±3.15efgh TM27 10.76±0.20ghij nt4-10 24.62±2.61a 注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 乳酸菌驯化前后胆固醇去除率
Table 2 Cholesterol removal rate of before and after lactic acid bacteria domestication
菌株 驯化前胆固醇去除率(%) 驯化后胆固醇去除率(%) SS2-6 18.21±3.02cd 36.86±2.48a BC17 19.04±0.99bcd 35.70±1.58a 4Y 22.62±1.76ab 34.79±1.41a nt4-10 24.62±2.61a 31.75±0.59b nt2-8 18.65±1.27bcd 30.85±0.33b qc2 18.58±2.48bcd 29.88±0.12b ntl5 20.59±0.51abc 29.06±0.79b SD8 16.22±1.26d 23.30±0.77c 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同乳酸菌甘油三酯去除率
Table 3 Triglyceride removal rate of different lactic acid bacteria
菌株 甘油三酯去除率(%) BC17 58.87±1.25a SD8 5.64±1.04e SS2-6 30.32±2.34c nt2-8 23.38±1.00d ntl5 25.21±1.25d nt4-10 41.13±1.04b qc2 32.34±1.00c 4Y − 注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);“−”表示未检出。 表 4 植物乳植杆菌BC17模拟胃肠道耐受性
Table 4 Simulated gastrointestinal tolerance of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BC17
指标 模拟胃液 模拟肠液 1 h 2 h 3 h 4 h 5 h 6 h 存活率(%) 89.80±0.03a 88.44±0.90b 79.52±0.51c 58.20±0.29d 56.54±0.29e 53.99±0.87f 活菌数(lg CFU/mL) 9.96±0.01a 8.95±0.00b 8.81±0.09c 7.92±0.05d 5.80±0.03e 5.63±0.03f 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] TAEBI R, MIRZAIEY R M, MAHMOODI M, et al. The effect of Curcuma longa extract and its active component (curcumin) on gene expression profiles of lipid metabolism pathway in liver cancer cell line (HepG2)[J]. Gene Reports,2019,18:100581.
[2] 陈继承, 何捷, 何国庆. 降血脂功能食品研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(23):333−338. [CHEN J C, HE J, HE G Q. Research progress on hypolipidemic nutraceuticals and fuctional foods[J]. Food Science,2011,32(23):333−338.] CHEN J C, HE J, HE G Q. Research progress on hypolipidemic nutraceuticals and fuctional foods[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(23): 333−338.
[3] 王炳艳. 瑞舒伐他汀治疗高血脂症合并颈动脉粥样硬化患者的效果及对其血清TC、TG和LDL-C水平的影响分析[J]. 中国医药指南,2019,17(15):158. [WANG B Y. The effect of rosuvastatin in the treatment of hyperlipidemia and carotid atherosclerosis and its effect on serum TC, TG and LDL-C levels were analyzed[J]. Chinese Medical Guide,2019,17(15):158.] WANG B Y. The effect of rosuvastatin in the treatment of hyperlipidemia and carotid atherosclerosis and its effect on serum TC, TG and LDL-C levels were analyzed[J]. Chinese Medical Guide, 2019, 17(15): 158.
[4] 曹蓝, 白玉芹, 余萍, 等. 降血脂鼠李糖乳杆菌的筛选及其对高脂模型地鼠血脂的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(7):48−54,69. [CAO L, BAI Y Q, YU P, et al. Screening of hypolipidemic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and exploration of its effect on high-fat hamster models[J]. The Mystery Inisde Food,2022,38(7):48−54,69.] CAO L, BAI Y Q, YU P, et al. Screening of hypolipidemic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and exploration of its effect on high-fat hamster models[J]. The Mystery Inisde Food, 2022, 38(7): 48−54,69.
[5] SINGH H, SINGH J V, GUPTA M K, et al. Benzoflavones as cholesterol esterase inhibitors:Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2017,27(4):850−854.
[6] ALYAR S, ŞEN T, ÖZMEN Ü Ö, et al. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterizations, enzyme inhibition, molecular docking study and DFT calculations of new Schiff bases of sulfa drugs[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2019,1185:416−424. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.03.002
[7] YE H D, XU Y, SUN Y N, et al. Purification, identification and hypolipidemic activities of three novel hypolipidemic peptides from tea protein[J]. Food Research International,2023,165:112450. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112450
[8] SHENG L, QIAN Z Y, ZHENG S G, et al. Mechanism of hypolipidemic effect of crocin in rats:Crocin inhibits pancreatic lipase[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2006,543(1-3):116−122. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.038
[9] KIM J, KIM C S, JO K, et al. POCU1b, the n-butanol soluble fraction of polygoni cuspidati rhizoma et radix, attenuates obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver, and insulin resistance via inhibitions of pancreatic lipase, cAMP-dependent PDE activity, AMPK activation, and SOCS-3 suppression[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(12):3612. doi: 10.3390/nu12123612
[10] CAVALIERE H, FLORIANO I, MEDEIROS-NETO G. Gastrointestinal side effects of orlistat may be prevented by concomitant prescription of natural fibers (psyllium mucilloid)[J]. International Journal of Obesity,2001,25(7):1095−1099. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801645
[11] PATEL D K, STANFORD F C. Safety and tolerability of new-generation anti-obesity medications:A narrative review[J]. Postgraduate Medicine,2018,130(2):173−182. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2018.1435129
[12] 秦晓雅. 黄酮类人胰脂肪酶抑制剂的发现及构效关系研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学, 2022. [QIN X Y. Discovery of flavonoid human pancreatic lipase inhibitors and their structure-activity relationship[D]. Shihezi University, 2022.] QIN X Y. Discovery of flavonoid human pancreatic lipase inhibitors and their structure-activity relationship[D]. Shihezi University, 2022.
[13] METTE K, SIGNA R J, KARINA V S, et al. Supplementation with dairy calcium and/or flaxseed fibers in conjunction with orlistat augments fecal fat excretion without altering ratings of gastrointestinal comfort[J]. Nutrition & Metabolism,2017,14(1):13.
[14] BECONCINI D, FABIANO A, ZAMBITO Y, et al. Cherry extract from Prunus avium L. to improve the resistance of endothelial cells to oxidative stress:Mucoadhesive chitosan vs. poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(7):1759. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071759
[15] BURAKOVA I, SMIRNOVA Y, GRYAZNOVA M, et al. The effect of short-term consumption of lactic acid bacteria on the gut microbiota in obese people[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(16):3384. doi: 10.3390/nu14163384
[16] JIANG S M, LIU A J, MA W Y, et al. Lactobacillus gasseri CKCC1913 mediated modulation of the gut-liver axis alleviated insulin resistance and liver damage induced by type 2 diabetes[J]. Food & Function,2023,14(18):8504−8520.
[17] KATARZYNA G. Anticancer activity of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology,2022,86(3):356−366.
[18] BANJOKO I O, ADEYANJU M M, ADEMUYIWA O, et al. Hypolipidemic effects of lactic acid bacteria fermented cereal in rats[J]. Lipids in Health and Disease,2012,11(1):170. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-170
[19] ALI S M, SALEM F E, ABOULWAFA M M, et al. Hypolipidemic activity of lactic acid bacteria:Adjunct therapy for potential probiotics[J]. PLoS One,2022,17(6):1−17.
[20] QIAN Y, LI M Y, WANG W, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus casei YBJ02 on lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic mice[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(12):3793−3803. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14787
[21] 许浩翔. 乳酸菌发酵刺梨汁对小鼠免疫力及肠道微生态影响的研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学, 2021. [XU H X. Study on the effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation of prickly pear juice on immunity and intestinal microecology in mice[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou University, 2021.] XU H X. Study on the effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation of prickly pear juice on immunity and intestinal microecology in mice[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2021.
[22] HASLAMD D W, JAES W P. Obesity[J]. The Lancet,2005,366(9492):1197−1209. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67483-1
[23] 印伯星. 乳酸菌发酵乳辅助降血脂效应与机制研究[D]. 扬州:扬州大学, 2019. [YIN B X. Study on the hypolipidemic effect and mechanism of lactic acid bacteria fermented milk[D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University, 2019.] YIN B X. Study on the hypolipidemic effect and mechanism of lactic acid bacteria fermented milk[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019.
[24] ZHAO Y T, ZHANG M, HOU X D, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of salicylanilides as novel allosteric inhibitors of human pancreatic lipase[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry,2023,91:117413.
[25] LI B J, ZHOU B H, LU H L, et al. Phosphaisocoumarins as a new class of potent inhibitors for pancreatic cholesterol esterase[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2010,45(5):1955−1963. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.01.038
[26] 凌代文, 东秀珠. 乳酸细菌分类鉴定及实验方法[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 1999. [LING D W, DONG X Z. Classification, identification and experimental methods of lactic acid bacteria[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 1999.] LING D W, DONG X Z. Classification, identification and experimental methods of lactic acid bacteria[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 1999.
[27] RUIZ M S, GONCALVES D S, MARIA T P. Screening of autochthonous lactic acid bacteria strains from artisanal soft cheese:Probiotic characteristics and prebiotic metabolism[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2019,114:108388.
[28] DENG L Q, LIU L M, FU T Y, et al. Genome sequence and evaluation of safety and probiotic potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LPJZ-658[J]. Microorganisms,2023,11(6):1620. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061620
[29] ZHANG Q, SONG X J, SUN W L, et al. Evaluation and application of different cholesterol-lowering lactic acid bacteria as potential meat starters[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2021,84(1):63−72. doi: 10.4315/JFP-20-225
[30] DING W R, SHI C, CHEN M, et al. Screening for lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Tibetan yak milk and evaluating their probiotic and cholesterol-lowering potentials in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,32:324−332. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.021
[31] 孟祥利. 耐高渗透压乳酸菌的驯化、应用及特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学, 2014. [MENG X L. The domestication, application and properties of the osmophilic lactic acid bacteria[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.] MENG X L. The domestication, application and properties of the osmophilic lactic acid bacteria[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.
[32] 苏建辉. 牡丹籽油及其复方降血糖、降血脂活性及机理研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [SU J H. The antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of peony seed oil with its formula and mechanism research[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017.] SU J H. The antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of peony seed oil with its formula and mechanism research[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[33] LI K X, GU Q Y, YANG W H, et al. In vitro screening and probiotic evaluation of anti-obesity and antioxidant lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Bioscience,2023,54:102844. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102844
[34] 张帆, 程路峰, 曹红, 等. 基于酶反应动力学理论优化脂肪酶活力测定体系[J]. 中国油脂,2023,48(5):146−52. [ZHANG F, CHENG L F, CAO H, et al. Optimization of lipase acticity assay system based on enzyme reaction kinetics theory[J]. Chinese Fats,2023,48(5):146−52.] ZHANG F, CHENG L F, CAO H, et al. Optimization of lipase acticity assay system based on enzyme reaction kinetics theory[J]. Chinese Fats, 2023, 48(5): 146−52.
[35] 张国文, 黎沙, 朱苗. 白杨素对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用及机制[J]. 南昌大学学报:理科版,2021,45(6):545−552. [ZHANG G W, LI S, ZHU M. Inhibitory interaction and mechanism of chrysin on pancreatic lipase[J]. Journal of Nanchang University:Science Edition,2021,45(6):545−552.] ZHANG G W, LI S, ZHU M. Inhibitory interaction and mechanism of chrysin on pancreatic lipase[J]. Journal of Nanchang University: Science Edition, 2021, 45(6): 545−552.
[36] 吴慧昊, 牛锋, 钟琦, 等. 高效降胆固醇降甘油三酯乳酸菌的分离鉴定和功能分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(14):157−162. [WU H H, NIU F, ZHONG Q, et al. Separation, identification and functional analysis of cholesterol-lowering and triglycerid-lowering lactic acid bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(14):157−162.] WU H H, NIU F, ZHONG Q, et al. Separation, identification and functional analysis of cholesterol-lowering and triglycerid-lowering lactic acid bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(14): 157−162.
[37] ZHANG X Y, LI D, WANG K X, et al. Hyperoside inhibits pancreatic lipase activity in vitro and reduces fat accumulation in vivo[J]. Food & Function,2023,14(10):4763−4776.
[38] AGUILERE-ANGEL E Y, ESPINAL-RUIZ M, NARVAEZ-CUENCA C E, et al. Pectic polysaccharides with different structural characteristics as inhibitors of pancreatic lipase[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,83:229−238. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.009
[39] AJAYI F F, MUDGIL P, GAN C Y, et al. Identification and characterization of cholesterol esterase and lipase inhibitory peptides from amaranth protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2021,12:100165.
[40] HYRONIMUS B, LE M C, HADJ S A, et al. Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2000,61:193−197. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00366-4
[41] VAN L M C, LYKLEMA J, NORDE W, et al. The role of bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1987,53(8):1893−1897. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1893-1897.1987
[42] GUO X H, KIM J M, NAM H M, et al. Screening lactic acid bacteria from swine origins for multistrain probiotics based on in vitro functional properties[J]. Anaerobe,2010,16(4):321−326. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.03.006
[43] BAO Y, ZHANG Y C, ZHANG Y, et al. Screening of potential probiotic properties of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from traditional dairy products[J]. Food Control,2010,21(5):695−701. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.10.010
[44] TOMÁS G C, AHMED M K, IRENE B, et al. Adhesion abilities of dairy Lactobacillus plantarum strains showing an aggregation phenotype[J]. Food Research International,2014,57:44−50. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.010
[45] 吴雨晗, 吴婷, 涂健, 等. 一株安庆六白猪源乳酸菌的分离鉴定及生物特性研究[J]. 动物营养学报,2022,34(8):5415−5425. [WU Y H, WU T, TU J, et al. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of a lactic acid bacteria from Anqing Liubai pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2022,34(8):5415−5425.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.08.061 WU Y H, WU T, TU J, et al. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of a lactic acid bacteria from Anqing Liubai pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(8): 5415−5425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.08.061





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
