Changes in Quality of Sauced Duck Necks during Cold Storage and Its Correlation with Microbial Community
-
摘要: 为探究酱卤鸭脖冷藏过程中品质变化与微生物菌群的相关性,以市售气调包装的酱卤鸭脖为研究对象,将其在4 ℃条件下冷藏1、4、7、10、13 d,分别测定其pH、硫代巴比妥酸反应产物(thiobarbituric acid reactive substances,TBARS)值、色泽、质构、菌落总数、总挥发性盐基氮(total volatile base nitrogen,TVB-N)含量以及微生物菌群等指标的变化。结果显示,酱卤鸭脖在冷藏过程中pH先下降后上升;亮度(L*)、红度(a*)、黄度(b*)和硬度均呈下降趋势,弹性、咀嚼性、内聚性和胶粘性先上升后下降;菌落总数、TVB-N和TBARS值均逐渐上升,其中菌落总数和TVB-N在第10 d超过可接受上限值。冷藏过程中微生物多样性逐渐降低,冷藏初期优势菌为红球菌属(Rhodococcus)、不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、尿素芽孢杆菌属(Ureibacillus)、共生短杆菌属(Symbiobacterium),冷藏末期优势菌为红球菌属、不动杆菌属、明串珠菌属(Leuconostoc)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)。主坐标分析(principal co-ordinates analysis,PCoA)表明两个主坐标叠加解释度为74.03%,贮藏4 d后菌群结构开始出现差异;相关性分析显示明串珠菌属与酱卤鸭脖冷藏过程中的pH、菌落总数、TVB-N含量和TBARS值呈正相关,表明明串珠菌属是酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程的主要腐败菌。Abstract: This study was undertaken in order to explore the correlation between the quality changes and microbial community in sauced duck necks during cold storage. Commercial sauced duck necks in modified atmosphere packaging were stored at 4 ℃ for 1, 4, 7, 10, and 13 days, and the changes in pH, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) value, color, texture, total bacterial count, total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N) content, and microbial community were analyzed. The results showed that the pH initially decreased and then increased with storage time, while brightness (L*), redness (a*), yellowness (b*) and hardness exhibited a decreasing trend, and elasticity, chewiness, cohesiveness and adhesiveness showed an initial increase followed by a decrease. The total bacterial count, TVB-N and TBARS values all gradually increased during storage, with the total bacterial count and TVB-N exceeding the acceptable limits on the 10th day. Microbial diversity diminished gradually with storage time. At the initial stage of storage, the dominant bacteria were Rhodococcus, Acinetobacter, Ureibacillus and Symbiobacterium, while those in the late storage period were Rhodococcus, Acinetobacter, Leuconostoc and Lactobacillus. Principal co-ordinate analysis indicated the two principal coordinates explained 74.03% of the variation, and differences in microbial community composition occurred after 4 days of storage. Correlation analysis showed that Leuconostoc was positively correlated with pH, total bacterial count, TVB-N content and TBARS value during cold storage of sauced duck necks, indicating that Leuconostoc was the primary spoilage bacteria during storage.
-
Keywords:
- sauced duck neck /
- quality change /
- microbial community /
- correlation
-
酱卤鸭肉制品属于我国传统肉制品,历史悠久。其肉质鲜嫩、酱香浓郁、别具风味,因此深受消费者喜爱[1]。市面上酱卤鸭肉销售方式通常以散卖或气调包装方式为主,然而这些销售方式存在贮藏期间品质不稳定、易腐败和货架期短等问题[2]。这是由于酱卤鸭肉制品在生产、运输和销售过程中极其容易受到外源微生物的污染[3],加上酱卤鸭肉制品营养丰富,水分较高,少数微生物得以迅速繁殖成为酱卤肉中的优势腐败菌,使肉制品变粘、变色、产生异味[4],最终导致腐败,进而严重影响其保质期和销售半径,造成巨大经济损失[5]。
目前,已经有大量关于酱卤肉制品腐败菌的研究报道。刘竹臻[6]发现酱牛肉贮藏期间优势菌属为肠杆菌属和芽孢杆菌属,这些优势菌属造成酱牛肉贮藏期间失水率不断下降,菌落总数和大肠杆菌数不断增加,总挥发性盐基氮(total volatile base nitrogen,TVB-N)值显著上升。叶可萍等[7]研究了气调包装的酱卤鸭翅贮藏过程菌群结构变化,结果表明,贮藏初期主要菌属为不动杆菌属,贮藏末期优势菌群为嗜冷杆菌、莫拉氏菌和链球菌等,其中嗜冷杆菌为主要优势菌群。而李雪等[8]测定了气调包装的酱卤鸭翅在贮藏期间品质变化情况(包括菌落总数、嫩度和硬度、TVB-N值等)。因此,酱卤肉制品在贮藏期间的腐败变质通常离不开微生物的作用,制定相应的微生物控制策略是延长酱卤肉制品货架期的关键。然而,关于酱卤鸭肉,尤其是气调包装的酱卤鸭肉在贮藏期间品质变化与微生物菌群之间关系的报道还比较少。
为此本实验以市售气调包装的酱卤鸭脖为研究对象,测定其在冷藏13 d期间pH、色泽、质构、菌落总数、TVB-N和硫代巴比妥酸反应产物(thiobarbituric acid reactive substances,TBARS)等理化指标,并且采取高通量测序技术,探究冷藏期间酱卤鸭脖的微生物菌群变化,分析理化性质与微生物菌群之间的关联,以期了解酱卤鸭脖在冷藏期间品质和微生物菌群之间关系,为酱卤鸭脖货架期的延长提供一定的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
国内知名品牌气调锁鲜盒装酱卤鸭脖(65% N2+35% CO2) 保质期10 d,购自江西省南昌市农贸市场,立即置于 4 ℃冰箱冷藏;三氯乙酸 天津风船化学试剂科技有限公司;2-硫代巴比妥酸 Solarbio公司;氧化镁 上海展云化工有限公司;盐酸 南昌鑫光精细化工厂;硼酸 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;平板计数琼脂培养基 Solarbio公司;E.Z.N.A.® Soil DNA Kit DNA抽提试剂盒 美国Omega公司;FastPfu DNA Polymerase高保真DNA聚合酶 北京全式金生物技术有限公司;AxyPrepDNA凝胶回收试剂盒 Axygen公司。
CR-10色差仪 日本柯尼卡公司;TA-TXplus质构分析仪 英国Stable Micro System公司;SW-CJ系列净化工作台 上海新苗医疗器械制造有限公司;SPX-150L生化培养箱 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;SKD-800自动凯氏定氮仪 上海沛欧分析仪器有限公司;TL-48R粉碎研磨仪 上海万柏生物科技有限公司;ABI GeneAmp®9700型PCR仪 美国ABI公司;DYY-6C电泳仪 北京市六一生物科技有限公司;NanoDrop2000超微量分光光度计 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific;Quantus™ FluorometerT微型荧光计 美国Promega公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原料贮藏条件
将同一批次的气调锁鲜盒装酱卤鸭脖置于4 ℃条件下,分别贮藏1、4、7、10、13 d后取样,依次编号为S1、S4、S7、S10、S13,每个样品重复测定3次,每次为1盒。
1.2.2 pH测定
依照GB 5009.237-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定》。
1.2.3 色差测定
采用手持色差仪测定鸭脖肉的亮度(L*)、红度(a*)、黄度(b*)。
1.2.4 质构特性测定
采用质构仪测定鸭脖的质构特性,将样品切成1 cm×1 cm×1 cm均匀块状(不含骨头),顺着肉纤维测定。质构仪参数为:探头为P6,触发力5 g,形变40%,测试速率为1 mm/s,测前和测后速率均为5 mm/s。
1.2.5 菌落总数测定
依照GB 4789.2-2016《食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》测定。
1.2.6 TVB-N含量测定
依照GB 5009.228-2016《食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》中的第二法自动凯氏定氮仪法测定。
1.2.7 TBARS值测定
依照GB 5009.181-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定》中的分光光度法测定。
1.2.8 DNA提取及高通量测序
1.2.8.1 细菌群落基因组DNA提取
根据E.Z.N.A.® Soil DNA Kit DNA试剂盒进行总基因组DNA抽提,添加0.3 g样品、适量磁珠和裂解液到2 mL离心管中,研磨仪破碎后具体提取步骤根据试剂盒说明书进行。
1.2.8.2 PCR扩增
选取样本16S rDNA基因V3~V4区进行PCR扩增,引物序列:338F 5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3',806R 5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3',PCR反应体系为:4 μL 5×FastPfu Buffer、2 μL 2.5 mmol/L dNTPs、0.8 μL上游引物(5 μmol/L)、0.8 μL下游引物(5 μmol/L)、0.4 μL FastPfu Polymerase、0.2 μL BSA、10 ng基因组DNA,加水补足至20 μL。扩增程序如下:95 ℃预变性3 min,循环1次;95 ℃变性30 s;53 ℃退火30 s,循环30次;72 ℃延伸45 s;72 ℃稳定延伸10 min,循环1次,10 ℃保存。使用2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测PCR产物,接着将PCR产物混合后进行切胶回收,得到纯化产物样本,并使用微型荧光计对样品进行定量,最后采用NEXTFLEX Rapid DNA-Seq Kit进行建库,在Illumina Miseq PE300平台进行测序。
1.2.8.3 高通量测序数据分析
采用Mothur软件[9]计算超Ⅰ指数(Chao1 index)、香农指数(Shannon index)和辛普森(Simpson)等α多样性指数,并采用Wilxocon秩和检验进行α多样性的组间差异分析;使用基于bray-curtis距离算法的主坐标分析检验样本间微生物群落结构的相似性,结合PERMANOVA非参数检验分析样本组间微生物群落结构差异是否显著。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均做3次平行,实验结果以平均值±标准偏差表示。采用Origin 2021绘图并利用Correlation plot进行相关性分析,SPSS 21.0软件进行统计分析,采用Duncan检验进行方差分析,P<0.05表示显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖pH的变化
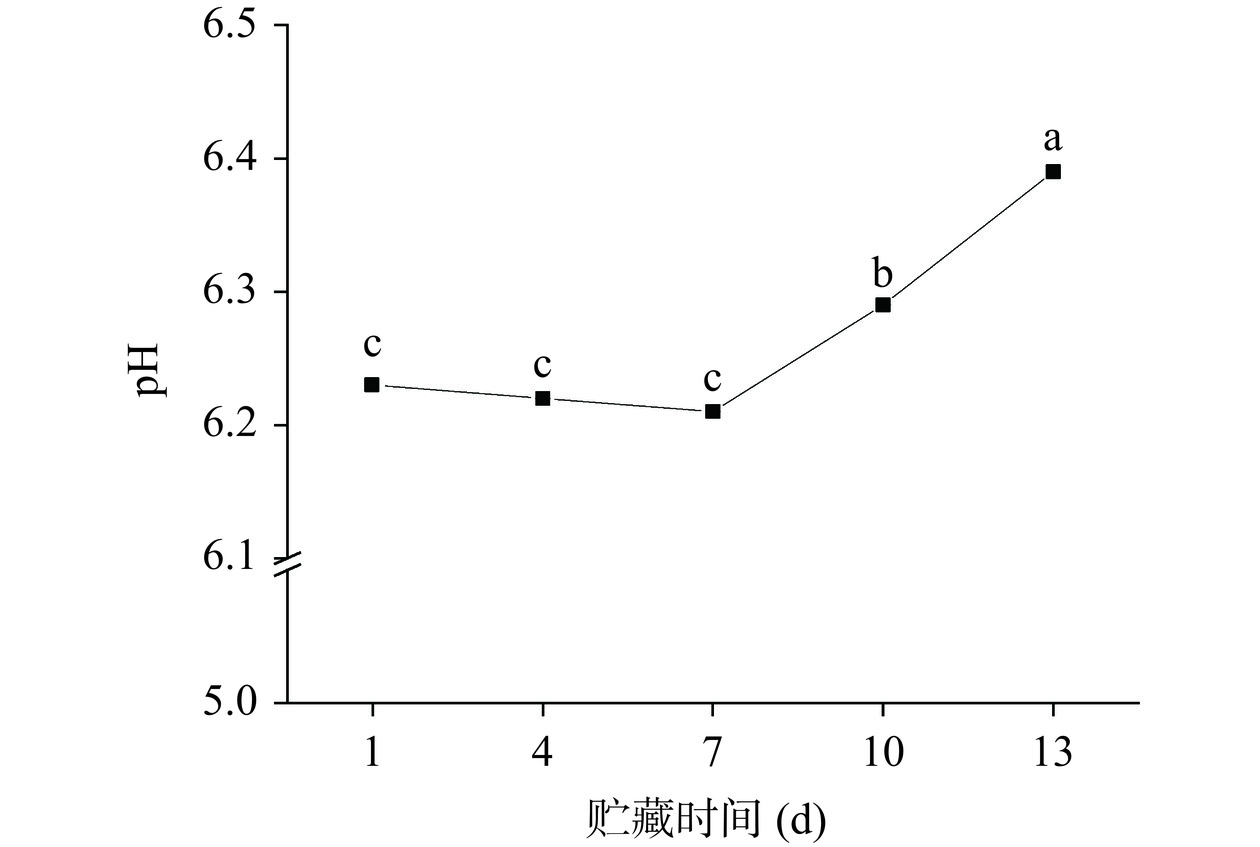
pH可以反映酱卤鸭脖新鲜度[10]。如图1所示,初始pH为6.23,在贮藏1~7 d期间,pH呈现出下降的趋势,但无明显差异(P>0.05),而在贮藏7~13 d期间,pH显著上升(P<0.05),且贮藏13 d后,pH上升至6.39。
2.2 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖TBARS值的变化
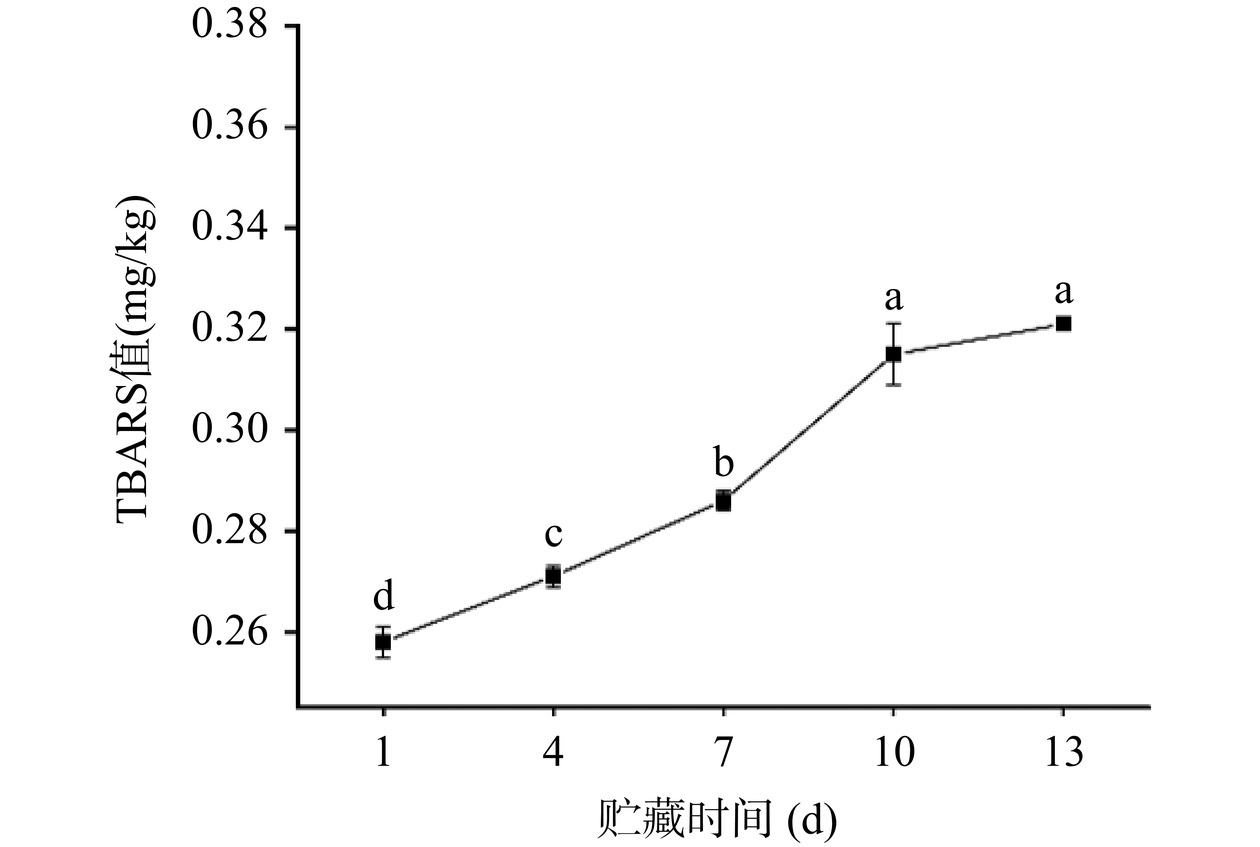
脂肪氧化是影响肉制品品质的重要因素,TBARS值可用于评估肉类脂肪氧化程度,TBARS值越高表明脂肪氧化程度越深[11]。如图2所示,酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间TBARS值缓慢升高,在1~10 d内存在显著差异(P<0.05),贮藏13 d后,其TBARS值达到0.32 mg/kg,与1 d相比增加了23.08%(P<0.05)。
2.3 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖色泽的变化
色泽是直接反映酱卤鸭脖新鲜度的参数,极大程度影响消费者的购买欲望[12]。由表1可以看出,随着贮藏时间的延长,酱卤鸭脖的L*、a*和b*值均显著下降(P<0.05)。L*值代表亮度,随着贮藏时间的增长,L*值逐渐降低,这可能是因为鸭脖的持水性下降,导致表面水分大量丧失,从而降低了肉表面的光反射率[13]。a*值代表红度,与肌红蛋白氧化密切相关,在贮藏的后期阶段,观察到pH持续上升,这对氧合肌红蛋白的形成产生不利影响。此外,大量微生物的繁殖会使气调包装酱卤鸭脖中氧分压降低,促进高铁肌红蛋白形成,由于高铁肌红蛋白呈褐色[14],最终导致a*值的下降。b*值代表黄度,b*值与脂质氧化程度相关,本研究中酱卤鸭脖b*值逐渐下降与贮藏过程中其TBARS值逐渐增加相吻合。类似地,段昌圣[15]研究也表明,酱卤鸭脖b*值显著下降可能是由于脂质氧化,导致肌肉颜色黄度下降。
表 1 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖色泽的变化Table 1. Changes in color of sauced duck neck during storage2.4 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖质构特性的变化
由表2可知,贮藏1 d时酱卤鸭脖硬度为745.86 g,10 d时显著下降(P<0.05)至630.76 g,13 d进一步下降至623.03 g;与1 d相比,贮藏13 d时硬度下降了16.47%。这可能是由于内源性酶与微生物共同作用于鸭脖中的蛋白结构,使肉中的肌动球蛋白分解,导致蛋白结构松散弹性提高,降低了肉的硬度[16]。贮藏期间,酱卤鸭脖弹性整体呈先上升后下降趋势,贮藏1 d时弹性为0.74 g,4 d时显著(P<0.05)上升至0.89 g,而后缓慢下降,但无显著性差异(P>0.05)。鸭脖弹性和持水力相关,贮藏初期,鸭脖保留一定的持水力,随着贮藏时间的延长,持水力下降,导致弹性下降[12]。另外,贮藏期间酱卤鸭脖咀嚼性、内聚性、胶粘性随着贮藏时间的延长呈波动下降趋势,且均在货架期内(前10 d)无明显变化(P>0.05),贮藏13 d后显著下降(P<0.05)。贮藏13 d酱卤鸭脖的咀嚼性、内聚性、胶粘性与贮藏1 d相比分别下降了38.34%、34.55%和46.53%,这可能是由于在微生物作用下,鸭脖中蛋白质等成分被降解,使其咀嚼性、内聚性和胶黏性慢慢下降,尤其是贮藏后期微生物大量繁殖,降解作用增强,导致咀嚼性、内聚性和胶黏性显著下降[17]。
表 2 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖质构特性的变化Table 2. Changes in texture of sauced duck neck during storage贮藏时间(d) 硬度(g) 弹性(g) 咀嚼性 内聚性 胶粘性 1 745.86±106.65a 0.74±0.03b 301.99±53.28ab 0.55±0.04ab 408.51±25.59a 4 733.31±76.53ab 0.89±0.07a 386.07±69.46a 0.60±0.11a 432.29±8.31a 7 704.85±39.58ab 0.88±0.09a 314.79±99.09a 0.51±0.14ab 352.97±24.56a 10 630.76±19.12b 0.87±0.02a 306.24±29.32a 0.47±0.06ab 349.17±28.04a 13 623.03±68.95b 0.85±0.06a 186.20±61.37b 0.36±0.14b 218.41±15.10b 2.5 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖菌落总数的变化
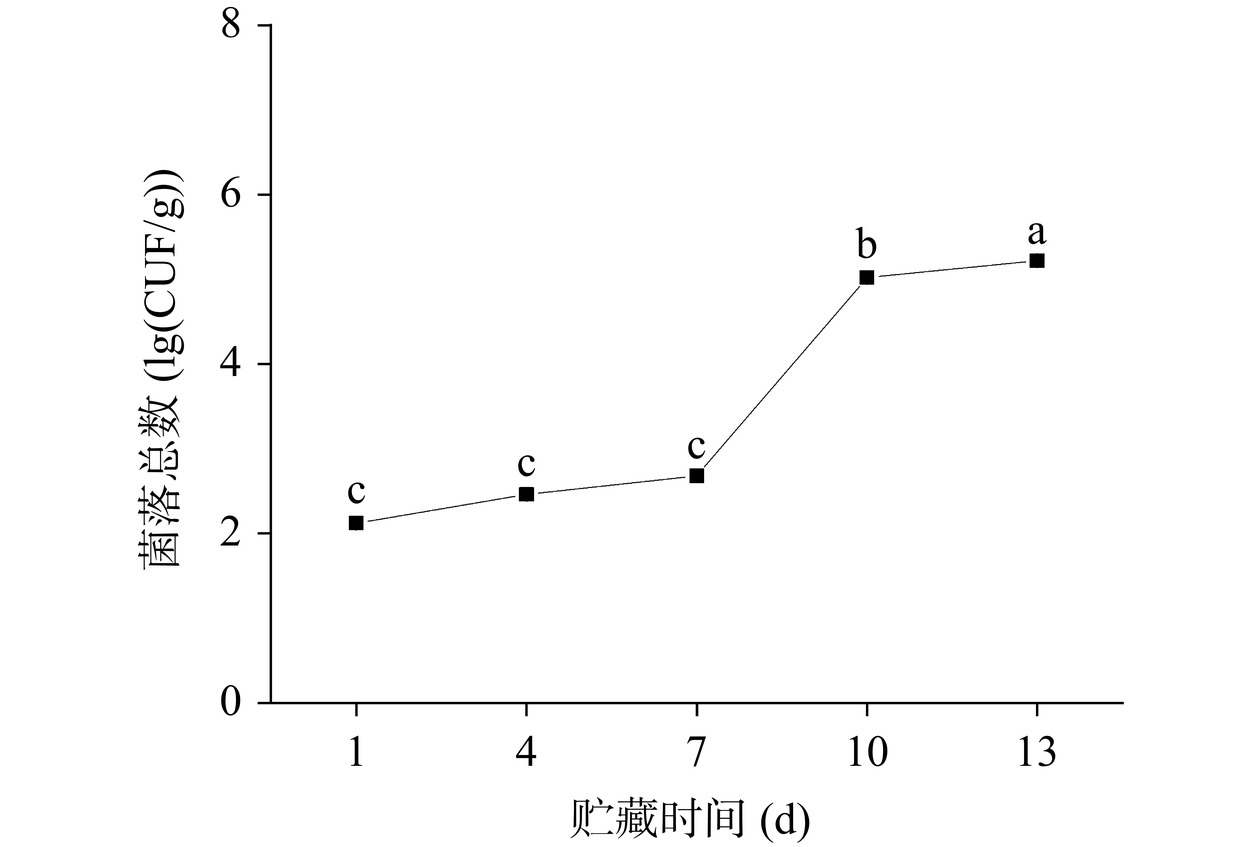
微生物是影响肉类保质期的主要因素之一,微生物数量的变化反映了腐败程度。根据我国《食品安全国家标准熟肉制品》(GB 2726-2016)规定,酱卤肉类菌落总数上限值为5.0 lg(CFU/g),超过视为腐败。由图3可知,酱卤鸭脖中的菌落总数在贮藏期间整体呈逐渐上升趋势,其中1~7 d上升缓慢,7~13 d上升显著(P<0.05),且在第10 d达到5.02 lg(CFU/g),超出熟肉可接受卫生水平,说明酱卤鸭脖在4 ℃下能贮藏10 d,贮藏结束时,菌落总数达到5.22 lg(CFU/g)。
2.6 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖TVB-N值的变化
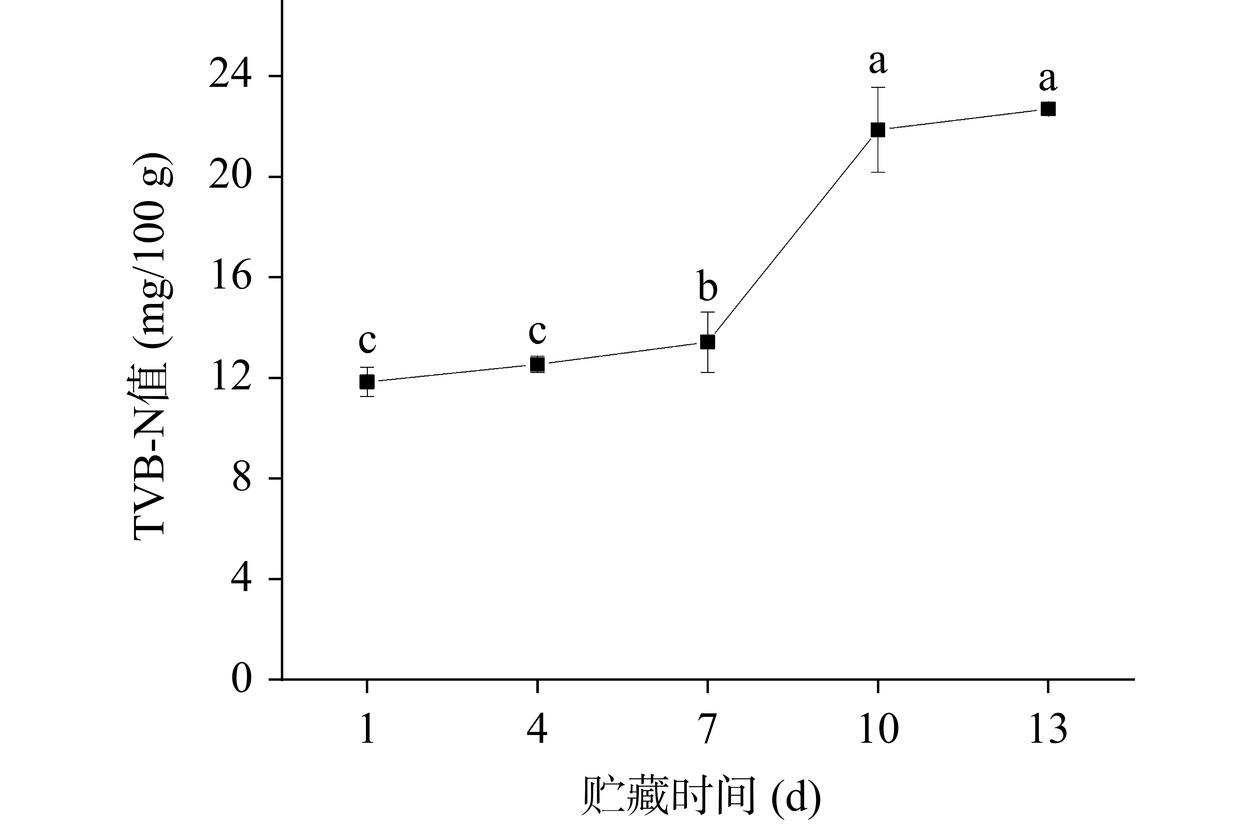
TVB-N与菌落总数密切相关,是指肉制品由于自身酶和微生物作用,使得蛋白质分解而产生氨及胺类等碱性含氮物质[18],TVB-N值越大,表明肉制品腐败变质越严重。由图4可知,酱卤鸭脖TVB-N值在贮藏期间不断上升,贮藏7 d后TVB-N值开始快速增加,而后趋于稳定,且10 d时TVB-N含量为21.87 mg/100 g,超过GB 2707-2016《鲜(冻)畜、禽产品》中的限定值(20 mg/100 g),贮藏结束后,TVB-N含量达到22.70 mg/100 g,相比1 d增加了1.92倍。
2.7 16S rDNA高通量测序结果分析
2.7.1 测序样本数据分析
高通量测序获得鸭脖不同贮藏时间的原始序列信息,经过筛选得到15个样本共647800条有效序列,样品有效序列数在不同贮藏时间均超过30000,平均长度范围在401~420 bp。
稀释曲线常用来反映测序数据是否科学,横坐标为随机从样本中抽取的序列数,纵坐标为对应的OTU数,曲线走势能够反映物种丰度。香农曲线能够反映测序深度对微生物多样性影响,当曲线走势趋向平缓时,说明该结果能够反映绝大多数的微生物多样性。如图5a所示,当测序量超过10000时,稀释曲线上升缓慢,达到3万时,曲线已经趋于平缓,且香农曲线(图5b)也已经达到饱和状态,表明抽样足够,数据科学,可以反映细菌多样性。
2.7.2 OTU聚类分析
酱卤鸭脖不同贮藏时间OTU聚类结果如表3所示。从表3可以看出,酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程中菌株序列OTU聚类结果总体呈现先上升后下降的趋势,贮藏7 d OTU聚类结果显示最大。
表 3 OTU聚类分析Table 3. Statistical analysis of OTU贮藏时间(d) 门 纲 目 科 属 种 1 19 63 152 247 421 582 4 24 67 147 177 400 560 7 31 76 175 282 490 698 10 24 56 137 221 378 535 13 28 68 167 248 410 568 2.7.3 α多样性分析
α多样性分析主要通过Chao1指数、Shannon指数和Simpson指数等来评估样本中菌群的丰富度和多样性[19],Chao1指数反映菌群丰度;Shannon和Simpson指数则反映菌群多样性,Shannon指数越大,说明菌群多样性越高,而Simpson指数越小,说明菌群多样性越高。样本测序的覆盖率越高,表明测序结果就越准确[20]。
由表4可知,样品覆盖率均大于0.99,表明测序结果可靠,可以用于后续微生物多样性分析。Chao1指数整体上呈现先上升后下降的趋势,表明酱卤鸭脖在贮藏期间菌群丰度先增加后减小,在贮藏7 d时Chao1指数最高,菌群丰度最高。Shannon指数在贮藏期间逐渐降低,而Simpson指数逐渐升高,说明酱卤鸭脖菌群多样性逐渐降低。菌群结果与菌落总数结果不一致,这可能是由于菌落总数是基于纯培养,难以同时培养出所有微生物[21]。
表 4 酱卤鸭脖样品微生物多样性指数Table 4. Microbial diversity indexes of sauced duck neck样品 Chao1指数 Shannon指数 Simpson指数 覆盖率 S1 381.05±150.54a 3.19±1.05a 0.24±0.20a 0.9990 S4 334.12±101.27a 2.00±0.49ab 0.38±0.08a 0.9985 S7 468.46±110.45a 1.71±0.19b 0.50±0.05a 0.9978 S10 315.81±89.85a 1.52±0.53b 0.54±0.10a 0.9985 S13 323.98±205.86a 1.33±1.02b 0.58±0.32a 0.9986 2.7.4 酱卤鸭脖OTU数目维恩图分析
对不同时期的样品中所含有的OTU数目绘制维恩图,可以对不同时期样品菌群进行分析。由图6可知,5个贮藏时期共有的OTU为211种,贮藏1、4、7、10、13 d分别有194、142、267、98、170种特有的OTU,表明贮藏7 d酱卤鸭脖特有的微生物种类更丰富。
2.7.5 酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间菌群门水平的变化
由图7可知,在门水平上,酱卤鸭脖菌群有放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)。1~10 d放线菌门逐渐增加,为优势菌门,13 d时厚壁菌门显著增加,与放线菌门共同构成优势菌门,放线菌门和厚壁菌门大都属于革兰氏阳性菌。其他研究也表明放线菌门和厚壁菌门是肉和肉制品中的优势菌门,例如莫然[22]研究发酵牦牛肉灌肠贮藏期间微生物变化情况,结果表明厚壁菌门为相对丰度最高的菌门。Song等[23]发现四川熏培根在4 ℃和25 ℃贮藏期间优势菌门均为厚壁菌门和变形菌门。
2.7.6 酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间菌群属水平的变化
为进一步研究酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程中微生物多样性差异,在属水平上选择相对丰度排名前20的细菌进行菌群结构分析。如图8所示,贮藏1 d时,酱卤鸭脖优势菌为:红球菌属(Rhodococcus)、不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、尿素芽孢杆菌属(Ureibacillus)、共生短杆菌属(Symbiobacterium)。第4 d优势菌发生了变化,除了红球菌属、不动杆菌属外,出现了产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes),和红球菌属、不动杆菌属构成优势微生物。第7 d红球菌属和不动杆菌属继续增加,两者相对丰度总占比达84.74%。第10 d红球菌属相对丰度占比达到最高,为72.22%,与不动杆菌属和产碱杆菌属成为主要微生物。至13 d时,出现了明串珠菌属(Leuconostoc)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus),与红球菌属和不动杆菌属成为主要菌属,其中红球菌属和明串珠菌属相对丰度总占比达73.11%,为优势菌属。
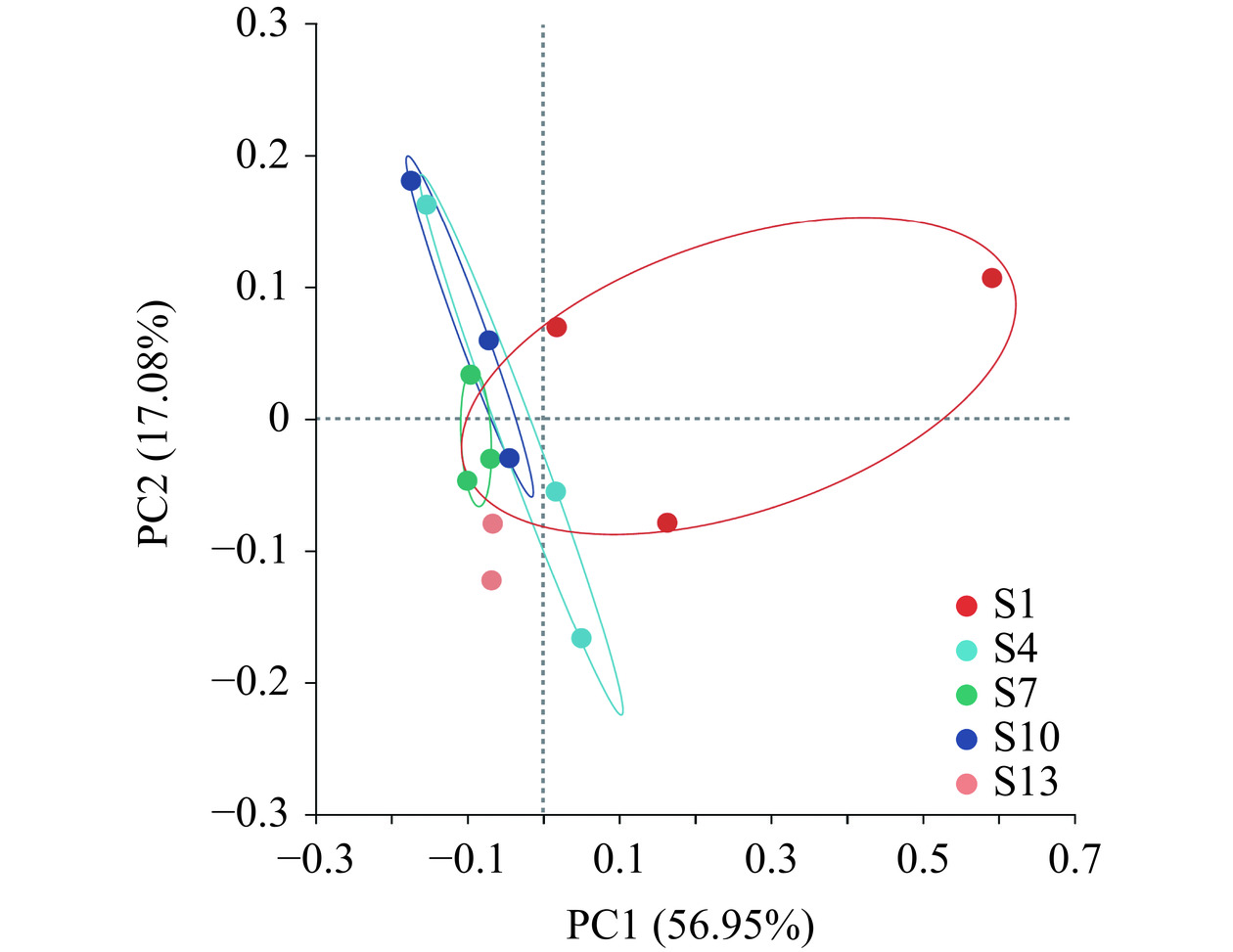
2.7.7 酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间菌群的主坐标分析(principal co-ordinates analysis,PCoA)
PCoA分析可用来研究样本菌群组成的相似性或差异性,距离越近,表明样本菌群组成相似度越高。如图9所示,横轴为第1主成分(PC1,56.95%),纵轴为第2主成分(PC2,17.08%),PC1和PC2叠加解释为74.03%。整体来看,1 d与4、7、10、13 d样品距离较远,表明贮藏4 d菌群结构开始出现差异;其中4、7、10、13 d样品互相聚集在一起,表明菌群组成差异较小。
2.8 酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程优势菌属与理化指标相关性分析
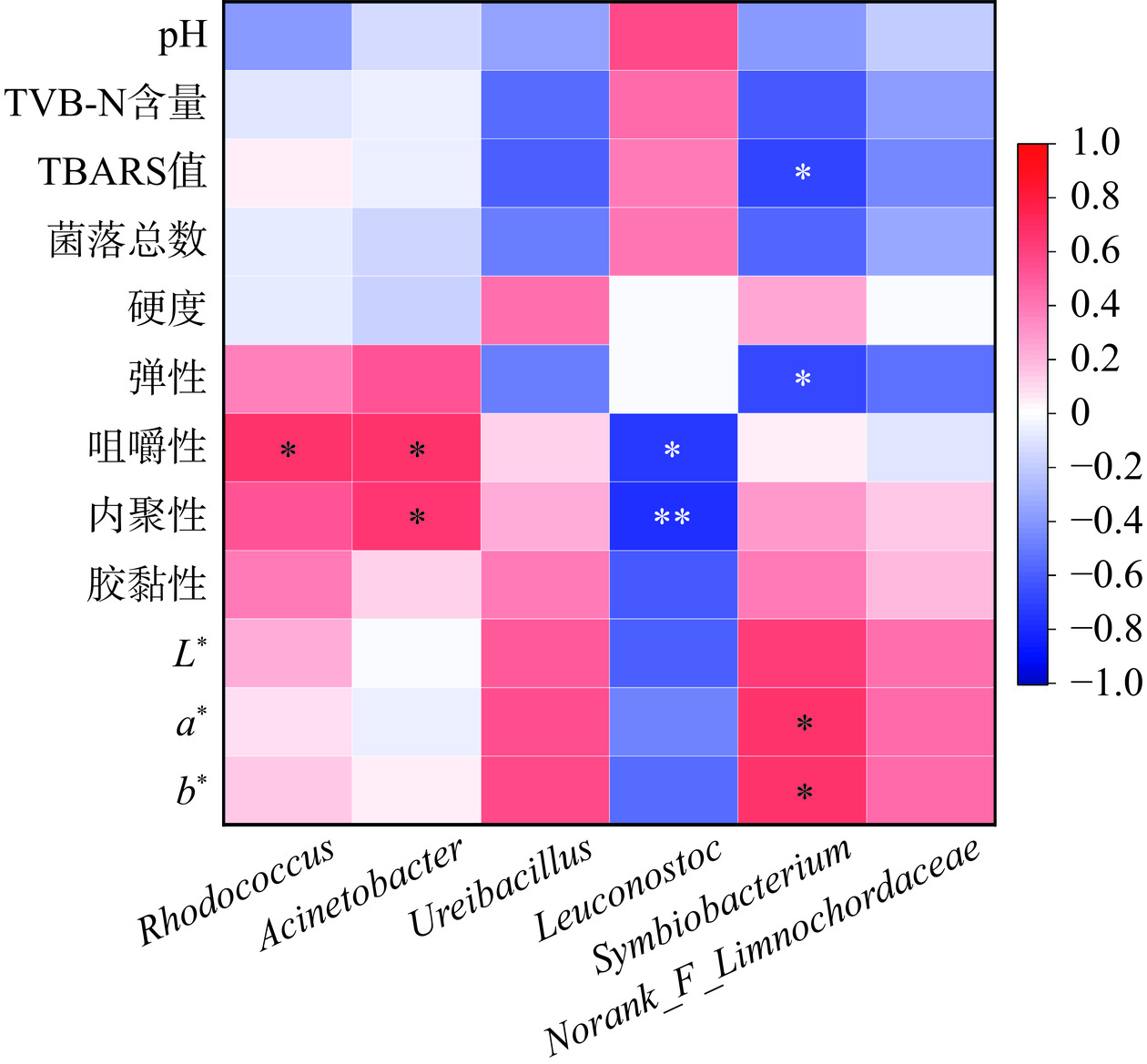
对酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程中的优势菌属与理化因子进行Pearson相关性分析。由图10可知,明串珠菌属与鸭脖腐败指标pH、菌落总数、TVB-N含量和TBARS值呈正相关,而芽孢杆菌属和共生短杆菌属与其呈负相关,其中共生短杆菌属与TBARS值呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。红球菌属与咀嚼性呈显著正相关。不动杆菌属与内聚性和咀嚼性呈显著正相关。明串珠菌属与咀嚼性呈显著负相关(P<0.05),与内聚性呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。共生短杆菌属与a*、b*均呈显著正相关,与弹性呈显著负相关。基于相关性的结果,表明明串珠菌属是酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程的主要腐败菌。
3. 讨论
本研究测定了酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间pH、TVB-N含量和TBARS值的变化。结果表明,各项理化指标均在贮藏7 d后变化速率开始加快,这与微生物数量在贮藏7 d后显著增加趋势一致。酱卤鸭脖在贮藏初始阶段中,由于鸭脖组织的糖原和ATP分解生成乳酸、磷酸和丙酮酸等酸性物质,以及二氧化碳的溶解[13],造成pH略有下降,随着贮藏时间的延长,由于鸭脖中大量微生物和内源酶分解蛋白质产生氨及胺类等碱性物质促使pH和TVB-N含量快速上升[24]。本研究中发现酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间存在产碱杆菌属,这类菌代谢产碱[25],也导致鸭脖的pH上升。此外,酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间TBARS值虽然逐渐上升,但含量都较低(0.26~0.32 mg/kg),表明脂质氧化不是酱卤鸭脖腐败的主要原因,这可能是由于低温冷藏并且采用气调包装,隔绝外界氧气,延缓了脂肪氧化[26]。陈雪等[27]和Guo等[28]也发现气调包装能够延缓肉制品脂肪氧化速率,与本研究结论类似。
酱卤鸭脖腐败与微生物数量和组成密切相关[29]。本研究分析了气调包装的酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间微生物菌群变化及组成。结果表明,鸭脖中微生物α多样性在贮藏1 d最高,之后逐渐降低,与Zotta等[30]研究结果类似,是优势菌生长所致。本研究中,酱卤鸭脖腐败时优势菌为放线菌门、变形菌门和厚壁菌门。在属水平上,红球菌属和不动杆菌属在整个贮藏期间相对丰度较高,而明串珠菌属和和乳杆菌属在贮藏13 d相对丰度较高,这些菌是肉及肉制品中常见腐败菌[31-33]。而殷雪[34]研究发现真空包装卤鸭脖在4 ℃贮藏期间优势腐败菌为乳酸菌、假单胞菌和耐热菌,可能是不同包装方式具有不同气体成分,从而影响微生物菌群变化及组成。
明确理化因子与微生物菌群相关性对于防腐保鲜具有重要意义。本研究发现,明串珠菌属与腐败相关理化因子pH、菌落总数、TVB-N含量和TBARS值呈正相关。明串珠菌属于兼性厌氧菌,肉制品厌氧包装条件有利于其生长繁殖[35]。Comi等[36]发现肠膜明串珠菌(L. mesenteroides)是培根贮藏过程中的主要腐败菌,引起培根菌落总数显著增加,pH有所下降,且分解培根中的糖类,降解含氮化合物产生酸类、醇类和酮类等挥发性物质,最终造成培根表面变粘、发绿。Jääskeläinen等[37]报道冷明串珠菌(L. gelidum)和伴气明串珠菌(L. gasicomitatum)是造成高氧包装牛肉异味的优势腐败菌,使得二乙酰、乙偶姻、壬醛、1-辛烯-3-醇和己酸含量的显著增加,且在接种了伴气明串珠菌的高氧包装猪肉中检测到乙偶姻、双乙酰、2,3-丁二醇、己醛、庚醛、乙酸的快速产生,这些物质赋予猪肉异味[38]。综上,本研究推测明串珠菌属是气调包装酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间的主要腐败微生物,但具体腐败菌株需进一步分析验证。
4. 结论
酱卤鸭脖贮藏13 d过程中,pH、色泽、质构、微生物数量、TVB-N含量和TBARS值均发生不同程度的变化,其品质逐渐发生劣变。鸭脖在贮藏10 d后的菌落总数和TVB-N超标。贮藏期间优势菌属为红球菌属、不动杆菌属、产碱杆菌属、明串珠菌属和乳杆菌属,其中明串珠菌属与腐败指标呈正相关,是酱卤鸭脖贮藏过程的主要腐败菌。本研究结果可以对酱卤鸭脖贮藏期间品质和微生物菌群变化有较为全面的了解,后期可以将优势菌属回接到酱卤鸭脖当中,确定具体的腐败菌株以及腐败菌株对酱卤鸭脖致腐作用,有助于开发靶向抑菌物质,从而延长酱卤鸭脖货架期。
-
表 1 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖色泽的变化
Table 1 Changes in color of sauced duck neck during storage
表 2 不同贮藏时间酱卤鸭脖质构特性的变化
Table 2 Changes in texture of sauced duck neck during storage
贮藏时间(d) 硬度(g) 弹性(g) 咀嚼性 内聚性 胶粘性 1 745.86±106.65a 0.74±0.03b 301.99±53.28ab 0.55±0.04ab 408.51±25.59a 4 733.31±76.53ab 0.89±0.07a 386.07±69.46a 0.60±0.11a 432.29±8.31a 7 704.85±39.58ab 0.88±0.09a 314.79±99.09a 0.51±0.14ab 352.97±24.56a 10 630.76±19.12b 0.87±0.02a 306.24±29.32a 0.47±0.06ab 349.17±28.04a 13 623.03±68.95b 0.85±0.06a 186.20±61.37b 0.36±0.14b 218.41±15.10b 表 3 OTU聚类分析
Table 3 Statistical analysis of OTU
贮藏时间(d) 门 纲 目 科 属 种 1 19 63 152 247 421 582 4 24 67 147 177 400 560 7 31 76 175 282 490 698 10 24 56 137 221 378 535 13 28 68 167 248 410 568 表 4 酱卤鸭脖样品微生物多样性指数
Table 4 Microbial diversity indexes of sauced duck neck
样品 Chao1指数 Shannon指数 Simpson指数 覆盖率 S1 381.05±150.54a 3.19±1.05a 0.24±0.20a 0.9990 S4 334.12±101.27a 2.00±0.49ab 0.38±0.08a 0.9985 S7 468.46±110.45a 1.71±0.19b 0.50±0.05a 0.9978 S10 315.81±89.85a 1.52±0.53b 0.54±0.10a 0.9985 S13 323.98±205.86a 1.33±1.02b 0.58±0.32a 0.9986 -
[1] SHAO L T, CHEN S S, WANG H D, et al. Advances in understanding the predominance, phenotypes, and mechanisms of bacteria related to meat spoilage[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,118:822−832.
[2] 李德红, 祝传海, 岳晓霞, 等. 气调包装酱卤鸭食管冷藏期间理化指标变化及优势腐败菌的分离鉴定[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(9):59−63. [LI D H, ZHU C H, YUE X X, et al. Sauced duck esophagus:Changes in physicochemical indexes during cold storage in modified atmosphere packaging and isolation and identification of dominant spoilage bacteria[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(9):59−63.] LI D H, ZHU C H, YUE X X, et al. Sauced duck esophagus: Changes in physicochemical indexes during cold storage in modified atmosphere packaging and isolation and identification of dominant spoilage bacteria[J]. Meat Research, 2019, 33(9): 59−63.
[3] SONG L, WU X, XIE J, et al. Kaempferia galanga Linn. Extract-A potential antibacterial agent for preservation of poultry products[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,147(3):111553.
[4] GRAM L, RAVN L, RASCH M, et al. Food spoilage-Interactions between food spoilage bacteria[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2002,78(1):79−97.
[5] XING S, LIU K, GONG H, et al. Predictive model for growth of Pseudomonas spp. on fresh duck breast as a function of temperature[J]. Poultry Science,2023,102(9):102868. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102868
[6] 刘竹臻. 中国传统酱卤制品初始菌相分析及酱牛肉货架期预测模型的研究[D]. 上海:上海应用技术大学, 2016. [LIU Z Z. Study on initial bacteria composition of Chinese traditional sauced meat and predictive model of shelf life for sauced beef[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Institute of Technology, 2016.] LIU Z Z. Study on initial bacteria composition of Chinese traditional sauced meat and predictive model of shelf life for sauced beef[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technology, 2016.
[7] 叶可萍, 刘佳, 刘梅, 等. 气调包装酱卤鸭翅贮藏过程中菌群结构分析[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(14):201−205. [YE K P, LIU J, LIU M, et al. Analysis of microbial communities of pot-stewed duck wings packaged in modified atmosphere during storage[J]. Food Science,2015,36(14):201−205.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201514039 YE K P, LIU J, LIU M, et al. Analysis of microbial communities of pot-stewed duck wings packaged in modified atmosphere during storage[J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(14): 201−205. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201514039
[8] 李雪, 王丽, 刘光宪, 等. 气调包装对酱卤鸭翅品质和保鲜效果的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(23):9171−9176. [LI X, WANG L, LIU G X, et al. Effects of modified atmosphere packaging on quality and preservation of sauced duck wings[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(23):9171−9176.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.23.spaqzljcjs202123027 LI X, WANG L, LIU G X, et al. Effects of modified atmosphere packaging on quality and preservation of sauced duck wings[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2021, 12(23): 9171−9176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.23.spaqzljcjs202123027
[9] SCHLOSS P D, WESTCOTT S L, RYABIN T, et al. Introducing mothur:open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2009,75(23):7537−7541. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09
[10] BASSEY A P, CHEN Y F, ZHU Z, et al. Assessment of quality characteristics and bacterial community of modified atmosphere packaged chilled pork loins using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing analysis[J]. Food Research International,2021,145:110412. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110412
[11] 柴子惠, 李洪军, 李少博, 等. 低盐腊肉贮藏期间菌相和理化性质的变化[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(11):201−206. [CHAI Z H, LI H J, LI S B, et al. Microbial, physical and chemical changes of low-salt Chinese bacon during storage[J]. Food Science,2019,40(11):201−206.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180615-309 CHAI Z H, LI H J, LI S B, et al. Microbial, physical and chemical changes of low-salt Chinese bacon during storage[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(11): 201−206. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180615-309
[12] 林柔汐. 卤鸭制品卤制过程香辛料主要成分迁移规律及品质保持研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2022. [LIN R X. Study on the migration law of main components and qualitymaintenance of spices in marinated duck products[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2022.] LIN R X. Study on the migration law of main components and qualitymaintenance of spices in marinated duck products[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
[13] MANCINI R A, HUNT M C. Current research in meat color[J]. Meat Science,2005,71(1):100−121. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.03.003
[14] 陈鹏. 冷鲜黄羽肉鸡储运过程中品质的变化及货架期预测模型的建立[D]. 南昌:江西农业大学, 2017. [CHEN P. Quality change of yellow broiler meat under chilled storage and establishment of predictive model for the shelf life[D]. Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017.] CHEN P. Quality change of yellow broiler meat under chilled storage and establishment of predictive model for the shelf life[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017.
[15] 段昌圣. 酱卤鸭脖的贮藏特性及其保水性研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2012. [DUAN C S. Study on storage characteristics and the water capacity of pot stewed duck neck[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012.] DUAN C S. Study on storage characteristics and the water capacity of pot stewed duck neck[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012.
[16] 王雨祺, 许必锋, 蔡克周, 等. 低钠配方对酱牦牛肉食用品质及氧化特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2024, 45(14):62-70. [WANG Y Q, XU B F, CAI K Z, et al. Effects of low sodium formula on edible quality and oxidation characteristics of sauced yak meat [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024, 45(14):62-70.] WANG Y Q, XU B F, CAI K Z, et al. Effects of low sodium formula on edible quality and oxidation characteristics of sauced yak meat [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(14): 62-70.
[17] ELISABETH H, STEVEN M L. Mechanisms of water-holding capacity of meat:The role of postmortem biochemical and structural changes[J]. Meat Science,2005,71(1):194−204. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.04.022
[18] SUN R, XU W, XIONG L, et al. The combined effects of ultrasound and plasma-activated water on microbial inactivation and quality attributes of crayfish during refrigerated storage[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2023,98:106517. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106517
[19] LI B, ZHANG X, GUO F, et al. Characterization of tetracycline resistant bacterial community in saline activated sludge using batch stress incubation with high-throughput sequencing analysis[J]. Water Research,2013,47(13):4207−4216. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.021
[20] 李侠, 温佳奇, 王秀娟, 等. 基于宏基因组学技术不同地区蛋源表面微生物的比较[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(10):139−145. [LI X, WEN J Q, WANG X J, et al. Metagenomic comparison of microbial communities on eggs from different areas of China[J]. Food Science,2021,42(10):139−145.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200402-026 LI X, WEN J Q, WANG X J, et al. Metagenomic comparison of microbial communities on eggs from different areas of China[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(10): 139−145. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200402-026
[21] 曾鹭, 刘淑集, 陈晓婷, 等. 基于Illumina MiSeq 测序技术探究冷藏菊黄东方鲀菌群演替规律[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(18):149−156. [ZENG L, LIU S J, CHEN X T, et al. Using Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing to explore the succession of microbial community in Takifugu flavidus during cold storage[J]. Food Science,2023,44(18):149−156.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221108-082 ZENG L, LIU S J, CHEN X T, et al. Using Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing to explore the succession of microbial community in Takifugu flavidus during cold storage[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(18): 149−156. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221108-082
[22] 莫然. 钠盐含量对牦牛肉灌肠加工及贮藏过程中品质变化和贮藏特性影响的研究[D]. 成都:西南民族大学, 2022. [MO R. Study on the effect of sodium content on the quality changes and storage characteristics of yak meat sausages during processing and storage[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Minzu University, 2022.] MO R. Study on the effect of sodium content on the quality changes and storage characteristics of yak meat sausages during processing and storage[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Minzu University, 2022.
[23] SONG Z, CAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of storage methods on the microbial community and quality of Sichuan smoked bacon[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,158:113−115.
[24] 杨汝晴, 陈玉磊, 孙乐常, 等. 鲈鱼在4 ℃冷藏过程中的肌肉品质变化[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(1):239−245. [YANG R Q, CHEN Y L, SUN L C, et al. Quality change of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) muscle during cold storage at 4 ℃[J]. Food Science,2023,44(1):239−245.] YANG R Q, CHEN Y L, SUN L C, et al. Quality change of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) muscle during cold storage at 4 ℃[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(1): 239−245.
[25] 万力婷, 吴祖芳, 张天龙, 等. 苋菜梗腌制过程细菌群落变化及风味的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,35(2):166−170. [WAN L T, WU Z F, ZHANG T L, et al. Study on bacterial community changes and its flavor components of pickled amaranth stem[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,35(2):166−170.] WAN L T, WU Z F, ZHANG T L, et al. Study on bacterial community changes and its flavor components of pickled amaranth stem[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 35(2): 166−170.
[26] 赵嘉越, 罗欣, 杨啸吟, 等. 气调包装对烤鸭腿货架期及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(19):272−280. [ZHAO J Y, LUO X, YANG X Y, et al. Effect of modified atmosphere packaging on shelf life andmicrobial diversity of roast duck legs[J]. Food Science,2019,40(19):272−280.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181015-126 ZHAO J Y, LUO X, YANG X Y, et al. Effect of modified atmosphere packaging on shelf life andmicrobial diversity of roast duck legs[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(19): 272−280. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181015-126
[27] 陈雪, 赵嘉越, 董鹏程, 等. 生物保鲜剂结合气调包装对烤鸭货架期及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(10):177−187. [CHEN X, ZHAO J Y, DONG P C, et al. Effects of biological preservative combined with modified atmosphere packaging on shelf-life and microbial diversity of roast duck[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(10):177−187.] CHEN X, ZHAO J Y, DONG P C, et al. Effects of biological preservative combined with modified atmosphere packaging on shelf-life and microbial diversity of roast duck[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(10): 177−187.
[28] GUO Y, HUANG J, SUN X, et al. Effect of normal and modified atmosphere packaging on shelf life of roast chicken meat[J]. Journal of Food Safety,2018,38(5):e12493. doi: 10.1111/jfs.12493
[29] MAO T T, XIA C L, ZENG T, et al. The joint effects of ultrasound and modified atmosphere packaging on the storage of sauced ducks[J]. Food Science and Technology,2023,177:114561.
[30] ZOTTA T, PARENTE E, IANNIELLO R G, et al. Dynamics of bacterial communities and interaction networks in thawed fish fillets during chilled storage in air[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2019,293:102−113. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.01.008
[31] 邱楚雯, 施永海, 王韩信, 等. 复合生物保鲜剂对冰鲜菊黄东方鲀微生物多样性变化的影响[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2023,50(2):267−274. [QIU W C, SHI Y H, WANG H X, et al. Effects of compound biological preservative on microbial community diversity of Takifugu flavidus during chilled storage[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2023,50(2):267−274.] QIU W C, SHI Y H, WANG H X, et al. Effects of compound biological preservative on microbial community diversity of Takifugu flavidus during chilled storage[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2023, 50(2): 267−274.
[32] 张莉, 马云昊, 王颖, 等. 冷藏过程中气调包装烧鸡的理化特性及腐败菌分析[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(15):188−195. [ZHANG L, MA Y H, WANG Y, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and spoilage bacteria of modified atmosphere packaged braised chicken during refrigeration[J]. Food Science,2023,44(15):188−195.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220914-122 ZHANG L, MA Y H, WANG Y, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and spoilage bacteria of modified atmosphere packaged braised chicken during refrigeration[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(15): 188−195. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220914-122
[33] 汤敏, 黄俊逸, 李聪, 等. 冷藏过程中不同包装德州扒鸡的微生物及理化特性[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(6):122−129. [TANG M, HUANG J Y, LI C, et al. Study on microbial and physicochemical characteristics of dezhou braised chicken by different packaging methed during chilled storage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(6):122−129.] TANG M, HUANG J Y, LI C, et al. Study on microbial and physicochemical characteristics of dezhou braised chicken by different packaging methed during chilled storage[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(6): 122−129.
[34] 殷雪. 低温禽肉制品(卤鸭脖)综合保鲜技术研究[D]. 武汉:武汉轻工大学, 2008. [YIN X. Study on synthetical preservation technology in pasteurized poultry product (spiced duck neck)[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2008.] YIN X. Study on synthetical preservation technology in pasteurized poultry product (spiced duck neck)[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2008.
[35] YANG X Y, ZHU L X, ZHANG Y M, et al. Microbial community dynamics analysis by high-throughput sequencing in chilled beef longissimus steaks packaged under modified atmospheres[J]. Meat Science,2018,141:94−102. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.03.010
[36] COMI G, ANDYANTO D, MANZANO M, et al. Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus sakei as bio-protective culture to eliminate Leuconostoc mesenteroides spoilage and improve the shelf life and sensorial characteristics of commercial cooked bacon[J]. Food Microbiology,2016,58:16−22. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2016.03.001
[37] JAASKELAINEN E, HULTMAN J, PARSHINTSEV J, et al. Development of spoilage bacterial community and volatile compounds in chilled beef under vacuum or high oxygen atmosphere[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2016,223:25−32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.01.022
[38] JAASKELAINEN E, JOHANSSON P, KOSTIAINEN O, et al. Significance of heme-based respiration in meat spoilage caused by Leuconostoc gasicomitatum[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2013,79(4):1078−1085. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02943-12
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 刘世昌,赵妍,刘旭光,龚志刚,吕好新. 不同温度对偏高水分玉米储藏品质变化规律的影响. 食品研究与开发. 2024(06): 40-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵品,范磊,燕照玲,韩启忠,苏磊,李建林. 有机鲜食玉米规范化种植及发展思考. 种业导刊. 2024(02): 3-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵琳,陈玉,骆乐谈,石江,王道泽. 不同保鲜方式下鲜食玉米品质变化规律的研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(08): 22-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李妍婷,张荣,姚研强,唐朝臣,韩金玲,王章英. 六个不同品种鲜食甘薯贮藏品质变化. 广东农业科学. 2024(08): 80-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邵子晗,张玮,宋玉,洪莹,陶澍,刘超,郄雪娇,龚勋,阮龙,曹磊. 鲜食糯玉米及其亲本贮藏过程中淀粉回生特性的研究. 玉米科学. 2024(08): 47-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 马正龙,石占军,郑高山,范兴忠,张正洁,杨文霞. 鲜食糯玉米新品种酒糯5006的选育及栽培和制种技术. 农业科技通讯. 2024(12): 141-143+146 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



