Effect of Zinc Sulphate Treatments on Key Active Components and the Molecular Mechanism of Thioglycoside Changes of Broccoli Sprouts
-
摘要: 为探究喷施不同浓度硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗活性成分积累和抗氧化活性的影响,并从分子水平探讨硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗中硫苷的调控机制,本文以7 d西兰花芽苗为试验材料,采用不同浓度(0、1、2、4、8 mmol/L)硫酸锌(Zinc sulphate,ZnSO4)处理西兰花芽苗,测定西兰花芽苗叶绿素、抗坏血酸、总黄酮、总酚、硫苷含量、黑芥子酶活以及DPPH自由基清除能力,研究不同浓度ZnSO4处理组对西兰花芽苗活性成分的影响,并且利用荧光定量PCR技术分析硫苷合成关键基因表达量的变化。结果表明,各处理组叶绿素含量均低于对照;抗坏血酸含量随硫酸锌浓度的增大呈上升趋势,各处理组均高于对照组。总酚含量在ZnSO4浓度为8 mmol/L时含量最高且显著高于对照组(P<0.05);总黄酮、总硫苷和RAA含量、黑芥子酶活性及DPPH自由基清除率在ZnSO4浓度为2 mmol/L时达最大值。在ZnSO4浓度为2 mmol/L时CYP83A1、CYP79F1与FMO-GSOX2基因表达量显著提高(P<0.05);FMO-GSOX2与总硫苷、RAA、脂肪族硫苷、黑芥子酶呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);CYP79F1、CYP83A1与总硫苷、RAA、脂肪族硫苷呈显著性正相关(P<0.05)。说明FMO-GSOX2、CYP79F1和CYP83A1表达量的上调促进了总硫苷、脂肪族硫苷和RAA的合成。本研究结果表明,外源喷施适量硫酸锌能促进硫苷合成相关基因的表达,其中2 mmol/L ZnSO4可有效增加西兰花芽苗中活性物质含量及抗氧化活性。Abstract: To investigated the effects of spray application of zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) solution on the accumulation of crucial bioactive components and antioxidant activity, and explored the regulatory mechanism of zinc sulfate on glucosinolates in broccoli flower buds and seedlings at the molecular level, seven-day-old broccoli sprouts were treated with one of four concentrations (1, 2, 4, and 8 mmol/L) of aqueous ZnSO4 solutions or water (0 mmol/L ZnSO4 as the control). The effects of each ZnSO4 treatment on the bioactive components of broccoli sprouts were investigated by determining the contents of chlorophyll, ascorbic acid, total flavonoids, total phenols, and total glucosinolates, as well as myrosinase activity and DPPH free-radical scavenging rate. The expression levels of glucosinolate synthesis structural genes in the sprouts were analyzed using a real-time quantitative PCR detection system. The results showed that the chlorophyll content of all ZnSO4 treatments was lower than that of the control. The ascorbic acid content tended to be elevated with an increase in ZnSO4 concentration and was higher than that of the control for all ZnSO4 treatments. The total polyphenol content was the highest in response to 8 mmol/L ZnSO4 treatment and was significantly (P<0.05) higher than that of the control. The contents of total flavonoid content, total glucosinolates, glucoraphanin, myrosinase activity and maximum DPPH free-radical scavenging rate were greatest after treatment with 2 mmol/L ZnSO4 solution. The expression levels of CYP83A1, CYP79F1, and FMO-GSOX2 were significantly (P<0.05) increased in response to 2 mmol/L ZnSO4 treatment. Thus, spray application of exogenous ZnSO4 promoted the expression of crucial genes involved in thioredoxin synthesis. FMO-GSOX2 showed highly significant (P<0.01) positive correlation with total glucosinolates, RAA, aliphatic glucosinolates, and myrosinase activity. CYP79F1 and CYP83A1 showed significant (P<0.05) positive correlation with total glucosinolates, RAA, and aliphatic glucosinolates. It indicated that the up-regulation of FMO-GSOX2, CYP79F1 and CYP83A1 expression promoted the synthesis of total glucosinolates, aliphatic glucosinolates and RAA. In conclusion, the results of this study showed that spray application of an appropriate concentration of exogenous ZnSO4 promoted up-regulation of the expression of critical glucosinolate synthesis-related genes, and that 2 mmol/L ZnSO4 solution effectively increased the contents of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in broccoli sprouts.
-
Keywords:
- broccoli sprouts /
- zinc sulphate /
- glucosinolate /
- active ingredient /
- antioxidant activity
-
西兰花(Brassica oleracea var. italica)是一种营养丰富的重要经济作物[1],因其具有较高含量的硫代葡萄糖苷(Glucosinolates,GS,以下简称硫苷),成为众多研究者的研究对象。西兰花芽苗中硫苷含量是成熟植株的10~100倍[2],硫苷的水解产物异硫氰酸酯(Isothiocyanate,ITCs)在黑芥子酶作用下形成[3],可以预防多种癌症,如乳腺癌、结肠癌、皮肤癌等,还可以降低人们患心血管疾病的风险,对自闭症和骨质疏松症也有帮助[4−6]。此外西兰花芽苗中还含有其他生物活性物质,如抗坏血酸、叶绿素、矿质元素、多酚、黄酮等[7],其中抗坏血酸是一种重要的抗氧化剂,在优化人体健康和预防疾病方面发挥着多种功能[8],在植物体内也起到促进新陈代谢作用[9]。从健康角度来看,酚类化合物因其具有强抗氧化活性,在维护人类健康如血脂调节功能、血管保护等方面具有重要作用[10−11]。叶绿素对人体健康也有益处,具有抗氧化和抗炎特性,可预防癌症等慢性疾病[12−13]。
添加适宜外源物质可以提高植物中活性成分含量。苗慧莹[14]研究发现葡萄糖协同JA促进芥蓝芽苗吲哚类硫代葡萄糖苷的积累。何锐等[15]向水培芥蓝中添加稀释1400倍的海藻肥,显著提高了芥蓝中总硫苷含量。AGHAJANZADEH等[16]研究发现,大白菜在10 μmol/L氯化锌处理下产量显著降低,但硫苷积累量提高。PEREZ等[17]对不同时期西兰花芽苗施用0、15、30、60 mg/L硫酸钾溶液,在芽苗9~12 d时,各浓度处理下的脂肪族硫苷含量以及总硫苷含量均高于清水处理。植物主要以硫酸盐的形式吸收硫[18],施用硫酸盐可以减少植物在生长过程中因为缺硫导致的硫苷分解,并具有提高硫苷含量的作用[19−20]。硫酸锌是一种含有植物生长发育所需的常量和微量元素的硫酸盐,锌对作物氮代谢和碳代谢具有重要作用,是多种酶的组成成分,能够促进作物体内的叶绿素、蛋白质、核糖核酸的形成,硫作为一种必需的常量营养素,在植物的生长发育中起着至关重要的作用[21−22]。喷施硫酸锌是一种有效且经济的营养品质调控方法。然而,喷施硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗活性成分的影响,尤其对硫苷合成过程中基因表达量的影响鲜有报道。
本研究以西兰花芽苗为试验材料,研究喷施不同浓度硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗中活性成分积累和抗氧化活性的影响,以及从分子机制水平探讨喷施硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗中硫苷的调控机制,为硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗中关键活性成分积累的影响提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
西兰花种子 品种B6,从京研益农(北京)种业科技有限公司进行采购;硫酸锌 北京沃凯生物科技有限公司;乙醇 天津市光复科技发展有限公司;无水碳酸钠 北京化工厂;硝酸铝、亚硝酸钠 阿拉丁;福林酚 北京博奥拓达科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼 梯希爱化成工业发展有限公司;氢氧化钠 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;试验所用试剂均为分析纯。
UV-1900i双光束紫外分光光度计 岛津公司(日本);Acquity UPLC/Xevo TQ-S micro超高效液相色谱串联质谱联用 Waters(美国);Infinite M1000 PRO型多功能酶标仪 TECAN公司(瑞士)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 西兰花芽苗种植及采收
将西兰花种子(B6)用蒸馏水在20 ℃下浸泡4 h,播种于塑料托盘中,在25 ℃、75%相对湿度和全黑暗的环境下催芽2 d,然后于25 ℃见光培养5 d。在此期间,每天喷洒15 mL不同浓度的硫酸锌溶液2次;对照喷洒去离子水。试验设计5个处理,3次重复,处理分别为去离子水,ZnSO4 1 mmol/L,ZnSO4 2 mmol/L,ZnSO4 4 mmol/L和ZnSO4 8 mmol/L。在芽苗生长的第7 d,对新鲜芽苗进行取样,一部分样品置于液氮中,再储存于−80 ℃冰箱待测定相关指标使用。另一部分芽苗样品,进行冷冻干燥处理,研磨成粉,储存在-20 ℃冰箱待测定相关指标使用。
1.2.2 抗坏血酸含量测定
参照刘萌[23]的方法测定抗坏血酸含量。取30 g新鲜西兰花芽苗于榨汁机中,加入200 mL 2%草酸榨取1 min。取5 mL样品于10 mL离心管中,在10000 r/min下离心10 min,将上清液用0.45 μm的水相滤膜过滤,弃去初滤液,取续滤液供液相色谱分析用。
1.2.3 叶绿素含量测定
参照刘萌[23]的方法测定叶绿素含量;称取西兰花粉末0.2 g于15 mL离心管中,加入10 mL 80%丙酮,振荡均匀后超声30 min,在3000 r/min下离心20 min。取上清液1 mL于10 mL离心管中,加入2 mL 80%丙酮和4 mL蒸馏水,以80%丙酮为空白,然后在663 nm和645 nm下测定其叶绿素含量。
叶绿素浓度计算:
Ca(mg/L)=12.7×A663−2.69×A645 Cb(mg/L)=22.9×A645−4.68×A663 总叶绿素浓度(mg/L)=Ca+Cb 叶绿素含量计算:
叶绿素含量(mg/g)=C×D×Vm 其中,C表示计算所得叶绿素浓度(mg/L);D表示稀释倍数;V表示提取液体积(L);m表示样品重量(g)。
1.2.4 总酚和总黄酮含量测定
参照田璐[24]的方法,测定总酚含量;称取0.5 g西兰花芽苗新鲜样品于50 mL离心管中,然后加入20 mL 70%乙醇,振荡均匀后超声30 min。取10 mL超声完的溶液于10 mL离心管中,在12000 r/min下离心30 min。取0.6 mL上清液加入3 mL稀释5倍福林酚再加3 mL 7%碳酸钠避光1 h,然后在720 nm下测定其多酚含量(70%乙醇调零)。标准曲线方程为y=0.1322x+0.0032(R2=0.999)。
总酚含量(µg/g)=C×D×Vm 其中,C表示从标曲上查得的多酚质量(mg/mL);D表示稀释倍数;V表示20%乙醇的体积(mL);m表示样品重量(g)。
参考柏夏琼等[25]的方法,测定总黄酮含量;称取0.5 g西蓝花新鲜样品于50 mL离心管中,然后加入20 mL 70%乙醇,振荡均匀后超声30 min。取10 mL超声完成的溶液于10 mL离心管中,在12000 r/min下离心30 min。取1 mL上清液添加1.4 mL蒸馏水,再加入0.4 mL亚硝酸钠摇匀静置6 min,之后加入0.4 mL硝酸铝摇匀静置6 min,加4 mL氢氧化钠,最后加入2.8 mL蒸馏水静置15 min后在500 nm下测定其黄酮含量。标准曲线方程为y=8.15x+0.0135(R2=0.9989)。
总黄酮含量(µg/g)=C×D×Vm 其中,C表示从标曲上查得的黄酮质量(μg/mL);D表示稀释倍数;V表示20%乙醇的体积(mL);m表示样品重量(g)。
1.2.5 硫苷含量测定
参照刘倩男等[26]方法,测定硫苷含量。称取液氮研磨成粉末状的样品0.5 g,放入15 mL离心管中。加入10 mL 70%甲醇,80 ℃下水浴处理20 min,然后超声处理30 min,3000 r/min离心30 min,上清液即为样品液。用一次性注射器吸1 mL样品液通过0.45 μm滤膜注入试管中。用移液枪吸取100 μL样品液与900 μL去离子水于小玻璃瓶中,涡旋1 min。之后进行液相色谱检测,记录峰面积。色谱条件如下:检测波长229 nm;流动相A:0.1%甲酸水;流动相B:甲醇;流速:0.2 mL/min;进样量:2 μL;柱温:30 ℃;采用苯甲基硫代葡萄糖苷作为内标,根据保留时间和峰面积对硫苷组分进行定量测定。利用相应因子和内标来计算硫苷含量,以mg/g 为单位。
1.2.6 黑芥子酶活性测定
参照WANG等[27]方法,测定黑芥子酶活性。称取0.5 g经液氮研磨后的西兰花样品,加入6 mL PBS溶液,在10000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心20 min,取0.5 mL上清液,加入0.5 mL 0.1 mg·mL−1烯丙基硫苷,在37 ℃下水浴15 min灭酶,选用葡萄糖试剂盒测定样品中葡萄糖的含量。以每分钟反应体系对被黑芥子酶转化生成1 nmol葡萄糖所需酶量为1个酶活力单位,酶活单位为nkat/g 。
1.2.7 DPPH自由基清除率测定
参照高诗薇等[3]方法,测定DPPH自由基清除率。称取干样0.5 g,加10 mL 50%甲醇于15 mL离心管中,在8000 r/min 10 min 4 ℃条件下离心。取1 mL样品溶液加入3 mL 0.1 mmol/L DPPH溶液,混合均匀后避光反应1 h,于517 nm下测定溶液的吸光度,无水乙醇作为参比。对照组(Acontrol)由1 mL甲醇与3 mL DPPH溶液组成;空白组(Ablank)由1 mL样品与3 mL甲醇组成;样品组(Asample)由1 mL样品与3 mL DPPH溶液组成。
清除率(%)=(1−Asample−AblankAcomtrol)×100 1.2.8 硫苷合成相关基因表达量检测
使用FsatPure® Plant Total RNA Isolation Kit RC411-C1试剂盒提取西兰花芽苗总RNA。使用Nanodrop 2000检测总RNA的纯度和浓度。使用HiScript® III All-in-one RT SuperMix Perfect for qPCR试剂盒将西兰花芽苗总RNA反转录成cDNA,所有操作均在冰上进行。使用Taq Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix试剂盒进行定量PCR分析,PCR程序为95 ℃ 30 sec,循环数40,95 ℃变性10 s和60 ℃退火/延伸30 s。所有基因表达分析以3个生物学重复,一个生物学重复对应3个技术重复进行。本研究内参基因和目的基因序列均在NCBI Primer-BLAST平台设计,引物由北京擎科生物科技股份有限公司合成,如表1所示。
表 1 基因特异性引物序列Table 1. Gene specific primer sequences基因 上游引物(5’-3’) 下游引物(5’-3’) Actin 3 CTGTTCCAATCTACGAGGGTTTC GCTCGGCTGTGGTGGTGAA AOP 3 TTGATGCGGAGTTGGGCTTA CTCGGTGATACGGTGAAGGG CYP83A1 TTCATATCCTACGGCAGGCG TTATCCGCGGCCTTGTTGAT CYP79F1 CCACCCTCGGGGGTTATTTC TCCCGACTTTAACACCCACG MAM1 AAATTCTGGCATTGCTCGTGG ATCACCAGATTCACCGCACG FMO-GSOX2 GACCGTGGTTACGGGAGACTTG GTAGCCATTGTATAACAAGCAACCC 1.3 数据处理
所有指标均采用3组样品重复测定,取平均值。使用SPSS 22.0软件和Microsoft Excel 2010进行数据处理和统计分析,用Duncan多重比较方法检验差异性显著(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
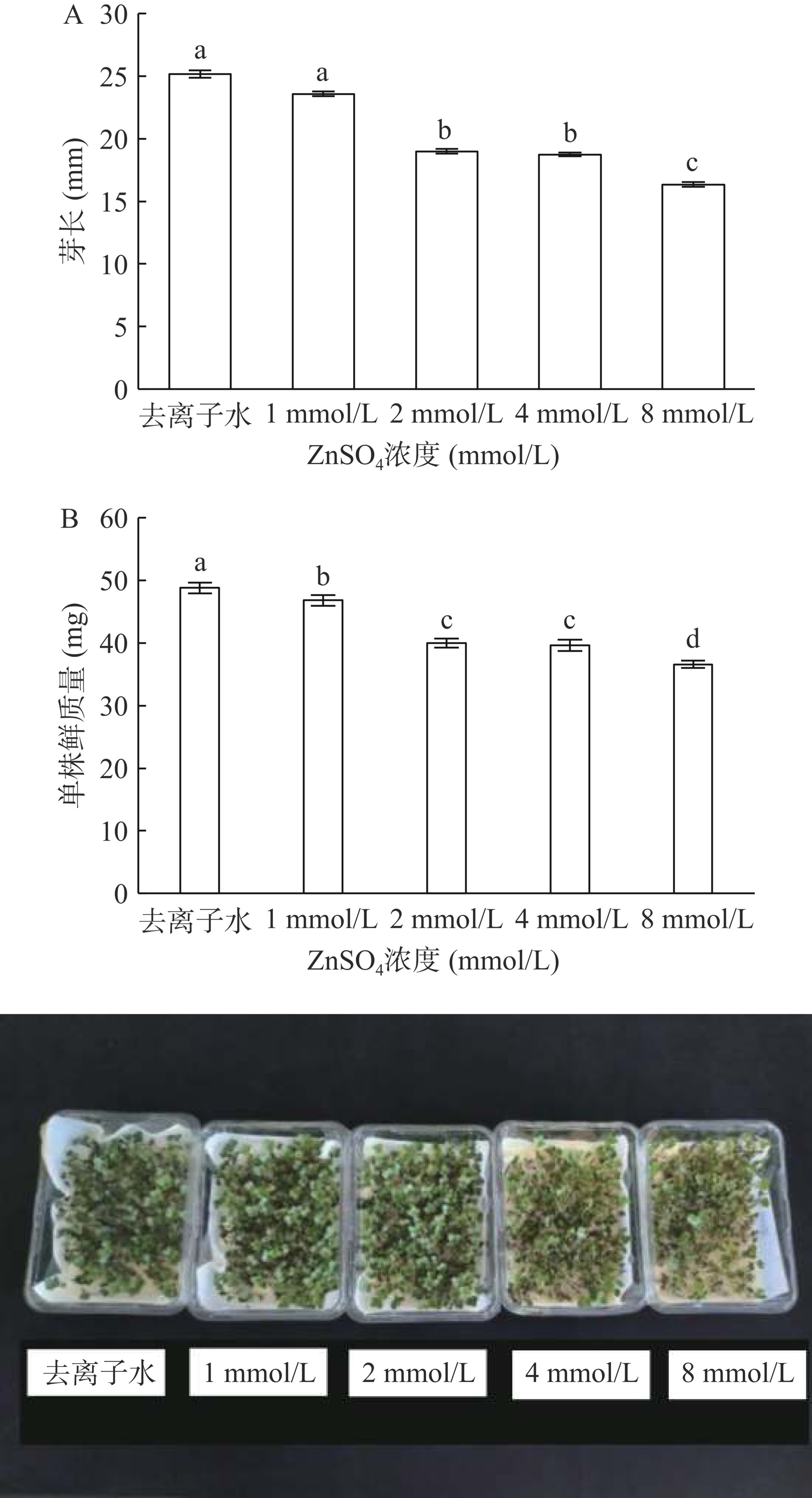
2.1 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗生长指标的影响
由图1A可知,喷施ZnSO4后各处理组芽长均低于对照组,ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组显著(P<0.05)低于其他处理,较对照组降低35.10%;ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理后芽苗的芽长与对照无显著性差异。由图1B可知,各处理组西兰花芽苗单株鲜质量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照组,其中1 mmol/L ZnSO4处理较对照组降低了4.00%,8 mmol/L ZnSO4处理后的西兰花芽苗单株鲜质量最小,较对照组降低了25.00%(P<0.05)。ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗生长造成了一定的胁迫作用,使其株高和产量都有一定程度的降低,ZnSO4浓度为1 mmol/L时,对西兰花芽苗生长影响较小。在实际生产中,选择合适的营养液处理浓度非常重要。
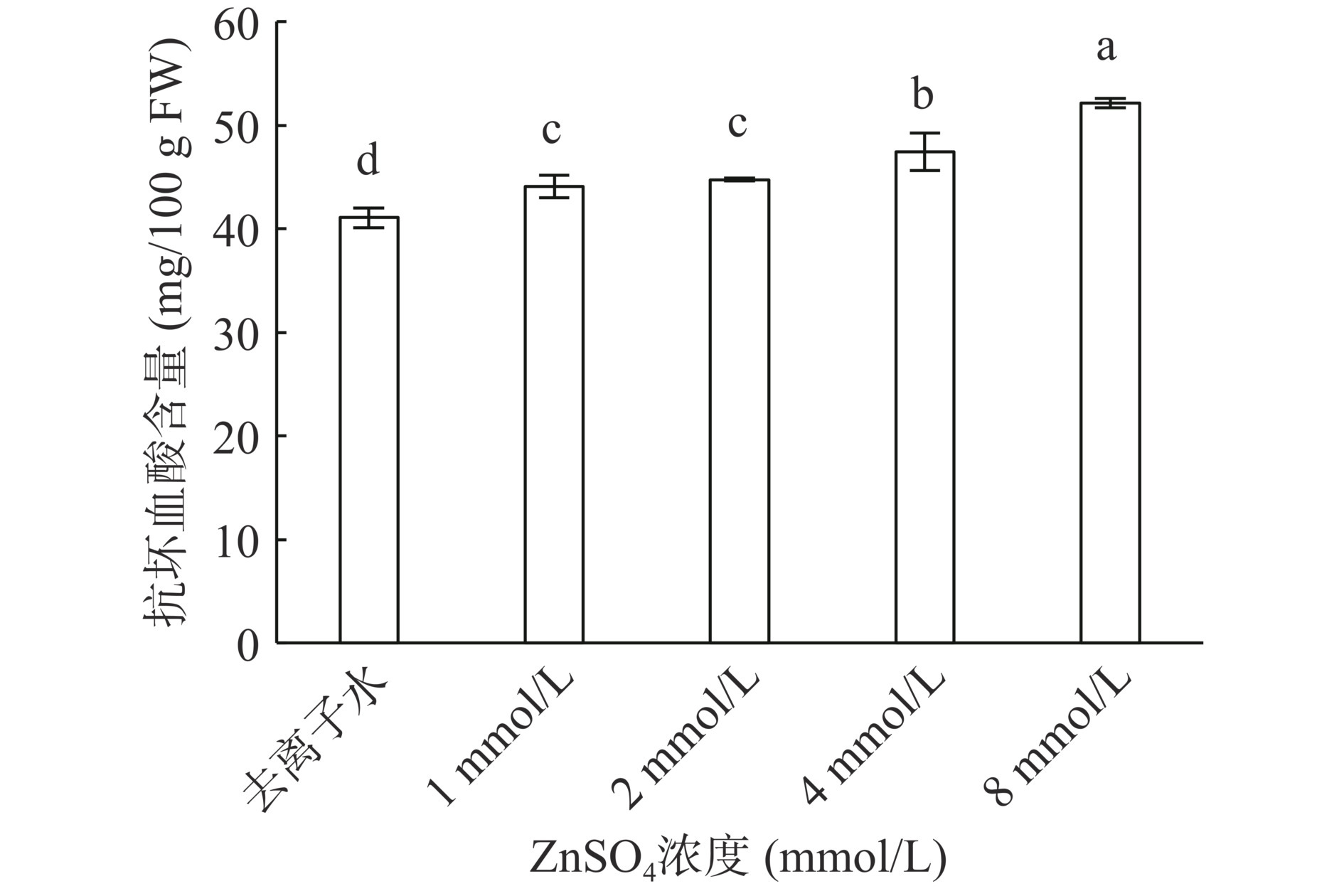
2.2 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗抗坏血酸含量的影响
抗坏血酸是衡量蔬菜营养质量的重要指标之一,也是人体不可或缺的物质。由图2可知,随着ZnSO4浓度的增加,西兰花芽苗中的抗坏血酸含量逐渐增加,各处理组含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照组,在ZnSO4浓度为8 mmol/L时含量达最大值,为52.17 mg/100 g,较去离子组与1~4 mmol/L ZnSO4浓度组分别增加了21.21%、15.40%、14.19%和9.01%。说明在本试验设定浓度范围内,喷施ZnSO4有利于西兰花芽苗中抗坏血酸含量的积累。本试验结果表明随着硫酸锌浓度的增加西兰花芽苗中抗坏血酸含量呈上升趋势,与郭强辉[28]研究结果相符。
2.3 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗中叶绿素含量的影响
叶绿素是光合作用中必不可少物质,并且具有一定抗氧化作用[29−30]。表2为不同ZnSO4处理下西兰花芽苗中的叶绿素含量。由表2可知,西兰花芽苗中去离子水处理的总叶绿素含量最高,为2.68 mg/g,ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组总叶绿素含量最低,为2.11 mg/g,二者差0.57 mg/g,去离子水处理与ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组的总叶绿素含量差异显著(P<0.05)。去离子水处理组叶绿素a含量最高,为1.86 mg/g,显著高于其他处理组,其他处理组间无显著性差异(P<0.05)。叶绿素b在去离子水处理组下达最大值0.83 mg/g,ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组的叶绿素b含量最低为0.63 mg/g,二者差异显著(P<0.05)。本试验结果与马原松等[31]对小白菜的研究以及杜新民[32]对菠菜幼苗的研究结论相似。西兰花芽苗中各处理组叶绿素含量均显著(P<0.05)低于去离子水处理组,其原因可能是喷施的ZnSO4浓度超过了芽苗呼吸和光合作用所需,抑制叶绿素的合成[33]。
表 2 ZnSO4 处理对西兰花芽苗叶绿素含量的影响Table 2. Effects of ZnSO4 treatment on the contents of chlorophyll in broccoli sprouts处理 总叶绿素(mg/g) 叶绿素a(mg/g) 叶绿素b(mg/g) 去离子水 2.68±0.14a 1.86±0.09a 0.83±0.05a ZnSO4 1 mmol/L 2.35±0.11b 1..62±0.07b 0.73±0.04b ZnSO4 2 mmol/L 2.24±0.02bc 1.57±0.02b 0.66±0.01bc ZnSO4 4 mmol/L 2.24±0.13bc 1.54±0.09b 0.70±0.04bc ZnSO4 8 mmol/L 2.11±0.06c 1.47±0.10b 0.63±0.04c 注:同列不同小写字母表示处理间显著差异(P<0.05);表3同。 2.4 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗中总酚和总黄酮含量的影响
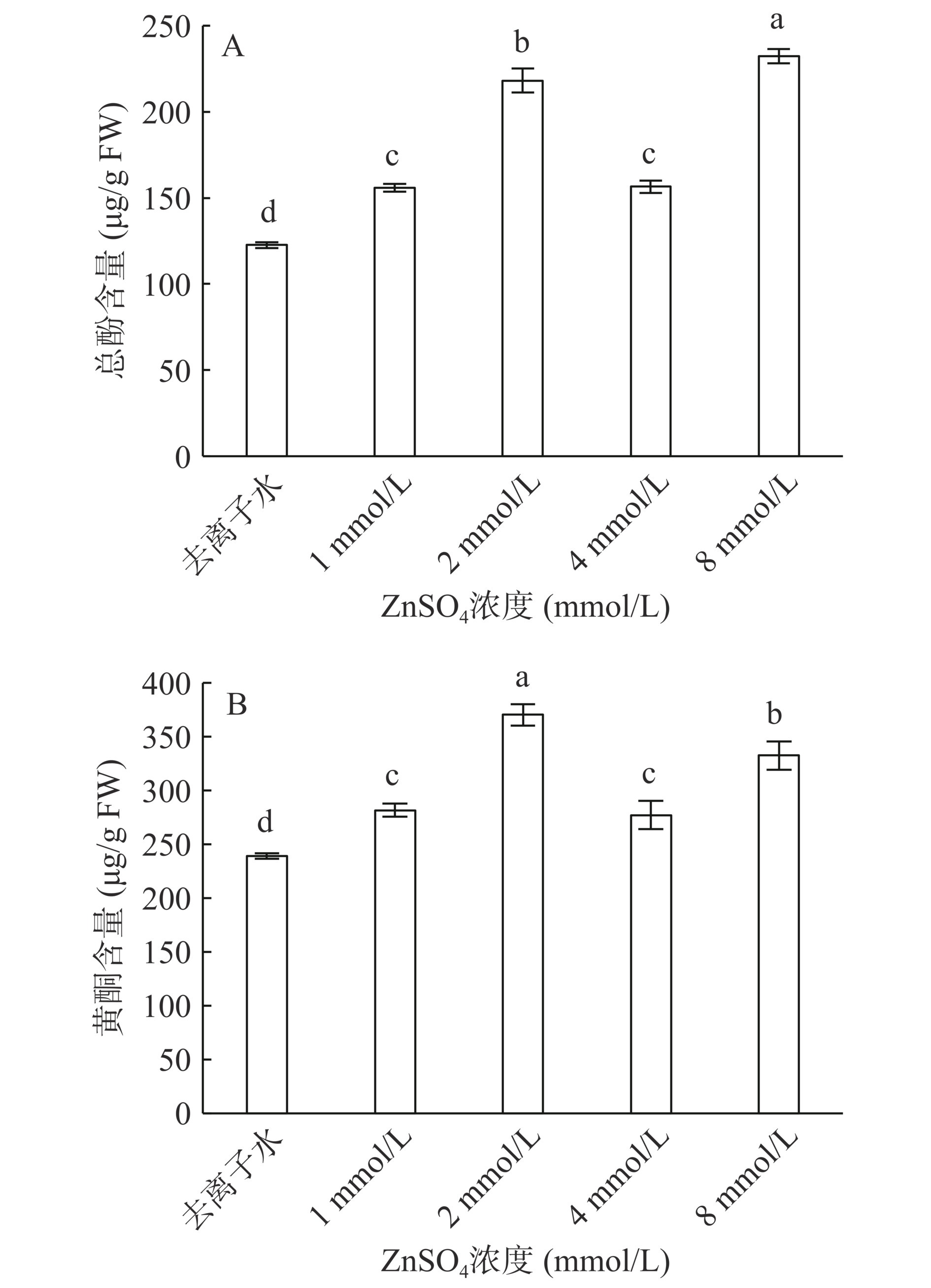
多酚和黄酮在保护生物机体免受外部刺激和消除活性氧(ROS)方面起着重要作用[34],还可以促进植物生长发育,调节植物开花结果。由图3A可以得知,各处理组总酚含量均显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组总酚含量最高,显著高于其他处理组(P<0.05),较去离子水处理组提高了47.15%。ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组显著高于去离子水处理组,较去离子水处理组提高了47.73%。ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理组和ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),较去离子水处理组分别显著提高了21.25%和21.57%(P<0.05)。由图3B可知,ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组总黄酮含量显著高于其他处理组(P<0.05),其总黄酮含量为370.43 μg/g,较去离子水处理组提高35.46%;ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组显著高于对照组(P<0.05),较去离子水处理组提高28.11%;ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理组与ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组间差异不显著(P>0.05),但也显著高于去离子水处理组(P<0.05),较去离子水处理组分别提高15.12%和13.76%。由此可见,适宜的ZnSO4浓度可以增加西兰花芽苗中总黄酮和总酚的含量。CHEN[35]以红树林植物为研究对象,证明施用低剂量ZnSO4可增加多酚含量,提高植物抗氧化能力,本文结果与其相似。
2.5 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗中硫苷含量的影响
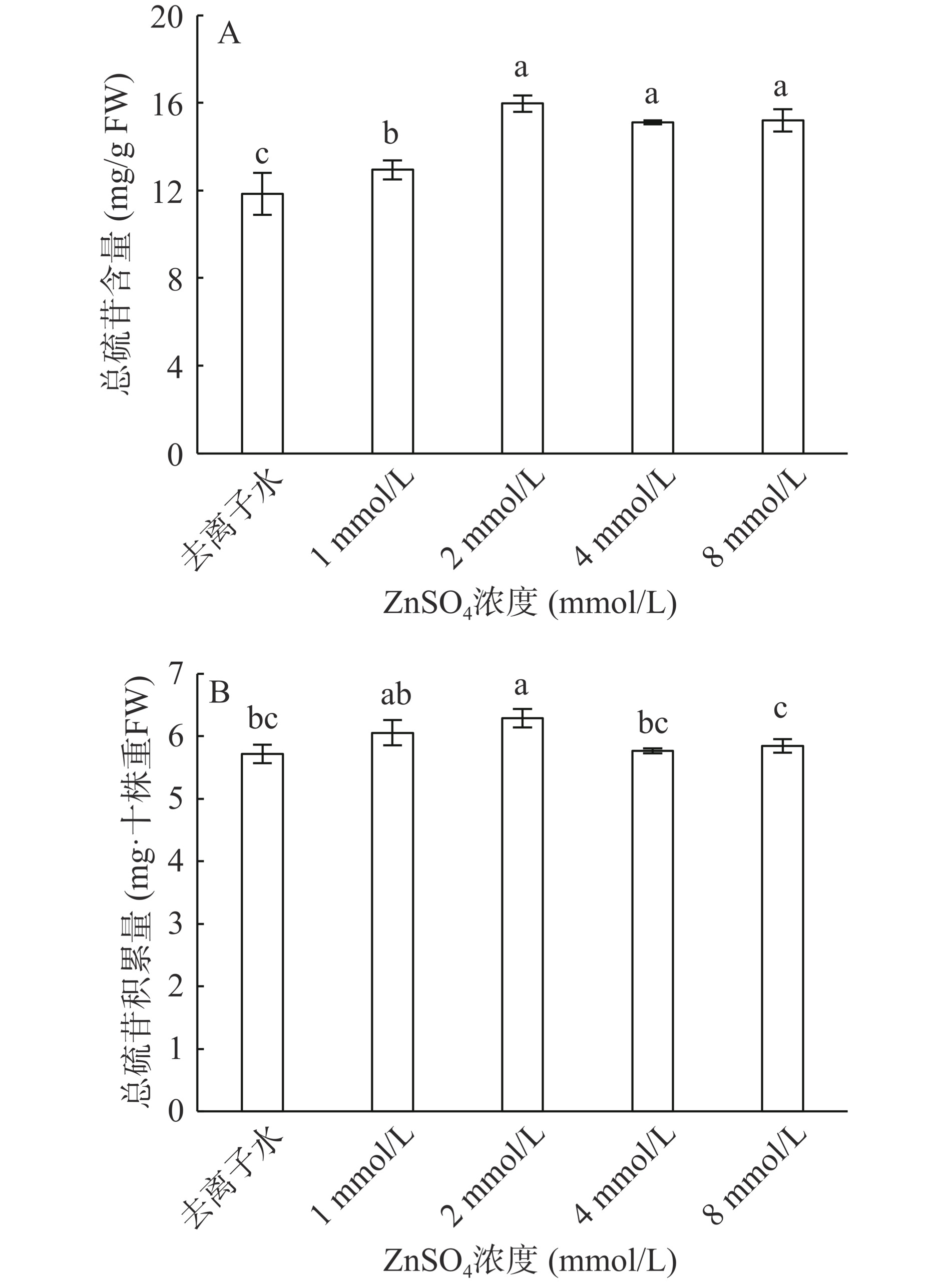
硫苷是一类广泛分布于十字花科植物中最具代表性的次级代谢产物。由图4A可知,随着ZnSO4浓度的增加,各处理组总硫苷含量均显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理组较对照组提高8.37%(P<0.05)。ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L较对照组分别提高25.72%、21.50%、21.98%(P<0.05),但彼此之间总硫苷含量无显著性差异(P>0.05)。可见,总硫苷含量在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组时含量最多。由图4B可知,十株重硫苷总含量在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组达最大值且显著高于对照组(P<0.05),说明ZnSO4浓度为2 mmol/L时更有利于西兰花芽苗硫苷的积累。初婷等[36]研究表明,MgSO4处理可以显著提高5 d西兰花芽苗中硫苷和萝卜硫素的含量。本试验施用ZnSO4同样使硫苷含量增加,可能是硫离子作为硫源,促进了甲硫氨酸的合成,进而影响硫苷的积累。
由表3可知,随着ZnSO4浓度的增加,硫苷组分RAA呈先上升后下降趋势,但在2~8 mmol/L ZnSO4之间差异不显著,在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组条件下含量最高,各处理组均显著高于去离子水处理组(P<0.05),ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理组较去离子水处理组提高了10.06%(P<0.05)。ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组之间差异不显著(P>0.05),分别较去离子水处理组提高26.62%、22.31%、21.85%。PRO在ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组达最大值,显著高于其他处理组,且较去离子水处理组、ZnSO4 1 mmol/L、ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组分别提高65.87%、55.42%、48.18%、68.34%(P<0.05)。ERU在ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组达最大值且显著高于对照组,但与ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组间差异不显著(P>0.05)。硫苷组分RAE含量呈先上升后下降趋势,在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组时达最大值且显著高于其他处理组(P<0.05),较去离子水、ZnSO4 1 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组分别提高了58.45%、53.67%、53.63%、58.60%。GBC各处理组均显著高于去离子水处理组(P<0.05),其中,以ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组促进效果较为明显,较去离子水处理组分别提高57.22%、46.30%、57.50%。4ME含量中,喷施ZnSO4各处理组均显著低于去离子水处理组(P<0.05),其中以ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组抑制效果最明显,与去离子水处理组相比下降了76.28%。总硫苷含量在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组下总硫苷含量最高,去离子水处理组的总硫苷含量最低。本试验结果表明,总硫苷与各硫苷组分含量大多在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L、ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组含量较高,说明喷施ZnSO4可以促进西兰花芽苗中硫苷含量的提高。
表 3 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗硫苷组分含量的影响(mg/g FW)Table 3. Effects of ZnSO4 treatment on glucosinolates content in broccoli sprouts (mg/g FW)硫苷 脂肪族硫苷 吲哚族硫苷 总硫苷 RAA PRO ERU ALY RAE GBC 4ME NEO 去离子水 10.05±0.94c 0.00±0.00b 1.03±0.04b 0.20±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 0.15±0.04c 0.15±0.00a 0.12±0.00bc 11.71±0.96c 1 mmol/L 11.17±0.33b 0.00±0.00b 0.92±0.10c 0.21±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 0.23±0.01b 0.05±0.00c 0.13±0.01b 12.71±0.43b 2 mmol/L 13.69±0.29a 0.01±0.00b 1.13±0.04ab 0.28±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.36±0.05a 0.04±0.01cd 0.11±0.00c 15.61±0.37a 4 mmol/L 12.93±0.25a 0.01±0.00a 1.14±0.04a 0.28±0.01a 0.00±0.00b 0.29±0.07ab 0.04±0.00d 0.14±0.00a 14.82±0.09a 8 mmol/L 12.85±0.49a 0.00±0.00b 1.13±0.03ab 0.29±0.00a 0.00±0.00b 0.36±0.03a 0.06±0.00 b 0.14±0.00a 14.84±0.50a 注:RAA表示4-甲基硫氧丁基硫苷;PRO表示2-羟基-3-丁烯基硫苷;ERU表示4-甲硫基丁烯基硫苷;ALY表示5-甲基亚磺酰基戊基硫苷;RAE表示4-甲基亚磺酰基-3-丁烯基硫苷;GBC表示4-甲硫基丁烯基硫苷;4ME表示4-甲基吲哚基-3甲基硫苷;NEO表示1-甲基吲哚基-3甲基硫苷。 2.6 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗中黑芥子酶活性的影响
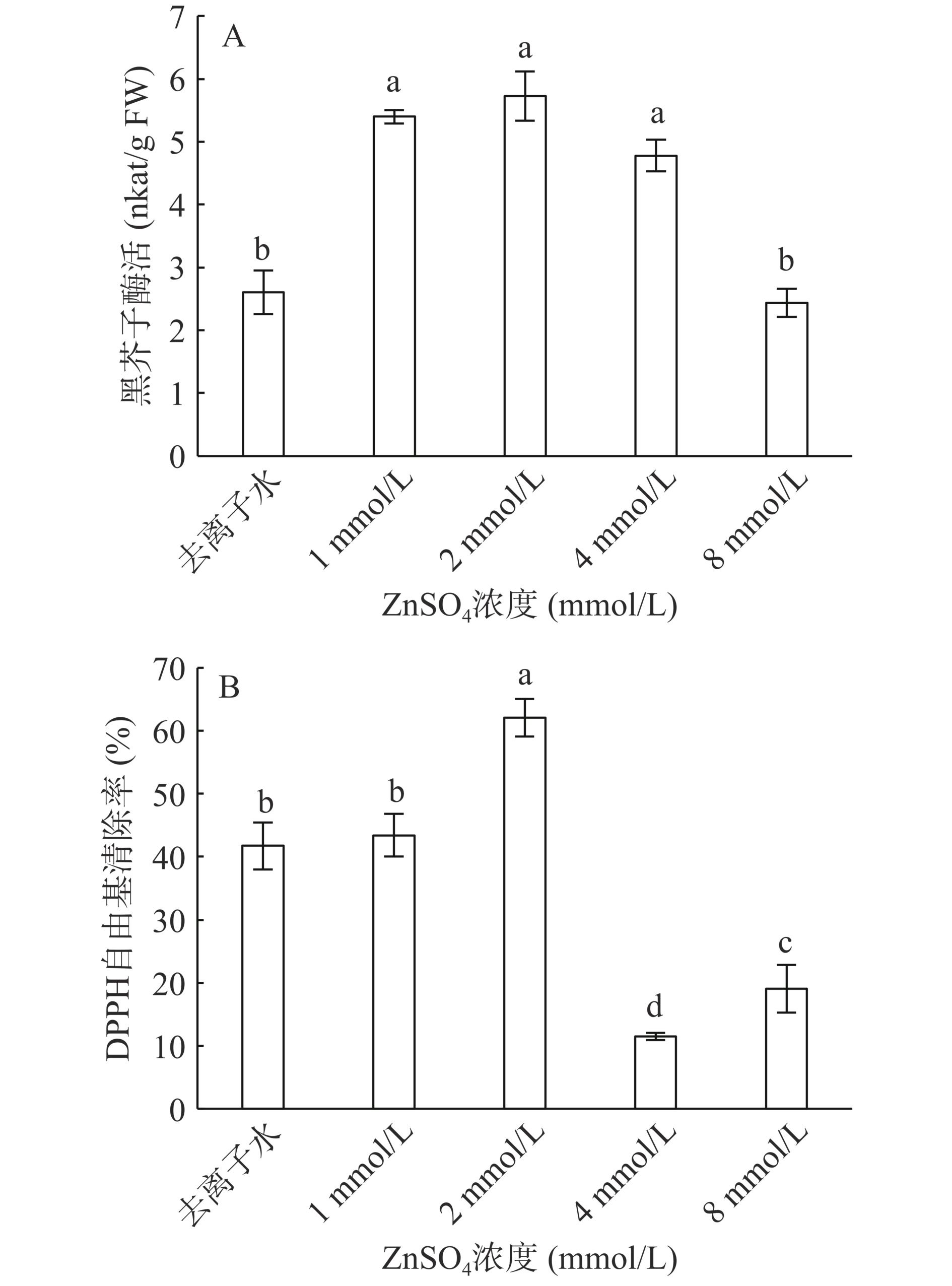
黑芥子酶广泛存在于十字花科植物中,能够促进硫代葡萄糖苷分解。喷施ZnSO4对黑芥子酶的活性影响如图5A所示,除ZnSO4 8 mmol/L处理组外,施用ZnSO4显著提高了西兰花芽苗中黑芥子酶活性。随着ZnSO4浓度的升高,黑芥子酶活性呈先上升后下降趋势,ZnSO4 1 mmol/L、ZnSO4 2 mmol/L、ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组间黑芥子酶活性差异不显著,ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组黑芥子酶活性最大,为5.73 nkat·g−1,较去离子水处理组提高54.50%(P<0.05)。Yang等[37]采用K2SO4、ZnSO4和Met 3三种硫源,结果表明经过ZnSO4处理后西兰花芽苗中黑芥子酶活性显著提高。所有植物的黑芥子酶活性都能被抗坏血酸激活[38],低浓度的抗坏血酸可以提高黑芥子酶活力,而高浓度抗坏血酸会降低黑芥子酶活性[36]。本研究结果也验证了这一点。
2.7 DPPH自由基清除率
测定DPPH自由基清除率可以探究抗氧化物质含量与抗氧化能力之间的关系。由图5B可知,西兰花芽苗DPPH自由基清除率随着ZnSO4浓度的升高,呈现先上升后下降再上升的趋势,最大值在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组,清除率为62.01%,最小值在ZnSO4 4 mmol/L处理组,清除率为11.50%,两者DPPH自由基清除率相差50.51%,差异显著(P<0.05)。ZnSO4 1 mmol/L处理组与去离子水处理组间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。本试验结果表明,DPPH自由基清除率呈先上升后下降再上升趋势,这与黄酮和多酚含量变化趋势相一致。
2.8 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗硫苷合成基因表达量的影响
硫苷按照R侧链氨基酸类型可分为三种:脂肪族硫苷、吲哚族硫苷以及芳香族硫苷,在西兰花中脂肪族硫苷含量较高。硫苷合成受多个基因调控,MAM1、CYP79F1、CYP83A1、AOP3主要参与脂肪族硫苷合成,受MYB28调控[39−40]。本研究选取总硫苷与脂肪族硫苷含量均最高的处理ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组(C2)与去离子水对照组(CK)进行西兰花芽苗中脂肪族硫苷合成路径较为关键的合成基因检测。如图6所示,在ZnSO4 2 mmol/L处理组下MAM1、CYP79F1、CYP83A1、AOP3、FMO-GSOX2基因表达量上调,其中CYP79F1、CYP83A1与FMO-GSOX2基因表达量较对照组显著提高(P<0.05),AOP3基因表达量虽然上调但与对照组无显著差异;MAM1基因表达量显著性下调(P<0.05)。说明ZnSO4处理可以通过调节硫苷合成途径中相关关键基因的表达来控制西兰花芽苗中硫苷的合成和积累。这些基因是硫苷合成过程中的关键基因,可能影响着甲硫氨酸的转化,而甲硫氨酸是硫苷合成过程中的主要氨基酸,这些基因表达量的变化可能与脂肪族硫苷以及总硫苷富集有关。
2.9 ZnSO4处理下硫苷含量、黑芥子酶活性及基因表达量之间相关性分析
为探究ZnSO4处理西兰花芽苗后硫苷含量、黑芥子酶活性以及相关基因表达量是否具有一致性,采用了Pearson相关系数来表示其相关性。结果如表4所示,总硫苷与脂肪族硫苷、RAA之间呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);MAM1与总硫苷、脂肪族硫苷、RAA、黑芥子酶呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);CYP79F1与总硫苷、脂肪族硫苷、RAA、黑芥子酶呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与MAM1呈显著负相关(P<0.01);CYP83A1与总硫苷、脂肪族硫苷、RAA呈显著正相关(P<0.05);FMO-GSOX2与总硫苷、脂肪族硫苷、RAA、黑芥子酶呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与MAM1极显著负相关(P<0.01),与CYP79F1显著正相关(P<0.05)。
表 4 ZnSO4处理硫苷含量、黑芥子酶活性及基因表达量之间相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of glucoside content, myrosinase activity and gene expression in ZnSO4 treatment相关性 总硫苷 脂肪族硫苷 RAA 黑芥子酶 MAM1 CYP79F1 CYP83A1 FMO-GSOX2 脂肪族硫苷 0.999** RAA 0.997** 0.998** 黑芥子酶 0.339 0.360 0.394 MAM1 −0.982** −0.983** −0.980** −0.996** CYP79F1 0.896* 0.893* 0.883* 0.860* −0.901* CYP83A1 0.855* 0.855* 0.858* 0.393 −0.414 0.305 FMO-GSOX2 0.946** 0.948** 0.944** 0.979** −0.971** 0.848* 0.235 AOP3 0.742 0.745 0.745 0.693 −0.689 0.615 0.513 0.626 注:**在0.01水平相关性显著;*在0.05水平相关性显著。 3. 结论
本研究以西兰花芽苗为试验材料,采用常规理化、UPLC以及分子机制水平初步探讨喷施硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗中硫苷的调控效应。结果表明,在ZnSO4浓度为2 mmol/L时,西兰花芽苗中总硫苷、萝卜硫苷(RAA)、黄酮含量以及DPPH自由基清除率与黑芥子酶活性均显著高于去离子水处理组(P<0.05)。在ZnSO4浓度为2 mmol/L时,CYP83A1、CYP79F1与FMO-GSOX2基因表达量显著提高(P<0.05)。施用2 mmol/L ZnSO4可以有效增加西兰花芽苗中活性物质含量,提高其抗氧化活性。
前人研究表明,外源物质可以通过调节基因表达水平促进蔬菜中硫苷的积累[39]。YIN等[41]研究发现,褪黑素提高了西兰花芽苗中CYP83A1基因表达量。LI等[42]通过施加纳米碳上调IPMI2、CYP79F1、FMOGS-OX2、AOP2和TGG1的表达水平,促进了西兰花中硫苷的积累。本研究表明,喷施适当浓度的硫酸锌可以有效促进西兰花芽苗中关键活性成分的积累,为西兰花芽苗品质调控奠定基础,下一步将采用氨基酸分析仪,从甲硫氨酸转变等角度,深入探究硫酸锌对西兰花芽苗关键活性成分的影响。
-
表 1 基因特异性引物序列
Table 1 Gene specific primer sequences
基因 上游引物(5’-3’) 下游引物(5’-3’) Actin 3 CTGTTCCAATCTACGAGGGTTTC GCTCGGCTGTGGTGGTGAA AOP 3 TTGATGCGGAGTTGGGCTTA CTCGGTGATACGGTGAAGGG CYP83A1 TTCATATCCTACGGCAGGCG TTATCCGCGGCCTTGTTGAT CYP79F1 CCACCCTCGGGGGTTATTTC TCCCGACTTTAACACCCACG MAM1 AAATTCTGGCATTGCTCGTGG ATCACCAGATTCACCGCACG FMO-GSOX2 GACCGTGGTTACGGGAGACTTG GTAGCCATTGTATAACAAGCAACCC 表 2 ZnSO4 处理对西兰花芽苗叶绿素含量的影响
Table 2 Effects of ZnSO4 treatment on the contents of chlorophyll in broccoli sprouts
处理 总叶绿素(mg/g) 叶绿素a(mg/g) 叶绿素b(mg/g) 去离子水 2.68±0.14a 1.86±0.09a 0.83±0.05a ZnSO4 1 mmol/L 2.35±0.11b 1..62±0.07b 0.73±0.04b ZnSO4 2 mmol/L 2.24±0.02bc 1.57±0.02b 0.66±0.01bc ZnSO4 4 mmol/L 2.24±0.13bc 1.54±0.09b 0.70±0.04bc ZnSO4 8 mmol/L 2.11±0.06c 1.47±0.10b 0.63±0.04c 注:同列不同小写字母表示处理间显著差异(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 ZnSO4处理对西兰花芽苗硫苷组分含量的影响(mg/g FW)
Table 3 Effects of ZnSO4 treatment on glucosinolates content in broccoli sprouts (mg/g FW)
硫苷 脂肪族硫苷 吲哚族硫苷 总硫苷 RAA PRO ERU ALY RAE GBC 4ME NEO 去离子水 10.05±0.94c 0.00±0.00b 1.03±0.04b 0.20±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 0.15±0.04c 0.15±0.00a 0.12±0.00bc 11.71±0.96c 1 mmol/L 11.17±0.33b 0.00±0.00b 0.92±0.10c 0.21±0.01b 0.00±0.00b 0.23±0.01b 0.05±0.00c 0.13±0.01b 12.71±0.43b 2 mmol/L 13.69±0.29a 0.01±0.00b 1.13±0.04ab 0.28±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.36±0.05a 0.04±0.01cd 0.11±0.00c 15.61±0.37a 4 mmol/L 12.93±0.25a 0.01±0.00a 1.14±0.04a 0.28±0.01a 0.00±0.00b 0.29±0.07ab 0.04±0.00d 0.14±0.00a 14.82±0.09a 8 mmol/L 12.85±0.49a 0.00±0.00b 1.13±0.03ab 0.29±0.00a 0.00±0.00b 0.36±0.03a 0.06±0.00 b 0.14±0.00a 14.84±0.50a 注:RAA表示4-甲基硫氧丁基硫苷;PRO表示2-羟基-3-丁烯基硫苷;ERU表示4-甲硫基丁烯基硫苷;ALY表示5-甲基亚磺酰基戊基硫苷;RAE表示4-甲基亚磺酰基-3-丁烯基硫苷;GBC表示4-甲硫基丁烯基硫苷;4ME表示4-甲基吲哚基-3甲基硫苷;NEO表示1-甲基吲哚基-3甲基硫苷。 表 4 ZnSO4处理硫苷含量、黑芥子酶活性及基因表达量之间相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of glucoside content, myrosinase activity and gene expression in ZnSO4 treatment
相关性 总硫苷 脂肪族硫苷 RAA 黑芥子酶 MAM1 CYP79F1 CYP83A1 FMO-GSOX2 脂肪族硫苷 0.999** RAA 0.997** 0.998** 黑芥子酶 0.339 0.360 0.394 MAM1 −0.982** −0.983** −0.980** −0.996** CYP79F1 0.896* 0.893* 0.883* 0.860* −0.901* CYP83A1 0.855* 0.855* 0.858* 0.393 −0.414 0.305 FMO-GSOX2 0.946** 0.948** 0.944** 0.979** −0.971** 0.848* 0.235 AOP3 0.742 0.745 0.745 0.693 −0.689 0.615 0.513 0.626 注:**在0.01水平相关性显著;*在0.05水平相关性显著。 -
[1] HAN J H, TAO W Y, HAO H K, et al. Physiology and quality responses of fresh-cut broccoli florets pretreated with ethanol vapor[J]. Journal of Food Science,2006,71(5):S385−S389.
[2] FAHEY J W, ZHANG Y, TALALAY P. Broccoli sprouts:An exceptionally rich source of inducers of enzymes that protect against chemical carcinogens[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,1997,94(19):67−72.
[3] 高诗薇, 朱禹蒙, 王齐蕾, 等. 等离子体处理对西兰花芽苗生产及活性物质含量的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(12):117−123. [GAO S W, ZHU Y M, WANG Q L, et al. Effects of cold plasma treatment on production and contents of bioactive substances in broccoli sprouts[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(12):117−123.] GAO S W, ZHU Y M, WANG Q L, et al. Effects of cold plasma treatment on production and contents of bioactive substances in broccoli sprouts[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(12): 117−123.
[4] NANDINI D B, RAO R S, DEEPAK BS, et al. Sulforaphane in broccoli:The green chemoprevention!! Role in cancer prevention and therapy[J]. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology:JOMFP,2020,24(2):405−407.
[5] VANGUCHOVA A, ANZENBACHER P, ANZENBACHEROVA E. Isothiocyanate from broccoli, sulforaphane, and its properties[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2019,22(2):121−126. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.0024
[6] ARORA I, SHARMA M, LI S, et al. An integrated analysis of the effects of maternal broccoli sprouts exposure on transcriptome and methylome in prevention of offspring mammary cancer[J]. Public Library of Science,2022,17(3):64858−64861.
[7] MAHN A, PEREZC E, ZAMBRANO V, BARRIENTOS H. Maximization of sulforaphane content in broccoli sprouts by blanching[J]. Foods,2022,11(13):1906−1907. doi: 10.3390/foods11131906
[8] NISHILIMI M, YAGI K. Molecular basis for the deficiency in humans of gulonolactone oxidase, a key enzyme for ascorbic acid biosynthesis[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1991,54(6):1203S−1208S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/54.6.1203s
[9] CARR A C, ROWE S. Factors affecting vitamin C status and prevalence of deficiency:A global health perspective[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(7):1963−1964. doi: 10.3390/nu12071963
[10] THEERIAULT A, CHAO J T, QI W, et al. Tocotrienol:A review of therapeutic potential[J]. Clinical Biochemistry,1999,32(5):309−319. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9120(99)00027-2
[11] HAN N M, MAY C Y. Determination of antioxidants in oil palm leaves (Elaeis guineensis)[J]. American Journal of Applied Sciences,2010,7(9):1243−1247. doi: 10.3844/ajassp.2010.1243.1247
[12] MA Q X, CAO X C, XIE Y N, et al. Effects of glucose on the uptake and metabolism of glycine in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) exposed to various nitrogen sources[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2017,17(1):1008−1010.
[13] DUAN Y, EDUARDO M S F, RODRIGUES R A, et al. Genotypic variation of flavonols and antioxidant capacity in broccoli[J]. Food Chemisyry,2021,338(4):1277−1289.
[14] 苗慧莹. 葡萄糖和植物激素协同调控十字花科植物中芥子油苷生物合成的机制研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2015. [MIAO H Y. Mechanism of glucose and phytohormone synergistic regulation of mustard oleosin biosynthesis in cruciferous plants[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2015.] MIAO H Y. Mechanism of glucose and phytohormone synergistic regulation of mustard oleosin biosynthesis in cruciferous plants[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015.
[15] 何锐, 谭星, 高美芳, 等. 添加不同浓度海藻肥对水培芥蓝生长及品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(11):2051−2059. [HE R, TAN X, GAO M F, et al. Effects of different concentrations of seaweed extract on growth and quality of Chinese kale in hydroponics[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2020,26(11):2051−2059.] doi: 10.11674/zwyf.20247 HE R, TAN X, GAO M F, et al. Effects of different concentrations of seaweed extract on growth and quality of Chinese kale in hydroponics[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(11): 2051−2059. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.20247
[16] AGHAJANZADEH T A, PEAJAPATI D H, BUROW M. Differential partitioning of thiols and glucosinolates between shoot and root in Chinese cabbage upon excess zinc exposure[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology,2020,244(1):1538−1542.
[17] PEREZ B S, MORENO D A, GARCIA V C. Glucosinolates in broccoli sprouts (Brassica oleracea var. italica) as conditioned by sulphate supply during germination[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,75(8):C673−C677.
[18] MORIKAWA I T, KIM S J, ALLAHHAM A, et al. Glucosinolate distribution in the aerial parts of sel1-10, a disruption mutant of the sulfate transporter SULTR1; 2, in mature arabidopsis thaliana plants[J]. Plants (Basel),2019,8(4):95−97. doi: 10.3390/plants8040095
[19] 李录山. 硫元素调控结球甘蓝生长和硫苷合成机理及BoMYC1功能研究[D]. 兰州:甘肃农业大学, 2022. [LI L S. Mechanism of sulfur regulation on growth and glucosinolate synthesis in cabbage and study on the function of BoMYC1[D]. Lanzhou:Gansu Agricultural University, 2022.] LI L S. Mechanism of sulfur regulation on growth and glucosinolate synthesis in cabbage and study on the function of BoMYC1[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2022.
[20] YIN Y Q, QUAN X L, CHENG Y, et al. Proteome reveals the mechanism of selenium-sulfur interaction in regulating isothiocyanate biosynthesis and the physiological metabolism of broccoli sprouts[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,426(15):1303−1307.
[21] CHAN K X, PHUA S Y, VAN B F. Secondary sulfur metabolism in cellular signalling and oxidative stress responses[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2019,70(16):4237−4250. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz119
[22] LI L S, ZHANG H, CHAI X H, et al. Transcriptome and proteome conjoint analysis revealed that exogenous sulfur regulates glucosinolate synthesis in cabbage[J]. Plants Basel,2021,10(10):2104−2108.
[23] 刘萌. 外源物质Na2SeO3和K2SO4对西兰花营养品质的影响及代谢调控机理研究[D]. 张家口:河北北方学院, 2022. [LIU M. Effects of exogenous substances Na2SeO3 and K2SO4 on nutritional quality and study on the metabolic regulation mechanism of broccoli[D]. Zhangjiakou:Hebei North University, 2022.] LIU M. Effects of exogenous substances Na2SeO3 and K2SO4 on nutritional quality and study on the metabolic regulation mechanism of broccoli[D]. Zhangjiakou: Hebei North University, 2022.
[24] 田璐. NaCl和CaCl2处理对西兰花芽苗菜营养与功能品质的影响[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2017. [TIAN L. Effect of NaCl and CaCl2 treatment on the nutritional and functional properties of broccoli sprouts[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.] TIAN L. Effect of NaCl and CaCl2 treatment on the nutritional and functional properties of broccoli sprouts[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
[25] 柏夏琼, 陈介南, 张林, 等. 发芽条件对西兰花芽苗菜总黄酮富集的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(1):105−110. [BAI X Q, CHEN J N, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of germination conditions on the enrichment of total flavonoids in broccoli sprouts[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(1):105−110.] BAI X Q, CHEN J N, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of germination conditions on the enrichment of total flavonoids in broccoli sprouts[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(1): 105−110.
[26] 刘倩男, 黄伟, 丁云花, 等. 青花菜中硫代葡萄糖苷RAA和GBC的近红外光谱快速测定[J]. 中国农业科学,2020,53(21):4497−4506. [LIU Q N, HUANG W, DING Y H, et al. Rapid determination of RAA and GBC in broccoli by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53(21):4497−4506.] doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.21.017 LIU Q N, HUANG W, DING Y H, et al. Rapid determination of RAA and GBC in broccoli by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(21): 4497−4506. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.21.017
[27] WANG J W, MAO S X, LIANG M T, et al. Preharvest methyl jasmonate treatment increased glucosinolate biosynthesis, sulforaphane accumulation, and antioxidant activity of broccoli[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2022,11(7):1298−1307. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071298
[28] 郭强晖. 西兰花芽苗异硫氰酸酯富集与调控技术研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2014. [GUO Q H. Study on isothiocyanates accumulation and regulation techniques in germinated broccoli sprouts[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014.] GUO Q H. Study on isothiocyanates accumulation and regulation techniques in germinated broccoli sprouts[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014.
[29] 商立超, 赵凤春, 弓志青, 等. 抗坏血酸联合乳酸链球菌素复合涂膜保鲜采后双孢蘑菇研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(20):346−351. [SHANG L C, ZHAO F C, GONG Z Q, et al. Preservation of postharvest agaricus bisporus by Vc/Nisin composite coating[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(20):346−351.] SHANG L C, ZHAO F C, GONG Z Q, et al. Preservation of postharvest agaricus bisporus by Vc/Nisin composite coating[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(20): 346−351.
[30] MICO V B, RAMOS M, LUZI F, et al. Effect of chlorophyll hybrid nanopigments from broccoli waste on thermomechanical and colour behaviour of polyester-based bionanocomposites[J]. Polymers (Basel),2020,12(11):2508−2515. doi: 10.3390/polym12112508
[31] 马原松, 朱晓琴, 陈道路, 等. 锌离子对温室水培小白菜硝酸盐积累及品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2020(4):53−57. [MA Y S, ZHU X Q, CHEN D L, et al. Effect of zinc ions on nitrate accumulation and quality of hydroponically grown cabbage in greenhouses accumulation and quality[J]. Northern Horticulture,2020(4):53−57.] MA Y S, ZHU X Q, CHEN D L, et al. Effect of zinc ions on nitrate accumulation and quality of hydroponically grown cabbage in greenhouses accumulation and quality[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020(4): 53−57.
[32] 杜新民. 锌对菠菜叶绿素含量及保护酶活性的影响[J]. 农业与技术,2016,36(19):37−38. [DU X M. Effect of zinc on chlorophyll content and protective enzyme activities in spinach[J]. Agriculture and Technology,2016,36(19):37−38.] DU X M. Effect of zinc on chlorophyll content and protective enzyme activities in spinach[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2016, 36(19): 37−38.
[33] 钟静, 王亮节, 曾国平, 等. 锌胁迫对薏苡种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2020(2):113−118. [ZHONG J, WANG L J, ZENG G P, et al. Effect of zinc stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Coix lacryma[J]. Northern Horticulture,2020(2):113−118.] ZHONG J, WANG L J, ZENG G P, et al. Effect of zinc stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Coix lacryma[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020(2): 113−118.
[34] ROISER M H, MULLER T, KRAUTLER B. Colorless chlorophyll catabolites in senescent florets of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(5):1385−1392. doi: 10.1021/jf5055326
[35] CHEN S. Mechanism of Zn alleviates Cd toxicity in mangrove plants (Kandelia obovata)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2023,2(13):1036−1039.
[36] 初婷, 彭畅, 郭丽萍. MgSO4处理对西兰花芽苗菜生理活性物质和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(11):53−59. [CHU T, PENG C, GUO L P. Effect of MgSO4 treatment on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in broccoli sprouts[J]. Food Science,2018,39(11):53−59.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201811009 CHU T, PENG C, GUO L P. Effect of MgSO4 treatment on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in broccoli sprouts[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(11): 53−59. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201811009
[37] YANG R, GUO L P, JIN X L, et al. Enhancement of glucosinolate and sulforaphane formation of broccoli sprouts by zinc sulphate via its stress effect[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2015,13(5):345−349.
[38] BHAT R, VYAS D. Myrosinase:insights on structural, catalytic, regulatory, and environmental interactions[J]. Critical Rev Biotechnol,2019,39(4):508−523. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2019.1576024
[39] KITAINDA V, JEZ J M. Structural studies of aliphatic glucosinolate chain-elongation enzymes[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2021,10(9):1500−1506. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091500
[40] WANG P, CAO W X, YANG L M, et al. Glucosinolate biosynthetic genes of cabbage:Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis[J]. Genes (Basel),2023,14(2):476−482. doi: 10.3390/genes14020476
[41] YIN Y Q, LIU Y, CHENG C, et al. ITRAQ-based proteomic and physiological analyses of broccoli sprouts in response to exogenous melatonin with ZnSO4 stress[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(20):12336−12347. doi: 10.1039/D1RA00696G
[42] LI Z S, LIU G M, HE H J, et al. Effects of nanocarbon solution treatment on the nutrients and glucosinolate metabolism in broccoli[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2022,12(15):10429−10431.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李琳,崔彦阁,赵娟娟,石晓丹,许军星,孙路. 调整膳食纤维和肠道菌群对延缓饮食诱导性肥胖的影响研究. 医学动物防制. 2025(02): 177-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王远利,王菲,张权,汤木果,陶亮,田洋. 海棠果果酱的研制及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(11): 175-186 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 毛欣欣,刘婧,梁文欧,蔡诗鸿,李彦勋. 果蔬加工副产物膳食纤维改性研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(08): 94-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李国巍,石雨,张正海,姬妍茹,杨庆丽,董艳,高宝昌,李柏阳. 黑海棠果多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(12): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李焱,林泳峰,刘文美,邹泽华,刘红,刘光明,刘庆梅. 食药同源植物多糖调控肠道稳态的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(02): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 雷延玲. 遮荫条件下栽培模式对草莓品质和产量的影响. 北方果树. 2022(05): 14-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



