Effects of Sophorolipids on the Structure and Properties of Zein-Quercetin Nanoparticles
-
摘要: 本研究制备了玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒(Zein-Q),采用扫描电子显微镜、傅里叶红外光谱和荧光光谱等方法分析了槐糖脂(SL)对Zein-Q颗粒结构的影响,并研究了Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的抗氧化活性和抑菌性质。结果表明,Zein-Q纳米颗粒为平均粒径128 nm的球形结构,包封率和载药量分别为25.8%±1.28%和3.98%±0.24%,对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除率为76.8%±0.9%和65.4%±1.2%。加入槐糖脂有助于形成分散性较好的纳米颗粒,且槐糖脂在氢键、静电作用力等作用下包覆于玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒外层,形成粒径较大的球形结构,当Zein-Q:SL为3:4时,Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的包封率和载药量分别增加至73.6%±1.80%和7.98%±0.41%,对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除率分别达到88.8%±1.0%和78.6%±1.5%。此外,复合纳米颗粒对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌显示出较好的抑制活性。由此表明,生物表面活性剂槐糖脂有潜力作为提高玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒结构稳定性和活性的修饰分子。
-
关键词:
- 槐糖脂 /
- 槲皮素 /
- 玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- 抑菌活性
Abstract: In this study, zein-quercetin (Zein-Q) nanoparticles were prepared and the effects of sophorolipids (SL) on the structure of Zein-Q nanoparticles were evaluated based on the combination of scanning electron microscopy, Fourier infrared spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. Their antioxidant and antibacterial properties were analyzed as well. The results showed that Zein-Q nanoparticles were spherical with an average particle size of 128 nm, the encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity were separately 25.8%±1.28% and 3.98%±0.24%, respectively, and its scavenging ability on DPPH· and ABTS+· were 76.8%±0.9% and 65.4%±1.2%. The addition of sophorolipids resulted in forming nanoparticles with good dispersion. The structural characteration results showed that sophorolipids were coated with the outer layer of zein-quercetin nanoparticles driven by the interaction of hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction, forming a spherical core-cell structure with a larger particle size. At Zein-Q:SL=3:4, the encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity of composite Zein-Q-SL nanoparticles were increased to 73.6%±1.80% and 7.98%±0.41%, respectively. The antioxidant activity of zein-quercetin nanoparticles was enhanced, which showed that the scavenging ability of composite Zein-Q-SL nanoparticles on DPPH· and ABTS+· reached 88.8%±1.0% and 78.6%±1.5%, respectively. In addition, the composite Zein-Q-SL nanoparticles showed a good inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Thus, it can be concluded that biosurfactant sophorolipids have potential to be excellent modifier for enhancing the structural stability and activity of zein-quercetin nanoparticles.-
Keywords:
- sophorolipids /
- quercetin /
- zein nanoparticles /
- antioxidant activity /
- antibacterial activity
-
槲皮素是一种类黄酮化合物,其结构为3,3',4',5,7-五羟基黄酮,广泛存在于如石榴、山楂、藕、冬枣、西兰花、山姜等植物的果实、花、叶、茎中,具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降血糖、降血压等功效[1]。但槲皮素难溶于水、稳定性差、生物利用度低,这极大限制了其在食品领域的广泛应用。目前,许多研究致力于采用纳米递送体系如纳米乳液、脂质体、胶体纳米颗粒等提高槲皮素的稳定性和生物利用度,取得了较好的效果[2−3]。其中蛋白质基纳米颗粒由于其采用生物大分子制备,生物可降解,载运效率高而受到广泛关注。此外,由于蛋白质基纳米颗粒结构中具有丰富的羟基、氨基和羧基,能够与多酚类化合物结合,形成高活性递送体系,提高多酚类化合物的应用范围。
玉米醇溶蛋白(Zein)是一类醇溶性蛋白质,其结构中超过50%的氨基酸是非极性的,能够溶于60%~90%乙醇水溶液。由于其天然的疏水特性,玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒可以通过反溶剂沉淀法制备,可作为用作包封和保护生物活性物质的载体[4−5]。邹艳[6]制备了玉米醇溶蛋白/酪朊酸钠-卡拉胶纳米颗粒作为槲皮素的口服输送体系,并证实了此递送体系抗氧化活性提高,并对HepG2细胞有较强的抑制作用。马娟娟[7]制备了玉米醇溶蛋白/槲皮素纳米颗粒,此颗粒粒径均在100 nm以下,槲皮素的包封率达95%,表现出较强的抗氧化活性。尽管玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒在提高生物活性物质稳定性和活性方面有诸多优势,但其易受到pH、热等加工环境的影响而发生聚集[8]。采用多糖、蛋白质等分子对玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒进行表面修饰[9−11],可以提高其稳定性、载药量和活性。马娟娟[7]进一步用壳聚糖、季铵盐壳聚糖、果胶修饰荷载槲皮素的玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒,发现果胶修饰的纳米颗粒显著提高了槲皮素的生物可及率。Yuan等[12]利用葡聚糖硫酸酯稳定玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒,所得到的复合颗粒具有由静电作用、氢键和疏水相互作用形成的球形结构,在不同pH、加热和储存中表现出良好的稳定性,且姜黄素的包封率提高至85.37%,同时表现出较高的储存稳定性和姜黄素的生物可及性。邓卓丹等[13]制备了玉米醇溶蛋白-卵磷脂-槲皮素纳米颗粒,发现随着卵磷脂质量比例增加,复合纳米颗粒的多分散性系数减小,稳定性更强,对槲皮素的包封率最高达73.2%。同样,Dai等[14]采用反溶剂共沉淀技术制备了玉米醇溶蛋白-卵磷脂复合纳米颗粒用于姜黄素的递送,发现姜黄素的包封率从玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒的42.03%显著提高到99.83%,卵磷脂修饰的玉米醇溶蛋白复合纳米颗粒显著提高了姜黄素对热处理、紫外线照射和高离子强度的稳定性。可见,表面活性剂对提升玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒的稳定性、包封率和活性起到有益效果。
槐糖脂是一类由微生物发酵产生的糖脂类生物表面活性剂,具有优良的表面活性[15],以及分散、润湿、保水等作用,还具有抑菌、抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤等活性[16−17],在石油、化工、食品、纳米技术等领域有广泛的应用[18−20]。研究证明,将槐糖脂应用于金属纳米颗粒的制备,可以提高金属纳米颗粒的分散性和细胞渗透性[21−22]。槐糖脂被应用于姜黄素纳米颗粒的制备,可以降低纳米颗粒的细胞毒性,提高药物的生物利用度[23−24]。目前,关于槐糖脂是否能够改善玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒的结构和性质的研究尚不清楚。
本文拟制备玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒(Zein-Q),并探讨槐糖脂(SL)对Zein-Q结构和性质的影响。具体分析了不同配比影响下复合纳米颗粒的粒径、ζ-电位和形貌变化;采用荧光光谱、傅里叶红外光谱等手段表征分析了两组分间的相互作用;并测定了复合纳米颗粒的抗氧化能力和抑菌性质,以期挖掘糖脂表面活性剂调控蛋白纳米颗粒结构和性质的潜力,并为开发高活性的槲皮素纳米递送体系提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玉米醇溶蛋白(纯度>98%)、槲皮素(纯度>99.9%)、2-苯基-4,4,5,5-四甲基咪唑啉-1-氧基酸盐(纯度>98%) 购于上海源叶生物科技有限公司;槐糖脂(纯度>90%) 购于陕西德冠生物公司;肉汤蛋白胨培养基 购于北京索莱宝科技有限公司;盐酸、氢氧化钠、无水乙醇等化学品 均为分析纯,购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli,E.coli,ATCC25922)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus,S. aureus,ATCC25923) 来源于美国ATCC生物标准品资源中心,由实验室保存。
EVO-LS 10扫描电子显微镜 德国蔡司;Q20差示量热扫描仪 上海斯迈欧分析仪器有限公司;Nicolet IS50傅里叶红外光谱 赛默飞世尔公司;Malvern Nano-ZS 90 Zeta电位仪 英国马尔文仪器有限公司;SpectraMax i3x多功能酶标仪 美谷分子仪器(上海)有限公司;SN-MS-9D磁力搅拌器 上海尚普仪器设备有限公司;RE-3000旋转蒸发器 上海贤德实验仪器有限公司;P5紫外/可见分光光度计 上海美普达仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素-槐糖脂纳米颗粒(Zein-Q-SL)的制备
根据Dai等[25]的方法制备了玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素-槐糖脂纳米颗粒(Zein-Q-SL)。具体操作是将玉米醇溶蛋白和槲皮素分别溶解于乙醇水溶液(70%,v/v)中,浓度分别为2.0 mg/mL和0.2 mg/mL,在室温下磁力搅拌500 r/min,搅拌3 h,然后在玉米醇溶蛋白溶液中加入槐糖脂,使玉米醇溶蛋白与槐糖脂的质量比为1:0(此比例条件制备玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒)、10:1、5:1、2:1和3:4。将玉米醇溶蛋白-槐糖脂溶液与等量的槲皮素溶液混合,在室温下500 r/min恒定搅拌2 h。按照体积比1:2.5,取混合溶液缓慢注入去离子水中,用0.1 mol/L NaOH或HCl将分散体调节到pH5.0,以1000 r/min的转速进行磁力搅拌30 min后,形成复合纳米颗粒分散体系,并于50 ℃下减压旋转蒸发除去乙醇和部分水。为了去除较大的纳米颗粒和游离的槲皮素,将纳米颗粒分散体系在1000×g下离心20 min,取上清,测定分散液的蛋白质浓度为3.6±0.3 mg/mL,样品储存于4 ℃或冷冻干燥成粉末后备用。上述制备的复合纳米颗粒在文中分别以Zein-Q、Zein-Q-SL 10:1、Zein-Q-SL 5:1、Zein-Q-SL 2:1和Zein-Q-SL 3:4表示。
1.2.2 Zein-Q-SL的粒径和ζ-电位
使用Malvern Nano-ZS 90 Zeta电位仪测定Zein-Q-SL的粒径分布、多分散系数(PDI)和ζ-电位。根据文献方法[13]并稍作调整,测定模式为Smoluchowski,折射率值为1.5,测试前放置平衡2 min。实验条件为25±0.1 ℃。每个样品重复测定3次,取平均值。
1.2.3 Zein-Q-SL形貌观察
采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察Zein-Q-SL的微观结构。根据文献方法[25]并作适当修改,将真空冷冻干燥后的纳米颗粒粘在不锈钢样品台上,镀金,随后在20 kV的加速电压下观察样品的微观形貌。
1.2.4 荧光光谱测定
按照文献方法[25],将Zein-Q-SL颗粒分散液蛋白浓度稀释至0.2 mg/mL。以Zein分子内的荧光基团作为探针,其中激发波长为280 nm(激发色氨酸荧光),发射波长范围为290~450 nm。激发和发射狭缝宽分别为5 nm和3 nm,进行荧光光谱扫描。
1.2.5 傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)测定
根据文献方法[25],采用溴化钾压片法测定样品的红外光谱。将冷冻干燥后的Zein-Q-SL样品与溴化钾以1:100比例进行混合。扫描条件设置为:光谱范围3500~500 cm−1,扫描次数64次,分辨率为4 cm−1。
1.2.6 包封率和载药量的测定
根据文献方法[26],测定不同Zein-Q-SL纳米颗粒中槲皮素的包封率(Encapsulation efficiency,EE)和载药量(Loading capacity,LC)。将Zein-Q-SL纳米颗粒分散体系用乙醇水溶液(80%,v/v)稀释,并采用超声辅助处理,条件为超声频率100 Hz,处理时间为15 min。将上述溶液置于比色皿中,测定374 nm处的吸光度,以槲皮素标品绘制标准曲线Y=0.078X−0.041,R2=0.997,计算纳米颗粒中槲皮素的含量,并计算槲皮素的EE和LC。计算公式如式(1)和式(2)所示:
(1) (2) 1.2.7 抗氧化活性的测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定
取2 mL纳米颗粒溶液(蛋白浓度稀释到2.0±0.5 mg/mL)与2 mL DPPH标准液(0.2 mmol/L DPPH溶于无水乙醇中)混合,并于25 ℃避光放置30 min。测定在517 nm处吸光度,DPPH自由基的清除率按公式(3)计算:
(3) 式中:A0、A1和A2分别是溶剂(去离子水)测试组、复合纳米颗粒样品测试组和空白(去离子水)的吸光度。
1.2.7.2 ABTS+自由基清除率测定
配制7.4 mmol/L ABTS和2.45 mmol/L K2S2O8的混合溶液,避光放置12~16 h,用去离子水稀释,使其在734 nm处的吸光度为0.700±0.001,得到ABTS+·。将4 mL纳米颗粒溶液(蛋白浓度稀释到2.0±0.5 mg/mL)与4 mL稀释的ABTS+·在暗处反应6 min,测定其在734 nm处的吸光度。ABTS+自由基清除率按公式(4)计算:
(4) 式中: A0、A1和A2分别是溶剂(去离子水)测试组、复合纳米颗粒样品测试组和空白(去离子水)的吸光度。
1.2.8 Zein-Q-SL抑菌性质
槐糖脂具有良好的抑菌活性。本实验采用大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli,E.coli)和金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus,S. aureus)作为研究对象,评价Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的抑菌活性。具体方法是将细菌的单菌落分别接种至100 mL LB培养基中,置于恒温振荡器(37 ℃,转速150 r/min)培养12 h。将培养后的菌液200 μL加到LB固体培养基中,迅速倒平板,待其凝固后进行打孔,然后分别将200 μL不同的Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒分散液样品加到孔中,平板置于37 ℃的恒温培养箱中24 h,比较抑菌圈的直径大小。设置对照组(孔中加入200 μL无菌水)和槐糖脂(浓度2.6 mg/mL,此为制备纳米颗粒时加入体系的最高浓度)处理组。
通过测定菌的密度OD值变化,计算抑菌率分析复合纳米颗粒的抑菌活性。具体将活化后对数期的菌稀释至105 CFU/mL,取100 μL菌液于96孔板中,每孔再分别加入100 μL不同的Zein-Q-SL纳米颗粒分散液。以加100 μL稀释后的菌液和100 μL无菌水为阳性空白对照,同时设置槐糖脂(浓度2.6 mg/mL)处理组,置于37 ℃的恒温培养箱中培养24 h,测定600 nm处的吸光值。抑菌率按照公式(5)计算:
(5) 式中,A0是菌的初始OD600值,A1是培养24 h后菌样品的OD600值。
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin 2021软件绘制图形,采用IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0软件整理并进行方差分析及差异显著性检验(P<0.05)。每个试验平行3次,结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 Zein-Q-SL的粒径、电位和形貌特征
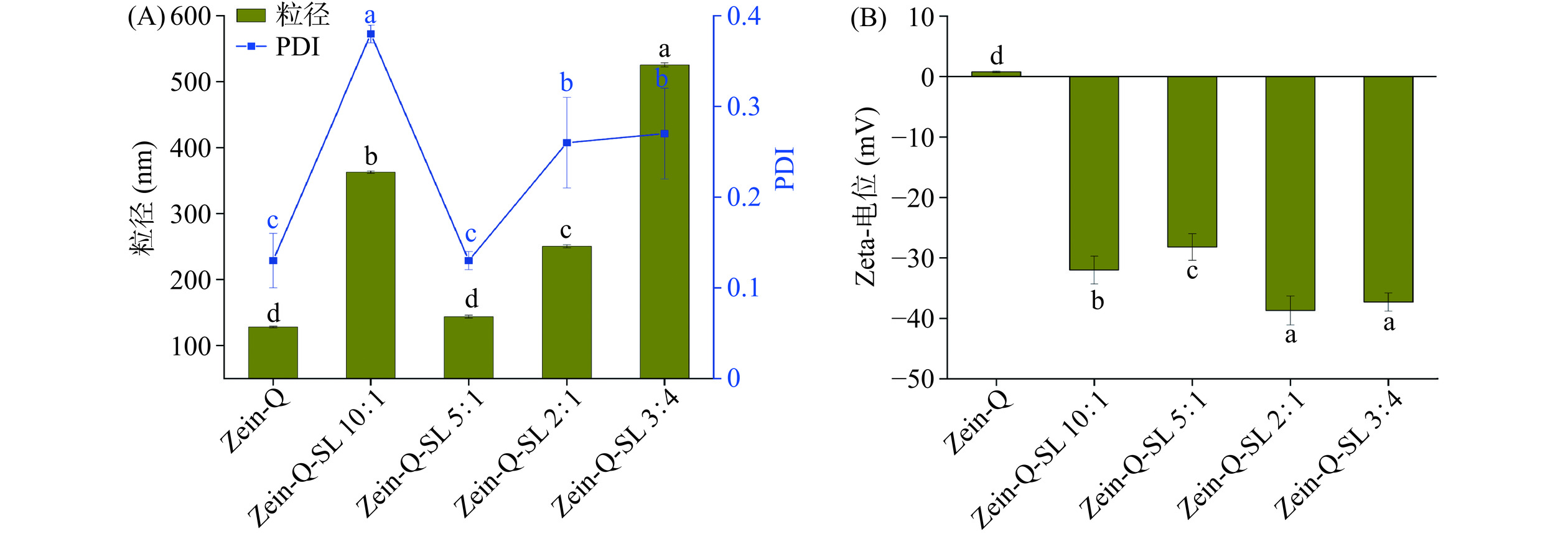
图1为Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的粒径、电位随Zein与SL不同比例的变化。由图1(A)可以看出,Zein-Q纳米颗粒的粒径为128 nm,随着槐糖脂的加入,Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的粒径变大,当Zein-Q:SL为10:1时,复合纳米颗粒的粒径达到362 nm,体系不稳定,有少许沉淀产生,这是由于少量槐糖脂加入,破坏了Zein-Q纳米体系的稳定,同时导致粒径变大。随着槐糖脂的比例升高,槐糖脂与Zein-Q纳米颗粒相互作用加强,体系逐渐趋于稳定,平均粒径有所减小,但在Zein-Q:SL为3:4时,复合纳米颗粒的平均粒径达到525 nm,这是可能由于过量的槐糖脂聚集于纳米颗粒表面,导致粒径变大。但此时体系的多分散性指数PDI值小于0.3,体系分子量分布较均一,制备过程无沉淀产生。粒径的增加可能与复合颗粒表面电荷情况也有关。从图1(B)可以看出,随着槐糖脂加入,Zein-Q的表面电荷从正变为负值,净电荷逐渐增加,且增加到−38 mV后变化较小,这是由于随着过量的槐糖脂包覆在复合纳米颗粒表面,产生静电斥力,逐渐形成稳定结构状态。Dai等[25]研究也发现鼠李糖脂能够包覆在姜黄素纳米颗粒表面,形成稳定的核壳结构。
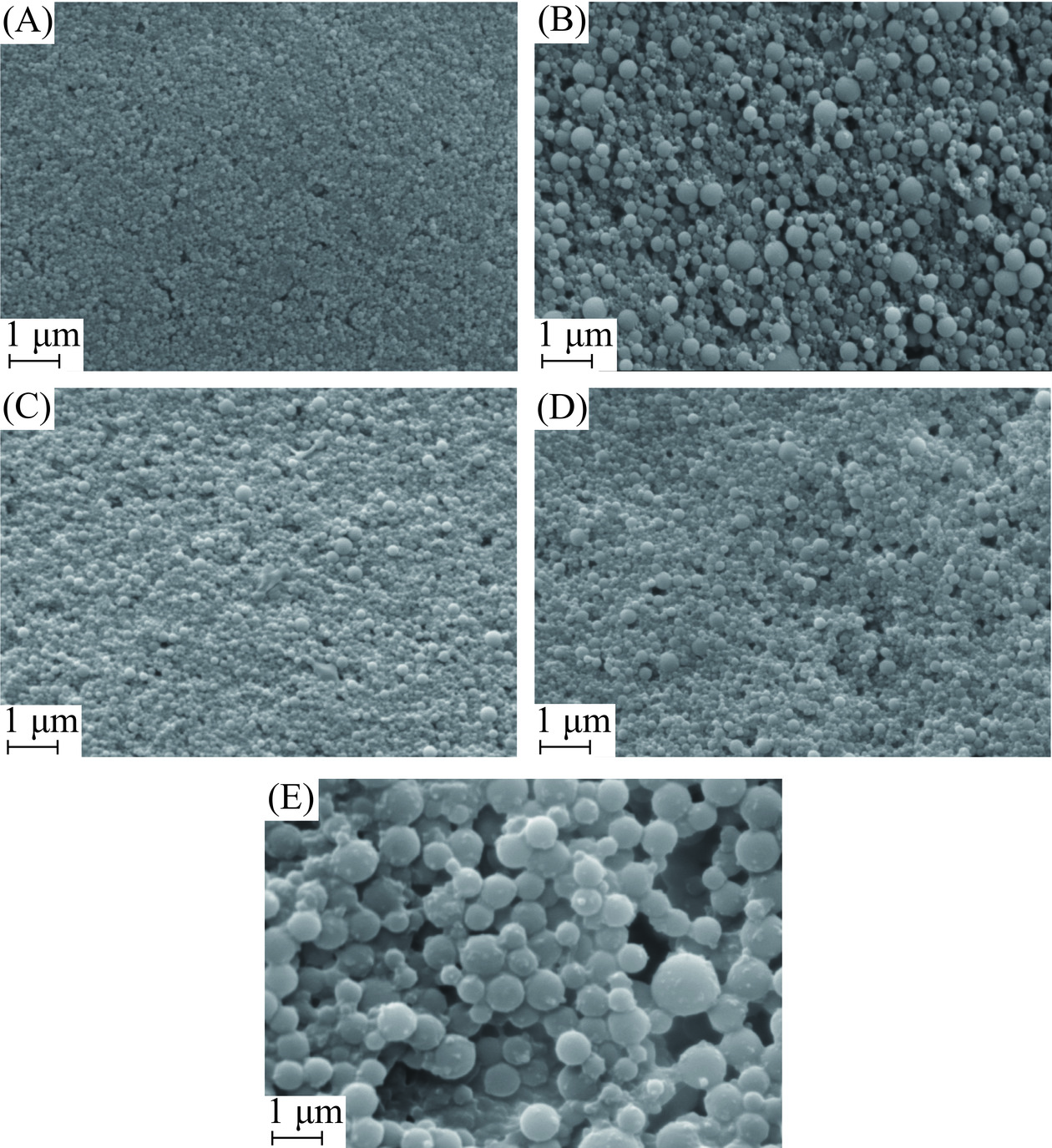
图2显示了不同槐糖脂比例对Zein-Q纳米颗粒形态的影响。从图中可以看出,不同条件下制备得到的纳米颗粒均为球形。随着槐糖脂加入,复合纳米颗粒逐渐变为表面均匀的较大球形结构,可能形成了以Zein-Q为核,以SL为壳的核壳结构。
2.2 荧光光谱分析
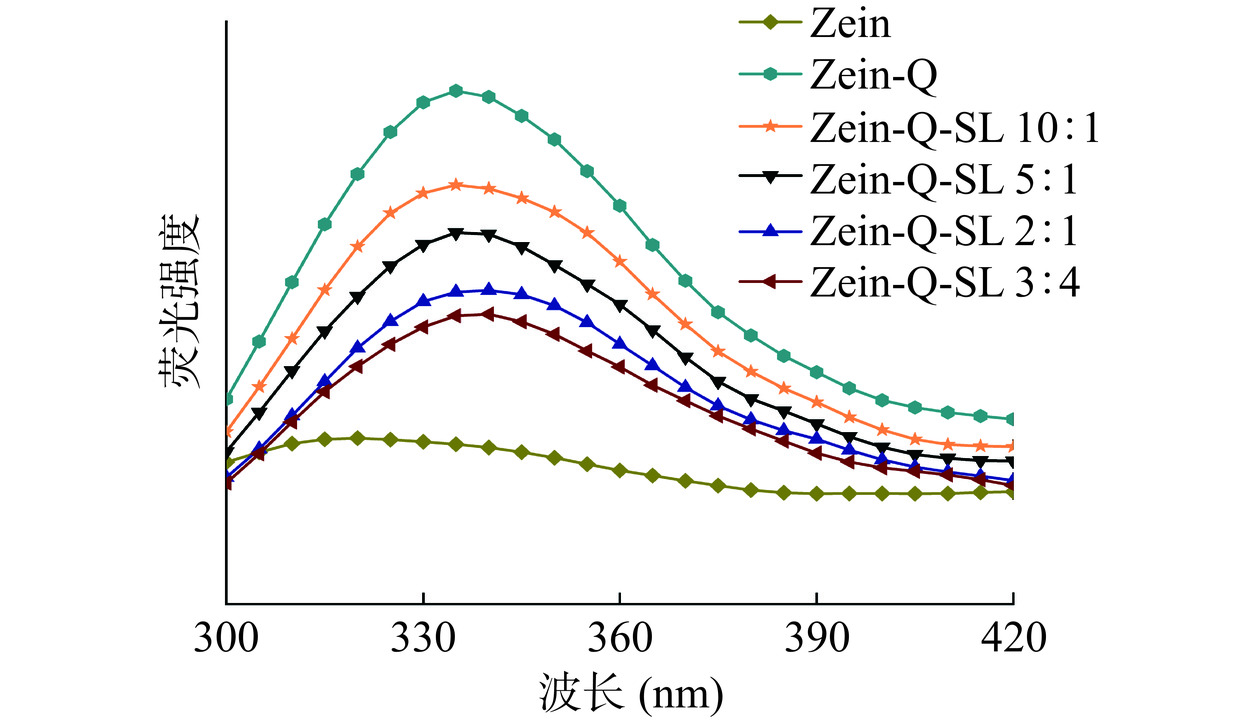
小分子和蛋白质之间的相互作用可以诱导氨基酸周围的极性变化,进而导致荧光位移或猝灭反应[27],因此,可以通过荧光光谱的变化反映纳米颗粒的分子间相互作用。图3为不同复合纳米粒子的荧光光谱。从图中可以看出,玉米醇溶蛋白在308 nm处有一个较强的荧光发射峰。在形成Zein-Q纳米颗粒后,其荧光发射强度增强,这是由于玉米醇溶蛋白与槲皮素相互作用时,玉米醇溶蛋白分子链展开,构象松弛,暴露更多的氨基酸残基,荧光强度增加[28]。同时,槲皮素的结合导致玉米醇溶蛋白发射峰的最大值发生红移至343 nm,说明蛋白的酪氨酸残基极性环境发生变化。这与Li等[28]研究结果一致,多酚小分子化合物与玉米醇溶蛋白结合,发生分子间相互作用,改变了蛋白的极性环境,引起荧光位移。
当槐糖脂加入到体系中,Zein-Q发射峰发生变化。当Zein-Q:SL为2:1和3:4时,Zein-Q发射峰的最大值发生红移至约346 nm处。此外,Zein-Q发射峰的荧光强度随着槐糖脂含量的增加而逐步降低,这是由于槐糖脂引起了荧光淬灭效应。这也进一步说明了槐糖脂与Zein-Q发生了分子间相互作用。根据报道,蛋白质的淬灭效应可能是由分子重排、激发态反应、基态络合物形成、能量转移和碰撞猝灭等分子相互作用引起的[29]。Dai等[25]研究也发现,鼠李糖脂导致的玉米醇溶蛋白荧光淬灭是由分子重排、能量转移等多种效应共同作用的结果。关于槐糖脂导致Zein-Q荧光淬灭的机制尚需进一步研究。
2.3 傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析
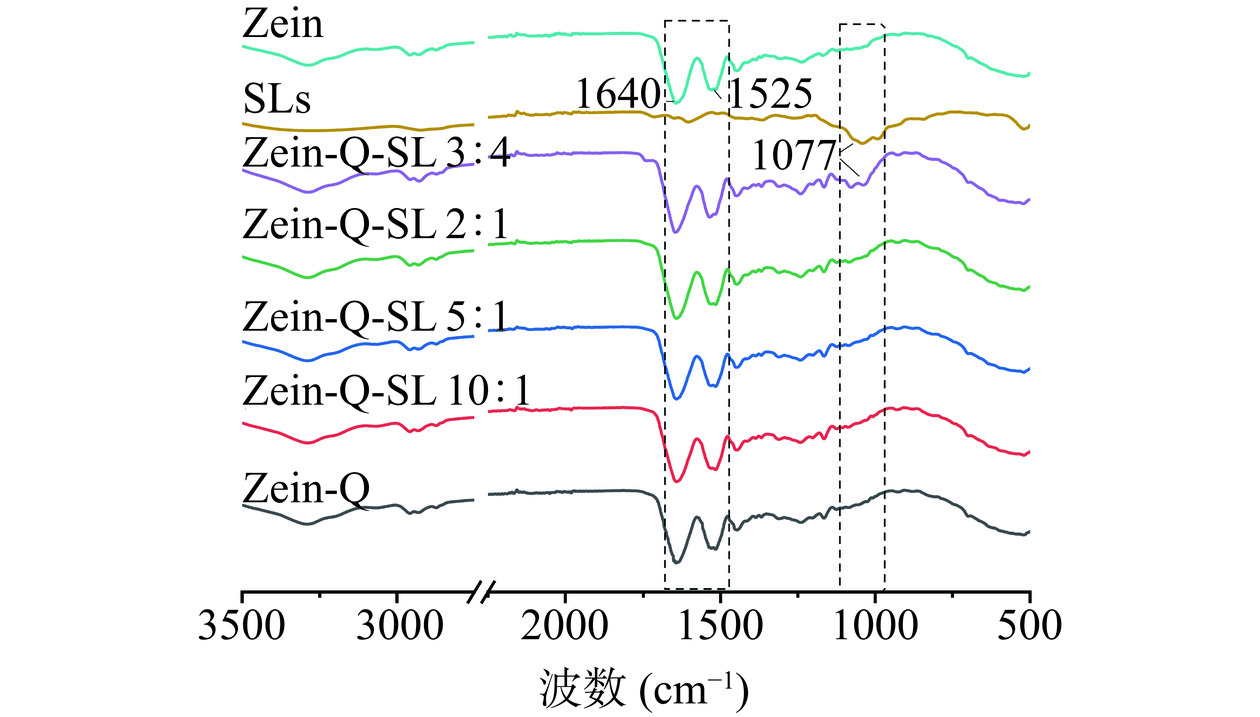
为解析不同组分之间的相互作用,分析了纳米颗粒的傅里叶红外光谱。从图4可以看出,槐糖脂和Zein-Q的O-H拉伸振动的特征峰分别为3320、3290 cm−1,在槐糖脂影响下,复合纳米颗粒Zein-Q:SL=10:1、Zein-Q:SL=5:1、Zein-Q:SL=2:1、Zein-Q:SL=3:4的O-H特征峰分别移至3292、3292、3294、3302 cm−1,O-H特征峰发生红移,羟基中的氧原子与氢键中的氢原子之间的键强度增加,振动频率降低,表明玉米醇溶蛋白、槲皮素和槐糖脂之间有氢键形成。
玉米醇溶蛋白在1640和1525 cm−1处有两个主要特征峰为酰胺I和酰胺II波段。通常,酰胺 I 带(1750~1600 cm−1)主要为C-O基和C-N基伸缩振动,而酰胺II带(1550~1510 cm−1)主要为N-H基弯曲振动和C-N基的伸缩振动[5,25]。与Zein-Q相比,加入槐糖脂并未引起酰胺I和酰胺II移动,但在Zein-Q-SL 3:4样品中,在1077 cm−1处出现了一个新峰,该峰为槐糖脂的特征峰,说明Zein-Q与SL发生了强相互作用,这是由于随着槐糖脂比例增加,玉米醇溶蛋白极性环境发生改变,分子链展开,更多的疏水基团暴露,纳米颗粒形成过程中,更容易与其他分子物质结合。此外,槐糖脂具有两亲性,其结构由两分子葡萄糖以1,2糖苷键连接构成槐糖基亲水部分,由饱和或不饱和的脂肪酸构成疏水部分[30]。在Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒形成过程中,槐糖脂亲水部分更易与蛋白的羟基等形成氢键,同时疏水基团间的疏水相互作用可能也是促使纳米核壳结构形成的重要驱动力。
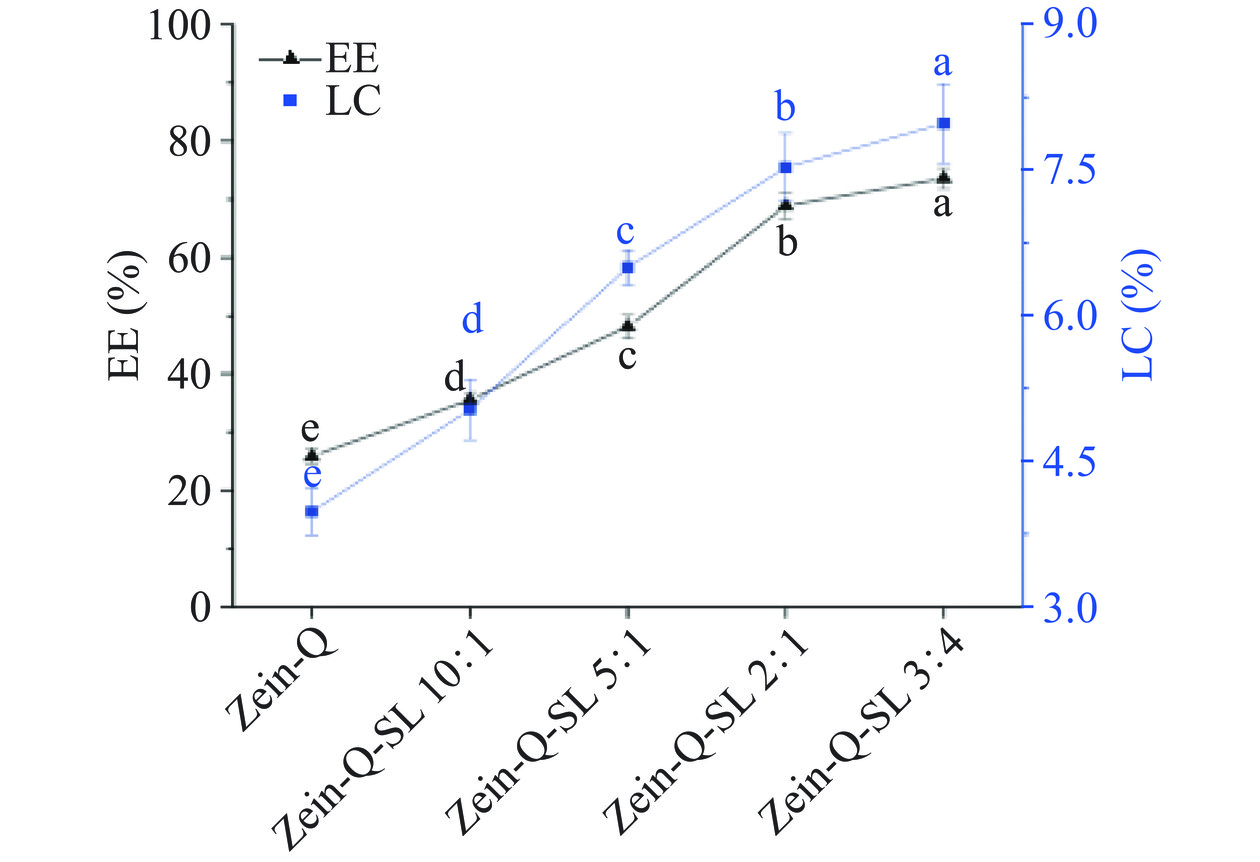
2.4 Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的包封率和载药量分析
图5为不同Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒对槲皮素的包封率和载药量结果。图中显示,Zein-Q纳米颗粒的包封率为25.8%±1.28%,载药量为3.98%±0.24%。随着槐糖脂的加入,复合纳米颗粒的包封率和载药量增加,当Zein-Q:SL为3:4时,包封率和载药量分别为73.6%±1.80%和7.98%±0.41%,显著高于Zein-Q纳米颗粒(P<0.05),说明了槐糖脂有助于提高玉米醇溶蛋白纳米颗粒对槲皮素的载运,其原因可能是槐糖脂与纳米颗粒中的Zein和槲皮素发生了相互作用,上述FTIR和荧光光谱结果也证实了这一点。
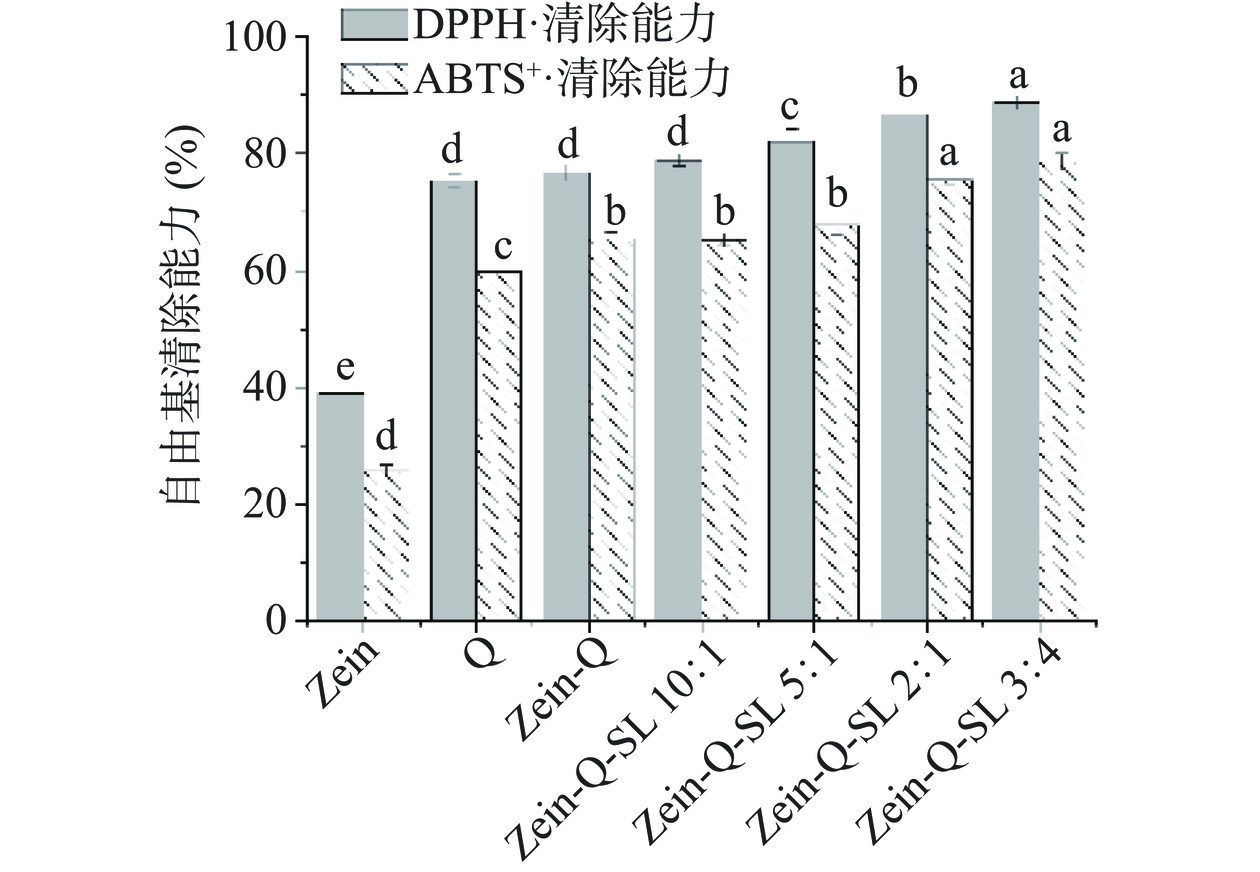
2.5 抗氧化活性分析
槲皮素具有很强的抗氧化活性,但槲皮素的溶解度低、性质不稳定,其在产品中的抗氧化活性难以发挥。本实验考察经纳米封装是否可以提高其抗氧化活性。Zein-Q-SL 复合纳米颗粒的抗氧化活性结果如图6所示。图中可以看出,Zein-Q 纳米颗粒(蛋白浓度为 2.0±0.5 mg/mL)具有清除 DPPH 自由基和 ABTS 阳离子自由基的能力,清除率分别为 76.8%±0.9% 和 65.4%±1.2%。随着槐糖脂加入,Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的抗氧化能力有一定的提高,当 Zein-Q:SL 为 3:4 时,对 DPPH 自由基和 ABTS 阳离子自由基清除率分别达到 88.8%±1.0% 和 78.6%±1.5%。可见,复合纳米颗粒提高了槲皮素的抗氧化活性。这可能是由于槐糖脂具有优越的表面性质[17],其包覆的纳米颗粒分散性好,稳定性提高,有助于其活性的发挥,同时由于槐糖脂也有一定的抗氧化活性[17,20],可能使体系呈现协同抗氧化效应。此 Zein-Q-SL 纳米颗粒作为抗氧化剂在食品中具有广泛的应用前景。
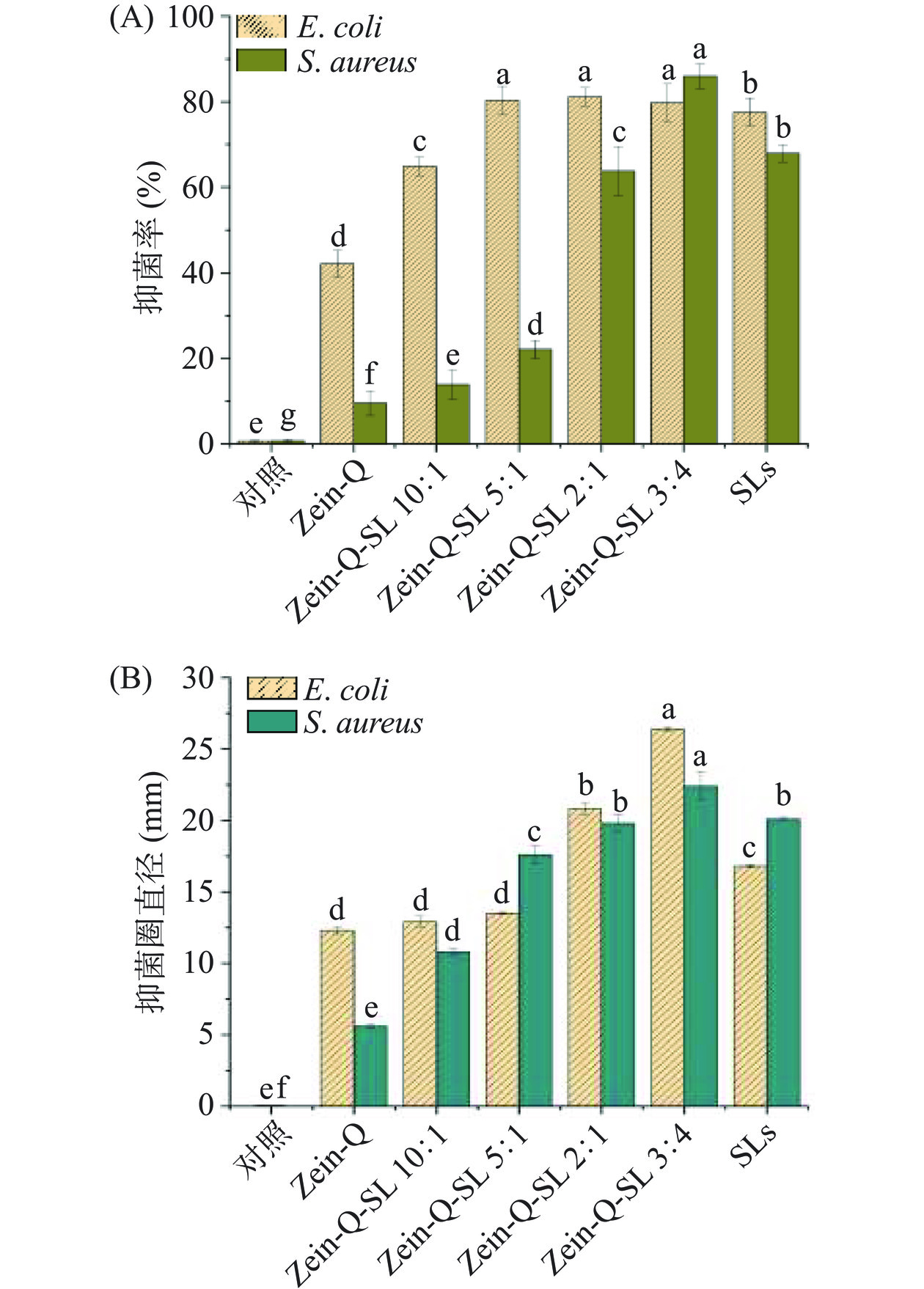
2.6 抑菌活性分析
槐糖脂具有优良的抑菌活性,作为抑菌剂或防腐剂在食品领域有潜在应用价值[31−32]。本实验采用食品常见病原菌E.coli和S. aureus作为研究对象,评价Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的抑菌活性,结果如图7所示。从图中可以看出, Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒对E.coli和S. aureus有较好的抑制作用。本实验条件下,槐糖脂对大肠杆菌的抑制率为77.5%±3.3%。Zein-Q纳米颗粒对大肠杆菌的抑制率为42.2%±3.1%,抑菌圈直径为12.3±0.3 mm,在槐糖脂的影响作用下,Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒的抑菌性能显著提升,当Zein-Q与SL比例为5:1时,复合纳米颗粒对大肠杆菌的抑制率提升至80.5%±2.1%,当Zein-Q与SL比例为3:4时,抑菌圈直径也随着逐渐增大至26.4±0.1 mm。
Zein-Q对革兰氏阳性菌S. aureus的抑菌作用较弱,与Zein-Q相比,Zein-Q-SL显示出优异的抑菌活性,当Zein-Q与SL比例为3:4时,Zein-Q-SL复合纳米颗粒对S. aureus的抑制率为85.9%±2.8%,抑菌圈直径也随着逐渐增大至22.4±0.9 mm,可见槐糖脂的添加提高了纳米颗粒的抑菌活性。胡静等[33]研究发现,槐糖脂作用于S. aureus后,使菌体出现细胞质固缩、凝集成块、空腔等现象,引起对细胞壁和细胞膜的破坏。由此可推断,槐糖脂包覆于纳米颗粒表面,其两亲性促使纳米颗粒能够与细胞结合,引起细胞壁和细胞膜结构发生改变,细菌细胞渗透性发生改变,导致细菌死亡,但具体的抑菌机制有待进一步解析。
3. 结论
玉米醇溶蛋白基纳米颗粒是多酚类化合物的优良递送系统,但其易受到加工环境的影响而降低递送性能。本研究采用生物表面活性剂槐糖脂对其进行结构修饰,发现槐糖脂通过氢键、静电作用力等作用包覆于玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗外层,形成较大的纳米颗粒结构。一方面提高了玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒的分散稳定性,使槲皮素的包封率和载药量显著提高(P<0.05),分别从25.8%±1.28%和3.98%±0.24%提高至73.6%±1.80%和7.98%±0.41%(Zein-Q:SL为3:4),另一方面使玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除率分别提高至88.8%±1.0%和78.6%±1.5%(Zein-Q:SL为3:4);此外还赋予了该纳米颗粒抑制革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性病原菌的活性。因此,经槐糖脂修饰的玉米醇溶蛋白-槲皮素纳米颗粒可作为抗氧化剂、抑菌剂等应用于食品防腐领域。本研究结果可为槐糖脂等生物表面活性调控蛋白基多酚纳米颗粒的结构和性质提供基础,也为提高槲皮素稳定性和生物利用提供了参考方法。后续可对此复合纳米颗粒的消化稳定性、细胞吸收活性等方面开展研究,以评价其在递送活性物质方面的应用潜力。
-
-
[1] 王亚茹, 袁满, 张丽, 等. 槲皮素抗氧化作用及相关机制研究进展[J]. 营养学报,2022,44(2):204−208. [WANG Yaru, YUAN Man, ZHANG Li, et al. Research process on antioxidantant actions and related mechanisms of quercetin[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2022,44(2):204−208.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0512-7955.2022.02.017 WANG Yaru, YUAN Man, ZHANG Li, et al. Research process on antioxidantant actions and related mechanisms of quercetin[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2022, 44(2): 204−208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0512-7955.2022.02.017
[2] LI Shufang, HU Tenggen, WU Hong. Fabrication of colon-targeted ethyl cellulose/gelatin hybrid nanofibers:Regulation of quercetin release and its anticancer activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,253(2):127175.
[3] SHIMUL I M, MOSHIKUR R M, NABILA F H, et al. Formulation and characterization of choline oleate-based micelles for co-delivery of luteolin, naringenin, and quercetin[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,429:136911. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136911
[4] XIE Hujun, LIU Chengzhi, GAO Jian, et al. Fabrication of Zein-lecithin-EGCG complex nanoparticles:Characterization, controlled release in simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,365:130542. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130542
[5] REN Gerui, SHI Jieyu, HUANG Sijie, et al. The fabrication of novel zein and resveratrol covalent conjugates:Enhanced thermal stability, emulsifying and antioxidant properties[J]. Food Chem,2022,374:131612. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131612
[6] 邹艳. 负载槲皮素的玉米醇溶蛋白复合纳米颗粒制备及其抗氧化活性研究[D]. 广州:广东药科大学, 2021. [ZOU Yan. Fabrication of quercetin-loaded zein composite nanoparticles:Antioxidant activity[D]. Guangzhou:Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2021.] ZOU Yan. Fabrication of quercetin-loaded zein composite nanoparticles: Antioxidant activity[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2021.
[7] 马娟娟. 基于玉米醇溶蛋白构建槲皮素输送载体的生物活性及生物利用度研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2021. [MA Juanjuan. Fabrication of zein-based delivery systems for quercetin on investigating its bioactivities and bioavailability[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2021.] MA Juanjuan. Fabrication of zein-based delivery systems for quercetin on investigating its bioactivities and bioavailability[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021.
[8] YUAN Yongkai, MA Mengjie, WANG Dongfeng, et al. A review of factors affecting the stability of zein-based nanoparticles loaded with bioactive compounds:From construction to application[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(25):7529−7545. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2047881
[9] CHENG C J, JONES O G. Stabilizing zein nanoparticle dispersions with ι-carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,69:28−35. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.022
[10] NICOLA A, AGNESE G, SILVIA V, et al. Strategies of stabilization of zein nanoparticles containing doxorubicin hydrochloride[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,243:125222−125222. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125222
[11] JONATHAN C, MARIO A, KAREM H, et al. Impact of molecular weight and deacetylation degree of chitosan on the bioaccessibility of quercetin encapsulated in alginate/chitosan-coated zein nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,242:124876−124876. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124876
[12] YUAN Yongkai, LI Hao, ZHU Junxiang, et al. Fabrication and characterization of zein nanoparticles by dextran sulfate coating as vehicles for delivery of curcumin[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,151:1074−1083. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.149
[13] 邓卓丹, 陈文学, 兰思琪, 等. 玉米醇溶蛋白-卵磷脂-槲皮素纳米颗粒的制备与抗氧化特性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(23):103−108. [DENG Zhuodan, CHEN Wenxue, LAN Siqi, et al. Preparation and antioxidant properties of zein-lecithin-quercetin nanoparticles[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(23):103−108.] DENG Zhuodan, CHEN Wenxue, LAN Siqi, et al. Preparation and antioxidant properties of zein-lecithin-quercetin nanoparticles[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(23): 103−108.
[14] DAI Lei, SUN Cuixia, LI Ruirui, et al. Structural characterization, formation mechanism and stability of curcumin in zein-lecithin composite nanoparticles fabricated by antisolvent co-precipitation[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,237:1163−1171. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.134
[15] PHAVIT W, MAGDA C, BEN D, et al. Food processing by-products as sources of hydrophilic carbon and nitrogen for sophorolipid production[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling,2022,185:106499.
[16] MA Xiaojing, WANG Tong, ZHANG Huimin, et al. Comparison of inhibitory effects and mechanisms of lactonic sophorolipid on different pathogenic bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,13:929932. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.929932
[17] 王彤. 基于槐糖脂的新型防腐保鲜用Pickering乳液的制备及功能评估[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2023. [WANG Tong. Preparation and performance evaluation of Pickering emulsion for preservative preservation based on sophorolipid[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2023.] WANG Tong. Preparation and performance evaluation of Pickering emulsion for preservative preservation based on sophorolipid[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2023.
[18] MA Enguang, CHEN Kai, SUN Liang, et al. Rapid construction of green nanopesticide delivery systems using sophorolipids as surfactants by flash nanoprecipitation[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(16):4912−4920. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00743
[19] NGUYEN B V G, NAGAKUBO T, TOYOFUKU M, et al. Synergy between sophorolipid biosurfactant and SDS increases the efficiency of P. aeruginosa biofilm disruption[J]. Langmuir,2020,36(23):6411−6420. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00643
[20] TANG Yujing, JIN Mingjie, CUI Tianyou, et al. Efficient preparation of sophorolipids and functionalization with amino acids to furnish potent preservatives[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(33):9608−9615. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03439
[21] KASTURE M, SINGH S, PATEL P, et al. Multiutility sophorolipids as nanoparticle capping agents:Synthesis of stable and water dispersible conanoparticles[J]. Langmuir,2007,23(23):11409−11412. doi: 10.1021/la702931j
[22] HUANG Cheng, HU Chunyan, SUN Gang, et al. Antimicrobial finish of cotton fabrics treated by sophorolipids combined with 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxyic acid[J]. Cellulose,2020,27(5):2859−2872. doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02925-9
[23] PENG Shengfeng, LI Zhiling, ZOU Liqiang, et al. Enhancement of curcumin bioavailability by encapsulation in sophorolipid-coated nanoparticles:An in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(6):1488−1479. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05478
[24] SINGH P K, WANI K, KAUL-GHANEKAR R, et al. From micron to nano-curcumin by sophorolipid co-processing:Highly enhanced bioavailability, fluorescence, and anti-cancer efficacy[J]. Royal Society of Chemistry,2015,5(28):22075−22075.
[25] DAI Lei, LI Ruirui, WEI Yang, et al. Fabrication of zein and rhamnolipid complex nanoparticles to enhance the stability and in vitro release of curcumin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,77:617−628. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.11.003
[26] XIAO Jie, NIAN Si, HUANG Qingrong. Assembly of kafirin/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles to enhance the cellular uptake of curcumin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,51:166−175. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.012
[27] KAYUKAWA C T M, DE OLIVEIRA M A S, KASPCHAK E, et al. Effect of tannic acid on the structure and activity of Kluyveromyces lactis β-galactosidase[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,275:346−353. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.107
[28] LI Shuangjian, LI Siyuan, GONG Minhui, et al. Development of zein/tannic acid nanoparticles as antioxidants for oxidation inhibition of blackberry seed oil emulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,403:134236. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134236
[29] PEREZ A A, CARRARA C R, SÁNCHEZ C C, et al. Interactions between milk whey protein and polysaccharide in solution[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,116(1):104−113. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.017
[30] MA Xiaojing, LI Hui, WANG Dongxue, et al. Sophorolipid production from delignined corncob residue by Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. Sophorolipid CGMCC 1576 and Cryptococcus curvatus ATCC 96219[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2014,98(1):475−483. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4856-3
[31] SRIJA P, NILOY C, ARUN KUMAR D, et al. Sophorolipids:A comprehensive review on properties and applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2023,313:102856. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.102856
[32] WANG Y, CHEN J, LIU X. A review on antimicrobial activity, anti-biofilm and synergistic effects of sophorolipids since their discovery[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology,2023,59(5):580−596. doi: 10.1134/S0003683823050174
[33] 胡静, 赵小慧, 朱春玉, 等. 槐糖脂对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌机理[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(5):33−36. [HU Jing, ZHAO Xiaohui, ZHU Chunyu, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanisms of sophorolipids against Staphyloccocus aureus[J]. Food Science,2012,33(5):33−36.] HU Jing, ZHAO Xiaohui, ZHU Chunyu, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanisms of sophorolipids against Staphyloccocus aureus[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(5): 33−36.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王喜庆,李成凤,郭丽,赵洪波,马雪,李杨,苏适,郭齐. 创新创业背景下“食品营养学”课程思政教学改革与实践. 食品与发酵科技. 2025(01): 188-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 隋晓楠,张妍,黄国,付昳丹,梁香玉,赵尚清,王思琦,杨爱峥,霍俊伟,江连洲. 省一流专业引领下“粮油加工副产物综合利用”课程创新创业元素的设计与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(13): 308-314 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李晓东,刘璐,李嘉钰,张秀秀,郑冬梅,崔立雪,张宏伟. 《乳品工艺学》课程思政教育的改革与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(19): 376-382 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 罗港. 高职院校思政元素融入Premiere课程的研究与探索. 辽宁师专学报(社会科学版). 2023(02): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 桂亚,马栎,李逸鹤,田林双. 高职院校粮食工程专业劳动教育的实践探究. 现代面粉工业. 2023(05): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 贺光祖,叶惠慧,李逢振,王治昕,魏莎,李静. 食品类专业实践教学体系化微课的创新路径. 现代畜牧科技. 2023(11): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
1. 杨攀平,李惠侠,胡亚美. 盐池滩羊肉品质特性及其潜在调控机理探讨. 草业学报. 2025(04): 223-232 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕玲燕,胡湘云,刘明君,顾国才,汪燕玲,韦明松,刘庆友,王献伟. 茉莉花渣对隆林黑山羊养分表观消化率、生长性能、屠宰性能、肉品质及血清生化指标的影响. 饲料研究. 2025(03): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘嘉东,韩晓娟,张桂杰,黄帅. 柠条青贮替代全株玉米青贮对滩羊生长性能、脂肪沉积和肉品质的影响. 动物营养学报. 2023(09): 5827-5836 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



