Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Sea Buckthorn in the Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Injury Based on Network Pharmacology
-
摘要: 目的:基于网络药理学预测沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤(Alcohol Liver Injury)的作用机制,并通过建立斑马鱼酒精性肝损伤动物模型来验证沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的功效。方法:通过中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology,TCMSP)、Uniprot数据库收集有效成分及其作用靶标,Venny2.1寻找交集靶点。通过GeneCards及OMIM数据库收集和筛选疾病靶点,STRING v12.0数据库进行PPI网络分析,PDB及PubChem进行蛋白质结构及小分子结构确认。通过Cytoscape(Version 3.9.1)软件网络图构建沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤关联网络。利用Metascape数据库对共有靶点进行基因本体(Gene Ontology,GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene,KEGG)数据库通路富集分析。通过斑马鱼实验进行功能验证:选取受精后3 d(3 dpf)野生型AB品系斑马鱼,正常组喂养于正常饲养用水,其余各组饲养于2%的无水乙醇溶液中建立酒精性肝损伤模型。沙棘组给予不同浓度的沙棘溶液,28 ℃处理2 d后,确定沙棘对酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼的最大耐受浓度(MTC)剂量,并根据MTC结果进行下一步给药,测定样品肝保护功效评价表型实验结果。结果:筛选后得到沙棘活性成分33个,主要包括槲皮素、花葵素、儿茶酸等;治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点1434个,主要包括ADH1C、CTNNB1、TGFB1等。调控这些核心靶点的信号通路主要富集在Lipid and atherosclerosis、Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis、PI3K-Akt signaling pathway等多条信号通路中。动物实验结果显示:与模型组相比,沙棘可显著降低酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼肝脏不透明值(P<0.01),改善肝脏和卵黄囊肿大(P<0.01),下调AST和ALT的活力值(P<0.001),改善肝细胞核肿大,减少肝组织脂肪空泡样变性的功效。结论:沙棘可改善酒精性肝损伤,其机制可能与改善脂肪酸氧化、细胞代谢和抑制细胞凋亡有关。Abstract: Objective: To predict the mechanism of sea buckthorn in the treatment of alcoholic liver injury based on network pharmacology, and to verify the efficacy of sea buckthorn in the treatment of alcoholic liver injury by establishing an animal model of alcoholic liver injury in zebrafish. Methods: Through the traditional chinese medicine systems pharmacology (TCMSP) and Uniprot database, the effective components and their targets were collected. Venny2.1 was used to find the intersection targets. GeneCards and OMIM databases were used to collect and screen disease targets. STRING v12.0 database was used for PPI network analysis. PDB and PubChem were used to confirm protein structure and small molecular structure. The correlation network of sea buckthorn in the treatment of alcoholic liver injury was constructed by Cytoscape (Version 3.9.1) software network diagram. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes (KEGG) database pathway enrichment analysis were performed on the common targets using the Metascape database. Functional verification was performed by zebrafish experiments: Wild-type AB strain zebrafish 3 days after fertilization (3 dpf) were selected. The normal group was fed with normal feeding water, and the other groups were fed in 2% anhydrous ethanol solution to establish an alcoholic liver injury model. Results: After screening, 33 active components of sea buckthorn were obtained, mainly including quercetin, sunflower, catechin and so on. There were 1434 potential targets for the treatment of alcoholic liver injury, including ADH1C, CTNNB1, TGFB1 and so on. The signaling pathways that regulate these core targets are mainly enriched in multiple signaling pathways such as lipid and atherosclerosis, fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. The results of animal experiments showed that sea buckthorn had the effect of reducing the opacity value of zebrafish liver in alcoholic liver injury model (P<0.01), improving the phenomenon of liver and yolk cyst enlargement (P<0.01), down-regulating the activity values of AST and ALT (P<0.001), improving the enlargement of liver nucleus and reducing the fatty vacuolar degeneration of liver tissue. Conclusion: Seabuckthorn can improve alcoholic liver injury, and its mechanism may be related to improving fatty acid oxidation, cell metabolism and inhibiting apoptosis.
-
Keywords:
- sea buckthorn /
- network pharmacology /
- alcoholic liver injury
-
酒精被公认为是导致慢性肝病的常见致病因素之一。肝脏是酒精代谢的重要器官,也是被酒精损伤的主要靶器官[1]。酒精性肝损伤(alcoholic liver injury)是慢性肝病死亡的最主要原因之一,乙醇在肝细胞中经乙醇脱氢酶代谢产生的乙醛不仅影响蛋白质的功能和DNA损伤恢复,还会诱导氧化应激、脂质蓄积和炎症反应而造成不同程度的肝损伤[2]。近年,饮酒人群数量增多,酒精性肝损伤发病人数上升,全世界超过7500万人面临与酒精有关的肝病风险,每年超过20万人死于酒精诱导的肝癌[3]。如何有效预防酒精性肝损伤是临床医学目前需要解决的问题。因此,寻找酒精性肝损伤的防治措施具有十分重要的意义[4]。
沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides L.)为胡颓子科酸刺属灌木或小乔木的成熟果实,是天然的高价值药食兼用资源,含有十分丰富的生物活性物质,有着“天然维生素宝库”的美誉[5]。沙棘中富含黄酮类、类胡萝卜素、甾醇类、生育酚、脂类等多种化合物[6],具有抗菌、消炎、调节血压、抗氧化、抗癌等多种作用[7]。沙棘中熊果酸通过降低肝脏和血浆中甘油三脂、胆固醇水平,降低脂质积累,改善血流流变学,对动脉粥样硬化起到防治作用[8−9]。沙棘中熊果酸可通过抑制NOX4/NLRP3炎症小体通路,减少细菌失衡逆转肝纤维化,并通过抑制胱天蛋白酶3减少肝细胞凋亡而减轻酒精诱导的肝损伤[10−11],对化学性肝损伤、药物性肝损伤及实验性肝癌具有保护作用[12],同时还具有安全有效、毒性低的特点[13]。本研究拟通过网络药理学预测沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在作用靶点及通路,利用斑马鱼的疾病生理、基因组与人类相似等优点,进行斑马鱼动物实验验证沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的疗效。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
受精后3 d(3 dpf)的斑马鱼270尾 由杭州环特生物科技股份有限公司提供,动物许可证号:SYXK(浙)2012-0171,饲养于28 ℃的养鱼用水中(水质:每1L反渗透水中加入200 mg速溶海盐,电导率为450~550 μS/cm;pH为6.5~8.5;硬度为50~100 mg/L CaCO3),饲养管理符合国际AAALAC认证(认证编号:001458)的要求;不同批次的沙棘粉末(SJ1、SJ2、SJ3、SJ4、SJ5、SJ6样) 广州市益尔乐生物科技有限公司提供,批号为200601、200602、200603、200604、200605、200606,湖南中医药大学药学院中药鉴定学教研室主任龚力民鉴定为胡颓子科植物中国沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi)的果实;无水乙醇、氨水、二甲苯 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;二甲基亚砜 德国默克生物科技公司;甲基纤维素 上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司;氯化钠注射液 杭州民生药业有限公司;谷丙转氨酶/ALT/GPT测试盒、谷草转氨酶/AST/GOT测试盒 南京建成生物研究所;4%组织细胞固定液 北京索莱科技有限公司;伊红染色液 诚汐医药科技有限公司;盐酸 分析纯,西陇化工有限公司;中性树胶 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;PBS 北京兰杰柯科技有限公司;软蜡、硬蜡 上海华永石蜡有限公司。
SZX7型解剖显微镜、CX31型生物显微镜 日本OLYMPUS公司;VertA1型CCD相机 上海土森视觉科技有限公司;CP214型精密天平 美国OHAUS公司;ST8型高速冷冻离心机 德国Thermo Fisher公司;FM70型雪花制冰机 北京长流科学仪器有限公司;KD-3368AM型切片机 金华科迪医疗器械有限公司;HHS-11-4型电子恒温不锈钢水浴锅 上海康路仪器销售有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 沙棘活性成分及靶点筛选
基于中药药理信息挖掘平台TCMSP(https://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php)及文献查阅,对沙棘的活性成分进行检索,依据各成分的毒药物动力学具体参数,类药性(DL)≥0.18,口服生物利用度(OB值)≥30%对检测结果进行筛选,并获得相应的靶点名[14]。依据蛋白序列和功能信息资源库UniProt(https:/www.uniprot.org),获得靶点对应的基因名[15]。
1.2.2 疾病靶点的获取与筛选
以“酒精性肝损伤”(Alcoholic Liver Injury)为关键词通过OMIM,GeneCards疾病数据库检索靶点[16],其中通过GeneCards数据库,筛选出酒精性肝损伤relevance score≥10的靶点。
1.2.3 “药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”的网络构建
以药物、活性成分与治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点,建立“药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”Excel文件,并导入Cytoscape 3.9.1构建“药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”网络图,以展示其交互作用关系[17−21]。
1.2.4 “药物-疾病靶点”PPI网络构建
以药物、活性成分与治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点,建立“药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”Excel文件,并导入Cytoscape 3.9.1构建“药物-疾病靶点”网络图,以展示其交互作用关系[22]。
1.2.5 GO功能及KEGG通路的富集分析
将沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点上传至Metascape平台,设定P<0.01,开展GO功能分析及KEGG信号通路的富集分析,并对其结果进行可视化分析[23−24]。
1.2.6 动物实验验证
1.2.6.1 实验分组、模型制备
随机把斑马鱼分为正常对照组、模型对照组、阳性对照组、沙棘实验组。参考戴文聪等[25]的研究,将斑马鱼除正常对照组外,其余各实验组均喂养于2%无水乙醇中,28 ℃处理2 d,建立斑马鱼酒精性肝损伤模型,正常对照组用正常养鱼用水处理斑马鱼。
1.2.6.2 最大耐受浓度(MTC)剂量实验给药
随机选取960尾受精后3 d(3 dpf)野生型AB品系斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔均处理30尾斑马鱼,分别水溶给予“1~6”样的沙棘样品使其饲养用水中沙棘浓度分别为125、250、500、1000、2000 μg/mL,同时设置正常对照组和模型组,除正常对照组外,其余各实验组均喂养于2%无水乙醇中,28 ℃处理2 d后,测定样品对模型斑马鱼的MTC[26]。
1.2.6.3 肝保护功效评价实验给药
随机选取270尾受精后3 d(3 dpf)野生型AB品系斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔均处理30尾斑马鱼,阳性药物组给予美他多辛使其饲养用水中美他多辛浓度为149 μg/mL,沙棘组(“1~6样”),每样均给予沙棘粉末使其饲养用水中沙棘浓度分别为250 μg/mL。除正常对照组外,其余各实验组均喂养于2%无水乙醇中,28 ℃处理2 d后,每个实验组随机选取10尾斑马鱼置于解剖显微镜下拍照,用NIS-Element D 3.20高级图像处理软件分析并采集数据,分析肝脏不透明平均值、肝脏面积和卵黄囊面积,以上述指标的统计学分析结果评价样品的肝保护功效。统计学结果采用mean±SE表示。用SPSS26.0软件进行统计学分析,P<0.05表明差异具有统计学意义[27]。
1.2.6.4 AST和ALT活力检测实验给药
随机选取270尾受精后3 d(3 dpf)野生型AB品系斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔均处理30尾斑马鱼,阳性药物组给予美他多辛使其饲养用水中美他多辛浓度为149 μg/mL,沙棘组(“1~6样”),每样均给予沙棘粉末使其饲养用水中沙棘浓度分别为250 μg/mL。除正常对照组外,其余各实验组均喂养于2%无水乙醇中。28 ℃处理2 d后,设置三个平行实验,每个实验组随机选取10尾斑马鱼,加入适量生理盐水匀浆上清液,分别用ALT测试盒和AST试剂盒检测各实验组ALT和AST活力,以上述指标的统计学分析结果评价样品的肝保护功效,并采用mean±SE形式表示[28]。
1.2.6.5 样品肝保护功效评价病理切片实验
用4%组织细胞固定液将斑马鱼固定,经系列脱水-包埋-切片-染色等步骤,对斑马鱼进行组织病理HE染色分析。通过肝脏组织病理分析,评价样品对斑马鱼肝脏结构的影响[29]。
1.3 数据处理
使用SPSS 26.0软件进行统计学分析,P<0.05表明差异具有统计学意义,Graphpad Prism9.0绘图,相关结果以柱形图的形式呈现。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 沙棘活性成分与预测靶点
通过TCMSP数据库及文献调研筛选中药的活性成分,汇总去重得到沙棘活性成分33个,主要成分有槲皮素、花葵素、儿茶酸、异鼠李素、豆甾醇等。依据蛋白序列和功能信息资源数据库UniProt,获得靶点对应的基因名,去重后最终得到活性成分对应靶点202个。
2.2 疾病靶点的预测
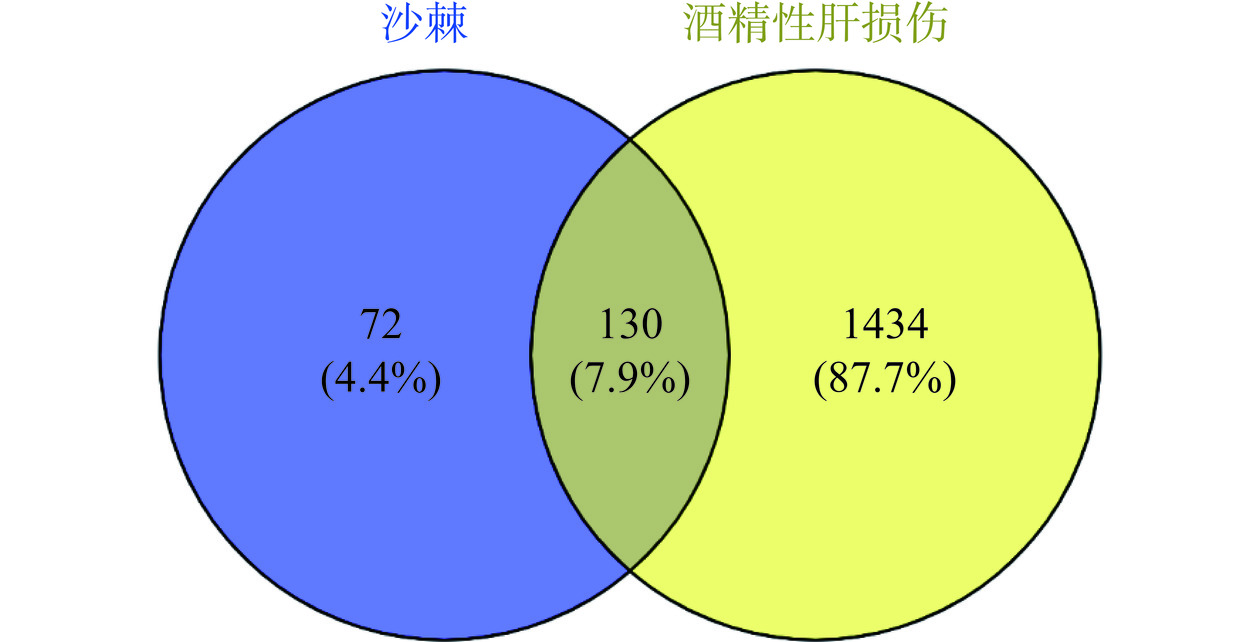
通过OMIM和GeneCard疾病数据库收集酒精性肝损伤疾病的相关靶点。以relevance score≥10为筛选条件,去除不符合条件的靶点,筛选出酒精性肝损伤相关靶点1434个。将疾病的靶点与沙棘活性成分靶点进行匹配,最终得到沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点130个,通过韦恩图可视化展示,如图1所示。
2.3 “药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”网络构建
通过Cytoscape 3.9.1软件,构建沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的“药物-活性成分-潜在靶点”网络图。共有122个节点,369条边,如图2所示。图中粉红色圆节点代表活性成分,橙色节点代表酒精性肝损伤相关靶点。该网络体现了沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤具有多成分、多靶点的特点。通过对沙棘成分分析,槲皮素、山奈酚、谷甾醇、异鼠李素结合靶点较多,可能是沙棘发挥药效作用的物质基础;沙棘活性成分和酒精性肝损伤连线排名靠前的有PIK3CG、CXCL8、CASP3、PRSS1、GABRA1等。
2.4 PPI网络构建
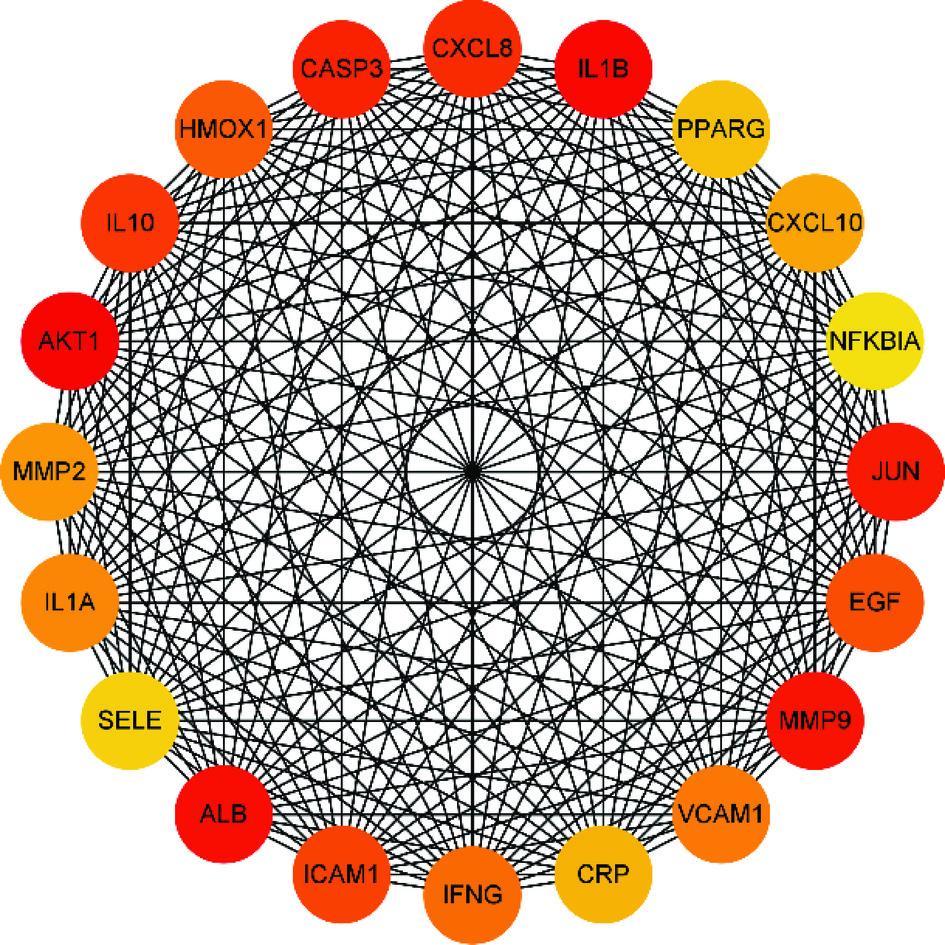
PPI网络结果显示共有103个节点,有2762条边,平均节点度为26.8。其中网络节点代表蛋白质,边缘代表蛋白质与蛋白质的结合,节点的连线越多代表蛋白等级越高,边缘连线越多代表蛋白关联度越大,其中关联度排名前二十蛋白靶点如图3所示,AKT1、IL1B、ALB、MMP9、JUN等节点颜色深,说明这些靶点可能在酒精性肝损伤的发展中起关键作用。
2.5 酒精性肝损伤靶点的GO和KEGG富集分析
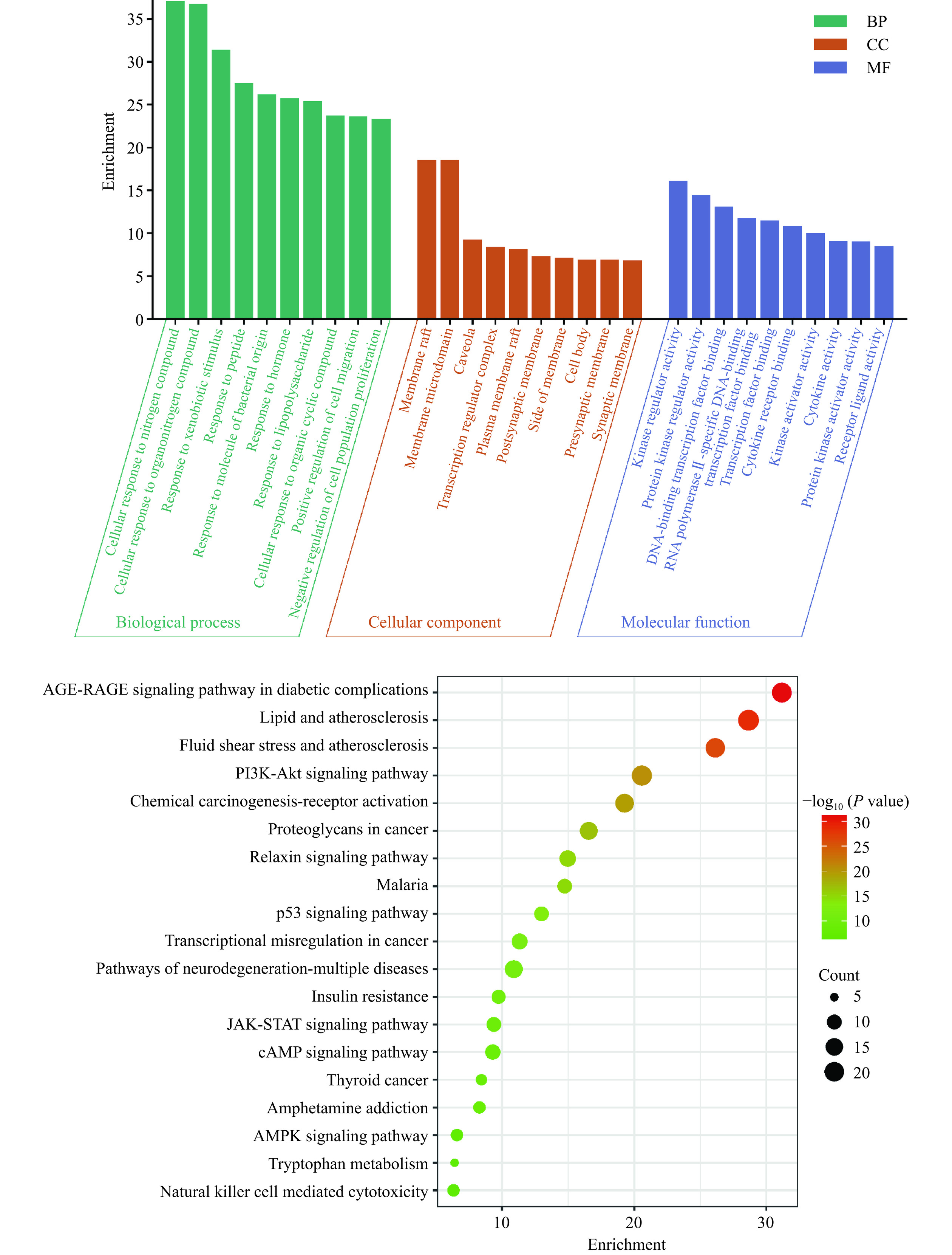
使用Metascape数据库对酒精性肝损伤靶点进行生物信息学分析,依据P<0.01筛选出排名靠前10的生物学过程、细胞组分、分子功能并进行可视化分析,结果见图4。在沙棘潜在抗炎靶点主要富集在细胞对氮化合物的反应、对外来刺激的反应。在GO-CC中主要参与膜囊泡、膜微区、细胞膜穴位内陷等。在GO-MF中主要为激酶调节剂活性、蛋白激酶调节剂活性、DNA结合转录因子结合。同时利用Metascape数据库将沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点进行KEGG通路分析,共获得20条信号通路,根据P值排序靠前的通路有Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity、Tryptophan metabolism、AMPK signaling pathway等通路,主要与脂肪酸氧化、细胞代谢有关,详见图4所示。
2.6 活性成分-交集靶点-通路网络的构建
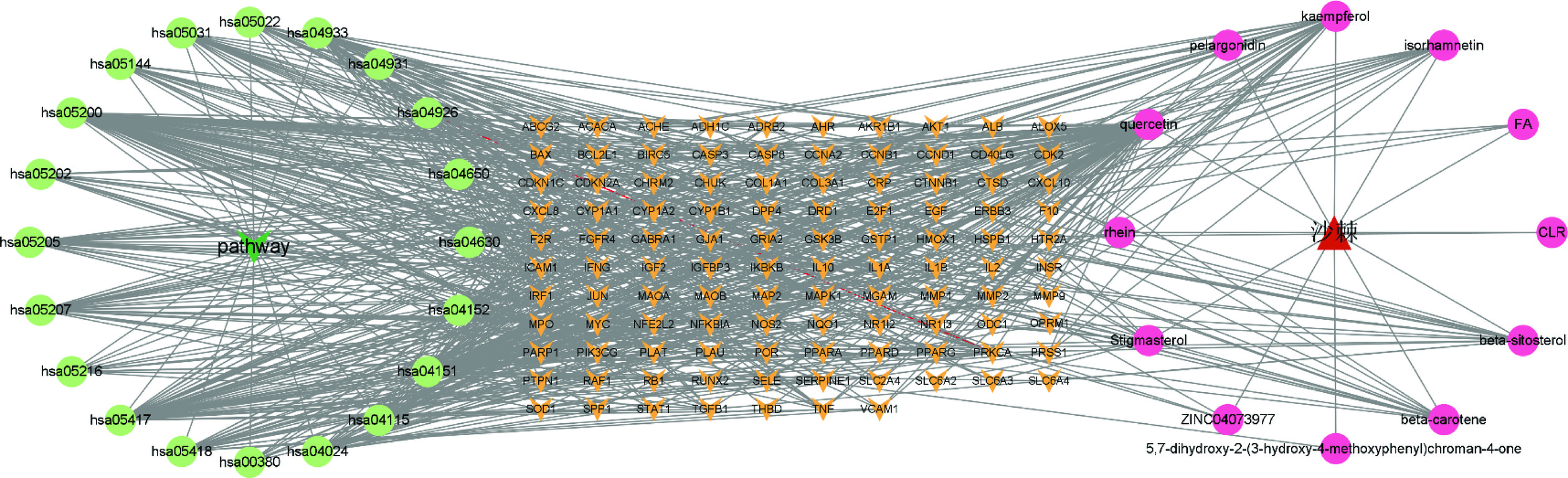
将筛选出的排名靠前的可能与酒精性肝损伤有关的通路,与沙棘的活性成分、作用靶点相结合共同构建活性成分-交集靶点-通路网络。所构建网络包括12个成分节点,107个靶基因节点,20条通路及671条边,见图5所示。图中粉红色圆形代表与酒精性肝损伤相关的沙棘活性成分,橙色V形节点代表作用靶点,绿色圆形代表与酒精性肝损伤相关通路。由图可知,沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的活性成分有12个,主要是槲皮素、山奈酚、谷甾醇、异鼠李素等,活性成分主要作用于Pathways in cancer、Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity、Pathways in cancer、Lipid and atherosclerosis、PI3K-Akt signaling pathway、Chemical carcinogenesis-rece等通路,前20条通路上富集的基因,其中Pathways in cancer通路对应的基因数最多为62个。
2.7 酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼MTC检测结果
正常对照组中斑马鱼游动正常,无明显异常情况发生;模型对照组中斑马鱼出现静止不动,没有活力症状;沙棘组中当沙棘浓度为125和250 μg/mL时,斑马鱼表现为游动正常,无明显异常情况发生、当沙棘浓度为500和1000 μg/mL时,斑马鱼表现为静止不动,没有活力,并出现部分死亡的现象、当沙棘浓度为2000 μg/mL时,斑马鱼全部死亡。因此得到沙棘对酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼的最大浓度耐受剂量(MTC)为250 μg/mL,详见表1。
表 1 样品肝保护功效浓度摸索实验结果(n=30)Table 1. Results of groping experiment on liver protection efficacy concentration of sample (n=30)组别 浓度(μg/mL) 死亡数(尾) 死亡率(%) 表现 正常对照组 − 0 0 游动正常 模型对照组 − 0 0 静止不动,没有活力 125 0 0 游动正常 250 0 0 游动正常 沙棘组 500 0 0 静止不动,没有活力 1000 3 10 静止不动,没有活力 2000 30 100 − 2.8 样品肝保护功效评价表型实验结果
实验结果如表2所示,“SJ1~6”组的斑马鱼的肝脏不透明度平均值相较于模型组有所降低且与模型组相比均具有显著性差异,说明“SJ1~6”沙棘具有改善肝脏透明度,改善酒精性肝损伤功效。“SJ2、SJ4、SJ6”沙棘组的斑马鱼肝脏面积相较于模型组有所降低且与模型组相比均具有显著性差异,肝脏肿大情况有所缓解,“SJ1、SJ3、SJ5”肝脏面积接近于模型组,数据与模型组相比无显著性差异,说明“SJ2、SJ4、SJ6”具有改善肝脏肿大功效。“SJ3、SJ4、SJ5、SJ6”沙棘均具有卵黄囊吸收延迟改善功效,“SJ1、SJ2”沙棘不具有卵黄囊吸收延迟改善功效。其样品处理后斑马鱼肝保护功效评价图如下图6所示。
表 2 样品肝保护功效评价表型实验结果(n=10)Table 2. Phenotypic experimental results of sample liver protection efficacy evaluation (n=10)组别 浓度
(μg/mL)肝脏不透明度
平均值肝脏面积 卵黄囊面积 正常对照组 − 0.258±0.008*** 33424±2081*** 27596±3476*** 模型对照组 − 0.333±0.010 56623±4391 56220±10606 美他多辛组 149 0.273±0.006*** 43711±2484*** 28766±3631*** SJ1 250 0.295±0.009*** 57740±2472* 63845±11267* SJ2 250 0.273±0.005*** 50165±2458*** 56114±13356 SJ3 250 0.284±0.004*** 58064±2907* 45855±9961* SJ4 250 0.283±0.003*** 53297±3187* 28463±6233*** SJ5 250 0.291±0.005*** 56257±3150 48801±8956* SJ6 250 0.287±0.002*** 51529±2977** 25266±4675* 注:与模型对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,表3同。 2.9 样品肝保护功效评价AST和ALT检测结果
检测结果如表3所示,“SJ1、SJ2、SJ3、SJ5、SJ6样”沙棘组的斑马鱼的组织中AST活力相比于模型对照组活力降低,而且数据相比于模型组具有显著性差异(P<0.001),说明“SJ1、SJ2、SJ3、SJ5、SJ6样”具有降低酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼体内AST活力功效作用,“SJ4样”降低酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼体内AST活力功效不明显。“SJ1~SJ6样”沙棘组的斑马鱼中的组织中ALT活力相比于模型对照组活力降低,而且数据相比于模型组具有显著性差异(P<0.001),说明“SJ1~SJ6样”沙棘具有降低酒精性肝损伤模型斑马鱼体内ALT活力功效作用。
表 3 样品肝保护功效评价AST和ALT检测结果Table 3. Evaluation of liver protection efficacy of samples AST and results of ALT组别 浓度(μg/mL) 组织中AST活力
(U/gprot)组织中ALT活力
(U/gprot)正常对照组 − 70.0±1.81*** 8.75±0.474*** 模型对照组 − 78.0±0.681 12.1±0.129 美他多辛组 149 61.3±3.20*** 8.21±1.01*** SJ1 250 65.2±6.82*** 8.17±0.819*** SJ2 250 54.5±3.87*** 8.37±0.064*** SJ3 250 62.2±0.833*** 7.42±0.692*** SJ4 250 79.7±4.62 5.56±0.646*** SJ5 250 59.7±4.27*** 6.42±0.156*** SJ6 250 66.3±2.46*** 10.7±0.181*** 2.10 斑马鱼肝脏组织病理切片实验结果
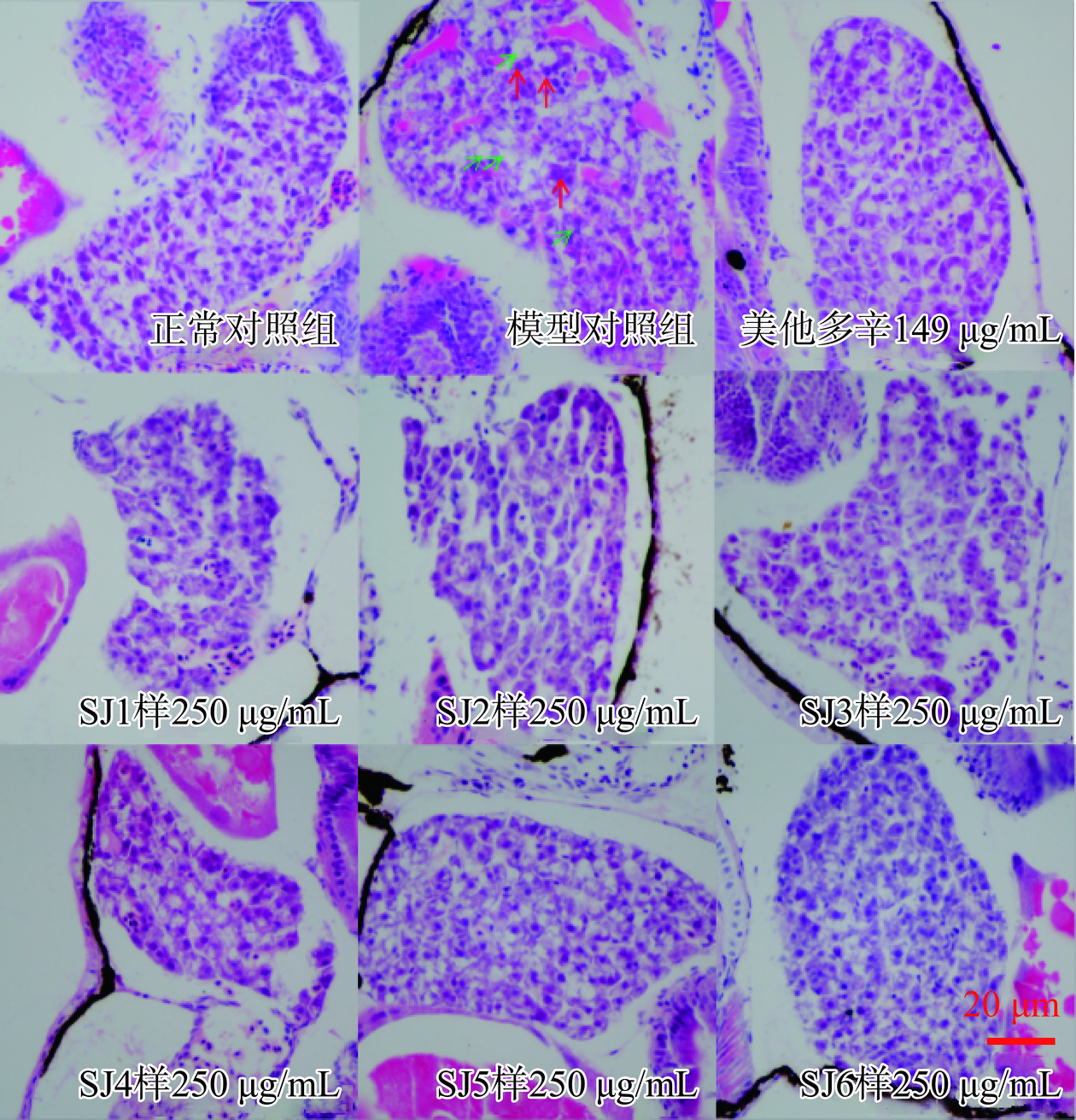
斑马鱼肝脏组织病理切片结果如图7所示,通过HE染色发现,正常对照组斑马鱼肝细胞核规则清晰,肝细胞结构正常,边缘清晰。模型对照组斑马鱼肝细胞结构模糊、肝细胞核肿大,肝组织出现脂肪空泡样变性,表示建模成功。阳性对照美他多辛组斑马鱼肝细胞较模型组清晰,肝细胞核肿大减少,肝组织脂肪空泡样变性减少,表明美他多辛对酒精引起的斑马鱼肝损伤有改善功效。“SJ1~SJ6样”沙棘组斑马鱼肝细胞结构较模型对照组清晰,肝细胞核肿大减少,肝组织脂肪空泡样变性减少,表明“SJ1~SJ6样”沙棘对酒精引起的斑马鱼损伤有改善功效。
3. 讨论
酗酒是一个全球性健康问题,尽管目前对酒精肝损伤的病理和发病机制研究取得了重大进展,但是酒精性肝损伤的许多特征仍然未确定,需要进一步深入研究[30]。有文献表明沙棘总黄酮具有肝脏保护作用,可明显降低损伤小鼠血清中碱性磷酸酶、谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶和MDA含量,提高肝脏过氧化物酶和超氧化物歧化酶活性[31];沙棘多糖通过降低扑热息痛诱导的AST和ALT水平,抑制TLR4和p-JNK表达,降低TNF-α和IL-6水平,对扑热息痛诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤组织发挥保护作用[32];沙棘多酚类成分对CCl4诱导的大鼠肝脏损伤液具有保护活性[33];沙棘叶提取物对醋酸铅致中毒大鼠的肝脏损伤具有保护作用[34];沙棘中熊果酸对酒精性肝损伤具有改善作用,其机制可能与调控肝细胞凋亡的关键蛋白Bcl-2、Bax、Cleaved caspase-3的表达水平有关[35]。
本研究通过网络药理学筛选活性成分,预测沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤的潜在靶点和潜在通路。结果显示,沙棘中槲皮素、山奈酚、谷甾醇、异鼠李素等活性成份作用于HSPB1、PPARG、CASP8、NOS2、PIK3CG、CXCL8、CASP3等信号靶点,从信号通路KEGG富集显示分析,沙棘治疗酒精性肝损伤主要涉及Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity、Tryptophan metabolism、AMPK signaling pathway等通路,通过改善脂肪酸氧化、细胞代谢和抑制细胞凋亡而改善酒精性肝损伤。
4. 结论
通过建立酒精性肝损伤的斑马鱼动物模型,并用沙棘粉末进行喂养,发现沙棘具有降低酒精性肝损伤斑马鱼模型的肝脏透明度,改善肝脏肿胀情况,改善卵黄囊吸收延迟的作用。此外还发现沙棘能降低酒精性肝损伤斑马鱼模型体内AST和ALT活力值。从斑马鱼肝脏HE染色切片图发现沙棘能使酒精性肝损伤斑马鱼模型肝细胞核肿大程度减少,肝组织脂肪空泡样变性程度减少,但本实验未对网络药理学预测的蛋白靶点和通道进行验证,这将在后续实验中继续研究。本研究对治疗酒精性肝损伤的药物开发提供了初步的理论基础,并为后续进一步的实验研究及临床应用提供依据。
-
表 1 样品肝保护功效浓度摸索实验结果(n=30)
Table 1 Results of groping experiment on liver protection efficacy concentration of sample (n=30)
组别 浓度(μg/mL) 死亡数(尾) 死亡率(%) 表现 正常对照组 − 0 0 游动正常 模型对照组 − 0 0 静止不动,没有活力 125 0 0 游动正常 250 0 0 游动正常 沙棘组 500 0 0 静止不动,没有活力 1000 3 10 静止不动,没有活力 2000 30 100 − 表 2 样品肝保护功效评价表型实验结果(n=10)
Table 2 Phenotypic experimental results of sample liver protection efficacy evaluation (n=10)
组别 浓度
(μg/mL)肝脏不透明度
平均值肝脏面积 卵黄囊面积 正常对照组 − 0.258±0.008*** 33424±2081*** 27596±3476*** 模型对照组 − 0.333±0.010 56623±4391 56220±10606 美他多辛组 149 0.273±0.006*** 43711±2484*** 28766±3631*** SJ1 250 0.295±0.009*** 57740±2472* 63845±11267* SJ2 250 0.273±0.005*** 50165±2458*** 56114±13356 SJ3 250 0.284±0.004*** 58064±2907* 45855±9961* SJ4 250 0.283±0.003*** 53297±3187* 28463±6233*** SJ5 250 0.291±0.005*** 56257±3150 48801±8956* SJ6 250 0.287±0.002*** 51529±2977** 25266±4675* 注:与模型对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,表3同。 表 3 样品肝保护功效评价AST和ALT检测结果
Table 3 Evaluation of liver protection efficacy of samples AST and results of ALT
组别 浓度(μg/mL) 组织中AST活力
(U/gprot)组织中ALT活力
(U/gprot)正常对照组 − 70.0±1.81*** 8.75±0.474*** 模型对照组 − 78.0±0.681 12.1±0.129 美他多辛组 149 61.3±3.20*** 8.21±1.01*** SJ1 250 65.2±6.82*** 8.17±0.819*** SJ2 250 54.5±3.87*** 8.37±0.064*** SJ3 250 62.2±0.833*** 7.42±0.692*** SJ4 250 79.7±4.62 5.56±0.646*** SJ5 250 59.7±4.27*** 6.42±0.156*** SJ6 250 66.3±2.46*** 10.7±0.181*** -
[1] BARAK A J, BECKENHAUER H C, TUMA D J. Methionine synthase:A possible prime site of the ethanolic lesion in liver[J]. Alcohol,2002,26(2):65−67. doi: 10.1016/S0741-8329(01)00201-4
[2] ZOU S P, WANG Y F, ZHOU Q, et al. Protective effect of kinsenoside on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia,2019,29(5):637−643. doi: 10.1016/j.bjp.2019.06.006
[3] XIAO J, WANG F, WONG N K, et al. Epidemiological realities of alcoholic liver injury:global burden, research trends, and therapeutic promise[J]. Gene Expression- The Journal of Liver Research,2020,20(2):105−118. doi: 10.3727/105221620X15952664091823
[4] 叶敬榕, 林彦, 段涵怡, 等. 天然药食单体防治酒精性肝损伤的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2023,39(10):2476−2484. [YE Jingrong, LIN Yan, DUAN Hanyi, et al. Research progress of natural medicinal and edible monomers in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatobiliary Disease,2023,39(10):2476−2484.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.10.029 YE Jingrong, LIN Yan, DUAN Hanyi, et al. Research progress of natural medicinal and edible monomers in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatobiliary Disease, 2023, 39(10): 2476−2484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.10.029
[5] 王宁宁, 郑文惠, 张凯雪, 等. 沙棘的化学成分、药理作用研究进展及其质量标志物的预测分析[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(21):5522−5532. [WANG Ningning, ZHENG Wenhui, ZHANG Kaixue, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of sea buckthorn and predictive analysis of its quality markers[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,46(21):5522−5532.] WANG Ningning, ZHENG Wenhui, ZHANG Kaixue, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of sea buckthorn and predictive analysis of its quality markers[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 46(21): 5522−5532.
[6] 丁肇俊, 叶健文, 马佳琪, 等. 沙棘叶化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 世界中医药,2023,18(5):714−720. [DING Zhaojun, YE Jianwen, MA Jiaqi, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of sea buckthorn leaves[J]. World Chinese Medicine,2023,18(5):714−720.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.05.023 DING Zhaojun, YE Jianwen, MA Jiaqi, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of sea buckthorn leaves[J]. World Chinese Medicine, 2023, 18(5): 714−720. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.05.023
[7] 王欣欣, 陈小艳, 张文莲, 等. 蒙药沙棘概况及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国民族医药杂志,2022,28(11):51−54. [WANG Xinxin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHANG Wenlian, et al. Research progress on the general situation and pharmacological effects of Mongolian medicine seabuckthorn[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnic Medicine,2022,28(11):51−54.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6810.2022.11.020 WANG Xinxin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHANG Wenlian, et al. Research progress on the general situation and pharmacological effects of Mongolian medicine seabuckthorn[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnic Medicine, 2022, 28(11): 51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6810.2022.11.020
[8] 梁奎英, 初霞. 熊果酸对肝细胞胆固醇代谢的影响[J]. 医药导报,2017,36(1):9−12. [LIANG Kuiying, CHU Xia. Effects of ursolic acid on cholesterol metabolism in hepatocytes[J]. Pharmaceutical Review,2017,36(1):9−12.] LIANG Kuiying, CHU Xia. Effects of ursolic acid on cholesterol metabolism in hepatocytes[J]. Pharmaceutical Review, 2017, 36(1): 9−12.
[9] 杨晓龙. 熊果酸对动脉粥样硬化大鼠血脂和血液流变学的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2018,16(11):1509−1512. [YANG Xiaolong. Effects of ursolic acid on blood lipids and hemorheology in atherosclerotic rats[J]. Journal of Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,2018,16(11):1509−1512.] doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2018.11.011 YANG Xiaolong. Effects of ursolic acid on blood lipids and hemorheology in atherosclerotic rats[J]. Journal of Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2018, 16(11): 1509−1512. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2018.11.011
[10] LIU Q, NIE Y, ZHANG W, et al. Ursolic acid reverses liver fibrosis by inhibiting NOX4/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways and bacterial dysbiosis[J]. Gut Microbes,2021,13:1972746. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1972746
[11] MA X Y, ZHANG M, FANG G, et al. Ursolic acid reduces hepatocellular apoptosis and alleviates alcohol-induced liver injury via irreversible inhibition of CASP3 in vivo[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin,2021,42(7):1101−1110. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00534-y
[12] 张男男, 戈娜. 熊果酸对实验性肝损伤的保护作用研究进展[J]. 华夏医学,2018,31(4):173−177. [ZHANG Nannan, GE na. Research progress on the protective effect of ursolic acid on experimental liver injury[J]. Huaxia Medicine,2018,31(4):173−177.] ZHANG Nannan, GE na. Research progress on the protective effect of ursolic acid on experimental liver injury[J]. Huaxia Medicine, 2018, 31(4): 173−177.
[13] 包艳红, 王强, 张文龙, 等. 沙棘熊果酸通过调节线粒体-细胞色素c抑制酒精性肝病大鼠模型肝细胞凋亡的作用分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2023,39(7):1617−1626. [BAO Yanhong, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Wenlong, et al. Analysis of the effect of seabuckthorn ursolic acid on inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis in a rat model of alcoholic liver disease by regulating mitochondria-cytochrome c[J]. Clinical Journal of Hepatobiliary Diseases,2023,39(7):1617−1626.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.07.016 BAO Yanhong, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Wenlong, et al. Analysis of the effect of seabuckthorn ursolic acid on inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis in a rat model of alcoholic liver disease by regulating mitochondria-cytochrome c[J]. Clinical Journal of Hepatobiliary Diseases, 2023, 39(7): 1617−1626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.07.016
[14] 吕晓飞, 蒋楠, 彭诚. 以网络药理学为基础探讨黄芩-厚朴治疗龋病的作用机制(英文)[J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版),2023,56(5):43−51. [LÜ Xiaofei, JIANG Nan, PENG Cheng. To explore the mechanism of scutellaria baicalensis-magnolia officinalis in the treatment of dental caries based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Nankai University (Natural Science Edition),2023,56(5):43−51.] LÜ Xiaofei, JIANG Nan, PENG Cheng. To explore the mechanism of scutellaria baicalensis-magnolia officinalis in the treatment of dental caries based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Nankai University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 56(5): 43−51.
[15] 范尧夫, 许娟, 孙洪平, 等. 基于网络药理学和动物实验探讨葛根芩连汤治疗2型糖尿病的作用[J]. 中成药,2023,45(10):3468−3475. [FAN Yaofu, XU Juan, SUN Hongping, et al. To explore the effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on type 2 diabetes based on network pharmacology and animal experiments[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine,2023,45(10):3468−3475.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.054 FAN Yaofu, XU Juan, SUN Hongping, et al. To explore the effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on type 2 diabetes based on network pharmacology and animal experiments[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine, 2023, 45(10): 3468−3475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.054
[16] 周颖东, 张梦娴, 王青玲, 等. 基于网络药理学和实验验证探讨补肾活血汤治疗中枢性老年性聋的机制[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2023,34(10):1398−1408. [ZHOU Yingdong, ZHANG Mengxian, WANG Qingling, et al. To explore the mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in the treatment of central presbycusis based on network pharmacology and experimental verification[J]. New Chinese Medicine and Clinical Pharmacology,2023,34(10):1398−1408.] ZHOU Yingdong, ZHANG Mengxian, WANG Qingling, et al. To explore the mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in the treatment of central presbycusis based on network pharmacology and experimental verification[J]. New Chinese Medicine and Clinical Pharmacology, 2023, 34(10): 1398−1408.
[17] 刘涛, 嵇晶, 王令充, 等. 基于LC-MS分析及网络药理学研究探讨多花黄精改善炎性疲劳的效应机制[J]. 南京中医药大学学报,2023(9):879−887. [LIU Tao, JI Jing, WANG Lingchong, et al. To explore the mechanism of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in improving inflammatory fatigue based on LC-MS analysis and network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023(9):879−887.] LIU Tao, JI Jing, WANG Lingchong, et al. To explore the mechanism of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in improving inflammatory fatigue based on LC-MS analysis and network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023(9): 879−887.
[18] 许彬洁, 孙绪光, 赵颀涵, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨赤芍抗血吸虫病及肝纤维化的作用机制[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2023,39(9):169−176,218. [XU Binjie, SUN Xuguang, ZHAO Qihan, et al. To explore the mechanism of anti-schistosomiasis and liver fibrosis of Radix Paeoniae Rubra based on network pharmacology[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023,39(9):169−176,218.] XU Binjie, SUN Xuguang, ZHAO Qihan, et al. To explore the mechanism of anti-schistosomiasis and liver fibrosis of Radix Paeoniae Rubra based on network pharmacology[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 39(9): 169−176,218.
[19] 李丁艾, 孙兆泉, 尚军. 基于数据挖掘和网络药理学探讨川贝母治疗肺系疾病的核心中药和机制[J]. 科学技术与工程,2023,23(27):11550−11561. [LI Dingai, SUN Zhaoquan, SHANG Jun. To explore the core traditional Chinese medicine and mechanism of Fritillariae Cirrhosae Bulbus in the treatment of lung diseases based on data mining and network pharmacology[J]. Science and Technology and Engineering,2023,23(27):11550−11561.] doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.27.11550 LI Dingai, SUN Zhaoquan, SHANG Jun. To explore the core traditional Chinese medicine and mechanism of Fritillariae Cirrhosae Bulbus in the treatment of lung diseases based on data mining and network pharmacology[J]. Science and Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(27): 11550−11561. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.27.11550
[20] 孙月梅, 韩星宇, 马江红, 等. 槟榔多酚对大鼠高原运动性疲劳的保护作用和网络药理学研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2023,39(10):1966−1972. [SUN Yuemei, HAN Xingyu, MA Jianghong, et al. Protective effect of areca nut polyphenols on exercise-induced fatigue in rats at high altitude and its network pharmacology[J]. China Pharmacology Bulletin,2023,39(10):1966−1972.] doi: 10.12360/CPB202208047 SUN Yuemei, HAN Xingyu, MA Jianghong, et al. Protective effect of areca nut polyphenols on exercise-induced fatigue in rats at high altitude and its network pharmacology[J]. China Pharmacology Bulletin, 2023, 39(10): 1966−1972. doi: 10.12360/CPB202208047
[21] 岳栋芳, 李彩霞, 官敏, 等. 基于网络药理学从线粒体自噬途径探讨八味沉香散抗缺血性心脏病的作用机制[J]. 中国药理学通报,2023,39(10):1957−1965. [YUE Dongfang, LI Caixia, GUAN Min, et al. Based on network pharmacology, the mechanism of Bawei Chenxiang Powder against ischemic heart disease was explored from the mitophagy pathway[J]. Chinese Pharmacology Bulletin,2023,39(10):1957−1965.] doi: 10.12360/CPB202301008 YUE Dongfang, LI Caixia, GUAN Min, et al. Based on network pharmacology, the mechanism of Bawei Chenxiang Powder against ischemic heart disease was explored from the mitophagy pathway[J]. Chinese Pharmacology Bulletin, 2023, 39(10): 1957−1965. doi: 10.12360/CPB202301008
[22] 张天栋, 彭青平, 刘欢, 等. 菟丝子治疗骨关节炎:网络药理学分析及实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28):4516−4521. [ZHANG Tiandong, PENG Qingping, LIU Huan, et al. Tusizi in the treatment of osteoarthritis:network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification[J]. China Tissue Engineering Research,2024,28(28):4516−4521.] ZHANG Tiandong, PENG Qingping, LIU Huan, et al. Tusizi in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification[J]. China Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4516−4521.
[23] 方欢乐, 陈衍斌, 张鑫, 等. 基于网络药理学-分子对接-实验验证的桃仁-红花药对干预动脉粥样硬化的作用机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2023,34(9):1245−1254. [FANG Huanle, CHEN Yanbin, ZHANG Xin, et al. Based on network pharmacology-molecular docking-experimental verification, the mechanism of action of peach kernel-safflower drug pair on atherosclerosis[J]. New Drugs and Clinical Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023,34(9):1245−1254.] FANG Huanle, CHEN Yanbin, ZHANG Xin, et al. Based on network pharmacology-molecular docking-experimental verification, the mechanism of action of peach kernel-safflower drug pair on atherosclerosis[J]. New Drugs and Clinical Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 34(9): 1245−1254.
[24] 孙医慧, 王祥斌, 李俊明, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS和网络药理学探讨黄精糕干预2型糖尿病的作用机制[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(9):1653−1663. [SUN Yihui, WANG Xiangbin, LI Junming et al. Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and network pharmacology, the mechanism of Polygonatum Cake in the intervention of type 2 diabetes mellitus was explored[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023,43(9):1653−1663.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2023.09.016 SUN Yihui, WANG Xiangbin, LI Junming et al. Based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and network pharmacology, the mechanism of Polygonatum Cake in the intervention of type 2 diabetes mellitus was explored[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(9): 1653−1663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2023.09.016
[25] 戴文聪, 刘莉, 王坤元, 等. 急性酒精性脂肪肝斑马鱼模型的建立[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2013,29(4):286−289. [DAI Wencong, LIU Li, WANG Kunyuan, et al. Establishment of acute alcoholic fatty liver zebrafish model[J]. Clinical Journal of Hepatobiliary Diseases,2013,29(4):286−289.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2013.04.012 DAI Wencong, LIU Li, WANG Kunyuan, et al. Establishment of acute alcoholic fatty liver zebrafish model[J]. Clinical Journal of Hepatobiliary Diseases, 2013, 29(4): 286−289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2013.04.012
[26] 范文彤. 海藻多糖急性毒性试验考察[J]. 中国医药科学,2020,10(23):77−82. [FAN Wentong. Acute toxicity test of seaweed polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Medical Science,2020,10(23):77−82.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0616.2020.23.018 FAN Wentong. Acute toxicity test of seaweed polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Medical Science, 2020, 10(23): 77−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0616.2020.23.018
[27] 陈林珍, 王璇, 张晓朦, 等. 基于斑马鱼模型的杠柳毒苷肝毒性评价[J]. 中国药物警戒,2023,20(7):742−748. [CHEN Linzhen, WANG Xuan, ZHANG Xiaomeng, et al. Evaluation of periplocoside hepatotoxicity based on zebrafish model[J]. Pharmacovigilance in China,2023,20(7):742−748.] CHEN Linzhen, WANG Xuan, ZHANG Xiaomeng, et al. Evaluation of periplocoside hepatotoxicity based on zebrafish model[J]. Pharmacovigilance in China, 2023, 20(7): 742−748.
[28] 史精干, 李燊星, 王恒, 等. 决明子分散片对大鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用及其谱效关系研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2023,58(14):1295−1304. [SHI Jinggan, LI Shenxing, WANG Heng, et al. Study on the protective effect of cassia seed dispersible tablets on acute liver injury in rats and its spectrum-effect relationship[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacy,2023,58(14):1295−1304.] doi: 10.11669/cpj.2023.14.006 SHI Jinggan, LI Shenxing, WANG Heng, et al. Study on the protective effect of cassia seed dispersible tablets on acute liver injury in rats and its spectrum-effect relationship[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacy, 2023, 58(14): 1295−1304. doi: 10.11669/cpj.2023.14.006
[29] 王斌杰, 付立斌, 叶昕宇, 等. 芬太尼对斑马鱼幼鱼的心脏和神经毒性及机制[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2023,37(10):767−773. [WANG Binjie, FU Libin, YE Xinyu, et al. Cardiac and neurotoxicity of fentanyl in zebrafish larvae and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology,2023,37(10):767−773.] doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2023.10.006 WANG Binjie, FU Libin, YE Xinyu, et al. Cardiac and neurotoxicity of fentanyl in zebrafish larvae and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2023, 37(10): 767−773. doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2023.10.006
[30] 孙悦, 张文龙, 李楠, 等. 沙棘熊果酸对酒精性肝损伤大鼠肝FXR信号通路的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(5):363−370. [SUN Yue, ZHANG Wenlong, LI Nan, et al. Effects of sea buckthorn ursolic acid on FXR signaling pathway in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food Industry Technology,2023,44(5):363−370.] SUN Yue, ZHANG Wenlong, LI Nan, et al. Effects of sea buckthorn ursolic acid on FXR signaling pathway in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food Industry Technology, 2023, 44(5): 363−370.
[31] 李淑珍, 武飞, 杨宁, 等. 沙棘叶黄酮对小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,39(5):765−769. [LI Shuzhen, WU Fei, YANG Ning, et al. Protective effect of seabuckthorn leaf flavonoids on acute liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2016,39(5):765−769.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2016.05.026 LI Shuzhen, WU Fei, YANG Ning, et al. Protective effect of seabuckthorn leaf flavonoids on acute liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 39(5): 765−769. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2016.05.026
[32] 王昕旭, 王雪, 张晓慧, 等. 沙棘多糖对扑热息痛诱导的小鼠肝损伤保护作用的研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(7):972−975. [WANG Xinxu, WANG Xue, ZHANG Xiaohui, et al. Protective effect of sea buckthorn polysaccharide on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology,2018,34(7):972−975.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2018.07.003 WANG Xinxu, WANG Xue, ZHANG Xiaohui, et al. Protective effect of sea buckthorn polysaccharide on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2018, 34(7): 972−975. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2018.07.003
[33] MAHESHWARI D T , KUMAR M S Y , VERMA S K , et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of phenolic rich fraction of Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaves[J]. Food & Chemical Toxicology, 2011, 49(9):2422−2428.
[34] ZARGAR R, RAGHUWANSHI P, KOUL A L, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of seabuckthorn leaf-extract in lead acetate-intoxicated Wistar rats[J]. Drug Chem Toxicol,2022,45(1):476−480. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2020.1775630
[35] 李可欣, 张男男, 侯瑞丽, 等. 沙棘熊果酸对酒精性肝病模型大鼠的保护作用[J]. 医药导报,2021,40(5):616−621. [LI Kexin, ZHANG Nannan, HOU Ruili, et al. Protective effect of seabuckthorn ursolic acid on alcoholic liver disease model rats[J]. Pharmaceutical Report,2021,40(5):616−621.] LI Kexin, ZHANG Nannan, HOU Ruili, et al. Protective effect of seabuckthorn ursolic acid on alcoholic liver disease model rats[J]. Pharmaceutical Report, 2021, 40(5): 616−621.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



