Construction and Application of a Lentinan-Specific Fluorescent Probe Based on a Carbohydrate-binding Module
-
摘要: 为构建得到香菇多糖特异性荧光探针以实现香菇多糖的原位可视化观察,本研究利用生物信息学技术从β-1,3-D-葡聚糖酶TlGluA中挖掘得到一个潜在具有香菇多糖结合能力的碳水化合物结合结构域,并对其进行了重组表达及分离纯化,重组蛋白命名为LBM,进一步利用微量滴定板法研究了LBM的结合特异性。结果表明LBM能够结合香菇多糖,但未表现出对大麦β-葡聚糖、凝结多糖或魔芋葡甘露聚糖的结合能力,这证实该蛋白对香菇多糖具有良好的结合特异性。此外,通过将LBM与绿色荧光蛋白EmGFP融合表达构建得到首个香菇多糖特异性荧光探针,命名为EmGFP-LBM,基于该探针实现了香菇多糖在香菇中的原位可视化观察。研究发现,香菇多糖不仅存在于菌丝细胞壁中,还以散在状态分布于菌丝细胞间隙与细胞内部。本研究成功构建得到首个香菇多糖特异性荧光探针,为香菇多糖的原位可视化观察提供了关键工具。
-
关键词:
- 香菇 /
- 香菇多糖 /
- 碳水化合物结合结构域 /
- 荧光探针 /
- 原位可视化
Abstract: This study aimed to obtain a lentinan-specific fluorescent probe for the in situ visualization of lentinan. A carbohydrate-binding module with potential lentinan-binding capacity was discovered in a β-1,3-D-glucanase by using the bioinformatics techniques, and further recombinantly expressed. The binding specificity of the expressed protein, which was named as LBM was determined by the microtiter plate assays. The results indicated that LBM displayed a desired specificity for lentinan. The protein exhibited positive binding signals to lentinan, while could not bind to several examined polysaccharides including barley β-glucan, curdlan, or konjac glucomannan. Furthermore, the first lentinan-specific fluorescent probe was successfully constructed by fusing LBM with a green fluorescent protein EmGFP, based on which the in situ visualization of lentinan in Lentinula edodes was realized. It was shown that lentinan was not only presented in the mycelial cell wall, but also amorphously distributed in the interstitial space and inside the cell. The construction of the EmGFP-LBM provided a promising tool for the in situ visualization of lentinan. -
我国食用菌产业发展迅速,已成为仅次于粮、油、果、菜的第五大农产品。香菇,作为我国产量最大的食用菌,具有重要经济价值和营养价值[1]。香菇多糖(Lentinan,LNT)是从香菇子实体中获得的一类多糖,主要活性成分结构为随机分布β-1,6-葡萄糖分支的β-1,3-葡聚糖[2−3]。香菇多糖具有抗癌、抗病毒、抗氧化、抗菌、抗抑郁和免疫调节等多种生物活性,目前已经作为注射剂、片剂及胶囊等处方药,应用于癌症的临床治疗[1,4−6]。除此之外,香菇多糖在世界范围内被广泛用作药物替代物和膳食补充剂[7]。可见,香菇多糖具有良好的应用前景和潜在的商业价值。
香菇多糖的原位研究是阐明香菇多糖在食品中的分布、香菇多糖与其他组分之间的相互作用以及香菇多糖对食品感官特性的影响机制等科学问题的关键。苯胺蓝染色剂为常用于β-1,3-葡聚糖原位研究的小分子染料[8],但其容易受到β-1,4-葡聚糖的干扰,在特异性上存在局限性。多糖特异性探针是多糖原位研究的重要工具[9],基于其特异性识别功能可详细定位食品中特定成分的原位分布[10]。目前,用于识别多糖的结合蛋白主要为单克隆抗体和碳水化合物结合结构域(Carbohydrate-binding module,CBM)。然而,多糖结构异质性高,免疫原性弱,抗体制备过程繁琐耗时,获取困难[11]。CBM是碳水化合物活性酶(carbohydrate-active enzymes,CAZymes)中天然存在的底物结合模块[12],具有精准的多糖结合能力,其结合特异性通常与其附着酶生物活性相匹配[13]。相较于抗体,CBM具有尺寸小、成本低、标记灵活等特点,可用于多糖的特异性检测分析[14]。CBM与荧光蛋白融合表达所构建的荧光探针[10]已广泛应用于木聚糖、纤维素、果胶等多糖的荧光显微观察[15−17]。目前香菇多糖CBM并未见报道,因此,挖掘香菇多糖CBM并构建特异性荧光探针对香菇多糖的荧光显微观察具有实际意义。
本研究利用生物信息学分析,在GH16_4家族的β-1,3-D-葡聚糖酶中发现了一个未知功能结构域。该结构域呈现β-sandwich折叠结构。众所周知,β-sandwich是CBMs最主要的折叠形式[14]。同时,CBM的结合能力通常与其附属酶的催化活性相匹配,鉴于此,推测这个未知功能结构域具有结合香菇多糖的能力。以分子生物学技术对该结构域进行克隆表达,分离纯化后得到重组蛋白,命名为LBM,随后确定LBM对香菇多糖的结合能力。并通过LBM与绿色荧光蛋白的融合表达,构建香菇多糖特异性荧光探针,并验证其应用于香菇多糖荧光显微观察的可行性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
香菇(Lentinula edodes) 青岛黄山路市场;香菇多糖 纯度≥96%,自制;魔芋葡甘露聚糖(纯度≥99%)、大麦β-葡聚糖(纯度≥95%) 上海麦克林公司;凝结多糖 纯度≥95%,北京博奥拓达科技有限公司;甲壳素 纯度≥99%,美国Sigma公司;纤维素(纯度≥99%)、四甲基联苯胺 北京索莱宝公司;pET28a(+)载体 美国Novagen公司;pRSET-EmGFP载体 美国Thermo Fisher公司;大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)感受态细胞 北京博迈德基因技术有限公司;96孔板 美国Corning公司;辣根过氧化物酶标记6×His标签的单克隆抗体 美国Proteintech公司。
Agilent 1260 HPLC高效液相色谱 Agilent;Milli-Q Advantage A10超纯水机 法国默克公司;3、10 kDa超滤离心管 美国密理博公司;iMark酶标仪 美国BioRad公司;ÄKTA Start蛋白纯化系统、HisTrapTM HP、HiPrepTM 26/10 Desalting 美国GE生命科学;FD5-3T冷冻干燥机 GOLD-SIM公司;Tanon5200全自动化学发光成像分析系统 上海天能科技有限公司;徕卡CM1860冷冻切片机 德国徕卡医疗;NanoDrop 美国Thermo Fisher公司;NIKON ECLIPSE Cl荧光显微镜 日本尼康;F-4600荧光分光光度计 日本HITACHI公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 香菇多糖的提取与检测
根据Wang等[3]的方法,利用水提醇沉提取香菇多糖,多糖结构为β-1,3-糖苷键连接的葡聚糖;多糖含量由苯酚硫酸法进行测定,随后由高效液相色谱进行检测是否呈现单一峰。高效液相色谱:Agilent 1260 HPLC;色谱柱:TSKgel SuperAW4000;检测器:RID;流动相:0.2 mol/L NaCl;流速:0.5 mL/min;柱温:40 ℃;检测器温度:35 ℃。
1.2.2 生物信息学分析
利用dbCAN[18]、CD-Search[19]、Interproscan[20]和SignalIP 5.0[21]等软件预测β-1,3-D-葡聚糖酶TlGluA的序列结构域架构,并使用AlphaFold2[22]预测蛋白TlGluA的三维结构。随后通过ExPASy计算重组蛋白的理论分子量和等电点[23]。
1.2.3 基因克隆与异源表达
编码结合蛋白LBM的基因序列委托上海生工进行合成,利用PCR技术扩增目的基因。利用正向5′-AGGAGATATACCATGGCCATGGGCGCAGACATTC-3′和反向引物5′-GGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCTCGAGACATCTCTTGACAATTTTAGGT-3′扩增编码LBM的基因序列。将PCR产物纯化并使用限制性内切酶NcoI/XhoI进行酶切,并连接到pET28a(+)载体中(保留N端His标签)。将重组质粒转化至大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)感受态细胞中。将成功转化的菌体接种于含有30 ng/μL卡那霉素的LB培养基中在37 ℃下培养至OD600达到0.4。在17 ℃下,利用0.5 mmol/L β-D-硫代半乳糖苷诱导16 h后收集菌体沉淀。将菌体重悬于20 mmol/L PBS(NaH2PO4-Na2HPO4)缓冲液(pH7.5)中,超声破碎,离心收集上清,得到含有LBM的粗蛋白溶液。
1.2.4 蛋白纯化
利用HisTrapTM HP柱和ÄKTA Start系统纯化来自细胞裂解物上清液中具有6×His标签的重组蛋白,并在0.3 mol/L NaCl的20 mmol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5)中以0~0.5 mol/L咪唑浓度进行线性梯度洗脱,收集紫外信号高的组分。使用HiPrepTM 26/10 Desalting以20 mmol/L PBS缓冲液(pH7.5)对样品进行脱盐。利用SDS-PAGE(160 V恒压,50 min)分析纯化蛋白、上样前的样品以及Ni柱流穿液的纯度和分子量(Mw)。使用NanoDrop测定蛋白质的浓度。纯化后的重组蛋白用于结合特异性的研究。
1.2.5 结合特异性研究
根据先前的微量滴定板法[24−25],将香菇多糖、大麦β-葡聚糖、凝结多糖和魔芋葡甘露聚糖溶解在包被(NaCl-Na2HPO4·12H2O-KH2PO4-KCl)缓冲液(pH7.5)中,多糖浓度均为50 μg/mL。取100 μL上述多糖样品添加至96孔板中,4 ℃下过夜孵育。随后用封闭缓冲液(含5%脱脂奶粉的包被缓冲液)封闭板中的剩余结合位点。超纯水洗涤后,依次加入100 μL利用包被缓冲液稀释的LBM(浓度分别为0.78、1.56、3.125、6.25、12.5、25、50、100 μg/mL)和辣根过氧化物酶标记6×His标签的单克隆抗体(0.2 μg/mL),每次反应2 h。使用四甲基联苯胺(TMB)显色15 min,并用1 mol/L HCl终止反应。最后,在450 nm处测量吸光度,当吸光度值>0.2时,判定结合蛋白LBM与多糖有结合。
1.2.6 荧光探针的构建
以含有结合蛋白LBM序列的重组质粒为模板钓取目的基因,正向引物和反向引物分别为5′-TCATGGTATGGCTAGCGCAGACATTCCTAAACCCAGACTCAC-3′和5′-TGGCGAATTCGGATCCACATCTCTTGACAATTTTAGGTGGTACCAAG-3′。将PCR产物纯化并使用限制性内切酶NheI/BamHI进行酶切,并连接到pRSET-EmGFP载体中。将携带重组质粒的大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)细胞在含有60 ng/μL氨苄青霉素的LB培养基中在37 ℃、160 r/min下进行培养。按照上述方法进行蛋白的表达和纯化。将荧光探针命名为EmGFP-LBM。
1.2.7 荧光显微测定实验
根据Kawakubo等[26]的方法研究荧光探针EmGFP-LBM与甲壳素和纤维素的结合能力,将2 mg上述多糖样品和100 μL荧光探针EmGFP-LBM溶液(1 mg/mL)添加至20 mmol/L PBS缓冲液(pH7.5)中,总体积为200 μL,并在25 ℃下振荡孵育30 min。离心(10000 r/min,5 min)除去上清中多余的蛋白,使用20 mmol/L PBS缓冲液(pH7.5)洗涤3次,以确保最小的背景荧光和高信噪比。将样品重悬于40 μL 20 mmol/L PBS缓冲液(pH7.5)中,取少量样品置于载玻片,用盖玻片覆盖,通过荧光显微镜进行分析。对于所有样品,以相同的曝光时间(1 s)记录图像,以检测信号强度的差异。实验过程中保持避光操作。
1.2.8 荧光探针的荧光特性研究
通过荧光分光光度计测定其最佳激发波长(Ex)和发射波长(Em)。在Ex和Em相等的情况下,将荧光强度定义为0。按照Patterson等[27]方法测定探针的pH稳定性,利用HCl或NaOH调节缓冲液(50 mmol/L磷酸氢二钠、50 mmol/L无水醋酸钠、50 mmol/L甘氨酸)的pH至3~10,以1:100的比例稀释荧光探针,利用荧光分光光度计在荧光探针的最佳激发波长、发射波长下进行定点测量。
1.2.9 香菇多糖的荧光显微观察
将新鲜香菇的组织包埋在OCT包埋剂中,于−20 ℃冷冻15 min后以10 μm进行切片。为实现香菇中多糖的共定位,向香菇组织切片中加入CFW与EmGFP-LBM的混合染液(1:9的混合比例),在室温下孵育30 min,20 mmol/L PBS缓冲液(pH7.5)下洗涤5 min,使用荧光显微镜收集蓝色通道和绿色通道图像。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验均重复进行3次,数据采用平均值±标准差表示。数据处理采用Excel、Origin和NIS等软件并作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 生物信息学分析
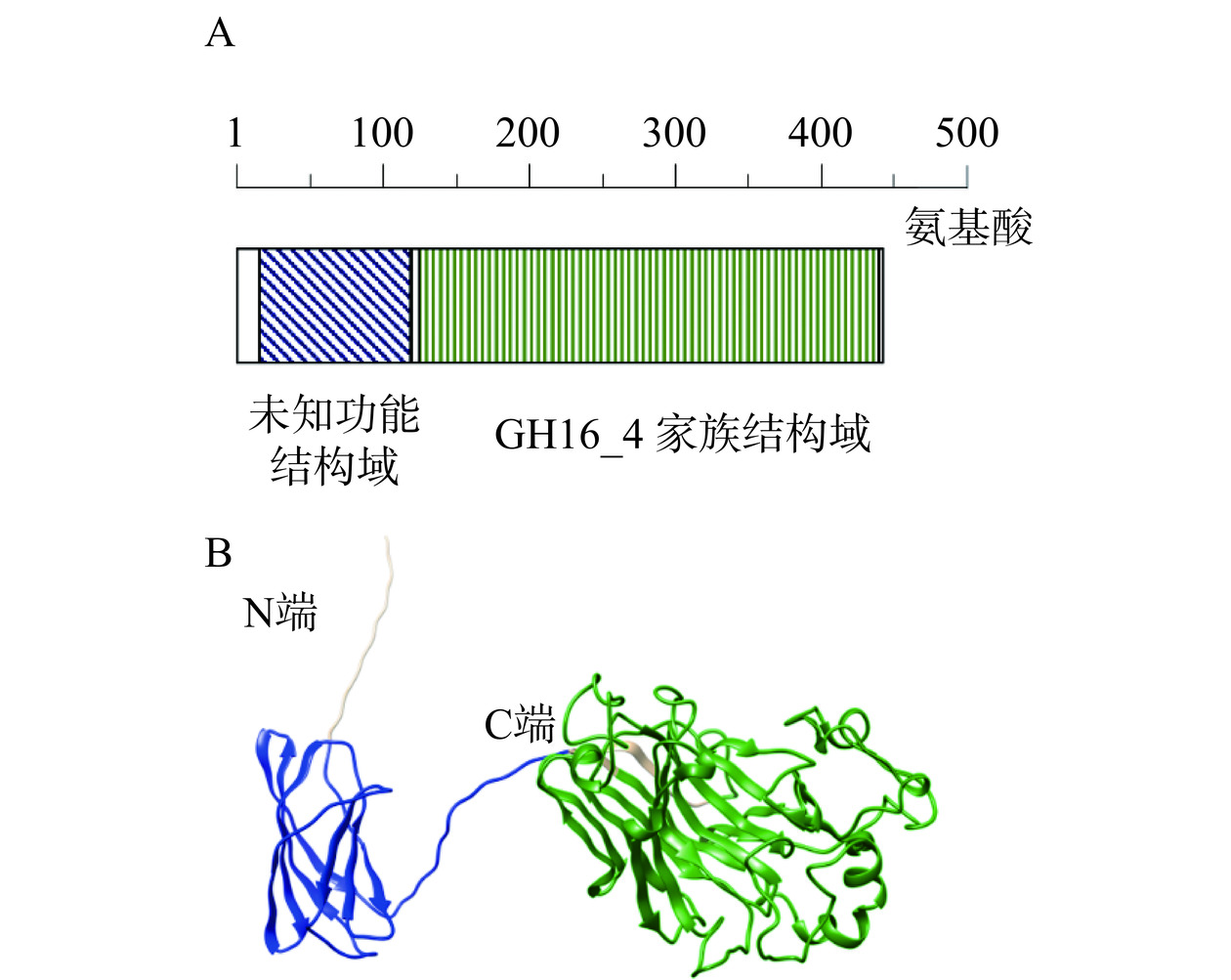
本研究利用生物信息学技术对CAZy数据库中β-1,3-葡聚糖酶的结构域架构进行分析,在GH16_4家族中发现了内切β-1,3-D-葡聚糖酶TlGluA(GenBank:AEE89454.1),其序列结构由N端信号肽(1~15位氨基酸)、GH16_4催化域(129~439位氨基酸)和一个未知功能的结构域(16~119位氨基酸)组成(图1A)。AlphaFold2蛋白结构预测结果显示,该未知功能结构域呈现β-sandwich折叠结构(图1B蓝色部分)。β-sandwich折叠是CBMs的主要折叠形式[14]。同时,鉴于CBM的结合能力通常与其附属酶的催化活性相一致,因此猜测该段未知功能结构域为一个具有香菇多糖结合能力的CBM。
2.2 克隆表达与结合特性研究
克隆LBM的基因片段,并在大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)中异源表达。随后通过镍亲和层析从胞内上清液中纯化具有6×His标签的重组LBM。纯化的LBM在SDS-PAGE分析上显示单一条带(图2A),Mw约为14 kDa,这与预期的理论Mw(13.3 kDa)接近,并且过Ni柱后穿透液在SDS-PAGE分析上条带明显减弱(图2C),表明蛋白已成功表达并纯化。为了进一步研究LBM对香菇多糖的结合能力,基于经典提取方法[3]提取香菇多糖,利用苯酚硫酸法测定多糖含量约为96%,利用Bradford法测定蛋白含量约为2%,通过HPLC检测发现呈现单一峰(图3A),表明香菇多糖纯度良好。微量滴定板法研究表明,蛋白LBM表现出对香菇多糖的阳性结合信号,提示该蛋白能够结合香菇多糖,这证实LBM为具有香菇多糖结合能力的CBM。此外,LBM未表现出对大麦β-葡聚糖、凝结多糖或魔芋葡甘露聚糖的结合能力(图3B)。上述结果表明,LBM具有对香菇多糖的良好结合特异性,这种特性有助于其作为探针对香菇多糖进行原位观察,可以有效避免其他多糖的干扰而造成实验结果的不可信性。
2.3 香菇多糖特异性荧光探针的构建
为实现香菇多糖的荧光显微观察,将LBM与绿色荧光蛋白EmGFP融合表达,成功构建荧光探针EmGFP-LBM。纯化的EmGFP-LBM在SDS-PAGE分析上显示单一条带(见图4A),Mw约为43 kDa,这与预期的理论Mw(40.7 kDa)接近,并且过Ni柱后穿透液在SDS-PAGE分析上条带明显减弱(图4C),表明目标蛋白已成功表达并纯化。
甲壳素和纤维素是β-1,4-葡聚糖,与香菇多糖的结构具有明显相似性,且均为香菇中存在的主要多糖[28−29]。结合特异性研究结果可以观察到随着EmGFP-LBM浓度的提高,其对香菇多糖的阳性结合信号呈上升趋势(图4D),表明该探针可以结合香菇多糖。由于该方法仅适用于结合蛋白对可溶性多糖的结合能力研究,对于EmGFP-LBM对甲壳素与纤维素的结合,采用荧光显微实验进行验证。结果显示,EmGFP-LBM对甲壳素和纤维素均没有显示出绿色荧光(图5C~5D),意味着该探针对甲壳素和纤维素均不具有结合能力。这提示EmGFP-LBM是香菇多糖特异性荧光探针。
3D全波长扫描结果显示,EmGFP-LBM的最佳激发波长和发射波长分别为480 nm和510 nm(图6A),与绿色荧光蛋白的荧光特性相似,这提示着LBM的引入并未对荧光蛋白的特性造成影响。EmGFP-LBM的荧光性能在pH6~10之间相对稳定(图6B),这表明该探针能够满足大多数食品体系中的应用。EmGFP-LBM为首个具有香菇多糖特异性结合能力的荧光探针,且该探针荧光性能稳定,具有良好的应用潜力。
2.4 香菇多糖特异性荧光探针在原位研究中的应用
香菇多糖的原位分析是阐明众多科学问题的关键,如香菇多糖在香菇中的原位分布,或在香菇加工过程中的原位变化。为获得香菇多糖原位可视化工具,进一步将LBM与绿色荧光蛋白EmGFP融合表达,成功构建得到香菇多糖特异性荧光探针EmGFP-LBM。为了评估所构建探针作为香菇多糖原位可视化工具的可行性,利用EmGFP-LBM对香菇中的香菇多糖进行了原位染色观察。同时为了考察香菇中不同多糖的分布,以卡尔科弗卢尔荧光增白剂(Calcofluor White Stain,简称CFW)对香菇中的甲壳素与纤维素进行染色[30−34]。如图7所示,在香菇组织切片中观察到了大量的绿色荧光和蓝色荧光。蓝色荧光分布于菌丝细胞壁(图7C),表明甲壳素和纤维素作为结构性多糖组成菌丝细胞壁;绿色荧光除分布于菌丝细胞壁上外,还随机分布于菌丝细胞内部和细胞间隙(图7D)。目前,尚未有报道关于香菇多糖在香菇中的原位分布研究,但这与之前描述的β-1,3-葡聚糖在双孢菇等其它真菌菌丝细胞壁中的分布大致相同[35]。由于EmGFP-LBM能特异性结合香菇多糖而不结合香菇中其他多糖,因此,推测香菇多糖不仅存在于菌丝细胞壁上,还以散在状态分布于菌丝细胞间隙和细胞内部。综上,EmGFP-LBM可以作为香菇多糖特异性荧光探针用于香菇多糖的原位可视化。
3. 结论
本研究从β-1,3-D-葡聚糖酶TlGluA中成功挖掘得到一个新型香菇多糖结合蛋白LBM,并对其进行克隆表达及功能验证。结果表明,LBM对香菇多糖具有良好的结合特异性。通过将LBM与绿色荧光蛋白EmGFP融合表达,成功构建出首个香菇多糖特异性荧光探针EmGFP-LBM。所构建探针荧光性能良好,适宜应用范围为pH6~10,能够满足大多数食品体系的应用。此外,以EmGFP-LBM为工具,配合显微成像技术,实现了香菇中香菇多糖的原位可视化。研究发现香菇多糖不仅存在于菌丝细胞壁中,还以散在状态分布于菌丝细胞间隙和细胞内部。EmGFP-LBM的构建为香菇多糖的原位研究提供了良好工具。
-
-
[1] NIEGO A G, RAPIOR S, THONGKLANG N, et al. Macrofungi as a nutraceutical source:Promising bioactive compounds and market value[J]. Journal of Fungi,2021,7(5):397. doi: 10.3390/jof7050397
[2] JEFF I B, YUAN X, SUN L, et al. Purification and in vitro anti-proliferative effect of novel neutral polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,52:99−106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.10.007
[3] WANG K, WANG J, LI Q, et al. Structural differences and conformational characterization of five bioactive polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes[J]. Food Research International,2014,62:223−232. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.02.047
[4] WASSER S P. Medicinal mushrooms in human clinical studies. Part I. Anticancer, oncoimmunological, and immunomodulatory activities:A review[J]. InternationaL Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms,2017,19(4):279−317. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.v19.i4.10
[5] MENG X, LIANG H, LUO L. Antitumor polysaccharides from mushrooms:A review on the structural characteristics, antitumor mechanisms and immunomodulating activities[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2016,424:30−41. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2016.02.008
[6] LU REN C P A Y. Antitumor activity of mushroom polysaccharides:A review[J]. Food & Function,2012(3):1118.
[7] ZHANG Y, LI S, WANG X, et al. Advances in lentinan:Isolation, structure, chain conformation and bioactivities[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(2):196−206. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.02.001
[8] MASON K N, EKANAYAKE G, HEESE A. Chapter 10-staining and automated image quantification of callose in arabidopsis cotyledons and leaves[J]. Methods in Cell Biology,2020,160:181−199.
[9] RYDAHL M G, HANSEN A R, KRAČUN S K, et al. Report on the current inventory of the toolbox for plant cell wall analysis:Proteinaceous and small molecular probes[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9.
[10] DOMOZYCH D S. The quest for four-dimensional imaging in plant cell biology:It's just a matter of time[J]. Annals of Botany,2012,110(2):461−474. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs107
[11] HERVÉ C, MARCUS S E, KNOX J P. Monoclonal antibodies, carbohydrate-binding modules, and the detection of polysaccharides in plant cell walls[J]. Methods Mol Biol,2011,715:103−113.
[12] SHOSEYOV O, SHANI Z, LEVY I. Carbohydrate binding modules:Biochemical properties and novel applications[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews,2006,70(2):283−295. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00028-05
[13] BORASTON A B, BOLAM D N, GILBERT H J, et al. Carbohydrate-binding modules:Fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition[J]. Biochem J,2004,382(Pt3):769−781.
[14] OLIVEIRA C, CARVALHO V, DOMINGUES L, et al. Recombinant cbm-fusion technology-applications overview[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2015,33(3−4):358−369. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.006
[15] DING S, XU Q, ALI M K, et al. Versatile derivatives of carbohydrate-binding modules for imaging of complex carbohydrates approaching the molecular level of resolution[J]. BioTechniques,2006,41(4):435−443. doi: 10.2144/000112244
[16] MCCARTNEY L, BLAKE A W, FLINT J, et al. Differential recognition of plant cell walls by microbial xylan-specific carbohydrate-binding modules[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences-PNAS,2006,103(12):4765−4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508887103
[17] BLAKE A W, MCCARTNEY L, FLINT J E, et al. Understanding the biological rationale for the diversity of cellulose-directed carbohydrate-binding modules in prokaryotic enzymes[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2006,281(39):29321−29329. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605903200
[18] TAMURA K, STECHER G, PETERSON D, et al. Mega6:Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution,2013,30(12):2725−2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197
[19] MARCHLER-BAUER A, BO Y, HAN L, et al. Cdd/sparcle:Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2017,45(D1):D200−D203. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1129
[20] QUEVILLON E, SILVENTOINEN V, PILLAI S, et al. Interproscan:Protein domains identifier[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2005,33(Web Server):W116−W120.
[21] WILKINS M R, GASTEIGER E, BAIROCH A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools in the expasy server[J]. Methods Mol Biol,1999,112:531−552.
[22] JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with alphafold[J]. Nature,2021,596(7873):583−589. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
[23] PETERSEN T N, BRUNAK S, VON HEIJNE G, et al. Signalp 4.0:Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions[J]. Nature Methods,2011,8(10):785−786. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701
[24] MCCARTNEY L, GILBERT H J, BOLAM D N, et al. Glycoside hydrolase carbohydrate-binding modules as molecular probes for the analysis of plant cell wall polymers[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,2004,326(1):49−54. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2003.11.011
[25] TORODE T A, SIMÉON A, MARCUS S E, et al. Dynamics of cell wall assembly during early embryogenesis in the brown algafucus[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2016,67(21):6089−6100. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw369
[26] KAWAKUBO T, KARITA S, ARAKI Y, et al. Analysis of exposed cellulose surfaces in pretreated wood biomass using carbohydrate-binding module (cbm)-cyan fluorescent protein (cfp)[J]. Biotechnol Bioeng,2010,105(3):499−508. doi: 10.1002/bit.22550
[27] PATTERSON G H, KNOBEL S M, SHARIF W D, et al. Use of the green fluorescent protein and its mutants in quantitative fluorescence microscopy[J]. Biophysical Journal,1997,73(5):2782−2790. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78307-3
[28] PÉREZ-BASSART Z, FABRA M J, MARTÍNEZ-ABAD A, et al. Compositional differences of β-glucan-rich extracts from three relevant mushrooms obtained through a sequential extraction protocol[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,402:134207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134207
[29] LI D, QIN X, TIAN P, et al. Toughening and its association with the postharvest quality of king oyster mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) stored at low temperature[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,196:1092−1100. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.060
[30] HOCH H C, GALVANI C D, SZAROWSKI D H, et al. Two new fluorescent dyes applicable for visualization of fungal cell walls[J]. Mycologia,2005,97(3):580−588. doi: 10.1080/15572536.2006.11832788
[31] HARRINGTON B J, HAGEAGE J R. Calcofluor white:A review of its uses and applications in clinical mycology and parasitology[J]. Laboratory medicine,2003,34(5):361−367. doi: 10.1309/EPH2TDT8335GH0R3
[32] HERBURGER K, HOLZINGER A. Aniline blue and calcofluor white staining of callose and cellulose in the streptophyte green algae zygnema and klebsormidium[J]. Bio-Protocol,2016,6(20):e1969.
[33] URSACHE R, ANDERSEN T G, MARHAVÝ P, et al. A protocol for combining fluorescent proteins with histological stains for diverse cell wall components[J]. The Plant Journal,2017,93(2):399−412.
[34] TSURKAN M V, VORONKINA A, KHRUNYK Y, et al. Progress in chitin analytics[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,252:117204. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117204
[35] IFUKU S, NOMURA R, MORIMOTO M, et al. Preparation of chitin nanofibers from mushrooms[J]. Materials,2011,4(8):1417−1425. doi: 10.3390/ma4081417
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 崔国梅,刘丽娜,田广瑞,王安建,禹子琪,高帅平. 响应面法优化香菇片硬化保脆工艺. 食品与机械. 2024(12): 102-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



