Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Apocynum venetum Polysaccharides
-
摘要: 本文以罗布麻叶为研究对象,探讨热水提取(HWE)、超声辅助提取(UE)、纤维素酶提取(CE)、果胶酶提取(PE)和超声微波协同提取(UME)对罗布麻多糖(Apocynum venetum Polysaccharides,AVP)理化性质及活性的影响。结果表明,多糖得率为:AVP-PE(13.6%)>AVP-CE(13.4%)>AVP-UME(12.4%)>AVP-UE(12.1%)>AVP-HWE(9.2%)。不同提取法所得多糖均主要由不同摩尔比的阿拉伯糖、葡萄糖及半乳糖组成,然而各单糖占比有所不同,其中AVP-HWE及AVP-CE中阿拉伯糖占比最高,另三种多糖中葡萄糖占比最高。不同多糖均显出了典型的多糖类化合物红外吸收峰,均不具有三螺旋结构,且表现出不同的表面结构。各多糖均具有较强的抗氧化活性,其中,AVP-HWE具有最强的DPPH及ABTS+自由基清除能力,半抑制浓度分别为0.219及0.072 mg/mL;AVP-UE具有最强的羟自由基清除能力,半抑制浓度为0.298 mg/mL;AVP-CE具有最强的亚铁离子螯合能力,半抑制浓度为0.107 mg/mL;不同多糖的总还原能力差距较小。综上,不同提取方法对AVP的结构及活性有显著的影响,UE和CE更适合罗布麻多糖的提取。本文将为罗布麻叶多糖资源的开发利用提供参考。Abstract: In this paper, the effects of hot water extraction (HWE), ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UE), cellulase assisted extraction (CE), pectinase assisted extraction (PE), and ultrasonic microwave assisted extraction (UME) on the physicochemical properties and activities of polysaccharide from Apocinae venetiana (AVP) were studied. The results showed that the extraction rate in the order of AVP-PE (13.6%)>AVP-CE (13.4%)>AVP-UME (12.4%)>AVP-UE (12.1%)>AVP-HWE (9.2%). The polysaccharides obtained by different extraction methods were mainly composed of arabinose, glucose and galactose in a different molar ratio, however, the proportion of each monosaccharide was different. The arabinose was the predominant monosaccharide for AVP-HWE and AVP-CE, and glucose for the others. Different polysaccharides exhibited typical infrared absorption peaks of polysaccharide compounds without a triple helix structure, and showed different surface structures. The polysaccharides demonstrated strong antioxidant activity, among which AVP-HWE had the strongest DPPH and ABTS+ free radicals scavenging ability, with half inhibition concentrations (IC50) of 0.219 and 0.072 mg/mL, respectively. AVP-UE had the strongest hydroxyl radical scavenging ability, with IC50 of 0.298 mg/mL. AVP-CE had the strongest ferrous ion chelating ability, with IC50 of 0.107 mg/mL, and there were few differences for the total reducing power between different polysaccharides. In summary, different extraction methods have a significant impact on the structure and activity of AVP, and UE and CE are more suitable for the extraction of AVP. This paper may be providing reference for the development and utilization of polysaccharides resources from Apocynum venetum leaves.
-
罗布麻(Apocynum venetum L.)为夹竹桃科植物罗布麻的叶,收载于《中国药典》2020年第一部,其具有清热平肝,利水消肿的功效,主治高血压、眩晕、头痛、心悸、失眠、水肿尿少[1]。罗布麻分布于欧洲及亚洲温带地区,在我国分布于新疆、青海、甘肃、陕西、山西、河南等省区,主要生在盐碱荒地和沙漠边缘及河流两岸、冲积平原、河泊周围及戈壁荒滩上[2]。罗布麻叶富含黄酮、有机酸、多糖、蛋白质、多酚及矿物质等多种成分[3−5]。现代药理学研究已证实罗布麻叶具有降压、降脂、降糖、抑菌、抗氧化、抗抑郁、抗动脉粥样硬化、保肝、调节肠道菌群及提高免疫力等功效[6−9]。多糖为罗布麻叶的主要生物活性成分之一,Wang等[10]通过水提法及分离纯化从罗布麻花中得到了两种分子量为7 kDa和9 kDa的具有抗凝血作用的多糖。Li等[11]从罗布麻根中分离得到了一种具有抗炎活性的中性多糖。Yuan等[12]报道富含多糖的罗布麻叶提取物显出较强的降糖、降血压及调节肠道菌群的作用。Chen等[13]从罗布麻茶残渣中分离得到了具有强乳化性能的多糖。郑思睿等[14]通过响应面法优化了罗布麻叶多糖提取工艺,当提取温度91℃、提取1.75 h、料液比1:82(g/mL)的条件下提取率为1.86%。研究表明作为入药部位的罗布麻叶,有关其多糖的相关研究仅限于其提取及活性筛选等。
多糖在自然界分布极广,随着多糖各类功能的逐渐挖掘,其广泛应用于食品、医疗、化妆品等领域;因其多种药理活性及功能特性,近些年来受到研究者们的广泛关注[15−17]。传统的热水提取法逐渐被超声辅助提取法、微波辅助提取法及酶提取法等新型提取方法取代。超声辅助提取法利用超声波的空化作用破坏细胞壁,从而加快多糖的析出;微波辅助提取法因其穿透力强、加热效率高等优点影响多糖的提取;酶提取法利用酶的专一性对多糖进行提取。新型辅助提取法克服了热水提取法耗时长、提取效率低等缺点,且对多糖的结构及生物活性的影响较为显著。Jing等[18]探究不同提取方法对黄精多糖的影响,得出碱提多糖因分子量高而显出较好的流变特性,酶解法及冻融法所得多糖因小分子量而显出较好的降脂活性。Tang等[19]报道不同方法提取的火龙果多糖提取率在3.78%~7.25%,多糖含量、单糖组成及分子量差距较大。白冰瑶等[20]比较不同提取方法对恰玛古多糖生物活性的影响,得出超声辅助提取多糖生物活性优于其他方法。不同的植物多糖因自身的理化性质差异最合适的提取方法也不同,决定着其应用的空间。因此,研究不同提取方法对多糖结构及活性的影响对于其在食品和医药领域的应用方面具有深远的意义。本文选择药效丰富的罗布麻叶为研究对象也为植物多糖的研究拓宽了领域。
多糖的提取为其分离分析、活性及产品研发的第一步,因此利用结构表征及活性评价,结合不同方法自身优缺点来筛选适合于罗布麻叶多糖的最优提取方法是本研究的主要目的。本文以罗布麻叶为研究对象,通过热水提法(Hot water extraction,HWE)、超声辅助提取法(Ultrasound-assisted extraction,UE)、酶提取法(Cellulase-assisted extraction,CE和Pectinase-assisted extraction,PE)及超声微波协同提取法(Ultrasound-Microwave assisted extraction,UME)等制备罗布麻叶多糖(Apocynum venetum polysaccharide,AVP)。通过紫外吸收光谱、红外吸收光谱、气相色谱、扫描电镜-X-射线能谱、刚果红实验等波谱学、色谱学及经典化学方法对罗布麻叶多糖结构进行表征。进一步利用自由基清除能力、总还原能力及亚铁离子螯合能力等评价抗氧化活性,并进行对比研究,从而筛选出适合于罗布麻叶多糖提取的最适方法。本文旨在为罗布麻叶多糖的进一步提取分离、结构鉴定及生物活性等提供实验基础,为罗布麻叶资源的充分利用和科学应用提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
罗布麻叶(Apocynum venetum L.) 购买于药材市场,产于新疆阿勒泰;纤维素酶(10000 U/g,从里氏木霉所得,最适pH为7)、果胶酶(500 U/mg,从黑曲霉所得,最适pH为5)、各单糖标准品均为分析纯 上海阿达玛斯试剂有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼、2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚(BHT)、菲啰嗪-钠盐、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐 均为分析纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;石油醚、无水乙醇、甲醇、乙酸酐、吡啶、水杨酸、氯化亚铁、氢氧化钠、盐酸羟胺 分析纯,天津市鑫铂特化工有限公司;三氟乙酸 分析纯,广州科檬生物科技有限公司;刚果红、硫酸亚铁、过氧化氢 分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司。
723N紫外可见分光光度计 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;Multiskan FC酶标仪 赛默飞世尔(上海)仪器有限公司;GC-2014气相色谱仪、IR Affinity1红外光谱仪 日本岛津检测技术有限公司;SUPRA 55vp场发射扫描电子显微镜 德国ZEISS公司;E-1045离子溅射仪 日本株式社会社日立高新技术那珂事业所;RE-2012旋转蒸发仪 上海兴创科学仪器设备有限公司;XH-300A超声微波协同提取仪 北京祥鹄科技发展有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 罗布麻叶的预处理
将罗布麻叶烘干进行粉碎处理,过100目筛。将粉碎后的罗布麻叶粉末按照溶剂和粉末1:5 g/mL比例加入石油醚,进行脱脂处理,重复三次,使粉末风干后进行脱色处理,按料液比1:5 g/mL加入85%乙醇溶液,90 ℃回流2 h,进行抽滤,重复至乙醇层颜色较淡后自然风干备用。
1.2.2 罗布麻叶多糖的提取
1.2.2.1 热水提取法
称取罗布麻叶粉末(20 g),在料液比、提取时间和提取温度分别为1:20 g/mL、2 h和90 ℃条件下进行提取。冷却至室温后,通过离心除去固体残留物(5000 r/min,5 min),得到离心上层清液。通过旋蒸仪将上清液浓缩至原始体积的三分之一,加入四倍体积95%的乙醇进行醇沉,静置12 h,将样品在4000 r/min下离心5 min,以获得沉淀,冷冻干燥,得到罗布麻叶粗多糖。实验重复三次,称重,按下式(1)计算得率。
粗多糖得率(%)=粗多糖质量罗布麻叶粉末质量×100 (1) 1.2.2.2 酶提取法
本次实验分别使用纤维素酶和果胶酶进行提取,称取20 g罗布麻叶粉末,加酶量1%,将溶液酸性调节至最适pH,料液比1:20 g/mL,45 ℃磁力搅拌下反应2 h,待反应结束,将温度加热到90 ℃反应10 min使酶灭活,冷却到室温,离心(4000 r/min,10 min),取上清,旋转蒸发仪浓缩,再离心(4000 r/min,5 min)。加入四倍乙醇,静置12 h,离心,冷冻干燥,分别得到纤维素酶及果胶酶提取的罗布麻叶粗多糖。重复三遍计算粗多糖的得率[21]。
1.2.2.3 超声辅助提取法
称取20 g罗布麻叶粉末,料液比1:20 g/mL加蒸馏水,在超声波处理器中反应,超声功率为500 W,提取温度为60 ℃,提取时间为60 min。提取结束后,冷却到室温,离心(4000 r/min,10 min),取上清,旋转蒸发仪浓缩,乙醇沉淀,静置12 h,离心(4000 r/min,5 min),冷冻干燥,得到超声辅助法提取的罗布麻叶粗多糖。实验重复三次,称重计算粗多糖的得率[21]。
1.2.2.4 超声微波协同提取法
取20 g罗布麻叶粉末按照料液比1:20 g/mL加入蒸馏水放入超声微波协同提取仪中反应。微波和超声功率400 W、提取温度为60 ℃,提取时间为15 min。提取后冷却到室温,离心(4000 r/min,10 min),取上清,旋转蒸发仪浓缩,最后加入4倍乙醇,静置12 h,离心(4000 r/min,5 min),冷冻干燥,得到超声微波协同提取法提取的罗布麻叶粗多糖,重复三遍,计算粗多糖的得率[22]。
1.2.3 罗布麻叶多糖的结构表征
1.2.3.1 紫外分光光度法
配制浓度为1 mg/mL的多糖溶液,通过紫外分光光度计,在400~200 nm的波长范围内进行全波长扫描。
1.2.3.2 傅里叶红外光谱法
取适量的多糖样品放置于红外分光光度计样品台上,记录多糖在4000~500 cm−1吸收光谱。
1.2.3.3 单糖组成
分别称取5 mg鼠李糖(Rha)、阿拉伯糖(Ara)、木糖(Xyl)、甘露糖(Man)、葡萄糖(Glc)及半乳糖(Gal)标准品,分别加入8 mg盐酸羟胺及0.5 mL吡啶,于90 ℃水浴反应30 min。取出,冷却至室温,分别加入0.5 mL乙酸酐,于90 ℃水浴反应30 min。待反应完毕,将反应液吹干,加入1 mL三氯甲烷,过0.22 μm滤膜,待气相色谱检测。分别称取5 mg多糖样品,加入3 mL三氯乙酸(2 mol/L),于120 ℃水解6 h。待水解完毕,加入3~4 mL甲醇将溶液旋干,重复三次。按照单糖标准品衍生化方法进行衍生化,待气相色谱检测[23]。
气相色谱条件:进样口及检测器温度280 ℃,进样量5 µL,程序升温条件如下:180 ℃保持5 min,以2 ℃/min的速率加热到220 ℃,保留10 min,最后以5 ℃/min的速率加热到280 ℃,保留10 min。
1.2.3.4 刚果红染色法
配制浓度为0.2 mmol/L的刚果红水溶液,浓度为1 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液,配制质量浓度为2 mg/mL的各个多糖母液。准确量取1 mL各多糖样品溶液,加1 mL刚果红试液,加入不同体积的氢氧化钠溶液,加水至4 mL,使溶液中氢氧化钠溶液的浓度为0~0.5 mol/L,混匀,室温反应5 min,用紫外分光光度计在400~700 nm波长范围内进行全波长扫描,记录最大吸收波长(λmax),氢氧化钠浓度为横坐标,λmax为纵坐标,绘制变化曲线,蒸馏水代替样品作为对照溶液[24]。
1.2.3.5 扫描电镜
取少量各多糖样品于样品台上,用离子溅射仪喷一层铂金。用扫描电镜仪在不同放大倍数下观察不同样品的表面结构形态。
1.2.4 抗氧化活性
1.2.4.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
配制0.2 mmol/L的DPPH-甲醇溶液和浓度为4 mg/mL的各个粗多糖样品母液。稀释样品至浓度为0.1~1 mg/mL,准确量取各稀释液1 mL,加入等体积DPPH-甲醇溶液避光反应30 min,在517 nm处用酶标仪测量吸光度。以2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚(BHT)作为阳性对照,按照公式(2)计算DPPH自由基清除率[25]。
自由基清除率(%)=(1−Ai−AjA0)×100 (2) 式中,Ai为样品混合液吸光度;Aj为蒸馏水代替显色溶液吸光度;A0为蒸馏水代替样品混合液吸光度。
1.2.4.2 羟自由基清除能力
配制6 mmol/L的硫酸亚铁溶液、6 mmol/L水杨酸-乙醇溶液和质量分数为0.1%的过氧化氢溶液,浓度为4 mg/mL的各个粗多糖样品母液。稀释样品至浓度为0.1~1 mg/mL,准确量取各稀释液1 mL,加入等体积硫酸亚铁溶液、水杨酸-乙醇溶液及过氧化氢溶液,放置反应30 min,于510 nm处测定吸光度。按照公式(2)计算羟自由基清除率[25]。
1.2.4.3 ABTS+自由基清除能力
配制在734 nm处的吸光度值为0.70±0.02的ABTS溶液,浓度为4 mg/mL的各个粗多糖样品母液。稀释样品至浓度为0.05~0.4 mg/mL,准确量取各稀释液20 μL,加入ABTS溶液180 μL,室温反应5 min,于734 nm测定吸光度。以BHT作为阳性对照,按照公式(2)计算ABTS+自由基清除率[25]。
1.2.4.4 亚铁离子螯合能力
配制浓度为5 mmol/L的菲啰嗪溶液和浓度为2 mmol/L的氯化亚铁溶液,浓度为8 mg/mL的各个多糖样品母液。稀释样品,准确量取各稀释液200 μL,加入氯化亚铁溶液20 μL与菲啰嗪溶液40 μL,室温反应5 min,于562 nm测定吸光度。以BHT作为阳性对照,按照公式(2)计算亚铁离子螯合能力[23]。
1.2.4.5 总还原能力
配制浓度为4 mg/mL的各多糖样品母液、磷酸缓冲溶液(PBS,0.2 mol/L,pH6.6)与铁氰化钾溶液(1%)。稀释样品,准确量取各稀释液800 μL,依次加入PBS和铁氰化钾溶液各400 μL,在50 ℃环境下反应50 min冷却至室温;再加入10%离心后的TCA水溶液400 μL,加入蒸馏水1.6 mL和400 μL三氯化铁水溶液(0.1%),室温放置10 min,700 nm处测定吸光度[25]。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复三次,所得数据采用OriginPro 21软件分析,采用均数±标准差表示,通过t检验,确认差异的显著性,以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
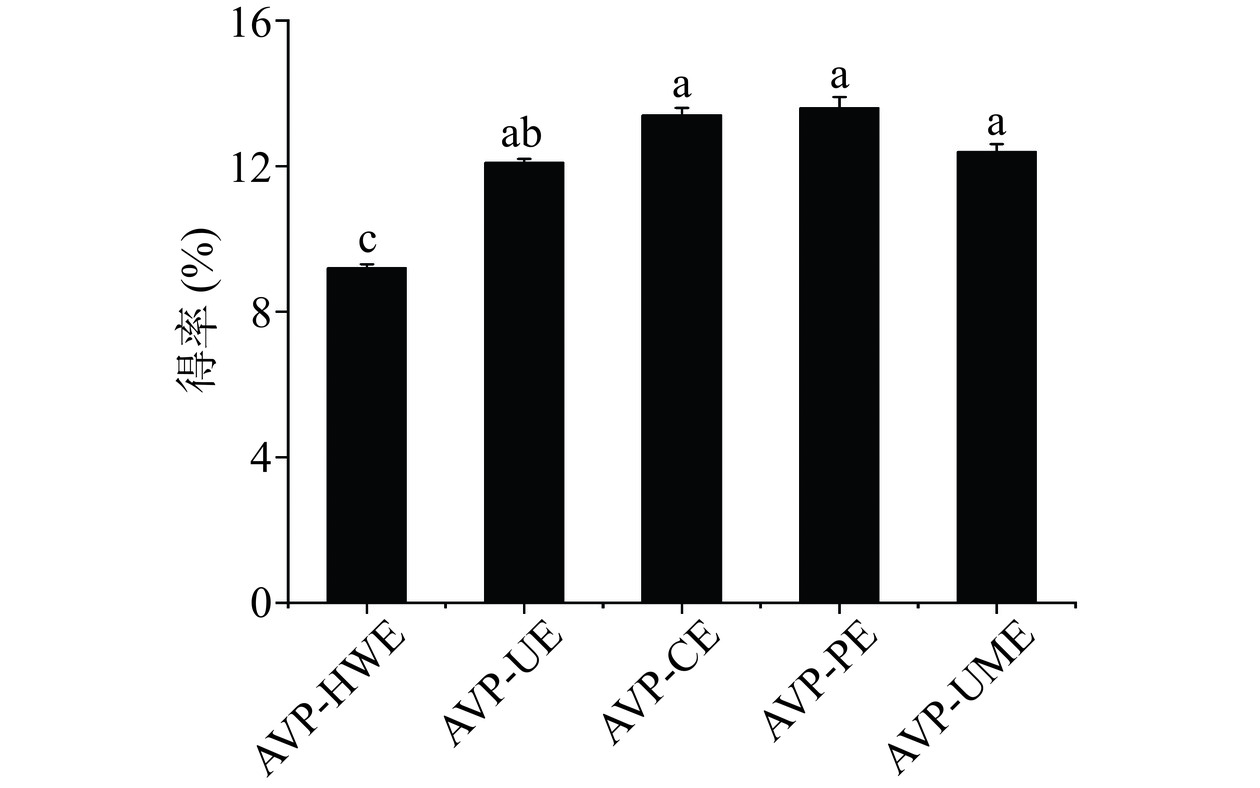
2.1 不同提取方法对罗布麻叶多糖得率的影响
热水提取法、超声辅助提取法、纤维素酶提取法、果胶酶提取法及超声微波协同提取等五种方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖的得率分别为9.2%±0.1%、12.1%±0.1%、13.4%±0.2%、13.6%±0.3%、12.4%±0.2%。如图1所示,HWE的提取率显著低于其他提取方法(P<0.01),酶提取法所得多糖的得率最高。HWE虽然条件较为温和,但其耗时长,提取效率低。超声波通过溶剂中产生的空化作用促进多糖的释放、扩散和溶解[21,26];纤维素酶及果胶酶能够在相对较低的温度下有效地解聚植物细胞壁中的纤维素及果胶,并能破坏细胞壁和细胞膜,促进所需多糖的分离,从而导致得率的升高[27−28]。因此,与HWE相比,新型辅助方法均可大幅度提高多糖的得率,此结果与较多文献报道结果一致[29−30]。Zhou等[5]分别使用不同的溶剂(0.05 mol/L和0.1 mol/L的盐酸及氢氧化钠、水)提取罗布麻叶多糖,得出酸、碱提取能够显著提高多糖的得率,以0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠为溶剂提取的多糖得率为水提法的4倍。赵东洋[31]通过热水提取法分别对罗布麻叶、茎、花及罗布麻茶多糖进行提取,得率分别为3.5%、15.8%、12.0%和15.0%。其中罗布麻叶多糖的得率显著低于本文中不同提取方法制备的AVP的得率。以上结果表明不同提取溶剂及提取方法对多糖得率有显著的影响。
2.2 罗布麻叶多糖的结构表征
2.2.1 单糖组成
混合标准品及不同提取方法制备的多糖的GC图进行比较得出罗布麻叶中的多糖主要含有阿拉伯糖(Ara)、葡糖糖(Glc)和半乳糖(Gal)三种单糖,含有少量的木糖(Xyl)和甘露糖(Man),不含有鼠李糖(Rha),结果如表1和图2所示。在五种多糖中阿拉伯糖(23.39%~37.98%)、葡糖糖(19.63%~48.32%)和半乳糖(21.42%~33.02%)含量最多,不同提取方法所得多糖的单糖含量也不同。如表1所示,经使用超声及酶解等辅助提取法,单糖组成变化较为明显,且多糖中的Glc含量均有所上升,Gal含量下降,此结果表明超声波、微波及酶的使用可能会将植物中不溶性糖降解为可溶性糖,且不同酶对其影响也有所差别,导致单糖组成的变化。从单糖组成可初步判断罗布麻叶多糖可能是由阿拉伯半乳聚糖组成的果胶类多糖。Wang等[10]研究表明罗布麻花两种纯化后的多糖由不同摩尔比的Rha、Ara、Xyl、Man、Glc及Gal组成,其中Gal及Ara为其主要单糖。Li等[11]报道罗布麻根多糖由摩尔比为35.10:34.18:23.67:7.04的Man、Ara、Glc及Gal组成,其主要单糖为Man及Ara。Yuan等[12]报道经热水提取及碱提取后的罗布麻叶多糖由Ara、Rha、Gal、Glc及GalA组成。魏柠柠[32]研究报道经水提醇沉及Sevag法脱蛋白后的罗布麻叶多糖由摩尔比为0.29:1.0:0.55:3.88:1.12:2.20:1.29的Man、Rha、葡萄糖醛酸(GlcA)、GalA、Glc、Gal及Ara组成。研究报道的罗布麻叶多糖的主要单糖组成与本文发现的一致,然而由于多糖制备方法及罗布麻植物来源的不同,各单糖摩尔比存在一定的差距。
表 1 罗布麻叶多糖的单糖组成(摩尔比%)Table 1. Yield and monosaccharide composition of AVP (molar ratio %)单糖 AVP-HWE AVP-UE AVP-CE AVP-PE AVP-UME Ara 37.98 23.39 37.25 28.88 26.33 Xyl − 2.06 − − − Man 9.37 − − − − Glc 19.63 43.88 33.93 46.07 48.32 Gal 33.02 30.67 28.82 28.05 21.42 注:AVP-HWE:罗布麻叶水提多糖,AVP-UE:罗布麻叶超声辅助提取多糖,AVP-CE:罗布麻叶纤维素酶提取多糖,AVP-PE:罗布麻叶果胶酶提取多糖,AVP-UME:罗布麻叶超声-微波协同提取多糖。 2.2.2 紫外吸收光谱结果
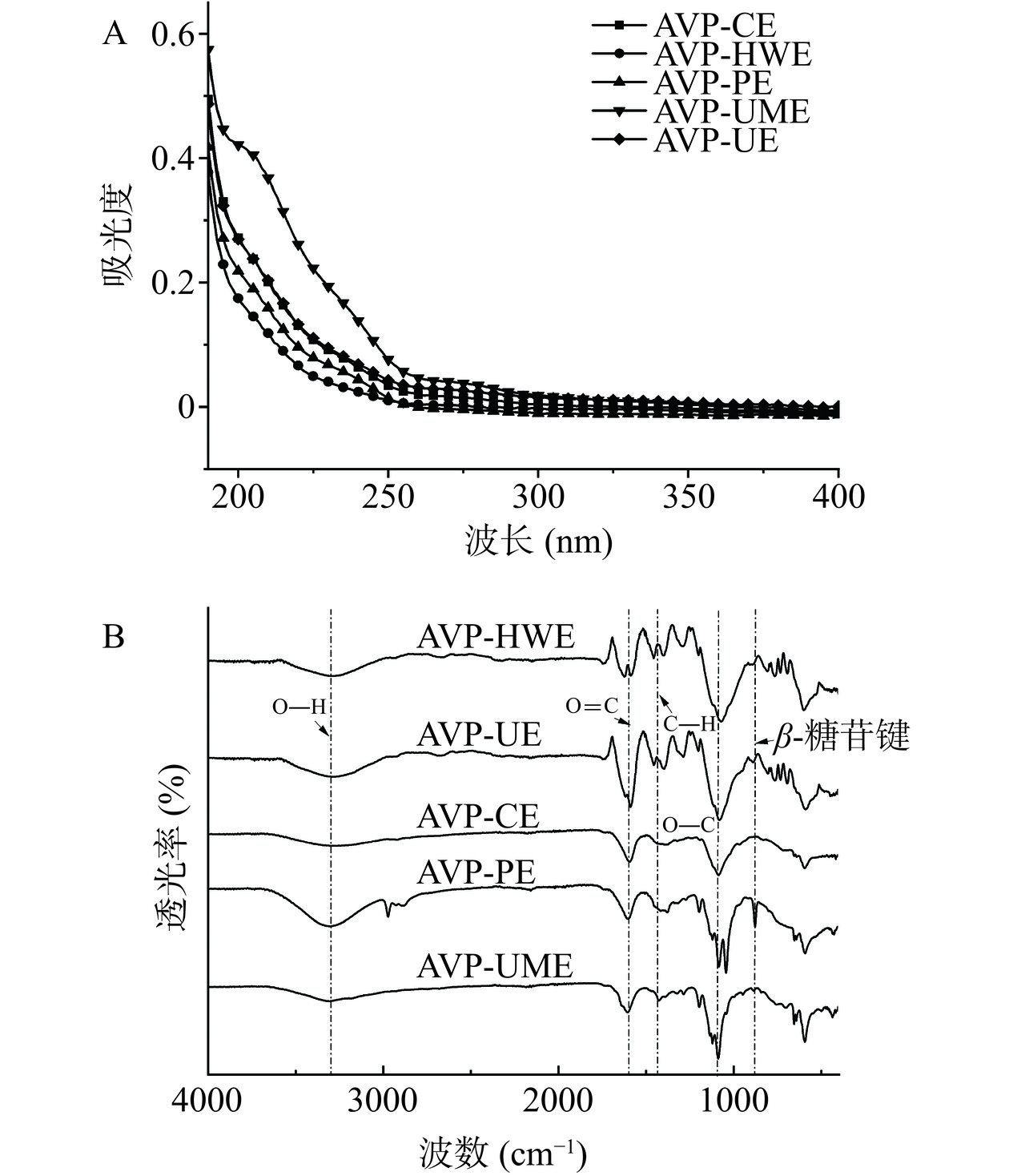
罗布麻多糖的紫外吸收光谱图如图3A所示。AVP-UE和AVP-UME在280 nm附近出现了微弱的吸收峰,说明其中含有极少量的蛋白,经BCA法测定后得出蛋白含量极少,可忽略不计。此研究结果与Zhou等[5]的研究报道一致。
2.2.3 红外吸收光谱结果
红外光谱可以用来分析多糖的糖苷键类型、官能团的类型以及糖环构型等。罗布麻叶多糖红外光谱图如图3B所示,五种多糖均在4000~500 cm−1范围内显出了相似的多糖吸收峰,说明多糖有相似的特征结构。3400 cm−1及2970 cm−1附近的吸收峰表示O-H及C-H的伸缩振动,1640 cm−1左右的吸收峰是C=O的伸缩振动,1475 cm−1左右的吸收峰是平面弯曲振动中的C-H,1200~1000 cm−1处的吸收峰为C-O-H键中C-O的拉伸振动,890 cm−1处出现吸收峰说明该多糖具有β-糖苷键,说明罗布麻叶多糖具有β-构型的糖苷键[33−34]。以上结果表明,不同的提取方法对罗布麻叶多糖的一级结构和糖苷键类型的影响较少。
2.2.4 刚果红染色试验结果
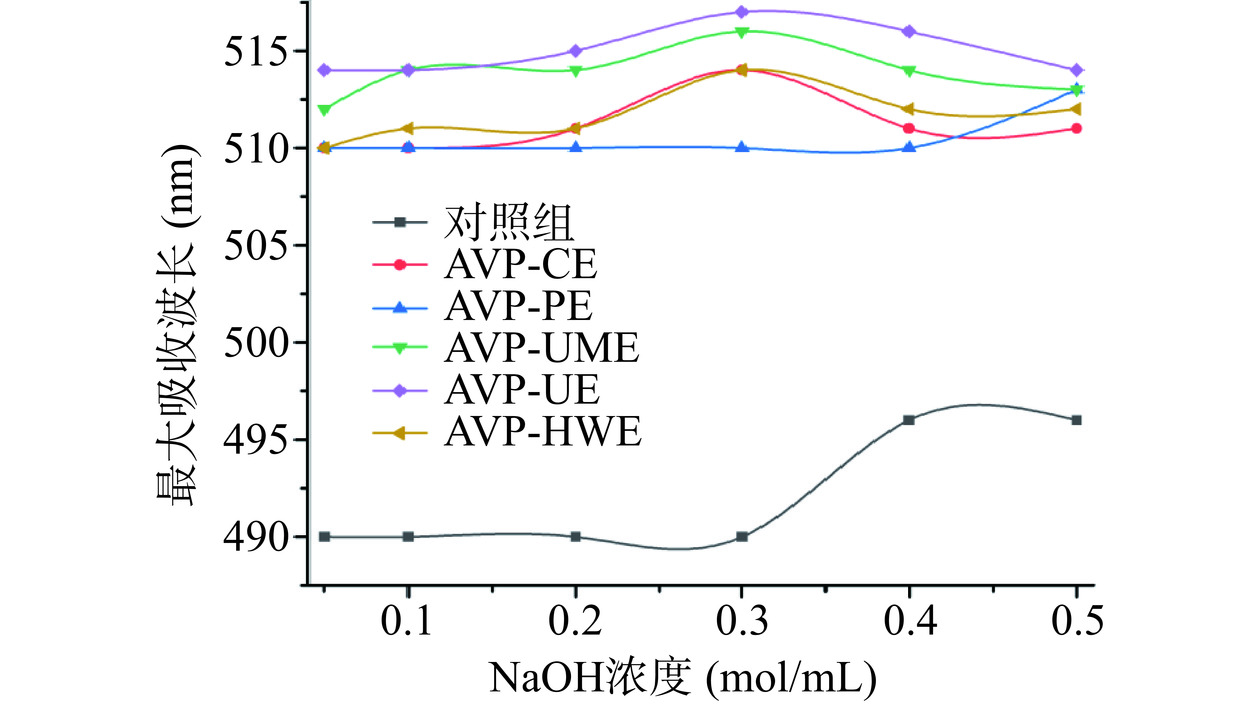
研究表明具有三螺旋结构的多糖在碱性条件下与刚果红生成红色络合物,络合物的λmax发生红移,且随着氢氧化钠浓度的升高三螺旋结构被破坏,λmax呈现下降趋势[35]。如图4所示,与阳性对照组相比,不同提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖与刚果红形成的络合物的λmax均发生红移。然而,随着NaOH浓度的升高,各络合物的λmax出现了不同的无规则变化,说明罗布麻叶多糖中可能不含有三螺旋结构,此结果与罗布麻根多糖报道一致[36]。其中,AVP-CE及AVP-UE显出先上升后降低趋势,AVP-PE显出先平缓再上升趋势,AVP-UME及AVP-HWE显出缓慢上升再降低的趋势,结果表明不同方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖具有不同的高级结构,不同提取方法所得罗布麻多糖的高级结构存在差异。
2.2.5 扫描电镜结果
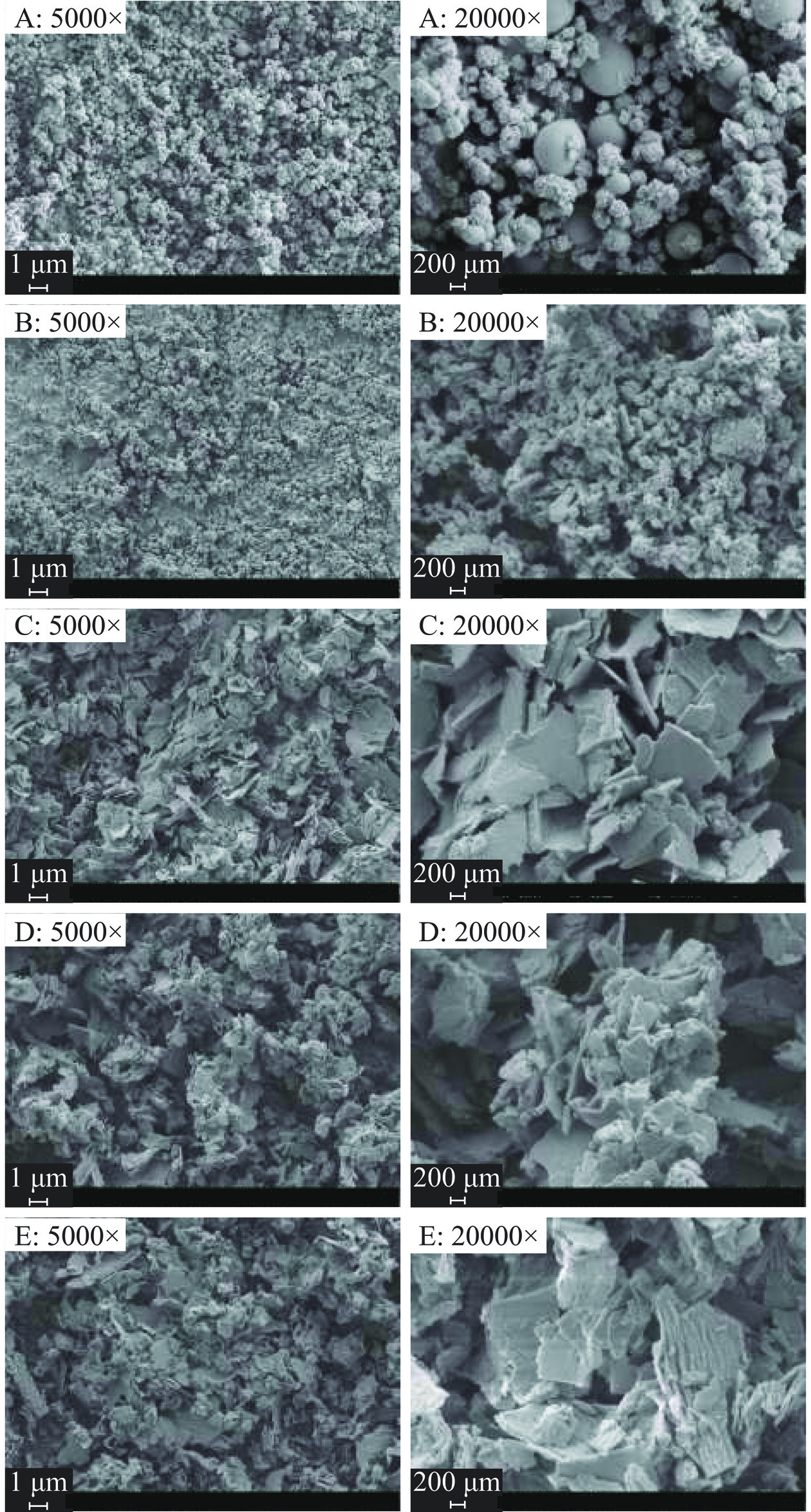
五种提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖在5000×和20000×放大倍数下的扫描电子显微镜图(SEM)如图5所示。AVP-HWE表面结构多表现为不规则的结构,放大至20000×可看出其主要是由不规则颗粒组成,表面较为粗糙(图5A)。AVP-UE显出球状及蜂窝状结构,球状颗粒表面较为光滑,而蜂窝状颗粒表面较为粗糙(图5B)。AVP-PE和AVP-CE表面都呈现出片状和块状混合结构,放大后发现AVP-PE片状结构较为完整,且较大,AVP-CE由片状结构较小、结构比较紧凑且多聚的结构组成(图5C和图5D)。AVP-UME由不规则大小的丝状与片状组成,表面较为粗糙(图5E),结果表明不同提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖表面形貌各不相同,不仅形状和颗粒大小,而且表面积等均有所不同。与传统水提法相比,超声辅助法、酶辅助法及超声-微波辅助法所制备的多糖可能由于在提取过程中超声、微波及酶的使用对植物细胞壁的破坏程度更大,处理方法在不同程度上破坏了多糖的原始链接方式,并导致了大小和形状的不同,说明不同的提取法对多糖的高级结构影响较大[37−38],此结果与刚果红实验结果一致。
2.3 罗布麻叶多糖的抗氧化活性
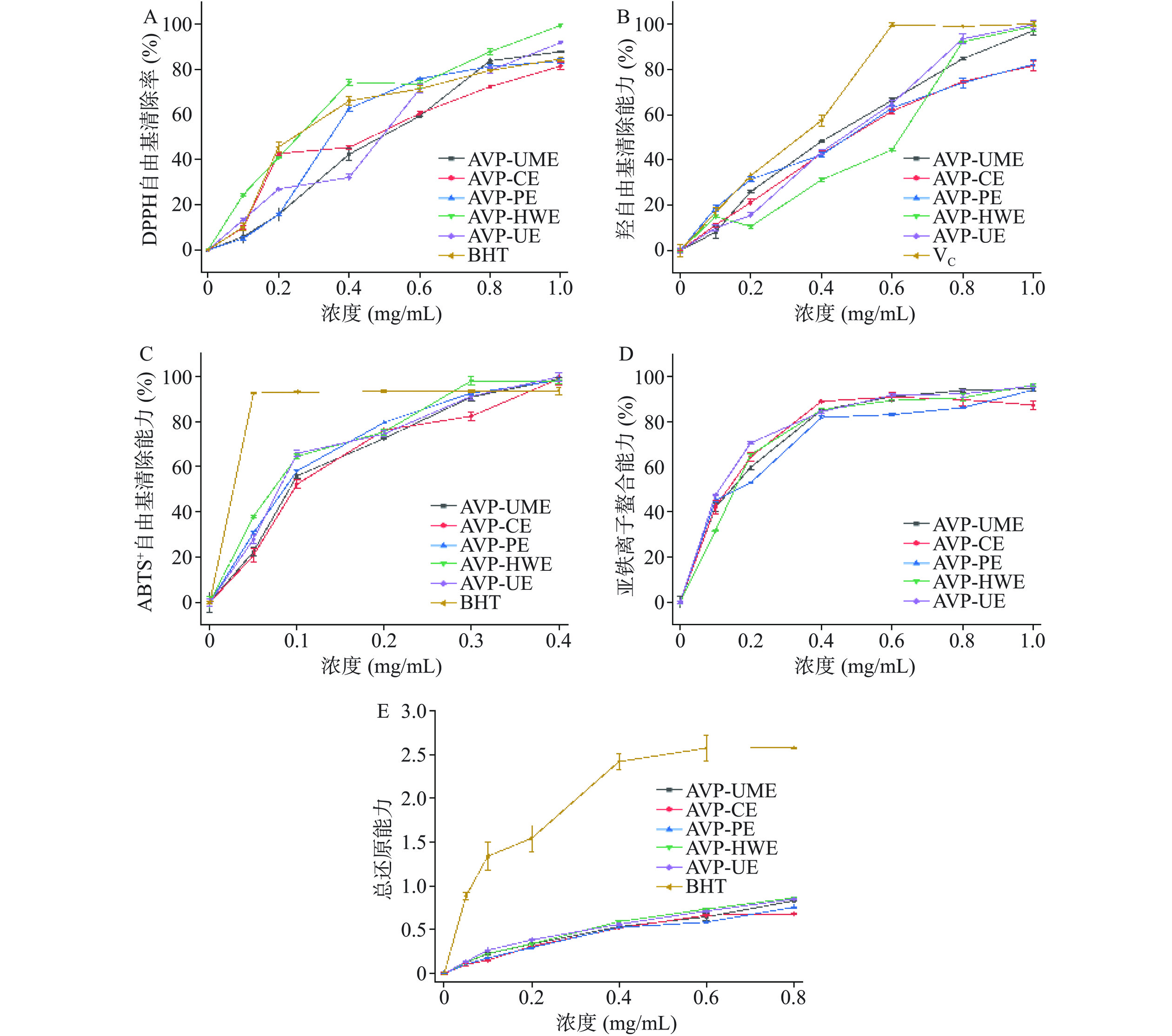
不同提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖的抗氧化活性结果如图6所示。随着浓度的升高,各多糖样品DPPH自由基清除能力均显出浓度依赖性关系(图6A)。当浓度为1 mg/mL时,AVP-HWE、AVP-UE及AVP-UME的DPPH自由基清除能力强于阳性对照BHT。其中,AVP-HWE的DPPH自由基清除能力最强,IC50值为0.219 mg/mL,其DPPH自由基清除能力显著强于其余多糖(P<0.05)。罗布麻叶多糖羟自由基清除能力结果如图6B所示,低浓度时五种多糖清除率均较差,随着浓度的升高AVP-HWE、AVP-UME和AVP-UE的清除能力迅速升高。通过对比IC50值可得出AVP-UE的羟自由基清除能力最强,IC50值为0.298 mg/mL。与DPPH及羟自由基清除能力相比,罗布麻叶多糖的ABTS+自由基清除能力及亚铁离子螯合能力较强。随着样品浓度的升高,ABTS+自由基清除能力及亚铁离子螯合能力均逐渐上升(图6C~6D),通过IC50值大小可以判断出AVP-HWE的ABTS+自由基清除能力最强,IC50值为0.072 mg/mL,AVP-CE和AVP-UE的亚铁离子螯合能力更强,IC50值分别为0.107 mg/mL和0.108 mg/mL,活性强于其余多糖。在测定浓度范围之内各多糖的总还原能力随着浓度的升高而增强,然而弱于阳性对照BHT,各样品之间无显著性差异,结果表明多糖对于自由基清除能力有一定的选择性。
Li等[7]研究报道罗布麻叶提取物当浓度为1 mg/mL时对DPPH、ABTS+及羟自由基的清除能力为57.4%、55.9%、83.1%,此结果显著低于罗布麻叶多糖的抗氧化活性。郑思睿等[14]报道热水提取后的罗布麻叶多糖具有较强的DPPH自由基清除能力和较弱的羟自由基清除能力,当浓度为6 mg/mL时其对羟自由基的清除能力低于50%。田立等[39]报道当浓度为1.2 mg/mL时,罗布麻叶多糖对羟自由基的清除能力为78.2%,同样浓度下总还原能力吸光度值达1.63。
研究表明多糖的生物活性与其结构的关系较为紧密。由于不同提取方法得到的多糖的结构差距较大,不同提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖显出的活性差距也较大。经对比不同提取方法制备的罗布麻叶多糖的IC50值(表2)可看出,不同种提取法制备的多糖具有不同的自由基清除能力。在羟自由基清除能力方面AVP-UE有较好的优势,AVP-CE亚铁离子螯合能力较强,在DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力中AVP-HWE的清除能力最好,各多糖在总还原能力方面差距较小。以上结果表明不同方法制备的罗布麻多糖均显出了不同的抗氧化活性。因此,原药材种类、产地,多糖的单糖组成、糖苷键链接方式及多糖的提取分离手段等均可能影响活性。
表 2 罗布麻叶多糖抗氧化活性的IC50( mg/mL)Table 2. IC50 of antioxidant activity of AVP (mg/mL)指标 AVP-HWE AVP-UE AVP-UME AVP-CE AVP-PE DPPH· 0.219b 0.358a 0.422a 0.388a 0.392a 羟自由基 0.342a,b 0.298b 0.333a,b 0.423a 0.368a 亚铁离子 0.149a 0.108a 0.132a 0.107a 0.136a ABTS+· 0.072a 0.084a 0.094a 0.083a 0.099a 注:同行不同字母表明有显著差异(P<0.05)。 3. 结论
本文通过热水提取、超声辅助提取、超声微波协同提取、纤维素酶及果胶酶提取等方法制备罗布麻叶多糖,通过UV、FT-IR、GC、SEM及刚果红染色等对多糖进行了结构初探,并通过体外自由基清除能力评价了抗氧化活性。结果表明果胶酶提取法得率最高(13.6%),热水提取法得率最低(9.2%)。罗布麻叶多糖主要含有Ara、Glc和Gal三种单糖,含有少量的Xyl和Man,FT-IR表明提取方法对多糖一级结构影响较小,均不含有三螺旋结构。抗氧化实验表明罗布麻叶多糖具有较强的DPPH、ABTS+、羟自由基清除能力及亚铁离子螯合能力,IC50分别为0.219~0.422、0.072~0.099、0.298~0.423、0.107~0.149 mg/mL。综上,不同提取方法对多糖结构及活性有显著的影响,经综合比较得出超声辅助提取法和纤维素酶提取法更适合于罗布麻叶多糖的提取。研究不同提取方法对罗布麻叶多糖结构以及活性的影响对于其在食品和药品原料开发方面具有深远的意义。有关于罗布麻叶多糖提取工艺优化、分离纯化、结构解析和生物活性关系研待进一步探究。
-
表 1 罗布麻叶多糖的单糖组成(摩尔比%)
Table 1 Yield and monosaccharide composition of AVP (molar ratio %)
单糖 AVP-HWE AVP-UE AVP-CE AVP-PE AVP-UME Ara 37.98 23.39 37.25 28.88 26.33 Xyl − 2.06 − − − Man 9.37 − − − − Glc 19.63 43.88 33.93 46.07 48.32 Gal 33.02 30.67 28.82 28.05 21.42 注:AVP-HWE:罗布麻叶水提多糖,AVP-UE:罗布麻叶超声辅助提取多糖,AVP-CE:罗布麻叶纤维素酶提取多糖,AVP-PE:罗布麻叶果胶酶提取多糖,AVP-UME:罗布麻叶超声-微波协同提取多糖。 表 2 罗布麻叶多糖抗氧化活性的IC50( mg/mL)
Table 2 IC50 of antioxidant activity of AVP (mg/mL)
指标 AVP-HWE AVP-UE AVP-UME AVP-CE AVP-PE DPPH· 0.219b 0.358a 0.422a 0.388a 0.392a 羟自由基 0.342a,b 0.298b 0.333a,b 0.423a 0.368a 亚铁离子 0.149a 0.108a 0.132a 0.107a 0.136a ABTS+· 0.072a 0.084a 0.094a 0.083a 0.099a 注:同行不同字母表明有显著差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopoeia[M]. Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020.] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopoeia[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020.
[2] 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 1977. [Editorial Board of Flora of China of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1977.] Editorial Board of Flora of China of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1977.
[3] SUN S W, ZHAO Y W, WANG L Y, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of bound phenolic compounds from the residue of Apocynum venetum tea and their antioxidant activities[J]. Food Bioscience,2022,47:101646. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101646
[4] SHAO D Y, GAO G, ABUBAKAR A S, et al. Total flavonoids extracts of Apocynum L. from the Ili river valley region at different harvesting periods and bioactivity analysis[J]. Molecules,2022,27:7343. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217343
[5] ZHOU J H, ZOU P, JING C L, et al. Chemical characterization and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Apocynum venetum leaves extracted by different solvents[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2019,14:244−253.
[6] PENG J, ABDULLA R, LI Y, et al. Potential anti-diabetic components of Apocynum venetum L. flowers:Optimization, chemical characterization and quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,115:104930. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104930
[7] LI C, HUANG G B, TAN F, et al. In vitro analysis of antioxidant, anticancer, and bioactive components of Apocynum venetum tea extracts[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2019,2019:1−13.
[8] ZHANG D, GU Z, WANG J, et al. Apocynum leaf extract suppresses the progress of atherosclerosis in rats via the FKN/SYK/p38 signal pathway[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2021,26:5524226.
[9] 杨杰, 付慧, 张晋, 等. 罗布麻提取物改善小鼠高脂饮食诱导的代谢失调与肠道菌群紊乱[J]. 陆军军医大学学报,2022,44:266−274. [YANG J, FU H, ZHANG J, et al. Apocynum venetum L. extract ameliorates metabolic dysbiosis and intestinal flora disorder induced by high-fat diet in mice[J]. Journal of Army Medical University,2022,44:266−274.] YANG J, FU H, ZHANG J, et al. Apocynum venetum L. extract ameliorates metabolic dysbiosis and intestinal flora disorder induced by high-fat diet in mice[J]. Journal of Army Medical University, 2022, 44: 266−274.
[10] WANG L L, ZHANG X F, NIU Y Y, et al. Anticoagulant activity of two novel polysaccharides from flowers of Apocynum venetum L.[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,124:1230−1237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.015
[11] LI D, WANG S Y, WANG G N, et al. Structural characterization and immunoregulatory activity of a neutral polysaccharide from the roots of Apocynum venetum L.[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,222:90−100. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.158
[12] YUAN Y, ZHOU J H, ZHENG Y F, et al. Beneficial effects of polysaccharide-rich extracts from Apocynum venetum leaves on hypoglycemic and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,127:110182.
[13] CHEN X Q, WANG C P, WANG C Y, et al. The emulsification properties of alkaline-extracted polysaccharide conjugates from Apocynum venetum L. tea residues[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107315. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107315
[14] 郑思睿, 杨婷, 依木然·马瑞士, 等. 响应面法优化罗布麻多糖提取工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39:93−97. [ZHENG S R, YANG T, EMRAN M, et al. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides in Apocynum venetum by response surface methods[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39:93−97.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.08.017 ZHENG S R, YANG T, EMRAN M, et al. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides in Apocynum venetum by response surface methods[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39: 93−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.08.017
[15] SU S Y, DING X, HOU Y L, et al. Structure elucidation, immuno-modulatory activity, antitumor activity and its molecular mechanism of a novel polysaccharide from Boletus reticulatus Schaeff[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12:647−661. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.067
[16] WEI C Y, YAO L, ZHANG L, et al. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of peach gum polysaccharides with different molecular weights and their impacts on gut microbiota[J]. Foods,2022,11:3970. doi: 10.3390/foods11243970
[17] SHI H M, LI J C, YU J, et al. Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from different parts of Hibiscus manihot L[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2024,1295:136598. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136598
[18] JING Y S, YAN M, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of extraction methods on the physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Foods,2023,12:2088. doi: 10.3390/foods12102088
[19] TANG Y Y, HE X M, LIU G M, et al. Effects of different extraction methods on the structural, antioxidant and hypoglycemic properties of red pitaya stem polysaccharide[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,405:134804. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134804
[20] 白冰瑶, 付超, 张春兰, 等. 不同提取方法对恰玛古多糖生物活性的比较[J]. 食品科技,2022,47:214−223. [BAI B Y, FU C, ZHANG C L, et al. Comparison on bioactivity of Brassica rapa L. Polysaccharides by different extraction methods[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47:214−223.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203031 BAI B Y, FU C, ZHANG C L, et al. Comparison on bioactivity of Brassica rapa L. Polysaccharides by different extraction methods[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47: 214−223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203031
[21] ABUDUWAILI A, ROZI P, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Effects of different extraction techniques on physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk[J]. Process Biochemistry,2019,83:189−197. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.05.020
[22] CAO W, WANG C, MAYHESUMU X, et al. Isolation, structural elucidation, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity of polysaccharides of Brassica rapa L.[J]. Molecules,2022,27(9):3002. doi: 10.3390/molecules27093002
[23] ABUDUWAILI A, NUERXIATI R, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Isolation, structural modification, characterization, and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Folium isatidis[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2022,176:114319. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114319
[24] LIU G R, KAMILIJIANG M, ABUDUWAILI A, et al. Isolation, structure elucidation, and biological activity of polysaccharides from Saussurea involucrata[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,222:154−166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.137
[25] ROZI P, ABUDUWAILI A, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Sequential extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,131:97−106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.029
[26] SOROURIAN R, KHAJEHRAHIMI A E, TADAYONI M, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Typha domingensis:Structural characterization and functional properties[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,160:758−768. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.226
[27] 方嘉沁, 郑青松, 文雨欣, 等. 不同提取方法的莲子心多糖结构与理化性质比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(1):92−103. [FANG J Q, ZHENG Q S, WEN Y X, et al. Comparison of the structures and physiochemical properties of polysaccharides extracted from Plumula Nelumbinis by different methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(1):92−103.] FANG J Q, ZHENG Q S, WEN Y X, et al. Comparison of the structures and physiochemical properties of polysaccharides extracted from Plumula Nelumbinis by different methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(1): 92−103.
[28] CHI Y, LI Y, ZHANG G, et al. Effect of extraction techniques on properties of polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera and their applicability in iron chelation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,181:616−623. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.104
[29] 马婷, 曲航, 杨海龙. 提取方法对羊栖菜多糖理化性质及体外生物活性的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(15):259−268. [MA T, QU H, YANG H L. Effects of extraction methods on physicochemical properties and in vitro biological activity of polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2023,14(15):259−268.] MA T, QU H, YANG H L. Effects of extraction methods on physicochemical properties and in vitro biological activity of polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2023, 14(15): 259−268.
[30] 覃引, 徐文慧, 吴凯, 等. 不同提取方法对黄精多糖理化特性和生物活性的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(3):142−152. [QIN Y, XU W H, WU K, et al. Effects of the physicochemical properties and biological activities of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides extracted by different extraction methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(3):142−152.] QIN Y, XU W H, WU K, et al. Effects of the physicochemical properties and biological activities of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides extracted by different extraction methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(3): 142−152.
[31] 赵东洋. 罗布麻系列多糖的提取、分离以及抑制半乳凝集素活性的研究[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2017. [ZHAO D Y. Studies on extraction and separation of polysaccharides from Apocynum and their anti-galectins effects[D]. Changchun:Northeast Normal University, 2017.] ZHAO D Y. Studies on extraction and separation of polysaccharides from Apocynum and their anti-galectins effects[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2017.
[32] 魏柠柠. 罗布麻叶多糖的分离纯化、结构分析以及与半乳凝集素的相互作用[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2010. [WEI N N. Isolation, purification and structure analysis of the polysaccharides from Apocynum venetum leaves and its interaction with Galectin-3[D]. Changchun:Northeast Normal University, 2010.] WEI N N. Isolation, purification and structure analysis of the polysaccharides from Apocynum venetum leaves and its interaction with Galectin-3[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2010.
[33] 陈晓乐, 李文文, 陈锵, 等. 牛蒡中性多糖结构分析与抗炎活性评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(12):45−54. [CHEN X L, LI W W, CHEN Q, et al. Structure analysis and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of neutral polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(12):45−54.
[34] 何思辰, 陈凌利, 陈慧, 等. 不同脱蛋白方法对青钱柳多糖的结构和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(16):81−89. [HE S C, CHEN L L, CHEN H, et al. Effect of different protein removal methods on the structure and antioxidant activity of the Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(16):81−89.] HE S C, CHEN L L, CHEN H, et al. Effect of different protein removal methods on the structure and antioxidant activity of the Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(16): 81−89.
[35] CUI Y L, WANG R, CAO S, et al. A galacturonic acid-rich polysaccharide from Diospyros kaki peel:Isolation, characterization, rheological properties and antioxidant activities in vitro[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,416:135781. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135781
[36] LIU D, WANG S Y, BAO Y L, et al. Extraction, purification and structural characterization of polysaccharides from Apocynum venetum L. roots with anti-inflammatory activity[J]. Process Biochemistry,2022,121:100−112. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2022.06.035
[37] CHEN H Y, ZENG J S, WANG B, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of Bletilla striata polysaccharide extracted by different methods[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,266:118149. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118149
[38] CHEN X H, CHEN G J, WANG Z R, et al. A comparison of a polysaccharide extracted from ginger (Zingiber officinale) stems and leaves using different methods:Preparation, structure characteristics, and biological activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,151:635−649. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.222
[39] 田立, 郭晓农, 孟杨, 等. 罗布麻多糖成分体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中兽医医药杂志,2016,35:5−8. [TIAN L, GUO X N, MENG Y, et al. Study on the antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Apocynum venetum in vitro[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary,2016,35:5−8.] TIAN L, GUO X N, MENG Y, et al. Study on the antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Apocynum venetum in vitro[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary, 2016, 35: 5−8.
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 曹雪丽,韩笑,李屿恺,王泽莹,董海钰,杨娟,郭晓. 响应面法优化泰山女儿茶总黄酮提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究. 广东化工. 2024(06): 7-10+60 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周志红,赵昕,胡勤,肖明明. 超声波处理与纤维素酶协同提取山楂总多酚的工艺优化研究. 当代化工研究. 2024(11): 152-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄月,向海芹,王双辉,龚意辉,陈致印. 穇子多酚的分离纯化及其抗氧化能力研究. 食品工业. 2023(01): 42-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾诗琴,梁强,李云成,赵玲,徐霞,熊伟,宣朴,姚英政. 浓香菜籽油SiO_2脱胶工艺优化及品质分析. 中国油脂. 2023(04): 21-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王媛媛,郝璟嵘,闫思颖,张甜甜,党玲,王晓婧. 沙棘冻干粉泡腾片的制备工艺优化及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(10): 235-241 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 杨春晖,王文平,续丹丹,崔宇倩,鞠岩,许春艳,吕小婷. 不同原料酿造酱油功能成分及抗氧化活性比较. 食品工业科技. 2023(14): 318-325 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 刘敏卓,张小月,张灵芝,曹孟君,叶素芳,吴泽华,张杰,曾志红. 竹茹总黄酮超声波处理与纤维素酶协同提取工艺优化及其体外抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(20): 221-229 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 张鑫,朱青永,徐慧敏,吴梦园,陈小娥,陈启和,刘政捷. 黄绿卷毛菇中原伊鲁烷型倍半萜芳基酯提取工艺优化及活性研究. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2023(06): 813-824 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 关玉婷,陈瑞瑞,蔡如玉,范蓓,孙晶,张瑞,张紫阳,常世敏. 超声辅助提取茄皮酚工艺优化及其降血糖功效研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



