Effect of Xylose on in Vitro Digestion of Starch and Its Action Mechanism
-
摘要: 淀粉是日常饮食中的主要碳水化合物来源,淀粉消化的快慢是影响机体餐后血糖水平的重要因素。本文以木糖为研究对象,探究了木糖对玉米淀粉体外消化特性的影响及其作用机理。通过体外模拟消化实验测定了不同添加量的木糖(5%、10%、15%)对淀粉体外消化性的影响,利用酶抑制动力学、分子对接、人体血糖生成指数(GI)测试研究了木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的作用机理及其对血糖波动的影响。结果表明,不同添加量的木糖均能抑制玉米淀粉的消化,木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的半数抑制浓度(IC50值)分别为205.35和4.75 mg/mL,抑制类型属于混合型抑制。木糖通过氢键与α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的氨基酸残基相互作用,其结合能分别为−3.05和−5.30 kcal/mol。添加木糖后,植物基肽素乳的GI值由58下降至45,表明木糖能够降低餐后血糖波动。该结果可为木糖在营养健康食品中的研究和应用提供科学的数据支持。Abstract: Starch was the main source of carbohydrates in people's daily diet, and its digestibility was an important factor affecting the body's postprandial blood glucose level. In this paper, the effect of xylose on the in vitro digestive properties of corn starch and its mechanism of action were investigated. The in vitro digestibility of starch was evaluated by an in vitro simulated digestion system after different additions of xylose (5%, 10%, and 15%), and the mechanisms of xylose on α-amylase and α-glucosidase, as well as its effect on blood glucose fluctuation through enzyme inhibition kinetics, molecular docking, and human glycemic index (GI) tests. The results showed that the digestive hydrolysis of corn starch was inhibited by different amounts of xylose, and the IC50 values of xylose on α-glucosidase and α-amylase were 205.35 and 4.75 mg/mL, respectively, which belonged to the mixed type inhibitors. Xylose interacted with amino acid residues of α-glucosidase and α-amylase through hydrogen bonding with binding energies of −3.05 and −5.30 kcal/mol, respectively. Additionally, the GI value of plant-based peptidoglycan milk decreased from 58 to 45 after the addition of xylose, which demonstrated that xylose was effective in decreasing the fluctuation of postprandial blood glucose. The results could provide scientific data to support the research and application of xylose in nutritional and health foods.
-
Keywords:
- xylose /
- starch digestibility /
- α-amylase /
- α-glucosidase /
- glucose fluctuations
-
随着生活节奏的加快、饮食习惯和膳食结构的变化及社会老龄化的加重,糖尿病、心血管疾病、肥胖症等慢性病发病率逐年提升,已成为目前全球性的重大公共卫生问题[1]。预防和控制上述疾病发生的关键在于科学合理的膳食结构,其中碳水化合物的质量十分重要。评价碳水化合物质量的一个重要生理参数为食物血糖生成指数(GI),低GI食物(GI值≤55)在胃肠道中消化吸收较慢,分解产生葡萄糖的速率低,从而可以维持餐后血糖稳态,有利于预防和治疗糖尿病等慢性疾病[2]。低GI饮食干预已被列入我国糖尿病及减重医学营养治疗指南,低GI饮食中重要的一点是选择优质碳水化合物,减少糖的摄入。淀粉是碳水化合物的主要来源,人体摄入过多的淀粉在体内消化,所释放出的葡萄糖是餐后血糖升高的主要原因,因此,筛选能够抑制淀粉消化的功能配料,对低GI产品的研发具有重要意义[3]。有研究表明,人体摄入一些功能糖有助于控制餐后血糖,这可能是由于其中一部分功能糖在小肠内难以被消化吸收;另一部分功能糖可能通过抑制消化酶(如α-葡萄糖苷酶)的活性,减缓或抑制碳水化合物的消化吸收,控制餐后高血糖的发生[4−5]。在此现状下,功能糖越来越受到生产者和消费者的青睐。
木糖作为一种功能性单糖,广泛存在于天然食物中(玉米芯、棉子壳等),其不代谢也不为人体提供能量,能够有效促进肠道内双歧杆菌的增殖[6],具有很大的应用前景。国外已有研究报道了木糖对餐后血糖波动具有有益作用,Asano等[7]的研究结果显示,食用含有10%(w/w)木糖的蔗糖饮料可以抑制小鼠血糖和胰岛素的快速升高;Jun等[8]通过血糖测试发现将木糖添加到饮料中有利于健康受试者和糖尿病受试者的餐后血糖控制。在我国,木糖主要作为木糖醇的半成品或原料,已有40年的生产历史,但并没有成为直接消费品,人们对其了解较少,而上世纪六十年代,日本已批准木糖作为无热量甜味剂[9]。国际上其他国家除了将木糖作为木糖醇的原料外,也将木糖作为食品添加剂用于代糖产品[10−11]。但目前,国内关于木糖的基础研究信息较少,其对淀粉消化及血糖波动的作用机理仍不明确。
本文以木糖为研究对象,通过体外模拟消化体系研究其对淀粉消化性质的影响,并测定了木糖对α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶的酶活性抑制作用,结合分子对接技术对木糖与α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶的作用位点进行挖掘,采用人体GI测试研究了木糖添加到植物基肽素乳后对餐后血糖波动的影响,以期为木糖在淀粉类食品和低GI食品中的开发利用提供理论依据和实践基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
木糖(≥99%) 济南圣泉唐和唐生物科技有限公司;玉米淀粉 河北田人嘉业农副产品有限公司;植物基肽素乳 宁波御坊堂生物科技有限公司;唾液淀粉酶(5 U/mg)、胃蛋白酶(250 U/mg)、胰酶(4×USP)、淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(120 U/mg)、α-淀粉酶(5 U/mg) 美国Sigma-aldrich公司;3号胆盐 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;可溶性淀粉、3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS)试剂、对硝基苯基-β-D-吡喃半乳糖苷(pNPG) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;α-葡萄糖苷酶(100 U/mg)、磷酸盐(PBS)试剂 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;F00-1-1葡萄糖测定试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;无水葡萄糖(食品级) 浙江一诺生物科技有限公司;其他化学试剂均为分析纯。
BSA224S电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;RC-806溶出试验仪 天津市鑫洲科技有限公司;Spectra Maxi3酶标仪 美国MD公司;DK-8D三温三控水槽 北京天林恒泰科技有限公司;台式pH计 梅特勒托利多;LGJ-10真空冷冻干燥机 北京松源华兴科技发展有限公司;MYP11-2A磁力搅拌器 上海梅颖浦仪器仪表制造有限公司;Beckman AU480全自动生化仪 贝克曼库尔特商贸(中国)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 玉米淀粉体外消化性测定
玉米淀粉体外消化性根据Brodkorb等[12]和Ding等[13]的方法测定并略有调整。模拟口腔液、胃液、小肠液配制方法如表1所示。称取200 mg玉米淀粉于离心管(50 mL)中,并分别称取5%、10%、15%的木糖(以玉米淀粉质量计)与玉米淀粉混合均匀,按1:1(W/W)加入模拟口腔液混匀,于200 r/min、37 ℃条件下模拟口腔消化2 min。而后将混合好的样品转移至溶出试验仪中并加入10 mL的模拟胃液,在200 r/min、37 ℃条件下模拟胃消化阶段1 h,随后加入NaOH将消化液调至pH7.0终止胃消化,并加入20 mg淀粉葡萄糖苷酶与10 mL模拟肠液充分混匀,于模拟肠消化阶段的0、20、40、60、90、120、150、180 min时间点吸取样品500 μL到10 mL离心管中,加入4.5 mL无水乙醇灭酶。将灭酶后的样品于5000 r/min离心5 min取上清液,用葡萄糖试剂盒测定样品中葡萄糖浓度。淀粉水解率的计算公式如下:
表 1 模拟体外消化液成分Table 1. Composition of simulated digestive fluid in vitro口腔液 胃液 小肠液 去离子水(mL) 500 1000 1000 NaCl(g) − 3.1 5.4 KCl(g) 0.562 1.1 0.65 CaCl2(g) − 0.15 − NaHCO3(g) 0.571 0.6 − KH2PO4(g) 0.252 − − MgCl2(H2O)6(g) 0.015 − − (NH4)2CO3(g) 0.003 − − CaCl2(H2O)2(g) 0.11 − 0.33 pH 7.0 2.0 7.0 酶 75 U/mL
唾液淀粉酶2000 U/mL
胃蛋白酶400 U/mL胰酶、
10 mmol/L胆汁盐水解率(%)=葡萄糖释放量(mg)×0.9淀粉质量(mg)×100 (1) 1.2.2 木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制率测定
木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用参照姚晓芬等[14]和Zhang等[15]的方法并略有修改。取200 µL不同浓度(100~500 mg/mL)的木糖加入200 µL α-葡萄糖苷酶(1.5 U/mL)混合均匀,于37 ℃水浴中反应5 min,随后加入200 µL pNPG(2.5 mmol/L)继续反应15 min,最后加入800 µL Na2CO3(0.2 mol/L)终止反应,并测定其在波长405 nm处的吸光值。
参照杨沁雪[16]和潘玥等[17]的方法测定木糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制活性。将木糖配制成不同浓度(2~10 mg/mL)的溶液,各吸取200 µL木糖溶液与200 µL 1%可溶性淀粉混合均匀,于37 ℃水浴条件下孵育10 min,随后加入200 µL α-淀粉酶溶液(5 U/mL)继续孵育10 min。而后加入400 µL的DNS试剂在沸水浴中煮5 min后置于冰水中迅速冷却,并加入4 mL去离子水稀释,测定其在波长540 nm处的吸光值。
每个样品至少平行测试3次,以阿卡波糖为阳性对照。根据如下公式计算木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的酶活抑制率,采用SPSS软件拟合计算木糖对酶的半数抑制浓度(IC50值)。
酶活性抑制率(%)=1−A样品−A样品背景A空白样品−A空白背景×100 (2) 式中,A样品为样品反应吸光值;A样品背景为样品背景反应吸光值;A空白样品为空白背景反应吸光值;A空白背景为空白背景反应吸光值。
1.2.3 木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制类型分析
取不同浓度的木糖(0、200 mg/mL),保持α-葡萄糖苷酶浓度不变(1.5 U/mL),改变底物pNPG的浓度(1、2、2.5 mmoL/L)[18],测定木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的酶促反应速率;木糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制类型测定是在1.2.2的基础上改变底物可溶性淀粉的浓度(3、5、10 mg/mL),保持α-淀粉酶的浓度不变(5 U/mL),测定不同浓度的木糖(0、4 mg/mL)对α-淀粉酶的酶促反应速率[19]。以底物浓度的倒数1/[S]为横坐标,以反应速度的倒数[1/V]为纵坐标,绘制双倒数曲线,分析木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制类型。
1V=ΔTOD2−OD1 (3) 式中,1/V为反应速率倒数;ΔT为底物与木糖反应时间;OD1和OD2为反应不同时间的吸光值。
1.2.4 分子对接分析
从PubChem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)下载木糖分子结构(CAS:58-86-6),α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的三维结构模型从PDB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)下载,其编号分别为:4X9Y和3A4A。对配体和受体进行去水、加氢、计算电荷、添加原子类型等前处理后采用Autodock 4.2.6软件进行对接,计算出靶点与化合物之间的结合能,采用Discovery Studio 4.5软件对结果进行可视化分析以解析木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶两种酶之间的相互作用[20−21]。
1.2.5 GI值测定
参照国际标准ISO 26642:2010《Food products-Determination of the glycemic index (GI) and recommendation for food classification》测定不含木糖和添加木糖的植物基肽素乳的GI值。受试者为健康成年人(年龄在18~60岁)男女各半,无其他不良嗜好,测试人数为10人。参考食物为葡萄糖,测定周期包括3~4次独立试食测定,其中参考食物2~3次,待测食物1次,采用随机设计。测试当日应当避免剧烈运动,受试者静坐10 min后开始试食测定。间隔5 min采集2次空腹指尖血样。在5~10 min内进食完所有受试物,从摄入第一口食物开始计时。分别于餐后15、30、45、60、90和120 min采集血样,离心取血清并用生化仪测定血糖浓度,按照下列公式计算GI值。本研究中国医学院北京协和医院伦理审查委员会许可(K22NO129),受试者在试验前均签署知情同意书。
GI=待测食物IAUC参比食物葡萄糖IAUC×100 (4) 式中,IAUC为血糖应答曲线下增幅面积。
1.3 数据处理
实验均重复3次,结果采用平均值±标准差表示。采用Origin 2022软件进行绘图,通过SPSS(IBM Statistics 22.0)软件进行显著性分析,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 木糖对淀粉体外消化性的影响
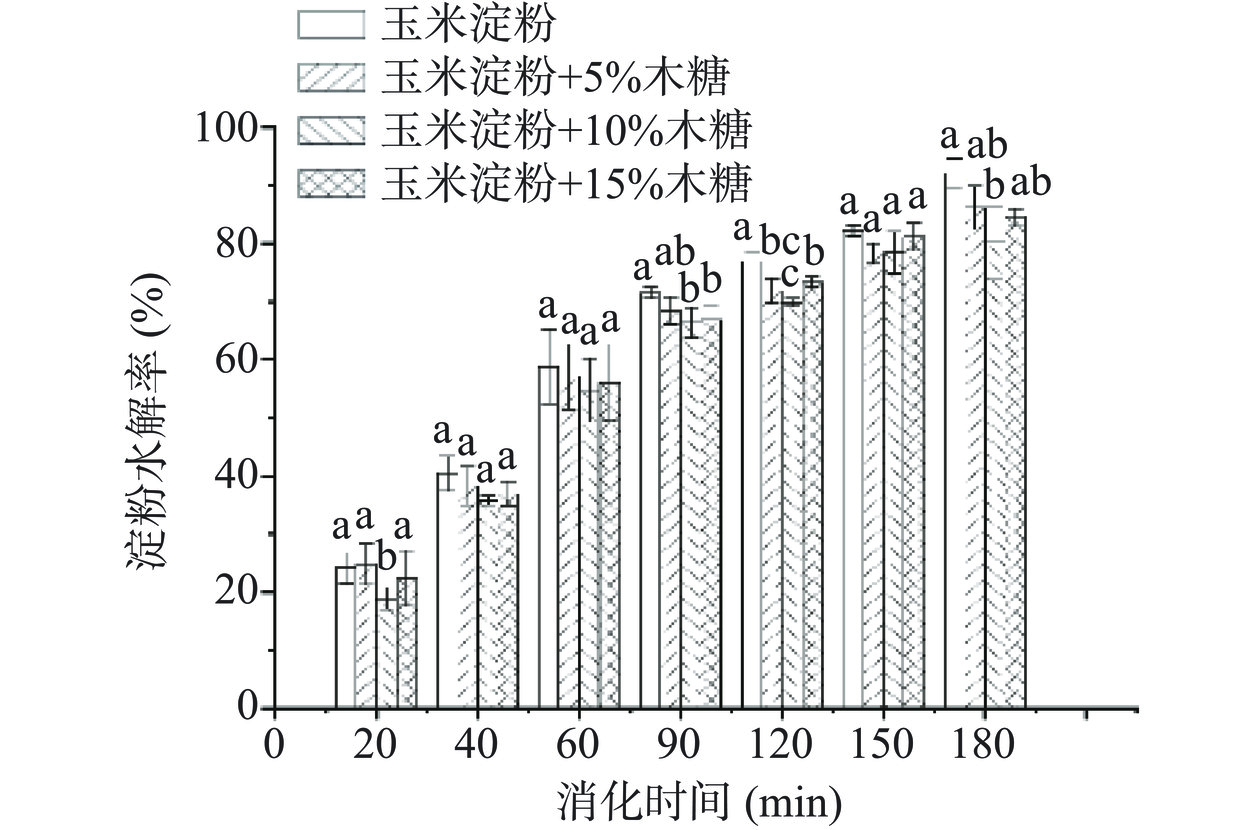
不同添加量(5%、10%、15%)的木糖对玉米淀粉体外消化性的影响如图1所示。从图1可以看出,随着消化时间的增加,所有样品的水解率均逐渐增加。当消化时间为180 min时,玉米淀粉的水解率为91.96%。进一步分析发现,加入木糖后,不同时间点的淀粉水解率均有所降低,木糖添加量为5%、10%和15%时,玉米淀粉在180 min时的水解率分别为86.11%、80.09%、84.55%,与未添加木糖时玉米淀粉的水解率相比,分别下降了5.85%、11.87%、7.41%。以上结果表明,木糖能够降低淀粉的水解率,其中当木糖添加量为10%时,玉米淀粉的消化率显著降低(P<0.05)。相关研究指出,木糖能够抑制两种消化关键酶α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性,降低淀粉与消化酶的接触,从而起到抑制淀粉水解的作用[8]。
2.2 木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制作用分析
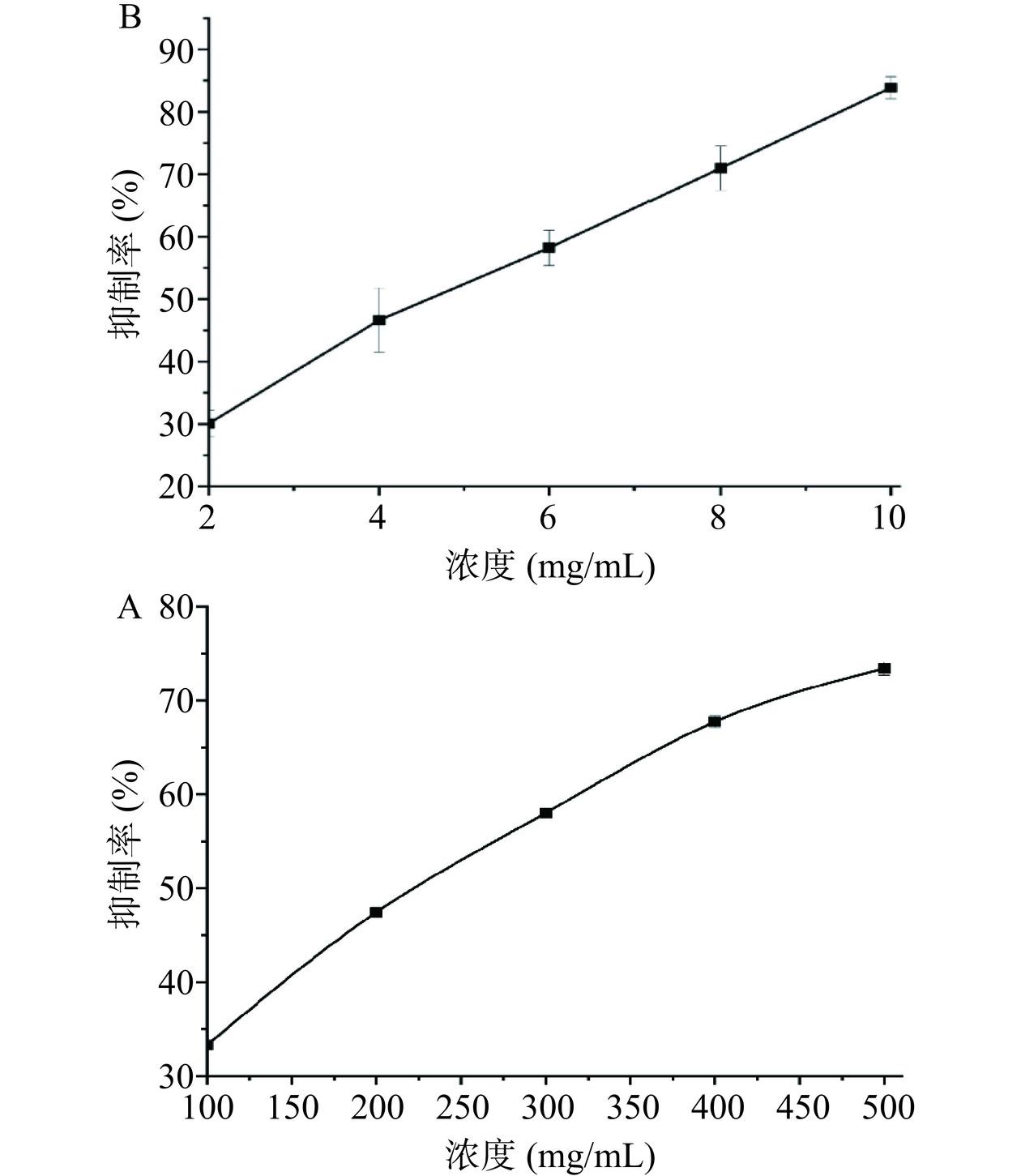
α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶是影响淀粉和其他碳水化合物在饮食消化和吸收中的关键酶,α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶活性被抑制,能够降低淀粉的消化率,并延迟淀粉的降解和葡萄糖的吸收[22−23]。不同浓度的木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制作用如图2所示。pNPG与α-葡萄糖苷酶水解产生的对硝基苯酚(PNP)在波长405 nm处呈现特异性吸收,可用于评估木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用[24]。从图2A可以看出,木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有一定的抑制效果,其抑制率随着浓度的增加而增加,呈现浓度依赖关系。木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的IC50值为205.35 mg/mL,高于阿卡波糖的IC50(0.04 µg/mL)。当木糖浓度为500 mg/mL时抑制率可达73.39%,具有良好的抑制作用。
淀粉在α-淀粉酶的水解作用下产生的还原糖与DNS共热产生棕红色氨基化合物,其在波长540 nm处成特异性吸收,可用于评估木糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用。从图2B可以看出,在不同浓度范围内,木糖对α-淀粉酶表现出一定的抑制能力,随着木糖浓度的增加,木糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制活性逐渐增加,通过计算得到其IC50值为4.75 mg/mL,高于阿卡波糖的IC50值(197.11 µg/mL)。当木糖浓度为10 mg/mL时,抑制率为83.85%,说明木糖对α-淀粉酶具有良好的活性抑制效果。
相比之下木糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制能力更强,表明木糖主要通过抑制该酶的水解活性从而减少葡萄糖的释放。谢静南[25]研究发现同为玉米芯中提取的甜玉米芯多糖经过分离纯化后对α-淀粉酶的IC50值为4.866 mg/mL,本实验研究结果与之相接近。
2.3 木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制类型分析
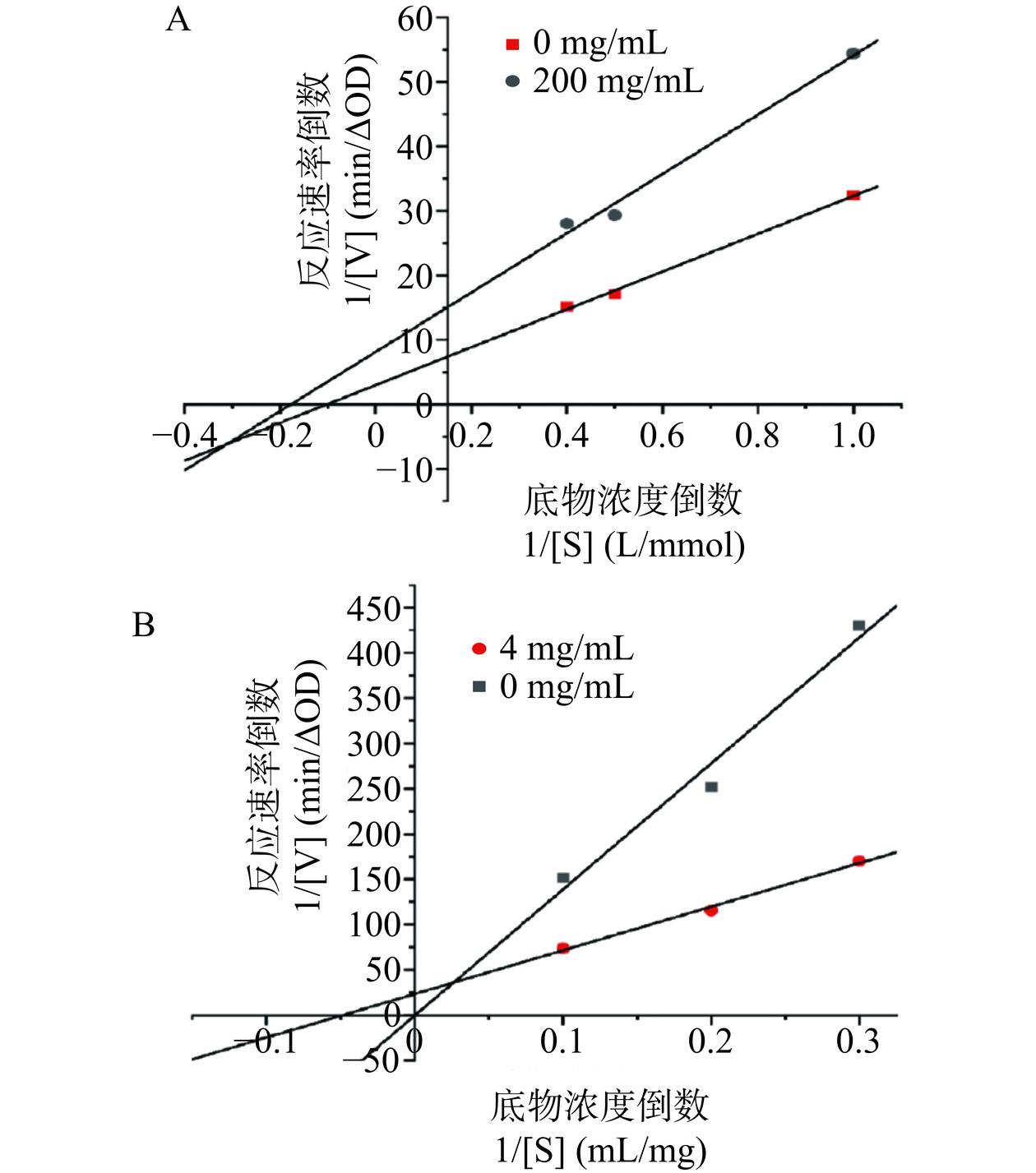
木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制动力学曲线如图3所示。从图3可以看出,木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的两条动力学拟合线分别相交于第三象限和第一象限,可判断木糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制类型均为混合型抑制[26],表明木糖既可以与酶的活性位点结合,又可以与酶-底物复合物结合[27]。
2.4 木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的分子对接分析
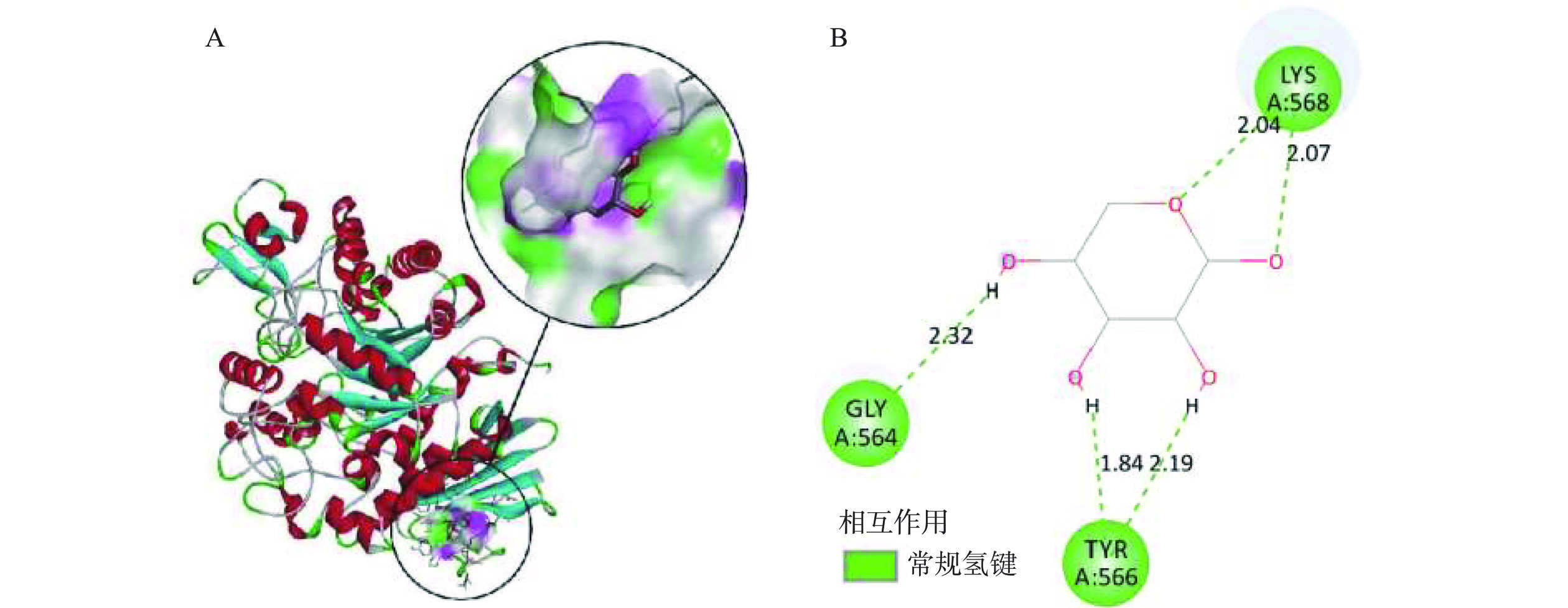
通过Autodock 4.2.6软件对木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶进行对接,得到木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶之间的结合能为−3.05 kcal/mol。当配体与靶蛋白间的结合能小于0 kcal/mol时为有效对接,对靶蛋白具有抑制作用,因此木糖是潜在的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂[28]。采用Discovery Studio 4.5软件解析配体与受体蛋白之间的相互作用并对其结果进行可视化分析,得到木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶的结合模式如图4所示,木糖与受体α-葡萄糖苷酶结合形成5条键长为2.04、2.07、2.19、1.84和2.32 Å的氢键,分别与受体蛋白上的GLY-564、TYR-566、LYS-568等3个氨基酸残基连接,其中TYR-566残基键长为1.84和2.19 Å、LYS-568残基键长为2.04和2.07 Å。分子对接结果表明,木糖能够通过氢键与α-葡萄糖苷酶上的氨基酸残基稳定结合,抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性。
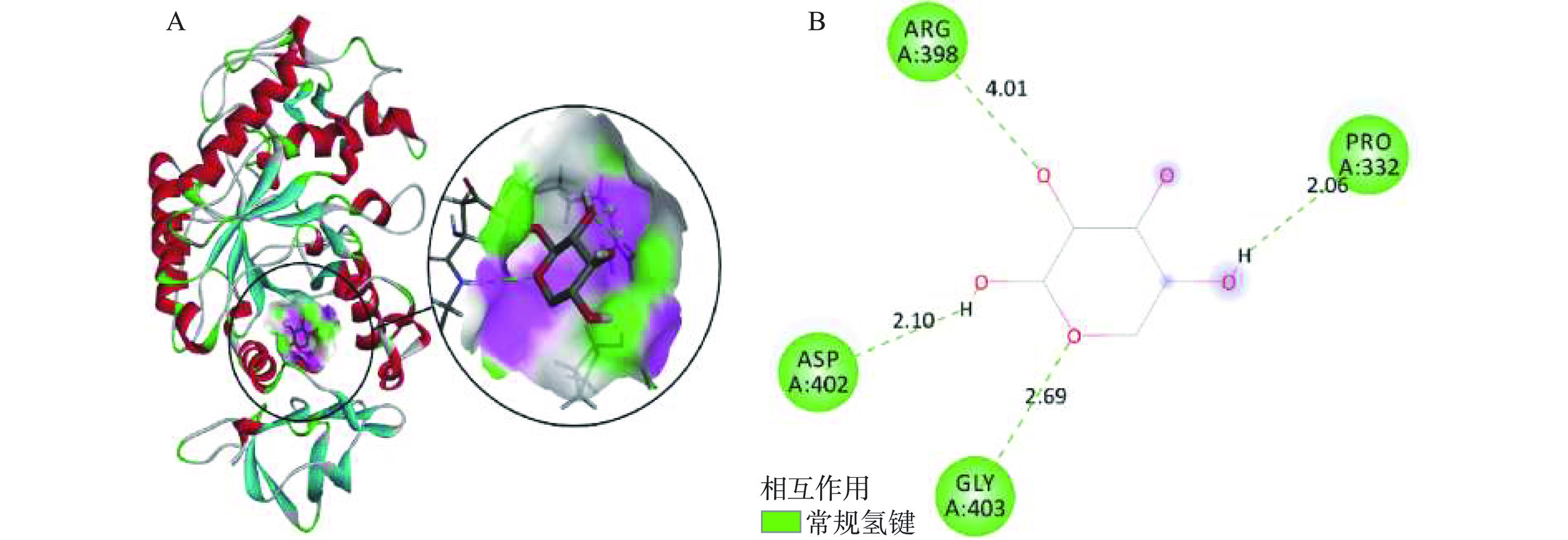
木糖与α-淀粉酶之间的结合能为-5.3 kcal/mol,当结合能低于−5.0 kcal/mol,表明活性成分与靶点具有较强的亲和活性[29]。结果显示,木糖能够与α-淀粉酶的酶活性位点进行结合从而影响酶的活性,其分子对接可视化结果如图5所示。由图5可知,木糖与α-淀粉酶的4个氨基酸残基PRO-332、ASP-402、GLY-403和ARG-398相互作用,形成4条键长分别为2.06、2.10、2.69和4.01 Å的氢键。以上结果表明,木糖与α-淀粉酶通过氢键相互作用,从而改变酶的空间结构,发挥其对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用。
2.5 木糖在植物基肽素乳中的应用
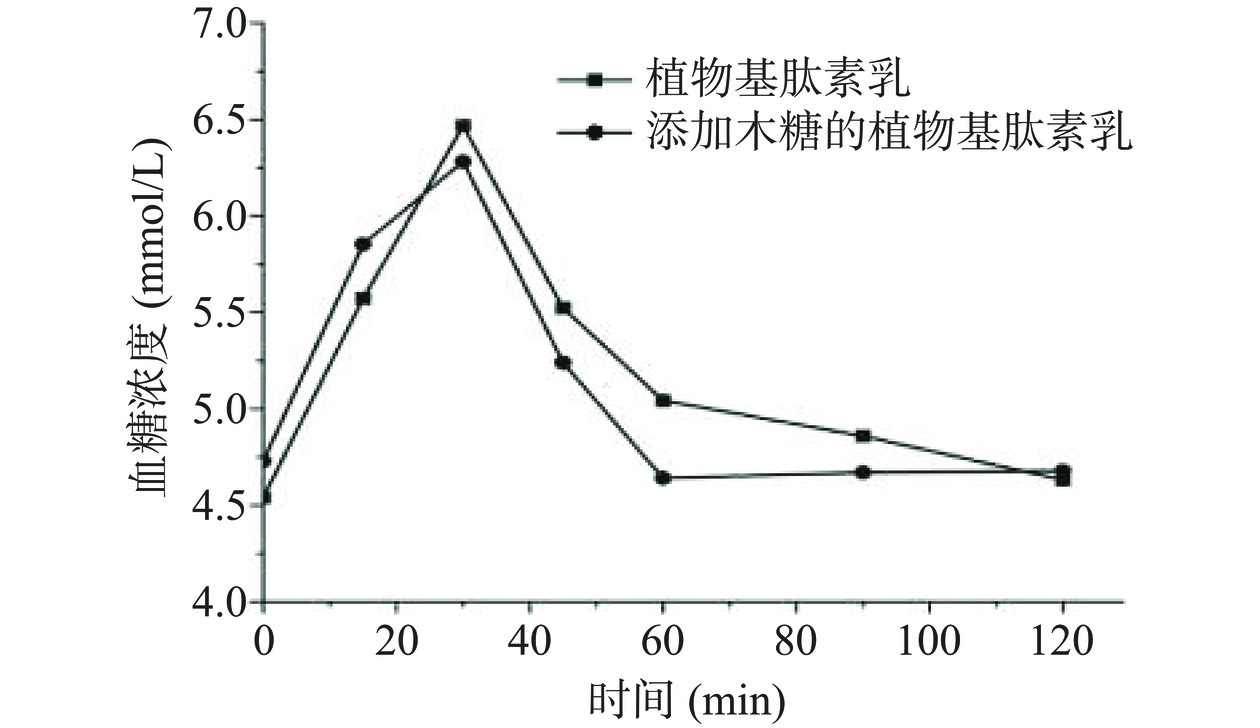
添加木糖前后,植物基肽素乳的血糖应答曲线如图6所示。从图6可以看出,添加木糖的植物基肽素乳血糖应答曲线在0~30 min时,血糖浓度达到峰值6.3 mmol/L,与食用未添加木糖的植物基肽素乳在30 min时的血糖峰值相比下降了10%,随后血糖浓度缓慢下降,食用添加木糖的植物基肽素乳的血糖应答曲线上升和下降趋势与食用未添加木糖的植物基肽素乳相比趋势均较缓慢,有利于血糖平稳。最终测得未添加木糖的植物基肽素乳GI值为58,添加10%木糖的植物基肽素乳GI值为45,添加10%木糖后植物基肽素乳GI值下降了13,且GI值≤55属于低GI食物,表明木糖具有降血糖作用。Pol等[30]研究指出木糖可能会降低摄入后的血糖和胰岛素反应,Bae等[31]研究发现,含有10%(w/w)木糖的蔗糖饮料与未添加木糖的蔗糖饮料相比,GI值降低了21.4%,受试者的胰岛素分泌降低了21.3%。可见,木糖有利于平稳餐后血糖的波动。
3. 结论
本研究揭示了木糖对淀粉消化性的影响及其对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的抑制作用和作用机理。不同添加量的木糖均能够抑制淀粉的水解,且对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶有良好的抑制活性,并通过混合型抑制方式与α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的活性位点相互作用。通过分子对接模拟木糖与α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的结合,木糖通过与两种酶的氨基酸残基形成氢键相互作用,从而降低酶的催化活性。此外,木糖的添加能够降低植物基肽素乳的餐后血糖波动,更有利于血糖的平稳。综上所述,木糖能够通过抑制两种关键消化酶的活性延缓淀粉的消化,降低餐后血糖的波动。该研究可为木糖在淀粉类食品中的应用和低GI产品的开发提供新的思路。
-
表 1 模拟体外消化液成分
Table 1 Composition of simulated digestive fluid in vitro
口腔液 胃液 小肠液 去离子水(mL) 500 1000 1000 NaCl(g) − 3.1 5.4 KCl(g) 0.562 1.1 0.65 CaCl2(g) − 0.15 − NaHCO3(g) 0.571 0.6 − KH2PO4(g) 0.252 − − MgCl2(H2O)6(g) 0.015 − − (NH4)2CO3(g) 0.003 − − CaCl2(H2O)2(g) 0.11 − 0.33 pH 7.0 2.0 7.0 酶 75 U/mL
唾液淀粉酶2000 U/mL
胃蛋白酶400 U/mL胰酶、
10 mmol/L胆汁盐 -
[1] 张卓琼, 郭军. 低血糖生成指数食品研究与开发应用现状[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(1):313−320. [ZHANG Z Q, GUO J. Research development and application status of low glycemic index foods[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(1):313−320.] ZHANG Z Q, GUO J. Research development and application status of low glycemic index foods[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(1): 313−320.
[2] 张阳. 低GI挤压重组米的配方优化及其食用品质和理化特性研究[D]. 重庆:西南大学, 2021. [ZHAO Y. Study on the formula optimization of low GI extruded rice and its edible quality and physical and chemical properties[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University, 2021.] ZHAO Y. Study on the formula optimization of low GI extruded rice and its edible quality and physical and chemical properties[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021.
[3] HESS A, KRESS S, RAKETE S, et al. Influence of the fat/carbohydrate component of snack food on energy intake pattern and reinforcing properties in rodents[J]. Behavioural Brain Research: An International Journal,2019,364:328−333. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.02.041
[4] 范光森, 许岱, 富志磊, 等. 血糖生成指数研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2016(10):56−68. [FAN G S, XU D, FU Z L, et al. Research progress of glycemic index[J]. Cereals & Oily,2016(10):56−68.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2016.10.003 FAN G S, XU D, FU Z L, et al. Research progress of glycemic index[J]. Cereals & Oily, 2016(10): 56−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2016.10.003
[5] 王怀槟, 彭星光, 刘宏生, 等. 碳水化合物食品GI值体外、内预测方法的研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2023(15):407−417. [WANG H B, PENG X G, LIU H S, et al. Current development of the in vitro and in vivo methods for predicting the Glycemic index values of carbohydrate foods Research progress of glycemic index[J]. Food Science, 2023(15):407−417.] WANG H B, PENG X G, LIU H S, et al. Current development of the in vitro and in vivo methods for predicting the Glycemic index values of carbohydrate foods Research progress of glycemic index[J]. Food Science, 2023(15): 407−417.
[6] 于中玉, 林楠, 黄佳琪, 等. 木糖对糯米淀粉糊化性质的影响−[J]. 粮食与油脂,2022,35(8):26−29,51. [YU Z Y, LIN N, HUANG J Q, et al. The effect of xylose on the gelatinization properties of waxy rice starch[J]. Cereals & Oily,2022,35(8):26−29,51.] YU Z Y, LIN N, HUANG J Q, et al. The effect of xylose on the gelatinization properties of waxy rice starch[J]. Cereals & Oily, 2022, 35(8): 26−29,51.
[7] ASANO T, YOSHIMURA Y, KUNUGITA K. Sucrase inhibitory activity of D-xylose and effect on the elevation of blood glucose in rats[J]. Journal of Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Sciences,1996,49(3):157−162. doi: 10.4327/jsnfs.49.157
[8] JUN Y J, LEE J, HWANG S, et al. Beneficial effect of xylose consumption on postprandial hyperglycemia in Korean:A randomized double-blind, crossover design[J]. Trials,2016,17(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1261-0
[9] 尤新, 朱路甲. 无热量甜味料—结晶木糖的性质功能和应用前景[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2009(1):52−56. [YOU X, ZHU L J. The functional characters and applications of xylose crystal—A non-calorie sweetener[J]. China Food Additives,2009(1):52−56.] YOU X, ZHU L J. The functional characters and applications of xylose crystal—A non-calorie sweetener[J]. China Food Additives, 2009(1): 52−56.
[10] 赵悦琪. 低GI韧性饼干的生产工艺研究及其品质分析[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2021. [ZHAO Y Q. Study on production technology and quality analysis of low GI toughness biscuit[D]. Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University, 2021.] ZHAO Y Q. Study on production technology and quality analysis of low GI toughness biscuit[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2021.
[11] JENKINS D J, WOLEVER T M, TAYLOR R H, et al. Glycemic index of foods:A physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1981,34(3):362−366. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.3.362
[12] BRODKORB A, EGGER L, ALMINGER M, et al. Infogest static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion[J]. Nature Protocols,2019,14(4):991−1014. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0119-1
[13] DING Q, NIE S P, HU J L, et al. In vitro and in vivo gastrointestinal digestion and fermentation of the polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,63:646−655. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.018
[14] 姚晓芬, 王鑫, 应茵, 等. L-阿拉伯糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性的体外试验研究[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志,2012,24(2):102−105. [YAO X F, WANG X, YING Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of L-arabinose on α-glucosidase tested in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2012,24(2):102−105.] YAO X F, WANG X, YING Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of L-arabinose on α-glucosidase tested in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2012, 24(2): 102−105.
[15] ZHANG H L, WU Q X, QIN X M. Camellia nitidissima Chi flower extracts inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase:In vitro by analysis of optimization of addition methods, inhibitory kinetics and mechanisms[J]. Process Biochemistry,2019,86:177−185. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.07.009
[16] 杨沁雪. 橡实仁内源多酚化合物对淀粉结构和体外消化性的影响[D]. 北京:北京林业大学, 2020. [YANG Q X. Effect of endogenous acorn kernel polyphenols on starch structure and in vitro digestibility[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University, 2020.] YANG Q X. Effect of endogenous acorn kernel polyphenols on starch structure and in vitro digestibility[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
[17] 潘玥, 刘小莉, 王英, 等. 蓝莓叶多酚对α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的体外抑制活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(4):579−587. [PAN Y, LIU X L, WANG Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of polyphenols from blueberry leaves on the activity of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(4):579−587.] PAN Y, LIU X L, WANG Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of polyphenols from blueberry leaves on the activity of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(4): 579−587.
[18] 宋晓童. 8-(6''-伞形酮)-芹菜素衍生物的抗糖尿病活性研究[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2018. [SONG X T. Anti-diabetic activity of 8-(6”-Umbelliferyl)-apigenin derivatives[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.] SONG X T. Anti-diabetic activity of 8-(6”-Umbelliferyl)-apigenin derivatives[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[19] WANG S, LI Y, HUANG D J, et al. The inhibitory mechanism of chlorogenic acid and its acylated derivatives on α-amylase and α-glucosidase[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,372:131334. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131334
[20] :潘若瑶, 任国艳, 马富利, 等. 芦荟大黄素对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用及机理[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业, 1−9:[2024-04-03]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036611. [PAN R Y, REN G Y, MA F L, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of aloe-emodin on α-glucosidase[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−9:[2024-04-03]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036611.] PAN R Y, REN G Y, MA F L, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of aloe-emodin on α-glucosidase[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−9: [2024-04-03]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036611.
[21] 史明威, 张梦玥, 初鸿, 等. 绿原酸对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用及其分子对接模拟[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2023,41(4):135−143. [SHI M W, ZHANG M Y, CHU H, et al. Inhibitory of chlorogenic acid on α-amylase and its molecular docking simulation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2023,41(4):135−143.] SHI M W, ZHANG M Y, CHU H, et al. Inhibitory of chlorogenic acid on α-amylase and its molecular docking simulation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 41(4): 135−143.
[22] XU J, CAO J Q, YUE J Y, et al. New triterpenoids from acorns of Quercus liaotungensis and their inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase, α-amylase and protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,41:232−239. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.054
[23] ZHENG Y X, YANG W H, SUN W X, et al. Inhibition of porcine pancreatic α-amylase activity by chlorogenic acid[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103587. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103587
[24] XU J, WANG X D, ZHANG H Y, et al. Synthesis of triterpenoid derivatives and their anti-tumor and anti-hepatic fibrosis activities[J]. Natural Product Research,2020,34(6):766−772. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1499642
[25] 谢静南. 甜玉米芯多糖SCP50分离及对大鼠小肠糖酶抑制作用的研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨商业大学, 2018. [XIE J N. Inhibition effects and separation of SCP50 on carbohydrase enzymes in the rat small intestine[D]. Harbin:Harbin University of Commerce, 2018.] XIE J N. Inhibition effects and separation of SCP50 on carbohydrase enzymes in the rat small intestine[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2018.
[26] 梁宗瑶, 魏园园, 任维维, 等. 橡子仁萃取物成分分析及对α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(17):47−55. [LIANG Z Y, WEI Y Y, REN W W, et al. Composition analysis and inhibitory effect against α-amylase and α-glucosidase of acorn kernel extractions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(17):47−55.] LIANG Z Y, WEI Y Y, REN W W, et al. Composition analysis and inhibitory effect against α-amylase and α-glucosidase of acorn kernel extractions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(17): 47−55.
[27] WANG M T, JIANG J, TIAN J H, et al. Inhibitory mechanism of novel allosteric inhibitor, Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) leaves proanthocyanidins against α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,56:286−294. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.026
[28] 於雨碟, 张佳妍, 张酥, 等. 桦褐孔菌子实体多糖的提取及体外降血糖活性[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(1):189−202. [YU Y D, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG S, et al. Molecular screening of medicinal fungus Inonotus obliquus and anti-breast cancer activity of its submerged fermentation broth[J]. Mycosystema,2021,40(1):189−202.] YU Y D, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG S, et al. Molecular screening of medicinal fungus Inonotus obliquus and anti-breast cancer activity of its submerged fermentation broth[J]. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(1): 189−202.
[29] LI X H, TANG H, TANG Q, et al. Decoding the mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction in treating pneumonia based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology,2021,9:638366. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.638366
[30] POL K, MARS M. L-arabinose and D-xylose:Sweet pentoses that may reduce postprandial glucose and insulin responses[J]. Food & Nutrition Research,2021,65:6254.
[31] BAE Y J, BAK Y K, KIM B, et al. Coconut-derived D-xylose affects postprandial glucose and insulin responses in healthy individuals[J]. Nutrition Research & Practice,2011,5(6):533−539.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 闫昱辛,何美军,李宇,袁晓曼,谭旭辉,程名,罗凯,廖璐婧. 铁皮石斛叶多糖美白和抗氧化活性. 植物研究. 2025(01): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代丽丽,王景,魏许瑞,马庆亚,王娜,都治香. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路研究灯盏花乙素对子宫内膜癌Ishikawa细胞的影响. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2024(01): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张琦,包小波,田冲冲. 灯盏花乙素增强4T1乳腺癌细胞对顺铂敏感性的体内外研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(05): 331-340 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王佳恩,殷子喻,马莉,李双良,符德欢. 灯盏乙素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展. 中草药. 2024(13): 4608-4621 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张琦,田冲冲,张洋,方晨曦,卜薇,李凤. 灯盏花乙素通过PPARγ-PGC1α-UCP1通路改善小鼠肥胖作用及机制. 药物评价研究. 2024(08): 1787-1796 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田冲冲,张琦,陈延绅. 基于肠道微生态探讨灯盏花乙素对乳腺癌小鼠的化疗增敏作用及其机制. 中国微生态学杂志. 2024(12): 1374-1381+1387 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



