Effect of Ultra High Pressure Combined with Partial Freezing on the Storage Quality of Chicken Soup
-
摘要: 传统鸡汤高温杀菌易对产品品质造成不利影响,且贮藏期短,无法满足现代便捷、营养消费需求。本研究将超高压结合微冻多栅栏技术应用于鸡汤保鲜,以期达到延长鸡汤贮藏期和降低鸡汤营养损失、提高品质的目的。研究分别以巴氏杀菌、高温高压与超高压(400 MPa,15 min)三种杀菌方式结合微冻(−2.5 ℃)贮藏对鸡汤品质进行对比分析,以鸡汤新鲜度(细菌总数、脂肪氧化、蛋白质氧化)、风味品质(可溶性蛋白、游离氨基酸、肌苷酸、挥发性物质)、感官品质(感官评定)等作为指标,考察三种杀菌方式结合微冻技术对鸡汤贮存保鲜效果的影响,并进一步探究超高压微冻技术对鸡汤贮藏期品质变化规律的影响。结果表明,超高压结合微冻处理鸡汤组在贮藏100 d 时,具有良好的微生物负荷值(菌落总数仅为2.11 log CFU/mL);三组不同处理方式鸡汤的丙二醛(MDA)由大到小依次是:高温高压组依次大于巴氏杀菌组和超高压组,且贮藏阶段超高压组MDA值始终低于其他两组;超高压组的可溶性蛋白含量最终为5.22 mg/mL,其含量始终高于其他两组;此外,超高压组风味物质(苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、肌苷酸、辛醛、2-庚酮、2-戊基呋喃)含量明显高于其他两组。可见,超高压结合微冻与传统热处理组相比,能够较好地减少营养物质损失,保护鸡汤感官品质,有效延长货架期等。Abstract: Traditional high-temperature sterilization of chicken soup can easily lead to adverse effects on product quality and result in a short storage period, which fails to meet the demands for modern convenience and nutritional consumption. In this study, ultra high pressure combined with partial freezing multi-fence technology was applied to preserve chicken soup, aiming to extend its storage period, reduce nutritional loss, and enhance overall quality. The quality of chicken soup was compared and analyzed using pasteurization, high temperature and high pressure treatment, as well as ultra high pressure (400 MPa for 15 min) combined with partial freezing (−2.5 ℃) storage. Freshness indicators (total bacterial count, fat oxidation, protein oxidation), flavor-related parameters (soluble protein content, free amino acid content, inosine acid content, volatile substances), sensory evaluation scores were used to investigate the effects of these three sterilization methods combined with partial freezing technology on the storage stability and freshness of chicken soup. Furthermore, the impact of ultra high pressure combined with partial freezing technology on changes in the quality attributes of chicken soup during storage was explored. Results demonstrated that the group treated with ultra high pressure combined with partial freezing exhibited favorable microbial load values (with a total colony count only at 2.11 log CFU/mL) after being stored for 100 days. Malondialdehyde (MDA) values differed among the three groups subjected to different treatment methods: Higher MDA levels were observed in the high temperature and high pressure group compared to both pasteurization group and ultra high pressure group. Consistently lower MDA values were found in the ultra high pressure group throughout storage stages when compared against other two groups. The soluble protein content in the ultra high pressure group remained consistently higher at 5.22 mg/mL than that in other two groups. Additionally, the ultra high pressure group exhibited significantly higher levels of flavor substances (phenylalanine, proline, inosine, octanaldehyde, 2-heptanone, 2-amylfuran) compared to the other two groups. These findings demonstrate that the combination of ultra high pressure and partial freezing is more effective than traditional heat treatment in minimizing nutrient loss, preserving sensory quality of chicken soup, and extending shelf life.
-
Keywords:
- chicken soup /
- ultra high pressure /
- storage quality /
- partial freezing preservation
-
鸡汤作为传统汤食制品,具有美味营养、风味醇厚等特点,在我国饮食文化中占有重要地位。鸡汤中蛋白质、氨基酸含量丰富,含有半胱氨酸、肌酸、肉毒碱等生理活性物质;且汤品更有利于营养物质的输送,促进消化,鸡汤更具有缓解感冒、增强人体免疫力[1−3]、消除炎症[4−5]、减少产妇产后出血和促进乳汁分泌[6−7]等功效。另外,鸡汤不仅可以单独作为美食,同时也可与其他食品互配形成各式各样种类繁多的产品,广受消费者喜爱,市场巨大。然而传统鸡汤炖煮,加工费时繁琐,且不利于工业化生产。现代都市生活的快节奏导致年轻群体时间成本越来越高[8],但消费者对健康、营养汤品的需求不断的扩大,这种矛盾下正是即食汤品的巨大市场。而今市场上,鸡汤保存期短且品质难以保证,即食鸡汤产品较少,亟需对传统鸡汤的加工及贮藏保鲜技术进行改进,以满足现代消费市场需求。
杀菌工艺是影响汤类产品品质重要影响因素之一。不同杀菌方式对延长汤汁产品的贮藏期均有一定的效果,但杀菌方式的差异性对产品的品质也会产生不同的影响。常见的食品杀菌方式主要包括热力杀菌和非热力杀菌两大类。其中巴氏杀菌处理温和,能极大保留产品中的营养成分;热力杀菌能够快速消灭食品中的致病微生物,有效延长食品贮藏期。徐卉等[9]发现巴氏杀菌组鱼汤生产成本低,但贮藏时间仅6周;热力杀菌组鱼汤贮藏时间长达20周,但会导致呈现蒸煮味的化合物相对含量增加,对鱼汤风味产生不良影响。可见,杀菌方式对汤品品质影响显著。传统的鸡汤生产方式以巴氏杀菌和高温高压炖煮为主,而鸡汤成品往往因贮存条件不适宜而快速腐败,或者高温易造成营养风味劣化,导致鸡汤在新鲜度、风味品质和感官品质等方面无法得到有效保障。超高压技术,又被称为静水压技术,它是将密封过的食品置于超高压设备中,以水或者其他液体为介质,对食品施加100~1000 MPa压力的一种冷杀菌技术[10−11]。超高压不仅具有杀菌的作用,还可以有效保留甚至改善食品品质。已有研究[12−13]证实了超高压处理对食品品质的影响,曾清清[12]对高压与常压熬煮方式进行比较,发现高压熬煮后鸡骨汤各理化指标均显著高于常压,但超高压技术对鸡汤品质仍需进一步系统研究。
除了杀菌方式,贮藏保鲜技术也是影响鸡汤贮藏品质的另一重要因素。低温冷藏是鸡汤保鲜较为常见的方式。微冻技术,是一种将食品贮藏在冰点以及冰点下1~2 ℃的新型贮藏保鲜方式[14]。微冻技术能够减少冷冻和解冻的时间,避免产品过度的解冻损伤损失。该技术较传统肉类冷藏方式延长1.4~4倍的货架期[15]。且微冻条件下的蛋白质降解及结构破坏较冻藏低[16]。王汉玲[17]探究了虹鳟在微冻的条件下,不同的处理方式对虹鳟微生物指标影响,发现微冻技术可以较好地抑制微生物的繁殖,延长货架期。李雅晶等[18]研究了微冻条件下贻贝品质变化,结果表明,微冻不仅能抑制微生物的繁殖,还能有效地抑制贻贝中内源酶的酶活,但目前将微冻技术应用于汤品,尤其是鸡汤保鲜贮藏的研究未见有报道。
因此本研究以鸡汤的新鲜度、风味品质、感官品质等为指标,以传统的巴氏杀菌、高温高压杀菌方式为对照,超高压杀菌方式为研究对象,对比评价三组鸡汤在微冻条件下的贮藏保鲜效果,同时探究超高压微冻栅栏技术对鸡汤贮藏期品质变化规律的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
氯化钠 分析纯,江苏强盛化学股份有限公司;碳酸钾、三氯乙酸、阿拉伯胶 分析纯,麦克林试剂公司;硫代巴比妥酸、环己酮 分析纯,中国医药(上海)化学试剂公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠 分析纯,上海振企化学公司;高氯酸、硼酸 分析纯,阿拉丁化学试剂有限公司;盐酸、甘油 分析纯,西陇科学服务有限公司;95%乙醇(分析纯)、甲醇(色谱级) 上海振兴化工;酒石酸钾钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;磷酸二氢钾 分析纯,无锡市亚盛化工厂有限公司;肌苷酸标品 标准品,北京索莱宝科技有限公司;食用盐 中盐东兴盐化股份有限公司;三黄鸡 180日龄,安徽老乡鸡餐饮有限公司。
JA503分析电子天平 常州幸运电子设备有限公司;DGT-G-C系列精密鼓风恒温干燥箱 河北润联科技开发有限公司;pHS-3C雷磁pH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;HH-M8型数显恒温水浴锅 江苏金坛市金城国胜实验仪器厂;PE-Lambda35紫外分光光度计 美国PE仪器有限公司;HPP600MPa/30-200L超高压处理设备 包头科发高压科技有限责任公司;L-8900氨基酸自动分析仪 日本Hitachi公司;Waters 2695液相 沃特世科技(上海)有限公司;7000E GC/MS气质三重四级杆 安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司;DHP-9402恒温培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;pen3电子鼻 德国AIRSENSE。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鸡汤的制备
前处理:将三黄鸡胴体清洗干净,去除内脏、头、脖、鸡爪,随后切成长宽为4 cm×3 cm大小,最后再用清水清洗鸡块。
焯水:将500 g鸡块倒入锅中,加入1000 g清水(屈臣氏蒸馏水),电磁炉功率为2000 W,时长8 min。
炖煮:冷水清洗焯过水的鸡块,然后将鸡块倒入锅中,水的添加量为鸡块重量的2倍。将电磁炉功率调到2000 W大火烧开,10 min后调至300 W,此过程持续2 h。最后,按料液比的0.36%加盐,出锅。
包装:待鸡汤冷却之后,用150目的三层纱布过滤,每袋装入150 g的鸡汤,真空热封口,得到袋装鸡汤。
1.2.2 鸡汤杀菌处理
热杀菌组:巴氏杀菌:将袋装鸡汤置于水浴锅中,80 ℃加热30 min,保证水浴时每袋鸡汤都要悬浮在水中。高温高压杀菌:杀菌条件为121 ℃,1.05~1.10 MPa,20 min。
冷杀菌组:超高压杀菌:对鸡汤样品施加400 MPa压力,时长15 min。
1.2.3 微冻贮藏
将经过灭菌处理的鸡汤放入冰箱中,微冻温度下贮藏,实验中测得鸡汤的冻结点为−0.3 ℃,因此取微冻贮藏温度−2.5 ℃。以0、25、50、75、100 d为固定时间间隔,分析3种不同灭菌方法对鸡汤质量的影响,每个样品重复3次。
1.2.4 鸡汤冻结曲线和冰点测定
将袋装鸡汤放入−18 ℃的冰箱中,鸡汤的中心温度初始值为13 ℃,使用自动温度记录仪记录鸡汤的实时变化,把温度记录仪放入鸡汤中心部位,每隔10 min记录一次温度值,共计4 h,最终绘制出鸡汤的冻结曲线,确定鸡汤的冰点。
1.2.5 新鲜度测定
1.2.5.1 微生物总数
参照GB 4789.2-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》[19]。
1.2.5.2 挥发性盐基氮
参照GB 5009.228-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》[20]。
1.2.5.3 丙二醛
参照GB 5009.181-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定》[21]。
1.2.6 风味品质
1.2.6.1 可溶性蛋白
参考周涛[22]的方法。采用双缩脲的测定方法,吸取0.5 mL的鸡汤样品,用纯水将其补足至1 mL,加入4 mL的双缩脲试剂,摇匀之后在室温下反应30 min,利用紫外分光光度计于540 nm测定吸光值。校正液配制是由纯水替换鸡汤,操作步骤同上。利用牛血清白蛋白溶液绘制标准曲线,回归方程为:Y=0.0467x−0.0041,R2=0.9994。
1.2.6.2 游离氨基酸
参考Kim等[23]的实验方法,并稍加修改。吸取适量鸡汤与4%磺基水杨酸混合,使用高速冷冻离心机在4 ℃、12000 r/min转速下运行30 min,得到上清液。利用一次性针管吸取上清液,并用0.22 μm水系膜过滤,然后转移到进样瓶中,使用氨基酸自动分析仪测定各游离氨基酸的含量。
1.2.6.3 肌苷酸(IMP)
参考Davidek等[24]的测定方法,并稍加修改。利用肌苷酸标品计算样品中肌苷酸的含量。配制1、2、5、10、25、50、100 μg/mL七个不同浓度的标品溶液,0.22 μm水系膜过滤,利用液相色谱仪测定标品的峰面积,并绘制标准曲线。回归方程为:Y=93685x−109528,R2=0.9989。
样品处理:吸取1 mL鸡汤到离心管中,加入4 mL 7%高氯酸,高速离心(12000 r/min,15 min)。用1 mol/L氢氧化钾将鸡汤pH调至4.5,随后再次离心15 min,离心完成后用一次性针管吸取上清液,并利用0.45 μm水系膜过滤。
色谱条件:C18柱子,流速:1.0 mL/min,进样量10 μL,柱温25 ℃。紫外检测波长为254 nm;流动相:98%溶剂A(0.05 mol/L磷酸二氢钾,pH4.5),2%溶剂B(甲醇),梯度洗脱运行30 min;梯度洗脱过程:0 min时,A相98%,B相2%;14 min时,A相85%,B相15%;21 min时,A相98%,B相2%。
1.2.6.4 挥发性物质
样品处理:精确称取5 g鸡汤样品至15 mL萃取瓶中,2 μL环己酮(1.11 μg/μL)作为内标,萃取器的萃取头插入顶空瓶,推出纤维萃取头,不能触碰到样品,50 ℃恒温水浴,吸附35 min。萃取结束后,收回纤维萃取头,立即将进样器插入气相色谱仪进样口,推出纤维萃取头,热解析3 min,同步开启气相色谱仪。
GC-MS条件:以氦气作为载气,注射口的温度为250 ℃,流速为1 mL/min。烘箱温度最开始为40 ℃,在此温度上保持3 min,然后以3 ℃/min的速度上升至70 ℃,随后又以5 ℃/min的速度上升至180 ℃,再以10 ℃/min速度上升至280 ℃,最后在此温度上保持5 min。
风味成分鉴定:利用NIST 11文库中的质谱数据对鸡汤的挥发性物质进行匹配,仅报道匹配度超过80%的物质。内标法定量,内标物为环己酮,通过各组分峰面积与内标物峰面积对比进行半定量分析,挥发性物质各组分含量=各组分峰面积/内标物峰面积×内标物浓度,含量单位为μg/μL。
1.2.7 感官评定
参考Badeka等[25]的方法。从冰箱中取出鸡汤,利用微波炉加热1 min,然后将鸡汤倒入一次性杯子中。事先选定好10位经验丰富、符合条件的同学,并组成评定小组。评定小组成员必须在一个干净、明亮和安静的环境下进行感官评定,并且每次品尝之后都要用清水漱口才能进行下一个样品的品尝。实验从鸡汤的色泽、滋味、香气、浮油4个方面进行评价,单项评定采取10分制,具体评分标准见表1。
表 1 感官评分Table 1. Evaluation of sensory score指标 0~2分 3~5分 6~8分 9~10分 色泽
(10分)鸡汤很浑浊
汤色很暗鸡汤浑浊度加大
汤色变暗鸡汤呈浅白色
略微浑浊色泽清亮
呈淡黄色滋味
(10分)口感很差
无回味
无鲜味口感清淡
回味不足
鲜味不足醇厚感不足
鲜味略微不足
回味稍差口感醇厚
鲜味适中
回味很足香气
(10分)肉香很差 肉香较差 肉香微淡 肉香浓郁 浮油
(10分)表面浮油厚重
口感很油腻表面有大量的浮油
口感较油腻表面有一层浮油
口感略微油腻表面有适量的浮油
口感适中1.3 数据处理
实验数据为平均值±标准差(Mean±SD),数据分析采用SPSS 24.0,ANOVA分析单因素方差分析,多重比较采用Duncan法,统计学显著定义为P<0.05,每个实验重复3次。
2. 结果与分析
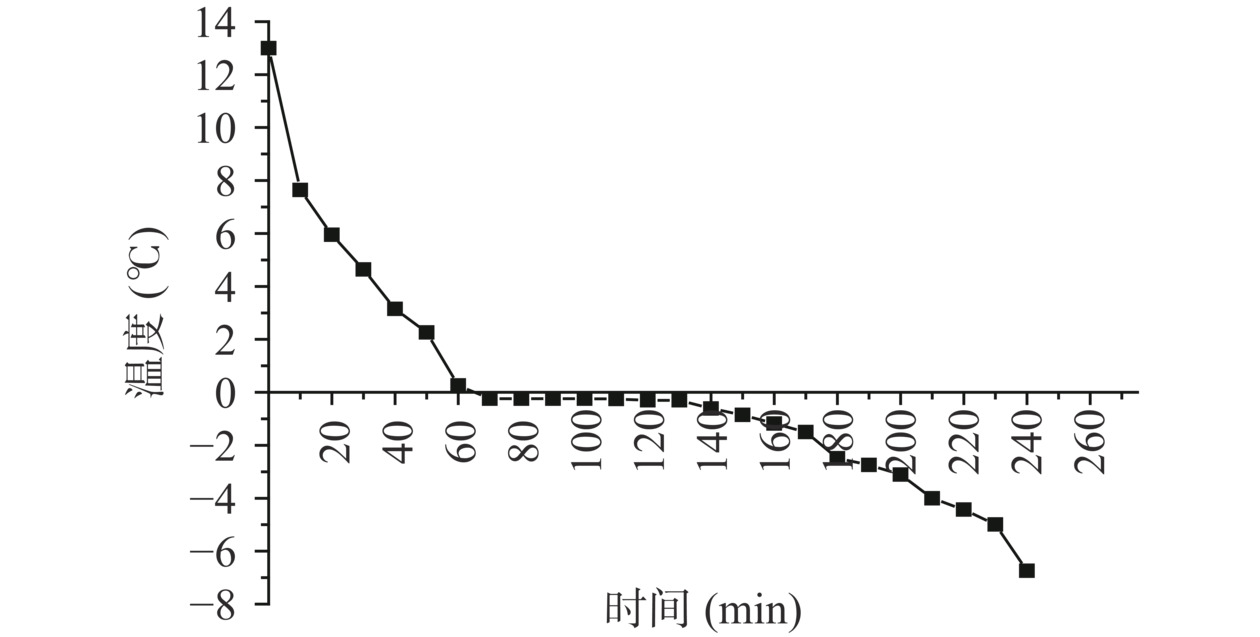
2.1 鸡汤冻结速率曲线图和冰点测定
微冻技术,又称“部分冷却技术”,是一种将食品贮藏在冰点以及冰点下1~2 ℃的新型贮藏保鲜方式,其原理是利用低温抑制微生物的繁殖及酶活力。由图1可知,鸡汤降温过程分为3个阶段:第一阶段,冷却阶段。由于冷却过程放出的热量是显热,数值较小,所以初温降得很快,并且温度变化平稳;第二阶段,被称为“最大冰晶生成区”。在此阶段,由于物料中水分开始结冰,放出大量潜热,致使其温度呈现相对稳定的阶段,此时的温度即为物料的冻结点。第三阶段,再继续冻结的过程中,所消耗的冷量一部分用于冰的降温,一部分消除余下液体冻结时放出的潜热,所以曲线的斜率小于冷却阶段。由图1可看出,鸡汤冻结过程中,出现典型的三个阶段。在实验前期鸡汤温度陡坡式下降,当温度达到0 ℃附近时,下降速度开始变得缓慢,在−0.3 ℃时,出现了一个较长时间的停滞过程,而在160 min时,鸡汤温度又再一次快速下降。最终,确定了鸡汤微冻温度为−2.5 ℃。
2.2 新鲜度指标
2.2.1 微生物总数
菌落总数的测定可以了解到鸡汤的微生物繁殖情况,它是评定食品品质的重要指标。由表2所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,超高压组和巴氏杀菌组的菌落总数逐步增加,超高压组鸡汤在整个贮藏期间,菌落总数有显著性差异(P<0.05),巴氏杀菌组也存在显著性差异(P<0.05),但高温高压组在整个贮藏过程中未有菌落检出,说明高温高压的杀菌能力比其他两种杀菌方式好,使得食品的贮藏期更长。段丽丽等[26]对比了不同杀菌方式对果酱的影响,研究结果表明,高温高压的杀菌效果最好。
表 2 不同杀菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的菌落总数影响(lg CFU/mL)Table 2. Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on total colony stored in chicken soup(lg CFU/mL)杀菌方式 贮藏时间(d) 0 25 50 75 100 超高压组 − − 1.32±0.07a 1.88±0.07bA 2.11±0.05cA 巴氏杀菌组 − − − 1.21±0.15aB 1.57±0.06bB 高温高压组 − − − − − 注:同行肩标不同小写字母代表组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);同列不同大写字母代表同一贮藏时间三种杀菌方式之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);“−”代表未检出。 贮藏期内,超高压组菌落总数上升趋势更快,但由于微冻这种贮藏方式,使得超高压组鸡汤在100 d的贮藏过程中,菌落总数为2.11 lg CFU/mL,低于6 lg CFU/mL[27],说明在此条件下,超高压组鸡汤有良好的微生物负荷值,既保留了营养和风味又达到贮藏保鲜效果。
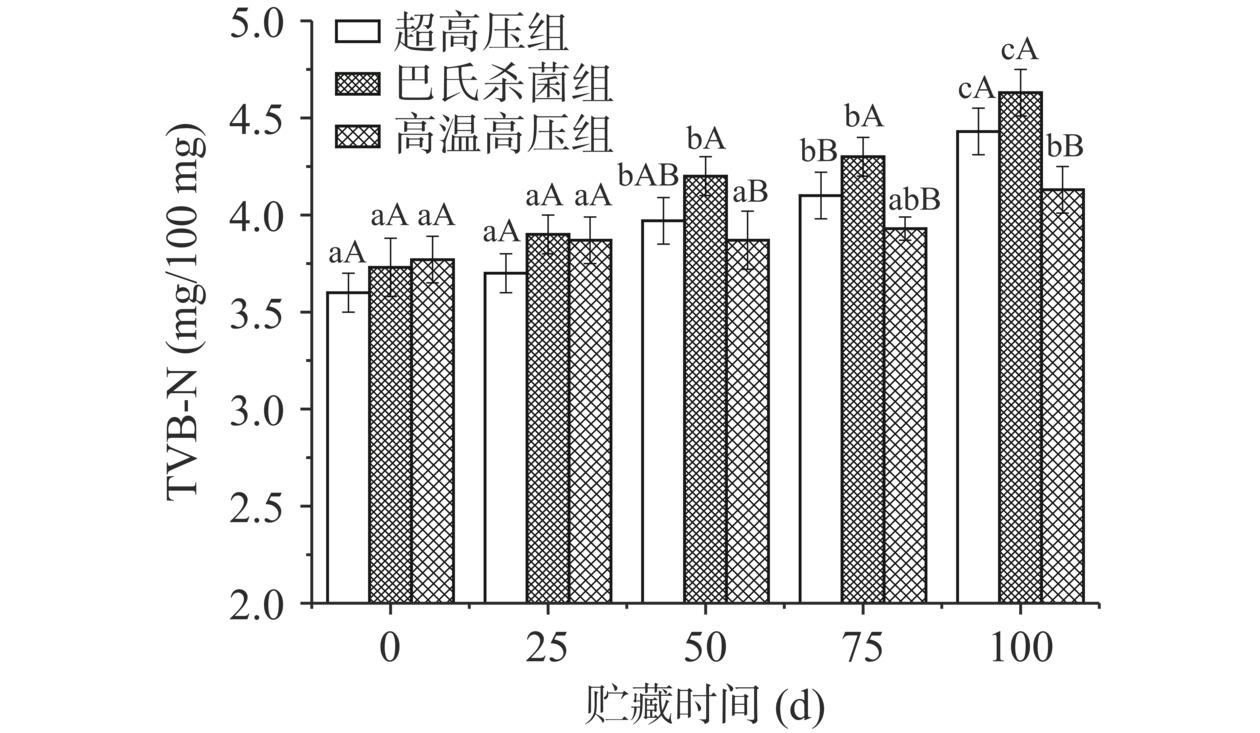
2.2.2 挥发性盐基氮含量
挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)是因为食品中蛋白质在酶或者微生物的作用下分解成的氨以及胺类等碱性含氮物质,是衡量蛋白质在贮藏过程中被氧化的程度,是测定食品新鲜度的重要指标[28]。由图2可知,三组的挥发性盐基氮呈现缓慢上升趋势,并从第50 d开始组间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。对比0 d时不同杀菌方式的鸡汤的挥发性盐基氮含量,发现三者没有显著性差异(P>0.05)。在0~25 d的贮藏期间,超高压组和巴氏杀菌组的挥发性盐基氮缓慢上升,但到了贮藏中后期,挥发性盐基氮含量上升速度加快,而高温高压组的挥发性盐基氮含量上升相对平缓,这与陈静茹等[29]的研究结论一致。总而言之,在微冻贮藏条件下,低温抑制了微生物的繁殖,导致三种不同杀菌方式鸡汤的挥发性盐基氮含量均低于15 mg/100 mg。
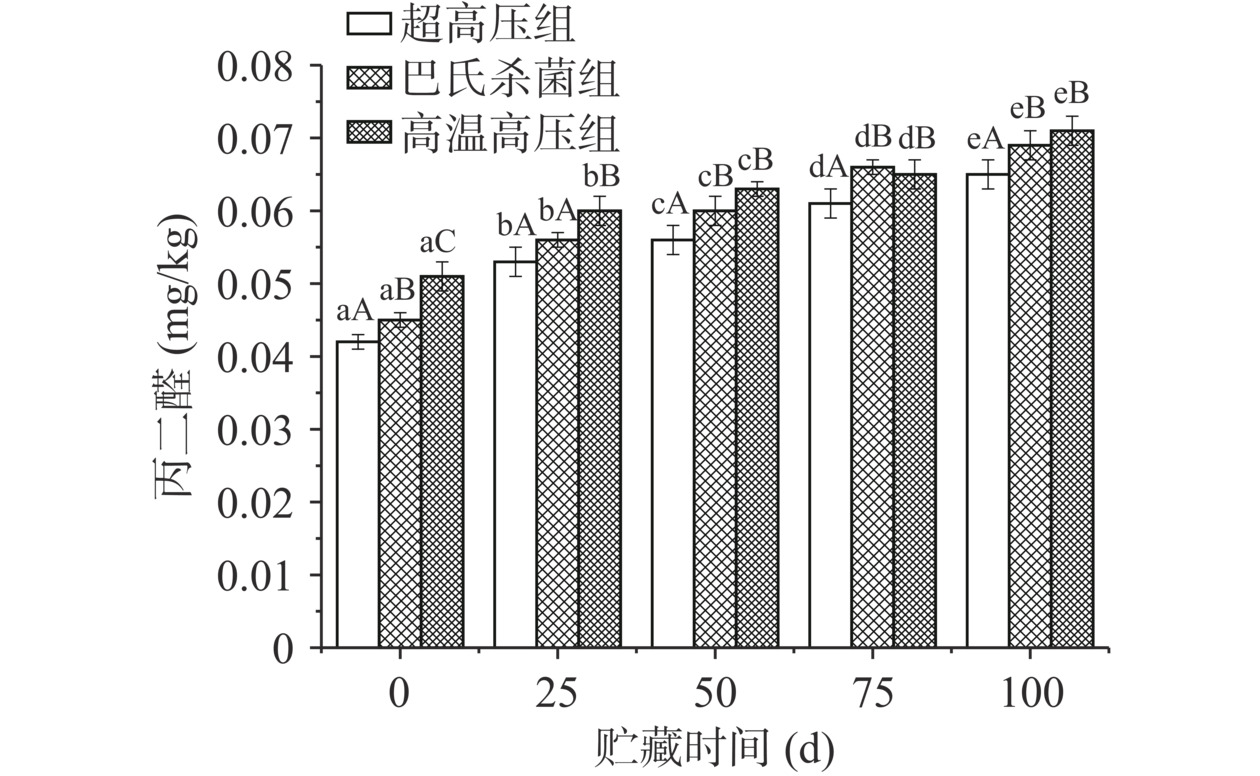
2.2.3 丙二醛含量
丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)是评价食品脂肪氧化程度和食品新鲜度的重要指标。脂肪氧化一般与加热温度、氧气、催化剂等有关。食品的脂肪氧化程度越高,其主要氧化产物丙二醛的含量越多[30]。由图3可知,三种不同杀菌方式得到的鸡汤,在贮藏期MDA含量均呈现缓慢上升趋势,且具有显著差异(P<0.05),与Tolasa等[31]、Mol[32]和Gadekar等[33]的研究结论一致。MDA值的变化主要是与脂肪氧化相关,对比0 d时三组的MDA值,发现三组实验存在显著差异(P<0.05),热处理增加了巴氏杀菌组和高温高压组的MDA值,而超高压属于冷杀菌,三组的MDA值由大到小依次是:高温高压组>巴氏杀菌组>超高压组。在0~50 d的贮藏期间,三组鸡汤的MDA值上升趋势较快,可能是因为袋中残存部分空气所致,到了贮藏中后期,MDA值上升速度放缓,可能是因为氧气消耗殆尽,何小峰[34]在研究瓦罐鸡汤时也发现了这一变化现象。
2.3 风味品质
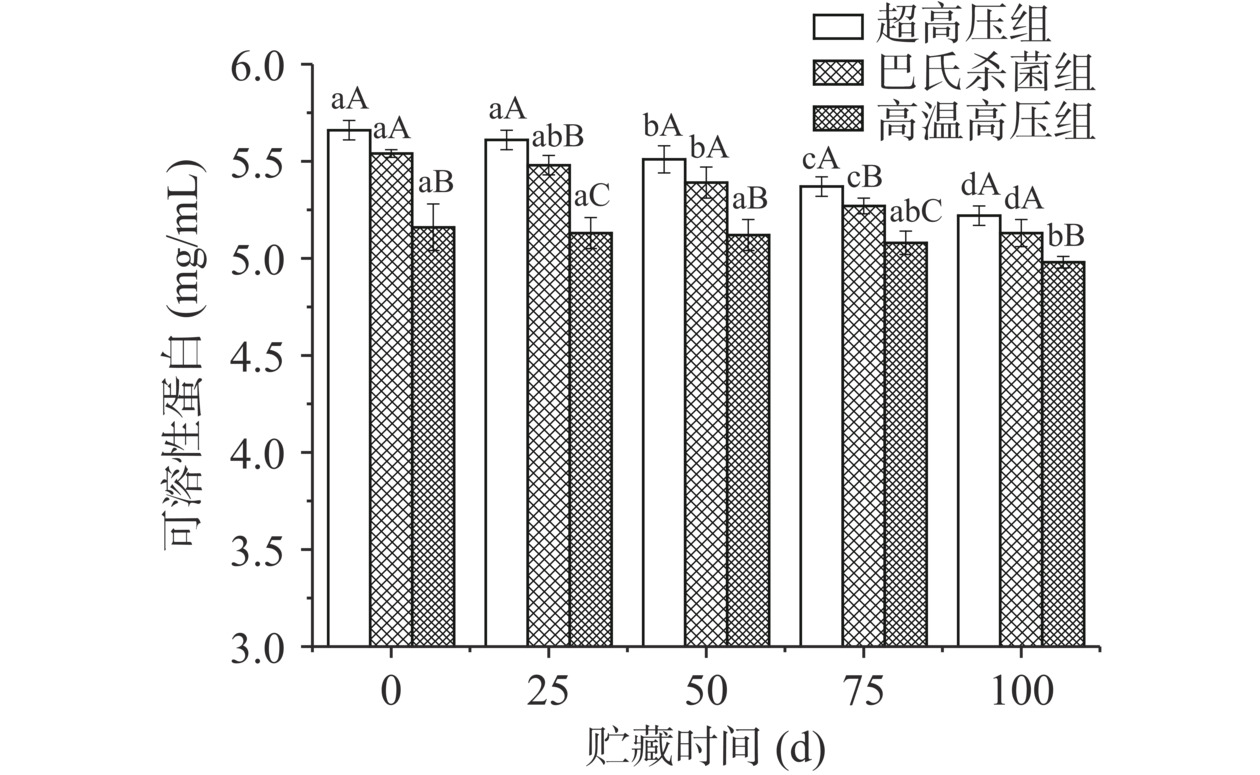
2.3.1 可溶性蛋白
鸡汤中的可溶性蛋白主要是一些肌原纤维蛋白和肌浆蛋白。由图4可知,三组实验的可溶性蛋白在贮藏期间呈现缓慢下降趋势。这种现象可能是因为鸡汤中的可溶性蛋白被微生物分解为氨和胺类碱性含氮物导致的[14]。超高压组可溶性蛋白含量下降速度是三组实验中最快的,在贮藏前期蛋白含量下降很慢,但到了第50 d时,可溶性蛋白含量快速下降,最终蛋白含量减少至5.22 mg/mL,贮藏期间的可溶性蛋白含量显著下降(P<0.05);巴氏杀菌组鸡汤的可溶性蛋白含量在0 d与25 d、25 d与50 d时无显著差异(P>0.05),但在50~100 d贮藏期内组间存在著性差异(P<0.05),整体上,可溶性蛋白含量在100 d贮存藏期内显著下降(P<0.05),在第100 d时的含量为5.13 mg/mL,低于超高压组而高于高温高压组;高温高压组的可溶性蛋白含量在整个贮藏期间下降非常缓慢,第100 d时的含量为4.98 mg/mL,明显低于其余两组第100 d时的可溶性蛋白含量,且组内与75 d无显著差异(P>0.05)。
2.3.2 游离氨基酸
游离氨基酸是一类十分重要的呈味物质,其中甜味、鲜味、苦味等氨基酸含量可以影响食品的整体滋味[35]。由表3所示,三种不同杀菌方式鸡汤中含有的主要游离氨基酸是Glu、Ser、Ala。纵观整个贮藏过程,发现三组游离氨基酸总量均显著下降(P<0.05)。Tian等[36]发现红曲酒经过18个月的贮藏,大部分游离氨基酸含量有所下降,比如赖氨酸。鸡汤中的游离氨基酸含量下降的原因主要是微生物的作用,这与余力等[14]、Li等[37]的分析结论一致。
表 3 不同灭菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的游离氨基酸的影响(mg/100 mL)Table 3. Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on free amino acid stored in chicken soup (mg/100 mL)游离氨基酸 超高压杀菌组 巴氏杀菌组 高温高压杀菌组 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 天冬氨酸Asp 3.30±0.08aA 3.23±0.15aA 3.15±0.13aA 3.14±0.11aA 3.03±0.13aA 3.23±0.16aB 3.15±0.13aA 3.17±0.09aA 3.11±0.03aA 3.06±0.05aA 3.21±0.20aB 3.20±0.21aA 3.11±0.11aA 3.07±0.17aA 2.91±0.14aA 苏氨酸Thr 8.13±0.54aA 7.64±0.37aA 7.42±0.21abA 7.26±0.05abA 7.18±0.08bA 7.43±0.38aA 6.81±0.52abB 6.75±0.24abB 6.70±0.28abB 6.57±0.50bB 6.52±0.62aB 6.46±0.47abB 6.58±0.63abC 6.51±0.67abC 6.48±0.69bB 丝氨酸Ser 14.35±0.06aA 14.33±0.25aA 14.23±0.28aA 13.95±0.35abA 13.51±0.49bA 14.18±0.11aA 14.17±0.04aAB 14.11±0.03aA 14.07±0.05aA 13.43±0.42bA 14.29±0.45aA 13.93±0.16abB 13.85±0.2abA 13.62±0.43bA 13.33±0.32bA 谷氨酸Glu 18.03±0.16aA 17.68±0.52abA 17.57±0.4abA 17.4±0.24bcA 16.96±0.06cA 17.92±0.45aA 17.38±0.23abA 17.31±0.24abA 17.21±0.29abA 16.75±0.64bA 17.43±0.51aB 16.99±0.55abA 16.89±0.55abA 16.78±0.48abA 16.3±0.16bA 甘氨酸Gly 8.19±0.45aA 8.11±0.23abA 7.75±0.36abA 7.70±0.31abA 7.40±0.21bA 8.15±0.07aA 8.09±0.03aA 8.10±0.02aA 7.67±0.41bA 7.19±0.07cA 7.98±0.10aA 7.52±0.43abB 7.52±0.43abB 7.45±0.40abA 7.19±0.22bA 丙氨酸Ala 12.04±0.04aA 12.07±0.46aA 11.76±0.42abA 11.69±0.53abA 11.11±0.39bA 12.15±0.19aA 12.06±0.39aA 11.76±0.61aA 11.47±0.85aA 11.18±0.93aA 11.46±0.66aA 11.24±0.59aA 11.16±0.58aA 10.94±0.82aA 10.77±0.49aA 半胱氨酸Cys 0.38±0.01abA 0.44±0.06aA 0.39±0.03abA 0.39±0.02abA 0.35±0.04bA 0.46±0.01aA 0.47±0.01aA 0.44±0.05aA 0.40±0.05aA 0.38±0.07aA 0.48±0.02aA 0.44±0.06abA 0.44±0.06bcA 0.38±0.03cA 0.36±0.01cA 缬氨酸Val 2.75±0.05aA 2.71±0.02aA 2.68±0.16aA 2.66±0.06aA 2.52±0.17aA 2.82±0.17aA 2.92±0.21aA 2.92±0.21aA 2.75±0.24aA 2.56±0.30aA 2.82±0.15aA 2.81±0.14aA 2.80±0.15aA 2.76±0.11aA 2.52±0.27aA 甲硫氨酸Met 1.39±0.16aA 1.32±0.02aA 1.28±0.04aA 1.26±0.04aA 1.25±0.04aA 1.37±0.08aA 1.25±0.05bAB 1.25±0.04bAB 1.22±0.05bAB 1.19±0.07bAB 1.32±0.03aA 1.26±0.07bB 1.25±0.09bcB 1.24±0.09bcB 1.17±0.08cB 异亮氨酸Ile 1.69±0.06aA 1.66±0.02aA 1.63±0.07aA 1.58±0.12aA 1.57±0.12aA 1.61±0.05aA 1.46±0.11abB 1.45±0.09abB 1.44±0.09abA 1.36±0.11bA 1.62±0.06aA 1.55±0.15bB 1.52±0.16bB 1.50±0.17bA 1.46±0.14bA 亮氨酸Leu 3.86±0.18aA 3.74±0.10aA 3.57±0.18abA 3.54±0.15abA 3.28±0.33bA 3.52±0.16aAB 3.42±0.19abAB 3.35±0.08abAB 3.31±0.03abB 3.23±0.12bA 3.41±0.35aB 3.45±0.30aB 3.42±0.26abB 3.4±0.26abC 3.39±0.25bA 酪氨酸Tyr 4.38±0.23aA 4.02±0.15bA 3.88±0.18bA 3.86±0.14bA 3.70±0.12bA 3.75±0.39aB 3.54±0.48aAB 3.53±0.47aAB 3.47±0.41aAB 3.33±0.29aAB 3.13±0.22aC 3.23±0.15aB 3.23±0.15aB 3.20±0.12aB 3.15±0.15aB 苯丙氨酸Phe 4.58±0.38aA 4.41±0.43aA 4.21±0.26aA 4.19±0.22aA 4.01±0.02aA 3.14±0.12abB 3.38±0.32aB 3.09±0.12abB 2.97±0.10bB 2.91±0.10bB 3.85±0.64aA 3.62±0.50abAB 3.59±0.50bcC 3.53±0.42cdC 3.37±0.27dC 赖氨酸Lys 3.30±0.37aA 3.14±0.15aA 2.98±0.22aA 2.91±0.12aA 2.87±0.18aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.00±0.08aA 2.98±0.06aA 2.66±0.45aA 2.62±0.49aA 2.62±0.49aA 2.60±0.47aA 2.54±0.44aA 组氨酸His 5.46±0.22aAB 5.51±0.02aA 5.45±0.10aA 5.31±0.23aA 5.12±0.23aA 5.53±0.33aA 5.49±0.23aA 5.46±0.23aA 5.24±0.21aA 5.10±0.18aA 4.88±0.35aB 5.08±0.39aA 5.04±0.41aA 5.03±0.41aA 4.96±0.49aA 精氨酸Arg 3.28±0.16aA 3.28±0.17aA 3.24±0.22aA 3.20±0.26aA 3.06±0.27aA 3.25±0.17aA 3.20±0.22aA 3.17±0.17aA 3.09±0.10aA 3.05±0.06aA 3.12±0.28aA 3.05±0.21aA 3.05±0.20aA 3.03±0.21aA 2.97±0.15aA 脯氨酸Pro 3.66±0.48aA 3.71±0.29aA 3.65±0.41aA 3.62±0.41aA 3.47±0.36aA 3.29±0.29aA 3.17±0.29aAB 3.15±0.26aAB 3.08±0.14aAB 3.03±0.09aAB 2.47±0.24aB 2.68±0.34aB 2.67±0.33aB 2.64±0.33aB 2.61±0.30aB 氨基酸总量TFAA 98.69±1.97aA 97.01±1.44abA 94.84±1.08bcA 93.67±1.40cA 90.38±1.42dA 94.54±1.60aB 92.97±1.17abB 92.02±1.16abB 90.21±1.96bcB 87.3±2.68cAB 90.64±2.01aC 89.13±1.67abC 88.74±1.83abC 87.68±1.76bcC 85.49±2.91cB 注:同行肩标不同小写字母代表组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);不同大写字母代表同一贮藏时间三种杀菌方法间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);表4同。 对比超高压、巴氏杀菌和高温高压杀菌的游离氨基酸含量,0 d时,三种不同杀菌方式的鸡汤中游离氨基酸含量有显著性差异(P<0.05),这是因为热处理加速了鸡汤发生美拉德反应[38],最终导致游离氨基酸的含量有所下降,且对各游离氨基酸含量均有不同程度的影响。在第50 d时,由于微生物的生长繁殖[14],超高压组的游离氨基酸被微生物分解,其含量开始快速下降,巴氏杀菌组则在第75 d才开始,高温高压组的游离氨基酸含量在整个贮藏期间下降相对平稳,这种趋势正好对应上文中的三种不同杀菌方式在贮藏期间的菌落总数变化。
在100 d的贮藏过程中,游离氨基酸总量由高到低依次是:超高压组>巴氏杀菌组>高温高压组。原因在于超高压这种冷杀菌技术保持了鸡汤中的游离氨基酸,这使得超高压组的初始值就比其他两组实验要高,留下较大的下降空间,同时微冻贮藏条件下,微生物总数不高,导致分解游离氨基酸的能力有限。
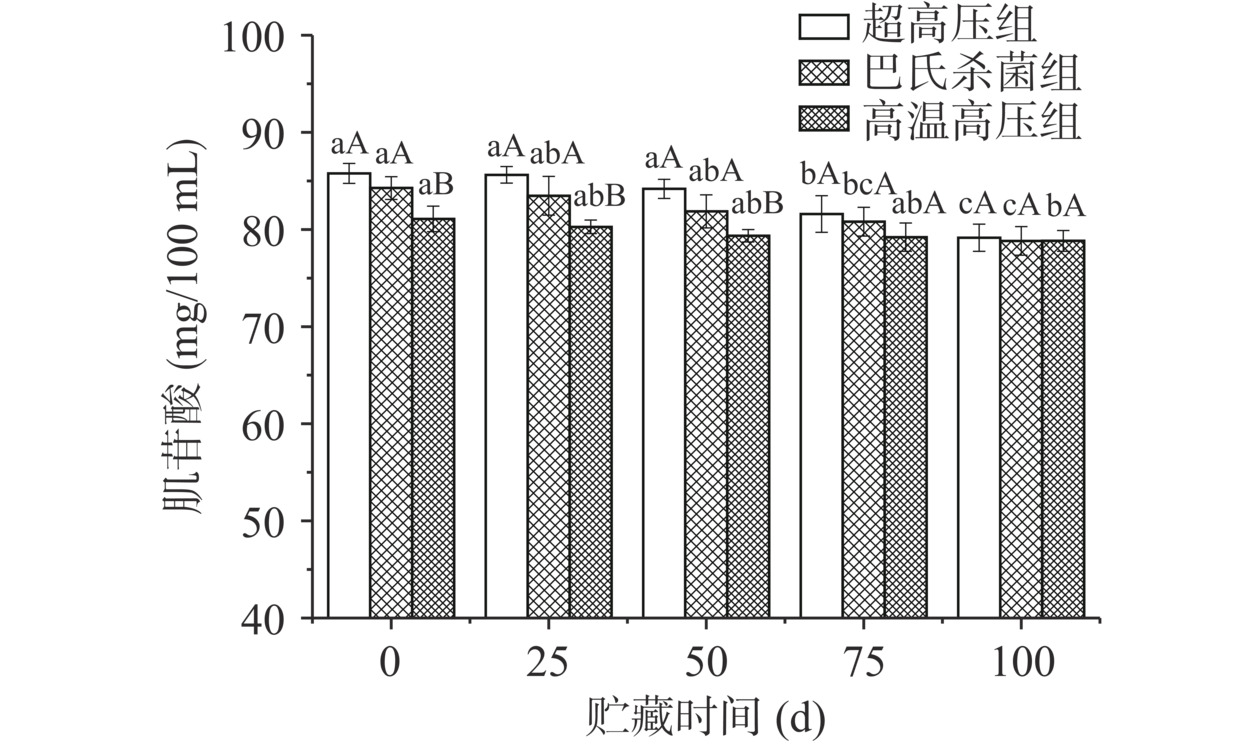
2.3.3 肌苷酸
肌苷酸(IMP)一直被认为是肉类的主要风味前体成分之一,在肌苷酸与腺苷一磷酸(AMP)协同作用条件下,会激发人的味觉,增加食品的甜度[37]。由图5可知,在整个贮藏过程中,三组实验的肌苷酸含量逐渐缓慢下降,且具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。在肌苷酸含量上,超高压组由85.77 mg/100 mL减少到79.15 mg/100 mL,巴氏杀菌组由84.27 mg/100 mL减少到78.82 mg/100 mL;而高温高压杀菌组下降速度缓慢,由81.09 mg/100 mL减少到78.83 mg/100 mL。鸡汤中肌苷酸含量下降原因在于微生物的作用。Li等[37]研究鸡汤在微生物的作用下,其肌苷酸含量呈下降的趋势,这与本实验结论是一致的。虽然超高压组的肌苷酸含量下降快,但在100 d的微冻条件下,其含量始终高于其他两组。低温贮存是食品保鲜的重要方式,能够有效抑制微生物生长,陈继兰等[39]研究室温和4 ℃下肌苷酸的变化,室温的肌苷酸含量下降最快,24 h后下降了55%;4 ℃的肌苷酸下降了6.3%,这佐证了本实验的结论,微冻贮藏可以抑制微生物生长进而降低鸡汤中肌苷酸的分解速度。
对比三种不同杀菌方式,其肌苷酸含量为超高压组>巴氏杀菌组>高温高压组,巴氏杀菌组和超高压杀菌组之间不存在显著性差异(P>0.05),巴氏杀菌组和超高压杀菌组与高温高压杀菌组相比,前50 d存在显著性差异(P<0.05),75 d开始无显著性差异(P>0.05),这可能是因为高温高压处理过程中,肌苷酸受热分解为肌苷和磷酸[40−41],同时巴氏杀菌组灭菌强度低于高温高压组导致的。由以上可知,高温高压杀菌明显降低了鸡汤的肌苷酸含量,由于杀菌效果好,在贮藏过程中,肌苷酸含量下降缓慢;超高压杀菌和巴氏杀菌对肌苷酸影响不大,但由于杀菌效果相对较弱,75 d之后肌苷酸的含量与高温高压杀菌组差异不显著。总体上,100 d的微冻条件下,超高压组肌苷酸含量高于其他两组。
2.3.4 挥发性物质
挥发性物质的种类、含量和感觉阈值是鸡汤呈香的重要因素[42]。从表4中可以看出,本次实验中检出烃类、醛类、醇类、酮类、呋喃类5类挥发性物质,共计21种,超高压杀菌组全部检出;巴氏杀菌组检出19种,十一烷、十二烷未检出;高温高压杀菌组检出17种,异十一醛、十一烷、十二烷、3-甲基-十五烷未检出;三组鸡汤在烃类物质种类上存在明显差异,其产生与脂肪氧化和大分子热降解有关,但烃类物质由于香味阈值很高,风味特征较弱,一般被认为对鸡汤呈香无特殊贡献[43]。
表 4 不同杀菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的挥发性物质的影响(μg/μL)Table 4. Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on volatile substances stored in chicken soup (μg/μL)挥发性物质 超高压杀菌组 巴氏杀菌组 高温高压杀菌组 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 醛类 辛醛 8.63±0.60aA 7.61±0.39bA 7.21±0.18bcA 7.01±0.11bcA 6.55±0.40cA 7.98±0.28aA 7.64±0.38aA 6.12±0.12aB 6.08±0.10bB 5.94±0.14bB 5.88±0.40aB 5.75±0.30aB 5.78±0.24aB 5.44±0.34abC 5.02±0.12bC 己醛 36.74±0.86aA 34.19±0.81bA 31.16±0.41cA 30.12±0.97cA 27.30±0.74dA 34.79±0.54aB 35.79±1.35abA 32.46±1.26bA 31.48±0.66cA 30.47±0.55cB 29.51±0.86aC 27.38±1.28bB 27.24±0.89bB 27.21±0.81bB 26.23±0.37bA 癸醛 1.33±0.11aA 1.26±0.08abA 1.15±0.12bcA 1.10±0.10bcA 1.01±0.06cA 1.18±0.14aAB 1.05±0.11abB 0.89±0.04bcB 0.88±0.07bcB 0.78±0.07cB 1.00±0.10aB 0.93±0.10abB 0.94±0.04abB 0.91±0.03abB 0.86±0.04bB 反-2-辛烯醛 5.47±0.32aA 4.71±0.36bA 4.37±0.23bcA 4.25±0.13bcA 4.03±0.07cA 5.11±0.22aA 4.88±0.18aA 4.27±0.26bA 4.04±0.02bB 3.94±0.08bB 3.78±0.40aB 3.54±0.29abB 3.49±0.10abB 3.44±0.05abC 3.26±0.14bB 壬醛 23.75±0.72aA 21.48±0.88bA 20.76±0.53bA 18.49±0.99cA 16.82±0.92dA 23.64±0.85aA 22.79±0.79aA 21.18±0.51bA 21.01±0.64bB 20.02±0.25bB 18.63±0.98aB 17.76±0.63abB 17.4±0.52bcB 17.12±0.28bcA 16.36±0.62cA 异十一醛 2.62±0.10a 2.53±0.14ab 2.35±0.16bc 2.26±0.12c 2.15±0.07c 2.29±0.24a 2.18±0.22ab 2.11±0.21ab 2.00±0.09ab 1.90±0.10b − − − − − 反式-2-癸烯醛 2.48±0.13aA 2.37±0.06abA 2.27±0.08bcA 2.11±0.07cdA 2.03±0.11dA 2.06±0.05aB 1.96±0.10abB 1.84±0.14bcB 1.80±0.09bcB 1.74±0.07cB 1.73±0.10aC 1.64±0.12abC 1.66±0.06abB 1.66±0.03abC 1.53±0.07bC 庚醛 4.57±0.41aA 4.13±0.22bA 3.99±0.13bA 3.94±0.08bA 3.71±0.09bA 4.70±0.32aA 4.19±0.14bA 3.86±0.13bcA 3.81±0.17cA 3.70±0.07cA 3.57±0.42aB 3.49±0.40aB 3.42±0.27aB 3.39±0.20aB 3.30±0.11aB 小计 85.58±1.49aA 78.28±2.12bA 73.27±0.23cB 69.28±0.61dB 63.59±0.35eB 81.76±1.28aB 80.48±1.75aA 72.74±1.59bA 71.10±0.20bA 68.49±0.65cA 64.09±1.37aC 60.5±0.48bB 59.94±0.34bC 59.17±0.34bC 56.55±1.13cC 醇类 1-辛烯-3-醇 13.04±0.75aA 11.97±0.37abA 11.20±0.7bcA 10.82±0.74bcA 10.20±0.42cA 11.57±0.48aB 11.00±0.6abB 10.45±0.16bcB 10.30±0.22bcA 9.94±0.24cA 10.36±0.54aC 10.11±0.40aB 9.77±0.23aB 9.94±0.43aA 9.73±0.12aA 庚醇 5.21±0.19aA 4.95±0.24aA 4.86±0.27aA 4.32±0.23bA 4.04±0.09bA 5.25±0.20aA 4.84±0.19bA 4.30±0.32cAB 4.14±0.14cA 3.94±0.12cA 4.84±0.30aA 4.69±0.20abA 4.68±0.12abB 4.48±0.21abA 4.42±0.19bB 小计 18.25±0.94aA 16.92±0.14bA 16.06±0.97bcA 15.14±0.72cdA 14.24±0.35dA 16.82±0.68aAB 15.84±0.72bAB 14.75±0.19cB 14.45±0.33cA 13.89±0.36cA 15.20±0.84aB 14.80±0.60aB 14.45±0.35aB 14.42±0.51aA 14.15±0.28aA 酮类 2-庚酮 5.60±0.09aA 5.22±0.20bA 5.00±0.10bA 4.59±0.28cA 4.03±0.16dA 4.87±0.20aB 4.27±0.21bB 4.03±0.14bcB 3.95±0.08cB 3.86±0.15cA 4.09±0.22aC 4.06±0.19aB 3.99±0.08aB 3.96±0.12aB 3.89±0.07aA 小计 5.60±0.09aA 5.22±0.20bA 5.00±0.10bA 4.59±0.28cA 4.03±0.16dA 4.87±0.20aB 4.27±0.21bB 4.03±0.14bcB 3.95±0.08cB 3.86±0.15cA 4.09±0.22aC 4.06±0.19aB 3.99±0.08aB 3.96±0.12aB 3.89±0.07aA 烃类 十一烷 1.18±0.03a 1.43±0.11b 1.53±0.10bc 1.62±0.08c 1.88±0.08d − − − − − − − − − − 十四烷 3.47±0.38abA 3.38±0.09aA 3.40±0.05aA 3.49±0.14abA 3.81±0.15bA 2.98±0.22aAB 3.29±0.11aA 3.74±0.21bB 3.83±0.11bB 4.01±0.17bA 2.78±0.05aB 2.82±0.02abB 2.84±0.01bC 2.91±0.02cB 2.93±0.02cA 十五烷 3.35±0.21aA 3.54±0.08abA 3.60±0.06bcA 3.78±0.11cA 4.08±0.10dA 2.80±0.27aA 3.38±0.36bA 3.71±0.39bA 3.85±0.09bA 3.91±0.15bA 1.64±0.35aB 1.86±0.07abB 1.88±0.06abB 1.92±0.03abB 2.00±0.04bB 十二烷 2.47±0.24a 2.61±0.09ab 2.70±0.11ab 2.83±0.08bc 3.02±0.14c − − − − − − − − − − 十六烷 2.05±0.11aA 2.20±0.10aA 2.52±0.08bA 2.54±0.08bA 2.84±0.10cA 1.96±0.09aA 2.21±0.31abA 2.43±0.31bcA 2.69±0.11cA 2.80±0.11cA 1.76±0.04aB 1.87±0.03bA 1.97±0.04cB 1.98±0.04cB 2.03±0.06cB 十七烷 3.62±0.19aA 3.76±0.17aA 3.83±0.09aA 3.83±0.13aA 4.25±0.18bA 3.35±0.29aA 3.64±0.22abA 3.95±0.07bcA 4.05±0.06cB 4.26±0.24cA 1.94±0.23aB 2.02±0.11aB 2.04±0.06aB 2.06±0.11aC 2.10±0.07aB 庚烷 1.53±0.08aA 1.65±0.11aA 1.62±0.08aA 1.67±0.05aA 1.87±0.04bA 1.37±0.14aA 1.62±0.11bA 1.89±0.09cB 1.97±0.07cB 2.05±0.06cB 1.02±0.13aB 1.13±0.08abB 1.15±0.07abC 1.14±0.05abC 1.27±0.06bC 辛烷 3.35±0.36aA 3.63±0.26abA 3.79±0.11bA 3.88±0.02bA 3.91±0.10bA 3.23±0.20aA 3.89±0.11bA 3.91±0.12bB 4.03±0.06bB 4.11±0.03bB 2.37±0.35aB 2.61±0.14abB 2.60±0.12abB 2.64±0.09abC 2.77±0.04bC 3-甲基-十五烷 1.59±0.18a 1.90±0.08b 1.92±0.05b 2.00±0.07bc 2.20±0.16c 1.50±0.19a 1.88±0.22b 1.91±0.09bc 2.01±0.11bc 2.18±0.07c − − − − − 小计 22.61±0.59dA 24.09±0.87cA 24.91±0.59bcA 25.64±0.45bA 27.87±0.20aA 17.20±0.41eB 19.9±0.39dB 21.55±0.22cB 22.43±0.30bB 23.32±0.52aB 9.75±0.87cC 10.45±0.26abC 10.51±0.17abC 10.68±0.23aC 11.08±0.01aC 呋喃类 2-戊基呋喃 6.97±0.39bA 7.11±0.24bA 7.26±0.27abA 7.38±0.14abA 7.71±0.18aA 6.86±0.25cA 6.97±0.16bcA 7.14±0.11abcA 7.23±0.08abA 7.34±0.16aB 6.39±0.44aA 6.40±0.33aB 6.44±0.24aB 6.58±0.29aB 6.86±0.10aC 小计 6.97±0.39bA 7.11±0.24bA 7.26±0.27abA 7.38±0.14abA 7.71±0.18aA 6.86±0.25cA 6.97±0.16bcA 7.14±0.11abcA 7.23±0.08abA 7.34±0.16aB 6.39±0.44aA 6.40±0.33aB 6.44±0.24aB 6.58±0.29aB 6.86±0.10aC 注:“−”:未检出。 醛类物质主要由鸡肉炖煮时脂肪氧化和热降解产生,其种类多且香气阈值较低,是形成鸡汤香气的主要的挥发性物质[44−45]。三组鸡汤中己醛含量均为最高,具有油脂香气[9],2-癸烯醛是鸡肉香味特征化合物中的重要成分,具有强烈的动物油脂味道[46],对鸡汤香气影响较大;在0 d时,超高压组的己醛含量(36.74±0.86 μg/μL)显著高于巴氏杀菌组(34.79±0.54 μg/μL)和高温高压组(29.51±0.86 μg/μL)(P<0.05),且在75 d时仍处于较高水平(30.12±0.97 μg/μL);在0~100 d微冻贮藏期内,超高压组2-癸烯醛含量始终显著高于其他两组(P<0.05),这可能是由于超高压的冷杀菌方式较好地保留了鸡汤中的醛类物质,但超高压组2-癸烯醛含量下降显著(0 d,2.48±0.13 μg/μL;100 d,2.03±0.11 μg/μL)(P<0.05),可能是由于400 MPa下杀菌效果弱于热杀菌组,导致贮藏期间部分醛类被微生物氧化还原而显著降低(P<0.05)。由此可见,醛类物质总量在100 d微冻贮藏期间呈下降趋势,但超高压组能将鸡汤中重要的醛类物质保持相对高的水平,减少了鸡汤脂香味损失。
醇类物质主要与脂肪氧化及醛的还原反应有关[46],实验中仅检出庚醇和1-辛烯-3-醇两种醇类物质。庚醇具有近似柑橘的香气,可能是由脂肪氧化或庚醛还原产生[47];1-辛烯-3-醇是一种亚油酸的氢过氧化物发生降解而产生的不饱和醇[48],是蒸煮鸡肉和鸡肉香精的特征风味物质之一,这种不饱和醇含量的增加会使鸡汤的肉香味有所增强[44]。在0 d时,超高压组的1-辛烯-3-醇含量(13.04±0.75 μg/μL)显著高于巴氏杀菌组(11.57±0.48 μg/μL)和高温高压杀菌组(10.36±0.54 μg/μL)(P<0.05),随着微冻贮藏时间的延长,三组鸡汤的1-辛烯-3-醇含量均呈下降趋势;75 d时,三组鸡汤的1-辛烯-3-醇含量已无统计学差异(超高压组10.82±0.74 μg/μL;巴氏杀菌组10.30±0.22 μg/μL;高温高压杀菌组9.94±0.43 μg/μL)(P>0.05),但超高压组的含量仍高于其余两组。由此可见,醇类物质总量贮藏期间呈下降趋势,超高压组能在0~75 d微冻贮藏期间保证鸡汤的肉香味,而75 d后三组鸡汤醇类含量并无显著差异(P>0.05)。
酮类物质、呋喃类物的形成也与脂肪氧化和热降解有关[44]。2-庚酮具有水果香气[47],在整个贮藏期间呈下降趋势。0~75 d贮藏期内,超高压组的2-庚酮含量(75 d,4.59±0.28 μg/μL)显著高于热杀菌组(P<0.05),可能是热处理方式减少了酮类含量。2-戊基呋喃是由亚油酸发生氧化而形成的[49],具有近似水果的香味[9],在0~100 d贮藏期内,三组鸡汤的2-戊基呋喃含量均呈上升趋势,且超高压组和巴氏杀菌组上升显著(P<0.05),高温高压组缓慢上升,但不具有显著性(P>0.05),这与张艳[50]的结论一致。由此可见,超高压组能较好保留鸡汤中的2-庚酮,但在2-戊基呋喃含量上,超高压组与巴氏杀菌组在0~75 d内无显著差异(P>0.05),仅在第100 d时高于热杀菌组,相对而言不具有明显优势;结合感官评价可发现,鸡汤中的果蔬芳香通常较为细微或被脂香掩盖而导致三组鸡汤在芳香气味上总体相似。
鸡汤的香气化合物主要是因为脂类的氧化、美拉德反应以及美拉德反应和脂类降解的相互作用产生[51]。总体上,超高压的杀菌方式在整个贮藏期间能较好保留鸡汤中重要的风味物质,己醛、2-癸烯醛、1-辛烯-3-醇维持了鸡汤的脂香、肉香,2-庚酮、2-戊基呋喃等使鸡汤风味产生细微差别;不同的杀菌方式对鸡汤挥发性物质影响显著(P<0.05),但在相同微冻条件下,鸡汤的挥发性物质变化趋势类似。
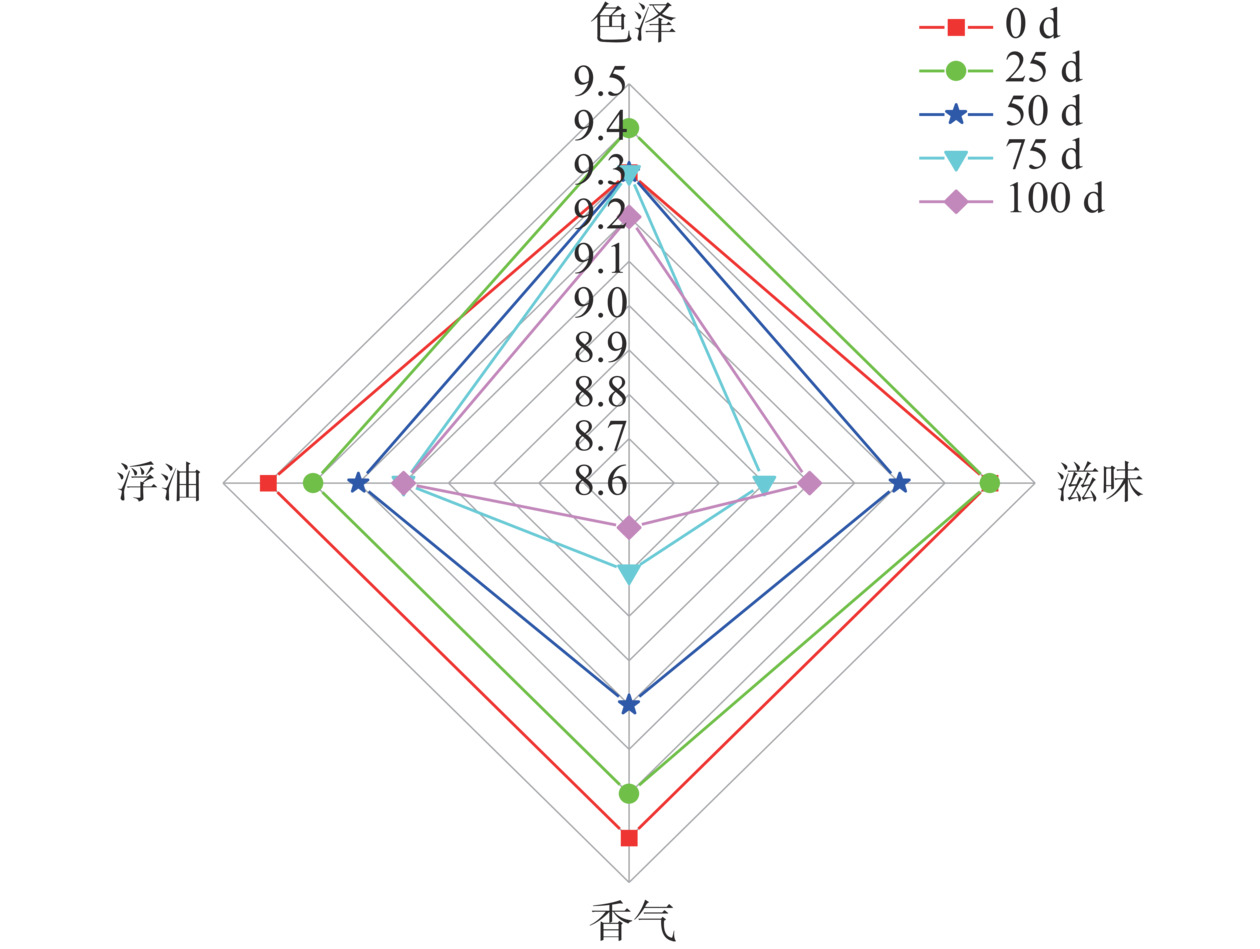
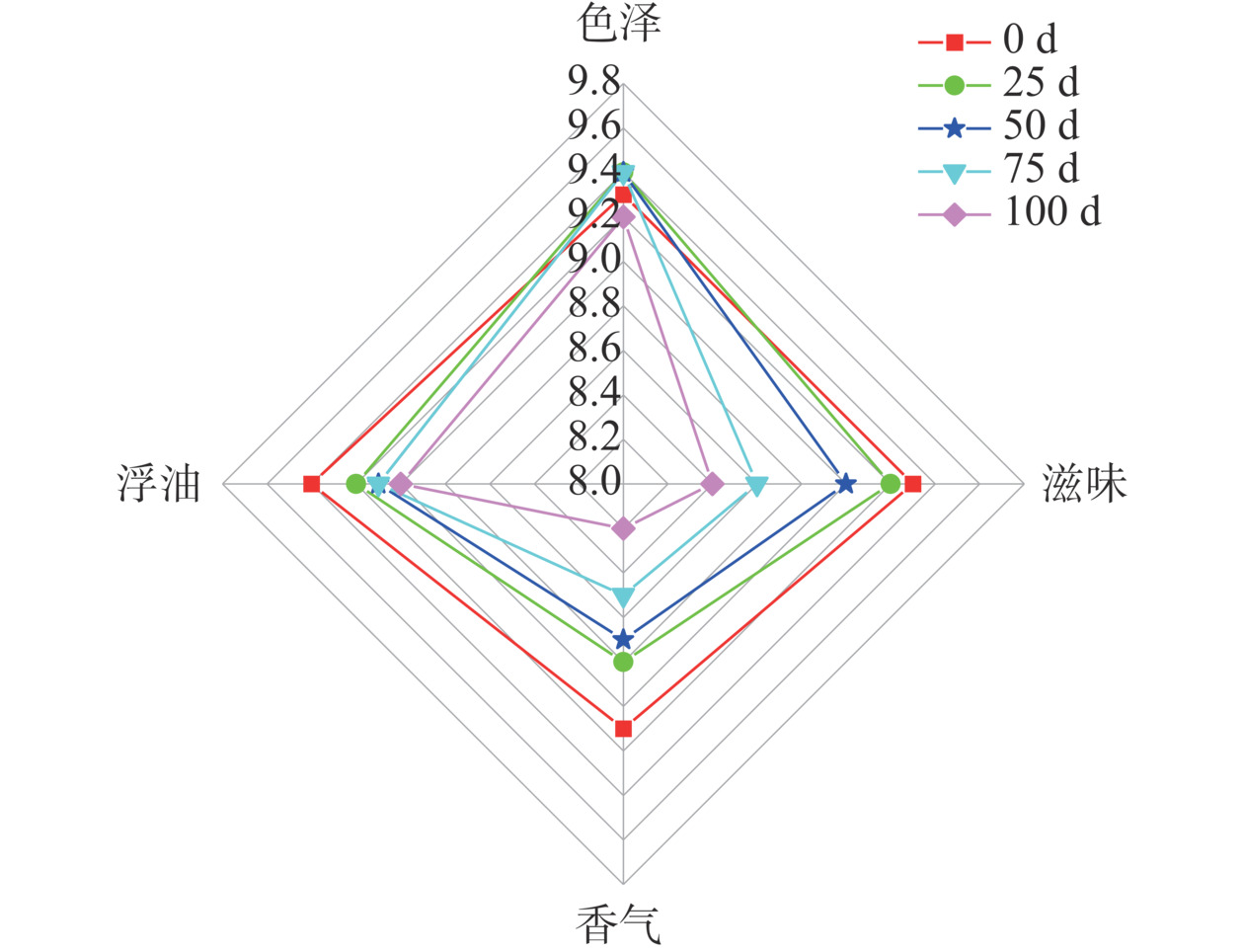
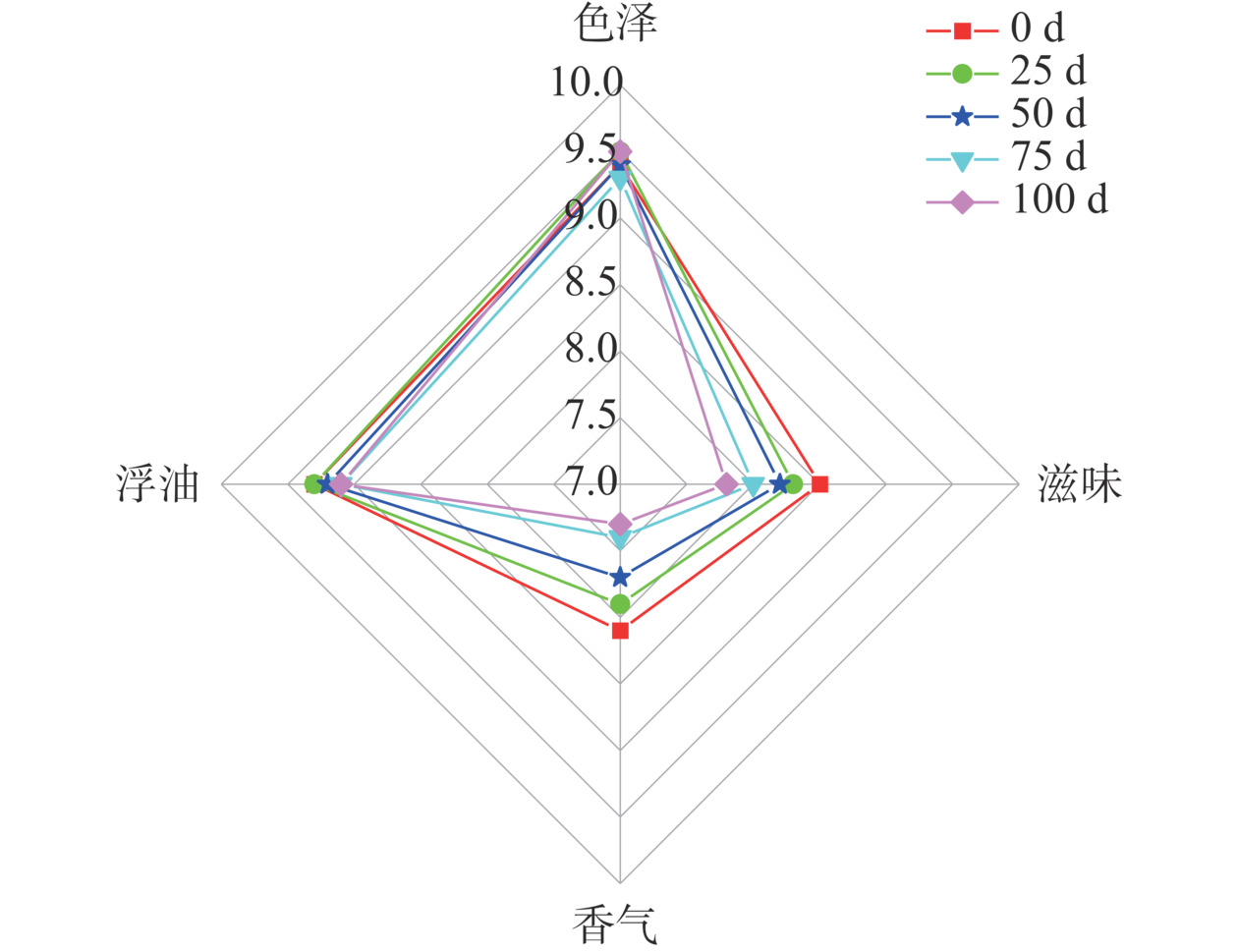
2.4 感官评定
感官评价是鸡汤风味品质的重要指标。经过100 d的贮藏时间,三组鸡汤的感官评分均有不同程度的下降(图6~图8),尤其是香气和滋味,但高温高压组的感官评分始终是三组中最低的。陈静茹等[29]发现油鸡的感官评分随着贮藏时间的延长而下降,这与本实验结论一致。对比0 d时三组鸡汤的感官得分,由高到低依次是:超高压组(37.4分)>巴氏杀菌组(37.0分)>高温高压组(35.3分)。结合前文中游离氨基酸、肌苷酸、挥发性物质等指标结果,发现热处理使得呈味物质下降,会导致鸡汤口感差,尤其是高温高压组的鸡汤口感醇厚不足,出现蒸煮味;而热处理又破坏了鸡汤中芳香族物质,致使鸡汤肉香味变淡,从而导致感官评分的下降。在整个贮藏过程中,因结合微冻技术,较好地抑制了微生物的繁殖,三种不同杀菌方式的鸡汤感官评分下降均较为缓慢。
3. 结论
本实验选定了超高压灭菌条件(400 MPa,15 min)和微冻的贮藏温度(−2.5 ℃),贮藏100 d,与巴氏杀菌组、高温高压组进行对比。发现三组处理条件下,鸡汤微生物指标在贮藏100 d内均符合产品微生物标准。贮藏过程中可溶性蛋白、游离氨基酸、肌苷酸含量呈下降趋势,而TVB-N含量呈上升趋势;超高压组鸡汤滋味指标高于热处理组,且超高压组鸡汤的鲜甜度更好;高温高压组的TVB-N值显著低于其他两组(P<0.05),但MDA值明显高于超高压组和巴氏杀菌组;在挥发性物质方面,超高压组的香气保持得较好,其挥发性物质种类和含量高于巴氏杀菌组和高温高压组;超高压组的感官得分显著高于巴氏杀菌组和高温高压组(P<0.05)。可见,在100 d的微冻条件下,超高压结合微冻的方式,使得鸡汤品质高于巴氏杀菌组和高温高压热处理组,并且100 d的贮藏时间比传统的0~4 ℃的保藏时间有显著提高。
利用压力结合微冻后多栅栏保鲜技术,开展其对鸡汤风味、脂质氧化等贮藏品质影响研究,有利于开发贮藏期长、鸡汤风味及营养保持度好的即食鸡汤产品,为拓展我国传统鸡汤产品品类,满足快速消费人群需求奠定研究基础。
-
表 1 感官评分
Table 1 Evaluation of sensory score
指标 0~2分 3~5分 6~8分 9~10分 色泽
(10分)鸡汤很浑浊
汤色很暗鸡汤浑浊度加大
汤色变暗鸡汤呈浅白色
略微浑浊色泽清亮
呈淡黄色滋味
(10分)口感很差
无回味
无鲜味口感清淡
回味不足
鲜味不足醇厚感不足
鲜味略微不足
回味稍差口感醇厚
鲜味适中
回味很足香气
(10分)肉香很差 肉香较差 肉香微淡 肉香浓郁 浮油
(10分)表面浮油厚重
口感很油腻表面有大量的浮油
口感较油腻表面有一层浮油
口感略微油腻表面有适量的浮油
口感适中表 2 不同杀菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的菌落总数影响(lg CFU/mL)
Table 2 Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on total colony stored in chicken soup(lg CFU/mL)
杀菌方式 贮藏时间(d) 0 25 50 75 100 超高压组 − − 1.32±0.07a 1.88±0.07bA 2.11±0.05cA 巴氏杀菌组 − − − 1.21±0.15aB 1.57±0.06bB 高温高压组 − − − − − 注:同行肩标不同小写字母代表组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);同列不同大写字母代表同一贮藏时间三种杀菌方式之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);“−”代表未检出。 表 3 不同灭菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的游离氨基酸的影响(mg/100 mL)
Table 3 Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on free amino acid stored in chicken soup (mg/100 mL)
游离氨基酸 超高压杀菌组 巴氏杀菌组 高温高压杀菌组 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 天冬氨酸Asp 3.30±0.08aA 3.23±0.15aA 3.15±0.13aA 3.14±0.11aA 3.03±0.13aA 3.23±0.16aB 3.15±0.13aA 3.17±0.09aA 3.11±0.03aA 3.06±0.05aA 3.21±0.20aB 3.20±0.21aA 3.11±0.11aA 3.07±0.17aA 2.91±0.14aA 苏氨酸Thr 8.13±0.54aA 7.64±0.37aA 7.42±0.21abA 7.26±0.05abA 7.18±0.08bA 7.43±0.38aA 6.81±0.52abB 6.75±0.24abB 6.70±0.28abB 6.57±0.50bB 6.52±0.62aB 6.46±0.47abB 6.58±0.63abC 6.51±0.67abC 6.48±0.69bB 丝氨酸Ser 14.35±0.06aA 14.33±0.25aA 14.23±0.28aA 13.95±0.35abA 13.51±0.49bA 14.18±0.11aA 14.17±0.04aAB 14.11±0.03aA 14.07±0.05aA 13.43±0.42bA 14.29±0.45aA 13.93±0.16abB 13.85±0.2abA 13.62±0.43bA 13.33±0.32bA 谷氨酸Glu 18.03±0.16aA 17.68±0.52abA 17.57±0.4abA 17.4±0.24bcA 16.96±0.06cA 17.92±0.45aA 17.38±0.23abA 17.31±0.24abA 17.21±0.29abA 16.75±0.64bA 17.43±0.51aB 16.99±0.55abA 16.89±0.55abA 16.78±0.48abA 16.3±0.16bA 甘氨酸Gly 8.19±0.45aA 8.11±0.23abA 7.75±0.36abA 7.70±0.31abA 7.40±0.21bA 8.15±0.07aA 8.09±0.03aA 8.10±0.02aA 7.67±0.41bA 7.19±0.07cA 7.98±0.10aA 7.52±0.43abB 7.52±0.43abB 7.45±0.40abA 7.19±0.22bA 丙氨酸Ala 12.04±0.04aA 12.07±0.46aA 11.76±0.42abA 11.69±0.53abA 11.11±0.39bA 12.15±0.19aA 12.06±0.39aA 11.76±0.61aA 11.47±0.85aA 11.18±0.93aA 11.46±0.66aA 11.24±0.59aA 11.16±0.58aA 10.94±0.82aA 10.77±0.49aA 半胱氨酸Cys 0.38±0.01abA 0.44±0.06aA 0.39±0.03abA 0.39±0.02abA 0.35±0.04bA 0.46±0.01aA 0.47±0.01aA 0.44±0.05aA 0.40±0.05aA 0.38±0.07aA 0.48±0.02aA 0.44±0.06abA 0.44±0.06bcA 0.38±0.03cA 0.36±0.01cA 缬氨酸Val 2.75±0.05aA 2.71±0.02aA 2.68±0.16aA 2.66±0.06aA 2.52±0.17aA 2.82±0.17aA 2.92±0.21aA 2.92±0.21aA 2.75±0.24aA 2.56±0.30aA 2.82±0.15aA 2.81±0.14aA 2.80±0.15aA 2.76±0.11aA 2.52±0.27aA 甲硫氨酸Met 1.39±0.16aA 1.32±0.02aA 1.28±0.04aA 1.26±0.04aA 1.25±0.04aA 1.37±0.08aA 1.25±0.05bAB 1.25±0.04bAB 1.22±0.05bAB 1.19±0.07bAB 1.32±0.03aA 1.26±0.07bB 1.25±0.09bcB 1.24±0.09bcB 1.17±0.08cB 异亮氨酸Ile 1.69±0.06aA 1.66±0.02aA 1.63±0.07aA 1.58±0.12aA 1.57±0.12aA 1.61±0.05aA 1.46±0.11abB 1.45±0.09abB 1.44±0.09abA 1.36±0.11bA 1.62±0.06aA 1.55±0.15bB 1.52±0.16bB 1.50±0.17bA 1.46±0.14bA 亮氨酸Leu 3.86±0.18aA 3.74±0.10aA 3.57±0.18abA 3.54±0.15abA 3.28±0.33bA 3.52±0.16aAB 3.42±0.19abAB 3.35±0.08abAB 3.31±0.03abB 3.23±0.12bA 3.41±0.35aB 3.45±0.30aB 3.42±0.26abB 3.4±0.26abC 3.39±0.25bA 酪氨酸Tyr 4.38±0.23aA 4.02±0.15bA 3.88±0.18bA 3.86±0.14bA 3.70±0.12bA 3.75±0.39aB 3.54±0.48aAB 3.53±0.47aAB 3.47±0.41aAB 3.33±0.29aAB 3.13±0.22aC 3.23±0.15aB 3.23±0.15aB 3.20±0.12aB 3.15±0.15aB 苯丙氨酸Phe 4.58±0.38aA 4.41±0.43aA 4.21±0.26aA 4.19±0.22aA 4.01±0.02aA 3.14±0.12abB 3.38±0.32aB 3.09±0.12abB 2.97±0.10bB 2.91±0.10bB 3.85±0.64aA 3.62±0.50abAB 3.59±0.50bcC 3.53±0.42cdC 3.37±0.27dC 赖氨酸Lys 3.30±0.37aA 3.14±0.15aA 2.98±0.22aA 2.91±0.12aA 2.87±0.18aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.01±0.07aA 3.00±0.08aA 2.98±0.06aA 2.66±0.45aA 2.62±0.49aA 2.62±0.49aA 2.60±0.47aA 2.54±0.44aA 组氨酸His 5.46±0.22aAB 5.51±0.02aA 5.45±0.10aA 5.31±0.23aA 5.12±0.23aA 5.53±0.33aA 5.49±0.23aA 5.46±0.23aA 5.24±0.21aA 5.10±0.18aA 4.88±0.35aB 5.08±0.39aA 5.04±0.41aA 5.03±0.41aA 4.96±0.49aA 精氨酸Arg 3.28±0.16aA 3.28±0.17aA 3.24±0.22aA 3.20±0.26aA 3.06±0.27aA 3.25±0.17aA 3.20±0.22aA 3.17±0.17aA 3.09±0.10aA 3.05±0.06aA 3.12±0.28aA 3.05±0.21aA 3.05±0.20aA 3.03±0.21aA 2.97±0.15aA 脯氨酸Pro 3.66±0.48aA 3.71±0.29aA 3.65±0.41aA 3.62±0.41aA 3.47±0.36aA 3.29±0.29aA 3.17±0.29aAB 3.15±0.26aAB 3.08±0.14aAB 3.03±0.09aAB 2.47±0.24aB 2.68±0.34aB 2.67±0.33aB 2.64±0.33aB 2.61±0.30aB 氨基酸总量TFAA 98.69±1.97aA 97.01±1.44abA 94.84±1.08bcA 93.67±1.40cA 90.38±1.42dA 94.54±1.60aB 92.97±1.17abB 92.02±1.16abB 90.21±1.96bcB 87.3±2.68cAB 90.64±2.01aC 89.13±1.67abC 88.74±1.83abC 87.68±1.76bcC 85.49±2.91cB 注:同行肩标不同小写字母代表组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);不同大写字母代表同一贮藏时间三种杀菌方法间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);表4同。 表 4 不同杀菌方式结合微冻对鸡汤贮藏的挥发性物质的影响(μg/μL)
Table 4 Effect of different sterilization methods combined with partial freezing on volatile substances stored in chicken soup (μg/μL)
挥发性物质 超高压杀菌组 巴氏杀菌组 高温高压杀菌组 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 0 d 25 d 50 d 75 d 100 d 醛类 辛醛 8.63±0.60aA 7.61±0.39bA 7.21±0.18bcA 7.01±0.11bcA 6.55±0.40cA 7.98±0.28aA 7.64±0.38aA 6.12±0.12aB 6.08±0.10bB 5.94±0.14bB 5.88±0.40aB 5.75±0.30aB 5.78±0.24aB 5.44±0.34abC 5.02±0.12bC 己醛 36.74±0.86aA 34.19±0.81bA 31.16±0.41cA 30.12±0.97cA 27.30±0.74dA 34.79±0.54aB 35.79±1.35abA 32.46±1.26bA 31.48±0.66cA 30.47±0.55cB 29.51±0.86aC 27.38±1.28bB 27.24±0.89bB 27.21±0.81bB 26.23±0.37bA 癸醛 1.33±0.11aA 1.26±0.08abA 1.15±0.12bcA 1.10±0.10bcA 1.01±0.06cA 1.18±0.14aAB 1.05±0.11abB 0.89±0.04bcB 0.88±0.07bcB 0.78±0.07cB 1.00±0.10aB 0.93±0.10abB 0.94±0.04abB 0.91±0.03abB 0.86±0.04bB 反-2-辛烯醛 5.47±0.32aA 4.71±0.36bA 4.37±0.23bcA 4.25±0.13bcA 4.03±0.07cA 5.11±0.22aA 4.88±0.18aA 4.27±0.26bA 4.04±0.02bB 3.94±0.08bB 3.78±0.40aB 3.54±0.29abB 3.49±0.10abB 3.44±0.05abC 3.26±0.14bB 壬醛 23.75±0.72aA 21.48±0.88bA 20.76±0.53bA 18.49±0.99cA 16.82±0.92dA 23.64±0.85aA 22.79±0.79aA 21.18±0.51bA 21.01±0.64bB 20.02±0.25bB 18.63±0.98aB 17.76±0.63abB 17.4±0.52bcB 17.12±0.28bcA 16.36±0.62cA 异十一醛 2.62±0.10a 2.53±0.14ab 2.35±0.16bc 2.26±0.12c 2.15±0.07c 2.29±0.24a 2.18±0.22ab 2.11±0.21ab 2.00±0.09ab 1.90±0.10b − − − − − 反式-2-癸烯醛 2.48±0.13aA 2.37±0.06abA 2.27±0.08bcA 2.11±0.07cdA 2.03±0.11dA 2.06±0.05aB 1.96±0.10abB 1.84±0.14bcB 1.80±0.09bcB 1.74±0.07cB 1.73±0.10aC 1.64±0.12abC 1.66±0.06abB 1.66±0.03abC 1.53±0.07bC 庚醛 4.57±0.41aA 4.13±0.22bA 3.99±0.13bA 3.94±0.08bA 3.71±0.09bA 4.70±0.32aA 4.19±0.14bA 3.86±0.13bcA 3.81±0.17cA 3.70±0.07cA 3.57±0.42aB 3.49±0.40aB 3.42±0.27aB 3.39±0.20aB 3.30±0.11aB 小计 85.58±1.49aA 78.28±2.12bA 73.27±0.23cB 69.28±0.61dB 63.59±0.35eB 81.76±1.28aB 80.48±1.75aA 72.74±1.59bA 71.10±0.20bA 68.49±0.65cA 64.09±1.37aC 60.5±0.48bB 59.94±0.34bC 59.17±0.34bC 56.55±1.13cC 醇类 1-辛烯-3-醇 13.04±0.75aA 11.97±0.37abA 11.20±0.7bcA 10.82±0.74bcA 10.20±0.42cA 11.57±0.48aB 11.00±0.6abB 10.45±0.16bcB 10.30±0.22bcA 9.94±0.24cA 10.36±0.54aC 10.11±0.40aB 9.77±0.23aB 9.94±0.43aA 9.73±0.12aA 庚醇 5.21±0.19aA 4.95±0.24aA 4.86±0.27aA 4.32±0.23bA 4.04±0.09bA 5.25±0.20aA 4.84±0.19bA 4.30±0.32cAB 4.14±0.14cA 3.94±0.12cA 4.84±0.30aA 4.69±0.20abA 4.68±0.12abB 4.48±0.21abA 4.42±0.19bB 小计 18.25±0.94aA 16.92±0.14bA 16.06±0.97bcA 15.14±0.72cdA 14.24±0.35dA 16.82±0.68aAB 15.84±0.72bAB 14.75±0.19cB 14.45±0.33cA 13.89±0.36cA 15.20±0.84aB 14.80±0.60aB 14.45±0.35aB 14.42±0.51aA 14.15±0.28aA 酮类 2-庚酮 5.60±0.09aA 5.22±0.20bA 5.00±0.10bA 4.59±0.28cA 4.03±0.16dA 4.87±0.20aB 4.27±0.21bB 4.03±0.14bcB 3.95±0.08cB 3.86±0.15cA 4.09±0.22aC 4.06±0.19aB 3.99±0.08aB 3.96±0.12aB 3.89±0.07aA 小计 5.60±0.09aA 5.22±0.20bA 5.00±0.10bA 4.59±0.28cA 4.03±0.16dA 4.87±0.20aB 4.27±0.21bB 4.03±0.14bcB 3.95±0.08cB 3.86±0.15cA 4.09±0.22aC 4.06±0.19aB 3.99±0.08aB 3.96±0.12aB 3.89±0.07aA 烃类 十一烷 1.18±0.03a 1.43±0.11b 1.53±0.10bc 1.62±0.08c 1.88±0.08d − − − − − − − − − − 十四烷 3.47±0.38abA 3.38±0.09aA 3.40±0.05aA 3.49±0.14abA 3.81±0.15bA 2.98±0.22aAB 3.29±0.11aA 3.74±0.21bB 3.83±0.11bB 4.01±0.17bA 2.78±0.05aB 2.82±0.02abB 2.84±0.01bC 2.91±0.02cB 2.93±0.02cA 十五烷 3.35±0.21aA 3.54±0.08abA 3.60±0.06bcA 3.78±0.11cA 4.08±0.10dA 2.80±0.27aA 3.38±0.36bA 3.71±0.39bA 3.85±0.09bA 3.91±0.15bA 1.64±0.35aB 1.86±0.07abB 1.88±0.06abB 1.92±0.03abB 2.00±0.04bB 十二烷 2.47±0.24a 2.61±0.09ab 2.70±0.11ab 2.83±0.08bc 3.02±0.14c − − − − − − − − − − 十六烷 2.05±0.11aA 2.20±0.10aA 2.52±0.08bA 2.54±0.08bA 2.84±0.10cA 1.96±0.09aA 2.21±0.31abA 2.43±0.31bcA 2.69±0.11cA 2.80±0.11cA 1.76±0.04aB 1.87±0.03bA 1.97±0.04cB 1.98±0.04cB 2.03±0.06cB 十七烷 3.62±0.19aA 3.76±0.17aA 3.83±0.09aA 3.83±0.13aA 4.25±0.18bA 3.35±0.29aA 3.64±0.22abA 3.95±0.07bcA 4.05±0.06cB 4.26±0.24cA 1.94±0.23aB 2.02±0.11aB 2.04±0.06aB 2.06±0.11aC 2.10±0.07aB 庚烷 1.53±0.08aA 1.65±0.11aA 1.62±0.08aA 1.67±0.05aA 1.87±0.04bA 1.37±0.14aA 1.62±0.11bA 1.89±0.09cB 1.97±0.07cB 2.05±0.06cB 1.02±0.13aB 1.13±0.08abB 1.15±0.07abC 1.14±0.05abC 1.27±0.06bC 辛烷 3.35±0.36aA 3.63±0.26abA 3.79±0.11bA 3.88±0.02bA 3.91±0.10bA 3.23±0.20aA 3.89±0.11bA 3.91±0.12bB 4.03±0.06bB 4.11±0.03bB 2.37±0.35aB 2.61±0.14abB 2.60±0.12abB 2.64±0.09abC 2.77±0.04bC 3-甲基-十五烷 1.59±0.18a 1.90±0.08b 1.92±0.05b 2.00±0.07bc 2.20±0.16c 1.50±0.19a 1.88±0.22b 1.91±0.09bc 2.01±0.11bc 2.18±0.07c − − − − − 小计 22.61±0.59dA 24.09±0.87cA 24.91±0.59bcA 25.64±0.45bA 27.87±0.20aA 17.20±0.41eB 19.9±0.39dB 21.55±0.22cB 22.43±0.30bB 23.32±0.52aB 9.75±0.87cC 10.45±0.26abC 10.51±0.17abC 10.68±0.23aC 11.08±0.01aC 呋喃类 2-戊基呋喃 6.97±0.39bA 7.11±0.24bA 7.26±0.27abA 7.38±0.14abA 7.71±0.18aA 6.86±0.25cA 6.97±0.16bcA 7.14±0.11abcA 7.23±0.08abA 7.34±0.16aB 6.39±0.44aA 6.40±0.33aB 6.44±0.24aB 6.58±0.29aB 6.86±0.10aC 小计 6.97±0.39bA 7.11±0.24bA 7.26±0.27abA 7.38±0.14abA 7.71±0.18aA 6.86±0.25cA 6.97±0.16bcA 7.14±0.11abcA 7.23±0.08abA 7.34±0.16aB 6.39±0.44aA 6.40±0.33aB 6.44±0.24aB 6.58±0.29aB 6.86±0.10aC 注:“−”:未检出。 -
[1] 李丹. 固始鸡鸡汤对小鼠免疫功能影响的研究[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学, 2006. [LI Dan. Study on the effect of Gushi chicken soup on mice's immunation[D]. Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University, 2006.] LI Dan. Study on the effect of Gushi chicken soup on mice's immunation[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2006.
[2] 施洪飞, 项平. 补益类药膳食疗方配方规律和烹饪特点研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2007,22(4):215−218. [SHI Hongfei, XIANG Ping. Compounding rules and cooking features of supplementing and boosting formulae in medicine-dietary therapy[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2007,22(4):215−218.] SHI Hongfei, XIANG Ping. Compounding rules and cooking features of supplementing and boosting formulae in medicine-dietary therapy[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2007, 22(4): 215−218.
[3] SALGANIK R, DIDALOVA A, DIKALOV S. Antioxidants selectively protecting neurochemical functions in rats over producing reactive oxygen species[J]. Journal of Anti-aging Medicine,2001,4(1):49−54. doi: 10.1089/109454501750225686
[4] SAKETKHOO K, JANUSZKIEWICZ A, SACKNER M A. Effects of drinking hot water, cold water, and chicken soup on nasal mucus velocity and nasal airflow resistance[J]. Chest,1978,74(4):408−410. doi: 10.1016/S0012-3692(15)37387-6
[5] BARBARA O, RENNARD B A. Chicken soup inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro[J]. Chest,2000,118(4):1150−1157. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.4.1150
[6] 刘媛珍, 陈文娟, 杨兰, 等. 手法刺激加速胎盘娩出对产后出血的影响[J]. 广西医学,2006,28(12):1883−1884. [LIU Yuanzhen, CHEN Wenjuan, YANG Lan, et al. Effect of manual stimulation on accelerated placental delivery on postpartum hemorrhage[J]. Guangxi Medical Journal,2006,28(12):1883−1884.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4304.2006.12.012 LIU Yuanzhen, CHEN Wenjuan, YANG Lan, et al. Effect of manual stimulation on accelerated placental delivery on postpartum hemorrhage[J]. Guangxi Medical Journal, 2006, 28(12): 1883−1884. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4304.2006.12.012
[7] 杨瑾. 产妇的饮食护理[J]. 护理学杂志,1996,11(3):190. [YANG Jin. Maternal dietary care[J]. Journal of Nursing,1996,11(3):190.] YANG Jin. Maternal dietary care[J]. Journal of Nursing, 1996, 11(3): 190.
[8] 朱琳芳. 方便鱼汤加工技术研究与开发[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2012. [ZHU Linfang. Research and development on processing technology of convenience[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2012.] ZHU Linfang. Research and development on processing technology of convenience[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2012.
[9] 徐卉, 陶宁萍, 俞骏, 等. 均质及杀菌处理对暗纹东方鲀鱼汤品质的影响[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2023,42(4):85−93. [XU Hui, TAO Ningping, YU Jun, et al. Effect of homogenization and sterilization treatment on the quality of Takifugu obscurus soup[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology,2023,42(4):85−93.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.04.010 XU Hui, TAO Ningping, YU Jun, et al. Effect of homogenization and sterilization treatment on the quality of Takifugu obscurus soup[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology, 2023, 42(4): 85−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.04.010
[10] BAUER B A, HARTMANN M, SOMMER K. Optical in situ analysis of starch granules under high pressure with a high pressure cell[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2004,5(3):293−298.
[11] TRUJILLO A J, CAPELLASS M, BUFFA M. Application of high pressure treatment for cheese production[J]. Food Research International,2000,33(3):311−316.
[12] 曾清清. 鸡骨高汤生产关键工艺的研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2014. [ZENG Qingqing. Study on the key production technologies of chicken bone stock[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2014.] ZENG Qingqing. Study on the key production technologies of chicken bone stock[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014.
[13] 杨玉宝. 两种工艺对鸡汤保质期的研究[J]. 肉类工业,2012(7):27−30. [YANG Yubao. Study on shelf life of chicken soup with two different technique[J]. Meat Industry,2012(7):27−30.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5467.2012.07.012 YANG Yubao. Study on shelf life of chicken soup with two different technique[J]. Meat Industry, 2012(7): 27−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5467.2012.07.012
[14] 余力, 贺稚非, 李洪军, 等. 不同贮藏方式对高压鸡汤品质的影响及货架期预测模型的建立[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(20):274−281. [YU Li, HE Zhifei, LI Hongjun, et al. Effect of different storage methods on quality of high pressure processed chicken broth and establishment of shelf life prediction model[J]. Food Science,2016,37(20):274−281.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620046 YU Li, HE Zhifei, LI Hongjun, et al. Effect of different storage methods on quality of high pressure processed chicken broth and establishment of shelf life prediction model[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(20): 274−281. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620046
[15] ZHOU G H, XU X L, LIU Y. Preservation technologies for fresh meat–A review[J]. Meat Science,2010,86(1):119−128. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.04.033
[16] GALLART-JORNET L, RUSTAD T, BARAT J M, et al. Effect of superchilled storage on the freshness and salting behaviour of atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,103(4):1268−1281. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.040
[17] 王汉玲. 不同处理方式对虹鳟在微冻条件下品质影响的研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学, 2018. [WANG Hanling. Effect of partial freezing with different conditions on quality of rainbow trout during storag[D]. Shihezi:Shihezi University, 2018.] WANG Hanling. Effect of partial freezing with different conditions on quality of rainbow trout during storag[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2018.
[18] 李雅晶, 周兵, 刘悦, 等. 微冻及真空包装对原汁整壳贻贝贮存期品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(2):267−272. [LI Yajing, ZHOU Bing, LIU Yue, et al. Effects of partial freezing and vacuum packaging on storage quality of whole shell mussel with original juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(2):267−272.] LI Yajing, ZHOU Bing, LIU Yue, et al. Effects of partial freezing and vacuum packaging on storage quality of whole shell mussel with original juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(2): 267−272.
[19] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 4789.2-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2016 National food safety standard Food microbiological examination Determination of total number of colonies[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2016 National food safety standard Food microbiological examination Determination of total number of colonies[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[20] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 5009.228-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 5009.228-2016 National food safety standard Determination of volatile basic nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 5009.228-2016 National food safety standard Determination of volatile basic nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB5009.181-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB5009.181-2016 National food safety standard Determination of malondialdehyde in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB5009.181-2016 National food safety standard Determination of malondialdehyde in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[22] 周涛. 热反应鸡汤呈味物质变化研究[D]. 重庆:西南大学, 2016. [ZHOU Tao. Study on the change of taste components in thermal-reaction chicken soup[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University, 2016.] ZHOU Tao. Study on the change of taste components in thermal-reaction chicken soup[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016.
[23] KIM S K, TAKEUCHI T, YOKOYAMA M, et al. Effect of dietary taurine levels on growth and feeding behavior of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus[J]. Aquaculture,2005,250(3-4):765−774. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.04.073
[24] DAVIDEK J, KHAN A W. Estimation of inosinic acid in chicken muscle and its formation and degradation during post-mortem aging[J]. Journal of Food Science,1967,32(2):155−157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1967.tb01282.x
[25] BADEKA A V, SAVVAIDIS I N, et al. Combined effect of freeze chilling and MAP on quality parameters of raw chicken fillets[J]. Food Microbiology,2008,25(4):575−581. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2008.02.008
[26] 段丽丽, 刘倩, 田怡. 不同杀菌方式对低糖香蕉柚子皮复合果酱的影响研究[J]. 四川旅游学院学报,2019(1):18−22. [DUAN Lili, LIU Qian, TIAN Yi. Impact of different sterilization methods on low-sugar banana and pomelo peel compound jam[J]. Journal of Sichuan Institute of Tourism,2019(1):18−22.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5432.2019.01.004 DUAN Lili, LIU Qian, TIAN Yi. Impact of different sterilization methods on low-sugar banana and pomelo peel compound jam[J]. Journal of Sichuan Institute of Tourism, 2019(1): 18−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5432.2019.01.004
[27] SHAPTON D A, SHAPTON N F. Principles and practices for safe processing of foods[M]. Oxford:Butterworth-Heineman Ltd, 1991:374-444.
[28] 施佩影, 李仁伟, 刘文营. 不同贮藏温度对南美白对虾黑变的影响[J]. 湖州师范学院学报,2014,36(8):35−39. [SHI Peiying, LI Renwei, LIU Wenying. The impact analysis of pacific white prawn blackening during storage[J]. Journal of Huzhou Normal University,2014,36(8):35−39.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1734.2014.08.007 SHI Peiying, LI Renwei, LIU Wenying. The impact analysis of pacific white prawn blackening during storage[J]. Journal of Huzhou Normal University, 2014, 36(8): 35−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1734.2014.08.007
[29] 陈静茹, 王梁, 吕学泽, 等. 北京油鸡肉4 ℃贮藏过程中的品质及风味变化[J]. 肉类研究,2018,32(8):1−6. [CHEN Jingru, WANG Liang, LÜ Xueze, et al. Changes in quality and flavor of Beijing-You chicken meat during storage at 4 ℃[J]. Meat Research,2018,32(8):1−6.] CHEN Jingru, WANG Liang, LÜ Xueze, et al. Changes in quality and flavor of Beijing-You chicken meat during storage at 4 ℃[J]. Meat Research, 2018, 32(8): 1−6.
[30] 康怀彬, 肖枫, 徐幸莲. 二次杀菌方式对烧鸡保质期影响的研究[J]. 食品科学,2007,28(7):174−177. [KANG Huaibin, XIAO Feng, XU Xinglian. Study on effects of two-stage sterilization on shelf life of roasted chicken[J]. Food Science,2007,28(7):174−177.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.07.037 KANG Huaibin, XIAO Feng, XU Xinglian. Study on effects of two-stage sterilization on shelf life of roasted chicken[J]. Food Science, 2007, 28(7): 174−177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.07.037
[31] TOLASA S, CAKLI S, KISLA D. Quality and shelf-life assessment of pasteurized trout soup during refrigerated storage[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2012,21(4):321−329. doi: 10.1080/10498850.2011.595054
[32] MOL S. Preparation and the shelf-life assessment of ready-to-eat fish soup[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2005,220(3/4):305−308.
[33] GADEKAR Y P, ANJANEYULU A S R, THOMAS R. Quality changes in soup from deboned chicken frames at refrigerated (4±1 ℃) and frozen (−18±1 ℃) storage[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2009,44(9):1763−1769. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2009.01994.x
[34] 何小峰. 瓦罐鸡汤工艺优、品质形成及储藏研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2010. [HE Xiaofeng. Study on processing optimizing, quality forming and storage of crock chicken soup[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010.] HE Xiaofeng. Study on processing optimizing, quality forming and storage of crock chicken soup[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010.
[35] KATO H, RHUE M R, NISHIMURA T. Role of free amino acids and peptides in food taste[J]. Agricultural and Food Sciences, Chemistry,1989,388(1):158−174.
[36] TIAN Y, HUANG J, XIE T, et al. Oenological characteristics, amino acids and volatile profiles of Hongqu rice wines during pottery storage:Effects of high hydrostatic pressure processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,203:456−464. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.116
[37] LI Xiao, ZHU Jing, QI Jun, et al. Superchilled storage (−2.5±1 ℃) extends the retention of taste-active and volatile compounds of yellow-feather chicken soup[J]. Animal Science Journal,2018,89(6):906−918. doi: 10.1111/asj.13004
[38] MOTTRAM D S, WEDZICHA B L, DODSON A T. Acrylamide is formed in the Maillard reaction[J]. Nature,2002,419(6906):448−449. doi: 10.1038/419448a
[39] 陈继兰, 文杰, 李建军, 等. 不同贮藏条件下鸡肉肌苷酸生成与降解规律的研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报,2004,35(3):276−279. [CHEN Jilan, WEN Jie, LI Jianjun, et al. Research on the formation and degradation of inosinic-5’-monophosphate in chicken muscle under different storage temperature[J]. Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2004,35(3):276−279.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2004.03.008 CHEN Jilan, WEN Jie, LI Jianjun, et al. Research on the formation and degradation of inosinic-5’-monophosphate in chicken muscle under different storage temperature[J]. Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2004, 35(3): 276−279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2004.03.008
[40] 杨炼, 沈燕霆, 李英雨, 等. 肌苷酸和鸟苷酸的热稳定性和酸稳定性[C]. 第十四届中国国际食品添加剂和配料展览会学术论文集. 2010:260-263. [YANG Lian, SHEN Yanting, LI Yingyu, et al. pH stability and thermostability of IMP and GMP[C]. Proceedings of the 14th China International Food Additives and Ingredients Exhibition. 2010:260-263.] YANG Lian, SHEN Yanting, LI Yingyu, et al. pH stability and thermostability of IMP and GMP[C]. Proceedings of the 14th China International Food Additives and Ingredients Exhibition. 2010: 260-263.
[41] 关随霞. 蒸煮温度对兔肉品质的影响[D]. 洛阳:河南科技大学, 2015. [GUAN Suixia. Cooking temperature effects on rabbit meat quality[D]. Luoyang:Henan University of Science and Technology, 2015.] GUAN Suixia. Cooking temperature effects on rabbit meat quality[D]. Luoyang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[42] 林泽原. 基于多肽组学的固始鸡源高汤Kokumi肽挖掘及风味特征研究[D]. 新乡:河南科技学院, 2022. [LIN Zeyuan. Peptide mining and flavor characteristics of Kokumi from Gushi chicken soup stock based on polypeptidomics[D]. Xinxiang:Henan University of Science and Technology, 2022.] LIN Zeyuan. Peptide mining and flavor characteristics of Kokumi from Gushi chicken soup stock based on polypeptidomics[D]. Xinxiang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2022.
[43] 唐春红, 陈旭华, 张春晖, 等. 不同卤制方法对鸡腿肉中挥发性风味化合物的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(14):123−129. [TANG Chunhong, CHEN Xuhua, ZHANG Chunhui, et al. Effect of different marinating methods on volatile flavor compounds in chicken thigh[J]. Food Science,2014,35(14):123−129.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201414024 TANG Chunhong, CHEN Xuhua, ZHANG Chunhui, et al. Effect of different marinating methods on volatile flavor compounds in chicken thigh[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(14): 123−129. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201414024
[44] 常思盎, 惠腾, 刘毅, 等. 杀菌和复热工艺对黄焖鸡挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2018,32(4):20−26. [CHANG Siang, HUI Teng, LIU Yi, et al. Effect of pasteurization and reheating on the volatile compounds of braised chicken product[J]. Meat Research,2018,32(4):20−26.] CHANG Siang, HUI Teng, LIU Yi, et al. Effect of pasteurization and reheating on the volatile compounds of braised chicken product[J]. Meat Research, 2018, 32(4): 20−26.
[45] 侯钰柯, 王鹏, 徐幸莲, 等. 不同鸡肉香精对鸡汤食用品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(4):77−87. [HOU Yuke, WANG Peng, XU Xinglian, et al. Effects of different chicken flavors on the quality of chicken soup[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(4):77−87.] HOU Yuke, WANG Peng, XU Xinglian, et al. Effects of different chicken flavors on the quality of chicken soup[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(4): 77−87.
[46] 贺紫琼, 张立彦. 粤式豉油鸡传统烹煮过程中的质地及风味变化[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(2):1−12. [HE Ziqiong, ZHANG Liyan. Texture and flavor changes of cantonese soya sauce chicken during traditional cooking[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(2):1−12.] HE Ziqiong, ZHANG Liyan. Texture and flavor changes of cantonese soya sauce chicken during traditional cooking[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(2): 1−12.
[47] 屠云洁, 栾德琴, 单艳菊, 等. 3种乌骨鸡肌肉中挥发性有机物差异分析[J]. 家畜生态学报,2023,44(11):36−41. [TU Yunjie, LUAN Deqin, SHAN Yanju, et al. Differential analysis of volatile organic compounds in muscle of three black bone chicken breeds[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology,2023,44(11):36−41.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2023.11.006 TU Yunjie, LUAN Deqin, SHAN Yanju, et al. Differential analysis of volatile organic compounds in muscle of three black bone chicken breeds[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2023, 44(11): 36−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1182.2023.11.006
[48] 徐莹莹. 即食龟肉的加工及其风味物质的研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2017. [XU Yingying. Processing of ready-to-eat turtle meat and its flavor compounds[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2017.] XU Yingying. Processing of ready-to-eat turtle meat and its flavor compounds[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2017.
[49] DRUMM T D, SPANIER A M. Chang in the content of lipid autoxidation and sulphur contaning compounds in cooked beef during storage[J]. Agricultural Food Chemistry,1991,39(2):336−343. doi: 10.1021/jf00002a023
[50] 张艳. 冻结速率对鸡汤品质特性的影响研究[D]. 重庆:西南大学, 2017. [ZHANG Yan. Study on the effect of different freezing rates on the quality of chicken soup[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University, 2017.] ZHANG Yan. Study on the effect of different freezing rates on the quality of chicken soup[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017.
[51] BRUNTON N P, CRONIN D A, MONAHAN F J. Volatile components associated with freshly cooked and oxidized off-flavours in turkey breast meat[J]. Flavour & Fragrance Journal,2002,17(5):327−334.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王馨,吴孟仙,陈媛媛,王林峰,杨生玉,李星科. 杜仲叶固态混菌发酵工艺优化及其体外活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2025(03): 29-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



