Extraction, Purification and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from White Lilacs
-
摘要: 采用酶辅助超声提取法提取白丁香花多糖,利用响应面试验(RSM)法系统分析了不同实验条件对白丁香花多糖得率的影响。将粗多糖经DEAE-52纤维素柱和Sephadex G-100凝胶柱层析进行纯化,用高效凝胶渗透色谱法(HPGPC)、离子色谱法(IC)、紫外光谱、傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)和扫描电镜(SEM)对多糖的初步结构进行了表征,并进行体外抗氧化活性研究。结果表明,白丁香花多糖最佳提取工艺:超声功率150 W、超声时间40 min、超声温度40 ℃、加酶量(纤维素酶、中性蛋白酶)2.2%、料液比1:40 g/mL,在此条件下白丁香花多糖的得率为3.03%±0.09%。经DEAE-52纤维素柱纯化后得到4个组分的多糖,收集主要组分SP-c;再经Sephadex G-100凝胶柱纯化后得到SP-c-1组分。得出SP-c-1的单糖组成及摩尔比为半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、葡萄糖醛酸、木糖=18.39:11.13:8.96:2.61:1:0.83:0.57。SP-c-1重均分子量(Mw)为14069 Da,数均分子量(Mn)为13637 Da,具有多糖特征吸收峰,含D-葡萄吡喃糖构型。SP-c-1对DPPH、ABTS+自由基的半抑制浓度(IC50)分别0.87、1.355 mg/mL。SP-c-1显示出良好的抗氧化活性。Abstract: Enzyme-assisted ultrasonic extraction was employed to extract polysaccharides from white lilacs. The effects of various experimental conditions on the yield of polysaccharides from white lilacs were systematically analyzed using the response surface methodology (RSM). The crude extract was purified through DEAE-52 cellulose column and Sephadex G-100 gel column chromatography. High-performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC), ion chromatography (IC), ultraviolet spectrum analysis, Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were utilized for characterization of the polysaccharide structure and its antioxidant activity in vitro was investigated. The results demonstrated that the optimal extraction process for polysaccharides from white lilacs involved ultrasonic power 150 W, ultrasonic time 40 min, ultrasonic temperature 40 ℃, enzyme dosage 2.2%, solid-liquid ratio 1:40 g/mL. Under these conditions, the yield of polysaccharides was 3.03%±0.09%. The polysaccharides were purified using a DEAE-52 cellulose column, and the main component SP-c was collected. Subsequently, SP-c-1 was obtained through a Sephadex G-100 gel column. The monosaccharide composition and molar ratio of SP-c-1 were galacturonic acid, arabinose, galactose, rhamnose, glucose, glucuronic acid, xylose=18.39:11.13:8.96:2.61:1:0.83:0.57, respectively. The weight-average molecular weight (Mw) of SP-c-1 was 14069 Da, and the numerical mean molecular weight (Mn) was 13637 Da. SP-c-1 had the characteristic absorption peak of polysaccharide and contained D-grape pyranose configuration. The half-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of SP-c-1 on DPPH and ABTS+ free radicals was 0.87 and 1.355 mg/mL, respectively. Overall results indicate that SP-c-1 exhibits significant antioxidant activity.
-
白丁香花(Syringa oblata Lindl.)为木犀科(Oleaceae)丁香属(Syringa Linn.)植物的干燥花序。其味苦,性寒,有清热解毒、利湿退黄之功效[1]。中国是丁香花栽种和培育的起源地,且很多地区都把丁香作为美化环境、净化空气的优质树种。丁香花中含有许多芳香类化合物,可制作成香料被用于日用品、化妆品中。当前对丁香的研究大多集中在精油[2]、酚类[3]、丁香苷[4]、黄酮[5]等活性物质的提取及药理活性的研究。多糖是一类天然大分子生物聚合物,由多种单糖通过糖苷键组成[6];作为一种天然活性物质,植物基多糖能够清除自由基或间接消耗易产生自由基的活性物质[7−8],且具有抗肿瘤[9]、抗炎[10]、降血糖血脂[11]、抗氧化[12]等方面活性,近年来已成为研究热点。当前对丁香多糖的研究大多集中在提取和测其含量。例如江蔚新等[13]对丁香花和丁香叶多糖含量进行对比,研究表明丁香叶中多糖含量为105.16 mg/g,丁香花中多糖含量为89.80 mg/g。徐蕊等[14]对不同采收时期的小叶丁香皮中黄酮和多糖含量进行比较,研究表明在4月是小叶丁香采摘的最佳时期。目前对多糖提取工艺优化、纯化及抗氧化活性鲜有报道,其资源尚未完全开发。
常见的多糖提取方法有水和酶提法[15],超声波辅助提取法等[16]。超声波辅助提取法是利用超声波振动而产生的强大压力使植物细胞壁破裂,从而促使活性物质溶出[17]。有研究表明植物多糖提取过程中可以通过添加纤维素酶或蛋白酶破环细胞壁和分解蛋白质等杂质[18],从而促进多糖的溶出,提高多糖得率,缩短提取时间。采用酶辅助超声法提取方式,结合了两者的优点,将提取时间大幅缩减,达到高效提取的效果[19]。例如,孙燕丽等[20]采用酶辅助超声提取马齿苋多糖的提取率为21.23 mg/g,明显高于单一超声波提取马齿苋多糖的提取率。
该研究以白丁香花为原料,酶辅助超声法提取白丁香花多糖,通过单因素实验及响应面试验(RSM)来确定该方法的最佳提取工艺[21],采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法(HPGPC)、离子色谱法(IC)、紫外光谱、傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)和扫描电子显微照片(SEM)对纯化后的白丁香多糖的初步结构表征进行分析并评估其抗氧化活性。这对丁香资源的开发利用和我国抗氧化物质的研究具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
白丁香花 采自东北林业大学校园内并经专家鉴定(采摘时间为2022年5月,阴干后粉碎过筛备用);中性蛋白酶(100 U/mg)、纤维素酶(10000 U/g)、透析袋1000 Da 上海生物源叶生物公司;超纯水 娃哈哈集团有限公司;2,2'-联氮-双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸(ABTS)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH) 分析纯,上海源叶科技有限公司;单糖标准品 博睿糖生物公司;所有试剂均为分析纯。
LG-04微型中药粉碎机 瑞安市百信制药机械有限公司;Neo15离心机 上海力申科学仪器有限公司;UH620H电子分析天平、UV-2600紫外可见分光光度计、IRAffinity-1傅里叶红外光谱仪 日本岛津公司;KQ-500DM-22.5超声波清洗仪 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;层析柱 瑞达恒辉有限公司;LC-10N-50A冷冻干燥机 湖南力辰仪器科技有限公司;LC-10A高效液相色谱仪、RI-10A示差检测器 Shimadzu;ICS5000离子色谱仪 ThermoFisher;JSM-7500F扫描电镜 日立。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 白丁香花多糖的提取
将干燥后的白丁香花粉碎,过80目筛。依次用石油醚、乙醇索氏回流至回流液无色,目的是除去脂类、色素及小分子等物质[22],置于50 ℃烘干箱中干燥24 h备用。
取一定量的白丁香花粉末放于三角瓶中,再加入白丁香花粉质量2.0%的复合酶[23](中性蛋白酶:纤维素酶=1:1),加入40 mL的去离子水,在50 ℃的环境下酶解1.0 h后灭活(100 ℃,10 min)。然后在超声功率150 W,温度40 ℃的超声条件下提取30 min,冷却至室温,10000 r/min 离心10 min,浓缩上清液至原溶液体积的1/4,向浓缩液中加入4倍的无水乙醇,4.0 ℃醇沉24 h,醇沉后经4000 r/min离心15 min 后去上清取沉淀,冻干后得白丁香花粗多糖。
1.2.2 白丁香花粗多糖含量的测定
苯酚-硫酸法测定多糖含量[24]。配制100 μg/mL的葡萄糖标准溶液,分别吸取0、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0 mL于7个10 mL离心管中,加入蒸馏水补充至2.0 mL,再依次加入1.0 mL 5.0%的苯酚溶液,迅速加入5.0 mL浓硫酸,混合均匀,室温静置5.0 min后在沸水中继续反应15 min。冷却至室温,在490 nm处测定吸光值。根据葡萄糖浓度和吸光值绘制葡萄糖标准曲线,得回归方程:y=3.345x+0.0139,R2=0.9991。多糖得率公式如下:
N(%)=C×V×BM×100 式中:N代表白丁香花多糖得率(%);C代表多糖的质量浓度(mg/mL);B代表稀释倍数;V代表多糖溶剂体积(mL);W代表白丁香花质量(mg)。
1.2.3 单因素实验
依据1.2.1的方法进行实验,采用酶结合超声辅助提取的方法提取多糖。分别考察酶添加量(1.0%、1.5%、2.0%、2.5%、3%)、料液比(1:20、1:30、1:40、1:50、1:60 g/mL)、超声时间(20、30、40、50、60 min)、超声温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃)、超声功率(100、125、150、175、200 W)5个因素对白丁香花多糖得率的影响,对白丁香花多糖的提取工艺进行优化。其中固定水平因素为加酶量2.0%,料液比1:40 g/mL,超声时间40 min,超声温度50 ℃,超声功率150 W。
1.2.4 响应面试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,采用响应面法进行优化,以料液比、超声功率、加酶量、超声温度四因素为X值和多糖得率为Y值进行四因素三水平的Box-Behnken Design优化试验,响应面因素水平见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平Table 1. Response surface experimental factor level水平 因素 A 超声温度(℃) B加酶量(%) C超声功率(W) D料液比(g/mL) −1 30 1.5 125 1:30 0 40 2.0 150 1:40 1 50 2.5 175 1:50 1.2.5 丁香粗多糖的分离纯化
1.2.5.1 蛋白质、色素的脱除
将冻干后的多糖溶于100 mL纯净水,加入其1/5体积的Sevage试剂(氯仿:正丁醇=1:4)。磁力搅拌器搅拌20 min,3000 r/min离心10 min,取上清,重复约7次,至无蛋白层为止。而后用2.0%活性炭脱色40 min,离心取上清。最后旋蒸后透析48 h,得到纯度较高的白丁香花多糖(Syringa polysaccharide,SP)。
1.2.5.2 DEAE-52纤维素柱层析
用纯净水以1.0 mL/min的流速平衡DEAE-52纤维素12 h,称取100 mg SP溶于10 mL纯净水中,多糖溶液经0.22 μm水系微孔滤膜过滤后上样,待多糖溶液完全浸入填料后,用0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4 mol/L的NaCl溶液依次洗脱[25],洗脱流速为1.0 mL/min。每管收集5.0 mL,采用苯酚-硫酸法测定每管吸光值,以收集管数为横坐标,吸光值为纵坐标绘制洗脱曲线。本研究选取含量最高的洗脱组分SP-c,并且合并0.2 mol/L NaCl洗脱出的收集液,经浓缩透析后冻干得到SP-c。
1.2.5.3 SephadexG-100葡聚糖凝胶柱层析
将经过DEAE-52纤维素柱层析出的SP-c溶于2.0 mL纯净水中进行上样,用纯净水作为洗脱溶剂,流速为0.5 mL/min,每管收集6.0 mL。用苯酚-硫酸法测定每管吸光值,绘制多糖Sephadex G-100层析柱洗脱曲线。随后收集洗脱峰,浓缩透析后冻干得到SP-c-1。
1.2.5.4 紫外光谱
将SP-c-1配制成1.0 mg/mL的丁香多糖水溶液,以纯净水作为空白,在200~400 nm范围内进行紫外全波长扫描。
1.2.5.5 分子量的测定
通过HPGPC测定SP-c-1的分子量和纯度。根据文献方法略作修改[26]。精密称取标准品和SP-c-1样品各5.0 mg溶于1.0 mL的0.2 mol/L NaCl溶液中,超声后离心(12000 r/min,10 min)。吸取上清液,用0.22 μm的水系微孔滤膜过滤,然后将样品转置于1.8 mL进样小瓶中。色谱条件:色谱柱(BRT105-104-102)、串联凝胶柱(8 mm×300 mm,5.0 µm);柱温:40 ℃;流动相:0.2 mol/L NaCl;流速0.8 mL/min;进样量25 μL。
将标准样品溶液置于进样盘中,选择上述色谱条件进行分析,得出lgMw-RT(Mw为重均分子量),lgMn-RT(Mn为数均分子量)标准曲线(lgMw-RT校正曲线方程为:y=−0.204x+10.99,R2=0.999 ;lgMn-RT校正曲线方程为:y=−0.205x+11.01,R2=0.999),得出分子量计算公式。将SP-c-1样品溶液置于进样盘中,得出色谱图及保留时间,代入标准曲线即可得出SP-c-1的相对分子质量。
1.2.5.6 单糖组成分析
采用离子色谱(IC)测定SP-c-1的单糖组成。根据文献方法略作修改[27]。首先取15种单糖配制成标准母液,取各单糖标准溶液精密配制成混标溶液。精密称量5 mg SP-c-1置于安瓿瓶中,加入3.0 mol/L TFA 2.0 mL,120 ℃水解3.0 h。吸取酸水解溶液转移至管中氮吹吹干,加入5.0 mL水涡旋混匀,吸取50 µL加入950 µL去离子水,离心(12000 r/min)5.0 min。取上清进IC分析。检测条件:色谱柱:Dionex CarbopacTM PA20 (3 mm×150 mm);流动相:A:H2O;B:15 mmol/L NaOH;C:15 mmol/L NaOH&100 mmol/L NaAc;流速:0.3 mL/min;进样量:25 µL;柱温:30 ℃。
1.2.5.7 红外光谱
将SP-c-1与KBr按质量比1:100充分研磨混匀后压片。以KBr为空白,置于红外光谱仪中,在4000~500 cm−1区间内进行红外光谱扫描。
1.2.5.8 扫描电镜
将SP-c-1放置载物台上与其紧密贴合,使其均匀分布于表面后喷金,用扫描电镜进行观察(放大倍数为1000倍率和3000倍率)。
1.2.6 体外抗氧化活性
1.2.6.1 SP-c-1对DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
配制不同浓度的SP-c-1溶液(0、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5 mg/mL),各取2.0 mL多糖溶液分别置于10 mL棕色避光离心管,加入2.0 mL 0.2 mmol/L的 DPPH-乙醇溶液,室温反应30 min(避光)。在517 nm处测定吸光值,各浓度多糖溶液以VC为阳性对照。重复3次[28−29]。计算DPPH自由基清除率公式如下:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0为蒸馏水和DPPH-乙醇在517 nm下吸光值;A1为SP-c-1和DPPH-乙醇在517 nm下吸光值;A2为SP-c-1和乙醇在517 nm下吸光值。
1.2.6.2 SP-c-1对ABTS+自由基清除能力的测定
首先配制ABTS储存液:用10 mL水溶解0.0384 g的ABTS,继续用10 mL水溶解0.0134 g过硫酸钾,将ABTS溶液与过硫酸钾溶液等体积混合后避光储存12 h,后得到ABTS+储存液。使用前需要用去离子水将ABTS+储存液稀释至在734 nm处的吸光值为0.7±0.02后得到ABTS+稀释液。吸取不同浓度的SP-c-1溶液(0、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5 mg/mL)0.2 mL于10 mL离心管中,加入3.8 mL ABTS+稀释液,混合均匀,待其反应6 min,于734 nm处测定吸光度[30−31]。各浓度多糖溶液以VC为阳性对照。计算ABTS+自由基清除率公式如下:
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0为蒸馏水和ABTS+稀释液在734 nm下吸光值;A1为SP-c-1和ABTS+稀释液在734 nm下吸光值;A2为SP-c-1和蒸馏水在734 nm下吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验进行3次重复,最终数据取平均值±方差表示;采用Origin 2021和Design-Expert 12进行数据分析和绘图,单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和沃勒-邓肯检验(P<0.05)采用SPSS 26.0 统计软件程序进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 白丁香花多糖提取单因素实验结果
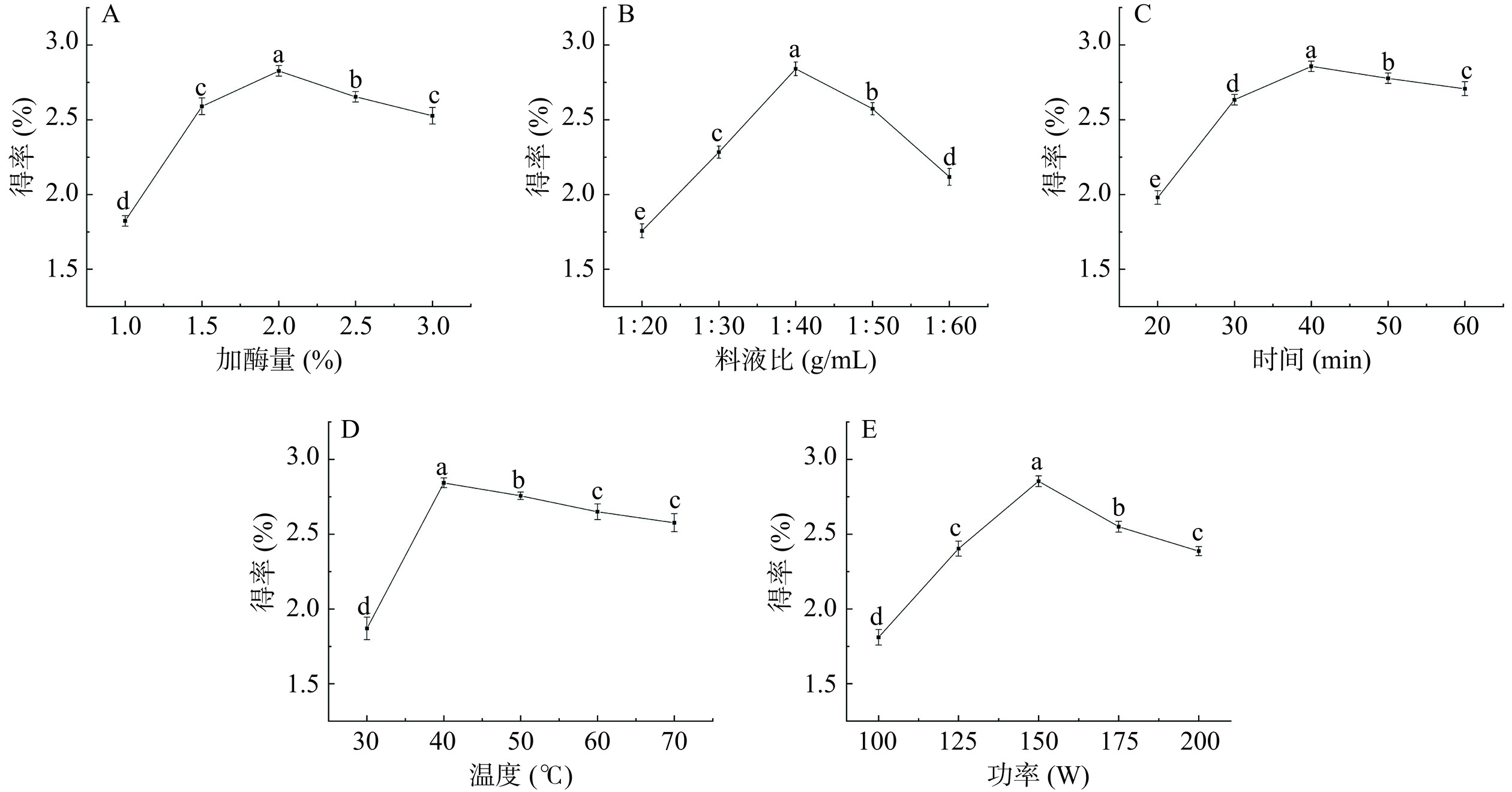
2.1.1 加酶量对白丁香花多糖得率的影响
由图1A可知,加酶量从1.0%增加至3.0%,多糖得率趋向于增加,然后逐渐减少。这是由于加入了纤维素酶和中性蛋白酶的影响使得植物细胞壁破裂,从而使多糖进一步溶出。当加酶量为2.0%时,多糖得率达到最大值。当加酶量大于2.0%时,多糖得率有下降趋势,这可能是因为酶与底物已达饱和状态,过量添加复合酶会使多糖的糖苷键水解,同时酶解产生的小分子蛋白在一定程度上对多糖有包埋作用,阻止了多糖的溶解[32],考虑到酶的成本较高,所以选取加酶量进行后续优化。综合考虑,加酶量选取1.5%~2.5%进行后续优化。
2.1.2 料液比对白丁香花多糖得率的影响
由图1B可知,当提取溶剂较少时,不能完全浸入材料[32],而随着料液比的增加,白丁香花粉与溶剂的接触面积也随之增大,可促进活性物质溶出。当料液比达到1:40 g/mL时,白丁香花多糖得率达到最高。当料液比进一步增大,多糖得率有下降趋势,因为多糖被过量溶剂完全溶解。溶剂会阻碍超声对溶质的空化作用,得率随着料液比的进一步增加而降低[33]。此外,由于溶液的体积过大,后续浓缩和乙醇沉淀步骤的成本增加。综合考虑,选取料液比1:30~1:50 g/mL进行后续优化。
2.1.3 超声时间对白丁香花多糖得率的影响
由图1C可知,随着超声波时间的增加,多糖得率呈先升后降的趋势。原因可能是超声空化作用使溶质高速剥离形成小的质团,提高了多糖的溶出率[34]。当超声时间在40 min内,多糖得率显著增加(P<0.05)。而长时间的超声波机械振动,会破坏多糖分子结构,从而导致得率有下降趋势[35]。由于超声时间对得率影响较小,为了节省耗能和提取时间,后续不对超声时间进行优化,故选择最佳超声时间为40 min。
2.1.4 超声温度对白丁香花多糖得率的影响
由图1D可知,随着超声温度的升高,多糖得率呈先升高后下降的趋势。这是因为较高的温度加速了溶液体系中分子扩散速度,导致分子运动更加剧烈,有利于活性成分的溶出。在40 ℃时,得率达到最大值。当温度超过40 ℃时,由于高温和超声波的机械粉碎的协同作用,多糖的产量明显下降,部分多糖结构降解[36],且温度过高容易引起溶剂汽化,影响溶剂与物料的接触[37]。超声温度对多糖得率影响较大。综上所述,选取30~50 ℃进行后续优化。
2.1.5 超声功率对白丁香花多糖得率的影响
由图1E可知,由于超声波的机械振荡作用随超声波功率的增加而逐渐增强,水溶剂加速进入植物细胞,从而使细胞内溶质的溶解度增加。但由于超声波的功率不断增强,会造成多糖分子的糖苷键断裂,从而导致得率降低。综合耗能和多糖得率,选取125~175 W超声功率进行后续优化。
2.2 响应面优化试验结果
2.2.1 响应模型的建立与显著性检验
将表2数据利用Design Expert 12软件进行多元回归拟合。以单因素为自变量,得率为响应值Y的响应面模型的二次多项回归方程如下:Y=2.95−0.0075A+0.0167B−0.0242C+0.025D+0.0075AB+0.0575AC−0.0225AD−0.01BC+0.0475BD+0.1350CD−0.2396A2−0.1958B2−0.1996C2−0.2333D2。
表 2 响应面试验方案及结果Table 2. Response surface experimental scheme and results试验号 A超声温度 B加酶量 C超声功率 D料液比 Y多糖得率
(%)1 0 0 1 −1 2.32±0.12 2 1 1 0 0 2.52±0.08 3 0 1 −1 0 2.62±0.07 4 1 0 0 −1 2.48±0.11 5 0 1 0 1 2.59±0.06 6 0 0 0 0 2.93±0.17 7 0 1 0 −1 2.48±0.13 8 −1 1 0 0 2.54±0.08 9 0 0 0 0 2.94±0.12 10 0 0 0 0 3.01±0.14 11 0 0 1 1 2.67±0.07 12 1 −1 0 0 2.48±0.08 13 0 0 0 0 2.92±0.12 14 −1 0 1 0 2.45±0.09 15 0 1 1 0 2.53±0.13 16 −1 0 0 −1 2.42±0.06 17 0 −1 0 −1 2.54±0.09 18 −1 0 0 1 2.52±0.10 19 1 0 −1 0 2.45±0.14 20 −1 −1 0 0 2.53±0.17 21 0 −1 −1 0 2.56±0.07 22 0 −1 0 1 2.46±0.12 23 0 0 −1 1 2.45±0.07 24 0 −1 1 0 2.51±0.15 25 1 0 1 0 2.54±0.05 26 0 0 0 0 2.95±0.12 27 1 0 0 1 2.49±0.03 28 0 0 −1 −1 2.64±0.14 29 −1 0 −1 0 2.59±0.07 根据表3分析,白丁香花多糖模型P值小于0.01,表明模型差异极显著。失拟项P值大于0.05,差异不显著,表明模型拟合较好,可用于试验结果分析。在影响因素中,C(超声功率)、D(料液比)、AC、BD、CD的P值小于0.01,表明对多糖得率有极显著影响,B(加酶量)的P值小于0.05,表明对多糖得率有显著影响,A(超声温度)、AB、AD、BC的P值均大于0.05,对多糖得率的影响不大。
表 3 响应面拟合回归方程方差分析结果Table 3. Response surface fitting regression equation variance analysis results来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 0.9085 14 0.0649 92.32 <0.0001 ** A 0.0007 1 0.0007 0.9602 0.3438 B 0.0033 1 0.0033 4.74 0.0470 * C 0.0070 1 0.0070 9.97 0.0070 ** D 0.0075 1 0.0075 10.67 0.0056 ** AB 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.3201 0.5805 AC 0.0132 1 0.0132 18.81 0.0007 ** AD 0.0020 1 0.0020 2.88 0.1118 BC 0.0004 1 0.0004 0.5690 0.4632 BD 0.0090 1 0.0090 12.84 0.0030 ** CD 0.0729 1 0.0729 103.70 <0.0001 ** A2 0.3723 1 0.3723 529.64 <0.0001 ** B2 0.2488 1 0.2488 353.87 <0.0001 ** C2 0.2584 1 0.2584 367.55 <0.0001 ** D2 0.3532 1 0.3532 502.37 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0098 14 0.0007 失拟项 0.0048 10 0.0005 0.3873 0.8980 不显著 纯误差 0.0050 4 0.0012 R2=0.9891 R2adj=0.9783 注:*表示差异性显著(P<0.05),**表示差异性极显著(P<0.01)。 由表3可知,模型的决定系数R2=0.9891,校正R2adj=0.9783,均大于0.9。结果显示,模型的拟合度良好,可用于实验结果的进一步分析和预测。
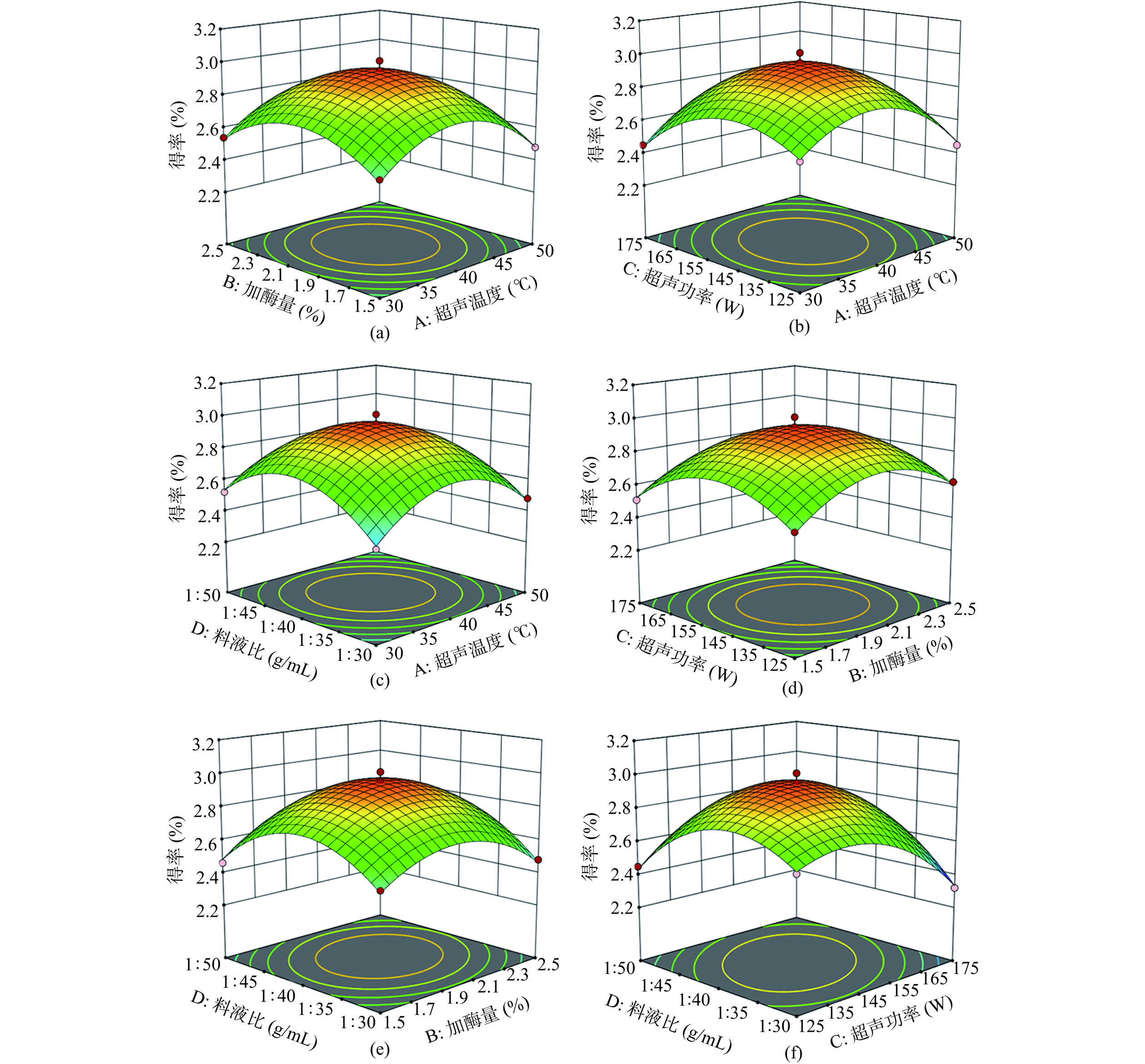
2.2.2 响应面优化曲面图
影响白丁香花多糖得率的四因素相互作用关系如图2所示。响应面图形的陡峭程度和底面等高线的椭圆或圆形可以直观地表现出各因素之间的交互作用是否显著[38],响应面越陡峭或等高线近似椭圆形,说明两因素交互作用差异极显著。
对图2(b)分析可知,在一定范围内,随着超声温度和超声功率的提升,多糖得率呈先升高,达到得率最大值,再逐渐降低的趋势。响应面坡度最陡,等高线图椭圆扁平程度最大,显示A、C两个因素以极显著的差异性表现出交互效果,其中C的曲面陡峭程度大于A,说明单因素C的影响程度大于A,即C>A。同理,由图2(e、f)可知,单因素D的影响程度大于B,D的影响程度大于C,即D>B、D>C。对图2(a、c、d)分析可知,等高线图均近似圆形,说明AB、AD、BC之间交互作用均表现为差异性不显著,且B的影响程度大于A,D的影响程度大于A,C的影响程度大于B,即B>A、D>A、C>B。综上所述,各因素对得率影响程度顺序为料液比>超声功率>加酶量>超声温度。与表3的结果一致。
2.2.3 回归模型的验证
基于上述模型,白丁香多糖最佳提取条件如下:料液比1:39.23 g/mL,超声时间40 min,超声温度41.10 ℃,加酶量2.18%,超声功率148.39 W,考虑到实际操作的需要,最佳工艺优化为:超声温度40 ℃,料液比1:40 g/mL,超声功率150 W,加酶量2.2%,超声时间40 min。Design Expert 12软件预测最优得率为3.17%,在此条件下进行三次重复性实验,此时多糖得率为3.03%±0.09%,与预测值吻合度较高,说明该优化条件可靠,也可说明实验结果的可靠性。
2.3 丁香多糖分离纯化结果
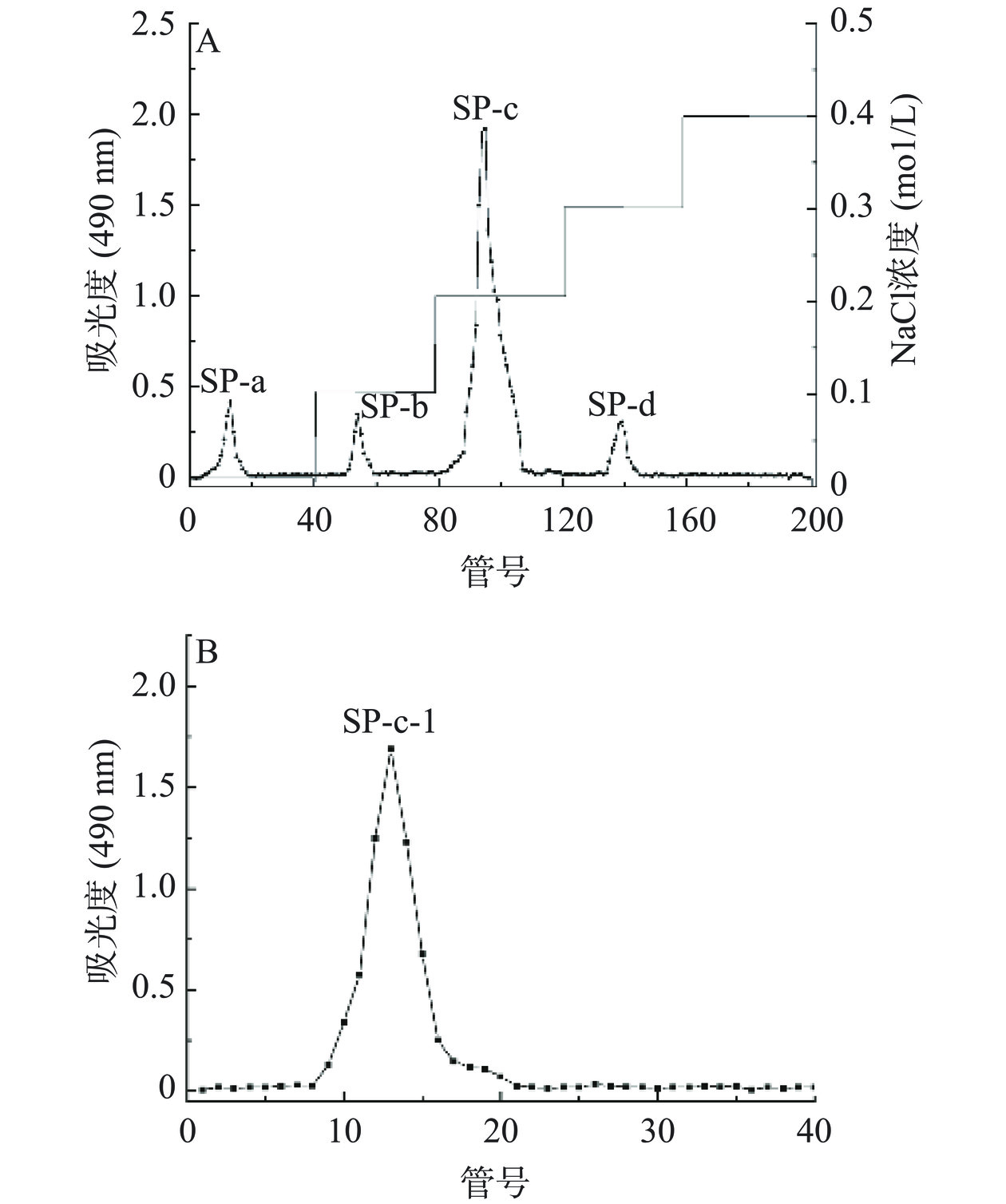
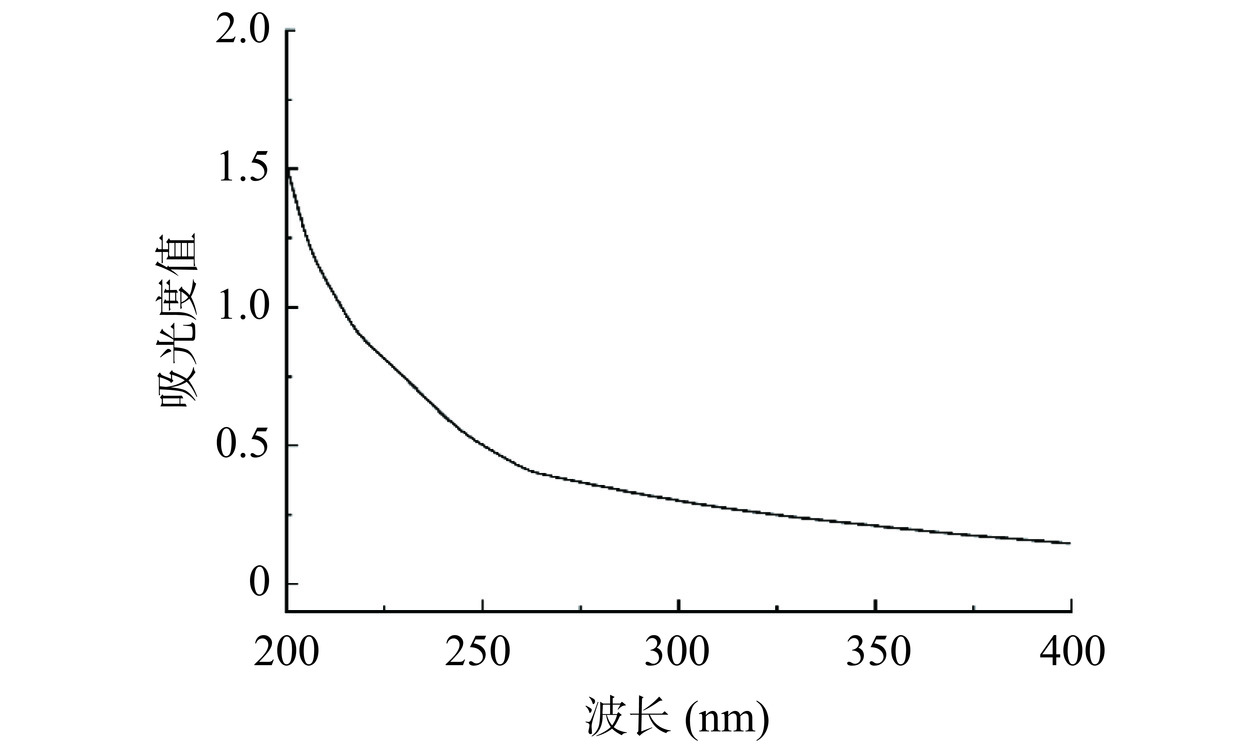
由图3A可知,分别用浓度为0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4 mol/L NaCl溶液梯度洗脱,得到4个单一洗脱峰,分别命名为SP-a、SP-b、SP-c、SP-d,其中0.2 mol/L为主要洗脱峰。本研究主要收集含量最高的洗脱组分,浓缩透析冻干得SP-c。再对其进行Sephadex G-100凝胶柱纯化后得到一个组分(命名为SP-c-1)呈现出单一对称的峰(图3B),说明经Sephadex G-100凝胶柱纯化后的多糖纯度较高,是分子量分布集中的均一多糖。用紫外光谱对SP-c-1全波长扫描,结果见图4,SP-c-1在260~280 nm没有明显的吸收峰,表明SP-c-1不含有核苷酸和蛋白质。通过苯酚-硫酸法检测到总糖含量为96.79%±1.63%。根据考马斯亮蓝,SP-c-1几乎没有检测到蛋白质含量,这与紫外光谱结果一致。表明白丁香花多糖SP-a-1的分离效果较好,纯度较高,可以用于后续的结构分析。
2.4 SP-c-1的相对分子量测定
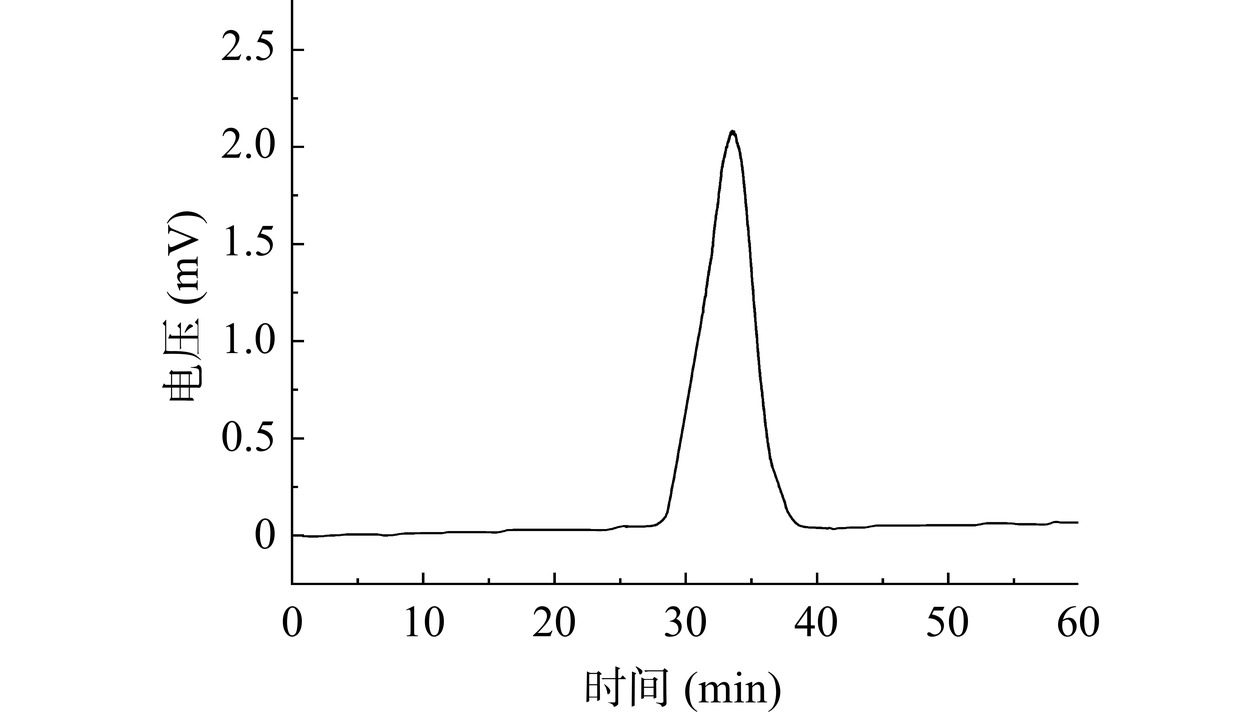
利用HPGPC法测定SP-c-1的相对分子质量,由SP-c-1的色谱图(图5)可看出,SP-c-1有一个单一对称峰,说明SP-c-1的纯度较高,为单一多糖。SP-c-1的保留时间为33.54 min,代入lgMw-RT、lgMn-RT校正曲线,根据标准品曲线,计算出SP-c-1的Mw为14069 Da, Mn为13637 Da。
2.5 SP-c-1的单糖组成
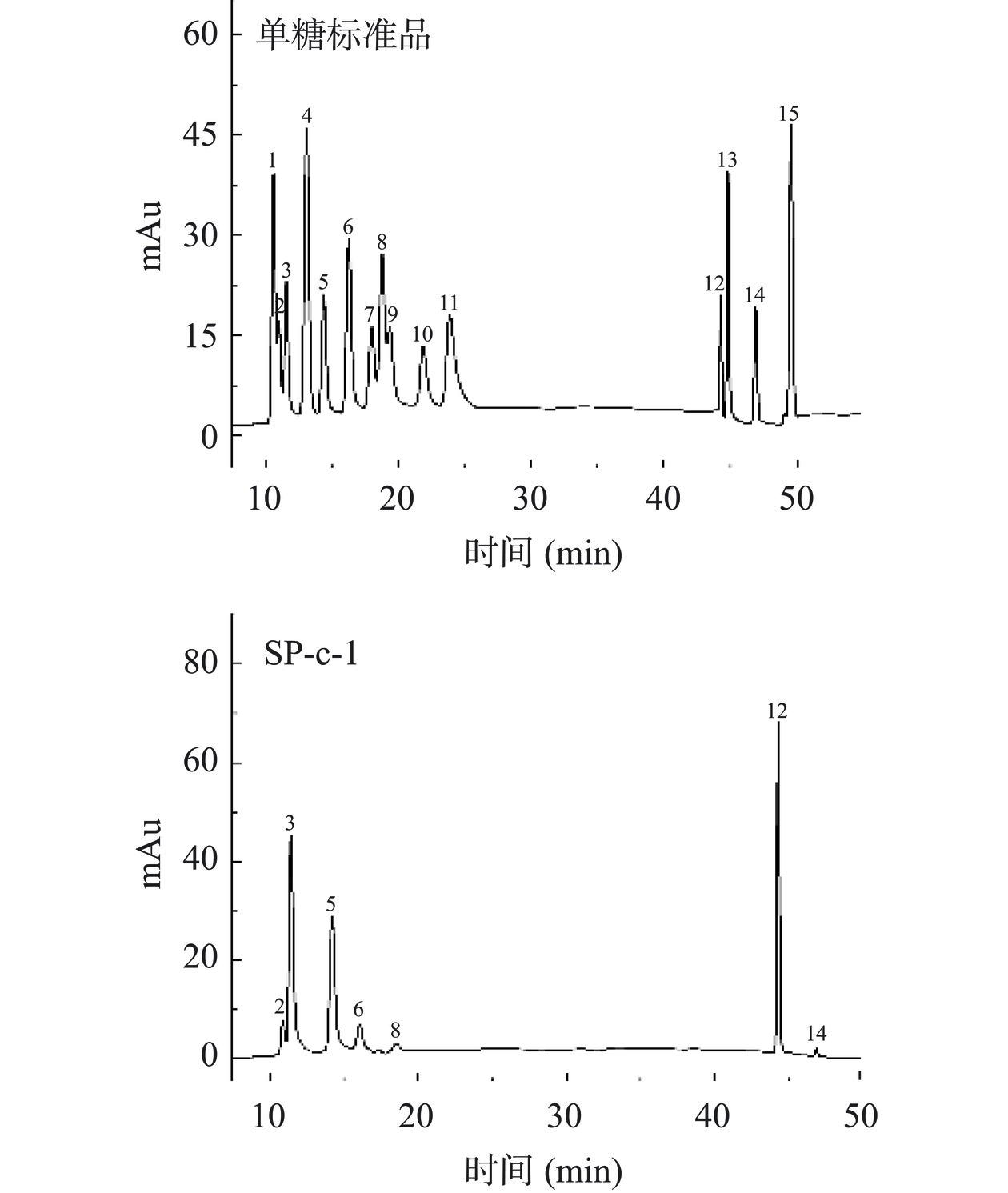
以单糖标准品做对照,采用离子色谱法测定SP-c-1的单糖组成,结果见图6。可看出SP-c-1是由半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、葡萄糖醛酸、木糖组成,其摩尔比为18.39:11.13:8.96:2.61:1:0.83:0.57。半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖是主要单糖。在SP-c-1中半乳糖醛酸比例最高为42.3%,其次是阿拉伯糖为25.4%和半乳糖为20.6%。
2.6 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
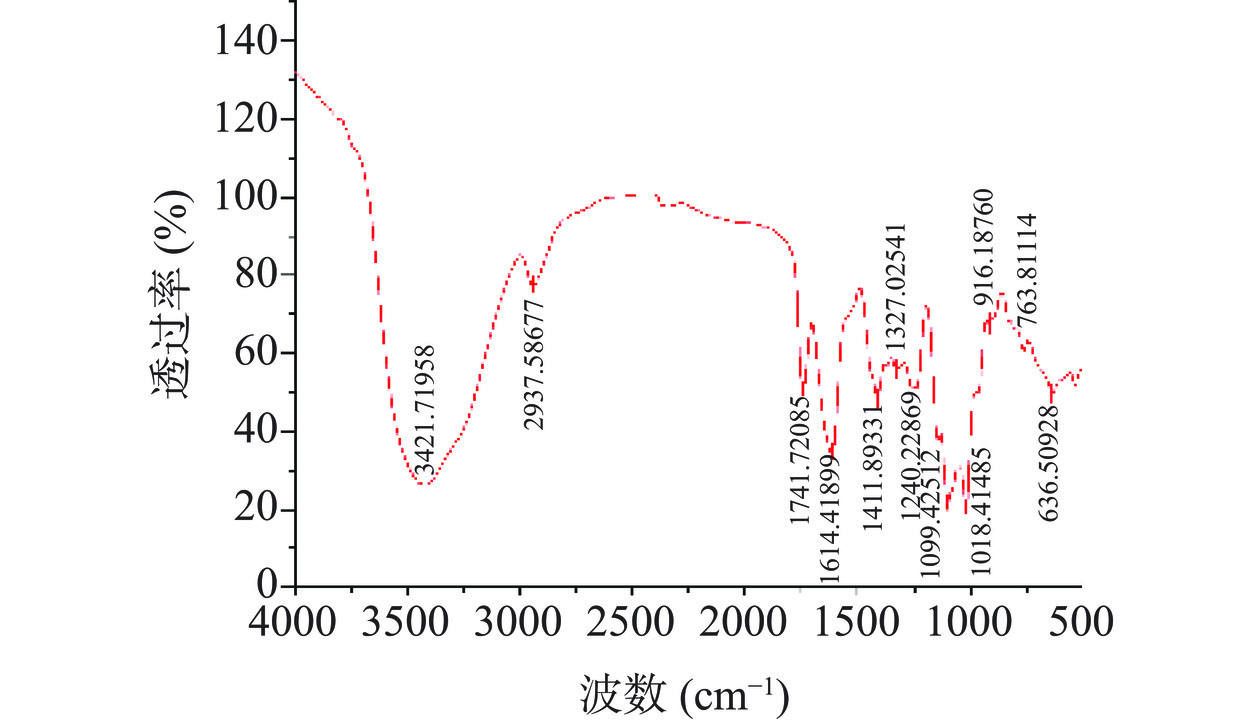
白丁香花多糖的红外光谱扫描如图7所示。发现白丁香花多糖具有典型的多糖特征峰,在3600~3200 cm−1区间为O-H的伸缩振动区。在3500~3300 cm−1区间的为分子间氢键。结合图示判断出3421.72 cm−1处强而宽的特征吸收峰为O-H的伸缩振动吸收峰,且白丁香花多糖具有分子间氢键;2937.59 cm−1处的较弱特征吸收峰为C-H的伸缩振动吸收峰。1411.89 cm−1处为C-O对称伸缩振动吸收峰。1240.23 cm−1处的峰属于S=O伸缩振动引起的,表明含有硫酸基[39]。在1327.03 cm−1处为C-N伸缩振动峰。在1741.72 cm−1的吸收峰归因于羧酸C=O的拉伸振动[40]。此结果与单糖组分分析中含有半乳糖醛酸结果一致。
在1200~1000 cm−1处吸收峰表示C-O伸缩的吡喃环振动[41]。所以在1099.43和1018.41 cm−1处可能是吡喃环上的C-O-C和C-O-H的伸缩振动引起的,表明白丁香花多糖存在吡喃糖苷。半乳糖和葡萄糖等己糖大都以吡喃糖的形式存在,这与单糖组分分析中结果一致。D-葡萄吡喃糖的C-O-C骨架非对称伸缩振动917±13 cm−1有吸收峰。所以在916.19 cm−1处的吸收峰为D-葡萄吡喃糖的C-O-C骨架非对称伸缩振动引起的[42]。综上所述,SP-c-1具有典型的多糖特征,且含有D-葡萄吡喃糖构型。
2.7 扫描电镜
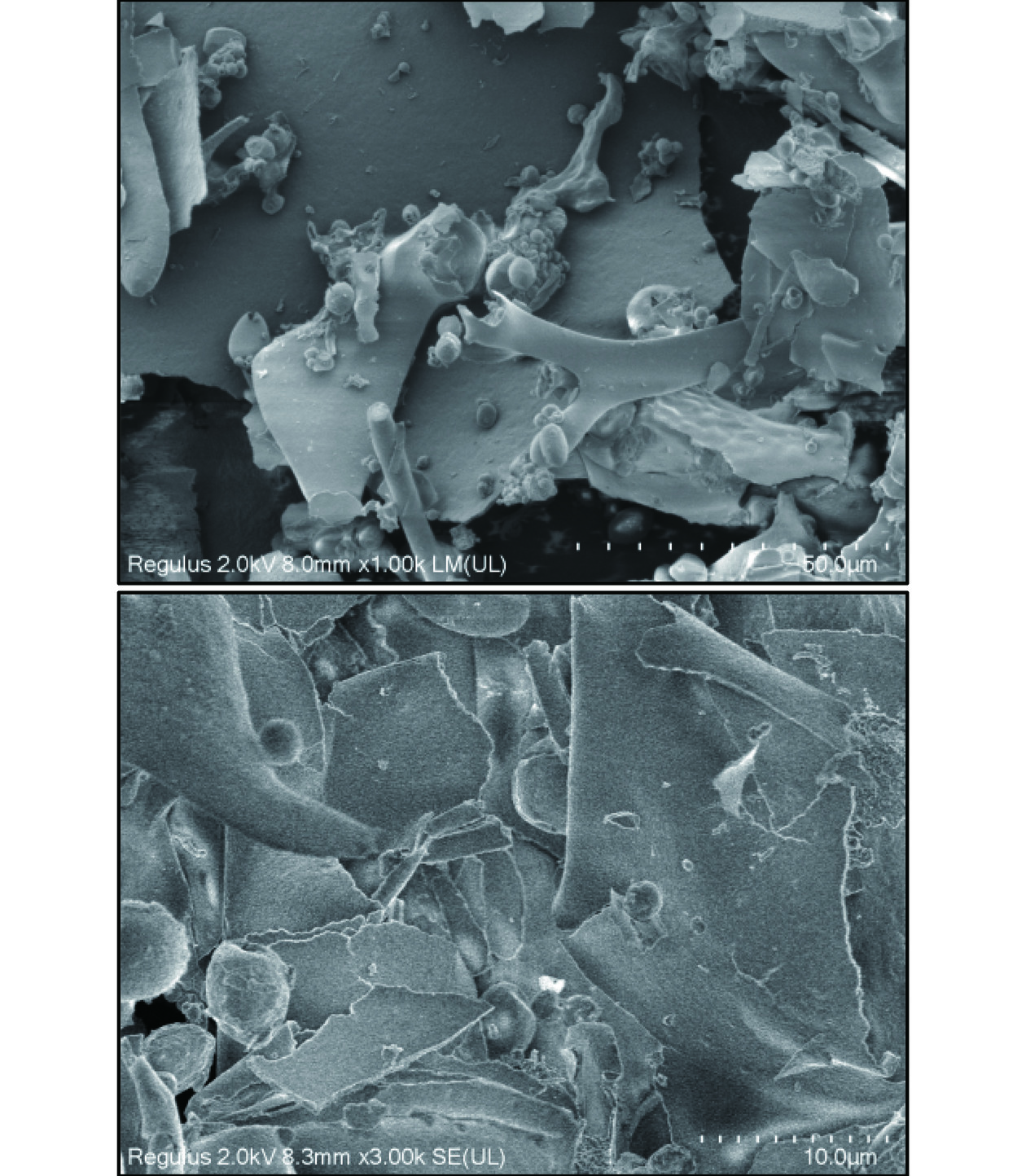
扫描电子显微镜可用作分析多糖表面形态的定性工具[43]。通过SEM图像提供了白丁香花多糖的表面形貌特征。图8为白丁香花多糖SP-c-1扫描电镜图,在1000倍率下可发现多糖样品表面大多数呈片状,有许多小的球状体和棒状结构附着在片状结构上,碎片结构不规则。在3000倍率下可发现片状多糖边缘褶皱,可能是冻干过程中造成的[44]。
2.8 白丁香花多糖体外抗氧化
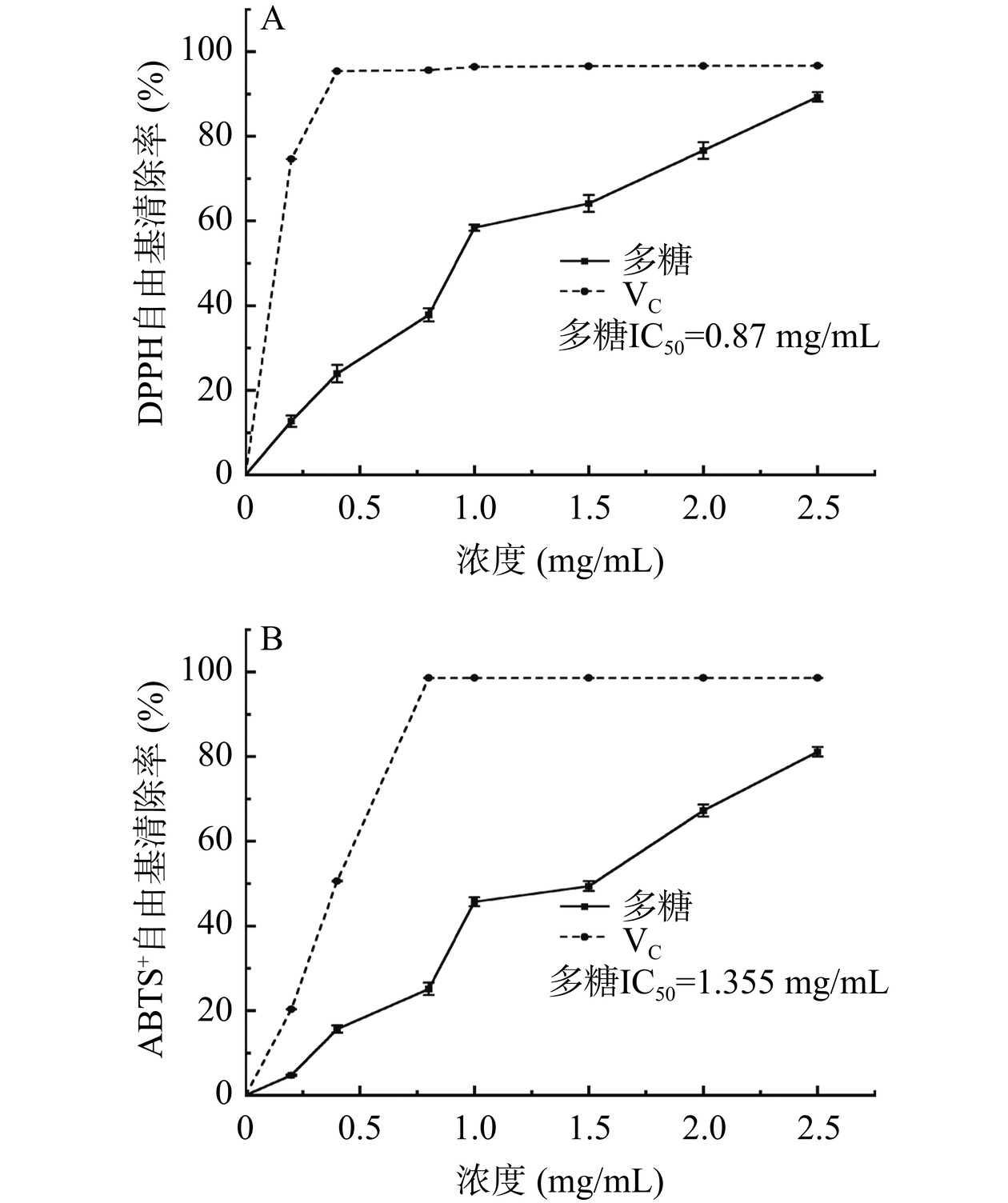
如图9所示,DPPH 和ABTS+自由基清除率在0~2.5 mg/mL 范围内,随着多糖浓度的增加,DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率也随之增大,这说明白丁香花多糖在一定浓度范围内清除自由基的能力与其浓度呈正相关。当多糖浓度达到2.5 mg/mL时,其DPPH自由基清除率和ABTS+自由基清除率分别为89.27%和78.78%。白丁香花多糖DPPH和ABTS+自由基半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为0.87、1.355 mg/mL。金花葵多糖的DPPH和ABTS+自由基半抑制浓度分别为1.22、4.43 mg/mL[45]。仙人掌多糖的ABTS+自由基半抑制浓度大于10 mg/mL[46]。IC50越小,其自由基清除率越强。表明白丁香花多糖具有良好的抗氧化活性。
3. 结论
采用酶辅助超声法从白丁香花中提取多糖,通过优化单因素和响应面试验得到最佳提取条件为:加酶量为2.2%,料液比1:40 g/mL,超声功率150 W,超声时间40 min,超声温度40 ℃。在此条件下,多糖得率为3.03%±0.09%。经DEAE-52纤维素柱和Sephadex G-100凝胶柱纯化出的SP-c-1主要是由半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、葡萄糖醛酸、木糖组成,其摩尔比为18.39:11.13:8.96:2.61:1:0.83:0.57。凝胶色谱图显示SP-c-1为均一多糖,其重均分子量(Mw)为14069 Da,数均分子量(Mn)为13637 Da。FT-IR分析显示SP-c-1具有典型的多糖吸收峰,含D-葡萄吡喃糖构型。扫描电镜显示SP-c-1大多数为片状结构,碎片结构不规则。此外,SP-c-1具有较强的抗氧化能力。白丁香花多糖对 DPPH 自由基和ABTS+自由基半抑制对应的浓度(IC50)分别为0.87、1.355 mg/mL。综上所述,SP-c-1可能是天然抗氧化剂的来源,具有功能性食品的潜在价值。本实验基于白丁花多糖进行分离、纯化及体外抗氧化活性分析,采用响应面法对白丁香花多糖提取工艺进行优化,为进一步研究和开发丁香多糖提供了理论依据。这项研究有助于深入了解白丁香花多糖的性质和潜在应用,为开发相关药物和保健品提供理论及实验基础。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平
Table 1 Response surface experimental factor level
水平 因素 A 超声温度(℃) B加酶量(%) C超声功率(W) D料液比(g/mL) −1 30 1.5 125 1:30 0 40 2.0 150 1:40 1 50 2.5 175 1:50 表 2 响应面试验方案及结果
Table 2 Response surface experimental scheme and results
试验号 A超声温度 B加酶量 C超声功率 D料液比 Y多糖得率
(%)1 0 0 1 −1 2.32±0.12 2 1 1 0 0 2.52±0.08 3 0 1 −1 0 2.62±0.07 4 1 0 0 −1 2.48±0.11 5 0 1 0 1 2.59±0.06 6 0 0 0 0 2.93±0.17 7 0 1 0 −1 2.48±0.13 8 −1 1 0 0 2.54±0.08 9 0 0 0 0 2.94±0.12 10 0 0 0 0 3.01±0.14 11 0 0 1 1 2.67±0.07 12 1 −1 0 0 2.48±0.08 13 0 0 0 0 2.92±0.12 14 −1 0 1 0 2.45±0.09 15 0 1 1 0 2.53±0.13 16 −1 0 0 −1 2.42±0.06 17 0 −1 0 −1 2.54±0.09 18 −1 0 0 1 2.52±0.10 19 1 0 −1 0 2.45±0.14 20 −1 −1 0 0 2.53±0.17 21 0 −1 −1 0 2.56±0.07 22 0 −1 0 1 2.46±0.12 23 0 0 −1 1 2.45±0.07 24 0 −1 1 0 2.51±0.15 25 1 0 1 0 2.54±0.05 26 0 0 0 0 2.95±0.12 27 1 0 0 1 2.49±0.03 28 0 0 −1 −1 2.64±0.14 29 −1 0 −1 0 2.59±0.07 表 3 响应面拟合回归方程方差分析结果
Table 3 Response surface fitting regression equation variance analysis results
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 0.9085 14 0.0649 92.32 <0.0001 ** A 0.0007 1 0.0007 0.9602 0.3438 B 0.0033 1 0.0033 4.74 0.0470 * C 0.0070 1 0.0070 9.97 0.0070 ** D 0.0075 1 0.0075 10.67 0.0056 ** AB 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.3201 0.5805 AC 0.0132 1 0.0132 18.81 0.0007 ** AD 0.0020 1 0.0020 2.88 0.1118 BC 0.0004 1 0.0004 0.5690 0.4632 BD 0.0090 1 0.0090 12.84 0.0030 ** CD 0.0729 1 0.0729 103.70 <0.0001 ** A2 0.3723 1 0.3723 529.64 <0.0001 ** B2 0.2488 1 0.2488 353.87 <0.0001 ** C2 0.2584 1 0.2584 367.55 <0.0001 ** D2 0.3532 1 0.3532 502.37 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0098 14 0.0007 失拟项 0.0048 10 0.0005 0.3873 0.8980 不显著 纯误差 0.0050 4 0.0012 R2=0.9891 R2adj=0.9783 注:*表示差异性显著(P<0.05),**表示差异性极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 尹承增. 紫丁香花挥发性物质定性分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2005(2):112−113. [YIN C Z. Analysis and appraisement of volatilisable substance in flowers of lilac[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2005(2):112−113.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2005.02.047 YIN C Z. Analysis and appraisement of volatilisable substance in flowers of lilac[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2005(2): 112−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2005.02.047
[2] PILONG P, CHUESIANG P, MISHRA D K, et al. Characteristics and antimicrobial activity of microfluidized clove essential oil nanoemulsion optimized using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2022,46(12):12.
[3] EL-MAATI M F A, MAHGOUB S A, LABIB S M, et al. Phenolic extracts of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) with novel antioxidant and antibacterial activities[J]. European Journal of Integrative Medicine,2016,8(4):494−504. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2016.02.006
[4] 王化, 周丽萍, 李梦莎, 等. 微波辅助提取暴马丁香中紫丁香苷和橄榄苦苷的工艺研究[J]. 植物研究,2016,36(1):141−145. [WANG H, ZHOU L P, LI M S, et al. Optimzation of microwave-assisted extraction of syringin and oleuroprin from Syringa reticulata[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research,2016,36(1):141−145.] doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2016.01.020 WANG H, ZHOU L P, LI M S, et al. Optimzation of microwave-assisted extraction of syringin and oleuroprin from Syringa reticulata[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(1): 141−145. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2016.01.020
[5] 周伟, 于笛, 迟治平, 等. 超声微波协同萃取紫丁香叶总黄酮工艺及其稳定性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2018(8):111−119. [ZHOU W, YU D, CHI Z P, et al. Study on ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction process and stability of total flavonoids from Syringa oblata leaves[J]. China Food Additives,2018(8):111−119.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.08.011 ZHOU W, YU D, CHI Z P, et al. Study on ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction process and stability of total flavonoids from Syringa oblata leaves[J]. China Food Additives, 2018(8): 111−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.08.011
[6] HUI Y, HUA J L, WANG C. Anti-oxidation and anti-aging activity of polysaccharide from Malus micromalus Makino fruit wine[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019, 121:1203−1212.
[7] YIN Z H, LIANG Z H, LI C Q, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from edible fungus: A review[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2021,10(4):393−400. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.04.001
[8] LI T T, HUANG S M, WANG J, et al. Alginate oligosaccharides protect against fumonisin B1-induced intestinal damage via promoting gut microbiota homeostasis[J]. Food Research International,2022,152:12.
[9] YU M L, YUE J, HUI N, et al. Anti-hyperlipidemia and gut microbiota community regulation effects of selenium-rich Cordyceps militaris polysaccharides on the high-fat diet-fed mice model[J]. Foods,2021,10(10):19.
[10] WU D T, HE Y, FU M X, et al. Structural characteristics and biological activities of a pectic-polysaccharide from okra affected by ultrasound assisted metal-free Fenton reaction[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,122:12.
[11] CUI R B, ZHU F. Ultrasound modified polysaccharides: A review of structure, physicochemical properties, biological activities and food applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,107:491−508.
[12] 景年华, 史俊友, 刘慧, 等. 枇杷叶多糖超声波辅助提取工艺优化[J]. 山东化工,2022,51(14):34−36, 39. [JING N H, SHI J Y, LIU H, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction process of polysaccharides from Eriobotrya japonica leaves[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2022,51(14):34−36, 39] JING N H, SHI J Y, LIU H, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction process of polysaccharides from Eriobotrya japonica leaves[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(14): 34−36, 39
[13] 江蔚新, 朱广伟, 李睿. 丁香叶与丁香花中多糖含量比较[J]. 中成药,2007(8):1251−1252. [JIANG W X, ZHU G W, LI R. Comparison of polysaccharide contents in lilac leaves and Lilac flowers[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2007(8):1251−1252.] JIANG W X, ZHU G W, LI R. Comparison of polysaccharide contents in lilac leaves and Lilac flowers[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2007(8): 1251−1252.
[14] 徐蕊, 郑友兰, 韩佳宏, 等. 不同采收期小叶丁香皮中黄酮和多糖含量的比较研究[J]. 人参研究,2011,23(3):19−23. [XU R, ZHENG Y L, HAN J H, et al. Comparative studies on the flavonoids and polysaccharides from skin of Syringa pubescens Turcz.in different harvest[J]. Ginseng Research,2011,23(3):19−23.] XU R, ZHENG Y L, HAN J H, et al. Comparative studies on the flavonoids and polysaccharides from skin of Syringa pubescens Turcz.in different harvest[J]. Ginseng Research, 2011, 23(3): 19−23.
[15] AHMAD A, ALKHARFY K M, WANI T A, et al. Application of Box-Behnken design for ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Paeonia emodi[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,72:990−997. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.10.011
[16] 王靓怡, 胡海燕, 李雪, 等. 植物多糖提取方法和提取动力学研究进展[J]. 化工科技,2022,30(3):65−68. [WANG L Y, HU H Y, LI X, et al. Research on plant polysaccharide extraction methods and extraction kinetics[J]. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry,2022,30(3):65−68.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0511.2022.03.014 WANG L Y, HU H Y, LI X, et al. Research on plant polysaccharide extraction methods and extraction kinetics[J]. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry, 2022, 30(3): 65−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0511.2022.03.014
[17] 游越, 杨菁菁, 姜壮壮, 等. 非热技术用于中药热不稳定成分提取研究进展[J]. 中医药学报,2021,49(12):117−121. [YOU Y, YANG J J, JIANG Z Z, et al. Research progress in non-thermal technologies for extraction of thermolabile components from Chinese medicinal[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology,2021,49(12):117−121.] YOU Y, YANG J J, JIANG Z Z, et al. Research progress in non-thermal technologies for extraction of thermolabile components from Chinese medicinal[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2021, 49(12): 117−121.
[18] 申红林, 王凤玲. 灰树花多糖复合酶协同微波辅助提取工艺及抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(22):124−131. [SHEN H L, WANG F L. Studies on compound enzymes synergistic microwave-assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of Frifola frondosa polysaccharide[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(22):124−131.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.22.021 SHEN H L, WANG F L. Studies on compound enzymes synergistic microwave-assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of Frifola frondosa polysaccharide[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(22): 124−131. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.22.021
[19] ZHAO Z Y, ZHANG Q, LI Y F, et al. Optimization of ultrasound extraction of Alisma orientalis polysaccharides by response surface methodology and their antioxidant activities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,119:101−109. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.052
[20] 孙燕丽, 吴晓青, 胡巧云. 超声波-复合酶法协同提取马齿苋多糖工艺的优化研究[J]. 饲料研究,2022,45(19):74−77. [SUN Y L, WU X Q, HU Q Y. Optimization of ultrasonic-complex enzymatic synergistic extraction of polysaccharides from Portulaca oleraces[J]. Feed Research,2022,45(19):74−77.] SUN Y L, WU X Q, HU Q Y. Optimization of ultrasonic-complex enzymatic synergistic extraction of polysaccharides from Portulaca oleraces[J]. Feed Research, 2022, 45(19): 74−77.
[21] HAMMI K M, HAMMAMI M, RIHOUEY C, et al. GC-EI-MS identification data of neutral sugars of polysaccharides extracted from Zizyphus lotus fruit[J]. Data in Brief,2018,18:680−683. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.085
[22] 纪鹏, 张蔓, 孙红国, 等. 响应面分析法优化当归粗多糖提取工艺[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2013,25(7):976−981,888. [JI P, ZHANG M, SUN H G, et al. Optimization of extraction process of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide using response sueface methodology[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2013,25(7):976−981,888.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.07.024 JI P, ZHANG M, SUN H G, et al. Optimization of extraction process of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide using response sueface methodology[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2013, 25(7): 976−981,888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.07.024
[23] 薛燕, 敢小双, 黄开丽, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖复合酶法提取工艺及其抗氧化性[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(3):215−219,225. [XUE Y, GAN X S, HUANG K L, er al. Extraction process of polysaccharide by compound enzymatic method of Dendrobium officnale and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(3):215−219,225.] XUE Y, GAN X S, HUANG K L, er al. Extraction process of polysaccharide by compound enzymatic method of Dendrobium officnale and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(3): 215−219,225.
[24] 王迎香, 唐子惟, 彭腾, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定酒蒸多花黄精多糖含量的优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):308−316. [WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol sulfuric acid method for the polysaccharide content of wine-steamed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(18):308−316.] WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol sulfuric acid method for the polysaccharide content of wine-steamed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(18): 308−316.
[25] JI X L, PENG B X, DING H H, et al. Purification, structure and biological activity of pumpkin polysaccharides:A Review[J]. Food Reviews International,2023,39(1):307−319. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.1904973
[26] QIAN S Q, FANG X H, DAN D M, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of a water soluble polysaccharide from dragon fruit peel and its antioxidant activity[J]. Rsc Advances,2018,8(73):42145−42152. doi: 10.1039/C8RA06449K
[27] WANG L, ZHANG B, XIAO J, et al. Physicochemical, functional, and biological properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,249:127−135. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.011
[28] MOHSEN S M, AMMAR A S M. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of corn tassel extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,112(3):595−598. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.014
[29] SUN X Y, HAO L, MA H, et al. Extraction and in vitro antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide by Pleurotus eryngii SI-02[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology,2013,44(4):1081−1088. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822013000400009
[30] 陈红惠, 牛念拉姆. 底圩茶多糖的超声波辅助提取及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(21):179−184. [CHEN H H, NIUNIAN L M. Ultrasonic extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Dixu tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(21):179−184.] CHEN H H, NIUNIAN L M. Ultrasonic extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Dixu tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(21): 179−184.
[31] DESEO M A, ELKINS A, ROCHFORT S, et al. Antioxidant activity and polyphenol composition of sugarcane molasses extract[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,314:10.
[32] XU Y Q, ZHANG L, YANG Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted compound enzymatic extraction and characterization of polysaccharides from blackcurrant[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,117:895−902. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.032
[33] WANG J, SUN B G, LIU Y L, et al. Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of arabinoxylan from wheat bran[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,150:482−488. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.121
[34] 王艳, 聂志勇, 贺瑛, 等. 超声波协同复合酶法提取姬松茸多糖[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2009,21(5):866−870. [WANG Y, NIE Z Y, HE Y, et al. Study on the extraction of Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharide with compound enzymes under ultraonic wave[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2009,21(5):866−870.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2009.05.034 WANG Y, NIE Z Y, HE Y, et al. Study on the extraction of Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharide with compound enzymes under ultraonic wave[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2009, 21(5): 866−870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2009.05.034
[35] CHO Y J, GETACHEW A T, SARAVANA P S, et al. Optimization and characterization of polysaccharides extraction from Giant African snail (Achatina fulica) using pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE)[J]. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre,2019,18:100179. doi: 10.1016/j.bcdf.2019.100179
[36] 千春录, 侯顺超, 殷健东, 等. 响应面试验优化水芹黄酮超声波辅助提取工艺及其抗氧化性[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(10):76−81. [QIAN C L, HOU S C, YIN J D, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Oenanthe javanica and their antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science,2016,37(10):76−81.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201610013 QIAN C L, HOU S C, YIN J D, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Oenanthe javanica and their antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(10): 76−81. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201610013
[37] 董红敏, 李素清, 牛小勇, 等. 正交实验优化川明参多糖超声提取工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(8):306−309,322. [DONG H M, LI S Q, NIU X Y, et al. Optimization ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from Chuanminshen violaceum based on orthogonal experiments design[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(8):306−309,322.] DONG H M, LI S Q, NIU X Y, et al. Optimization ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from Chuanminshen violaceum based on orthogonal experiments design[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(8): 306−309,322.
[38] YUAN S, XU C Y, XIA J, et al. Extraction of polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula by fermentation with response surface methodology[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(12):6660−6669.
[39] HAN L, SONG H, FU L C, et al. Effect of extraction method on the chemical profiles and bioactivities of soybean hull polysaccharides[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2021,9(11):5928−5938.
[40] LI Q, YU N W, WANG Y P, et al. Extraction optimization of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza polysaccharides with radical scavenging activities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,96(1):148−155. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.054
[41] CHENG H, HUANG G L. The antioxidant activities of carboxymethylated garlic polysaccharide and its derivatives[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,140:1054−1063. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.204
[42] 阮征, 胡筱波, 陈浩, 等. 香菇多糖L-2A的结构表征[J]. 光谱实验室,2007(3):496−500. [RUAN Z, HU X B, CHEN H, et al. Characterization of polysaccharide L-2A isolated from Lentinus edodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory,2007(3):496−500.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2007.03.057 RUAN Z, HU X B, CHEN H, et al. Characterization of polysaccharide L-2A isolated from Lentinus edodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, 2007(3): 496−500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2007.03.057
[43] JI X L, HOU C Y, YAN Y Z, et al. Comparison of structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,149:1008−1018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.018
[44] 韦志, 阮心眉, 戴涛涛, 等. 碱提砂仁多糖的结构表征及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):87−93. [[WEI Z, RUAN X M, DAI T T, et al. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Amomum villosum extracted with alkaline solution[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(24):87−93.] [WEI Z, RUAN X M, DAI T T, et al. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Amomum villosum extracted with alkaline solution[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(24): 87−93.
[45] 储启明, 魏洪玲, 田叙晨, 等. 金花葵多糖提取工艺优化及结构表征和抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(8):236−243. [CHU Q M, WEI H L, TIAN X C, et al. Optimization of extraction technology, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Hibiseus manihot L J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(8):236−243.
[46] AMAMOU S, LAZREG H, HAFSA J, et al. Effect of extraction condition on the antioxidant, antiglycation and α-amylase inhibitory activities of Opuntia macrorhiza fruit peels polysaccharides[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,127:109411. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109411
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 向芳. 食品减盐策略研究进展. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(06): 350-358 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵亚丽,张香美,卢涵,杨贝,文港. 传统腌腊肉制品质量安全管理研究. 食品与机械. 2023(01): 55-60+156 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘东,夏金龙. 低钠酱鹿肉的配方优化及贮藏期特性研究. 中国调味品. 2023(03): 67-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李智,牛超杰,邹爱军,常超. 肉制品加工减盐技术及其应用. 武汉轻工大学学报. 2023(04): 31-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张彦慧,郑红霞,刘楠,高彦祥,毛立科. 胶体结构设计在减盐食品中的应用. 食品科学. 2022(01): 213-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吕广英,孔君,郑润愽. 一种低钠休闲香肠的加工技术研究. 肉类工业. 2022(05): 16-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 芮李彤,李海静,张婷婷,郭琦,李子豪,夏秀芳. 食盐对肉制品品质形成的作用及减盐技术研究进展. 肉类研究. 2022(07): 61-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 孙悦,李震,王鹏,徐幸莲. 响应面优化减盐鸡肉松热加工工艺及品质测定. 食品工业科技. 2022(20): 263-273 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 周平萍. 咸味剂咸度分析研究方法进展. 现代食品. 2022(17): 23-26+37 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



