Research Status of Peptide-Calcium Chelation and Absorption Mechanism
-
摘要: 钙是人体必需的常量元素之一,科学补钙对维持生命健康具有重要意义,具有良好钙结合能力和高生物利用度的肽-钙螯合物也备受关注。本文综述了肽-钙螯合物中钙与肽的结合位点、结合模式、分子间作用力等内容。通过阐明游离钙和螯合钙的吸收途径,分析螯合钙易被肠道吸收的特点。肽-钙螯合物作为新型钙补充剂,来源丰富且生物利用度高,具有良好的经济开发价值和广阔的发展前景。在肽-钙螯合物的安全性、物理化学稳定性、消化稳定性以及螯合钙被肠道吸收后Ca2+的释放机制等方面的研究需要继续开展。本文旨在为新型钙补充剂的开发提供思路。Abstract: Calcium is one of the essential macro-elements in the human body. The scientific calcium supplementation is greatly significant to maintaining life and health. The peptide-calcium chelates with good calcium binding capacity and high bioavailability have attracted more attention. This work reviews the binding sites, binding modes, and intermolecular forces between calcium and peptides in peptide-calcium chelates. Compared with free calcium, chelated calcium is more easily absorbed in the intestine according to the summarization of the calcium absorption pathways. Peptide-calcium chelates, as a new generation of calcium supplements, have a rich source of raw materials, high bioavailability, good economic value, and broad development prospects. Further research is needed on the safety, physicochemical stability, digestive stability, and Ca2+ release mechanism of peptide-calcium chelates after intestinal absorption. This paper aims to provide new insight into the development of novel calcium supplements.
-
Keywords:
- calcium /
- peptide-calcium chelates /
- calcium supplements /
- calcium absorption
-
钙是人体内最重要的矿物质元素之一,与人体生命健康息息相关。机体内的钙,构成人体的骨骼和牙齿[1],参与各种生理功能和代谢过程,影响器官组织的活动,例如,钙能维持肌肉的收缩和神经冲动的传递;通过调节心脏的搏动,保持心脏连续交替地收缩和舒张;通过刺激血小板,促使伤口处的血液凝结[2−4]。此外,机体中的钙可以与酶结合,如凝血酶、ATP酶、脂酶、蛋白水解酶等,形成具有相应活性的构象[5]。当机体钙摄入不足时会出现生理性钙透支,导致血钙水平下降,当血钙水平下降到一定阈值时,会促使甲状旁腺分泌甲状旁腺素,甲状旁腺素具有破骨作用,即将骨骼中的钙反抽调出来,以维持血钙水平,从而导致骨质疏松、骨质增生、儿童佝偻病、手足抽搐症以及高血压、肾结石、结肠癌、老年痴呆等疾病的发生[6−7]。我国居民钙摄入量一直处于较低的水平,根据第三次中国健康与营养调查结果显示,膳食营养素中钙缺乏最为严重,其摄入量仅为推荐摄入量的50%,某些地区儿童佝偻病的发病率高达40%,中老年骨质疏松症也颇为严重[8]。因此,对于我国居民来说科学合理地补钙十分重要。
人体摄入钙的主要途径是饮食,乳及乳制品、豆类及豆制品、海产品和蔬菜都能为人体提供丰富的钙质。这些食物中的钙被胃酸消化后以离子形态到达小肠,但由于小肠内的碱性环境会导致钙离子形成沉淀[9]。除了膳食补钙外,还可以通过服用补钙制剂进行补钙。近年来,研究人员发现,小分子肽能够与钙发生螯合反应形成可溶性螯合物,进而避免游离钙离子(Ca2+)形成不溶性沉淀,减少钙损失,促进钙吸收。目前市场上已开发有钙酪蛋白磷酸肽咀嚼片、可溶性海藻钙肽粉、胶原蛋白钙肽粉等产品[10],肽-钙螯合物作为新一代钙补充剂,具有较好的经济价值和广阔的开发前景。肽-钙螯合物是指具有钙螯合能力的生物活性肽与Ca2+结合形成的较稳定螯合物[11]。研究肽-钙螯合物的结合机制和生物利用度具有重要的现实意义,为其作为食品功能性成分提高钙生物利用度提供理论基础。研究人员从不同的蛋白来源中分离鉴定出了具有钙螯合能力的肽链,并对肽-钙螯合物的补钙效果进行了验证[12−14]。钙依赖于肽链上的活性位点与肽结合,不同的肽可能具有不同的结合模式,钙与肽链之间的分子间作用力能够影响螯合物的稳定性。螯合钙和游离钙两种钙存在形式在肠道中的吸收机制有所不同,因此,在钙的生物利用度方面可能存在一定差异。本文的目的是综述现有文献对钙与肽螯合的方式和螯合钙影响钙吸收方式的研究结果,总结螯合钙补钙的优势,旨在阐明肽-钙螯合物作为新一代补钙制剂的广阔应用前景。
1. 钙补充方式
通过食物摄入补钙质,除了食物中的钙含量之外更重要的是提高钙的吸收率。钙在维生素D的作用下,才能被吸收利用并沉积到骨骼中。仅摄入富含钙的食物而不搭配摄入维生素D,这种膳食补钙方式见效慢且补钙效果并不理想。作为药品或者保健品的钙片中通常包含提供Ca2+的成分的无机钙(碳酸钙)、有机钙(醋酸钙、葡萄糖酸钙、乳酸钙),还含有促进钙吸收的维生素D。碳酸钙这类无机补钙制剂含钙量很高,但其溶解度较低,使部分钙以难溶盐形式被排出体外,生物利用率不高[12],此外,过量摄入碳酸钙可能会导致胃肠道副作用,包括便秘、胃肠胀气和腹胀[15]。有机钙如醋酸钙、葡萄糖酸钙、乳酸钙等,这类钙补充剂虽然含钙量相对较低,但吸收率高,补钙效果优于无机钙制剂。有机钙也存在一定的副作用,醋酸钙LD50值为52 mg/kg(小鼠,皮下),急性毒性较大,易导致肾结石、心脏痉挛、血管钙化和软组织钙化,所以一直未通过FDA认证作为钙补充剂,仅在临床上被用作高血磷症的降血磷药剂;葡萄糖酸钙含钙量很低(8.9%),且高糖成分不适合糖尿病患者服用[16]。
除了有机钙、无机钙这类补钙制剂以外,小分子肽螯合钙受到越来越多的关注。小分子肽鳌合钙具有吸收快、不易饱和、耗能低且与其他金属离子的吸收无竞争等特点。研究指出位于五元环或六元环络合物中心的金属元素可以通过小肠绒毛刷状缘,以小肽的形式被吸收[17],维持钙在小肠内的溶解状态,增加小肠对钙的吸收及其在体内的蓄积。另外,与普通补钙制剂相比,肽-钙螯合物的吸收不需要维生素D参与,Ca2+在螯合状态下主要通过肽的吸收通道被吸收,而不是通过金属离子的吸收通道,因而能够避免与利用同一通道吸收的其他金属离子拮抗竞争[18],从而提高吸收效率。此外,肽-钙螯合物吸收速度快,生化路径简单,节约机体能量消耗[19]。肽鳌合钙进入细胞以鳌合物的形式缓释Ca2+[20],供机体利用,能够避免血清中Ca2+浓度过高所致的肾排钙量增加或高钙血症,减轻钙结合蛋白的转运负荷。
2. 肽与钙的螯合
2.1 结合位点
在已有研究中,具有钙螯合能力的肽分子量没有特定范围,来源不同的钙螯合肽的分子量有一定差异,通常分子量较小的肽具有更高的钙结合活性[21]。结合活性位点主要包括酸性氨基酸的羧基,包括谷氨酸(Glutamicacid,Glu)的γ-COO-和天冬氨酸(Asparticacid,Asp)的β-COO-,氨基(-NH2),组氨酸(Histidine,His)的咪唑基(-C3H3N2)[22]以及磷酸基(Pi)。此外,钙的结合能力还与疏水性氨基酸含量相关。活性位点的研究主要通过傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)、X射线光子光谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS)和核磁共振波谱(Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy,NMR)等多种技术进行检测分析。
Xu等[13]利用分子对接技术发现Ca2+与贻贝肽Leu-Gly-Lys-Asp-Gln-Val-Arg-Thr中Asp残基的羧基发生相互作用,Wang等[23]的研究中也得到了相同的结论。另外,有研究发现Glu的羧酸氧是Ca2+的结合位点[24−26]。而Cui等[14]从海参卵子中鉴定出具有钙结合能力的肽链Asn-Asp-Glu-Glu-Leu-Asn-Lys,认为钙结合位点可能涉及肽中两个谷氨酸和一个天冬氨酸残基的羧基氧和氨基氮原子。以上几项研究中鉴定出的具有钙结合能力的多肽都含有酸性氨基酸残基,酸性氨基酸的羧基和氨基可能是多肽与钙的结合位点。
除了酸性氨基酸的羧基与氨基外,组氨酸的咪唑基也是多肽与钙的结合位点。Huang等[27]通过电喷雾串联质谱(ESI/MS/MS)从虾中鉴定出的钙结合肽Thr-Cys-His中含有组氨酸残基,但不含有天冬氨酸或谷氨酸残基,组氨酸的咪唑基可能是多肽与钙的结合位点。另外,Charoenphun等[28]通过自动Edman降解从罗非鱼中鉴定出的钙结合肽Trp-Glu-Trp-Leu-His-Tyr-Trp,除谷氨酸残基外,肽链上的组氨酸也是多肽与钙的结合位点。
Lee等[29]、Chen等[30]、Cui等[14]、李超楠[31]分别从猪血、罗非鱼、海参卵子、碎米中得到的具有钙结合能力的肽,肽链中除了都含有酸性氨基酸外还含有疏水性氨基酸。另外,一些具有钙结合能力的多肽虽然不含有酸性氨基酸或组氨酸[32−33],但都含有疏水性氨基酸。因此,钙结合能力可能与疏水性氨基酸有直接关系。
研究发现,许多酪蛋白磷酸肽具有相同的序列,即Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu,已被确定能与金属离子结合[34],磷酸化丝氨酸已被证实是Ca2+的主要结合位点,磷酸化修饰有助于Ca2+与肽的结合[35]。Luo等[36]利用分子动力学可视化酪蛋白磷酸肽的结合模式,发现钙结合位点包括谷氨酸残基的羰基和磷丝氨酸残基的磷酸基。蛋黄中的卵黄高磷蛋白是含磷最多的天然蛋白质,磷含量约为10%[37],其中超过50%的蛋白质磷酸化,在液体中具有聚阴离子性质,在肠内可以部分水解为磷酸肽,具有比原始卵黄高磷蛋白更强的金属螯合能力[38]。因此,卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽中的磷酸化丝氨酸能与Ca2+、Mg2+、Zn2+等金属离子结合,并促进这些矿物质的肠道吸收[39]。Si等[18]选用新型卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸化五肽(Glu-Asp-Asp-(P)Ser-(P)Ser,EddPSPS)制备了EddPSPS-钙复合物(EddPSPS-Ca),并对其钙结合机制进行了研究,结果证实了磷丝氨酸的磷酸基是Ca2+结合位点之一。以上研究表明,除了酸性氨基酸、组氨酸、疏水性氨基酸之外,磷酸化修饰即磷酸基也能够显著影响肽与钙的结合(表1)。
表 1 鉴定出的部分钙结合肽链及其结合位点Table 1. Some of the identified calcium-binding peptide chains and the binding sites来源 序列 结合位点 参考
文献贻贝 Leu-Gly-Lys-Asp-Gln-Val-Arg-Thr 天冬氨酸的羧基 [13] Gln-Glu-Glu-Ile-Ser-Lys 谷氨酸的羧基 [23] 乳清蛋白 Glu-Gly 谷氨酸的羧基、羰基、氨基 [24] 鱼副产物 Val-Leu-Ser-Gly-Gly-Thr-Thr-Met-Tyr-Ala-Ser-Leu-Tyr-Ala-Glu 谷氨酸的羧基 [25] 小麦 Phe-Val-Asp-Val-Thr 天冬氨酸的羧基 [26] 海参卵子 Asn-Asp-Glu-Glu-Leu-Asn-Lys 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸的羧基氧和氨基氮原子,疏水性氨基酸 [14] 虾 Thr-Cys-His 组氨酸的咪唑基 [27] 罗非鱼 Trp-Glu-Trp-Leu-His-Tyr-Trp 谷氨酸的羧基,组氨酸的咪唑基 [28] Asp-Gly-Asp-Asp-Gly-Glu-Ala-Gly-Lys-Ile-Gly 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸,疏水性氨基酸 [29] 裂壶藻 Phe-Tyr 疏水性氨基酸 [30] 鱼骨架 Val-Leu-Ser-Gly-Gly-Thr-Thr-Met-Ala-Met-Tyr-Thr-Leu-Val 疏水性氨基酸 [31] 猪血 Val-Ser-Gly-Val-Glu-Asp-Val-Asn 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、疏水性氨基酸 [32] 大米 Asn-Arg-Gly-Asp-Glu-Phe-Gly-Ala-Phe 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、疏水性氨基酸 [33] 酪蛋白 Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu 谷氨酸的羰基和磷丝氨酸残基的磷酸基 [34] 卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽 Glu-Asp-Asp-(P)Ser-(P)Ser 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸的羧基、氨基,磷丝氨酸的磷酸基 [18] α-乳白蛋白 Lys-Phe-Leu-Asp-Asp-Asp-Leu-Thr-Asp-Asp-Asp 天冬氨酸的羧基 [40] 2.2 结合模式
现有研究报道了Ca2+与肽上羧酸基团和磷酸基团的结合模式,其中Ca2+螯合到肽上羧酸基团(COO-)的主要方式是单齿、双齿、桥接和α模式[41]。如图1所示,在单齿模式下,金属离子仅与-COO-基团的一个氧原子相互作用;当金属离子与-COO-基团上的两个氧原子相互作用时,为双齿模式;如果-COO-基团中的两个氧原子各自与金属离子结合,为桥接模式;当Ca2+与羧酸基团的一个氧原子和另一个配体原子(O、N、S等)螯合时,则为α模式[42]。α-乳白蛋白(α-Lactalbumin,α-LA)是牛奶中一种含有两个Ca2+结合位点的小分子(Mr 14200)酸性(PI4~5)蛋白,是一种重要的Ca2+结合蛋白[43]。α-LA的一个强钙结合位点是由三个Asp残基(82、87和88)的羧基和肽链的两个羰基(Lys79和Asp84)在两个螺旋之间的环上形成的氧配体,Ca2+结合环的序列为Lys79-Phe-Leu-Asp-Asp-Asp-Leu-Thr-Asp-Asp-Asp88,在不同物种的α-LA中高度保守[40]。肽的羧酸基团与Ca2+的结合存在多种模式,如太平洋鳕鱼骨来源的十肽与Ca2+具有单齿、双齿和α模式三种结合模式[44]。此外,磷酸基团与Ca2+的结合也可以通过三种模式发生,即单齿、双齿和三齿,具体的结合模式取决于参与结合的磷酸基团或其他基团的数量。Luo等[36]观察到单齿、双齿、三齿三种螯合模式中,磷酸肽以1:6的比例与Ca2+结合。以上研究表明,Ca2+与肽的结合具有复杂性和不确定性。
2.3 分子间作用力
解析肽分子与Ca2+间的相互作用有助于解释肽分子Ca2+结合能力的构效关系。Sun等[24]通过ITC测量磷虾肽和Ca2+的热力学参数,发现磷虾肽和Ca2+之间存在静电相互作用。Si等[18]通过研究一种磷酸化五肽(Glu-Asp-Asp-(P)Ser-(P)Ser,EddPSPS)与Ca2+之间的分子作用力得到了同样的结论。除了静电相互作用,在肽-钙螯合物中,肽中的氧和氮原子主要作为电子供体,而金属离子主要作为形成配位键的电子受体[45−46]。Lin等[47]在比较Ca2+结合前后肽的Zeta电位后,观察到其绝对值显著降低,并且在相同pH下螯合物的电位低于肽,表明肽和Ca2+还可通过配位键结合。此外,Zhang等[48]用具有不同作用位点的解离剂处理肽-钙螯合物,发现当高能疏水相互作用和氢键被破坏时,螯合物会分解,这一结果说明螯合物的形成和稳定还取决于氢键和疏水相互作用。以上结果说明,肽与Ca2+的分子间作用主要包括氢键、静电相互作用、配位键和疏水相互作用,由于以上分子间作用力的存在肽和Ca2+能够稳定结合,且具有一定的结合强度。而随着温度的升高,氢键的强度会逐渐减弱。温度、pH、离子强度也会影响疏水相互作用的强度。考虑到加工过程及人体胃肠消化过程中环境的变化,应对螯合钙在不同环境中的稳定性进行进一步研究。
3. 钙吸收机制
3.1 游离Ca2+在体内的吸收机制
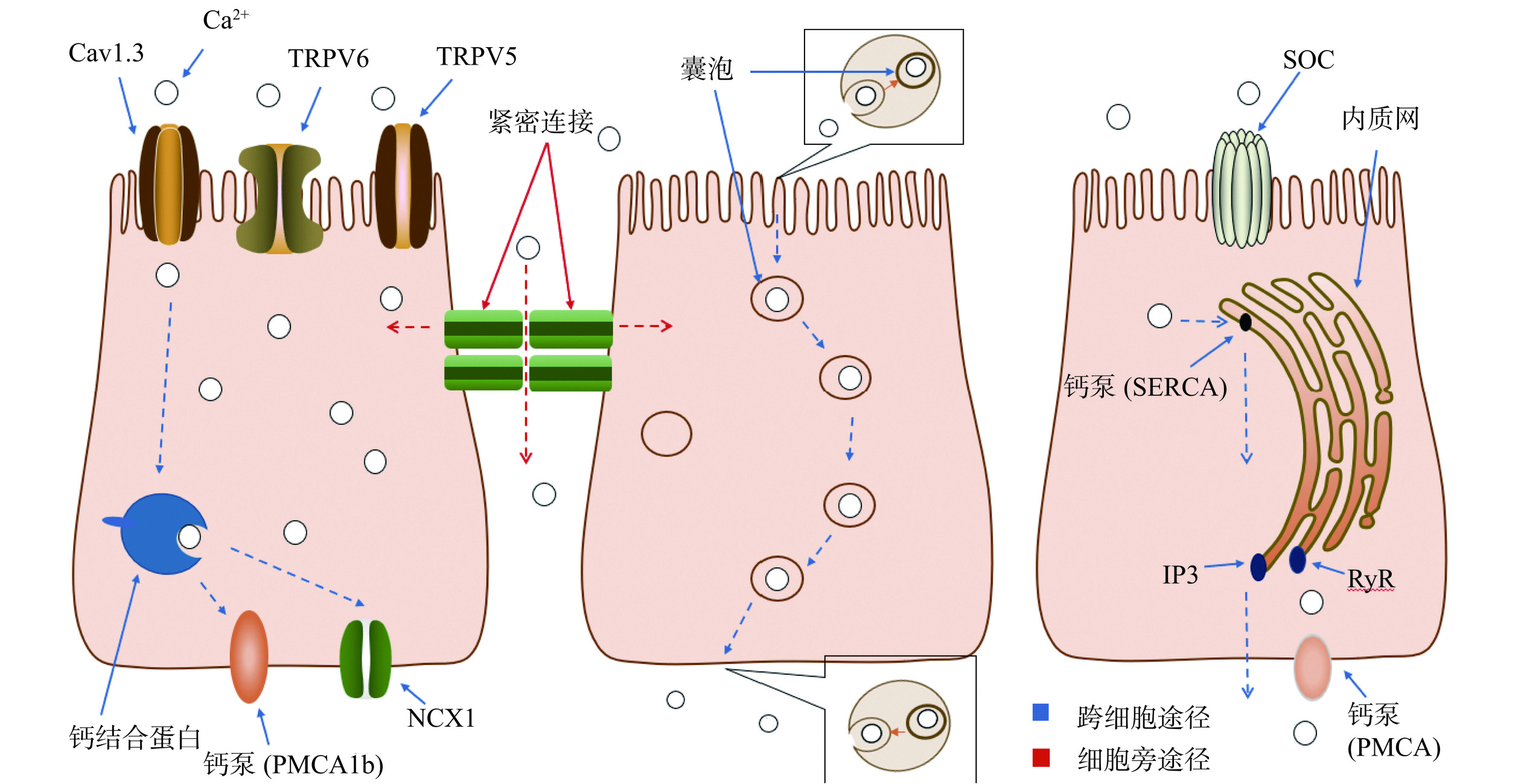
人体内钙的吸收主要发生在肠道的回肠部分[49]。钙有两种吸收途径,分别是跨细胞途径和细胞旁途径(图2)。其中跨细胞途径包括主动运输和被动运输,维生素D能够调节这两种运输途径,促进肠道对钙的吸收。经肠道吸收的钙进入血液循环后,最终大部分沉积在骨骼中,形成骨钙[18]。
3.1.1 跨细胞途径转运Ca2+
跨细胞途径主要包括三个步骤。首先,Ca2+穿过刷状边界膜(BBM)进入细胞;然后,细胞中的Ca2+从刷状边界膜移动到基底侧膜;最后,钙通过基底侧膜进入血液[50]。目前有三种转吞钙摄取模型,分别为促进扩散、囊泡转运和内质网转运[51]。
3.1.1.1 促进扩散
Ca2+通过上皮钙离子通道TRPV6、TRPV5和Cav1.3进入肠细胞。进入后,Ca2+与钙结合蛋白结合并通过细胞质运输到基底膜。最终,Ca2+从钙结合蛋白转移到亲和力更高的钙ATP酶(PMCA1b)或钠钙交换蛋白(NCX1)上[38,52],两者都参与Ca2+从肠细胞排到血液的过程。这种模型为非饱和扩散模型。
3.1.1.2 囊泡运输
刷状边界膜周围Ca2+浓度的快速增加会破坏靠近钙通道中的细丝的活性,引发内吞囊泡的形成。新形成的含有Ca2+的囊泡通过微管运输,有些与溶酶体融合。最后,囊泡或溶酶体被转运到基底侧膜与膜融合,而Ca2+被挤出到细胞外[51]。
3.1.1.3 内质网转运
Ca2+通过钙通道(SOC)进入肠细胞,然后被钙泵(SERCA)泵在内质网上,释放通道IP3和RyR集中在基底外侧膜附近的内质网部分,从内质网释放的Ca2+最终通过PMCA释放到血液中[53]。
3.1.1.4 维生素D促进Ca2+的跨细胞转运
维生素D是促进肠道钙吸收的重要因素,能够调节主动运输和被动运输两种运输途径。Ca2+在维生素D的帮助下,吸收并利用沉积到骨骼中。维生素D与维生素D受体(VDR)结合后进入细胞核,加快DNA转录成为mRNA,促进Ca2+转运相关蛋白(TRPV6、钙结合蛋白、PMCA1b等)的生物合成;活性维生素D还刺激基底膜腺苷酸环化酶的活化,在Ca2+-ATP酶联合作用下,经主动耗能,使Ca2+向血液转运[54];另外,有研究证明维生素D与VDR对钙的细胞旁被动运输也具有调节作用,维生素D通过上调紧密连接蛋白的表达,促进钙的被动运输[55]。
3.1.2 细胞旁途径转运Ca2+
如图2所示,细胞旁途径主要由细胞之间的紧密连接结构(Tight Junctions,TJ)组成,这些结构是位于肠细胞顶端膜和基底外侧膜之间的特殊膜结构域[56]。这些连接由跨膜蛋白、细胞骨架成分和细胞质斑块组成。TJ的跨膜蛋白在邻近细胞中合成,包括闭塞带-1、闭塞蛋白和claudin[57],所有这些都在细胞之间连接并限制物质通过细胞旁空间的自由运动。离子通过紧密连接处的运动主要取决于渗透离子的浓度梯度和穿过上皮的电梯度。当肠腔内Ca2+浓度较高时,一部分Ca2+就能通过细胞旁路途径,顺着浓度梯度直接弥散入血。这种吸收形式不消耗能量,但是吸收的钙仅占总量的极少部分,常被忽略不计。
3.2 肽-钙螯合物在体内的吸收机制
不同于游离Ca2+的吸收,研究表明,肽-钙螯合物能够抵抗胃消化,并以小分子肽的形式通过肽的吸收途径在小肠中被吸收[58]。因此,了解肠细胞转运肽的途径有助于确定肽-钙螯合物促进钙吸收的特定机制,并且在与上文阐述的游离Ca2+吸收机制的对比之下,显示出肽螯合钙在钙吸收方面的优点。如图3所示,目前已知的通过肠细胞转运肽的主要途径是PepT1途径、细胞穿透肽途径这类跨细胞途径(类似于Ca2+跨细胞途径)以及细胞旁途径[59]。
3.2.1 跨细胞途径转运肽
PepT1途径是一种广泛特异性的肽转运蛋白,能够转运几乎所有的二肽和三肽[58]。转运到细胞内的肽可以通过其他转运蛋白进入血液,也可以留在细胞中供细胞使用;细胞穿透肽可以在质膜上易位,同时携带某些物质进入细胞。穿透肽表面有一个阳离子区域,可以与质膜上的负电荷结合,从而导致质膜结构形状的变化[59]。这些途径有两种主要形式,包括直接运输穿过细胞或通过囊泡运输。细胞穿透肽可用于新型营养输送,以克服细胞屏障的不可穿透性[60]。酪蛋白磷酸肽是一种细胞穿透肽,能够通过插入细胞质膜形成钙选择性通道,从而促进钙吸收[61]。因此,肽螯合钙能够避免与其他离子竞争离子通道,提高钙离子的吸收效率。
3.2.2 细胞旁途径转运肽
细胞旁肽途径也通过细胞之间紧密连接的结构(TJ)发生。由于紧密连接结构的孔径较小,所以该途径主要运输3~5个氨基酸的短肽。一些分子量较大的肽可以在水解后通过细胞旁途径运输,如从豆豉中鉴定出的降血糖肽SFLLR(Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg)被消化系统部分降解为SFLL(Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu)、SFL(Ser-Phe-Leu)和SF(Ser-Phe)等小片段。SFL可以通过细胞旁途径和PepT1途径运输,SFLLR和SFLL仅通过细胞旁途径[62]。从蛋清中提取的抗高血压三肽LKP(Leu-Lys-Pro)和IQW(Ile-Gln-Trp)既可以通过PepT1途径运输也可以通过细胞旁途径运输[63]。
3.2.3 其他肽螯合钙的吸收途径
肽螯合钙的吸收机制具有复杂性和不确定性,除了以小分子肽的形式被吸收,还存在其他形式,如脱盐鸭蛋清多肽与钙结合形成可溶性螯合物后,既能以小分子肽形式被肠上皮细胞吸收,又能通过与瞬时受体电位相互作用调控肠上皮细胞的增殖和分化。据报道,蛋清肽-钙螯合物促进钙吸收的途径包括Ca2+通道Cav1.3、胞吞途径和细胞旁路途径[64]。卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽(PPP)和PPP-Ca能够提高碱性磷酸酶(ALP)的活性,降低抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase,TRAP)活性,同时显著影响信号通路(OPG、RANKL、NFATC-1、RANK)mRNA的表达情况,并通过上调CalbindinD9K mRNA的表达增加钙的转运量[65]。鱼鳞蛋白水解物-钙复合物(FSPH-Ca)通过促进TRPV6通道开放和mRNA表达,促进钙进入Caco-2细胞[47]。这些研究表明,肽螯合钙并不是只通过肽的吸收途径被吸收,可能具有多种吸收途径,能够通过影响通道的开放及上调通道蛋白、钙结合蛋白的表达量增加钙的吸收速率以达到促进钙吸收的效果。目前还没有研究报道螯合钙固有的吸收机制,因此,不同来源的肽螯合钙的吸收机制需进一步研究。
4. 结论与展望
本文综述了Ca2+与肽的结合位点、结合模式及两者之间的相互作用关系,对传统补钙制剂和肽-钙螯合物的吸收机制进行了总结,阐述了相较于无机钙和有机钙,肽-钙螯合物在钙的生物利用度方面的优势。肽-钙螯合物中Ca2+主要与肽链上酸性氨基酸的羧基、组氨酸的咪唑基、疏水性氨基酸及磷酸基结合,结合模式具有复杂性。螯合物的稳定性主要依赖于氢键和疏水相互作用的存在。肽-钙螯合补钙制剂能够减少钙在小肠内的沉积,维持溶解状态。肽螯合钙以小分子肽的形式被吸收,能够避免与其他金属离子竞争离子通道,提高吸收效率,节约机体能量。螯合物缓释Ca2+可避免血清中Ca2+浓度过高所致的肾排钙量增加或高钙血症,减轻钙结合蛋白的转运负荷。因此,肽-钙螯合物作为新型钙补充剂具有较好的开发价值和广阔的应用前景。
目前针对肽-钙的螯合机理开展的研究较多,而对肽-钙螯合物释放Ca2+或控制Ca2+缓释的规律缺乏深入研究。为明确肽-钙螯合物在人体内的补钙作用,提高补钙效果,未来需要研究肽-钙螯合物在加工过程中的物理化学稳定性(温度、湿度、pH等),以及人体内胃肠道消化稳定性。另外,还需进行毒理学研究,确保其对人体不产生急性、亚急性或慢性毒性,为肽-钙螯合物成为新型的高效钙补充剂提供理论支撑。
-
表 1 鉴定出的部分钙结合肽链及其结合位点
Table 1 Some of the identified calcium-binding peptide chains and the binding sites
来源 序列 结合位点 参考
文献贻贝 Leu-Gly-Lys-Asp-Gln-Val-Arg-Thr 天冬氨酸的羧基 [13] Gln-Glu-Glu-Ile-Ser-Lys 谷氨酸的羧基 [23] 乳清蛋白 Glu-Gly 谷氨酸的羧基、羰基、氨基 [24] 鱼副产物 Val-Leu-Ser-Gly-Gly-Thr-Thr-Met-Tyr-Ala-Ser-Leu-Tyr-Ala-Glu 谷氨酸的羧基 [25] 小麦 Phe-Val-Asp-Val-Thr 天冬氨酸的羧基 [26] 海参卵子 Asn-Asp-Glu-Glu-Leu-Asn-Lys 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸的羧基氧和氨基氮原子,疏水性氨基酸 [14] 虾 Thr-Cys-His 组氨酸的咪唑基 [27] 罗非鱼 Trp-Glu-Trp-Leu-His-Tyr-Trp 谷氨酸的羧基,组氨酸的咪唑基 [28] Asp-Gly-Asp-Asp-Gly-Glu-Ala-Gly-Lys-Ile-Gly 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸,疏水性氨基酸 [29] 裂壶藻 Phe-Tyr 疏水性氨基酸 [30] 鱼骨架 Val-Leu-Ser-Gly-Gly-Thr-Thr-Met-Ala-Met-Tyr-Thr-Leu-Val 疏水性氨基酸 [31] 猪血 Val-Ser-Gly-Val-Glu-Asp-Val-Asn 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、疏水性氨基酸 [32] 大米 Asn-Arg-Gly-Asp-Glu-Phe-Gly-Ala-Phe 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、疏水性氨基酸 [33] 酪蛋白 Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu 谷氨酸的羰基和磷丝氨酸残基的磷酸基 [34] 卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽 Glu-Asp-Asp-(P)Ser-(P)Ser 谷氨酸、天冬氨酸的羧基、氨基,磷丝氨酸的磷酸基 [18] α-乳白蛋白 Lys-Phe-Leu-Asp-Asp-Asp-Leu-Thr-Asp-Asp-Asp 天冬氨酸的羧基 [40] -
[1] 王培霞, 张勤, 周石仙, 等. 骨质疏松症营养干预研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(3):409−412,443. [WANG Peixia, ZHANG Qin, ZHOU Shixian, et al. Advances in nutritional intervention of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2023,29(3):409−412,443.] WANG Peixia, ZHANG Qin, ZHOU Shixian, et al. Advances in nutritional intervention of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis, 2023, 29(3): 409−412,443.
[2] ZHANG Xiaowei, JIA Qi, LI Mengyu, et al. Isolation of a novel calcium-binding peptide from phosvitin hydrolysates and the study of its calcium chelation mechanism[J]. Food Research International,2021,141:110169. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110169
[3] LIU Ting, LI Tao, XU Dandi, et al. Small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in the heart:Expression, regulation and pathological implications[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences,2023,378(1879):20220171. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0171
[4] QI Liwei, WANG Kangyu, ZHOU Jiaojiao, et al. Phosphorylation modification of bovine bone collagen peptide enhanced its effect on mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells via improving calcium-binding capacity[J]. Food Chemistry,2024(433):137365.
[5] 李奕, 程永强, 唐宁. 肠道中钙和铁相互作用对其吸收影响的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(4):323−335. [LI Yi, CHENG Yongqiang, TANG Ning. Review on effects of calcium and iron interactions on their absorptions in the intestine[J]. Food Science,2024,45(4):323−335.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230313-132 LI Yi, CHENG Yongqiang, TANG Ning. Review on effects of calcium and iron interactions on their absorptions in the intestine[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(4): 323−335. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230313-132
[6] CUI Qun, LI Na, NIE Fujiao, et al. Vitamin K2 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Arch Oral Biol,2021,124:105057. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2021.105057
[7] 石景, 邹烨, 马晶晶, 等. 食源肽螯合钙的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(11):460−467. [SHI Jing, ZOU Hua, MA Jingjing, et al. Research progress in food-derived calcium chelated peptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(11):460−467.] SHI Jing, ZOU Hua, MA Jingjing, et al. Research progress in food-derived calcium chelated peptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(11): 460−467.
[8] 中国营养学会骨营养与健康分会, 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症患者的营养和运动管理专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2020,13(5):396−410. [Bone Nutrition and Health Branch-Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Society of Osteoporosis And Bone Mineral Research. Expert consensus on nutritional and exercise management of patients with primary osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism,2020,13(5):396−410.] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20200408-00261 Bone Nutrition and Health Branch-Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Society of Osteoporosis And Bone Mineral Research. Expert consensus on nutritional and exercise management of patients with primary osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2020, 13(5): 396−410. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20200408-00261
[9] 李侠, 许翠萍, 顾帅, 等. 绿豆中植酸和单宁对钙吸收的影响[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2016,38(3):364−368. [LI Xia, XU Cuiping, GU Shuai, et al. Effects of phytic acid and tannin from mung bean on calcium absorption[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2016,38(3):364−368.] LI Xia, XU Cuiping, GU Shuai, et al. Effects of phytic acid and tannin from mung bean on calcium absorption[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2016, 38(3): 364−368.
[10] 赵梓月, 王思远, 廖森泰, 等. 多肽螯合钙的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(5):218−224. [ZHAO Ziyue, WANG Siyuan, LIAO Sentai, et al. Progress in research on peptide chelated calcium[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(5):218−224.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.05.033 ZHAO Ziyue, WANG Siyuan, LIAO Sentai, et al. Progress in research on peptide chelated calcium[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(5): 218−224. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.05.033
[11] 金子琪. 蛋清肽螯合钙的结构表征及其促钙吸收途径的研究[D]. 大连:大连工业大学, 2019:5−10. [JIN Ziqi. Study on the structural characterization of egg white peptide chelated calcium and its pathways of promoting calcium absorption[D]. Dalian:Dalian Polytechnic University, 2019:5−10.] JIN Ziqi. Study on the structural characterization of egg white peptide chelated calcium and its pathways of promoting calcium absorption[D]. Dalian: Dalian Polytechnic University, 2019: 5−10.
[12] MICHOS E D, CAINZOS-ACHIRICA M, HERAVI A S, et al. Vitamin D, calcium supplements, and implications for cardiovascular health[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology,2021(4):77.
[13] XU Zhe, HAN Shiying, CHEN Hui, et al. Characterization of chelation and absorption of calcium by a mytilus edulis derived osteogenic peptide[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:840638. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.840638
[14] CUI Pengbo, LIN Songyi L, JIN Ziqi, et al. In vitro digestion profile and calcium absorption studies of sea cucumber ovum derived heptapeptide-calcium complex[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(9):4521−5026.
[15] 苑晴晴, 罗琴, 何凯鑫, 等. 肽钙螯合物的研究进展[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2023,30(2):24−26. [YUAN Qingqing, LUO Qin, HE Kaixin, et al. Progress of calcium chelate of microalgal peptide[J]. Cereal and Food Industry,2023,30(2):24−26.] YUAN Qingqing, LUO Qin, HE Kaixin, et al. Progress of calcium chelate of microalgal peptide[J]. Cereal and Food Industry, 2023, 30(2): 24−26.
[16] 郭艳. 水解米渣蛋白及制备氨基酸螯合钙的工艺研究[D]. 成都:四川大学, 2006:5−10. [GUO Yan. Hydrolysis of rice residue protein and synthesis of complex amino acid with calcium[D]. Chengdu:Sichuan University, 2006:5−10.] GUO Yan. Hydrolysis of rice residue protein and synthesis of complex amino acid with calcium[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2006: 5−10.
[17] 孙小东. 核桃蛋白肽改善骨质疏松活性评价和钙螯合肽的制备与结构表征[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学, 2021:10−13. [SUN Xiaodong. Evaluation of the activity of walnut protein peptide in improving osteoporosis and preparation and structural characterization of calcium chelating peptide[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021:10−13.] SUN Xiaodong. Evaluation of the activity of walnut protein peptide in improving osteoporosis and preparation and structural characterization of calcium chelating peptide[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021: 10−13.
[18] SI Kai, GONG Tingting, DING Suyun, et al. Binding mechanism and bioavailability of a novel phosvitin phosphopeptide (Glu-Asp-Asp-pSer-pSer) calcium complex[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,404(PtA):134567.
[19] FERRARETTO A, GRAVAGHI C, FIORILLI A, et al. Casein-derived bioactive phosphopeptides:Role of phosphorylation and primary structure in promoting calcium uptake by HT-29 tumor cells[J]. FEBS Letters,2003,551(1−3):92−98. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00741-5
[20] 刘卫震, 王冠华, 袁延佩, 等. 酪蛋白磷酸肽-钙螯合物的分级、表征及持钙特性[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(10):93−100. [LIU Weizhen, WANG Guanhua, YUAN Yanpei, et al. Fractionation, characterization and calcium-holding properties of casein phosphopeptide-calcium chelates[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(10):93−100.] LIU Weizhen, WANG Guanhua, YUAN Yanpei, et al. Fractionation, characterization and calcium-holding properties of casein phosphopeptide-calcium chelates[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(10): 93−100.
[21] 李雪芬, 杜斌, 丁轲, 等. 金属螯合肽分离纯化及其抗氧化活性的研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2016,22(3):35−39. [LI Xuefen, DU Bin, DING Ke, et al. Progress in the isolation and purification of metal-chelating peptides and their antioxidant activity[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2016,22(3):35−39.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2016.03.008 LI Xuefen, DU Bin, DING Ke, et al. Progress in the isolation and purification of metal-chelating peptides and their antioxidant activity[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2016, 22(3): 35−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2016.03.008
[22] STORCKSDIECK S, BONSMANN G, HURRELL R F. Iron-binding properties, amino acid composition, and structure of muscle tissue peptides from in vitro digestion of different meat sources[J]. Journal of Food Science,2007,72(1):19−29.
[23] WANG Li, DING Yuanyuan, ZHANG Xinxia, et al. Isolation of a novel calcium-binding peptide from wheat germ protein hydrolysates and the prediction for its mechanism of combination[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,239(15):416−426.
[24] SUN Na, HU Shengjie, WANG Di, et al. Calcium delivery systems assembled using antarctic krill derived heptapeptides:Exploration of the assembly mechanism, in vitro digestion profile, and calcium absorption behavior[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022(6):70.
[25] HUANG Guangrong, REN Lie, JIANG Jiaxin. Purification of a histidine-containing peptide with calcium binding activity from shrimp processing byproducts hydrolysate[J]. European Food Research & Technology,2011,232(2):281−287.
[26] JUNG W K, KIM S K. Calcium-binding peptide derived from pepsinolytic hydrolysates of hoki (Johnius belengerii) frame[J]. European Food Research & Technology,2007,224:763−767.
[27] HUANG Shunli, ZHAO Lina, CAI Xixi, et al. Purification and characterisation of a glutamic acid-containing peptide with calcium-binding capacity from whey protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Dairy Research,2015,82(1):29−35. doi: 10.1017/S0022029914000715
[28] CHAROENPHUN N, CHEIRSILP B, SIRINUPONG N, et al. Calcium-binding peptides derived from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) protein hydrolysate[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2013,236(1):57−63. doi: 10.1007/s00217-012-1860-2
[29] LEE S H, SONG K B. Article isolation of a calcium-binding peptide from enzymatic hydrolysates of porcine blood plasma protein[J]. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry,2009,52(3):290−294. doi: 10.3839/jksabc.2009.051
[30] CHEN Da, MU Xinmin, HUANG Hai, et al. Isolation of a calcium-binding peptide from tilapia scale protein hydrolysate and its calcium bioavailability in rats[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2014,6:575−584. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.12.001
[31] 李超楠. 米蛋白肽-钙螯合物的制备及其性质研究[D]. 大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2019:3-5. [LI Chaonan. Preparation and properties of rice protein peptide-calcium chelate[D]. Daqing:Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019:3-5.] LI Chaonan. Preparation and properties of rice protein peptide-calcium chelate[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019: 3-5.
[32] CAI Xixi, LIN Jiaping, WANG Shaoyun. Novel peptide with specific calcium-binding capacity from Schizochytrium sp. protein hydrolysates and calcium bioavailability in Caco-2 cells[J]. Marine Drugs,2017,15(1):2−14.
[33] JUNG W K, KARAWITA R, HEO S J, et al. Recovery of a novel Ca-binding peptide from Alaska Pollack (Theragra chalco gramma) backbone by pepsinolytic hydrolysis[J]. Process Biochemistry,2006,41(9):2097−2100. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2006.05.008
[34] JIANG Lan, LI Shuhong, WANG Nan, et al. Preparation of dextran-casein phosphopeptide conjugates, evaluation of its calcium binding capacity and digestion in vitro[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,352:129332. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129332
[35] LIU Guo, GUO Baoyan, LUO Minna, et al. A comprehensive review on preparation, structure-activities relationship, and calcium bioavailability of casein phosphopeptides[J]. Food Science and Nutrition,2024,64(4):996−1014.
[36] LUO Minna, XIAO Jie, SUN Shengwei, et al. Deciphering calcium-binding behaviors of casein phosphopeptides by experimental approaches and molecular simulation[J]. Food & Function,2020,11:5284−5292.
[37] YILMAZ B, DUYGU A. Bioactivities of hen's egg yolk phosvitin and its functional phosphopeptides in food industry and health[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85(10):2969−2976. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15447
[38] CHAKRABARTI S, REN Jiandong, WU Jianping. Phosvitin derived phospho-peptides show better osteogenic potential than intact phosvitin in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(10):2998. doi: 10.3390/nu12102998
[39] SAMARAWEERA H, MOON S, LEE E, et al. Characterisation of phosvitin phosphopeptides using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,165(15):98−103.
[40] LONNERDAL B, GLAZIER C. Calcium binding by alpha-lactalbumin in human milk and bovine milk[J]. Journal of Nutrition,1985,115:1209−1216. doi: 10.1093/jn/115.9.1209
[41] AN Jiulong, ZHANG Yinxiao, YING Zhiwei, et al. The formation, structural characteristics, absorption pathways and bioavailability of calcium-peptide chelates[J]. Foods,2022,11(18):2762. doi: 10.3390/foods11182762
[42] NARA M, MORII H, TANOKURA M. Coordination to divalent cations by calcium-binding proteins studied by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes,2013,1828(10):2319−2327. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.11.025
[43] PERMYAKOV E. α-Lactalbumin, amazing calcium-binding protein[J]. Biomolecules,2010(9):1210.
[44] PENG Zhe, HOU Hu, ZHANG Kai, et al. Effect of calcium-binding peptide from Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) bone on calcium bioavailability in rats[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,221:373−378. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.078
[45] ZHANG Y, STOCKMANN R, NG K, et al. Opportunities for plant-derived enhancers for iron, zinc, and calcium bioavailability:A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2020,20(1):652−685.
[46] KHARE E, HOLTEN-ANDERSEN N, BUEHLER M. Transition-metal coordinate bonds for bioinspired macromolecules with tunable mechanical properties[J]. Nature Reviews Materials,2021,6:421−436. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-00270-z
[47] LIN Yanlan, CAI Xixi, WU Xiaoping, et al. Fabrication of snapper fish scales protein hydrolysate-calcium complex and the promotion in calcium cellular uptake[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,65:103717.
[48] ZHANG J, LIANG L, TIAN Z, et al. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of calcium-induced soy protein isolate nanoparticles and their formation mechanism study[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,133(2):390−399. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.049
[49] 宋丽, 朱临娴, 宋璐杉, 等. 钙结合卵黄高磷蛋白磷酸肽的制备及其肽钙螯合物的结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(6):125−133. [SONG Li, ZHU Linxian, SONG Lushan, et al. Preparation of calcium-binding phosvitin phosphopeptide and structural characterization of its calcium chelate[J]. Food Science,2023,44(6):125−133.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220414-167 SONG Li, ZHU Linxian, SONG Lushan, et al. Preparation of calcium-binding phosvitin phosphopeptide and structural characterization of its calcium chelate[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(6): 125−133. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220414-167
[50] 刘佳琛, 程永强, 唐宁. 钙的生物利用度与多肽螯合钙研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(23):354−365. [LIU Jiachen, CHENG Yongqiang, TANG Ning. Progress on bioavailability of calcium and calcium-peptide chelates[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(23):354−365.] LIU Jiachen, CHENG Yongqiang, TANG Ning. Progress on bioavailability of calcium and calcium-peptide chelates[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(23): 354−365.
[51] PEREZ A, PICOTTO G, CARPENTIERI A, et al. Minireview on regulation of intestinal calcium absorption. Emphasis on molecular mechanisms of transcellular pathway[J]. Digestion,2008,77(1):22−34. doi: 10.1159/000116623
[52] KHANAL R C, NEMERE I. Regulation of intestinal calcium transport[J]. Annual Review of Nutrition,2008(28):179−196.
[53] DEBARBOZA G D, GUIZZARDI S, DETALAMONI N T, et al. Molecular aspects of intestinal calcium absorption[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2015,1(23):7142−7154.
[54] NEED A, O'LOUGHLIN P D, MORRIS, H A, et al. Vitamin D metabolites and calcium absorption in severe vitamin d deficiency[J]. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research,2008(23):1859−1863.
[55] FLEET J C. Vitamin D-mediated regulation of intestinal calcium absorption[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(16):3351. doi: 10.3390/nu14163351
[56] TSUKITA S, FURUSE M, ITOH M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2001,2(4):285−293. doi: 10.1038/35067088
[57] FUJITA H, SUGIMOTO K, INATOMI S, et al. Tight junction proteins claudin-2 and -12 are critical for vitamin D-dependent Ca2+ absorption between enterocytes[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell,2008,19(5):1912−1921.
[58] PETERSEN O H, FEDIRKO N V. Calcium signalling:Store-operated channel found at last[J]. Current Biology,2001,11(13):520−523. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00309-8
[59] WANG Xueqi, ZHANG Zhen, XU Hongyan, et al. Preparation of sheep bone collagen peptide–calcium chelate using enzymolysis-fermentation methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis[J]. The Royal Society of Chemistry,2020,10(20):11624−11633.
[60] KATIMBA H A, WANG Rongchun, CHENG Cuiling. Current findings support the potential use of bioactive peptides in enhancing zinc absorption in humans[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(19):3959−3979. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1996328
[61] FERNANDEZ-MUSOLES R, SALOM J B, CASTELLO-RUIZ M, et al. Bioavailability of antihypertensive lactoferricin B-derived peptides:Transepithelial transport and resistance to intestinal and plasma peptidases[J]. International Dairy Journal,2013,32(2):169−174. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.05.009
[62] PALM C, JAYAMANNE M, KJELLANDER M, et al. Peptide degradation is a critical determinant for cell-penetrating peptide uptake[J]. BBA–Biomembranes,2007,1768(7):1769−1776. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.03.029
[63] YU Songfeng, WANG Wenjun, BU Tingting, et al. Digestion, absorption, and transport properties of soy-fermented Douchi hypoglycemic peptides VY and SFLLR under simulated gastrointestinal digestionand Caco-2 cell monolayers[J]. Food Research International,2023,164:112340. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112340
[64] XU Qingbiao, FAN Hongbing, YU Wenlin, et al. Transport study of egg-derived antihypertensive peptides (LKP and IQW) using Caco-2 and HT29 coculture monolayers[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(34):7406−7414. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02176
[65] GILBERT E R, WONG E A, WEBB K E. Board-invited review:Peptide absorption and utilization:Implications for animal nutrition and health[J]. Journal of Animal Science,2008,86(9):2135. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0826





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
