Establishment of UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Fingerprints and Antioxidant Spectroscopic Relationship of Ethanol-eluting Sites of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Macroporous Resin
-
摘要: 目的:研究三叶青提取物与其抗氧化活性的谱效关系,初步明确其发挥抗氧化活性的质量标志物。方法:制备三叶青提取物上大孔树脂柱,分别使用浓度为10%、30%、50%、70%、90%和100%的乙醇进行洗脱,得到6个不同洗脱部位;采用超高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间串联质谱法(UPLC-Q-TOF-MS)建立三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位的指纹图谱并筛选特征峰;以1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)自由基清除率为抗氧化指标,考察三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位的抗氧化活性;再综合Pearson相关系数法和正交偏最小二乘(OPLS)法分析研究特征峰与抗氧化活性的谱效关系,筛选其质量标志物并分析鉴定其化学成分。结果:在正、负离子模式下,三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位分别筛选出57、92个特征峰;综合Pearson相关系数与OPLS分析结果,其中14个离子峰对抗氧化活性贡献较大,分别为香兰素(P2)、儿茶素(P13、N19)、芦丁(P27、N54)、异槲皮苷(P28)、山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷(P33、N61)、原花青素B(N18)、原花青素C(N22)以及离子峰N23、N25、N26、N29。结论:建立了三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位的UPLC-Q-TOF-MS指纹图谱,揭示了三叶青抗氧化活性的质量标志物,为三叶青的质量标准制定及资源开发利用提供技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 三叶青 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- 超高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间串联质谱 /
- 谱效关系 /
- 质量标志物
Abstract: Objective: To study the spectrum-effect relationship between the extracts of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and its antioxidant activity, and to clarify the quality markers of its antioxidant activity. Methods: The extract was prepared and separated by macroporous resin elution, six different elution sites were obtained using ethanol at concentrations of 10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, 90% and 100%. The fingerprints of the Tetrastigma hemsleyanum extract and each elution site were established by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and the characteristic peaks were screened. The free radical scavenging rate of 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine (DPPH) was used as an antioxidant index to investigate the antioxidant activity of the extract and each elution site of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. The Pearson correlation coefficient method and orthogonal partial least squares (OPLS) method were combined to analyze and study the spectrum-effect relationship between the characteristic peaks and the antioxidant activity, to screen the quality markers, and to analyze and identify the chemical compositions. Results: Under the positive and negative ion modes, 57 and 92 characteristic peaks were identified in the extract and each elution site of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum, respectively. The combined results of Pearson correlation coefficient and OPLS analysis showed that 14 ion peaks contributed more to the antioxidant activity, which was vanillin (P2), catechin (P13, N19), rutin (P27, N54), and isoquercitrin (P28), kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (P33, N61), proanthocyanidin B (N18), proanthocyanidin C (N22), and ion peaks N23, N25, N26, and N29, respectively. Conclusion: UPLC-Q-TOF-MS fingerprints of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum extract and each elution site were established, and the quality markers of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum antioxidant activity were revealed to provide technical support for the formulation of quality standards and resource development and utilization of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. -
三叶青(Tetrastigma hemsleyanum)学名三叶崖爬藤,为葡萄科崖爬藤属植物[1],是我国特有珍稀濒危植物[2],于2018年入选浙江省新“浙八味”。三叶青被称作“植物抗生素”[3],具有抗氧化[4−6]、抗肿瘤[7−8]、抗炎[9−10]等多种活性,民间常将其作为药食两用的食材,三叶青在药品、食品领域有着广泛的应用[11−12]。三叶青主要含有黄酮、多糖、酚类、鞣质、萜类以及甾体类等[13]成分,其中黄酮、多糖、酚类为主要活性成分[14]。
现有三叶青的研究多为提取工艺[15]、质量控制[16]以及抗肿瘤功效[17]等方向。关于三叶青抗氧化活性及药效成分的研究较少,其质量评价体系和质量标志物研究基础薄弱。而目前谱效关系已广泛应用于植物原料抗氧化活性物质基础研究中,杨锡金等[18]运用偏最小二乘回归分析和灰色关联分析谱效关系筛选出景天三七中抗氧化活性关键成分分别为:表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷;李东辉等[19]运用偏最小二乘分析、灰色关联分析及Pearson相关系数法对其抗氧化活性进行谱效分析,筛选出大黄饮片中共有峰1、2、3、7(芦荟大黄素-8-O-葡萄糖苷)、8、9(芦荟大黄素)、10(大黄酸)、12(大黄素)、14(大黄素甲醚)为发挥抗氧化活性的关键成分;刘翰飞[20]通过将刺梨不同极性部位提取物的HPLC指纹图谱和抗氧化抑菌药效数据相结合,运用偏最小二乘法、灰色关联度法筛选出共有峰8、10、12、13、15、16、17为发挥抗氧化活性的关键成分。为探究三叶青发挥抗氧化活性的质量标志物,通过建立三叶青指纹图谱和抗氧化活性之间谱效关系,将指纹图谱的化学成分信息与药物活性关联,初步探索三叶青抗氧化活性的物质基础。
综上所述,本研究以DPPH自由基清除率为抗氧化活性指标,通过大孔树脂对三叶青提取物进行洗脱分离,运用UPLC-Q-TOF-MS建立三叶青不同洗脱部位的指纹图谱,再联合Pearson相关系数法和OPLS法建立抗氧化谱效关系模型,筛选出三叶青发挥抗氧化活性的质量标志物并分析鉴定其化学成分。本研究以期为三叶青在抗氧化方面的应用提供参考,也为其质量控制及资源开发利用提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
三叶青 采自浙江台州,经南京野生植物综合利用研究所陈斌研究员鉴定为葡萄科崖爬藤属植物三叶青Tetrastigma hemsleyanum的干燥块根;甲醇 色谱级,默克化工技术(上海)有限公司;乙腈、甲酸 质谱级,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;无水乙醇 分析级,成都科隆化学品有限公司;盐酸、氢氧化钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH) 批号为Z6B8N-TF,梯希爱(上海)化成工业发展有限公司;AB-8大孔树脂 安徽三星树脂科技有限公司。
Waters ACQUITY UPLC超高效液相色谱仪、Waters Xevo G2-XS QTof高分辨质谱仪 美国Waters公司;ML204T/02电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;DZF-6050真空干燥箱、HWS-12水浴锅 上海恒一科学仪器有限公司;KQ-400DE超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;RE-6000AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;PURELAB flex 2超纯水系统 英国埃尔格公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 三叶青提取物制备
根据前期实验研究结果[4],将三叶青块根粉碎后过50目筛,烘干至恒重,得到样品粉末。称取三叶青粉末300 g,加入60%乙醇溶液9 L,于83 ℃回流提取60 min,共提取2次,布氏漏斗抽滤后,于旋转蒸发仪减压浓缩至无醇味,得到三叶青提取物S7,备用。
1.2.2 大孔树脂洗脱
1.2.2.1 大孔树脂预处理
参考文献[21−22]方法,采用AB-8大孔树脂对三叶青提取物进行洗脱分离。将AB-8大孔树脂放入95%乙醇中浸泡24 h后装柱,以95%乙醇冲洗至流出液澄清;再使用去离子水冲洗,至流出液无醇味;然后依次分别使用3% HCl和3% NaOH溶液冲洗、浸泡树脂层4 h;最后用去离子水洗至流出液中性,备用。
1.2.2.2 样品吸附
采用静态吸附法,将三叶青提取物S7以1:10的比例在水中均匀分散,与活化后的AB-8型大孔树脂1:10混合,静态吸附24 h,期间每隔2 h搅拌一次,使之充分吸附。
1.2.2.3 装柱
将静态吸附后的大孔树脂缓慢倒入玻璃层析柱中,使用去离子水以1 BV/h的流速反复冲洗约2个柱体积,使柱内的树脂充分压紧,并达到除去杂质的目的。
1.2.2.4 洗脱收集
去离子水洗脱除杂后,分别用浓度为10%、30%、50%、70%、90%和100%的乙醇以1 BV/h 的流速缓慢冲洗,直至洗脱液近无色,再用下一浓度的乙醇进行洗脱。洗脱液分别减压浓缩至浸膏状,真空干燥,得到三叶青10%(S1)、30%(S2)、50%(S3)、70%(S4)、90%(S5)、100%(S6)乙醇洗脱部位粉末。
1.2.3 三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位UPLC-Q-TOF-MS图谱的建立
1.2.3.1 供试品溶液制备
精密称取上述三叶青各洗脱部位S1~S6粉末以及三叶青提取物粉末S7各50 mg,加入纯甲醇进行溶解,定容至1 mg/mL,过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,得到供试品溶液,备用。
1.2.3.2 UPLC条件
色谱柱为Waters BEH C18柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm),流动相为0.1%甲酸水(A)-0.1%甲酸乙腈(B),梯度洗脱(0~10 min,2%~10%B;10~16 min,10%~12%B;16~24 min,12%~15%B;24~30 min,15%~40%B;30~40 min,40%~2%B);流速为0.3 mL/min;检测波长为360 nm;柱温为40 ℃;进样量为2 μL。
1.2.3.3 质谱条件
Waters Xevo G2-XS QTof质谱仪采用ESI电喷雾离子源在正、负离子模式进行高灵敏度扫描,扫描范围为m/z 50~1200 Da,正、负离子模式毛细管电压分别为2.0与−2.0 kV,温度135 ℃,锥孔电压为15~35 V,锥孔流量为50 L/hr,碰撞电压为6 V,脱溶剂气温度为500 ℃,脱溶剂气流速为800 L/hr。采用全扫描模式进行数据收集,频率为0.2 s,采集时间为0~40 min。
根据正、负离子模式离子流图等信息,通过质荷比、二级谱图,借助Reaxys、Pubchem等数据库进行检索,对各峰进行初步鉴定[23−24]。再根据二级质谱裂解规律结合崖爬藤属植物相关文献[25−27]所报道数据进一步对比推测化学成分。
1.2.3.4 指纹图谱建立
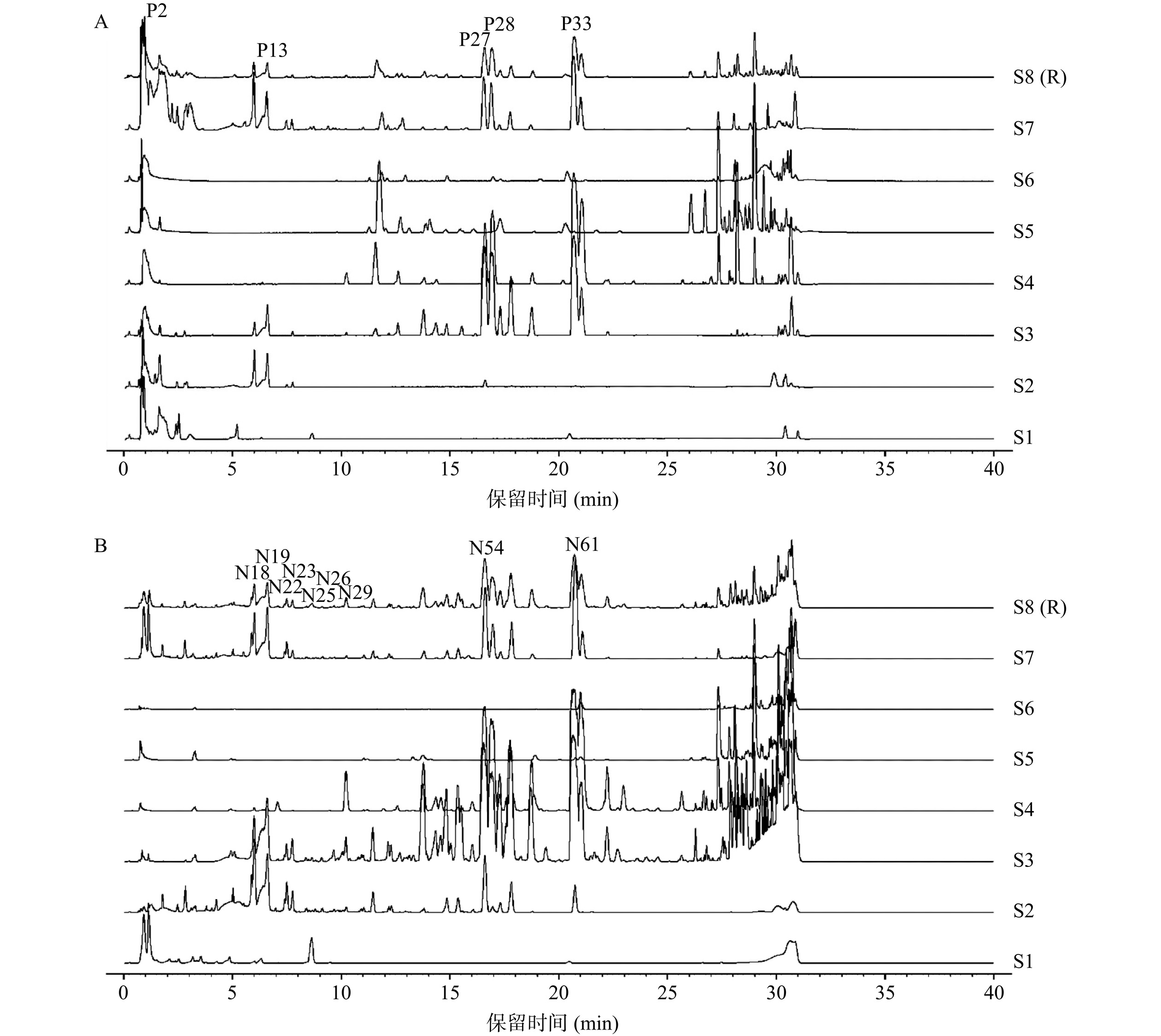
取三叶青样品S1~S7供试品溶液,按“1.2.3.2”“1.2.3.3”项下色谱与质谱条件进样分析,于正、负离子扫描模式下采集三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位S1~S7的图谱,利用masslnyx软件对三叶青各样品的质谱数据进行处理,提取并积分总离子流图,导出离子峰峰面积、峰高和保留时间等信息,建立.txt格式数据文件再将其导入“中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统(2012版)”进行分析,以S7为参照图谱,采用中位数法生成对照图谱S8(R),经多点校正和自动匹配建立三叶青各洗脱部位指纹图谱。
1.2.4 抗氧化活性评价
参考文献[18,28]方法,DPPH自由基清除率测定:取适量DPPH粉末,使用无水乙醇溶解,制成浓度为0.04 mg/mL的DPPH溶液。将各洗脱部位粉末配制成0.1 mg/mL的供试液。其中取1 mL的供试液与1 mL的DPPH溶液混合均匀,为A组;取1 mL的DPPH溶液与1 mL的无水乙醇混合均匀,为B组;取1 mL的供试液与1 mL的无水乙醇混合均匀,为C组。各组在室温环境下避光反应30 min,于波长517 nm下测定吸光度。实验平行重复3次,得到各洗脱部分DPPH自由基清除率。DPPH自由基清除率计算公式为:
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 26软件进行Pearson相关系数分析;采用Simca14.1软件进行OPLS分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 三叶青提取物及各洗脱部位UPLC-Q-TOF-MS指纹图谱的建立
将三叶青各洗脱部位正、负离子模式质谱数据导入“中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统(2012版)”进行分析,结果如图1所示。由正、负离子模式特征图谱可知,三叶青各洗脱部位化学成分、含量均有所不同,于正离子模式指纹图谱中挑选出峰面积大于4000的57个离子峰P1~P57,于负离子模式指纹图谱中挑选出峰面积大于4000的92个离子峰N1~N92,用于后续谱效关联度分析。
2.2 抗氧化活性评价
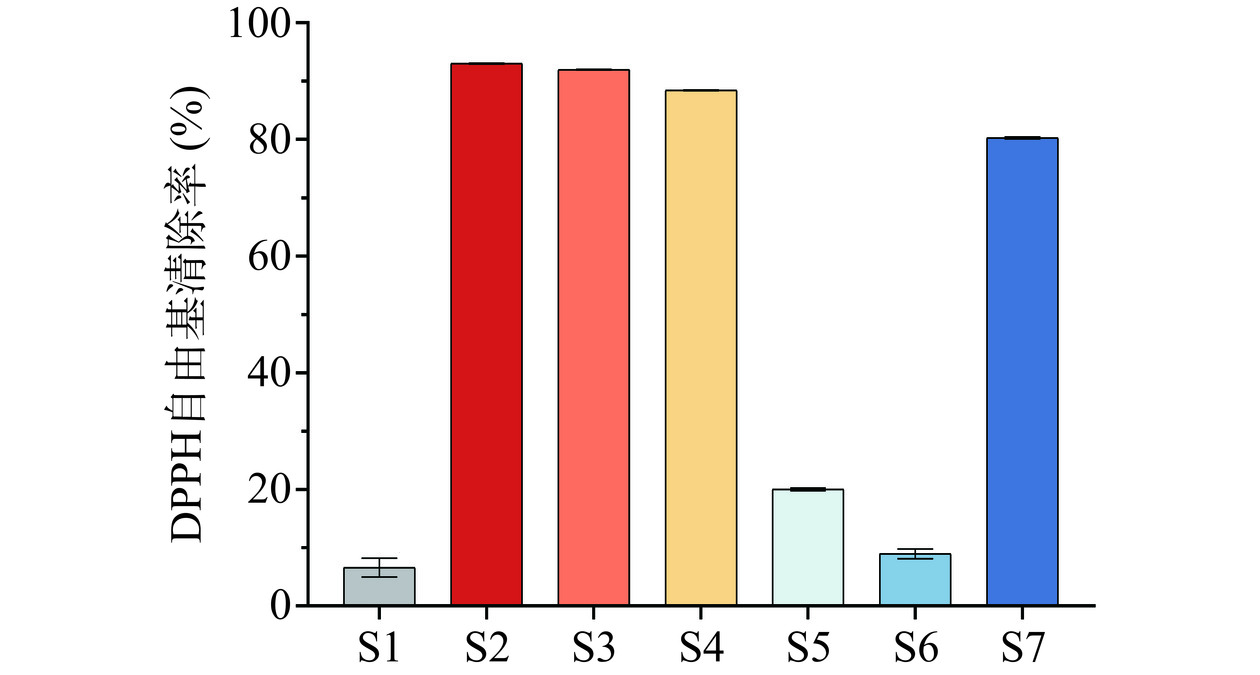
三叶青各洗脱部位及三叶青提取物的DPPH自由基清除率结果如图2所示。三叶青各洗脱部位中,10%、30%、50%、70%、90%、100%乙醇洗脱部位S1~S6的DPPH自由基清除率分别为6.61%、93.04%、91.99%、88.44%、20.05%以及8.94%,而洗脱纯化前的三叶青提取物S7的DPPH自由基清除率为80.29%。结果显示,经大孔树脂洗脱后,三叶青提取物30%乙醇洗脱部位S2的DPPH自由基清除率较三叶青提取物S7提升了12.75%,表明大孔树脂洗脱对三叶青抗氧化活性物质进行了有效的富集和分离。
2.3 三叶青抗氧化谱效关系分析
2.3.1 Pearson相关系数
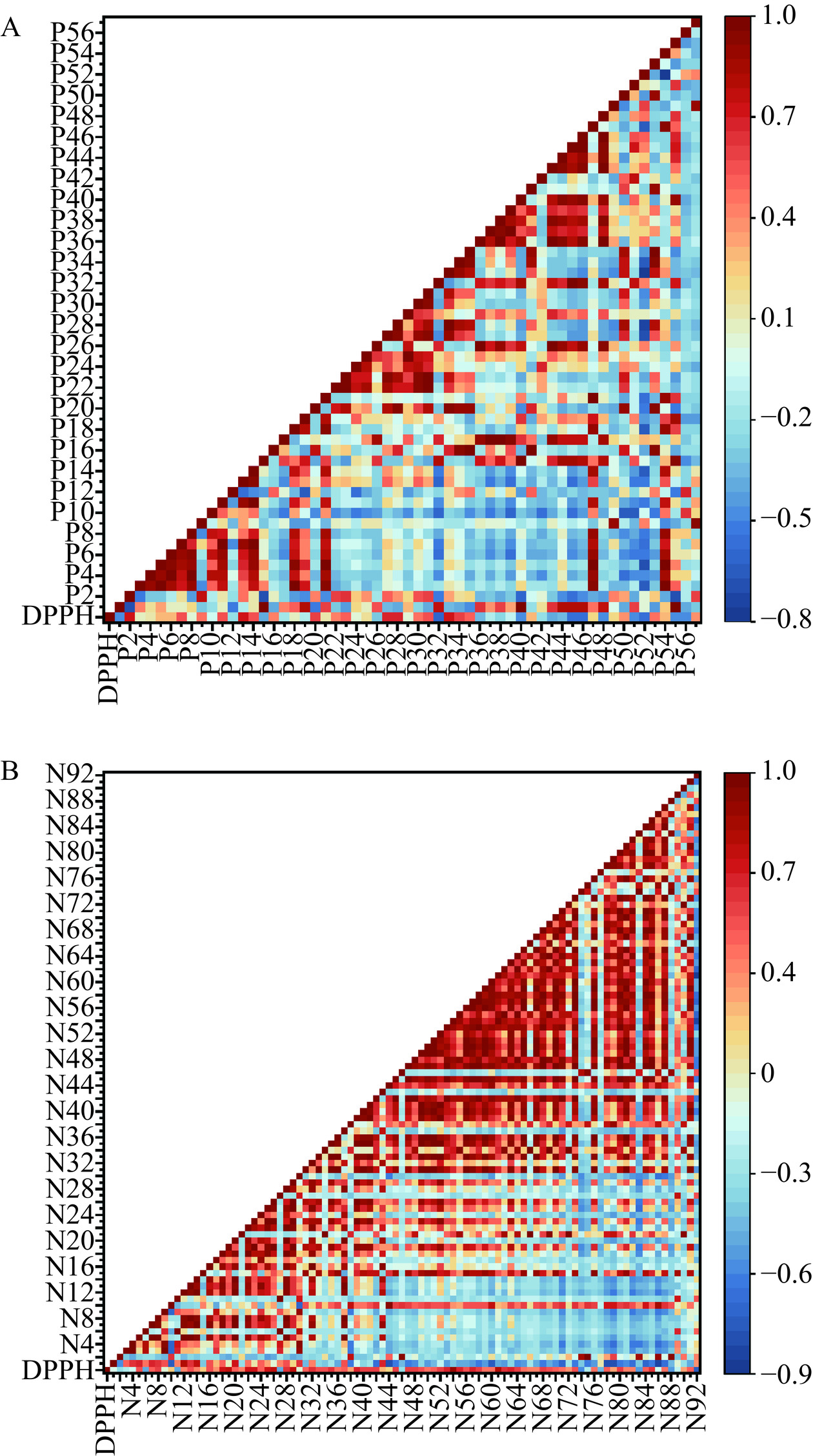
Pearson相关系数是一种统计方法,可以定量地度量变量之间的相关性,广泛应用于谱毒或谱效的相关分析[29−30]。运用Pearson相关系数法,计算得到在正、负离子模式下三叶青提取物各洗脱部位各离子峰之间及其与抗氧化活性指标的相关系数,如表1所示。正离子模式下,得到5个特征峰与抗氧化活性呈显著性正相关(Pearson相关系数>0.6),且相关系数具有显著性(P<0.05),分别为P2、P13、P27、P28、P33,相关系数热图如图3A所示。负离子模式下,得到9个特征峰与抗氧化活性呈显著性正相关(Pearson相关系数>0.6),且相关系数具有显著性(P<0.05),分别为N18、N19、N22、N23、N25、N26、N29、N54、N61,其相关系数热图如图3B所示。在样本量有限的情况下,为避免数据多重共线性和模型过拟合等问题,采用OPLS分析来进一步分析验证特征峰与药效指标的关系。
表 1 正、负离子模式下各离子峰与抗氧化活性的Pearson相关系数分析Table 1. Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of each ion peak with antioxidant activity in positive and negative ion modes峰号 保留时间T(min) 离子模式 Pearson相关系数 P值 P2 0.687 [M+H]+ 0.7 0.04 P13 6.581 [M+H]+ 0.705 0.038 P27 16.577 [M+H]+ 0.682 0.046 P28 16.919 [M+H]+ 0.676 0.048 P33 20.707 [M+H]+ 0.704 0.039 N18 6.005 [M–H]– 0.681 0.046 N19 6.606 [M–H]– 0.757 0.024 N22 7.507 [M–H]– 0.691 0.043 N23 7.764 [M–H]– 0.713 0.036 N25 8.388 [M–H]– 0.686 0.044 N26 8.518 [M–H]– 0.725 0.033 N29 9.117 [M–H]– 0.729 0.032 N54 16.619 [M–H]– 0.872 0.005 N61 20.743 [M–H]– 0.777 0.02 2.3.2 OPLS分析
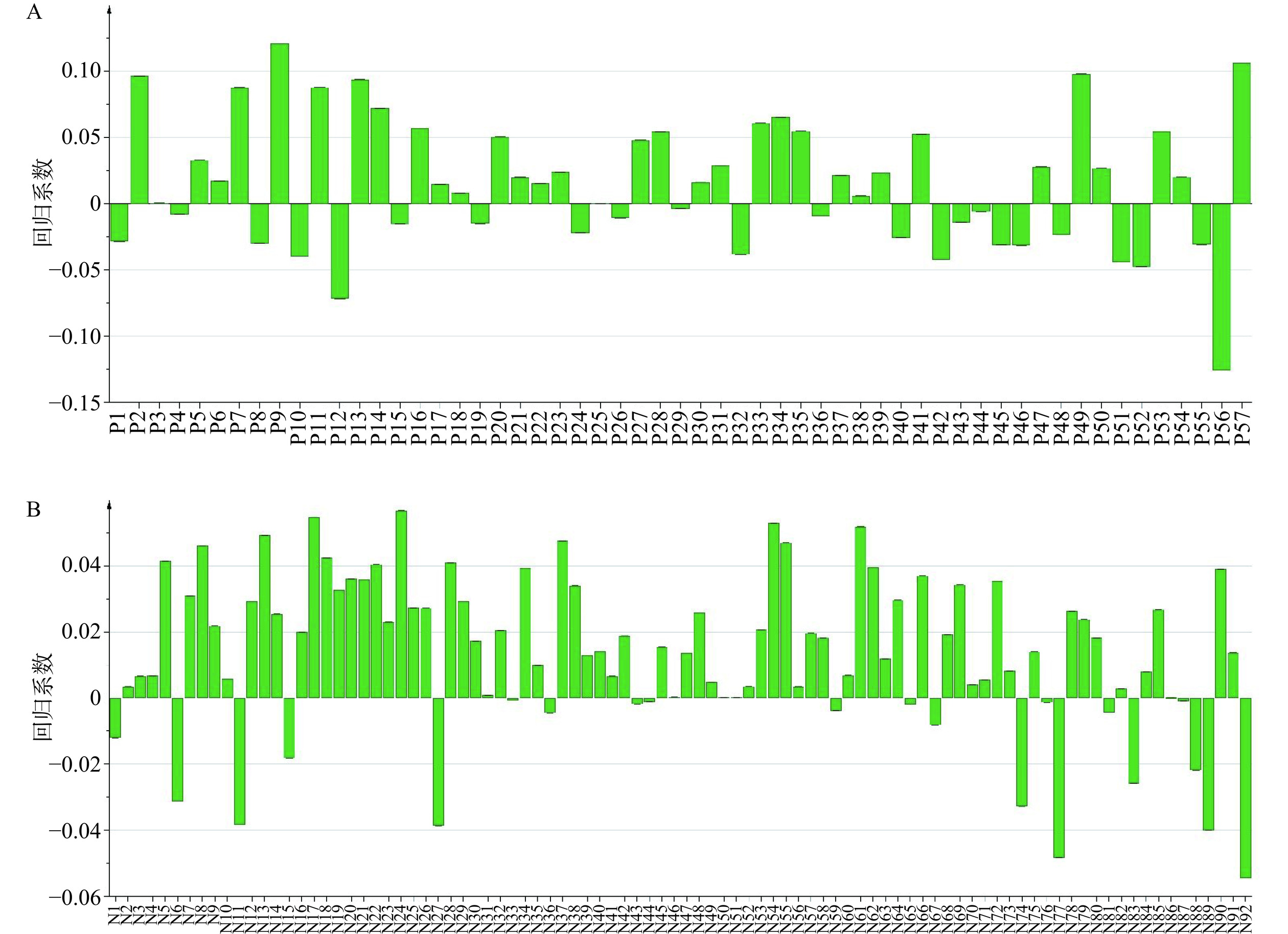
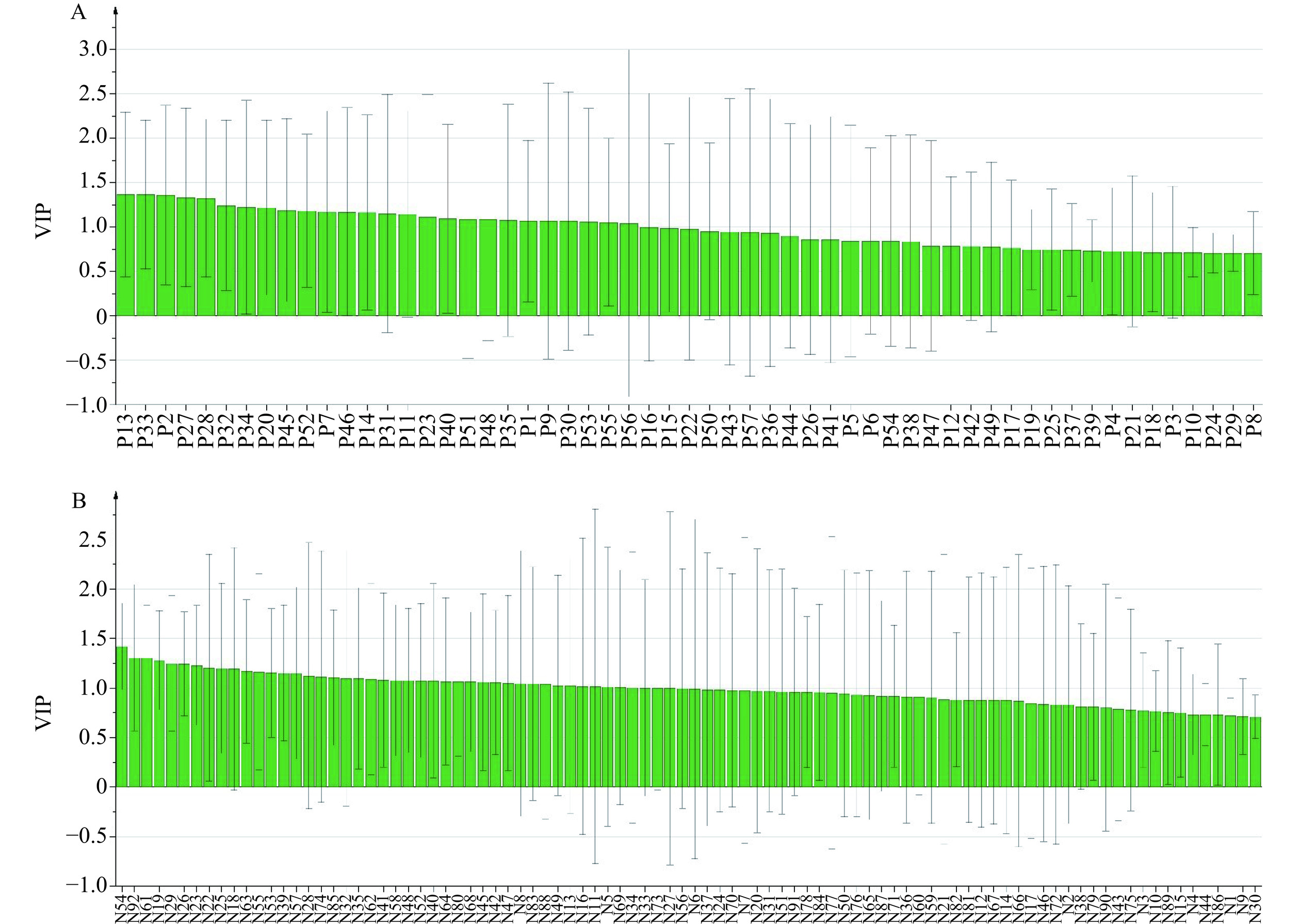
OPLS是一种多因变量对多自变量的回归建模方法,适用于小样本,可以克服多变量共线性的问题,避免数据干扰,提高模型的解释性和预测的可靠性从而使模型变得简单和易于解释[31−32]。在OPLS分析中,回归系数可反映特征峰与活性指标的相关性,回归系数大于0,则表明特征峰与活性指标呈正相关关系,否则反之;变量重要性投影(VIP)值表示特征峰对活性指标的重要程度,当VIP>1时,则表明自变量对因变量有重要影响。由回归系数图4可知,在正离子模式下三叶青提取物各洗脱部位共有34个离子峰与抗氧化活性呈正相关,而在负离子模式下共有71个离子峰与抗氧化活性呈正相关。由图5可知,正离子模式下共有27个离子峰VIP值>1,筛选出其中排名前10的离子峰。结合回归系数图,其中共有7个离子峰满足与抗氧化活性正相关,且VIP>1,分别为P2、P13、P20、P27、P28、P33以及P34。同样负离子模式下共有41离子峰VIP值>1,筛选出其中排名前10且与抗氧化活性呈正相关的离子峰共9个,分别为N18、N19、N22、N23、N25、N26、N29、N54以及N61。
2.3.3 Pearson系数和OPLS联合分析
综合Pearson相关系数和OPLS分析结果,将Pearson相关系数大于0.6且P<0.05的离子峰与OPLS分析中VIP>1且回归系数大于0的离子峰进行整合,选取其中同时满足二者条件的离子峰,得出在正、负离子模式下离子峰P2、P13、P27、P28、P33、N18、N19、N22、N23、N25、N26、N29、N54以及N61与抗氧化活性呈正相关,初步推测该14个峰对应的化合物为三叶青发挥抗氧化活性的质量标志物。
2.4 三叶青抗氧化质量标志物的化学成分鉴定
根据上文1.2.3.3项下数据分析方法,对三叶青发挥抗氧化活性的14个离子峰进行化学成分分析鉴定,推测结果如表2所示。
表 2 三叶青抗氧化质量标志物的化学成分分析鉴定Table 2. Chemical composition analysis and identification of antioxidant quality markers in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum峰号 保留时间T(min) 离子模式 分子式 质荷比(m/z) 分子量 化合物 准分子离子峰 二级碎片离子 P2 0.687 [M+H]+ C8H8O3 153.0321 125、110、81 152.0473 香兰素 P13 6.581 [M+H]+ C15H14O6 291.0860 162、139 290.0790 儿茶素 P27 16.577 [M+H]+ C27H30O16 611.1620 465、304、303 610.1534 芦丁 P28 16.919 [M+H]+ C21H20O12 465.1055 304、303 464.0955 异槲皮苷 P33 20.707 [M+H]+ C27H30O15 595.1691 449、287 594.1585 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 N18 6.005 [M–H]– C30H26O12 577.1373 451、407、289 578.1424 原花青素B N19 6.606 [M–H]– C15H14O6 289.0733 151、125、109 290.0790 儿茶素 N22 7.507 [M–H]– C45H38O18 865.2001 577、407、289 866.2058 原花青素C N23 7.764 [M–H]– − 561.1398 475、289 − 未知 N25 8.388 [M–H]– − 849.2046 720、577、451 − 未知 N26 8.518 [M–H]– − 867.2364 849、720、577 − 未知 N29 9.117 [M–H]– − 849.2046 712、583、447 − 未知 N54 16.619 [M–H– C27H30O16 609.1450 301、300 610.1534 芦丁 N61 20.743 [M–H]– C27H30O15 593.1504 285、284、255 594.1585 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 化合物P2在正离子模式下的母离子m/z 153.0321,母离子脱去1个CO分子得到碎片离子m/z 125,再脱去一个CH3分子得到碎片离子m/z 110,然后再脱去一个CHO分子得到碎片离子m/z 81,结合文献资料[33−34],推测化合物P2为香兰素。化合物P13在正离子模式下的母离子m/z 291.0860,母离子失去2分子C2H2O和1中性分子CO2得到m/z 162,母离子C环的1,3键断裂(1,3A−)得到m/z 139,结合文献资料[35−36],推测化合物P13为儿茶素。化合物P27在正离子模式的母离子m/z 611.1620,母离子脱去1分子鼠李糖产生碎片离子m/z 465,再脱去1分子葡萄糖得到特征碎片离子m/z 304,再脱去1个H得到特征碎片m/z 303,结合文献资料[37],推测化合物P27为芦丁。化合物P28在正离子模式下的母离子m/z 465.1055,母离子糖苷键断裂后失去1分子葡萄糖苷得到2个特征碎片离子m/z 304和303,结合文献资料[38],推测化合物P28为异槲皮苷。化合物P33在正离子模式下的母离子m/z 595.1691,母离子失去1分子鼠李糖苷得到碎片离子m/z 449,母离子失去1分子C12H20O9得到特征离子碎片m/z 287,结合文献资料[39−40],推测化学成分P33为山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷。
化合物N18在负离子模式下的母离子m/z 577.1373,母离子开环脱去3分子C2H2O得到碎片离子m/z 451,再经过RDA反应并脱去1分子H2O后得到特征碎片离子m/z 407,母离子C4-C8键断裂脱去1分子儿茶素即特征碎片离子m/z 289,结合文献资料[36,41],推测化合物N18为原花青素B。化合物N19在负离子模式下的母离子m/z 289.0733,母离子经RDA裂解产生碎片离子m/z 151和m/z 109,母离子发生分子内断裂失去1分子C9H12O7得到特征碎片离子m/z 125,结合文献资料[42−43],推测化合物N18为儿茶素。化合物N22在负离子模式下的母离子m/z 865.2001,母离子脱去1分子儿茶素分别得到碎片离子m/z 289和m/z 577,碎片离子m/z 577发生RDA反应再脱去1分子H2O后得到特征碎片离子m/z 407,结合文献资料[36,44],推测化合物N22为原花青素C。化合物N54在负离子模式下的母离子m/z 609.1450,母离子失去1分子葡萄糖、1分子鼠李糖产生特征离子碎片m/z 301,再脱去1个H得到特征离子碎片m/z 300,结合文献资料[45],推测化合物N54为芦丁。化合物N61在负离子模式下的母离子m/z 593.1504,母离子脱去1分子C12H20O9得到特征碎片离子m/z 285,再脱去1个H得到碎片离子m/z 284,碎片离子m/z 285再脱去1分子CH2O得到碎片离子m/z 255,结合文献资料[40],推测化合物N61为山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷。
经UPLC-UPLC-Q-TOF-MS定性分析,鉴定出其中10种化学成分,多为黄酮类成分,分别为香兰素[46](P2)、儿茶素[47](P13、N19)、芦丁[47−48](P27、N54)、异槲皮苷[49](P28)、山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷[50](P33、N61)、原花青素B[51](N18)以及原花青素C[52](N22),以上鉴定出的化学成分抗氧化功效与文献报道一致。
3. 结论
本研究利用UPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术建立三叶青提取物及各大孔树脂洗脱部位的正、负离子模式指纹图谱,综合Pearson相关系数与OPLS分析对其抗氧化谱效关系进行研究,将Pearson相关系数大于0.6且P<0.05的离子峰与OPLS分析中VIP>1且回归系数大于0的离子峰进行整合,推测出与抗氧化活性相关的离子峰共14个,分别为P2、P13、P27、P28、P33、N18、N19、N22、N23、N25、N26、N29、N54以及N61。经分析鉴定出其中10种化学成分,分别为香兰素(P2)、儿茶素(P13、N19)、芦丁(P27、N54)、异槲皮苷(P28)、山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷(P33、N61)、原花青素B(N18)以及原花青素C(N22)。本研究首次基于谱效关系分析挖掘三叶青抗氧化活性的质量标志物,但本研究中抗氧化指标仍待完善,无法综合全面评价三叶青的抗氧化作用,且目前只指认部分质量标志物离子峰,因此,后续会进一步探究三叶青中发挥抗氧化活性的质量标志物。
综上所述,本研究发现三叶青的抗氧化活性主要源于黄酮类物质,并指认出香兰素、儿茶素、芦丁、异槲皮苷、山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷、原花青素B以及原花青素C为三叶青抗氧化活性的质量标志物,为三叶青抗氧化活性质量标志物的确定和质量标准的制定提供了参考依据。
-
表 1 正、负离子模式下各离子峰与抗氧化活性的Pearson相关系数分析
Table 1 Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of each ion peak with antioxidant activity in positive and negative ion modes
峰号 保留时间T(min) 离子模式 Pearson相关系数 P值 P2 0.687 [M+H]+ 0.7 0.04 P13 6.581 [M+H]+ 0.705 0.038 P27 16.577 [M+H]+ 0.682 0.046 P28 16.919 [M+H]+ 0.676 0.048 P33 20.707 [M+H]+ 0.704 0.039 N18 6.005 [M–H]– 0.681 0.046 N19 6.606 [M–H]– 0.757 0.024 N22 7.507 [M–H]– 0.691 0.043 N23 7.764 [M–H]– 0.713 0.036 N25 8.388 [M–H]– 0.686 0.044 N26 8.518 [M–H]– 0.725 0.033 N29 9.117 [M–H]– 0.729 0.032 N54 16.619 [M–H]– 0.872 0.005 N61 20.743 [M–H]– 0.777 0.02 表 2 三叶青抗氧化质量标志物的化学成分分析鉴定
Table 2 Chemical composition analysis and identification of antioxidant quality markers in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum
峰号 保留时间T(min) 离子模式 分子式 质荷比(m/z) 分子量 化合物 准分子离子峰 二级碎片离子 P2 0.687 [M+H]+ C8H8O3 153.0321 125、110、81 152.0473 香兰素 P13 6.581 [M+H]+ C15H14O6 291.0860 162、139 290.0790 儿茶素 P27 16.577 [M+H]+ C27H30O16 611.1620 465、304、303 610.1534 芦丁 P28 16.919 [M+H]+ C21H20O12 465.1055 304、303 464.0955 异槲皮苷 P33 20.707 [M+H]+ C27H30O15 595.1691 449、287 594.1585 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 N18 6.005 [M–H]– C30H26O12 577.1373 451、407、289 578.1424 原花青素B N19 6.606 [M–H]– C15H14O6 289.0733 151、125、109 290.0790 儿茶素 N22 7.507 [M–H]– C45H38O18 865.2001 577、407、289 866.2058 原花青素C N23 7.764 [M–H]– − 561.1398 475、289 − 未知 N25 8.388 [M–H]– − 849.2046 720、577、451 − 未知 N26 8.518 [M–H]– − 867.2364 849、720、577 − 未知 N29 9.117 [M–H]– − 849.2046 712、583、447 − 未知 N54 16.619 [M–H– C27H30O16 609.1450 301、300 610.1534 芦丁 N61 20.743 [M–H]– C27H30O15 593.1504 285、284、255 594.1585 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 -
[1] HU W, ZHENG Y, XIA P, et al. The research progresses and future prospects of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum:A valuable Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,271:113836. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113836
[2] 陈海杰, 周永逸, 薛佳, 等. 基于UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS技术分析三叶崖爬藤不同部位的多元活性成分[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2023,35(8):1322−1337,1363. [CHEN H J, ZHOU Y Y, XUE J, et al. Analysis of multiple active constituents in different parts of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg based on UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2023,35(8):1322−1337,1363.] CHEN H J, ZHOU Y Y, XUE J, et al. Analysis of multiple active constituents in different parts of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg based on UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2023, 35(8): 1322−1337,1363.
[3] BAI Y, JIANG L, LI Z, et al. Flavonoid metabolism in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg based on metabolome analysis and transcriptome sequencing[J]. Molecules,2022,28(1):83. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010083
[4] 徐志杰, 黄子洳, 马方芳, 等. 响应面法优化三叶青总黄酮提取工艺及不同产地三叶青的质量评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(6):158−167. [XU Z J, HUANG Z R, MA F F, et al. Optimization of total favonoids extraction process of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and its quality evaluation from different origins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(6):158−167.] XU Z J, HUANG Z R, MA F F, et al. Optimization of total favonoids extraction process of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and its quality evaluation from different origins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(6): 158−167.
[5] WANG B, LIN Y, ZHOU M, et al. Polysaccharides from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating TLR4/COX-2/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2022,155:113755. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113755
[6] SUN Y, LI H, HU J, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolics in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(44):10507−10515. doi: 10.1021/jf4037547
[7] SUN L, LU J J, WANG B X, et al. Polysaccharides from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum:Optimum extraction, monosaccharide compositions, and antioxidant activity[J]. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology,2022,52(4):383−393. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2021.1952600
[8] 吴舟涛, 朱玲燕, 吴学谦, 等. 三叶青化学成分和抗肿瘤作用研究进展[J]. 中南药学,2017,15(3):319−324. [WU Z T, ZHU L Y, WU X Q, et al. Research progress in the chemical compositions and anti-tumor effect of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2017,15(3):319−324.] doi: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2017.03.015 WU Z T, ZHU L Y, WU X Q, et al. Research progress in the chemical compositions and anti-tumor effect of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2017, 15(3): 319−324. doi: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2017.03.015
[9] WEI C, ZHAO Y, JI T, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 identified as the target protein in the antitumor activity of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Frontiers in Oncology,2022,12:865409. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.865409
[10] 汪传宝, 陈静文, 王可, 等. 仿野生种植三叶青不同部位总黄酮分析及其抗炎、抗氧化能力比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):321−329. [WANG C B, CHEN J W, WANG K, et al. Analysis of total flavonoids in different parts of wild planting Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and comparison of their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(6):321−329.] WANG C B, CHEN J W, WANG K, et al. Analysis of total flavonoids in different parts of wild planting Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and comparison of their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(6): 321−329.
[11] WANG C Y, JANG H J, HAN Y K, et al. Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells[J]. Molecules,2018,23(6):1445. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061445
[12] 程晓阳, 廖明, 何全光, 等. 三叶青超微粉对酒精性肝损伤大鼠肠道菌群的调节作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(18):415−424. [CHENG X Y, LIAO M, HE Q G, et al. Effects of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum superfine powder on intestinal microflora in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(18):415−424.] CHENG X Y, LIAO M, HE Q G, et al. Effects of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum superfine powder on intestinal microflora in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(18): 415−424.
[13] KRISHNA T P A, MAHARAJAN T, KRISHNA T P A, et al. Insights into metabolic engineering of bioactive molecules in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels & Gilg:A traditional medicinal herb[J]. Current Genomics,2023,24(2):72−83. doi: 10.2174/0113892029251472230921053135
[14] 伍婷, 李振斌, 杜家会, 等. 三叶青质量控制方法研究进展[J]. 中国民族民间医药,2023,32(10):49−54. [WU T, LI Z B, DU J H, et al. Research progress on quality control methods of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy,2023,32(10):49−54.] WU T, LI Z B, DU J H, et al. Research progress on quality control methods of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2023, 32(10): 49−54.
[15] 李兆慧, 师砚首, 喻晓雁, 等. 三叶青黄酮的提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 中南药学,2023,21(8):2035−2040. [LI Z H, SHI Y S, YU X Y, et al. Optimization of extraction of flavonoids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and its antioxidant activities[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2023,21(8):2035−2040.] LI Z H, SHI Y S, YU X Y, et al. Optimization of extraction of flavonoids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and its antioxidant activities[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2023, 21(8): 2035−2040.
[16] 李鹤, 陈伟东. 不同产地三叶青HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 中药材,2021,44(12):2896−2898. [LI H, CHEN W D. Study on the HPLC fingerprints of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum from different origins[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2021,44(12):2896−2898.] LI H, CHEN W D. Study on the HPLC fingerprints of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum from different origins[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2021, 44(12): 2896−2898.
[17] 赵文菊, 朱勇, 鲁正学. 三叶青多糖增强Lewis肺癌小鼠抗肿瘤免疫反应[J]. 中国肺癌杂志,2023,26(8):559−571. [ZHAO W J, ZHU Y, LU Z X. Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyanum promotes antitumor immune response in Lewis lung cancer mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer,2023,26(8):559−571.] doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.106.16 ZHAO W J, ZHU Y, LU Z X. Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyanum promotes antitumor immune response in Lewis lung cancer mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer, 2023, 26(8): 559−571. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.106.16
[18] 杨锡金, 王艳, 陈梓瀚, 等. 基于HPLC-ECD研究景天三七抗氧化活性的谱效关系[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(16):15−24. [YANG X J, WANG Y, CHEN Z H, et al. Study on the spectrum effect relationship of antioxidant activity of Sedum aizoon L. based on HPLC-ECD[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(16):15−24.] YANG X J, WANG Y, CHEN Z H, et al. Study on the spectrum effect relationship of antioxidant activity of Sedum aizoon L. based on HPLC-ECD[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(16): 15−24.
[19] 李东辉, 吴红伟, 李国峰, 等. 大黄总多酚、总蒽醌含量测定及体外抗氧化作用的谱效关系研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(4):541−552. [LI D H, WU H W, LI G F, et al. Study on content of total polyphenols and total anthraquinones in rhubarb and its spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation in vitro[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(4):541−552.] LI D H, WU H W, LI G F, et al. Study on content of total polyphenols and total anthraquinones in rhubarb and its spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation in vitro[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(4): 541−552.
[20] 刘翰飞. 刺梨抗氧化抑菌作用的谱效关系研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学, 2021. [LIU H F. Study on the spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation and bacteriostasis of Rose roxburghii[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou University, 2021.] LIU H F. Study on the spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation and bacteriostasis of Rose roxburghii[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2021.
[21] 何志贵, 徐祥林, 崔莹莹, 等. 三叶青原花青素纯化工艺及抗氧化、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(6):178−185. [HE Z G, XU X L, CUI Y Y, et al. Study on purification process and antioxidative activity and α-glucosidas inhibitory activity of proanthocyanidins from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(6):178−185.] HE Z G, XU X L, CUI Y Y, et al. Study on purification process and antioxidative activity and α-glucosidas inhibitory activity of proanthocyanidins from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(6): 178−185.
[22] 许海顺, 吴学谦, 熊科辉, 等. 三叶青不同洗脱组分的抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2015,33(8):1968−1971,2068. [XU H X, WU X Q, XIONG K H, et al. Antioxidant activity of different elution fractions from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,33(8):1968−1971,2068.] XU H X, WU X Q, XIONG K H, et al. Antioxidant activity of different elution fractions from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 33(8): 1968−1971,2068.
[23] 王昱涵, 王志萍, 谢谭芳, 等. UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS技术在中药及中药复方制剂研究中的应用[J]. 中国药师,2022,25(1):114−118. [WANG Y H, WANG Z P, XIE T F, et al. Application of UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technique to the study of tradition Chinese medicine and herbal compound preparations[J]. China Pharmacist,2022,25(1):114−118.] WANG Y H, WANG Z P, XIE T F, et al. Application of UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technique to the study of tradition Chinese medicine and herbal compound preparations[J]. China Pharmacist, 2022, 25(1): 114−118.
[24] ZHANG L, SHEN H, XU J, et al. UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS-guided isolation and purification of sulfur-containing derivatives from sulfur-fumigated edible herbs, a case study on ginseng[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,246:202−210. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.151
[25] ZHU R, XU X, YING J, et al. The phytochemistry, pharmacology, and quality control of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels & Gilg in China:A review[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020,11:550497. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.550497
[26] LUO Y, YANG Y, YANG X, et al. Quality evaluation of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum different parts based on quantitative analysis of 42 bioactive constituents combined with multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Phytochemical Analysis,2022,33(5):754−765. doi: 10.1002/pca.3127
[27] GUO Z, CHEN L, LIANG X. Components research on Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg:Identification and effect of drying methods on the content of ten main constituents by targeting metabolomics method[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2023,229:115375. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115375
[28] 郭其洪, 李兴丽, 范江平, 等. 辣木籽抗氧化肽的分离鉴定及其稳定性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):41−47. [GUO Q H, LI X L, FANG J P, et al. Isolation, identification and stability analysis of antioxidant peptides from Moringa oleifera seeds[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):41−47.] GUO Q H, LI X L, FANG J P, et al. Isolation, identification and stability analysis of antioxidant peptides from Moringa oleifera seeds[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(5): 41−47.
[29] LI Y, YANG Y, KANG X, et al. Study on the anti-inflammatory effects of Callicarpa nudiflora based on the spectrum-effect relationship[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2022,12:806808. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.806808
[30] SHI J W, LI Z Z, WU J S, et al. Identification of the bioactive components of Banxia Xiexin decoction that protect against CPT-11-induced intestinal toxicity via UPLC-based spectrum-effect relationship analyses[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,266:113421. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113421
[31] QI J, ZHANG Q, LI L, et al. Spectrum-effect relationship between UPLC-Q-TOF-MS fingerprint and anti-AUB effect of Clinopodium chinense (Benth.) O. Kuntze[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2022,217:114828. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114828
[32] WUBULI A, ABDULLA R, ZANG D, et al. Spectrum-effect relationship between UPLC fingerprints and melanogenic effect of Ruta graveolens L[J]. Journal of Chromatography B-analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences,2023,1221:123683. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2023.123683
[33] 钟洪祥, 王素方, 蔡继宝, 等. 香兰素的热解研究[J]. 烟草科技,2004(7):22−26. [ZHONG H X, WANG S F, CAI J B, et al. Study on pyrolysis of vanillin[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology,2004(7):22−26.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2004.07.009 ZHONG H X, WANG S F, CAI J B, et al. Study on pyrolysis of vanillin[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 2004(7): 22−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2004.07.009
[34] 宁霄, 何欢, 金绍明, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定食品中麦芽酚、乙基麦芽酚、香兰素、甲基香兰素和乙基香兰素[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2017,8(7):2555−2562. [NING X, HE H, JIN S M, et al. Simultaneous determination of vanillin, methyl vanillin, ethyl vanillin, maltol and ethyl maltol in foods by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2017,8(7):2555−2562.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.07.028 NING X, HE H, JIN S M, et al. Simultaneous determination of vanillin, methyl vanillin, ethyl vanillin, maltol and ethyl maltol in foods by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(7): 2555−2562. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.07.028
[35] 沈淑双. 鸡树条荚蒾药用部位化学成分分析[D]. 佳木斯:佳木斯大学, 2023. [SHEN S S. Analysis of chemical constituents of medicinal parts of Viburnum sargentii[D]. Jiamusi:Jiamusi University, 2023.] SHEN S S. Analysis of chemical constituents of medicinal parts of Viburnum sargentii[D]. Jiamusi: Jiamusi University, 2023.
[36] 王晴, 卢志威, 刘月红, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF/MSE结合诊断离子过滤方法快速分析大黄中酚类成分[J]. 中国中药杂志,2017,42(10):1922−1931. [WANG Q, LU Z W, LIU Y H, et al. Rapid analysis on phenolic compounds in Rheum palmatum based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MSE combined with diagnostic ions filter[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2017,42(10):1922−1931.] WANG Q, LU Z W, LIU Y H, et al. Rapid analysis on phenolic compounds in Rheum palmatum based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MSE combined with diagnostic ions filter[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(10): 1922−1931.
[37] 李晓, 石慧, 丁晶鑫, 等. 不同基原八爪金龙药材中黄酮、香豆素类化学成分分析[J]. 中国药房,2021,32(4):443−452. [LI X, SHI H, DING J X, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents as flavonoids and coumarins in Radix Ardisiae from different sources[J]. China Pharmacy,2021,32(4):443−452.] doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.04.10 LI X, SHI H, DING J X, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents as flavonoids and coumarins in Radix Ardisiae from different sources[J]. China Pharmacy, 2021, 32(4): 443−452. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.04.10
[38] YASIR M, SULTANA B, ANWAR F. LC-ESI-MS/MS based characterization of phenolic components in fruits of two species of Solanaceae[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55(7):2370−2376. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2702-9
[39] CAO J, XIA X, DAI X, et al. Chemical composition and bioactivities of flavonoids-rich extract from Davallia cylindrica Ching[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol,2014,37(2):571−579. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.01.011
[40] 沈瑶, 黄思红, 刘依茹, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS分析覆盆子不同部位的化学成分及其9种成分含量的快速测定[J]. 中草药,2023,54(15):4789−4803. [SHEN Y, HUANG S H, LIU Y R, et al. Analysis of chemical components in different parts of Rubus chingii and rapid determination of its nine main components by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2023,54(15):4789−4803.] SHEN Y, HUANG S H, LIU Y R, et al. Analysis of chemical components in different parts of Rubus chingii and rapid determination of its nine main components by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2023, 54(15): 4789−4803.
[41] 李开敏, 刘育辰, 刘刚, 等. 血人参中化学成分鉴定及其保肝活性研究[J]. 中成药,2023,45(11):3826−3833. [LI K M, LIU Y C, LIU G, et al. Identification of chemical components in Indigofera stachyodes and their hepatoprotective activities[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2023,45(11):3826−3833.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.11.056 LI K M, LIU Y C, LIU G, et al. Identification of chemical components in Indigofera stachyodes and their hepatoprotective activities[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2023, 45(11): 3826−3833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.11.056
[42] 蔡定吉. 岩白菜的化学成分及COX-2抑制活性研究[D]. 南昌:江西中医药大学, 2023. [CAI D J. Chemical constituents and COX-2 inhibitory activity of Bergenia purpurascens[D]. Nanchang:Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2023.] CAI D J. Chemical constituents and COX-2 inhibitory activity of Bergenia purpurascens[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2023.
[43] 杨祖凡, 王倩, 赵晴, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS技术的沙棘黄酮类成分分析[J]. 化学试剂,2024,46(2):95−106. [YANG Z F, WANG Q, ZHAO Q, et al. Identification and characterization of flavonoid compounds from Hippophae rhamnoides L. by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS[J]. Chemical Reagents,2024,46(2):95−106.] YANG Z F, WANG Q, ZHAO Q, et al. Identification and characterization of flavonoid compounds from Hippophae rhamnoides L. by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2024, 46(2): 95−106.
[44] 翁倩倩, 杨滨, 李斌, 等. 瓜拉纳化学成分的UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(15):68−75. [WENG Q Q, YANG B, LI B, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in Paullinia cupana dried seeds by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2021,27(15):68−75.] WENG Q Q, YANG B, LI B, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in Paullinia cupana dried seeds by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2021, 27(15): 68−75.
[45] 陆石英, 王海波, 袁光蔚, 等. UPLC-Q-Exactive技术分析民族药石笔木化学成分[J]. 中国新药杂志,2019,28(16):2032−2039. [LU S Y, WANG H B, YUAN G W, et al. Study on chemical constituents of Tutcheria championi Nakai by UPLC-Q-Exactive[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs,2019,28(16):2032−2039.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2019.16.018 LU S Y, WANG H B, YUAN G W, et al. Study on chemical constituents of Tutcheria championi Nakai by UPLC-Q-Exactive[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2019, 28(16): 2032−2039. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2019.16.018
[46] 杨庆明, 丁兰, 杨红, 等. 食用香料——香兰素的抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2007(1):85−88. [YANG Q M, DING L, YANG H, et al. Study on the antioxidant effect of vanillin in in vitro experiment[J]. Food Research and Development,2007(1):85−88.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2007.01.026 YANG Q M, DING L, YANG H, et al. Study on the antioxidant effect of vanillin in in vitro experiment[J]. Food Research and Development, 2007(1): 85−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2007.01.026
[47] 刘长梅, 陈悦鸣, 胡煜. 不同茶叶中儿茶素、芦丁含量和抗氧化性效果研究[J]. 中国卫生工程学,2022,21(3):453−455,458. [LIU C M, CHEN Y M, HU Y. Study on the content and antioxidant effects of catechins and rutin in different teas[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health Engineering,2022,21(3):453−455,458.] LIU C M, CHEN Y M, HU Y. Study on the content and antioxidant effects of catechins and rutin in different teas[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health Engineering, 2022, 21(3): 453−455,458.
[48] 郑妍, 秦梦洋, 岳松烨, 等. 苦荞麦芦丁提取工艺及抗氧化评价[J]. 食品安全导刊,2023(24):148−150,155. [ZHENG Y, QIN M Y, YUE S Y, et al. Extraction technology and antioxidant evaluation of rutin from tartary buckwheat[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2023(24):148−150,155.] ZHENG Y, QIN M Y, YUE S Y, et al. Extraction technology and antioxidant evaluation of rutin from tartary buckwheat[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2023(24): 148−150,155.
[49] AHMAD R, AHMAD N, NAQVI A A, et al. Antioxidant and antiglycating constituents from leaves of Ziziphus oxyphylla and Cedrela serrata[J]. Antioxidants,2016,5(1):9. doi: 10.3390/antiox5010009
[50] WANG J, FANG X, GE L, et al. Antitumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of kaempferol and its corresponding glycosides and the enzymatic preparation of kaempferol[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(5):e0197563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197563
[51] 洪苏贞. 雷公藤临床应用文献研究与不同产地原花青素萃取分析及抗氧化作用[D]. 杭州:浙江中医药大学, 2022. [HONG S Z. The clinical literature review, procyanidins extraction methods development and antioxidant activity evaluation in Tripterygium wilforsii Hook. F[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 2022.] HONG S Z. The clinical literature review, procyanidins extraction methods development and antioxidant activity evaluation in Tripterygium wilforsii Hook. F[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 2022.
[52] SONG J H, LEE H J, KANG K S. Procyanidin C1 activates the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway to prevent glutamate-induced apoptotic HT22 cell death[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(1):142. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010142
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 杨敏,张密,叶贤胜,曾长立,马爱民,牛蒙亮,许丹云. 大球盖菇多肽的制备、抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性的研究. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 123-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏磊,景炳年,李宁洁,金饶,谢晓阳,刘雨晴,马艳妮,梁雅辉,王韬,王伟. 赤松茸乙醇提取物不同萃取相生物活性对比. 食品研究与开发. 2025(04): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王小平,刘忠莹,钟洋,张定秋,陆阳,朱敏敏,郑红毅,何叶馨,王鑫,黄韬睿,江祖彬. 基于离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析木耳、香菇、松茸和茶树菇中砷形态分布. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 韦菡燕,蒋军文. 等离子体对松茸多糖抗疲劳作用的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(10): 128-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄磊,何春梅,司灿,石鸿宇,段俊. 大球盖菇栽培研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2023(03): 8-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 魏磊,王伟,谢晓阳,周雍,刘雨晴,马艳妮,宁二娟,王韬,李宁洁,景炳年. 响应面优化博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺及其抑菌和抗氧化活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(15): 213-220 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 曹燕妮,华蓉,邓雅元,王娟,游金坤. 食用菌中维生素测定方法研究. 中国食用菌. 2022(09): 44-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



