AlphaLISA Detection Method for Quinolone Residues in Milk
-
摘要: 本文旨在建立一种可检测牛奶中喹诺酮类药物(Quinolones,QNS)残留的均相光激化学发光免疫分析方法(Amplifiedluminescent proximity homogeneous assay linkedimmune sorbent assay,AlphaLISA)。采用EDC/NHS活泼酯法在诺氟沙星分子连接6-氨基己酸作为间隔臂,制备生物素修饰诺氟沙星半抗原(Biotin-6AS-NOR),并在受体微球上偶联QNS单克隆抗体,Biotin-6AS-NOR可与牛奶样品中的QNS竞争结合喹诺酮抗体;通过优化受体微球的QNS抗体偶联量,Biotin-6AS-NOR及供/受体微球的用量等参数,以及牛奶样品的稀释方案,建立了牛奶中QNS残留的AlphaLISA检测方法。采用1:5牛奶样品稀释方案,所建立牛奶中QNS残留的AlphaLISA检测方法的检出限和定量限分别为0.19 ng/mL和0.46 ng/mL,回收率在85.97%~110.11%之间,日内和日间变异系数均小于10%,与诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星、环丙沙星、氧氟沙星、培氟沙星、达氟沙星和洛美沙星的交叉反应率均高于70%。本研究所建立AlphaLISA检测方法具有灵敏度和准确度高、重复性好等优点,且在整个检测过程中不需要繁琐洗涤操作,具有较高的应用和推广价值。Abstract: This article aimed to establish an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay linked immune sorbent assay (AlphaLISA) for detecting quinolones (QNS) residues in milk. The EDC/NHS active ester method was used to connect 6-aminocaproic acid as the spacer arm on the norfloxacin molecule to prepare biotin-modified norfloxacin hapten (Biotin-6AS-NOR), and QNS monoclonal antibody was coupled on the receptor microsphere. Biotin-6AS-NOR could compete with QNS in the sample to bind quinolone antibodies. A competitive indirect AlphaLISA for QNS residues in milk was established by optimizing the parameters including QNS antibody coupling amount on receptor microspheres, Biotin-6AS-NOR, the dosage of donor/receptor microspheres, and dilution schemes for milk samples. By using the 1:5 milk sample dilution scheme, the limit of detection and the limit of quantification of the established AlphaLISA for QNS in milk were 0.19 ng/mL and 0.46 ng/mL, respectively. The recovery values ranged from 85.97% and 110.11%, and the intraday and interday variation were both less than 10%. The cross-reactivity values for norfloxacin, enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, pefloxacin, ofloxacin, and lomefloxacin were all higher than 70%. In conclusion, the established AlphaLISA showed high sensitivity, accuracy and good repeatability, without the need of tedious wash steps throughout the detection process; therefore, it is easy to achieve automated detection of chemical hazards residue in milk and has high application and promotion value.
-
Keywords:
- quinolones /
- hapten /
- biotin /
- AlphaLISA
-
近年来,抗生素在食品动物养殖过程中的滥用引起了全球范围内对其残留危害的关注[1−4]。2000~2015年,全球抗生素的使用增加了65%,预计到2030年将增加至200%,达到每日1280亿剂[5−7]。喹诺酮类药物是一种人工合成的广谱抗菌药物,包括氧氟沙星、双氟沙星、环丙沙星等,对革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性菌均具有杀菌作用[8−9],具有抗菌能力强,价格低廉、给药方便等优点[10−13]。喹诺酮类药物超剂量或者不按休药期使用,会导致该类药物在动物源食品中的残留[14−16];长期摄入喹诺酮类药物可能会引起轻度胃肠道刺激或不适,出现头痛、头晕、睡眠不良等症状,严重时可能造成肝损害[17−18];不仅如此,药物滥用还会引起细菌耐药性、生态环境污染等问题[19−20]。喹诺酮类药物的不规范使用会对细菌产生选择性压力,导致耐药菌的产生和扩散,进而通过食物链传播,对人类健康构成威胁[21−24]。针对上述危害,我国GB 31650-2019《食品安全国家标准 食品中兽药最大残留限量》中规定了肉、奶等食品动物中喹诺酮类药物的最大残留限量为100 μg/kg[25]。
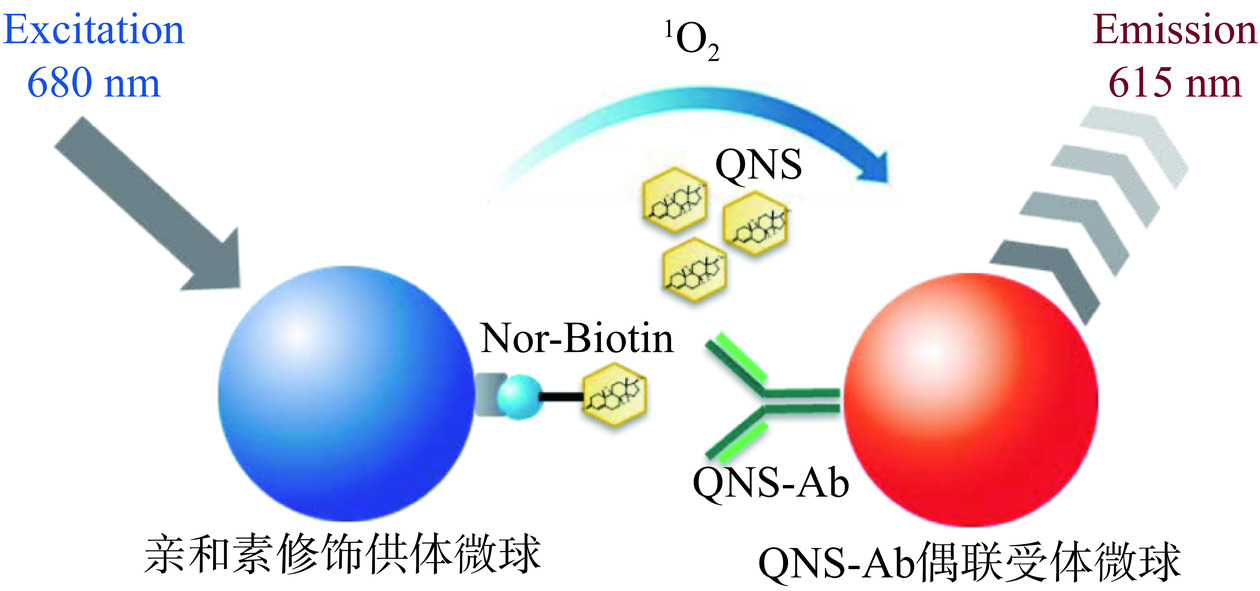
均相光激化学发光免疫分析方法(Amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay linked immune sorbent assay,AlphaLISA)基于近距离能量共振转移的原理,通过抗原和抗体的相互作用形成供体微珠-抗原-抗体-受体微珠复合物,在680 nm波长处的激光作用下发生荧光共振能量转移,产生了一个可检测的615 nm波长信号[26];与传统免疫检测方法相比,AlphaLISA具有均相反应、免洗涤、灵敏度高、操作简便等优点。本文基于偶联喹诺酮抗体的受体微球、Nor-biotin和亲和素修饰的供体微球开展牛奶样品中喹诺酮类药物的AlphaLISA检测方法研究。当样品中无QNS存在时,受体微球上的抗体特异性识别/结合Nor-biotin,然后供体微球通过亲和素-biotin作用与受体微球相互接近。在680 nm激光照射下,供体微球上的光敏剂将周围环境中的氧气转化为单体氧,单体氧扩散至受体微球,并与其上的化学发光剂反应、激活受体微球的荧光基团,使之发出波长520~620 nm荧光。单体氧的半衰期大概4 μs,在溶液中的扩散距离约为200 nm。若样品中存在QNS时,QNS与Nor-biotin竞争性地识别/结合受体微球,从而使得部分受体微球和供体微球无法相互靠近,激光照射产生的单体氧无法扩散至受体微球,则不会产生可检测的荧光信号,可通过检测荧光信号强弱的变化来计算样品中喹诺酮类药物的浓度[27]。
基于上述原理,本研究拟建立一种检测牛奶中喹诺酮类药物残留的AlphaLISA方法,检测原理如图1所示,并对其灵敏度、准确性、重复性等指标进行测定,评价其在乳品安全检测中应用的可行性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牛奶样品 北京(北京昭阳牧场)、内蒙(犇腾牧业第一牧场,双翔牧业)、河北(河北牧兴顺牧业,河北锦程牧业)地区的牛原奶,-20 ℃以下运输/保存;诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星、环丙沙星、氧氟沙星、培氟沙星、达氟沙星、沙拉沙星、麻保沙星、双氟沙星、洛美沙星、氟甲喹、恶喹酸、D-生物素、O-(羧甲基)羟胺半盐酸盐、氰基硼氢化钠 Sigma-Aldrich西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司;受体微球(20 mg/mL)、链霉亲和素修饰供体微球(5 mg/mL)、微孔板(OptiPlate™-96) PerkinElemer公司;6-氨基己酸(99%)、1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺(EDC,95%)、N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺(NHS,99%) 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;恩诺沙星抗体Mab-QNS-3E4 北京维德维康生物技术有限公司;二氯甲烷、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺、Tween 20(沪试) 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
PE EnVision®多功能酶标仪 PerkinElemer公司;BPG-9106A型鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;Z 216 MK型低温高速离心机 HERMLE贺默(上海)仪器科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 生物素修饰喹诺酮半抗原的合成
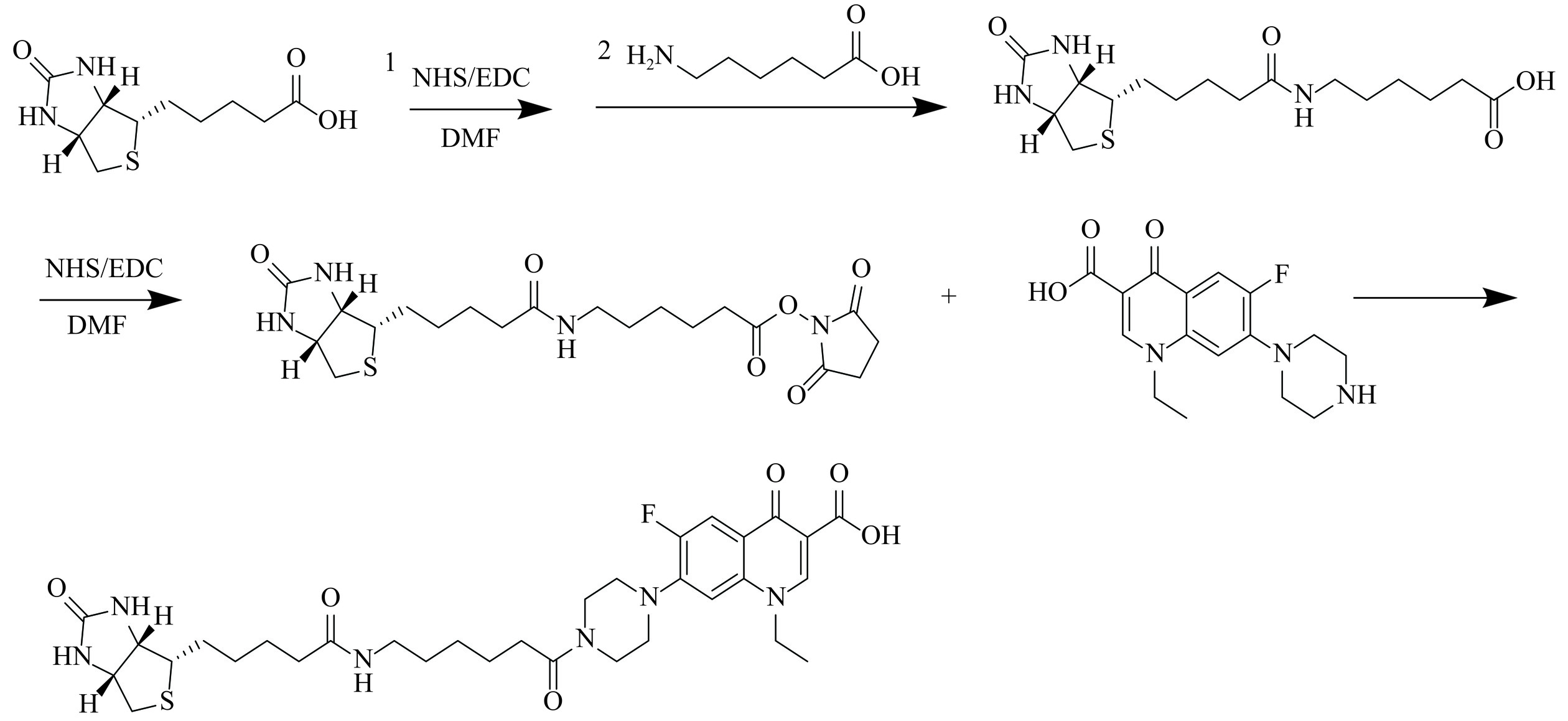
采用活泼酯法进行生物素修饰半抗原的合成[29],合成路线见图2,具体方法如下:向100 mL圆底烧瓶中投入D-生物素2440 mg,N,N-二甲基甲酰胺50 mL,搅拌均匀后加入NHS 1380 mg,EDC 2300 mg室温搅拌反应16 h;然后,在反应液中加入6-氨基己酸1320 mg室温反应24 h,析出白色固体,过滤,用20 mL二氯甲烷洗涤滤饼,40 ℃鼓风干燥10 h得到约1050 mg生物素-6氨基己酸(Biotin-6AS)白色固体。
将上述合成的1050 mg Biotin-6AS投入250 mL反应瓶中,N,N-二甲基甲酰胺100 mL,搅拌均匀后加入NHS 921 mg,EDC 1535 mg室温搅拌反应24 h,反应液中加入诺氟沙星2555 mg室温反应24 h,析出白色固体,过滤,用50 mL二氯甲烷洗涤滤饼,40 ℃鼓风干燥10 h得到约4220 mg生物素-6氨基己酸-诺氟沙星(Biotin-6AS-NOR)白色固体。
1.2.2 受体微球的标记
参照PerkinElmer提供的AlphaLISA研发指南,进行了受体微球的标记,具体方法如下[30]:取50 μL受体微球(20 mg/mL)置于1.5 mL离心管中,加入100 μL磷酸盐缓冲液(20 mmol/L,pH8.0),振荡混匀后16000×g 离心15 min弃上清;加入1.0 mL磷酸盐缓冲液(130 mmol/L,pH8.0)复溶微球,然后加入8 μL QNS抗体(2.3 mg/mL),振荡混匀后加15 μL 10% Tween 20,100 μL氰基硼氢化钠(25 mg/mL),混匀后37 ℃避光静置反应42 h;加入100 μL新鲜配制的CMO溶液(65 mg/mL),混匀后37 ℃避光静置反应1 h;16000×g离心15 min清洗3次(20 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液),使用20 mmol/L PBS按照5 mg/mL微球重悬,超声混匀后4 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3 均相化学发光检测步骤
采用竞争性AlphaLISA方法检测牛奶中喹诺酮类药物残留,具体检测步骤如下[31]:取20 μL待测样品或添标样品(添加有不同浓度QNS标准物质,用于建立标准曲线)分别加入到白色、不透明的96微孔板中,加入10 μL上述标记的受体微球(0.01 mg/mL),室温振荡反应30 min;再加入10 μL Biotin-6AS-NOR混匀,室温振荡反应30 min;然后使用20 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液将链霉亲和素修饰的供体微球(5 mg/mL)稀释至0.025 mg/mL,避光条件下向每个反应孔中加入10 μL链霉亲和素修饰的供体微球(0.025 mg/mL),混匀后室温避光振荡反应30 min;最后,使用PE EnVision®多功能酶标仪选择AlphaScreen模式检测615 nm信号值。
1.2.4 牛奶样品稀释方案的筛选
牛奶样品的成分较为复杂,含有大量蛋白质、脂肪、糖类等,会对受体微球和供体微球结合过程的信号产生及检测造成干扰,且不同来源样品的各成分含量及pH存在差异,不可避免地会影响免疫检测的准确性[32]。为了提高方法的可靠性,本研究使用20 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2)对样品进行不同比例稀释后检测,考察的稀释比例(牛奶:磷酸盐缓冲液)包括1:0、1:1、1:2、1:3、1:5、1:7和1:10。
1.2.5 方法学评价
1.2.5.1 标准曲线测定
在喹诺酮类药物阴性的牛奶样本中添加梯度浓度的诺氟沙星,终浓度依次为:0、0.1、0.3、1.0、3.0、10.0、30.0、100.0 ng/mL,按照1.2.3所述步骤进行检测。每个浓度水平重复测试5次,取平均值,然后以样本中添加的诺氟沙星终浓度为X值,各浓度对应的检测信号值为Y值进行四参数曲线拟合[33]。
1.2.5.2 检出限及定量限
取20份诺氟沙星阴性牛奶样品,按照1.2.3所述步骤进行检测,并依据1.2.5.1所建立的标准曲线,利用20份样本检测结果的平均值(¯X)和标准差(s)计算所建立均相光激化学发光免疫分析方法的检出限(Limit of detection,LOD)和定量限(Limit of quantification,LOQ),计算公式如下[34]:
检出限:LOD=¯X+3s (1) 定量限:LOQ=¯X+10s (2) 1.2.5.3 特异性测定
按照1.2.5.1所述步骤测试其它喹诺酮类药物,包括:恩诺沙星、环丙沙星、氧氟沙星、培氟沙星、达氟沙星、沙拉沙星、麻保沙星、双氟沙星、洛美沙星、氟甲喹、恶喹酸;依据标准曲线,分别计算各结构类似物的半数抑制浓度(Half maximal inhibitory concentration,IC50),然后依据下式计算各药物的交叉反应率(Cross reaction rate,CR):
CR(%)=IC50(诺氟沙星)/IC50(类似物)×100 (3) 1.2.5.4 准确度和重复性测定
将空白牛奶样品中分别添加终浓度为0.5、1.0和2.0 ng/mL诺氟沙星,每个浓度做3个平行,采用1.2.3所述步骤和1.2.5.1标准曲线进行检测。在3个不连续的工作日内重复测定3次,按照下述公式计算批内和批间变异系数:
CV(%)=(s/¯X)×100 (4) 1.3 数据处理
本研究使用Origin 2018和Adobe Illustrator软件进行图形绘制及四参数标准曲线的拟合。采用SPSS 20软件对牛奶样稀释方案进行单因素方差统计分析,P<0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 牛奶样品稀释方案的确定
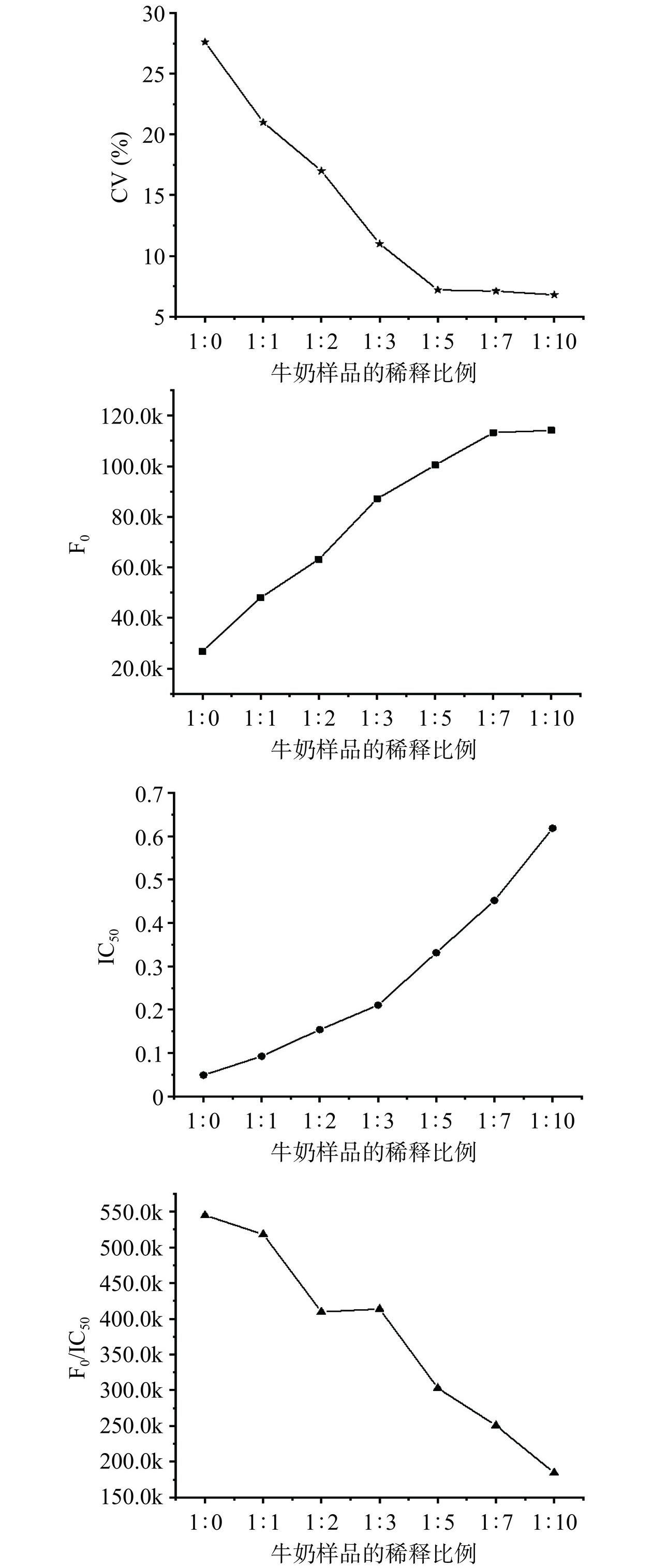
使用20 mmol/L磷酸盐对牛奶样品稀释不同比例后,采用AlphaLISA方法测试的结果如图3所示。随着牛奶样品稀释倍数的增加,AlphaLISA方法的F0与IC50逐渐上升,而CV值则相应下降。通过降低样品中干扰物质的浓度(蛋白质、脂肪、糖类等),调节样品溶液pH,可以显著提高反应体系的信号强度;同时,对样品的稀释也使得检测样品溶液中QNS药物浓度降低,进而导致AlphaLISA方法的灵敏度下降。牛奶样品在1:0~1:5比例范围内稀释时,高比例稀释可以显著减少检测结果的变异系数(P<0.05):5份不同来源的牛奶样品,检测结果变异系数均高于29.8%,1:5稀释后检测结果的变异系数下降至7.1%。因此,最终选择1:5作为牛奶样品的稀释方案,F0值为10413.5,IC50大小为0.33 ng/mL和CV值为7.1%,均能满足牛奶中QNS免疫快检的方法学需求。
2.2 标准曲线的建立
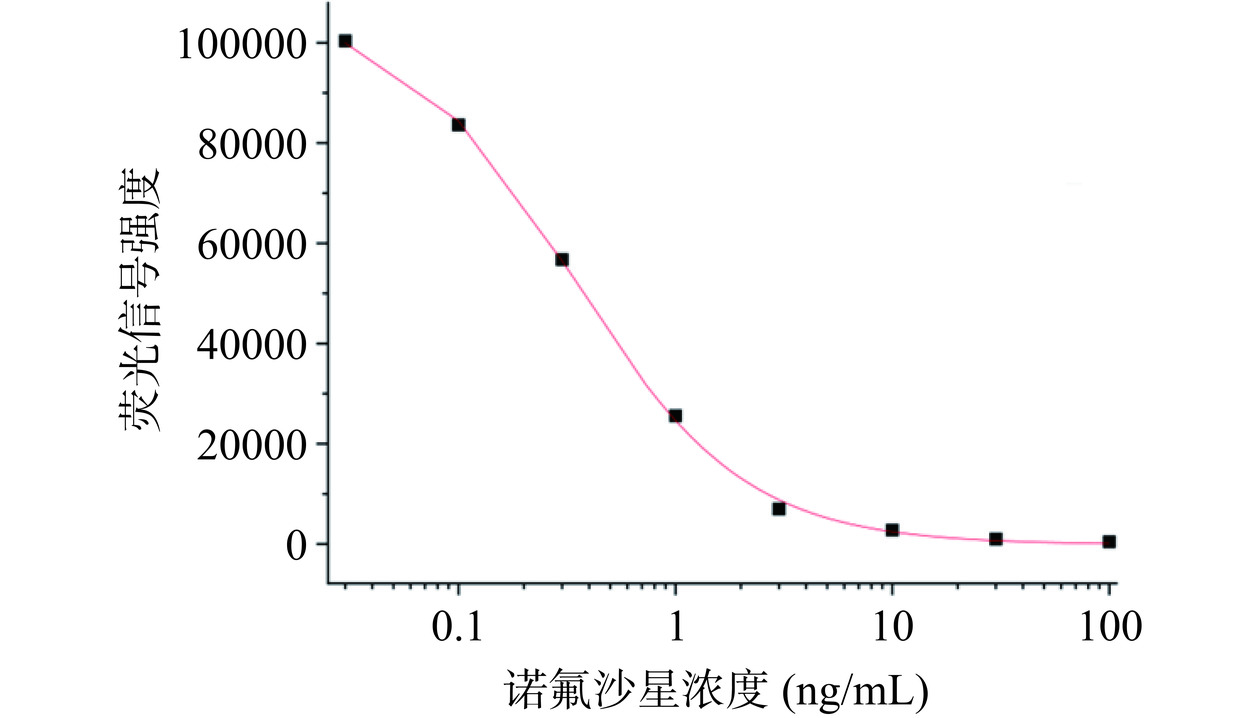
测试添加了梯度浓度诺氟沙星的牛奶样本,以诺氟沙星系列浓度为X轴,对应AlphaLISA方法的检测信号作为Y轴,使用软件Origin 2018进行四参数曲线拟合,结果如图4所示,线性方程为:Y=−98.69+107349.93/ (1+(X/0.33)1.09),IC50为0.33 ng/mL,决定系数R2=0.99953。从图4中可以看出,相对于传统的ELISA方法,本研究所建立的AlphaLISA具有更宽的检测范围。
2.3 检出限与定量限
采用本研究所建立的均相光激化学发光免疫分析方法测试20份QNS阴性牛奶样品,检测结果如表1所示。检出限和定量限分别为0.19 ng/mL和0.46 ng/mL。
表 1 QNS阴性牛奶样品的测定结果(ng/mL)Table 1. Determination of NOR negative milk samples (ng/mL)实验序号 测定值(n=20) 平均值 标准差 检出限 定量限 1~5 0.128 0.047 0.090 0.083 0.119 0.072 0.039 0.19 0.46 6~10 0.106 0.060 0.024 0.075 0.012 11~15 0.056 0.027 0.130 0.091 0.086 16~20 0.032 0.038 0.112 0.016 0.109 2.4 特异性
测得其他12种喹诺酮类药物的IC50及交叉反应率数据如表2所示。诺氟沙星、恩诺沙星、环丙沙星、氧氟沙星、培氟沙星、达氟沙星和洛美沙星的交叉反应率均高于70%,其中,洛美沙星、培氟沙星、氧氟沙星、诺氟沙星禁止被用于食用动物的养殖过程[35]。此外,沙拉沙星、麻保沙星、双氟沙星、氟甲喹和恶喹酸的交叉反应率均低于60%。
表 2 其他QNS的交叉反应率Table 2. Cross-reaction rates of other QNS药品名称 IC50(ng/mL) 交叉率(%) 诺氟沙星 0.33 100.0 恩诺沙星 0.28 117.9 环丙沙星 0.31 106.5 氧氟沙星 0.39 84.6 培氟沙星 0.37 89.2 达氟沙星 0.46 71.7 沙拉沙星 1.29 25.6 麻保沙星 1.97 16.8 双氟沙星 1.14 28.9 洛美沙星 0.43 76.7 氟甲喹 0.58 56.9 恶喹酸 1.15 28.7 2.5 准确度和重复性结果
鉴于国标方法GB 29692-2013《牛奶中喹诺酮类药物多残留的测定 高效液相色谱法》[36]的检出限为1~25 μg/kg,灵敏度低于本方法,因此本研究仅通过空白样品添加的方法进行准确性和重复性的评价。结果显示,本研究所建立AlphaLISA方法的添加回收率为85.97%~110.11%,日内变异系数为3.44%~9.79%,日间变异系数为8.36%~9.92%,两者均小于10%(表3)。上述数据表明,本研究所建立的牛奶中喹诺酮类药物残留的AlphaLISA方法具有良好的准确度和重复性。
表 3 准确度和重复性的测试结果Table 3. Results of accuracy and repeatability添加浓度(ng/mL) 重复 日内 日间 平均值±标准差(ng/mL) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 平均值±标准差(ng/mL) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 0.5 1 0.504±0.032 106.81 6.34 0.484±0.053 95.73 8.34 2 0.488±0.038 97.61 7.91 3 0.429±0.014 85.97 3.44 1.0 1 0.984±0.086 98.45 8.81 1.026±0.065 102.57 9.92 2 0.992±0.071 99.2 7.10 3 1.101±0.102 110.11 9.28 2.0 1 1.819±0.072 90.97 3.99 1.867±0.156 93.35 8.36 2 2.141±0.181 107.08 8.47 3 1.74±0.1462 87.1 8.40 3. 结论
喹诺酮类药物是一类人畜共用的抗菌药物,其在动物源性食品中的残留可能会随着食物链传播,引起人类病原菌的耐药性及消费者的不良反应。本研究基于AlphaLISA的原理,建立了一种牛奶中QNS残留的均相光激化学发光免疫分析方法。其中,牛奶样品基质的复杂性是该方法检测喹诺酮类药物的最大挑战。研究发现,对牛奶样品稀释(1:5)可有效降低样品差异的影响,提高检测结果的准确性和可靠性。AlphaLISA为一种液体均相光激化学发光检测反应,具有较高的检测灵敏度,且由于不涉及繁复的洗板过程,可更有效控制变异并缩短检测时间。由此可见,随着AlphaLISA相关检测试剂和检测装置国产化带来检测成本的降低,使其在食品安全检测领域亦具有较高的应用价值。
-
表 1 QNS阴性牛奶样品的测定结果(ng/mL)
Table 1 Determination of NOR negative milk samples (ng/mL)
实验序号 测定值(n=20) 平均值 标准差 检出限 定量限 1~5 0.128 0.047 0.090 0.083 0.119 0.072 0.039 0.19 0.46 6~10 0.106 0.060 0.024 0.075 0.012 11~15 0.056 0.027 0.130 0.091 0.086 16~20 0.032 0.038 0.112 0.016 0.109 表 2 其他QNS的交叉反应率
Table 2 Cross-reaction rates of other QNS
药品名称 IC50(ng/mL) 交叉率(%) 诺氟沙星 0.33 100.0 恩诺沙星 0.28 117.9 环丙沙星 0.31 106.5 氧氟沙星 0.39 84.6 培氟沙星 0.37 89.2 达氟沙星 0.46 71.7 沙拉沙星 1.29 25.6 麻保沙星 1.97 16.8 双氟沙星 1.14 28.9 洛美沙星 0.43 76.7 氟甲喹 0.58 56.9 恶喹酸 1.15 28.7 表 3 准确度和重复性的测试结果
Table 3 Results of accuracy and repeatability
添加浓度(ng/mL) 重复 日内 日间 平均值±标准差(ng/mL) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 平均值±标准差(ng/mL) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 0.5 1 0.504±0.032 106.81 6.34 0.484±0.053 95.73 8.34 2 0.488±0.038 97.61 7.91 3 0.429±0.014 85.97 3.44 1.0 1 0.984±0.086 98.45 8.81 1.026±0.065 102.57 9.92 2 0.992±0.071 99.2 7.10 3 1.101±0.102 110.11 9.28 2.0 1 1.819±0.072 90.97 3.99 1.867±0.156 93.35 8.36 2 2.141±0.181 107.08 8.47 3 1.74±0.1462 87.1 8.40 -
[1] 陆向梅, 胡波, 宫平, 等. 动物源性食品中氟喹诺酮类药物残留检测前处理技术的比较研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2023(13):130−132,145. [LU X M, HU B, GONG P. et al. Comparative study on pretreatment techniques for detection of fluoroquinolone residues in food of animal origin[J]. Journal of Food Safety,2023(13):130−132,145.] LU X M, HU B, GONG P. et al. Comparative study on pretreatment techniques for detection of fluoroquinolone residues in food of animal origin[J]. Journal of Food Safety, 2023(13): 130−132,145.
[2] 袁丽, 丁磊, 杨希, 等. 高效液相色谱-荧光检测法对动物源性食品中氟喹诺酮类药物残留的检测[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022(14):84−86. [YUAN L, DING L, YANG X, et al. Detection of fluoroquinolone residues in animal derived foods using high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection[J]. Journal of Food Safety,2022(14):84−86.] YUAN L, DING L, YANG X, et al. Detection of fluoroquinolone residues in animal derived foods using high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection[J]. Journal of Food Safety, 2022(14): 84−86.
[3] 田雨超, 谷学佳, 薛丽. 高效液相色谱法检测猪肉中4种氟喹诺酮类药物残留方法的优化[J]. 现代畜牧兽医,2021(10):25−29. [TIAN Y C, GU X J, XUE L. Optimization of high-performance liquid chromatography for the detection of four fluoroquinolone residues in pork[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2021(10):25−29.] TIAN Y C, GU X J, XUE L. Optimization of high-performance liquid chromatography for the detection of four fluoroquinolone residues in pork[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021(10): 25−29.
[4] 施元旭, 盛华栋, 张水锋, 等. 同位素稀释法-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定豆芽中6种喹诺酮类药物残留[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(11):3551−3557. [SHI Y X, SHENG H D, ZHANG S F, et al. Determination of 6 quinolones drug residues in bean sprouts by isotope internal standard- ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2020,11(11):3551−3557.] SHI Y X, SHENG H D, ZHANG S F, et al. Determination of 6 quinolones drug residues in bean sprouts by isotope internal standard- ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2020, 11(11): 3551−3557.
[5] KLEIN E Y, VAN BOECKEL T P, MARTINEZ E M, et al. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015[J]. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America,2018(15):3463−3470.
[6] QIU W H, LIU T, LIU X J, et al. Enrofloxacin induces intestinal microbiota-mediated immunosuppression in zebrafish[J]. Environmental Science Technology,2022,56(12):8428−8437. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c08712
[7] 吴晓晓, 俞进, 热孜万古力·赛麦提, 等. 分析动物源性食品中抗生素残留的快速检测方法[J]. 食品界,2023(6):102−105. [WU X X, YU J, SAIMAITI R Z W G L, et al. A rapid detection method for analyzing antibiotic residues in animal derived foods[J]. Food Industry,2023(6):102−105.] WU X X, YU J, SAIMAITI R Z W G L, et al. A rapid detection method for analyzing antibiotic residues in animal derived foods[J]. Food Industry, 2023(6): 102−105.
[8] PATYRA E, KWIATEK K, NEBOY C, et al. Quantification of veterinary antibiotics in pig and poultry feces and liquid manure as a non-invasive method to monitor antibiotic usage in livestock by liquid chromatography mass-spectrometry[J]. Molecules,2020,25(14):3265. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143265
[9] KIRCHHELLE C. Pharming animals:a global history of antibiotics in food production (1935-2017)[J]. Palgrave Communications,2018,4(1):1−13. doi: 10.1057/s41599-017-0055-7
[10] FU H G, LI Z W, HU X X, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of quinoline derivatives as a novel class of broad-spectrum antibacterial agents[J]. Molecules,2019,24(3):548. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030548
[11] VASUNDHARA D, RAJU V N, HEMALATHA R, et al. Vaginal & gut microbiota diversity in pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis & effect of oral probiotics:An exploratory study[J]. Indian Journal of Medical Research,2021,153(4):492−502. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_350_19
[12] BRACHA D, WALLS M T, WEI M T, et al. Mapping local and global liquid phase behavior in living cells using photo-oligomerizable seeds[J]. Cell,2018,175(6):1467−1480. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.048
[13] 王宁, 阿斯喀·夏热甫汉, 李艳美, 等. QuEChERS-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定动物尿液中14种喹诺酮类和8种糖皮质类兽药残留[J]. 分析科学学报,2023,39(4):417−423. [WANG N, ASHIKA X R F H, LI Y M, et al. Simultaneous determination of 14 quinolones and 8 glucocorticoid residues in animal urine using QuEChERS high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2023,39(4):417−423.] WANG N, ASHIKA X R F H, LI Y M, et al. Simultaneous determination of 14 quinolones and 8 glucocorticoid residues in animal urine using QuEChERS high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2023, 39(4): 417−423.
[14] 王勇, 龚勇, 卢明华, 等. 氟喹诺酮类药物残留检测方法的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2017,44(8):2509−2516. [WANG Y, GONG Y, LU M H, et al. Research progress on detection methods of fluoroquinolones residue[J]. Chinese Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2017,44(8):2509−2516.] WANG Y, GONG Y, LU M H, et al. Research progress on detection methods of fluoroquinolones residue[J]. Chinese Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(8): 2509−2516.
[15] ZHOU X, CHEN W Q, DING Y Q, et al. Rapid determination of sulfonamides in chicken using two-dimensional online cleanup mode with three columns coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2019,1114:110−118.
[16] 林萍萍, 史云鹏, 安鹏天. 动物源性食品中喹诺酮类药物残留检测方法研究进展[J]. 中国口岸科学技术,2022,4(2):45−49. [LIN P P, SHI Y P, AN P T. Research progress on detection methods of quinolones residues in animal-derived food[J]. Science and Technology of China Port,2022,4(2):45−49.] LIN P P, SHI Y P, AN P T. Research progress on detection methods of quinolones residues in animal-derived food[J]. Science and Technology of China Port, 2022, 4(2): 45−49.
[17] PAN S D, XU Q H, GUO Y B, et al. Simultaneous determination of 11 quinolone residues in freshwater fish samples by magnetic solid-extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of separation science,2021,44(21):4017−4024. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202100554
[18] 王雪奇. 奶豆腐中6种喹诺酮类药物残留检测技术及不同工艺对药物残留的研究[D]. 通辽:内蒙古民族大学, 2022. [WANG X Q. A study on the detection techniques and different processes of six quinolone drug residues in milk tofu[D]. Tongliao:National University of The Inner Mongol, 2022.] WANG X Q. A study on the detection techniques and different processes of six quinolone drug residues in milk tofu[D]. Tongliao: National University of The Inner Mongol, 2022.
[19] 汪阿鹏, 冯连顺. 氟喹诺酮类抗菌药的最新研究进展[J]. 国外医药(抗生素分册),2019,40(3):171−179,170. [WANG A P, FENG L S. Research progress of fluoroquinolones[J]. Foreign Medicine (Antibiotics Division),2019,40(3):171−179,170.] WANG A P, FENG L S. Research progress of fluoroquinolones[J]. Foreign Medicine (Antibiotics Division), 2019, 40(3): 171−179,170.
[20] HUA J H, JIAO Y, WANG M, et al. Determination of norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin by carbon dots fluo rescence enhancement using magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent[J]. Mikrochimica Acta An International Journal for Physical & Chemical Methods of Analysis,2018,185(2):137.
[21] 李倩, 王甲, 张玉洁, 等. 动物性食品中喹诺酮类药物残留检测方法研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(8):3016−3022. [LI Q, WANG J, ZHANG Y J, et al. Research progress on detection methods for quinolone residues in animal foods[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2021,12(8):3016−3022.] LI Q, WANG J, ZHANG Y J, et al. Research progress on detection methods for quinolone residues in animal foods[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing, 2021, 12(8): 3016−3022.
[22] 刘发全, 许世富, 束玲玲. 喹诺酮类兽药在鸡蛋中残留危害分析[J]. 中国动物保健,2021,23(9):4−5. [LIU F Q, XU S F, SHU L L. Hazard analysis of quinolone veterinary drugs residues in eggs[J]. China Animal Health,2021,23(9):4−5.] LIU F Q, XU S F, SHU L L. Hazard analysis of quinolone veterinary drugs residues in eggs[J]. China Animal Health, 2021, 23(9): 4−5.
[23] 刘佩怡, 伍宏凯, 梁祺琦, 等. HPLC-MS/MS同位素内标法测定鸡蛋中14种喹诺酮类药物残留量[J]. 广东畜牧兽医科技,2022,47(5):28−34. [LIU P Y, WU H K, LIANG Q Q, et al. Determination of 14 quinolone drug residues in eggs using HPLC-MS/MS isotope internal standard method[J]. Guangdong Livestock and Veterinary Science and Technology,2022,47(5):28−34.] LIU P Y, WU H K, LIANG Q Q, et al. Determination of 14 quinolone drug residues in eggs using HPLC-MS/MS isotope internal standard method[J]. Guangdong Livestock and Veterinary Science and Technology, 2022, 47(5): 28−34.
[24] WANG R, LI S, CHEN D W, et al. Selective extraction and enhanced-sensitivity detection of fluoroquinolones in swine body fluids by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry:Application in long-term monitoring in livestock[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,341:128269. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128269
[25] 中华人民共和国农业农村部, 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 31650-2019食品安全国家标准 食品中兽药最大残留限量[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2019. [Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 31650-2019 National standard for food safety. Maximum residue limit of veterinary drugs in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2019.] Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 31650-2019 National standard for food safety. Maximum residue limit of veterinary drugs in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019.
[26] YAMANISHI C D, CHIU J H, TAKAYAMA S C. Systems for multiplexing homogeneous immunoassays[J]. Bioanalysis,2015,7(12):1545−1556. doi: 10.4155/bio.15.78
[27] CHEN D J, WANG D, WANG C X, et al. Application of an AlphaLISA method for rapid sensitive detection of African swine fever virus in porcine serum[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2021,105(11):4751−4759. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11339-2
[28] 熊玉锋. 基于均相免疫分析技术检测蛋白质相互作用的方法建立及其在新药研发中的应用[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2018. [XIONG Y F. Establishment of a method for detecting protein interactions based on homogeneous immunoassay technology and its application in new drug development[D]. Guangzhou:Southern Medical University, 2019.] XIONG Y F. Establishment of a method for detecting protein interactions based on homogeneous immunoassay technology and its application in new drug development[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2019.
[29] SHEN H, WAN Y P, WU X S, et al. Hapten designs based on aldicarb for the development of a colloidal gold immunochromatographic quantitative test strip[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:976284. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.976284
[30] PERKINELMER. AlphaLISA® assay development guide [EB/OL]. (2019-04-17) [2023-11-03]. https://resources.perkinelmer.com/corporate/content/manuals/gde_alphalisadevelopmentguide.pdf.
[31] 张力文. 11种毒素AlphaLISA检测体系的建立[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学, 2020. [ZHANG L W. The establishment of AlphaLISA detection system for 11 kinds of toxin[D]. Hefei:Anhui Medical University, 2020.] ZHANG L W. The establishment of AlphaLISA detection system for 11 kinds of toxin[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2020.
[32] 严祖浩, 李晓薇, 夏曦. 牛奶中69种兽药残留的超高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间质谱快速筛查[J]. 分析测试学报,2023,42(10):1309−1318. [YAN Z H, LI X W, XIA X. Rapid screening of 69 veterinary drug residues in milk by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2023,42(10):1309−1318.] YAN Z H, LI X W, XIA X. Rapid screening of 69 veterinary drug residues in milk by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2023, 42(10): 1309−1318.
[33] MA L C, WANG Z H, LIU H B, et al. Monoclonal antibody production and the development of a quantitative time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for rifaximin in milk[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2019,30(1):P1135−P1147. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2019.1669538
[34] 国家粮食局. LS/T 6402-2017 粮油检验设备和方法标准适用性验证及结果评价一般原则[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2017. [National Food and strategic reserves administration. LS/T 6402-2017 Inspection of grain and oils-the general principle of standard adaptability verification and evaluation results for equipments and testing methods[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2017.] National Food and strategic reserves administration. LS/T 6402-2017 Inspection of grain and oils-the general principle of standard adaptability verification and evaluation results for equipments and testing methods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[35] 中华人民共和国农业部. 中华人民共和国农业部公告第2292号[EB/OL]. 中华人民共和国农业部公报, 2015(9):61-62. [Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China No.2292[EB/OL]. Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2015(9):P61-P62.] Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China No.2292[EB/OL]. Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2015(9): P61-P62.
[36] 中华人民共和国农业部, 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 29692-2013牛奶中喹诺酮类药物多残留的测定 高效液相色谱法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2013. [Ministry of Agriculture, National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 29692-2013 Determination of quinolone residues in milk by high performance liquid chromatography[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2013.] Ministry of Agriculture, National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 29692-2013 Determination of quinolone residues in milk by high performance liquid chromatography[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 韩银涛,庞李艳,廖柳媚,陈粉娜,孙洁,唐涛,张秋韵,罗国强,次仁玉珍,吴凯. 一种检测牛奶中喹诺酮类药物的高效液相色谱-串联质谱方法. 国外畜牧学(猪与禽). 2024(05): 81-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



