Antifungal Activity of Ethanol Extract of Polytrichum commune Hedw. Against Four Plant Pathogenic Fungi
-
摘要: 为给植物源杀菌剂的研发提供备选材料,采用菌丝生长速率法和孢子萌发法测定大金发藓(Polytrichum commune Hedw.)茎叶和假根的乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌灰葡萄孢菌(Botrytis cinerea)、茄病镰刀菌甘薯专化型(Fusarium solani f. sp. batatas)、茄病镰刀菌(Fusarium solani)和细极链格孢菌(Alternaria tenuissima)菌丝生长和孢子萌发的抑制率及其抑制中浓度(EC50),对抑菌活性进行分析。结果表明,浓度在1~8 mg/mL时,大金发藓茎叶醇提液和假根醇提液对4种植物病原真菌产生极显著抑菌效果(P<0.01),且随提取液使用浓度增加,对4种病原菌菌丝生长和分生孢子萌发的抑制率增强;在相同浓度下,茎叶醇提液对4种植物病原真菌的抑制效果显著优于假根醇提液(P<0.05);茄病镰刀菌(甘薯)对大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液的抑菌作用最敏感,EC50值分别仅为0.42和0.35 mg/mL。综合而言,大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液对4种植物病原真菌存在较强抑菌效果,茎叶醇提液抑菌效果优于假根,二者在植物源杀菌剂的研发中具有一定的应用潜力。Abstract: In order to exploit new botanic fungicide, the antifungal activities of the ethanol extracts of stem-leaf and rhizoid of P. commune were studied by the mycelia growth rate method and the spore germination method based on the determination of their mycelia growth inhibition rates, spore germination inhibition rates and median inhibition concentration values (EC50) on B. cinerea, F. solani f. sp. batatas, F. solani and A. brassicicola. The results showed that the antifungal activities of the ethanol extracts of P. commune against the four plant pathogenic fungi were extremely significant (P<0.01) in the concentration range of 1 to 8 mg/mL and the antifungal activities were proportional to the concentration of ethanol extracts of P. commune. Furthermore, under the same concentration, the antifungal activity of the alcohol extracts of the stem-leaf of P. commune against the four plant pathogenic fungi was significantly higher than that of the rhizoid of P. commune (P<0.05). Finally, among the four plant pathogenic fungi, F. solani f. sp. batatas was the most sensitive to the antifungal activity of the ethanol extracts of the stem-leaf and rhizoid of P. commune, with the EC50 values of stem-leaf and rhizoid only 0.42 and 0.35 mg/mL, respectively. In summary, the ethanol extracts of the stem-leaf and rhizoid of P. commune had strong antifungal activities against the four plant pathogenic fungi, and the antifungal activity of the stem-leaf was better than that of the rhizoid. Both of them had certain potential application in the development of new botanical fungicides.
-
微生物病害易给农业生产来带损失,由真菌感染的约占70%~80%[1],其中草莓灰霉病,一种由灰葡萄孢菌(B. cinerea)引起的真菌性病害普遍流行,危害较大,主要发生在低温、潮湿的环境中,易染病期主要在花期;甘薯根腐病由多种镰孢菌(Fusarium)引起,其中包括茄病镰刀菌(F. solani),主要发生在育苗期和大田生长期;芹菜根腐病由茄病镰刀菌(F. solani)和侧雄腐霉菌(Pythium paroecandrum)引起;花椰菜黑斑病的主要致病菌是链格孢菌(Alternaria),其中包括细极链格孢菌(A. tenuissima),主要危害叶片。化学性杀菌剂广泛应用于防治植物病原真菌引起的植物病害,但其毒性大,长期使用容易对农产品产生一定的安全隐患,而且植物致病菌可能会对多种化学杀菌剂产生抗性[2−3]。植物源杀菌剂可代替化学性杀菌剂应用于多种植物真菌病害的防治[4−6],是将植物中具有抑菌活性的成分分离纯化得到的生物合成农药,具有高效、易降解、无二次环境污染等优点[7],这些抑菌活性成分主要为植物次生代谢的产物,由天然植物资源中直接提取获得,但受天然植物资源及其开发成本的限制,亟需筛选更多更有效且易于获取的植物供体材料。
大金发藓(P. commune Hedw.),是藓纲、金发藓目、金发藓科、金发藓属植物[8],广泛分布于我国南北各地的林下湿地,其药用价值开发较早,据《本草纲目》和《中华本草》记载,其全草入药,味甘、性凉,对高夫克氏球菌、金色葡萄菌、肺炎球菌、结核杆菌均有抗性[9],并对淋巴细胞白血病等癌症有一定的抑制作用[10]。大金发藓次生代谢产物丰富,富含皂苷、生物碱、黄酮类、酚类、香豆素及萜类化合物[11],可能赋予其一定的抵御病害入侵的能力,研究大金发藓提取物对植物病原微生物菌丝生长及孢子萌发的抑制作用,对植物源杀菌剂的合成和开发提供具有参考价值。植物活性成分提取中,不同提取剂所提取出的活性成分种类不同[12−13],成晓霞等[14]研究表明,大金发藓乙醇提取物中含有生物碱、黄酮、皂苷、蒽酮、香豆素类化合物,氯仿成分中主要含有生物碱类化合物,乙酸乙酯组分中主要以黄酮类化合物为主,正丁醇组分中主要含有皂苷类化合物,其中乙酸乙酯组分在抗氧化和抗癌方面具有一定的作用,但是,针对大金发藓提取物在抑制植物病原菌方面的研究还未见报道。有研究表明,5种瑞香科植物的乙醇提取物[15]和丝瓜乙醇提取物[16]均对植物病原真菌具有较好的抑菌活性,而大金发藓乙醇提取物中所含活性成分种类最多[14]。因此,本研究以乙醇为提取剂,对大金发藓不同器官的乙醇提取物在不同浓度条件对灰葡萄孢菌(B. cinerea)、茄病镰刀菌甘薯专化型(F. solani f. sp. batatas)、茄病镰刀菌(F. solani)和细极链格孢菌(A. tenuissima)的抑制效果进行分析,以期为植物源杀菌剂的开发利用提供备选原料。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大金发藓 采自贵州省安顺市紫云县宗地村(海拔1765 m,33°28'N,33°28'E),供试部位为茎叶和假根;灰葡萄孢菌(B. cinerea)、茄病镰刀菌(F. solani f. sp.)(甘薯专化型)、茄病镰刀菌(F. solani)、细极链格孢菌(A. tenuissima) 分别从发病的草莓(草莓灰霉病)、甘薯(根腐病)、芹菜(根腐病)、花椰菜(黑斑病)植株上分离纯化而来,分子鉴定结果见表1;马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(PDA) 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;乙醇 分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂。
表 1 本研究所用菌种Table 1. Bacteria tested in this study名称 DNA鉴定结果 相似度(%) 灰葡萄孢菌 Botrytis cinerea 100.00 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) Fusarium solani f. sp. batatas 99.73 茄病镰刀菌 Fusarium solani 99.87 细极链格孢菌 Alternaria tenuissima 100.00 GZX-9246型电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂;KS-400KDE型旋钮超声波清洗器 昆山洁力美超声仪器有限公司;RE-2010型旋转蒸发仪 上海爱朗仪器有限公司;GR85DA型全自动立式高压灭菌器 致微(厦门)仪器有限公司;SW-CJ-2F型双人双面净化工作台 苏州净化设备有限公司;RXZ-430L型智能型人工气候箱 韶关市科力仪器有限公司;AS2型全自动菌落计数仪 杭州迅数科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大金发藓乙醇提取物的制备
将新鲜大金发藓在流水下冲洗干净,分成茎叶与假根两部分,于50 ℃电热鼓风干燥箱烘干至恒重,将烘干后的大金发藓粉碎,过42目筛,制成粉末干样,保存备用。
采用传统的溶剂浸提法结合超声促提技术提取大金发藓醇提物[17−18]。按料液比1:5(g:mL),分别称取大金发藓茎叶和假根干粉样100 g置于带橡胶塞的三角瓶中,用500 mL 80%乙醇密闭混合静置72 h进行浸提,然后超声浸提(50 ℃,30 min),抽滤,收集到的液体为初提物。用90%乙醇采用以上提取步骤重复浸提滤渣3次,合并4次滤液,于旋转蒸发仪(60 r/min,水浴锅温度设为50 ℃)旋转蒸发浓缩,测定浓缩后提取液的提取率及浓度。将醇提液置于4 ℃冰箱保存,待制作大金发藓醇提液-PDA培养基。
1.2.2 大金发藓乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌菌丝生长抑制活性的测定
1.2.2.1 菌种的活化
将分离保存的菌种从冰箱取出,于无菌条件将菌饼接种于已经准备好的无菌PDA固体培养基上,封上封口膜,做好菌株标记,25 ℃恒温培养7 d。
1.2.2.2 抑菌活性测定
于无菌条件下,将大金发藓茎叶和假根提取液经0.22 µm有机微孔滤膜过滤后进行稀释,分别与灭菌后未凝固的PDA培养基混合均匀,制成带药PDA培养基平板,配制成1、2、4、8 mg/mL 4个浓度梯度[19],以不同体积乙醇取代提取液为空白对照(CK),共9个处理,每个处理平行5次。用无菌打孔器在活化后的4种病原菌菌落边缘打取菌饼(6 mm),并将菌饼接种于含药平板和空白对照平板中央,每个平板接种一个病原菌菌饼。将接种后的平板封好封口膜并用报纸包好后于25 ℃恒温培养箱培养5 d[20−21]。当空白对照的菌落长到平板直径的3/4左右时,采用全自动菌落计数仪十字交叉法测量菌落直径,计算菌丝生长抑制率[22],计算公式如下:
(1) 将各处理菌落拍照留存,利用DPS软件建立毒力回归方程,计算大金发藓不同器官提取物及不同使用浓度下的EC50值,进行毒力分析。
1.2.3 大金发藓乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌分生孢子萌发相对抑制率的测定
于无菌条件下,取活化后的4种病原真菌于10 mL无菌水中,用涂布棒将分生孢子和菌丝体刮下,3层纱布过滤掉菌丝体,滤液采用显微镜和血细胞计数板确定孢子浓度,最后配制成1×107 CUF/mL的孢子悬浮液[22]。用一定量的N,N-二甲基甲酰胺溶解大金发藓醇提物,经0.22 µm有机微孔滤膜过滤后与PDA培养基混合均匀,配制成0.25、0.50、1.00、2.00、4.00和8.00 mg/mL的带药培养基,并分别滴于载玻片上,待凝固后,将20 µL孢子悬浮液滴于培养基表面,涂布均匀,以含有等比例的N,N-二甲基甲酰胺的无菌水为空白对照,每个处理重复5次。处理好的载玻片置于25 ℃培养箱中暗培养6 h,待对照组孢子萌发率>95%后,于显微镜下观察各处理组的孢子萌发情况,计算萌发率与相对抑制率[23],计算公式如下:
(2) (3) 1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS19.0软件,对大金发藓醇提物不同使用浓度的抑菌效果进行单因素方差分析,多重比较采用Duncan法,对大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提物的抑菌效果进行T检验,P<0.05表示抑菌效果差异显著,P<0.01表示抑菌效果差异极显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 大金发藓醇提物对灰葡萄孢菌的抑菌效果
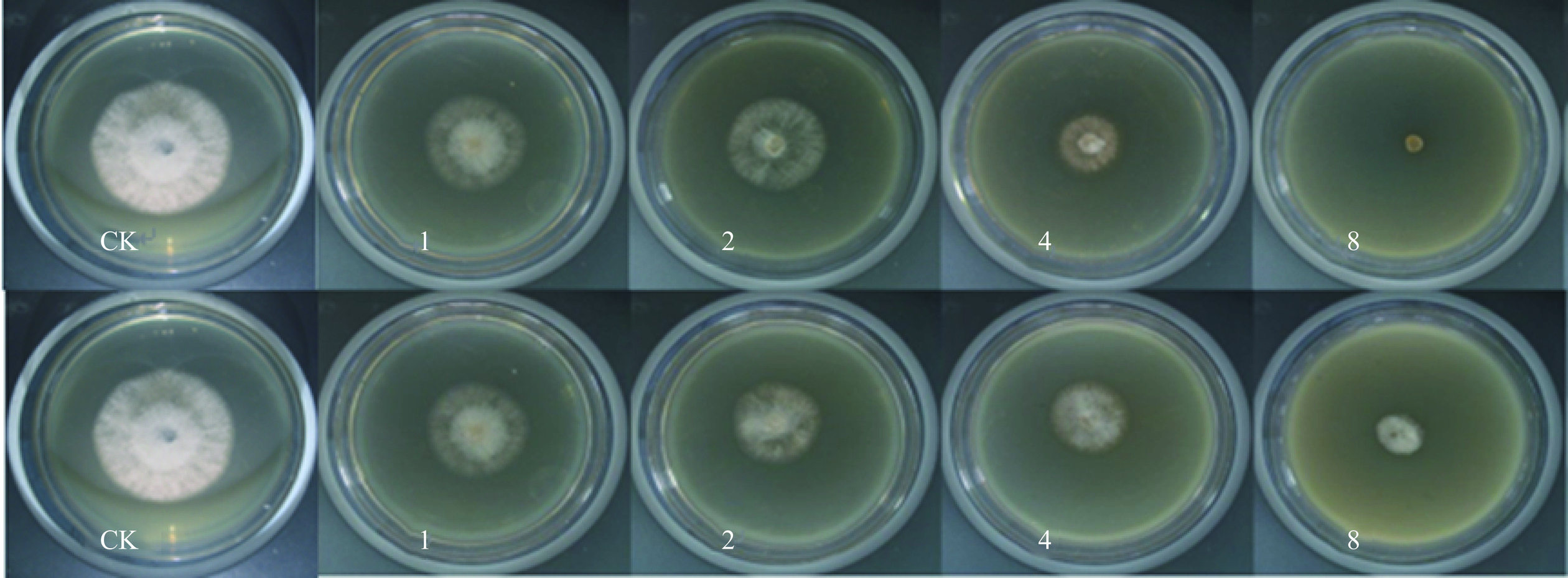
药用植物提取物使用量的确定对于其后期活性开发至关重要。由表2和图1可知,与对照(CK)相比,大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液对灰葡萄孢菌菌丝的抑制作用显著(P<0.05),抑菌效果与使用浓度正相关,在1.5 mg/mL浓度下,山芝麻提取物对灰霉菌的抑制率在40%左右[23],本研究的大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提物在1、2、4、8 mg/mL 4个浓度下对灰葡萄孢菌的菌丝生长抑制率均优于山芝麻提取物。
表 2 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对灰葡萄孢菌的抑菌效果Table 2. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on B. cinerea.浓度
(mg·mL−1)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 68.21±0.29a 68.21±0.29a − − 1 35.46±0.43b 36.40±0.54b 52.65±0.70d 51.13±0.87d 2 32.77±0.49c 32.03±0.30c 56.97±0.78c 58.15±0.48c 4 20.64±0.37d 28.77±0.22d** 76.47±0.60b 63.40±0.35b** 8 6.79±0.03e 17.24±0.24e** 98.74±0.04a 81.93±0.39a** 注:每一列不同小写字母代表不同使用浓度下菌落生长的差异极显著(P<0.01);同一行两组数据后的“*”代表同一浓度下,与茎叶相比,假根醇提液处理菌落生长的数据存在显著差异(P<0.05),“**”代表差异极显著(P<0.01);表3~表5同。 茎叶醇提液浓度≥4 mg/mL时,对灰葡萄孢菌的菌丝生长抑制率高于假根醇提液,菌落直径小于假根醇提液(P<0.01),但在梁财等[23]的研究中,根对灰霉菌的抑菌效果与叶片相当。胡秀荣等[24]采用生长速率法研究柑桔提取物对8种植物病原真菌的抑制作用,结果表明,桔皮醇提液对供试8种病原菌的抑制率均在70%以上,种子醇提液对供试8种病原菌的抑制率均在75%以上,种子醇提液的抑菌率均高于桔皮醇提液。药用植物体内起抑菌活性作用的主要是次生代谢产物,而次生代谢产物在不同植物、不同器官及不同生境条件下是不同的,因此抑菌活性也不同[25]。综上,大金发藓醇提液对灰葡萄孢菌菌丝生长产生极显著抑制作用,且随使用浓度增加抑制效果增强,其中,茎叶醇提液的抑菌效果优于假根醇提液。
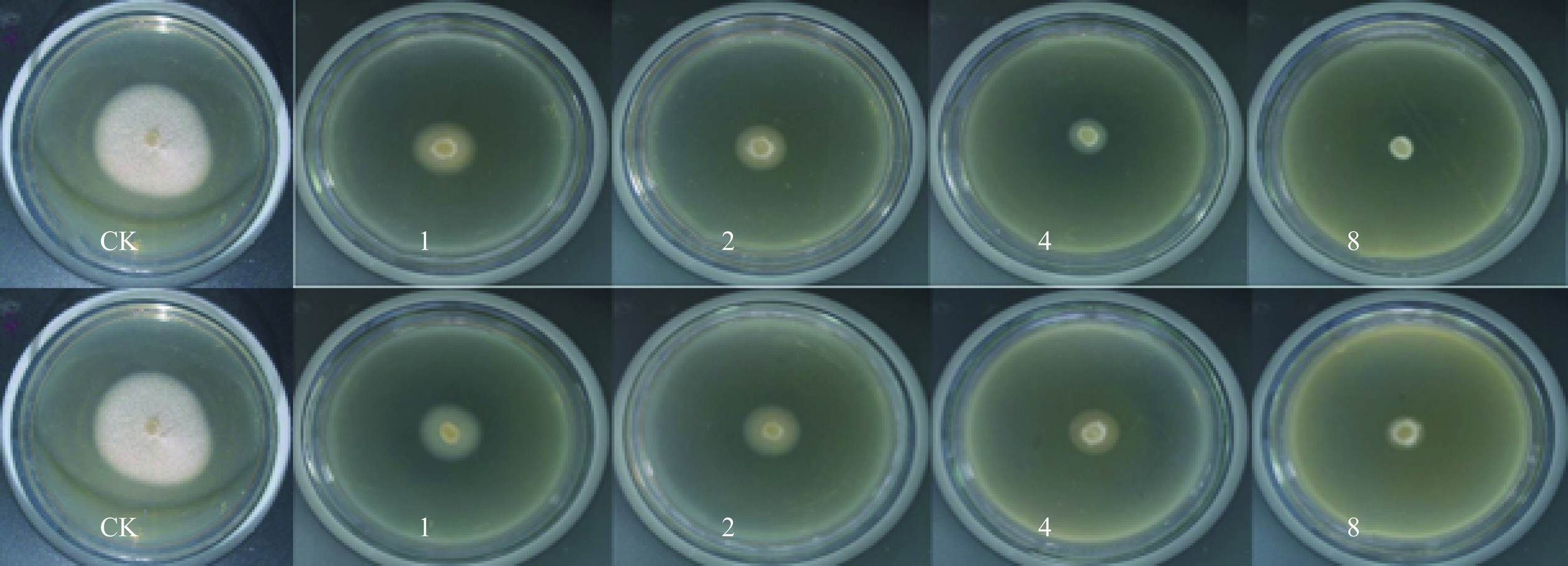
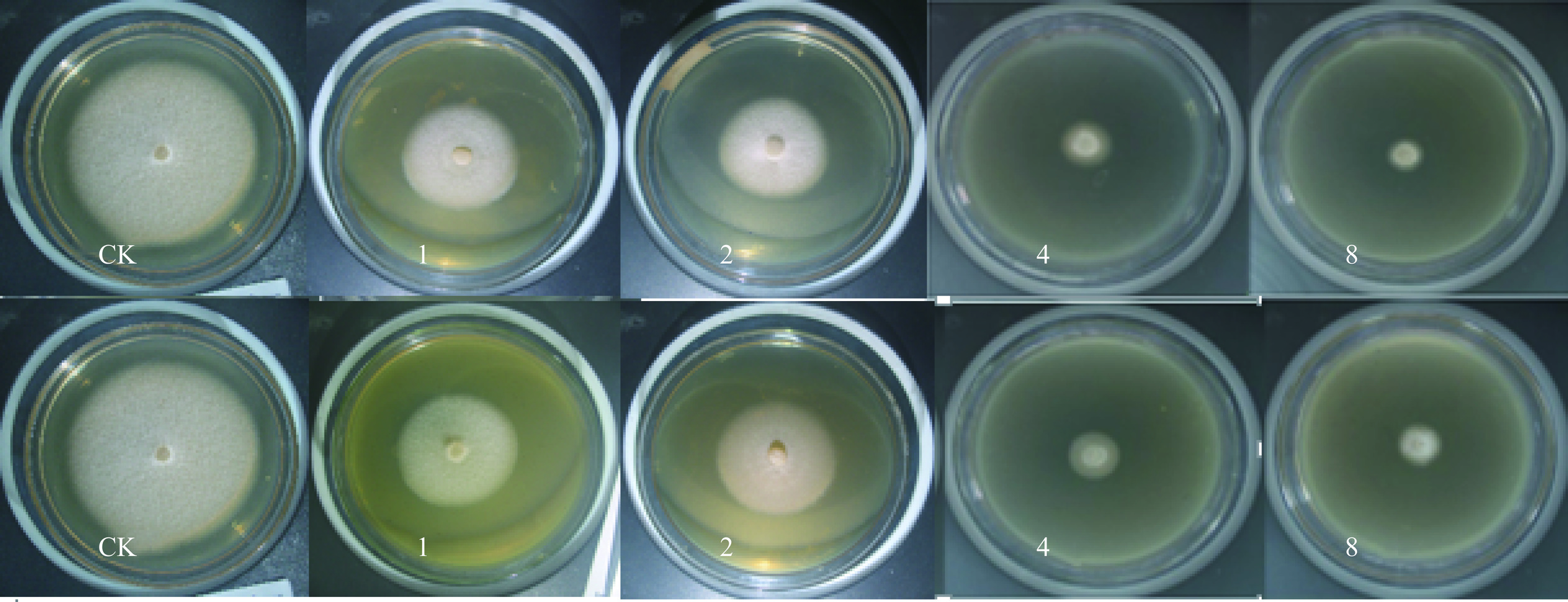
2.2 大金发藓醇提物对茄病镰刀菌的抑菌效果
茄病镰刀菌是导致多种植物根腐病的病原菌之一,药用植物活性代谢产物对其活性有抑制作用[26−27]。由表3~表4和图2~图3可知,与CK相比,大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液对茄病镰刀菌甘薯专化型和茄病镰刀菌菌丝生长的抑制作用极显著(P<0.01),且抑制效果与使用浓度正相关。在2.0 mg/mL时,中南鱼藤枝叶提取物对茄病镰刀菌的抑制率最高,为63.82%[28],但本实验结果表明,8 mg/mL大金发藓茎叶醇提液对茄病镰刀菌的抑菌率高达90%以上。茎叶醇提液在≥2 mg/mL浓度,对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)菌丝生长的抑制率极显著高于假根醇提液(P<0.01),菌落直径小于假根醇提液(P<0.01),茎叶醇提液在≥1 mg/mL浓度,对茄病镰刀菌菌丝生长的抑制率显著高于假根醇提液(P<0.05),菌落直径小于假根醇提液(P<0.05)。综上,大金发藓醇提液对茄病镰刀菌菌丝生长产生极显著抑制作用,且随使用浓度增加抑制效果增强,其中,茎叶醇提液的抑菌效果优于假根醇提液(P<0.01)。
表 3 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)的抑菌效果Table 3. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on F. solani f. sp. batatas (sweet potato type)浓度
(mg·mL−1)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 51.10±0.13a 51.10±0.13a − − 1 22.78±0.59b 23.58±0.26b 62.79±1.30d 61.01±0.58d 2 18.52±0.10c 20.74±0.14c** 72.23±0.21c 67.32±0.30c** 4 14.32±0.49d 17.84±0.13d** 81.56±1.09b 73.75±0.30b** 8 9.18±0.05e 14.10±0.61e** 92.94±0.10a 82.05±1.35a** 表 4 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对茄病镰刀菌的抑菌效果Table 4. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on F. solani浓度
(mg/mL)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 80.66±0.76a 80.66±0.76a − − 1 44.22±0.62b 46.53±0.75b** 48.81±0.83d 45.71±1.01d** 2 42.69±0.39c 44.21±0.75c* 50.86±0.52c 48.83±1.00c * 4 15.66±0.39d 17.85±0.78d* 87.07±0.52b 84.13±1.05b* 8 8.580±0.43e 11.69±0.74e* 96.54±0.58a 92.38±0.99a* 2.3 大金发藓醇提物对细极链格孢菌的抑菌效果
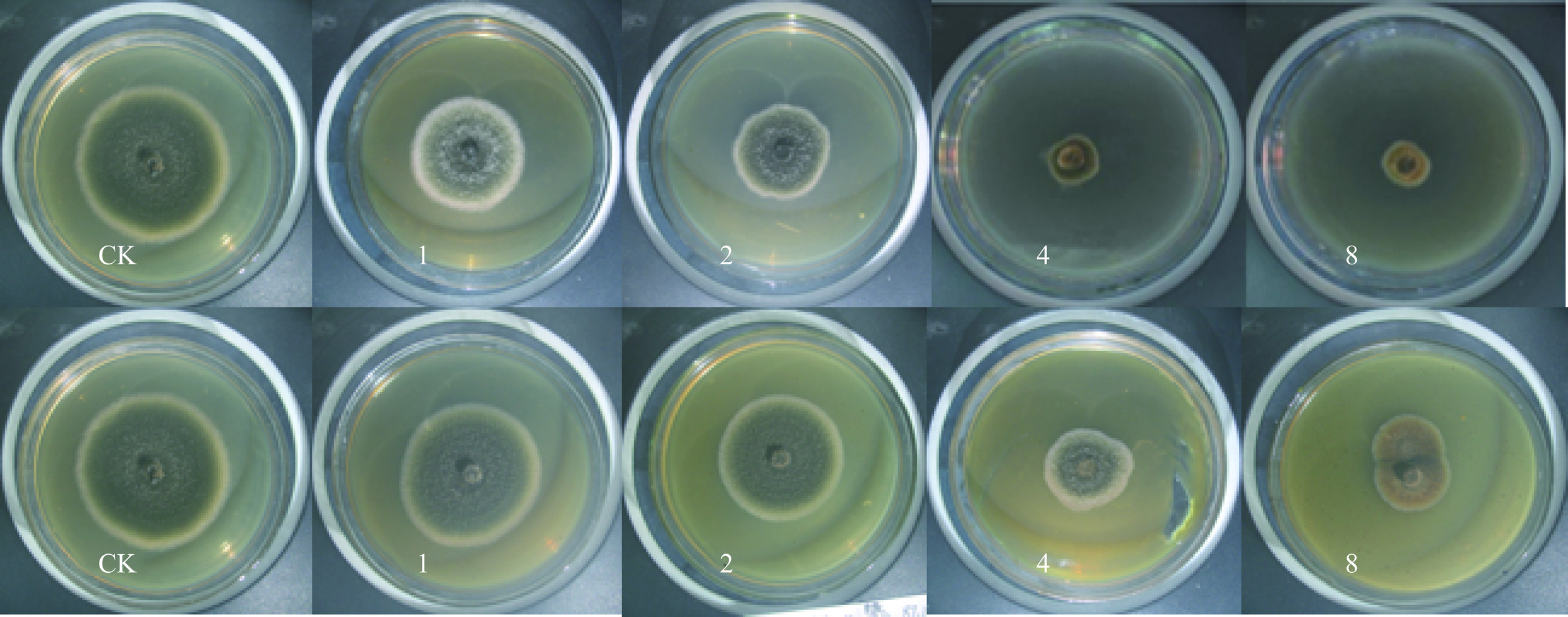
与CK相比,大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液对细极链格孢菌菌丝生长的抑制作用极显著且抑制效果与使用浓度正相关(表5、图4)。相比于其他3种真菌,大金发藓醇提物对细极链格孢菌菌丝生长的抑制效果最差,但在最高浓度8 mg/mL下,抑制率仍达到81.84%(茎叶)和70.86%(假根),有必要对更高浓度的使用进行进一步研究。在≥1 mg/mL浓度下,茎叶醇提液对细极链格孢菌菌丝生长抑制率极显著高于假根醇提液(P<0.01),菌落直径极显著小于假根醇提液(P<0.01)。综合而言,大金发藓醇提液对细极链格孢菌菌丝生长产生显著抑制作用,且随使用浓度增加抑制效果增强,茎叶醇提液的抑菌效果优于假根醇提液。
表 5 不同浓度大金发醇提物对细极链格孢菌的抑制效果Table 5. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on A. tenuissima浓度
(mg/mL)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 75.08±0.77a 75.08±0.77a − − 1 40.79±0.58b 51.02±2.16b* 49.64±0.85d 34.83±3.12c* 2 35.27±1.14c 43.32±0.57c** 57.63±1.65c 45.97±0.82b** 4 20.08±0. 19d 26.33±0.82d** 79.61±0.28b 70.58±1.19a** 8 18.55±0.70e 26.13±0.13e** 81.84±1.02a 70.86±0.19a** 2.4 大金发藓醇提物对4种植物病原真菌分生孢子萌发抑制效果的比较
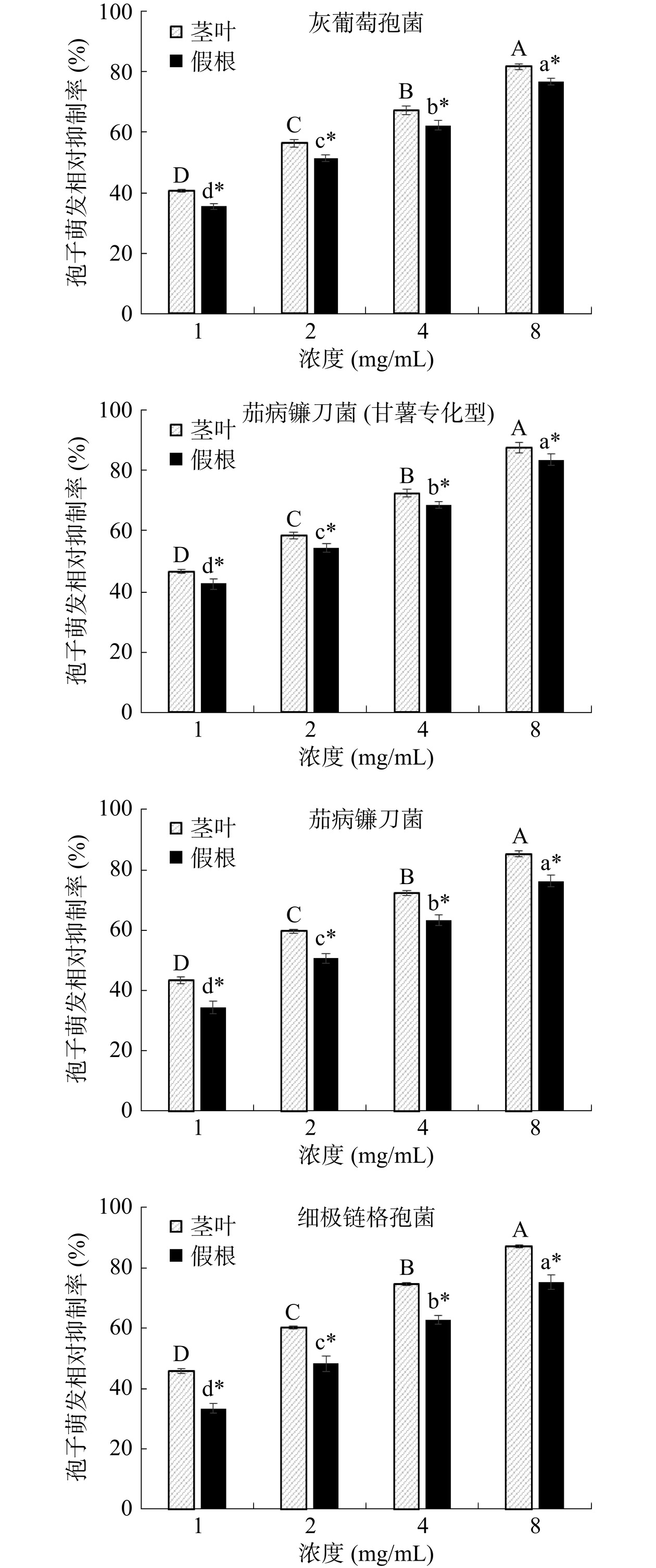
如图5所示,大金发藓茎叶醇提液对4种植物病原菌分生孢子萌发具有极显著的抑制作用,且随用量增加,抑制作用增强(P<0.01),假根醇提液的作用效果与之相同,但处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。茎叶醇提液对4种病原菌孢子萌发的相对抑制率在最低浓度1 mg/mL时即大于40%,在最高用量8 mg/mL时,对4种病原菌孢子萌发的相对抑制率均在80%以上,其中,对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)分生孢子萌发的相对抑制率最高(87.68%),其次为细极链格孢菌(87.10%)。假根醇提液对4种病原菌孢子萌发也产生显著抑制作用,且随使用浓度增加抑制作用增强(P<0.05),对于4种病原菌孢子萌发而言,假根醇提液的抑制作用均显著低于茎叶醇提液(P<0.05)。
![]() 图 5 大金发藓乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌分生孢子萌发的相对抑制率注:同一系列4组数据上的不同大写字母代表不同使用浓度间孢子萌发抑制率的单因素方差分析结果差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05);同一使用浓度下,茎叶和假根处理组数据上的“*”代表茎叶和假根醇提液处理之间孢子萌发抑制率的T检验结果差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 5. Relative inhibitory rates of the alcohol extracts from P. commune on the conidial germination of the four plant disease fungi
图 5 大金发藓乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌分生孢子萌发的相对抑制率注:同一系列4组数据上的不同大写字母代表不同使用浓度间孢子萌发抑制率的单因素方差分析结果差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05);同一使用浓度下,茎叶和假根处理组数据上的“*”代表茎叶和假根醇提液处理之间孢子萌发抑制率的T检验结果差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 5. Relative inhibitory rates of the alcohol extracts from P. commune on the conidial germination of the four plant disease fungi2.5 大金发藓醇提物对4种植物病原真菌的毒力分析
EC50为半数效应浓度,是物质对病原菌抑制效率达到50%时的使用浓度[29]。由表6可知,大金发藓茎叶醇提液对4种植物病原真菌的EC50排序为茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)<细极链格孢菌<茄病镰刀菌<灰葡萄孢菌,茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)对大金发藓茎叶醇提液的敏感性最高,EC50仅为0.42 mg/mL。由表7可知,大金发藓假根醇提液对4种植物病原真菌的EC50顺序为茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)<灰葡萄孢菌<茄病镰刀菌<细极链格孢菌,茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)对大金发藓假根醇提液的敏感性最高,EC50仅为0.35 mg/mL,结合菌丝生长抑制实验,在1 mg/mL浓度下,大金发藓醇提液对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)菌丝生长抑制率达到60%以上。有研究发现大镰刀藓的醇提液对立枯丝核菌的抑菌活性显著,EC50为0.878 mg/mL,但对于不同器官提取物的抑菌效果未做深入研究[30],本研究结果显示,大金发藓茎叶和假根醇提液对4种植物病原真菌均有抑制作用,其中对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)的EC50数值最小,抑制效果最好。
表 6 大金发藓茎叶醇提物对4种病原菌的EC50Table 6. Medium concentration of alcohol extracts from the shoots of P. commune against four pathogenic bacteria真菌名称 毒力回归方程 相关系数 EC50(mg/mL) 灰葡萄孢菌 y=52.409x+47.54 0.9339 2.95 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) y=33.151x+62.411 0.9976 0.42 茄病镰刀菌 y=55.57x+42.702 0.9877 1.35 细极链格孢菌 y=39.387x+49.395 0.9425 1.04 表 7 大金发藓假根醇提物对4种病原菌的EC50Table 7. Medium concentration of alcohol extracts from the rhizoids of P. commune against 4 pathogenic bacteria真菌名称 毒力回归方程 相关系数 EC50(mg/mL) 灰葡萄孢菌 y=32.438x+49.006 0.9149 1.07 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) y=23.099x+60.605 0.9953 0.35 茄病镰刀菌 y=58.237x+41.466 0.9483 1.41 细极链格孢菌 y=44.081x+35.654 0.9126 2.14 3. 结论
本研究结果表明,大金发藓茎叶和假根乙醇提取物对灰葡萄孢菌、茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)、茄病镰刀菌和细极链格孢菌菌丝生长和分生孢子萌发均具有较强的抑制作用,且随使用浓度增加抑菌作用增强,其中茎叶乙醇提取物的抑菌效果显著高于假根,二者在植物源杀菌剂的开发利用中均具备一定的应用潜力。本研究对大金发藓乙醇提取液设了4个使用浓度(1、2、4、8 mg/mL),结果显示,8 mg/mL使用浓度下,4种植物病害真菌菌丝生长的抑制率均达到85%以上,最高可达到98.74%(灰葡萄孢菌),但是高于8 mg/mL浓度的抑菌活性和更确切的抗菌组分还有待进一步研究。
-
图 5 大金发藓乙醇提取物对4种植物病原真菌分生孢子萌发的相对抑制率
注:同一系列4组数据上的不同大写字母代表不同使用浓度间孢子萌发抑制率的单因素方差分析结果差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05);同一使用浓度下,茎叶和假根处理组数据上的“*”代表茎叶和假根醇提液处理之间孢子萌发抑制率的T检验结果差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5. Relative inhibitory rates of the alcohol extracts from P. commune on the conidial germination of the four plant disease fungi
表 1 本研究所用菌种
Table 1 Bacteria tested in this study
名称 DNA鉴定结果 相似度(%) 灰葡萄孢菌 Botrytis cinerea 100.00 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) Fusarium solani f. sp. batatas 99.73 茄病镰刀菌 Fusarium solani 99.87 细极链格孢菌 Alternaria tenuissima 100.00 表 2 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对灰葡萄孢菌的抑菌效果
Table 2 Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on B. cinerea.
浓度
(mg·mL−1)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 68.21±0.29a 68.21±0.29a − − 1 35.46±0.43b 36.40±0.54b 52.65±0.70d 51.13±0.87d 2 32.77±0.49c 32.03±0.30c 56.97±0.78c 58.15±0.48c 4 20.64±0.37d 28.77±0.22d** 76.47±0.60b 63.40±0.35b** 8 6.79±0.03e 17.24±0.24e** 98.74±0.04a 81.93±0.39a** 注:每一列不同小写字母代表不同使用浓度下菌落生长的差异极显著(P<0.01);同一行两组数据后的“*”代表同一浓度下,与茎叶相比,假根醇提液处理菌落生长的数据存在显著差异(P<0.05),“**”代表差异极显著(P<0.01);表3~表5同。 表 3 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型)的抑菌效果
Table 3 Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on F. solani f. sp. batatas (sweet potato type)
浓度
(mg·mL−1)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 51.10±0.13a 51.10±0.13a − − 1 22.78±0.59b 23.58±0.26b 62.79±1.30d 61.01±0.58d 2 18.52±0.10c 20.74±0.14c** 72.23±0.21c 67.32±0.30c** 4 14.32±0.49d 17.84±0.13d** 81.56±1.09b 73.75±0.30b** 8 9.18±0.05e 14.10±0.61e** 92.94±0.10a 82.05±1.35a** 表 4 不同浓度大金发藓醇提物对茄病镰刀菌的抑菌效果
Table 4 Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on F. solani
浓度
(mg/mL)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 80.66±0.76a 80.66±0.76a − − 1 44.22±0.62b 46.53±0.75b** 48.81±0.83d 45.71±1.01d** 2 42.69±0.39c 44.21±0.75c* 50.86±0.52c 48.83±1.00c * 4 15.66±0.39d 17.85±0.78d* 87.07±0.52b 84.13±1.05b* 8 8.580±0.43e 11.69±0.74e* 96.54±0.58a 92.38±0.99a* 表 5 不同浓度大金发醇提物对细极链格孢菌的抑制效果
Table 5 Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of alcohol extracts from P. commune on A. tenuissima
浓度
(mg/mL)菌落直径(mm) 菌丝生长抑制率(%) 茎叶 假根 茎叶 假根 CK 75.08±0.77a 75.08±0.77a − − 1 40.79±0.58b 51.02±2.16b* 49.64±0.85d 34.83±3.12c* 2 35.27±1.14c 43.32±0.57c** 57.63±1.65c 45.97±0.82b** 4 20.08±0. 19d 26.33±0.82d** 79.61±0.28b 70.58±1.19a** 8 18.55±0.70e 26.13±0.13e** 81.84±1.02a 70.86±0.19a** 表 6 大金发藓茎叶醇提物对4种病原菌的EC50
Table 6 Medium concentration of alcohol extracts from the shoots of P. commune against four pathogenic bacteria
真菌名称 毒力回归方程 相关系数 EC50(mg/mL) 灰葡萄孢菌 y=52.409x+47.54 0.9339 2.95 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) y=33.151x+62.411 0.9976 0.42 茄病镰刀菌 y=55.57x+42.702 0.9877 1.35 细极链格孢菌 y=39.387x+49.395 0.9425 1.04 表 7 大金发藓假根醇提物对4种病原菌的EC50
Table 7 Medium concentration of alcohol extracts from the rhizoids of P. commune against 4 pathogenic bacteria
真菌名称 毒力回归方程 相关系数 EC50(mg/mL) 灰葡萄孢菌 y=32.438x+49.006 0.9149 1.07 茄病镰刀菌(甘薯专化型) y=23.099x+60.605 0.9953 0.35 茄病镰刀菌 y=58.237x+41.466 0.9483 1.41 细极链格孢菌 y=44.081x+35.654 0.9126 2.14 -
[1] WANG H, TIAN R Z, CHEN Y. In vivo and in vitro antifungal activities of five alkaloid compounds isolated from Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn against plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,2022,188(3):67−73.
[2] FERNANDEZ-ORTUNO D, TORES J A, PEREZ-GARCIA A, et al. First report of fenpyrazamine resistance in Botrytis cinerea from strawberry fields in Spain[J]. Plant Health Progress,2018,19(1):45. doi: 10.1094/PHP-12-17-0075-BR
[3] COSSEBOOM S D, IVORS K L, SCHNABEL G, et al. Within-season shift in fungicide resistance profiles of Botrytis cinerea in California strawberry fields[J]. Plant Disease,2018,103(1):59−64.
[4] 王帆帆, 唐涛, 郭杰, 等. 植物源杀菌剂对白术叶斑病菌的室内毒力和田间防效[J]. 中国植保导刊,2020,40(9):77−80. [WANG Fanfan, TANG Tao, GUO Jie, et al. Toxicity test and field control effect of botanical fungicides on the leaf spot of Atractylodes macrociphala[J]. China Plant Protection,2020,40(9):77−80.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2020.09.015 WANG Fanfan, TANG Tao, GUO Jie, et al. Toxicity test and field control effect of botanical fungicides on the leaf spot of Atractylodes macrociphala[J]. China Plant Protection, 2020, 40(9): 77−80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2020.09.015
[5] 赵茜. 一种防治南瓜白粉病和蔓枯病植物源杀菌剂的研究[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2021(7):35−37. [ZHAO Qian. Study on a plant-derived fungicide for the control of pumpkin powdery mildew and gummy stem blight[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2021(7):35−37.] doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2021.07.0035 ZHAO Qian. Study on a plant-derived fungicide for the control of pumpkin powdery mildew and gummy stem blight[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021(7): 35−37. doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2021.07.0035
[6] 郑安可, 路妍, 黄家英, 等. 9种植物源杀菌剂对向日葵锈病的防效分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2023,45(3):623−628. [ZHENG Anke, LU Yan, HUANG Jiaying, et al. Control effects of 9 botanical fungicides on Puccinia helianthi[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Science,2023,45(3):623−628.] ZHENG Anke, LU Yan, HUANG Jiaying, et al. Control effects of 9 botanical fungicides on Puccinia helianthi[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Science, 2023, 45(3): 623−628.
[7] 丁仁惠, 何小娥, 王文龙, 等. 柑橘采后主要病害植物源杀菌剂的筛选及抑菌效果分析[J]. 河南农业科学,2019,48(2):91−97. [DING Renhui, HE Xiaoe, WANG Wenlong, et al. Screening of plant-derived fungicides for main diseases of postharvest Gitrus and analysis of antifungal effects[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2019,48(2):91−97.] DING Renhui, HE Xiaoe, WANG Wenlong, et al. Screening of plant-derived fungicides for main diseases of postharvest Gitrus and analysis of antifungal effects[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 48(2): 91−97.
[8] 成晓霞. 大金发藓抗癌活性组分分析及其对白血病细胞杀伤机制研究[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2013. [CHENG Xiaoxia. Analysis of anti-cancer active components of Polytrichum commune and its killing mechanism on leukemia cells[D]. Xi’an:Shaanxi Normal University, 2013.] CHENG Xiaoxia. Analysis of anti-cancer active components of Polytrichum commune and its killing mechanism on leukemia cells[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2013.
[9] 郭玲, 雷成康, 袁文娟, 等. 大金发藓乙酸乙酯提取物对K562细胞膜的损伤效应[J]. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(5):89−93. [GUO Ling, LEI Chengkang, YUAN Wenjuan, et al. Damage of effect of ethyl acetate extract of Polytrichum commune on membrane of human leukemia K562 cell[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2016,44(5):89−93.] GUO Ling, LEI Chengkang, YUAN Wenjuan, et al. Damage of effect of ethyl acetate extract of Polytrichum commune on membrane of human leukemia K562 cell[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(5): 89−93.
[10] 成晓霞, 张志琪, 汤薇, 等. 大金发藓化学成分预试及其肿瘤细胞毒活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2014,26(11):1733−1738. [CHENG Xiaoxia, ZHANG Zhiqi, TANG Wei, et al. Chemical components and cytotoxic activity of Polytrichum commune L. ex Hedw[J]. Natural Production Research and Development,2014,26(11):1733−1738.] CHENG Xiaoxia, ZHANG Zhiqi, TANG Wei, et al. Chemical components and cytotoxic activity of Polytrichum commune L. ex Hedw[J]. Natural Production Research and Development, 2014, 26(11): 1733−1738.
[11] 陈圆圆, 郭水良, 娄玉霞, 等. 大金发藓和小蛇苔化学他感作用的生物测定[J]. 植物研究,2009,29(1):108−112. [CHEN Yuanyuan, GUO Shuiliang, LOU Yuxia, et al. Bioassay on the allelopathic effects of Polytrichum commune and Conocephalum japonicum[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Rsearch,2009,29(1):108−112.] doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2009.01.022 CHEN Yuanyuan, GUO Shuiliang, LOU Yuxia, et al. Bioassay on the allelopathic effects of Polytrichum commune and Conocephalum japonicum[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Rsearch, 2009, 29(1): 108−112. doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2009.01.022
[12] LI W Y, CHIU L C M, LAM W S, et al. Ethyl acetate extract of Chinese medicinal herb Sancandra glabra induces growth inhibition on human leukemic HL-60 cells, associated with cell cycle arrest and up-regulation of pro-apoptotic Bax/Bcl-2 ratio[J]. Oncology Reports,2007,17(2):425−431.
[13] LIU Q W, GE X D, CHEN L G, et al. Purification and analysis of the composition and antioxidant activity of poly-saccharides from Heliaeres angustifolin L.[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,107:2262−2268. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.095
[14] 成晓霞, 李欣怡, 李微, 等. 大金发藓极性组分与抗氧化能力相关性研究[J]. 西安文理学院学报,2022,25(2):72−78. [CHENG Xiaoxia, LI Xinyi, LI Wei, et al. Research on the correlation between polar components of Polytrichum commune Hedw and its antioxidant capacity[J]. Journal of Xian University(Natural Science Edition),2022,25(2):72−78.] CHENG Xiaoxia, LI Xinyi, LI Wei, et al. Research on the correlation between polar components of Polytrichum commune Hedw and its antioxidant capacity[J]. Journal of Xian University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 25(2): 72−78.
[15] 陈云坤, 胡春艳, 张知宇, 等. 5种瑞香科植提取物对7种植物病原真菌的抑菌活性测定[J]. 中国农学通报,2022,38(13):148−156. [CHEN Yunkun, HU Chunyan, ZHANG Zhiyu, et al. Antimicrobial activity of extracts from five thymelaeaceae plants aginst seven plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Chinese Agricultural Sciences Bulletin,2022,38(13):148−156.] doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0784 CHEN Yunkun, HU Chunyan, ZHANG Zhiyu, et al. Antimicrobial activity of extracts from five thymelaeaceae plants aginst seven plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Chinese Agricultural Sciences Bulletin, 2022, 38(13): 148−156. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0784
[16] 邢小霞, 李秀岚. 丝瓜乙醇提取物对几种植物病原菌真菌抑菌活性的研究[J]. 北方园艺,2015(13):131−133. [XING Xiaoxia, LI Xiulan. Study on antifungal activity of several plant pathogenit fungi from ethanol extract of Luffa[J]. North Horticulture,2015(13):131−133.] XING Xiaoxia, LI Xiulan. Study on antifungal activity of several plant pathogenit fungi from ethanol extract of Luffa[J]. North Horticulture, 2015(13): 131−133.
[17] 刘星宇, 廖艺超, 王壹, 等. 超声波联用技术在植物活性成分提取中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(14):319−327. [LIU Xingyu, LIAO Yichao, WANG Yi, et al. Reasearch progress on application of ultrasound hyphenated technique in extraction of active phytochemicals[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(14):319−327.] LIU Xingyu, LIAO Yichao, WANG Yi, et al. Reasearch progress on application of ultrasound hyphenated technique in extraction of active phytochemicals[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(14): 319−327.
[18] CARREIRACASAIS A, OTERO P, GARCIAPEREZ P, et al. Benefits and drawbacks of ultrasound-assisted extraction for the recovery of bioactive compounds from marine algae[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2021,18(17):9153. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179153
[19] 刘立萍, 王宁, 雷小红, 等. 食品包装用箬叶提取物抑菌活性的初步研究[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(6):257−262. [LIU liping, WANG Ning, LEI Xiaohong, et al. Primary study of the antimicrobial activity of the extracts from Indocalamus tessellatus leaves for food packaging [J]. Food Science and Technology, 22022, 47(6):257−262.] LIU liping, WANG Ning, LEI Xiaohong, et al. Primary study of the antimicrobial activity of the extracts from Indocalamus tessellatus leaves for food packaging [J]. Food Science and Technology, 22022, 47(6): 257−262.
[20] SRIDHAR R A, RAMCHANDER E R U G U M, MADHUSUDANA R J. Antibacterial and antifungal studies of prenylated isoflavones and prenylated 3-aryl coumarins isolated from Derris scandens Bengh.[J]. Journal of Pharmacognosy,2012,3(2):51−54.
[21] LIN Z, ANJANEYA S R, SUNDAR R K, et al. Anti-fungal and antibacterial activities of ethanol extracts of selected traditional Chinese medicinal herbs[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine,2013,6(9):673−681. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(13)60117-0
[22] 方中达. 植病研究方法[M]. 第3版. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2007:142−156. [FANG Zhongda. Method of plant disease research[M]. 3rd. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2007:142−156.] FANG Zhongda. Method of plant disease research[M]. 3rd. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2007: 142−156.
[23] 梁材, 陈颖, 李昌恒, 等. 山芝麻提取物对10种植物病原菌的抑菌活性初探[J]. 广西植物,2020,40(5):715−726. [LIANG Cai, CHEN Ying, LI Changheng, et al. Antifungal activity of extracts of Helicteres ngustifolia against ten plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Guihaia,2020,40(5):715−726.] doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201901051 LIANG Cai, CHEN Ying, LI Changheng, et al. Antifungal activity of extracts of Helicteres ngustifolia against ten plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Guihaia, 2020, 40(5): 715−726. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201901051
[24] 胡秀荣, 杜丹超, 黄振东, 等. 柑桔提取物对8种植物病原真菌的抑制作用研究[J]. 中国南方果树,2011,40(5):1−4. [HU Xiurong, DU Danchao, HUANG Zhendong, et al. Study on fugistasis effects of extracts to 8 Phytopathogenic fungi[J]. China Northern fruit Tree,2011,40(5):1−4.] HU Xiurong, DU Danchao, HUANG Zhendong, et al. Study on fugistasis effects of extracts to 8 Phytopathogenic fungi[J]. China Northern fruit Tree, 2011, 40(5): 1−4.
[25] 周冬宇, 李杨, 邢咏梅, 等. 药用植物微生物组及其与药用植物次生代谢产物的关系[J]. 微生物学通报,2022,49(9):3989−4003. [ZHOU Dongyu, LI Yang, XING Yongmei, et al. Microbiome of medicinal plants and its effect on medicinal plant secondary metabolites:A review[J]. Microbioloty China,2022,49(9):3989−4003.] ZHOU Dongyu, LI Yang, XING Yongmei, et al. Microbiome of medicinal plants and its effect on medicinal plant secondary metabolites: A review[J]. Microbioloty China, 2022, 49(9): 3989−4003.
[26] 武文豪, 李开杰, 王庆, 等. 草珊瑚不同提取物抑菌活性研究[J]. 现代农业研究, 2023, 29(2):96−100. [WU Wenhao, LI Kaijie, WANG Qing, et al. Study on antibacterial activity of different extracts from sarcandra Glabra (Thenb. Nakai)[J]. 2023, 29(2):96−100.] WU Wenhao, LI Kaijie, WANG Qing, et al. Study on antibacterial activity of different extracts from sarcandra Glabra (Thenb. Nakai)[J]. 2023, 29(2): 96−100.
[27] ROZIHAWATI Z, NORMALA H, AHMAD S S, et al. Bio-antifungal activity of selected medicinal plant extracts against root rot of fungal disease[J]. Journal of Plant Sciences,2014,2(1):31−36.
[28] 刘启凤, 张北京, 尹丰满, 等. 中南鱼藤枝叶提取物对植物病原真菌的抑菌活性[J]. 热带生物学报,2022,13(3):227−234. [LIU Qifeng, ZHANG Beijing, YIN Fengman, et al. Fungistatic activity of the extracts from the twigs and leavies of Derris fordii againse plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology,2022,13(3):227−234.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2022.3.hnrdnydxxb202203005 LIU Qifeng, ZHANG Beijing, YIN Fengman, et al. Fungistatic activity of the extracts from the twigs and leavies of Derris fordii againse plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2022, 13(3): 227−234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7054.2022.3.hnrdnydxxb202203005
[29] KHANM R, OMOLOSO A D, BAREWAI Y. Antimicrobial activity of the Derris dlliptica, Derris indica and Derris trifoliate extractives[J]. Fitoterapia,2006,77(4):327−330. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2006.03.007
[30] 程辉彩, 赵建成, 张丽萍, 等. 三种苔藓植物提取物对植物病原菌的抑菌性研究[J]. 微生物学杂志,2005(3):82−84. [CHENG Huicai, ZHAO Jiancheng, ZHANG Liping, et al. Antifungal activity of three bryothytes extracts on plant pathogen[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2005(3):82−84.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2005.03.021 CHENG Huicai, ZHAO Jiancheng, ZHANG Liping, et al. Antifungal activity of three bryothytes extracts on plant pathogen[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2005(3): 82−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2005.03.021
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李晓娟. 电子束辐照降解诺丽多糖溶液的工艺及抗氧化活性研究. 酿酒科技. 2025(01): 35-39+44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任晓莉,杨璐,乔鹏,缪奕锴,杨懿昂,代秋红,张贤德. 复合酶法提取槐花多糖的工艺优化及其抗氧化活性. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 8-14 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 米圣成,徐晓杰,魏菱鸽,路祺,朱明华,包怡红,陈春霞. 元宝枫种仁多糖提取纯化、结构表征以及降糖活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(08): 29-38 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 寇先勇,吴燕,王峣姿,冯文博,郑佳贝,尤祥宇,苏江涛. 5种中药粗多糖水凝胶的制备及其促伤口愈合能力研究. 轻工学报. 2024(02): 43-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 叶文斌,樊亮,孙娜,秦芳,韩媛,王志文. 响应面结合模糊数学感官评价法优化槐花蜜饯配方及品质测定. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 56-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 赵钜阳,刘静,杨斐然,王婷,刘轲晗,刘珈成,顾丽雅. 槐花提取物对东北肉糜肠贮藏品质的影响及其货架期预测. 肉类研究. 2024(10): 52-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



