Preparation and Properties of Oligo-chitosan Cross-linked Gelatin Biodegradable Films
-
摘要: 目的:研究壳寡糖改性对明胶基薄膜性能的影响。方法:以废猪皮中提取明胶为基质,以壳寡糖和聚乙烯醇为改性交联剂,制备得到了明胶基薄膜。利用红外光谱、X射线衍射、扫描电子显微镜、分光光度法、拉力试验测试法对其结构和力学性能进行了测定,并测试了明胶基薄膜在抗氧化、抗菌、水稳定性和生物降解方面的性能。结果:交联改性后明胶薄膜的力学性能得到显著提升,断裂应力最高可达37.09 MPa,最大撕裂能为56.71 kJ/m2,且浸泡于水中48 h仍能维持良好的物理形态,此外,薄膜还拥有优异透光性(最大可达92.32%),良好抗氧化性(自由基的清除率最高可达75.12%),优异抗菌性和生物降解性(完全降解时间<45 h)。结论:壳寡糖改性一定程度上改善了明胶基薄膜的力学性能和生物降解性能,赋予了薄膜良好抗菌性和抗氧化能力,表明其在食品包装上存在较大潜在应用价值。Abstract: Objective: The aim was to evaluate the effect of oligo-chitosan modification on the properties of gelatin-based films. Methods: The gelatin-based films were prepared by using gelatin extracted from scrap pig skin as a cheap raw material and chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol as cross-linking agents. The structural and mechanical properties were characterized by Fourier infrared spectroscopy, X-ray power diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, spectroscopy, and tensile test. Meanwhile, the ability of gelatin-based films in antioxidant, antibacterial, water stability and biodegradation were evaluated. Results: The multi-cross-linked gelatin-based films showed excellent mechanical properties, with a highest fracture stress of 37.09 MPa, a maximum tearing energy of 56.71 kJ/m2, and a good physical form maintained after 48 h of immersion in water. In addition, the films possessed excellent light transmission (up to 92.32%), good oxidation resistance (radical scavenging capacity up to 75.12%), excellent antimicrobial and biodegradability (complete degradation time <45 h). Conclusions: The addition of oligo-chitosan has changed the properties of gelatin-based films in mechanics and biodegradation, and endowed the films with good antibacterial and antioxidant capacity, indicating that it had great potential application value in food packaging.
-
Keywords:
- gelatin /
- oligo-chitosan /
- crosslinking /
- biodegradable film /
- property
-
食品易受到微生物污染而导致其保质期变短,若储存不佳极易造成大量浪费[1]。薄膜材料因具有良好的阻断性、保温性、防潮性和机械性,而被广泛应用于食品包装,对延长食品保质期起着至关重要的作用[2−3]。然而,日常生活中食品包装薄膜的应用多为“一次性”[4],且大多是由石油基高分子聚合物所构成的。这些被废弃后的食品包装薄膜难以降解,其大量应用不仅会造成严重的环境污染,影响人们的身体健康,而且还会加剧人类在化石资源上的短缺危机。因此,寻求一种可生物降解的非石油基食品包装薄膜显得尤为必要。
明胶作为胶原的变性产物,因其具有良好的生物降解性、成膜性和无毒性等优势,而成为制备食品包装薄膜的一种理想材料[5]。在天然皮革的生产过程中,约有占原皮重30%~50%的皮革材料被丢弃,因此可从皮革生产工业被废弃的生皮边角料中提取廉价明胶[6]。然而,未经过任何处理的明胶薄膜自身却存在较多缺陷,如吸湿性强、脆性高和耐水性差等,极大限制了其在食品包装领域的应用[7−9]。针对这些固有缺陷,通过交联剂与明胶分子间的交联,可有效改善明胶薄膜在吸湿性和力学方面的性能。陈书霖等[10]将戊二醛添加到罗非鱼明胶中,发现改性后明胶薄膜的阻湿性和耐水性得到显著提升,但其机械性能却发生了一定程度降低。Chou等[11]发现向明胶纤维膜中添加碳二亚胺后,明胶膜的生物稳定性和热稳定性得到明显改善。陶忠等[12]对比了酶交联剂谷氨酰胺转移酶和化学交联剂戊二醛应用于改性明胶性能中的效果,发现谷氨酰胺转移酶的改性能提升明胶薄膜的耐水性能和机械性能。然而,这些交联剂的加入并不能让明胶基薄膜获得高强韧性,拥有较好的抗氧化和抗菌性能,更为严重的是其中部分化学交联剂,如戊二醛存在一定毒副作用,使得其改性后薄膜不宜直接应用于食品包装。
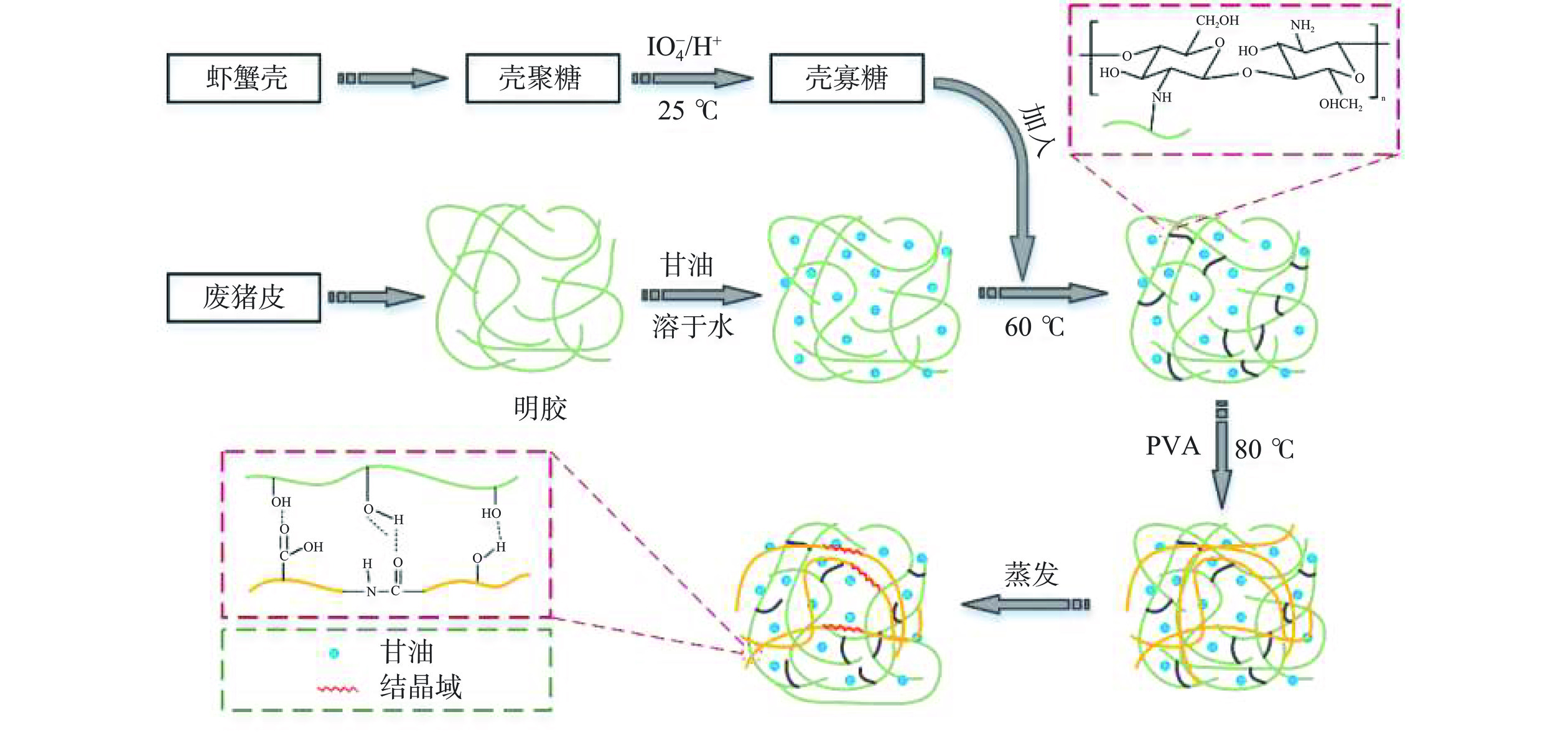
壳寡糖是壳聚糖或甲壳素的降解产物,因其特殊的阳离子氨基结构,使得壳寡糖具有良好的抑菌活性和抗氧化性,在抑菌材料的制备方面显示出潜在的应用价值[13],同时,壳寡糖安全且无毒副作用,具有优良成膜性而在食品领域应用较为广泛。林碧莲等[14]将可控制备得到三组不同聚合度的壳寡糖分别添加到预包装豆腐中,发现均显示出良好的抑菌效果,可有效延长豆腐腐败变质的时间。Castillo等[15]发现将壳寡糖添加到热塑性玉米淀粉薄膜后,改性后淀粉薄膜在抑制酵母菌和霉菌方面显示出良好的效果,而成为一种在食品包装方面存在潜在应用价值的材料。目前,壳寡糖可以以废弃的虾蟹壳为原料进行制备提取[16],若能将其应用于明胶基薄膜的制备当中,不仅可以实现“变废为宝”,还能为明胶基食品薄膜包装材料制备提供理论依据。本研究以从废弃皮革中提炼的明胶为原材料,通过与氧化壳寡糖的交联反应提高明胶的机械性能、抗湿性能、抗菌性能和抗氧化性,此外,利用聚乙烯醇作为第二网络引入到明胶基薄膜中以进一步提升其机械性能,可为生物降解新型食品薄膜的开发与应用提供新选项。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
明胶(从废弃猪皮中提取,Mn≈100000) 宁德市夏威食品有限公司;壳聚糖(从虾蟹壳中提取,Mn≈100000,脱乙酰度90%) 潍坊海之源生物制品有限公司;聚乙烯醇(聚合度=1750±50)、甘油、NaIO4、无水乙醇 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;大肠杆菌(CMCC 44103)、金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC 25932) 中国工业微生物菌种保藏管理中心;活性污泥 活性≥0.4 kg COD removed/kg VSS.d,购自武汉市黄浦路污水处理厂。
XPR504型电子分析天平 上海梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;KQ-600KDE型超声波清洗机 江苏省昆山市超声仪器有限公司;HHS-2型恒温水浴锅 上海博讯医疗设备有限公司;9052B型鼓风干燥箱 广东宏展科技有限公司;Nicolet iS50R型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国Thermo Scientific公司;D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪 荷兰帕纳科有限公司;Lambda 35型紫外-可见分光光度计 美国PerkinElmer公司;DR-6000A电子万能试验机 扬州德瑞仪器设备有限公司;Nava 450型扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 荷兰FEI公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 壳寡糖的制备
称取10.0 g壳聚糖于120 mL去离子水中,磁力搅拌使其充分溶解,使用稀H2SO4溶液调节溶液pH4.0,将一定量的NaIO4(与壳聚糖单体单元的摩尔比为1:1)加入到反应体系,在避光条件下于25 ℃、150 r/min水浴中搅拌反应24 h,然后,向反应体系加入浓度为90%乙醇溶液让产物沉淀,并反复洗涤直至无碘化物检出,随后,将所制备得到产物进行冷冻干燥,即得到氧化壳寡糖。
1.2.2 多交联明胶薄膜的制备
称取一定量明胶和甘油于去离子水中,搅拌至完全溶解,配制成质量分数为5.0%明胶溶液,然后将不同剂量所制备的氧化壳寡糖加入到该溶液中,制备得到相对于明胶质量分数分别为0.0%、3.0%、6.0%、9.0%、12.0%和15.0%的壳寡糖-明胶混合溶液,60 ℃条件下反应1.5 h,再向混合溶液中加入相对于明胶质量分数为15.0%的聚乙烯醇(PVA),80 ℃条件下搅拌反应1 h,制备得到多交联明胶成膜溶液。最后,将40 mL成膜溶液倒入到尺寸为10 cm×10 cm聚四氟乙烯方型模具中,放入鼓风干燥箱于45 ℃干燥成膜,制备得到多交联明胶薄膜,如图1所示。将含有不同剂量壳寡糖的明胶薄膜分别命名为MPK-0、MPK-3、MPK-6、MPK-9、MPK-12和MPK-15,未加聚乙烯醇,仅加入质量分数为9.0%壳寡糖的明胶薄膜命名为MK-9。将所制备薄膜置于相对湿度为50%、温度为25 ℃的恒湿恒温环境中存放3 h,再进行各项性能指标的测试。
1.2.3 多交联明胶薄膜性能测定
1.2.3.1 红外光谱(FTIR)测定
将待测薄膜置于干燥器内放置7 d,然后在相对湿度的环境中,将薄膜剪切成直径为20 mm的圆形样品,并固定在红外光谱仪的样品架上,设置波数范围为400~4000 cm−1进行全波段扫描,重复扫描32次,分辨率设置为4 cm−1。
1.2.3.2 X射线衍射(XRD)测定
将待测薄膜切割成2.0 cm×2.0 cm的方块进行X射线衍射扫描,扫描角度范围为5°~50°,电流为40 mA,电压为40 V,扫描速度为4°/min。
1.2.3.3 力学性能测试
依据ASTM D-882的规定,采用单轴拉伸法测试所制备薄膜的断裂应力和断裂应变,将待测薄膜切割成哑铃状(2.0 mm×40.0 mm),并置于电子万能试验机中进行测试,设置试验机的拉伸速度为10 mm/min。使用电子千分尺测定待测薄膜样品的厚度。薄膜杨氏模量主要是从所测量应力-应变曲线初始弹性阶段中获得。
采用“裤型”撕裂方式测定薄膜的撕裂能(Γ):将待测薄膜切割成矩形(10 mm×30 mm),在量规段中间切开一条10 mm长的裂缝,将其置于电子万能试验机进行最大撕裂力(F)测试,依据公式(1),撕裂能(Γ)由薄膜的最大撕裂力(F)和薄膜的平均厚度(d)计算。
Γ(kJ/m2)=2Fd (1) 1.2.3.4 薄膜的溶胀溶解测定
将待测薄膜切成4.0 cm×4.0 cm的方块,在50 ℃条件下干燥至恒重,称重(m0),室温下置于去离子水中浸泡24 h后取出,用滤纸迅速吸干其表面水分,称重(m1),然后,在50 ℃条件下干燥至恒重,称重(m2)。按公式(2)和公式(3)计算薄膜的溶胀率和溶解率。
溶胀率(%)=m1−m0m0×100 (2) 溶解率(%)=m0−m2m0×100 (3) 1.2.3.5 薄膜透光性测定
将表面平整、光滑且无瑕疵的待测薄膜切割成合适尺寸大小1 cm×5 cm的方形,然后,将其紧贴于石英比色皿的一侧,置于紫外-可见分光光度计内的样品池中,以空比色皿做空白对照,在波长为200~800 nm范围内测定薄膜光的透过率,待测薄膜的透明程度采用光的透过率表示。
1.2.3.6 抗氧化性测定
通过测定薄膜清除DPPH自由基和ABTS+自由基的效率来评价其抗氧化性能。其中,参照文献[17]中方法进行DPPH自由基清除率的测定:称取5.0 mg待测薄膜置于5.0 mL浓度为0.4 mmol/L的DPPH甲醇溶液中,在避光条件下振荡处理30 min,然后,使用紫外-可见分光光度计在517 nm处测定其吸光度,依据公式(4)计算DPPH自由基的清除率。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (4) 式中,A0为DPPH甲醇溶液吸光度;A1为DPPH甲醇溶液与待测薄膜作用后吸光度;A2为待测薄膜与相同体积去离子水作用后吸光度。
依照文献[18]中方法进行ABTS+自由基清除率的测定:将4.0 mmol/L ABTS溶液与1.4 mmol/L过硫化钾溶液按1:1搅拌混合均匀,室温下避光氧化16 h,得到ABTS母液。使用蒸馏水将ABTS母液稀释至其在734 nm处的吸光度约为0.7时即可使用,并将其吸光度作为A0。然后,称取5.0 mg待测薄膜置于5.0 mL稀释后ABTS溶液中,避光条件下放置30 min后测定溶液吸光度A1,依据公式(5)计算ABTS+自由基的清除率。
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 (5) 1.2.3.7 抗菌性测定
通过抑菌圈法测定明胶基薄膜抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的强弱。将预培养18 h的细菌溶液(浓度为1×106~1×107 CFU/mL的菌悬液,0.1 mL)分配到预置有营养琼脂培养基的无菌培养皿中,用无菌三角棒将其均匀涂布。将待测明胶基薄膜裁剪成直径为40 mm的圆形,45 min紫外杀菌处理后,使用无菌镊子将其贴于存在菌悬液的培养皿表面。将贴有薄膜片的培养皿倒置,并将其置于温度为37±1 ℃条件下孵化24 h,观察并测试抑菌圈的直径。
1.2.3.8 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)测试
将待测薄膜剪切成2.0 mm×6.0 mm的长条,横断面朝上固定于样品台上,真空喷金处理约12 min后,将处理好的待测薄膜样品置于场扫描电镜中进行薄膜横断面微观形貌扫描,测试加速电压为10 kV。
1.2.3.9 薄膜生物降解性能评估
以活性污泥作为模拟土壤测试薄膜的生物降解性能。将待测薄膜切割成2.0 cm×2.0 cm的方块,称重(m1),将其置于活性污泥中,在温度为28±0.5 ℃,湿度为50%±2%的培养箱中培育,每隔5 h取出残存薄膜样品并用去离子水清洗,50 ℃条件下烘干并恒重,称重(m2),以损失的质量对薄膜降解性能进行评价,依据公式(6)计算薄膜的降解率。同时,为了参照和对比,采用相同实验条件,测试了聚乙烯(PE)薄膜的降解率。
降解率(%)=m1−m2m1×100 (6) 1.3 数据处理
每组实验至少平行测定3次,数据采用平均值±标准差表示。所得数据采用SPSS 24.0进行显著性分析(P<0.05),利用Origin 2021软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 结构分析
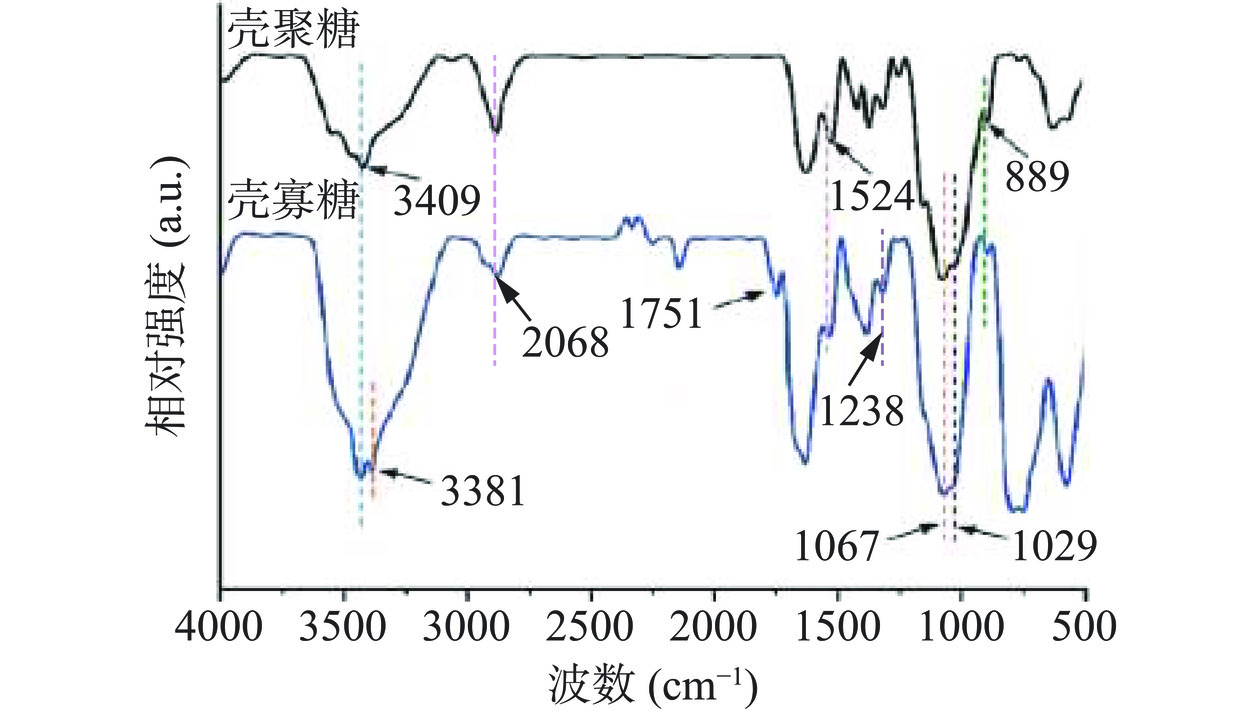
图2为壳聚糖和壳寡糖的红外光谱图。从图中可看出,壳聚糖与壳寡糖的红外光谱特征相类似,在3409 cm−1左右处吸收峰是与壳聚糖和壳寡糖结构中N-H的伸缩振动,以及与-OH的分子内或分子间氢键耦合相关[19]。1524 cm−1左右处吸收峰与结构中酰胺II带相关,1067和1029 cm−1附近吸收峰主要是由分子结构中C-O键振动引起的,889 cm−1附近吸收峰则与壳聚糖中存在的β-(1→4)糖苷键相关[20]。而壳聚糖经过高碘酸氧化后,壳寡糖在1751 cm−1附近出现了一个新的吸收峰,其可能是由壳寡糖中所新生成醛羰基的伸缩振动引起的[21]。同时,壳寡糖在3409 cm−1处吸收峰偏移到3381 cm−1附近,其可能是与壳聚糖被高碘酸氧化后,壳寡糖分子内-OH和-NH2官能团数量减少,进而导致形成分子内或分子间氢键数量减少相关[22]。由此,表明壳聚糖被高碘酸氧化后会在壳寡糖中形成醛基。
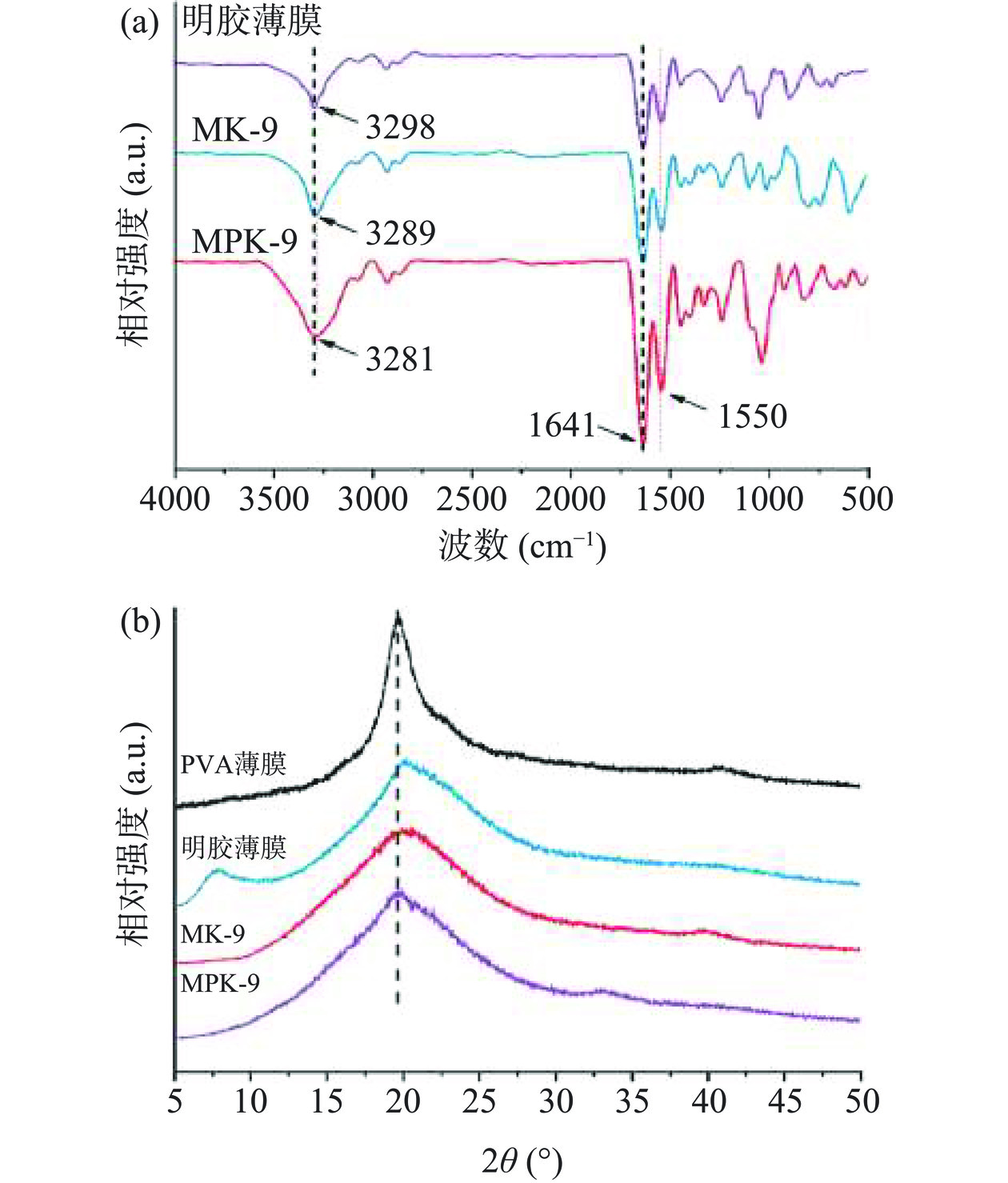
为了研究交联前后明胶薄膜结构上的变化,如图3所示,分别测试了不同薄膜的红外光谱和XRD谱图。图3(a)为明胶、MK-9和MPK-9的红外光谱图。可以看出,所有明胶薄膜均能够明显的观察到酰胺-A带、酰胺-B带、酰胺-Ⅰ带、酰胺-Ⅱ带和酰胺-Ⅲ带的特征吸收峰[23]。在3298和2068 cm−1左右处分别为明胶结构中酰胺-A带和酰胺-B带的特征吸收峰,其与-OH通过氢键与N-H耦合引起的伸缩振动相关[24];在1641、1550和1238 cm−1左右处分别为酰胺-Ⅰ带、酰胺-II带和酰胺-Ⅲ带的特征吸收峰,其中酰胺-Ⅰ带与酰胺键结构中C=O的伸缩振动相关,酰胺-Ⅱ则与C-N键的伸缩振动以及N-H键的弯曲振动的共同作用相关,酰胺-Ⅲ带则是由明胶分子内脯氨酸和甘氨酸中侧链上-CH2的摇摆振动以及C-N键的伸缩振动共同引起的。
与明胶薄膜相比,壳寡糖的加入使MK-9薄膜的酰胺-A带向低波数方向移动,从3298 cm−1偏移到了3289 cm−1,其可能的原因是明胶分子中氨基与壳寡糖中醛基发生了席夫碱反应形成共价交联,而所形成的共价键会阻碍明胶分子链重组为类胶原三股螺旋结构,使得明胶分子链间N-H与-OH耦合而形成的氢键减少。当加入壳寡糖和PVA后,可以看出MPK-9薄膜的酰胺-A带偏移到3281 cm−1,进一步向低波数方向偏移,这表明薄膜中PVA的引入会进一步减少明胶分子链间N-H与-OH耦合的氢键。该研究结果与文献[21]中所观察到的现象基本一致。
采用XRD对不同薄膜聚集态结构进行分析,图3(b)为PVA、明胶、MK-9和MPK-9薄膜的XRD谱图。可以看出,PVA薄膜分别在2θ≈20°,2θ≈23°和2θ≈41°处存在三个明显的衍射峰,分别对应其晶体上(101)、(200)和(102)平面。明胶薄膜分别在2θ≈8°和2θ≈20°处存在两个明显的结晶衍射峰,分别对应明胶中类胶原三股螺旋结构的结晶和单链的非晶相,其与明胶在水中的重组作用相关[25]。而加入壳寡糖和PVA后,MK-9和MPK-9薄膜均仅在2θ≈20°保留了一个宽的衍射峰,其与明胶分子链呈现无定型的状态相关。但随着PVA的掺入,MPK-9薄膜在2θ=20°左右的衍射峰向低角度发生轻微偏移,其衍射峰与PVA晶体上(101)平面的衍射峰一致,表明掺入PVA后的MPK-9薄膜依然保留PVA中的结晶域,并与明胶分子中单链的非晶相共同形成该衍射峰。因此,依据FTIR和XRD的测试结果可以看出,壳寡糖和PVA的加入,使得明胶分子链难以重组并形成类胶原三股螺旋结构,这与明胶分子间形成共价交联和氢键的协同作用存在直接关系。
2.2 力学分析
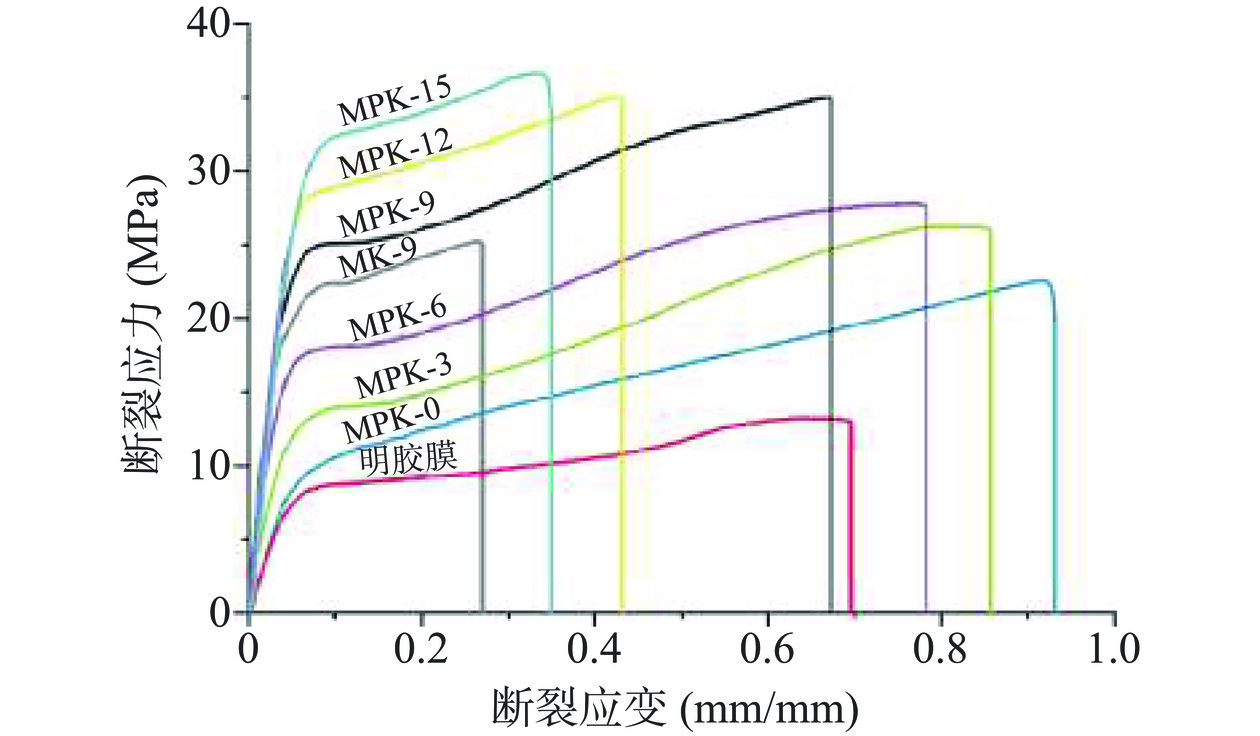
图4和表1为不同类型明胶基薄膜的力学性能。可以看出,明胶薄膜的断裂应力仅为12.92±0.42 MPa,断裂应变为0.68±0.13 mm/mm,显示出较差力学性能。当以壳寡糖作为交联剂,掺入改性后MK-9薄膜的断裂应力提升较大,高达25.26±1.59 MPa(P<0.05),但其断裂应变和杨氏模量并未得到明显改善。而当选择壳寡糖和PVA作为交联剂协同改性明胶,改性后明胶薄膜的断裂应力和杨氏模量均获得了较大提高,最大断裂应力可达37.09±1.48 MPa(P<0.05),最大杨氏模量为568.51±16.44 MPa(P<0.05),最大撕裂能为56.71±4.93 kJ/m2(P<0.05),其机械性能明显优于商用聚氯乙烯薄膜和聚乙烯薄膜[26−27]。同时,随着壳寡糖剂量的增加,改性后MPK薄膜的断裂应力、杨氏模量和撕裂能均呈现不断增加趋势,而断裂应变则不断减小。这是因为明胶分子在重组作用下形成的三股螺旋结构以及明胶分子链间的弱氢键会在受外力时能够耗散能量,导致明胶薄膜具有一定力学强度。而随着壳寡糖的加入,其会与明胶分子链形成共价交联,故能显著提升了薄膜的断裂应力。并且随着壳寡糖剂量的增加,与明胶分子链间的交联程度也相应增大,因而导致高剂量壳寡糖的添加后明胶薄膜的断裂应力、杨氏模量和撕裂能均不断增加,而对应断裂应变则不断减小。该变化趋势与Lake-Thomas模型中交联密度增大,薄膜刚度增加,韧性减小的趋势相一致[28]。
表 1 不同类型明胶基薄膜的断裂应力、断裂应变、杨氏模量和撕裂能Table 1. Fracture stress, fracture strain, Young’s modulus and tearing energy of different gelatin-based films样品 断裂应力(MPa) 断裂应变(mm/mm) 杨氏模量(MPa) 撕裂能
(kJ/m2)明胶膜 12.92±0.42a 0.68±0.13c 145.87±11.32a 20.06±2.97a MK-9 25.26±1.59c 0.27±0.07a 143.63±14.59a 25.68±3.59a MPK-0 22.49±1.42b 0.93±0.10d 172.49±13.18a 23.54±3.26a MPK-3 26.31±1.81c 0.86±0.06d 219.41±15.43a 26.31±4.12a MPK-6 27.59±1.54c 0.78±0.11d 286.75±16.21b 33.11±3.98b MPK-9 34.96±2.13d 0.67±0.09c 399.34±18.26c 38.90±4.51c MPK-12 35.15±1.89d 0.43±0.07b 489.26±13.11d 48.86±5.29d MPK-15 37.09±1.48d 0.35±0.06b 568.51±16.44d 56.71±4.93d 注:同列中不同字母代表差异显著性(P<0.05)。 2.3 溶胀溶解性能
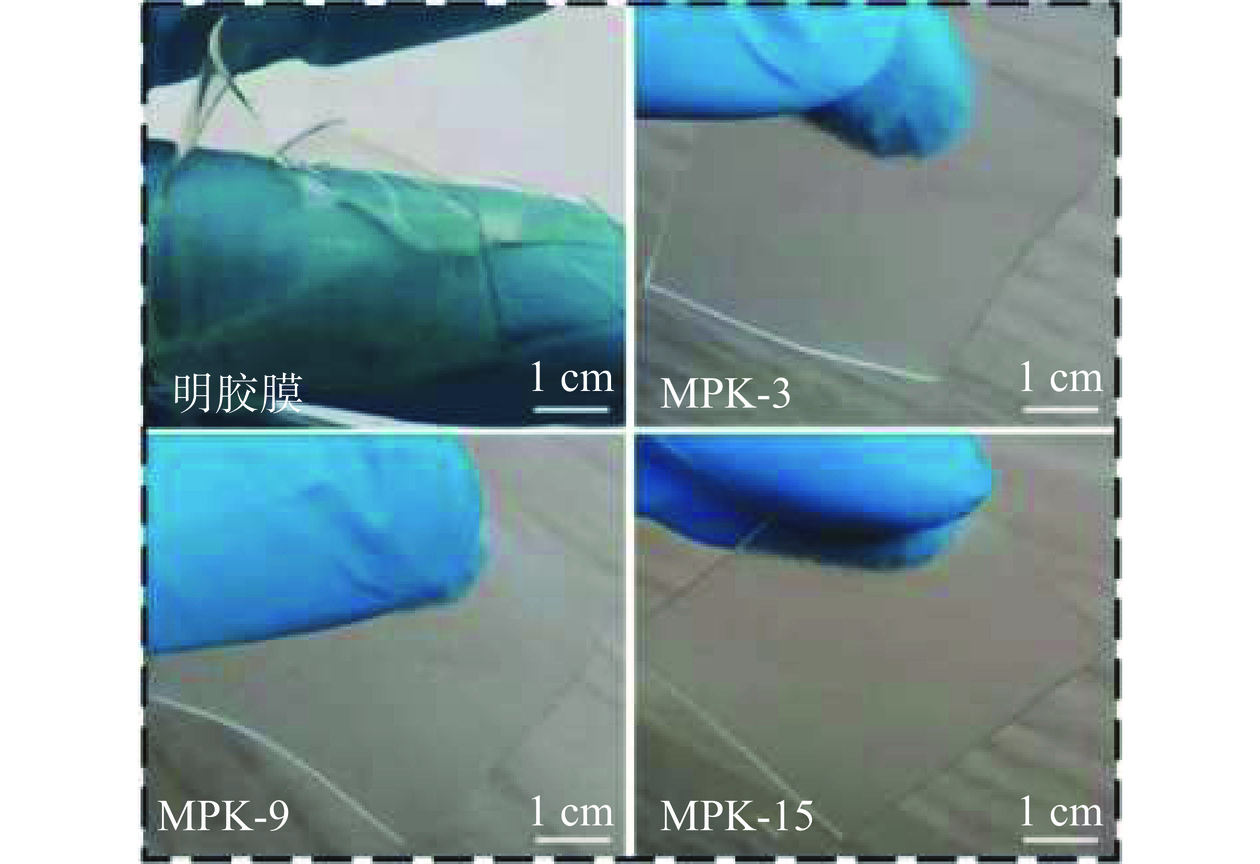
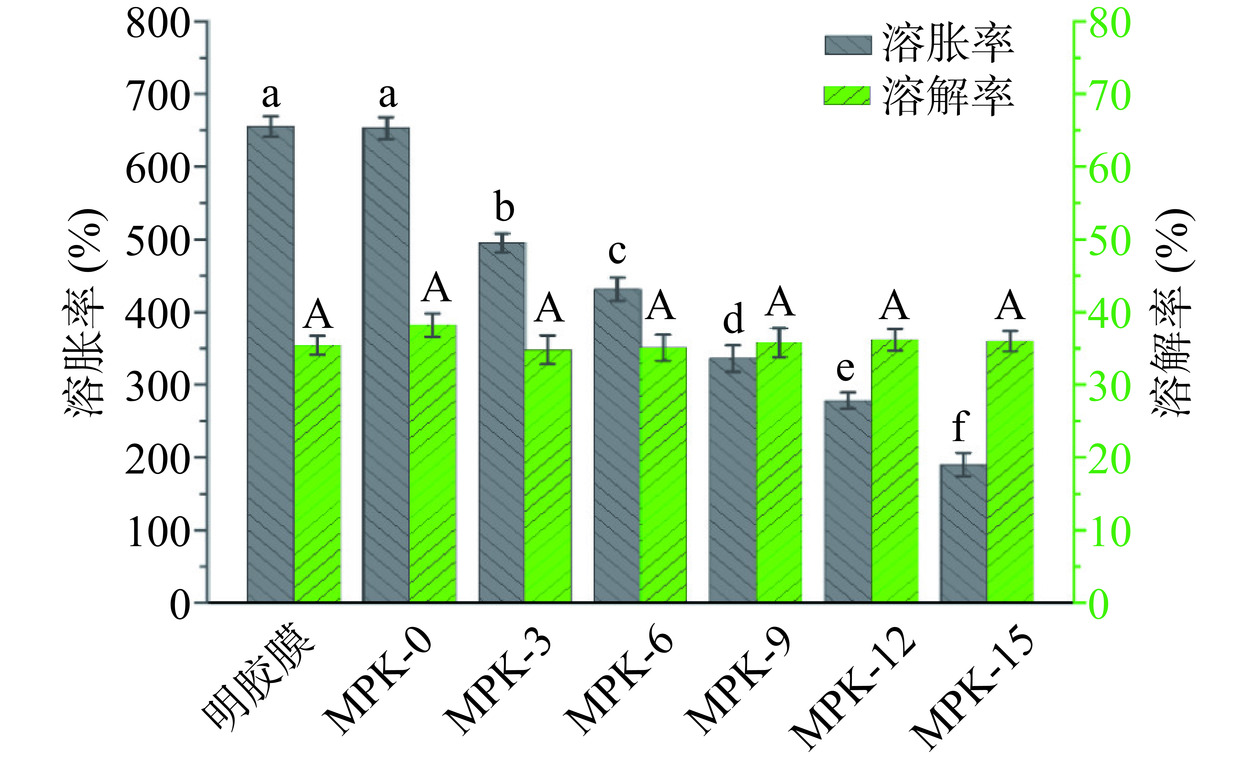
耐湿性直接影响到薄膜的实际应用价值,可通过测试薄膜的溶胀率和溶解率对其耐湿性能进行评价[29]。图5为不同类型明胶基薄膜的溶胀率和溶解率,可以看出,水中浸泡48 h后未交联明胶薄膜的溶胀率高达654.23%±23.56%,同时,溶胀后明胶薄膜稍微触碰就会破碎(图6),显示出极差的耐湿特性和脆弱的机械性能,其原因与明胶分子中存在大量亲水基团,显示较强吸水性,水分子的存在会破坏明胶分子链间的氢键,进而使得其机械性能较差。当加入PVA后,MPK-0的溶胀率和溶解率几乎不变。而壳寡糖的掺入改性可明显改善MPK薄膜的溶胀性能,并且随着壳寡糖掺入剂量的不断增加,薄膜溶胀率不断降低,当壳寡糖的掺入剂量为15.0%时,MPK薄膜的溶胀率显著降低至190.89%±27.65%(P<0.05)且能维持较好的物理形态(图6)。这是因为掺入的壳寡糖能够与明胶分子交联并形成共价网络结构,而该结构可在水中稳固存在,因而导致改性后MPK薄膜的溶胀率发生了降低,同时薄膜机械性能也得到提升,并且不断增加的壳寡糖掺入量会提升其与明胶分子间的交联程度,进而使得改性后MPK薄膜的溶胀率不断降低。此外,从图5还可以看出,所有MPK薄膜的溶解率均为35%左右,未显示出明显的变化趋势,可能的原因是在长时间的浸泡过程中,薄膜质量损失仅与明胶基中甘油析出和少量游离水蒸发有关。
2.4 透光性测定
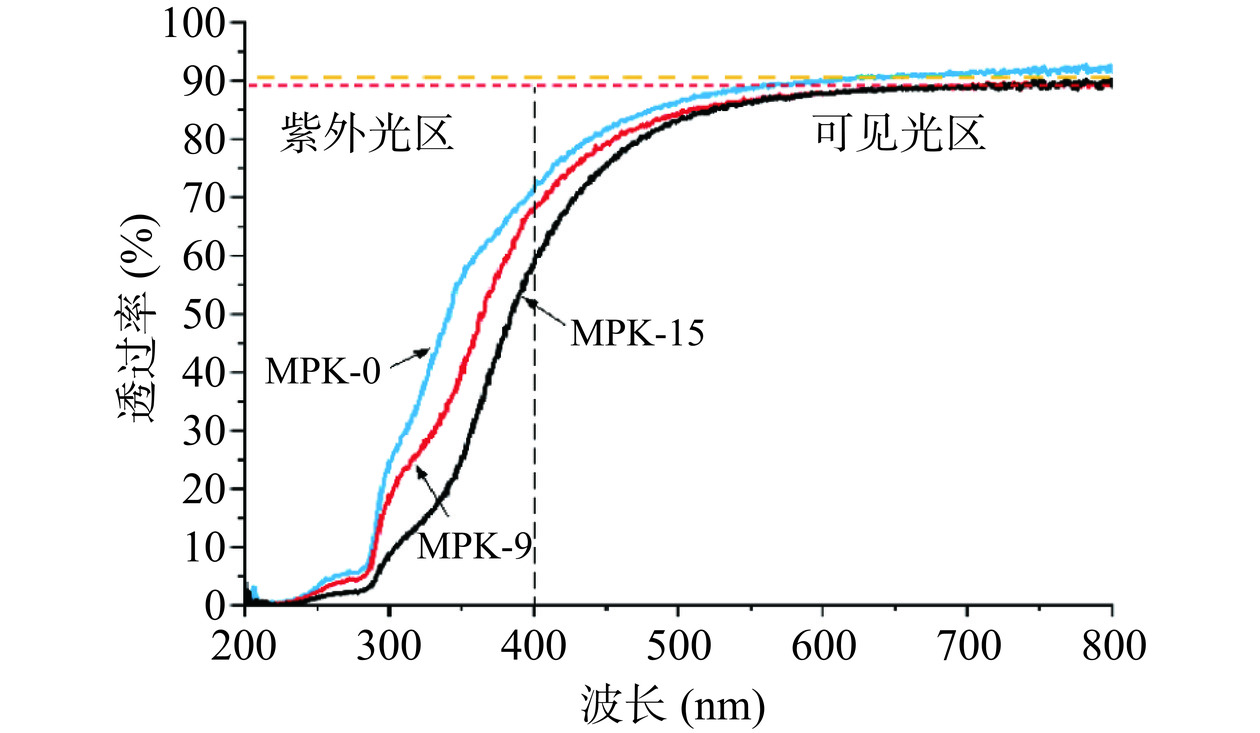
采用紫外-可见分光光度计对明胶基薄膜的透光性能进行测试。如图7所示,所有薄膜在紫外光区(200~400 nm)的透光性较差,显示出一定的抗紫外能力,其与明胶中芳香氨基酸结构存在直接关系。而在可见光区(400~760 nm)明胶薄膜的光透过率最高可达 92.84%,显示出良好的透光性。随着 PVA 和壳寡糖的加入,MPK-15和MPK-9的光透过率与MPK-0相差不大,这表明薄膜中所形成的多交联结构以及PVA和壳寡糖中存在的部分结晶并不会对明胶基薄膜的透光性造成显著影响,明胶基薄膜的透光特性揭示其在食品包装领域拥有十分广阔的应用前景。
2.5 抗氧化和抗菌性能测定
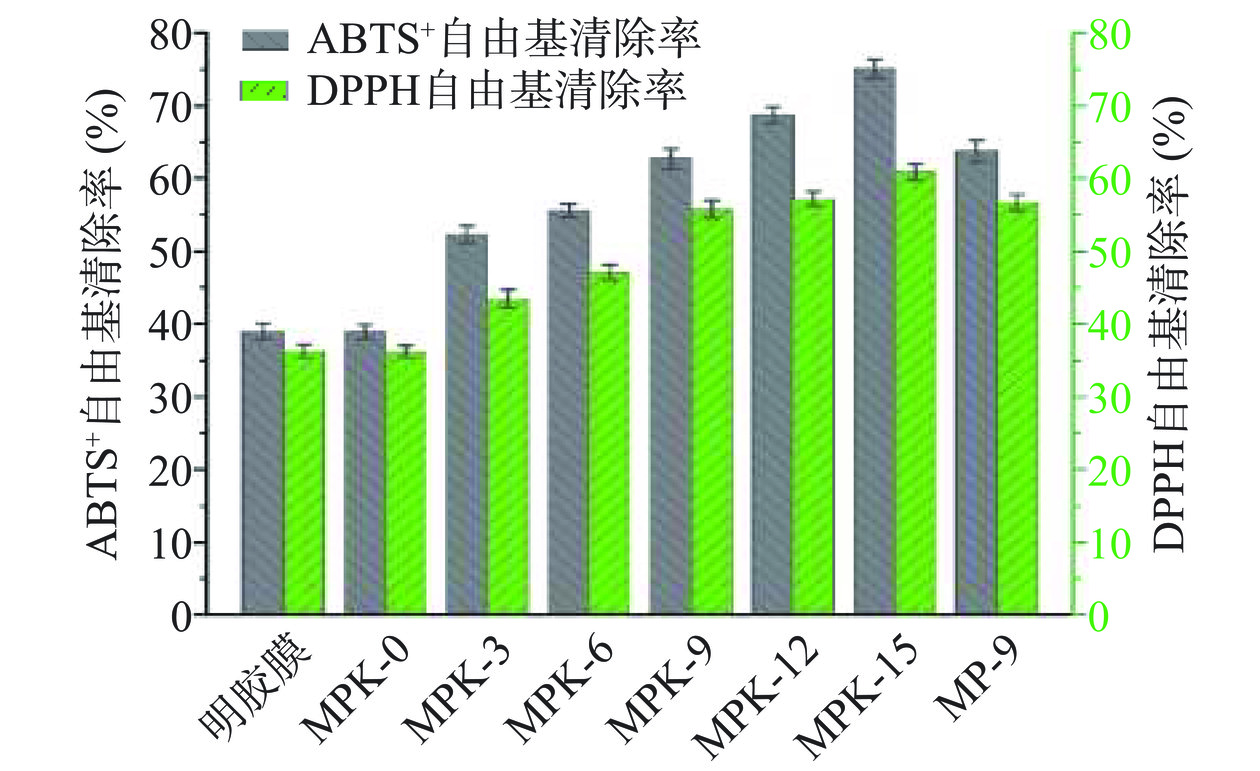
在食品的储存过程中,薄膜的抗氧化性和抗菌性会直接影响到其保存期长短。DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力被认为评估抗氧化性能的标准方法之一[30]。图8为不同明胶基薄膜清除DPPH和ABTS+自由基的效率,可以看出明胶薄膜拥有一定清除DPPH和ABTS+自由基的能力,对应的清除率分别为39.04%±1.32%和36.30%±1.08%,其与明胶分子链上氨基酸相关,可作为供电子体来清除自由基[31]。MPK-0清除DPPH和ABTS+自由基能力与明胶薄膜相差不大,表明PVA的引入并不会明显影响到明胶基薄膜在清除自由基方面的能力。随着壳寡糖掺入剂量的增加,MPK薄膜清除DPPH和ABTS+自由基能力不断提升,当壳寡糖的掺入剂量为15.0%时,MPK-15清除DPPH和ABTS+自由基的效率最高可分别达75.12%±1.98%和60.94%±1.46%,其与壳寡糖分子中脱水葡萄糖单元的C2-OH和C6-OH相关,可作为电子供体协同清除自由基。因此,MPK薄膜在延长食品保质期方面具有较大潜在应用价值。
薄膜的抗菌性能主要是通过测定其对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果进行评价。表2为不同类型明胶基薄膜的抑菌效果,可以看出,明胶薄膜和MPK-0的抑菌圈直径均为0 mm,表明均不具备抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的能力。而MPK-3、MPK-9、MPK-15和MK-9在大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌中的抑菌圈直径均超过了12 mm,显示出良好的抑菌效果,并且随着壳寡糖掺入量的不断增加,明胶基薄膜的抑菌效果也不断增强。因此,由抑菌实验结果可知,明胶基薄膜的抑菌能力与壳寡糖的添加有关,而与明胶分子和PVA分子的存在无关。
表 2 不同类型明胶基薄膜的抑菌效果Table 2. Antibacterial effect of different gelatin-based films细菌类型 抑菌圈直径(mm) 明胶膜 MPK-0 MPK-3 MPK-9 MPK-15 MK-9 大肠杆菌 0.00 0.00 13.42±0.13 14.28±0.19 14.61±0.09 15.19±0.11 金黄色葡
萄球菌0.00 0.00 12.84±0.34 16.67±0.25 23.31±0.41 16.09±0.29 2.6 微观形貌
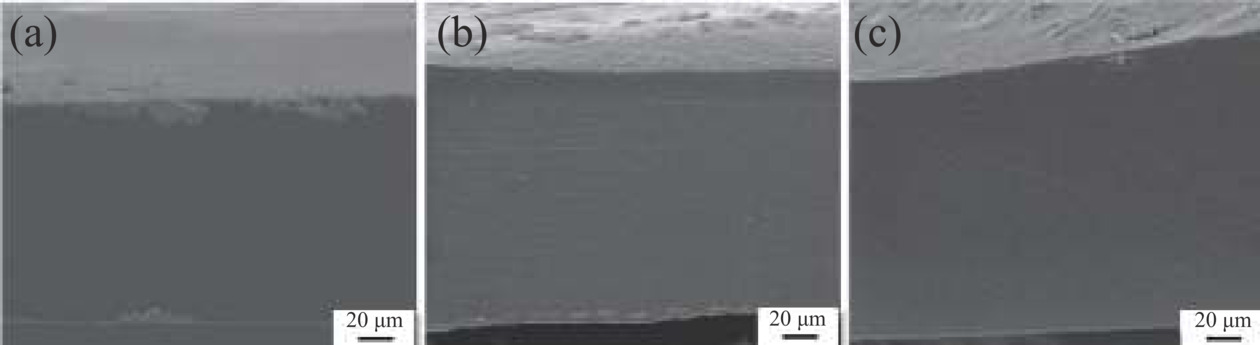
图9为明胶薄膜、MPK-0和MPK-9的表面和断截面微观形貌图,由图9(a)可以看出,明胶薄膜截面呈现出均匀且紧致的结构,同时,其表面十分平整和光滑。当加入PVA后,MPK-0横断面与明胶薄膜相类似,没有出现明显相分离问题,同样呈现出十分均匀和紧致的特征(图9(b)),可能的原因是PVA中羟基可与明胶中氨基、羧基、羟基和酰胺键等官能团间形成氢键,增强PVA与明胶的相容性,使得MPK-0薄膜对外呈现出均一紧致的结构特征。而当加入壳寡糖后,MPK-9截面同样没有出现相分离现象,对外也呈现紧致均一的结构特征(图9(c)),其原因与壳寡糖分子中羟基、氨基等官能团易与明胶中官能团形成氢键,从而确保它们之间拥有良好的相容性有关。
2.7 生物降解性测试
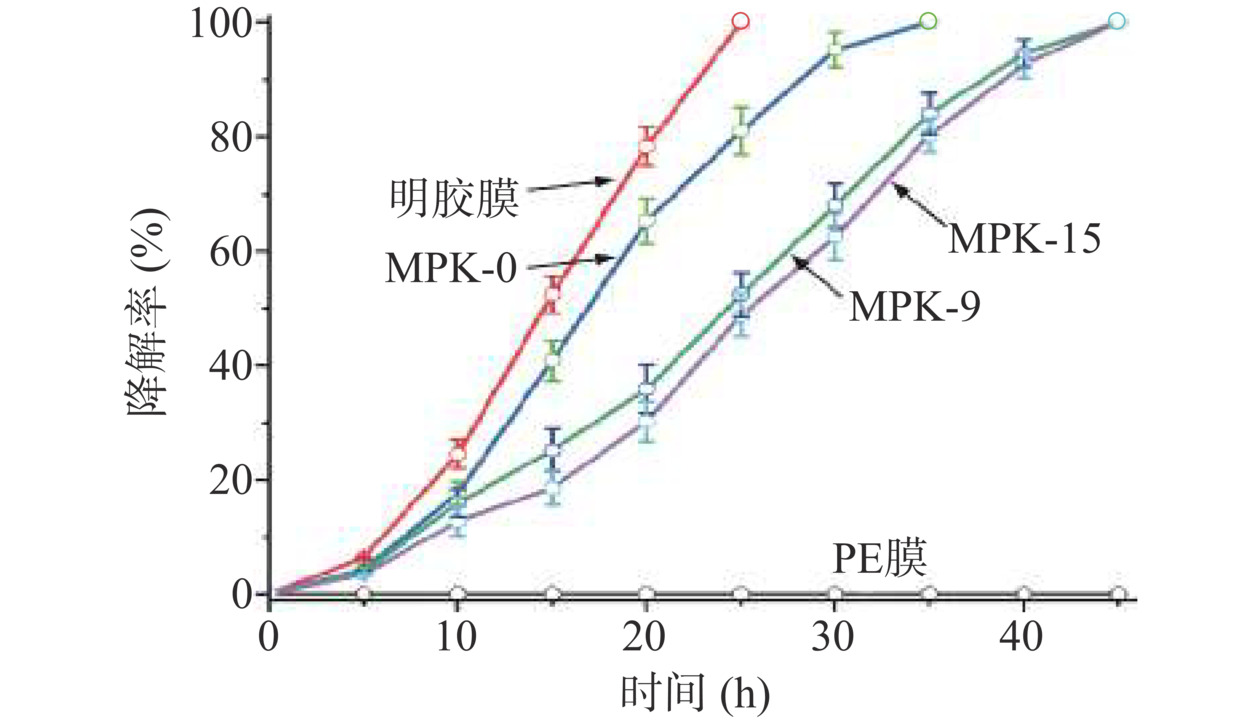
本文选择活性污泥模拟自然土壤来评价薄膜的生物降解性能。图10为不同类型薄膜在活性污泥中的降解率随时间变化的曲线,可以看出,一定时间后明胶薄膜及MPK在活性污泥中均能完全降解。其中,明胶薄膜的降解速率最快,15 h内降解率超过50%,25 h内能完全降解。而随着壳寡糖掺入剂量的增加,MPK薄膜的降解速率变得更加缓慢,最长需要45 h才能完全降解。这是因为相比于明胶薄膜而言,MPK薄膜中加入的壳寡糖会与明胶分子链间形成共价键而降低了其薄膜的溶胀性,使得微生物需要更长的时间进入到MPK基质中,因而减缓了其降解速度。同时,MPK基质中壳寡糖拥有较好的抑菌性,其不利于微生物在明胶基质上生长和繁殖,这同样也会延缓MPK薄膜的降解速度。
3. 结论
利用从废弃猪皮中提取的明胶为原材料,从虾蟹壳中提取的壳寡糖以及PVA为改性交联剂,制备得到了一种高强度可生物降解的多交联明胶基薄膜。所形成多交联结构使得改性后明胶基薄膜的断裂应力最大可达37.09±1.48 MPa,杨氏模量最高为568.51±16.44 MPa,撕裂能最大为56.71±4.93 kJ/m2,同时,薄膜的耐水性、抗氧化性和抗菌性也得到显著提高。此外,壳寡糖和PVA的协同改性并未影响到明胶基薄膜的透光性和生物降解性能。改性明胶基薄膜的综合性能显示其在食品包装方面具有较大潜在应用价值,可替代传统石油基薄膜,助力社会与环境的可持续发展。
-
表 1 不同类型明胶基薄膜的断裂应力、断裂应变、杨氏模量和撕裂能
Table 1 Fracture stress, fracture strain, Young’s modulus and tearing energy of different gelatin-based films
样品 断裂应力(MPa) 断裂应变(mm/mm) 杨氏模量(MPa) 撕裂能
(kJ/m2)明胶膜 12.92±0.42a 0.68±0.13c 145.87±11.32a 20.06±2.97a MK-9 25.26±1.59c 0.27±0.07a 143.63±14.59a 25.68±3.59a MPK-0 22.49±1.42b 0.93±0.10d 172.49±13.18a 23.54±3.26a MPK-3 26.31±1.81c 0.86±0.06d 219.41±15.43a 26.31±4.12a MPK-6 27.59±1.54c 0.78±0.11d 286.75±16.21b 33.11±3.98b MPK-9 34.96±2.13d 0.67±0.09c 399.34±18.26c 38.90±4.51c MPK-12 35.15±1.89d 0.43±0.07b 489.26±13.11d 48.86±5.29d MPK-15 37.09±1.48d 0.35±0.06b 568.51±16.44d 56.71±4.93d 注:同列中不同字母代表差异显著性(P<0.05)。 表 2 不同类型明胶基薄膜的抑菌效果
Table 2 Antibacterial effect of different gelatin-based films
细菌类型 抑菌圈直径(mm) 明胶膜 MPK-0 MPK-3 MPK-9 MPK-15 MK-9 大肠杆菌 0.00 0.00 13.42±0.13 14.28±0.19 14.61±0.09 15.19±0.11 金黄色葡
萄球菌0.00 0.00 12.84±0.34 16.67±0.25 23.31±0.41 16.09±0.29 -
[1] 迟敏, 李利元, 黄东杰. 淀粉基食品薄膜在肉制品保鲜中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(12):117−225. [CHI M, LI L Y, HUANG D J. Application of starch-based food films in the preservation of meat products[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2023,14(12):117−225.] CHI M, LI L Y, HUANG D J. Application of starch-based food films in the preservation of meat products[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2023, 14(12): 117−225.
[2] CALVA-ESTRADA S J, JIMÉNEZ-FERNÁNDEZ M, LUGO-CERVANTES E. Protein-based films:Advances in the development of biomaterials applicable to food packaging[J]. Food Engineering Reviews,2019,11:78−92. doi: 10.1007/s12393-019-09189-w
[3] ZHAO Y, DU J, ZHOU, H, et al. Biodegradable intelligent film for food preservation and real-time visual detection of food freshness[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,129:107665−107672. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107665
[4] FAHMY H M, ELDIN R E S, SEREA E S A, et al. Advances in nanotechnology and antibacterial properties of biodegradable food packaging materials[J]. RSC advances,2020,10(35):20467−20484. doi: 10.1039/D0RA02922J
[5] 陈良. 多重交联明胶基可生物降解薄膜的构效调控[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2023. [CHEN L. Structure and performance regulation of gelatin-based multi-cross-linked biodegradable film[D]. Xi'an:Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2023.] CHEN L. Structure and performance regulation of gelatin-based multi-cross-linked biodegradable film[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2023.
[6] SAVCHUK O, RAKSHA N, OSTAPCHENKO L, et al. Extraction and characterization of collagen obtained from collagen-containing wastes of the leather industry[J]. Solid State Phenomena,2017,267:172−176. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.267.172
[7] 杨帅帅, 李海朝. 明胶膜改性研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2018,47(3):599−602. [YANG S S, LI H C. Research progress in modification of gelatin film[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2018,47(3):599−602.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.03.042 YANG S S, LI H C. Research progress in modification of gelatin film[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(3): 599−602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.03.042
[8] AKRAMI-HASAN-KOHAL M, GHORBANI M, MAHMOODZADEH F, et al. Development of reinforced aldehyde-modified kappa-carrageenan/gelatin film by incorporation of halloysite nanotubes for biomedical applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,160:669−676. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.222
[9] OLAD A, HAGH H B K. Graphene oxide and amin-modified graphene oxide incorporated chitosan-gelatin scaffolds as promising materials for tissue engineering[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering,2019,162:692−702. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.040
[10] 陈书霖, 陶忠, 吴菲菲, 等. 鱼皮明胶蛋白膜的制备及其性质改良[J]. 集美大学学报(自然科学版),2012,17(5):335−342. [CHEN S L, TAO Z, WU F F, et al. Preparation and improvement of gelatin films based on tilapia skin[J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science),2012,17(5):335−342.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7405.2012.05.003 CHEN S L, TAO Z, WU F F, et al. Preparation and improvement of gelatin films based on tilapia skin[J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2012, 17(5): 335−342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7405.2012.05.003
[11] CHOU S F, LUO L J, LAI J Y, et al. Role of solvent-mediated carbodiimide cross-linking in fabrication of electrospun gelatin nanofibrous membranes as ophthalmic biomaterials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C,2017,71:1145−1155.
[12] 陶忠, 郑惠彬, 翁武银. 化学交联与酶法交联对鱼糜-明胶复合膜性质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(5):25−30. [TAO Z, ZHENG H B, WENG W Y. Effect of chemical and enzymatic cross-linking on the properties of surimi-gelatin composite films[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(5):25−30.] TAO Z, ZHENG H B, WENG W Y. Effect of chemical and enzymatic cross-linking on the properties of surimi-gelatin composite films[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2013, 39(5): 25−30.
[13] SÁNCHEZ Á, MENGÍBAR M, RIVERA-RODRÍGUEZ G, et al. The effect of preparation processes on the physicochemical characteristics and antibacterial activity of chitooligosaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,157:251−257. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.055
[14] 林碧莲, 陈浩, 代传芝, 等. 壳寡糖的酶法可控制备及其在预包装豆腐保鲜中的应用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(12):136−143. [LIN B L, CHEN H, DAI C Z, et al. Enzymatic controlled preparation of chitosan oligosaccharides and its application in preservation of pre-packaged tofu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(12):136−143.] LIN B L, CHEN H, DAI C Z, et al. Enzymatic controlled preparation of chitosan oligosaccharides and its application in preservation of pre-packaged tofu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(12): 136−143.
[15] CASTILLO L A, FARENZENA S, PINTOS E, et al. Active films based on thermoplastic corn starch and chitosan oligomer for food packaging applications[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2017,14:128−136. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2017.10.004
[16] 王亚珍. 壳聚糖基复合膜的制备、性能及应用[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2015. [WANG Y Z. Preparation, properties and application of chitosan based composite films[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2015.] WANG Y Z. Preparation, properties and application of chitosan based composite films[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2015.
[17] BAO S, XU S, WANG Z. Antioxidant activity and properties of gelatin films incorporated with tea polyphenol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2009,89(15):2692−2700. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.3775
[18] QIANG T, CHEN L, YAN Z, et al. Evaluation of a novel collagenous matrix membrane cross-linked with catechins catalyzed by laccase:A sustainable biomass[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(5):1504−1512. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05810
[19] TAN W, DONG F, ZHANG J, et al. Physical and antioxidant properties of edible chitosan ascorbate films[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(9):2530−2539. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04567
[20] VERLEE A, MINCKE S, STEVENS C V. Recent developments in antibacterial and antifungal chitosan and its derivatives[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,164:268−283. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.001
[21] CHEN L, QIANG T, CHEN X, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of biodegradable multi-cross-linked mulch film based on waste gelatin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,419:129639−129650. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129639
[22] CHEN L, QIANG T, CHEN X, et al. Tough and biodegradable gelatin-based film via the synergistic effect of multi-cross-linking[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials,2021,4(1):357−368.
[23] LIN J, PAN D, SUN Y, et al. The modification of gelatin films:Based on various cross-linking mechanism of glutaraldehyde at acidic and alkaline conditions[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2019,7(12):4140−4146.
[24] AHMAD M, BENJAKUL S, PRODPRAN T, et al. Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin film from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket incorporated with essential oils[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,28(1):189−199. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.12.003
[25] SANWLANI S, KUMAR P, BOHIDAR H B. Hydration of gelatin molecules in glycerol-water solvent and phase diagram of gelatin organogels[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2011,115(22):7332−7340. doi: 10.1021/jp201877d
[26] ASHORI A, KIANI H, MOZAFFARI S A. Mechanical properties of reinforced polyvinyl chloride composites:Effect of filler form and content[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2011,120(3):1788−1793. doi: 10.1002/app.33378
[27] JORDAN J L, CASEM D T, BRADLEY J M, et al. Mechanical properties of low-density polyethylene[J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials,2016,2:411−420. doi: 10.1007/s40870-016-0076-0
[28] LI J, ILLEPERUMA W R, SUO Z, et al. Hybrid hydrogels with extremely high stiffness and toughness[J]. ACS Macro Letters,2014,3(6):520−523. doi: 10.1021/mz5002355
[29] CAZÓN P, VÁZQUEZ M, VELAZQUEZ G. Composite films with UV-barrier properties of bacterial cellulose with glycerol and poly (vinyl alcohol):Puncture properties, solubility, and swelling degree[J]. Biomacromolecules,2019,20(8):3115−3125. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00704
[30] ABD EL-HACK M E, EL-SAADONY M T, SHAFI M E, et al. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications:A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:2726−2744. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.153
[31] ANRAKU M, GEBICKI J M, IOHARA D, et al. Antioxidant activities of chitosans and its derivatives in in vitro and in vivo studies[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,199:141−149. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.016
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 闫昱辛,何美军,李宇,袁晓曼,谭旭辉,程名,罗凯,廖璐婧. 铁皮石斛叶多糖美白和抗氧化活性. 植物研究. 2025(01): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代丽丽,王景,魏许瑞,马庆亚,王娜,都治香. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路研究灯盏花乙素对子宫内膜癌Ishikawa细胞的影响. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2024(01): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张琦,包小波,田冲冲. 灯盏花乙素增强4T1乳腺癌细胞对顺铂敏感性的体内外研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(05): 331-340 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王佳恩,殷子喻,马莉,李双良,符德欢. 灯盏乙素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展. 中草药. 2024(13): 4608-4621 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张琦,田冲冲,张洋,方晨曦,卜薇,李凤. 灯盏花乙素通过PPARγ-PGC1α-UCP1通路改善小鼠肥胖作用及机制. 药物评价研究. 2024(08): 1787-1796 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田冲冲,张琦,陈延绅. 基于肠道微生态探讨灯盏花乙素对乳腺癌小鼠的化疗增敏作用及其机制. 中国微生态学杂志. 2024(12): 1374-1381+1387 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



