Optimization of Sulfation Process of Zizania latifolia Polysaccharide by Response Surface and Its Antioxidant Activity Analysis
-
摘要: 为提高茭白多糖抗氧化活性,对茭白多糖进行硫酸化修饰,并探索其最佳修饰条件。以茭白为原料,利用水提醇沉法提取并纯化一种新型水溶性多糖,采用三氧化硫-吡啶法,以甲酰胺为溶剂,对多糖进行硫酸改性,以硫酸根取代度(DS)为指标,利用响应面法对茭白多糖进行硫酸改性条件优化,同时通过体外自由基清除率实验对比改性前后体外抗氧化活性。结果表明:采用响应面法辅助茭白多糖硫酸化修饰条件优化得到最佳反应条件为多糖样品100 mg,酯化时间4 h,酯化温度70 ℃,三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量2.6 g,得到最佳DS为1.79;热重分析显示茭白多糖在46.38 ℃时失重最快,失重率为16.48%;硫酸化茭白多糖在65.04 ℃时失重最快,失重率为2.92%。在体外抗氧化实验中,茭白多糖对于DPPH·、·OH以及ABTS+·清除能力的IC50值分别为3.49、3.28和12.70 mg/mL;硫酸化茭白多糖为0.39、1.00和1.82 mg/mL;阳性对照(VC)为0.069、0.17和0.077 mg/mL。综上表明,硫酸化修饰能提高茭白多糖的热稳定性;同时一定程度上增强其自由基清除能力。Abstract: In order to improve the antioxidant activity of Zizania latifolia polysaccharides, sulfate it and explore the optimum modification conditions. Polysaccharides was extracted by water extraction and alcohol precipitation method from Zizania latifolia, then it was separated and purified to obtain a new type of water-soluble polysaccharide. Using formamide as solvent, polysaccharides were sulfated by sulfur trioxide-pyridine method. The degree of substitution (DS) was set as the examination index, the optimal sulfonation conditions were selected by response surface method. Through the free radical scavenging rate trial in vitro, compared with natural polysaccharides, to explore the changes of antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharides in vitro. The results showed that the optimum reaction conditions obtained as polysaccharide 100 mg, time 4 h, temperature 70 ℃, sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex 2.6 g. The optimum DS was 1.79. Thermogravimetric analysis showed that the fastest weight loss rate of Zizania latifolia polysaccharides was 16.48% at 46.38 ℃, and the sulfated polysaccharides was 2.92% at 65.04 ℃. In the antioxidant test in vitro, the IC50 of free radical scavenging ability of Zizania latifolia polysaccharides to DPPH·, ·OH and ABTS+· were 3.49, 3.28 and 12.70 mg/mL respectively. The sulfated polysaccharides of Zizania latifolia polysaccharides were 0.39, 1.00 and 1.82 mg/mL respectively, and the positive control (VC) was 0.069, 0.17 and 0.077 mg/mL respectively. In summary, sulfation modification can enhance the thermal stability of Zizania latifolia polysaccharides and enhance its free radical scavenging ability to some extent.
-
Keywords:
- Zizania latifolia /
- polysaccharide /
- sulfated /
- response surface methodology /
- antioxidant activity
-
茭白(Zizania latifolia),又称菰瓜、高瓜、高笋等,原产于中国及东南亚,是禾本科孤属多年生宿根水生草本植物感染菰黑粉菌后长成的变态肉质茎[1],其口感肥嫩鲜美,是浙江最受欢迎的蔬菜之一[2]。茭白中含有糖类、蛋白质、维生素、多酚等多种营养物质[3],具有化浊降脂、生津止渴、预防肝硬化[4]等保健功能,在中国以及东南亚部分地区,茭白也作为传统中药被使用[5],其优越的抗氧化能力已经被证明[6−9]。
多糖是一种天然大分子活性物质,广泛存在于自然界中,具有多种与人类生活紧密相关的重要生物活性,如降血糖、抗肿瘤、抗氧化、提高免疫功能[10−14]等,同时多糖具有无毒、可生物降解、成本低易获取[15]等优点,已成为食药领域研究热点。茭白中含有丰富的多糖类物质,水溶性多糖含量约为10%~20%[4,16]。目前茭白多糖的研究主要集中于抗氧化[7]、免疫调节[7,17]、缓解急性酒精中毒[5]以及复合生物膜[9]等方面。
天然多糖活性相对较弱,大量研究表明采用生物、化学等方法对多糖进行修饰能不同程度地改善多糖活性。硫酸化是多糖改性的一种常用方法,已被广泛应用于增强多糖的抗氧化活性[14,18]。其中,氯磺酸-吡啶法、浓硫酸法、三氧化硫-吡啶法等是多糖硫酸化改性最常用的几种化学修饰方法[19]。Gong等[20]研究发现随着硫酸盐基团的引入,罗汉果多糖对DPPH·和O2−·清除能力增强。Xu等[21]研究发现硫酸化修饰显著提高了大麦多糖的体外抗氧化及抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的能力,且呈剂量依赖性。多糖的抗氧化特性是由于多糖链上的电子给体或氢给体官能团[14],当这些官能团被硫酸基团取代时,其分子量、结构以及生物活性便会发生相应改变。张子木等[22]研究发现,壶瓶碎米荠多糖抗氧化活性随着取代度的增加呈现先升后降并整体上升的趋势;刘玉凤等[23]研究发现,不同取代度的硫酸化肠浒苔多糖其抗氧化程度不同,且随着多糖取代度的增加而增加。
本文旨在对茭白多糖进行硫酸酯化,得到硫酸化茭白多糖,并对酯化时间、酯化温度以及酯化剂添加量进行优化,提高茭白多糖硫酸基取代度从而提高其体外抗氧化能力,同时比较了天然茭白多糖与改性多糖的抗氧化活性,为硫酸化茭白多糖作为天然的抗氧化剂的开发提供了可能,同时也为进一步开发茭白多糖提供了理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜茭白 产地安徽省安庆市岳西县,双季茭白,10月季;浓硫酸、苯酚、三氯甲烷、氯化钡 购于天津市化学试剂厂;无水乙醇、三氟乙酸、正丁醇、冰醋酸、氢氧化钠、甲醇、硫酸钾 购于天津江天化工技术有限公司;DEAE-52、S6-ff琼脂糖凝胶、无水葡萄糖、半乳糖醛酸、考马斯亮蓝G-250、牛血清白蛋白(BSA)、葡聚糖标准品、单糖标品、刚果红、还原糖含量检测试剂盒、植物总酚(TP)含量检测试剂盒 购于北京索莱宝科技有限公司;溴化钾 购于上海吉至生化科技有限公司;三氧化硫-吡啶复合物、甲酰胺、明胶 购于上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;所用试剂均为分析纯。
GZX-9070MBE电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司;SE-2000高速粉碎机 浙江永康市圣象电器有限公司;B600型低速自动平衡离心机 长沙湘仪仪器有限公司;Model 680酶标仪 美国伯腾仪器有限公司;BS-100A自动部分收集器 上海沪西仪器分析厂;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;FD-1A-50真空冷冻干燥机 上海比郎仪器有限公司;VECTOR-220傅里叶红外光谱仪 美国尼高利仪器有限公司;Agilent 1260 高效液相色谱仪 德国安捷伦仪器有限公司;CARY 50紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津仪器有限公司;JJ500型精密电子天平、ESJ205-4电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;FE28-Standard pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;DF-101油浴锅 苏州威尔实验用品有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 茭白多糖的提取与纯化
新鲜茭白洗净,切成0.5 cm左右薄片,于60 ℃烘箱中烘干24 h,粉碎机粉碎后80目过筛,得到茭白原料粉末。称取定量茭白原料粉末,按1:30料液比于95 ℃热水提取3 h,离心取上清,沉淀重复2次上述步骤重新提取上清液,旋蒸浓缩,加入三倍体积无水乙醇4 ℃醇沉24 h,离心取沉淀。60 ℃旋蒸除掉酒精后重溶于蒸馏水,用Savag法除去蛋白,透析3 d,冷冻干燥后得到茭白粗多糖。
粗多糖得率(%)=粗多糖质量原料质量×100 将冻干后的茭白粗多糖分别经过DEAE-52纤维素层析柱分离(样品用量:100 mg;样品浓度:10 mg/mL;洗脱剂:0、0.1、0.3、0.5 mol/L NaOH;流速1.5 mL/min)、琼脂糖凝胶S-6ff纯化柱洗脱纯化(样品用量:40 mg;样品浓度:20 mg/mL;洗脱剂:去离子水;流速2.5 mL/min),冷冻干燥得到纯化后的茭白多糖(ZLP)。
1.2.2 茭白多糖硫酸化工艺优化
1.2.2.1 单因素实验
方法参考文献[24−25]稍作改变。将100 mg茭白多糖溶于25 mL甲酰胺中,室温搅拌使多糖完全溶解。边升温边加入一定量三氧化硫-吡啶复合物,待温度达到所需反应温度后开始计时,反应完成后立即冰水浴冷却,2 mol/L NaOH调pH至中性,75%乙醇醇沉,4 ℃静置24 h使多糖沉淀完全。离心收集沉淀,吹干除去乙醇,用水复溶,透析3 d,冷冻干燥得硫酸化茭白多糖(S-ZLP)。
对酯化温度、酯化时间以及三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量进行单因素实验,以取代度(DS)为考察指标。实验均重复3次。
酯化温度:设定茭白多糖为100 mg、酯化时间为3 h、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物量为2 g和甲酰胺量为25 mL,调节温度为50、60、70、80、90 ℃;酯化时间:设定茭白多糖为100 mg、酯化温度为70 ℃、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物量为2 g和甲酰胺量为25 mL,调节时间1、2、3、4、5 h;三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量:设定茭白多糖为100 mg、酯化时间为3 h、酯化温度为70 ℃和甲酰胺量为25 mL,调节三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量为1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0 g。
1.2.2.2 响应面试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,选取反应温度(A)、反应时间(B)、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量(C)为考察因子,选择3因素3水平,具体试验因素水平见表1,以Box-Behnken设计安排进行试验, Design-Expert 13.0.1.0 Trial进行数据分析及响应曲面作图。
表 1 Box-Behnkens 试验因素水平设计Table 1. Box-Behnkens test factor level design因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 酯化温度(℃) A 60 70 80 酯化时间(h) B 3 4 5 三氧化硫-吡啶(g) C 2 2.5 3 1.2.3 取代度的测定
采用氯化钡-明胶比浊法测定硫酸根含量,参照邱芳萍等[26]的方法。以硫酸钾为标准品,建立标准回归曲线。以标曲同样方法测定样品硫元素含量(S%)。标准回归方程如下:y=1.6043x−0.0478,R2=0.9981。
代入公式(1)计算样品取代度(DS)。
DS=1.62×S%32−1.02×S% (1) 1.2.4 红外光谱分析
通过傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)对ZLP和S-ZLP的特征吸收峰进行测定。称取1.2 mg茭白多糖和硫酸化茭白多糖,加入140 mg干燥的KBr于玛瑙研钵中迅速研磨均匀,在12 MPa压力下压缩成1 mm左右的薄片,400~4000 cm−1区间扫描透射光谱16次。
1.2.5 总糖含量测定
总糖含量采用苯酚-硫酸法进行测定,参考Chen等[27]的方法。以葡萄糖为标准品建立标准回归曲线。代入样品溶液的光吸收值计算总糖的含量。标准曲线方程为:y=6.1676x+0.1475,R2=0.9970。
1.2.6 蛋白质含量测定
蛋白质含量测定采用考马斯亮蓝法,按照沈育伊等[28]的方法稍作修改。准备1 mg/mL BSA标准试剂及考马斯亮蓝G-250试剂,在4 ℃避光存储。
向试管中加入0.1 mL BSA标准试剂(0、0.01、0.02、0.04、0.05、0.06、0.08、0.10 mg/mL),随后加入5 mL G-250试剂。待混合均匀后,室温静置5 min,于595 nm处测定吸光度值。绘制标准曲线,分别代入两种多糖溶液的吸光度值计算蛋白质的含量。标准曲线方程为:y=3.587x+0.5756,R2=0.9943。
1.2.7 糖醛酸含量测定
糖醛酸含量测定采用间羟基联苯法,参照米合热尼沙等[29]的方法。以半乳糖醛酸为标准品建立标准回归曲线。代入样品吸光度值计算糖醛酸的含量。标准曲线方程为:y=5.2041+0.1104,R2=0.9921。
1.2.8 还原糖和总酚含量测定
还原糖测定使用还原糖含量检测试剂盒(可见光分光光度法);总酚测定使用植物总酚(TP)含量检测试剂盒(可见分光光度法)。
1.2.9 紫外全波长扫描分析
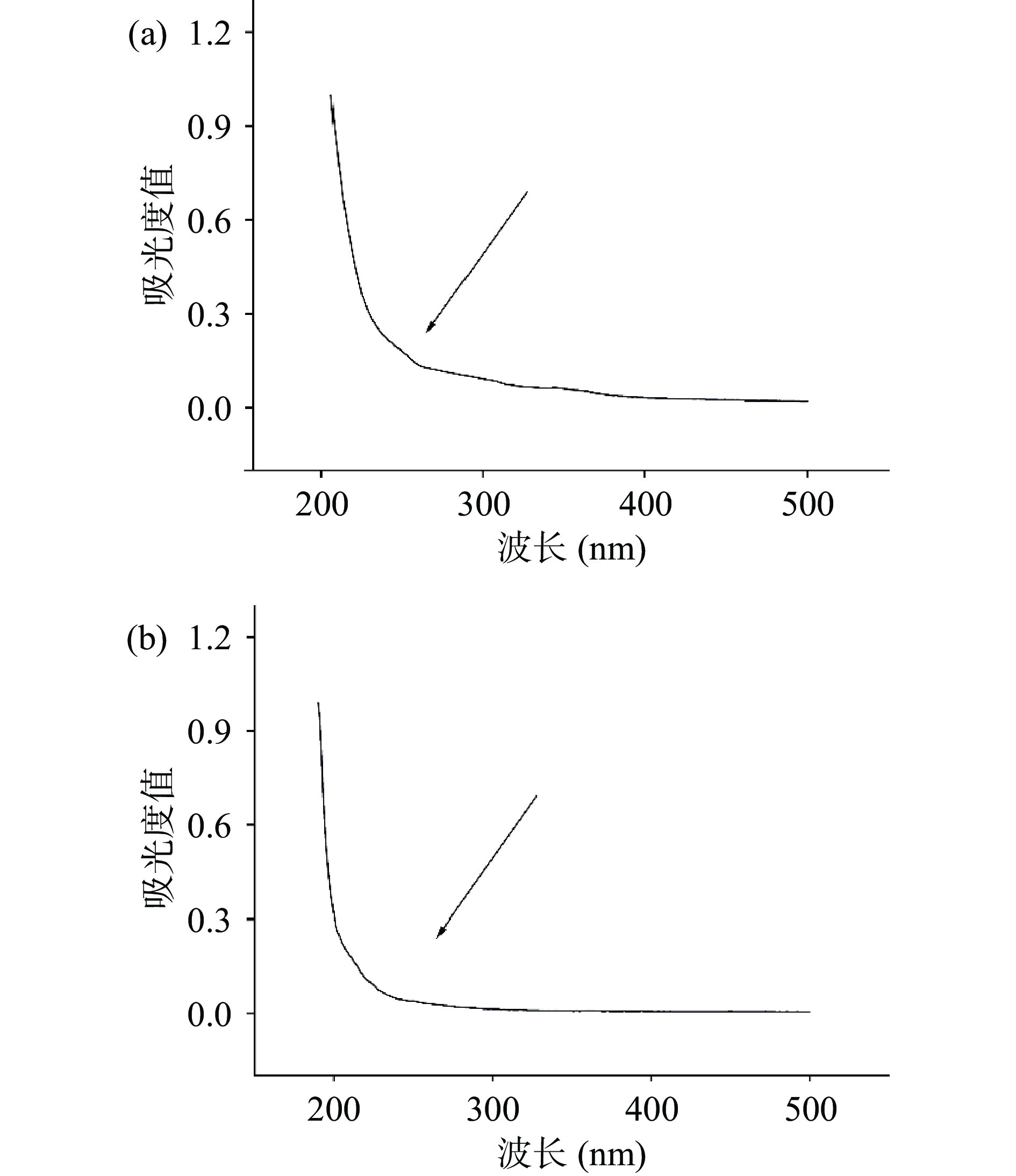
通过紫外-可见光分光光度计对ZLP和S-ZLP的纯度进行评估。将两种多糖溶于超纯水配制成浓度为1 mg/mL的溶液,以超纯水为参比校准基线,在200~500 nm范围内扫描多糖溶液。通过测定260和280 nm处的吸收峰,即可评估核酸、蛋白质及总酚在两种多糖样品中的存在情况[30]。
1.2.10 多糖分子量的检测
以不同分子量的葡聚糖T-10(10 kDa)、T-40(40 kDa)、T-110(110 kDa)、T-500(500 kDa)、T-1000(1000 kDa)、T-2000(2000 kDa)为标准品,通过HPGPC对ZLP和S-ZLP的分子量进行评估。以超纯水配制1 mg/mL的待测样品。以超纯水为流动相,洗脱流速为0.6 mL/min,进样体积20 µL,检测温度35 ℃,柱温30 ℃,示差检测器,Tsk-gel G4000PWxl(7.8 mm×300 mm)色谱柱,测定各个标准品的保留时间,建立lg Mw-Rt标准曲线。以一致的运行条件测定样品溶液的保留时间,带入标准曲线即可计算出ZLP和S-ZLP的分子量分布情况。标准曲线方程为:lg Mw=−0.3555Rt+9.3736,R2=0.9906。
1.2.11 多糖微观结构的扫描电子显微镜观察
使用SEM观察ZLP和S-ZLP的分子形态[31]。在显微镜的金属支架上固定碳导电双面胶,两种多糖样品冻干后平铺到双面胶上,并吹扫掉多余的样品。随后利用离子溅射喷镀仪在导电胶上均匀地沉积一层薄金涂层进行观察。
1.2.12 多糖热力学性质的检测
通过TGA测定ZLP和S-ZLP 热稳定性。在微量天平中分别称量5 mg多糖粉末,将样品置于分析仪的氧化铝坩埚中,以氮气为载气,流速为20 mL/min,设置初始和结束温度分别为30 ℃ 和600 ℃,以10 ℃/min的速度进行加热测试。
1.2.13 抗氧化活性的检测
1.2.13.1 DPPH·清除活性测定
参考 Wu等[32]的方法稍作修改,配制0.2 mmol/L DPPH 溶液并在黑暗中贮存。分别准备0.05、0.1、0.3、0.5、1、3、5、8、10 mg/mL ZLP和S-ZLP溶液。在96孔板中,取60 μL多糖溶液与120 μL 0.2mmol/L DPPH溶液,混合静置30 min,测量510 nm处吸光度。以维生素C(VC)为阳性对照,平行3次。根据公式(2)计算ZLP和S-ZLP DPPH·清除率。
A(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (2) 式中:A—DPPH·清除率,%;A0—去离子水代替样品溶液的吸光度;A1—样品溶液吸光度;A2—无水乙醇代替DPPH溶液的吸光度。
1.2.13.2 ·OH清除活性测定
采用Fenton反应体系法[33]。参照宋佳敏等[34]的方法稍作修改。使用去离子水配制不同浓度的样品溶液。在96孔板中,将160 μL样品溶液与40 μL 9 mmol/L FeSO4溶液和40 μL 8.8 mmol/L H2O2溶液充分混合,再加入20 μL 9 mmol/L水杨酸-乙醇溶液混合均匀后,于37 ℃静置30 min,并于酶标仪上测定510 nm处吸光度。以VC作为阳性对照,平行3次。吸光度值代入公式(3)计算·OH清除率:
A(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (3) 式中:A—·OH清除率,%;A0—去离子水代替样品溶液的吸光度;A1—样品溶液吸光度;A2—去离子水代替H2O2工作液的吸光度。
1.2.13.3 ABTS+·清除活性测定
ABTS+·清除率参考樊海燕等[35]的方法稍作修改。7 mmol/L ABTS溶液与2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾溶液按照1:1混合均匀,避光放置12 h以上。用去离子水调734 nm吸光度为0.7±0.01,即ABTS+·工作液。
使用去离子水配制不同浓度的多糖溶液。在96孔板中,将40 μL多糖溶液与120 μL ABTS+·工作液溶液混合均匀,在室温下静置5 min,并于酶标仪上测定734 nm处吸光度。VC作为阳性对照,以去离子水替代多糖溶液作为空白,每组设置3个重复孔,计算ABTS+·清除率:
A(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (4) 式中:A—ABTS+·清除率,%;A0—去离子水代替样品溶液的吸光度;A1—样品溶液吸光度;A2—去离子水代替ABTS+·工作液的吸光度。
1.2.13.4 亚铁离子还原力的测定
样品还原能力的测定参考Zhou等[11]的方法稍作修改。离心管中分别加入2.5 mL配制好的0.2 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH6.6)、1%铁氰化钾溶液、10%的三氯乙酸溶液和0.1%的氯化铁溶液以及1 mL不同浓度ZLP和S-ZLP溶液,混匀。50 ℃水浴30 min后以5000 r/min离心20 min,取2.5 mL上清液加入2.5 mL去离子水和1.5 mL 0.1%氯化铁溶液,静置10 min后测量700 nm处吸光度值。平行测定3 次,以VC作为对照。测得吸光度越大说明样品还原力越强[36]。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS进行单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和Duncan多重比较,Microsoft Excel 2021、Design expert13、Origin 2022进行统计分析及绘图。其中,P<0.05被认为是显著的。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 茭白多糖的提取与纯化
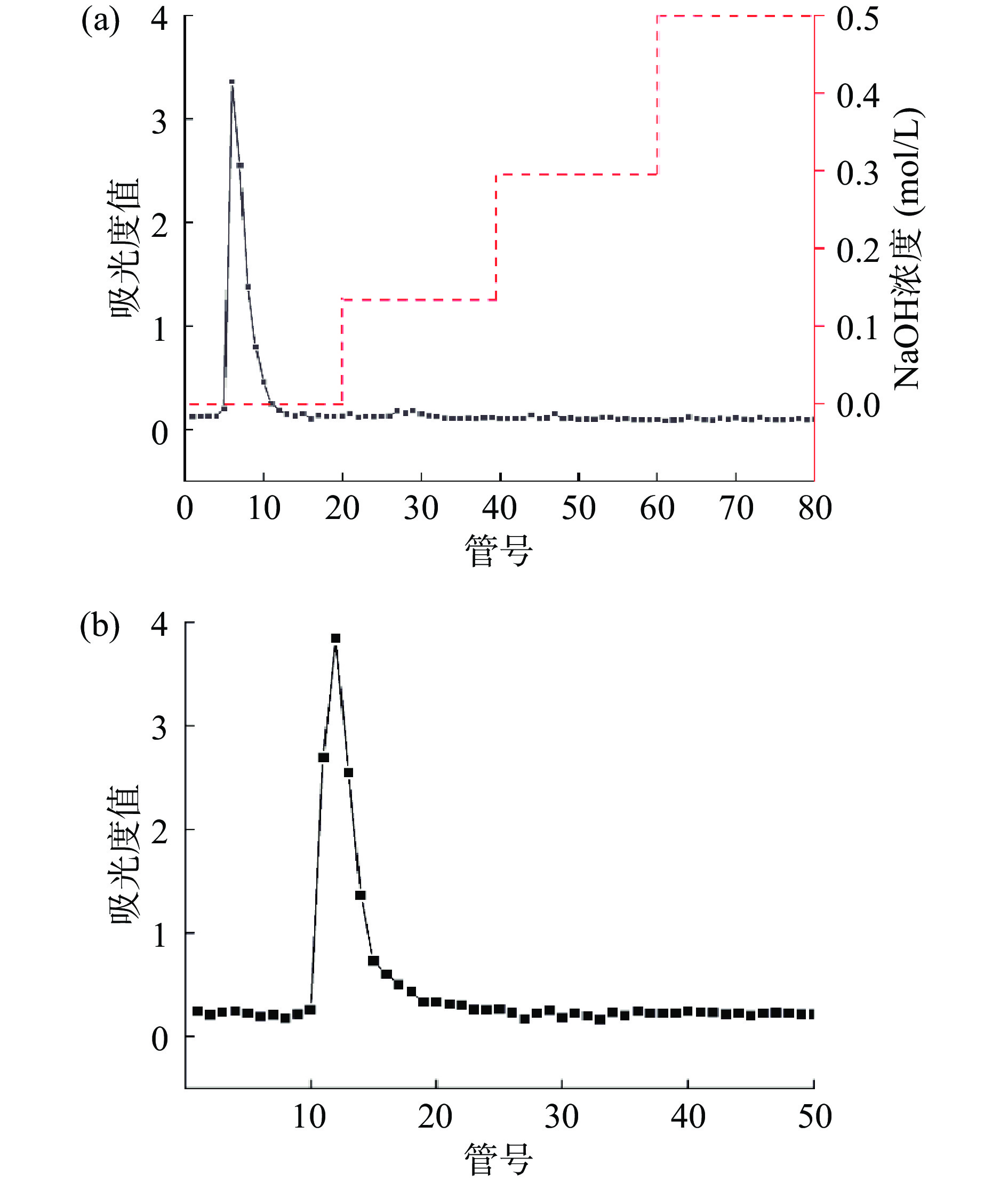
透析后得到的茭白粗多糖,得率为3.56%±0.46%。如图1a,通过DEAE-52纤维素分离柱洗脱,发现其只在去离子水洗脱出峰,收集峰上洗脱液,冷冻干燥后利用琼脂糖凝胶S-6ff纯化柱纯化,如图1b,只产生对称单峰,表明纯化后的多糖为分子量相对均一的化合物。将洗脱液冻干得到的多糖组分命名为ZLP,得率为2.73%±0.26%。
2.2 茭白多糖硫酸化
2.2.1 单因素实验
2.2.1.1 酯化温度对DS的影响
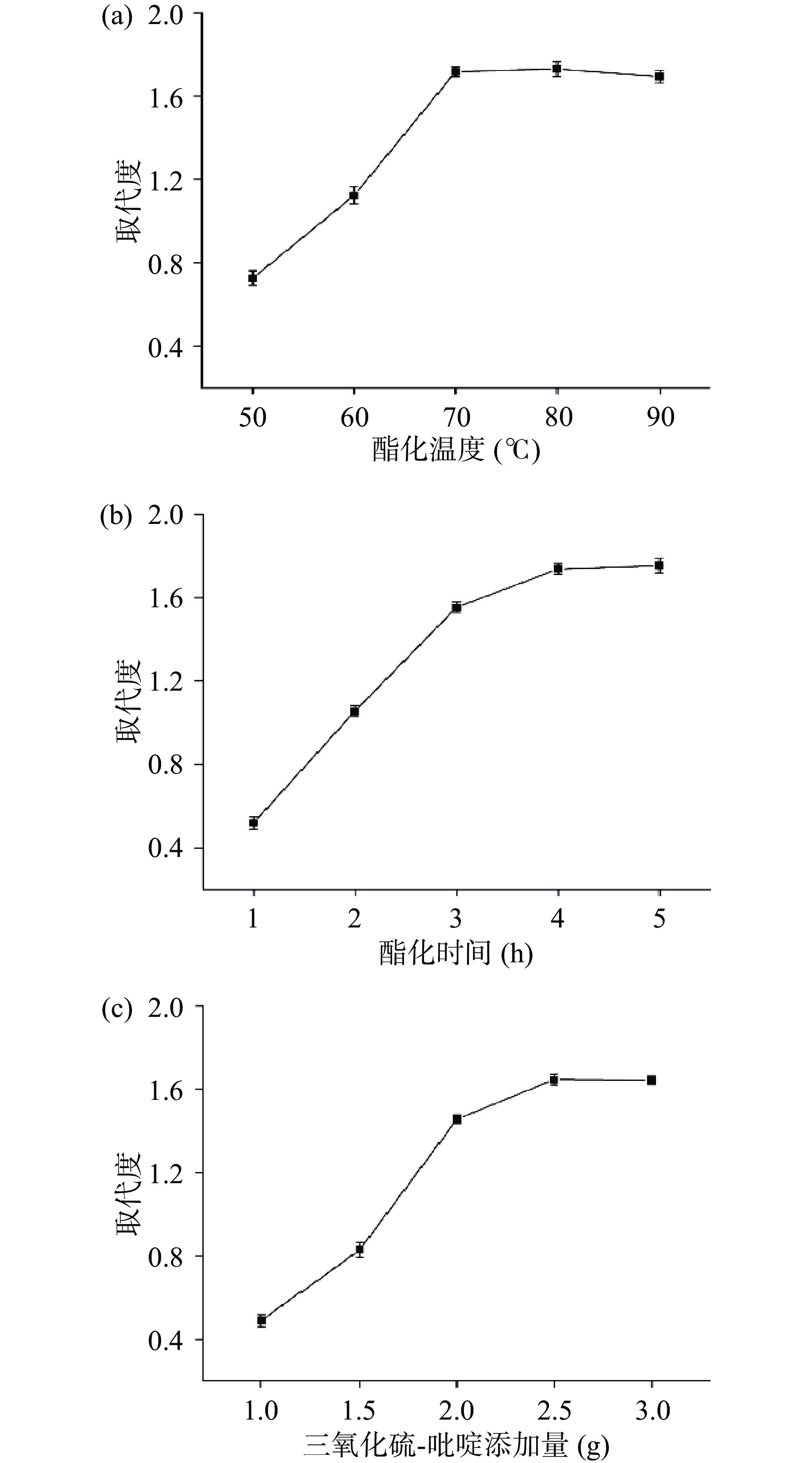
多糖取代度随酯化温度上升而增加,在50~70 ℃时,DS增加显著(P<0.05),由0.73上升至1.72;70 ℃以后,DS提高缓慢甚至有所下降(图2a)。这与周艳等[37]、郭金英等[38]研究结果相同。可能是由于温度升高,酯化剂副反应增大,抑制硫酸基团的取代[39]。同时考虑节能问题,选择70 ℃为酯化温度。
2.2.1.2 酯化时间对DS的影响
茭白多糖取代度随时间增长而增加,4 h时DS达到最大值1.74,继续酯化,DS变化不明显(图2b)。这与郭金英等[38]、Jayawardena等[40]研究结果相同。说明在一定范围内延长酯化时间可提高DS。但由于酯化反应可逆性,随着时间延长取代度增加变得平缓,继续酯化,可能会引起多糖部分降解[39],使酯化率降低。因此,选择4 h为茭白多糖硫酸化反应时间。
2.2.1.3 三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量对DS的影响
酯化剂量由1 g增加到2.5 g,DS由0.44增大到1.66。继续增加三氧化硫-吡啶复合物量,DS不再增加甚至有下降趋势(图2c)。这与Zhang等[39]的研究结果是相一致的,即由于酯化剂用量过大导致反应不均匀[41]。同时考虑到经济成本问题,选择酯化剂量为2.5 g。
2.2.2 响应面试验
试验安排及结果见表2,其中第13~17组为5次重复的中心点试验用于验证模型的准确性[24]。
表 2 试验设计及结果Table 2. Experimental scheme and results试验号 A:酯化温度
(℃)B:酯化时间
(h)C:三氧化硫-吡啶
复合物添加量(g)取代度 1 60 3 2.5 1.33 2 80 3 2.5 1.45 3 60 5 2.5 1.42 4 80 5 2.5 1.58 5 60 4 2 1.4 6 80 4 2 1.52 7 60 4 3 1.52 8 80 4 3 1.56 9 70 3 2 1.45 10 70 5 2 1.58 11 70 3 3 1.53 12 70 5 3 1.66 13 70 4 2.5 1.83 14 70 4 2.5 1.85 15 70 4 2.5 1.81 16 70 4 2.5 1.83 17 70 4 2.5 1.84 对试验数据进行回归分析,得二次多元回归方程如下:DS=1.83+0.055A+0.06B+0.04C+0.01AB−0.02AC+0.000BC−0.221A2−0.166B2−0.111C2。
方差分析(表3)表明,回归模型极显著(F值=129.91,P<0.0001),失拟项不显著(F=3.03,P>0.05),拟合系数R2=0.9940,模型拟合程度比较好,试验误差较小。
表 3 回归模拟方差分析Table 3. Regression simulation analysis of variance来源 平方和 自由度 标准差 F值 P值 模型 0.4810 9 0.0534 129.91 <0.0001 ** A-酯化温度 0.0242 1 0.0242 58.82 0.0001 ** B-酯化时间 0.0288 1 0.0288 70.00 <0.0001 ** C-三氧化硫-吡啶
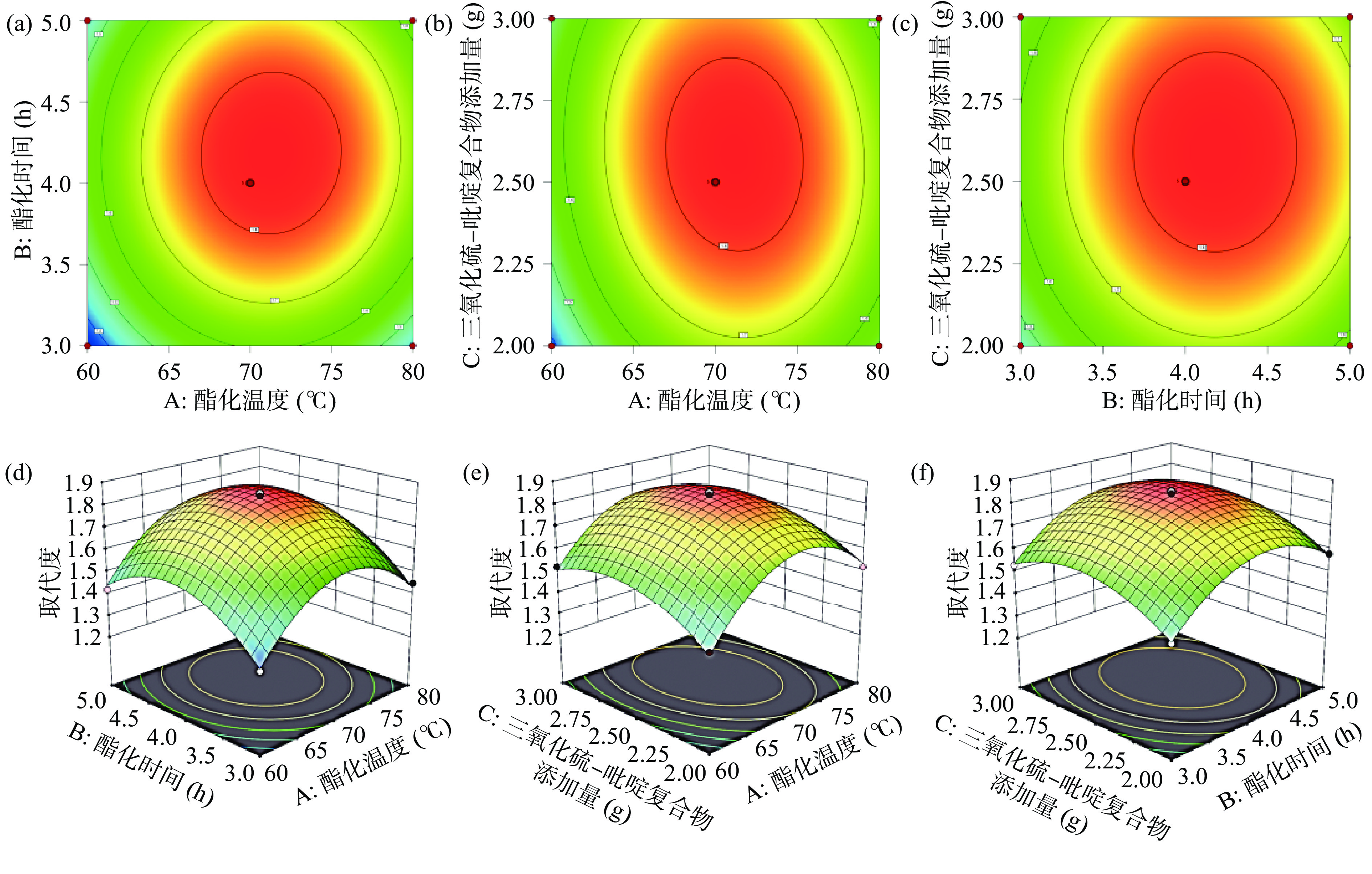
复合物添加量0.0128 1 0.0128 31.11 0.0008 ** AB 0.0004 1 0.0004 0.9722 0.3570 AC 0.0016 1 0.0016 3.89 0.0892 BC 0.0000 1 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 A2 0.2056 1 0.2056 499.83 <0.0001 ** B2 0.1160 1 0.1160 282.01 <0.0001 ** C2 0.0519 1 0.0519 126.09 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0029 7 0.0004 失拟项 0.0020 3 0.0007 3.03 0.1561 纯误差 0.0009 4 0.0002 总和 0.4839 16 结合显著性检验,比较响应曲面(图3),得到优化区域中各因素对茭白多糖取代度影响的显著程度为,酯化时间>酯化温度>三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量。拟给出的茭白多糖硫酸酯化的最优条件为:温度71.21 ℃、时间4.18 h、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物加入量2.58 g,产品的DS为1.84。
![]() 图 3 酯化时间、酯化温度、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量及交互作用对茭白多糖硫酸基取代度的影响的等高线图(a、b、c)及三维响应面图(d、e、f)Figure 3. Contour plots (a, b, c) and three-dimensional response surface plots (d, e, f) about the effects of esterification time, esterification temperature, addition amount of sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex and interaction on the DS ofsulfate of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide
图 3 酯化时间、酯化温度、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量及交互作用对茭白多糖硫酸基取代度的影响的等高线图(a、b、c)及三维响应面图(d、e、f)Figure 3. Contour plots (a, b, c) and three-dimensional response surface plots (d, e, f) about the effects of esterification time, esterification temperature, addition amount of sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex and interaction on the DS ofsulfate of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide考虑到实际操作方便,为验证响应面法所得结果的准确性和可靠性,将工艺参数修正为酯化时间4 h、酯化温度70 ℃、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物加入量2.6 g,试验重复3次,验证响应面法拟给出的结果可靠性。得到实际的DS为1.79±0.3,相对误差为2.72%,故基于响应面法所得的优化工艺参数准确可靠。
2.2.3 傅里叶红外光谱分析
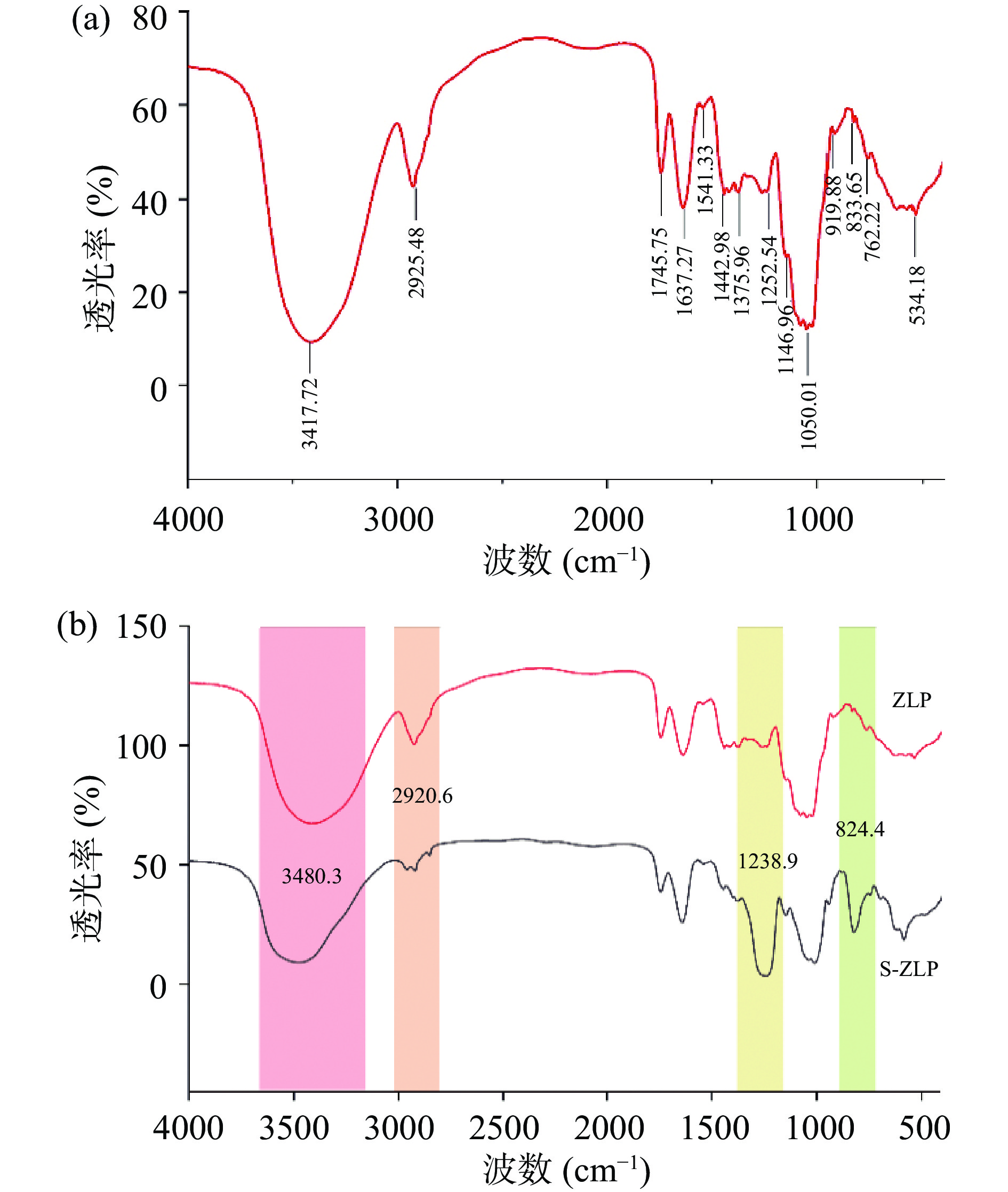
图4a为ZLP红外光谱, 3417.72 cm−1处为OH 的伸缩振动峰;2925.48 cm−1为C-H 的伸缩振动的吸收峰;1637.27 cm−1 处为C=O 的伸缩振动引起;1442.98 cm−1处为 C-H 的振动峰;以上四处是多糖的特征吸收峰;1745.75 cm−1 及1252.54 cm−1处的吸收峰证明了O-乙酰基的存在[42];1050.01 cm−1处为C-O-C不对称伸缩振动,表明吡喃糖的存在;919.88 cm−1表明ZLP含有β-型糖苷键;833.65 cm−1处为α-型糖苷键[13]。
图4b为茭白多糖及其硫酸化产物红外光谱对比图。3600~3200 cm−1间为多糖中-OH的吸收峰,峰形变窄说明羟基数量减少[24],在1240 cm−1附近有-O-SO3的S=O伸缩振动吸收峰,850~820 cm−1间有-C-O-S的伸缩振动峰[43],说明硫酸基团已经成功结合到茭白多糖分子上,利用硫酸钡-明胶比浊法测定其DS为1.79。
2.3 多糖组成测定
如图5所示,通过紫外-可见光分光光度计对ZLP(a)和S-ZLP(b)进行紫外全波长扫描,发现二者在260以及280 nm处没有明显吸收峰,说明其基本不含或含有极少量蛋白质、核酸和总酚。其基本理化性质如表4 所示。由于取代度的增加会降低硫酸化多糖的总糖含量导致S-ZLP总糖含量降低[44]。
表 4 茭白多糖及其硫酸化产物基本组成Table 4. Basic compositions of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide and its sulfated products含量(%) ZLP S-ZLP 总糖 94.48±0.3 50.58±0.4 硫酸根 − 49.86±0.1 还原糖 − − 糖醛酸 5.93±0.45 4.49±0.27 蛋白质 0.52±0.07 0.33±0.09 总酚 − − 2.4 多糖分子量的检测
通过高效液相色谱对ZLP、S-ZLP样品进行色谱测定,ZLP样品保留时间为8.870 min,如图6a;S-ZLP样品保留时间为9.243 min,如图6b 。根据葡萄糖标准回归曲线计算可得,ZLP分子量约为1.66×106 Da,S-ZLP分子量约为1.22×106 Da。陈群[45]的研究发现不同方法对茯苓多糖硫酸化后得到的硫酸化产物分子量均小于天然茯苓多糖;Zhang等[39]对慈姑多糖进行研究,发现硫酸化后慈姑多糖分子量由为576.9 kDa逐渐降低到最低水平129.6 kDa,与天然慈姑多糖相比降低了77.5%。导致此现象的原因可能是改性过程中酸的氧化使部分糖链发生断裂导致多糖分子量减小。由色谱图可以得知,ZLP和S-ZLP均为均匀对称的单峰,说明其纯化程度较高,多糖组分较纯。
2.5 扫描电子显微镜分析
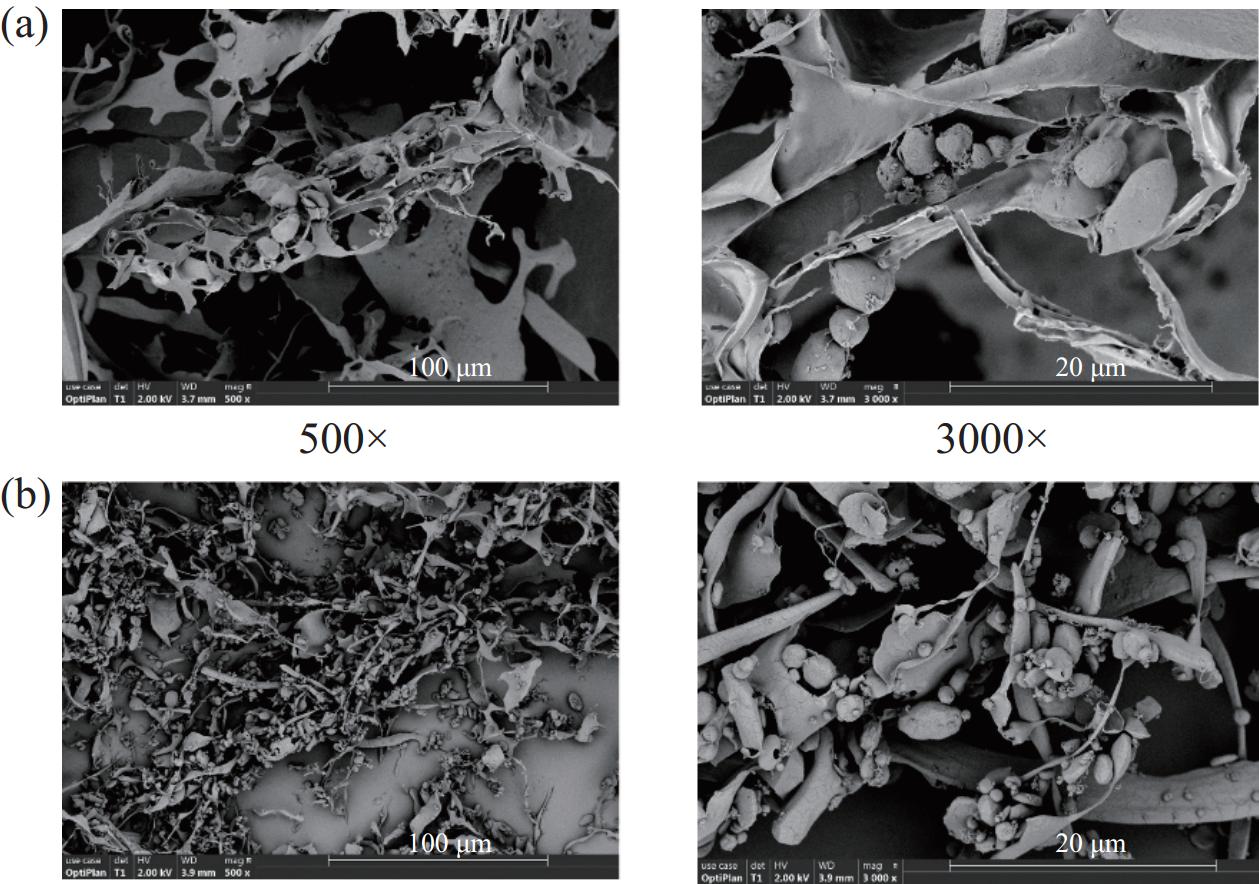
如图7 为不同放大倍数下ZLP和S-ZLP扫描电子显微镜微观结构观测图,多糖形态的差异表明各组分具有不同的链构象[46]。由图可知,茭白多糖主要为脉络状结构,中间附有少量球状结构;而经过硫酸化修饰后,茭白多糖的微观结构发生明显改变,组织更加细碎,脉络结构变少,球状组织增多。可能是由于硫酸基团的取代导致分子间缔合作用力变弱[47],片层卷曲形成球状。
2.6 热力学性质分析
ZLP和S-ZLP的TG曲线(图8)显示,在测定范围内ZLP、S-ZLP共出现了三次质量损失过程。第一阶段,在25~100 ℃左右,开始失去吸附水;ZLP在46.38 ℃时失重最快,失重率为16.48%;S-ZLP在65.04 ℃时失重最快,失重率为2.92%。
第二阶段,温度变化范围为200~400 ℃ ,此阶段失重最为明显,表明多糖在该温度范围内发生了剧烈的分解;ZLP降解速率在336.44 ℃时达到最大值,此阶段的失重率为73.54%,S-ZLP降解速率在331.05 ℃时达到最大值,此阶段的失重率为81.02%。
第三阶段,温度变化范围是400~600 ℃ ,此阶段样品的重量变化趋于平缓,为缓慢碳化阶段,大部分样品在此阶段内分解为灰分和无机成分[47]。
以上结果说明多糖在200 ℃以下的环境中内具有良好的热稳定性,且S-ZLP热稳定性要优于ZLP。
2.7 体外抗氧化活性测定
活性氧引起的氧化应激和氧化损伤已成为机体各种器官疾病和衰老的重要原因[11]。由图9 可知,ZLP和S-ZLP能一定程度上清除DPPH·(a)、·OH(b)、ABTS+·(c)及还原Fe2+(d)且均呈剂量依赖性。S-ZLP对于四者的还原能力均优于ZLP但均低于阳性对照。ZLP对于DPPH·、·OH以及ABTS+·清除能力的IC50值分别为3.49、3.28和12.70 mg/mL;S-ZLP为0.39、1.00和1.82 mg/mL;阳性对照VC为0.069、0.17和0.077 mg/mL。IC50值越小,其自由基清除能力越强。从IC50结果来看,ZLP和S-ZLP对三种自由基清除能力均低于阳性对照,硫酸化后茭白多糖的自由基清除能力有一定程度上的提高,且对于DPPH·和ABTS+·清除能力提高更优。Khan等[15]研究发现含有硫酸根的紫菜多糖对·OH及ABTS+·的清除能力要高于不含硫酸根的多糖;Gong等[20]研究发现,罗汉果多糖硫酸衍生物具有清除DPPH·、·OH和超氧阴离子的能力,且清除能力随多糖浓度的增加而增强。与本研究结果具有相似性,这证实了硫酸化改性对多糖的抗氧化能力的改善作用。
3. 结论
本研究采用水提醇沉法从茭白膨大茎中提取出一种新型的水溶性多糖。在单因素基础上,对硫酸化茭白多糖响应面优化,得到的最优酯化方案为:茭白多糖100 mg,酯化温度70 ℃,酯化时间4 h,三氧化硫-吡啶复合物质量2.6 g及甲酰胺量25 mL条件下,DS为1.79±0.3(n=3)。结合红外光谱证明,硫酸基团已经结合到多糖分子链上。体外抗氧化实验证明,茭白多糖具有一定的体外抗氧化活性;与硫酸化茭白多糖对比发现,硫酸改性能在一定程度上提高ZLP的抗氧化活性,但IC50值仍低于阳性对照,并且二者对体外抗氧化活性表现出不同的质量浓度依赖性。这也为硫酸化茭白多糖在医药领域作为天然的抗氧化剂提供了可能,同时也为进一步开发茭白多糖提供了理论基础。
由于本研究获得的多糖分子量较大,其结构特征可能更为复杂,因此研究主要集中于硫酸化茭白多糖的提取纯化、简单的成分及活性探究。后续将利用核磁等方法对其结构进行深入解析,并对其构效关系进行进一步的研究。
-
图 3 酯化时间、酯化温度、三氧化硫-吡啶复合物添加量及交互作用对茭白多糖硫酸基取代度的影响的等高线图(a、b、c)及三维响应面图(d、e、f)
Figure 3. Contour plots (a, b, c) and three-dimensional response surface plots (d, e, f) about the effects of esterification time, esterification temperature, addition amount of sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex and interaction on the DS ofsulfate of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide
表 1 Box-Behnkens 试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Box-Behnkens test factor level design
因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 酯化温度(℃) A 60 70 80 酯化时间(h) B 3 4 5 三氧化硫-吡啶(g) C 2 2.5 3 表 2 试验设计及结果
Table 2 Experimental scheme and results
试验号 A:酯化温度
(℃)B:酯化时间
(h)C:三氧化硫-吡啶
复合物添加量(g)取代度 1 60 3 2.5 1.33 2 80 3 2.5 1.45 3 60 5 2.5 1.42 4 80 5 2.5 1.58 5 60 4 2 1.4 6 80 4 2 1.52 7 60 4 3 1.52 8 80 4 3 1.56 9 70 3 2 1.45 10 70 5 2 1.58 11 70 3 3 1.53 12 70 5 3 1.66 13 70 4 2.5 1.83 14 70 4 2.5 1.85 15 70 4 2.5 1.81 16 70 4 2.5 1.83 17 70 4 2.5 1.84 表 3 回归模拟方差分析
Table 3 Regression simulation analysis of variance
来源 平方和 自由度 标准差 F值 P值 模型 0.4810 9 0.0534 129.91 <0.0001 ** A-酯化温度 0.0242 1 0.0242 58.82 0.0001 ** B-酯化时间 0.0288 1 0.0288 70.00 <0.0001 ** C-三氧化硫-吡啶
复合物添加量0.0128 1 0.0128 31.11 0.0008 ** AB 0.0004 1 0.0004 0.9722 0.3570 AC 0.0016 1 0.0016 3.89 0.0892 BC 0.0000 1 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 A2 0.2056 1 0.2056 499.83 <0.0001 ** B2 0.1160 1 0.1160 282.01 <0.0001 ** C2 0.0519 1 0.0519 126.09 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0029 7 0.0004 失拟项 0.0020 3 0.0007 3.03 0.1561 纯误差 0.0009 4 0.0002 总和 0.4839 16 表 4 茭白多糖及其硫酸化产物基本组成
Table 4 Basic compositions of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide and its sulfated products
含量(%) ZLP S-ZLP 总糖 94.48±0.3 50.58±0.4 硫酸根 − 49.86±0.1 还原糖 − − 糖醛酸 5.93±0.45 4.49±0.27 蛋白质 0.52±0.07 0.33±0.09 总酚 − − -
[1] WU W J, HAN Y C, NIU B, et al. Recent advances in Zizania latifolia:A comprehensive review on phytochemical, health benefits and applications that maximize its value [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2023.
[2] 韦满棋. 茭白种植现状及发展建议[J]. 新农业,2021(17):44−45. [WEI M Q. Current situation of Zizania latifolia planting and development suggestions[J]. Modern Agriculture,2021(17):44−45.] WEI M Q . Current situation of Zizania latifolia planting and development suggestions[J]. Modern Agriculture,2021 (17 ):44 −45 .[3] HUANG J, WU W, FANG X, et al. Zizania latifolia cell wall polysaccharide metabolism and changes of related enzyme activities during postharvest storage[J]. Foods,2022,11(3):392. doi: 10.3390/foods11030392
[4] 汪名春, 赵士伟, 朱培蕾, 等. 茭白水溶性多糖提取工艺及单糖组成的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(17):211−214,219. [WANG M C, ZHAO S W, ZHU P L, et al. Study on extraction process of water soluble polysaccharides from Zizania latifolia and determine component of monosaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(17):211−214,219.] WANG M C, ZHAO S W, ZHU P L, et al . Study on extraction process of water soluble polysaccharides from Zizania latifolia and determine component of monosaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015 ,36 (17 ):211 −214,219 .[5] GAO Y, CHEN H, LIU R, et al. Ameliorating effects of water bamboo shoot ( Zizania latifolia) on acute alcoholism in a mice model and its chemical composition[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,378:132122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132122
[6] YAN N, DU Y, LIU X, et al. Morphological characteristics, nutrients, and bioactive compounds of Zizania latifolia, and health benefits of its seeds[J]. Molecules,2018,23(7):1561. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071561
[7] WANG M, ZHU P, ZHAO S, et al. Characterization, antioxidant activity and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from the swollen culms of Zizania latifolia[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,95:809−817. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.010
[8] YU X, YANG T, QI Q, et al. Comparison of the contents of phenolic compounds including flavonoids and antioxidant activity of rice ( Oryza sativa) and Chinese wild rice ( Zizania latifolia)[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,344:128600. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128600
[9] HUANG J, WU W, NIU B, et al. Characterization of Zizania latifolia polysaccharide-corn starch composite films and their application in the postharvest preservation of strawberries [J]. LWT, 2023, 173.
[10] 王晓烨, 吴旭. 生物活性多糖的研究现状及展望[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(19):318,324. [WANG X Y, WU X. Research status and prospects of bioactive polysaccharide[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015(19):318,324.] WANG X Y, WU X. Research status and prospects of bioactive polysaccharide[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015(19): 318,324.
[11] ZHOU S, HUANG G, HUANG H. Extraction, derivatization and antioxidant activities of onion polysaccharide[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,388:133000. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133000
[12] CHEN F, HUANG G, HUANG H. Preparation, analysis, antioxidant activities in vivo of phosphorylated polysaccharide from Momordica charantia[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,252:117179. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117179
[13] JIA R B, LI Z R, WU J, et al. Physicochemical properties of polysaccharide fractions from Sargassum fusiforme and their hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,147:428−438. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.243
[14] AHMAD M M. Recent trends in chemical modification and antioxidant activities of plants-based polysaccharides:A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications,2021,2(25):100045.
[15] KHAN B M, QIU H M, XU S Y, et al. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of sulphated polysaccharides derived from Porphyra haitanensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,145:1155−1161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.040
[16] 李天一, 苏超, 高婷, 等. 超声辅助法提取茭白多糖工艺的优化研究[J]. 农产品加工,2023(11):20−23,26. [LI T Y, SU C, GAO T, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of water-white polysaccharide[J]. Farm Products Processing,2023(11):20−23,26.] LI T Y, SU C, GAO T, et al . Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of water-white polysaccharide[J]. Farm Products Processing,2023 (11 ):20 −23,26 .[17] WANG M, ZHAO S, ZHU P, et al. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of water extractable polysaccharides from the swollen culms of Zizania latifolia [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 107(Pt A):882−890.
[18] PEI Y, YANG S T, XIAO Z B, et al. Structural characterization of sulfated polysaccharide isolated from red algae ( Gelidium crinale) and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in macrophage cells[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2021,9:794818. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.794818
[19] WANG Z, XIE J, SHEN M, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides:Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,74:147−157.
[20] GONG P, WANG M, GUO Y, et al. Structure characterization, in vitro antioxidant and anti-tumor activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Siraitia grosvenorii[J]. Foods,2023,12(11):2133. doi: 10.3390/foods12112133
[21] XU Y, GAO Y, LIU F, et al. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharides from blackcurrant and their antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109:1344−1354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.164
[22] 张子木, 黄秀芳, 张琴, 等. 壶瓶碎米荠多糖硫酸化结构修饰及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(12):28−33. [ZHANG Z M, HUANG X F, ZHANG Q, et al. Sulfated structure modification and antioxidant activity of Cardamine Hupingshanensis polysaccharide[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021,36(12):28−33.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2021.12.006 ZHANG Z M, HUANG X F, ZHANG Q, et al . Sulfated structure modification and antioxidant activity of Cardamine Hupingshanensis polysaccharide[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021 ,36 (12 ):28 −33 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2021.12.006[23] 刘玉凤, 贾淑颖, 刘飞飞, 等. 不同取代度的硫酸化肠浒苔多糖抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(19):142−147, 152. [LIU Y F, JIA S Y, LIU F F, et al. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharides with different substituting degrees from Enteromorpha intestinalis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(19):142−147,152.] LIU Y F, JIA S Y, LIU F F, et al . Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharides with different substituting degrees from Enteromorpha intestinalis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016 ,37 (19 ):142 −147,152 .[24] 白冶宇, 钱建亚. 氨基磺酸法制备硫酸化大麦多糖[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(3):203−208. [BAI Y Y, QIAN J Y. Preparation of sulfated barley polysaccharide with sulfamic acid[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,40(3):203−208.] BAI Y Y, QIAN J Y . Preparation of sulfated barley polysaccharide with sulfamic acid[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015 ,40 (3 ):203 −208 .[25] 孔倩, 周婷, 武改兰, 等. 南瓜水溶性多糖的制备及硫酸酯化初步研究[J]. 食品科学,2009,30(16):73−77. [KONG Q, ZHOU T, WU G L, et al. Preparation and sulfation of polysaccharides from pumpkin[J]. Food Science,2009,30(16):73−77.] KONG Q, ZHOU T, WU G L, et al . Preparation and sulfation of polysaccharides from pumpkin[J]. Food Science,2009 ,30 (16 ):73 −77 .[26] 邱芳萍, 张玲, 于健. 硫酸钡比浊法对鹿茸多糖中硫酸基含量的测定[J]. 长春工业大学学报(自然科学版),2005(4):268−270. [QIU F P, ZHANG L, YU J. Determination of sulfate group in antler polysaccharides by barium sulfate turbidimetric method[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Techonology (Natural Science Edition),2005(4):268−270.] QIU F P, ZHANG L, YU J . Determination of sulfate group in antler polysaccharides by barium sulfate turbidimetric method[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Techonology (Natural Science Edition),2005 (4 ):268 −270 .[27] CHEN P, DING S, YAN Z, et al. Structural characteristic and in-vitro anticancer activities of dandelion leaf polysaccharides from pressurized hot water extraction[J]. Nutrients,2022,15(1):80. doi: 10.3390/nu15010080
[28] 沈育伊, 覃香香, 滕秋梅, 等. 荸荠多糖中蛋白含量的测定[J]. 微量元素与健康研究,2019,36(6):50−52. [SHEN Y Y, TAN X X, TENG Q M, et al. Determination of protein content in Eleocharis dulcis polysacchaeides[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health,2019,36(6):50−52.] SHEN Y Y, TAN X X, TENG Q M, et al . Determination of protein content in Eleocharis dulcis polysacchaeides[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health,2019 ,36 (6 ):50 −52 .[29] 米合热尼沙·阿木热江, 胡晟, 任国瑞, 等. 库尔勒香梨酸性多糖PSAP-1的分离纯化及其糖醛酸含量测定[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(22):7454−7460. [MIHERENISHA A M R J, HU S, REN G R, et al. Separation and purification of acidic polysaccharide PSAP-1 from Pyrus sinkiangensis Yu. and its uronic acid content determination[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(22):7454−7460.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.22.spaqzljcjs202222038 MIHERENISHA A M R J, HU S, REN G R, et al . Separation and purification of acidic polysaccharide PSAP-1 from Pyrus sinkiangensis Yu. and its uronic acid content determination[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022 ,13 (22 ):7454 −7460 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.22.spaqzljcjs202222038[30] YU S, JI H, DONG X, et al. FAS/FAS-L-mediated apoptosis and autophagy of SPC-A-1 cells induced by water-soluble polysaccharide from Polygala tenuifolia[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,150:449−458. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.010
[31] ZHAO B, ZHAO J, LÜ M, et al. Comparative study of structural properties and biological activities of polysaccharides extracted from Chroogomphus rutilus by four different approaches[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,188:215−225. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.025
[32] WU Q, QU H, JIA J, et al. Characterization, antioxidant and antitumor activities of polysaccharides from purple sweet potato[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,132:31−40. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.045
[33] 贾之慎, 邬建敏, 唐孟成. 比色法测定Fenton反应产生的羟自由基[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,1996(2):184−186,193. [JIA Z S, WU J M, TANG M C. The hydroxyl radical produced by Fenton reaction was determined by colorimetric method[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics,1996(2):184−186,193.] JIA Z S, WU J M, TANG M C . The hydroxyl radical produced by Fenton reaction was determined by colorimetric method[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics,1996 (2 ):184 −186,193 .[34] 宋佳敏, 王鸿飞, 孙朦, 等. 响应面法优化金蝉花多糖提取工艺及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(4):275−281. [SONG J M, WANG H F, SUN M, et al. Optimization of extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Cordyceps cicadae by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2018,39(4):275−281.] SONG J M, WANG H F, SUN M, et al . Optimization of extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Cordyceps cicadae by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2018 ,39 (4 ):275 −281 .[35] 樊海燕, 蔡云飞, 杨彭鹏, 等. ABTS法和DPPH法测定锁阳多糖抗氧化活性的适用性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2023,43(S1):315−316. [FAN H Y, CAI Y F, YANG P P, et al. Applicability of ABTS and DPPH assays for determination of antioxidant acitivity of Cynomorium songaricum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2023,43(S1):315−316.] FAN H Y, CAI Y F, YANG P P, et al . Applicability of ABTS and DPPH assays for determination of antioxidant acitivity of Cynomorium songaricum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2023 ,43 (S1 ):315 −316 .[36] 吴丹. 富硒香菇多糖和富硒平菇多糖体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2010,38(11):5841−5843,5856. [WU D. Study on antioxidative activity of selenium-rich lentinan and selenium-rich oyster mushroom polysaccharide in vitro[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2010,38(11):5841−5843,5856.] WU D . Study on antioxidative activity of selenium-rich lentinan and selenium-rich oyster mushroom polysaccharide in vitro[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2010 ,38 (11 ):5841 −5843,5856 .[37] 周艳, 林中瑞, 张聪, 等. 响应面法优化猴头菌硫酸化多糖[J]. 生物技术,2019,29(5):492−497. [ZHOU Y, LIN Z R, ZHANG C, et al. Optimization of the sulfated polysaccharide of Hericium erinaceus by response surface methodology[J]. Biotechnology,2019,29(5):492−497.] ZHOU Y, LIN Z R, ZHANG C, et al . Optimization of the sulfated polysaccharide of Hericium erinaceus by response surface methodology[J]. Biotechnology,2019 ,29 (5 ):492 −497 .[38] 郭金英, 朱蓓茹, 任国艳, 等. 发菜胞外多糖硫酸化条件的优化及红外光谱分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(24):61−67. [GUO J Y, ZHU B R, REN G Y, et al. Optimization of sulfation conditions and infrared spectroscopy analysis of Nostoc flagelliforme exopolydsaccharide[J]. Food Science,2016,37(24):61−67.] GUO J Y, ZHU B R, REN G Y, et al . Optimization of sulfation conditions and infrared spectroscopy analysis of Nostoc flagelliforme exopolydsaccharide[J]. Food Science,2016 ,37 (24 ):61 −67 .[39] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, NI G, et al. Sulfated modification, basic characterization, antioxidant and anticoagulant potentials of polysaccharide from Sagittaria trifolia[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2023,16(7):104812. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104812
[40] JAYAWARDENA U T, WANG L, SANJEEWA A K K, et al. Antioxidant potential of sulfated polysaccharides from Padina boryana; protective effect against oxidative stress in in vitro and in vivo zebrafish model[J]. Marine Drugs,2020,18(4):212. doi: 10.3390/md18040212
[41] QIAN J Y, BAI Y Y, TANG J, et al. Antioxidation and a-glucosidase inhibitory activities of barley polysaccharides modified with sulfation[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,64(1):104−111. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.05.034
[42] FATEMEH N B, TAHMASEBI E S. FT-IR study of the polysaccharides isolated from the skin juice, gel juice, and flower of Aloe vera tissues affected by fertilizer treatment[J]. Organic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2012,2(1):33. doi: 10.1186/2191-2858-2-33
[43] SUDHARSAN S, SUBHAPRADHA N, SEEDEVI P, et al. Antioxidant and anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria debilis (Forsskal)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,81:1031−1038. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.09.046
[44] 阿得力江·吾斯曼, 萨比热·热夏提, 希尔艾力·阿不力克木, 等. 葫芦多糖及其硫酸化修饰物抗新城疫病毒活性[J]. 中国兽医学报,2022,42(8):1640−1646. [WUSIMAN A D L J, REXIATI S B R, ABULIKEMU X E A L, et al. Anti-Newstle disease virus activity of Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) standl polysaccharide and sulfated modifications[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2022,42(8):1640−1646.] WUSIMAN A D L J, REXIATI S B R, ABULIKEMU X E A L, et al . Anti-Newstle disease virus activity of Lagenaria siceraria (Molina) standl polysaccharide and sulfated modifications[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,2022 ,42 (8 ):1640 −1646 .[45] 陈群. 茯苓硫酸酯化多糖的制备及其核磁共振波谱分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2010,38(1):45−47. [CHEN Q. Preparation and NMR spectral characterization of pachyman sulfate[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2010,38(1):45−47.] CHEN Q . Preparation and NMR spectral characterization of pachyman sulfate[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2010 ,38 (1 ):45 −47 .[46] CHEN Z, ZHAO Y, ZHANG M, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of a new polysaccharide from Bletilla striata fibrous roots[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 227.
[47] 符玉霞, 郭欣, 魏亚博, 等. 红枣多糖的硫酸酯化修饰及其结构特性的研究[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(8):33−38. [FU Y X, GU X, WEI Y B, et al. Study on sulfated modification and structural properties of jujube polysaccharides[J]. The Food Industry,2022,43(8):33−38.] FU Y X, GU X, WEI Y B, et al . Study on sulfated modification and structural properties of jujube polysaccharides[J]. The Food Industry,2022 ,43 (8 ):33 −38 . -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 吴霞,周攀,吴科锋,叶华,邓路铭. 羊栖菜多糖脱色工艺优化及其抗氧化活性评价. 广东医科大学学报. 2025(02): 157-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘盈,张欣,刘会平. 不同修饰方法对西瓜皮多糖结构和抗氧化性的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(10): 119-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杜宇明,邓利玲,汪娟,赵祎,经琳,钟耕. 微波辅助过氧化氢半干法降解魔芋葡甘聚糖工艺优化及其特性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 189-197 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 尹智慧,李志宇,李怡鹏,潘素君,李魏. 茭白孕茭机制的研究进展. 生物灾害科学. 2024(04): 512-516 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 温华建,牟建,杨睿,温柔,温华勇,黄毅华,南占东. 富硒茭白的营养保健成分及其功能产品开发探讨. 现代食品. 2024(20): 161-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



