Study on the Mechanism of Enzymatic Browning and Its Inhibitors during Lonicera caerulea Fruit Pulp Beating
-
摘要: 为解决蓝靛果打浆工艺单元的酶促褐变现象,提高蓝靛果的利用价值。实验研究蓝靛果在打浆工艺中主要参与酶促褐变反应的酚类底物及其抑制能力,并分析酚类底物与表儿茶素对多酚氧化酶(Polyphenol oxidase,PPO)反应的相互作用,进而确定酶促褐变机理。并进一步通过对比抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸、氯化钙、EDTA-2Na、柠檬酸添加量对褐变抑制率的影响,筛选出效果最佳的三种抑制剂。结果表明,蓝靛果打浆工艺中参与酶促褐变的首要影响因素是表儿茶素,并且表儿茶素对PPO的淬灭机制为静态淬灭。响应面优化试验确定复合抑制剂的最佳组合为:抗坏血酸添加量0.11%、L-半胱氨酸添加量0.11%、EDTA-2Na添加量0.08%,该条件下蓝靛果汁的褐变抑制率为93.17%。说明选用以上复合抑制剂可抑制蓝靛果打浆工艺中的酶促褐变。Abstract: In order to solve the enzymatic browning phenomenon in the pulping unit of Lonicera caerulea fruits and improve its utilization value. The main phenolic substrates involved in the enzymatic browning reaction in the pulping process of Lonicera caerulea fruits and the inhibition ability were investigated, and the interactions between phenolic substrates and epicatechin on the reaction of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) were analyzed and its mechanism of enzymatic browning was also determined. The three most effective inhibitors were further selected by comparing the effects of ascorbic acid, L-cysteine, calcium chloride, EDTA-2Na, and citric acid additions on the browning inhibition rate. The results showed that epicatechin was the primary influencing factor involved in enzymatic browning in the pulping process of Lonicera caerulea fruits, and the quenching mechanism of epicatechin on PPO was static quenching. The response surface optimization test determined the optimal combination of composite inhibitors as 0.11% ascorbic acid, 0.11% L-cysteine, and 0.08% EDTA-2Na, and the browning inhibition rate of Lonicera caerulea fruits juice under this condition was 93.17%. It indicates that the above composite inhibitors can inhibit the enzymatic browning in the pulping process of Lonicera caerulea fruits.
-
Keywords:
- Lonicera caerulea fruits /
- enzymatic browning /
- mechanism of browning /
- inhibitor
-
浆果在打浆过程中,会受到机械损伤,并发生酶促褐变反应,严重影响了果汁的色泽及活性成分。这也是目前影响浆果果汁加工的一种常见的问题。蓝靛果(Lonicera caerulea L.),属茜草目,忍冬科忍冬属,常见名称有山茄子果、羊奶子等,是一种新兴的野生浆果[1−3],具有较高的营养价值[4−5]。研究表明,蓝靛果中含有丰富的矿物质、VC、多酚、多糖等活性成分[6−8]。并且蓝靛果具有清热解毒、抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤和降血糖等功效,对人体健康起到一定的积极促进作用[9−12]。
蓝靛果在打浆过程中极易发生酶促褐变,在工业生产过程中严重影响蓝靛果汁品质以及经济效益。因此,有必要进一步对蓝靛果打浆工艺酶促褐变机理及其抑制进行研究。研究发现,存在浆果液泡内的多酚与存在于质体和细胞质内的多酚氧化酶(Polyphenol oxidase,PPO)相互接触,可能是引起浆果打浆过程中的酶促褐变的一个重要原因[13]。Wang等[14]在研究葡萄加工过程中酶促褐变机理时同样认为PPO是造成其褐变的主要原因。董乐[15]研究了龙眼果皮的褐变产物,研究发现酶促褐变的产物主要为蒽醌类化合物。李琳玲等[16]在研究板栗酶促褐变产物时也得出了相似的结论,即蒽醌类化合物为酶促褐变的主要产物。一些研究发现,通过加入抑制剂,可以在一定程度上抑制果汁的酶促褐变,并提高果汁的货架期及贮藏性。蓝靛果在打浆过程中同样存在相似问题。因此,通过研究蓝靛果打浆过程中酶促褐变机理,可以控制并减少褐变反应,以提高产品的品质。目前,酶促褐变抑制剂主要包括还原剂、酶蛋白制剂、螯合剂和酸化剂。常用的还原剂主要包括抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸等;酶蛋白制剂主要包括氯化物、蛋白酶等;螯合剂主要包括EDTA及其衍生物等;酸化剂主要包括柠檬酸、苹果酸等。熊忠飞等[17]研究了柠檬酸、抗坏血酸和L-半胱氨酸三种抑制剂对‘黄元帅’苹果汁品质及褐变的影响,研究发现浓度为0.12%的柠檬酸与0.15%的L-半胱氨酸复合可使苹果汁的褐变抑制效果最佳。Özoğlu等[18]在研究不同抗褐变剂对苹果汁褐变抑制的影响时发现,L-半胱氨酸、抗坏血酸和肉桂酸有较好的抑制效果,当三者组合时抑制效果优于单独的抑制效果,并且发现当L-半胱氨酸的浓度较高时,会产生不良气味和漂白作用。Xu等[19]同样发现加入适当的抗坏血酸能够更好地缓解苹果汁的酶促褐变,并提高苹果汁的品质。因此,选择合适的抑制剂并控制抑制剂的使用量,可抑制果汁的酶促褐变。
针对蓝靛果在打浆过程中极易出现酶促褐变影响果汁品质的问题,实验采用高效液相色谱法测定了蓝靛果所含的酚类成分,通过研究酚类底物与PPO反应时的酶活,结合通径分析的方法确定主要参与酶促褐变反应的酚类底物,并采用荧光光谱法分析底物与酶之间的相互作用。同时,通过单因素实验研究对比抑制剂添加量对褐变抑制率的影响,筛选出抑制效果最佳的三种抑制剂进行响应面优化试验确定最优的复合抑制剂组合,以期提高蓝靛果汁的品质,为蓝靛果加工利用提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
蓝靛果 ‘蓓蕾’品种,产自黑龙江省勃利县,鲜果采摘于6~7月份,冷冻保藏;聚乙烯吡咯烷酮 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;1,8-二羟基蒽醌 标准品,上海麦克林生化有限公司;抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸、氯化钙、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、柠檬酸 食品级,河南万邦化工科技有限公司;其余试剂均为国产分析纯。
FL1963榨汁机 温州福菱科技有限公司;UV-5200紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;TD5A台式高速离心机 湖南凯达科学仪器有限公司;LDZX-50FBS高压蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;Sartorious-PB-10 pH计 广州市深华生物科技有限公司;PHS-2F精密酸度计 上海雷磁仪电科学仪器有限公司;HL-2B数显恒流泵 上海沪西分析仪器有限公司;HJ-3恒温磁力搅拌器 荣华仪器制造有限公司;HWS-26电热恒温水浴锅 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;DHP-9082电热恒温培养箱 上海百典设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蓝靛果打浆基本工艺
蓝靛果贮藏于−18 ℃中保存,在室温条件下解冻,在蓝靛果添加量60%、打浆时间3 min、打浆强度32000 r/min工艺条件下以榨汁机打浆,打浆后过滤,得到蓝靛果果浆。
1.2.2 蓝靛果中酚类物质的测定
将蓝靛果经过打浆和过滤操作后,经4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液进行指标的测定。将蓝靛果汁稀释100倍后,取10 mL稀释液溶于甲醇(体积比1:1),在10000 r/min条件下离心10 min,取上清液用0.45 µm微孔滤膜过滤,得待测样液。参照魏敏[20]的方法,以高效液相色谱(HPLC)法测定蓝靛果汁中酚类物质。
1.2.3 酶促褐变底物鉴定
1.2.3.1 PPO对酚类底物催化酶活性测定
参照陈军等[21]方法提取待测液PPO得到粗酶液,并测定PPO活性。在试管中加入3 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.2 mol/L,pH6.8),1 mL不同反应底物(0.5 mol/L),置于28 ℃水浴中,加热5 min,然后加入1 mL粗酶液,混合均匀,在420 nm波长下测定其在反应4 min内的吸光度值,每隔30 s测1次,以每分钟ΔA值变化0.001为1个酶活力单位。酶活计算见公式(1)[22]:
PPO活性=ΔA×Vt×VS×W×0.001 (1) 式中,ΔA为反应时间内吸光度值的变化;V为提取酶液总体积,mL;t为反应时间,min;VS为测定时所取酶液体积,mL;W为取样质量,g。
1.2.3.2 酚类底物含量变化通径分析
分别测定蓝靛果中不同反应底物在4 ℃贮藏过程中含量的变化和生成物蒽醌含量的变化以及褐变度的变化,采用相关性分析和通径分析的方法鉴定酶促褐变的底物。
通径分析计算[23]:根据相关系数和通径系数,通过公式(2)和(3)计算决定系数d,根据公式(4)计算剩余通径系数Pe。决定系数表示各因素对结果的相对决定程度,剩余通径系数表示未被考虑的一切可能影响Y的因素和试验误差。
单因素对Y的决定系数:di=P2i (2) 两因素对Y的决定系数:dij=2rijPiPj (3) 剩余通径系数:Pe=√1−∑d (4) 式中,Y表示应变量褐变度;i,j为不同因素(绿原酸、表儿茶素、蒽醌);Pi为因素i的通径系数;Pj为因素j的通径系数;rij为因素i和j的相关系数。
1.2.4 PPO和表儿茶素相互作用的研究
多种氨基酸残基存在于PPO分子中,其中包括色氨酸、苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸等。这些氨基酸残基可以发射内源荧光,因此可通过内源荧光的变化来研究表儿茶素和PPO之间的相互作用以及表儿茶素对PPO构象的影响。荧光光谱是研究酚类底物与PPO相互作用的一种常用方法,本文采用荧光光谱分析研究表儿茶素与PPO体系中的淬灭类型、结合常数和结合位点[24]。
1.2.4.1 储备液的配制
取不同质量的表儿茶素溶解于磷酸缓冲溶液(pH6.8)中,配制成浓度分别为0.34、0.69、1.03、1.38、1.72 mmol/L的表儿茶素溶液,备用。
1.2.4.2 淬灭类型的研究
在25 ℃条件下将不同浓度的表儿茶素与PPO混合,静置反应2 h后进行荧光光谱检测。荧光光谱的仪器参数:激发波长λex为280 nm,激发与发射狭缝宽度均为10 nm,电压为600 V,发射波长λem为550~580 nm。PPO的荧光淬灭过程使用Stern-Volmer方程分析[25],Stern-Volmer方程见公式(5):
F0F=1+Kqτ0[Q]=1+Ksv[Q] (5) 式中,F0为未加入淬灭剂时的荧光峰值;F为加入不同浓度淬灭剂时的荧光峰值;τ0为不存在淬灭剂时荧光分子的平均寿命;[Q]为淬灭剂的浓度;Ksv为动态淬灭常数;Kq为静态猝灭常数。
1.2.4.3 结合常数和结合位点数的研究
对于静态淬灭,当生物小分子与大分子相结合时,结合常数Ka与结合位点数n通过Lineweaver-Burk双对数方程进行计算[26],Lineweaver-Burk双对数方程见公式(6):
lgF0−FF=lgKa+nlg[Q] (6) 式中,F0为未加入淬灭剂时的荧光峰值;F为加入不同浓度淬灭剂时的荧光峰值;Ka为结合常数;n为结合位点数;[Q]为淬灭剂的浓度。
1.2.5 酶促褐变抑制剂筛选单因素实验
1.2.5.1 抗坏血酸添加量对抑制效果的影响
在蓝靛果汁中分别添加0.02%、0.04%、0.06%、0.08%、0.10%、0.12%的抗坏血酸,分别测定褐变度,以褐变抑制率为指标考察抗坏血酸对其的抑制程度。
1.2.5.2 L-半胱氨酸添加量对抑制效果的影响
在蓝靛果汁中分别添加0.02%、0.04%、0.06%、0.08%、0.10%、0.12%的L-半胱氨酸,分别测定褐变度,以褐变抑制率为指标考察L-半胱氨酸对其的抑制程度。
1.2.5.3 氯化钙添加量对抑制效果的影响
在蓝靛果汁中分别添加0.02%、0.04%、0.06%、0.08%、0.10%、0.12%的氯化钙,分别测定褐变度,以褐变抑制率为指标考察氯化钙对其的抑制程度。
1.2.5.4 EDTA-2Na添加量对抑制效果的影响
在蓝靛果汁中分别添加0.02%、0.04%、0.06%、0.08%、0.10%、0.12%的EDTA-2Na,分别测定褐变度,以褐变抑制率为指标考察EDTA-2Na对其的抑制程度。
1.2.5.5 柠檬酸添加量对抑制效果的影响
在蓝靛果汁中分别添加0.05%、0.15%、0.25%、0.35%、0.45%、0.55%的柠檬酸,分别测定褐变度,以褐变抑制率为指标考察柠檬酸对其的抑制程度。
1.2.6 复合酶促褐变抑制剂筛选响应面优化试验
通过单因素实验筛选出抑制效果最佳的三种抑制剂,利用Box-Behnken设计-响应面分析法,以褐变抑制率为响应值进行各因素间的交互作用分析,研究抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸、EDTA-2Na添加量对蓝靛果汁褐变抑制率的影响。设计因素和水平见表1。
表 1 褐变抑制试验因素水平Table 1. Factors and levels of browning inhibition test水平 因素 A 抗坏血酸添加量
(%)B L-半胱氨酸添加量
(%)C EDTA-2Na
(%)−1 0.08 0.08 0.06 0 0.10 0.10 0.08 1 0.12 0.12 0.10 1.2.7 理化指标的测定
1.2.7.1 蒽醌含量的测定
将不同浓度1, 8-二羟基蒽醌标准品的甲醇溶液500 μL经挥干后,加入质量分数为0.5%的醋酸镁-甲醇溶液并定容至10 mL,充分混合均匀后测定508 nm吸光值[27],得到标准曲线(Y=0.0577X+0.0064,R2=0.9995),并根据标准曲线计算蒽醌含量。
1.2.7.2 褐变抑制率的测定
以分光光度计于420 nm处测定蓝靛果汁的褐变度,褐变抑制率计算见公式:
T(%)=A0−AiA0×100 (7) 式中,T为褐变抑制率;A0为未加抑制剂的蓝靛果汁在420 nm处的吸光值;Ai为加入抑制剂的蓝靛果汁在420 nm处的吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
以SPSS 22.0对数据进行处理及相关性分析,并以Origin 2018作图,响应面分析以Design-Expert进行,实验平行进行3次并以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蓝靛果中酚类物质的鉴定
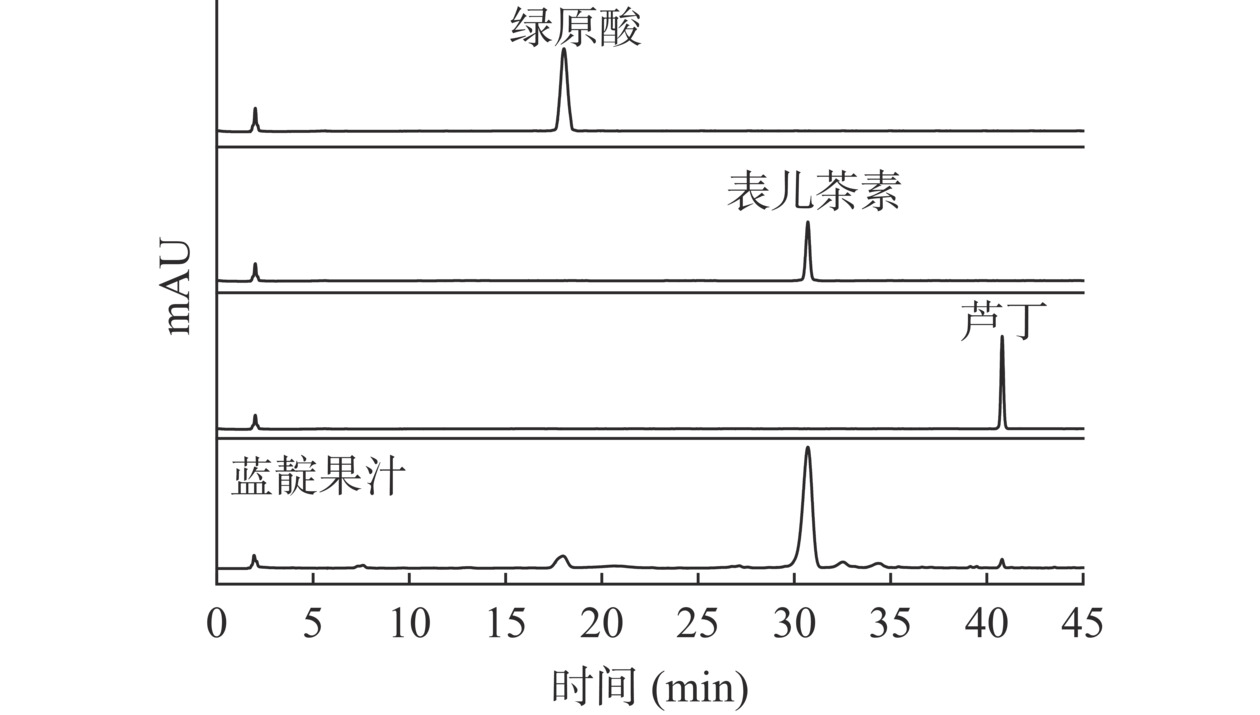
由HPLC测定蓝靛果汁中的酚类物质与多种标准溶液进行对比,根据保留时间确定蓝靛果中的酚类组成,将蓝靛果中含量较高的三种酚类物质对应的标准溶液和蓝靛果汁进行测定,结果如图1所示。
分别配制不同浓度的绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁标准品进行标准曲线的绘制,标准曲线的线性回归方程如表2所示。
表 2 酚类物质标准品保留时间及线性回归方程Table 2. Retention time and linear regression equation of phenolic reference materials样品名称 保留时间(min) 线性方程 决定系数(R2) 绿原酸 17.918 y=12.486x−1.3594 0.9998 表儿茶素 30.702 y=8.0243x−27.34 0.9995 芦丁 40.876 y=8.3314x+20.648 0.9996 由图1可知,蓝靛果汁中主要的酚类物质为绿原酸、表儿茶素和芦丁。将图1中蓝靛果汁色谱图的纵坐标带入表2中的线性回归方程可以得出,蓝靛果汁中表儿茶素的含量最高,为166.71 µg/mL,其次绿原酸的含量为11.25 µg/mL,芦丁的含量最低,为1.07 µg/mL。
2.2 PPO催化酚类底物酶活性测定
分别通过测定绿原酸、表儿茶素和芦丁与PPO反应过程中在420 nm处吸光度值的变化,计算得到PPO对不同酚类底物的催化酶活,如表3所示。
表 3 蓝靛果多酚氧化酶对不同酚类底物催化酶活性Table 3. Catalytic activity of Lonicera edulis fruits PPO on different phenolic substrates序号 反应底物 酶活(U/g) 1 绿原酸 163.67±5.87 2 表儿茶素 157.00±6.81 3 芦丁 未检出 由表3可以看出,绿原酸和表儿茶素作为反应底物时,PPO的活性较高,分别为163.67和157.00 U/g;芦丁作为反应底物时,未检测到PPO的活性。说明绿原酸和表儿茶素是蓝靛果汁中参与酶促褐变反应的底物,芦丁未参与蓝靛果汁中酶促褐变的反应。
2.3 蓝靛果中酚类物质含量以及褐变度的变化
2.3.1 褐变度与酚类物质含量变化相关性分析
表4为蓝靛果汁在贮藏过程中酶促褐变反应物含量(绿原酸和表儿茶素)、生成物含量(蒽醌)以及褐变度的变化,将表4中的X1、X2、X3与Y1进行相关性分析得到表5。由表5可以看出,绿原酸和表儿茶素含量的变化与褐变度变化的相关系数分别为-0.964和-0.983,呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),并且此时表儿茶素相关性系数(绝对值)要大于绿原酸;蒽醌含量的变化与褐变度变化的相关性系数为0.985,呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。说明蓝靛果汁中绿原酸和表儿茶素为主要的致褐因子,可通过蒽醌含量的变化判断果汁酶促褐变的程度。
表 4 蓝靛果汁在不同贮藏时间褐变度等指标的变化Table 4. Changes of browning degree of Lonicera edulis fruit juice at different storage time贮藏时间(d) X1:绿原酸(µg/mL) X2:表儿茶素(µg/mL) X3:蒽醌(µg/mL) Y1:褐变度 0 11.25 166.71 4.83 0.292 2 9.14 150.83 9.42 0.368 4 7.52 137.47 11.74 0.453 6 5.43 131.85 14.26 0.536 8 3.16 125.31 15.11 0.527 10 2.67 121.54 15.75 0.579 表 5 致褐因子与褐变度变化的相关系数Table 5. Correlation coefficient between browning factor and browning degree change致褐因子 相关性系数 P值 绿原酸 −0.964** 0.002 表儿茶素 −0.983** 0.000 蒽醌 0.985** 0.000 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3.2 褐变度与酚类物质含量变化通径分析
X1、X2、X3和Y1之间的相关系数见表6,通径系数为各个因子对改变Y值的相对重要性的统计数。设Pi为各个因子对Y的直接通径系数,Pij为间接通径系数,计算公式如下:
表 6 各因子间相关系数Table 6. Correlation coefficient of each factor因子 X1 X2 X3 Y1 X1 1 −0.964 X2 0.974 1 −0.983 X3 −0.966 −0.994 1 0.985 直接通径系数:[1r12r13r211r23r31r321][P1P2P3]=[r1r2r3]
将表5中的数据带入:[10.974−0.9660.9741−0.994−0.966−0.9941] [P1P2P3]=[−0.964−0.9830.985]
解得:P1=−0.150;P2=−0.221;P3=0.620,即为绿原酸、表儿茶素、蒽醌对褐变度的直接通径系数。
间接通径系数:Pij=rijPj
得:P12=−0.215;P13=−0.599;P21=−0.146;P23=−0.616;P31=0.145;P32=0.220。
由直接通径系数和间接通径系数得通径系数见表7。
表 7 通径系数Table 7. Path coefficient因子 X1 X2 X3 X1 −0.150* −0.215 −0.599 X2 −0.146 −0.221* −0.616 X3 0.145 0.220 0.620* 注:*为直接通径系数;其余为间接通径系数。 决定系数是指各因素对结果的相对决定程度,用d表示,结果为:d1=0.023;d2=0.049;d3=0.384;d12=0.065;d13=0.180;d23=0.272。
Ʃd=0.973;Pe=√(1−0.973)=0.164
根据致褐因子对褐变度的决定系数可以看出,d3>d23>d13>d12>d2>d1,说明蒽醌是影响褐变度的决定因素;表儿茶素和蒽醌的交互作用是影响褐变度的第二决定因素;绿原酸和蒽醌的交互作用是影响褐变度的第三决定因素;绿原酸和表儿茶素的交互作用是影响褐变度的第四决定因素;表儿茶素是影响褐变度的第五影响因素;绿原酸是影响褐变度的第六影响因素。Pe代表剩余通径系数,为0.164,说明考虑了影响蓝靛果汁酶促褐变的主要因素。
直接通径系数、间接通径系数以及致褐因子对褐变度的决定系数结果表明,表儿茶素含量的变化对褐变度的影响大于绿原酸,并且表儿茶素参加酶促反应生成蒽醌的含量大于绿原酸。蒽醌为影响蓝靛果褐变度的决定因素,而表儿茶素和蒽醌的交互作用为影响褐变度的第二决定因素,因此,综合分析认为蓝靛果汁中主要参加酶促褐变反应的反应物为表儿茶素,其次为绿原酸,在本实验中,主要探究表儿茶素与PPO的相互作用。
2.4 PPO和表儿茶素相互作用的结果
2.4.1 内源荧光光谱和淬灭类型确定
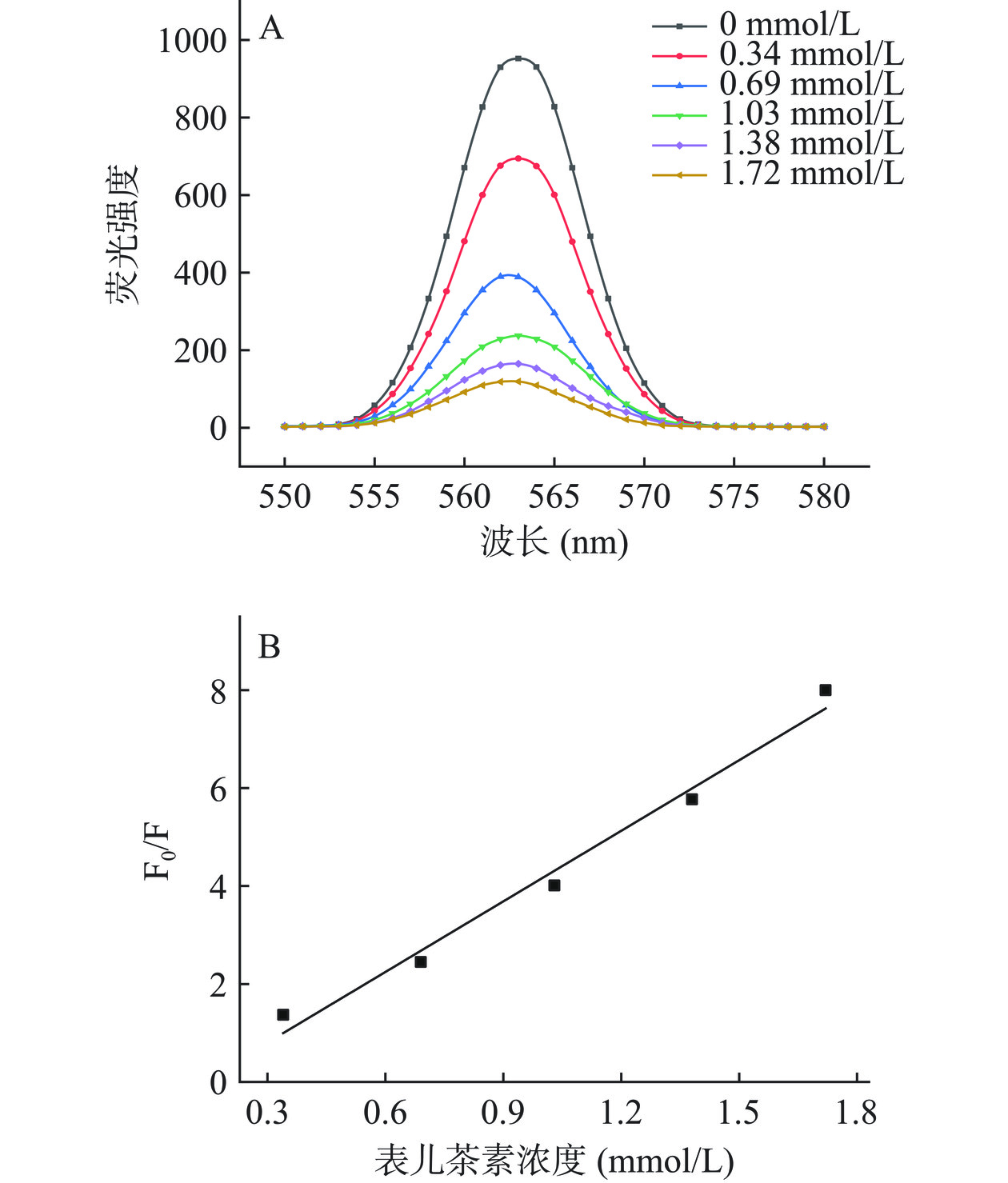
由图2可以看出,随着表儿茶素浓度的增加,荧光强度逐渐降低,说明表儿茶素导致PPO发生了酶促氧化,并导致PPO发生了荧光淬灭[28]。将表儿茶素与PPO相互作用的内源荧光光谱进行Stern-Volmer方程拟合,R2为0.98,表明F0/F与表儿茶素的浓度呈现良好线性关系。由表8可知,淬灭常数为4.8×103,较高的淬灭常数值表明表儿茶素与PPO之间有较强的相互作用[29]。生物大分子的荧光存在时间一般为10−8 s,由此得出淬灭速率常数为4.8×1011 mol·L−1·s−1,远高于2×1010[28],因此认为表儿茶素对PPO的淬灭机制为静态淬灭。
表 8 表儿茶素和PPO相互作用的Stern-Volmer常数Table 8. Stern-Volmer constants of the interaction between epicatechin and PPO温度(℃) 淬灭常数Ksv 淬灭速率常数Kq(mol·L−1·s−1) R2 25 4.8×103 4.8×1011 0.98 2.4.2 结合常数和结合位点数
将图2(A)中的数据代入公式(6)计算出结合常数和结合位点数,结果如表9所示。
表 9 表儿茶素和PPO相互作用的结合常数与结合位点数Table 9. Binding constants and number of binding sites of the interaction between epicatechin and PPO温度(℃) 结合常数Ka 结合位点数n 25 7.32×105 1.81 由表9可以看出,表儿茶素与PPO的结合常数为7.32×105,远大于104数量级,说明表儿茶素与PPO之间具有较强的相互作用[30]。结合位点数为1.81,说明表儿茶素与PPO大约有1~2个结合位点数。由于主要参加蓝靛果酶促褐变的反应物为表儿茶素,其与PPO结合引起酶促褐变,为进一步解决蓝靛果加工过程中酶促褐变的问题,实验通过筛选与表儿茶素或PPO结合的抑制剂,使表儿茶素和PPO二者之间的结合减少,进而达到减少酶促褐变的目的。
2.5 酶促褐变抑制剂的筛选
2.5.1 抑制剂筛选单因素实验结果
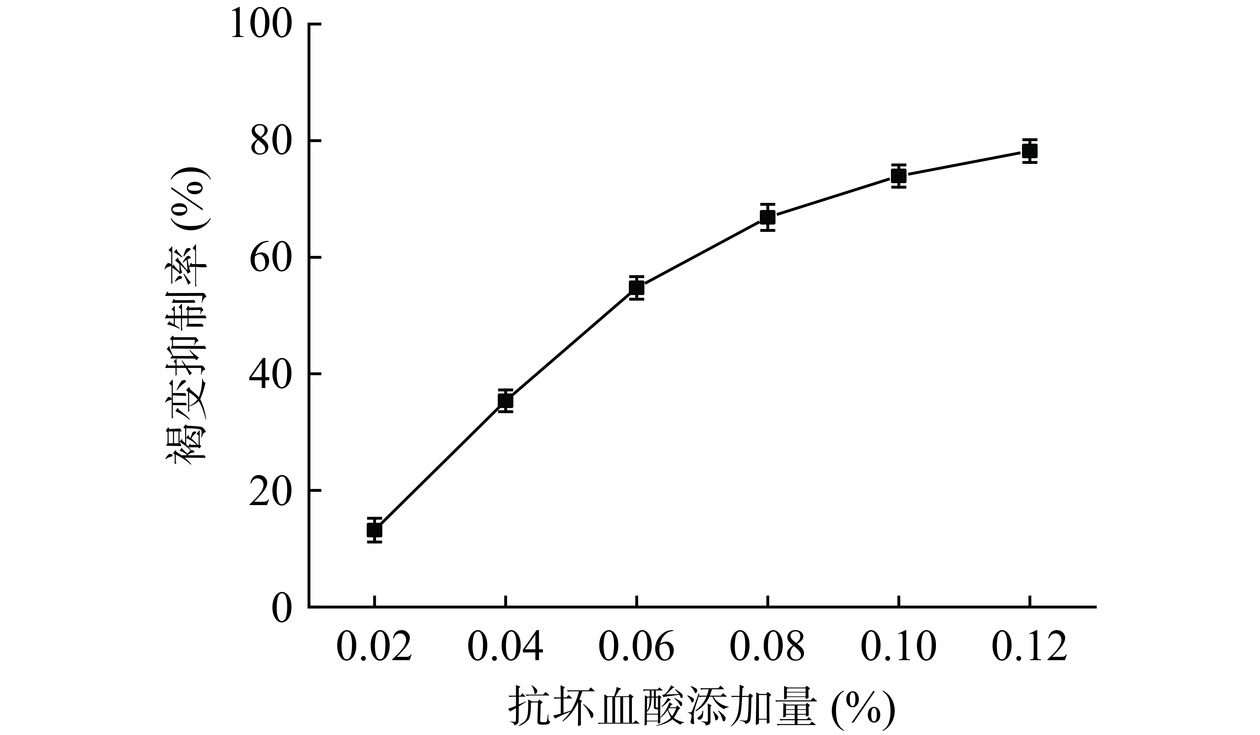
如图3所示,随着抗坏血酸添加量的增加,褐变抑制率逐渐增加,说明褐变抑制率与抗坏血酸的添加量呈一定的剂量效应关系。抗坏血酸添加量较少时,其被醌类物质氧化消耗后会继续发生酶促褐变反应;抗坏血酸添加量增多后,既能将中间产物邻二醌还原成邻二酸,阻止黑色素的产生,还能与PPO的辅基铜离子发生螯合,降低PPO的活性[31]。当添加量为0.10%和0.12%时的褐变抑制率分别为73.93%和78.21%,具有明显的抑制效果。但当抗坏血酸添加量超过0.10%时,邻二醌的转化和螯合反应基本完全,并且过量的抗坏血酸降解,生成醛类物质,自身发生褐变[32]。所以,选择最佳的抗坏血酸添加量为0.10%。
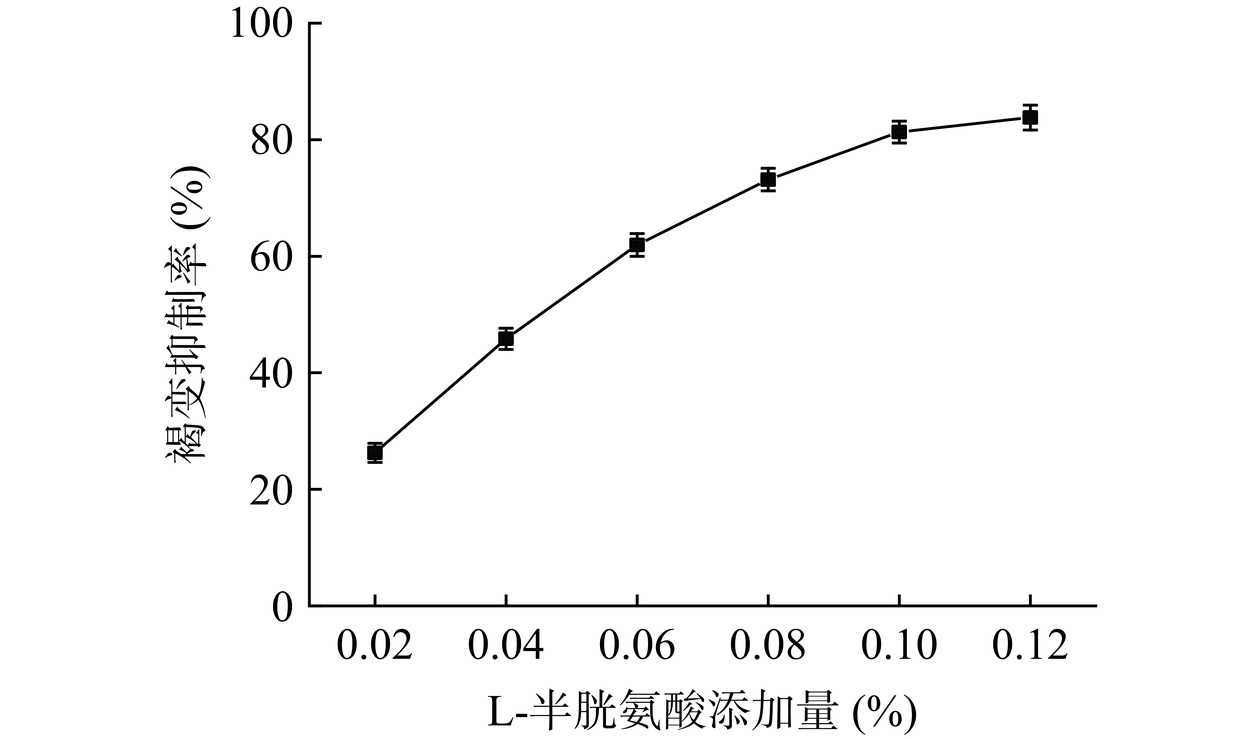
如图4所示,随着L-半胱氨酸添加量的增加,褐变抑制率逐渐增加,当添加量超过0.10%时,褐变抑制率变化趋于平稳。当添加量为0.10%和0.12%时,褐变抑制率分别为81.32%和83.81%,具有明显的抑制效果。主要是因为L-半胱氨酸中含有-SH的氨基酸,可与表儿茶素等酚类底物反应生成醌类物质结合形成无色的硫氢化合物,从而抑制酶促褐变反应的发生[33]。但当添加量超过0.10%时,体系内底物发生反应接近饱和,褐变抑制率增加平缓,并且,过量的L-半胱氨酸溶解后自身带有的微臭味会引起蓝靛果汁产生不良气味。因此,选择最适的L-半胱氨酸添加量为0.10%。
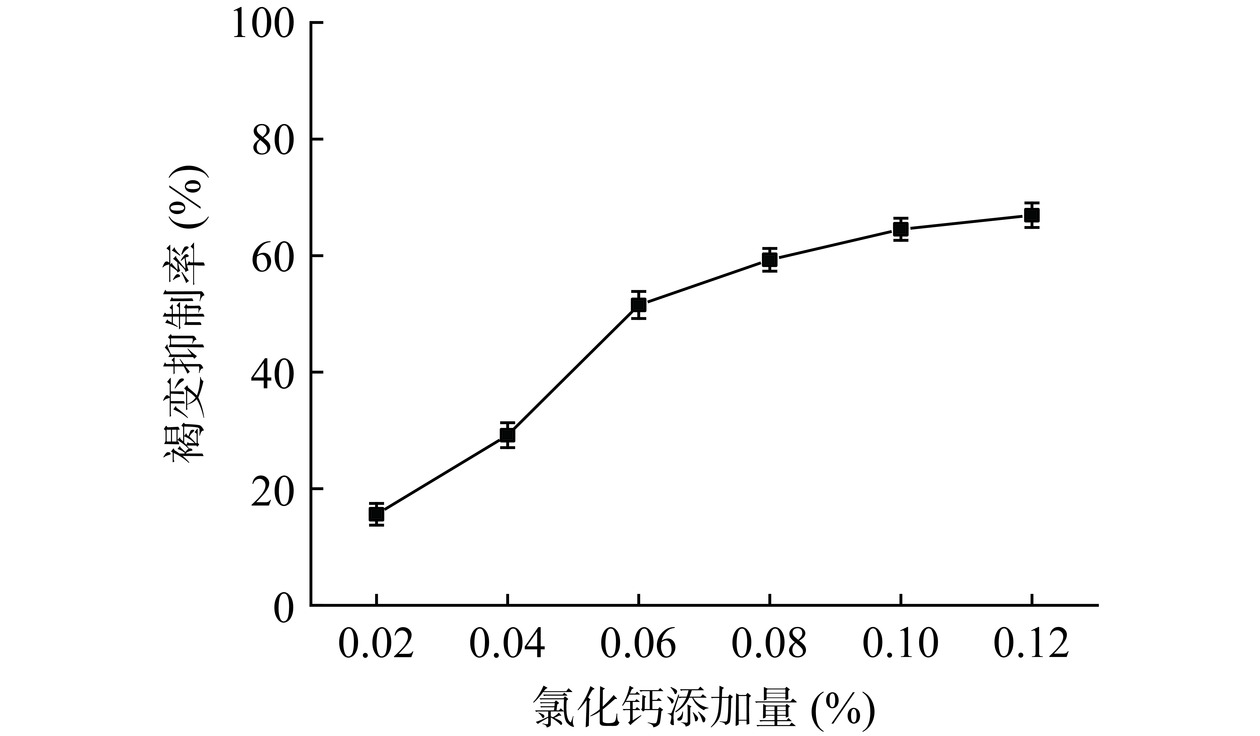
如图5所示,随着氯化钙添加量的增加,褐变抑制率逐渐增加,说明褐变抑制率与氯化钙添加量呈一定的剂量效应关系。氯化钙主要通过钙离子与PPO中的羧基化合物结合,降低PPO的活性,减少表儿茶素等酚类物质与PPO的反应来减少酶促褐变反应的发生[34]。随着钙离子与PPO结合基本完全,后续褐变抑制率逐渐平缓。当氯化钙添加量为0.12%时,褐变抑制率为66.93%。
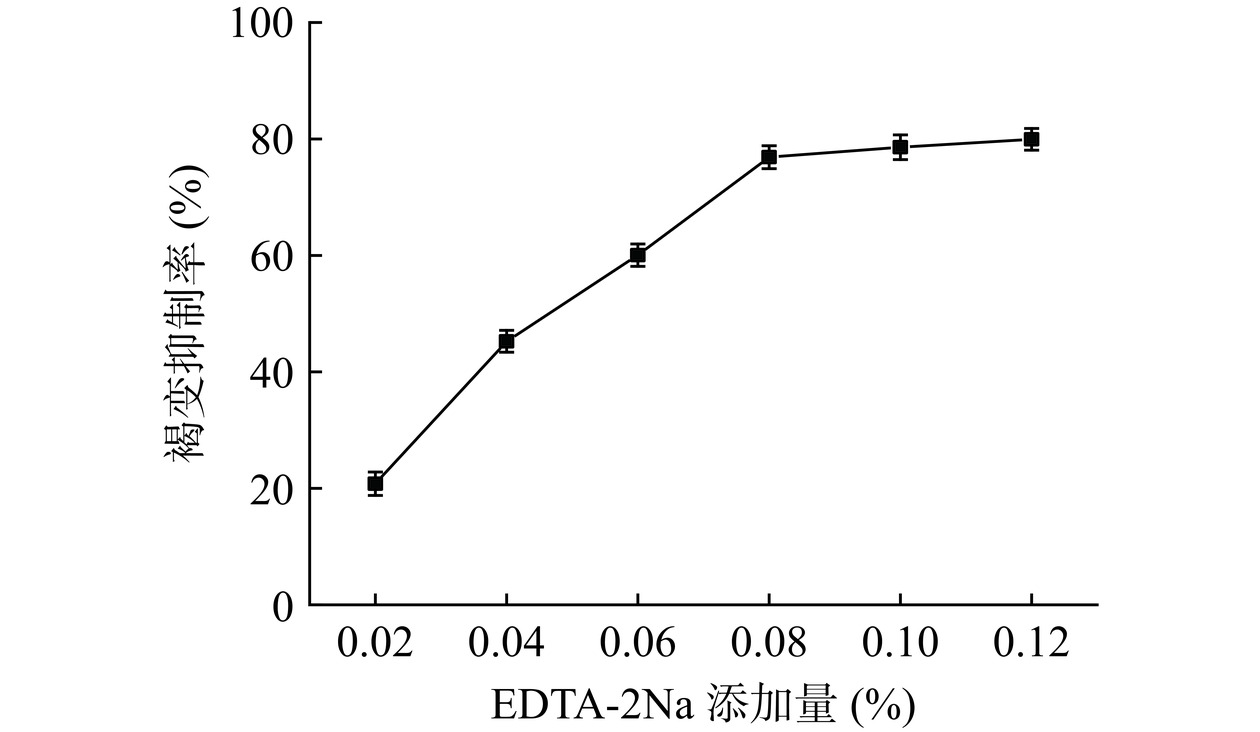
如图6所示,随着EDTA-2Na添加量的增加,褐变抑制率逐渐增加,当添加量超过0.08%时,褐变抑制率变化趋于平稳。EDTA-2Na作为金属离子螯合剂,主要通过与底物竞争和PPO结合,降低PPO和酚类底物的结合浓度,抑制果汁的酶促褐变[35]。添加量为0.08%时,褐变抑制率为76.87%,有较好的抑制效果。当添加量超过0.08%时,PPO和EDTA-2Na的结合反应基本完全,并且蓝靛果果汁中的果胶和蛋白类物质可能与过量的EDTA-2Na发生结合,产生少量的絮状物,影响产品的质量。所以EDTA-2Na的最适添加量为0.08%。
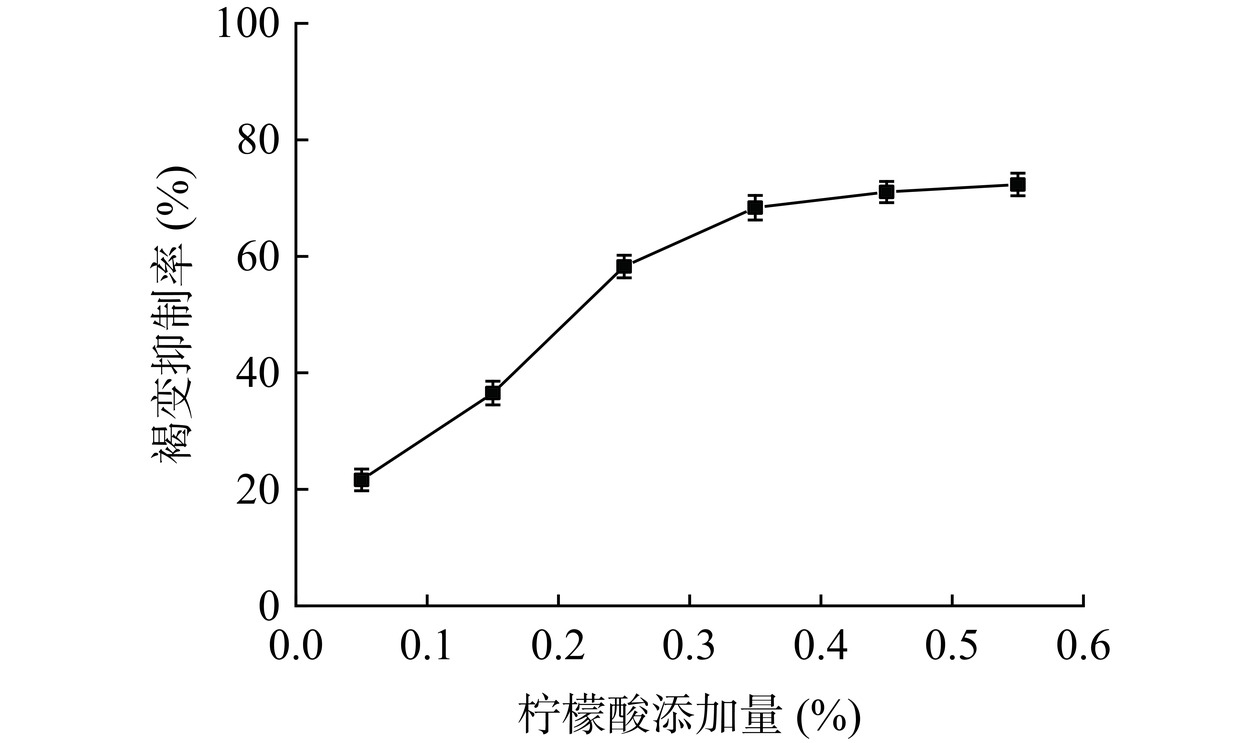
如图7所示,随着柠檬酸添加量的增加,褐变抑制率逐渐增加,当添加量超过0.35%时,褐变抑制率逐渐趋于平稳。添加量为0.55%时,褐变抑制率为72.34%。柠檬酸抑制酶促褐变反应一方面是加入柠檬酸后,果汁的pH降低,使PPO中的辅基铜离子解离出来,降低了PPO的活性;另一方面是当果汁pH过低时,导致蛋白质变性,降低了PPO的活性[36]。当柠檬酸添加量较少时,褐变抑制程度不明显;当柠檬酸添加量较多时,虽然褐变抑制率有所提升,但会导致蓝靛果汁过酸,影响产品的风味。
2.5.2 响应面优化试验结果
为进一步优化工艺,选择单因素实验已考察的抑制褐变率效果最佳的三种抑制剂(抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸、EDTA-2Na)的添加量对蓝靛果汁褐变抑制率的影响,进一步确定复合抑制剂最优组合条件,试验设计及结果见表10。
表 10 响应面设计模型及结果Table 10. Response surface design model and results试验号 A B C Y:褐变抑制率(%) 1 0 0 0 92.56 2 0 0 0 93.04 3 −1 0 −1 84.73 4 −1 1 0 86.47 5 0 0 0 92.74 6 1 0 1 88.58 7 −1 0 1 85.97 8 0 −1 1 84.86 9 0 0 0 92.92 10 0 1 1 89.03 11 −1 −1 0 82.85 12 1 0 −1 88.54 13 1 1 0 90.57 14 1 −1 0 85.23 15 0 1 −1 87.91 16 0 −1 −1 84.32 17 0 0 0 93.15 2.5.3 回归模型的建立与分析
对表10中的数据回归拟合后得到蓝靛果汁褐变抑制率的二次多项回归方程为:Y=92.88+1.61A+2.09B+0.3675C+0.43AB−0.3AC+0.145BC−3.09A2−3.51B2−2.84C2。根据表11可以得出,模型中P<0.0001(极显著),失拟项P=0.4189>0.05(不显著),方程拟合度和相关性很好,误差较小,模型合理。总决定系数R2=0.9979,校正系数R2Adj=0.9952,说明预测值与实际值高度一致[37],模型可用来预测抗坏血酸添加量、L-半胱氨酸添加量、EDTA-2Na添加量对果汁褐变抑制率的影响。因此,采用该模型分析和预测蓝靛果汁的褐变抑制率,可有效反映真实值。
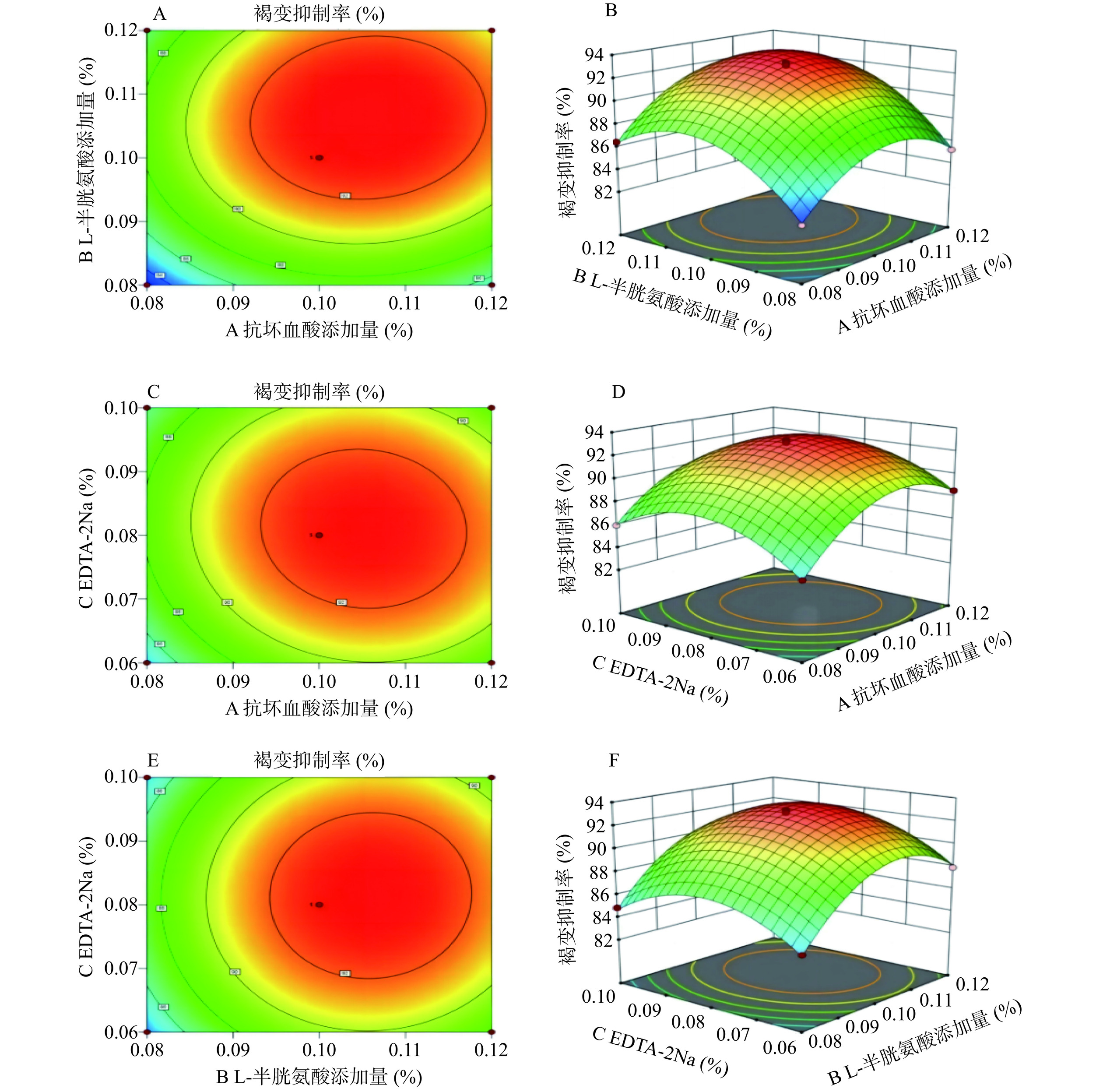
表 11 回归模型方差分析结果Table 11. Regression model analysis of variance results方差来源 平方和 自由度 平均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 198.74 9 22.08 367.53 <0.0001 ** A 20.80 1 20.80 346.21 <0.0001 ** B 34.94 1 34.94 581.61 <0.0001 ** C 1.08 1 1.08 17.98 0.0038 ** AB 0.7396 1 0.7396 12.31 0.0099 ** AC 0.3600 1 0.3600 5.99 0.0442 * BC 0.0841 1 0.0841 1.40 0.2754 − A2 40.16 1 40.16 668.47 <0.0001 ** B2 51.98 1 51.98 865.10 <0.0001 ** C2 33.92 1 33.92 564.63 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.4206 7 0.0601 失拟项 0.1985 3 0.0662 1.19 0.4198 − 纯误差 0.2221 4 0.0555 总离差 199.16 16 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示差异显著(P<0.05);“−”表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。 进一步对回归模型进行方差分析和交互作用分析,确定影响蓝靛果汁褐变抑制率的因素依次为:EDTA-2Na添加量<抗坏血酸添加量<L-半胱氨酸添加量。通过P值判断回归系数的显著性:一次项A、B、C、交互项AB、二次项A2、B2和C2均极显著(P<0.01),交互项AC为显著水平(P<0.05),交互项BC不显著(P>0.05)。由图8所示,交互项AB等高线图呈现椭圆形,3D图曲面陡峭,这说明抗坏血酸和L-半胱氨酸添加量在交互作用下极显著影响蓝靛果汁的褐变抑制率。因此,实验结果同样揭示了复合抑制剂更能够降低蓝靛果打浆过程中的褐变率。
2.5.4 最佳工艺验证
根据软件对数据进行响应面结果分析,预测蓝靛果汁酶促褐变最佳抑制剂条件为:抗坏血酸添加量为0.1056%、L-半胱氨酸添加量为0.1063%、EDTA-2Na添加量为0.0811%,在此条件下预测果汁褐变抑制率可以达到93.45%。但在实际操作中这一条件很难控制,因此考虑到实际的可操作性且能准确地验证预测的合理性,实际操作验证选取抗坏血酸添加量为0.11%、L-半胱氨酸添加量为0.11%、EDTA-2Na添加量为0.08%,该条件下经过3次实验取平均值,得到蓝靛果汁的褐变抑制率为93.17%,与理论预测值基本一致。说明所建模型有效可行,可以对蓝靛果汁酶促褐变抑制剂进行优化、分析和预测。
3. 结论
实验研究了蓝靛果在加工过程中酶促褐变机理,以及不同褐变抑制剂对褐变抑制率的影响,采用通径分析的方法得出蓝靛果中主要参与酶促褐变反应的酚类底物为表儿茶素,其次为绿原酸。通过荧光光谱分析PPO与酚类底物的相互作用,得出淬灭常数为4.8×103,淬灭速率常数为4.8×1011 mol·L−1·s−1,说明表儿茶素对PPO的淬灭机制为静态淬灭。结合常数为7.32×105,说明表儿茶素与PPO之间具有较强的相互作用,且约有1~2个结合位点数。明确褐变机理后为进一步解决打浆工艺后酶促褐变的问题,通过单因素实验研究抗坏血酸、L-半胱氨酸、氯化钙、EDTA-2Na、柠檬酸添加量对褐变抑制率的影响,并通过响应面优化试验得到最优的复合抑制剂组合为抗坏血酸添加量0.11%、L-半胱氨酸添加量0.11%、EDTA-2Na添加量0.08%,在此条件下褐变抑制率达到93.17%。实验可为蓝靛果加工工艺提供理论参考。
-
表 1 褐变抑制试验因素水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of browning inhibition test
水平 因素 A 抗坏血酸添加量
(%)B L-半胱氨酸添加量
(%)C EDTA-2Na
(%)−1 0.08 0.08 0.06 0 0.10 0.10 0.08 1 0.12 0.12 0.10 表 2 酚类物质标准品保留时间及线性回归方程
Table 2 Retention time and linear regression equation of phenolic reference materials
样品名称 保留时间(min) 线性方程 决定系数(R2) 绿原酸 17.918 y=12.486x−1.3594 0.9998 表儿茶素 30.702 y=8.0243x−27.34 0.9995 芦丁 40.876 y=8.3314x+20.648 0.9996 表 3 蓝靛果多酚氧化酶对不同酚类底物催化酶活性
Table 3 Catalytic activity of Lonicera edulis fruits PPO on different phenolic substrates
序号 反应底物 酶活(U/g) 1 绿原酸 163.67±5.87 2 表儿茶素 157.00±6.81 3 芦丁 未检出 表 4 蓝靛果汁在不同贮藏时间褐变度等指标的变化
Table 4 Changes of browning degree of Lonicera edulis fruit juice at different storage time
贮藏时间(d) X1:绿原酸(µg/mL) X2:表儿茶素(µg/mL) X3:蒽醌(µg/mL) Y1:褐变度 0 11.25 166.71 4.83 0.292 2 9.14 150.83 9.42 0.368 4 7.52 137.47 11.74 0.453 6 5.43 131.85 14.26 0.536 8 3.16 125.31 15.11 0.527 10 2.67 121.54 15.75 0.579 表 5 致褐因子与褐变度变化的相关系数
Table 5 Correlation coefficient between browning factor and browning degree change
致褐因子 相关性系数 P值 绿原酸 −0.964** 0.002 表儿茶素 −0.983** 0.000 蒽醌 0.985** 0.000 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 表 6 各因子间相关系数
Table 6 Correlation coefficient of each factor
因子 X1 X2 X3 Y1 X1 1 −0.964 X2 0.974 1 −0.983 X3 −0.966 −0.994 1 0.985 表 7 通径系数
Table 7 Path coefficient
因子 X1 X2 X3 X1 −0.150* −0.215 −0.599 X2 −0.146 −0.221* −0.616 X3 0.145 0.220 0.620* 注:*为直接通径系数;其余为间接通径系数。 表 8 表儿茶素和PPO相互作用的Stern-Volmer常数
Table 8 Stern-Volmer constants of the interaction between epicatechin and PPO
温度(℃) 淬灭常数Ksv 淬灭速率常数Kq(mol·L−1·s−1) R2 25 4.8×103 4.8×1011 0.98 表 9 表儿茶素和PPO相互作用的结合常数与结合位点数
Table 9 Binding constants and number of binding sites of the interaction between epicatechin and PPO
温度(℃) 结合常数Ka 结合位点数n 25 7.32×105 1.81 表 10 响应面设计模型及结果
Table 10 Response surface design model and results
试验号 A B C Y:褐变抑制率(%) 1 0 0 0 92.56 2 0 0 0 93.04 3 −1 0 −1 84.73 4 −1 1 0 86.47 5 0 0 0 92.74 6 1 0 1 88.58 7 −1 0 1 85.97 8 0 −1 1 84.86 9 0 0 0 92.92 10 0 1 1 89.03 11 −1 −1 0 82.85 12 1 0 −1 88.54 13 1 1 0 90.57 14 1 −1 0 85.23 15 0 1 −1 87.91 16 0 −1 −1 84.32 17 0 0 0 93.15 表 11 回归模型方差分析结果
Table 11 Regression model analysis of variance results
方差来源 平方和 自由度 平均方差 F值 P值 显著性 模型 198.74 9 22.08 367.53 <0.0001 ** A 20.80 1 20.80 346.21 <0.0001 ** B 34.94 1 34.94 581.61 <0.0001 ** C 1.08 1 1.08 17.98 0.0038 ** AB 0.7396 1 0.7396 12.31 0.0099 ** AC 0.3600 1 0.3600 5.99 0.0442 * BC 0.0841 1 0.0841 1.40 0.2754 − A2 40.16 1 40.16 668.47 <0.0001 ** B2 51.98 1 51.98 865.10 <0.0001 ** C2 33.92 1 33.92 564.63 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.4206 7 0.0601 失拟项 0.1985 3 0.0662 1.19 0.4198 − 纯误差 0.2221 4 0.0555 总离差 199.16 16 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示差异显著(P<0.05);“−”表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。 -
[1] MACLEAN A, SILVA Y, JIAO G, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins from Haskap berries (Lonicera caerulea L.) using a deep eutectic solvent (DES)[J]. Food Technol Biotech,2021,59(1):56−62. doi: 10.17113/ftb.59.01.21.6869
[2] SENICA M, STAMPAR F, MIKULIC-PETKOVSEK M. Blue honeysuckle (Lonicera cearulea L. subs. edulis) berry; A rich source of some nutrients and their differences among four different cultivars[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2018,238:215−221. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.04.056
[3] WANG X, LUO Y, MA R, et al. Effect of Lonicera edulis polysaccharide on reducing oral dyeing of Lonicera edulis juice[J]. Applied Biological Chemistry,2022,65(1):1−13. doi: 10.1186/s13765-021-00671-w
[4] KUCHARSKA A Z, ANNA S T, JAN O, et al. Iridoids, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of edible honeysuckle berries (Lonicera caerulea var. Kamtschatica Sevast)[J]. Molecules,2017,22(3):405. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030405
[5] LIU X, LV Y, ZHENG M, et al. Polyphenols from blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea var. edulis) berry inhibit lipid accumulation in adipocytes by suppressing lipogenesis[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacol,2021,279:114403. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114403
[6] LEE H J, LEE D Y, CHUN Y, et al. Effects of blue honeysuckle containing anthocyanin on anti-diabetic hypoglycemia and hyperlipidemia in ob/ob mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2022,89:104959. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.104959
[7] CAPRIOLI G, IANNARELLI R, INNOCENTI M, et al. Blue honeysuckle fruit (Lonicera caerulea L.) from Eastern Russia:Phenolic composition, nutritional value and biological activities of its polar extracts[J]. Food & Function,2016,7(4):1892−1903.
[8] WANG Y, ZHU J, MENG X, et al. Comparison of polyphenol, anthocyanin and antioxidant capacity in four varieties of Lonicera caerulea berry extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,197:522−529. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.006
[9] DE S, RUPASINGHE H. Polyphenols composition and anti-diabetic properties in vitro of Haskap (Lonicera caerulea L.) berries in relation to cultivar and harvesting date[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2020,88:103402. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103402
[10] ZDARILOVA A, SVOBODOVA A, CHYTILOVÁ K, et al. Polyphenolic fraction of Lonicera caerulea L. fruits reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory markers induced by lip polysaccharide in gingival fibroblasts[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2017,48(6):1555−1561.
[11] AN M, EO H, SON H, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of leaf and branch extracts of honeyberry (Lonicera caerulea) on lipopolysaccharide stimulated RAW264.7 cells through ATF3 and Nrf2/HO1 activation[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2020,22(6):5219−5230. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11638
[12] GHARIBZAHEDI S, JAFARI S. The importance of minerals in human nutrition:Bioavailability, food fortification, processing effects and nanoencapsulation[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,62:119−132.
[13] 张亚伟,. 陈义伦. 不同品种梨汁酶促褐变因子及相关性[J]. 中国农业科学,2011,44(9):1880−1887. [ZHANG. Y W, CHEN Y L, Enzymatic browning factors of pear juice in different varieties and its correlation with enzymatic browning[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2011,44(9):1880−1887.] ZHANG. Y W, CHEN Y L, Enzymatic browning factors of pear juice in different varieties and its correlation with enzymatic browning[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(9): 1880−1887.
[14] WANG Z L, YUAN J L, YANG J H, et al. Effects of Guankou grape polyphenol oxidase on enzymatic browning[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2021,46(1):458−465.
[15] 董乐. 龙眼果皮酶促褐变产物的提取、稳定性及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2012,28(28):174−181. [DONG L. Study on the extraction, stability and antioxidational effects of the enzymatic browning product in Dimocarpus longan pericarp[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(28):174−181.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.28.032 DONG L. Study on the extraction, stability and antioxidational effects of the enzymatic browning product in Dimocarpus longan pericarp[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(28): 174−181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.28.032
[16] 李琳玲, 郑永良, 张雪花, 等. 罗田板栗褐变产物的分离及稳定性研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2018,57(1):93−96. [LI L L, ZHENG Y L, ZHANG X H, et al. Isolation and stability analysis of the browning product in Luotian chestnut[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2018,57(1):93−96.] LI L L, ZHENG Y L, ZHANG X H, et al. Isolation and stability analysis of the browning product in Luotian chestnut[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 57(1): 93−96.
[17] 熊忠飞, 李惠, 付岩吉, 等. 响应面法优化“黄元帅”苹果浓缩汁防褐变工艺研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2019,30(12):143−151. [XIONG Z F, LI H, FU Y J, et al. Study on optimization of anti-browning process of apple concentrate by response surface analysis[J]. China Food Additives,2019,30(12):143−151.] XIONG Z F, LI H, FU Y J, et al. Study on optimization of anti-browning process of apple concentrate by response surface analysis[J]. China Food Additives, 2019, 30(12): 143−151.
[18] ÖZOĞLU H, BAYNDRL A. Inhibition of enzymic browning in cloudy apple juice with selected antibrowning agents[J]. Food Control,2002,13(4):213−221.
[19] XU J, ZHOU L, MIAO J Y, et al. Effect of cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsion combined with ascorbic acid on enzymatic browning of cloudy apple juice[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2020,13(4):1−11.
[20] 魏敏. 鲜切苹果酶促褐变底物研究[J]. 现代园艺, 2015(15):56, 31. [WEI M. Study on the enzymatic browning substrate of fresh-cut apples [J]. Xiandai Horticulture, 2015(15):56, 31.] WEI M. Study on the enzymatic browning substrate of fresh-cut apples [J]. Xiandai Horticulture, 2015(15): 56, 31.
[21] 陈军, 鲁豪. 鲜切苹果不同部位酶促褐变机理研究[J]. 宿州学院学报,2020,35(11):72−75. [CHEN J, LU H. Study on the mechanism of enzymatic browning on different parts of fresh-cut apples[J]. Journal of Suzhou University,2020,35(11):72−75.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2006.2020.11.016 CHEN J, LU H. Study on the mechanism of enzymatic browning on different parts of fresh-cut apples[J]. Journal of Suzhou University, 2020, 35(11): 72−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2006.2020.11.016
[22] ZHOU L, LIU W, TEREFE N S. The inactivation kinetics of soluble and membrane-bound polyphenol oxidase in pear during thermal and high-pressure processing[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2018,11(5):1039−1049. doi: 10.1007/s11947-018-2070-0
[23] 朱丹, 颜飞翔, 朱立斌, 等. 沙棘酒贮藏期间非酶褐变研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):336−341. [ZHU D, YAN F X, ZHU L B, et al. Research on non-enzymatic browning of sea buckthorn wine during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):336−341.] ZHU D, YAN F X, ZHU L B, et al. Research on non-enzymatic browning of sea buckthorn wine during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 336−341.
[24] JIANG H W, ZHOU L, SUN Y F, et al. Polyphenol oxidase inhibited by 4-hydroxycinnamic acid and naringenin:Multi-spectroscopic analyses and molecular docking simulation at different pH[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 396: 133662.
[25] 李春翼, 田勇, 杨雅轩, 等. 植物多酚与蛋白质互作机制表征方法研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(13):262−268. [LI C Y, TIAN Y, YANG Y X, et al. Characterization methods for investigating interaction mechanisms between plant polyphenols and proteins:A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(13):262−268.] LI C Y, TIAN Y, YANG Y X, et al. Characterization methods for investigating interaction mechanisms between plant polyphenols and proteins: A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(13): 262−268.
[26] 何文妮, 陈开意, 邵波. 对氨基苯甲酸与牛血清白蛋白相互作用的荧光分析[J]. 河南化工,2020,37(9):23−28. [HE W N, CHEN K Y, SHAO B. Fluorescence analysis on the interaction between p-aminobenzoic acid and bovine serum albumin[J]. Henan Chemical Industry,2020,37(9):23−28.] HE W N, CHEN K Y, SHAO B. Fluorescence analysis on the interaction between p-aminobenzoic acid and bovine serum albumin[J]. Henan Chemical Industry, 2020, 37(9): 23−28.
[27] 马永强, 戴传荣, 王鑫, 等. 抑制剂对蓝莓果汁加工过程的酶促褐变研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2017(2):124−129. [MA Y Q, DAI C R, WANG X, et al. Study of inhibitorsusage on preventing enzymatic browning of blueberry juice[J]. China Food Additives,2017(2):124−129.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.02.012 MA Y Q, DAI C R, WANG X, et al. Study of inhibitorsusage on preventing enzymatic browning of blueberry juice[J]. China Food Additives, 2017(2): 124−129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.02.012
[28] 候增超, 原江锋, 赖钰婷, 等. 微波对没食子酸和PPO相互作用特性的影响[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(6):68−75, 83, 8−9. [HOU Z C, YUAN J F, LAI Y T, et al. Effect of microwave on interaction properties between gallic acid and polyphenol oxidase[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology:Natural Science,2021,42(6):68−75, 83, 8−9.] HOU Z C, YUAN J F, LAI Y T, et al. Effect of microwave on interaction properties between gallic acid and polyphenol oxidase[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology: Natural Science, 2021, 42(6): 68−75, 83, 8−9.
[29] OUYANG J, SUN F, FENG W, et al. Antimicrobial activity of galangin and its effects on murein hydrolases of vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) strain Mu50[J]. Chemotherapy,2018,63(1):20−28. doi: 10.1159/000481658
[30] ZHU L, ZHU L, MURTAZA A, et al. Ultrasonic processing induced activity and structural changes of polyphenol oxidase in orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck)[J]. Molecules,2019,24(10):1922. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101922
[31] GAO M, FENG L, JIANG T. Browning inhibition and quality preservation of button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) by essential oils fumigation treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,149(8):107−113.
[32] 甘笑静, 陈志周, 李绍振, 等. 超声-抗坏血酸复合处理对新梨7号梨汁的褐变及营养品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(11):51−58, 65. [GAN X J, CHEN Z Z, LI S Z, et al. Effect of ultrasound-ascorbic acid combination treatment on browning and nutritional quality of Xinli No. 7 pear juice[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(11):51−58, 65.] GAN X J, CHEN Z Z, LI S Z, et al. Effect of ultrasound-ascorbic acid combination treatment on browning and nutritional quality of Xinli No. 7 pear juice[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(11): 51−58, 65.
[33] WU X, GUO X, ZHU K. Inhibition of L-cysteine on the browning of fresh wet noodles[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland),2021,10(6):1156−1156.
[34] 谷会, 朱世江, 侯晓婉, 等. 氯化钙处理对菠萝采后黑心病及贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(9):161−167. [GU H, ZHU S J, HOU X W, et al. Effect of calcium chloride treatment on internal browning and storage quality of pineapple after harvest[J]. Food Science,2020,41(9):161−167.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190425-326 GU H, ZHU S J, HOU X W, et al. Effect of calcium chloride treatment on internal browning and storage quality of pineapple after harvest[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(9): 161−167. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190425-326
[35] TASHOOQ A, ABDUL H, SYED Z, et al. Efficacy of ascorbic acid, citric acid, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and 4-hexylresorcinol as inhibitors of enzymatic browning in osmo-dehydrated fresh cut kiwis[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2021,15(5):1−17.
[36] SOMMANO S, CHANASUT U, KUMPOUN W. Enzymatic browning and its amelioration in fresh-cut tropical fruit[J]. Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables, 2020:51−76.
[37] XUE H, LI J, LIU Y, et al. Optimization of the ultrafiltration-assisted extraction of Chinese yam polysaccharide using response surface methodology and its biological activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:1186−1193. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.126
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



