Preparation, Structure Characterization and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Selenized Gastrodia elata Polysaccharides
-
摘要: 本文以天麻多糖(Gastrodia elata Blume polysaccharides,GEP)和亚硒酸钠为原料,以硒含量为指标,利用单因素实验和响应面试验优化硝酸-亚硒酸钠(HNO3-Na2SeO3)法制备硒化天麻多糖(Selenated Gastrodia elata polysaccharides,SeGEP)的工艺。采用紫外光谱、红外光谱、核磁共振、粒径和Zeta电位、刚果红试验、碘-碘化钾试验、扫描电镜等对GEP和SeGEP进行结构表征分析;并采用体外抗氧化活性试验研究硒化修饰对天麻多糖的活性影响。结果表明,硒化天麻多糖最佳制备工艺条件为:反应温度74 ℃、硝酸浓度0.041%、反应时间8.4 h,在此条件下SeGEP的硒含量为3891.05±10.86 μg/g;结构表征结果显示天麻多糖被成功硒化修饰,硒化修饰后可使GEP粒径降低、Zeta电位的绝对值变大、多糖溶液的稳定性改善,同时发现GEP和SeGEP可能具备三股螺旋结构,且含有较长的侧链和支链结构;扫描电镜分析显示硒化修饰可改变GEP的微观形态。体外抗氧化活性实验表明,在浓度为10 mg/mL时,SeGEP对DPPH自由基清除率为98%±1.52%、最大铁还原力为0.99±0.24,在浓度为1 mg/mL时SeGEP对ABTS+自由基清除率为97.49%±1.16%,均比天麻多糖高,表明硒化修饰可提高天麻多糖抗氧化能力。本研究可为硒化天麻多糖相关的补硒制剂、功能食品开发提供理论基础。Abstract: In this paper, the preparation of Selenized Gastrodia elata polysaccharides (SeGEP) was conducted through HNO3-Na2SeO3 method using GEP and sodium nitrite as the raw materials, and the modification conditions were optimized by single factor experiment combined with response surface method using selenium content as the index. Ultraviolet spectrum (UV), infrared spectrum (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), particle size test, zeta potential test, Congo red test, iodine-potassium iodide test, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) techniques were carried out to explore the structure of GEP and SeGEP. Antioxidant tests were conducted to evaluate the effect of selenylation modification on GEP in vitro. The results showed that the optimum selenylation parameters were as follows: Reaction temperature 74 ℃, nitric acid concentration 0.041%, reaction time 8.4 h, and under the optimum conditions, the selenium content could be reached to 3891.05±10.86 μg/g. Structural characterization analysis showed that SeGEP had been successfully accomplished, and SeGEP had reduced the particle size, increased the absolute value of Zeta potential and improved the stability in solution by comparing with GEP. It was also found that both GEP and SeGEP might possess triple helix with long side branched chain structures, whereas selenylation modification could change the micromorphology of GEP. The in vitro antioxidant results showed that the DPPH radical scavenging rate of SeGEP at 10 mg/mL was 98%±1.52% and the maximum iron reducing power was 0.99±0.24, and the ABTS+ radical scavenging rate of SeGEP at 1 mg/mL was 97.49%±1.16%, respectively. SeGEP exhibited higher antioxidant activities than that of GEP, indicating that selenylation modification could improve the antioxidant ability of GEP. This study provided a theoretical basis for the development of selenium supplement and functional food related to selenized Gastrodia elata polysaccharides.
-
天麻(Gastrodia elata Blume)为兰科真菌营养型多年生草本植物天麻的干燥块茎,是我国一种传统珍贵的中药材,最早记载于《神农本草经》[1−2]。天麻主产于我国贵州、云南、湖北、陕西等地,在我国已有2000多年的应用历史,具有息风止痉、平抑肝阳、祛风通络等功效,主要用于治疗头痛、小儿惊风、肢体麻木、癫痫等病症[3],同时还具有健脑、抗衰老等作用[4]。除了有药用价值外,天麻还被国家卫生健康委员会列为药食两用资源植物[5],因此天麻及其多糖在药品、食品、保健品等领域具有广泛的应用前景。天麻多糖为天麻的活性成分之一,研究表明天麻多糖具有抗氧化[6]、免疫调节[7]、抗肿瘤[8]、神经保护[9]、抑菌[10]等作用。
硒(Selenium,Se)是人体内必需的微量元素,在抗肿瘤、抗氧化、免疫调节、降血糖等方面都发挥着重要的作用[11−13]。缺硒会导致人体生殖功能下降,免疫力低下,还会引起糖尿病、高血压、心脑血管病等多种疾病,严重缺硒还可引起克山病和大骨节病[14]。我国是一个缺硒大国,约占国土面积的2/3地区为缺硒地区,其中30%地区为严重缺硒地区,约7亿人生活在低硒地区[15]。有报道指出,我国居民硒平均摄入量只有44.4 μg/d[16],远低于《中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量第3部分:微量元素(WT/T 578.3-2017)》中成人推荐硒的摄入量60 μg/d[17]。硒在人体内无法合成,只能通过外源摄取,因此补硒剂越来越受到人们的关注。补硒剂主要有两类:一是无机硒,如亚硒酸钠、硒酸钠,但其毒性大,人体吸收利用率低[18];二是有机硒,包括有机硒制剂、富硒地区出产的天然产品以及人工生物转化的各种动、植物和微生物产品。与无机硒相比,有机硒通常以硒蛋白或硒多糖等形式存在,具有生物活性高、毒性低、易被吸收等特点[19−20]。
目前除少数富硒区出产的个别产品中硒多糖含量较高外,大部分地区产品中硒多糖含量较低[21],无法满足人们补硒的需求。人工干预方法是提高硒多糖产量的便捷途径之一,已经成为了补硒制剂研究的热点[22]。目前,人工合成硒多糖的方法有:植物转化法、化学合成法和微生物转化法[23]等,硒多糖的化学合成法主要是利用多糖链上的羟基等活性基团与硒化试剂中的硒结合,从而使硒共价结合到多糖分子上,形成硒多糖[24−25]。其中硝酸-亚硒酸钠法具有反应过程简单、操作性强、环境污染小、安全性高、产物回收方便的优点,在硒多糖的制备合成中广泛应用[26]。许多国内外学者采用硝酸-亚硒酸钠法合成出硒化多糖,如硒化冬虫夏草多糖[27]、硒化梅花马尾藻多糖[28]、硒化食用灰树花多糖[29]、硒化紫花苜蓿根多糖[30]、硒化黄大枣多糖[31]等。
目前关于硒化天麻多糖的研究还未见相关报道,研究天麻多糖的硒化修饰工艺和抗氧化活性,可为天麻资源的综合利用和补硒产品的进一步开发提供科学依据。本研究采用硝酸-亚硒酸钠法合成硒化天麻多糖SeGEP,采用响应面法优化天麻多糖的硒化修饰制备工艺,并研究硒化修饰前后天麻多糖的结构变化以及GEP、SeGEP的抗氧化活性,为开发研制硒化天麻多糖相关的补硒制剂、功能食品开发等提供科学基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
天麻 购自贵州乌蒙腾菌业有限公司,并经贵州师范大学陈华国教授鉴定为兰科植物天麻(Gastrodia elata Blume)的块茎,样本保存在贵阳学院食品科学与工程学院,编号2021060263;石油醚、无水乙醇、三氯甲烷、正丁醇、丙酮、甲苯 分析纯,天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;活性炭 分析纯,天津市光复科技发展有限公司;硝酸、高氯酸 分析纯,成都市科隆化学品有限公司;盐酸、三氯化铁 分析纯,国药集团化学有限公司;亚硒酸钠 分析纯,山东西亚化学股份有限公司;碳酸氢钠 分析纯,天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;抗坏血酸(Vitamin C,VC)、刚果红、碘、碘化钾、三氯乙酸 分析纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;邻苯二胺、过硫酸钾 分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠(Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt,DETA-2Na) 分析纯,天津市登峰化学试剂厂;重水(D2O) 分析纯,上海泰坦科技股份有限公司;2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基(2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(2,2-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate),ABTS) 分析纯,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;磷酸盐缓冲溶液 标准物质,坛墨质检科技股份有限公司;铁氰化钾 分析纯,成都金山化学试剂有限公司;MD44(8000~14000 D)透析袋 北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
XMTD-204恒温水浴锅 上海梅香仪器有限公司;DF-101S恒温加热磁力搅拌器 巩义市予华仪器有限公司;RE-52A旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;FA124电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;TDZ25-WS离心机 湖南平凡科技有限公司;LC-12N-50A真空冷冻干燥机 上海力辰邦西仪器科技有限公司;Cary 60 UV-Vis紫外光谱仪 安捷伦科技有限公司;PerkinElmer Spectrum Two傅里叶变换衰减全放射红外光谱仪 珀金埃尔默企管理(上海)有限公司;NS-90Z纳米粒度及电位分析仪 珠海欧美克仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 天麻多糖的提取
参考文献[32],稍作改动。称取干燥至恒重的天麻粉末10.0 g,依次经石油醚、无水乙醇50 mL回流脱脂60 min,用活性炭进行脱色素处理。滤渣加水300 mL在80 ℃下提取2 h后过滤,重复多次提取。滤液收集后,减压浓缩至20 mL,重复多次加入Sevag试剂(氯仿:正丁醇=4:1)10 mL以除去游离蛋白质直至无白色沉淀。取上清液加入4倍无水乙醇,静置过夜,离心(4000 r/min)5 min过滤。用乙醇、丙酮洗涤沉淀,然后加蒸馏水溶解,冷冻干燥,得到天麻多糖提取物(GEP)。
1.2.2 硒化天麻多糖的制备
参考胡润峰等[33]和王峙力等[34]的方法,稍作改动。称取0.5 g天麻多糖放入锥形瓶中,加入一定浓度的硝酸溶液50 mL,加热搅拌溶解多糖,得到10 mg/mL的天麻多糖溶液。加入一定量的亚硒酸钠,在一定的温度、时间条件下搅拌反应。反应结束后冷却至室温,用碳酸氢钠调pH至5~6。反应液离心(4000 r/min)5 min、抽滤,滤液用纯净水透析72 h。取少量的透析液加入抗坏血酸进行显色检测,若无红色时则停止透析。透析液减压浓缩至20 mL、冷冻干燥得到硒化天麻多糖(SeGEP)。称重,计算硒含量和硒化多糖得率。
1.2.3 硒化天麻多糖中硒含量的测定
1.2.3.1 硒含量标准曲线的绘制
参考李丽彩等[35]的方法,采用邻苯二胺法检测SeGEP的硒含量。用Na2SeO3配制0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.3 μg/mL不同浓度系列的硒标准溶液25 mL,分别加入10 g/L EDTA-2Na溶液2 mL,用1 mol/L的盐酸调节pH2,加入10 g/L邻苯二胺2.5 mL,暗处反应40 min,加入10 mL甲苯,振荡萃取5 min取上层甲苯层,在波长334 nm处测定吸光值。以硒的质量浓度为横坐标X,以吸光值A为纵坐标Y绘制标准曲线。
1.2.3.2 硒含量测定与计算
取20 mg硒化天麻多糖置于锥形瓶中加入10 mL浓硝酸、4 mL高氯酸,常温放置18 h以上,在电热炉上加热消化,等溶液变无色或微黄色时,加入4 mol/L盐酸10 mL,加热至溶液为10 mL左右,冷却定容至25 mL,后续操作按照硒含量标准曲线的测定方法,得到吸光值并代入标准曲线计算硒含量,硒含量计算公式如式(1):
硒含量(μg/g)=c×Vm (1) 式中:c表示根据吸光度值计算出的硒质量浓度,μg/mL;V表示消化液定容体积,mL;m表示硒化天麻多糖的质量,g。
1.2.4 硒化天麻多糖中得率的计算
得率计算公式如式(2):
得率(%)=m2m1×100 (2) 式中:m1表示天麻多糖的质量,g;m2表示硒化修饰天麻多糖的质量,g。
1.2.5 单因素实验
1.2.5.1 反应温度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
按照1.2.2的方法,硝酸浓度0.05%、反应时间8 h、亚硒酸钠用量(亚硒酸钠:天麻多糖)为1:1,改变反应温度分别为50、60、70、80、90 ℃测定硒化多糖硒含量及其得率,考察反应温度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响。
1.2.5.2 硝酸浓度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
按照1.2.2的方法,在反应温度70 ℃、反应时间8 h亚硒酸钠用量为1:1条件下,改变硝酸浓度分别为0.01%、0.03%、0.05%、0.07%、0.09%制备硒化天麻多糖,测定硒化多糖硒含量及其得率,探究硝酸浓度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响。
1.2.5.3 反应时间对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
按照1.2.2的方法,固定反应温度70 ℃、硝酸浓度0.05%、亚硒酸钠用量为1:1,改变反应时间分别为4、6、8、10、12 h,制备硒化天麻多糖,测定硒化多糖硒含量及其得率,探究反应时间对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响。
1.2.5.4 亚硒酸钠的用量对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
按照1.2.2的方法,在反应温度70 ℃、硝酸浓度0.05%,反应时间8 h,改变亚硒酸钠的用量分别为0.6:1、0.8:1、1:1、1.2:1、1.4:1,制备硒化天麻多糖,测定硒化多糖硒含量及其得率,探究亚硒酸钠的用量对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响。
1.2.6 响应面试验
在单因素实验结果分析的硒含量和显著水平的基础上,采用Box-Behnken(BBD)法进行响应面设计。选择反应温度(℃)、硝酸浓度(%)、反应时间(h),以硒化天麻多糖的硒含量作为响应值,进行响应面法工艺优化试验,因素水平见表1。
表 1 响应面法试验的因素及水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface methodology水平 因素 A反应温度(℃) B硝酸浓度(%) C反应时间(h) −1 60 0.03 6 0 70 0.05 8 1 80 0.07 10 1.2.7 硒化天麻多糖的表征
1.2.7.1 紫外光谱分析
配制0.1 mg/mL的Na2SeO3、GEP、SeGEP溶液,以蒸馏水作空白,于200~400 nm范围扫描测定。
1.2.7.2 红外光谱分析
称取干燥恒重的Na2SeO3、GEP、SeGEP 100 mg研磨压片,于红外光谱仪中,4000~400 cm−1范围内扫描测定。
1.2.7.3 核磁共振分析
称取20 mg的SeGEP,溶解于0.5 mL重水(D2O)中,冷冻干燥,再用0.5 mL的D2O复溶,加入到核磁管中,测定其1H-NMR、13C-NMR。
1.2.7.4 粒径及Zeta电位分析
取适量GEP和SeGEP溶于去离子水中,配制成浓度为2 mg/mL的多糖溶液,在25 ℃的条件下,使用纳米粒度及电位移仪测量多糖样品的粒径分布和Zeta电位,每个样品测3次。
1.2.7.5 刚果红实验
通过刚果红(Congo red)实验测定GEP和SeGEP是否具有三股螺旋[36]。分别用蒸馏水配制2.5 mg/mL的GEP、SeGEP溶液,移取2 mL多糖溶液与2 mL 80 μmol/L的刚果红溶液混合,逐渐加入NaOH溶液,使溶液中NaOH的浓度分别为0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mol/L避光反应5 min,在190~600 nm波长范围扫描,测定最大吸收波长,绘制最大吸收波长与NaOH浓度变化曲线。
1.2.7.6 碘-碘化钾试验
称取0.2 g KI,定容到100 mL,加入0.02 g I2,充分溶解后,称取GEP与SeGEP各2 mg,分别溶解在1.2 mL配制好的溶液中,稀释至一定浓度,在300~700 nm范围进行紫外光谱扫描[37]。
1.2.7.7 扫描电镜(SEM)分析
分别取干燥的GEP和SeGEP均匀分散在铝板上,在真空环境下镀金。喷金后将样品置于扫描电镜下室温扫描,观察硒化前后多糖的表面形状。
1.2.8 体外抗氧化实验
1.2.8.1 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
参考文献[38]中的方法,分别配制成每组2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL的VC、GEP和SeGEP溶液、取1 mL样品溶液加入0.01% DPPH-乙醇溶液2 mL,摇匀,在暗处反应30 min,用紫外分光光度计测定517 nm处的吸光值。DPPH自由基清除率计算方法如式(3):
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (3) 式中:A1,多糖与DPPH溶液混合的吸光值;A2,多糖与无水乙醇混合后的吸光值;A0,DPPH溶液与无水乙醇混合后的吸光值。
1.2.8.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力的测定
根据文献[33,39]的方法,适量修改后,制备ABTS自由基溶液,将7 mmol/L ABTS母液与2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾混合,在室温下暗反应16 h,用10 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH6.6)稀释,直至在734 nm处的吸光度为0.70±0.02 Abs,得到ABTS工作液。配制VC、GEP、SeGEP溶液(0.0625、0.125、0.25、0.5、1 mg/mL)置于试管中1 mL,每组加入2 mL ABTS工作液,室温暗反应反应6 min,用紫外分光光度仪在734 nm处测定吸光度。ABTS+自由基清除率计算方法如式(4):
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(1−Aa−AcAb)×100 (4) 式中:Aa,样品与ABTS工作液混合的吸光值;Ac,样品与水混合后的吸光值;Ab,ABTS工作液与水混合后的吸光值。
1.2.8.3 铁还原能力
参考文献[40]中的方法,适量修改后,将待测样品(VC、GEP、SeGEP)配制为2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL的溶液,分别取1 mL于试管中,加入0.2 mol/L pH6.6磷酸盐缓冲液2.5 mL,1%铁氰化钾1 mL,于50 ℃下反应20 min,加入10%三氯乙酸5 mL,4000 r/min条件下离心10 min,取上清液2.5 mL,加入2.5 mL蒸馏水,0.1%三氯化铁0.5 mL,静置10 min。于波长700 nm处测定吸光度。铁还原力计算如式(5):
铁还原力 =A1−A2 (5) 式中:A1,样品与反应溶液体系混合的吸光值;A2,样品与用去离子水代替0.1%三氯化铁的反应溶液体系混合的吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据用3次独立重复实验结果的平均值±标准差表示,采用SPSS Statistics 26软件进行方差分析,P<0.05表示差异显著,采用OMNIC软件处理红外数据和绘图,采用MestReNova软件处理核磁共振数据和绘图,其他数据采用Origin 2021软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 硒含量标准曲线绘制
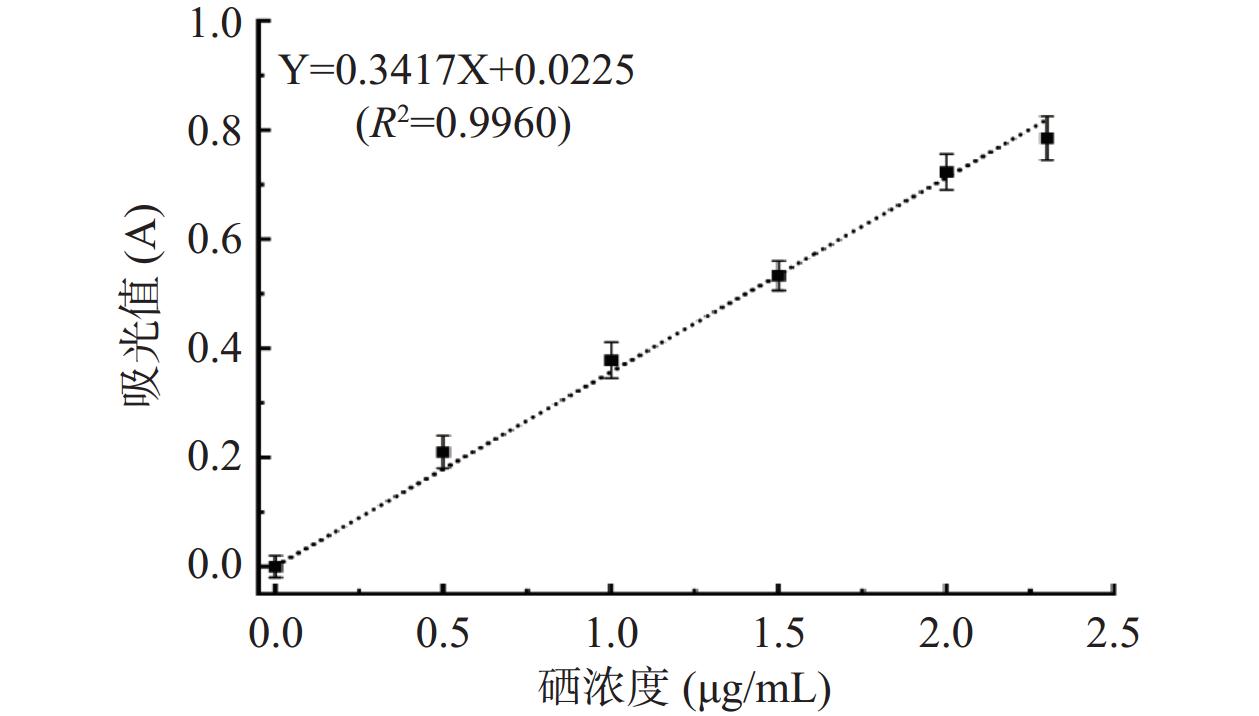
以硒的质量浓度为横坐标X,以吸光值A为纵坐标Y绘制标准曲线并建立回归方程:Y=0.3417X+0.0225(R2=0.9960)(图1)。
2.2 单因素实验
2.2.1 反应温度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
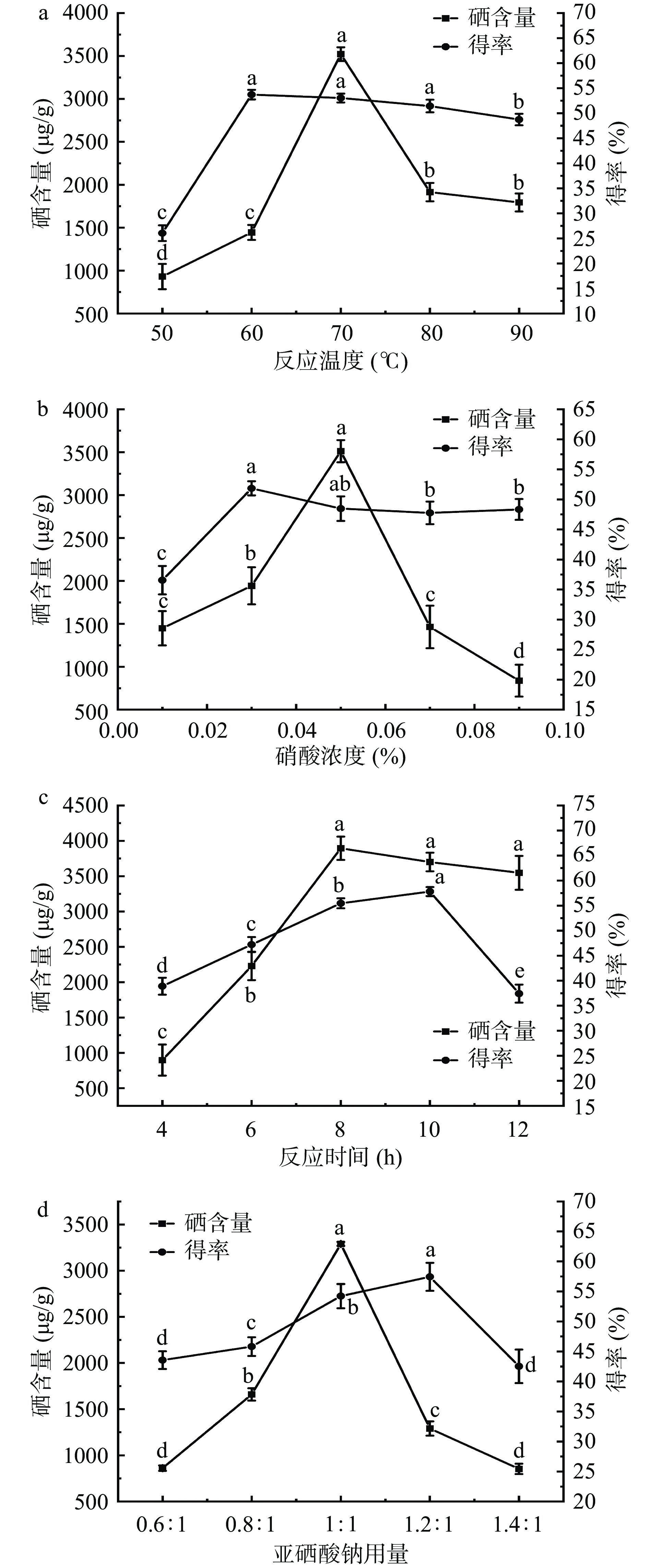
结果如图2a所示,当反应温度在50~70℃范围内,硒含量,得率显著增加(P<0.05);在60 ℃时,得率达到最大值53.72%±0.96%;在70 ℃时,硒含量达到最大值为3521.65±79.81 µg/g,此时得率为53.04%±0.89%;当反应温度大于70 ℃,硒含量、得率下降。这可能由于硒多糖在高温度条件下易分解[41],硒与多糖解离速度大于结合速度。因此,选择60、70、80 ℃进行响应面优化。
2.2.2 硝酸浓度对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
结果如图2b所示,当SeGEP在硝酸浓度0.01%~0.05%范围内时,SeGEP的硒含量、得率随着硝酸浓度的增加而显著增加(P<0.05);在浓度为0.03%时,得率达到最大值51.84%±1.18%;在浓度为0.05%时,硒含量达到最大值3511.645±128.95 µg/g,此时得率为48.46%±2.04%;当硝酸浓度大于0.05%时,硒化天麻多糖的硒含量、得率下降,这可能是因为过高的硝酸浓度会导致已经结合在多糖上的硒氧键C-O-Se断裂而发生解离作用,进而导致硒含量下降[42]。因此,选择0.03%、0.05%、0.07%进行响应面优化。
2.2.3 反应时间对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
结果如图2c所示,当硒化天麻多糖的反应时间小于8 h,硒含量、得率随着反应时间的增加而逐渐显著增大(P<0.05);在反应时间为8 h时,硒含量达到最大值为3894.72±164.28 µg/g,此时得率为55.46%±1.00%;在反应时间为10 h时,有最大的得率57.8%±0.9%;当反应时间大于8 h和10 h,硒含量、得率分别随着反应时间的增加而缓慢减小,当硒化时间过长时,GEP在高温和酸性条件下发生降解,影响硒化反应进行。因此,选择6、8、10 h进行响应面优化。
2.2.4 亚硒酸钠的用量对天麻多糖硒化修饰的影响
结果如图2d所示,当GEP与Na2SeO3质量比低于1:1时,随着Na2SeO3用量的增加,SeGEP 中硒含量、得率呈现显著上升趋势(P<0.05);当用量比为1:1时,硒含量达到最大为3289.79±21.26 µg/g,得率为54.22%±2.02%;当Na2SeO3用量大于1:1和1.2:1时,随着Na2SeO3用量的增加,硒含量、得率分别呈下降趋势,这可能硒与多糖的键合达到饱和状态,Na2SeO3的用量比的增大可能导致其平衡状态被破坏,从而导致硒含量下降[43]。
2.3 响应面试验结果与分析
2.3.1 回归方程的建立与方差分析
响应面试验设计与结果见表2。以硒含量为响应值,利用Design-Expert 11软件分析拟合得到硒化天麻多糖的硒含量的二次多元回归方程:Y=3736.73+308.25A−241.56B+634.45C−83.37AB+196.70AC−12.22BC−531.47A2−359.40B2−1649.24C2,并对此设计的模型进行方差分析,结果见表3。
表 2 响应面试验设计与结果Table 2. Design and result of response surfacemethod test试验号 A反应温度
(℃)B硝酸浓度
(%)C反应时间
(h)硒含量
(μg/g)1 60 0.03 8 2598.39±65.12 2 80 0.03 8 3625.83±25.37 3 60 0.07 8 2232.64±54.61 4 80 0.07 8 2926.58±34.84 5 60 0.05 6 915.55±51.28 6 80 0.05 6 894.46±61.32 7 60 0.05 10 1824.19±95.27 8 80 0.05 10 2589.88±64.82 9 70 0.03 6 1314.87±51.67 10 70 0.07 6 905.56±39.24 11 70 0.03 10 2575.07±43.98 12 70 0.07 10 2116.87±56.17 13 70 0.05 8 3859.08±102.31 14 70 0.05 8 3792.07±86.54 15 70 0.05 8 3761.27±75.43 16 70 0.05 8 3691.47±84.58 17 70 0.05 8 3579.78±73.91 表 3 方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型项 1.87E+7 9 2.08E+6 84.62 0.0001 显著 A 7.60E+5 1 7.60E+5 31 0.0008 ** B 4.67E+5 1 4.67E+5 19.04 0.0033 ** C 3.22E+6 1 3.22E+6 131.32 0.0001 ** AB 27805.56 1 27805.56 1.13 0.3223 AC 1.55E+5 1 1.55E+5 6.31 0.0403 * BC 597.56 1 597.56 0.0244 0.8804 A² 1.19E+6 1 1.19E+6 48.5 0.0002 ** B² 5.44E+5 1 5.44E+5 22.18 0.0022 ** C² 1.15E+7 1 1.15E+7 467.05 0.0001 ** 残差 1.72E+5 7 24521.41 失拟项 1.26E+5 3 42111.29 3.72 0.1185 不显著 纯误差 45316.02 4 11329 总和 1.89E+7 16 注:**P<0.01,差异极显著;*P<0.05,差异显著。 如表3所示,对回归模型进行方差分析,该回归模型极显著(P<0.01),失拟项不显著(P>0.05),模型决定系数R2=0.9909,校正后决定系数R2adj=0.9792,说明模型拟合度较高,能预测97.92%的响应值,可以利用此模型对硒化天麻多糖的制备工艺的优化。由回归模型的显著性可知,一次项A、B、C,二次项A2、B2、C2的影响极显著(P<0.01),交互项AC的影响显著(P<0.05),交互项AB、BC的影响不显著(P>0.05)。由F值可知,各因素对硒化天麻多糖的硒含量的影响顺序:C>A>B。
2.3.2 响应面曲面结果分析
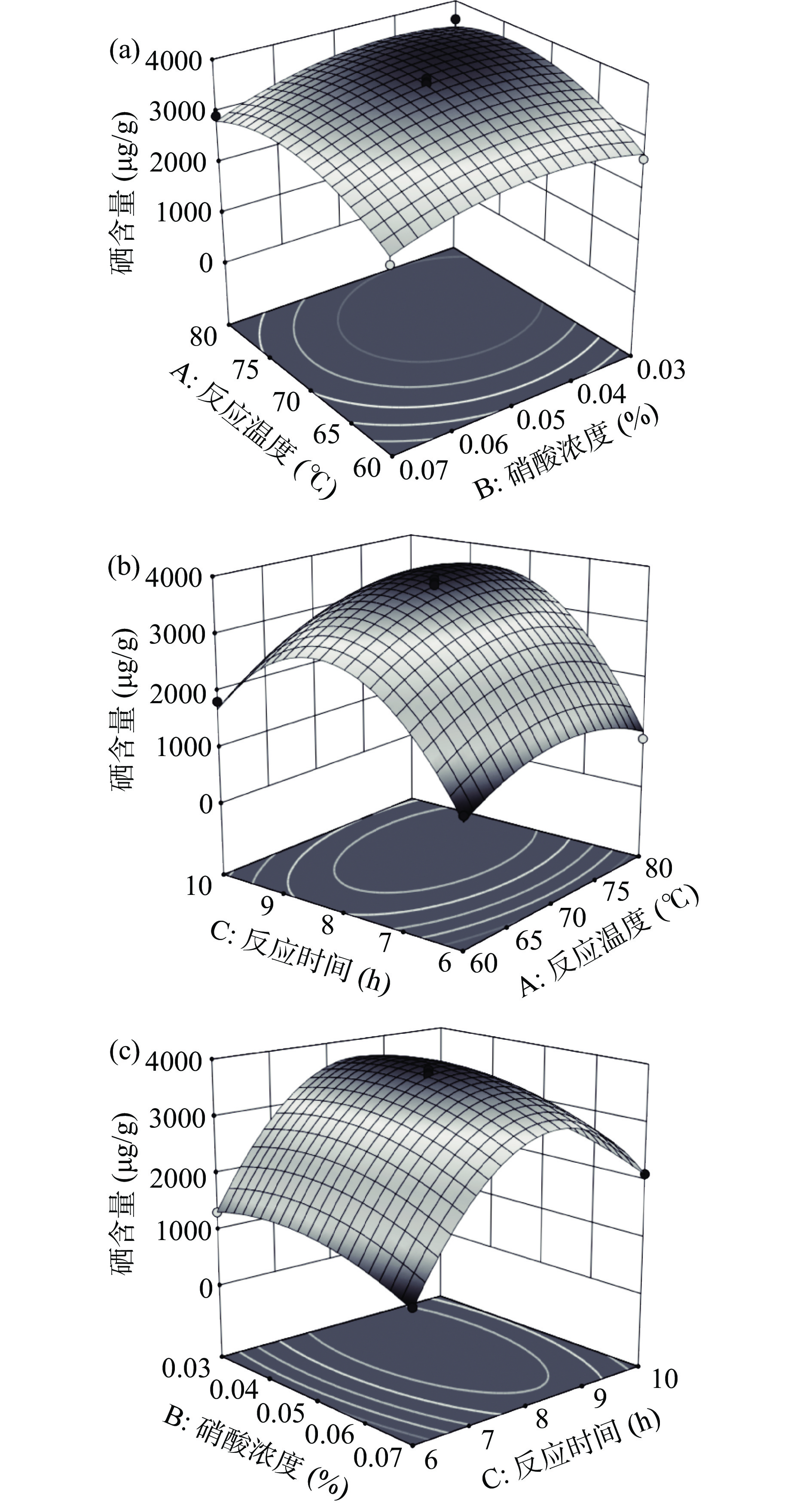
根据分析软件拟合得到的三维图来反映出反应温度、硝酸浓度、反应时间三个因素两两交互作用对天麻多糖的硒化修饰影响。由图3看出,AB响应面不陡峭,等高线接近圆形,说明AB交互作用相对不显著;AC、BC响应面陡峭,等高线呈椭圆形,说明AC、BC交互作用显著,这与方差结果分析较为一致。
2.3.3 验证试验
通过分析软件模型的建立,当反应温度为73.91 ℃、硝酸浓度为0.041%、反应时间为8.42 h时,预测硒化天麻多糖的硒含量为3904.07 μg/g。考虑实际操作,将最佳硒化天麻多制备工艺改为反应温度74 ℃、硝酸浓度0.041%、反应时间8.4 h,重复3次。在此条件下得到的硒含量为3891.05±10.86 μg/g,得率为49.63%±1.49%,与预测值硒含量对比仅相差0.33%,表明模型准确可靠。
2.4 紫外光谱结果分析
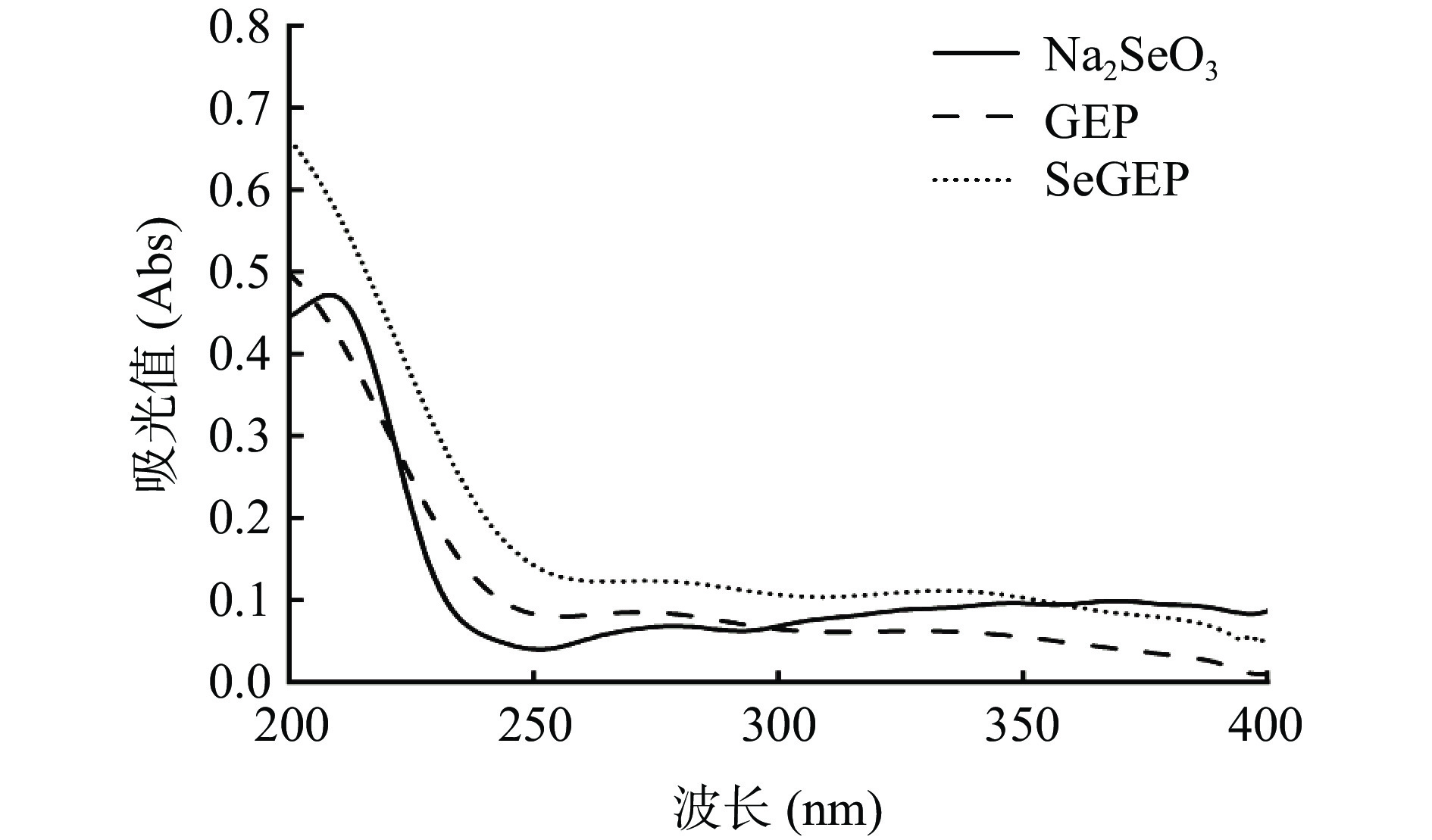
如图4所示,Na2SeO3在208 nm处有较强的吸收峰,这与张春岭等[44]的研究相符合。GEP和SeGEP在260、280 nm没有明显的核酸和蛋白质的特征吸收峰,说明多糖中大部分蛋白质和核酸已经除去[45]。
2.5 红外光谱结果分析
亚硒酸钠、天麻多糖硒化前后的红外光谱如图5所示。在717、445 cm−1处有吸收峰为Na2SeO3的特征吸收峰[46]。其中3292 cm−1(GEP)、3307 cm−1(SeGEP)处的特征峰为-OH的伸缩振动特征吸收峰(3600~3200 cm−1),2902 cm−1(GEP、SeGEP)处的吸收峰为C-H的伸缩振动(2900 cm−1),1591 cm−1(GEP)、1645 cm−1(SeGEP)处的吸收峰为C=O的伸缩振动(2200~1350 cm−1),1406 cm−1(GEP、SeGEP)处的吸收峰为C-H的变形振动(1450~1360 cm−1),1230 cm−1(GEP)、1246 cm−1(SeGEP)处的吸收峰为C-O-C的伸缩振动[47],1149 cm−1(GEP)、1148 cm−1(SeGEP)处的吸收峰为β-型糖苷键的特征吸收峰[34],760 cm−1(GEP)、759 cm−1(SeGEP)为吡喃环骨架的特征吸收峰[48],以上特征吸收峰说明了天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖都具有含β-型糖苷键连接以吡喃环为骨架的多糖结构。而硒化天麻多糖在1016、896、605 cm−1处产生新的弱吸收峰,其中1016 cm−1处的吸收峰为O-Se-O的特征吸收峰[49](1040~1010 cm−1),896 cm−1处的吸收峰为Se=O特征吸收峰[50](900~850 cm−1),605 cm−1处的吸收峰为C-O-Se特征吸收峰[51](700~600 cm−1),这说明硒以亚硒酸酯的形式与天麻多糖上的羟基结合生成硒化天麻多糖。
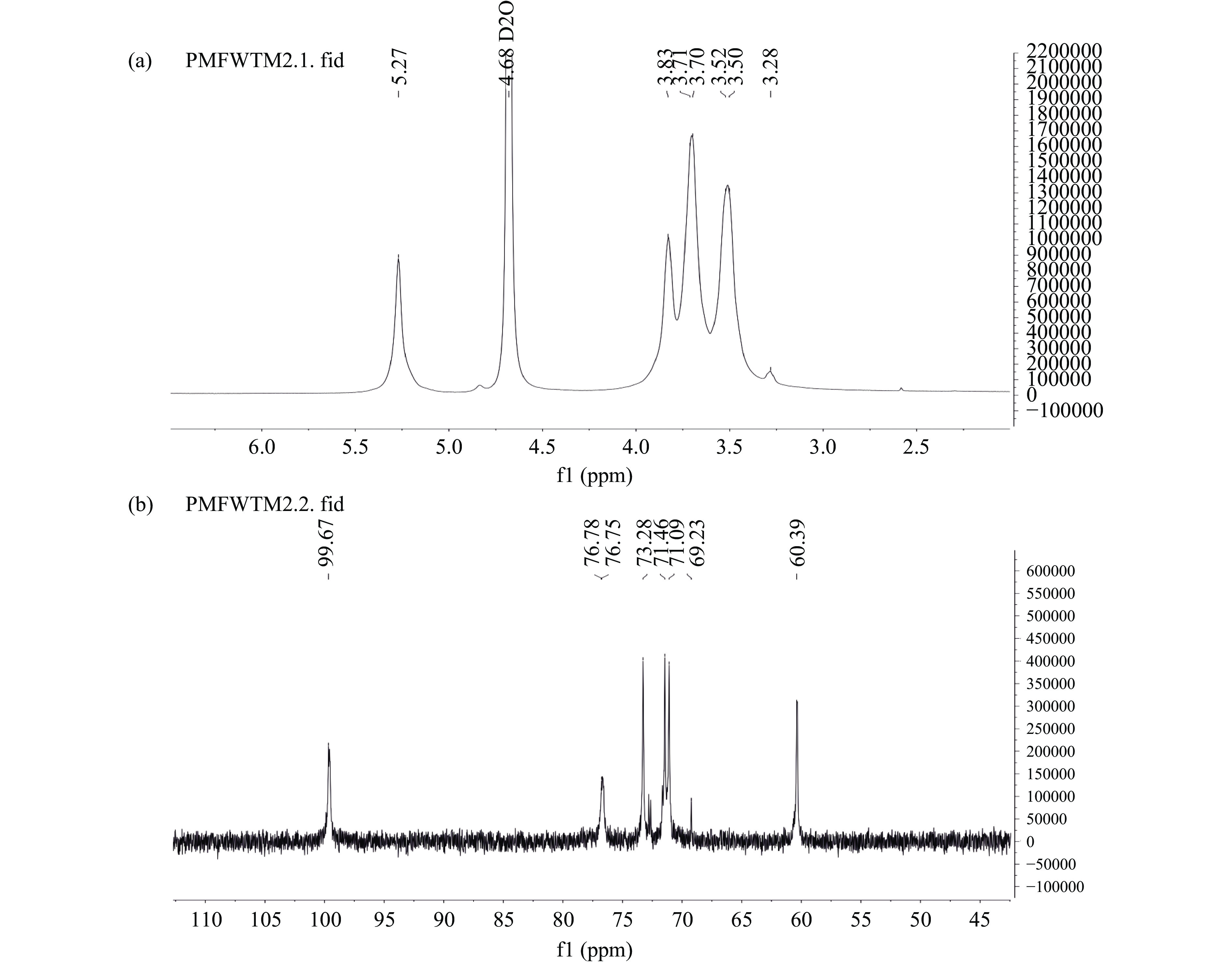
2.6 核磁共振结果分析
如图6所示,SeGEP的1H-NMR谱图的化学位移有3.28、3.50、3.70、3.83、5.27 ppm,这些信号可以指征为多糖的特征峰[28],其中3.28、3.50、3.70、3.83 ppm来源于单糖上的H-2~H-6[52]。在一般情况下,异头氢H-1在5.50~4.90 ppm范围内属于α-构型,在4.90~4.0 ppm范围内属于β-构型,SeGEP在这两个范围内只有信号5.27 ppm,通过1H-NMR谱说明硒化天麻多糖的糖苷键主要为α构型。
SeGEP的13C-NMR谱图的化学位移有60.39、69.23、71.09、71.46、73.28、76.75、99.67 ppm。其中60.39 ppm处为C-6信号,69.23 ppm处为C-5信号,71.09、71.46 ppm处为C-2信号,出现裂峰,73.28 ppm处为C-3信号,76.75 ppm处为C-4信号,99.67 ppm处为异头碳C-1信号,异头碳信低于100 ppm也验证了SeGEP的构型为α构型[53]。
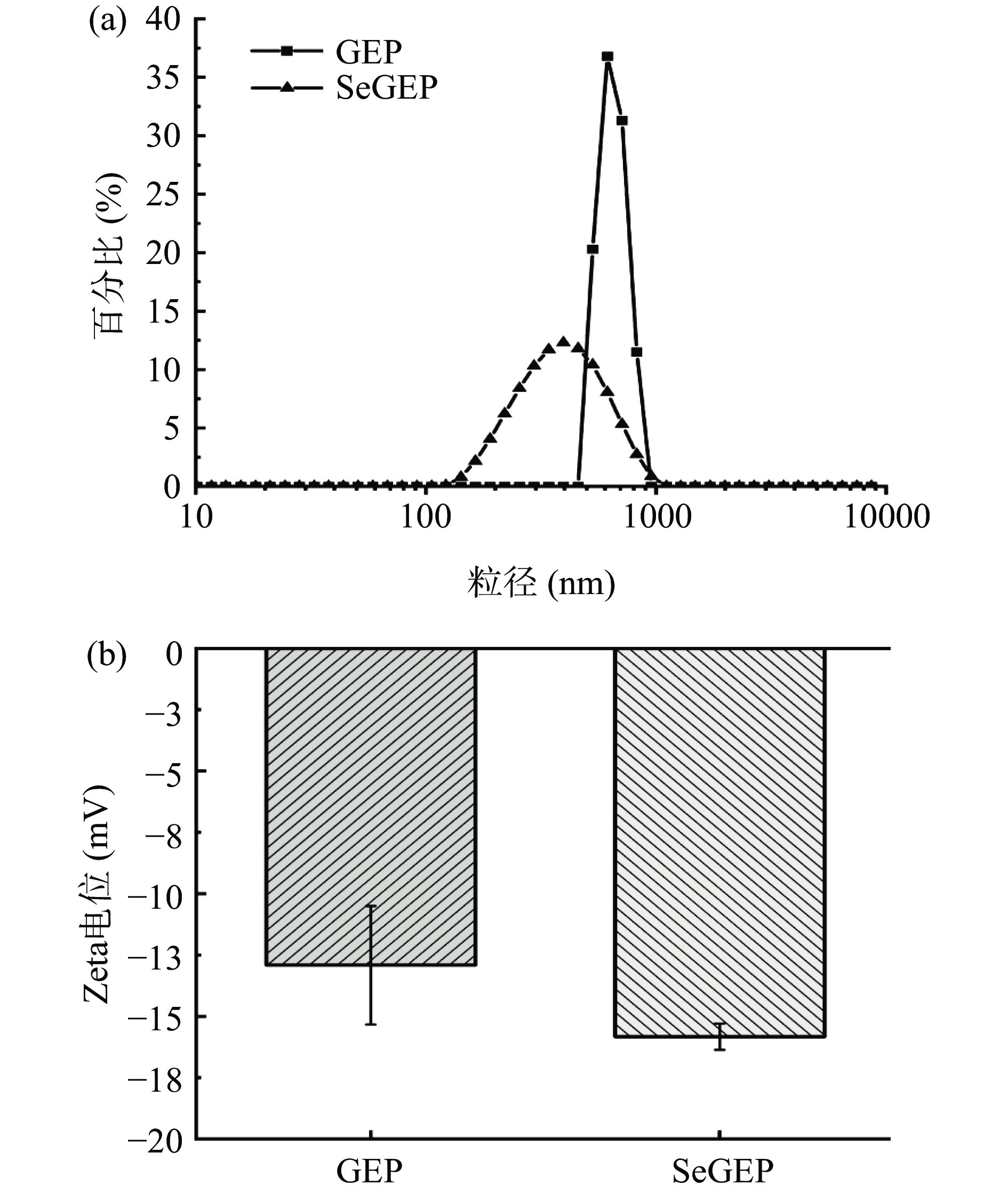
2.7 粒径及Zeta电位结果分析
多糖的流体力学性质如粒径分布和电势电位可以在一定程度上反映其稳定性,一般来说,多糖分子的粒径越小、Zeta电位的绝对值越大,说明多糖分子在体系中越容易分散或溶解,反之则多糖分子越容易聚集[54]。如图7a所示,在2 mg/mL的浓度下,GEP的平均粒径为647.33±43.11 nm,SeGEP的平均粒径为486±60 nm,SeGEP的粒径比GEP减少了24.92%。该结果显示天麻多糖在硒化反应过程中,因亚硒酸酯基团的引入使天麻多糖高级结构发生改变,更易紧密聚合成粒径更小的形态;图7b中GEP的平均Zeta电位为−12.92±2.42 mV,SeGEP的平均Zeta电位−15.83±0.53 mV,SeGEP的Zeta电位绝对值比GEP大22.52%。结果显示硒化多糖形成后,因SeGEP表面的亚硒酸酯基团的羟基比GEP表面的羟基基团电离程度强,使SeGEP表面带的负电荷增加,表现出SeGEP的Zeta电位绝对值比GEP大。这与Ru等[55]研究结果一致,表明硒化修饰能提高天麻多糖在溶液体系的稳定性、分散性。
2.8 刚果红实验结果分析
刚果红是一种酸性染料,其可与具有三股螺旋链构象的多糖形成络合物,该络合物在一定的碱性溶液中保持稳定,但当氢氧化钠溶液浓度大于某一数值后,由于碱性过高使多糖高级结构开始破坏导致最大吸收波长急剧下降,由此可对多糖中是否含有三股螺旋结构进行判断[56],并推断硒化修饰是否对多糖的三股螺旋结构产生影响。由图8a可知,随着NaOH浓度的增大,刚果红的最大吸收波长在下降,发生蓝移现象。GEP和SeGEP的最大吸收波长相比于刚果红的最大吸收波长有发生红移现象,但变化程度较少,最大吸收波长整体处于蓝移趋势。综上所述,天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖可能具备三股螺旋结构[57],且硒化修饰过程不会对天麻多糖的螺旋结构产生影响。
2.9 碘-碘化钾试验结果分析
当多糖与碘试剂混匀后,碘与分支较少或侧链较短的多糖的结合位点少,无法络合,通过紫外扫描只有碘在565 nm处的最大吸收峰,碘与分支较多或侧链较长的多糖的结合位点多,能使碘与多糖形成络合物,紫外扫描发生蓝移现象[58],通过碘-碘化钾实验推断硒化修饰是否对天麻多糖的分支结构产生影响。如图8b所示,在330~380 nm范围内,天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖都有一个明显的吸收峰,说明天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖都具有分支结构,但565 nm处无最大吸收峰,说明天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖均存在较长的侧链和支链,这与于闯[59]和蔡佳欣[60]研究结果相似。
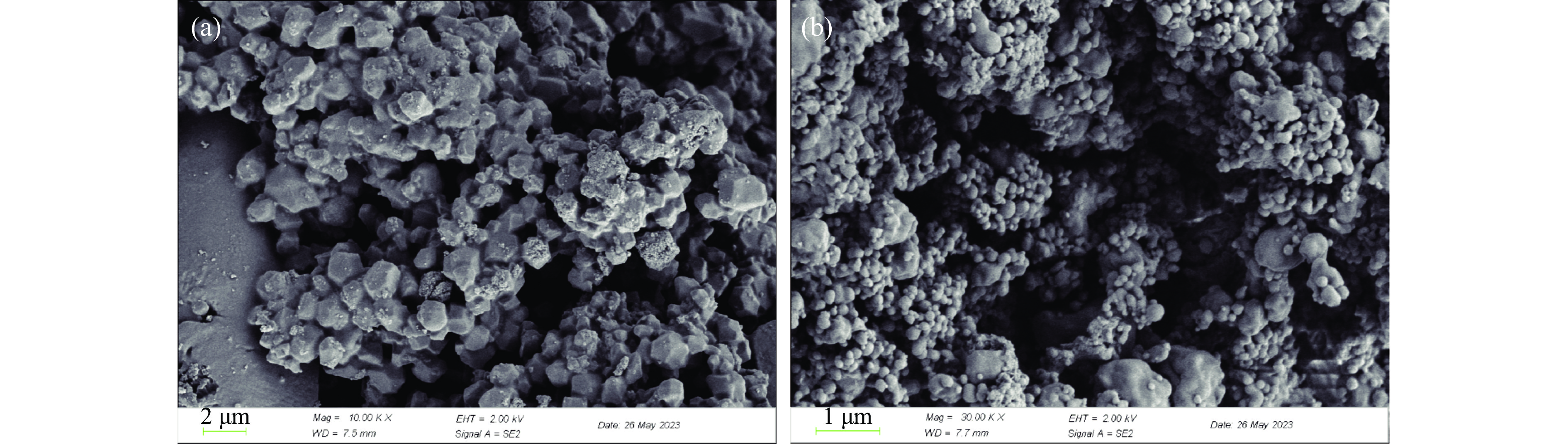
2.10 扫描电镜(SEM)结果分析
扫描电子显微镜主要是利用二次电子信号成像来观察样品的表面形态,即用极狭窄的电子束去扫描样品,通过电子束与样品的相互作用产生各种效应,其中主要是样品的二次电子发射。二次电子能够产生样品表面放大的形貌像,从而获得形貌、结构、成分和结晶学信息等优点,通过SEM分析推断硒化修饰是否对天麻多糖的微观结构产生影响。图9a、b分别为GEP和SeGEP扫描电镜图。由图9a可知,GEP的表面比较光滑、规则,具有棱角的团状晶体结构;由图9b可知,SeGEP的表面粗糙,有大小不一,产生更小的粒径、致密的球状物聚集存在,这与粒径分析的结果一致。这种变化可能是硒化修饰对天麻多糖的高级结构产生较大的影响,改变了天麻多糖的微观表观形态。
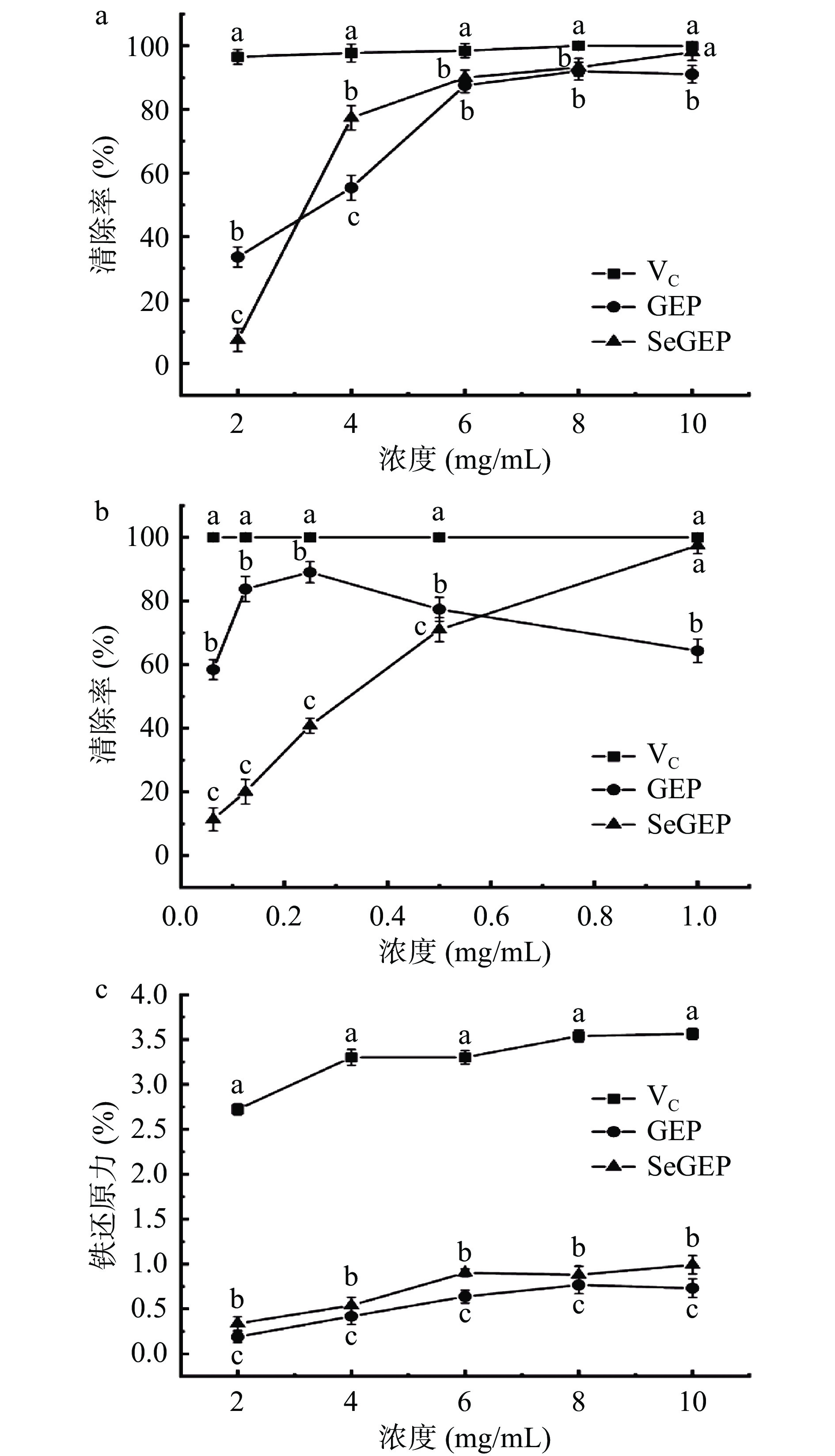
2.11 清除DPPH自由基能力结果分析
DPPH是一种稳定的自由基,分子内部存在有非共有电子的氮原子中心(N·),当抗氧化剂向DPPH自由基转移一个氢原子或一个电子,氮原子中心会转化为稳定的结构(N-H),这样使DPPH自由基性质不再存在[61]。通过DPPH自由基清除实验,推断硒化修饰是否对天麻多糖清除DPPH自由基的影响。如图10a所示,GEP和SeGEP对DPPH自由基的清除率均表现出剂量依赖关系,随着多糖浓度的增加,DPPH自由基清除率越高。在浓度>3 mg/mL时,相同的浓度下,SeGEP的DPPH自由基清除率显著大于GEP(P<0.05)。在浓度10 mg/mL时,SeGEP有最大的DPPH自由基清除率为98%±1.52%,这与阳性对照的VC清除率为100%接近。SeGEP上的亚硒酸酯基团比GEP表面的羟基基团更活泼,更有利于与DPPH的氮原子中心孤对电子配对,使DPPH自由基性质不再存在。综上所述,说明硒化修饰可以增加天多糖对DPPH自由基的清除效果。
2.12 清除ABTS+自由基能力结果分析
ABTS作为一种过氧化氢酶底物,能与氧化物反应生成稳定的绿色ABTS+自由基,并在734 nm处有最大紫外吸收。其与抗氧化剂反应时,ABTS+自由基与一个游离电子配对变成非自由基形式,溶液由绿色变为无色[62]。通过此试验,考察硒化修饰对天麻多糖清除ABTS+自由基的影响。如图10b所示,GEP、SeGEP都具有对ABTS+自由基清除作用。浓度在1 mg/mL时SeGEP的清除作用显著比GEP强(P<0.05),在硒化天麻多糖浓度为1 mg/mL时SeGEP的清除率为97.49%±1.16%,这与阳性对照的VC清除率为100%接近。天麻多糖的中羟基基团比较活泼,其易向ABTS+自由基提供氢原子,使天麻多糖具有抗氧化活性,且活性的强弱直接和供氢能力相关,硒化修饰后硒基团的存在可以进一步激活天麻多糖中的氢原子,从而增强其清除自由基的能力。综上所述,表明硒化修饰后的天麻多糖在一定的浓度范围内提高抗氧化能力。
2.13 铁还原能力结果分析
抗氧化试剂可以使铁氰化钾(K3Fe(CN)6)的三价铁变为二价铁,K3Fe(CN)6中二价铁和三氯化铁反应生成普鲁士蓝,在700 nm处有特定的吸收值[63]。如图10c所示,GEP和SeGEP的铁还原能力均表现出剂量依赖关系,随着多糖浓度的增加,还原能力越高,但上升的趋势缓慢。相同的浓度下,SeGEP的还原能力显著强于GEP(P<0.05)。在浓度10 mg/mL时,GEP有最大的还原力为0.73±0.17,而SeGEP还原力为0.99±0.24。SeGEP中的硒基团的存在可提供电子的能力更强,还原铁氰化钾中三价铁生成二价铁的能力也更强,表现为SeGEP的铁还原力比GEP强,这说明硒化修饰可以增强天麻多糖的铁还原能力。
3. 结论
本研究以硒含量为指标,采用HNO3-Na2SeO3法制备硒化天麻多糖,并通过单因素和响应面法优化制备工艺,得出最佳的硒化天麻多糖的制备工艺条件为反应温度74 ℃、硝酸浓度0.041%、反应时间8.4 h,在此条件下的硒含量为3891.05±10.86 μg/g;红外光谱显示,天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖均有吡喃环的多糖,在硒化修饰后在1016、896、605 cm−1处产生新的吸收峰,分别为O-Se-O、Se=O、C-O-Se特征吸收峰。核磁共振显示,SeGEP主要为有α构型、吡喃环的硒化天麻多糖;硒化修饰使粒径变小、Zeta电位的绝对值变大、改变了天麻多糖的微观形态,并提高了天麻多糖在溶液体系中的稳定性;刚果红试验和碘-碘化钾试验表明,天麻多糖和硒化天麻多糖可能具备三股螺旋结构并含有较长的侧链和支链结构,且硒化修饰过程不会对天麻多糖的螺旋结构、侧链、支链结构产生影响。抗氧化结果显示,硒化天麻多糖对DPPH自由基最大清除率为98%±1.52%、对ABTS+自由基最大清除率为97.49%±1.16%,均与VC相当,最大铁还原能力为0.99±0.24。以上三种抗氧化测试发现硒化天麻多糖的自由基清除率、铁还原力比天麻多糖高,表明硒化修饰提高了天麻多糖的抗氧化能力。
-
表 1 响应面法试验的因素及水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface methodology
水平 因素 A反应温度(℃) B硝酸浓度(%) C反应时间(h) −1 60 0.03 6 0 70 0.05 8 1 80 0.07 10 表 2 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 2 Design and result of response surfacemethod test
试验号 A反应温度
(℃)B硝酸浓度
(%)C反应时间
(h)硒含量
(μg/g)1 60 0.03 8 2598.39±65.12 2 80 0.03 8 3625.83±25.37 3 60 0.07 8 2232.64±54.61 4 80 0.07 8 2926.58±34.84 5 60 0.05 6 915.55±51.28 6 80 0.05 6 894.46±61.32 7 60 0.05 10 1824.19±95.27 8 80 0.05 10 2589.88±64.82 9 70 0.03 6 1314.87±51.67 10 70 0.07 6 905.56±39.24 11 70 0.03 10 2575.07±43.98 12 70 0.07 10 2116.87±56.17 13 70 0.05 8 3859.08±102.31 14 70 0.05 8 3792.07±86.54 15 70 0.05 8 3761.27±75.43 16 70 0.05 8 3691.47±84.58 17 70 0.05 8 3579.78±73.91 表 3 方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis
项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型项 1.87E+7 9 2.08E+6 84.62 0.0001 显著 A 7.60E+5 1 7.60E+5 31 0.0008 ** B 4.67E+5 1 4.67E+5 19.04 0.0033 ** C 3.22E+6 1 3.22E+6 131.32 0.0001 ** AB 27805.56 1 27805.56 1.13 0.3223 AC 1.55E+5 1 1.55E+5 6.31 0.0403 * BC 597.56 1 597.56 0.0244 0.8804 A² 1.19E+6 1 1.19E+6 48.5 0.0002 ** B² 5.44E+5 1 5.44E+5 22.18 0.0022 ** C² 1.15E+7 1 1.15E+7 467.05 0.0001 ** 残差 1.72E+5 7 24521.41 失拟项 1.26E+5 3 42111.29 3.72 0.1185 不显著 纯误差 45316.02 4 11329 总和 1.89E+7 16 注:**P<0.01,差异极显著;*P<0.05,差异显著。 -
[1] 杨世林, 兰进, 徐锦堂. 天麻的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2000, 31(1):66−69. [YANG S L, LAN J, XU J T. Research progress of Gastrodia elata [J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine 2000, 31 (1):66−69. YANG S L, LAN J, XU J T. Research progress of Gastrodia elata [J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine 2000, 31 (1): 66−69.
[2] 韩大荣. 天麻研究新进展[J]. 中国处方药,2018,16(4):19−21. [HAN Darong. New research progress of Gastrodia elata[J]. Chinese Prescription Drugs,2018,16(4):19−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-945X.2018.04.012 HAN Darong . New research progress of Gastrodia elata[J]. Chinese Prescription Drugs,2018 ,16 (4 ):19 −21 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-945X.2018.04.012[3] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典:一部[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020:59−60. [State Pharmacopoeia Committee. People’s Republic of China Pharmacopoeia:Part one [M]. Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Publishing House, 2020:59−60. State Pharmacopoeia Committee. People’s Republic of China Pharmacopoeia: Part one [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Publishing House, 2020: 59−60.
[4] HUANG H, JIANG N, ZHANG Y W, et al. Gastrodia elata Blume ameliorates circadian rhythm disorder-induced mice memory impairment[J]. Life Sciences in Space Research,2021,31:51−58.
[5] 国家卫生健康委. 关于对党参等9种物质开展按照传统既是食品又是中药材的物质管理试点工作的通知:国卫食品函[2019]311号[EB]. (2019-11-25)[2020-01-06]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7885/202001/1ec2cca04146450d9b14acc2499d854f.shtml. [National Health and Health Commission. Notice on carrying out the pilot work on the material management of Codonopsis pilosula and other nine substances that are traditionally both food and traditional Chinese medicine:Guowei Food letter (2019) No. 311 [EB]. (2019-11-25) [2020-01-06]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7885/202001/1ec2cca04146450d9b14acc2499d854f.shtml. National Health and Health Commission. Notice on carrying out the pilot work on the material management of Codonopsis pilosula and other nine substances that are traditionally both food and traditional Chinese medicine: Guowei Food letter (2019) No. 311 [EB]. (2019-11-25) [2020-01-06]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/sps/s7885/202001/1ec2cca04146450d9b14acc2499d854f.shtml.
[6] CHEN L, ZHANG Y P, JIN L X. Preparation, characterization and anti-ageing activity of Gastrodia elata Blume polysaccharide[J]. Acta Alimentaria,2018,47(2):210−219. doi: 10.1556/066.2018.47.2.10
[7] GUAN H, LING X, XU J, et al. Structural characterization of polysaccharide derived from Gastrodia elata and its immunostimulatory effect on RAW264.7 cells[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(22):8059.
[8] KIM N H, XIN M J, CHA J Y, et al. Antitumor and immunomodulatory effect of Gastrodia elata on colon cancer in vitro and in vivo[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2017,45(2):319−335. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500203
[9] ZHOU B, TAN J, ZHANG C, et al. Neuroprotective effect of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata Blume against corticosterone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated pathway[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2018,17(1):1182−1190.
[10] 陈琛, 李鑫鑫, 付昀东, 等. 汉中天麻多糖抗菌活性研究[J]. 江苏农业科学,2018,46(11):156−159 [CHEN C, LI X X, FU Y D, et al. Study on antibacterial activity of Gastrodia elata polysaccharides in Hanzhong[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(11):156−159. CHEN C, LI X X, FU Y D, et al . Study on antibacterial activity of Gastrodia elata polysaccharides in Hanzhong[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018 ,46 (11 ):156 −159 .[11] ROMAN M, JITARU P, BARBANTE C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health[J]. Metallomics,2014,6(1):25−54. doi: 10.1039/C3MT00185G
[12] 段亮亮. 硒的生理功能和富硒保健食品开发[J]. 现代食品,2018(1):42−45. [DUAN L L. Physiological function of seleniumand development of selenium-rich health food[J]. Modern Food,2018(1):42−45. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2018.01.014 DUAN L L . Physiological function of seleniumand development of selenium-rich health food[J]. Modern Food,2018 (1 ):42 −45 . doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2018.01.014[13] SURHIO M M, WANG Y, XU P, et al. Antihyperlipidemic and hepatoprotective properties of selenium modified polysaccharide from Lachnum sp[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,99(7):88−95.
[14] ZHANG L, ZENG H, CHENG W H. Beneficial and paradoxical roles of selenium at nutritional levels of intake in health plan and longevity[J]. Journal of Nutrition,2018,148(1):22−40. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxx005
[15] 李春生. 开阳县硒资源农业开发利用研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州师范大学, 2000. [LI C S. Research on agricultural development and utilization of selenium resources in Kaiyang County[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou Normal University, 2000. LI C S. Research on agricultural development and utilization of selenium resources in Kaiyang County[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2000.
[16] 王立平, 唐德剑, 沈亚美, 等. 硒的营养缺乏现状及补充方式[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(1):339−343 [WANG L P, TANG D J, SHEN Y M, et al. Nutritional deficiency status and supplement methods of selenium[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(1):339−343. WANG L P, TANG D J, SHEN Y M, et al . Nutritional deficiency status and supplement methods of selenium[J]. Food Industry,2020 ,41 (1 ):339 −343 .[17] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量第3部分:微量元素(WS/T 578.3-2017)[S]. 2017. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. Reference Intake of dietary nutrients for Chinese Part 3:Trace element(WS/T 578.3-2017)[S]. 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. Reference Intake of dietary nutrients for Chinese Part 3: Trace element(WS/T 578.3-2017)[S]. 2017.
[18] 王明祥, 李翼斌, 祝俊, 等. 黔南州部分7~14岁学生头发微量元素检测分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2012,39(7):1660−1661. [WANG M X, LI Y B, ZHU J, et al. Analysis of trace elements in hair of students aged 7 to 14 years in Qiannan Prefecture[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2012,39(7):1660−1661. WANG M X, LI Y B, ZHU J, et al . Analysis of trace elements in hair of students aged 7 to 14 years in Qiannan Prefecture[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2012 ,39 (7 ):1660 −1661 .[19] 李洁, 祝振洲, 程水源, 等. 硒形态检测方法在富硒食品标准中的应用与进展[J]. 食品科技,2019,46(12):8−14 [LI J, ZHU Z Z, CHENG S Y, et al. Application and progress of selenium morphology detection method in selenium rich food standard[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,46(12):8−14. LI J, ZHU Z Z, CHENG S Y, et al . Application and progress of selenium morphology detection method in selenium rich food standard[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019 ,46 (12 ):8 −14 .[20] CHEN N, ZHAO C, ZHANG T. Selenium transformation and selenium-rich foods[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,40(4):100875.
[21] 周亚龙, 彭敏, 成杭新, 等. 全国主要农耕区富硒土地资源调查与开发利用模式[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2022,44(6):833−841. [ZHOU Y L, PENG M, CHENG H X, et al. Investigation, development and utilization model of selenium-rich land resources in major agricultural areas in China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Computing Technology,2022,44(6):833−841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2022.06.14 ZHOU Y L, PENG M, CHENG H X, et al . Investigation, development and utilization model of selenium-rich land resources in major agricultural areas in China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Computing Technology,2022 ,44 (6 ):833 −841 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2022.06.14[22] 齐鹏翔, 陈玉颖, 陈山. 硒多糖的合成方法及其特性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(1):332−336. [QI P X, CHEN Y Y, CHEN S. Progress in synthesis and properties of selenium polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2019,40(1):332−336. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.01.059 QI P X, CHEN Y Y, CHEN S . Progress in synthesis and properties of selenium polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2019 ,40 (1 ):332 −336 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.01.059[23] 景永帅, 张钰炜, 李佳瑛, 等. 硒多糖的合成方法、结构特征和生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,542(7):374−381. [JING Y S, ZHANG Y W, LI J Y, et al. Progress in synthesis, structure and biological activity of selenium polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,542(7):374−381. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020050188 JING Y S, ZHANG Y W, LI J Y, et al . Progress in synthesis, structure and biological activity of selenium polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,542 (7 ):374 −381 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020050188[24] WANG J, LI Q, BAO A, et al. Synthesis of selenium-containing Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharides:Solution conformation and anti-tumor activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,152(5):70−78.
[25] FIORITO S, EPIFANO F, PREZIUSO F, et al. Selenylated plant polysaccharides:A survey of their chemical and pharmacological properties[J]. Phytochemistry,2018,153:1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.05.008
[26] HOU R, CHEN J, YUE C, et al. Modification of lily polysaccharide by selenylation and the immune-enhancing activity[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,142(20):73−81.
[27] WANG L, LI X, WANG B. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of selenium modified polysaccharides from Hohenbuehelia serotina[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 120(Part B): 1362−1368.
[28] XIAO H, CHEN C, LI C, et al. Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of selenized polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,132(1):308−315.
[29] LI Q, ZHU L, QI X, et al. Immunostimulatory and antioxidant activities of the selenized polysaccharide from edible Grifola frondosa[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2022,10(4):1289−1298.
[30] GAO P, BIAN J, XU S, et al. Structural features, selenization modification, antioxidant and anti-tumor effects of polysaccharides from alfalfa roots[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,149(15):207−214.
[31] 马晓宁, 秦令祥, 冀晓龙, 等. Design-Expert软件设计优化内黄大枣多糖的硒化修饰及其抗氧化、抗疲劳作用研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(10):164−172. [MA X N, QIN L X, JI X L, et al. Design-Expert software was designed to optimize the selenization modification, antioxidant and anti-fatigue effects of Neihuang jujube polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2023,14(10):164−172. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2023.10.020 MA X N, QIN L X, JI X L, et al . Design-Expert software was designed to optimize the selenization modification, antioxidant and anti-fatigue effects of Neihuang jujube polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2023 ,14 (10 ):164 −172 . doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2023.10.020[32] 马风伟, 李莹, 潘成, 等. 不同采收期乌天麻中多糖的提取及含量测定[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(22):47−51,90. [MA F W, LI Y, PAN C, et al. Extraction and determination of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata in different harvest periods[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(22):47−51,90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.22.009 MA F W, LI Y, PAN C, et al . Extraction and determination of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata in different harvest periods[J]. Food Research and Development,2018 ,39 (22 ):47 −51,90 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.22.009[33] 胡润锋, 李浚哲, 李鹏飞, 等. 响应面法优化硒化桑叶多糖的制备工艺及其体外抗氧化活性[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2022,42(8):148−157. [HU R F, LI J Z, LI P F, et al. Optimization of selenized mulberry leaf polysaccharides preparation by response surface methodology and determination of the antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2022,42(8):148−157. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2022.08.015 HU R F, LI J Z, LI P F, et al . Optimization of selenized mulberry leaf polysaccharides preparation by response surface methodology and determination of the antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2022 ,42 (8 ):148 −157 . doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2022.08.015[34] 王峙力, 王鑫, 韩烨, 等. 甜玉米芯硒多糖的制备及其对淀粉酶抑制作用[J]. 包装工程,2021(21):33−41. [WANG Z L, WANG X, HAN Y, et al. Preparation of selenium polysaccharide from sweet corncob and its inhibitory effect on amylase[J]. Packaging Engineering,2021(21):33−41. doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2021.21.005 WANG Z L, WANG X, HAN Y, et al . Preparation of selenium polysaccharide from sweet corncob and its inhibitory effect on amylase[J]. Packaging Engineering,2021 (21 ):33 −41 . doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2021.21.005[35] 李丽彩, 王留成, 程相林, 等. 紫外分光光度法测定富硒麦芽中微量元素硒的含量[J]. 应用化工,2016,45(4):771−774. [LI L C, WANG L C, CHENG X L, et al. Determination of trace element selenium in selenium-rich malt by ultraviolet spectrophotometry[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2016,45(4):771−774. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20160115.010 LI L C, WANG L C, CHENG X L, et al . Determination of trace element selenium in selenium-rich malt by ultraviolet spectrophotometry[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2016 ,45 (4 ):771 −774 . doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20160115.010[36] 于瑞莹. 兴安杜鹃多糖的纯化修饰、结构表征及其抗氧化活性研究报告[D]. 延边:延边大学, 2022. [YU R Y. Purification, modification, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of rhododendron polysaccharide from Xing'an[D]. Yanbian:Yanbian University, 2022. YU R Y. Purification, modification, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of rhododendron polysaccharide from Xing'an[D]. Yanbian: Yanbian University, 2022.
[37] 符玉霞. 红枣多糖硫酸酯化、羧甲基化修饰及其抗氧化活性研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学, 2022. [FU Y X. Study on sulfation, carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of jujube polysaccharides[D]. Shihezi:Shihezi University, 2022. FU Y X. Study on sulfation, carboxymethylation modification and antioxidant activity of jujube polysaccharides[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2022.
[38] HOU R, LI Q, LIU J, et al. Selenylation modification of Atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. Advances in Polymer Technology,2019,2019:8191385.
[39] 王诗宝. 茯苓多糖的提取、硫酸化修饰及其抑制胃癌细胞MGC803增殖作用的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2022. [WANG S B. Extraction, sulfation and modification of Poria polysaccharide and its inhibitory effect on proliferation of gastric cancer cells MGC803 [D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2022. WANG S B. Extraction, sulfation and modification of Poria polysaccharide and its inhibitory effect on proliferation of gastric cancer cells MGC803 [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
[40] 吕青青. 小麦麸皮多糖的结构表征、硒化改性及生理活性研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2020. [LÜ Q Q. Study on structural characterization, selenization modification and physiological activity of wheat bran polysaccharide[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2020. LÜ Q Q. Study on structural characterization, selenization modification and physiological activity of wheat bran polysaccharide[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020.
[41] 李晓娇, 段绍丽, 曹凯红, 等. 硒化铁皮石斛多糖的制备工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2022,35(7):1548−1554. [LI X J, DUAN S L, CAO K H, et al. Study on preparation technology and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Dendrobium candidum selenide[J]. Journal of Southwest Agriculture,2022,35(7):1548−1554. doi: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2022.7.008 LI X J, DUAN S L, CAO K H, et al . Study on preparation technology and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Dendrobium candidum selenide[J]. Journal of Southwest Agriculture,2022 ,35 (7 ):1548 −1554 . doi: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2022.7.008[42] 侯巍, 朱小庆, 楚婧, 等. 硒化玉米须多糖的工艺条件及硒含量测定研究[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2012,29(7):621−624. [HOU W, ZHU X Q, CHU J, et al. Study on technological conditions and determination of selenium content of selenized corn whisker polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Modern Applied Pharmacy,2012,29(7):621−624. doi: 10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.2012.07.007 HOU W, ZHU X Q, CHU J, et al . Study on technological conditions and determination of selenium content of selenized corn whisker polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Modern Applied Pharmacy,2012 ,29 (7 ):621 −624 . doi: 10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.2012.07.007[43] 李晓娇, 闵诗碧, 曹凯红, 等. 龙陵紫皮石斛多糖的硒化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,443(20):117−124. [LI X J, MIN S B, CAO K H, et al. Selenium modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Dendrobium candidum[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,443(20):117−124. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.20.015 LI X J, MIN S B, CAO K H, et al . Selenium modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Dendrobium candidum[J]. Food Research and Development,2022 ,443 (20 ):117 −124 . doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.20.015[44] 张春岭, 吴校卫, 陈大磊, 等. 硒化红枣多糖制备工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(22):241−244. [ZHANG C L, WU J W, CHEN D L, et al. Optimization of preparation technology of selenized jujube polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(22):241−244. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.22.044 ZHANG C L, WU J W, CHEN D L, et al . Optimization of preparation technology of selenized jujube polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014 ,35 (22 ):241 −244 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.22.044[45] WANG L, ZHANG P, SHEN J, et al. Physicochemical properties and bioactivities of original and Se-enriched polysaccharides with different molecular weights extracted from Pleurotus ostreatus[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,141(1):150−160.
[46] 姚万玲. 党参多糖的硒化修饰及其抗氧化和增强免疫活性的研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2011. [YAO W L. Study on selenization modification of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides and its antioxidant and enhanced immune activity[D]. Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011. YAO W L. Study on selenization modification of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides and its antioxidant and enhanced immune activity[D]. Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011.
[47] 董慧茹. 仪器分析[M]. 第三版. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2016:199−205. [DONG H R. Instrumental analysis [M]. The third edition. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2016:199−205. DONG H R. Instrumental analysis [M]. The third edition. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016: 199−205.
[48] PETKOVA N T, SHEROVA G, DENEV P P. Characterization of inulin from Dahlia tubers isolated by microwave and ultrasound-assisted extractions[J]. International Food Research Journal,2018,25(5):1876−1884.
[49] 徐碧辉. 硒的化学、生物化学及其在生命科学中的应用[M]. 武汉:华中理工大学出版社, 1994, 12:66−67. [XU B H. Chemistry and biochemistry of selenium and its application in life science[M]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press 1994, 12:66−67. XU B H. Chemistry and biochemistry of selenium and its application in life science[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press 1994, 12: 66−67.
[50] WEI D F, CHEN T, YAN M F. et al. Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant activity and neuroprotective effects of selenium polysaccharide from Radix hedysari[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,125(10):161−168.
[51] YUAN B, YANG X Q, KOU M, et al. Selenylation of polysaccharide from the sweet potato and evaluation of antioxidant, antitumor, and antidiabetic activities[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(3):605−617. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04788
[52] 张治国. 超声法辅助富硒甘薯多糖提取、结构表征及其抗氧化分析[D]. 沈阳:辽宁大学, 2022. [ZHANG Z G. Ultrasound-assisted extraction, structural characterization and antioxidant analysis of selenium-enriched sweet potato polysaccharides[D]. Shenyang:Liaoning University, 2022. ZHANG Z G. Ultrasound-assisted extraction, structural characterization and antioxidant analysis of selenium-enriched sweet potato polysaccharides[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2022.
[53] 丁佳玉. 硒化牡蛎多糖制备及其生物活性研究[D]. 大连:大连海洋大学, 2019. [DING J Y. Preparation and biological activity of selenized oyster polysaccharides [D]. Dalian:Dalian Ocean University, 2019. DING J Y. Preparation and biological activity of selenized oyster polysaccharides [D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2019.
[54] LIU G Y, YANG X, ZHANG J X, et al. Synthesis, stability and anti-fatigue activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,179(15):418−428.
[55] RU Y, LIU K, KONG X, et al. Synthesis of selenylated polysaccharides from Momordica charantia L. and its hypoglycemic activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,152(1):295−304.
[56] YANG X, XUE Z, FANG Y, et al. Structure-immunomodulatory activity relationships of Hedysarum polysaccharides extracted by a method involving a complex enzyme combined with ultrasonication[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(2):1146−1158.
[57] 程素盼. 天麻多糖分离纯化、结构表征及抗肿瘤活性研究[D]. 济南:山东中医药大学, 2020. [CHENG S P. Isolation, purification, structural characterization, and anti-tumor activity of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata [D]. Ji’nan:Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020. CHENG S P. Isolation, purification, structural characterization, and anti-tumor activity of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata [D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[58] YAMADA H, YANAHIRA S, KIYOHARA H, et al. Water-soluble glucans from the seed of Coix lacryma-jobi var. ma-yuen[J]. Phytochemistry,1985,25(1):129−132. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)94516-3
[59] 于闯. 富硒方式对茶多糖的影响研究[D]. 上海:上海师范大学, 2018. [YU C. Study on the effect of selenium enrichment on tea polysaccharide [D]. Shanghai:Shanghai normal University, 2018. YU C. Study on the effect of selenium enrichment on tea polysaccharide [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai normal University, 2018.
[60] 蔡佳欣. 硒化和酶解修饰改性对荔枝多糖结构和生物活性的影响[D]. 广州:广东药科大学, 2019. [CAI J X. Effects of selenization and enzymolysis modification on the structure and biological activity of litchi polysaccharides [D]. Guangzhou:Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2019. CAI J X. Effects of selenization and enzymolysis modification on the structure and biological activity of litchi polysaccharides [D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2019.
[61] 熊双丽, 卢飞, 史敏娟, 等. DPPH自由基清除活性评价方法在抗氧化剂筛选中的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(8):380−383. [XIONG S L, LU F, SHI M J, et al. Research progress of DPPH free radical scavenging activity evaluation methods in antioxidant screening[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(8):380−383. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.08.022 XIONG S L, LU F, SHI M J, et al . Research progress of DPPH free radical scavenging activity evaluation methods in antioxidant screening[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012 ,33 (8 ):380 −383 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.08.022[62] 钟胜男, 禹小波, 胡烨, 等. 海绵胶煤炱菌(竹燕窝)多糖的组成及体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(6):62−66. [ZHONG S N, YU X B, HU Y, et al. The antioxidant activity and monosaccharide composition analysis of the polysaccharide from Scorias spongiosa[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(6):62−66. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060281 ZHONG S N, YU X B, HU Y, et al . The antioxidant activity and monosaccharide composition analysis of the polysaccharide from Scorias spongiosa[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (6 ):62 −66 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060281[63] YOU Q, YIN X, ZHANG S, et al. Extraction, purification, and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Tricholoma mongolicum Imai[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,99(2):1−10.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 高雅文,吴国鹏,韩博,王荣武,娄方明. 硒化芹菜素的制备及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2025(04): 109-116 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 袁永旭,闫馨慈,吕炀,周扬,何文兵,夏光辉,裴世春. 磨盘草多糖的提取工艺优化、结构表征及其抗氧化活性. 饲料研究. 2025(02): 109-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵向豪,栗宁,玛依拉·米吉提,刘亚茹. 产业集群视域下新疆富硒果蔬产业发展策略研究. 中国果树. 2024(08): 140-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨文,刘媛. 硒化高分子多糖的研究进展. 农业与技术. 2024(17): 28-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王清,曹珍,刘涛,高歌,郑雪珂,涂剑秋,桑大席. 微波辅助硒化葡聚糖的合成及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品科技. 2024(08): 279-288 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 袁永旭,黄志程,贡永鹏,闫馨慈,吕炀,周扬,李明,崔艳艳. 榛子青皮多糖的提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性评价. 饲料研究. 2024(16): 79-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



