Protective Effect and Mechanism of Chinese Yam Total Protein on High D-Glucose Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
-
摘要: 探究山药总蛋白对高浓度D-葡萄糖(High concentrations of D-glucose,HG)诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞(Human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs)氧化应激损伤的保护作用及其机制。利用50 mmol/L HG建立HUVECs损伤模型。将HUVECs随机分为对照组、模型组、山药总蛋白低剂量组(0.5 mg/mL)以及山药总蛋白高剂量组(1 mg/mL),评估山药总蛋白对HG处理的HUVECs的细胞活力、细胞形态及血管生成能力的影响;检测细胞中活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)的水平和超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)的活力;以及培养基上清液中一氧化氮(Nitric oxide,NO)、8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(8-Hydroxy deoxyguanosine,8-OHdG)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、白介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、白介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)的水平;测定B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)、Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)、硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白(Txnip)、NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)、半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶剪切体-1(Cleaved caspase-1)和IL-1β蛋白的表达水平。结果显示,山药总蛋白能显著提高HG处理后的HUVECs的细胞活力(P<0.01),改善细胞凋亡形态,并显著升高SOD和CAT的活力(P<0.05或P<0.01)以及凋亡相关蛋白(Bcl-2/Bax)的比值、血管形成能力、NO分泌量。此外,山药总蛋白还显著降低了HUVECs的ROS、MDA、8-OHdG、IL-1β和IL-6的水平(P<0.05或P<0.01)及炎症相关蛋白(Txnip、NLRP3、cleaved Caspase-1、IL-1β)的表达水平(P<0.05或P<0.01),并且上述指标的变化均呈现明显的浓度依赖性。本研究结果表明,山药总蛋白可能通过抑制Txnip/NLRP3信号通路从而保护HUVECs拮抗HG诱导的氧化应激,恢复HUVECs内的氧化平衡,进一步减轻细胞的炎症反应。
-
关键词:
- 山药总蛋白 /
- 人脐静脉内皮细胞 /
- 氧化应激 /
- 炎症反应 /
- Txnip/NLRP3信号通路
Abstract: To explored the protective effect and mechanism of Chinese yam total protein in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with high-concentration D-glucose (HG)-induced oxidative stress injury. The HUVECs injury model was established by 50 mmol/L HG. HUVECs were randomly divided into control, model, low-dose Chinese yam total protein (0.5 mg/mL), and high-dose Chinese yam total protein (1 mg/mL) groups. The effects of Chinese yam total protein on the viability, morphology, and angiogenetic ability of HUVECs treated with HG were evaluated. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities in cells were determined. The nitric oxide (NO), 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), malondialdehyde (MDA), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in culture medium supernatant were measured. Protein expression levels of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), Bcl-2-associated X (Bax), thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip), NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), cleaved Caspase-1, and IL-1β were determined. The results showed that Chinese yam total protein could significantly increased the cell viability of HUVECs treated with HG (P<0.01), improved cell apoptotic morphology, and significantly increased the activities of SOD and CAT (P<0.05, P<0.01) and ratio of apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-2/Bax), angiogenetic ability and nitric oxide (NO) secretion. Moreover, Chinese yam total protein significantly decreased the levels of ROS, MDA, 8-OHdG, IL-1β, and IL-6 (P<0.05, P<0.01) and the expression levels of inflammation-related proteins (Txnip, NLRP3, cleaved Caspase-1, and IL-1β) (P<0.05, P<0.01). Changes in these indicators showed a significant concentration-dependent manner. The results indicate that Chinese yam total protein may protect against HG-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting the Txnip/NLRP3 signaling pathway, restoring the oxidative balance, and reducing the inflammatory response of HUVECs. -
糖尿病(Diabetes mellitus,DM)是一种由糖代谢紊乱引起的、严重危害人类健康的全身性代谢疾病[1]。DM可导致血管疾病、视网膜病变、肾病和神经损伤等多种并发症,其中大血管病变是DM并发症患者致死、致残的重要原因,死亡率高达70%~80%[2]。由于内皮是位于血管内表面的单层细胞,可促进血管生成并产生活性物质,具有调节血管收缩和舒张平衡的作用,故其在维持血管稳态中发挥关键作用。然而,高血糖引起的内皮功能障碍是大血管病变发生的共同病理基础和推动剂[3−4],因此,寻找能够修复内皮损伤的功能性食品对于改善或延缓DM血管疾病具有重要意义。
山药是薯蓣科薯蓣的干燥根茎,是我国传统的药食同源佳品,含有丰富的多糖、皂苷类、氨基酸、维生素、脂肪酸等营养成分,具有抗炎、免疫调节、降血糖、抗肿瘤、抗氧化、预防心血管疾病等多种生物学功能[5−8]。山药蛋白作为山药中的有效成分,具有促进外周免疫器官的发育以及免疫活性物质的分泌表达,提高机体免疫能力等作用[9−10]。山药蛋白防治DM的研究主要是通过降低促炎细胞因子白介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(Tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)的合成,提高一氧化氮合酶(Endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)、环磷鸟嘌呤核苷(Cyclic guanosinc monophosphate,cGMP)含量,以降低内皮细胞中的活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)的水平,来改善微血管内皮细胞的生理功能[10−13],但其对大血管内皮细胞的修复作用机制尚不明确。本研究以大血管内皮细胞-人脐静脉内皮细胞(Human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs)作为研究对象,利用高浓度D-葡萄糖(High concentrations of D-glucose,HG)建立内皮细胞损伤模型,深入探究山药总蛋白对HG诱导的内皮功能障碍的保护作用,为山药防治DM相关血管疾病提供数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
山药总蛋白 蛋白含量为40%,制备参考本课题组前期方法,由长春中医药大学大健康创新中心制备[14];HUVECs 中国科学院上海细胞库;RIPA(Radio immunoprecipitation assay)裂解液(20210115)、苯甲磺酰氟(Phenylmethyl sulfonyl fuoride,PMSF) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、一氧化氮(Nitric oxide,NO)、8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(8-Hydroxy deoxyguanosine,8-OHdG)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、白介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、IL-6酶联免疫吸附(Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)试剂盒 上海优选生物科技有限公司;ROS检测试剂盒、聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯(Bicinchoninic acid,BCA)蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(092221211217)、化学发光(Efficient chemiluminescence,ECL)试剂盒、2×蛋白上样缓冲溶液(P0015B)、4,6-联脒-2-苯基吲哚(4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole,DAPI)染色液 上海碧云天公司;B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)、Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)、甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH)抗体 美国Bioworld公司;半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶剪切体-1(cleaved Caspase-1)抗体 武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司;硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白(Txnip)抗体 美国CST公司;NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)、IL-1β抗体 美国Abcam公司;F-12K培养基 武汉普诺赛生命科技有限公司;M199培养基 美国Sigma公司;Matrigel基质胶 美国Corning公司;CCK-8试剂盒 美国Bioss公司;磷酸盐缓冲溶液(Phosphate buffer saline,PBS,AH30026711) 美国HyClone公司;其余试剂均为分析纯;水 超纯水。
iBright FL 1000型智能成像系统、3111型CO2细胞培养箱、EVOS FL Auto荧光显微镜 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;Infnite 200 PRO型酶标仪 美国Life Sciences公司;Mini Protean型电泳仪 美国Bio-rad公司;TS-200型摇床 江苏其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
HUVECs用含有1%青霉素/链霉素溶液和10%胎牛血清的F-12K培养基培养,将细胞置于37 ℃培养箱中,贴壁培养2~3 d后用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化传代。使用血球计数板进行细胞计数。
1.2.2 山药总蛋白溶液制备
将山药总蛋白冻干粉末溶解于50 mmol/L HG溶液中,充分混匀后使用0.22 μm过滤器过滤除菌,实验前,使用50 mmol/L HG溶液稀释至实验所需浓度。
1.2.3 山药总蛋白对HG损伤的HUVECs的细胞存活率的影响
取处于对数生长期的HUVECs以2×104/mL细胞密度,每孔100 μL均匀铺至96孔板中,待细胞贴壁,弃去培养基,更换成F-12K基础培养基饥饿培养24 h。将细胞分为对照组(F-12K完全培养基,100 μL)、模型组(50 mmol/L HG,100 μL)和山药总蛋白组(50 mmol/L HG+0.5、1 mg/mL山药总蛋白,100 μL)培养48 h。培养结束后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,将培养板置于37 ℃培养箱中,避光条件下孵育1 h,酶标仪450 nm处测定各孔OD值,计算细胞存活率。细胞存活率计算公式如下:
细胞存活率(%)=A实验组−A空白组A对照组−A空白组×100 式中;A实验组为模型组和不同剂量山药总蛋白组测得的OD值;A对照组为正常培养液培养的细胞测得的OD值;A空白组为只加正常培养液未加细胞测得的OD值。
1.2.4 DAPI染色法观察细胞形态变化
HUVECs按“1.2.3”项下方法分组和给药后,用PBS(pH7.2,0.0067 mol/L)漂洗3次,加入4%多聚甲醛固定30 min,弃去固定液。PBS漂洗3次,加入DAPI染色液,常温下避光5 min。于倒置荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.2.5 Western Blot实验
HUVECs按“1.2.3”项下方法分组和给药后,收集各组细胞,用RIPA裂解液提取细胞总蛋白,BCA法测蛋白浓度并调整至浓度一致。每100 μL样品加2×蛋白上样缓冲液100 μL,共同煮沸5 min,利用十二烷基磺酸钠-聚丙稀酰胺凝胶电泳(Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electropheresis,SDS-PAGE)分离,湿转条件为电压110 V,90 min进行转印,转膜完毕后在5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭1 h,0.05% PBST(含有0.05%吐温的PBS)洗涤3次后,分别用Bcl-2、Bax、Txnip、NLRP3、cleaved Caspase-1、IL-1β、GAPDH一抗(稀释比例1:1000)4 ℃孵育过夜;0.05% PBST洗涤3次,加入二抗(稀释比例1:1000),室温孵育1 h;0.05% PBST洗涤3次后,利用ECL化学发光试剂在iBright FL1000成像系统中进行成像,并利用Image J软件分析灰度值。
1.2.6 血管生成实验
将Matrigel基质胶按每孔50 μL涂覆至预冷的96孔培养板底,在37 ℃培养箱中放置30 min。HUVECs按“1.2.3”项下方法分组和给药后,收集各组细胞,制备37 ℃培养箱中孵育12 h,使用倒置显微镜进行拍照并对其结节数量、管腔数、总血管长度计数。
1.2.7 活性氧水平测定
HUVECs按“1.2.3”项下方法分组和给药后,利用无血清培养基础以1:1000稀释2',7'-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(2',7'-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate,DCFH-DA),配制其终浓度为10 μmol/L。去除孔板中细胞培养基,PBS洗涤3次,加入1 mL浓度为10 μmol/L的DCFH-DA,在37 ℃细胞培养箱内孵育20 min,无血清细胞培养基洗涤细胞3次,在酶标仪488/525 nm处测定荧光强度。
1.2.8 ELISA检测试剂盒检测生化指标
HUVECs按“1.2.3”项下方法分组和给药后48 h后,3000 r/min离心10 min,收集各组细胞以及培养基的上清液,再向细胞中加入RIPA裂解液(含1 mmol/L的PMSF)150 μL,裂解5 min后12000 r/min离心10 min,取细胞裂解液。利用ELISA检测试剂盒测定细胞裂解液中的SOD、CAT活力及培养基的上清液中的NO、MDA、8-OHdG、IL-1β、IL-6的水平。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据至少进行3次生物学重复,数据均采用(¯x±s)表示,数据采用GraphPad Prism 6.0 软件中t test或One-way ANOVA方法进行统计分析,P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 山药总蛋白对HG致HUVECs损伤的保护作用
2.1.1 山药总蛋白对HG损伤模型细胞活力的影响
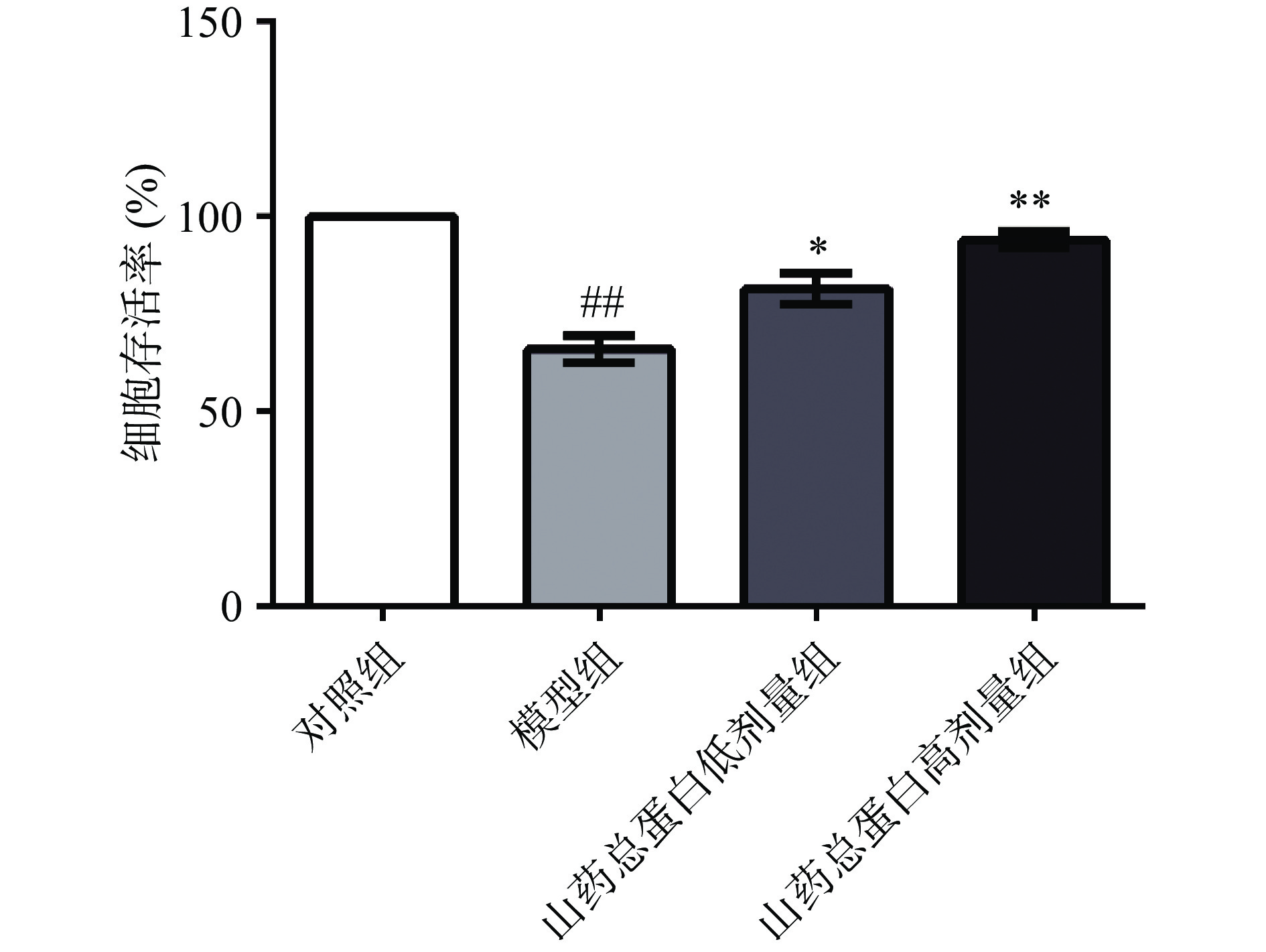
HG环境会抑制血管内皮细胞增殖并产生的过量ROS对细胞造成严重损伤,细胞活力降低。并且随着HG浓度的不断增加及培养时间的延长,细胞活力与之呈现明显的负相关[15]。如图1所示,HG处理HUVECs 48 h后,与对照组比较,模型组细胞存活率极显著降低至60.57%(P<0.01),表明造模成功;山药总蛋白低剂量组细胞存活率为85.76%,显著高于模型组(P<0.05),山药总蛋白高剂量组细胞存活率为93.78%,极显著高于模型组(P<0.01)。以上结果表明,山药总蛋白可改善HG造成的HUVECs活力降低。
2.1.2 山药总蛋白对HG损伤模型细胞凋亡的影响
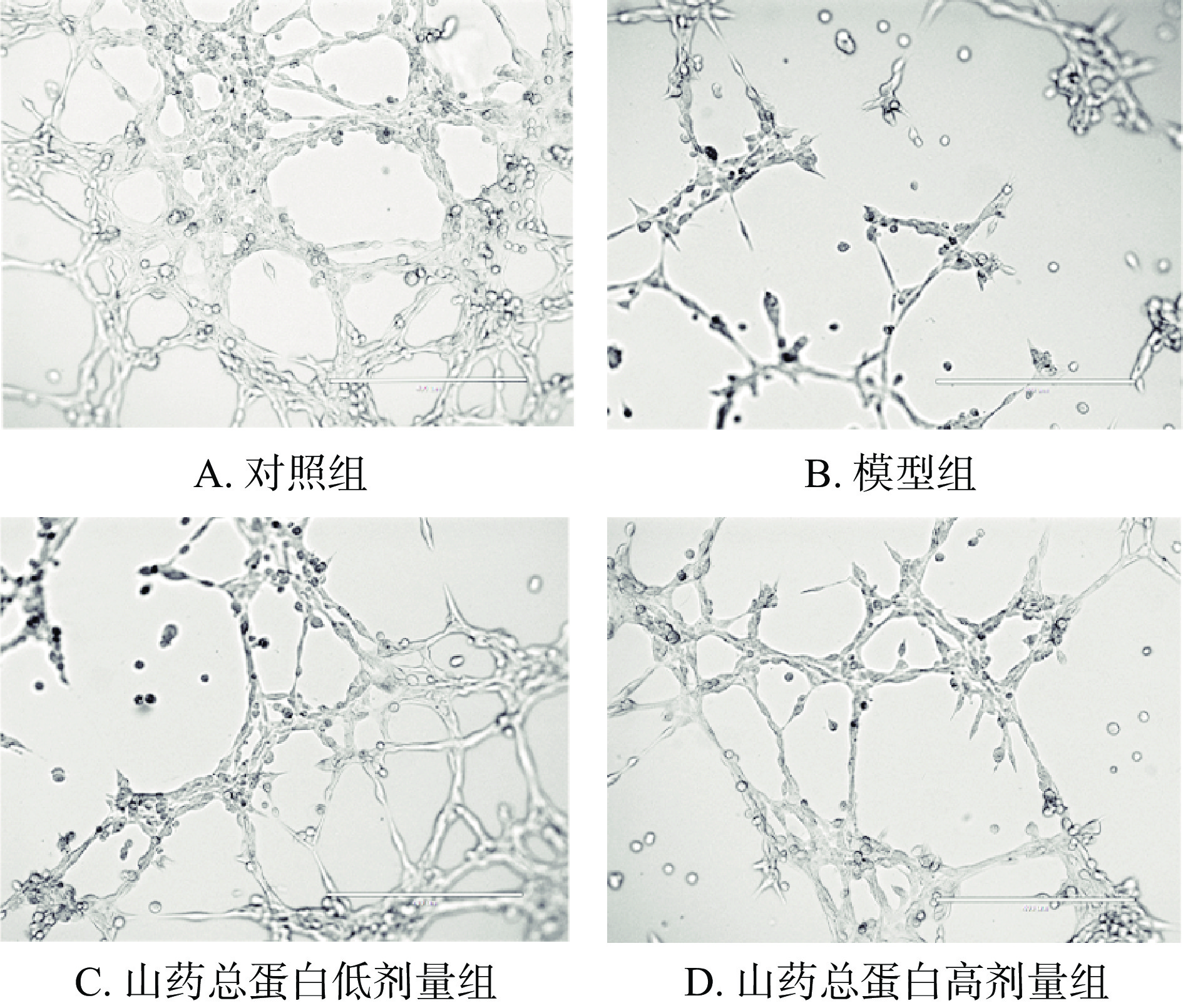
染色体DNA降解是细胞凋亡典型特征。DAPI荧光染料可穿透完整的细胞膜,与细胞内DNA强力结合,从而反应细胞的凋亡程度[16]。如图2所示,与对照组相比,模型组细胞核皱缩,体积变小呈不规则形状,核内呈现致密浓染的块状凝聚强荧光,表明HUVECs的凋亡程度增强。此外,凋亡相关蛋白Bcl-2/Bax的比值也决定了细胞凋亡[17]。由图3可知,HG诱导后HUVECs的Bcl-2的表达显著下调,Bax的表达显著上调,使Bcl-2/Bax的比值极显著降低(P<0.01),与DAPI染色的结果相一致,说明HG能显著诱导HUVECs产生凋亡。山药总蛋白干预48 h后,与模型组相比,山药总蛋白低剂量组Bcl-2/Bax的比值显著升高(P<0.05),山药总蛋白高剂量组Bcl-2/Bax的比值极显著升高(P<0.01)且呈现明显的浓度依赖性。表明山药总蛋白可抑制HG造成的HUVECs凋亡。
2.1.3 山药总蛋白对HG损伤模型中内皮功能的影响
利用体外血管形成实验模拟山药总蛋白对血管生成的影响。通过图4和表1可以明显观察到,给予山药总蛋白治疗48 h后,山药总蛋白低剂量组能够显著改善HG对HUVECs成管的结节数量、管腔数和总血管长度的抑制作用(P<0.05),山药总蛋白高剂量组能够极显著改善HG对HUVECs成管的结节数量、管腔数和总血管长度的抑制作用(P<0.01),提高HUVECs的血管生成能力。并且内皮细胞分裂以及迁移生成血管的同时可分泌NO来维持血管稳态,NO的释放量增加对维持内皮功能有着重要意义[18−19]。结果如表1所示,与对照组相比,模型组可极显著抑制NO的释放量(P<0.01),山药总蛋白作用48 h后,山药总蛋白低剂量组可显著缓解HG对HUVECs的抑制作用(P<0.05),山药总蛋白高剂量组可极显著缓解HG对HUVECs的抑制作用(P<0.01),修复HG诱导的HUVECs功能损伤。
表 1 山药总蛋白对HG损伤的HUVECs结节数量、管腔数、总血管长度以及NO分泌量的影响Table 1. Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the number of nodules and lumens, the length of total blood vessels and NO levels in HG-injured HUVECs组别 结节数量(个) 管腔数(个) 总血管长度(μm) NO(μmol/L) 对照组 489.1±74.2 37.0±5.3 15346.5±619.5 124.8±5.3 模型组 136.1±18.2## 6.4±1.3## 6474.1±900.4## 91.6±7.1## 山药总蛋白低剂量组 222.3±17.0* 16.3±1.5* 9676.1±737.7* 105.9±5.2* 山药总蛋白高剂量组 283.4±7.1** 20.7±2.1** 11630.7±1148.2** 117.7±7.9** 注:与对照组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01;与模型组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;表2~表3同。 2.2 山药总蛋白对HG诱导的HUVECs损伤的保护作用机制研究
2.2.1 对氧化应激相关因子水平的影响
HG环境下,机体对自由基的清除功能遭到破坏,平衡被打破,导致过量ROS生成,同时产生大量的MDA和8-OHdG堆积,致使细胞内抗氧化系统失衡SOD、CAT活力下降[20]。通过表2可知HG诱导48 h后,与对照组相比,模型组中的8-OHdG水平显著升高(P<0.05),ROS、MDA水平极显著升高(P<0.01),SOD和CAT活力显著降低(P<0.01)。说明HG环境可诱导HUVECs产生氧化应激反应[21]。山药总蛋白干预48 h后,与模型组相比,山药总蛋白低剂量组ROS、MDA、8-OHdG水平显著降低(P<0.05),SOD和CAT活力无显著性差异(P>0.05);山药总蛋白高剂量组ROS、MDA、8-OHdG水平极显著降低(P<0.01),SOD和CAT活力显著升高(P<0.05),表明山药总蛋白可拮抗HG诱导的氧化应激,恢复HUVECs的抗氧化系统的平衡。
表 2 山药总蛋白对HG损伤的HUVECs氧化应激水平的影响Table 2. Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the levels of oxidative stress in HG-injured HUVECs组别 ROS SOD(U/mL) CAT(U/mL) MDA(nmol/mL) 8-OHdG(pg/mL) 对照组 100.1±0.1 271.6±12.8 154.3±9.6 2.5±0.6 423.4±10.8 模型组 245.4±3.3## 222.3±8.8## 128.5±3.9## 3.5±0.2## 461.7±14.8# 山药总蛋白
低剂量组213.5±2.2* 229.3±9.8 133.1±7.4 2.9±0.1* 437.8±7.1* 山药总蛋白
高剂量组194.3±2.7** 237.8±5.3* 139.4±8.3* 2.7±0.1** 425.3±7.4** 2.2.2 对炎症相关因子水平的影响
氧化应激状态往往伴随炎症反应并产生IL-1β和IL-6等一系列炎症因子,加剧内皮细胞的功能紊乱[22]。结果如表3所示,HG诱导后,与对照组相比,模型组IL-1β水平极显著升高(P<0.01),IL-6水平显著升高(P<0.05),说明HG环境能够诱发HUVECs的炎症反应[23]。不同剂量山药总蛋白干预48 h后,与模型组相比,山药总蛋白低剂量组IL-1β水平显著降低(P<0.05),IL-6水平无显著性差异(P>0.05);山药总蛋白高剂量组IL-1β水平极显著降低(P<0.01),IL-6水平显著性降低(P<0.05),表明山药总蛋白可减少HG诱导的炎症因子的分泌,抵御氧化应激损伤,改善HUVECs的功能。
表 3 山药总蛋白对炎症相关因子水平的影响Table 3. Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the levels of inflammatory factors组别 IL-1β(pg/mL) IL-6(pg/mL) 对照组 0.39±0.02 0.36±0.02 模型组 0.48±0.05## 0.47±0.03# 山药总蛋白低剂量组 0.42±1.03* 0.45±0.13 山药总蛋白高剂量组 0.39±0.21** 0.41±0.02* 2.2.3 对炎症相关蛋白表达的影响
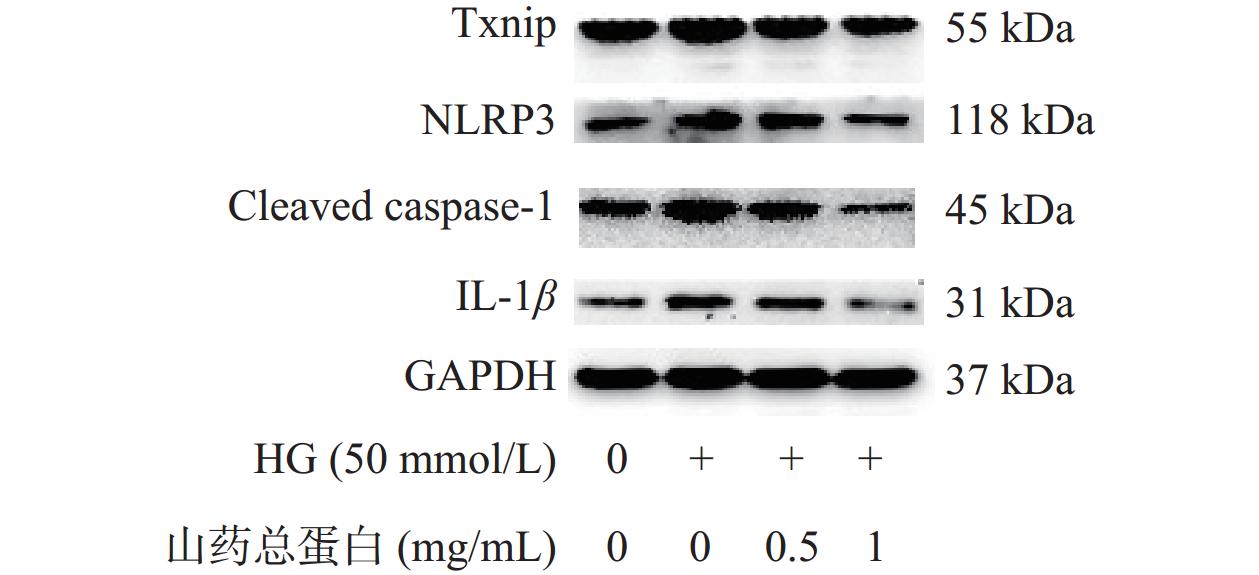
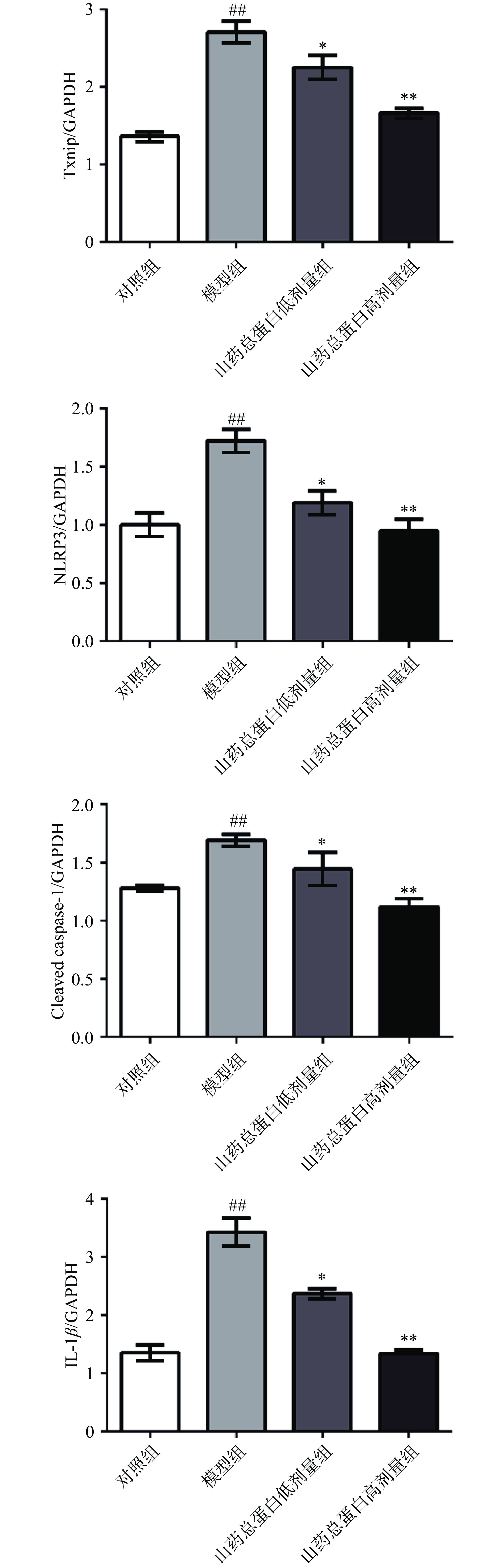
Txnip/NLRP3通路的激活与炎症反应的发生密切相关,Txnip蛋白在ROS的刺激下引起NLRP3炎性小体的活化,激活TXNIP/NLRP3通路,发挥其促炎作用[24]。由图5和图6所示,HG诱导48 h后,与对照组相比,模型组Txnip、NLRP3、Cleaved caspase-1、IL-1β蛋白表达极显著升高(P<0.01)。不同剂量山药总蛋白干预48 h后,与模型组相比,山药总蛋白低剂量组Txnip、NLRP3、Cleaved caspase-1、IL-1β蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.05);山药总蛋白高剂量组Txnip、NLRP3、Cleaved caspase-1、IL-1β蛋白表达极显著降低(P<0.01),说明山药总蛋白对HG诱导的HUVECs炎症反应的抑制作用可能与调控Txnip/NLRP3信号通路相关。
3. 讨论与结论
长期以来,内皮功能障碍与DM血管并发症的关系一直是学者研究的热点之一,DM引起的内皮细胞的结构及功能变化都可能影响血管疾病的发病进程。已有研究发现,可修复内皮细胞功能的天然产物在DM血管并发症的预防和治疗领域具有广阔的前景[25]。
HG损伤模型能模拟DM大血管疾病病理情况下的细胞状态,是DM大血管内皮功能障碍的经典细胞模型。因此,本研究以HG诱导的HUVECs氧化应激损伤建立体外研究模型,探讨山药总蛋白对HG诱导的内皮细胞氧化损伤的保护机制。结果表明,山药总蛋白可显著改善HG诱导所致的HUVECs活力降低。细胞凋亡是由多种因子或蛋白参与的复杂的病理生理过程,其中抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2与促凋亡蛋白Bax相互作用失衡是启动细胞凋亡的重要开关[26],当细胞收到凋亡信号后,Bcl-2和Bax通过形成同源二聚体引起Bcl-2抑制,从而促进细胞凋亡。本研究的结果表明,山药总蛋白能够增加凋亡相关蛋白Bcl-2/Bax的比值,并减弱DAPI染色的HUVECs的蓝色荧光强度,降低HUVECs凋亡,减少细胞损伤,进一步提升内皮细胞的抗氧化应激能力,增强对DM大血管相关疾病的抵抗力。
内皮细胞最重要的功能是维持血管稳态,是血管的第一防线。一方面,内皮细胞通过分裂及迁移生成血管,在胚胎生长、子宫内膜增殖、伤口愈合、组织修复等生理过程发挥着关键作用[27−28]。另一方面,内皮细胞通过分泌多种生物活性物质(如NO)确保血管正常的收缩和舒张[29−30]。本研究发现,HG损伤后细胞血管样结构的形成能力以及NO的释放量显著降低,表明HG诱导下HUVECs发生了内皮功能障碍。山药总蛋白干预后,HUVECs血管生成能力及NO的水平显著提高。以上结果说明,山药总蛋白对HG诱导的内皮功能障碍具有明显的保护作用。
DM患者在高血糖刺激下,血管内皮细胞发生严重的氧化应激,造成体内抗炎因子和促炎因子表达失衡,引起炎症损伤,导致内皮功能障碍。因此减轻氧化应激和炎症反应是改善DM患者内皮功能障碍的有效策略[31−33]。Txnip/NLRP3信号是很有前景的DM血管疾病治疗靶点。研究表明,Txnip是ROS的重要调节剂:其启动子上的碳水化合物反应元件结合蛋白(ChREBP)易被高血糖激活而使表达量上调,诱导ROS过量产生,通过合成脂质过氧化物MDA、抑制抗氧化酶SOD和CAT活性、刺激氧化应激标志物8-OHdG生成等方式诱发氧化应激[34−36]。此外,Txnip表达升高是激活NLRP3炎症小体的重要机制,炎症小体复合物的组装是引发炎症反应的关键环节[37−38]。研究表明,Txnip激活后,促进NLRP3与接头蛋白(ASC)相互作用,招募胞内Caspase-1前体组装成炎症小体复合物,同时激活Caspase-1,剪切胞浆中pro-IL-1β、pro-IL-6,诱导具有促炎功能的IL-1β、IL-6成熟和分泌,发生炎症反应[39−40]。因此,抑制Txnip/NLRP3信号通路是阻滞内皮细胞氧化应激和炎症反应,进而修复内皮功能的关键。本研究通过HG诱导后发现细胞中氧化应激产物ROS、MDA和8-OHdG水平增加,抗氧化酶SOD和CAT活力降低,细胞中炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6水平升高,发现是HG的诱导使HUVECs发生了氧化应激和炎症反应,最终造成内皮细胞损伤。同时Txnip、NLRP3、Caspase-1、IL-1β蛋白表达量的显著升高,表明了HG诱导的HUVECs氧化损伤的过程加重了炎症反应。山药总蛋白干预后,上述指标均得到了显著改善,说明山药总蛋白可拮抗HG诱导的HUVECs氧化应激损伤和炎症反应,这种作用可能与山药总蛋白对Txnip/NLRP3信号通路的抑制有关,未来还需深入研究来验证这一推测。
与过往对DM采用的抑制P38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的治疗方式不同[41−42],本研究利用HG环境建立的体外HUVECs氧化应激损伤模型,验证了山药总蛋白对大血管内皮细胞的修复作用,证实了山药总蛋白能有效抑制HG诱导的HUVECs氧化应激损伤,提高细胞中抗氧化酶的活力,降低促炎因子分泌及细胞炎症,改善HUVECs的细胞形态及生理功能。此外,本研究对山药总蛋白在功能性食品开发及DM相关疾病的治疗领域奠定了实验基础,并为进一步探索山药总蛋白在抑制Txnip/NLRP3信号通路方面的相关研究提供了理论支持。
-
表 1 山药总蛋白对HG损伤的HUVECs结节数量、管腔数、总血管长度以及NO分泌量的影响
Table 1 Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the number of nodules and lumens, the length of total blood vessels and NO levels in HG-injured HUVECs
组别 结节数量(个) 管腔数(个) 总血管长度(μm) NO(μmol/L) 对照组 489.1±74.2 37.0±5.3 15346.5±619.5 124.8±5.3 模型组 136.1±18.2## 6.4±1.3## 6474.1±900.4## 91.6±7.1## 山药总蛋白低剂量组 222.3±17.0* 16.3±1.5* 9676.1±737.7* 105.9±5.2* 山药总蛋白高剂量组 283.4±7.1** 20.7±2.1** 11630.7±1148.2** 117.7±7.9** 注:与对照组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01;与模型组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;表2~表3同。 表 2 山药总蛋白对HG损伤的HUVECs氧化应激水平的影响
Table 2 Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the levels of oxidative stress in HG-injured HUVECs
组别 ROS SOD(U/mL) CAT(U/mL) MDA(nmol/mL) 8-OHdG(pg/mL) 对照组 100.1±0.1 271.6±12.8 154.3±9.6 2.5±0.6 423.4±10.8 模型组 245.4±3.3## 222.3±8.8## 128.5±3.9## 3.5±0.2## 461.7±14.8# 山药总蛋白
低剂量组213.5±2.2* 229.3±9.8 133.1±7.4 2.9±0.1* 437.8±7.1* 山药总蛋白
高剂量组194.3±2.7** 237.8±5.3* 139.4±8.3* 2.7±0.1** 425.3±7.4** 表 3 山药总蛋白对炎症相关因子水平的影响
Table 3 Effect of Chinese yam total protein on the levels of inflammatory factors
组别 IL-1β(pg/mL) IL-6(pg/mL) 对照组 0.39±0.02 0.36±0.02 模型组 0.48±0.05## 0.47±0.03# 山药总蛋白低剂量组 0.42±1.03* 0.45±0.13 山药总蛋白高剂量组 0.39±0.21** 0.41±0.02* -
[1] TERENTES D, IOAKEIMIDIS N, ROKKAS K, et al. Interactions between erectile dysfunction, cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular drugs[J]. Nature Reviews Neurology,2022,19(1):59−74.
[2] 杨华, 刘云涛. 血清脂肪细胞脂肪酸结合蛋白与2型糖尿病大血管病变的相关性研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2014,22(9):784−786. [YANG H, LIU Y T. The correlation between serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein and macroangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes,2014,22(9):784−786.] YANG H, LIU Y T. The correlation between serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein and macroangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes, 2014, 22(9): 784−786.
[3] MICHIELS C. Endothelial cell functions[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2003,196(3):430−443. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10333
[4] YUAN T, YANG T, CHEN H, et al. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis[J]. Redox Biology,2019,20:247−260. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.09.025
[5] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia [M]. Beijing:China Medical Science Press, 2020.] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020.
[6] 杨雁, 孙羽灵, 孙建梅, 等. 山药活性成分药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2022, 41(12):55−60. [YANG Y, SUN Y L, SUN J M, et al. Progress on pharmacological effects of active ingredients in Chinese Yam[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2022, 41(12):55−60.] YANG Y, SUN Y L, SUN J M, et al. Progress on pharmacological effects of active ingredients in Chinese Yam[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2022, 41(12): 55−60.
[7] 崔艺钒, 张璐佳, 丰宇, 等. 山药活性成分及营养功能研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(7):372−383. [CUI Y F, ZHANG L J, FENG Y, et al, Research progress on active components and nutritional functions of Chinese yam[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(7):372−383.] CUI Y F, ZHANG L J, FENG Y, et al, Research progress on active components and nutritional functions of Chinese yam[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(7): 372−383.
[8] 陈梦雨, 刘伟, 侴桂新, 等. 山药化学成分与药理活性研究进展[J]. 中医药学报,2020,48(2):62−66. [CHEN M Y, LIU W, CHOU G X, et al. Research progress on cemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Dioscorea opposita thunb[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology,2020,48(2):62−66.] CHEN M Y, LIU W, CHOU G X, et al. Research progress on cemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Dioscorea opposita thunb[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2020, 48(2): 62−66.
[9] 樊乃境, 王冬梅, 高悦, 等. 山药蛋白肽对免疫能力低下小鼠的免疫调节作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(6):101−107. [FAN N J, WANG D M, GAO Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of the iron yam peptides on mice with immunocompromised[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(6):101−107.] FAN N J, WANG D M, GAO Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of the iron yam peptides on mice with immunocompromised[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(6): 101−107.
[10] 李懿轩, 赵大庆, 王思明, 等. PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路介导山药蛋白对肾阳虚大鼠阴茎勃起功能障碍的改善作用[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(24):2607−2611. [LI Y X, ZHAO D Q, WANG S M, et al. PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway mediated the amelioration effect of Chinese yam protein on penile erectile dysfunction in kidney-yang deficiency rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2022,42(24):2607−2611.] LI Y X, ZHAO D Q, WANG S M, et al. PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway mediated the amelioration effect of Chinese yam protein on penile erectile dysfunction in kidney-yang deficiency rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2022, 42(24): 2607−2611.
[11] LEE W, JEONG S Y, GU M J, et al. Inhibitory effects of compounds isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne peel on particulate matter-induced pulmonary injury in mice[J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A,2019,82(12):727−740. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2019.1646174
[12] WANG L S, BAI Y Y, YANG Y, et al. Diabetes mellitus stimulates pancreatic cancer growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated metastasis via a p38 MAPK pathway[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(25):38539−38550. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9533
[13] 邢欣, 赵大庆, 王思明, 等. 基于转录组测序技术分析山药蛋白防治糖尿病性勃起功能障碍的作用机制[J]. 中国药房,2021,32(23):2859−2868. [XING X, ZHAO D Q, WANG S M, et al. Analysis of the mechanism of yam protein in the prevention and treatment of diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction based on RNA-Seq technology[J]. China Pharmacy,2021,32(23):2859−2868.] XING X, ZHAO D Q, WANG S M, et al. Analysis of the mechanism of yam protein in the prevention and treatment of diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction based on RNA-Seq technology[J]. China Pharmacy, 2021, 32(23): 2859−2868.
[14] 韩冰, 赵大庆, 白雪媛, 等. 山药总蛋白对大鼠睾丸损伤后生精功能的修复[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报, 1−9[2024-03-07]. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2020.6070. [HAN B, ZHAO D Q, BAI X Y, et al. Yam total protein for repairing testicular spermatogenic injury in rats[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 1−9[2024-03-07]. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2020.6070.] HAN B, ZHAO D Q, BAI X Y, et al. Yam total protein for repairing testicular spermatogenic injury in rats[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 1−9[2024-03-07]. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2020.6070.
[15] 谢利亚, 张虹, 陆吴霞, 等. 黄芪甲苷通过SIRT1/AMPK抑制高糖诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞衰老[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志,2023,33(3):225−229. [XIE L Y, ZHANG H, LU W X, et al. Astragaloside IV inhibits high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell senescence through activation of the SIRT1/AMPK signaling[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,2023,33(3):225−229.] XIE L Y, ZHANG H, LU W X, et al. Astragaloside IV inhibits high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell senescence through activation of the SIRT1/AMPK signaling[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2023, 33(3): 225−229.
[16] 朱澂, 林辰涛. 一种新型的DNA荧光染料—DAPI的光学特性及其应用[J]. 武汉植物学研究,1986(1):91−102. [ZHU C, LIN C T. Optical proterties and applications of a new DNA fluochrome 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylndole[J]. Plant Science Journal,1986(1):91−102.] ZHU C, LIN C T. Optical proterties and applications of a new DNA fluochrome 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylndole[J]. Plant Science Journal, 1986(1): 91−102.
[17] 高赛红, 张小良, 杨迎春, 等. 聚肌苷酸聚胞苷酸对高血脂大鼠脑缺血/再灌注后Bcl-2和Bax表达的影响及神经保护作用[J]. 解剖学报, 2023, 54(2):175−180. [GAO S H, ZHANG X L, YANG Y C, et al. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid affecting the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in hyperlipidemic rats and its neuroprotective effect[J]. Acta Anatomica Sinica, 2023, 54(2):175−180.] GAO S H, ZHANG X L, YANG Y C, et al. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid affecting the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in hyperlipidemic rats and its neuroprotective effect[J]. Acta Anatomica Sinica, 2023, 54(2): 175−180.
[18] HEIN T W, OMAE T, XU W, et al. Role of arginase in selective impairment of endothelium-dependent nitric oxide synthase-mediated dilation of retinal arterioles during early diabetes[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science,2020,61(5):36.
[19] 章玉兰, 王梅, 叶文凤. 硝苯地平治疗妊娠期高血压的有效性及对患者内皮功能和妊娠结局的影响[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2023,7(8):139−141. [ZHANG Y L, WANG M, YE W F. Efficacy of nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension in pregnancy and its effect on endothelial function and pregnancy outcome in patients[J]. Modern Medicine and Health Research Electronic Journal,2023,7(8):139−141.] ZHANG Y L, WANG M, YE W F. Efficacy of nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension in pregnancy and its effect on endothelial function and pregnancy outcome in patients[J]. Modern Medicine and Health Research Electronic Journal, 2023, 7(8): 139−141.
[20] LI H L, TANG Z Y, CHU P, et al. Neuroprotective effect of phosphocreatine on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo:Involvement of dual PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2018,120:228−238. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.014
[21] 江颖娟, 蒋作锋, 岑俊林, 等. 槲皮素预处理高糖环境培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞氧化应激、内质网应激反应观察[J]. 山东医药,2022,62(6):39−43. [JIANG Y J, JIANG Z F, CEN J L, et al. Effects of quercetin on oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by high glucose[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2022,62(6):39−43.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2022.09.009 JIANG Y J, JIANG Z F, CEN J L, et al. Effects of quercetin on oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by high glucose[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2022, 62(6): 39−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2022.09.009
[22] 吴俊荣, 张嘉琳, 吕贵东, 等. 瓜蒌皮提取物通过调控NQO1对高糖诱导的人肾小管上皮细胞炎症因子表达的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(8):1585−1589. [WU J R, ZHANG J L, LÜ G D, et al. Effect of pericarpium trichosanthis extract on expressions of inflammatory factors in human renal tubular epithelial cells induced by high glucose by regulating NQO1[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology,2023,39(8):1585−1589.] WU J R, ZHANG J L, LÜ G D, et al. Effect of pericarpium trichosanthis extract on expressions of inflammatory factors in human renal tubular epithelial cells induced by high glucose by regulating NQO1[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2023, 39(8): 1585−1589.
[23] 黄柳慧. 糖肾宝对高糖培养小鼠肾脏内皮细胞Fli-1表达的影响[D]. 南宁:广西中医药大学, 2020. [HUANG L H. Effect of Sugar Nephro on the expression of Fli-1 in renal endothelial cells of mice cultured with high glucose[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.] HUANG L H. Effect of Sugar Nephro on the expression of Fli-1 in renal endothelial cells of mice cultured with high glucose[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[24] LU L, LU Q, CHEN W, et al. Vitamin D3 protects against diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting high-glucose-induced activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway[J]. Journal of Diabetes Resarch,2018,2018:8193523.
[25] KOCAMAN G, ALTINOZ E, ERDEMLI ME, et al. Crocin attenuates oxidative and inflammatory stress-related periodontitis in cardiac tissues in rats[J]. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2021,30(5):517−524. doi: 10.17219/acem/133753
[26] 李攀登, 王永红, 肖芸, 等. 氢醌对人白血病细胞凋亡及相关蛋白Bcl-2、Bax及Caspase-3表达的影响[J]. 现代预防医学,2018,45(5):878−882. [LI P D, WANG Y H, XIAO Y, et al. Effects of hydroquinone on apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 in human leukemia cells[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2018,45(5):878−882.] LI P D, WANG Y H, XIAO Y, et al. Effects of hydroquinone on apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 in human leukemia cells[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2018, 45(5): 878−882.
[27] AZIZ N S, YUSOP N, AHMAD A. Importance of stem cell migration and angiogenesis study for regenerative cell-based therapy:A review[J]. Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy,2020,15(3):284−299.
[28] ZHANG Y, WANG S, CHEN X, et al. Liraglutide prevents high glucose induced HUVECs dysfunction via inhibition of PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2022,545:111560. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111560
[29] LI C Y, WANG L X, DONG S S, et al. Phlorizin exerts direct protective eeffects on palmitic acid (PA)-induced endothelial dysfunction by activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway and increasing the levels of nitric xxide (NO)[J]. Medical Science Monitor Basic Research,2018,24:1−9. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.907775
[30] WILSON A J, GILL E K, ABUDALO R A, et al. Reactive oxygen species signalling in the diabetic heart:Emerging prospect for therapeutic targeting[J]. Heart,2018,104(4):293−299. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2017-311448
[31] FEILLET C C, FOURET G, VIGOR C, et al. Long-term measures of dyslipidemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat/high-fructose diet[J]. Lipids,2019,54(1):81−97. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12128
[32] FORBES J M, COOPER M E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications[J]. Physiological Reviews,2013,93(1):137−188. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
[33] SHARMA D, KANNEGANTI T D. The cell biology of inflammasomes:Mechanisms of inflammasome activation and regulation[J]. Journal of Cell Biology,2016,213(6):617−629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201602089
[34] DOMINGUETI C P, DUSSE L M, CARVALHO M, et al. Diabetes mellitus:The linkage between oxidative stress, inflammation, hypercoagulability and vascular complications[J]. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications,2016,30(4):738−745. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.12.018
[35] VALLANCE P, CHAN N. Endothelial function and nitric oxide:Clinical relevance[J]. Heart,2001,85:342−350. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.3.342
[36] RAMUS S M, CILENSEK I, PETROVIC M G, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the Trx2/TXNIP and TrxR2 genes of the mitochondrial thioredoxin antioxidant system and the risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications,2016,30(2):192−198. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.11.021
[37] LÜ H, ZHU C, WEI W, et al. Enhanced Keap1-Nrf2/Trx-1 axis by daphnetin protects against oxidative stress-driven hepatotoxicity via inhibiting ASK1/JNK and Txnip/NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Phytomedicine,2020,71:153241. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153241
[38] FAN Z, YANG J, YANG C, et al. MicroRNA-24 attenuates diabetic vascular remodeling by suppressing the NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine,2020,45(5):1534−1542.
[39] SHARMA B R, KANNEGANTI T D. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases[J]. Nature Immunology,2021,22(5):550−559. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00886-5
[40] FENG S, FOX D, MAN S M. Mechanisms of gasdermin family members in inflammasome signaling and cell death[J]. Journal of Molecular Bilogy,2018,430(18PtB):3068−3080.
[41] 张超. 四妙勇安汤对糖尿病大鼠肢体缺血的治疗作用及对Akt、p38MAPK通路的影响[D]. 北京:首都医科大学, 2014. [ZHANG C. Therapeutical effect of simiaoyongan recipe on diabetic rats of limb ischemia via Akt and p38MAPK signal pathways[D]. Beijing:Capital Medical University, 2014.] ZHANG C. Therapeutical effect of simiaoyongan recipe on diabetic rats of limb ischemia via Akt and p38MAPK signal pathways[D]. Beijing: Capital Medical University, 2014.
[42] 孙艳. LncRNA HOTTIP通过调节p38-MAPK信号通路来促进糖尿病视网膜病变[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2019. [SUN Y. LncRNA hottip promotes diabetic retinopathy by regulating p38-MAPK sognaling pathways[D]. Jinan:Shandong University, 2019.] SUN Y. LncRNA hottip promotes diabetic retinopathy by regulating p38-MAPK sognaling pathways[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 史文锦,刘仁慧. 山药在糖尿病及其并发症治疗中的作用机制研究进展. 山东医药. 2025(01): 144-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



