Progress on the Extraction, Structure Characterization and Bioactivity of Schisandra chinensis Polysaccharides
-
摘要: 五味子是木兰科植物五味子(Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill),或华中五味子(Schisandra sphenanchera Rehd. etWils.)的干燥成熟果实,富含多糖、木脂素、挥发油、多酚等多种活性成分。多糖作为其主要的活性成分,提取工艺有双水相萃取、酶解法、超声法、微波法、超声微波协同、微波酶法协同、水提法等,其中双水相萃取效率最高,超声法和水提法应用最广泛。五味子多糖主要由鼠李糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖、阿拉伯糖和半乳糖醛酸组成,平均分子量大致范围在103~105 Da。现代药理学研究表明,五味子多糖具有显著的抗氧化、免疫调节、抗肿瘤、保肝、降血糖、血脂等功效,在食品、医药领域高值化开发具有重要的意义。因此,本文对近年来国内外五味子多糖提取工艺、结构特征和生物活性及其相关机制进行系统总结,并对其研究方向与应用前景进行展望,以期为五味子深入研究和应用开发提供参考。Abstract: Schisandra chinensis refers to the dried mature fruit of the plant Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill from the Magnoliaceae family, or Schisandra sphenanchera Rehd. etWils. It is rich in various active components such as polysaccharides, lignans, volatile oils, and polyphenols. Polysaccharides, as its main active ingredients, are extracted by biphasic extraction, enzymatic method, ultrasonic method, microwave method, ultrasonic-microwave synergy, microwave-enzymatic synergy, and aqueous extraction, among which biphasic extraction has the highest efficiency, and ultrasonic and aqueous extraction are the most widely used methods. Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides are mainly composed of rhamnose, mannose, glucose, galactose, arabinose and galacturonic acid, and the average molecular weight roughly ranges from 103~105 Da. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides have significant antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antitumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering efficacy, and they are of significant significance for the development of high-value in the field of food and medicine. Therefore, this paper systematically summarizes the extraction process, structural characteristics and biological activities of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides and their related mechanisms at home and abroad in recent years, and looks forward to its research direction and application prospects, with a view to providing reference for the in-depth research and application development of Schisandra chinensis.
-
Keywords:
- Schisandra chinensis /
- polysaccharide /
- extraction process /
- structure /
- biological activity
-
五味子是木兰科植物五味子(Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.)Baill),或华中五味子(Schisandra sphenanchera Rehd. etWils.)的干燥成熟果实,前者习称“北五味子”,后者习称“南五味子”,是我国传统的药食同源植物(图1)。唐代《新修本草》记载“五味皮肉甘酸,核中辛苦,都有咸味”,故有五味子之名。五味子广泛分布于中国、俄罗斯远东地区以及朝鲜、日本等地[1−3]。《中华人民共和国药典》(2020版)记载五味子作为一种药食同源的植物,具有收敛固涩,益气生津,补肾宁心的功效,可用于久嗽虚喘,梦遗滑精,遗尿尿频,久泻不止,自汗盗汗,津伤口渴,内热消渴,心悸失眠等病症。
五味子含有蛋白质、脂质、维生素C等营养物质,同时还含有多糖、木脂素、挥发油、多酚等活性物质。现代药理学表明五味子具有抗氧化、抗炎、保肝、镇静、抗衰老等功效。其中多糖因其特殊的结构以及丰富的生物活性和保健作用而受到广大研究者青睐。五味子多糖主要由鼠李糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖、阿拉伯糖和半乳糖醛酸组成[4],具有显著的抗氧化、免疫调节、抗肿瘤、保肝、降血糖、血脂等生物活性[5−9]。目前五味子多糖的研究主要集中在药物活性和物化特性方面,其在保健品、食品领域的应用潜力也在不断发掘。因此本文对五味子多糖的提取工艺、结构特征和生物活性及其相关机制进行综述,旨在为五味子多糖的深入研究和在食品、保健品领域的应用开发提供理论支撑。
1. 五味子多糖提取方法
五味子是药食同源的常用滋补性中药,基于提取效率、经济、时间、能耗等层面考虑,五味子多糖提取方法、工艺优化研究一直是研究的热点。多糖的提取因其种类的多样性、结构组成的复杂性以及多糖分子量大、极性大的特点,给其分离纯化带来了很大困难。五味子果实中多糖含量高,活性强,大多学者以果实为原料提取多糖。一般干果在多糖提取前需要用95%乙醇或30~60 ℃石油醚索氏提取作脱脂预处理。本部分概括了近年来对五味子多糖提取的方法。
1.1 双水相萃取
双水相萃取是基于两种互不相溶的溶剂(一般是有机溶剂和水)形成两个不同的相,并利用两相之间的分配和分离效应实现目标物质的提取方法[10]。李化等[11]基于Box-Behnken响应面法优化五味子多糖的PEG6000-K2HPO4双水相提取工艺,得到最佳工艺:药液量5 mL,K2HPO4用量1.0 g,PEG6000用量1.8 g,提取率达64.38%±2.42%。同时K2HPO4相可以抑制不纯蛋白质的溶解,PEG6000相可以提高五味子多糖的稳定性。此方法提取率远远高于传统提取方法,但继续寻找最优提取条件、对溶剂选择和溶剂耗费等问题进行优化极为重要。
1.2 酶辅助提取
酶是具有高度特异性和催化活性的蛋白质或者RNA,可以在相对温和的条件下促进特定化学反应的进行[12]。可成友等[13]通过酶解法对五味子多糖提取工艺进行优化,最佳工艺条件为:1%的纤维素酶,提取3 h,温度55 ℃,缓冲液pH为6.0,多糖得率达14.87%。宋海燕等[14]利用响应面法优化纤维素酶提取五味子多糖工艺,最佳提取条件为:酶解温度65 ℃,酶解时间为2.98 h,提取液pH7.98,酶用量2.06%,料液比1:40(g/mL),药材粒径80目,此条件下多糖提取率为19.38%,比传统的水提醇沉法提高了50%以上。五味子多糖酶法提取大多使用纤维素酶、果胶酶和木瓜蛋白酶。酶的催化活性易受到温度、pH等条件的影响,需要进行精确的控制和调节以最大程度保持酶的活性,因此酶的选择和优化需要一定的研究和开发。
1.3 超声辅助提取
超声波辅助提取是一种利用超声波在液体中产生的机械效应、热效应和空化效应[15−16]来促进目标物质的提取的方法。张莹等[17]利用超声技术提取五味子多糖,得到最优工艺:提取温度100 ℃、液料比10:1,提取时间3 h,醇沉浓度80%,平均得率9.35%。谭晓虹等[18]利用正交法优化多糖提取工艺,得到最佳条件为:提取时间40 min,浸泡时间90 min,固液比1:25,多糖平均提取率为11.07%。超声辅助提取多糖的实验发现:超声功率对提取率影响最大,其次为温度。随着功率增大,多糖得率呈现先增后减的趋势。得率下降是因为超声较强的机械剪切作用,破坏了多糖结构。
1.4 微波辅助提取
微波辅助提取是利用高频电磁波穿透使细胞破裂,使胞内有效成分快速流出与有机溶剂相结合的一种方法[19]。程振玉等[20]设计正交试验优化五味子多糖微波提取工艺,得到最优条件为:料液比1:15(g/mL)、温度100 ℃、时间25 min、功率900 W,多糖得率为20.08%。该方法通常和其他提取方法如酶法、浸提法相结合,同时提取时需要综合考虑样品特性、提取要求以此来更好地保留多糖的生物活性。
1.5 超声-微波协同提取
超声-微波提取将超声波与微波结合,通过两者的协同作用来促进目标物质的提取[21]。Zhang等[22]基于Box-Behnken响应面法,利用超声-微波协同作用提取五味子多糖,确定最佳提取工艺:提取温度65 ℃,微波功率550 W,超声波功率60 W,时间15 min,料液比1:25,在此条件下多糖提取率为13.23%。宋海燕等[23]研究超声-微波协同法提取北五味子多糖的工艺条件,最优工艺为:温度100 ℃,提取时间80 min,微波功率600 W,料液比1:40,药材粒径80目,多糖提取率为11.68%。这种方法充分利用超声波和微波的物理效应,能够加速多糖的提取速度,有效提高多糖得率。
1.6 微波辅助酶法提取
微波辅助酶法提取是一种将微波辐射技术与酶法提取技术相结合的方法,用于从植物材料、动物组织等生物样品中提取目标活性成分[24]。Cheng等[25]建立一种微波辅助酶提取法,采用响应面和正交试验设计优化得出的最优工艺条件为:温度48 ℃,pH4.8,纤维素酶、果胶酶和木瓜蛋白酶的酶用量为1.5%,微波时间10 min,此条件下多糖提取率为7.38%±0.21%。薛俊礼等[26]设计正交试验和响应面优化试验对复合酶的组成和微波辅助复合酶法提取多糖的工艺条件进行优化,得到最优条件为:由1%纤维素酶、2%木瓜蛋白酶和2%的果胶酶组成复合酶,酶解时间1.2 h,酶解温度58 ℃,微波辐射时间10 min,pH4.0,多糖平均得率为14.87%。然而,微波加热会造成温度分布不均匀,可能导致部分区域的温度过高或过低,使酶的活性受到影响,存在酶失活的风险。此外,微波辐射对一些底物可能产生化学或物理的影响,导致底物结构的改变或损坏。
1.7 热水浸提法
热水浸提作为一种传统的多糖提取工艺,易受组分的化学性质、浸提条件和杂质影响。Zhao等[27]对200 g五味子沸水提取3次,每次3 h,4 ℃下80%乙醇沉淀,离心,冻干,得到23 g多糖。唐静等[28]研究响应面法优化五味子多糖提取工艺,得出最优条件为:提取时间3 h,液固比20:1,提取温度75 ℃,多糖提取率为3.14%。许梦然等[29]通过正交分析法优化五味子多糖水提工艺,得到最优条件为料液比1:40,提取3次,提取时间3.0 h,提取温度为90 ℃,此条件下多糖最高得率为10.72%。通常热水浸提的温度在75~90 ℃,提取时间3~9 h,以确保多糖一定的提取率和保留活性成分。
表1对五味子多糖的7种提取方法的优缺点、多糖得率进行总结对比。目前五味子多糖提取工艺主要有双水相萃取、酶解法、超声法、微波法、超声微波协同、微波酶法协同、水提法等。主旨都是在提取过程中避免多糖降解失活。随着科学技术的发展及社会需求,五味子多糖提取工艺更趋向于工业化、商业化,传统提取方法显然达不到要求,需要创新出更多新兴技术。
表 1 五味子多糖不同提取方法的优缺点比较Table 1. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of different extraction methods序号 提取方法 优点 缺点 多糖得率 参考文献 1 双水相萃取 适用范围广
选择性强
操作简便
提取效果好溶剂选择受限
溶剂耗费大64.38% [11] 2 酶辅助 反应条件温和
高选择性
环境友好
可再利用价格昂贵
反应对象单一
反应条件难控制14.87%~
19.38%[13-14] 3 超声辅助 提取效率高
节省时间
作用温和能量消耗大
设备昂贵、成本高1.107%~
9.35%[17-18] 4 微波辅助 高效节能
节省时间
操作简单加热均匀性差
多糖结构易破坏20.08% [20] 5 超声-微波
联合省时高效节能
工业化前景广阔设备昂贵
成本能耗较大11.68%~
13.23%[22-23] 6 微波-酶 节省时间
提取效率更高设备成本较高
温度控制困难
可能造成样品变性7.38%~
14.87%[25-26] 7 热水浸提 操作简单
条件温和
对多糖结构友好耗时长
提取率较低
产物纯度低3.14%~
10.72%[27-29] 2. 五味子多糖结构
不同的提取纯化方法会导致多糖的结构和性质存在差异。多糖的生物活性与其分子量、单糖组成、糖苷键连接方式以其主侧链基本构型等有紧密的相关性,其结构复杂、生物活性强,因此探究植物多糖的结构对研究其生物活性及潜在的构效关系十分重要[30]。五味子多糖的主要结构特征(单糖组成、生物活性、分子量、结构特征)见表2。
表 2 五味子多糖结构特征Table 2. Structural characteristics of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides序号 多糖名称 单糖组成 生物活性 分子量(Da) 结构特征 参考文献 1 SSPW1 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶
Glc=13.52∶5.69∶3.92∶
41.28∶35.59抗氧化
降血糖1.91×105 蛋白质∶中性糖∶糖醛酸=48.92%∶42.83%∶5.56% [5] 2 SSPP11 Man∶Gal∶Glc=
1∶1.29∶1.77抗氧化 5.30×103 T-D-Manp(1→, →1)-D-Man-(6→, T-D-Glup(1→, T-D-Galp(1→, →1)-D-Manp-(2→, →1)-D-Glup(4→, →1)-D-Glup-(6→, →1)-D-Galp-(4→, →1)-D-Galp-(4,6→ and →1)-D-Manp-(3,6→ 其比例为1.1∶4.8∶6.2∶5.2∶4.8∶15.4∶21.6∶20.8∶1∶11.4 [27] 3 SCPP22 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶Xyl=3.04∶1.21∶2.91∶
11.37∶100.67∶1.00免疫调节 14.30×104 主链:1,4-α-D-Glup
侧链:通过O-6与主链的1,4-β-D-Glup连接(由T-α-D-Galp组成)[31] 4 SCFP-1 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶Rib∶Xyl=2.7∶133.6∶1∶
1.4∶302.2∶11.9∶1.7镇咳 3.18×104 碳水化合物∶糖醛酸=96.9%∶14.2% [32] 5 SCP
SSPSSP
Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=22.3∶34.6∶15.0∶11.5
SCP
Man∶Gal∶Glc=
11.7∶8.6∶67.6∶免疫调节
1.70×104
1.70×105SCP/SSP
糖:78.45%;51.04%
蛋白质:12.55%;35.35%
糖醛酸:4.78%;12.81%
多酚:3.28%;3.43%[6] 6 SCP-1 Rha∶Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=1.19∶2.29∶5.01∶73.32∶
18.19抗肿瘤 3.05×104 主链:→4)-α-Glcp-(1→
侧链:8种类型[8] 7 SCP-3-1 Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶
GalA=0.13∶0.09∶2.08∶
19.82∶0.19_ 8.49×104 α-糖苷键连接的吡喃型多糖 [33] 8 SFP Rha∶Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=0.68∶6.17∶7.37∶83.85∶ 0.34 镇痛 _ 不含核酸和蛋白质 [34] 9 WSP Rha∶Ara
Man∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA∶=
9.3∶4.5∶12.2∶13.3∶
23.3∶37.4治疗腹泻 _ 碳水化合物∶糖醛酸=95.7%∶36.4% [35] 10 SCAP Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=3.68∶4.30∶1.36∶
7.25∶30.19∶53.60保肝 _ 总糖含量∶糖醛酸含=61.4%∶52.2% [36] 11 SCP Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc=
0.17∶1.32∶44.10∶54.41抗疲劳 2.65×104 蛋白质由12种氨基酸组成 [37] 12 SCP2-1 Gal∶Glc=
8.78∶1.23改善认知,抗炎 0.54×104 1,4-α-D-Glcp
1,4-β-D-Galp
1,4,6-β-Galp
1-β-Galp[38] 2.1 单糖组成
单糖以不同的比例组成五味子多糖分子,而具体的组成比例可能会因不同的品种、生长环境和提取方法而有所差异。一般采用高效液相色谱(HPLC)/气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)/气相色谱(GC)分析方法测定五味子多糖单糖组成。由表2可知,五味子多糖主要是由5种单糖和1种糖醛酸组成,其中单糖分别是鼠李糖(rhamnose, Rha),阿拉伯糖(arabinose, Ara),甘露糖(mannose, Man),半乳糖(galactose, Gal)和葡萄糖(glucose, Glc),糖醛酸只有半乳糖醛酸(galacturonic acid, GalA)。在样品中含量较高的是Glc。在报道的单糖中,Gal和Glc均可被检测到。仅Zhao等[31]和Hong等[32]检测到木糖(xylose, Xyl),仅Hong等[32]检测到核糖(ribose, Rib)。Chen等[6]对北五味子和南五味子多糖进行单糖分析,研究发现两种多糖主要由Ara、Glc和Gal组成,但含量差异较大,SSP含有较多的GalA。
2.2 平均分子量
多糖的理化特性、生物活性与其分子量有很大关系。一般通过高效凝胶渗透色谱(HPGPC)或多角度激光光散射(MALLS)分析方法测定其相对分子质量。五味子多糖的平均分子量大致范围在103~105 Da。Chen等[6]通过HPGPC测得北五味子多糖和南五味子多糖分子量分别为1.7×104 Da和1.7×105 Da。在五味子多糖平均分子质量测定中,造成分子量大小差异可能跟五味子提取方法、分离纯化方法、测定方法等的不同有关。
2.3 化学结构
不同的糖苷键连接方式可以影响多糖分子的立体构型、稳定性、溶解性以及与其他生物分子的相互作用。五味子多糖主链主要由Glc和Gla组成,其中Gla仅Zhao等[27]对五味子多糖(SSPP11)糖苷键类型和主支链结构进行了较好的表征,研究发现SSPP11具有十个不同的糖苷键,同时刚果红实验发现SSPP11具有三股螺旋结构。Huang等[8]发现→4)-α-Glcp-(1→作为SCP-1主链的重复单元,其在C-3和C-6处具有分支点,被不同类型的酸性和中性侧链取代以形成多个分支。
3. 五味子多糖生物活性及作用机制
3.1 抗氧化活性
氧化应激与许多疾病密切相关,包括心血管疾病、癌症、神经退行性疾病等。而抗氧化剂能够通过捕捉活性氧的自由基,减少或中和其反应活性,保护细胞免受氧化损伤,抑制体内的氧化应激反应[39]。研究发现五味子叶多糖对DPPH自由基、羟基自由基、ABTS+自由基和超氧阴离子自由基具有较好的清除效果,EC50达到0.735、1.677、0.626、0.253 mg/mL[40]。另有研究指出,从五味子多糖分离纯化得到的SSPW1组分对超氧阴离子自由基、羟基自由基和DPPH自由基的清除率分别达到了62.08%、39.27%和41.83%。此外,SSPW1可显著降低小鼠血清MDA含量,提高GSH-Px、SOD和CAT活性,充分表明其在体内体外具有良好的抗氧化特性[5]。研究表明,硒化五味子多糖(sSCP)能够显著提高细胞活力和SOD、CAT和GSH-Px的活性,降低细胞凋亡和LDH、AST、ALT和MDA含量,下调p-JNK1、p-ERK1/2、p-p38、Bax、Caspase3和细胞色素C蛋白,上调Bcl-2蛋白。研究指出sSCP是通过调节MAPKs和线粒体诱导凋亡通道的蛋白表达来保护经H2O2诱导的肝细胞的氧化损伤[41]。研究发现,SCP能够通过增强Trx-1表达和促进TXNIP/Trx-1复合物的分离来预防心肌肥大。TXNIP作为Trx-1的内源性抑制剂,SCP与TXNIP结合使Trx-1解离,Trx-1发挥抗氧化作用。氧化应激是参与心肌肥大发病的重要机制,因此,SCP可作为TXNIP抑制剂,在减缓氧化应激中发挥作用。表明SCP具有治疗心肌肥大的潜在作用[42]。
有研究指出,虽然葡萄糖是一种还原性单糖,但其含量的多少与抗氧化效果没有关系,在所有单糖成分中,鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖和半乳糖的含量与抗氧化效果密切相关。此外,含有一定量半乳糖醛酸的多糖具有较高的抗氧化能力。五味子多糖对不同自由基的清除效果不同,可能因为提取方法有所不同导致多糖本身的纯度和结构存在差异。总之,多糖的抗氧化能力不是由单一因素决定的,而是由几个相关因素共同决定的。
综上所述,五味子多糖具有显著的抗氧化能力,能够减轻氧化应激引起的氧化损伤,保护细胞免受自由基的侵害,维护细胞的正常功能,并在预防和治疗氧化应激相关的疾病中发挥作用。
3.2 免疫调节作用
天然多糖可以调节细胞因子的产生和释放,影响免疫细胞的互作和信号传导,调节免疫细胞的分化和功能,从而维持免疫系统的稳定性和平衡性[43]。研究发现,SSP和SCP均能够加强RAW264.7细胞的吞噬能力和促进巨噬细胞产生NO。经过100 μg/mL浓度以上处理,SCP和SSP会产生更多活性更强的酸性磷酸酶,表明SCP和SSP均有较好的免疫调节作用[6]。此实验中SCP和SSP均为粗多糖,并未经过纯化步骤,为深入研究五味子多糖调节免疫活性的作用机制,可以通过分离纯化或富集操作,表征出发挥重要作用的成分,更清楚的阐述其中的机理。经分离纯化得到的SCP-IIa可以提高免疫抑制小鼠的胸腺和脾脏指数,且与灌胃剂量成正比。同时SCP-IIa显著增加了环磷酰胺免疫抑制小鼠的血清溶血素形成,增强了小鼠的体液免疫功能[6]。研究发现经水提、超滤得到的较低分子质量的五味子多糖浓度在500.00 μg/mL以上时,对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7的吞噬能力、NO分泌水平、IL-1β和TNF-α含量有普遍的促进作用,且活性强于大分子量多糖[44]。另有研究表明SCP能够有效改善葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[45]。
以上体现出五味子多糖具有较好的免疫调节活性,且有望成为一种免疫调节剂并用于药物治疗。多糖是通过多途径、多靶点来实现免疫调节功能的,其中的机制涉及各种免疫细胞上的众多受体,同时对细胞间的信使分子有一定的调节作用,这需要研究者在研究过程中从多个层面探讨其机制。
3.3 抗肿瘤活性
多糖通过改变巨噬细胞的功能、刺激抗癌抗体的产生、增加NO和干扰自由基等方式来抑制癌细胞的生长[46]。研究发现,SCPP11可以显著提高胸腺指数,增强腹腔巨噬细胞的吞噬活性,促进溶血素的形成,增加CTX诱导的免疫抑制小鼠的球蛋白、IL-2和TNF-α水平,改善小鼠的免疫调节活性,从而发挥抗肿瘤特性[47]。研究指出WSLSCP可以显著提高携带荷瘤小鼠的生存率,同时可以诱导受刺激的巨噬细胞产生NO和TNF-α等非活性分子,且NO产生量随浓度成正比,以此间接发挥抗肿瘤的作用[48]。研究发现在低氧或常氧条件下,SCP能够显著抑制Caki-1细胞的VEGF产生,且与SCP浓度成相关,反映出SCP的抗血管生成能力。同时还发现SCP通过上调Bax和p53基因表达以及下调Bcl-2基因表达来引起Caki-1荷瘤小鼠的癌细胞凋亡[49]。
综上所述,五味子多糖通过抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡、抑制肿瘤血管生成和调节免疫功能等多个机制,发挥抗肿瘤的作用。五味子多糖可作为一种具有免疫调节活性的新型抗肿瘤药物,应用于功能食品和医药领域,但其在免疫调节中的详细结构特征和构效关系,尤其是高级结构体现的生物活性的影响作为未来研究重点有待进一步研究。
3.4 保肝作用
研究表明,五味子多糖具有显著的的保肝作用[50]。Wu等[51]利用经CsA诱导的小鼠模型,发现SCP通过激活Nrf2来增加下游脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)的释放来发挥保肝作用。Yuan等[52]建立乙醇诱导小鼠肝损伤模型和HepG2细胞肝损伤模型并评估五味子酸性多糖(SCAP)的保护作用及其机制,结果表明,SCAP能显著降肝损伤和HepG2细胞中AST、ALT水平。通过HE染色发现SCAP对小鼠酒精性肝损伤具有一定的保护作用,并且能够降低血清、肝组织和HepG2细胞MDA含量,提高SOD活性;通过蛋白质印迹法发现SCAP是通过抑制CYP2E1蛋白的表达,减轻乙醇诱导的氧化应激损伤。Che等[36]研究五味子酸性多糖(SCAP)对APAP所致小鼠急性肝损伤的影响及其机制,研究发现,SACP可显著降低小鼠血清丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)、天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)水平。同时,SCAP能够显著降低MDA含量和GSH消耗,降低Bax/Bcl比例,抑制caspase-3的表达,并提高p-AMPK、p-Akt、GSK 3β、Nrf2和HO-1蛋白水平,表明SCAP对APAP诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用与其抗氧化、抗炎和抗凋亡等作用有关。Chen等[53]利用Con A诱导的免疫性肝损伤小鼠模型,结果发现SCP可提高小鼠肝脏中SOD活性,降低MDA和NO水平,降低血清中AST、ALT、肿瘤坏死因子-α、干扰素-γ、白细胞介素(IL)-1β和IL-6水平,表明SCP可减轻免疫性肝损伤中的氧化应激和炎症反应,减轻ConA引起的代谢紊乱。
3.5 降血糖、降血脂作用
多种天然多糖已经被证实具有降低血糖,治疗糖尿病的功效。糖尿病与脂质代谢异常密切相关[54],五味子多糖有良好的降血糖、血脂功能,有望成为一种天然的降糖降脂药物。Zhao等[27]对小鼠注射四氧嘧啶建立高血糖小鼠模型。糖尿病小鼠经过五味子多糖(ESCP)治疗后,高血糖小鼠血清胆固醇,三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白有所下降,且优于阳性对照组(格列本脲),同时给药组小鼠肝糖原含量显著提高,推断ESCP通过影响糖原代谢途径发挥其降血糖作用。此外还发现ESCP可改善四氧嘧啶糖尿病小鼠的脂质代谢,降低心血管疾病的发生风险。但由于多糖的制备和纯化技术有限,大多数是多糖或糖蛋白的粗制剂,其作用机制尚不清楚,通过何种途径发挥降血糖作用还需要更多的研究。
3.6 其他作用
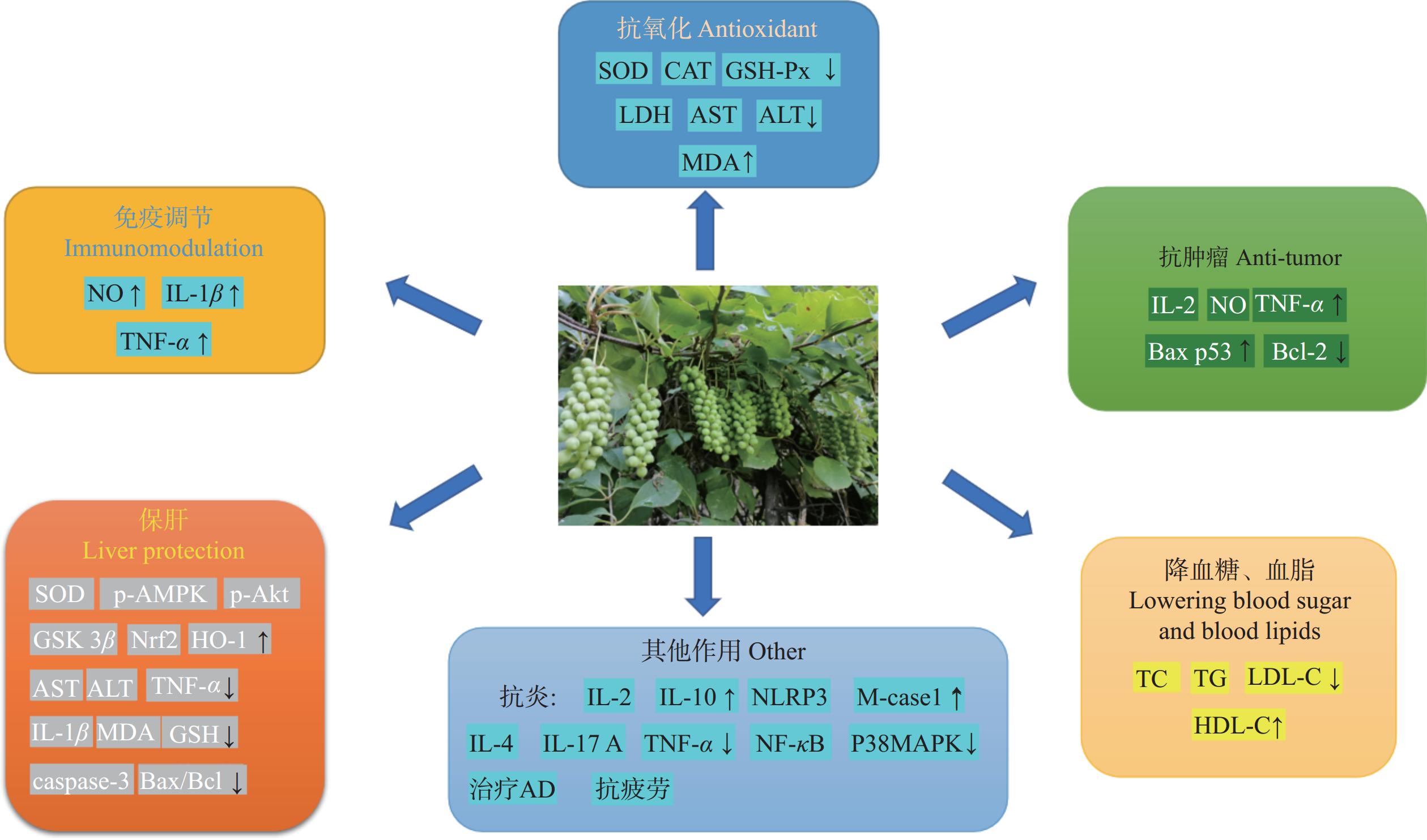
除上述生物活性外,五味子多糖还具有其他生物活性。疲劳是工作和活动中能量消耗引起的身体生理变化,持续工作一段时间后人体会出现疲劳,使工作功能下降。疲劳也是机体集体避免损害的一种自然保护反应[55−56]。Chi等[37]探讨了五味子多糖(SCP)对慢性疲劳综合征(CFS)的治疗作用及其代谢机制,实验表明,SCP组大鼠的体重、Morris水迷宫试验中寻找平台的次数和旷场试验中的站立次数均有显著提高。同时,Morris水迷宫试验中搜索平台时间和尾部悬吊试验中的静止时间均显著降低,表明SCP治疗对CFS的治疗效果显著。尿液代谢组学发现,SCP通过TCA循环代谢和丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢两种代谢途径来缓解小鼠的不平衡代谢。Xu等[38]评估分离纯化得到的SCP2-1对由过度神经炎症引起的小鼠的认知功能障碍的改善机制,实验发现,SCP2-1能明显改善小鼠Y迷宫实验中探索的新臂时间,增加NOR实验中新目标的探索时间,缩短小鼠MWM实验中的逃避潜伏期。对脑组织进行HE染色发现,SCP2-1对小鼠神经元具有一定的保护作用,作用机制是通过抑制TNF-α、IL-1β等促炎细胞因子的持续释放,调节IL-4、IL-10等抗炎细胞因子的水平,平衡星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞的过度活化,进而通过提高NLRP3和M-case1的表达,降低Aβ的吞噬作用。此外,SCP2-1还可抑制NF-κB的核转位和P38 MAPK通路的过度磷酸化,从而减轻过度炎症反应。Fu等[57]发现纯化后的SCP2具有改善AD大鼠的学习和记忆能力,减少神经炎症和恢复肠道屏障,以及调节内源性代谢物,改善肠道微生物群紊乱的功能。Qi等[35]建立抗腹泻性大鼠模型,发现经WSP治疗后大鼠回肠和结肠炎性细胞浸润明显减少,同时提高IL-2、IL-10水平,降低IL-4、IL-17A、TNF-α水平,发现WSP能够增加布劳特氏菌属Blautia、肠杆菌属Intestinibacter和毛螺菌科-UCG-008属丰度,降低瘤胃球菌属-1、瘤胃菌科-UCG-014属和丹毒荚膜菌属Erysipelatoclostridium丰度。五味子多糖的生物学功能见图2。
4. 总结与展望
近些年来,学者研究分离出多种具有不同生物活性的五味子多糖,主要包括抗氧化、免疫调节、抗肿瘤、保肝、降血糖、血脂等生物活性。有关五味子多糖的提取、结构表征和生物活性等方面的研究取得了一定进展,但是还有仍值得探索的领域。
第一,提取和纯化技术的改进:不同提取方法及纯化条件所得到的五味子多糖在含量上仍有一定差异,得到的多糖会含有木脂素、蛋白质等杂质,可能会导致其结构和生物活性发生变化,给多糖功效测定标准的确定带来困难。随着提取技术的不断进步,多糖提取工艺逐渐趋向于工业化、商业化,这就要求在现有提取方法上做出高质量创新,并制定严格的提取标准,以争取低成本、高产率,得到更高质量的五味子多糖。
第二,结构与活性关系的深入研究:由于五味子多糖分子量大,结构复杂,目前对于多糖结构与活性之间的关系仍存在一定的模糊性。多糖分子的碳水化合物组成、分支度、空间构型等因素都可以影响其与生物分子的相互作用,从而调节其生物活性。例如,多糖的分支结构可能增加其溶解性,促进其与受体结合,进而影响免疫调节、抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤等活性。通过研究多糖的构效关系与生物活性之间的关系,可以了解多糖分子结构与其与生物分子的相互作用、信号传导等关联,揭示多糖在生物体内的作用机制,从而推动多糖在医药、食品、生物材料等领域的开发和创新。
第三,改性与活性关系的深入研究:多糖改性是通过对多糖分子的化学修饰或结构调整来改变其性质和活性。改性可以增强多糖的稳定性、溶解性,改善其生物利用度,从而影响其药理效果。不同的改性方式可能导致多糖的活性增强或减弱,例如,酯化、醚化能够改变多糖结构和性质;硫酸化、甲基化、磷酸化、修饰官能团能够影响其生物活性;交联,包覆可增加其黏度和稳定性。多糖改性的具体方法和效果会因多糖种类、目标应用和改性程度而异。在进行多糖改性时,需要综合考虑所需的特定性质和应用要求,确保改性后的多糖能够在特定环境中发挥出最佳的功能和效果。
第四,分子质量与活性的深入研究:多糖分子质量和活性之间的关系取决于多种因素:分子的类型、结构、环境条件等。分子质量可以影响化合物的生物利用度、分布和相互作用。在某些情况下,分子质量较大的化合物可能更难渗透细胞膜,从而影响其生物活性。然而,分子质量与活性之间的关系不是线性的,一些生物活性物质可能在适度的分子质量范围内表现出最佳的效果。此外,分子质量也可能影响药物代谢、药动学等因素,从而进一步影响活性。在研究和应用中,应深入研究多糖的特性,理解其与生物体内活性之间的相互关系,进而提高多糖在药物传递系统、食品保健品开发、指导生物材料设计等领域的效能。
第五,新方法的开发:现阶段,基于组学技术,包括转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学、单细胞技术、高通量筛选等是研究多糖生物活性的新型方法。通过这些新型方法能够了解多糖是如何影响细胞信号传导、基因表达、蛋白质功能等,以及全面的揭示多糖与细胞、分子之间的复杂相互作用,提供更准确的机制阐释。
第六,临床试验的扩大:尽管在体外和动物实验中多糖表现出一定的生物活性,但目前仍缺乏足够的临床试验验证其疗效和安全性。因此,需要扩大临床试验的规模,并进行更多的临床研究,进一步研制适当的剂量与剂型,以确定多糖在临床应用中的实际效果和潜在风险。
第七,研究开发不足:目前五味子仅被作为中药利用,在未来,以五味子多糖为主要成分的具有更高生物活性的药剂或功能性食品仍是重要研究方向。例如制作五味子茶、五味子饮料、五味子营养品等,强调其抗氧化、免疫调节、保健等功效;根据五味子在不同地区的资源分布和特点,开发符合当地文化和消费需求的高值化产品,推动地方特色产业发展等。充分发挥五味子所含的丰富生物活性成分,将其应用于药物、食品、农业等领域,以提高产值、促进产业发展,同时满足人们对健康、天然和可持续发展的需求。
-
表 1 五味子多糖不同提取方法的优缺点比较
Table 1 Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of different extraction methods
序号 提取方法 优点 缺点 多糖得率 参考文献 1 双水相萃取 适用范围广
选择性强
操作简便
提取效果好溶剂选择受限
溶剂耗费大64.38% [11] 2 酶辅助 反应条件温和
高选择性
环境友好
可再利用价格昂贵
反应对象单一
反应条件难控制14.87%~
19.38%[13-14] 3 超声辅助 提取效率高
节省时间
作用温和能量消耗大
设备昂贵、成本高1.107%~
9.35%[17-18] 4 微波辅助 高效节能
节省时间
操作简单加热均匀性差
多糖结构易破坏20.08% [20] 5 超声-微波
联合省时高效节能
工业化前景广阔设备昂贵
成本能耗较大11.68%~
13.23%[22-23] 6 微波-酶 节省时间
提取效率更高设备成本较高
温度控制困难
可能造成样品变性7.38%~
14.87%[25-26] 7 热水浸提 操作简单
条件温和
对多糖结构友好耗时长
提取率较低
产物纯度低3.14%~
10.72%[27-29] 表 2 五味子多糖结构特征
Table 2 Structural characteristics of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides
序号 多糖名称 单糖组成 生物活性 分子量(Da) 结构特征 参考文献 1 SSPW1 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶
Glc=13.52∶5.69∶3.92∶
41.28∶35.59抗氧化
降血糖1.91×105 蛋白质∶中性糖∶糖醛酸=48.92%∶42.83%∶5.56% [5] 2 SSPP11 Man∶Gal∶Glc=
1∶1.29∶1.77抗氧化 5.30×103 T-D-Manp(1→, →1)-D-Man-(6→, T-D-Glup(1→, T-D-Galp(1→, →1)-D-Manp-(2→, →1)-D-Glup(4→, →1)-D-Glup-(6→, →1)-D-Galp-(4→, →1)-D-Galp-(4,6→ and →1)-D-Manp-(3,6→ 其比例为1.1∶4.8∶6.2∶5.2∶4.8∶15.4∶21.6∶20.8∶1∶11.4 [27] 3 SCPP22 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶Xyl=3.04∶1.21∶2.91∶
11.37∶100.67∶1.00免疫调节 14.30×104 主链:1,4-α-D-Glup
侧链:通过O-6与主链的1,4-β-D-Glup连接(由T-α-D-Galp组成)[31] 4 SCFP-1 Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶Rib∶Xyl=2.7∶133.6∶1∶
1.4∶302.2∶11.9∶1.7镇咳 3.18×104 碳水化合物∶糖醛酸=96.9%∶14.2% [32] 5 SCP
SSPSSP
Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=22.3∶34.6∶15.0∶11.5
SCP
Man∶Gal∶Glc=
11.7∶8.6∶67.6∶免疫调节
1.70×104
1.70×105SCP/SSP
糖:78.45%;51.04%
蛋白质:12.55%;35.35%
糖醛酸:4.78%;12.81%
多酚:3.28%;3.43%[6] 6 SCP-1 Rha∶Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=1.19∶2.29∶5.01∶73.32∶
18.19抗肿瘤 3.05×104 主链:→4)-α-Glcp-(1→
侧链:8种类型[8] 7 SCP-3-1 Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶
GalA=0.13∶0.09∶2.08∶
19.82∶0.19_ 8.49×104 α-糖苷键连接的吡喃型多糖 [33] 8 SFP Rha∶Ara∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=0.68∶6.17∶7.37∶83.85∶ 0.34 镇痛 _ 不含核酸和蛋白质 [34] 9 WSP Rha∶Ara
Man∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA∶=
9.3∶4.5∶12.2∶13.3∶
23.3∶37.4治疗腹泻 _ 碳水化合物∶糖醛酸=95.7%∶36.4% [35] 10 SCAP Rha∶Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc∶GalA=3.68∶4.30∶1.36∶
7.25∶30.19∶53.60保肝 _ 总糖含量∶糖醛酸含=61.4%∶52.2% [36] 11 SCP Ara∶Man∶Gal∶Glc=
0.17∶1.32∶44.10∶54.41抗疲劳 2.65×104 蛋白质由12种氨基酸组成 [37] 12 SCP2-1 Gal∶Glc=
8.78∶1.23改善认知,抗炎 0.54×104 1,4-α-D-Glcp
1,4-β-D-Galp
1,4,6-β-Galp
1-β-Galp[38] -
[1] YANG K, QIU J, HUANG Z C, et al. A comprehensive review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. and Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. etWils.[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2022,284:114759. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114759
[2] YI Q Z, YAN L, BO W, et al. New triterpenoids and a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan from the leaves of Schisandra chinensis[J]. Phytochemistry Letters,2023,54:57−62. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2023.01.020
[3] HONG C P, KIM C K , LEE D J , et al. Long-read transcriptome sequencing provides insight into lignan biosynthesis during fruit development in Schisandra chinensis[J]. BMC Genomics,2022,23(1):1−14. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08243-4
[4] ZHAO T, GUO Y H, YAN S Y, et al. Preparation, structure characterization of carboxymethylated Schisandra polysaccharides and their intervention in immunotoxicity to polychlorinated biphenyls[J]. Process Biochemistry,2022,15:30−41.
[5] NIU J M, XU G Y, JIANG S, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities and anti-diabetic effect of a polysaccharide from Schisandra sphenanthera in rats with type 2 diabetes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,94:154−160. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.015
[6] CHEN X Y, TANG R, LIU T T, et al. Physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity and immunological effects in vitro of polysaccharides from Schisandra sphenanthera and Schisandra chinensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,131:744−751. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.129
[7] YANG S F, DONG W W, LI G M, et al. A recombinant vaccine of Riemerella anatipestifer OmpA fused with duck IgY Fc and Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide adjuvant enhance protective immune response[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2019,1336:103707.
[8] HUANG Y X, LIANG J, CHAI J H, et al. Structure of a highly branched galacturonoglucan from fruits of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill.[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2023,313:120844. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120844
[9] ZHANG G J, ZHANG J B, YAN S, et al. Study on the plasma metabolomics of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide against ulcerative colitis and its correlation with gut microbes metabolism[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 100244.
[10] BASAVARAJ S N, REGUPATHI I, BELUR P D. Simultaneous extraction of four different bioactive compounds from Garcinia indica and their enrichment using aqueous two-phase systems[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing,2019,114:185−195. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2019.01.002
[11] 李化, 柯华香, 李发洁, 等. Box-Behnken响应面法优选五味子多糖双水相提取工艺[J]. 中药材,2016,39(3):593−597. [LI H, KE H X, LI F J, et al. Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction of polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis using response surface methodology with box-behnken design[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2016,39(3):593−597. LI H, KE H X, LI F J, et al . Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction of polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis using response surface methodology with box-behnken design[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2016 ,39 (3 ):593 −597 .[12] PETER K R. Enzymes:principles and biotechnological applications[J]. Essays In Biochemistry,2015,59:1−41. doi: 10.1042/bse0590001
[13] 可成友, 梁宏斌, 边蔷, 等. 北五味子多糖的酶法提取工艺研究[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2010,24(2):47−50. [KE C Y, LIANG H B, BIAN Q, et al. Study on enzyme extraction processes of the coarse polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines,2010,24(2):47−50. KE C Y, LIANG H B, BIAN Q, et al . Study on enzyme extraction processes of the coarse polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines,2010 ,24 (2 ):47 −50 .[14] 宋海燕, 程振玉, 马朝红. 响应面优化酶法提取五味子多糖的工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(3):159−163. [SONG H Y, CHENG Z Y, MA C H. Enzyme-assisted extraction technology of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis Baill by RSM and its antioxidation activity[J]. The Food Industry,2016,37(3):159−163. SONG H Y, CHENG Z Y, MA C H . Enzyme-assisted extraction technology of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis Baill by RSM and its antioxidation activity[J]. The Food Industry,2016 ,37 (3 ):159 −163 .[15] LI Y C, ZHAO M, LAURA P G, et al. Investigation of enzyme-assisted methods combined with ultrasonication under a controlled alkali pretreatment for agar extraction from Gelidium sesquipedale[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,120:106905. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106905
[16] WANG N, SHI N N, FEI H L, et al. Physicochemical, structural, and digestive properties of pea starch obtained via ultrasonic-assisted alkali extraction[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2022,89:106136. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106136
[17] 张莹, 王洪源, 周宇航, 等. 超声波辅助提取和热水浸提五味子多糖的比较研究[J]. 特产研究,2015,37(3):52−57. [ZHANG Y, WANG H Y, ZHOU Y H, et al. Study on the extraction of Schisandra chinensis Biall polysaccharides by ultrasonic wave and hot water method[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research,2015,37(3):52−57. ZHANG Y, WANG H Y, ZHOU Y H, et al . Study on the extraction of Schisandra chinensis Biall polysaccharides by ultrasonic wave and hot water method[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research,2015 ,37 (3 ):52 −57 .[18] 谭晓虹, 王治宝, 卫娇娇, 等. 正交实验优化南五味子多糖的超声提取工艺[J]. 神经药理学报,2012,2(6):36−39. [TAN X H, WANG Z B, WEI J J, et al. Study on extraction polysaccharide from fructus Schisandrae sphenantherae by orthogonal ultrasound-assisted method[J]. Acta Neuropharmacologica,2012,2(6):36−39. TAN X H, WANG Z B, WEI J J, et al . Study on extraction polysaccharide from fructus Schisandrae sphenantherae by orthogonal ultrasound-assisted method[J]. Acta Neuropharmacologica,2012 ,2 (6 ):36 −39 .[19] GAO F Y, ZHOU C C, WANG Z H, et al. Solid-oil separation of coal tar residue to reduce polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via microwave-assisted extraction,[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2023,337:117679. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117679
[20] 程振玉, 杨英杰, 刘治刚. 微波辅助提取北五味子多糖工艺研究[J]. 吉林化工学院学报,2014,31(3):18−22. [CHENG Z Y, YANG Y J, LIU Z G. Study on microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology,2014,31(3):18−22. CHENG Z Y, YANG Y J, LIU Z G . Study on microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology,2014 ,31 (3 ):18 −22 .[21] GARCÍA-VILLALBA W G, RODRÍGUEZ-HERRERA R, OCHOA-MARTÍNEZ L A, et al. Comparative study of four extraction methods of fructans (agavins) from Agave durangensis:Heat treatment, ultrasound, microwave and simultaneous ultrasound-microwave[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,415:135767. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135767
[22] ZHANG X Y, WANG J Q, YUE X, et al. Optimization of The extraction process of polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2019,1176(6):062032.
[23] 宋海燕, 程振玉, 马朝红, 等. 正交试验优化超声波-微波协同法萃取北五味子多糖工艺研究[J]. 吉林化工学院学报,2015,32(6):12−16. [SONG H Y, CHENG Z Y, MA C H, et al. Study on optimization of ultrasound/microwave - assisted extraction technology of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis by orthogonal test[J]. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology,2015,32(6):12−16. SONG H Y, CHENG Z Y, MA C H, et al . Study on optimization of ultrasound/microwave - assisted extraction technology of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis by orthogonal test[J]. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology,2015 ,32 (6 ):12 −16 .[24] TIAN S Q, DU K, YAN F, et al. Microwave-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat germ albumin to prepare polypeptides and influence on physical and chemical properties[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131707. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131707
[25] CHENG Z Y, SONG H Y, YANG Y J, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction of polysaccharides from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis Baill[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,76:161−168. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.01.048
[26] 薛俊礼, 吕洋, 杨艳艳, 等. 微波辅助复合酶法提取北五味子多糖的工艺研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(6):61−67,73. [XU J L, LÜ Y, YANG Y Y, et al. Study on extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis Baill. polysaccharide using microwave-assisted complex enzymatic meth[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2020,41(6):61−67,73. XU J L, LÜ Y, YANG Y Y, et al . Study on extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis Baill. polysaccharide using microwave-assisted complex enzymatic meth[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2020 ,41 (6 ):61 −67,73 .[27] ZHAO T, MAO G H, FENG W W, et al. Isolation, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,105:26−33. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.059
[28] 唐静, 金利华, 李英英, 等. 响应曲面法优化南五味子多糖的提取工艺[J]. 化学与生物工程,2017,34(10):49−53. [TANG J, JIN L H, LI Y Y, et al. Optimization in extraction process of polysaccarides from Schisandra sphenanthera Rehe. etWils by response surface methodology[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2017,34(10):49−53. TANG J, JIN L H, LI Y Y, et al . Optimization in extraction process of polysaccarides from Schisandra sphenanthera Rehe. etWils by response surface methodology[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2017 ,34 (10 ):49 −53 .[29] 许梦然, 王迦琦, 高婧雯, 等. 北五味子多糖提取工艺优化及其对LPS刺激巨噬细胞线粒体膜电位的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(20):33−40. [XU M R, WANG J Q, GAO J W, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide and its protective effect on LPS induced mitochondrial membrane potential in macrophages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(20):33−40. XU M R, WANG J Q, GAO J W, et al . Optimization of extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide and its protective effect on LPS induced mitochondrial membrane potential in macrophages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (20 ):33 −40 .[30] YANG X L, WEI S Q, LU X M, et al. A neutral polysaccharide with a triple helix structure from ginger:Characterization and immunomodulatory activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,350:129261. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129261
[31] ZHAO T, WANG F, GUO Y C, et al. Structural characterization of a novel Schisandra polysaccharides and nutritional intervention in immunotoxicity to PCBs[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,258:117380. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117380
[32] HONG S Z, LIU X D, NIE Y C, et al. Antitussive activity of the Schisandra chinensis fruit polysaccharide (SCFP-1) in guinea pigs models[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2016,194:378−385. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.08.008
[33] 张红梅, 李方怿, 赵春霞, 等. 五味子多糖的分离、纯化及结构表征[J]. 天津中医药,2022,39(4):509−515. [ZHANG H M, LI F Y, ZHAO C X, et al. Isolation, purification and characterization of polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,39(4):509−515. ZHANG H M, LI F Y, ZHAO C X, et al . Isolation, purification and characterization of polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022 ,39 (4 ):509 −515 .[34] YE C, HAN N, TENG F K, et al. Extraction optimization of polysaccharides of Schisandrae fructus and evaluation of their analgesic activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,57:291−296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.03.025
[35] QI Y L, CHEN L X, GAO K, et al. Effects of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on rats with antibiotic-associated diarrhea[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,124:627−634. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.250
[36] CHE J Y, YANG S, QIAO Z J, et al. Schisandra chinensis acidic polysaccharide partialy reverses acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences,2019,140(3):248−254. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2019.07.008
[37] CHI A P, ZHANG Y, KANG Y J, et al. Metabolic mechanism of a polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis to relieve chronic fatigue syndrome[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,93:322−332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.08.042
[38] XU M J, YAN T X, GONG G W, et al. Purification, structural characterization, and cognitive improvement activity of a polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:497−507. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.275
[39] BARRY H. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), oxygen radicals and antioxidants:Where are we now, where is the field going and where should we go?[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2022,633:17−19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.08.098
[40] 王鑫, 耿一丁, 王丽红, 等. 五味子叶多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(9):75−82. [WANG X, GEN Y D, WANG L L H, et al. Optimization of extraction process of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis leaves and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(9):75−82. WANG X, GEN Y D, WANG L L H, et al . Optimization of extraction process of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis leaves and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2022 ,33 (9 ):75 −82 .[41] YUE C J, CHEN J, HOU R R, et al. The antioxidant action and mechanism of selenizing Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide in chicken embryo hepatocyte[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,98:506−514. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.015
[42] SHI X W, HAN B J, ZHANG B, et al. Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides prevent cardiac hypertrophy by dissociating thioredoxin-interacting protein/thioredoxin-1 complex and inhibiting oxidative stress[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2021,139:111688.
[43] ZHANG M Z, TIAN X H, WANG Y, et al. Immunomodulating activity of the polysaccharide TLH-3 from Tricholoma lobayense in RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,107:2679−2685. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.165
[44] 崔石阳, 姜帆, 韩建春, 等. 北五味子多糖对RAW264.7细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(19):201−205. [CUI S Y, JIANG F, HAN J C, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. Food Science,2017,38(19):201−205. CUI S Y, JIANG F, HAN J C, et al . Immunomodulatory effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. Food Science,2017 ,38 (19 ):201 −205 .[45] SU L L, MAO C Q, WANG X C, et al. The anti-colitis effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide is associated with the regulation of the composition and metabolism of gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology,2020,10:519479. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.519479
[46] WANG X L, LI N, LI Y, et al. A novel polysaccharide from Paeonia lactiflora exerts anti-tumor activity via immunoregulation[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2022,15(10):104132. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104132
[47] ZHAO T, FENG Y, LI J, et al. Schisandra polysaccharide evokes immunomodulatory activity through TLR 4-mediated activation of macrophages[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014(65):33−40.
[48] XU C L, LI Y H, D M, et al. Inhibitory effect of Schisandra chinensis leaf polysaccharide against L5178Y lymphoma[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,88(1):21−25. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.047
[49] QU H M, LIU S J, ZHANG C Y, et al. Antitumor and antiangiogenic activity of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide in a renal cell carcinoma model[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,66:52−56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.025
[50] 朱天仪. 五味子多糖对CCl_4致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用研究[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2022. [ZHU T Y. Study on the protective effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccaride on CCl4-induced liver injury in mice[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. ZHU T Y. Study on the protective effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccaride on CCl4-induced liver injury in mice[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.
[51] WU Q W, LIU C, ZHANG J N, et al. Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide protects against cyclosporin A-induced liver injury by promoting hepatocyte proliferation[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,87:104799. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104799
[52] YUAN R S, TAO X, LIANG S, et al. Protective effect of acidic polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis on acute ethanol-induced liver injury through reducing CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2018,99:537−542.
[53] CHEN L H, SHAN Y Y, WANG C M, et al. Metabolomics study on the therapeutic mechanism of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on concanavalin A-induced immunological liver injury in mice[J]. Pharmacognosy Magazine,2021,17(74):293−301. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_255_20
[54] MARIE-CHRISTINE S, ANNA L R, CORINNA W, et al. Distinct alterations of gut morphology and microbiota characterize accelerated diabetes onset in nonobese diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2020,295(4):969−980. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)49908-X
[55] WAN J J, QIN Z, WANG P Y, et al. Muscle fatigue:general understanding and treatment[J]. Experimental and Molecular Medicine,2017,49:e384. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.194
[56] ZHU J Q, YI J J, KANG Q Z, et al. Anti-fatigue activity of hemp leaves water extract and the related biochemical changes in mice[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2021,150:112054. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112054
[57] FU J, LI J X, SUN Y Z, et al. In-depth investigation of the mechanisms of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide mitigating Alzheimer's disease rat via gut microbiota and feces metabolomics[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,232:123488. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123488
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 尉洁,张玲芳,胡顺安,秦孟春,马琳,李丹,段翠翠. 长白山区发酵酱菜中高产胞外多糖乳酸菌的筛选及多糖抗氧化性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(02): 110-117 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 赵丹,赵守祺,王烁,陈曦,杜仁鹏. 融合魏斯氏菌P2胞外多糖对巨噬细胞RAW264.7增殖及免疫调节活性的影响. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报. 2024(02): 200-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 虞宁馨,于连升,齐心彤,葛菁萍,杜仁鹏. 肠膜明串珠菌葡聚糖蔗糖酶的生物信息学分析. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报. 2024(05): 544-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 于连升,葛菁萍,平文祥,杜仁鹏. 环二鸟苷酸调控细菌胞外多糖生物合成的研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2023(09): 422-430 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 张孟雨,李尧,彭嘉屹,陈禹豪,曾凤婷,钟青萍. 高产EPS乳酸片球菌的航天育种及其EPS性能研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(17): 158-167 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 李旭阳,郭润晴,路江浩,鄢梦洁,张鹏,刘明月,杨玲. 嗜热链球菌S131对巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2023(16): 247-252 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 罗伟,杨立军,崔晨旭,王玉娇,陈琼,王锐丽,叶润. 内生菌协同发酵对半夏多糖及其生物活性的影响. 中南农业科技. 2023(08): 52-56+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨立军,花娇娇,崔晨旭,贾艳娇,陈琼,赫丁轩. 一株高产胞外多糖半夏内生真菌的鉴定、发酵条件优化及生物活性测定. 中国酿造. 2023(11): 109-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 唐华英,罗欣锦,张云野,杨睿睿,叶广彬,王长丽. 假肠膜明串珠菌GX-3产胞外多糖条件优化及其理化性质研究. 中国乳品工业. 2022(08): 15-19+26 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 兰冬雪,瞿茜楠,黄天,姚国强,扎木苏,彭传涛,李兆杰. 益生菌活性代谢产物的研究及应用进展. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 11-20 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



