Prediction Model of Aztec Apples Quality Based on the Fusion of Multi-maturity Spectral Information
-
摘要: 不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质变化大,会显著影响采后贮藏与销售效益。本研究以江苏宿迁四个成熟阶段的阿森泰克苹果为研究对象,首先利用主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)和线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)分析其色泽(L*、a*、b*值)、硬度(firmness,FI)、可溶性固形物(soluble solid content,SSC)、可滴定酸(titratable acidity,TA)、水分含量(moisture content,MC)、干物质(dry matter content,DMC)的变化规律;同时,基于可见-近红外(visible and near-infrared,Vis-NIR)与近红外(near-infrared,NIR)光谱技术结合连续投影(successive projections algorithm,SPA)、竞争性自适应重加权(competitive adaptive reweighted sampling,CARS)、无信息变量消除(uninformative variable elimination,UVE)算法进行相关特征变量筛选,基于偏最小二乘(partial least squares,PLS)与支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)建立阿森泰克苹果品质预测模型。结果表明,SSC、a*、L*、b*对不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的聚类贡献率较高,510~680、1170~1270、2300 nm为高相关度特征波段。SPA-PLS、SPA-SVM模型能很好地预测不同成熟度阿森泰克的L*、b*、a*值,相对预测偏差(relative percent deviation,RPD)均高于3.00,CARS-PLS模型可以很好地预测SSC,RPD为3.19,但FI、TA、MC、DMC的SPA-PLS模型预测精度相对较低,RPD分别为2.27、2.21、2.32、2.42。研究结果证明Vis-NIR和NIR光谱方法能够预测不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果品质,为阿森泰克苹果采收管理与质量安全控制提供技术参考。Abstract: The quality of Aztec apples varies significantly at different maturity stages, which can have a significant impact on postharvest storage and sales efficiency. This study focused on Aztec apples at four different maturity stages in Suqian, Jiangsu Province. Firstly, the variations in color (L*, a*, b* values), firmness (FI), soluble solid content (SSC), titratable acidity (TA), moisture content (MC) and dry matter content (DMC) were analyzed using principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). Simultaneously, visible and near-infrared (Vis-NIR) and near-infrared (NIR) spectral techniques, along with the successive projections algorithm (SPA), competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) and uninformative variable elimination (UVE) algorithms were employed for selecting relevant characteristic variables. Subsequently, partial least squares (PLS) and support vector machine (SVM) were utilized to establish quality prediction models for Aztec apples. The results revealed that SSC, a*, L* and b* had a significant impact on the categorization of Aztec apples at different maturity stages. Notably, wavelength bands in the ranges of 510 to 680 nm, 1170 to 1270 nm and 2300 nm exhibited strong correlations with characteristic attributes. The SPA-PLS and SPA-SVM models demonstrated remarkable performance in predicting the L*, b* and a* values of Aztec apples at different maturity stages, with all relative percent deviation (RPD) values exceeding 3.00. The CARS-PLS model effectively predicted SSC with an RPD of 3.19. However, the prediction accuracy of SPA-PLS models for FI, TA, MC and DMC was comparatively lower, with RPD values of 2.27, 2.21, 2.32 and 2.42, respectively. The results demonstrated that Vis-NIR and NIR spectroscopy methods could predict the quality of Aztec apples at different maturity stages, providing valuable technical references for the harvest management and quality control of Aztec apples.
-
阿森泰克苹果(Malus domestica Borkh. cv. Aztec Fuji)是在新西兰选育的富士浓红型芽变品种,一般在10月中旬成熟。在不套袋栽培条件下品质表现优良,果型端正、果实大,平均着色面积80%以上,甜脆多汁,糖含量达14%以上,耐贮藏[1]。目前阿森泰克苹果的栽培面积不断扩大,在陕西千阳、甘肃宁县、江苏宿迁等地均有种植,市场逐渐扩大。现有研究发现阿森泰克苹果相比于Mollie's Delicious苹果具有更高的可溶性固形物含量(soluble solid content,SSC),但可滴定酸含量(titratable acid,TA)较低[2];与富士6629、富士Suprema相比硬度(firmness,FI)较高[3]。上述研究已证明商业成熟的阿森泰克苹果品质与传统富士存在较大品质差异性,但对于不同成熟阶段的阿森泰克苹果品质研究报道较少。
目前,苹果理化品质特性分析测定主要依靠一系列破坏性检测技术,如质构仪、糖度计、色谱质谱等,虽然检测精度高,但前处理较复杂、具有时滞性,无法实现快速在线检测。近年来,可见-近红外光谱(visible and near-infrared,Vis-NIR)和近红外光谱(near-infrared,NIR)技术,依靠快速无损、易于自动化的优势,已被成功应用于苹果SSC、TA、FI等重要理化指标的快速检测[4−6]。Yao等[7]利用Vis-NIR光谱技术有效实现了山东烟台等产地的富士苹果SSC预测,其预测集决定系数(determination coefficient of prediction,Rp2)为0.87、预测集均方根误差(root mean square error of prediction,RMSEP)为0.7%。姚亚楠[8]基于富士苹果在NIR波段下的14个筛选特征波长构建了TA的反向传播神经网络模型,Rp2为0.74,RMSEP为0.02%。Fan等[9]研究表明基于Vis-NIR光谱和二阶导数预处理建立的偏最小二乘(partial least squares,PLS)模型能够实现红富士苹果FI的有效预测,Rp2为0.81,RMSEP为0.53 kg/cm2。这些研究展示了Vis-NIR和NIR光谱技术对于富士苹果品质特征的良好评价潜力,但现有报道模型对于阿森泰克苹果品质的评价潜力还有待研究。
上述研究仅集中于商业成熟度下苹果近红外光谱品质模型的构建与优化。同时,苹果在收获时的成熟度极大地影响果实的口感风味,是影响采后贮藏品质变化的关键因素[10]。成熟度过低时,苹果果实淀粉含量高、糖含量低、口感较差,成熟度过高则会导致果实变得绵软,不耐贮藏[10]。不同生理阶段的果实,其物理特性、化学成分可能有所不同,这些特性会影响光学特性[11]。因此,应将多个收获期的果实进行建模,提高模型的适应性。Sharabiani等[12]基于200~1100 nm光谱数据预测不同成熟阶段嘎啦苹果的SSC,所建立的混合人工神经网络模型Rp2为0.92,RMSEP为0.17%。Pourdarbani等[13]在400~1000 nm 范围内研究应用近红外光谱检测不同成熟度富士苹果TA的可行性,建立人工神经网络预测模型,模型Rp2为0.86。这些研究均考虑了果实成熟阶段对模型性能的影响,且说明近红外光谱对苹果成熟阶段品质检测具有一定可行性,然而基于Vis-NIR和NIR光谱对阿森泰克苹果在不同成熟阶段品质的预测暂无报道。
因此,本研究以四个不同成熟阶段的阿森泰克苹果果实为研究对象,测定其在400~1000 nm、900~2500 nm范围内的反射率和理化指标,分析成熟过程中果实漫反射光谱差异和理化指标变化。最后利用化学计量学方法建立融合不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果品质的定量预测模型,实现对阿森泰克苹果成熟过程中品质的快速无损检测,以期为预测阿森泰克苹果的质量参数提供理论依据与实际指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
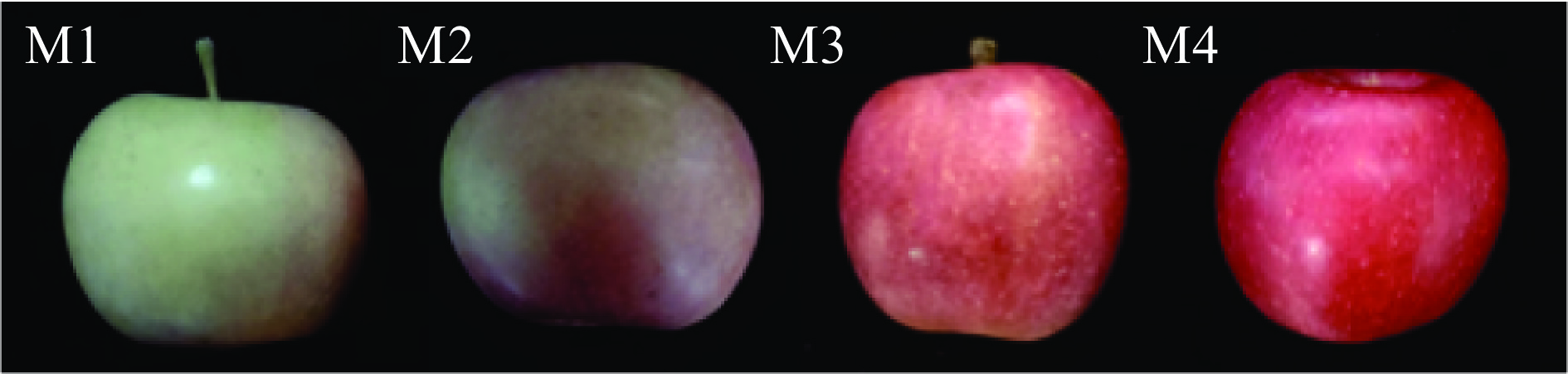
供试材料为阿森泰克苹果 采摘自江苏省宿迁市江苏福瑞斯农业有限公司,果实商业成熟期在十月中旬,分四个阶段进行收获,分别为M1(2022年9月25日)、M2(2022年10月5日),M3(2022年10月15日)和M4(2022年10月25日)(图1)。每个阶段40个苹果样本,采集样本后,筛选大小相对一致,表面没有疤痕的样本。样本置于室温(20 ℃左右)24 h后用纯水擦拭样品表面并自然晾干、编号。在每个样本沿赤道方向每120°进行标记,共三个标记位置,作为光谱扫描及检测取样点。
CR-13便携式色差计 日本美能达公司;PAL-1手持式糖度仪 日本爱拓公司;Easy ACID F5酸度计 日本爱拓公司;TMS-Pro质构仪 美国FTC公司;LC-20A高效液相色谱(配有蒸发光散射检测器) 日本岛津公司;可见-近红外光谱采集系统:PG2000-Pro光谱仪、FIB-600-L-UV直通光纤、FIB-Y-600-L(2)-UV光纤、FVA-UV光纤可调衰减器 上海复享光学股份有限公司;LS-HA卤素光源 台湾超微光学;近红外光谱采集系统:NIR2500近红外光谱仪、FIB-Y-600-L(2)-NIR光纤 上海复享光学股份有限公司;ASBN-100-L卤钨光源 美国Spectronics公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 理化指标测定
用CR-13型色差仪测定苹果果实标记部位(沿赤道方向每120°),测量亮度(L*)、红度(a*)、黄度(b*),测定结果取平均值;硬度(firmness,FI)测定采用质构仪[14],使用直径为6 mm的圆柱形探头在标记区域进行穿刺,触发力为0.3 N,检测速度为120 mm/min,穿刺距离为8 mm,回程速度为200 mm/min,测定结果用牛顿(N)表示;可溶性固形物测定采用手持式糖度计,将标记区域的果肉用无菌纱布包裹挤汁进行测定,测定结果用白利糖度(°Brix)表示;可滴定酸测定采用酸度计[15],对标记区域的果肉挤汁,测定结果用百分比(%)表示;水分含量(moisture content,MC)测定参考GB 5009.3-2016,采用直接干燥法测定,取约5 g果肉在105 ℃下烘干至恒重,测定结果用百分比(%)表示;干物质含量(dry matter content,DMC)采用烘干法测定,取约8 g果肉在60 ℃下烘干48 h至恒重,干重与鲜重的比值为干物质含量,测定结果用百分比(%)表示;果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖含量测定参考You等[14]报道的方法,采用高效液相色谱法测定,总可溶性糖含量用葡萄糖、果糖和蔗糖的总含量表示[14],测定结果用mg/g表示。
1.2.2 可见-近红外、近红外光谱检测
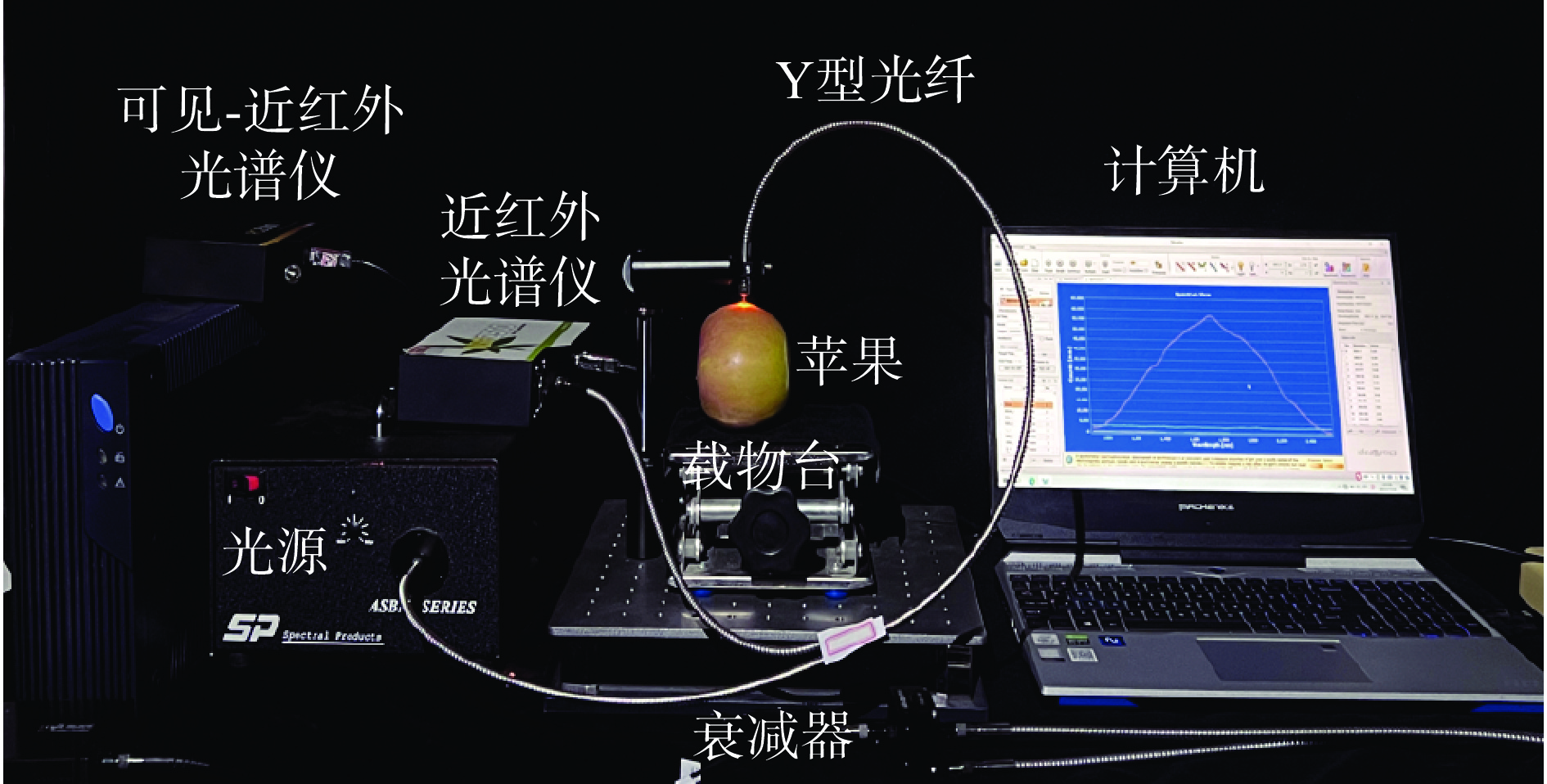
实验室搭建的近红外光谱检测系统如图2所示,主要由光源、Y型光纤、光谱仪和计算机组成。将光源和光纤衰减器通过直通光纤连接,Y型光纤的六孔端连接光纤衰减器的另一端,单孔端连接光谱仪,光谱仪的另一端通过USB与计算机连接。光谱数据可直接通过软件Morpho 3.2采集获得。三个标记部位各进行一次光谱采集,获得的3次光谱信息取平均值作为该样本的漫反射光谱,共采集160个不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果的光谱信息。按照2:1的比例划分建模集与预测集。
光谱采集参数:可见-近红外波段(400~1000 nm):积分时间为45 ms,平均次数为10,窗口平滑为5。近红外波段(900~2500 nm):积分时间为5 ms,平均次数为10,窗口平滑为5。
光纤探头直接对准标准白板或样品进行光谱信号采集。首先对光谱进行校正,通过关闭和打开光源来采集标准白板的反射光谱,然后分别作为用于参考的暗光谱和光源光谱。每个样品的光谱反射率按照公式(1)进行计算:
(1) 其中:R是相对于标准白板的样品光谱反射率;R0是样品光谱反射率;RD是暗光谱反射率;RW是光源光谱反射率。
1.3 光谱处理
1.3.1 光谱预处理
由于环境、仪器、人为操作等影响,光谱可能会受到噪声的干扰,有必要在建模之前需要对原始光谱进行预处理[16]。标准正态变量变换(standard normalized variate,SNV)是较为常用的预处理方法之一,用于光散射校正,减少光程的变化对光谱信息的干扰[17]。因此本研究对所有原始光谱数据进行SNV预处理。
1.3.2 特征波长筛选
为了消除原始光谱中无用变量,提高模型性能,加快模型检测速度,对光谱进行特征波段筛选。连续投影算法(successive projections algorithm,SPA)是一种前向变量选择算法,消除原始光谱矩阵中的冗余信息,最小化光谱中变量的共线性[18]。竞争性自适应重加权算法(competitive adaptive reweighted sampling,CARS)算法是一种基于PLS和达尔文进化论原理“适者生存”的变量选择算法,通过绝对回归系数大小筛选波长,剔除权重小的变量带[19]。无信息变量消除法(uninformative variable elimination,UVE)算法是基于PLS回归系数,将随机噪声变量加到光谱数据后,通过交叉验证去除无关变量[20]。因此,本研究采用SPA、CARS以及UVE这3种算法对光谱进行特征波段筛选。
1.3.3 模型建立与性能评价
PLS广泛用于定量分析,该方法能够结合矩阵的分解与回归,同时考虑浓度矩阵Y(品质参数)和光谱矩阵X[21]。支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)是基于非参数内核的学习算法,将问题从低维空间映射到高维空间,并使用线性算法在高维空间中寻找最优超平面,可以解决原始特征空间中的非线性关系[22]。本研究为预测不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的理化指标,采用PLS、SVM算法建立预测模型。
模型的性能用校正集决定系数(determination coefficient of calibration,Rc2)、校正集均方根误差(root mean square error of calibration,RMSEC)、预测集决定系数、预测集均方根误差以及相对预测偏差(relative percent deviation,RPD)来评估。RPD值大于2.50表示模型稳健性很好,介于2.00和2.50之间表示模型具有较好的稳健性,小于2.00表明模型稳健性较差[23]。
1.4 数据处理
使用数据处理软件OriginPro 2022b绘制各种理化指标的变化趋势、相关性分析、主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA),使用IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0软件进行方差分析(P<0.05)和线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)。使用MATLAB R2016a中PLS toolbox 7.5工具箱对光谱数据进行预处理、特征波段挑选并建立定量模型。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的理化指标变化
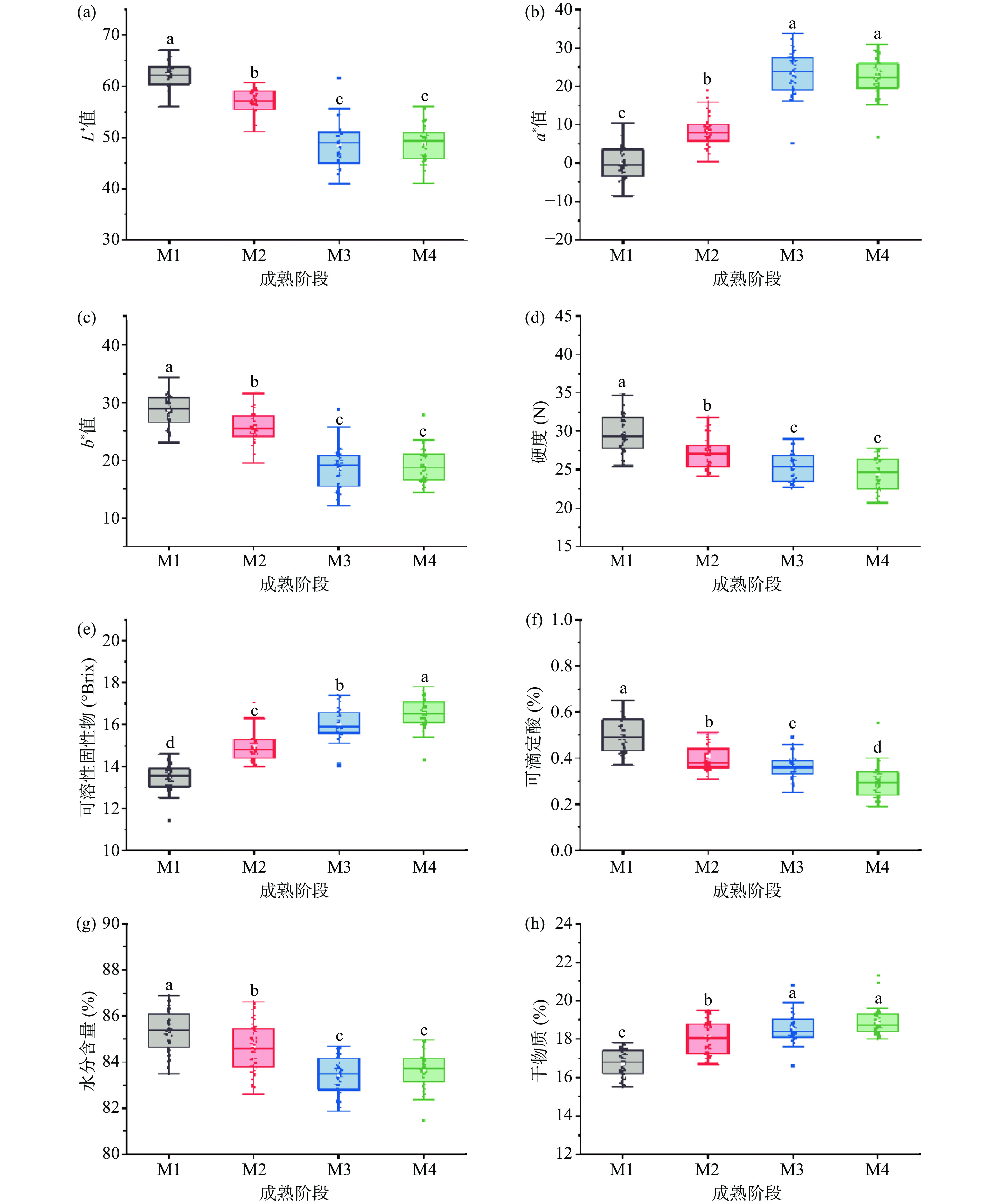
由图3所示,与成熟后期相比(M3到M4),在成熟前期(M1、M2)阿森泰克苹果的物理指标(L*、a*、b*值和FI)变化程度更剧烈。色泽是评价果实外观品质的重要指标,随着苹果不断成熟,苹果果皮的L*值逐渐降低,表明果皮亮度降低(图3a)。a*值不断升高(图3b),b*值逐渐降低(图3c),表明阿森泰克苹果果皮逐渐退绿而呈红色,主要是由于果实细胞中叶绿素分解,花青素、类胡萝卜素等含量增加[24]。M3、M4阶段的果实L*、a*、b*值均没有显著性差异(P>0.05),表明成熟后期果实的色泽较为稳定,这与Iglesias等[3]对阿森泰克苹果的研究结论一致。在成熟过程中,随着苹果果实成熟,果皮细胞间的果胶分解,细胞壁中的原果胶在果胶酶的作用下逐渐降解为可溶性果胶,FI开始下降[25]。阿森泰克苹果的FI从29.69 N显著降低至24.44 N(P<0.05)(图3d),下降率为17.68%,这明显低于张猛胜[26]在不同成熟度的富士苹果研究中FI的下降率(21.26%)因此,相较于富士,阿森泰克的硬度变化更小。
![]() 图 3 不同成熟阶段(M1、M2、M3、M4)阿森泰克苹果的理化指标注:不同字母表示不同成熟度苹果果实的不同指标差异显著(P<0.05);图4同。Figure 3. Physical and chemical indicators of Aztec apples at different maturity levels (M1, M2, M3 and M4)
图 3 不同成熟阶段(M1、M2、M3、M4)阿森泰克苹果的理化指标注:不同字母表示不同成熟度苹果果实的不同指标差异显著(P<0.05);图4同。Figure 3. Physical and chemical indicators of Aztec apples at different maturity levels (M1, M2, M3 and M4)此外,阿森泰克苹果在不同成熟阶段的化学指标(SSC、TA、MC和DMC)也存在明显变化。SSC和TA是影响苹果口感的重要因素,随着阿森泰克苹果成熟,SSC从13.5°Brix显著上升到16.5°Brix(图3e),TA则从0.50%显著降低到0.30%(P<0.05)(图3f)。张猛胜[26]发现富士苹果在成熟过程中SSC从12.69%增加到14.62%,TA从0.28%下降到0.22%,其变化幅度均明显低于阿森泰克苹果,这表明阿森泰克苹果与富士苹果在成熟过程中的SSC和TA的差异性。MC、DMC是判断水果成熟度的重要指标,如图3g所示,随着成熟度增加,苹果果实MC整体呈下降趋势,M1、M2和M3组阿森泰克苹果的含水量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。这是由于苹果成熟过程中,SSC积累,且细胞分裂,纤维素、半纤维素等不溶性固体增加,DMC增加,导致MC逐渐下降。阿森泰克苹果的DMC含量在成熟阶段从16.74%显著升至18.91%(P<0.05)(图3h),Vieira等[27]研究发现富士在成熟阶段DMC也呈上升趋势,但含量低于阿森泰克,因为DMC与水果中的淀粉、糖分含量直接相关,阿森泰克的糖含量高于富士。
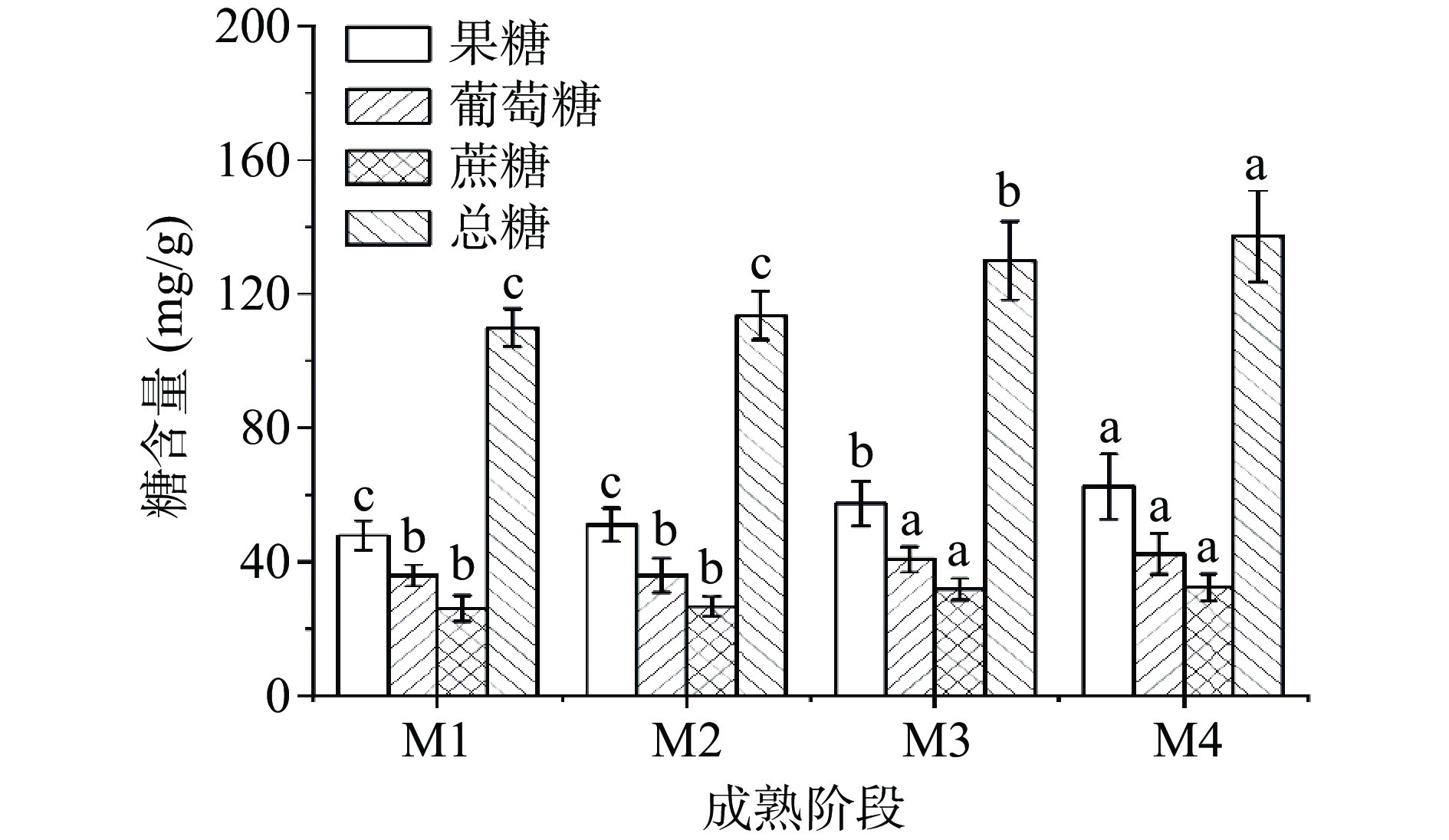
苹果的可溶性糖主要包括果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖,属于果糖积累型果实[28]。整体上阿森泰克苹果的可溶性糖呈上升趋势,与李千里[28]研究结论一致。主要是大多数碳水化合物通过糖酵解和三羧酸循环快速代谢,在发育的早期阶段,苹果中糖分积累量低,成熟过程中,淀粉水平开始下降,可溶性糖含量增加,随着有机酸水平的下降,甜度值达到最大[29]。由图4所示,阿森泰克的可溶性糖以果糖为主,约占总可溶性糖的45%左右,其次是葡萄糖,蔗糖最低。而蜜脆、金冠、玉林等品种成熟后蔗糖高于葡萄糖含量,烟富8号中蔗糖(24.0 mg/g)和葡萄糖含量(22.0 mg/g)相当,但均低于阿森泰克苹果(蔗糖:32.35 mg/g,葡萄糖:42.40 mg/g)[28]。
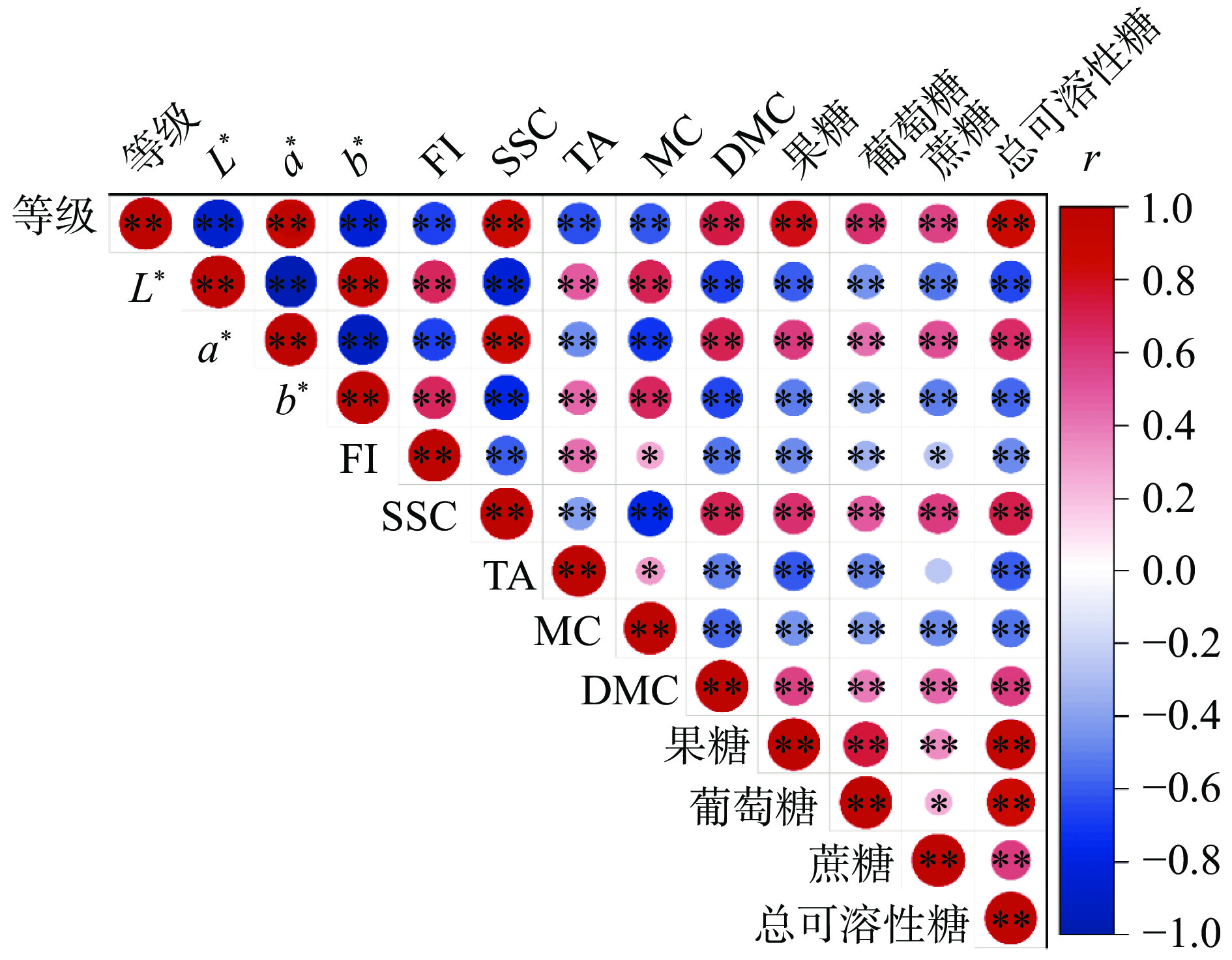
2.2 不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果理化指标的关联性分析
为了明确阿森泰克苹果成熟过程中各理化指标之间的关联性,对其进行Pearson相关性分析以及主成分分析,结果如图5所示。阿森泰克苹果的成熟度等级与所有指标都呈现极显著相关性(P<0.01),与a*值相关性最强,相关系数(correlation coefficient,r)为0.88,与SSC、果糖、总糖呈强正相关,r分别为0.85、0.80和0.85,与L*值、b*值呈强负相关,r分别为−0.87、−0.84。表明阿森泰克成熟过程中色泽、糖含量变化显著。DMC与成熟度等级的相关性也较强,r为0.73。通过Pearson相关性分析发现,在阿森泰克苹果的成熟过程中,色泽、FI、SSC、TA、可溶性糖、DMC、MC等品质都发生了较大变化。
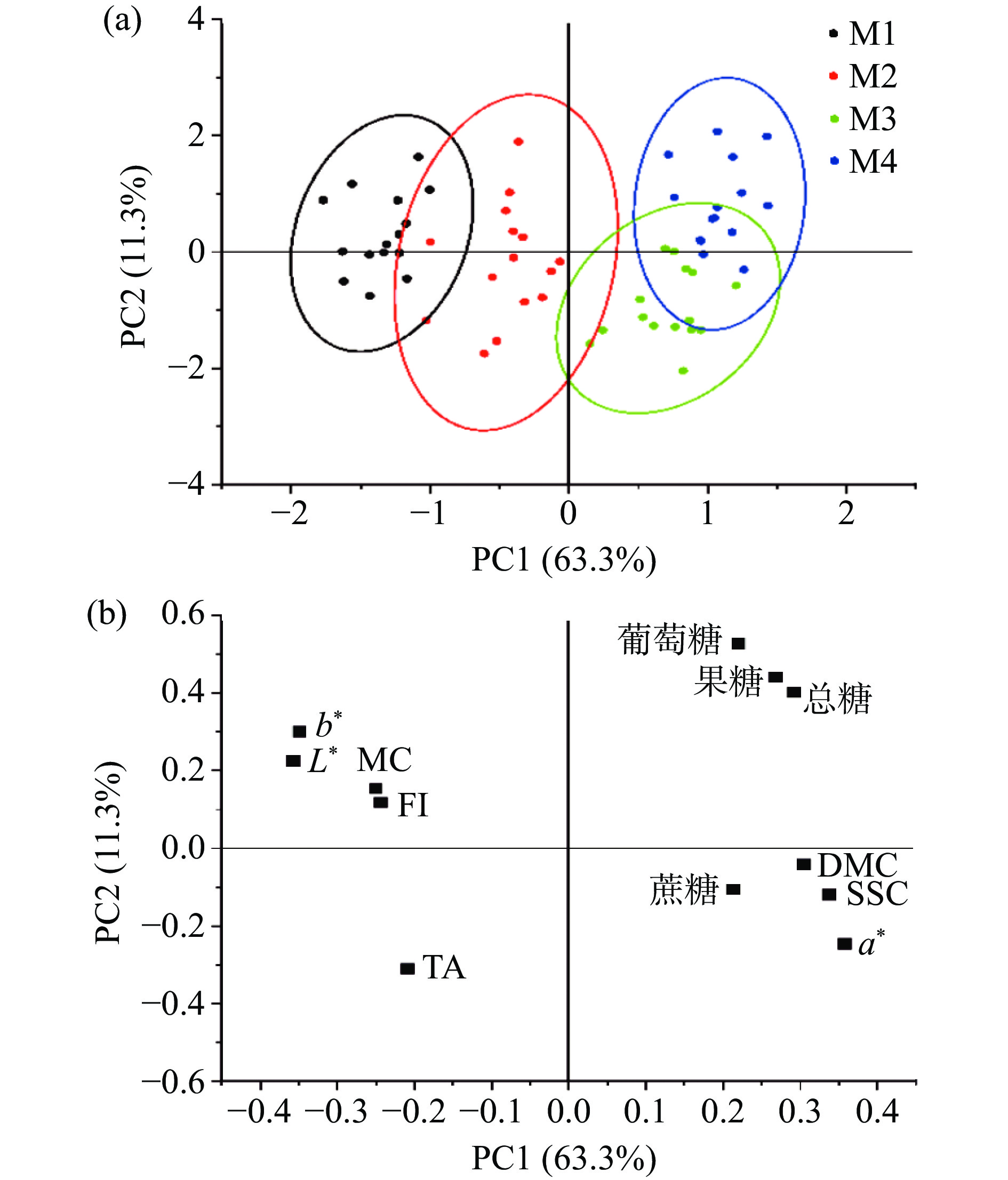
2.3 不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果理化指标的主成分聚类分析
由图6所示,第一主成分(PC1)和第二主成分(PC2)累计贡献率达到74.6%,能够表征原始变量的特征差异。PCA结果显示,处于不同成熟阶段的苹果理化指标在PC1上呈现有规律的分布,根据PC1可以实现对不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的区分(图6a),其中M1、M2组苹果样品分布在第二、三象限,M3、M4组的样品分布在第一、四象限。说明不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果在品质上有显著差异。PC1与SSC、a*值呈高度正相关,与L*值、b*值呈高度负相关(图6b)。表明本研究中对阿森泰克苹果样本聚类贡献率较大的是SSC、a*值、L*值、b*值,有助于区分果实的不同成熟阶段。同时PCA结果中贡献率大的理化指标与上述相关性分析结果较吻合。
2.4 不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的光谱变化
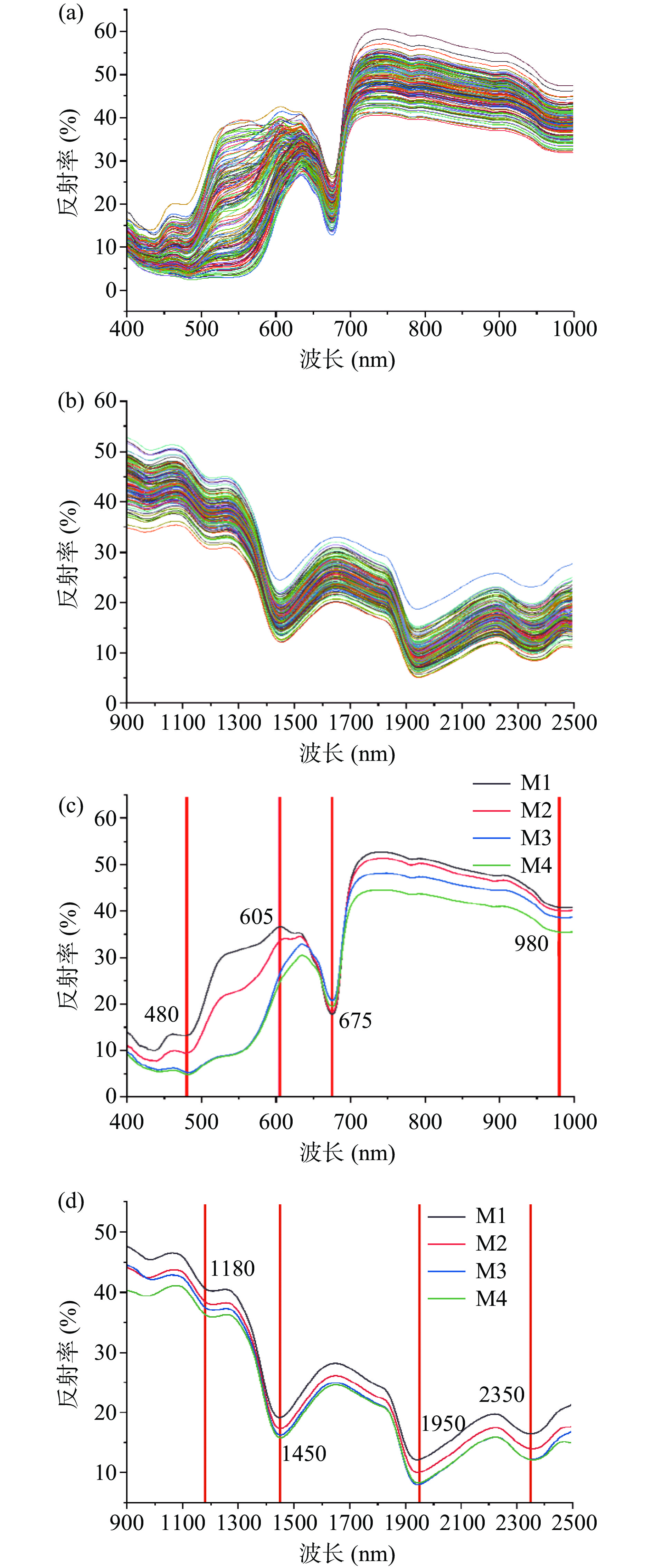
由图7a和7b所示,各样本的光谱曲线具有相同趋势,但因内部物质含量变化而产生光谱反射率差异,低成熟度苹果的光谱反射率高于高成熟度苹果。Zhang等[30]观察到不同成熟期富士苹果在Vis-NIR波段也有类似的下降趋势。在Vis-NIR波段范围内,480~675 nm范围处,M1、M2组与M3、M4组果实光谱差异明显(图7c),因为发育前期阿森泰克的颜色差异大,而后期色泽差异不明显。其中480~605 nm区域的光谱受花青素含量的影响,不同成熟阶段积累的花青素水平存在差异,约675 nm处的波谷与C-H基团的二级倍频有关,是苹果中叶绿素的吸收峰,980 nm处为O-H键拉伸带在水中的第二个泛音,与果实内部的水分变化相关[30]。在NIR波段范围内,光谱反射率差异主要是成熟过程中阿森泰克的糖含量变化引起的。其中1180 nm处的吸收峰(图7d),可能是碳水化合物中的C-H的延伸[31]。在1450和1950 nm附近的强吸收峰,主要与C-H拉伸的第二泛音、O-H拉伸和弯曲振动有关[32]。2350 nm附近的吸收峰与糖、有机酸的C-H有关[33]。
2.5 不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的光谱聚类分析
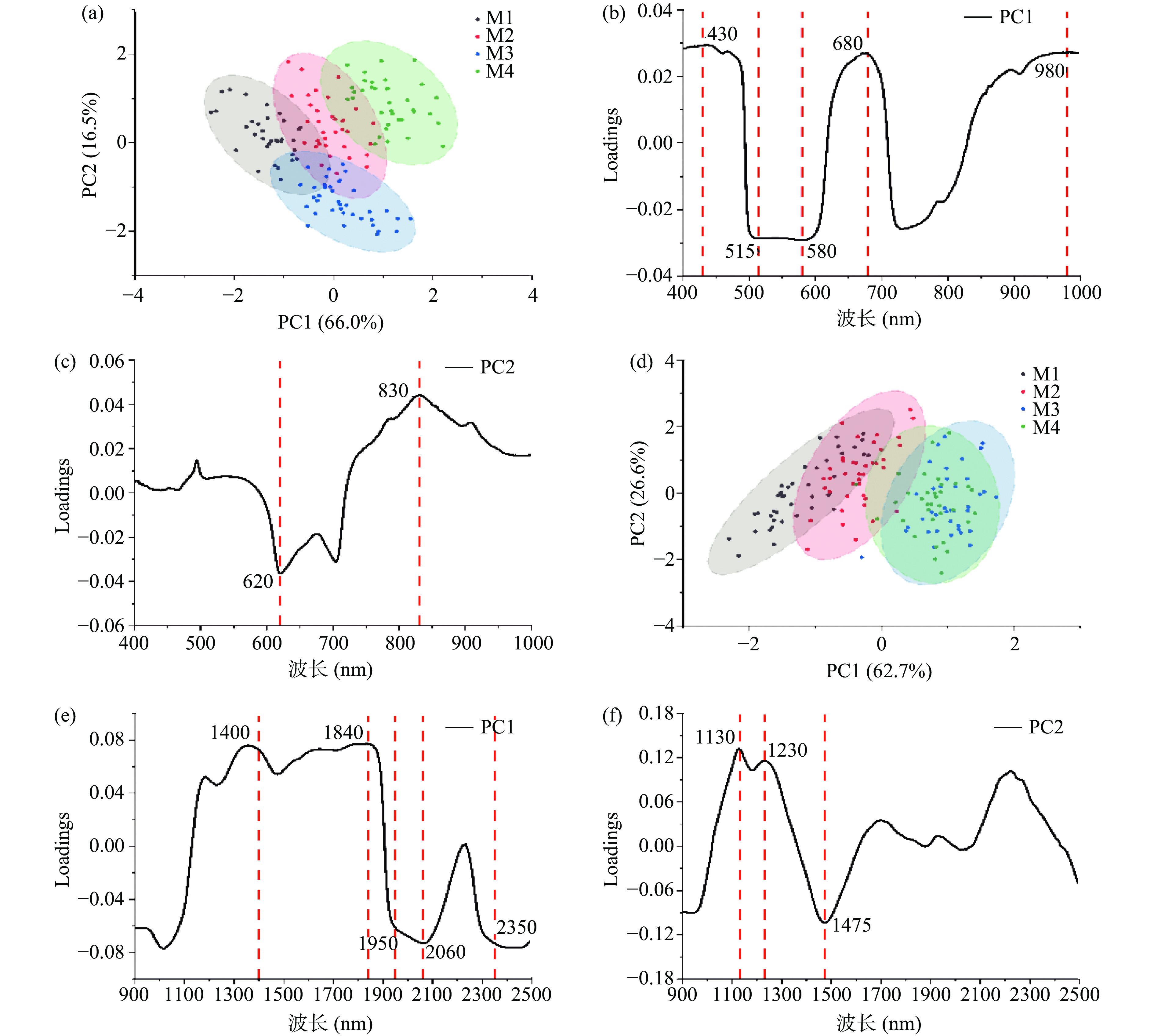
分别对不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果Vis-NIR、NIR范围内的全光谱数据进行PCA聚类分析,在Vis-NIR(400~1000 nm)波段下,PC1和PC2的累计贡献率为82.5%(图8a),不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的光谱信息无法实现良好的聚类效果。图8b和图8c分别显示了Vis-NIR波段下PC1和PC2的载荷图,430、515~580、680和980 nm波段对PC1的贡献率最大,620、830 nm波段对PC2具有主要贡献,主要是与花青素、类胡萝卜素、叶绿素、水分子的吸收有关[30]。在NIR(900~2500 nm)范围内,PC1、PC2的累计贡献率为89.3%,M1、M2组苹果样品主要聚集在PC1的负半轴,M3、M4组则主要分布在PC1的正半轴,重叠更明显,且不易区分(图8d)。PC1中1400、1840、1950~2060、2350 nm波段的贡献较大(图8e),1130~1230、1475 nm是PC2的主要贡献波段(图8f),这些波段主要与水分、糖有关[33]。综上所述,基于各成熟度苹果的光谱信息,PCA无法区分不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果。
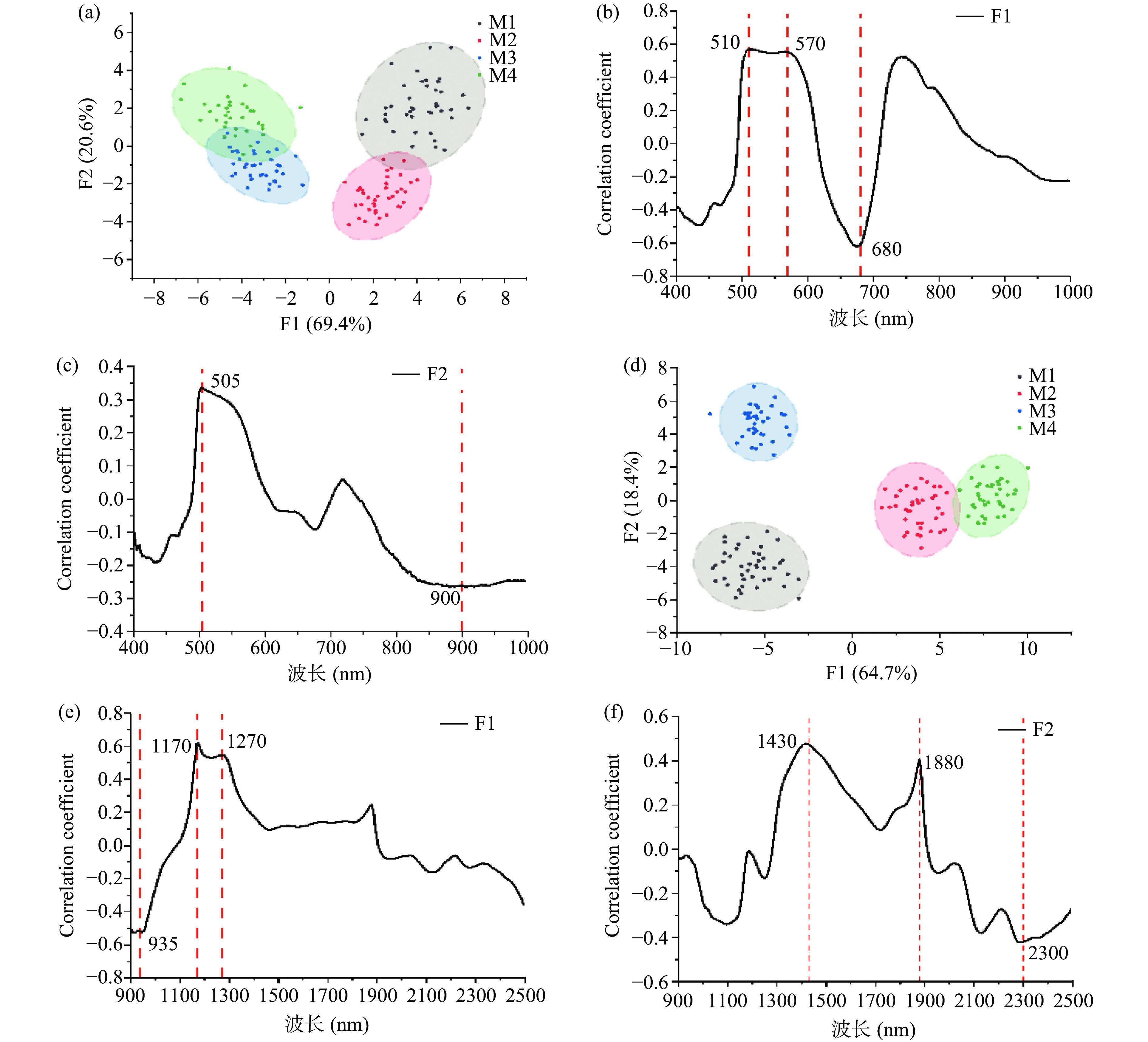
PCA无法准确划分各个成熟度的阿森泰克苹果的界限,因此需要有监督模式识别方法。LDA可提供更好的分类,有助于更好地理解特征数据的分布[34]。对Vis-NIR波段下光谱信息进行LDA,第一判别因子(F1)、第二判别因子(F2)累计贡献率为90.0%。M1、M2组苹果样品分布在F1正半轴,M3、M4组分布在F1负半轴,尽管M3、M4组仍存在少数重叠,但能够明显区分不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果(图9a)。在Vis-NIR范围内,F1与680 nm处的反射率呈负相关,与510~570 nm呈现正相关(图9b)。F2与505 nm附近的反射率呈正相关,与800~1000 nm呈负相关(图9c)。表明阿森泰克苹果在成熟过程中颜色以及水分含量的变化造成Vis-NIR光谱反射率存在差异。在NIR范围内,四个成熟度等级的阿森泰克苹果可以实现明显的区分(图9d)。F1与935、1170~1270 nm范围附近的反射率呈正相关(图9e),该区域的反射率可能与水分损失和糖含量有关[35]。F2得分与1430和1880 nm附近的反射率呈正相关(图9f),其中1880 nm可能与O-H和NH的组合有关,与2300 nm附近的反射率呈负相关,对应糖或有机酸C-H的组合[33]。
综上所述,基于多成熟度光谱信息,LDA可以区分不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果,510~680、1170~1270、2300 nm是主要贡献波段,为后续定量模型的建立提供依据。
2.6 基于全波长建立融合不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质预测模型
分别在Vis-NIR(400~1000 nm)与NIR(900~2500 nm)波段范围下,经SNV预处理全波段光谱后,构建了阿森泰克苹果理化指标(L*、a*、b*、FI、SSC、TA、MC和DMC)的PLS和SVM预测模型。结果如表1所示,除a*值,其余理化指标的PLS模型的预测效果均好于SVM模型。这表明不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果品质与光谱信息间存在大量的线性关联,更适合采用PLS等线性算法进行预测。当预测的苹果成分与叶绿素变化无强相关性时,NIR范围可以提供比Vis-NIR范围更多的信息,而Vis-NIR波段中化学成分键的相对强度较弱[36]。Ignat等[36]采用NIR技术预测苹果SSC、TA和FI获得更好的结果。本研究中也有相同结论,在NIR范围内FI、SSC、TA、MC、DMC的模型性能好于Vis-NIR范围。
表 1 基于Vis-NIR和NIR全波段预测阿森泰克苹果品质的PLS和SVM模型Table 1. PLS and SVM models for prediction of quality indexes of Aztec apples based on full wavebands in Vis-NIR and NIR理化指标 范围 标准差 波段范围 (nm) PLS SVM Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD L* 40.9~67.1 6.7 400~1000 0.95 1.4 0.94 1.8 4.03 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 3.99 900~2500 0.94 1.5 0.93 1.9 3.83 0.90 1.9 0.89 2.6 2.81 a* −8.6~33.8 11.0 400~1000 0.98 1.6 0.95 2.5 4.29 0.97 2.0 0.96 2.1 5.11 900~2500 0.93 2.9 0.91 3.4 3.28 0.92 3.0 0.90 3.7 3.00 b* 12.1~34.3 5.2 400~1000 0.92 1.5 0.92 1.5 3.45 0.91 1.5 0.91 1.7 3.10 900~2500 0.89 1.7 0.88 1.7 2.80 0.90 1.6 0.77 2.2 2.13 FI(N) 20.70~34.73 2.97 400~1000 0.84 1.11 0.82 1.25 2.26 0.53 1.90 0.47 2.05 1.37 900~2500 0.85 1.01 0.82 1.12 2.32 0.73 1.48 0.71 1.39 1.88 SSC(°Brix) 12.5~17.8 1.3 400~1000 0.91 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.02 0.86 0.5 0.82 0.5 2.38 900~2500 0.92 0.3 0.91 0.4 3.25 0.91 0.4 0.86 0.5 2.52 TA(%) 0.17~0.69 0.10 400~1000 0.82 0.04 0.80 0.04 2.24 0.75 0.04 0.70 0.05 1.85 900~2500 0.87 0.03 0.85 0.04 2.49 0.92 0.03 0.80 0.05 1.87 MC(%) 81.88~86.89 1.17 400-1000 0.79 0.53 0.78 0.54 2.14 0.74 0.61 0.66 0.67 1.71 900-2500 0.82 0.56 0.82 0.56 2.31 0.82 0.59 0.75 0.66 1.94 DMC(%) 15.5~19.9 1.1 400~1000 0.81 0.4 0.80 0.5 2.26 0.82 0.4 0.78 0.5 2.14 900~2500 0.87 0.4 0.81 0.5 2.26 0.80 0.4 0.78 0.5 2.08 对于色泽(L*、a*、b*)的预测,基于Vis-NIR范围开发的模型性能更佳。因为Vis-NIR范围包括叶绿素、花青素等的吸收光谱。其中L*、b*值的PLS模型性能略优于SVM模型,其Rp2分别为0.94、0.92。a*值的最优模型为SVM,Rp2为0.96。L*、a*、b*值的模型预测结果很好,RPD均大于3.00,具有很高的精度与稳健性。李磊[37]在400~1000 nm范围内预测不同采收期富士苹果的L*值,PLS模型Rp2为0.86。相比之下,本研究的模型精度更高,可能是由于阿森泰克苹果不套袋种植,颜色变化更大。FI的PLS模型Rp2为0.82,而Zhang等[38]建立包含六个不同成熟阶段富士苹果的FI预测模型,Rp2为0.86,高于本研究FI的模型精度,考虑是其研究的成熟期范围更大,扩大样品的成熟度范围可以消除成熟度变化对硬度预测的影响。
SSC的PLS预测模型Rp2为0.91,RPD为3.25。Guo等[39]分别在Vis-NIR、NIR波段下预测商业成熟的富士苹果SSC,发现NIR范围能更好的预测SSC,Rp2为0.81,RPD为2.27。对比之下本研究模型精度更高,这可以通过所有成熟度中SSC具有更高变异性来解释,多成熟度模型具有较高预测精度。TA的预测模型Rp2为0.85,RPD为2.49。Mcglone等[40]构建含有成熟早期至晚期的皇家嘎拉苹果的TA预测模型,Rp2为0.38,RPD为1.54,精度显著低于本研究的模型,可能是数据集的TA分布非常窄(标准差为0.08%),本研究TA标准差为0.10%。MC的最优模型为PLS,Rp2为0.82,相较于Abasi等[41]基于350~2500 nm范围内光谱构建的PLS模型(Rp2为0.60),本研究精度更高,这可能与所选择的光谱变量范围(900~2500 nm)有关,减少部分无关信息。DMC的最优模型为PLS,Rp2分别为0.81,精度高于Zhang等[42]通过NIR波段建立的四个成熟度的蜜脆苹果的DMC模型(Rp2为0.76),因为蜜脆苹果在成熟过程中DMC的变化小,导致其预测模型精度较低。
2.7 基于特征波长建立融合不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质预测模型
为建立快速、准确的预测模型,使用SPA、CARS和UVE对Vis-NIR、NIR波段范围进行特征波长提取,确定与阿森泰克苹果品质相关的特征波长,以提高模型性能,结果如表2所示。与基于全波段光谱建立的L*、a*、b*、DMC、MC的最优模型相比,SPA挑选的特征波段所建立的预测模型效果得到提升。因为SPA采用简单的投影运算来选择共线性最小的变量,能降低光谱信息维度,剔除冗余信息[18]。
表 2 基于SPA、CARS、UVE算法筛选的特征波段的阿森泰克苹果品质PLS和SVM模型Table 2. PLS and SVM models for quality indexes of Aztec apples based on feature bands from SPA, CARS and UVE algorithms理化指标 波段范围 (nm) 波段选择方式 波长数目 PLS SVM Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD L* 400~1000 SPA 18 0.95 1.5 0.95 1.7 4.32 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 3.89 CARS 74 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.7 4.08 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 4.05 UVE 422 0.95 1.5 0.93 1.9 3.78 0.94 1.6 0.93 1.9 3.84 900~2500 SPA 18 0.91 1.9 0.91 2.2 3.27 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.4 2.99 CARS 21 0.91 1.8 0.91 2.2 3.20 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.3 3.11 UVE 72 0.93 1.6 0.93 2.0 3.55 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.4 2.94 a* 400~1000 SPA 10 0.96 2.1 0.96 2.1 5.05 0.96 2.2 0.97 2.0 5.34 CARS 12 0.96 2.2 0.96 2.2 4.72 0.93 2.8 0.91 3.1 3.43 UVE 117 0.97 2.0 0.94 2.5 4.20 0.96 2.3 0.95 2.4 4.36 900~2500 SPA 26 0.93 2.9 0.93 2.9 3.89 0.92 2.9 0.91 3.4 3.22 CARS 35 0.92 2.9 0.91 3.3 3.39 0.92 3.1 0.90 3.6 3.07 UVE 89 0.94 2.5 0.92 3.2 3.48 0.91 3.2 0.88 3.9 2.83 b* 400~1000 SPA 20 0.93 1.4 0.92 1.5 3.51 0.91 1.6 0.92 1.6 3.28 CARS 148 0.93 1.4 0.90 1.6 3.14 0.93 1.4 0.90 1.7 3.02 UVE 154 0.92 1.5 0.88 1.9 2.79 0.91 1.6 0.88 1.8 2.84 900~2500 SPA 15 0.86 2.0 0.85 1.8 2.55 0.85 2.0 0.78 2.1 2.15 CARS 30 0.90 1.6 0.85 1.9 2.46 0.92 1.5 0.83 1.9 2.38 UVE 82 0.90 1.7 0.85 1.9 2.47 0.91 1.6 0.80 2.1 2.17 FI(N) 400~1000 SPA 25 0.75 1.37 0.74 1.43 1.97 0.57 1.83 0.52 1.96 1.44 CARS 56 0.78 1.29 0.71 1.52 1.86 0.63 1.71 0.61 1.81 1.55 UVE 383 0.71 1.46 0.65 1.74 1.62 0.53 1.87 0.49 2.05 1.37 900~2500 SPA 24 0.80 1.25 0.80 1.15 2.27 0.71 1.52 0.66 1.52 1.71 CARS 26 0.77 1.36 0.77 1.24 2.11 0.72 1.49 0.70 1.41 1.84 UVE 49 0.80 1.25 0.76 1.29 2.02 0.74 1.45 0.70 1.42 1.83 SSC(°Brix) 400~1000 SPA 25 0.90 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.05 0.87 0.5 0.84 0.5 2.50 CARS 32 0.91 0.4 0.88 0.5 2.76 0.89 0.5 0.85 0.5 2.60 UVE 54 0.89 0.5 0.82 0.6 2.17 0.85 0.5 0.80 0.6 2.16 900~2500 SPA 20 0.90 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.04 0.88 0.4 0.86 0.5 2.54 CARS 16 0.91 0.4 0.91 0.4 3.19 0.91 0.4 0.90 0.5 2.90 UVE 63 0.91 0.4 0.85 0.5 2.55 0.89 0.4 0.84 0.5 2.44 TA(%) 400~1000 SPA 26 0.82 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.23 0.74 0.04 0.72 0.05 1.88 CARS 64 0.81 0.04 0.78 0.04 2.13 0.78 0.04 0.76 0.04 2.01 UVE 544 0.83 0.03 0.77 0.04 2.04 0.74 0.04 0.73 0.05 1.89 900~2500 SPA 20 0.83 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.21 0.81 0.04 0.77 0.05 1.98 CARS 21 0.82 0.04 0.80 0.04 2.17 0.83 0.04 0.79 0.04 2.11 UVE 74 0.83 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.20 0.82 0.04 0.78 0.05 2.05 MC(%) 400~1000 SPA 15 0.80 0.53 0.79 0.52 2.19 0.75 0.59 0.68 0.65 1.78 CARS 28 0.80 0.52 0.78 0.53 2.14 0.82 0.50 0.78 0.54 2.11 UVE 915 0.82 0.50 0.79 0.53 2.15 0.77 0.57 0.70 0.62 1.84 900~2500 SPA 23 0.82 0.56 0.82 0.56 2.32 0.78 0.65 0.78 0.64 2.02 CARS 23 0.83 0.55 0.73 0.68 1.89 0.83 0.56 0.77 0.61 2.12 UVE 106 0.84 0.53 0.75 0.68 1.90 0.87 0.48 0.72 0.68 1.90 DMC(%) 400~1000 SPA 26 0.76 0.5 0.76 0.5 2.03 0.63 0.6 0.61 0.7 1.61 CARS 28 0.81 0.5 0.77 0.5 2.04 0.61 0.6 0.56 0.7 1.53 UVE 206 0.77 0.5 0.70 0.6 1.76 0.62 0.6 0.60 0.7 1.60 900~2500 SPA 15 0.83 0.4 0.83 0.5 2.42 0.74 0.5 0.58 0.7 1.55 CARS 31 0.82 0.4 0.75 0.5 2.02 0.80 0.4 0.76 0.6 2.05 UVE 42 0.80 0.4 0.80 0.5 2.26 0.76 0.5 0.76 0.6 2.00 L*、b*值的最优模型为SPA-PLS模型,Rp2分别为0.95、0.92;a*值的最优模型为SPA-SVM模型,Rp2为0.97,L*、a*、b*的模型RPD均大于3.00,表明模型可应用于不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的色泽预测。由表3所示,建立的L*、a*、b*值最优模型,筛选出的特征光谱变量主要位于400~680 nm波段区域,这与2.5中对Vis-NIR光谱的LDA结果一致,500~570 nm和680 nm等波段范围的贡献较大,在这些波段下不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的光谱反射率差异较大。预测FI时,使用全波长建立的模型效果最好,但模型的变量数过多,FI的SPA-PLS预测模型的Rp2为0.80,模型精度与全光谱相比略有降低,主要是由于经过SPA算法挑选24个变量,与全波段相比,变量减少90.36%,其中损失部分与硬度相关的有效信息,这可能是导致模型效果略差的原因。
表 3 用于构建不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质预测最优模型的特征波段Table 3. Characteristic bands for building optimal prediction models for the quality of Aztec apples at different maturity levels理化指标 波段范围(nm) 最优模型 波长数目 特征波段(nm) L* 400~1000 SPA-PLS 18 400.06,405.02,418.45,423.04,433.26,455.76,508.86,549.41,577.31,599.26,627.25,649.34,665.92,687.51,699.27,730.07,812.45,954.16 a* 400~1000 SPA-SVM 10 401.48,456.11,508.86,549.07,597.55,623.17,649.68,664.91,692.22,867.87 b* 400~1000 SPA-PLS 20 400.42,405.02,415.62,423.04,433.26,448.39,482.37,507.12,549.07,574.91,597.21,622.14,649.68,666.26,681.45,690.87,711.35,755.37,907.54,983.9 FI 900~2500 SPA-PLS 24 906.67,913.22,919.77,945.95,965.56,991.66,1063.24,1173.33,1250.72,1443.33,1520.13,1609.66,1673.58,1731.13,1820.7,1884.76,1936.08,2038.94,2142.2,2219.97,2258.97,2304.59,2448.8,2475.18 SSC 900~2500 CARS-PLS 16 900.11,913.22,952.49,1004.7,1571.3,1833.5,2058.27,2142.2,2155.14,2174.57,2239.46,2245.96,2304.59,2429.05,2435.63,2494.99 TA 900~2500 SPA-PLS 20 906.67,913.22,919.77,939.41,959.02,991.66,1037.24,1173.33,1257.16,1366.41,1430.52,1558.51,1718.34,1891.17,2032.5,2122.81,2206.99,2258.97,2369.97,2488.38 MC 900~2500 SPA-PLS 23 900.11,913.22,919.77,945.95,965.56,1011.21,1082.71,1173.33,1257.16,1353.57,1488.14,1622.44,1711.94,1820.7,1871.94,1929.66,2032.5,2109.88,2181.05,2337.24,2429.05,2475.18,2494.99 DMC 900~2500 SPA-PLS 15 919.77,965.56,1004.7,1082.71,1173.33,1257.16,1724.73,1820.7,1942.5,2026.06,2103.43,2239.46,2343.78,2429.05,2494.99 SSC的CARS-PLS预测模型精度与全光谱模型接近,Rp2为0.91,RPD为3.19,提取的波长数量更少,减少93.57%,模型运行速度更快。所挑选的特征波段主要分布在1450~1840 nm和1950~2400 nm区域,这些波段与碳水化合物中的C-H有关[33]。TA、MC和DMC的预测最优模型为SPA-PLS模型,Rp2分别为0.81、0.82、0.83,RPD均大于2.00,表明模型预测能力较好。SPA算法挑选的MC特征波段中970、1480、1930 nm等与O-H基团伸缩振动相关,是水的吸收峰[32]。DMC特征波段与SSC特征波段有部分处于重叠,如1004、2239、2429、2495 nm,说明干物质与苹果中的淀粉、糖分含量直接相关。
基于算法挑选的特征波段与2.5中分析的阿森泰克苹果的光谱特征吻合较好,且SPA-PLS、SPA-SVM模型能很好地预测不同成熟度阿森泰克的L*、b*、a*值,RPD高于3.00,CARS-PLS模型可以很好地预测SSC,RPD为3.19,FI、TA、MC和DMC的最优预测模型SPA-PLS的RPD均大于2.00,表明模型具有一定的实际应用价值。
3. 结论
本研究首先通过PCA、LDA探究了阿森泰克苹果在成熟过程中色泽(L*、a*、b*值)、FI、SSC、TA、MC、DMC和可溶性糖的变化规律,基于Vis-NIR与NIR光谱技术结合SPA、CARS、UVE三种算法进行特征波段挑选,再基于PLS和SVM算法建立融合不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的品质预测模型。结果表明,随着苹果不断成熟,阿森泰克的a*、SSC、DMC、可溶性糖增加,L*、b*、FI、TA、和MC降低。其中SSC、a*、L*、b*对不同成熟度阿森泰克苹果的聚类贡献率较高,510~680、1170~1270、2300 nm是相关度较高的特征波段。SPA-PLS、SPA-SVM模型能很好地预测不同成熟度阿森泰克的L*、b*、a*值,RPD分别为4.32、3.51、5.34,CARS-PLS模型可以很好地预测SSC,RPD为3.19,但FI、TA、MC、DMC的SPA-PLS模型预测精度相对较低,RPD分别为2.27、2.21、2.32、2.42。研究结果证明可见-近红外和近红外光谱方法能够预测不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质,避免模型只适用于某种成熟度的阿森泰克苹果,为阿森泰克苹果采收管理与质量安全控制提供技术参考。
-
图 3 不同成熟阶段(M1、M2、M3、M4)阿森泰克苹果的理化指标
注:不同字母表示不同成熟度苹果果实的不同指标差异显著(P<0.05);图4同。
Figure 3. Physical and chemical indicators of Aztec apples at different maturity levels (M1, M2, M3 and M4)
表 1 基于Vis-NIR和NIR全波段预测阿森泰克苹果品质的PLS和SVM模型
Table 1 PLS and SVM models for prediction of quality indexes of Aztec apples based on full wavebands in Vis-NIR and NIR
理化指标 范围 标准差 波段范围 (nm) PLS SVM Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD L* 40.9~67.1 6.7 400~1000 0.95 1.4 0.94 1.8 4.03 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 3.99 900~2500 0.94 1.5 0.93 1.9 3.83 0.90 1.9 0.89 2.6 2.81 a* −8.6~33.8 11.0 400~1000 0.98 1.6 0.95 2.5 4.29 0.97 2.0 0.96 2.1 5.11 900~2500 0.93 2.9 0.91 3.4 3.28 0.92 3.0 0.90 3.7 3.00 b* 12.1~34.3 5.2 400~1000 0.92 1.5 0.92 1.5 3.45 0.91 1.5 0.91 1.7 3.10 900~2500 0.89 1.7 0.88 1.7 2.80 0.90 1.6 0.77 2.2 2.13 FI(N) 20.70~34.73 2.97 400~1000 0.84 1.11 0.82 1.25 2.26 0.53 1.90 0.47 2.05 1.37 900~2500 0.85 1.01 0.82 1.12 2.32 0.73 1.48 0.71 1.39 1.88 SSC(°Brix) 12.5~17.8 1.3 400~1000 0.91 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.02 0.86 0.5 0.82 0.5 2.38 900~2500 0.92 0.3 0.91 0.4 3.25 0.91 0.4 0.86 0.5 2.52 TA(%) 0.17~0.69 0.10 400~1000 0.82 0.04 0.80 0.04 2.24 0.75 0.04 0.70 0.05 1.85 900~2500 0.87 0.03 0.85 0.04 2.49 0.92 0.03 0.80 0.05 1.87 MC(%) 81.88~86.89 1.17 400-1000 0.79 0.53 0.78 0.54 2.14 0.74 0.61 0.66 0.67 1.71 900-2500 0.82 0.56 0.82 0.56 2.31 0.82 0.59 0.75 0.66 1.94 DMC(%) 15.5~19.9 1.1 400~1000 0.81 0.4 0.80 0.5 2.26 0.82 0.4 0.78 0.5 2.14 900~2500 0.87 0.4 0.81 0.5 2.26 0.80 0.4 0.78 0.5 2.08 表 2 基于SPA、CARS、UVE算法筛选的特征波段的阿森泰克苹果品质PLS和SVM模型
Table 2 PLS and SVM models for quality indexes of Aztec apples based on feature bands from SPA, CARS and UVE algorithms
理化指标 波段范围 (nm) 波段选择方式 波长数目 PLS SVM Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD Rc2 RMSEC Rp2 RMSEP RPD L* 400~1000 SPA 18 0.95 1.5 0.95 1.7 4.32 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 3.89 CARS 74 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.7 4.08 0.94 1.6 0.94 1.8 4.05 UVE 422 0.95 1.5 0.93 1.9 3.78 0.94 1.6 0.93 1.9 3.84 900~2500 SPA 18 0.91 1.9 0.91 2.2 3.27 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.4 2.99 CARS 21 0.91 1.8 0.91 2.2 3.20 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.3 3.11 UVE 72 0.93 1.6 0.93 2.0 3.55 0.91 1.8 0.90 2.4 2.94 a* 400~1000 SPA 10 0.96 2.1 0.96 2.1 5.05 0.96 2.2 0.97 2.0 5.34 CARS 12 0.96 2.2 0.96 2.2 4.72 0.93 2.8 0.91 3.1 3.43 UVE 117 0.97 2.0 0.94 2.5 4.20 0.96 2.3 0.95 2.4 4.36 900~2500 SPA 26 0.93 2.9 0.93 2.9 3.89 0.92 2.9 0.91 3.4 3.22 CARS 35 0.92 2.9 0.91 3.3 3.39 0.92 3.1 0.90 3.6 3.07 UVE 89 0.94 2.5 0.92 3.2 3.48 0.91 3.2 0.88 3.9 2.83 b* 400~1000 SPA 20 0.93 1.4 0.92 1.5 3.51 0.91 1.6 0.92 1.6 3.28 CARS 148 0.93 1.4 0.90 1.6 3.14 0.93 1.4 0.90 1.7 3.02 UVE 154 0.92 1.5 0.88 1.9 2.79 0.91 1.6 0.88 1.8 2.84 900~2500 SPA 15 0.86 2.0 0.85 1.8 2.55 0.85 2.0 0.78 2.1 2.15 CARS 30 0.90 1.6 0.85 1.9 2.46 0.92 1.5 0.83 1.9 2.38 UVE 82 0.90 1.7 0.85 1.9 2.47 0.91 1.6 0.80 2.1 2.17 FI(N) 400~1000 SPA 25 0.75 1.37 0.74 1.43 1.97 0.57 1.83 0.52 1.96 1.44 CARS 56 0.78 1.29 0.71 1.52 1.86 0.63 1.71 0.61 1.81 1.55 UVE 383 0.71 1.46 0.65 1.74 1.62 0.53 1.87 0.49 2.05 1.37 900~2500 SPA 24 0.80 1.25 0.80 1.15 2.27 0.71 1.52 0.66 1.52 1.71 CARS 26 0.77 1.36 0.77 1.24 2.11 0.72 1.49 0.70 1.41 1.84 UVE 49 0.80 1.25 0.76 1.29 2.02 0.74 1.45 0.70 1.42 1.83 SSC(°Brix) 400~1000 SPA 25 0.90 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.05 0.87 0.5 0.84 0.5 2.50 CARS 32 0.91 0.4 0.88 0.5 2.76 0.89 0.5 0.85 0.5 2.60 UVE 54 0.89 0.5 0.82 0.6 2.17 0.85 0.5 0.80 0.6 2.16 900~2500 SPA 20 0.90 0.4 0.90 0.4 3.04 0.88 0.4 0.86 0.5 2.54 CARS 16 0.91 0.4 0.91 0.4 3.19 0.91 0.4 0.90 0.5 2.90 UVE 63 0.91 0.4 0.85 0.5 2.55 0.89 0.4 0.84 0.5 2.44 TA(%) 400~1000 SPA 26 0.82 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.23 0.74 0.04 0.72 0.05 1.88 CARS 64 0.81 0.04 0.78 0.04 2.13 0.78 0.04 0.76 0.04 2.01 UVE 544 0.83 0.03 0.77 0.04 2.04 0.74 0.04 0.73 0.05 1.89 900~2500 SPA 20 0.83 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.21 0.81 0.04 0.77 0.05 1.98 CARS 21 0.82 0.04 0.80 0.04 2.17 0.83 0.04 0.79 0.04 2.11 UVE 74 0.83 0.04 0.81 0.04 2.20 0.82 0.04 0.78 0.05 2.05 MC(%) 400~1000 SPA 15 0.80 0.53 0.79 0.52 2.19 0.75 0.59 0.68 0.65 1.78 CARS 28 0.80 0.52 0.78 0.53 2.14 0.82 0.50 0.78 0.54 2.11 UVE 915 0.82 0.50 0.79 0.53 2.15 0.77 0.57 0.70 0.62 1.84 900~2500 SPA 23 0.82 0.56 0.82 0.56 2.32 0.78 0.65 0.78 0.64 2.02 CARS 23 0.83 0.55 0.73 0.68 1.89 0.83 0.56 0.77 0.61 2.12 UVE 106 0.84 0.53 0.75 0.68 1.90 0.87 0.48 0.72 0.68 1.90 DMC(%) 400~1000 SPA 26 0.76 0.5 0.76 0.5 2.03 0.63 0.6 0.61 0.7 1.61 CARS 28 0.81 0.5 0.77 0.5 2.04 0.61 0.6 0.56 0.7 1.53 UVE 206 0.77 0.5 0.70 0.6 1.76 0.62 0.6 0.60 0.7 1.60 900~2500 SPA 15 0.83 0.4 0.83 0.5 2.42 0.74 0.5 0.58 0.7 1.55 CARS 31 0.82 0.4 0.75 0.5 2.02 0.80 0.4 0.76 0.6 2.05 UVE 42 0.80 0.4 0.80 0.5 2.26 0.76 0.5 0.76 0.6 2.00 表 3 用于构建不同成熟度的阿森泰克苹果品质预测最优模型的特征波段
Table 3 Characteristic bands for building optimal prediction models for the quality of Aztec apples at different maturity levels
理化指标 波段范围(nm) 最优模型 波长数目 特征波段(nm) L* 400~1000 SPA-PLS 18 400.06,405.02,418.45,423.04,433.26,455.76,508.86,549.41,577.31,599.26,627.25,649.34,665.92,687.51,699.27,730.07,812.45,954.16 a* 400~1000 SPA-SVM 10 401.48,456.11,508.86,549.07,597.55,623.17,649.68,664.91,692.22,867.87 b* 400~1000 SPA-PLS 20 400.42,405.02,415.62,423.04,433.26,448.39,482.37,507.12,549.07,574.91,597.21,622.14,649.68,666.26,681.45,690.87,711.35,755.37,907.54,983.9 FI 900~2500 SPA-PLS 24 906.67,913.22,919.77,945.95,965.56,991.66,1063.24,1173.33,1250.72,1443.33,1520.13,1609.66,1673.58,1731.13,1820.7,1884.76,1936.08,2038.94,2142.2,2219.97,2258.97,2304.59,2448.8,2475.18 SSC 900~2500 CARS-PLS 16 900.11,913.22,952.49,1004.7,1571.3,1833.5,2058.27,2142.2,2155.14,2174.57,2239.46,2245.96,2304.59,2429.05,2435.63,2494.99 TA 900~2500 SPA-PLS 20 906.67,913.22,919.77,939.41,959.02,991.66,1037.24,1173.33,1257.16,1366.41,1430.52,1558.51,1718.34,1891.17,2032.5,2122.81,2206.99,2258.97,2369.97,2488.38 MC 900~2500 SPA-PLS 23 900.11,913.22,919.77,945.95,965.56,1011.21,1082.71,1173.33,1257.16,1353.57,1488.14,1622.44,1711.94,1820.7,1871.94,1929.66,2032.5,2109.88,2181.05,2337.24,2429.05,2475.18,2494.99 DMC 900~2500 SPA-PLS 15 919.77,965.56,1004.7,1082.71,1173.33,1257.16,1724.73,1820.7,1942.5,2026.06,2103.43,2239.46,2343.78,2429.05,2494.99 -
[1] 孟云, 王晶晶, 田惠惠, 等. 阿珍富士苹果在陕西千阳的引种表现[J]. 落叶果树,2020,52(1):30−32. [MENG Y, WANG J J, TIAN H H, et al. Performance and cultivation techniques of apple variety Malus domestica Borkh. cv. Aztec Fuji[J]. Deciduous Fruits,2020,52(1):30−32.] MENG Y, WANG J J, TIAN H H, et al . Performance and cultivation techniques of apple variety Malus domestica Borkh. cv. Aztec Fuji[J]. Deciduous Fruits,2020 ,52 (1 ):30 −32 .[2] ALI M T, MEHRAJ S, MIR M S, et al. Deciphering the response of thirteen apple cultivars for growth, fruit morphology and fruit physico-chemical attributes during different years[J]. Heliyon,2023,9(6):e17260. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17260
[3] IGLESIAS I, ECHEVERRIA G, LOPEZ M L. Fruit color development, anthocyanin content, standard quality, volatile compound emissions and consumer acceptability of several 'Fuji' apple strains[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2012,137:138−147. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.01.029
[4] HASANZADEH B, ABBASPOUR-GILANDEH Y, SOLTANI-NAZARLOO A, et al. Non-destructive measurement of quality parameters of apple fruit by using visible/near-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate regression analysis[J]. Sustainability,2022,14(22):14918. doi: 10.3390/su142214918
[5] MARECKOVA M, DANKOVA V, ZELENY L, et al. Non-destructive near infrared spectroscopy externally validated using large number sets for creation of robust calibration models enabling prediction of apple firmness[J]. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy,2022,30(2):97−104. doi: 10.1177/09670335211054299
[6] XU X, MO J C, XIE L J, et al. Influences of detection position and double detection regions on determining soluble solids content (SSC) for apples using on-line visible/near-infrared (vis/nir) spectroscopy[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2019,12(9):2078−2085. doi: 10.1007/s12161-019-01530-7
[7] YAO Y N, MA K, ZHU J F, et al. Non-destructive determination of soluble solids content in intact apples using a self-made portable NIR diffuse reflectance instrument[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology,2023,132:104714.
[8] 姚亚楠. 红富士苹果品质测定及近红外便携式无损检测仪的研发[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2022. [YAO Y N. Quality determination of red Fuji apple and development of near infrared portable nondestructive detector[D]. Urumchi:Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.] YAO Y N. Quality determination of red Fuji apple and development of near infrared portable nondestructive detector[D]. Urumchi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.
[9] FAN G Q, ZHA J W, DU R, et al. Determination of soluble solids and firmness of apples by Vis/NIR transmittance[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2009,93(4):416−420. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.02.006
[10] 王志华, 王文辉, 姜云斌, 等. 不同采收期对苹果常温贮藏品质和衰老的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(7):300−306. [WANG Z H, WANG W H, JIANG Y B, et al. Effect of different harvesting periods on the quality and aging of apples stored at room temperature[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(7):300−306.] WANG Z H, WANG W H, JIANG Y B, et al . Effect of different harvesting periods on the quality and aging of apples stored at room temperature[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020 ,36 (7 ):300 −306 .[11] SEIFERT B, ZUDE M, SPINELLI L, et al. Optical properties of developing pip and stone fruit reveal underlying structural changes[J]. Physiologia Plantarum,2015,153(2):327−336. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12232
[12] SHARABIANI V R, SABZI S, POURDARBANI R, et al. Inner properties estimation of gala apple using spectral data and two statistical and artificial intelligence based methods[J]. Foods,2021,10(12):2967. doi: 10.3390/foods10122967
[13] POURDARBANI R, SABZI S, ROHBAN M H, et al. Using metaheuristic algorithms to improve the estimation of acidity in Fuji apples using NIR spectroscopy[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal,2022,13(6):101776. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2022.101776
[14] YOU S C, JIANG M W, LAN W J, et al. Assessment of the optical properties with physicochemical properties and cell wall polysaccharides of 'Korla' pear flesh during Alternaria alternata-induced disease development[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,409(3):135302.
[15] 江梦薇, 兰维杰, 屠康, 等. 冬枣黑斑病的光学特性检测方法建立[J/OL]. 食品工业科技:1−15[2023-07-31]. doi:10.13386/j. issn1002-0306.2022100082. [JIANG M W, LAN W J, TU K, et al. Method establishment for the detection of black spot disease on winter jujubes based on optical properties[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry:1−15 [2023-07-31]. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022100082.] JIANG M W, LAN W J, TU K, et al. Method establishment for the detection of black spot disease on winter jujubes based on optical properties[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−15 [2023-07-31]. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022100082.
[16] MISHRA P, ROGER J M, RUTLEDGE D N, et al. Sport pre-processing can improve near-infrared quality prediction models for fresh fruits and agro-materials[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,168(6):111271.
[17] CEN H Y, HE Y. Theory and application of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in determination of food quality[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2007,18(2):72−83.
[18] ZHANG Z X, LIU H L, CHEN D Y, et al. Smote-based method for balanced spectral nondestructive detection of moldy apple core[J]. Food Control,2022,141(3):109100.
[19] KAMRUZZAMAN M, KALITA D, AHMED T M, et al. Effect of variable selection algorithms on model performance for predicting moisture content in biological materials using spectral data[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2022,1202:339390. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339390
[20] GUO Z M, WANG M M, SHUJAT A, et al. Nondestructive monitoring storage quality of apples at different temperatures by near-infrared transmittance spectroscopy[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(7):3793−3805.
[21] 秦浩, 林志娟, 陈景武. 偏最小二乘回归原理、分析步骤及程序[J]. 数理医药学杂志,2007,20(4):450−451. [QIN H, LIN Z J, CHEN J W. Partial least squares regression principles, analytical steps and procedures[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine,2007,20(4):450−451.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2007.04.008 QIN H, LIN Z J, CHEN J W . Partial least squares regression principles, analytical steps and procedures[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine,2007 ,20 (4 ):450 −451 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2007.04.008[22] NOBLE W S. What is a support vector machine?[J]. Nature Biotechnology,2006,24(12):1565−1567. doi: 10.1038/nbt1206-1565
[23] CRUZ-TIRADO J P, AMIGO J M, BARBIN D F. Determination of protein content in single black fly soldier ( Hermetia illucens L.) larvae by near infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) and chemometrics[J]. Food Control,2023,143(6):109266.
[24] SOLOVCHENKO A E, CHIVKUNOVA O B, MERZLYAK M N, et al. Relationships between chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments during on- and off-tree ripening of apple fruit as revealed non-destructively with reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2005,38(1):9−17. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.05.004
[25] POSE S, PANIAGUA C, MATAS A J, et al. A nanostructural view of the cell wall disassembly process during fruit ripening and postharvest storage by atomic force microscopy[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,87:47−58.
[26] 张猛胜. 基于可见/近红外光谱的苹果成熟度无损检测方法和便携式仪器研发[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学, 2021. [ZHANG M S. Research and development of nondestructive detection method and portable device for apple maturity based on visible and near infrared spectroscopy[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University, 2021.] ZHANG M S. Research and development of nondestructive detection method and portable device for apple maturity based on visible and near infrared spectroscopy[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2021.
[27] VIEIRA M J, ARGENTA L C, MATTHEIS J P, et al. Relationship between dry matter content at harvest and maturity index and post-harvest quality of 'Fuji' apples[J]. Revista Brasileira De Fruticultura,2018,40(2):e596.
[28] 李千里. 阿克苏不同苹果品种果实发育动态、果实品质及淀粉染色图谱构建研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2022. [LI Q L. Construction of fruit development dynamics, fruit quality and starch staining atlas of different apple varieties in Aksu[D]. Urumchi:Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.] LI Q L. Construction of fruit development dynamics, fruit quality and starch staining atlas of different apple varieties in Aksu[D]. Urumchi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.
[29] LI M J, LI D X, FENG F J, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals dynamic regulation of fruit development and sugar and acid accumulation in apple[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2016,67(17):5145−5157. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw277
[30] ZHANG M S, ZHANG B, LI H, et al. Determination of bagged 'Fuji' apple maturity by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy combined with a machine learning algorithm[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology,2020,111:103529.
[31] DONG J L, GUO W C. Nondestructive determination of apple internal qualities using near-infrared hyperspectral reflectance imaging[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2015,8(10):2635−2646. doi: 10.1007/s12161-015-0169-8
[32] ZHANG D Y, XU Y F, HUANG W Q, et al. Nondestructive measurement of soluble solids content in apple using near infrared hyperspectral imaging coupled with wavelength selection algorithm[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology,2019,98:297−304.
[33] LAN W J, JAILLAIS B, LECA A, et al. A new application of NIR spectroscopy to describe and predict purees quality from the non-destructive apple measurements[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,310:125944. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125944
[34] THAPNGAM T, YU S, ZHOU W. Ddos discrimination by linear discriminant analysis (LDA)[C]. International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC). Deakin University, Burwood, VIC 3125, Australia:2012:532-536.
[35] CAMPS C, GUILLERMIN P, MAUGET J C, et al. Discrimination of storage duration of apples stored in a cooled room and shelf-life by visible-near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy,2007,15(3):169−177. doi: 10.1255/jnirs.726
[36] IGNAT T, LURIE S, NYASORDZI J, et al. Forecast of apple internal quality indices at harvest and during storage by VIS-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2014,7(10):2951−2961. doi: 10.1007/s11947-014-1297-7
[37] 李磊. 苹果成熟度与品质关联因子无损检测方法研究[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学, 2018. [LI L. Research on apple maturity and associated quality factors based on nondestructive detection[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University, 2018.] LI L. Research on apple maturity and associated quality factors based on nondestructive detection[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018.
[38] ZHANG M S, SHEN M S, LI H, et al. Modification of the effect of maturity variation on nondestructive detection of apple quality based on the compensation model[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2022,267(11):120598.
[39] GUO Z M, HUANG W Q, PENG Y K, et al. Color compensation and comparison of shortwave near infrared and long wave near infrared spectroscopy for determination of soluble solids content of 'Fuji' apple[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2016,115:81−90. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.12.027
[40] MCGLONE V A, JORDAN R B, MARTINSEN P J. Vis/NIR estimation at harvest of pre- and post-storage quality indices for 'Royal Gala' apple[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2002,25(2):135−144. doi: 10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00180-6
[41] ABASI S, MINAEI S, JAMSHIDI B, et al. Rapid measurement of apple quality parameters using wavelet de-noising transform with Vis/NIR analysis[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2019,252:7−13. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.085
[42] ZHANG Y Y, NOCK J F, AL SHOFFE Y, et al. Non-destructive prediction of soluble solids and dry matter contents in eight apple cultivars using near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2019,151(4):111−118.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



