Protective Effect of Tartaty Buckwheat Extract Fermented with Pleurotus eryngii on Alcoholic Liver and Stomach Injury in Mice
-
摘要: 目的:研究杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物的体外抗氧化活性及体内对酒精性肝脏、胃黏膜损伤的保护作用。方法:本实验检测杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物中功能成分的含量,并分析提取物的抗氧化能力;以Lieber-DeCarli酒精液体饲料建立小鼠慢性酒精性肝脏、胃黏膜损伤模型,考察发酵后的苦荞提取物在低、高剂量(1.5 g/kg B.W.、3.0 g/kg B.W.)对肝脏和胃粘膜损伤的保护作用。结果:杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液中含有较多的抗氧化成分,其中多酚、黄酮、三萜含量分别为11.40±0.32 mg GAE/g DW、17.19±0.30 mg RE/g DW、7.59±0.24 mg/g,黄酮类物质:芦丁和槲皮素含量分别为13.55±0.05、0.665±0.01 mg/g;杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的铁离子还原抗氧化能力及其对DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率分别为:16.66±0.65、33.49±1.26、15.68±1.17 μmol Trolox/g DW;与模型组相比,高、低剂量组均能显著降低丙二醛(P<0.05)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(P<0.01)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(P<0.01)、乳酸脱氢酶(P<0.05)、白细胞介素1β(P<0.05)水平,并显著提高超氧化物歧化酶(P<0.01)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(P<0.01)水平,下调了活性氧(P<0.01)、鼠肉瘤蛋白(P<0.01)、丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(P<0.01)、细胞外信号调节激酶(P<0.05)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶(P<0.05)的蛋白表达量。结论:杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物具有较好的抗氧化活性,并对小鼠慢性酒精性肝脏、胃黏膜损伤具有明显的保护作用。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the antioxidant activity of fermented tartaty buckwheat extract of Pleurotus eryngii in vitro as well as its protective effect on alcohol-induced liver and gastric mucosa injury in vivo. Methods: The study involved determining the contents of functional components in fermented tartary buckwheat extract and observing its antioxidant capacity. Mice models of chronic alcoholic liver and gastric mucosa injury were established using Lieber-DeCarli liquid feed. The protective effects of fermented tartary buckwheat extract at low and high doses (1.5 g/kg B.W., 3.0 g/kg B.W.) were investigated for both liver and gastric mucosa injury. Results: The extract of fermented buckwheat with Pleurotus eryngii contained more antioxidant components, the contents of polyphenols, flavonoids and triterpenes were 11.40±0.32 mgGAE/g DW, 17.19±0.30 mg RE/g DW and 7.59±0.24 mg/g, respectively. The contents of rutin and quercetin were as follows: 13.55±0.05 and 0.665±0.01 mg/g. The iron reducing antioxidant capacity and DPPH and ABTS+ free radical scavenging efficiency of Tartary buckwheat extract were 16.66±0.65, 33.49±1.26 and 15.68±1.17 μmol Trolox/g DW, respectively. Compared with the model group, both high-dose and low-dose groups significantly reduced malondialdehyde (P<0.05), aspartate aminotransferase (P<0.01), alanine aminotransferase (P<0.01), lactate dehydrogenase (P<0.05), and interleukin-1β (P<0.05) levels and significantly increased levels of superoxide dismutase (P<0.01) and glutathione peroxidase (P<0.01), downregulated protein expression levels of reactive oxygen species (P<0.01), rat sarcoma (P<0.01), rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (P<0.01), extracellular signal-regulated kinases (P<0.05), and mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (P<0.05). Conclusion: Fermented tartaty buckwheat extract of Pleurotus eryngii has good antioxidant activity, and has obvious protective effect on chronic alcoholic liver and gastric mucosa injury in mice.
-
饮酒已成为当今人们一种普遍的社交娱乐方式。长期饮酒会导致酒精性肝炎、肝纤维化、胃溃疡等[1],严重危害人们的身体健康。肝脏无法及时分解的酒精在体内会经一系列反应产生大量的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS),从而破坏肝脏氧化还原平衡;经常摄入酒精会导致胃黏膜变薄,上皮细胞坏死脱落,微血管内皮损伤,从而造成胃黏膜糜烂和溃疡形成[2]。近年来,我国酒精性肝病、胃病的发病率正在逐年上升。因此,开发具有缓解酒精性肝、胃损伤的天然抗氧化活性提取物已成为全球关注的热点。
苦荞(Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn.)是一种传统的药食两用特色杂粮,含有丰富的多酚、黄酮、植物甾醇等活性成分[3]。现代医学也证实,苦荞具有降三高、抗氧化、抗菌消炎、免疫调节等功效,具有很高的食用价值和药用价值[4]。食用菌发酵食品是一种新型的功能性食品,菌丝体在基质中发酵能使活性代谢产物增加,在提高其营养价值的同时赋予其独特的保健功效[5−6]。杏鲍菇(Pleurotus eryngii)作为一种食用菌,具有成本低,菌种扩繁的操作方法简便,生长速度快等优点,其菌体中含有多种活性成分,可以降血压、降血脂、降低胆固醇和增强机体免疫力等[7]。大量的体内吸收代谢研究也表明,口服膳食类黄酮的吸收能力差、生物利用度低[8]。但通过发酵产生的各种生化反应,可以改变食品中营养成分和抗营养成分组成,提高食品的生物活性和消化利用率。
本研究将苦荞与杏鲍菇菌种进行混合固态发酵,以有效丰富苦荞中活性成分的种类、提升活性成分的含量。研究通过HPLC技术分析杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物中活性成分的含量,以铁离子还原抗氧化能力、DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率来综合评价体外抗氧化活性。实验构建了小鼠慢性酒精性肝、胃粘膜损伤模型,通过测定小鼠血清中天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT),肝脏及胃组织中炎症指标和氧化应激指标,并通过分析肝脏中鼠肉瘤蛋白(rat sarcoma,Ras)、丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶(rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma,Raf)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase,MEK)、细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinases,ERK)的蛋白表达情况,阐明了与杏鲍菇菌种混合发酵后的苦荞提取物对于慢性酒精性肝、胃损伤的保护作用,并为苦荞产品的开发和利用提供了数据支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
苦荞(西荞1号) 分别于四川简阳收集到5批(S1~S5),于四川凉山收集到5批(S6~S10),于四川美姑县收集到5批(S11~S15);杏鲍菇菌种(XBG-1,Pleurotus eryngii) 农业农村部杂粮加工重点实验室;6周龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠(18~22 g) 斯贝福(北京)生物技术有限公司,生产许可证号:SCXK(京)2016-0006;小鼠普通固体饲料 成都达硕实验动物有限公司;Lieber-DeCarli液体饲料 南通特洛菲饲料科技有限公司;实验期间小鼠饲养在成都大学食品与生物工程学院动物房中,饲养温度保持在(25±2) ℃,湿度保持在50%±5%,12 h光暗交替,动物饲养条件符合实验动物伦理委员会的要求;西米替丁(Cimetidine,CMD,JSK2208) 青岛捷世康生物科技有限公司;水飞蓟素(Silymarin,SM,S0292)、2,2-二(4-叔辛基苯基)-1-苯基肼基(DPPH)、2,2’-叠氮-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)(ABTS)、2,4,6-三(2-吡啶)-1,3,5-三嗪(TPTZ)、奎诺二甲基丙烯酸酯(Trolox) Sigma-Aldrich公司;福林酚(Folin-Ciocalteu)试剂 美国Sigma公司;没食子酸(Gallic acid,GAE) 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;芦丁、槲皮素标准品(纯度>98%) 四川省维克奇生物科技有限公司;天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST,C010-2-1)测定试剂盒、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT,C009-2-1)测定试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT,A007-1-1)测定试剂盒、谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH,A006-2-1)测定试剂盒、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px,A005-1)测定试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD,A001-3)测定试剂盒、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA,A003-1)测定试剂盒、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH,A020-2)测定试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α,E-EL-M3063)测定试剂盒、白细胞介素1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β,E-EL-M0037c)测定试剂盒、白细胞介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6,E-EL-M0044c)测定试剂盒、白细胞介素10(interleukin-10,IL-10,E-EL-M0046c)测定试剂盒、前列腺素E2(Prostaglandin E2,PGE2,E-EL-0034c)测定试剂盒 武汉伊莱瑞特生物科技股份有限公司;抗GAPDH(ab9485)、抗β-Actin(ab213262)、抗Ras(ab52939)、抗Raf1(ab181115)、抗ERK1+ERK2(ab184699)、抗MEK1+MEK2(ab178876)、抗ERK1(pT202/pY204)+ERK2(pT185/pY187)(ab76299)、抗MEK1+MEK2(phospho S218+S222)(ab194754) 艾博抗(上海)贸易有限公司;抗ROS(3287T) 赛信通(上海)生物试剂有限公司。
1260 Infinity Ⅱ 液相色谱系统 安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司;Wes TM全自动蛋白表达分析系统 普诺森生物科技(上海)有限公司;Biotek Synergy HTX 多功能酶标仪 美国伯腾仪器有限公司北京代表处;CPA-225D精密电子天平 德国赛多利斯;ST16R高速冷冻离心机 赛默飞世尔科技;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;800A多功能粉碎机 永康市红太阳机电有限公司;DZKW-S-4电热恒温水浴锅 北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司;SB-800DTD超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌种的扩繁
称取200 g玉米为杏鲍菇菌种扩繁基质,清洗后浸泡8 h,预先蒸煮20 min后装入500 mL的锥形瓶中,利用透气不透菌的封口膜密封,放入高压灭菌锅中灭菌,选取在马铃薯琼脂培养基(PDA)中活化的杏鲍菇菌种接种于玉米基质中,于28 ℃的恒温培养箱中进行菌种扩繁,6 d后结束扩繁。
1.2.2 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的制备
称取200 g苦荞,洗净后浸泡10 h,预蒸煮10 min后装入500 mL的锥形瓶中进行高压灭菌,冷却后在无菌操作台上接种10 颗长满杏鲍菇菌种的玉米粒,置于温度28 ℃的恒温培养箱中发酵5 d,将发酵产物冻干粉碎,过65目筛,得到与杏鲍菇菌种混合发酵后的苦荞粉样品原料,在−20 ℃下储存。精密称取该样品原料1.00 g,加入15 mL 70%(v/v)的乙醇溶液,功率为500 W 超声提取30 min,然后在4 ℃下以8000 r/min离心15 min,保留上清进行后续实验。
1.2.3 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液总酚含量的测定
采用修改后的Folin-Ciocalte法[9],测定样品的总酚含量。准确吸取100 μL提取液样品,再加500 μL福林酚试剂,充分摇匀后静置4 min,然后加入400 μL 20% Na2CO3溶液,反应30 min,于765 nm下测定反应液的吸光度。采用相同的方法,以没食子酸(gallic acid,GAE)标准品溶液的浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,总酚含量以每克干质量样品原料中所含没食子酸的当量毫克数表示(简写为 mg GAE/g DW)。所有样品均测定3次。
1.2.4 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液总黄酮含量的测定
参照罗娅等[10]的方法略作修改,取100 μL稀释样品,加入4 mL 70%乙醇,再加30 μL 5% NaNO2摇匀,反应6 min,然后加入30 μL 10% Al(NO3)3反应6 min,加入400 μL NaOH后在室温下静置反应25 min。待反应结束后,于510 nm下测定吸光值。以芦丁(rutoside,RE)标准品溶液的浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,总黄酮含量以每克干质量样品原料中所含芦丁的当量毫克数表示(简写为 mg RE/g DW)。所有样品均测定3 次。
1.2.5 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液总三萜含量的测定
采用修改后的香草醛-冰醋酸法[11−12],测定三萜含量。精密称取10 mg齐墩果酸(oleanolic acid,OAE)标准品,以无水乙醇为溶剂配制成浓度为1 mg/mL的齐墩果酸标准品溶液,分别吸取20、40、60、80、100 μL齐墩果酸标准品溶液于10 mL试管中,在90 ℃水浴锅中水浴挥干溶剂,依次加入200 μL 5%的香草醛-冰乙酸(w/v)和800 μL高氯酸混匀,70 ℃水浴孵育20 min,取出试管于冰上冷却,加入5 mL乙酸乙酯,于550 nm处测定吸光度。以齐墩果酸的含量(mg)为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。然后吸取样品提取液100 μL,以上述标准曲线测定样品中总三萜含量,样品中的总三萜含量表示为mg/g。所有样品测定均进行3次重复。
1.2.6 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的含量测定以及指纹图谱的建立
色谱柱:Pursuit C18柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 µm);流动相:乙腈(A)-0.5%乙酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱:5% A(0~5 min),5%~10% A(5~7 min),10% A(7~19 min),10%~15% A(19~20 min),15% A(20~28 min),15%~20% A(28~31 min),20% A(31~38 min),20%~30% A(38~39 min),30%~35% A(39~44 min),35%~40% A(44~46 min),40%~45% A(46~51 min),45%~95% A(51~55 min),95% A(55~60 min),95%~5% A(60~61 min),5% A(61~71 min)。柱温:30 ℃,进样量:10 μL,检测波长:254 nm。
对照品溶液的制备:精密称定芦丁、槲皮素对照品10 mg,加入甲醇制成浓度分别为 1 mg/mL的混合对照品储备液。
供试样品溶液的制备:取“1.2.2”项下制备的杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液稀释10倍,用 0.22 μm 的针式过滤器过滤,进样。
1.2.7 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的铁离子还原抗氧化能力(ferric reducing antioxidant power, FRAP)测定
参考Li等[13−14]的方法,取20 μL提取液样品加入380 μL TPTZ工作液(由300 mmol醋酸盐缓冲液25 mL、10 mmol/L TPTZ溶液2.5 mL、20 mmol/L FeCl3溶液2.5 mL组成)混匀后37 ℃下孵育10 min,于593 nm测定吸光度,以Trolox作为标准,每一样品平行测3次,铁离子还原抗氧化能力以每克杏鲍菇发酵苦荞干重的Trolox当量(μmol Trolox/g DW)表示。
1.2.8 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的DPPH自由基清除能力
取待测样品溶液25 μL,加入200 μL DPPH乙醇溶液,混匀并在室温下孵化30 min。于517 nm测定吸光度,以Trolox作为标准,每一样品平行测3次,DPPH自由基清除能力以每克杏鲍菇发酵苦荞干重的Trolox当量(μmol Trolox/g DW)表示[13−15]。
1.2.9 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的ABTS+自由基清除能力
将10 mL 7 mmol/L ABTS溶液和10 mL 2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾水溶液混合,在室温、避光的条件下静置过夜,用磷酸盐缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH7.4)稀释ABTS+自由基溶液,使其在734 nm处的吸光度为0.750±0.02。然后,将200 μL ABTS+自由基工作溶液与20 μL待测样品在96孔微孔板中,在30 ℃下反应20 min。于734 nm测定吸光度。以Trolox为标准,每一样品平行测3次,ABTS+自由基清除能力以每克杏鲍菇发酵苦荞干重的Trolox当量(μmol Trolox/g DW)表示[13−15]。
1.2.10 小鼠慢性酒精性肝脏及胃黏膜损伤模型的建立和样品采集
将C57BL/6J小鼠随机分成6组,每组10只小鼠,体重18~22 g。小鼠用Lieber-DeCarli液体饲料喂养。所有小鼠食用对照液体饲料适应5 d后,除对照组外,其余各组小鼠换成含酒精的液体饲料喂养、造模,前5 d饲料的酒精含量由1%(v/v)逐天递增到5%(v/v),然后5%(v/v)维持10 d后,升高到8%(v/v)维持7 d,期间连续灌胃给药,对照组(Control)、模型组(Ethanol)小鼠灌胃生理盐水,胃黏膜阳性组(CMD)灌胃西米替丁100 mg/kg B.W.、肝脏阳性组(SM)灌胃水飞蓟素100 mg/kg B.W.、杏鲍菇发酵苦荞低剂量组(FTB-Low)灌胃提取液冻干粉混悬液1.5 g/kg B.W.、杏鲍菇发酵苦荞高剂量组(FTB-High)灌胃3.0 g/kg B.W.,所有药物均混悬于DMSO中。酒精饲料喂养22 d后禁食12 h,次日早上给小鼠单次灌胃浓度为42%的基酒(剂量为0.2 mL/10 g B.W.),对照组灌胃相同剂量的糊精。9 h后进行眼球取血并脱颈处死,然后立刻以3500 r/min离心10 min取血清储存在-80 ℃,取肝脏右叶和完整胃用4%多聚甲醛固定,用于病理切片及H&E染色,肝脏左叶和剖开的胃组织储存在−80 ℃用于生化指标分析。
1.2.11 血清、肝脏及胃组织中的生理生化指标测定
分别取肝脏、胃组织,加入9倍体积重量的预先冰冻过的生理盐水,匀浆,制成10%的匀浆液,整个匀浆过程在冰上进行。将匀浆液以3500 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,按照试剂盒说明书检测各组织中炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6、IL-10,氧化应激指标CAT、MDA、SOD、GSH、GSH-Px、LDH,以及血清中ALT、AST的含量变化。
1.2.12 免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测肝脏中蛋白表达情况
每只动物取肝组织40 mg于离心管中,切碎,加入400 μL预冷的RIPA裂解缓冲液,置于冰上30 min,每5 min混合一次,使组织得到充分的裂解。裂解完全后,在4 ℃以10000×g离心5 min后,取出上清液,先用BCA法计算蛋白质浓度,然后对其进行稀释,使蛋白质浓度保持在相同的浓度水平。按照试剂盒说明书,检测小鼠肝脏的蛋白表达情况。ERK包括ERK1和ERK2(简写为 ERK1/2),磷酸化激活的细胞外信号调节激酶(phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases,p-ERK)包括p-ERK1和p-ERK2(简写为 p-ERK1/2);MEK包括MEK1和MEK2(简写为 MEK1/2),磷酸化激活的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶(phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase,p-MEK)包括p-MEK1和p-MEK2(简写为 p-MEK1/2)。分别以靶标蛋白Ras、Raf比内参蛋白GAPDH来表示Ras和Raf的蛋白表达量;以靶标蛋白ROS比内参蛋白β-Actin来表示ROS的蛋白表达量;以p-ERK1/2比ERK1/2表示ERK的蛋白表达量;以p-MEK1/2比MEK1/2来表示MEK的蛋白表达量。样品分析采用分离度为12~230 kD的Simple Western试剂盒,遵循试剂盒使用指南加样,结果用Compass for SW 3.1.8.0软件(ProteinSimple)进行分析。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据均以平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示,组间显著性分析采用SPSS 19.0数据处理软件进行,实验数据采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)比较组间差异,以P<0.05作为差异具有统计学意义的判断标准。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液中活性物质的含量测定
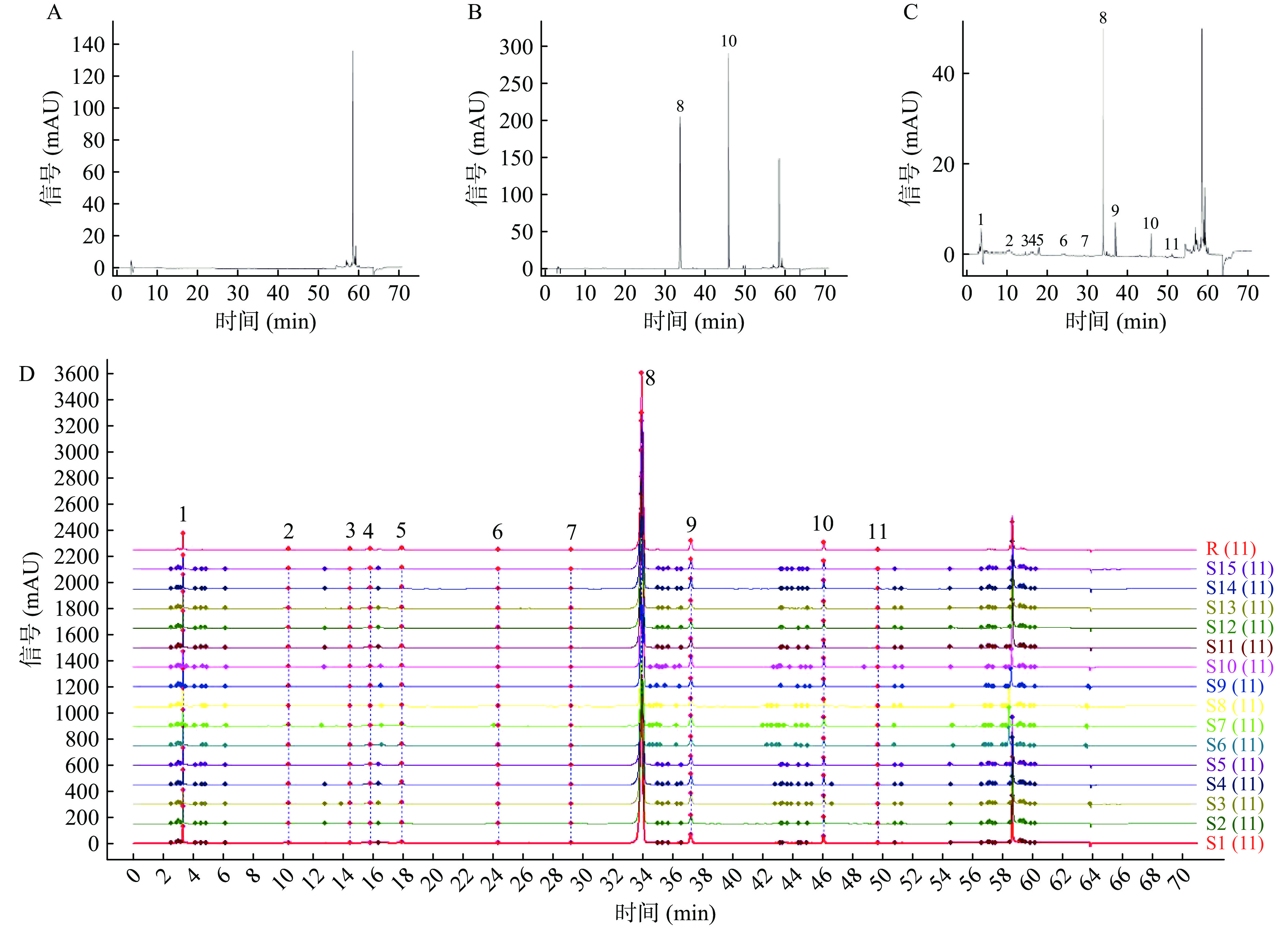
酚类化合物广泛存在于谷物中,具有抗癌、抗肿瘤、清除自由基、降血脂等多种生物活性。酚类化合物结构复杂、种类繁多,主要包括黄烷醇类、黄烷酮类、异黄酮类、花色素类等[16]。如表1和图1A、B、C所示,与杏鲍菇菌种混合发酵后的苦荞提取物中含有较多的抗氧化成分,多酚、黄酮含量分别为:11.40±0.32 mg GAE/g DW、17.19±0.30 mg RE/g DW,黄酮类物质以芦丁和槲皮素含量较高,分别是:13.55±0.05、0.665±0.01 mg/g;杏鲍菇含有较多的三萜类化合物,具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤等功效。本实验采用杏鲍菇菌种与苦荞混合发酵,测定其三萜含量为7.59±0.24 mg/g,略高于藜蒿茎中三萜化合物含量[17],与李志华等[18]测定的苹果和孙培龙[19]测定的灵芝中含量相似。实验说明杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物具有一定的药用价值和开发价值,具有成为功能性食品的潜力。
表 1 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物中活性物质含量Table 1. Antioxidant content of fermented tatary buckwheat extracts from apricot mushroom样品 多酚含量
(mg GAE/g DW)黄酮含量
(mg RE/g DW)三萜含量
(mg/g)芦丁含量(mg/g) 槲皮素含量(mg/g) 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物 11.40±0.32 17.19±0.30 7.59±0.24 13.55±0.05 0.665±0.01 2.2 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液指纹图谱的建立
如图1D所示,将15批苦荞(S1~S15)与杏鲍菇菌种进行固态混合发酵后所得样品的色谱数据导入国家药典委员会颁布的中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统。以S1为参照图谱,时间窗宽度设置为0.1 min,中位数法生成对照谱,经Mark峰匹配后生成的15批杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液叠加图谱和对照指纹图谱(R),共找出11个共有峰,S1~S15的相似度为0.992~0.999,通过与对照品比对,8号峰为芦丁,10号峰为槲皮素。
2.3 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液抗氧化能力
苦荞中酚类物质、黄酮类物质、芦丁均与总还原力、DPPH自由基清除能力有较强的相关性[20],本实验中杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液的FRAP、DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率分别为:16.66±0.65、33.49±1.26、15.68±1.17 μmol Trolox/g DW,结果表明杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取液中含有抗氧化物质,食用与杏鲍菇菌种混合发酵后的苦荞可能对健康有益,同时具有作为功能性食品配料的潜力,可提高苦荞的附加值。
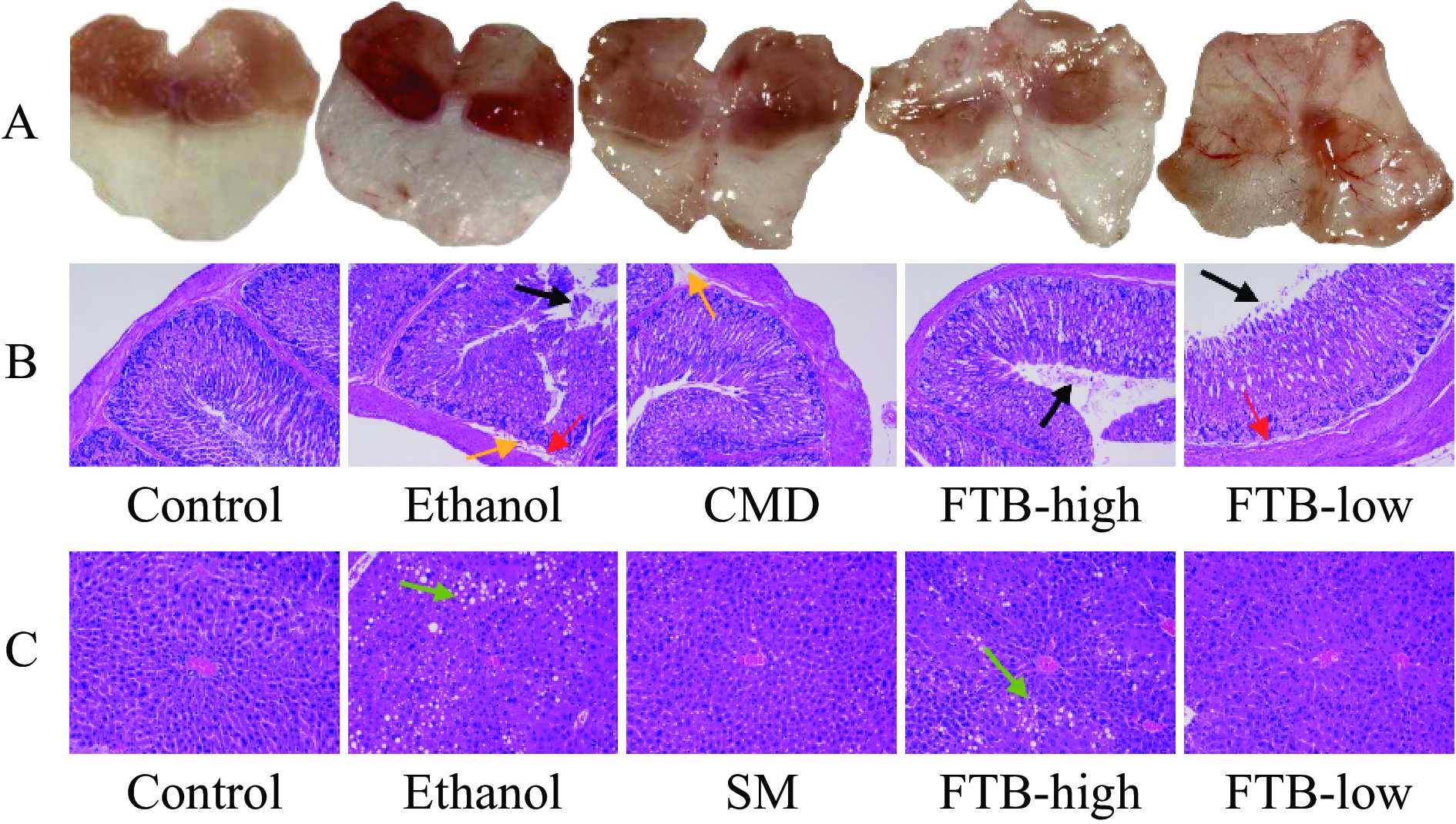
2.4 小鼠肝脏、胃粘膜组织的病理改变
图2A可见,对照组(Control)胃粘膜无明显破损、充血及水肿,表面呈粉红色,胃粘膜皱壁光滑、完整、走向规则;模型组小鼠胃粘膜损伤严重,可见明显充血、水肿,粘膜表面呈暗红色,甚者可见粘膜糜烂,点状、线状出血;给药高剂量组(FTB-High)小鼠胃粘膜损伤情况明显轻于模型组,粘膜完整,出血性损伤明显较少;胃黏膜阳性组(CMD)和给药低剂量组(FTB-Low)有部分充血,但损伤程度减轻[21]。图2B显示对照组(Control)小鼠胃黏膜各层结构完整清晰,细胞形态完整,腺体排列规则,未见组织缺损、出血、炎症等异常病变;模型组小鼠黏膜层细胞弥散性坏死脱落情况严重,黏膜层中可见大量红细胞,细胞肿大、排列松散,有炎细胞浸润和水肿;小鼠灌胃西米替丁和杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物后,症状有所减轻,CMD组小鼠的粘膜层水肿,部分细胞排列松散;FTB-Low和FTB-High组小鼠的部分黏膜上皮细胞坏死脱落,黏膜层中有少量红细胞和炎细胞浸润。图2C为H&E染色进行的肝脏组织病理学检查,观察发现对照组的健康小鼠具有清晰的肝小叶结构和肝索的放射性排列[22]。然而,过度饮酒的小鼠肝细胞轮廓不清晰、排列紊乱,胞质疏松,有炎性细胞浸润及脂肪沉积[23]。与模型组相比,肝脏阳性组(SM,给予水飞蓟素)和杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物处理的小鼠,肝细胞脂肪变性相对减少,肝损伤程度明显减轻,但FTB-High组的缓解程度相对较弱,肝脏中有部分脂肪沉积。
2.5 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对小鼠胃黏膜中氧化应激指标的影响
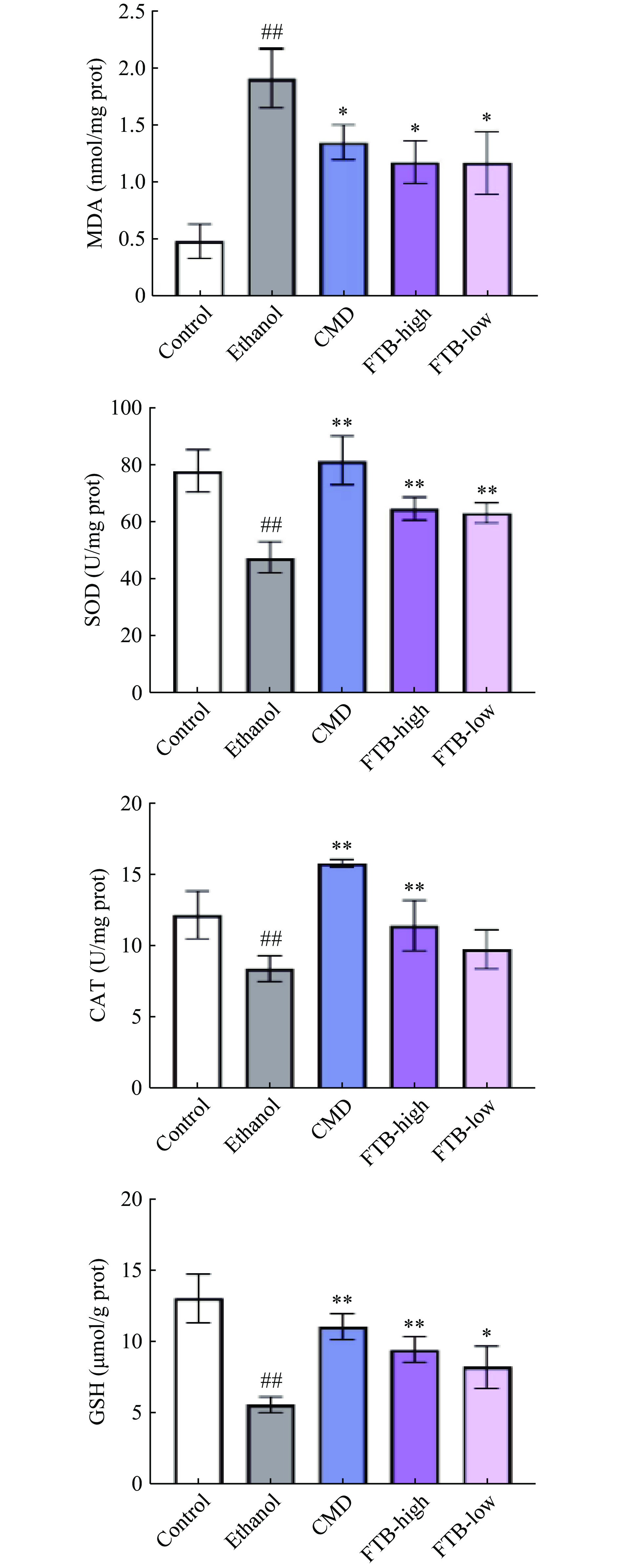
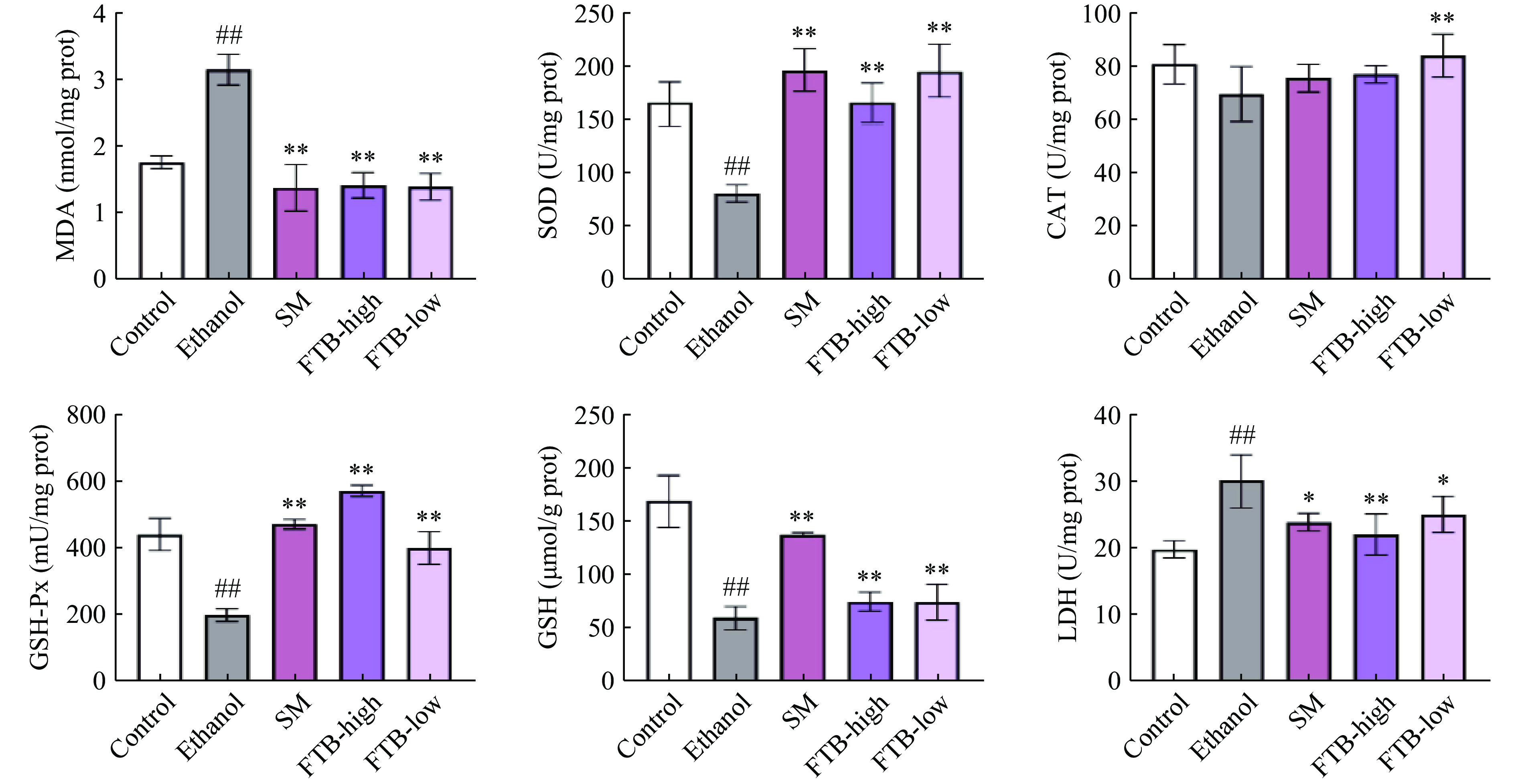
如图3所示,与对照组相比,模型组酒精引起的胃黏膜损伤使得小鼠胃组织中CAT水平(P<0.01)、SOD水平(P<0.01)和GSH水平(P<0.01)极显著降低,而MDA水平极显著增加(P<0.01),与Xie等[24]的结果相似。灌胃高、低剂量的杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物均能显著抑制小鼠胃组织中SOD水平的降低(P<0.01)与MDA水平的升高(P<0.05),从而缓解酒精导致的小鼠慢性酒精性胃黏膜损伤,而低剂量的杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物显著增加了GSH(P<0.05)水平,但对CAT水平影响不显著,高剂量可极显著增加CAT和GSH(P<0.01)水平。结果表示杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物具有较好的体内抗氧化活性。
![]() 图 3 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对酒精性胃黏膜损伤的影响(小鼠胃黏膜氧化应激指标变化)注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示与模型组相比差异显著(P<0.05),**表示与模型组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);图4~图8同。Figure 3. Effect of fermented tartary buckwheat extract of Pleurotus eryngii on alcoholic gastric mucosal injury (Changes of oxidative stress indexes of gastric mucosa in mice)
图 3 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对酒精性胃黏膜损伤的影响(小鼠胃黏膜氧化应激指标变化)注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示与模型组相比差异显著(P<0.05),**表示与模型组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);图4~图8同。Figure 3. Effect of fermented tartary buckwheat extract of Pleurotus eryngii on alcoholic gastric mucosal injury (Changes of oxidative stress indexes of gastric mucosa in mice)2.6 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对小鼠胃黏膜中炎症因子的影响
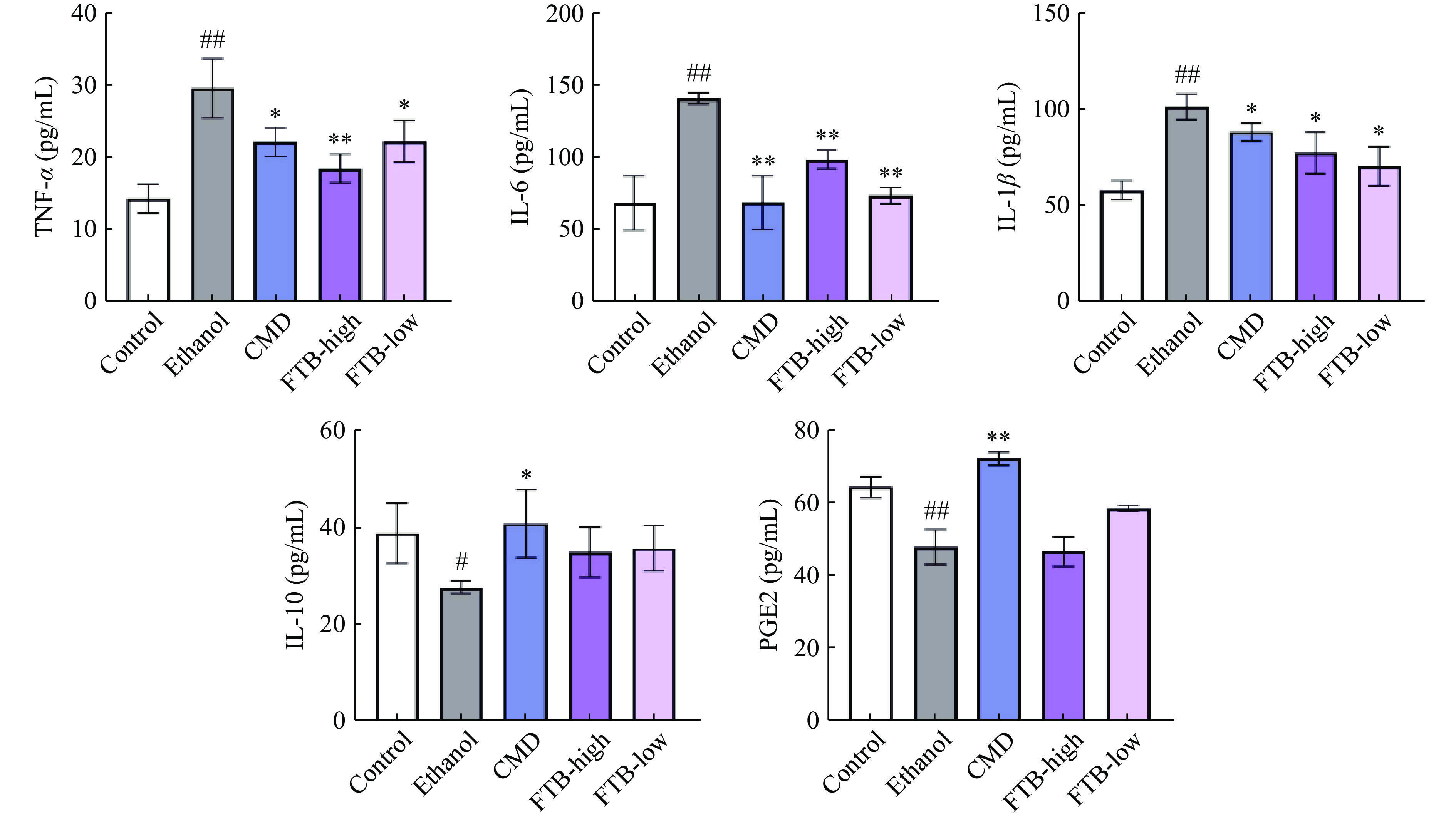
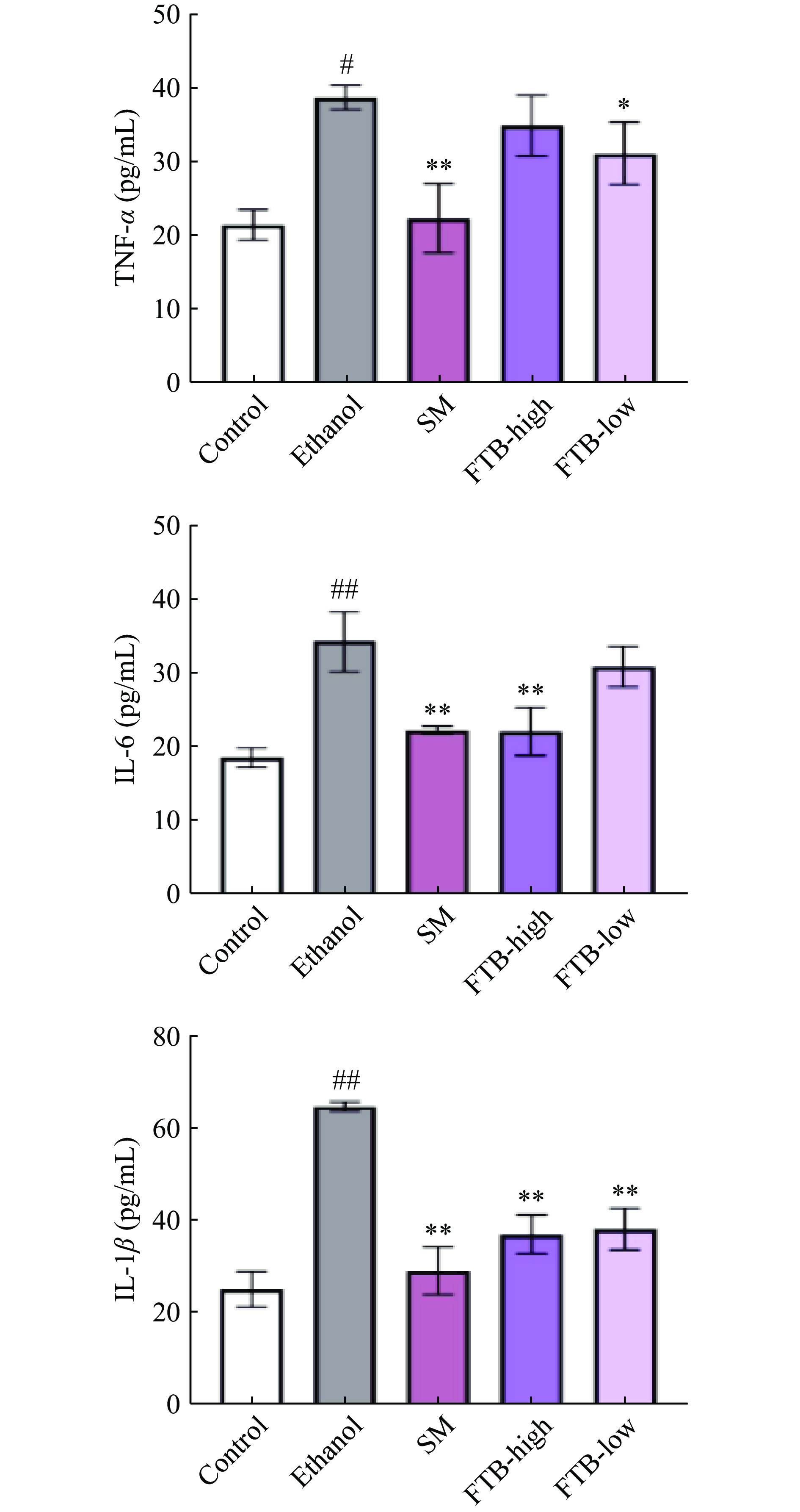
如图4所示,酒精引起的胃黏膜损伤,显著增加了小鼠胃组织中TNF-α(P<0.01)、IL-6(P<0.01)、IL-1β(P<0.01)水平,减少了抗炎因子IL-10(P<0.05)和PGE2(P<0.01)水平,与Lu等[25]和Zhang等[26]的结果相似。给药组高、低剂量能显著缓解酒精所造成的TNF-α(P<0.01、P<0.05)、IL-6(P<0.01)和IL-1β(P<0.05)水平的上升,但是高、低剂量杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对IL-10和PGE2的影响不显著。
2.7 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对小鼠肝脏中氧化应激指标的影响
如图5所示,与对照组相比,酒精引起的酒精性肝损伤,极显著降低了小鼠肝脏中SOD(P<0.01)、GSH(P<0.01)和GSH-Px(P<0.01)水平,CAT水平降低不显著,并使MDA(P<0.01)、LDH(P<0.01)水平极显著增加。FTB-Low组均能极显著缓解酒精对小鼠肝脏中SOD(P<0.01)水平、GSH(P<0.01)水平、GSH-Px(P<0.01)水平、CAT(P<0.01)水平和MDA(P<0.01)水平的影响,并显著降低了LDH(P<0.05)水平;肝脏阳性组(SM)和FTB-High组对CAT水平影响不显著,但是SM组显著降低了LDH(P<0.05)、MDA(P<0.01)的表达,增加了SOD、GSH、GSH-Px的水平(P<0.01);FTB-High组极显著抑制了MDA、LDH指标的上升(P<0.01),并提高了SOD、GSH、GSH-Px的水平(P<0.01)。
2.8 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对小鼠肝脏中炎症因子的影响
如图6所示,酒精引起的肝脏损伤使得小鼠肝脏组织中TNF-α(P<0.05)、IL-6(P<0.01)、IL-1β(P<0.01)水平显著上升;水飞蓟素均可以缓解酒精导致的小鼠肝脏中炎症因子TNF-α(P<0.01)、IL-6(P<0.01)、IL-1β(P<0.01)水平的上升;低剂量杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物显著降低了TNF-α(P<0.05)、IL-1β(P<0.01)的水平,高剂量杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物极显著降低了IL-6、IL-1β水平(P<0.01),但对TNF-α的调节作用不显著。
2.9 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对小鼠血清中ALT、AST的影响
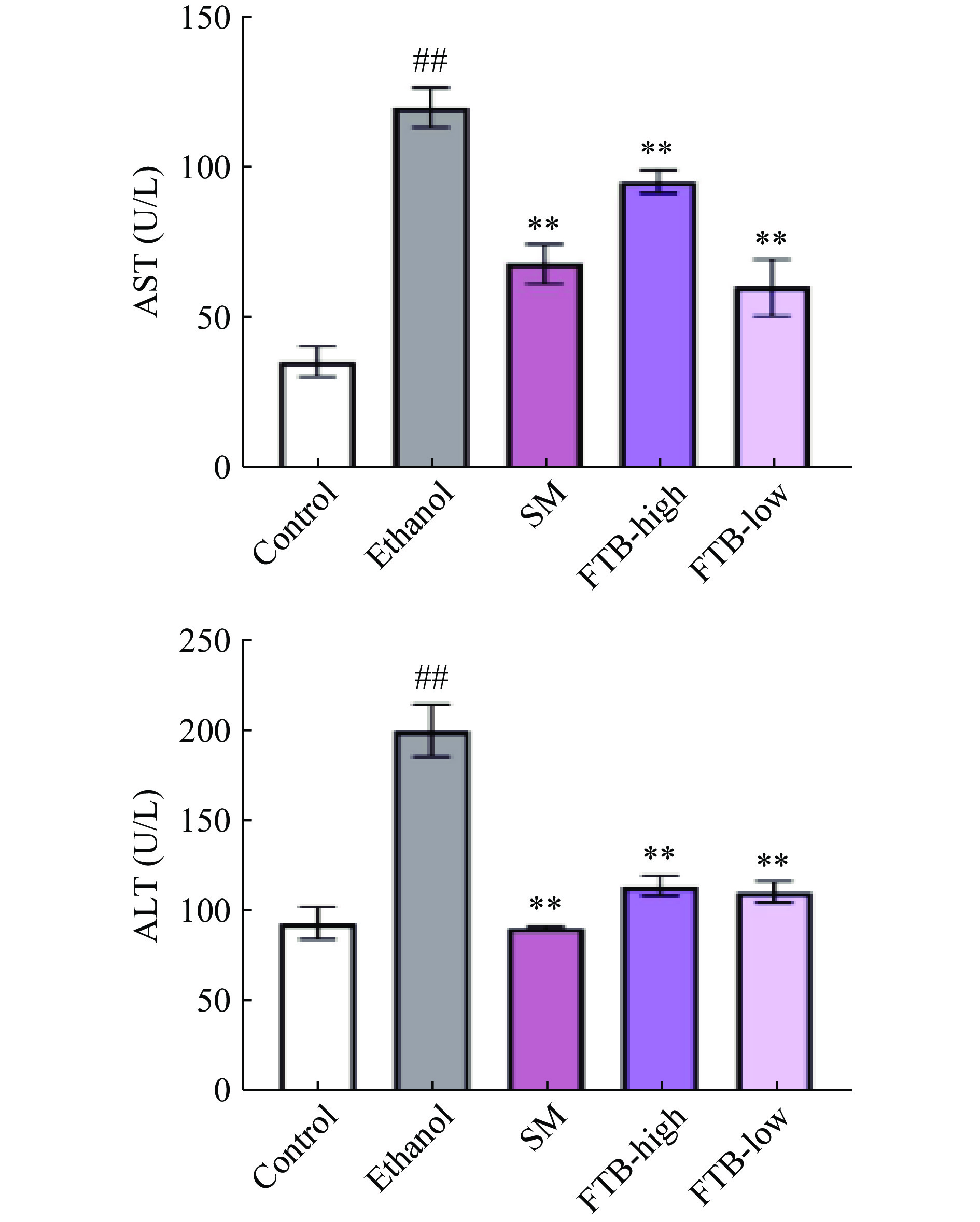
由图7可知,模型组小鼠血清中ALT和AST水平均极显著高于对照组(P<0.01),表明长期饮酒会导致肝功能出现异常。而相比于模型组,SM组、FTB-High组和FTB-Low组的小鼠血清ALT及AST的水平均极显著下降(P<0.01),结果表明给予杏鲍菇发酵的苦荞提取物可以有效缓解酒精对肝脏造成的损害。
2.10 免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测肝组织蛋白表达情况
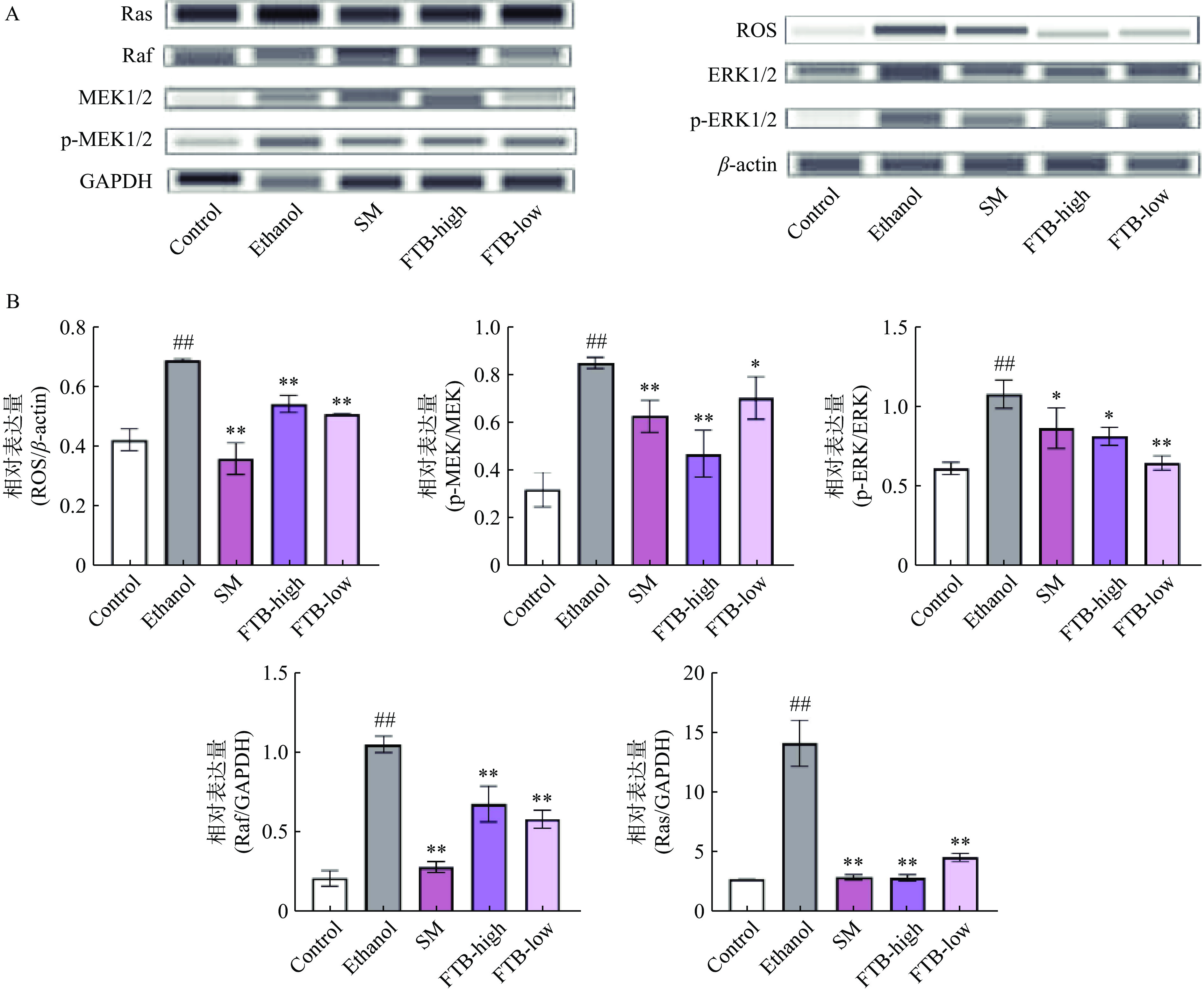
众所周知,ROS在体内的信号传导和细胞代谢中起着非常重要的作用,同时ROS也是乙醇代谢的另一副产物,当机体的氧化平衡被破坏时,ROS可在体内大量积累[27],与乙醛共同作用引起氧化应激,诱发细胞毒性。此外,也有研究表明Ras与ROS密切相关,Ras通过调节ROS的数量来调节促凋亡和抗凋亡。Ras属于小G蛋白家族,一旦Ras与GTP结合,就会导致Ras募集Raf1激酶并使其磷酸化。磷酸化的Raf1导致MEK的下游活化和磷酸化,MEK是一种双特异性酪氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,可以活化激活ERK,从而调节细胞的生长、分化以及炎性因子表达[28]。如图8所示,与对照组相比,长期饮用酒精饲料的小鼠,ERK、MEK、Ras、Raf、ROS的蛋白表达均极显著上升(P<0.01),给予阳性药物水飞蓟素后能显著降低ROS(P<0.01)、Ras(P<0.01)、Raf(P<0.01)、ERK 1/2(P<0.05)、MEK 1/2(P<0.01)蛋白的表达。给予高剂量杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物后能显著减少ERK 1/2(P<0.05)的蛋白表达,极显著减少ROS(P<0.01)、Ras(P<0.01)、Raf(P<0.01)、MEK 1/2(P<0.01)的蛋白表达,而低剂量组显著降低了MEK 1/2(P<0.05)的蛋白表达,极显著降低了ROS(P<0.01)、Ras(P<0.01)、Raf(P<0.01)和ERK 1/2(P<0.01)的蛋白表达,结果显示杏鲍菇发酵的苦荞提取物可能是通过调节MAPK通路的Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号传导途径来缓解小鼠的慢性酒精性肝损伤。
3. 讨论与结论
固态发酵可以产生不同的水解酶,分解植物材料中的大分子物质,经过丝状真菌固态发酵以后会显著提升总酚、花青素含量和抗氧化活性,在增加被发酵物活性成分的同时能够加入食用菌中的营养成分和活性成分[29−30]。选择富含活性成分的可食用真菌进行混合固态发酵,能够最大程度地丰富和提高苦荞中的活性成分,因此本研究将杏鲍菇菌种与苦荞进行混合发酵,发现其提取物具有较好的抗氧化能力,初步检测出了苦荞发酵后多酚、黄酮和三萜等功能成分。国内外研究也表明了荞麦的乙醇提取物均有较强的抗氧化活性和明显的自由基清除效果,这可能与荞麦的品种、提取物中的总酚含量相关[31−32]。
苦荞中黄酮类化合物成分作为一种天然产物能有效缓解酒精性肝损伤,能通过多种机制调控酒精性肝损伤的发生和发展,起到缓解酒精性肝病的效果[33]。Yang等[22]在酒精暴露大鼠的急性和慢性肝损伤中发现,服用苦荞提取物能显著降低血清天冬氨酸氨基转移酶和丙氨酸氨基转移酶水平的升高,改善肝脏指数。本研究成功建立了小鼠慢性酒精性肝脏、胃黏膜损伤模型,小鼠肝组织可见明显的病理变化,同时TNF-α、IL-6及IL-1β水平,以及MDA、LDH活性均显著升高,SOD、GSH等活性显著降低(P<0.05),给予杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物后,均能改善上述情况。有研究发现MAPK通路在药物性肝损伤中出现异常激活,其中RAS的激活可能通过磷酸化逐渐激活下游蛋白,导致复杂的级联反应[34],因此本实验通过测定RAS-Raf信号蛋白及下游蛋白MEK/ERK的表达情况,发现杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物能极显著降低Ras、ROS的表达(P<0.01),这表明RAS-Raf信号可能是参与小鼠肝损伤的关键因素。
此外,饮酒会导致急性、慢性酒精性胃黏膜损伤,包括粘膜细胞膜的破坏、胃上皮细胞的坏死和炎性细胞的增生[35]。虽然胃内酒精代谢在整个酒精代谢途径中的作用不如肝脏明显,但酒精性胃粘膜损害在临床上并不少见,目前国内相关领域的研究甚少,有待于进一步研究。本实验中酒精损伤的模型组小鼠胃部出现大小不一的出血性糜烂,在灌胃西米替丁或杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物后,均能减少损伤的面积。酒精会使胃黏膜产生大量氧自由基而引起胃黏膜细胞受损[36],造成氧化应激与炎症因子大量分泌,通过降低胃组织中炎症因子可减轻炎症程度,调节黏膜防御屏障[24,37]。本研究结果显示长期饮用酒精会导致小鼠胃黏膜的氧化应激水平升高,TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10的水平也与胃黏膜炎症反应的严重程度有关。而给予杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物后,对乙醇诱导的小鼠慢性酒精性肝脏、胃黏膜损伤均有一定的治疗效果。
综上所述,经杏鲍菇发酵过的苦荞提取物中含有较多的酚类物质和三萜类物质,能发挥较好的抗氧化活性;同时杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对体内慢性酒精性胃黏膜损伤和肝损伤两个动物模型都有治疗作用,其机制可能与调节肝损伤和胃黏膜损伤相关炎症因子、氧化应激有关。本实验明确了苦荞提取物的功效特点,并为苦荞未来合理应用提供实验依据。
-
图 3 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物对酒精性胃黏膜损伤的影响(小鼠胃黏膜氧化应激指标变化)
注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示与模型组相比差异显著(P<0.05),**表示与模型组相比差异极显著(P<0.01);图4~图8同。
Figure 3. Effect of fermented tartary buckwheat extract of Pleurotus eryngii on alcoholic gastric mucosal injury (Changes of oxidative stress indexes of gastric mucosa in mice)
表 1 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物中活性物质含量
Table 1 Antioxidant content of fermented tatary buckwheat extracts from apricot mushroom
样品 多酚含量
(mg GAE/g DW)黄酮含量
(mg RE/g DW)三萜含量
(mg/g)芦丁含量(mg/g) 槲皮素含量(mg/g) 杏鲍菇发酵苦荞提取物 11.40±0.32 17.19±0.30 7.59±0.24 13.55±0.05 0.665±0.01 -
[1] 孟宪军, 朱安宁, 徐伟伟. 葛花解酲汤的现代相关研究与运用[J]. 光明中医,2015,30(7):1561−1564. [MENG X J, ZHU A N, XU W W. Modern research and application of Gehua Jiejie Tang[J]. Guangming TCM,2015,30(7):1561−1564.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2015.07.107 MENG X J, ZHU A N, XU W W. Modern research and application of Gehua Jiejie Tang[J]. Guangming TCM, 2015, 30(7): 1561−1564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2015.07.107
[2] CHEN Y, LI Q, KUANG Z, et al. Inhibitory effect of flavonoid extract of lotus leaf on alcohol-induced gastric injury by antioxidant capacity in mice[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2020,2020(17):1−11.
[3] ZOU L, WU D, REN G, et al. Bioactive compounds, health benefits, and industrial applications of tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum)[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(5):657−673. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1952161
[4] 柴多, 王美婷, 姜雨萌, 等. 苦荞麦不同部位代谢轮廓及活性成分分布[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):212−217. [CHAI D, WANG M T, JIANG Y M, et al. Metabolic profiles and distribution of active ingredients in different parts of buckwheat[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):212−217.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191023-245 CHAI D, WANG M T, JIANG Y M, et al. Metabolic profiles and distribution of active ingredients in different parts of buckwheat[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(2): 212−217. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191023-245
[5] 张余, 黄小燕, 刘昌敏, 等. 苦荞营养保健成分及其食品开发研究进展与展望[J]. 粮食与油脂,2019,32(8):12−14. [ZHANG Y, HUANG X Y, LIU C M, et al. Progress and prospects of research on nutritional and health components of buckwheat and its food development[J]. Grain and Oil,2019,32(8):12−14.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2019.08.004 ZHANG Y, HUANG X Y, LIU C M, et al. Progress and prospects of research on nutritional and health components of buckwheat and its food development[J]. Grain and Oil, 2019, 32(8): 12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2019.08.004
[6] 许莹莹, 廖烨, 李德海, 等. 食用菌发酵液中功能性成分研究及应用[J]. 包装与食品机械,2018,36(1):57−62. [XU Y Y, LIAO Y, LI D H, et al. Research and application of functional ingredients in edible mushroom fermentation broth[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2018,36(1):57−62.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2018.01.012 XU Y Y, LIAO Y, LI D H, et al. Research and application of functional ingredients in edible mushroom fermentation broth[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2018, 36(1): 57−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2018.01.012
[7] 郭美英. 珍稀食用菌杏鲍菇生物学特性的研究[J]. 福建农业学报,1998,13(3):44−9. [GUO M Y. Study on the biological characteristics of the rare edible mushroom abalone[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture,1998,13(3):44−9.] GUO M Y. Study on the biological characteristics of the rare edible mushroom abalone[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture, 1998, 13(3): 44−9.
[8] 于航, 郑瑞芳, 苏文灵, 等. 基于肠道菌的黄酮类成分代谢特征及药理学思考[J]. 药学学报,2021,56(7):1757−1768. [YU H, ZHENG R F, SU W L, et al. Metabolic characteristics and pharmacological considerations of flavonoid components based on intestinal bacteria[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2021,56(7):1757−1768.] YU H, ZHENG R F, SU W L, et al. Metabolic characteristics and pharmacological considerations of flavonoid components based on intestinal bacteria[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021, 56(7): 1757−1768.
[9] 潘瑶, 郑时莲, 邹兴平, 等. 葡萄、芒果、草莓乙醇提取物抗氧化活性组分分析及其抗氧化相互作用[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(4):133−140. [PAN Y, ZHENG S L, ZOU X P, et al. Analysis of antioxidant activity fractions of ethanolic extracts of grapes, mangoes and strawberries and their antioxidant interactions[J]. Food Science,2017,38(4):133−140.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201704022 PAN Y, ZHENG S L, ZOU X P, et al. Analysis of antioxidant activity fractions of ethanolic extracts of grapes, mangoes and strawberries and their antioxidant interactions[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(4): 133−140. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201704022
[10] 罗娅, 王小蓉, 张勇, 等. 不同提取条件对草莓果实抗氧化物质和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(14):108−112. [LUO Y, WANG X R, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of different extraction conditions on antioxidant substances and antioxidant activity of strawberry fruits[J]. Food Science,2011,32(14):108−112.] LUO Y, WANG X R, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of different extraction conditions on antioxidant substances and antioxidant activity of strawberry fruits[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(14): 108−112.
[11] 刘智慧, 何宏魁, 曹润洁, 等. 灵芝及其制品中总三萜含量检测方法条件的优化及其验证[J]. 酿酒,2022,49(3):72−75. [LIU Z H, HE H K, CAO R J, et al. Optimization of method conditions for the determination of total triterpenes in Ganoderma lucidum and its products and its validation[J]. Brewing,2022,49(3):72−75.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8110.2022.03.021 LIU Z H, HE H K, CAO R J, et al. Optimization of method conditions for the determination of total triterpenes in Ganoderma lucidum and its products and its validation[J]. Brewing, 2022, 49(3): 72−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8110.2022.03.021
[12] 李娇妹. 杏鲍菇三萜类化合物提取纯化工艺及抑制肿瘤活性研究[D]. 天津:天津大学, 2015. [LI J M. Extraction and purification process and tumor suppression activity of triterpenoids from Agaricus blazei[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University, 2015.] LI J M. Extraction and purification process and tumor suppression activity of triterpenoids from Agaricus blazei[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2015.
[13] LI D, ZHU L, WU Q, et al. Different interactions between tartary buckwheat protein and tartary buckwheat phenols during extraction:Alterations in the conformation and antioxidant activity of protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,418:135711. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135711
[14] LI H Y, YUAN Q, YANG Y L, et al. Phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacities, and inhibitory effects on digestive enzymes of different kiwifruits[J]. Molecules,2018,23(11):2957. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112957
[15] 张婷, 李琛, 罗安伟, 等. 8 种猕猴桃不同组织部位的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(19):88−93. [ZHANG T, LI C, LUO A W, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities of different tissue parts of eight species of kiwifruit[J]. Food Science,2016,37(19):88−93.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201619015 ZHANG T, LI C, LUO A W, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities of different tissue parts of eight species of kiwifruit[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(19): 88−93. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201619015
[16] 王璐瑶, 张笃芹, 牛猛, 等. 固态发酵对藜麦营养成分、酚类物质含量及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(24):130−138. [WANG L Y, ZHANG D Q, NIU M, et al. Effects of solid-state fermentation on the nutrient composition, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of quinoa[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2022,43(24):130−138.] WANG L Y, ZHANG D Q, NIU M, et al. Effects of solid-state fermentation on the nutrient composition, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of quinoa[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(24): 130−138.
[17] 辛欣, 余宙, 范青生, 等. 藜蒿三萜分离纯化及其体外抗氧化、抗菌活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2009,21(2):312−318. [XIN X, YU Z, FAN Q S, et al. Isolation and purification of triterpenes from Artemisia quinquefolium and their in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities[J]. Natural Products Research and Development,2009,21(2):312−318.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2009.02.032 XIN X, YU Z, FAN Q S, et al. Isolation and purification of triterpenes from Artemisia quinquefolium and their in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities[J]. Natural Products Research and Development, 2009, 21(2): 312−318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2009.02.032
[18] 李志华, 宋晓凯, 赵艳敏, 等. 不同品种苹果果皮和果肉中总三萜含量的测定[J]. 食品研究与开发,2014,35(11):87−90. [LI Z H, SONG X K, ZHAO Y M, et al. Determination of total triterpene content in the peel and flesh of apples of different varieties[J]. Food Research and Development,2014,35(11):87−90.] LI Z H, SONG X K, ZHAO Y M, et al. Determination of total triterpene content in the peel and flesh of apples of different varieties[J]. Food Research and Development, 2014, 35(11): 87−90.
[19] 孙培龙. 三萜类物质的提取及抗肿瘤活性研究[D]. 上海:上海应用技术大学, 2016. [SUN P L. Extraction and antitumor activity of triterpenoids[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai University of Applied Science and Technology, 2016.] SUN P L. Extraction and antitumor activity of triterpenoids[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Applied Science and Technology, 2016.
[20] 田汉英, 国旭丹, 李五霞, 等. 不同处理温度对苦荞抗氧化成分的含量及其抗氧化活性影响的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2014,29(11):19−23,50. [TIAN H Y, GUO X D, LI W X, et al. Study on the effect of different treatment temperatures on the content of antioxidant components and their antioxidant activity of buckwheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2014,29(11):19−23,50.] TIAN H Y, GUO X D, LI W X, et al. Study on the effect of different treatment temperatures on the content of antioxidant components and their antioxidant activity of buckwheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2014, 29(11): 19−23,50.
[21] PEREIRA JUNIOR L C, NASCIMENTO F G, OLIVEIRA S, et al. Protective effect against gastric mucosa injury of a sulfated agaran from Acanthophora spicifera[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,261:117829. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117829
[22] YANG Q, LUO C, ZHANG X, et al. Tartary buckwheat extract alleviates alcohol-induced acute and chronic liver injuries through the inhibition of oxidative stress and mitochondrial cell death pathway[J]. American Journal of Translational Research,2020,12(1):70−89.
[23] 孟海涛, 汪鹤, 查学强, 等. 霍山石斛不同提取物抗小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤活性的比较研究[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(13):229−234. [MENG H T, WANG H, CHA X Q, et al. Comparative study on the anti-acute alcoholic liver injury activity of different extracts of Dendrobium Huoshan[J]. Food Science,2015,36(13):229−234.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201513042 MENG H T, WANG H, CHA X Q, et al. Comparative study on the anti-acute alcoholic liver injury activity of different extracts of Dendrobium Huoshan[J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(13): 229−234. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201513042
[24] XIE L, GUO Y L, CHEN Y R, et al. A potential drug combination of omeprazole and patchouli alcohol significantly normalizes oxidative stress and inflammatory responses against gastric ulcer in ethanol-induced rat model[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2020,85:106660. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106660
[25] LU S, KONG S, WANG Y, et al. Gastric acid-response chitosan/alginate/tilapia collagen peptide composite hydrogel:Protection effects on alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2022,277:118816. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118816
[26] ZHANG Y, SUN L, LAI X, et al. Gastroprotective effects of extract of Jasminum grandiflorum L. flower in HCl/EtOH-induced gastric mucosal ulceration mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2021,144:112268. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112268
[27] TESCHKE R. Alcoholic liver disease:Alcohol metabolism, cascade of molecular mechanisms, cellular targets, and clinical aspects[J]. Biomedicines,2018,6:106. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040106
[28] 黄欣, 张思遥, 王薛, 等. HBx基因通过ERK1/2信号通路促肝细胞增殖及炎性因子表达[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2020,42(8):790−798. [HUANG X, ZHANG S Y, WANG X, et al. HBx gene promotes hepatocyte proliferation and inflammatory factor expression through ERK1/2 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of the Third Military Medical University,2020,42(8):790−798.] HUANG X, ZHANG S Y, WANG X, et al. HBx gene promotes hepatocyte proliferation and inflammatory factor expression through ERK1/2 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of the Third Military Medical University, 2020, 42(8): 790−798.
[29] 秦宇, 马硕晗, 徐恩波, 等. 绿色加工全谷物的结构及膳食纤维, 酚类物质变化研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2022,41(11):10−21. [QIN Y, MA S H, XU E B, et al. Progress of structural and dietary fiber and phenolic changes in green processed whole grains[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology,2022,41(11):10−21.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.11.002 QIN Y, MA S H, XU E B, et al. Progress of structural and dietary fiber and phenolic changes in green processed whole grains[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology, 2022, 41(11): 10−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.11.002
[30] LEE I H, HUNG Y H, CHOU C C. Solid-state fermentation with fungi to enhance the antioxidative activity, total phenolic and anthocyanin contents of black bean[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2008,121(2):150−156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.09.008
[31] 何永艳. 荞麦乙醇提取物的抗氧化活性研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2008. [HE Y Y. Antioxidant activity of buckwheat ethanol extract[D]. Yanling:Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2008.] HE Y Y. Antioxidant activity of buckwheat ethanol extract[D]. Yanling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2008.
[32] LAN-SOOK L, EUN-JI C, CHANG-HEE K, et al. Contribution of flavonoids to the antioxidant properties of common and tartary buckwheat[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2016,68:181−186. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2015.07.005
[33] LIANG Q, SHENG Y, PING J, et al. The gender-dependent difference of liver GSH antioxidant system in mice and its influence on isoline-induced liver injury[J]. Toxicology,2011,280(1-2):61−69. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.11.010
[34] ZHAO J, LUO Z. Discovery of Raf family is a milestone in deciphering the Ras-mediated intracellular signaling pathway[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23:5158. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095158
[35] PARK S W, OH T Y, KIM Y S, et al. Artemisia asiatica extracts protect against ethanol-induced injury in gastric mucosa of rats[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,2008,23(6):976−84. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05333.x
[36] 孙阳, 杜军, 陈敏, 等. 不同浓度酒精对慢性饮酒大鼠胃黏膜细胞增殖的影响[J]. 南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2004,24(4):348−350. [SUN Y, DU J, CHEN M, et al. Effects of different concentrations of alcohol on the proliferation of gastric mucosal cells in rats with chronic alcohol consumption[J]. Journal of Nanjing Medical University:Natural Science Edition,2004,24(4):348−350.] SUN Y, DU J, CHEN M, et al. Effects of different concentrations of alcohol on the proliferation of gastric mucosal cells in rats with chronic alcohol consumption[J]. Journal of Nanjing Medical University:Natural Science Edition, 2004, 24(4): 348−350.
[37] 毛湘君芝, 陆震鸣, 耿燕, 等. 猴头菌粉对小鼠急性酒精性胃损伤的预防作用[J]. 食用菌,2018,40(4):4. [MAO X J Z, LU Z M, GENG Y, et al. Prophylactic effect of powdered monkey head mushroom on acute alcoholic gastric injury in mice[J]. Edible Mushrooms,2018,40(4):4.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2018.04.027 MAO X J Z, LU Z M, GENG Y, et al. Prophylactic effect of powdered monkey head mushroom on acute alcoholic gastric injury in mice[J]. Edible Mushrooms, 2018, 40(4): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2018.04.027
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张敏杰,杨武德,代叶,李玮,魏晴,梁珊珊. 黔产不同商品规格金钗石斛质量评价研究. 亚太传统医药. 2024(04): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林鑫静,张明,李鑫,周春阳,蒲跃,袁斌,范艺缤,范润勇,夏天琴,尤俊,杨晓曦,胥正敏. 调脏舒秘合剂小鼠急性毒性实验研究. 现代中医药. 2023(02): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨吉容,石京山. 金钗石斛破壁粉对自发性高血压大鼠血压及心功能的影响. 遵义医科大学学报. 2022(06): 699-705 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
