Effect of Vacuum Pre-cooling on the Circulation and Shelf Quality of Postharvest Baby Cabbage
-
摘要: 为优选娃娃菜真空预冷的处理条件,维持采后娃娃菜的新鲜品质,在分析不同真空预冷终温(0、2和4 ℃)和不同真空预冷终压(400、600、800和1000 Pa)对采后娃娃菜预冷效果的基础上,进行了二因素三水平的中心复合响应面试验。结果显示,与不经预冷处理的对照和终温0 ℃的预冷组相比,在终压600 Pa条件下,2~4 ℃的预冷终温处理可更好地维持采后娃娃菜的外观品质,抑制其呼吸速率和丙二醛(MDA)含量的升高。在终温2 ℃条件下,与不经预冷处理的对照和终压1000 Pa的预冷组相比,400~800 Pa的预冷终压处理可更好地维持采后娃娃菜的外观品质,抑制其呼吸速率及MDA含量的升高。进一步的中心复合响应面试验结果显示,采后娃娃菜的真空预冷最优条件为终温4.0 ℃、终压600 Pa,该真空预冷条件不仅可维持采后娃娃菜的较好品质,而且可使活性物质可溶性蛋白、总酚和抗坏血酸的含量分别提高18.78%、18.47%和33.23%。因此,适宜的真空预冷处理是一种极具潜力的商品化处理技术,能有效维持采后娃娃菜在流通及货架期间的良好品质。Abstract: To optimize the treatment conditions for vacuum pre-cooling of baby cabbage and maintain the fresh quality of postharvest baby cabbage, a central composite response surface experiment with two factors and three levels was conducted on the basis of analyzing the effects of different vacuum pre-cooling final temperature (0, 2 and 4 ℃) and different vacuum pre-cooling final pressure (400, 600, 800 and 1000 Pa) on the pre-cooling of postharvest baby cabbage. The results showed that compared with the control without pre-cooling and the pre-cooling group with final temperature of 0 ℃, the pre-cooling with final temperature of 2~4 ℃ at the final pressure of 600 Pa could better maintain the appearance quality of postharvest baby cabbage, inhibit the increase of respiratory rate and malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Under the condition of final temperature of 2 ℃, compared with the control without pre-cooling and the pre-cooling group with a final pressure of 1000 Pa, pre-cooling with final pressures of 400~800 Pa could also better maintain the appearance quality of postharvest baby cabbage, inhibit the increase of respiratory rate and MDA content. Further central composite response surface experiments showed that the optimal conditions for vacuum pre-cooling of postharvest baby vegetables were final temperature of 4.0 ℃ and final pressure of 600 Pa. The vacuum pre-cooling condition not only maintained good quality of postharvest baby vegetable, but also increased the content of soluble protein, total phenols, and ascorbic acid by 18.78%, 18.47% and 33.23%, respectively. Therefore, appropriate vacuum pre-cooling treatment is a highly potential commercialization technology that could effectively maintain the good quality of postharvest baby vegetable during circulation and shelf life.
-
Keywords:
- vacuum pre-cooling /
- baby cabbage /
- final temperature /
- final pressure /
- total phenol /
- soluble protein /
- ascorbic acid /
- shelf life
-
娃娃菜(Brassica pekinensis)属于十字花科芸薹属白菜亚种,结球类叶菜,半耐寒性蔬菜。因其外形精致、色泽鲜艳,口感清脆等特点而深受消费者青睐[1]。娃娃菜含有丰富的矿物质元素和营养物质,如钙、铁、酚类物质、蛋白质和抗坏血酸等。另外,娃娃菜还含有硫苷等药用活性物质,其水解产物萝卜硫素更具有抗炎、抗菌及抗肿瘤等作用[2]。然而,娃娃菜由于叶表面积较大,很容易在修整过程中遭受机械伤损害,加之其采后呼吸代谢旺盛,很容易导致大量病原菌浸入组织伤口,从而加速腐烂变质过程,严重影响其商品特性。为此,国内外许多学者也在积极探索维持采后娃娃菜货架品质的技术措施。例如,张映瞳等[3]通过中强度脉冲电场处理有效延缓了娃娃菜的衰老进程,增强了其营养品质;陈少霞等[4]的研究表明,相较常温对照和其他包装材料,低温环境及纳米包装材料可以维持采后娃娃菜较好的品质;李翠红等[5]研究发现,0.1%的溶菌酶可有效抑制鲜切娃娃菜茎部褐变和营养物质的降解;陈皖豫等[6]则通过建立低O2+高CO2的气体微环境,阐明了自发气调包装处理可维持采后娃娃菜的较高营养品质;此外,1-甲基环丙烯熏蒸处理在维持采后娃娃菜营养品质降解及抗氧化活性方面也显现出有益的效果[2]。
真空预冷技术(Vacuum cooling)是通过降低环境压力使水的沸点降低,从而蒸发叶表水分达到吸热降温的原理。真空预冷可以迅速去除果蔬田间热,具有降温均匀迅速、高效维持食品营养品质等特点。目前,该技术已广泛应用于叶菜保鲜领域。例如,安容慧等[7]的研究表明,真空预冷可以维持采后上海青良好的货架品质;杨腾达等[8]通过研究发现真空预冷可以延缓桑叶菜的采后木质化,延缓其品质劣变。赵安琪等[9]阐明了真空预冷可以显著维持采后鸡毛菜较高的营养品质,延缓其有害物质丙二醛和亚硝酸盐含量的升高。He等[10]研究发现真空预冷同步酸性电解水处理可有效提高鲜枸杞的贮藏品质,延长其货架期。戚军洋等[11]的研究表明真空预冷可应用于杨梅的生产销售,解决杨梅在梅雨季节中保鲜运输等问题。尽管真空预冷处理在菠菜[12]、黄花菜[13]和西兰花[14]上也显示出了有益的保鲜效果。然而不适当的真空预冷也会导致蔬菜发生冻害、失水严重等问题[15]。不同类型的蔬菜由于组织结构的不同,对预冷关键参数的要求也不同。例如,娃娃菜的叶梗类似于海绵组织,不适宜的真空预冷压力会导致贮藏/货架期娃娃菜出现组织“凹陷”的伤害;不适宜的真空预冷温度,会导致娃娃菜组织出现冻害。然而截至目前,尚未见对娃娃菜采后真空预冷中关键参数预冷终温和预冷终压阈值的报道。
基于此,本研究以娃娃菜为对象,以真空预冷终温和终压为因素,以真空预冷效果、娃娃菜流通期及货架期间的总酚类物质、可溶性蛋白、抗坏血酸、亚硝酸盐和丙二醛等指标作为响应值,研究了适宜采后娃娃菜真空预冷的工艺参数,以期为娃娃菜快速、精准真空预冷提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
娃娃菜 购自江苏省南京市高邮娃娃菜基地,采购后3 h内送回江苏省农业科学院农业设施与装备研究所实验室,挑选大小均匀、无病虫害的娃娃菜作为实验材料;甲醇、酚酞、硫脲、蒽酮、盐酸萘乙二胺、乙醇、抗坏血酸 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;乙酸锌、草酸、磷酸二氢钾、氢氧化钾、对氨基苯磺酸、考马斯亮蓝G-250、硫代巴比妥酸、异丙醇 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;硼酸、无水葡萄糖、亚硝酸钠、亚铁氰化钾 西陇科学股份有限公司;浓硫酸 南京化学试剂股份有限公司;福林酚、三氯乙酸 上海源叶生物技术有限公司。
PL202-L电子天平、Seven Multi pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;3K15高速冷冻离心机 德国Sigma公司;UV-1102型紫外-可见分光光度计 上海天美科学仪器有限公司;A11 Basic型液氮研磨器 艾卡(广州)仪器设备有限公司;GC7890 气相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;全功能微电脑控制振动实验台 上海华仪器设备有限公司;FR-400A手压式塑料薄膜封口机 上海义光包装设备制造有限公司;KMS 500型真空预冷机 东莞科美斯科技实业有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 不同预冷终温参数的筛选
将挑选好的娃娃菜(每组处理约3±0.2 kg)放入塑料筐中,将塑料筐放入真空预冷室,将温度感应器插在娃娃菜最外层与次外层叶片中间,关闭真空预冷舱门。在预冷终压为600 Pa的条件下,设置三个预冷终温处理:0、2和4 ℃。启动真空预冷机,待预冷终温降至设定温度,预冷结束,取出塑料筐,记录娃娃菜达到预设终温时所需的时间、失水率及能耗情况。以同样量的不进行真空预冷的娃娃菜为对照,该对照组在常温条件(30±1 ℃)下贮藏。预冷结束后统一采用打孔聚丙烯防雾袋(厚度为20 μm)进行包装,每袋装3颗,每组处理12袋,将袋子封口后先于相对湿度85%~90%、低温(4±1 ℃)冷库模拟流通1 d,之后于相对湿度85%~90%、常温(25±1 ℃)冷库模拟货架销售12 d,货架期间每3 d取一次样,取避开主脉的外部叶片为实验材料,迅速用液氮冷冻,贮存于−80 ℃冰箱保存,用于相关指标的测定。取样期间观察表型变化并对呼吸速率进行检测。
1.2.2 不同预冷终压参数的筛选
将挑选好的娃娃菜(每组处理约3±0.2 kg)放入塑料筐中,将塑料筐放入真空预冷室,将温度感应器插在娃娃菜最外层与次外层叶片中间,关闭真空预冷舱门。在预冷终温为2 ℃的条件下,分别调节真空预冷机预冷终压400、600、800和1000 Pa。启动真空预冷机,待预冷终温降至设定温度,预冷结束,取出塑料筐,记录娃娃菜达到预设终温时所需的时间、失水率及能耗情况。以同样量的不进行真空预冷的娃娃菜为对照,该对照组在常温条件(25±1 ℃)下贮藏,预冷结束后的包装、流通、模拟货架期等方法同1.2.1。
1.2.3 娃娃菜真空预冷工艺条件的优化
基于单因素实验的结果,采用响应面中心复合设计方案进行二因素三水平实验设计,优化娃娃菜真空预冷过程的关键工艺参数。以娃娃菜的预冷终温(2~4 ℃)和预冷终压(400~800 Pa)作为自变量,以预冷时长、失水率及能耗和货架3 d时娃娃菜的可溶性蛋白含量、抗坏血酸含量、丙二醛含量和亚硝酸盐含量作为响应值。以不进行任何处理的娃娃菜为对照,进行中心复合响应面试验。表1为中心复合响应面试验的因素及水平情况。
表 1 中心复合响应面试验的因素及水平Table 1. Factors and levels of central composite response surface experimental因素 水平 −1 0 1 预冷终温(℃) 2.0 3.0 4.0 预冷终压(Pa) 400 600 800 1.2.4 预冷前后温度和压强的测定
采用真空预冷机预冷腔室温度计探针测定预冷前后温度,通过真空预冷机数据显示屏读取温度和压强,单位分别以℃和Pa表示。
1.2.5 预冷前后失水率的测定
采用电子秤分别称量预冷前后娃娃菜的重量,通过预冷前后娃娃菜的重量变化率来计算失水率。每个处理重复3次。单位以%表示。
1.2.6 能耗的测定
采用独立电表箱记录预冷前后预冷机耗电情况,通过预冷前后电量变化来计算能耗。每个处理重复3次。单位以kWh表示。
1.2.7 丙二醛(MDA)含量的测定
采用硫代巴比妥酸法测定[16]。取0.5 g娃娃菜样品,加入5 mL 5%的三氯乙酸(TCA)溶液,研磨匀浆,浸提10 min,离心后取上清,低温备用。取2 mL上清加2 mL 0.67%的硫代巴比妥酸(TBA),混匀后,100 ℃沸水浴20 min,取出后冷却,于450、532和600 nm处测定吸光度,计算MDA含量。计算公式如下。
式中:V表示提取液总体积,mL;V1表示反应液总量,mL;V2表示反应液中的提取液体积,mL;W表示样品重量,g。
1.2.8 呼吸速率的测定
采用气相色谱法[17],取450 g娃娃菜放进密闭容器中3 h后,用30 mL的无菌注射器抽取25 mL气体备用。气体样品用气相色谱来分析CO2的成分,呼吸速率的表示单位为 mg·(kg·h)−1。测定其中的CO2含量,以计算呼吸速率,共测定3次,取平均值,计算公式如下。
式中:φ1表示气相色谱测定的样品气体中CO2体积分数,%;φ0表示气相色谱测定的空白气体中CO2体积分数,%;V表示密闭容器体积,mL;m表示样品质量,kg;t表示测定时间,h。
1.2.9 可溶性蛋白含量的测定
参照Bradford[18]的方法测定,取0.5 g娃娃菜样品,加入0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2)5 mL,匀浆,离心取上清0.1 mL,加入0.9 mL蒸馏水和5 mL考马斯亮蓝G-250试剂,混匀于595 nm处测定吸光度。计算公式如下。
式中:C表示标准曲线查得蛋白质含量,mg;V表示上清液总体积,mL;V1表示反应液中的上清体积,mL;W表示样品重量,g。
1.2.10 总酚含量的测定
参照Ghasemnezhd等[19]的方法,略有改动。取0.5 g娃娃菜样品,加入2.5 mL 80%乙醇,匀浆,离心,取上清0.1 mL,加入0.9 mL蒸馏水,再加入0.5 mL福林酚试剂,25 ℃反应3 min,再加入1 mL饱和Na2CO3,25 ℃反应1 h,反应结束,于760 nm处测定吸光度,计算公式如下。
式中:C表示标准曲线查得总酚含量,mg;V表示上清液总体积,mL;V1表示反应液中的上清体积,mL;W表示样品重量,g。
1.2.11 抗坏血酸含量的测定
参照An等[20]的方法,略有改动。采用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法进行测定。称取0.5 g娃娃菜样品,加入5 mL草酸溶液,匀浆,离心后取上清4 mL,转移至锥形瓶中,用2,6-二氯靛酚滴定,溶液呈粉红色且15 s不褪色为止,同时吸取4 mL草酸溶液做空白实验,用1.0 mg/mL的抗坏血酸标准液进行标定,计算公式如下。
式中:V表示滴定试样所消耗2,6-二氯靛酚溶液的体积,mL;V0表示滴定空白所消耗2,6-二氯靛酚溶液的体积,mL;T表示2,6-二氯靛酚溶液的滴定度,mg/mL;A表示稀释倍数;W表示样品重量,g。
1.2.12 亚硝酸盐含量的测定
采用盐酸萘乙二胺法[21],称取0.5 g娃娃菜样品,加入2.5 mL 50 g/L的饱和硼砂溶液,充分混匀,再加入2.5 mL 70 ℃左右蒸馏水,于沸水浴中加热15 min,取出冷却10 min,边转边加入1 mL 106 g/L的亚铁氰化钾溶液,再加入1 mL 220 g/L的乙酸锌溶液,摇匀后静置30 min,离心。取上清2.5 mL,加入2 mL 4 g/L的对氨基苯磺酸溶液,静置5 min,加入1 mL 2 g/L的盐酸萘乙二胺溶液,常温静置15 min,于538 nm处测定吸光度,计算公式如下。
式中:m1表示测定用样液中亚硝酸钠的质量,µg;V0表示测定用样液总体积,mL;W表示样品重量,g;V1表示测定用样液体积,mL。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据均重复平行测定3次,数据采用平均值±标准误差,使用SPSS软件进行统计分析,采用ANOVA进行差异分析(P<0.05为差异显著)。用Design-Expert 12.0进行中心复合响应面设计以及二次回归拟合和预测,并用Origin 21.0软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同预冷终温对娃娃菜保鲜效果的影响
2.1.1 不同预冷终温对娃娃菜预冷时间的影响
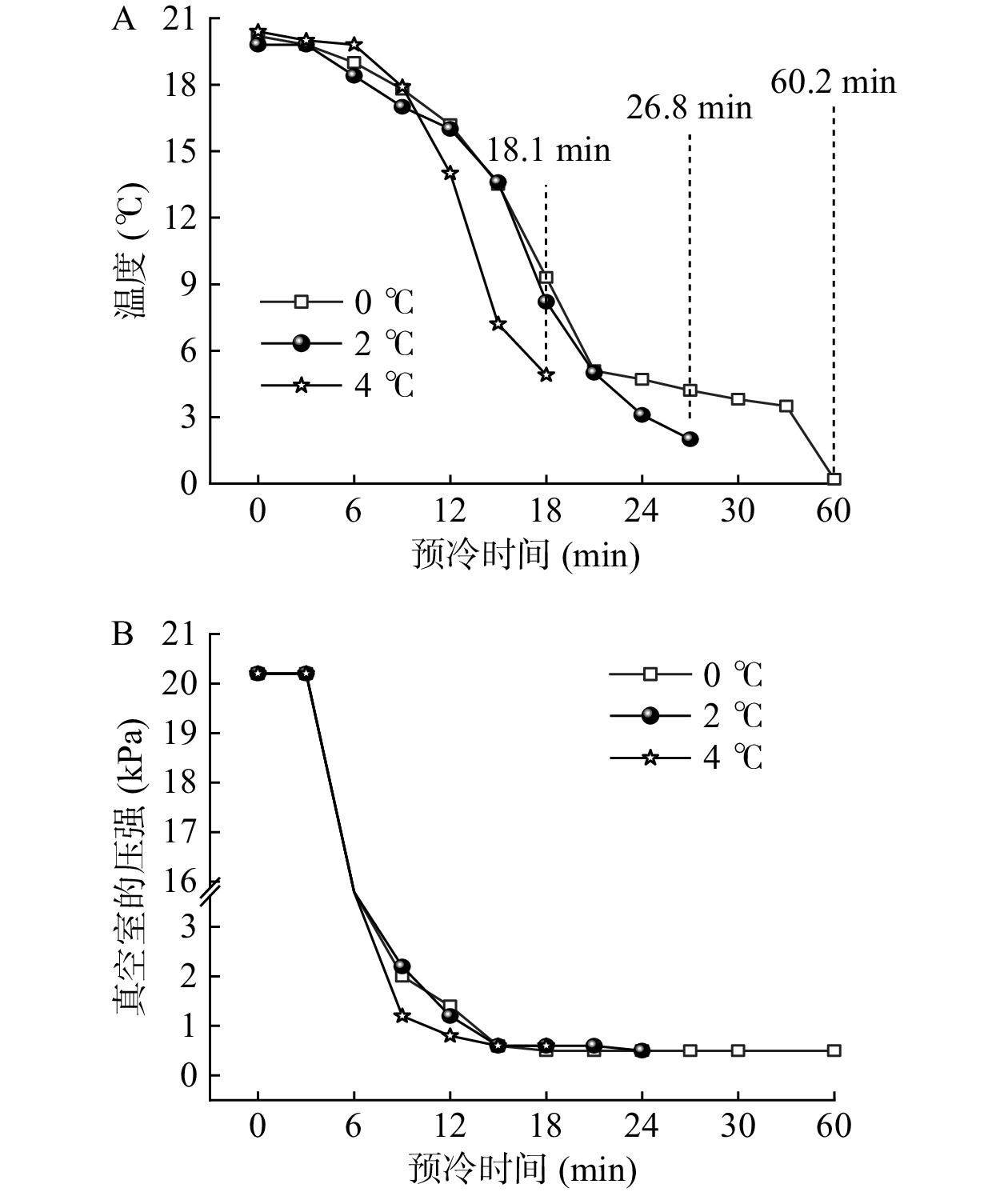
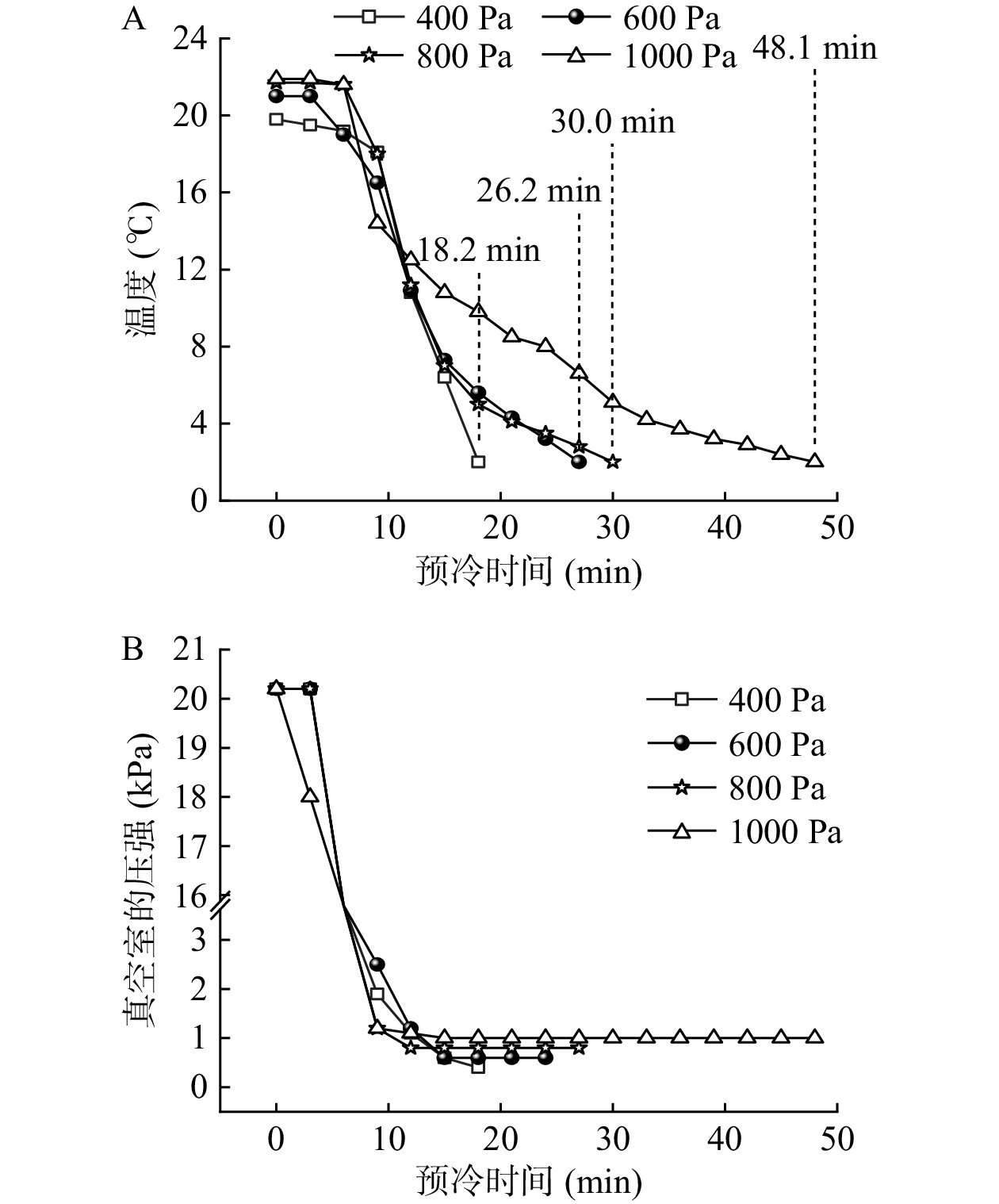
图1A为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜预冷时间的影响情况。可看出,当娃娃菜预冷终温为0、2和4 ℃时,相应的预冷时间分别为60.2、26.8和18.1 min。可见,预冷终温为0 ℃的耗时分别是终温2和4 ℃的2.25倍和3.33倍。
图1B为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜预冷真空室压强的影响情况。可看出,在前3 min内,所有处理真空室的压强均保持稳定状态,从第4 min开始,各处理组真空室内的压强开始迅速下降,最终于15 min左右达到预设终压并趋于稳定。可见,不同预设终温对于真空室压降速率的变化影响不大。
2.1.2 不同预冷终温对娃娃菜流通及货架期间外观品质的影响
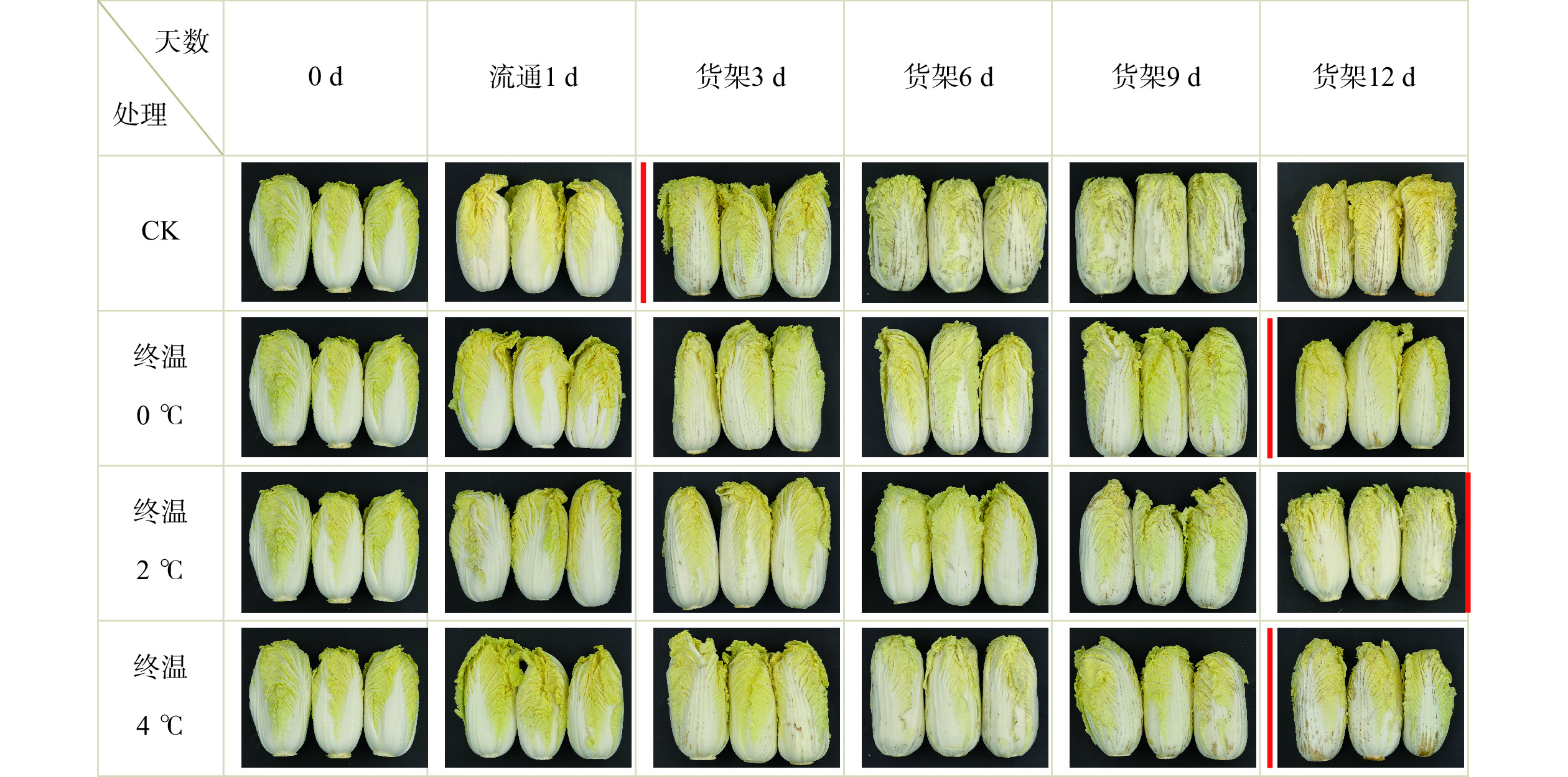
图2为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间外观品质的影响。可看出,从货架3 d开始,对照组娃娃菜开始出现腐烂现象,然而终温4 ℃预冷组娃娃菜的外观品质在货架第9 d才出现腐烂现象,终温2 ℃预冷组在9~12 d时仅出现了轻微的腐烂斑点。总体上经过真空预冷处理的娃娃菜外观品质要明显优于对照。尤其是预冷终温为2和4 ℃的处理组,在货架第9 d时仍可以保持娃娃菜较好的外观品质。
![]() 图 2 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜外观品质的影响注:图中红线右代表失去商品价值;图7同。Figure 2. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the appearance quality of postharvest baby cabbage
图 2 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜外观品质的影响注:图中红线右代表失去商品价值;图7同。Figure 2. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the appearance quality of postharvest baby cabbage2.1.3 不同预冷终温对娃娃菜失水率的影响
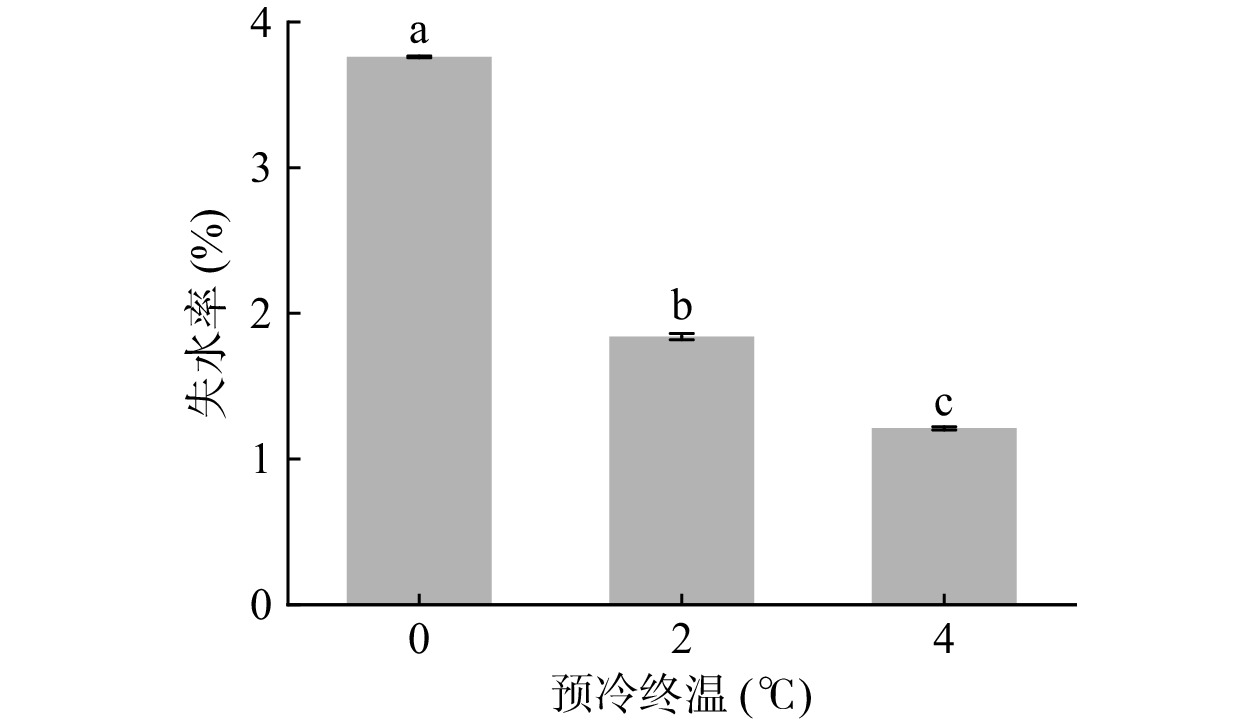
图3为真空预冷过程中不同预冷终温对娃娃菜失水率的影响,可看出,在预冷终压600 Pa条件下,预冷终温为0、2和4 ℃处理组娃娃菜的失水率分别为3.76%、1.85%和1.21%。可见,当预冷终温为0 ℃时,娃娃菜的失水率远高于终温2和4 ℃的预冷处理,因此,应在2~4 ℃内调节预冷终温,避免由于失水率过高引发品质劣变。
2.1.4 不同预冷终温对预冷机能耗的影响
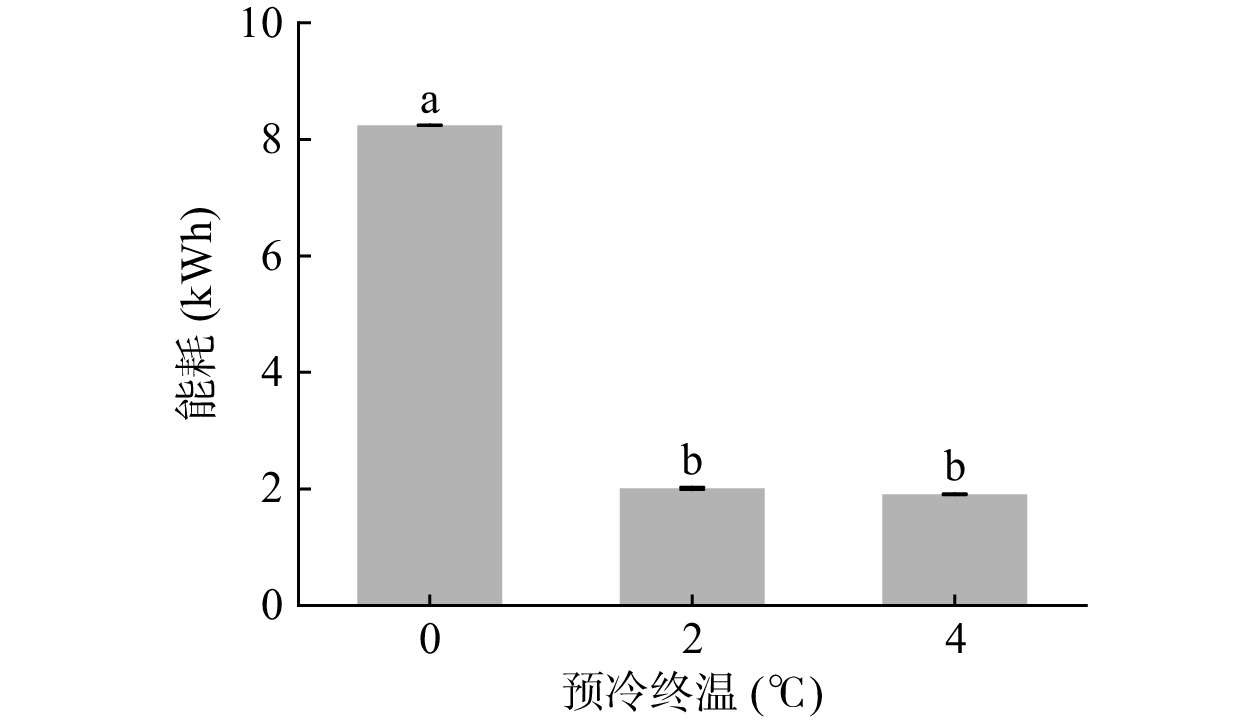
图4为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对真空预冷能耗的影响,由图可看出,当预冷终温为0、2和4 ℃时,真空预冷的能耗分别为8.24、2.01和1.91 kWh,可见,当预冷终温为0 ℃时,其能耗显著高于预冷终温2 ℃和4 ℃的预冷处理(P<0.05),后二者之间的能耗无显著差异(P>0.05),因此,从节约资源的角度考虑,应在2~4 ℃内调节预冷终温。
2.1.5 不同预冷终温对娃娃菜流通及货架期间丙二醛含量(MDA)及呼吸速率的影响
图5A为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间丙二醛含量的影响,可看出,随着流通及货架时间的延长,所有娃娃菜中的丙二醛含量总体均呈上升趋势。与对照相比,真空预冷处理可显著延缓采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间丙二醛含量的升高(P<0.05)。尤其在货架后期,这种效果愈加显著。例如,在货架第12 d时,对照组娃娃菜的丙二醛含量为2.32 μmol/g,预冷终温0、2和4 ℃处理组娃娃菜的丙二醛含量分别为1.93、1.75和2.12 μmol/g,分别比同期对照组低了16.81%、24.57%和8.62%。可见,真空预冷可显著延缓采后娃娃菜中丙二醛含量的升高。
![]() 图 5 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜丙二醛含量(A)及呼吸速率(B)的影响注:不同小写字母表示相同时间不同组别差异显著(P<0.05),图10同。Figure 5. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the malondialdehyde content (A) and respiration rate (B) of postharvest baby cabbage
图 5 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜丙二醛含量(A)及呼吸速率(B)的影响注:不同小写字母表示相同时间不同组别差异显著(P<0.05),图10同。Figure 5. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the malondialdehyde content (A) and respiration rate (B) of postharvest baby cabbage图5B为终压600 Pa条件下,不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间呼吸速率的影响,可看出,真空预冷结束后,娃娃菜的呼吸速率从43.11 mg·(kg·h)−1降到19.68~20.22 mg·(kg·h)−1。在流通1 d的时候,对照组娃娃菜的呼吸速率为26.22 mg·(kg·h)−1,较最初下降了39.18%,但仍显著高于真空预冷处理组的呼吸速率(P<0.05)。在随后的货架期间,尽管所有娃娃菜的呼吸速率总体呈上升趋势,但真空预冷可以显著延缓采后娃娃菜呼吸速率的升高,尤其是终温为2 ℃的处理组。例如,在货架第12 d时,终温0、2和4 ℃的预冷组相较同期对照组娃娃菜的呼吸速率分别降低了14.21%、23.48%和15.14%。因此,真空预冷可以降低采后娃娃菜的呼吸速率并抑制其在货架期间的升高。
2.1.6 不同预冷终温单因素实验结果分析总述
综上,与对照相比,终温2和4 ℃预冷组可以较好地维持采后娃娃菜的外观品质,延缓呼吸速率及丙二醛含量的升高;与预冷终温0 ℃的处理组相比,终温2和4 ℃的预冷组降低了失水率及能耗的损失,节约了资源,提升了经济效益。同时亦可以维持娃娃菜较好地外观及营养品质。但预冷终温2~4 ℃间相差了2 ℃,究竟何种温度可以达到最优预冷及保鲜效果,本研究将基于此在后续进一步开展中心复合响应面试验,以此探究采后娃娃菜真空预冷最优终温条件。
2.2 不同预冷终压对娃娃菜保鲜效果的影响
2.2.1 不同预冷终压对娃娃菜预冷时长的影响
图6A为终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对采后娃娃菜预冷时间的影响情况。可看出,当娃娃菜预冷终压为400、600、800和1000 Pa时,相应的预冷时间分别为18.2、26.2、30.0和48.1 min。可见,终压为400 Pa时的耗时最短,终压为1000 Pa的耗时最长,该值显著高于其他终压处理(P<0.05),分别是终压400、600和800 Pa耗时的2.99、1.84和1.60倍。
图6B为终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对采后娃娃菜预冷真空室压强的影响情况。可看出,在前3 min内,终压400~800 Pa处理组真空室的压强保持稳定状态,从第4 min开始,各处理组真空室内的压强开始迅速下降,于16 min左右达到预设终压并趋于稳定。终压1000 Pa处理组真空室的压强从预冷开始较快地进入了降压模式,于12 min左右趋于稳定。最终各处理组的压强稳定在设定值内。
2.2.2 不同预冷终压对娃娃菜流通及货架期间外观品质的影响
图7为预冷终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间外观品质的影响,可看出,对照组娃娃菜在货架第3 d便出现腐烂迹象。相比之下,真空预冷处理明显减轻了货架期娃娃菜的腐烂症状。另也发现,不同终压处理对采后娃娃菜的外观品质显示出了不同的影响。例如, 终压400 Pa处理组的娃娃菜在货架12 d时出现了明显的腐烂症状;然而终压600 Pa和终压800 Pa处理仍能较好地维持货架12 d娃娃菜的外观品质,当预冷终压为1000 Pa时,娃娃菜从货架第6 d开始便出现腐烂斑点。因此,调节预冷终压在400~800 Pa范围内变化可以相对较好地维持娃娃菜的外观品质。
2.2.3 不同预冷终压对娃娃菜失水率的影响
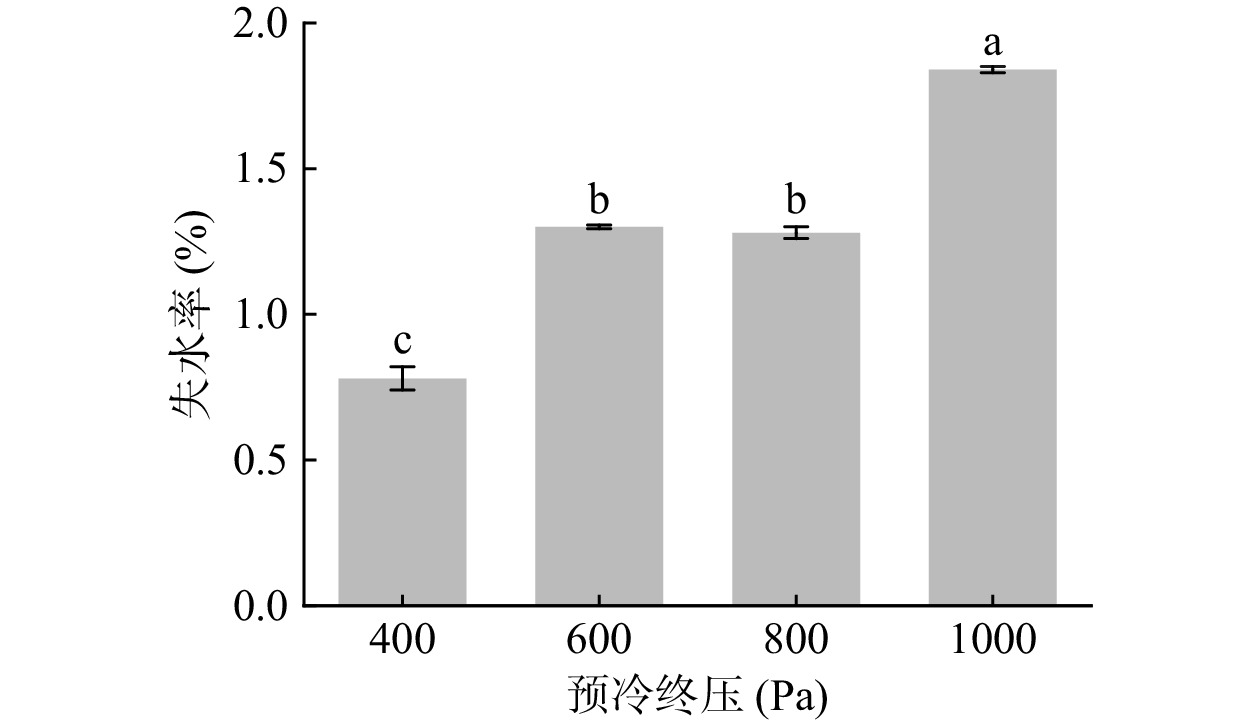
图8为终温为2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对娃娃菜失水率的影响,可看出,在预冷终压为400、600、800和1000 Pa时,其失水率分别为0.79%、1.30%、1.28%和1.84%。可见,当预冷终压为1000 Pa时,其失水率远高于其他三个终压处理(400、600和800 Pa),因此,应根据不同需求在400~800 Pa范围内调节预冷终压,避免失水率过高。
2.2.4 不同预冷终压对预冷能耗的影响
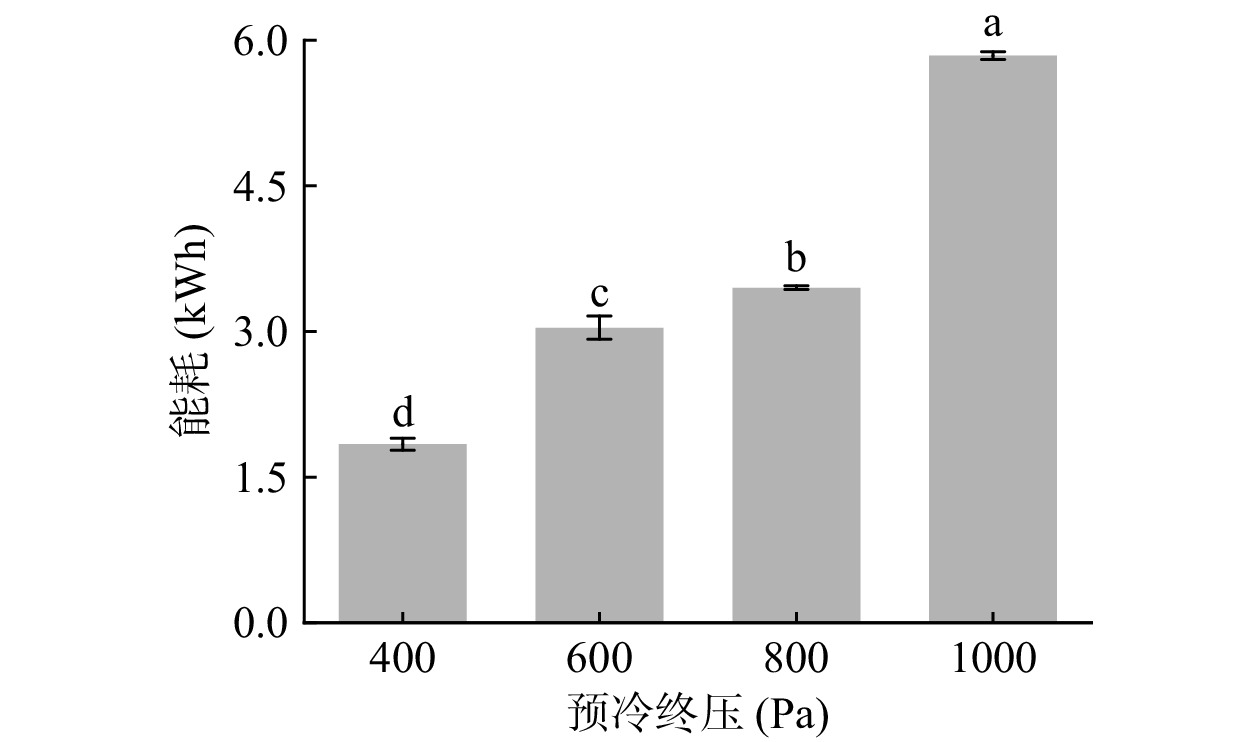
图9显示了在终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对真空预冷能耗的影响,可以看出,当预冷终压为400、600、800和1000 Pa时,其能耗分别为1.84、3.04、3.45和5.84 kWh。可见,在预冷终压400~1000 Pa的范围内,随着预冷终压的增加,能耗显著增加(P<0.05)。当预冷终压为1000 Pa时,其预冷能耗分别为终压400、600和800 Pa处理组的3.17、1.92和1.69倍。因此,在400~800 Pa范围内调节预冷终压,不仅可以显著降低采后娃娃菜的失水率,而且可降低能耗。
2.2.5 不同预冷终压对娃娃菜流通及货架期间丙二醛(MDA)含量和呼吸速率的影响
图10A为终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对娃娃菜丙二醛含量的影响,可看出,随着流通及货架时间的延长,采后娃娃菜组织丙二醛含量总体呈上升趋势,真空预冷可显著抑制其丙二醛含量的累积。例如,在货架第12 d时,终压400、600、800和1000 Pa处理组娃娃菜的丙二醛含量分别为1.71、1.57、1.63和2.08 μmol/g,而同期对照组娃娃菜组织的丙二醛含量已经高达2.21 μmol/g,分别是终压400、600、800和1000 Pa处理组的1.29、1.41、1.36和1.06倍。可见,真空预冷可以延缓采后娃娃菜丙二醛含量的积累,保护细胞膜的完整性。
图10B为终温2 ℃条件下,不同预冷终压对娃娃菜呼吸速率的影响,可看出,与对照相比,真空预冷可以显著降低娃娃菜的呼吸速率(P<0.05),当真空预冷结束后,娃娃菜的呼吸速率从29.01 mg·(kg·h)−1降至15.79~16.81 mg·(kg·h)−1。在随后的货架期间,真空预冷均可以显著抑制采后娃娃菜呼吸速率的升高(P<0.05)。尤其是终压400、600和800 Pa的处理组,相较对照和终压1000 Pa处理组,这三个处理组对呼吸速率的抑制效果更加明显。例如,在货架第9 d时,终压400、600和 800 Pa处理组娃娃菜的呼吸速率为24.61、23.42和24.31 mg·(kg·h)−1,该值比同期对照组低了15.17%、19.27%和16.20%,同样,在货架12 d时,终压400、600和 800 Pa处理组娃娃菜的呼吸速率值比同期对照组也低了14.28%、17.18%和16.35%。可见,真空预冷过程中,不同终压条件对娃娃菜呼吸速率具有明显的影响,尤其是400~800 Pa终压的效果更理想。
2.2.6 不同预冷终压单因素实验结果分析总述
综上,与对照相比,终压400、600和800 Pa的预冷组可以较好地维持采后娃娃菜的外观品质,延缓呼吸速率及丙二醛含量的升高;与预冷终压1000 Pa的处理组相比,终压400、600和800 Pa的预冷组明显降低了预冷时间、失水率及能耗,节约了资源,同时亦可以维持娃娃菜较好的品质。但400~800 Pa之间相差400 Pa,究竟何种终压可以达到最优预冷及保鲜效果,本研究将基于此在后续进一步开展中心复合响应面试验,以此探究采后娃娃菜真空预冷最优的终温及终压条件。
2.3 娃娃菜真空预冷参数优化
2.3.1 中心复合响应面试验设计、回归方程及方差分析
根据单因素实验结果,综合采后娃娃菜真空预冷效果、外观品质、呼吸速率和丙二醛含量,优选预冷终温2~4 ℃和预冷终压400~800 Pa的参数进行进一步优化试验;通过响应面中心点法对数据进行拟合处理,建立娃娃菜真空预冷终温和终压二因素与预冷时长、失水率、能耗、可溶性蛋白含量、总酚含量、抗坏血酸含量、丙二醛含量及亚硝酸盐含量的数学回归模型,表2为中心复合响应面试验设计及结果,表3为回归方程的方差分析结果(模型列及各一次项、二次项及交互项P值均达到显著水平,失拟项不显著,表明该模型合理)。
表 2 中心复合响应面试验设计及结果Table 2. Design and results of central composite response surface试验号 X1预冷终温
(℃)X2预冷终压
(Pa)Y1预冷时间
(min)Y2失水率
(%)Y3能耗
(kWh)Y4可溶性蛋白
含量(mg/g)Y5总酚含量
(mg/g)Y6抗坏血酸
含量(mg/100 g)Y7丙二醛含量
(μmol/g)Y8亚硝酸盐
含量(mg/kg)1 3.0 320 12.96±1.15 0.84±1.18 1.73±0.02 53.33±0.69 2.75±0.01 58.90±0.58 0.90±0.01 1.75±0.02 2 2.0 800 30.20±1.22 1.56±0.29 3.45±0.26 52.11±0.26 2.71±0.02 57.83±1.06 0.92±0.01 1.81±0.02 3 4.4 600 15.12±1.13 1.01±0.04 1.88±0.43 51.91±0.21 2.67±0.03 57.18±0.51 0.95±0.01 1.82±0.01 4 3.0 880 27.67±0.84 1.48±0.01 3.01±0.36 52.52±0.24 2.69±0.01 56.75±0.59 0.93±0.01 1.81±0.02 5 4.0 800 17.68±0.92 1.09±0.21 2.01±0.04 50.04±0.22 2.62±0.05 56.18±0.51 1.00±0.02 1.94±0.03 6 2.0 400 16.60±0.54 0.87±0.42 1.82±0.16 50.08±0.20 2.65±0.01 55.75±0.23 0.97±0.02 1.86±0.07 7 3.0 600 24.10±0.22 1.33±0.31 2.80±1.22 55.06±0.28 2.87±0.02 61.78±0.58 0.71±0.03 1.45±0.04 8 3.0 600 23.60±0.87 1.27±0.20 2.60±0.80 55.71±0.13 2.91±0.01 62.21±023 0.71±0.04 1.41±0.02 9 3.0 600 23.90±0.37 1.31±0.02 2.66±0.12 55.56±0.10 2.92±0.02 61.78±0.59 0.73±0.02 1.40±0.02 10 4.0 400 12.60±1.08 0.77±0.01 1.69±0.22 53.65±0.16 2.80±0.01 58.76±0.58 0.88±0.01 1.62±0.10 11 3.0 600 23.10±1.02 1.22±0.92 2.67±0.58 56.12±0.18 2.92±0.01 62.05±1.01 0.73±0.06 1.37±0.06 12 3.0 600 23.40±0.28 1.41±0.33 2.74±0.38 55.56±0.14 2.90±0.01 61.50±0.51 0.74±0.01 1.43±0.02 13 1.6 600 24.20±0.63 1.39±0.25 2.88±0.48 49.56±0.37 2.62±0.06 55.90±0.59 1.01±0.03 1.94±0.10 对照组 45.43±0.10 2.49±0.01 38.52±0.24 1.26±0.19 2.35±0.07 注:X1代表预冷终温;X2代表预冷终压;表3同。 表 3 回归方程的方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of regression model方差来源 模型 F值 残差 失拟项 R2 X1 X2 X1·X2 X12 X22 预冷时间 368.75b 107.76b 194.86b 18.15b 31.54b 22.59b 4.3 3.28c 0.9895 失水率 0.75b 0.15b 0.46b 0.035a 0.046a 0.072a 0.045 0.31c 0.9436 能耗 3.76b 1.11b 1.75b 0.43b 0.25b 0.27b 0.064 0.23c 0.9833 可溶性蛋白含量 62.88b 2.39b 1.01a 8.24b 42.02b 14.88b 1.12 0.57c 0.9825 总酚含量 0.17b 2.277E-003a 5.043E-003b 0.016b 0.11b 0.052b 1.503E-003 1.064E-004c 0.9910 抗坏血酸含量 80.78b 1.27a 1.58a 5.45b 51.54b 29.96b 1.48 0.84c 0.9820 丙二醛含量 0.17b 1.363E-003a 1.672E-003a 6.356E-003b 0.11b 0.063b 1.327E-003 9.436E-004c 0.9921 亚硝酸盐含量 0.58b 9.787E-003a 0.014a 0.034b 0.36b 022a 9.265E-003 6.008E-003c 0.9842 注:a代表差异显著(P<0.05);b表示差异极显著(P<0.01);c表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。 2.3.2 预冷终温及预冷终压对娃娃菜预冷效果的影响
图11A为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜预冷时间的影响,娃娃菜的预冷时间即由采摘后3 h内运至实验室的初始温度降至预设预冷终温所需的时间。随着预冷终压的升高及终温的降低,娃娃菜的预冷时长也随之逐渐增大。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y1=−130.84148+32.53112X1+0.15328X2−0.010650X1X2−2.12937X12−4.50469E-005X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9895表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
图11B为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜失水率的影响,失水率即娃娃菜预冷前后重量的损失。随着预冷终压的增大,娃娃菜的失水率也逐渐增大。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y2=−5.29936+1.27781X1+7.52369E−003X2−4.68229E−004X1X2−0.081052X12−2.53728E-006X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9436,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
图11C为采后娃娃菜真空预冷过程的能耗情况,能耗即娃娃菜预冷前后真空预冷机耗能情况。由图可看出,随着预冷终压的增大,其能耗也逐渐增大。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y3=−14.03558+3.26247X1+0.019714X2−1.6375E−003X1X2−0.18950X12−4.92500E-006X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9833,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
2.3.3 预冷终温及预冷终压对娃娃菜可溶性蛋白、总酚和抗坏血酸含量的影响
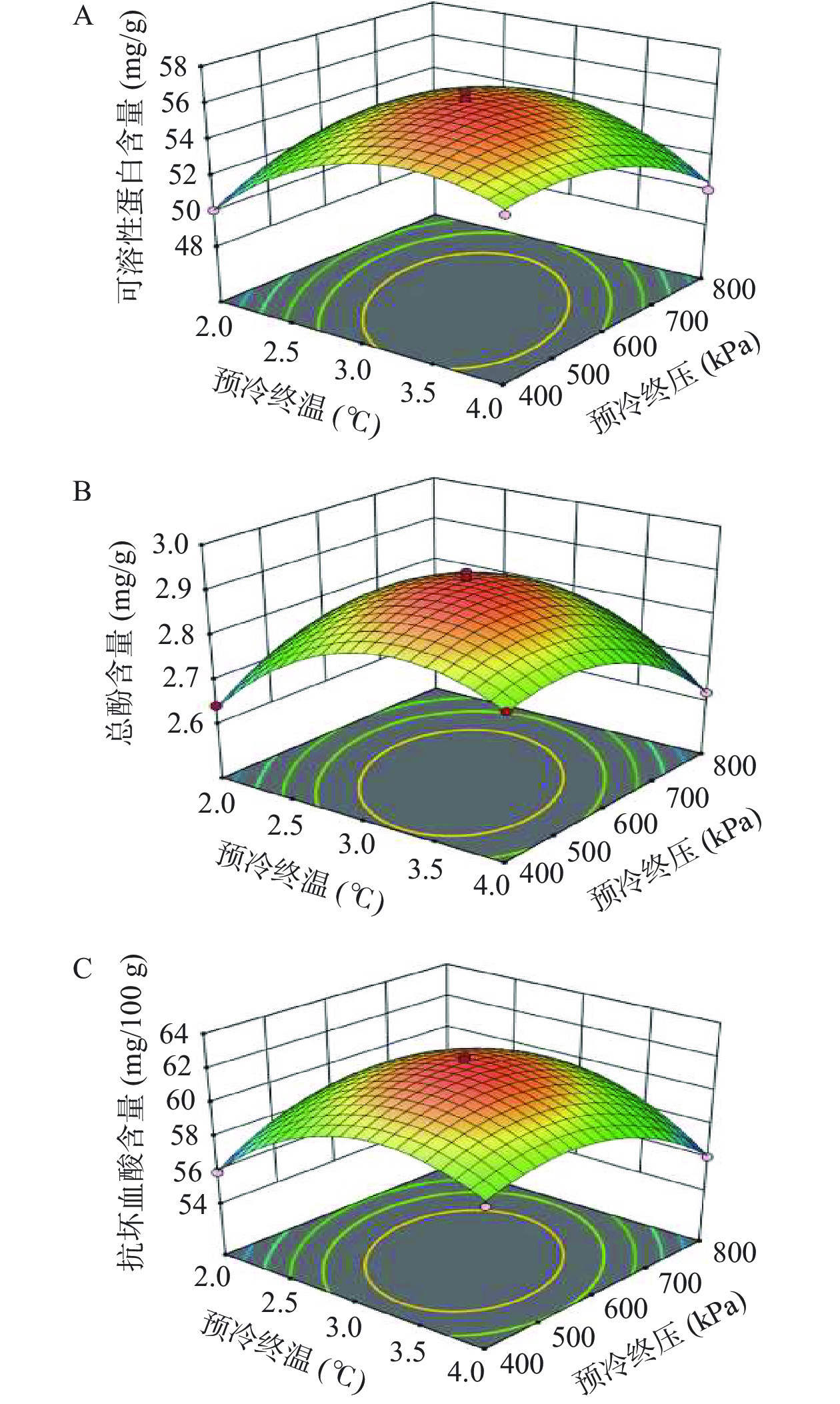
图12A为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜可溶性蛋白含量的影响,可溶性蛋白可以提高细胞的保水能力、保护细胞膜的完整性。本研究中,随着预冷终温、终压的增加,娃娃菜组织的可溶性蛋白含量均呈先升高后降低的趋势。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y4=−110.84835+35.25789X1+0.09233X2−7.17500E−003X1X2−2.45763X12−3.65667E−005X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9825,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
总酚是重要的抗氧化物质。图12B为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜总酚含量的影响,随着预冷终温及终压的升高,总酚含量总体呈先升高后降低的趋势。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y5=−5.36619+1.95644X1+4.65683E−003X2−3.14277E−004X1X2−0.12507X12−2.15203E−006X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9910,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
图12C为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜抗坏血酸含量的影响,随着预冷终温及终压的升高,娃娃菜组织抗坏血酸含量变化与总酚和可溶性蛋白的变化趋势相似,均呈先上升后下降的趋势。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y6=−116.06961+42.00661X1+0.10090X2−5.83693E-003X1X2−2.72180X12−5.18813E−005X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9820,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
2.3.4 预冷终温及预冷终压对娃娃菜丙二醛及亚硝酸盐含量的影响
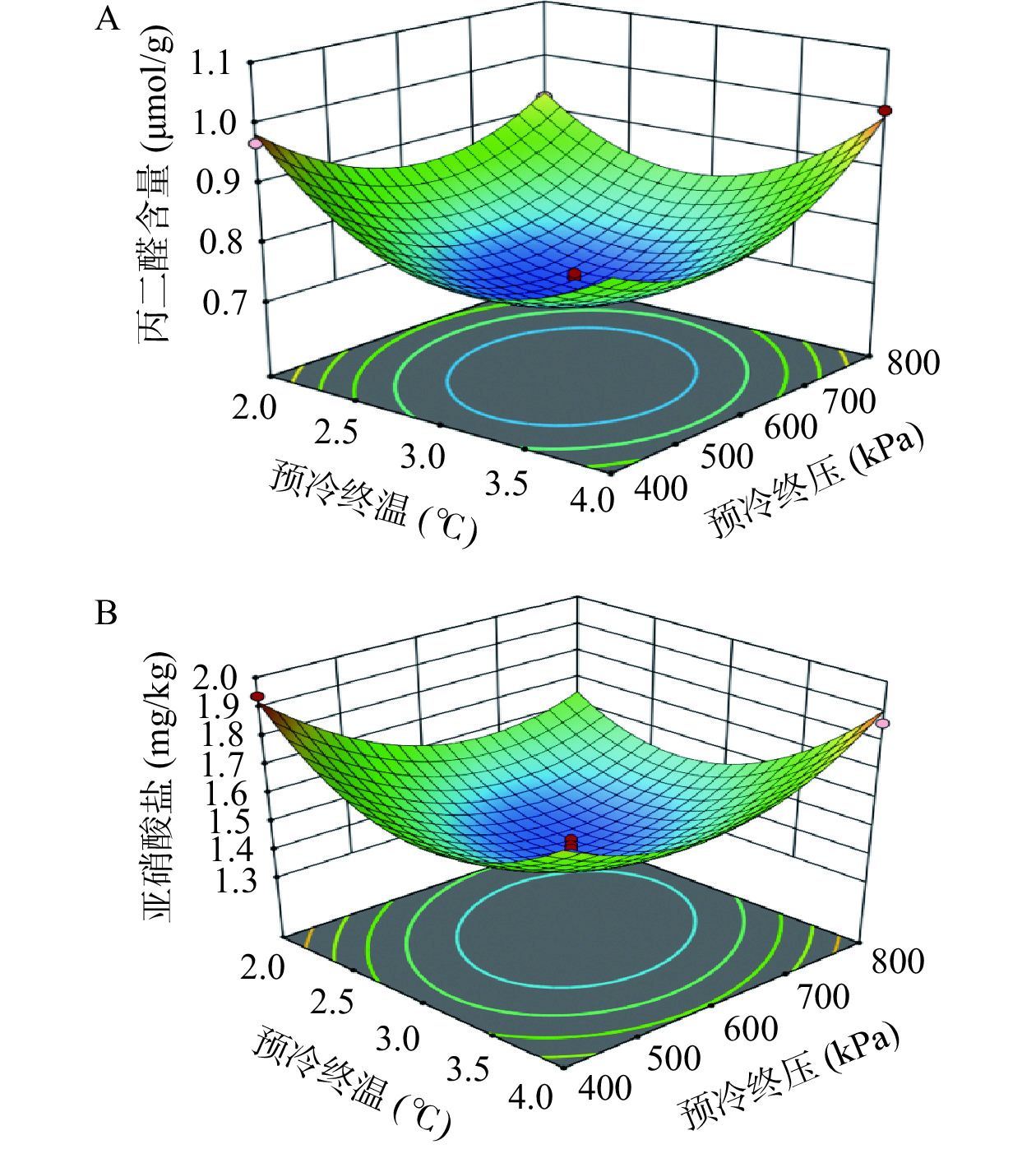
丙二醛是膜脂过氧化的重要产物,累积过多会对细胞膜造成损伤,图13A为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜丙二醛含量的影响,可看出,随着预冷终温、终压的增加,娃娃菜组织的丙二醛含量总体呈先下降后上升的趋势。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y7=8.71388−1.91758X1−4.18625E−003X2+1.99312E−004X1X2+0.12750X12+2.38613E−006X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9921,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
图13B为真空预冷对采后娃娃菜亚硝酸盐含量的影响,随着预冷终温及终压的升高,其组织总体变化趋势与丙二醛含量变化相似,均呈先下降后上升的趋势。对实验数据进行回归拟合,得到方程如下:Y8=16.28451−3.51595X1−8.35447E−003X2+4.64202E−004X1X2+0.22875X12+4.43109E-006X22。如表3所示,采用ANOVA进行显著性检验及方差分析可知,回归方程模型的P值均<0.01,说明模型差异极显著;失拟项P值均˃0.05,表明失拟不显著,实验模型的决定系数R2为0.9842,表明模型的预测结果与实际值拟合度高,因此该模型能够很好地预测和分析响应值。
2.3.5 预冷条件的优化与验证
使用Design Expert软件进行条件优化,设置各响应值目标和等级,得到最佳处理条件为预冷终温X1=3.11 ℃,预冷终压X2=570 Pa,此时预测的各响应值为预冷时间22.40 min,失水率1.26%,能耗2.58 kWh,可溶性蛋白55.70 mg/g,总酚2.90 mg/g,抗坏血酸62.04 mg/100 g,丙二醛0.72 μmol/g,亚硝酸盐1.41 mg/kg。为了检验模型准确性和考虑实际情况,将最优工艺修改为预冷终温4.0 ℃,预冷终压600 Pa,在此条件下平行实验3次,得出各个指标的综合分为预冷时间20.9 min,失水率1.33%,能耗2.52 kWh,可溶性蛋白53.96 mg/g,总酚2.95 mg/g,抗坏血酸60.18 mg/100 g,丙二醛0.70 μmol/g,亚硝酸盐1.47 mg/kg。由此可见综合评分的验证实验值与模型预测值比较接近,达到预测的93.30%~105.56%,表明预测结果较优。
3. 讨论与结论
真空预冷是指在真空环境下迅速蒸发产品水分,从而达到迅速降温的非热加工保鲜技术[22]。果蔬在采收后,呼吸作用会成为其新陈代谢的主导过程。采后呼吸作用越旺盛,衰老越快。这就导致其外观、营养品质很容易发生劣变[23]。为了使其在送达终端消费者时保持最佳状态。需要采取一定的保鲜技术措施来延缓其品质下降[24]。因此新鲜的果蔬在采收后通常需要先进行预冷处理,其作用即将刚采收后的果蔬温度从田间环境温度快速降至适宜的常温贮藏或低温运输温度[25]。真空预冷作为冷链保鲜的首要环节,不仅可以在源产地迅速除去田间热,降低营养成分的消耗,而且可以高效避免后续果蔬在进入冷藏车和冷库时消耗过多的冷量,引起车温或库温波动,从而造成水汽凝结引发品质劣变[26]。本研究结果显示,真空预冷可以有效维持采后娃娃菜流通及货架期间较好地外观品质,延缓其总酚类和抗坏血酸等营养物质的降解,提高娃娃菜的保鲜效果。
普通叶类蔬菜,外层叶片可以最大化地暴露在空气中,便于气孔蒸发水分吸收热量,从而快速达到降温预冷。而娃娃菜不同于这些叶类蔬菜,属于结球型叶菜,叶球合抱,是预冷蜡质类的典型代表。由于其致密的包裹形态,就会导致内层叶子产生水分蒸发阻力。预冷降温过程中,外部叶片与茎部中心会存在一定温差。董杰 [27]的研究表明,预冷蜡质类蔬菜娃娃菜在真空预冷过程中,其叶表存在低于茎部中心(3.5±0.5 ℃)的温差。吴欣蔚 [28]通过研究证实了叶菜的包裹形态和紧密程度在影响预冷时间和预冷温差方面起主要作用。此外,Zhu等[29]通过研究发现,叶类蔬菜在真空预冷过程中,温度从叶脉向叶缘逐渐降低。维管束主要由韧皮部和木质部组成,是植物体内运输水分和营养成分的主要通道,被称为叶片中的叶脉,叶类蔬菜从叶片中脉分支出来的侧脉延伸到叶缘并变薄,这意味着水分输送路径变窄和输送能力减弱,水分的蒸发受到叶肉细胞中水分的限制,叶脉边缘的水分无法得到及时补充。这就会导致叶类蔬菜在真空预冷过程中,其叶片边缘部位温度要低于叶脉部位温度。因此,本研究将真空预冷机温度感应器插入娃娃菜最外层与次外层叶片中间。可以最大限度地保护其外层叶片及边缘部位免受冷害侵袭。此外,娃娃菜叶片附着一层具有抗击外界胁迫功能的表皮蜡质层,其疏水结构在组织表面起极其重要的防卫功能[23]。
本研究结果表明,正确的预冷参数可以显著维持娃娃菜的品质,然而,不适宜的预冷参数同样也会对娃娃菜的品质产生不良的影响。例如,不同预冷终温对娃娃菜预冷过程起到了差异化的影响。当预冷终温为0 ℃时,其预冷时长为60.2 min,预冷机能耗高达8.24 kWh,显然,其预冷时间和能耗相对较高,不够经济。相比之下,终温2和4 ℃处理组的预冷时间及能耗要明显低于终温0 ℃的处理组,不仅使预冷时间缩短了69.93%和55.48%、能耗降低了75.61%和76.82%,而且可较好地抑制丙二醛的累积;同理,真空预冷过程中预冷压力的变化也会对蔬菜产生不同的作用效果。本研究结果显示,终温一定时,预冷终压越低,娃娃菜预冷时间越短,失水率越低,能耗越小,但如果终压过低会导致娃娃菜组织发生冻害。相反,如果随着预冷终压的升高会使娃娃菜表面的失水率显著增加,导致组织失去鲜态品质。因此,娃娃菜的真空预冷应将压力参数控制在一定范围。在本研究中,如当预冷终压为400和1000 Pa时,在货架后期(9~12 d),其外观品质要劣于终压600和800 Pa的预冷处理。本研究结果还表明,终压每降低200 Pa,大约可以降低娃娃菜预冷时间10~18 min。Zhu等[29]的研究还表明,快速减压模式可以显著提高小白菜的冷却效率并延缓其品质下降,而适度减压模式则有助于更好的降温均匀和最大限度保护外观品质[30]。因此,应根据不同的流通及货架需求,在保证预冷效果的同时,选择适宜的预冷参数。
综上,本研究基于中心响应面试验设计,建立了真空预冷终温X1、终压X2与娃娃菜真空预冷时间、失水率、能耗以及货架期间营养品质指标之间的数学回归方程,以及工艺参数的优选,得到采后娃娃菜真空预冷工艺的最优组合为预冷终温4 ℃+预冷终压600 Pa,该真空预冷条件不仅可提高娃娃菜的预冷效果,而且可维持货架期娃娃菜中可溶性蛋白、总酚及抗坏血酸的含量,并可抑制有害物质丙二醛及亚硝酸盐的积累。研究结果可为娃娃菜产地真空预冷提供理论依据和技术参考。
-
图 2 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜外观品质的影响
注:图中红线右代表失去商品价值;图7同。
Figure 2. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the appearance quality of postharvest baby cabbage
图 5 不同预冷终温对采后娃娃菜丙二醛含量(A)及呼吸速率(B)的影响
注:不同小写字母表示相同时间不同组别差异显著(P<0.05),图10同。
Figure 5. Effects of different pre-cooling final temperatures on the malondialdehyde content (A) and respiration rate (B) of postharvest baby cabbage
表 1 中心复合响应面试验的因素及水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of central composite response surface experimental
因素 水平 −1 0 1 预冷终温(℃) 2.0 3.0 4.0 预冷终压(Pa) 400 600 800 表 2 中心复合响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Design and results of central composite response surface
试验号 X1预冷终温
(℃)X2预冷终压
(Pa)Y1预冷时间
(min)Y2失水率
(%)Y3能耗
(kWh)Y4可溶性蛋白
含量(mg/g)Y5总酚含量
(mg/g)Y6抗坏血酸
含量(mg/100 g)Y7丙二醛含量
(μmol/g)Y8亚硝酸盐
含量(mg/kg)1 3.0 320 12.96±1.15 0.84±1.18 1.73±0.02 53.33±0.69 2.75±0.01 58.90±0.58 0.90±0.01 1.75±0.02 2 2.0 800 30.20±1.22 1.56±0.29 3.45±0.26 52.11±0.26 2.71±0.02 57.83±1.06 0.92±0.01 1.81±0.02 3 4.4 600 15.12±1.13 1.01±0.04 1.88±0.43 51.91±0.21 2.67±0.03 57.18±0.51 0.95±0.01 1.82±0.01 4 3.0 880 27.67±0.84 1.48±0.01 3.01±0.36 52.52±0.24 2.69±0.01 56.75±0.59 0.93±0.01 1.81±0.02 5 4.0 800 17.68±0.92 1.09±0.21 2.01±0.04 50.04±0.22 2.62±0.05 56.18±0.51 1.00±0.02 1.94±0.03 6 2.0 400 16.60±0.54 0.87±0.42 1.82±0.16 50.08±0.20 2.65±0.01 55.75±0.23 0.97±0.02 1.86±0.07 7 3.0 600 24.10±0.22 1.33±0.31 2.80±1.22 55.06±0.28 2.87±0.02 61.78±0.58 0.71±0.03 1.45±0.04 8 3.0 600 23.60±0.87 1.27±0.20 2.60±0.80 55.71±0.13 2.91±0.01 62.21±023 0.71±0.04 1.41±0.02 9 3.0 600 23.90±0.37 1.31±0.02 2.66±0.12 55.56±0.10 2.92±0.02 61.78±0.59 0.73±0.02 1.40±0.02 10 4.0 400 12.60±1.08 0.77±0.01 1.69±0.22 53.65±0.16 2.80±0.01 58.76±0.58 0.88±0.01 1.62±0.10 11 3.0 600 23.10±1.02 1.22±0.92 2.67±0.58 56.12±0.18 2.92±0.01 62.05±1.01 0.73±0.06 1.37±0.06 12 3.0 600 23.40±0.28 1.41±0.33 2.74±0.38 55.56±0.14 2.90±0.01 61.50±0.51 0.74±0.01 1.43±0.02 13 1.6 600 24.20±0.63 1.39±0.25 2.88±0.48 49.56±0.37 2.62±0.06 55.90±0.59 1.01±0.03 1.94±0.10 对照组 45.43±0.10 2.49±0.01 38.52±0.24 1.26±0.19 2.35±0.07 注:X1代表预冷终温;X2代表预冷终压;表3同。 表 3 回归方程的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of regression model
方差来源 模型 F值 残差 失拟项 R2 X1 X2 X1·X2 X12 X22 预冷时间 368.75b 107.76b 194.86b 18.15b 31.54b 22.59b 4.3 3.28c 0.9895 失水率 0.75b 0.15b 0.46b 0.035a 0.046a 0.072a 0.045 0.31c 0.9436 能耗 3.76b 1.11b 1.75b 0.43b 0.25b 0.27b 0.064 0.23c 0.9833 可溶性蛋白含量 62.88b 2.39b 1.01a 8.24b 42.02b 14.88b 1.12 0.57c 0.9825 总酚含量 0.17b 2.277E-003a 5.043E-003b 0.016b 0.11b 0.052b 1.503E-003 1.064E-004c 0.9910 抗坏血酸含量 80.78b 1.27a 1.58a 5.45b 51.54b 29.96b 1.48 0.84c 0.9820 丙二醛含量 0.17b 1.363E-003a 1.672E-003a 6.356E-003b 0.11b 0.063b 1.327E-003 9.436E-004c 0.9921 亚硝酸盐含量 0.58b 9.787E-003a 0.014a 0.034b 0.36b 022a 9.265E-003 6.008E-003c 0.9842 注:a代表差异显著(P<0.05);b表示差异极显著(P<0.01);c表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。 -
[1] OSHER Y, CHALUPOWICZ D, MAURER D, et al. Summer storage of cabbage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,145:144−150. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.07.006
[2] 安容慧, 陈皖豫, 胡花丽, 等. 1-甲基环丙烯对娃娃菜贮藏品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(20):194−203. [AN R H, CHEN W Y, HU H L, et al. Effect of 1-methylcyclopropene on storage quality and antioxidant activity of baby cabbage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(20):194−203.] AN R H, CHEN W Y, HU H L, et al. Effect of 1-methylcyclopropene on storage quality and antioxidant activity of baby cabbage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2021, 47(20): 194−203.
[3] 张映曈, 张元元, 赵欢欢, 等. 中强度脉冲电场对娃娃菜活性物质含量及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(19):183−193. [ZHANG Y T, ZHANG Y Y, ZHAO H H, et al. Effect of moderate intensity pulsed electric field on the contents of bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of baby cabbage (Brassica pekinensis L. var. gemmifera Zenk. )[J]. Food Science,2021,42(19):183−193.] ZHANG Y T, ZHANG Y Y, ZHAO H H, et al. Effect of moderate intensity pulsed electric field on the contents of bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of baby cabbage (Brassica pekinensis L. var. gemmifera Zenk. )[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(19): 183−193.
[4] 陈少霞, 周丹丹, 潘磊庆, 等. 不同包装材料对娃娃菜贮藏过程中品质指标的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(3):270−276, 284. [CHEN S X, ZHOU D D, PAN L Q, et al. Effect of different packaging materials on quality indices of Brassica campestris during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(3):270−276, 284.] CHEN S X, ZHOU D D, PAN L Q, et al. Effect of different packaging materials on quality indices of Brassica campestris during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(3): 270−276, 284.
[5] 李翠红, 魏丽娟, 李长亮, 等. 不同保鲜剂对鲜切娃娃菜贮藏品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2021,21(3):22−28. [LI C H, WEI L J, LI C L, et al. Effects of different preservatives on the quality and antioxidant activity of fresh-cut baby cabbages during storage[J]. Preservation and Processing,2021,21(3):22−28.] LI C H, WEI L J, LI C L, et al. Effects of different preservatives on the quality and antioxidant activity of fresh-cut baby cabbages during storage[J]. Preservation and Processing, 2021, 21(3): 22−28.
[6] 陈皖豫, 安容慧, 胡花丽, 等. 薄膜包装对娃娃菜采后贮藏品质的影响[J]. 包装工程,2020,41(7):33−42. [CHEN W Y, AN R H, HU H L, et al. Effect of film packaging on postharvest storage quality of brassica pekinensis[J]. Packaging Engineering,2020,41(7):33−42.] CHEN W Y, AN R H, HU H L, et al. Effect of film packaging on postharvest storage quality of brassica pekinensis[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2020, 41(7): 33−42.
[7] 安容慧, 周宏胜, 罗淑芬, 等. 真空预冷及不同流通方式对上海青货架品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(13):241−248. [AN R H, ZHOU H S, LUO S F, et al. Effects of vacuum precooling and different circulation modes on the shelf quality of pakchoi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis)[J]. Food Science,2021,42(13):241−248.] AN R H, ZHOU H S, LUO S F, et al. Effects of vacuum precooling and different circulation modes on the shelf quality of pakchoi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis)[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(13): 241−248.
[8] 杨腾达, 陈于陇, 曾凡坤, 等. 真空预冷调控桑叶菜采后木质化的机理初探[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(4):131−138. [YANG T D, CHENG Y L, ZENG F K, et al. A preliminary study on the regulating mechanism of vacuum precooling on the lignification of mulberry leaf vegetables after harvest[J]. Modern Food Technology,2021,37(4):131−138.] YANG T D, CHENG Y L, ZENG F K, et al. A preliminary study on the regulating mechanism of vacuum precooling on the lignification of mulberry leaf vegetables after harvest[J]. Modern Food Technology, 2021, 37(4): 131−138.
[9] 赵安琪, 安容慧, 王馨渝, 等. 真空预冷中的雾化微酸性电解水处理对鸡毛菜低温流通及其货架期品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(3):218−227. [ZHAO A Q, AN R H, WANG X Y, et al. Effect of atomized slightly acidic electrolyzed water treatment in vacuum precooling on the quality of postharvest Chinese little greens during low temperature circulation and shelf[J]. Food Science,2023,44(3):218−227.] ZHAO A Q, AN R H, WANG X Y, et al. Effect of atomized slightly acidic electrolyzed water treatment in vacuum precooling on the quality of postharvest Chinese little greens during low temperature circulation and shelf[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(3): 218−227.
[10] HE X L, WU C, LU L. et al. Influence of acidic electrolyzed water combined with vacuum precooling treatment on quality and antioxidant performance of fresh Lycium barbarum L.[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2022,46(12):2−9.
[11] 戚军洋, 孙红红, 柴春燕. 真空预冷对慈溪杨梅预冷效果的研究及应用[J]. 浙江农业科学,2022,63(2):342−344,410. [QI J Y, SUN H H, CHAI C Y. Research and application of vacuum pre-cooling effect on pre-cooling of Cixi prunes[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Science,2022,63(2):342−344,410.] QI J Y, SUN H H, CHAI C Y. Research and application of vacuum pre-cooling effect on pre-cooling of Cixi prunes[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Science, 2022, 63(2): 342−344,410.
[12] 郭淑婷, 薛健翼, 李锋, 等. 真空预冷压力对菠菜采后贮藏保鲜品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(5):265−269. [GUO S T, XUE J Y, LI F, et al. Effects of vacuum precooling pressure on postharvest preservative quality of spinach[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(5):265−269.] GUO S T, XUE J Y, LI F, et al. Effects of vacuum precooling pressure on postharvest preservative quality of spinach[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(5): 265−269.
[13] 王娟, 马晓艳, 王通, 等. 预冷方式对黄花菜贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(10):215−221. [WANG J, MA X Y, WANG T, et al. Effect of pre-cooling methods on storage quality of daylily[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(10):215−221.] WANG J, MA X Y, WANG T, et al. Effect of pre-cooling methods on storage quality of daylily[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2020, 46(10): 215−221.
[14] DIRAPAN P, BOONYAKIAT D, POONLARP P. Improving shelf life, maintaining quality, and delaying microbial growth of broccoli in supply chain using commercial vacuum cooling and package icing[J]. Horticulturae,2021,7(11):506−506. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7110506
[15] LIU E H, HU X B, LIU S Y. Theoretical simulation and experimental study on effect of vacuum pre-cooling for postharvest leaf lettuce[J]. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research,2014,2(8):443−449. doi: 10.12691/jfnr-2-8-3
[16] 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2013:142−154. [CAO J K, JIANG W B, ZHAO Y M. Postharvest physiological and biochemical experimental guidance of fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2013:142−154.] CAO J K, JIANG W B, ZHAO Y M. Postharvest physiological and biochemical experimental guidance of fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2013: 142−154.
[17] 姜爱丽, 胡文忠, 田密霞, 等. 水杨酸处理对采后番茄果实后熟衰老的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2009,35(5):205−209. [JIANG A L, HU W Z, TIAN M X, et al. Effect of salicylic acid treatment on postharvest senescence of tomato fruit after ripening[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2009,35(5):205−209.] JIANG A L, HU W Z, TIAN M X, et al. Effect of salicylic acid treatment on postharvest senescence of tomato fruit after ripening[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2009, 35(5): 205−209.
[18] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1976,72(12):248−254.
[19] GHASEMNEZHAD M, SHERAFATI M, PAYVAST G A. Variation in phenolic compounds, ascorbic acid and antioxidant activity of five coloured bell pepper (Capsicum annum) fruits at two different harvest times[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2011,3(1):44−49. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.02.002
[20] AN R H, LUO S F, ZHOU H S, et al. Effects of hydrogen-rich water combined with vacuum precooling on the senescence and antioxidant capacity of pakchoi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis)[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2021,289:110469. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110469
[21] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中亚硝酸盐与硝酸盐的测定 GB 5009.33-2016[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016:10−12. [China Food and Drug Administration. National food safety standard determination of nitrites and nitrates in foods GB 5009.33-2016[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016:10−12.] China Food and Drug Administration. National food safety standard determination of nitrites and nitrates in foods GB 5009.33-2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016: 10−12.
[22] WANG N, KAN A, MAO S, et al. Study on heat and mass transfer of sugarcane stem during vacuum pre-cooling[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2021,292:110288. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110288
[23] CHENG H P, HSUEH C F. Multi-stage vacuum cooling process of cabbage[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2007,79(1):37−46. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.01.027
[24] VERA T, PHILIPPE V, CATHIE M. Effect of elevated temperature on tomato post-harvest properties[J]. Plants,2021,10(11):1−2.
[25] 王馨渝, 安容慧, 赵安琪, 等. 真空预冷与雾化ε-聚赖氨酸共处理对采后上海青品质的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2022,40(6):103−115. [WANG X Y, AN R H, ZHAO A Q, et al. Effect of vacuum pre-cooling co-treated with atomized ε-polylysine on postharvest quality of pakchoi[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,40(6):103−115.] WANG X Y, AN R H, ZHAO A Q, et al. Effect of vacuum pre-cooling co-treated with atomized ε-polylysine on postharvest quality of pakchoi[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 40(6): 103−115.
[26] KEHINDE P A, ZHU Z W, SUN D W. Transport phenomena and their effect on microstructure of frozen fruits and vegetables[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,101:63−72.
[27] 董杰. 真空预冷实验与理论分析[D]. 天津:天津商业大学, 2018:23−29. [DONG J. Vacuum precooling experiment and theoretical analysis[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Commerce, 2018:23−29.] DONG J. Vacuum precooling experiment and theoretical analysis[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Commerce, 2018: 23−29.
[28] 吴欣蔚. 真空预冷同步结合气调技术对叶类蔬菜保鲜的研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2017:10−19. [WU X W. Study on preservation of leaf vegetables by vacuum cooling synchronously coupled with modified atmosphere technique[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2017:10−19.] WU X W. Study on preservation of leaf vegetables by vacuum cooling synchronously coupled with modified atmosphere technique[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017: 10−19.
[29] ZHU Z W, GENG Y, SUN D W. Effects of pressure reduction modes on vacuum cooling efficiency and quality related attributes of different parts of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.)[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2021,173(6):111409.
[30] 陆伟杰, 郑伟尉, 吴砚农, 等. 十字花科植物蜡质形成特性及分子机制研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报,2021,38(1):205−213. [LU W J, ZHENG W W, WU Y N, et al. Research review on features and molecular mechanism of wax formation in Brassicaceae[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University,2021,38(1):205−213.] LU W J, ZHENG W W, WU Y N, et al. Research review on features and molecular mechanism of wax formation in Brassicaceae[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, 2021, 38(1): 205−213.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王馨,吴孟仙,陈媛媛,王林峰,杨生玉,李星科. 杜仲叶固态混菌发酵工艺优化及其体外活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2025(03): 29-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



