Effects of Different Concentrations of Carrageenan on the Gel Properties and Structure of Hemp Protein Isolate
-
摘要: 为阐明不同浓度的卡拉胶(0.4%、0.8%、1.2%、1.6%、2.0%,w/w)对汉麻分离蛋白凝胶特性和结构的影响,以未添加卡拉胶的汉麻分离蛋白凝胶为对照,测定复合凝胶的持水能力、质构、流变特性,同时检测了卡拉胶的加入对复合凝胶水分分布、蛋白结构及分子间作用力的影响。结果表明:添加卡拉胶显著(P<0.05)提高了汉麻分离蛋白凝胶持水能力和凝胶强度,改变了蛋白结构。与对照组相比,0.8%卡拉胶的添加显著(P<0.05)提高凝胶的硬度、弹性模量并降低了凝胶的频率依赖性,并与水分子结合最为紧密,α-螺旋向β-折叠和无规卷曲转变,增加凝胶刚性结构;此时维持凝胶结构的主要作用力由疏水相互作用力向二硫键转变,凝胶网络更加致密,电镜结果证明了这一结论。因此,添加0.8%的卡拉胶可显著(P<0.05)提高汉麻分离蛋白的凝胶性质并改善其结构,为提高汉麻分离蛋白在食品领域的应用提供了理论和实验基础。Abstract: To elucidate the influence of different concentrations of carrageenan (CA, 0.4%, 0.8%, 1.2%, 1.6%, 2.0%, w/w) on the gelation properties and structure of hemp protein isolate (HPI), with the hemp protein isolate without adding CA as the control, the water-holding capacity, texture, rheological properties of the composite gels were determined. Meanwhile, the effect of CA addition on the water distribution, protein structure and intermolecular forces in the composite gels was also investigated. The results showed that the addition of CA significantly (P<0.05) improved the water-holding capacity and gel strength, and changed the protein structure. Compared to the control group, adding 0.8% CA significantly increased the hardness, elastic modulus and reduced the frequency dependence of the gel compared to the control group (P<0.05). And most tightly bound to water molecules, with a shift from α-helix to β-sheet and random curling, increasing the rigid structure of the gel. At this time, the primary force maintaining the gel structure shifted from hydrophobic interaction force to disulfide bonding and the gel network became denser, which was proved by scanning electron microscopy results. Therefore, the addition of 0.8% carrageenan could significantly (P<0.05) improve the gel properties and structure of hemp isolate protein, which would provide a theoretical and experimental foundation for the application of hemp protein isolate in the food industry (P<0.05).
-
Keywords:
- carrageenan /
- hemp protein isolate /
- gel properties /
- secondary structure
-
汉麻分离蛋白(Hemp Protein Isolate,HPI)是一种由球蛋白和白蛋白组成的蛋白六聚体,具有乳化性、起泡性、高消化率、低致敏性、高必需氨基酸含量等特点[1−2]。基于HPI的功能特点,常作为营养添加剂添加到食品中提高配方食品产品质量。目前,已经开发出汉麻乳、能量棒等产品,但由于HPI过于紧凑的蛋白结构影响其溶解度、凝胶性、乳化性等功能性质,限制了HPI在食品工业中的应用及发展[2−3]。HPI的改性已得到研究者的广泛关注。通过热处理[4]或化学交联剂[5−6]能够促进蛋白分子的交联进而提高HPI的凝胶性质,如加热或高压均质处理引起蛋白质变性重新排列凝胶网络,添加京尼平促进凝胶网络的形成[5,7]。
多糖可吸附在蛋白质表面促进蛋白交联,常在食品工业中用作胶凝剂和稳定剂[8−11]。卡拉胶(Carrageenan,CA)作为硫酸化线性多糖,可较好改善食品凝胶性质,常作为胶凝剂、增稠剂、乳化剂等广泛应用于食品工业领域[12−14]。CA形成的三维网络通过双螺旋之间的缔合形成分子间弱连接区或形成分子间接合区,从而提高体系的稳定性[15]。已有研究发现添加CA可以提高大豆分离蛋白的凝胶性质和抗氧化能力,促进更加致密的凝胶网络的形成[16−17],将CA与大豆分离蛋白结合可改善香肠、鱼丸[18]等特定食品的品质。但CA对HPI凝胶性质和结构的影响还鲜有报道。
因此,本研究旨在探讨添加CA对HPI凝胶性能及结构的影响。采用质构、流变学测量、持水能力来表征HPI-CA凝胶性能;通过溶解度、巯基含量、傅里叶光谱等方法分析CA的添加对HPI凝胶结构的影响及其相互作用;通过扫描电镜分析蛋白凝胶微观结构。本研究为HPI在新型食品领域的开发及应用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
脱脂汉麻粕(蛋白质干基含量70.20%,脂肪干基含量2.90%,水分含量9.80%,灰分含量11.30%) 购自辽宁省辽宁俏牌生物科技有限公司;卡拉胶(试剂级)、5,5'-二硫代双(2-硝基苯甲酸)(5,5'-Dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid),DTNB) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;甘氨酸(Glycine,Gly)、2-氨基-2-羟甲基-1,3-丙二醇(2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol,Tris)、考马斯亮蓝(Coomassie brilliant blue G-250) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)、氯化钠(NaCl)、尿素、β-巯基乙醇(β-ME) 天津市天力化学试剂有限公司;所有化学药品均为分析纯。
Spectrum Two红外光谱仪 美国PerkinElmer公司;TG16-WS高速离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;FTT2-2500T粉碎机 东莞市房太电器有限公司;PhS-3C型pH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;OS20-S精密增力电动搅拌器 常州丹瑞实验仪器设备有限公司;AlpHa-1560紫外分光光度计 上海谱元仪器有限公司;TA. new plus质构仪 美国ISENSO公司;MCR 102高级旋转流变仪 安东帕(上海)商贸有限公司;Zeiss supra55扫描式电子显微镜 德国蔡司;NMI20核磁共振成像分析仪 上海纽迈电子科技有限公司;Alpha 1-2 LDplus 冷冻干燥机 德国Christ集团;XHF-DY高速分散器 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 HPI的提取
HPI的提取参照Hadnađev等[19]的方法并稍作修改。将脱脂汉麻粕粉碎,过80目筛备用。过筛后的脱脂汉麻粉与去离子水混合(w:v=1:20),2.0 mol/L NaOH调整溶液pH为9.0,45 ℃水浴2 h。水浴后的脱脂汉麻粉溶液在4000 r/min条件下离心20 min,收集上清液。使用2.0 mol/L HCl调节上清液pH为5.0,得悬浊液,4 ℃条件下静置12 h。弃去上清液后,4000 r/min离心15 min,收集沉淀,使用去离子水反复冲洗3次,并调整pH为7.0,冷冻干燥,得HPI冻干粉备用(凯氏定氮测定蛋白终浓度为89%)。
1.2.2 HPI-CA复合凝胶的制备
将HPI粉末溶于去离子水(总浓度固定为12%),室温条件下(25 ℃)磁力搅拌器500 r/min搅拌4 h,随后在4 ℃条件下水化12 h,使蛋白与水充分相溶,制得HPI分散液。将不同浓度的CA(0.4%、0.8%、1.2%、1.6%、2.0%,w/w)与水化好的HPI分散液混合,制备HPI-CA溶胶。复合溶胶在25 ℃下400 r/min搅拌1 h,4 ℃下储存2 h备用。随后将HPI-CA混合熔胶在95 ℃恒温水浴中加热30 min后立即转移至冰水浴中冷却20 min,制得HPI-CA复合凝胶,4 ℃储存,备用。
1.2.3 持水性的测定
持水性(Water Holding Capability,WHC)测定参照Ma等[20]方法并稍作改动。凝胶样品在5000 r/min离心15 min,离心后吸去多余水分,根据下式计算持水性:
WHC(%)=m−(m1−m2)m×100 式中:m为离心前凝胶的总质量(g);m1为离心前离心管和凝胶的总质量(g);m2为离心后离心管和凝胶的总质量(g)。
1.2.4 HPI-CA凝胶质构测定
参照Liu等[21]方法并稍加改动,凝胶样品在25 ℃下静置30 min,用直径2 cm打孔器均匀取出等高圆柱体凝胶测定其质构性质。预测试速度和测试速度分别为1 mm/s和5 mm/s;触发力5.0 g。根据TPA曲线计算硬度、弹性、内聚性和回弹性。
1.2.5 HPI-CA流变特性的测定
参考Li等[22]的方法稍作修改。使用MCR102流变仪(PP50平板探头)进行动态温度扫描和动态频率扫描。温度扫描条件为直径40 mm的不锈钢平行板之间的间隙为1 mm,样品在25 ℃条件下平衡10 min后,以5.83 ℃/min的速率从25 ℃上升至95 ℃,在95 ℃条件下10 min后,以相同速率从95 ℃降至25 ℃,记录动态扫描期间凝胶的弹性模量(G')的变化;频率扫描恒定应变0.5%(线性粘弹区域内)。在0.1~100 Hz频率范围内对每个样品进行频率扫描测试,记录弹性模量(G')、粘性模量(G'')的变化趋势。弹性模量(G')和粘性模量(G'')的频率依赖性由幂律拟合公式表示:
G'=K'×ωn' G''=K''×ωn' 式中,K'和K''对应G'和G''的幂律指数;n'和n''对应G'和G''的频率指数;ω为角频率。
1.2.6 HPI-CA凝胶水分状态的分布
弛豫时间(T2)的测量方法参照Kang等[23]方法并稍加改动。用直径10 mm的打孔器轻取高10 mm的圆柱形样品放入直径15 mm的核磁玻璃管内,将玻璃管插入核磁探头采样。单次采样参数:主频率SF(MHz)=18;90º脉宽P1=14;TD=1020;W=1500;SW(kHz)=100;RFD(ms)=0.002;RGI=20;DRG1=3;DR=1;NS=1。伪彩图采用ImageSystem软件(美国)分析。
1.2.7 溶解度的测定
蛋白溶解度的测定参照Li等[17]的方法并稍加改动。称取25 mg样品溶于5 mL去离子水中,涡旋搅拌1 min后,4 ℃下8000 r/min离心10 min。取1 mL上清液,与5 mL考马斯亮蓝充分混合5 min,595 nm处测定吸光值,根据下式计算样品蛋白溶解度。以牛血清蛋白标曲(y=0.0007x+0.0087,R2=0.9996;其中x为牛血清蛋白浓度、y为对应吸光度)计算蛋白质含量。
蛋白溶解度(%)=C1C×100 式中,C1为样品上清液可溶性蛋白含量(mg/mL);C为样品总蛋白含量(mg/mL)。
1.2.8 游离巯基含量的测定
游离巯基含量参照Li等[24]方法并稍加修改。称取15 mg样品溶于5 mL Tris-Gly缓冲液(A液:0.086 mol/L Tris,0.09 mol/L Gly,4 mmol/L EDTA,pH8.0)室温条件下混合均匀后,将50 μL Ellman(4 mg/mL DNTB)试剂加入混匀的样品中,涡旋混匀,避光反应1 h;在4℃ 10000 r/min离心10 min,412 nm处测定上清液吸光值,以A液为空白对照。
游离巯基计算公式如下:
游离巯基(µmol/g)=73.53×A412C 式中,A412为样品在412 nm处吸光值;C为所测样品质量浓度(mg/mL);73.53为Ellman试剂在pH8.0时的摩尔消光系数。
1.2.9 HPI-CA凝胶二级结构测定
使用Spectrum Two红外光谱仪在400~4000 cm−1的波数范围内进行扫描;其中测力计压力为58,分辨率为4 cm−1。获得的原始光谱经ATR(校正)、修订基线、平滑和标准化处理后得到红外光谱。利用Peakfit4.12软件对蛋白质二级结构的变化进行反卷积分析,计算蛋白质二级结构(α-螺旋、β-折叠、β-转角及无规卷曲)的相对百分含量。
1.2.10 HPI-CA凝胶分子间作用力的测定
分子间作用力的测定参照Mi等[25]的方法并稍作修改。取0.5 g的HPI-CA凝胶样品分别放入5 mL SA(0.05 mol/L NaCl)、SB(0.6 mol/L NaCl)、SC(0.6 mol/L NaCl+1.5 mol/L尿素)、SD(0.6 mol/L NaCl+8 mol/L尿素)和SE(0.6 mol/L NaCl+8 mol/L尿素+1.5 mol/L β-ME)中,用高速分散器分散30 s,4 ℃条件下保存2 h,使凝胶与蛋白充分混合,4℃ 10000 r/min离心15 min,收集上清液。上清液蛋白浓度采用考马斯亮蓝法测定。各化学键计算公式如下:
离子键=SB−SA 氢键=SC−SB 疏水相互作用=SD−SC 二硫键=SE−SD 1.2.11 HPI-CA凝胶微观结构
使用扫描电镜对样品冻干粉的微观结构进行观察,参照Zhang等[26]方法并稍加修改。将粉末附着在双面碳上,15 kV加速电压下在1000倍和5000倍倍率下观察测试样品的表面形貌。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均在同一实验条件下重复3次,并计算其平均值±标准差。使用SPSS对数据进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)检验(P<0.05)。使用Origin 2021Pro软件绘制图。
2. 结果与分析
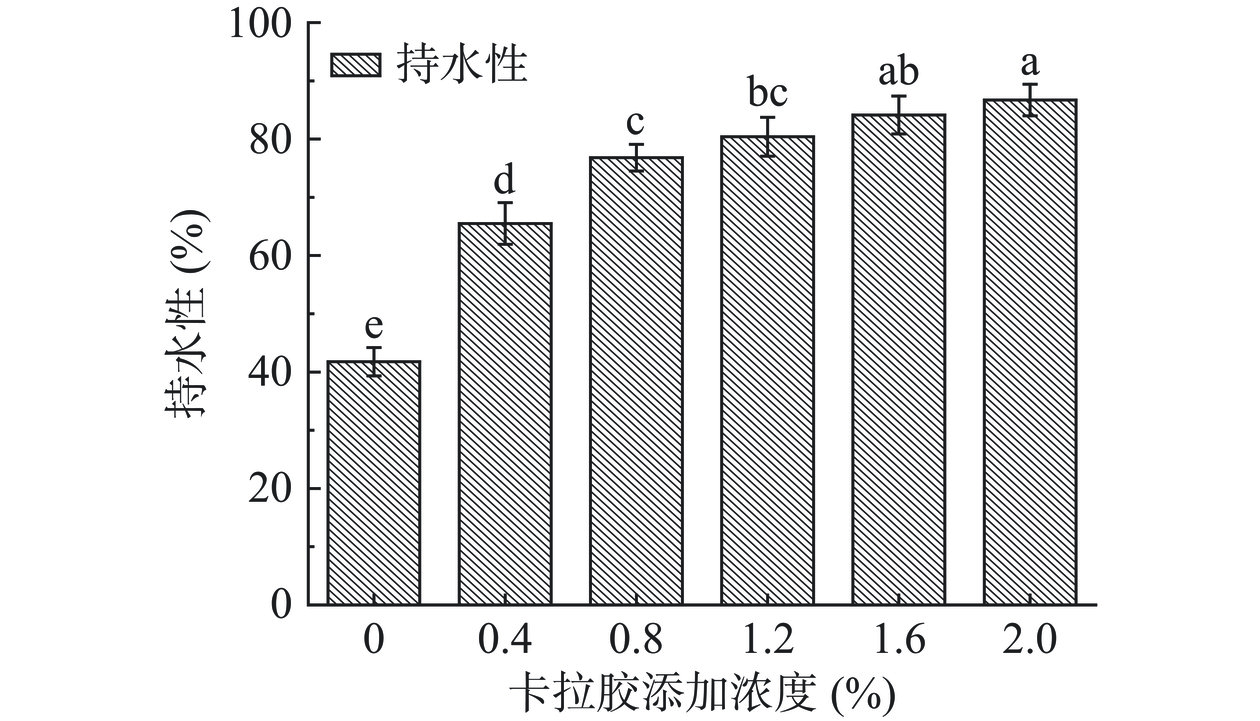
2.1 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶WHC的影响
WHC是可以体现蛋白质与水分子结合能力的指标,主要反映蛋白与水之间的非共价相互作用[27]。添加不同浓度CA的HPI凝胶持水能力变化如图1所示。与对照组相比较,CA浓度的增加对HPI凝胶的WHC提高有着显著的影响(P<0.05)。随CA浓度从0增加到2.0%,HPI-CA凝胶的WHC升高了2.07倍(对照组41.76%,最大值86.71%),可能是由于HPI与CA在糖基化反应过程中形成的小分子接枝共聚物避免了蛋白分子的快速交联,形成了更加致密的凝胶网络[28−29]。因此,离心时不易断裂,使水分子紧密的缠绕在凝胶网络中,提高了复合凝胶持水能力。Wang等[28]在研究中也发现多糖可以增加凝胶网络致密性,显著提高凝胶的持水性。结果表明,CA的添加可以显著(P<0.05)提升HPI-CA凝胶的持水能力,可能是添加CA形成的致密凝胶网络可以抵抗外部施加的压力保留内部水分子。
2.2 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶质构的影响
质构是判定凝胶性能的重要指标,不同浓度CA对复合凝胶性质的影响如表1所示。结果表明,与对照组相比,添加CA后HPI-CA凝胶的硬度、弹性、内聚性和回弹性均表现出显著变化(P<0.05)。HPI凝胶硬度随着CA浓度的增加逐渐增加,添加浓度为2.0%时,凝胶硬度最大(2405.04 g),与对照组相比复合凝胶硬度增加了约40倍。这可能是由于加入CA生成的接枝共聚物促进致密凝胶网络的形成,使维持凝胶的网络的主要作用力由非共价相互作用向共价相互作用转变[29]。同时体系中未与蛋白接枝的CA填充在凝胶网络中,增加凝胶硬度[30],流变及分子间作用力也证实了这一结论。弹性反映凝胶在第一次形变循环后的物理回弹能力[31]。表1可知,CA添加浓度为0~0.8%时,HPI凝胶的弹性随着CA浓度增加而增大(最大值0.927,P<0.05),这表明凝胶抗第一次形变循环施加的作用力能力增强;而当CA添加浓度为0.8%~2.0%时,凝胶弹性逐渐降低,表明第一次形变循环施加的作用力使凝胶分解成较小碎片,凝胶抗压能力减弱[30−31]。弹性的变化表明添加0.8% CA形成的凝胶网络具有抵御第一次形变的能力。内聚性与凝胶内部结构承受应力二次破坏的能力有关[31]。当CA浓度0~0.8%时内聚性增加,可能是0.8%的CA促进分子间共价交联且增加β-折叠含量,凝胶刚性结构增强,所以凝胶的抗第二次形变能力增强,内聚性增加;CA浓度高于0.8%后,CA在凝胶网络中填充,阻碍蛋白分子间交联,破坏凝胶网络完整性,从而导致凝胶抵御二次形变能力下降,内聚性降低。所有样品回弹性均处于0.4~0.5之间,表明施加压力破坏了混合凝胶的内部网络,释放力后凝胶不会立即恢复到原始状态,凝胶在第一个形变周期内恢复能力变弱,与弹性变化相同。凝胶强度的提高与Chu等[12]结果相似,多糖可与蛋白结合提高凝胶硬度。因此,CA添加浓度为0.8%时凝胶网络抵抗外力能力最强。
表 1 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶质构的影响Table 1. Effects of different concentrations of CA on the texture of HPI-CA gels浓度(%) 硬度(g) 弹性 内聚性(gּּ·s−1) 回弹性 0 62.02±1.45f 0.867±0.025d 0.27±0.02c 0.040±0.005c 0.4 256.82±8.16e 0.996±0.001a 0.37±0.02b 0.049±0.001b 0.8 725.47±43.98d 0.927±0.051b 0.48±0.01a 0.046±0.001b 1.2 1497.57±43.51c 0.889±0.411c 0.44±0.02b 0.044±0.003bc 1.6 2116.45±34.59b 0.880±0.019c 0.40±0.06b 0.049±0.002b 2.0 2405.04±78.00a 0.846±0.061e 0.38±0.03b 0.055±0.003a 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 2.3 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶流变性能的影响
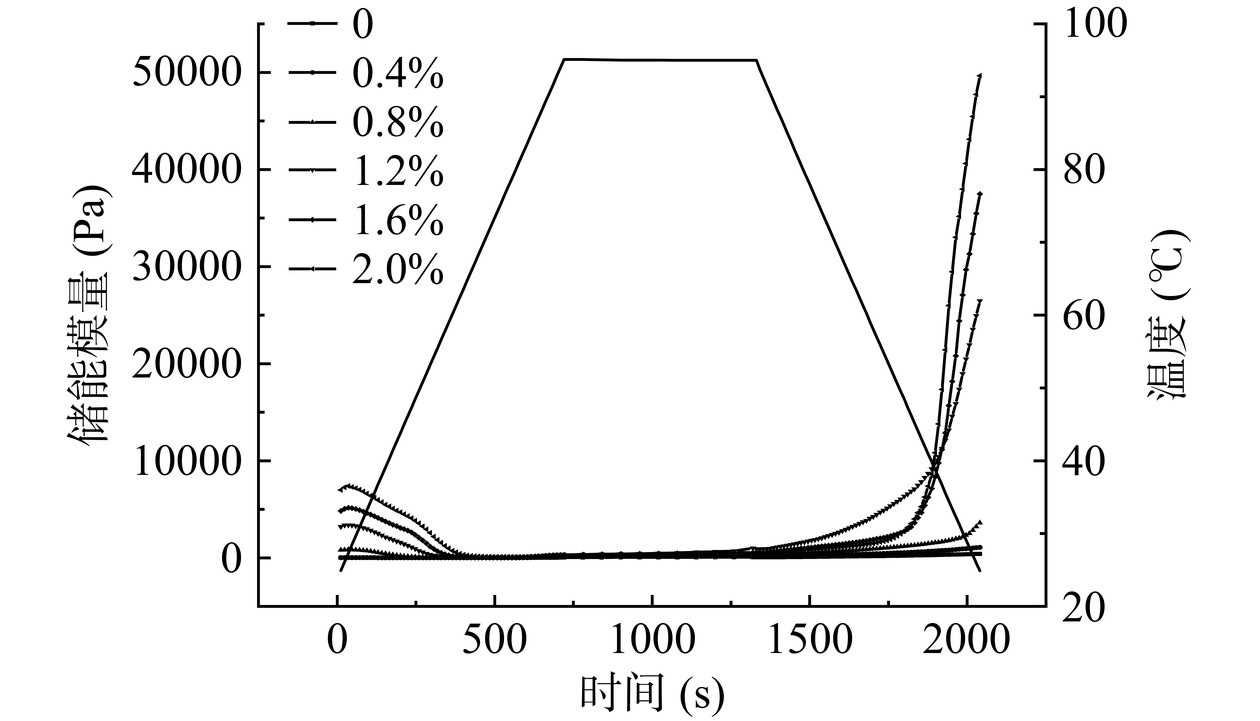
添加不同浓度CA的HPI-CA凝胶随温度-时间流变曲线均表现出典型的熔胶-凝胶转变特征(图2)。温度扫描结果与凝胶硬度结果一致,弹性模量G'随着CA浓度的增加显著增加(P<0.05),当浓度为2.0% G'达到最大值(49646 Pa)。G'的增加表明,CA浓度的增加表明HPI-CA凝胶间的分子间交联逐渐增强,非共价交联逐渐向共价交联转变。当CA添加浓度高于0.8%时,蛋白的空间位阻阻碍多糖-蛋白、蛋白-蛋白分子间的连接,未与蛋白质交联形成凝胶网络的CA作为被动填料填充在凝胶网络中,支撑凝胶网络,增加凝胶硬度[30]。电镜结果证实了CA添加量高于0.8%时在凝胶在基质中的填充。所有凝胶样品在加热升温阶段(25~28 ℃)储能模量先小幅度上升后开始下降,这是典型的Suwari预凝胶阶段,ε-(γ-谷氨酰基)赖氨酸交联形成初始凝胶网络,弹性模量增加[22]。温度继续升高(28~95 ℃),初始凝胶网络被破坏,凝胶流动性增加,G'开始减小。G'在恒温阶段缓慢上升,冷却阶段迅速上升,温度降至25 ℃时达到最大值。温度下降过程中,蛋白质分子通过非共价相互作用相互交联,形成大量疏水相互作用、氢键等,凝胶网络逐渐完整,凝胶粘弹性增加[27]。
为了进一步观测凝胶性质的变化,采用幂律模型对凝胶的G'、G''与角频率进行拟合(表2)。K'和K''代表G'和G''与凝胶的粘弹性有关的幂律常数。K'和K''值随着CA浓度的增加升高,说明添加CA凝胶提高了HPI-CA凝胶的弹性和粘性[32]。n'和n''为频率指数,所有样品的n'和n''均大于0.05,表明复合凝胶为弱凝胶且具有一定的频率依赖性。随着CA浓度增加,n'与n''值逐渐减小,表明添加CA可以降低HPI-CA凝胶的频率依赖性。温度扫描结果表明,HPI-CA凝胶为弱凝胶,添加CA可以通过促进分子间共价交联提高HPI-CA凝胶的粘弹性并降低其频率依赖性。
表 2 HPI-CA凝胶在不同CA浓度下的幂律模型参数拟合结果Table 2. Power law model parameters fitting results of HPI-CA gels at various CA concentrations浓度(%) G'=K'ωn' R2 G''=K''ωn'' R2 K' n' K'' n'' 0 327.47±0.62f 0.136±0.002a 0.999 46.89±0.67f 0.168±0.004a 0.986 0.4 897.19±3.00e 0.129±0.001b 0.996 142.86±2.24e 0.164±0.005a 0.988 0.8 3339.72±13.48d 0.121±0.001c 0.997 589.86±5.04d 0.153±0.003b 0.988 1.2 7237.34±17.96c 0.097±0.001d 0.999 905.61±11.03c 0.149±0.002b 0.985 1.6 22367.96±143.78b 0.095±0.002d 0.998 7868.98±24.34b 0.127±0.002c 0.976 2 84596.49±197.36a 0.095±0.001d 0.996 18632.48±195.16a 0.113±0.004d 0.979 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 2.4 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶水分分布的影响
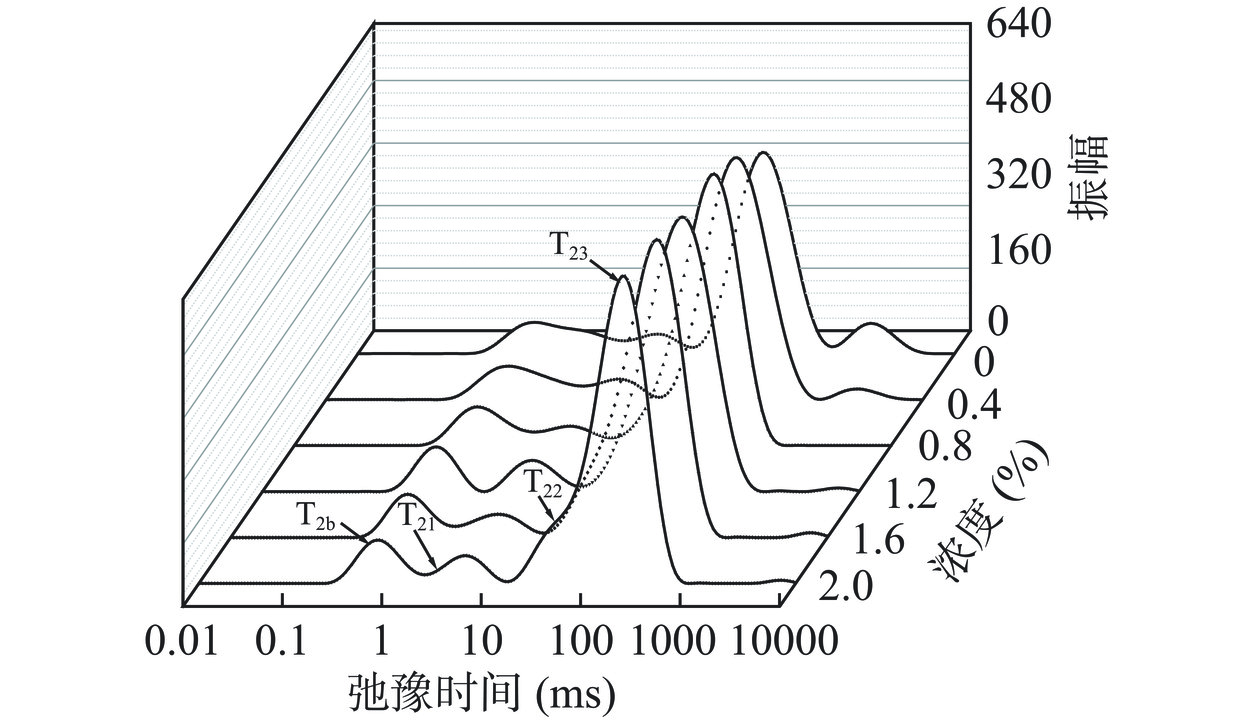
水分子在凝胶网络中的存在状态影响蛋白凝胶性质,低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)弛豫时间T2的变化可直观显示水分子的存在状态[23]。图3显示了HPI-CA复合凝胶的T2b、T21、T22和T23弛豫时间分布。T2b(0~1 ms)主要由结合较紧密C-H质子组成,代表自由度极低的强束缚水;T21(1~10 ms)为与蛋白基团结合相对紧密的水;T22(10~100 ms)为与分子适度结合的水;T23(100~10000 ms)主要代表被样品内部结构中被困住的自由水[33]。CA添加为0~0.8%时,T22峰值随着CA浓度的增加逐渐升高,添加浓度为0.8%时达到最大值(85.02%)。T22峰面积的增加表明凝胶中的水分子与蛋白紧密结合,同时T22向更短弛豫时间迁移,这表明凝胶中的水受到完整凝胶网络的限制,高速离心条件下凝胶网络更不易被破坏[34]。继续增加CA浓度(0.8%~2.0%),T22峰面积减小,T23峰面积增加且出现了额外的T23峰,表明凝胶网络中存在更易释放的水分子[11]。CA堆积在凝胶网络中阻碍了氢键等非共价相互作用的形成,凝胶网络形成不均匀,水分子无法与蛋白发生更紧密结合,影响凝胶持水性质[35]。虽然WHC结果表明持水能力与CA浓度呈正相关,但低场核磁结果显示除添加浓度为0.8%时均存在额外的T23峰值,这可能是CA吸收凝胶网络渗透的水分子,使其不易被离心力甩出。Zhuang等[11]同样发现添加过量多糖会导致复合凝胶发生相分离,持水能力下降。
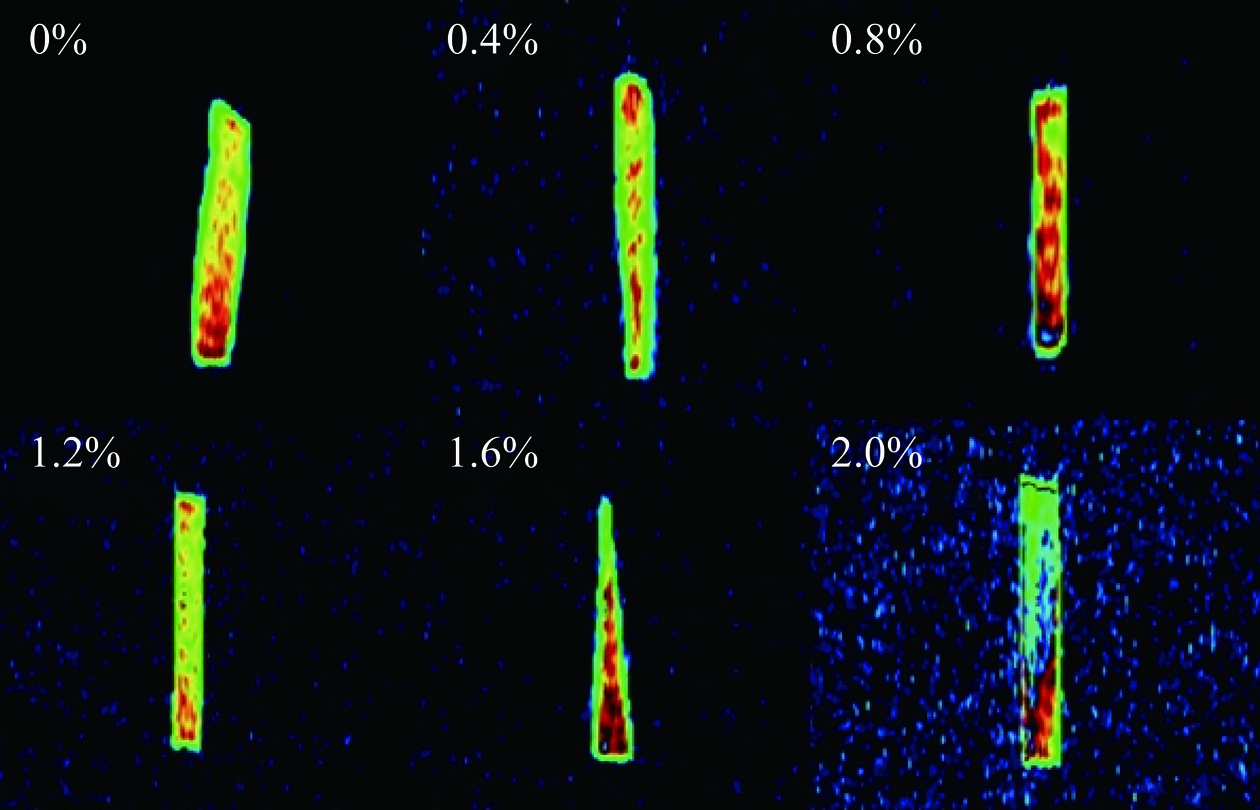
通过核磁共振成像对复合凝胶水分分布进一步分析(图4)。未添加CA组分有较多的绿色区域,表明凝胶中的水大多以自由水形式存在;当CA浓度增加至0.8%时,复合凝胶红色区域增加,红绿色分布均匀,与蛋白更紧密的水分子被均匀分布在凝胶网络中;CA浓度大于0.8%时,绿色区域逐渐增加,红色区域减少且红绿颜色区域分布逐渐不均匀,自由水增多,与图3结果相符,过高浓度的多糖破坏了蛋白质之间的相互作用,使其与水分子结合能力变弱[30]。综上,添加0.8% CA可使蛋白分子与水分子紧密结合,而添加量高于0.8%时,蛋白凝胶网络保留水分子能力下降。
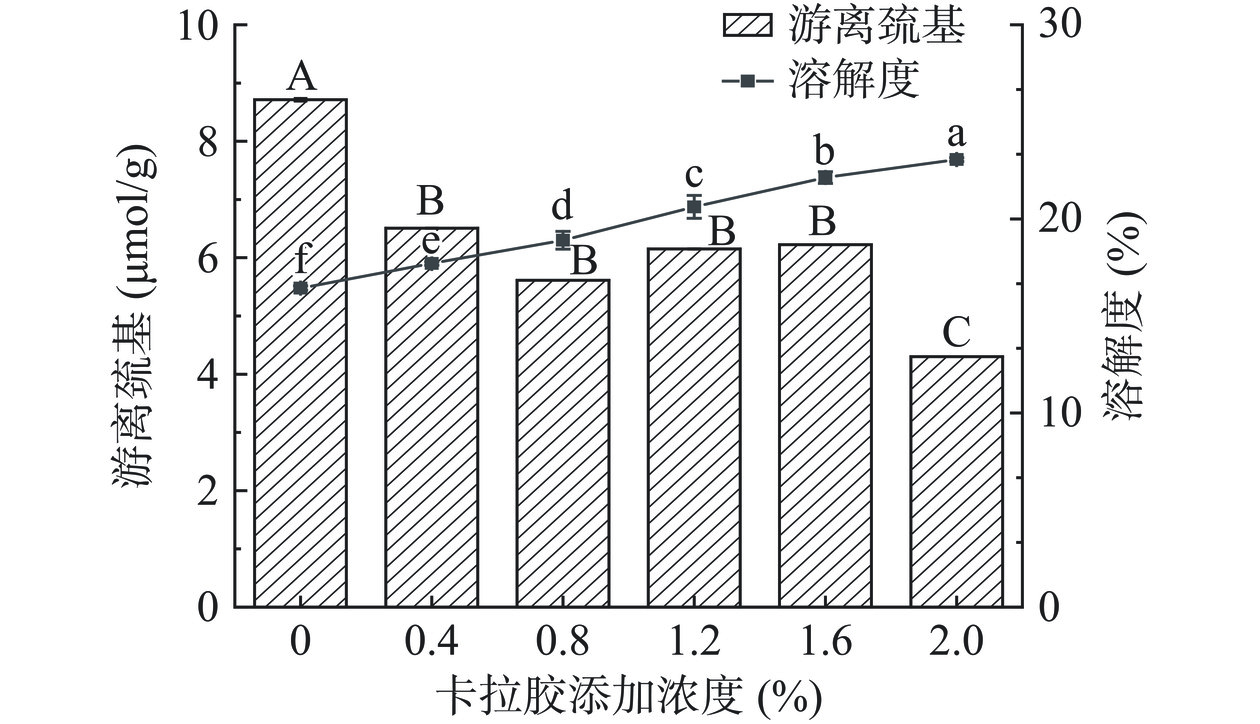
2.5 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶游离巯基含量和蛋白溶解度的影响
游离巯基含量的变化可以反映蛋白质分子内和分子间二硫键的断裂与形成[36]。HPI-CA凝胶的游离巯基及溶解度变化如图5所示。CA添加浓度为0~0.8%时,加热使蛋白质结构展开,分子内二硫键向分子间二硫键转变,游离巯基含量减少,二硫键含量增加,促进了蛋白质凝胶网络的形成[37]。当CA添加量大于0.8%时,CA在凝胶网络中的堆积及糖基化反应抑制二硫键的形成,游离巯基含量增加[34]。当CA添加量为2.0%时,游离巯基含量降低(最低值4.301 μmol/g),这可能是由于CA为多糖分子,当多糖与蛋白在同一体系中存在,在一定温度下发生美拉德反应,生成美拉德产物,这些产物的存在组织游离巯基暴露,降低巯基含量[38]。
溶解度是蛋白质重要的功能性质。随着CA浓度的增加,蛋白质溶解度逐渐增加,添加至2.0%时溶解度达到最大值54.64%。可能是由于CA为亲水多糖,携带大量亲水基团,热处理条件下与HPI发生接枝反应,生成小分子接枝共聚体,增加了与水分子的相容性[29]。同时加热使蛋白分子展开,新生成的接枝共聚体埋藏了蛋白的非极性基团,减弱了蛋白分子间的疏水相互作用和范德华力,增减了蛋白溶解度[22]。游离巯基含量和溶解度的增加表明CA促进了蛋白凝胶的形成,凝胶性质得到改善。以上结果表明,添加CA可以促进蛋白分子间二硫键交联并增加蛋白溶解度。
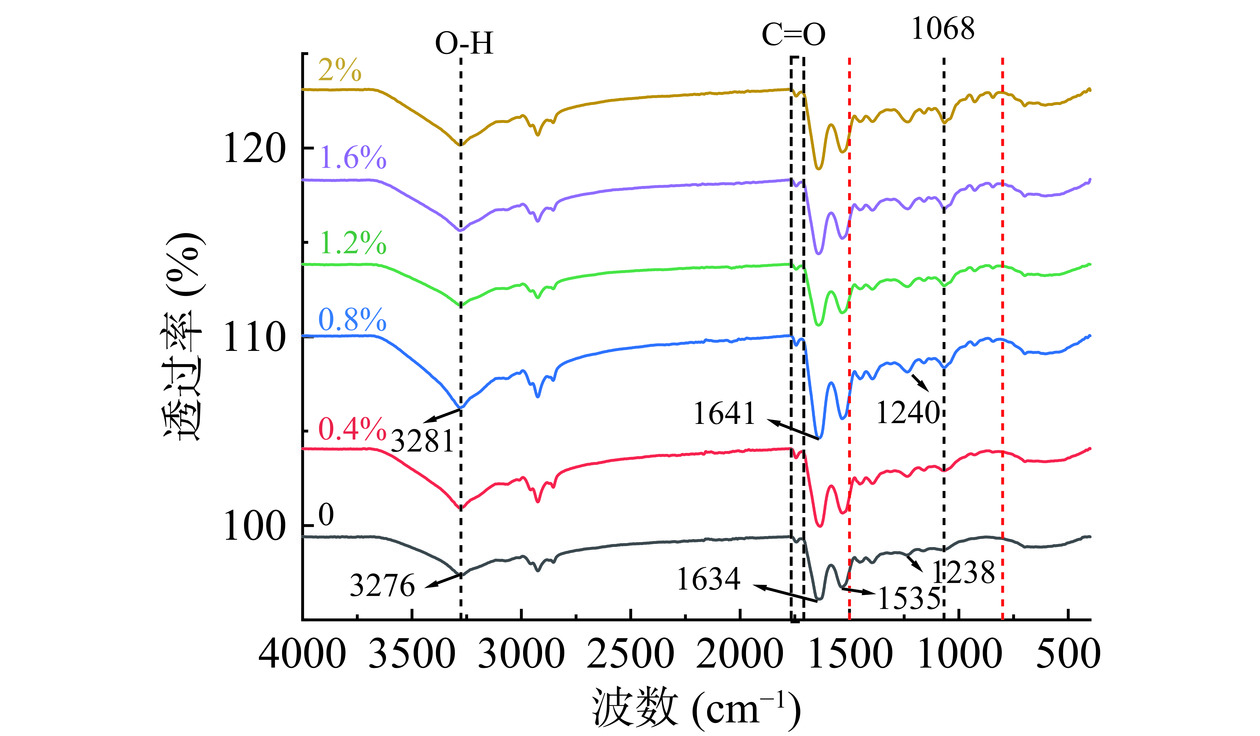
2.6 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶二级结构的影响
傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)常用于观察蛋白质结构及其官能团特征[29]。HPI-CA凝胶在400~4000 cm−1范围内FTIR光谱及二级结构变化如图6、表3所示。酰胺I区(1700~1600 cm−1)和酰胺II区(1600~1500 cm−1)的吸收峰为HPI典型吸收带,是由C=O伸缩振动、C-N伸缩振动和N-H弯曲振动引起的[12]。1068、1238 cm−1波长处吸收峰红移及800~1800 cm−1处出现的吸收峰表明糖基化反应的发生[39]。1535和1634 cm−1处吸收峰逐渐增强,C=O键、C-N键和N-H键维持凝胶三维结构,同时酰胺III带(1400~1200 cm−1)伸缩振动增强,维持β-折叠中C-N振动的能量增加,凝胶结构更加稳定[39]。3280 cm−1波长处为主要为O-H拉伸,可反应蛋白分子间氢键的相互作用。CA浓度增加,O-H拉伸增强,蛋白分子间氢键作用增强。CA为阴离子多糖,与蛋白接枝反应后新生成的团聚体携带亲水基团,增加了分子间氢键的交联[12],同时提高蛋白溶解度(图5),增强凝胶性质。CA浓度大于0.8%时,大量CA堆积在凝胶网络中,阻碍蛋白之间的交联,3280 cm−1波长及酰胺III带处伸缩振动逐渐减小,氢键相互作用减弱,β-折叠含量降低,对凝胶性质产生负面影响(表3)。
表 3 添加不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶二级结构的影响Table 3. Effects of adding different concentrations of CA on the secondary structure of HPI-CA gels卡拉胶浓度(%) α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规卷曲(%) 0 15.07±1.68a 47.03±0.21e 23.48±1.88a 14.42±0.31c 0.4 12.61±0.17b 57.38±1.10b 14.00±0.90c 16.00±0.55ab 0.8 11.12±1.33b 61.11±2.21a 11.90±0.40c 15.87±0.49ab 1.2 15.38±15.38a 52.92±1.88c 17.43±0.92b 14.27±0.18c 1.6 15.76±0.82a 50.62±0.39cd 18.28±0.76b 15.33±0.93bc 2.0 15.58±0.55a 49.75±1.77de 17.84±0.22b 16.83±1.01a 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 对酰胺I带峰面积进行计算得出蛋白二级结构含量,进而分析二级结构对凝胶性质的影响。由表3可知,随着CA浓度的增加,α-螺旋含量先降低在升高,在浓度为0.8%时含量最低(11.12%),β-折叠变化趋势与α-螺旋含量呈负相关(61.11%)。凝胶化过程中,α-螺旋区域的ε-氨基基团与CA的羰基发生糖基化反应导致α-螺旋含量降低[40]。同时加热使蛋白分子去折叠,α-螺旋向β-折叠和无规卷曲转变,使α-螺旋含量降低,增强凝胶刚性结构。与Zhao等[41]结论一致,α-螺旋减少,β-折叠和无规卷曲增加,更有利于蛋白的凝胶化。Lei等[42]对添加不同浓度CA的藻蓝蛋白凝胶红外光谱分析也得出了类似结论。
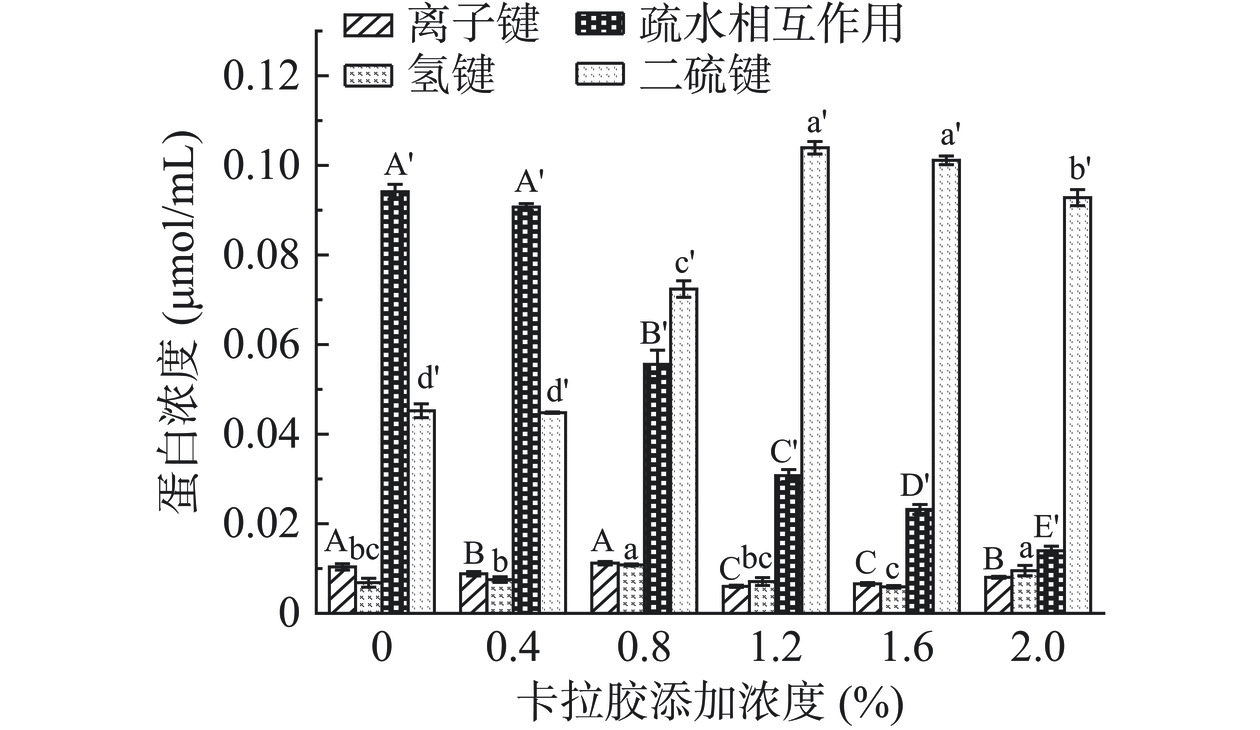
2.7 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA复合凝胶分子间作用力的影响
凝胶形成过程中分子间相互作用的变化如图7所示,维持凝胶网络的主要作用力受CA浓度的影响。当CA添加浓度低于0.8%时,疏水相互作用为维持凝胶网络的主要作用力;CA添加浓度高于0.8%时,维持凝胶网络的主要作用力由疏水相互作用向二硫键转变。对照组以疏水相互作用为主要作用力,热处理使蛋白分子肽链展开,分子内二硫键断裂,游离巯基及疏水基团暴露,蛋白分子通过疏水相互作用和二硫键快速聚集,形成不均匀的凝胶网络,凝胶性质较差[17]。随着CA的加入(0.4%~0.8%),通过糖基化反应生成的小分子接枝物掩埋了暴露的疏水基团,增加了蛋白的亲水性,逐渐减弱分子间疏水相互作用,延缓了蛋白分子的快速交联,避免大分子团聚体的生成,有利于凝胶形成更致密的凝胶网络,这与蛋白溶解度(图5)的结果一致[29]。继续增加CA浓度(>0.8%),未与蛋白接枝的CA堆积在凝胶通路中,影响凝胶形成致密均匀的网络且阻碍蛋白分子间疏水基团交联,维持凝胶的主要作用力由疏水相互作用逐渐向二硫键转变。在疏水相互作用和二硫键足够强的条件下,HPI-CA凝胶不以离子键作为维持凝胶网络稳定的主要吸引力[43]。CA的加入对氢键有积极的影响,添加量为0.8%时,破坏氢键溶液的上清液中蛋白浓度最大,但随着CA浓度增加,蛋白体系中存在一部分未与展开蛋白相结合的多糖分子阻碍氢键的交联致使蛋白浓度逐渐降低[22,30]。因此,疏水相互作用和二硫键是维持凝胶的主要作用力。
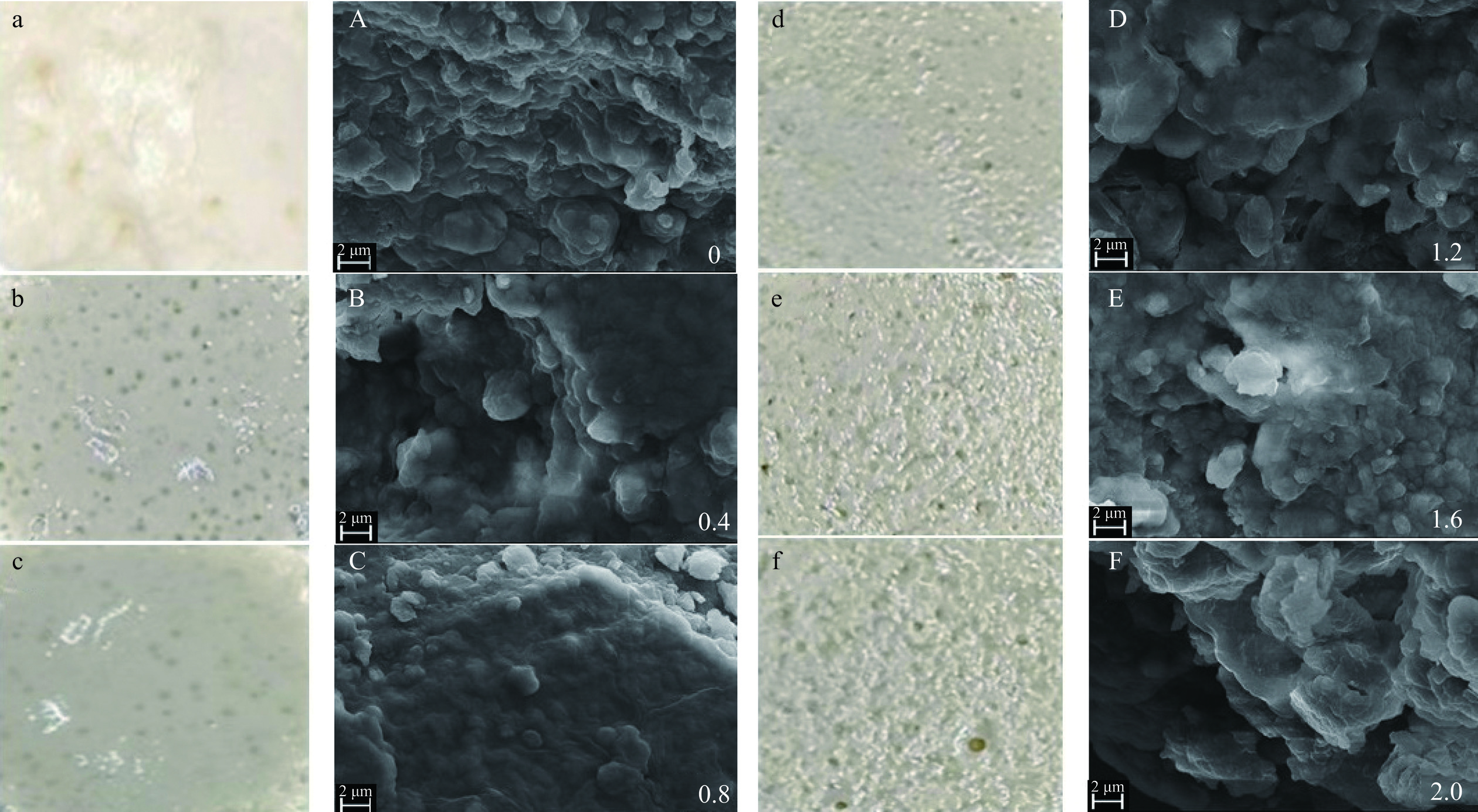
2.8 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA复合凝胶微观结构的影响
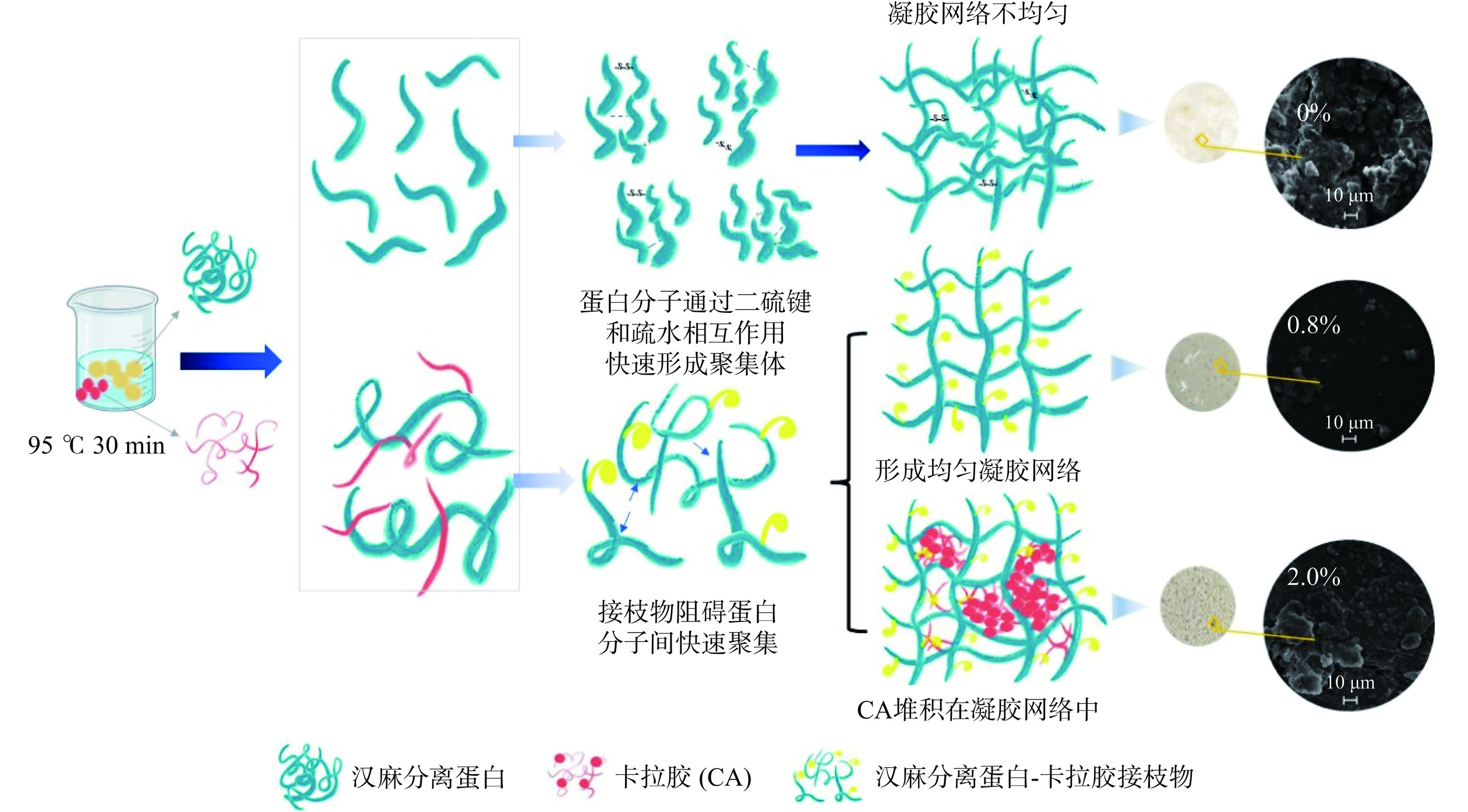
图8为不同CA浓度下HPI凝胶和HPI-CA复合凝胶直观图和电镜图。对照组HPI凝胶表面粗糙不平整,直观图可见不均匀孔洞,孔洞周围凝胶易坍塌,凝胶强度较差(图8a)。与对照组相比较,随着CA的添加,HPI-CA凝胶结构更加致密均匀,孔洞逐渐减小。当浓度为0.8%时,凝胶表面光滑、致密,孔隙分布均匀(图8C),形成了更加规则均匀的网状结构。在热处理条件下,HPI的氨基与CA的羰基发生糖基化反应,生成小分子接枝共聚物,这些接枝共聚物紧密结合,形成均匀致密的结构,增强了凝胶网络的稳定性[38]。CA浓度大于0.8%时,体系中存在未与蛋白发生接枝反应的CA堆积在凝胶网络中,阻碍凝胶形成均匀的网络,凝胶表面逐渐粗糙不平滑(图8D~图8F)。虽然填充在凝胶基质的CA提高了凝胶的硬度,但对凝胶网络的均匀性产生负面影响,降低凝胶性质。Li等[17]也发现,相同条件下,蛋白与多糖结合形成互穿网络对凝胶性质的改善要优于多糖作为填料对凝胶性质的改善。结合直观图与微观结构可以得到,添加量0.8% CA的HPI-CA凝胶结构更加致密均匀。
2.9 HPI-CA凝胶形成机制分析
HPI-CA凝胶机制图如图9所示。与对照组相比,CA的加入对HPI凝胶性质和结构有着显著的影响(P<0.05)。随着CA浓度的增加(0~2.0%),HPI-CA凝胶的持水能力、硬度和储能模量增加,微观结构从疏松结构到致密结构再到疏松结构的转变(添加0.8%时最致密)。未添加CA的HPI凝胶网络粗糙且分布不均匀。CA添加量为0.4%和0.8%时,CA与HPI在加热过程中形成的小分子聚集体与HPI分子相互交联形成互穿聚合物凝胶网络,形成更均匀致密的凝胶网络(图8)。当CA添加量高于0.8%时,多糖分子在蛋白通路中堆积,阻碍了蛋白质疏水基团的相互连接形成较大孔径,破坏了均匀凝胶网络的形成。
3. 结 论
上述分析结果表明,添加不同浓度的CA对HPI-CA凝胶的凝胶性质及理化结构有着不同的影响。低浓度的CA(<0.8%)提高了HPI凝胶的WHC、硬度,促进了α-螺旋向β-折叠的转变,有利于蛋白的凝胶化。0.8%浓度的卡拉胶增强蛋白质之间的相互作用(包括氢键、疏水相互作用和二硫键),形成的凝胶具有更高的G'和G''(G'>G'')的凝胶网络。而高浓度的CA(>0.8%)会穿插在凝胶网络中阻碍均匀凝胶网络的形成,阻碍疏水基团之间的相互作用,破坏凝胶网络之间的相互作用,导致凝胶网络结构松散。结果表明,CA添加浓度为0.8%时,可以获得性质较优的凝胶。本研究有助于了解蛋白-多糖相互作用体系,且为提高HPI凝胶性能提供了一种新思路。
-
表 1 不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶质构的影响
Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of CA on the texture of HPI-CA gels
浓度(%) 硬度(g) 弹性 内聚性(gּּ·s−1) 回弹性 0 62.02±1.45f 0.867±0.025d 0.27±0.02c 0.040±0.005c 0.4 256.82±8.16e 0.996±0.001a 0.37±0.02b 0.049±0.001b 0.8 725.47±43.98d 0.927±0.051b 0.48±0.01a 0.046±0.001b 1.2 1497.57±43.51c 0.889±0.411c 0.44±0.02b 0.044±0.003bc 1.6 2116.45±34.59b 0.880±0.019c 0.40±0.06b 0.049±0.002b 2.0 2405.04±78.00a 0.846±0.061e 0.38±0.03b 0.055±0.003a 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 HPI-CA凝胶在不同CA浓度下的幂律模型参数拟合结果
Table 2 Power law model parameters fitting results of HPI-CA gels at various CA concentrations
浓度(%) G'=K'ωn' R2 G''=K''ωn'' R2 K' n' K'' n'' 0 327.47±0.62f 0.136±0.002a 0.999 46.89±0.67f 0.168±0.004a 0.986 0.4 897.19±3.00e 0.129±0.001b 0.996 142.86±2.24e 0.164±0.005a 0.988 0.8 3339.72±13.48d 0.121±0.001c 0.997 589.86±5.04d 0.153±0.003b 0.988 1.2 7237.34±17.96c 0.097±0.001d 0.999 905.61±11.03c 0.149±0.002b 0.985 1.6 22367.96±143.78b 0.095±0.002d 0.998 7868.98±24.34b 0.127±0.002c 0.976 2 84596.49±197.36a 0.095±0.001d 0.996 18632.48±195.16a 0.113±0.004d 0.979 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 表 3 添加不同浓度CA对HPI-CA凝胶二级结构的影响
Table 3 Effects of adding different concentrations of CA on the secondary structure of HPI-CA gels
卡拉胶浓度(%) α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规卷曲(%) 0 15.07±1.68a 47.03±0.21e 23.48±1.88a 14.42±0.31c 0.4 12.61±0.17b 57.38±1.10b 14.00±0.90c 16.00±0.55ab 0.8 11.12±1.33b 61.11±2.21a 11.90±0.40c 15.87±0.49ab 1.2 15.38±15.38a 52.92±1.88c 17.43±0.92b 14.27±0.18c 1.6 15.76±0.82a 50.62±0.39cd 18.28±0.76b 15.33±0.93bc 2.0 15.58±0.55a 49.75±1.77de 17.84±0.22b 16.83±1.01a 注:同组数据以不同小写字母表示样品间差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 孟妍, 曾剑华, 李美莹, 等. 汉麻籽分离蛋白提取技术优化及其组成和乳化性表征[J]. 中国食品学报, 2021, 21(5):250-262. [MENG Y, ZENG J H, LI M Y, et al. Optimization of extraction technology, composition and emulsification characterization of protein isolate from sesame seed[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2019, 21(5):250-262.] MENG Y, ZENG J H, LI M Y, et al. Optimization of extraction technology, composition and emulsification characterization of protein isolate from sesame seed[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2019, 21(5): 250-262.
[2] WANG Q L, XIONG Y L. Processing, nutrition, and functionality of hempseed protein:A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2019,18(4):936−952. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12450
[3] 朱秀清, 王子玥, 李美莹, 等. 热处理对汉麻乳稳定性的影响及蛋白结构表征[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(7):68−73. [ZHU X Q, WANG Z Y, LI M Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the stability of sesame milk and characterization of protein structure[J]. Food Science, 2019, 42(7):68−73.] ZHU X Q, WANG Z Y, LI M Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the stability of sesame milk and characterization of protein structure[J]. Food Science, 2019, 42(7): 68−73.
[4] RAIKOS V, DUTHIE G, RANAWANA V. Denaturation and oxidative stability of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate as affected by heat treatment[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition,2015,70:304−309. doi: 10.1007/s11130-015-0494-5
[5] WANG Q L, JIANG J, XIONG Y L. Genipin-aided protein cross-linking to modify structural and rheological properties of emulsion-filled hempseed protein hydrogels[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,2019,67(46):12895−12903. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05665
[6] TEH S S, BEKHIT A E D A, CARNE A, et al. Antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysates produced by the proteases AFP, HT, Pro-G, actinidin, and zingibain[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 203:199–206.
[7] WANG Q, JIN Y, XIONG Y L. Heating-aided pH shifting modifies hemp seed protein structure, cross-linking, and emulsifying properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(41):10827−10834. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03901
[8] SHAO P, MA H, ZHU J, et al. Impact of ionic strength on physicochemical stability of o/w emulsions stabilized by ulva fasciata polysaccharide[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,69:202−209. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.039
[9] LI C, CHEN G, RAN C, et al. Adlay starch-gluten composite gel:Effects of delay starch on rheological and structural properties of gluten gel to molecular and physicochemical characteristics[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,289:121−129. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.030
[10] WANG Y R, YANG Q, LI-SHA Y J, et al. Structural, gelation properties and microstructure of rice glutelin/sugar beet pectin composite gels:Effects of ionic strengths[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,346:128956. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128956
[11] ZHUANG X, HAN M, BAI Y, et al. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel improved by insoluble dietary fiber[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,74:219−226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.08.015
[12] CHU L, YANG L, LI J, et al. Effect of Smilax china L. starch on the gel properties and interactions of calcium sulfate-induced soy protein isolate gel[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:127−132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.130
[13] YANG X, LI A, LI D, et al. Applications of mixed polysaccharide-protein systems in fabricating multi-structures of binary food gels—A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,109:197−210.
[14] LI L, NI R, SHAO Y, et al. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery[J]. Carbohydrate polymers,2014,103:1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.008
[15] TAO H, GUO L, QIN Z, et al. Textural characteristics of mixed gels improved by structural recombination and the formation of hydrogen bonds between curdlan and carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,129:107678. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107678
[16] MAN H, JIA Y, SONG H, et al. Effects of κ-carrageenan addition and chlorogenic acid covalent crosslinking on protein conformation and gelling properties of soy protein hydrogels[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2023,174:114434. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114434
[17] LI M, YANG R, FENG X, et al. Effects of low-frequency and high-intensity ultrasonic treatment combined with curdlan gels on the thermal gelling properties and structural properties of soy protein isolate[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,127:107506. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107506
[18] WALAYAT N, WANG X, LIU J, et al. Kappa-carrageenan as an effective cryoprotectant on water mobility and functional properties of grass carp myofibrillar protein gel during frozen storage[J]. LWT-Food Science Technology,2022,154:112675. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112675
[19] HADNAĐEV M, DAPČEVIĆ-HADNAĐEV T, LAZARIDOU A, et al. Hempseed meal protein isolates prepared by different isolation techniques. Part I. Physicochemical properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,79:526−533. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.015
[20] MA Z, LI L, WU C, et al. Effects of combined enzymatic and ultrasonic treatments on the structure and gel properties of soybean protein isolate[J]. LWT-Food Science Technology,2022,158:113123. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113123
[21] LIU F, FENG S, GUO Y, et al. The rheological characteristics of soy protein isolate-glucose conjugate gel during simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Structure,2021,29:100210. doi: 10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100210
[22] LI J, WU M, WANG Y, et al. Effect of pH-shifting treatment on structural and heat induced gel properties of peanut protein isolate[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,325:126921. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126921
[23] KANG Z, BAI R, LU F, et al. Effects of high pressure homogenization on the solubility, foaming, and gel properties of soy 11S globulin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107261. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107261
[24] LI Y, WAN Y, MAMU Y, et al. Protein aggregation and Ca2+-induced gelation of soymilk after heat treatment under slightly alkaline conditions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107274. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107274
[25] MI H, LI Y, WANG C, et al. The interaction of starch-gums and their effect on gel properties and protein conformation of silver carp surimi[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106290. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106290
[26] ZHANG J, JIANG L, YANG J, et al. Effect of calcium chloride on heat-induced Mesona chinensis polysaccharide-whey protein isolation gels:Gel properties and interactions[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,155:112907. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112907
[27] ZHAO H, CHEN J, HEMAR Y, et al. Improvement of the rheological and textural properties of calcium sulfate-induced soy protein isolate gels by the incorporation of different polysaccharides[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,310:125983. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125983
[28] WANG W, SHEN M, JIANG L, et al. Influence of Mesona blumes polysaccharide on the gel properties and microstructure of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,313:126125. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126125
[29] WU Y, ZHANG Y, DUAN W, et al. Ball-milling is an effective pretreatment of glycosylation modified the foaming and gel properties of egg white protein[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2022,319:110908. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2021.110908
[30] ZHUANG X, WANG L, JIANG X, et al. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel influenced by konjac glucomannan:Moisture stability and phase separation behavior[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,339:127941. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127941
[31] CORTEZ-TREJO M C, LOARCA-PIñA G, FIGUEROA-CÁRDENAS J D, et al. Gel properties of acid-induced gels obtained at room temperature and based on common bean proteins and xanthan gum[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,132:107873. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107873
[32] BI C H, WANG P L, SUN D Y, et al. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on gelling and rheological properties of soybean protein isolate emulsion gel[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2020,277:109923. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.109923
[33] XIA S, XUE Y, XUE C, et al. Structural and rheological properties of meat analogues from Haematococcus pluvialis residue-pea protein by high moisture extrusion[J]. LWT-Food Science Technology,2022,154:112756. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112756
[34] SHENG L, LIU Q, DONG W, et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound assisted glycosylation on the gel properties of ovalbumin:Texture, rheology, water state and microstructure[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,372:131215. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131215
[35] LIU S, ZHAO P, ZHANG J, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) myofibrillar protein glycated with konjac oligo-glucomannan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,67:216−223. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.018
[36] WANG W, SHENG H, ZHOU J, et al. The effect of a variable initial pH on the structure and rheological properties of whey protein and monosaccharide gelation via the Maillard reaction[J]. International Dairy Journal,2021,113:104896. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2020.104896
[37] LEI Y, MA L, OUYANG H, et al. Influence of soy protein isolate on the gel properties of walnut protein isolate-κ-carrageenan treated with NaCl[J]. Journal of Future Foods,2023,3(4):364−373. doi: 10.1016/j.jfutfo.2023.03.007
[38] DOOST A S, NASRABADI M N, WU J, et al. Maillard conjugation as an approach to improve whey proteins functionality:A review of conventional and novel preparation techniques[J]. Trends in Food Science Technology,2019,91:1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgs.2019.06.011
[39] ZHAO C, YIN H, YAN J, et al. Structure and acid-induced gelation properties of soy protein isolate–maltodextrin glycation conjugates with ultrasonic pretreatment[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106278. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106278
[40] HATTORI M, NAGASAWA K, AMETANI A, et al. Functional changes in beta-lactoglobulin by conjugation with carboxymethyl dextran[J]. Food Chemistry,1994,42(10):2120−2125. doi: 10.1021/jf00046a009
[41] ZHAO Y, ZHOU G, ZHANG W. Effects of regenerated cellulose fiber on the characteristics of myofibrillar protein gels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,209:276−281. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.042
[42] LEI Y, ZHAO X, LI D, et al. Effects of kappa-Carrageenan and guar gum on the rheological properties and microstructure of phycocyanin gel[J]. Foods,2022,11(5):734. doi: 10.3390/foods11050734
[43] JONES O G, MCCLEMENTS D J. Recent progress in biopolymer nanoparticle and microparticle formation by heat-treating electrostatic protein-polysaccharide complexes[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2011,167(1−2):49−62. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2010.10.006
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 闫昱辛,何美军,李宇,袁晓曼,谭旭辉,程名,罗凯,廖璐婧. 铁皮石斛叶多糖美白和抗氧化活性. 植物研究. 2025(01): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代丽丽,王景,魏许瑞,马庆亚,王娜,都治香. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路研究灯盏花乙素对子宫内膜癌Ishikawa细胞的影响. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2024(01): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张琦,包小波,田冲冲. 灯盏花乙素增强4T1乳腺癌细胞对顺铂敏感性的体内外研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(05): 331-340 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王佳恩,殷子喻,马莉,李双良,符德欢. 灯盏乙素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展. 中草药. 2024(13): 4608-4621 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张琦,田冲冲,张洋,方晨曦,卜薇,李凤. 灯盏花乙素通过PPARγ-PGC1α-UCP1通路改善小鼠肥胖作用及机制. 药物评价研究. 2024(08): 1787-1796 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田冲冲,张琦,陈延绅. 基于肠道微生态探讨灯盏花乙素对乳腺癌小鼠的化疗增敏作用及其机制. 中国微生态学杂志. 2024(12): 1374-1381+1387 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



