Impact of Chlorine Dioxide Slow-releasing Preservative on Quality and Key Anthocyanins of Litchi during Low Temperature Storage
-
摘要: 荔枝采后易由花青素降解、呼吸代谢等导致其品质劣变,而二氧化氯(ClO2)有护色和抑制呼吸的多重作用。为探明ClO2对采后荔枝的综合影响,本研究分别采用0.1 g(T1)、0.4 g(T2)和1.2 g(T3)ClO2缓释剂处理荔枝,以0 g(CK)为对照,通过品质指标、色泽指标、花青素等评价其保鲜效果,并通过相关性分析探讨它们间的联系。结果表明,T1组荔枝贮藏品质最佳。贮藏7 d时,T1组荔枝可溶性固形物、a*值分别比同期CK组显著(P<0.05)提高了2.93%和10.13%,而呼吸速率显著(P<0.05)降低了34.54%。与此相反,T3组荔枝第7 d相对电导率达最高值35.84%,a*达降到最低值18.38,说明细胞结构破坏、漂白明显,贮藏品质最差。为进一步探明色泽变化与花青素的关系,筛选出荔枝中10种关键花青素,含7种原花青素,它们占总花青素达66.96%。相关性分析表明,在贮藏期内,T1、T2、T3组中色泽a*值与矢车菊素半乳糖苷的相关系数分别为0.980、0.548、0.360,与矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷的相关系数为0.985、0.488、0.402。T1组维持了最好的色泽,可能与其维持以上2种关键红色花青素较慢分解有关,而T3组加速了花青素的分解。本研究可为提高荔枝采后品质提供参考。Abstract: Litchi is prone to deterioration in quality after harvest due to degradation of anthocyanins and respiratory metabolism, and chlorine dioxide (ClO2) has multiple effects on color protection and respiratory inhibition. In this study, 0.1 g (T1), 0.4 g (T2), and 1.2 g (T3) of ClO2 slow-releasing preservatives were used to treat lychees with 0 g (CK) as the control to evaluate the preservation effect by quality index, color index and anthocyanin, and correlation analysis was applied to explore the association between them. The results showed that the litchi of the T1 showed the optimal qualities. On the 7 th day, the total soluble solids and a* values of litchi in the T1 were significantly (P<0.05) increased by 2.93% and 10.13%, respectively, while the respiration rate was significantly (P<0.05) decreased by 34.54% compared to the CK group in the same period. On the contrary, the relative conductivity of the T3 litchi reached the highest value of 35.84% on the 7 th day, and a* decreased to the lowest value of 18.38, indicating significant damage to cell structure, bleaching, and the worst storage quality. To further investigate the relationship between color changes and anthocyanins, 10 key anthocyanins were selected from litchi, including 7 proanthocyanins, which accounted for 66.96% of the total. The correlation analysis showed that the correlation coefficients between a* value and cyanidin-3-O-galactoside in the T1, T2, and T3 groups were 0.980, 0.548, and 0.360, respectively, and the correlation coefficients with cyanidin-3-O-glucoside were 0.985, 0.488, and 0.402 during storage. The T1 maintained the best color, possibly due to the slower decomposition of the two key red anthocyanins above, while the T3 accelerated the decomposition of anthocyanins. This study could provide valuable insights for enhancing the postharvest quality of litchi.
-
Keywords:
- litchi /
- ClO2 slow-releasing preservative /
- anthocyanin /
- storage quality /
- correlation analysis
-
荔枝(Litchi chinensis Sonn.)属于无患子科,是原产于我国的热带、亚热带水果,其富含花青素,以营养丰富而闻名[1]。荔枝采收于气温高湿度大的夏季,采后呼吸强度大,贮藏期易发生果实破损、褐变以及腐烂等问题[2−3]。海南是我国荔枝最早上市的区域[4],常年气候湿热,荔枝采后品质劣变问题最为突出[5]。
ClO2能有效抑制果蔬褐变和微生物生长,目前已在荔枝、提子等水果的保鲜上应用。郭芹等[6]使用不同浓度ClO2处理荔枝,发现80、120 mg/L的ClO2可明显抑制荔枝采后病害的发生,减缓褐变程度。李奕星等[7]用ClO2、1-MCP以及两者联合处理无核荔枝,发现皆能提高好果率、抑制褐变。但高浓度的气体ClO2不易保存,还有一定的爆炸风险[8]。因此,不需要现配现用、安全性高的ClO2缓释剂成为果蔬保鲜研究热点[9]。此外,花青素是荔枝[10]、蓝莓[11]、苹果[12]等水果的主要呈色物质,也是判断果实品质的重要指标,但花青素在果实贮藏过程中易分解,大大降低水果商业价值。目前,ClO2对热带水果贮藏期间花青素的影响还未有系统报道。
综上,本研究选用3组不同浓度的ClO2缓释剂应用于荔枝采后保鲜中。通过评价荔枝关键品质、色泽指标和花青素的影响,通过相关性分析得到荔枝保鲜效果最佳的ClO2缓释剂用量,并对其护色机理进行了初步阐述,本研究结果可为荔枝贮运流通提供应用参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
糯米糍荔枝 海口市南北水果批发市场;ClO2缓释剂 海南省农业科学院农产品加工设计研究所研制;乙腈、甲醇 色谱级,德国Merck公司;亚氯酸钠 天津市大茂化学厂;酒石酸 天津市北辰方正试剂厂;碘化钾 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;硫代硫酸钠 天津市登科化学试剂有限公司;常规试剂 均为国产分析纯;20种花青素混标(纯度≥95%) 上海甄准生物科技有限公司;原花青素A1、A2、B1、B2、B3、B4、C1(纯度≥95%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
MettlerXS204分析天平 美国Mettler Toledo公司;UNIVERSAL320R高速冷冻离心机 德国Hettich公司;NS800分光测色仪 深圳三恩施科技有限公司;SK-GH10果蔬呼吸测定仪 三克重庆仪器有限公司;FNV-55数显糖度计 河南绥净环保科技有限公司;AR8211+电导率仪 东莞万创电子制品有限公司;Ultimate 3000超高效液相色谱仪 美国Thermo公司;三重四极杆质谱仪 配有电喷雾离子源(ESI) 美国AB公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 ClO2缓释剂的制备
参考邓浩等[9] 将m(亚氯酸钠):m(酒石酸):m(硅胶):m(硅藻土)=3:1:0.5:0.5:0.5,漩涡混合后加入无纺布袋中封口。
1.2.2 ClO2缓释剂处理荔枝
挑选无损伤、大小相近的2.5 kg荔枝置于5 L泡沫箱中,每组分别放置0、0.1、0.4、1.2 g ClO2缓释剂,命名为CK、T1、T2、T3组,每组共3个平行,密封后在8 ℃、相对湿度85%条件下贮藏。
1.2.3 品质指标的测定
1.2.3.1 可溶性固形物
按NY/T 2637-2014《水果和蔬菜可溶性固形物含量的测定 折射仪法》进行测定,贮藏第1、3、5、7 d各测一次,单位为%。
1.2.3.2 可滴定酸
可滴定酸(TA)含量,采用酸碱滴定法,参照曹建康等[13]的方法测定,单位为%。
1.2.3.3 呼吸强度
每组取250 g果实,采用SK-GH10果蔬呼吸测定仪测定,每组测3次,单位为mg/(kg·h)。
1.2.3.4 相对电导率
每组取5个果,用打孔器将果赤道面对称的部位,打成直径约10 mm的果皮圆片,每个果2个孔,共10个孔果皮置于50 mL离心管内,同时加入30 mL蒸馏水静置20 min后,测定电导率P1;之后将离心管沸水浴加热10 min,冷却至25℃后测定电导率P2。相对电导率为P1/P2,每组测3次,单位为%。
1.2.4 色泽指标的测定
对10个果实表面赤道部位对角4个方向果皮的L*、a*。其中,L*表示亮度,正值越大则样品表面越光亮;a*表示红绿色差,正值越大则越红。
1.2.5 花青素含量的测定
样品前处理:称取磨碎的果皮1 g,加10 mL乙腈,加2粒陶瓷均质子,混匀10 min,超声10 min,10000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液1 mL,稀释5倍,过0.22 μm有机滤膜,上机检测。色谱柱:Phenomenex Luna Omega Polar C18(1.6 μm,2.1 mm×100 mm);柱温30 ℃;进样量5.0 μL;流速0.3 mL/min;流动相A:甲醇;流动相B:水;梯度洗脱程序0~2 min,0~20% B;2~3 min,80% B;3~3.5 min,80% B~20% B;3.5~5 min,20% B。质谱:离子源:ESI源,正离子和负离子模式;扫描模式:选择反应监测(SRM)模式;电喷雾电压:4500和-4500 V;离子源温度:550 ℃;雾化气:50 psi;加热气:50 psi;气帘气:25 psi;碰撞室入口电压:10 V。花青素质量分数计算公式如下:
花青素质量分数X(mg/kg)=C×V×Dm×1000 式中,X为样品花青素质量分数,mg/kg;C为样品浓度,ng/mL;V为样品体积,mL;m为样品称样量,g;D为稀释倍数。
1.3 数据处理
每个样品重复3次测定,实验数据采用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计分析,按照邓肯氏新复极差法进行组间比较,P<0.05表示差异显著;使用OriginPro 2021软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 ClO2缓释剂对荔枝贮藏期品质指标的影响
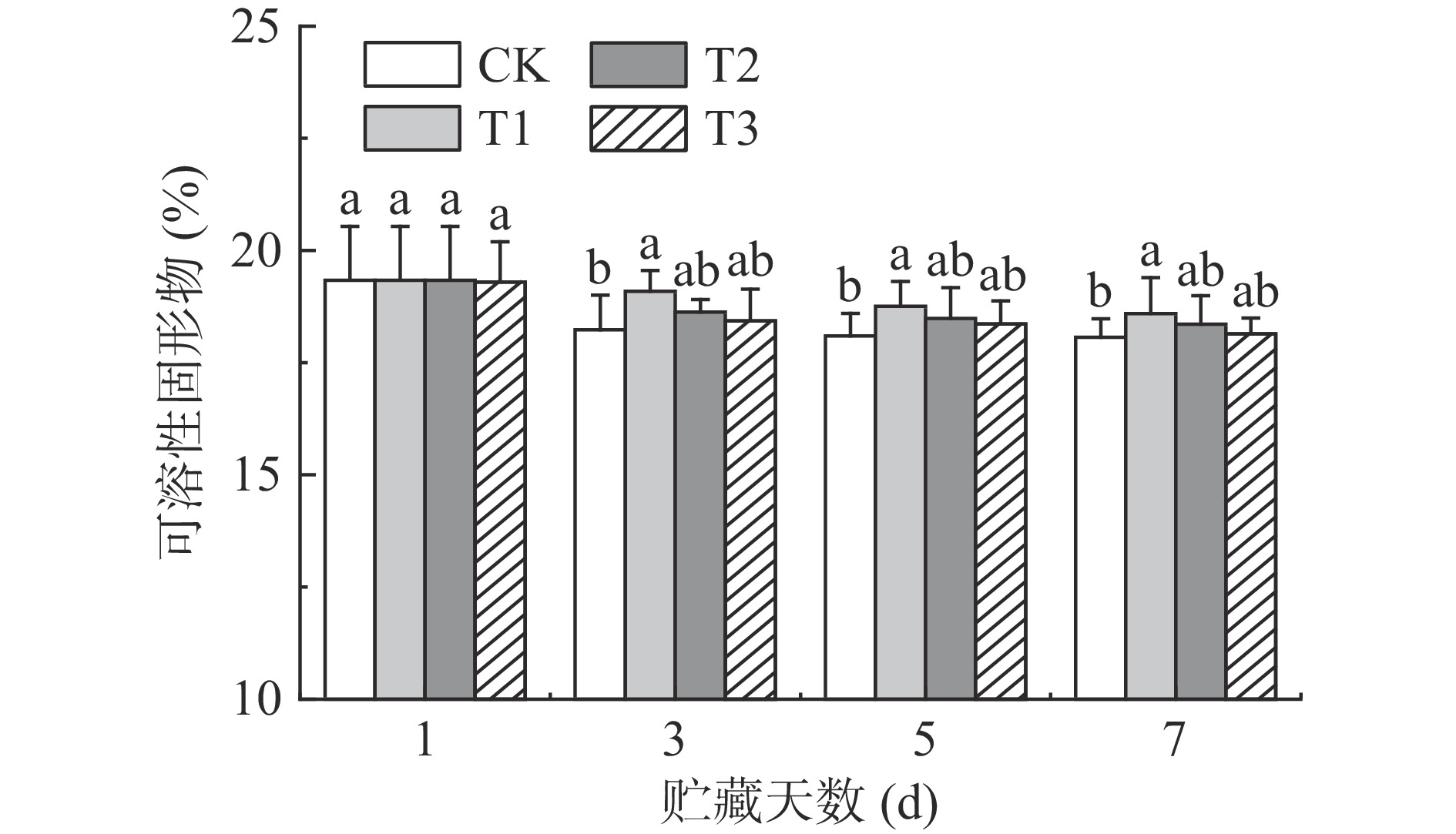
可溶性固形物(total soluble solids,TSS)主要是指可溶性糖类,即单糖、双糖、多糖等,是参与采后代谢活动的底物[14]。如图1所示,各组的荔枝在贮藏过程中的TSS含量均有不同程度的下降,说明TSS参与果实采后代谢活动并被不断消耗。在整个贮藏期间,T1组的TSS含量都显著(P<0.05)高于CK组,贮藏7 d时为18.43%,仅比第1 d下降4.6%。说明低浓度的ClO2处理能延缓荔枝TSS含量的下降,维持荔枝的良好品质。研究表明较低浓度的ClO2处理能延缓木奶果[15]、葡萄[16]等果实TSS含量的下降,这与本研究的结果相一致。
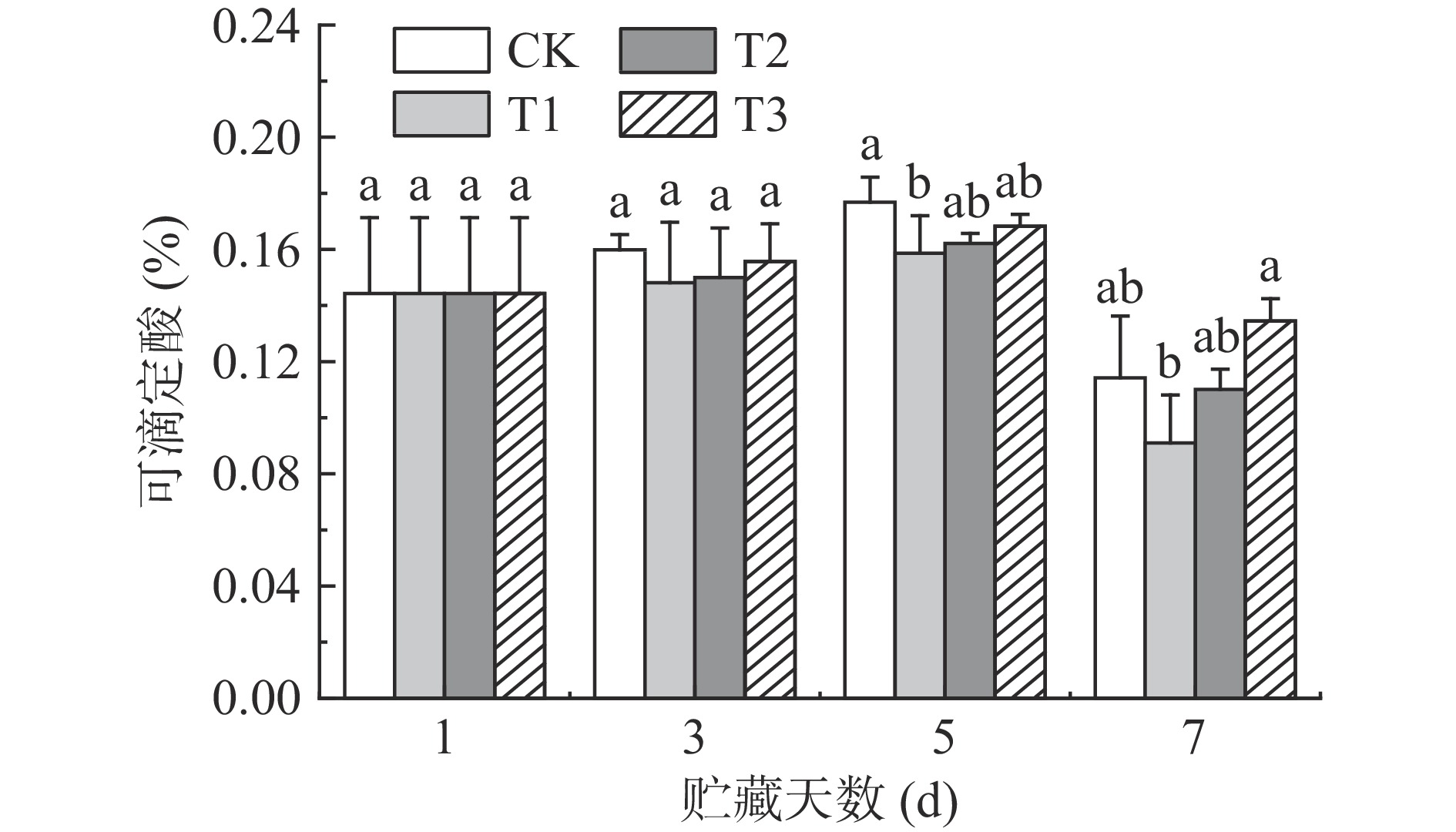
可滴定酸(titratable acid,TA)是荔枝口感及风味变化的重要因素[17−18]。如图2所示,TA含量在整个贮藏期间呈先上升后下降的趋势。贮藏5 d时,CK组的TA含量上升至0.177%,而T1组的TA含量显著(P<0.05)低于CK组。TA含量的上升是因为荔枝中酸性转化酶活性增加,促进糖转化成酸,造成TSS含量的降低[19]。与CK组相比,T1组可能通过抑制酸性转化酶活性,减缓荔枝中糖转化成酸的生物过程。贮藏7 d时,各组的TA含量均有下降,可能是荔枝中有机酸作为基质被呼吸代谢所消耗[20]。
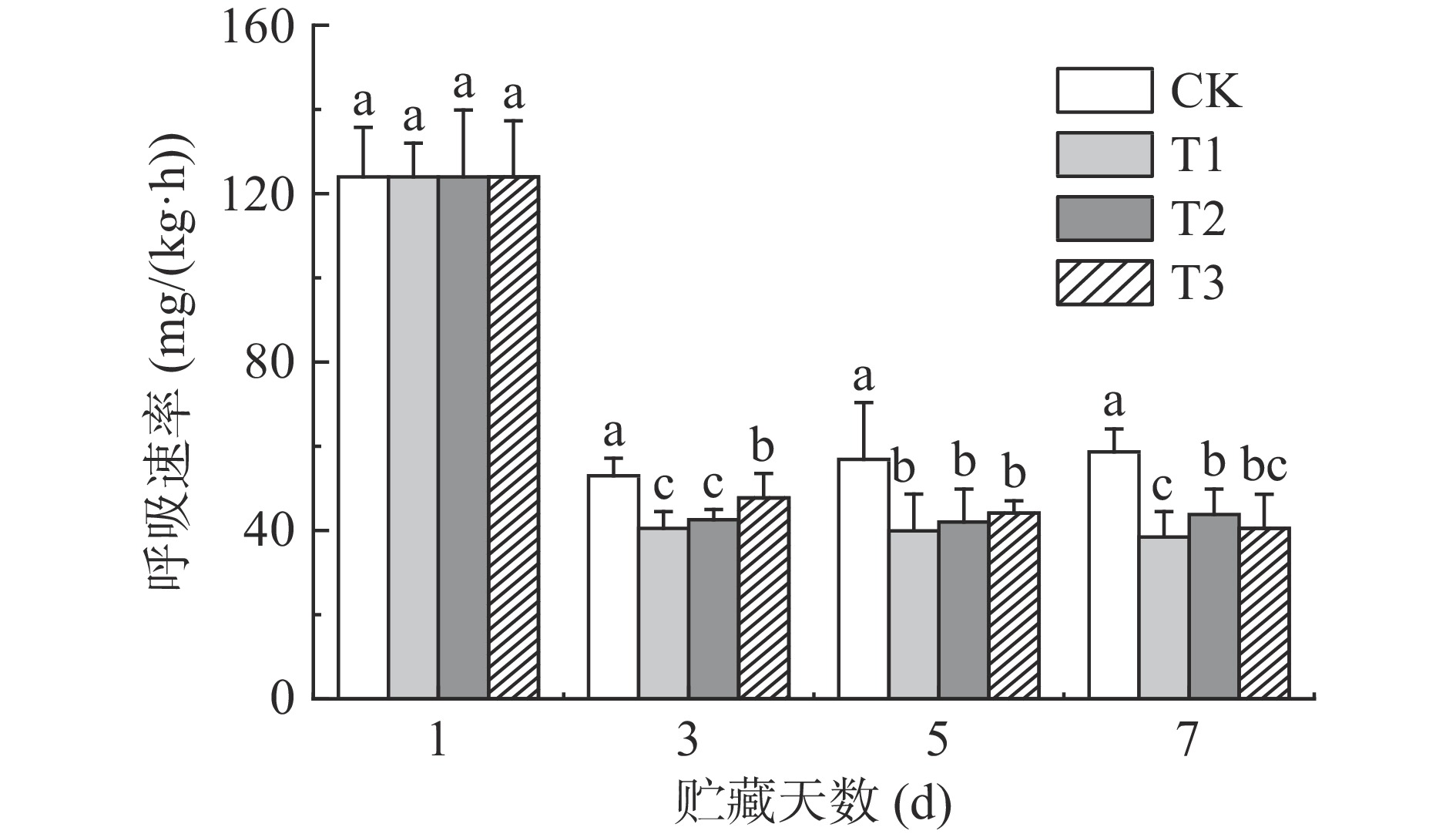
果蔬采后会自主呼吸,呼吸速率越高,受损害程度越大[21−23]。如图3所示,荔枝的呼吸速率在贮藏后迅速下降。3个ClO2缓释剂组荔枝的呼吸速率在整个贮藏期间均显著(P<0.05)低于CK组,说明ClO2处理可有效抑制荔枝呼吸作用。有研究表明,ClO2能通过抑制在有氧呼吸中发挥重要作用的环氧合酶(COX)基因来阻断线粒体电子传输链[24]。贮藏7 d时,T1组荔枝的呼吸速率为38.40 mg/(kg·h),保持了最低的呼吸速率,说明T1处理组可以通过减少呼吸过程中有机物质的消耗来减缓荔枝的品质劣变。
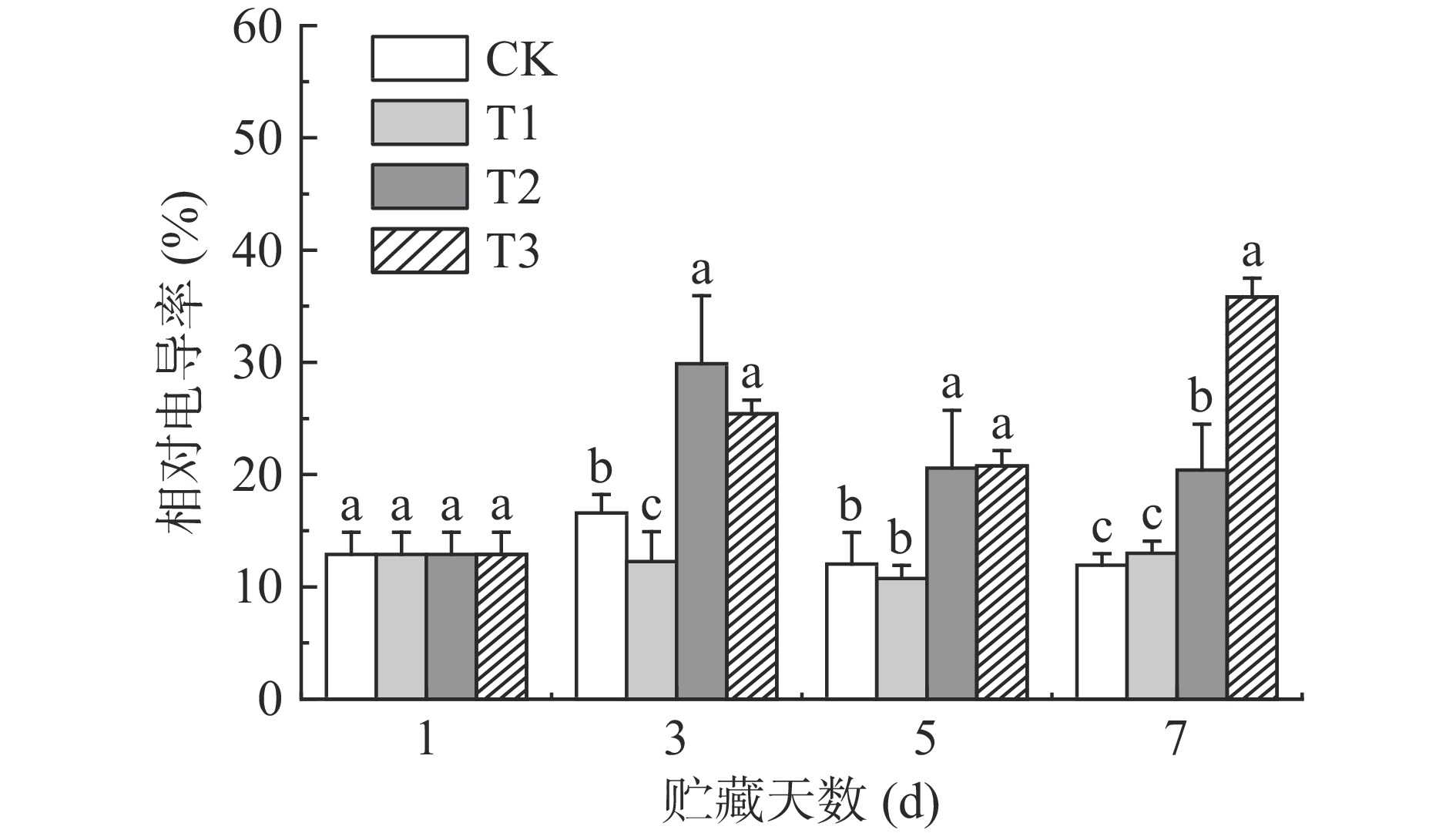
相对电导率可评价果蔬的受损伤程度,果蔬组织破损导致细胞液外渗,相对电导率就会增大[25]。如图4所示,T2、T3组荔枝在贮藏期间保持了较高的相对电导率,并显著(P<0.05)高于CK和T1组。贮藏7 d时,T3组荔枝的相对电导率达到峰值35.84%,较同期CK组增加了200.31%,说明高浓度的ClO2严重破坏了荔枝细胞膜的完整性。但T1组的相对电导率与CK组在贮藏中后期没有显著(P<0.05)差异,说明低浓度的ClO2缓释剂对荔枝细胞无明显不利影响。
2.2 ClO2缓释剂对荔枝色泽指标影响
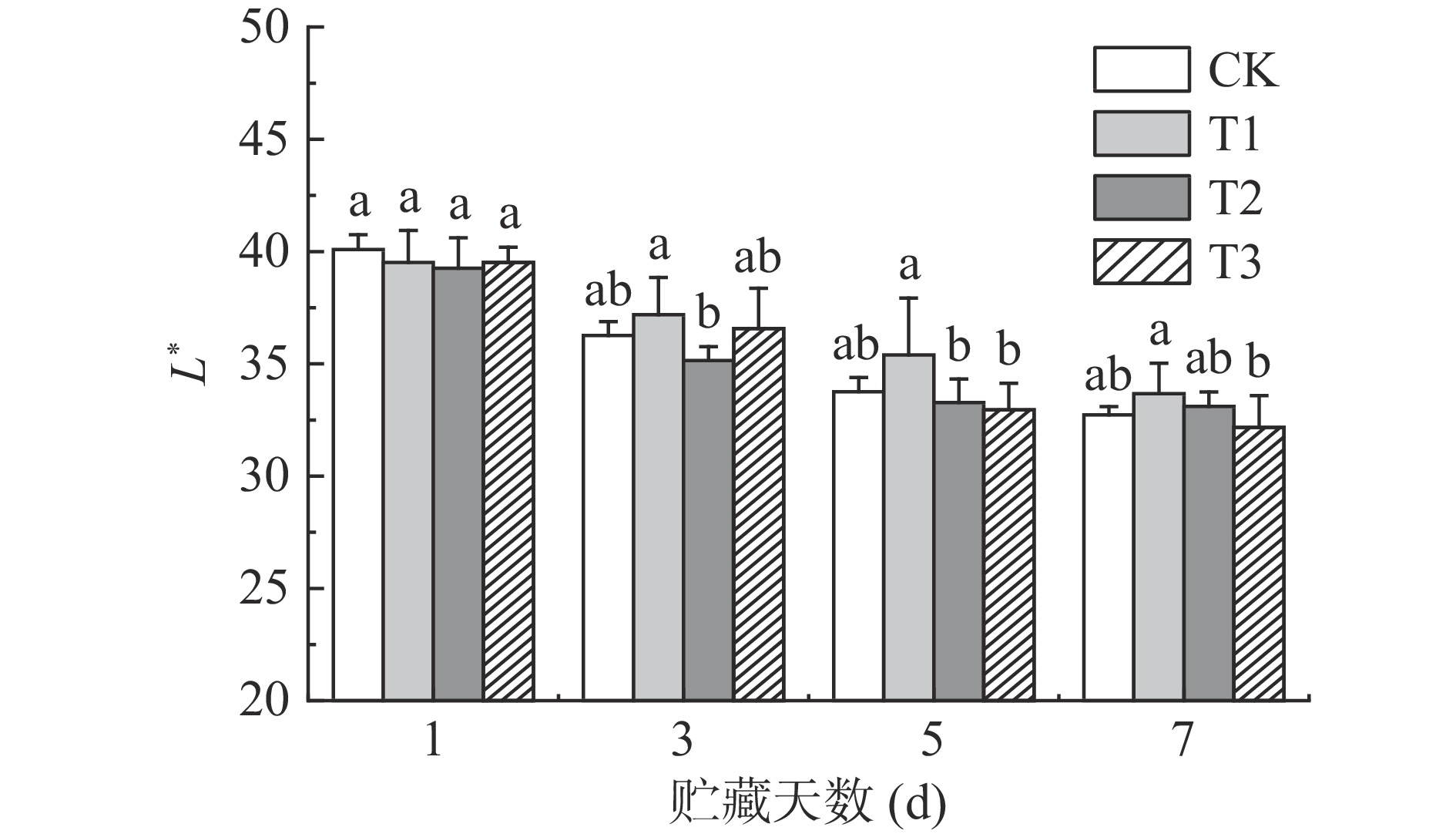
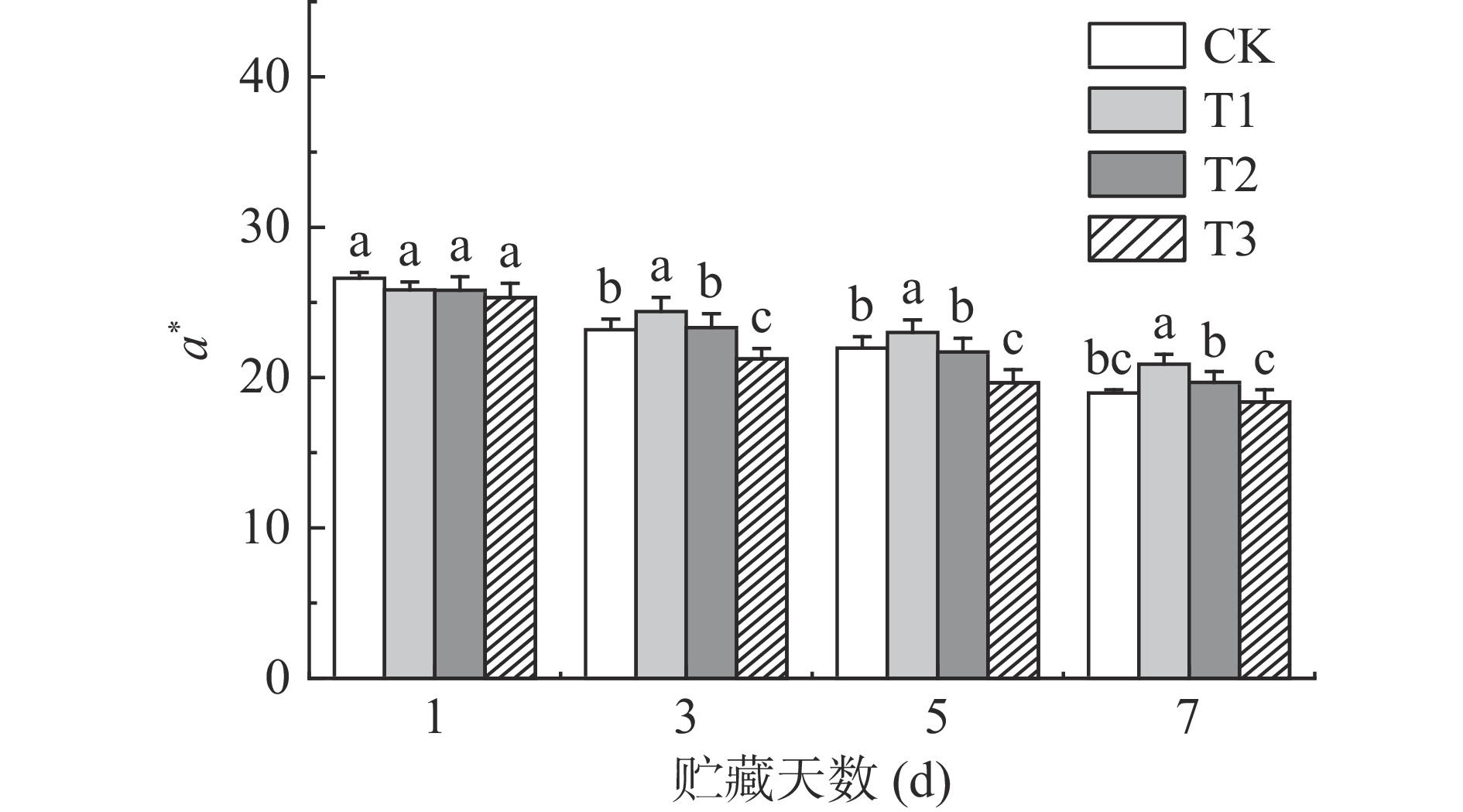
果蔬采后的色泽指标变化可反映果蔬的褐变程度[7]。如图5~图6所示,色泽指标L*、a*值在贮藏期间均有不同程度的下降,说明果实随着贮藏时间的延长而变暗,果皮的红色也逐渐褪去,品相变差。T1组荔枝保持了较高的L*值,并且a*值始终显著(P<0.05)高于同期其它组。贮藏7 d时,T1组荔枝L*值与a*值为33.67和20.89,比同期CK组分别高2.88%和10.13%。有研究表明,适当浓度ClO2可以有效减缓荔枝褪色[6],维持荔枝色泽,这与本研究的结果一致。
综上,T1组荔枝贮藏期间综合品质最佳。贮藏7 d时,T1组荔枝可溶性固形物、a*分别比同期CK组显著提高2.93%,10.13%(P<0.05),而呼吸速率显著降低34.54%(P<0.05)。与此相反,T3组荔枝第7 d时相对电导率达最高值36%,a*达降到最低值18.38,说明细胞结构破坏、漂白明显,贮藏品质最差。由于低浓度ClO2有护色保鲜的效果,而高浓度ClO2有强氧化性,且有漂白作用,不利于保鲜。不同浓度ClO2对荔枝色泽、花青素降解规律尚不清楚,因此需要开展进一步探讨。
2.3 ClO2缓释剂对荔枝花青素的影响
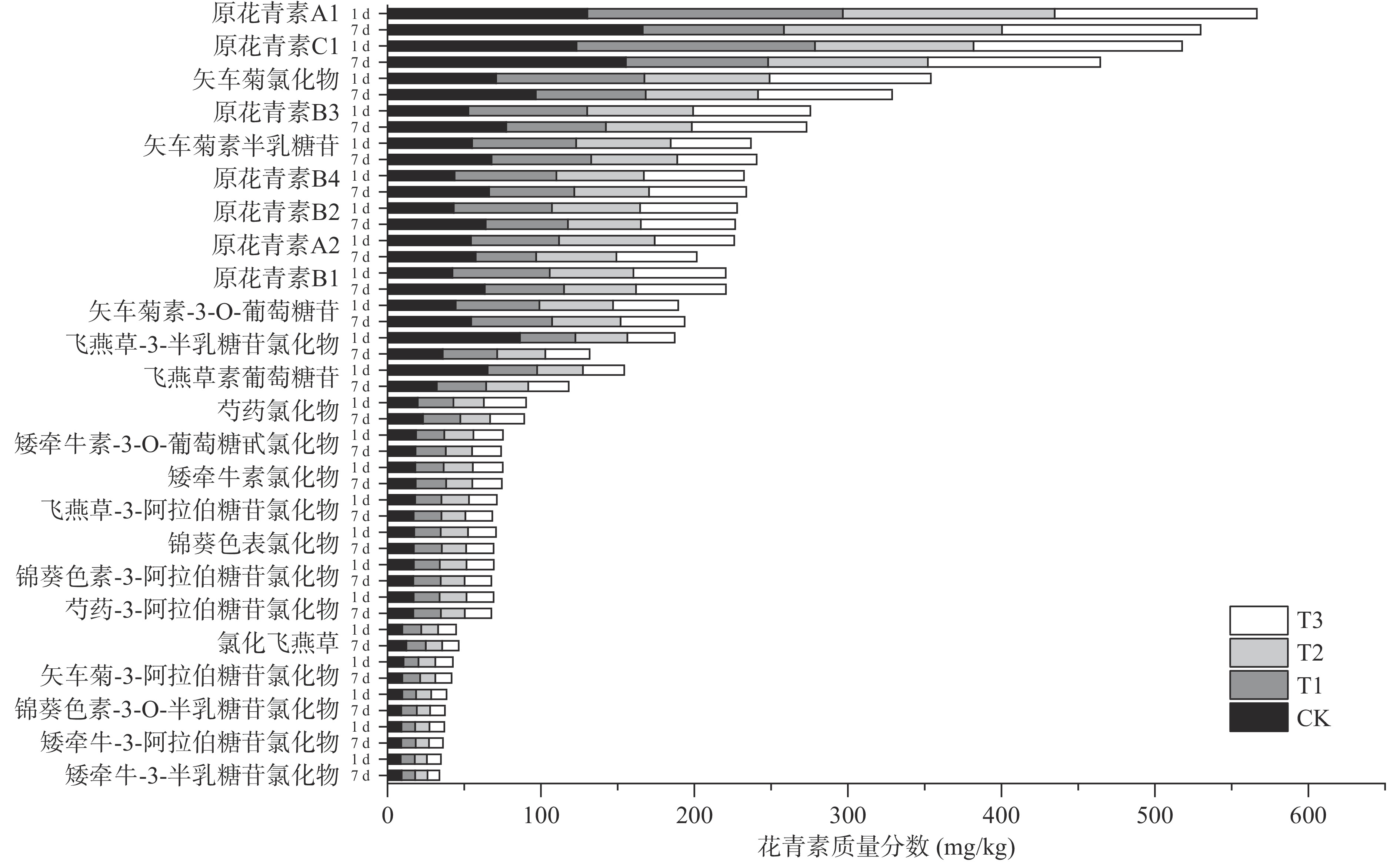
花青素是一种广泛存在于植物中的类黄酮色素,使荔枝呈现红色[26],其含有大量羟基并且会随采后贮藏时间的延长或褐变而下降[27−29]。如图7所示,与第1 d相比,荔枝经7 d贮藏大多数花青素都发生了明显降解,其中原花青素A1、原花青素C1、矢车菊氯化物、原花青素A2、飞燕草-3-半乳糖苷氯化物、飞燕草素葡萄糖苷降解最多。在1 d,原花青素A1、A2、B1、B2、B3、B4、C1、矢车菊氯化物、矢车菊素半乳糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷占全部24种花青素达66.96%,其中7种原花青素占比49.68%,它们对荔枝贮藏期间颜色变化起关键性作用。Sui等[30]对荔枝果皮中的原花青素进行了分离鉴定,发现原花青素A1、A2是主要花青素,这与本文结果一致。原花青素富羟基,有较强的抗氧化能力,用以保护细胞膜免受损伤[31]。ClO2作为一种强氧化剂,在荔枝贮藏期间能氧化原花青素中的羟基,造成花青素的分解。
2.4 荔枝色泽指标与关键花青素相关性分析
为进一步探明ClO2对荔枝中花青素与色泽指标的影响,定义占比超60%的10种花青素为关键花青素。10种关键花青素和色泽指标L*、a*值相关性结果如表1所示:CK组荔枝在贮藏过程中,色泽L*、a*值逐渐降低,颜色加深,红色逐渐丢失。推测10种关键的花青素处于活跃的合成分解平衡,因此无一花青素与色泽指标有显著相关。T1组荔枝在贮藏期间,矢车菊素半乳糖苷与色泽L*值有极显著(P<0.01)正相关,相关系数为0.999,与色泽a*值也显著正相关,相关系数为0.980。矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷与色泽L*值有显著(P<0.05)正相关,相关系数为0.985。说明最佳浓度的ClO2处理能减少荔枝的褐变,维持红色色泽,可能与其维持矢车菊素半乳糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷较慢分解有关。有研究表明,7种原花青素为无色,而矢车菊素半乳糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷为山楂[32]、苹果[33]中呈现红色的主要花青素。随着ClO2浓度增大,这两种红色花青素的合成分解平衡被打破,T1、T2、T3组矢车菊素半乳糖苷与色泽a*值相关系数分别为0.980、0.548、0.360。与此相似的是,3个处理组的矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷与色泽a*值相关系数也从0.985降至0.402。其中,最高ClO2浓度T3组中2种红色花青素与色泽指标相关性最差,说明高浓度ClO2打破了花青素合成分解平衡,对荔枝色泽产生了不利影响。有研究表明氧化剂过氧化氢对黑米花青素[34]、木枣果皮花青素[35]有明显的破坏作用,且与氧化剂浓度显著相关。此外,Qu等[36]通过转录组学和蛋白质组学联合分析认为参与荔枝花色素苷生物合成的查尔酮酶和降解的过氧化物酶同时上调,荔枝花青素降解多于生物合成,降解与合成不平衡,造成荔枝果皮褐变。Khushboo等[37]同样发现查尔酮酶和过氧化物酶参与荔枝花青素合成与降解,任何一个酶的变化都可引起降解与合成不平衡。推测3种不同浓度的氧化剂ClO2处理对参与荔枝花色素苷生物合成的查尔酮酶和降解的过氧化物酶产生了破坏作用,打破且加速了荔枝花青素的合成分解平衡。值得注意的是,原花青素A2与T2组的a*值和L*值呈显著(P<0.05)正相关,可能是由于原花青素A2分子结构中含有苯环和偏二苯甲烷基,能够吸收红光的波长,反射出红色。当荔枝果实中原花青素A2的含量降低时,由于分子结构的特异性,荔枝果实的红色程度也会随之降低,从而导致荔枝色泽a*值的下降。整个调控网络需进一步研究。
表 1 荔枝色泽指标与关键花青素含量变化相关性Table 1. Correlation between color indicators and key anthocyanin contents of litchi处理组 色泽指标 原花青素
A1原花青素
C1矢车菊
氯化物原花青素
B3矢车菊素
半乳糖苷原花青素
B4原花青素
B2原花青素
A2原花青素
B1矢车菊素-3-O-
葡萄糖苷CK L* −0.117 0.024 −0.333 −0.540 −0.773 −0.504 −0.507 0.185 −0.540 −0.791 a* −0.366 −0.239 −0.567 −0.730 −0.883 −0.699 −0.703 −0.076 −0.730 −0.914 T1 L* 0.883 0.359 −0.092 0.363 0.999** 0.240 0.250 0.670 0.363 0.985* a* 0.834 0.208 −0.248 0.215 0.980* 0.088 0.104 0.705 0.215 0.945 T2 L* −0.031 −0.490 −0.006 −0.019 0.406 −0.002 0.103 0.953* −0.019 0.304 a* −0.354 −0.209 0.346 0.302 0.548 0.312 0.396 0.992** 0.302 0.488 T3 L* −0.416 −0.249 −0.116 −0.391 0.069 −0.373 −0.384 −0.489 −0.391 0.107 a* −0.372 −0.183 −0.070 −0.370 0.360 −0.375 −0.368 −0.455 −0.370 0.402 注:*表示相关性显著(P<0.05),**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 3. 结论
本研究使用不同浓度ClO2缓释剂进行荔枝保鲜实验,并分析了ClO2缓释剂处理的荔枝中关键花青素与荔枝色泽变化的关系。结果表明:T1组(0.1 g ClO2缓释剂)处理可提高荔枝采后品质、防止褐变。贮藏7 d时,T1组荔枝可溶性固形物、a*值分别比同期CK组显著提高了2.93%和10.13%(P<0.05),而呼吸速率显著降低了34.54%(P<0.05)。与此相反,T3组(1.2 g ClO2缓释剂)处理荔枝在第7 d相对电导率达最高值35.84%,a*达降到最低值18.38,细胞结构破坏、漂白明显,贮藏品质最差。荔枝中原花青素A1、A2、B1、B2、B3、B4、C1、矢车菊氯化物、矢车菊素半乳糖苷、矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷等10种关键花青素与色泽指标的相关性分析表明:在贮藏期内,T1、T2、T3组中色泽a*值与矢车菊素半乳糖苷的相关系数分别为0.980、0.548、0.360,与矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷的相关系数为0.985、0.488、0.402。T1组维持了最好的色泽,而T3组打破且加速了花青素的分解与平衡,加速了褐变。该研究对ClO2缓释剂在荔枝保鲜中的应用提供了理论基础,荔枝花青素的合成与分解调控机理仍需更深入的研究。
-
表 1 荔枝色泽指标与关键花青素含量变化相关性
Table 1 Correlation between color indicators and key anthocyanin contents of litchi
处理组 色泽指标 原花青素
A1原花青素
C1矢车菊
氯化物原花青素
B3矢车菊素
半乳糖苷原花青素
B4原花青素
B2原花青素
A2原花青素
B1矢车菊素-3-O-
葡萄糖苷CK L* −0.117 0.024 −0.333 −0.540 −0.773 −0.504 −0.507 0.185 −0.540 −0.791 a* −0.366 −0.239 −0.567 −0.730 −0.883 −0.699 −0.703 −0.076 −0.730 −0.914 T1 L* 0.883 0.359 −0.092 0.363 0.999** 0.240 0.250 0.670 0.363 0.985* a* 0.834 0.208 −0.248 0.215 0.980* 0.088 0.104 0.705 0.215 0.945 T2 L* −0.031 −0.490 −0.006 −0.019 0.406 −0.002 0.103 0.953* −0.019 0.304 a* −0.354 −0.209 0.346 0.302 0.548 0.312 0.396 0.992** 0.302 0.488 T3 L* −0.416 −0.249 −0.116 −0.391 0.069 −0.373 −0.384 −0.489 −0.391 0.107 a* −0.372 −0.183 −0.070 −0.370 0.360 −0.375 −0.368 −0.455 −0.370 0.402 注:*表示相关性显著(P<0.05),**表示相关性极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 谢翀, 林琳, 吴戈仪, 等. 荔枝生理落果中A型原花青素提取纯化鉴定及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(3):81−87. [XIE C, LIN L, WU G Y, et al. Extraction and purification of a-type proanthocyanidins from physiological fruit drop of litchi and study of antioxidant activity[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(3):81−587.] XIE C, LIN L, WU G Y, et al. Extraction and purification of a-type proanthocyanidins from physiological fruit drop of litchi and study of antioxidant activity[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(3): 81−587.
[2] 黄方, 唐杰, 黄敏, 等. 低温结合气调包装对荔枝保鲜作用[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(10):51−55. [HUANG F, TANG J, HUANG M, et al. The effect of low temperature combined with air conditioning packaging on the preservation of litchi[J]. Food Industry,2022,43(10):51−55.] HUANG F, TANG J, HUANG M, et al . The effect of low temperature combined with air conditioning packaging on the preservation of litchi[J]. Food Industry,2022 ,43 (10 ):51 −55 .[3] 蒋璇靓, 王南, 陈洪彬, 等. 激光微孔保鲜袋包装对采后荔枝果实的保鲜效应[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(24):124−130. [JIANG X L, WANG N, CHEN H B, et al. Preservation effect of laser microporous preservation bag packaging on postharvest litchi fruits[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(24):124−130.] JIANG X L, WANG N, CHEN H B, et al . Preservation effect of laser microporous preservation bag packaging on postharvest litchi fruits[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022 ,48 (24 ):124 −130 .[4] 吴小巧, 朱镕, 钟于秀, 等. 海南荔枝养分投入限量标准及减量潜力分析[J/OL]. 热带作物学报:1−14 [2024-02-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.s.20230106.1013.002.html. [WU X Q, ZHU R, ZHONG Y X, et al. Analysis of nutrient input limit standards and reduction potential of litchi in Hainan [J/OL]. Journal of Tropical Crops:1−14 [2024-02-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.s.20230106.1013.002.html.] WU X Q, ZHU R, ZHONG Y X, et al. Analysis of nutrient input limit standards and reduction potential of litchi in Hainan [J/OL]. Journal of Tropical Crops: 1−14 [2024-02-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.s.20230106.1013.002.html.
[5] 吕润, 梁彩红, 邹海平, 等. 海南妃子笑荔枝精细化农业气候区划研究[J]. 热带农业科学,2021,41(12):117−122. [LÜ R, LIANG C H, ZOU H P, et al. Refined agro-climatic zoning of litchi in Hainan[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science,2021,41(12):117−122.] LÜ R, LIANG C H, ZOU H P, et al . Refined agro-climatic zoning of litchi in Hainan[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science,2021 ,41 (12 ):117 −122 .[6] 郭芹, 张玉丽, 王吉德, 等. 二氧化氯处理对荔枝采后贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2013,38(6):46−50,53. [GUO Q, ZHANG Y L, WANG J D, et al. Effect of chlorine dioxide treatment on postharvest storage quality of litchi[J]. Food Science and Technology,2013,38(6):46−50,53.] GUO Q, ZHANG Y L, WANG J D, et al . Effect of chlorine dioxide treatment on postharvest storage quality of litchi[J]. Food Science and Technology,2013 ,38 (6 ):46 −50,53 .[7] 李奕星, 陈娇, 李芬芳, 等. ClO2结合1-MCP对无核荔枝的常温保鲜效果研究[J]. 保鲜与加工,2021,21(3):29−34. [LI Y X, CHEN J, LI F F, et al. Study on the effect of ClO2 combined with 1-MCP on the freshness of seedless litchi at room temperature[J]. Preservation and Processing,2021,21(3):29−34.] LI Y X, CHEN J, LI F F, et al . Study on the effect of ClO2 combined with 1-MCP on the freshness of seedless litchi at room temperature[J]. Preservation and Processing,2021 ,21 (3 ):29 −34 .[8] 赵琪琪, 胡文忠, 陈晨, 等. 二氧化氯气体处理对果蔬采后生理代谢及质量安全的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):387−396. [ZHAO Q Q, HU W Z, CHEN C, et al. Effects of chlorine dioxide gas treatment on post-harvest physiological metabolism and quality and safety of fruits and vegetables[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(18):387−396.] ZHAO Q Q, HU W Z, CHEN C, et al . Effects of chlorine dioxide gas treatment on post-harvest physiological metabolism and quality and safety of fruits and vegetables[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (18 ):387 −396 .[9] 邓浩, 张容鹄, 吴广, 等. 二氧化氯缓释剂的制备及对龙眼保鲜效果综合评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(6):149−155. [DENG H, ZHANG R H, WU G, et al. Preparation and evaluation of slow-releasing chlorine dioxide preservative on longan[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(6):149−155.] DENG H, ZHANG R H, WU G, et al . Preparation and evaluation of slow-releasing chlorine dioxide preservative on longan[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023 ,49 (6 ):149 −155 .[10] 胡雅馨, 李京, 惠伯棣, 等. 蓝莓果实中主要营养及花青素成分的研究[J]. 食品科学,2006(10):600−603. [HU Y X, LI J, HUI B D, et al. Study on the main nutritional and anthocyanin components in blueberry fruits[J]. Food Science,2006(10):600−603.] HU Y X, LI J, HUI B D, et al . Study on the main nutritional and anthocyanin components in blueberry fruits[J]. Food Science,2006 (10 ):600 −603 .[11] 赵宗方, 谢嘉宝, 吴桂法, 等. 富士苹果果皮花青素发育的相关因素分析[J]. 果树科学,1992(3):134−137. [ZHAO Z F, XIE J B, WU G F, et al. Analysis of factors related to anthocyanin development in Fuji apple pericarp[J]. Fruit Tree Science,1992(3):134−137.] ZHAO Z F, XIE J B, WU G F, et al . Analysis of factors related to anthocyanin development in Fuji apple pericarp[J]. Fruit Tree Science,1992 (3 ):134 −137 .[12] 杨胜平, 谢晶, 钱韻芳, 等. 壳聚糖复合保鲜剂涂膜与MAP保鲜“妃子笑”荔枝[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(8):279−283. [YANG S P, XIE J, QIAN Y F, et al. Chitosan composite preservative coating and MAP for preserving "Fei Zi Xiao" litchi[J]. Food Science,2013,34(8):279−283.] YANG S P, XIE J, QIAN Y F, et al . Chitosan composite preservative coating and MAP for preserving "Fei Zi Xiao" litchi[J]. Food Science,2013 ,34 (8 ):279 −283 .[13] 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅, 等. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2007. [CAO J K, JIANG W B, ZHAO Y M, et al. Postharvest physiological and biochemical experimental guidance for fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2007.] CAO J K, JIANG W B, ZHAO Y M, et al. Postharvest physiological and biochemical experimental guidance for fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2007.
[14] DINESH R, SHARMAI P D, KUMAR S. Effect of total soluble solid during storage of litchi fruits under different temperatures[J]. Advances in Applied Science Research,2014,5(2):117−121.
[15] 孔方南, 李文砚, 罗培四, 等. 二氧化氯对木奶果保鲜效果的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2021,21(2):20−27. [KONG F N, LI W Y, LUO P S, et al. Effect of chlorine dioxide on the freshness of wooden milk fruits[J]. Preservation and Processing,2021,21(2):20−27.] KONG F N, LI W Y, LUO P S, et al . Effect of chlorine dioxide on the freshness of wooden milk fruits[J]. Preservation and Processing,2021 ,21 (2 ):20 −27 .[16] 许萍, 乔勇进, 周慧娟, 等. 固体二氧化氯保鲜剂对夏黑葡萄保鲜效果的影响[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(10):282−286. [XU P, QIAO Y J, ZHOU H J, et al. Effect of solid chlorine dioxide preservatives on the freshness of summer black grapes[J]. Food Science,2012,33(10):282−286.] XU P, QIAO Y J, ZHOU H J, et al . Effect of solid chlorine dioxide preservatives on the freshness of summer black grapes[J]. Food Science,2012 ,33 (10 ):282 −286 .[17] CHEN Y H, SUN J Z, LIN H T, et al. Salicylic acid reduces the incidence of Phomopsis longanae Chi infection in harvested longan fruit by affecting the energy status and respiratory metabolism[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,160:111035. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111035
[18] IBARRA-GARZA I P, RAMOS-PARRA P A, HERNÁNDEZ-BRENES C, et al. Effects of postharvest ripening on the nutraceutical and physicochemical properties of mango ( Mangifera indica L. cv Keitt)[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2015,103:45−54. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.02.014
[19] 李海登, 蒋佳男, 张春萌, 等. 纳米ZnO保鲜膜对苹果保鲜效果的研究[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(10):33−36. [LI H D, JIANG J N, ZHANG C M, et al. Study on the effect of nano-ZnO cling film on apple freshness preservation[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(10):33−36.] LI H D, JIANG J N, ZHANG C M, et al . Study on the effect of nano-ZnO cling film on apple freshness preservation[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019 ,44 (10 ):33 −36 .[20] PARVIN N, RAHMAN A, ROY J, et al. Chitosan coating improves postharvest shelf-life of mango ( Mangifera indica L.)[J]. Horticulturae,2023,9(1):64. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae9010064
[21] LIN Y X, LIN H T, CHEN Y H, et al. The role of ROS-induced change of respiratory metabolism in pulp breakdown development of longan fruit during storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,305:125439. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125439
[22] PÉREZ-LÓPEZ A, CHÁVEZ-FRANCO S H, VILLASEÑOR-PEREA C A, et al. Respiration rate and mechanical properties of peach fruit during storage at three maturity stages[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2014,142:111−117. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.06.007
[23] 卢倩倩, 冯琳骄, 王爽, 等. 复合盐碱胁迫对鲜食葡萄生理生化指标的影响[J]. 中国农学通报,2023,39(1):62−70. [LU Q Q, FENG L J, WANG S, et al. Effects of complex salinity stress on physiological and biochemical indicators of fresh grapes[J]. Chinese Agronomy Bulletin,2023,39(1):62−70.] LU Q Q, FENG L J, WANG S, et al . Effects of complex salinity stress on physiological and biochemical indicators of fresh grapes[J]. Chinese Agronomy Bulletin,2023 ,39 (1 ):62 −70 .[24] GUO Q, WU B, PENG X Y, et al. Effects of chlorine dioxide treatment on respiration rate and ethylene synthesis of postharvest tomato fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2014,93:9−14. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.01.013
[25] 陈爱葵, 韩瑞宏, 李东洋, 等. 植物叶片相对电导率测定方法比较研究[J]. 广东教育学院学报,2010,30(5):88−91. [CHEN A K, HAN R H, LI D Y, et al. A comparative study on the determination of relative conductivity of plant leaves[J]. Journal of Guangdong College of Education,2010,30(5):88−91.] CHEN A K, HAN R H, LI D Y, et al . A comparative study on the determination of relative conductivity of plant leaves[J]. Journal of Guangdong College of Education,2010 ,30 (5 ):88 −91 .[26] FANG F, ZHANG X L, LUO H H, et al. An intracellular laccase is responsible for epicatechin-mediated anthocyanin degradation in litchi fruit pericarp[J]. Plant Physiology,2015,169(4):2391−408.
[27] XIE C, WANG K, LIU X W, et al. Characterization and bioactivity of A-type procyanidins from litchi fruitlets at different degrees of development[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,405:134855.
[28] ZHAO Q, ZHONG X L, CAI X, et al. Comparative physiological analysis of lignification, anthocyanin metabolism and correlated gene expression in red toona sinensis buds during cold storage[J]. Agronomy,2023,13(1):119.
[29] YAN Y F, PICO J, GERBRANDT E M, et al. Comprehensive anthocyanin and flavonol profiling and fruit surface color of 20 blueberry genotypes during postharvest storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2023,199:112274. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2023.112274
[30] SUI Y, ZHENG Y, LI X P, et al. Characterization and preparation of oligomeric procyanidins from Litchi chinensis pericarp[J]. Fitoterapia,2016,112:168−174. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.06.001
[31] MIRANDA-HERNÁNDEZ A M, MUÑIZ-MÁRQUEZ D B, WONG-PAZ J E, et al. Characterization by HPLC–ESI–MS2 of native and oxidized procyanidins from litchi ( Litchi chinensis) pericarp[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,291:126−131. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.020
[32] 张烘维. 山楂杂交后代果皮颜色变异规律初步研究[D]. 秦皇岛:河北科技师范学院. 2019. [ZHANG H W. Preliminary research on color variation of pericarp in hawthorn hybrid offspring[D]. Qinghuangdao:Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology, 2019.] ZHANG H W. Preliminary research on color variation of pericarp in hawthorn hybrid offspring[D]. Qinghuangdao: Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[33] 刘玉莲, 车飞, 郭延平, 等. 苹果着色期花青苷和糖组分含量变化及关联性[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(17):47−52. [LIU Y L, CHE F, GUO Y P, et al. Correlation between changes in soluble sugars and anthocyanins contents during fruit coloration[J]. Food Science,2013,34(17):47−52.] LIU Y L, CHE F, GUO Y P, et al . Correlation between changes in soluble sugars and anthocyanins contents during fruit coloration[J]. Food Science,2013 ,34 (17 ):47 −52 .[34] 田喜强, 董艳萍, 赵东江. 黑米花青素的浸提工艺优化及稳定性研究[J]. 中国酿造,2016,35(6):161−164. [TIAN X Q, DONG Y P, ZHAO D J. Optimization of extraction process and stability study of black rice anthocyanins[J]. China Brewing,2016,35(6):161−164.] TIAN X Q, DONG Y P, ZHAO D J . Optimization of extraction process and stability study of black rice anthocyanins[J]. China Brewing,2016 ,35 (6 ):161 −164 .[35] 郭浩, 杨卫民, 王建勋. 木枣果皮花青素稳定性研究[J]. 北京农业,2011,464(3):13−15,17. [GUO H, YANG W M, WANG J X. Study on the stability of anthocyanins in the peel of jujube[J]. Beijing Agriculture,2011,464(3):13−15,17.] GUO H, YANG W M, WANG J X . Study on the stability of anthocyanins in the peel of jujube[J]. Beijing Agriculture,2011 ,464 (3 ):13 −15,17 .[36] QU S S, LI M M, WANG G, et al. Transcriptomic, proteomic and LC-MS analyses reveal anthocyanin biosynthesis during litchi pericarp browning[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2021,289(17):110443.
[37] KHUSHBOO A, HIDAYATULL A M, TUSHAR R J, et al. Expression profiling of candidate genes for insight to pericarp browning in Litchi ( Litchi chinensis Sonn)[J]. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology,2019,33(2):1−10.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张桐,马路凯,刘东杰,王锋,柳建良. 常见加工型荔枝的品质分析及干燥规律研究. 农产品加工. 2024(09): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 荆红彭,刘明,李小燕,任桂芹,黄国华,李佥. 不同授粉方式对火龙果座果率及果实贮藏品质的影响. 天津农业科学. 2024(05): 18-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 白玲,张光友. 过硫酸氢钾复合物和二氧化氯泡腾片对禽流感病毒、新城疫病毒消毒效果的评价. 中国家禽. 2024(11): 159-164 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨娟,周婷婷,邓庆,唐新容,刘浩,毛译轩. 天然食用色素在食品中的应用及其稳定性探讨. 食品安全导刊. 2024(36): 134-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



