Progress of Exogenous Enzymes Application in Black Tea Processing
-
摘要: 红茶是世界上最主要的茶类之一,颇受世人欢喜。我国夏秋季茶资源广茂,加工成红茶或深加工产品是其重要的利用途径,过程中添加具有良好功能特性的外源酶进行辅助加工,能够有效提升夏秋季红茶和深加工产品的品质。本文综述了近年来外源酶在红茶加工中的应用现状及存在问题,常用外源酶的种类及其作用机制,外源酶在红茶加工重要工艺萎凋、揉捻及发酵中促进茶叶内含物质的有益转化,利用外源酶促进红茶特征成分茶黄素的合成及其含量提升,以及外源酶在红茶深加工中带来的品质变化。探索茶资源的酶法加工利用途径,可以为今后利用外源酶调控改善夏秋红茶的风味品质及深加工产品开发提供理论参考。Abstract: Black tea is the most important in the world tea production, and is very popular in the world tea market. China has abundant tea resources, especially unused tea leaves in summer and autumn, and there are a few new ways to develop them, such as processing black tea or deep processed products. Application of exogenous enzymes with good functional characteristics, can improve the quality of summer and autumn black teas, and their deep processed products. This article reviews that, the current status and existing problems of exogenous enzymes application in black tea processing in recent years, as well as the types and acting mechanisms of frequently-used exogenous enzymes, transformation of tea components catalyzed by exogenous enzymes during withering, rolling, and fermentation in black tea processing. Utilizing exogenous enzymes to promote the synthesis of theaflavins, a unique component of black tea, and the quality changes in deep-processing of black tea, are also summarized. Exploring the enzymatic processing methods, could promote the efficient utilization of tea resources, and regulate quality of summer and autumn black tea, as well as their deep-processed products, in the future.
-
Keywords:
- exogenous enzyme /
- black tea /
- processing /
- deep-processing /
- mechanism
-
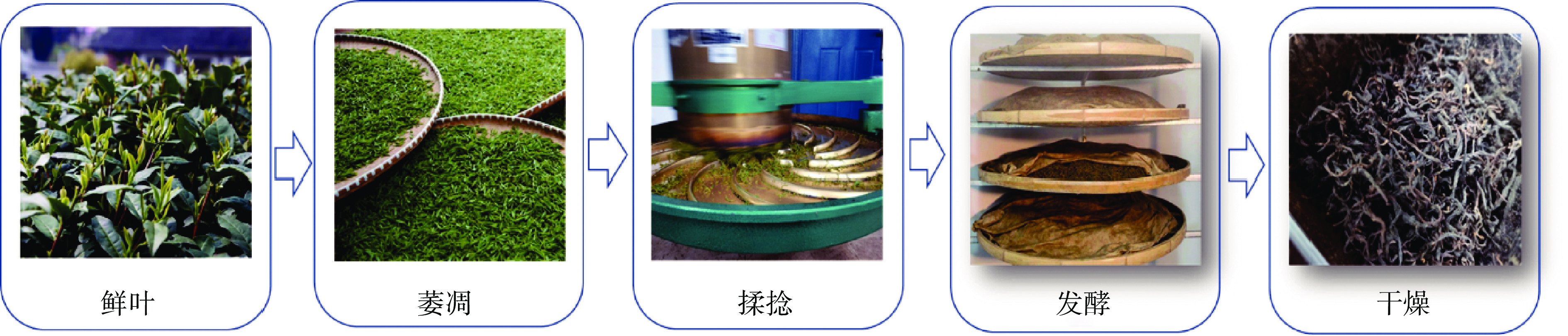
茶叶是我国非常重要的农产品。近年来,我国的茶叶产量、茶园面积等产业规模稳居世界前列[1]。茶是世界上消费量仅次于水的第二大饮料[2]。根据加工工艺不同,可以将茶叶分为绿茶、红茶、乌龙茶、白茶、黄茶和黑茶六大类。红茶是世界上消费量最大的茶类,具有红汤红叶、香味甜醇等品质特征,受到众人喜爱,其中夏秋红茶产量已被认为茶生产高峰[3],根据茶树一年可以萌发多轮新梢的生长规律,夏秋茶产量占全年总产量的60%以上[4]。根据加工工艺的不同,可将红茶分为条形茶和红碎茶,其中条形红茶又可分为工夫红茶和小种红茶。红茶加工工序主要为萎凋、揉捻、发酵和干燥,如图1所示。
酶具有专一性、催化高效性、作用条件温和、活性可调节等良好的功能特性,作为生态友好的生物催化剂受到了全世界的关注,利用外源酶来提升红茶品质已经成为红茶研究的热点。有研究人员发现,在萎凋、揉捻、发酵三个步骤中分别添加相应的外源酶,对红茶加工工艺及品质都有明显影响,甚至可以节省时间成本,趋势向好。中国是世界茶叶的主要生产国,春季绿茶和夏秋红茶成为了采茶叶生产的高峰。夏秋两季的茶,由于环境因素、茶树体内代谢水平的变化等,造成了夏秋茶多酚类物质含量较高,氨基酸、芳香物质等含量偏低,从而导致夏茶品质远不及春茶[5−6]。现有部分研究报道表明,添加外源酶能够改善夏秋季红茶或深加工产品的品质[7]。在制备红茶浓缩液时,加入单宁酶、果胶酶、纤维素酶、淀粉酶和蛋白酶制得的成品滋味丰富,增加甜感,并且能够提升回甘[8]。利用木瓜蛋白酶、单宁酶和谷氨酰胺酶改良过的抹茶,其风味物质得到很大的改善,抹茶茶汤清澈均匀稳定,色泽翠绿,醇厚甘爽,茶氨酸质量浓度达到2.135 g/L[9]。多酚氧化酶催化儿茶素合成四种茶黄素的合成率可以达到30.66%[10]。纤维素酶、果胶酶、漆酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶复合处理陈年武夷岩茶增香效果最好,其香气总量为6455.96 μg/L,是对照组的2.14倍[11]。基于此,文章综述了红茶加工中常应用的外源酶种类及其作用原理,红茶加工中主要外源酶的作用机制以及外源酶在红茶加工及其深加工中的应用效果,为今后如何高效、快捷地应用外源酶来改善夏秋红茶品质提供理论借鉴,促进夏秋茶资源得到充分利用,提高其附加值,进一步提高茶叶生产效益。
1. 红茶加工中常用外源酶类介绍
在当前生物技术时代,酶作为一种天然、绿色、高效的生物催化剂在食品工业领域具有广阔的应用前景。不同的外源酶在红茶加工中的作用效果不同,本文主要介绍红茶加工中常用的外源酶:水解酶类和氧化酶类。水解酶类主要有单宁酶、纤维素酶、果胶酶和蛋白酶;氧化酶类主要有多酚氧化酶、漆酶、过氧化物酶。纤维素酶和果胶酶具有消化细胞壁、提高茶叶可溶性糖和水浸出物含量等作用,木瓜蛋白酶可以提高茶叶中游离氨基酸含量,单宁酶对降低茶汤的苦涩味具有很好的效果,多酚氧化酶促进红茶色素的形成,这些外源酶应用于红茶加工中发挥各自的功能特性,使红茶品质得到进一步提升。
1.1 水解酶类及其作用原理
水解酶是催化水解反应的一类酶,它们是一类特殊的转移酶,以水作为被转移基团的受体。单宁酶又称鞣酸酶,是一种单宁酰基水解酶,在食品单宁转化过程中起着至关重要的作用,目前已经成为最常用的生物催化剂之一[12]。它已经在许多真菌菌株中鉴定出来,并且表现出较高的单宁耐受性[13]。单宁酶常应用在食品加工中,如去除速溶茶中的单宁[14]和澄清苹果汁[15],以减少其苦涩味和饮料浑浊现象。蛋白酶是一种蛋白水解酶,可分解蛋白质,释放出较多的小肽分子或游离氨基酸。在食品工业中,蛋白酶通常用于肉类嫩化、蛋白质水解物的生产,以及果汁和啤酒的澄清[16]。果胶酶是指催化植物细胞中果胶聚合物降解的酶,在全球食品和饮料酶市场中占有25%的份额,也是最早被开发且应用广泛的商品酶[17−18]。目前,果胶酶常应用于食品工业和化学工业中,在不同种类的发酵工艺技术上,主要用来提取、澄清和浸渍。例如植物纤维的沤解和脱胶、茶和咖啡的发酵、榨油、果汁和葡萄酒的澄清等[19]。纤维素酶是降解纤维素生成葡萄糖的一组酶的总称,是一种复合酶。据报道,纤维素酶在高温下比其他植物细胞壁降解酶更稳定[20]。除了上述水解酶之外,越来越多的天然水解酶资源,也作为新起之秀应用于红茶的生产加工中,如糖苷酶、脂肪酶、淀粉酶等水解酶,它们发挥其自有的特性,从滋味、颜色、香气、时间等各个维度进一步改善红茶品质。
1.2 氧化酶类及其作用原理
氧化酶是作用于不同底物的一类酶,可以将氧还原成过氧化氢。多酚氧化酶(Polyphenol oxidase,PPO)是红茶生产中的关键酶,催化多酚氧化形成茶色素,即茶黄素、茶红素和茶褐素[21]。根据其底物特异性和结构的不同,多酚氧化酶分为酪氨酸酶、儿茶酚氧化酶和漆酶[22]。在一些果蔬中,该酶可能会引起一些不良变化,如颜色褐变,然而在红茶发酵中添加外源多酚氧化酶则是有益于茶叶色泽的生成。漆酶是一种含铜的多酚氧化酶,它能催化多种芳香族和非芳香族化合物的转化,同时将分子氧还原为水,这一特性使漆酶成为绿色催化剂[23]。近年来,漆酶常用于果汁澄清、啤酒加工稳定性和食品感官品质的改善,它可以使油脱氧,去除可可和橄榄的苦味以及其他令人不快的味道,改善食品色泽[24]。研究发现,漆酶能有效地将茶叶中的茶多酚转化为茶色素,使茶黄素、茶红素和茶褐素含量均有明显提高,并且在适宜条件下,利用漆酶的氧化作用可有效提高红茶茶汤的品质[25]。过氧化物酶是在过氧化氢存在下催化基质氧化的一种酶,广泛存在于动物、植物和微生物中,它与多酚氧化酶一样,参与红茶发酵过程中色素的形成[26]。红茶发酵过程中,因有机酸的增加,导致多酚氧化酶逐渐失去活性,而后过氧化物酶逐渐位于主导地位。向绿茶茶汤中加入含有多酚氧化酶和过氧化物酶的果蔬果浆,再进行有氧搅拌发酵,经过一系列加工可得高茶黄素红茶饮料[27]。可见,氧化酶类是红茶加工中重要的一员,它与红茶加工过程中茶色素的形成紧密相关,不仅能催化发酵液色泽的形成,增加红茶中茶黄素的含量,还能有效改善茶汤品质。
2. 红茶加工中主要外源酶的作用机制
2.1 单宁酶
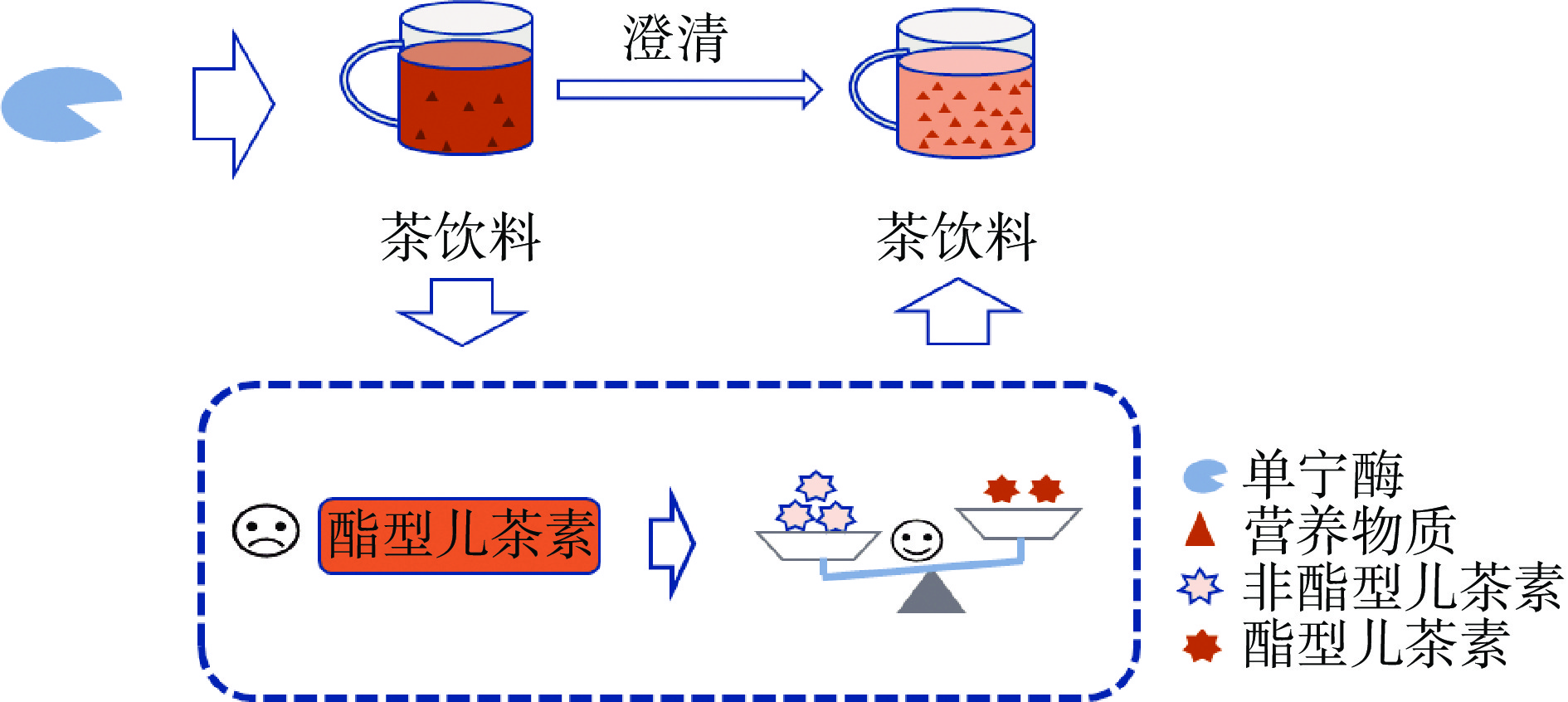
酯型儿茶素是茶叶苦涩味特性的主要原因,单宁酶在茶叶中主要用于水解没食子单宁中的酯键、缩酚键,使具有苦涩味的酯型儿茶素被水解成非酯型儿茶素,促进没食子酸以及葡萄糖释放,使茶汤、茶饮料的营养物质在不被破坏的前提下,减轻其苦涩味,提高澄清度,并且在一定程度上增加营养物质的溶出,降低酯型儿茶素与非酯型儿茶素的比值,提升产品品质[28−31],如图2所示。单宁酶可以增加茶汤的抗氧化能力[32],其应用于茶饮料中还具有提高茶叶提取率和水溶性,防止茶汤冷后浑等作用[33−34]。
2.2 多酚氧化酶
红茶汤色红亮、香气甜香、滋味甜醇是其特有的品质[35−37]。多酚氧化酶能使茶叶多酚类中的没食子儿茶素及没食子酸酯先氧化为邻醌,再逐步氧化缩合经过一系列反应生成茶黄素和茶红素[38−39],如图3所示。添加外源多酚氧化酶所制的红茶汤色红艳明亮,叶底红亮,滋味醇厚爽口,香气甜香持久[41−42]。据报道,水果中的多酚氧化酶对改善夏秋红茶感官品质具有不错的效果[43],常用于红茶的加工和深加工中。如苹果、梨、香蕉中所含有的多酚氧化酶不仅可以降低夏秋红茶的苦涩味,还能赋予茶叶果香[44−45]。
2.3 纤维素酶
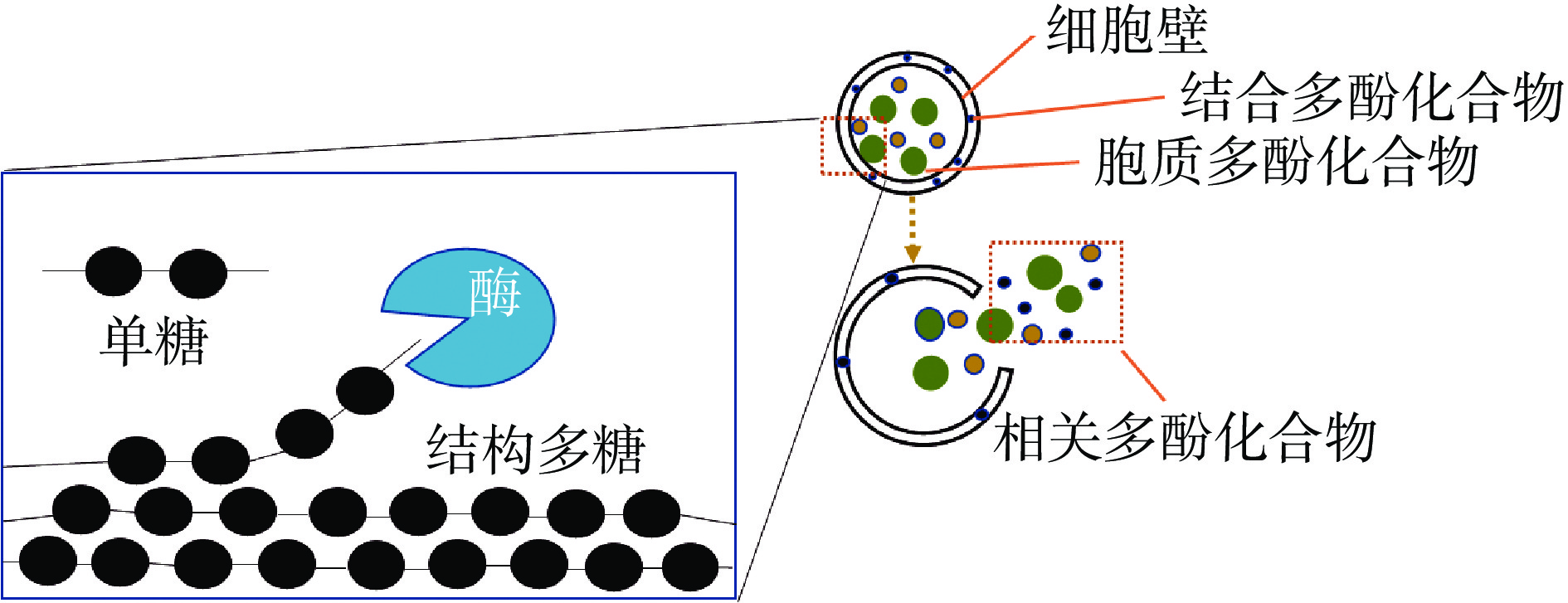
纤维素是一种相当稳定的大分子多糖,难以降解[46]。纤维素酶可以转化不溶性纤维素成葡萄糖,以及在果蔬汁中破坏细胞壁从而提高果汁得率。纤维素酶应用于红茶发酵过程中,可以提高茶黄素和茶红素含量[47]。研究发现,在红茶萎凋、揉捻和发酵过程中添加一定量的果胶酶和纤维素酶,前者有助于破坏茶叶细胞壁中存在的果胶,后者能水解细胞壁中的纤维素,更利于其浸提茶叶中有效成分和水浸出物的含量及芳香性物质的释放,还可以缩短发酵时间[48]。如图4所示,果胶酶、纤维素酶等酶促降解植物细胞壁,促使生物活性物质释放。
2.4 其他酶
β-葡萄糖苷酶是糖苷酶之一,通过水解糖苷化合物来增强红茶的香气,如芳樟醇、香叶醇和水杨酸甲酯等挥发性化合物,这些化合物具有果味花香,对红茶具有一定的增香能力[50−51]。在红茶加工揉捻过程中添加碱性蛋白酶,一定条件下,可以促进茶叶中的蛋白质水解,从而使茶汤中的游离氨基酸含量有所增加,提高茶汤营养价值[52],同时释放了多酚-蛋白复合物中的多酚类物质,增加红茶中多酚类物质的含量[1]。α-淀粉酶能将茶汤中淀粉物质切断成长短不一的短链糊精和少量的低分子糖类,从而使淀粉糊的黏度迅速下降,红茶汤中添加木瓜蛋白酶和α-淀粉酶均能起到提高茶汤透光率和澄清茶汤的作用,且两种酶效果相当[53]。在红茶生产过程中,脂肪酶可以催化许多酯类化合物的水解,同时产生挥发性物质,使红茶具有特定的风味特性,从而突出了脂肪酶在风味改善中的重要性[54]。
3. 外源酶在红茶加工过程中的应用研究
3.1 萎凋
萎凋是红茶加工的第一道工序,该阶段会发生一系列的物理变化过程,如叶片水分蒸发和萎缩、细胞汁浓度提高、叶绿素部分被破坏、一些水解酶、氧化酶活性增强等。现有学者尝试新的萎凋工艺去提高红茶品质,例如采用红光萎凋、添加外源酶等[55]。罗晶晶等[56]研究在萎凋过程中添加不同浓度的木聚糖酶、纤维素酶及木瓜蛋白酶,结果表明,添加350 U/mL的木聚糖酶能明显提高萎凋后茶叶的氨基酸含量,而同样浓度的木瓜蛋白酶反而降低了氨基酸的含量。冯花等[7]研究了添加外源酶对夏季红茶品质的影响,萎凋中添加木瓜蛋白酶、纤维素酶和单宁酶,均显著降低了氨基酸含量、提高了水浸出物总量与酚氨比。可见,木瓜蛋白酶对红茶氨基酸含量的作用不明显,反而使其含量有所降低。红茶萎凋工序中外源酶对茶叶氨基酸总量的影响上存在一定差异,分析认为可能与研究本身采取的红茶新工艺有关,因萎凋前期采取了摇青处理适度破坏了叶细胞结构,导致外源酶的作用效果发生变化。因此,在传统的红茶萎凋过程中可以尝试选择喷洒一定量的木聚糖酶来提高茶氨酸的含量,或者纤维素酶去水解茶叶细胞壁中的纤维素并提高茶叶中可溶性成分的含量。
3.2 揉捻
揉捻是借助外力使萎凋后的茶叶迅速卷曲成条,是塑造红茶外形的重要工序,在揉捻过程中,茶叶细胞组织破损,茶汁适度流出,使叶片中的多酚类化合物、蛋白质、氨基酸等物质附着于茶叶表面,这些物质与多酚氧化酶、氧气等充分接触,进行酶促氧化。林剑峰等[1]在揉捻工序中加入木瓜蛋白酶、纤维素酶和单宁酶,研究三种外源酶单独或混合使用对红茶主要成分的影响,认为木瓜蛋白酶能提高红茶内含成分含量,是较优的外源酶选择。Chiang等[57]研究发现红茶在揉捻1 min后喷洒纤维素酶溶液(30 U/mL)和发酵开始0 min喷洒多酚氧化酶溶液(5.0 U/mL)和过氧化物酶溶液(5.45 U/mL)制得的红茶品质较好。可见,在红茶揉捻过程中,纤维素酶的添加有利于促进茶叶内含物质的溶出,多酚氧化酶和过氧化物酶添加到发酵过程较为合适,所以在选择外源酶应用于红茶揉捻工序时,需要考虑酶的浓度和添加的种类。
3.3 发酵
发酵是红茶加工的关键工序,在茶叶发酵过程中添加外源酶能够提升茶叶品质,改善茶叶的发酵效果[58]。叶飞等[59]利用丰水梨多酚氧化酶改善夏秋红茶品质的试验中发现,茶汤的苦涩味减少,甜醇类物质增加,同时香气、汤色和滋味等感官品质得分都有明显的提高,并且茶叶的原有风味也得到了保留。红茶经过金水1号砂梨品种的多酚氧化酶处理后也有类似的效果[60]。林世锋等[61]在葛叶红茶发酵工序中采用了葡萄糖苷酶酶促发酵,不但去除了葛叶的涩味,增添了独特的香甜味,而且转化形成新产物,使其具有良好的营养保健功能。仝佳音等[62]通过在发酵过程中添加不同浓度的多酚氧化酶和纤维素酶,结果发现,添加多酚氧化酶和纤维素酶的茶样氨基酸、茶多酚、茶黄素等的含量都有不同程度的提高。可见,在发酵过程添加葡萄糖苷酶会增强茶叶香气,而添加丰水梨多酚氧化酶不仅可以改善成品茶的滋味品质,增强香气,还不会破坏茶叶原有风味,且使其综合感官品质得以提高。
4. 外源酶在红茶深加工中的应用
4.1 茶黄素提取制备
茶黄素组分(Theaflavins,TFs)是红茶中的主要功能成分和品质组分,在红茶中的含量仅在1%左右,但却是衡量红茶品质重要的化学成分,且具有很强的天然抗氧化作用和多种药理功能[63]。红茶中茶黄素含量低,直接提取较为困难,通过添加外源酶酶促合成茶黄素成为了工业化生产的关键途径。据报道,多酚氧化酶可以将黄烷醇氧化成茶黄素和茶红素[64]。前人研究发现,多酚氧化酶同工酶谱带多,酶活性就大,合成茶黄素的能力强,而丰水梨果实中的多酚氧化酶同工酶谱带比贡梨、雪梨、香梨、水晶梨多,因此,红茶加工中也常常选择水果中合成能力相对较强的丰水梨多酚氧化酶来提高茶黄素含量[65]。徐洪梅[66]利用丰水梨多酚氧化酶与红茶原液进行反应,结果发现茶黄素含量提高了17%左右。Xia等[67]利用单宁酶进行酶水解市售茶黄素提取物后,TF的含量增加了约3倍。可见,与丰水梨多酚氧化酶相比,单宁酶主要提高TF含量来提升茶黄素的总量,且效果更佳。其他果蔬中的多酚氧化酶应用于茶黄素的提取也有不错的效果,如马铃薯[68]、山药[10]等多酚氧化酶。研究发现,蘑菇中的酪氨酸酶比漆酶、胆红素氧化酶和粗茶多酚氧化酶能更有效地产生茶黄素[69]。Li等[70]以茶多酚为反应底物,利用马铃薯多酚氧化酶合成茶黄素类产量为651.75 μg/mL。酶对茶黄素的形成至关重要,茶黄素含量的提高与底物儿茶素有着密切的关系,多酚氧化酶促进儿茶素的消耗,同时合成茶黄素。不同酶源、外源添加儿茶素和不同比例的关键儿茶素对茶黄素的形成都有影响[1]。酶促氧化成为现研究阶段常使用制备茶黄素的方法之一,可通过调控底物儿茶素及其比例使外源酶发挥合成茶黄素的最佳效果,并为茶黄素合成技术的改进提供新的见解。
4.2 红茶饮料加工
4.2.1 速溶茶系列固体饮料
速溶茶是一种以传统茶叶为原料,经提取、澄清、浓缩、转溶、干燥等工艺加工而成的茶制品,具有快捷、方便等优点。速溶茶粉是重要的茶叶深加工产品,但是速溶茶的澄清度、滋味品质等是速溶茶发展的一项阻碍因素,因此出现很多速溶茶提取技术,其中酶技术可以改善速溶茶的感官品质和稳定性[38],是改良速溶茶粉及其加工产品风味的重要途径。有研究表明,一种生产冷水可溶性茶浓缩物或茶粉末的工艺,通过单宁酶处理红茶提取物,使茶的涩味和颜色得到改善,而且没有浑浊[71]。在速溶茶生产中添加单宁酶或木瓜蛋白酶,从而减少红茶提取物或速溶茶生产中茶乳酪的形成,并降低速溶茶中的苦涩口感,使得速溶茶品质更加趋于稳定[72]。绿茶提取液经过多酚氧化酶处理也可以加工成速溶红茶,能够有效地提高茶黄素的含量和改善速溶红茶的感官品质[73],而过氧化物酶与多酚氧化酶协同作用比单一酶的效果好,且使茶汤色泽更加红亮[74]。最新研究发现,液态发酵中酶和底物之间的反应更能有效地增加速溶红茶的抗氧化作用,酶法发酵与酶辅助萃取相结合的方法,可以制备感官品质优良、茶黄素含量高的速溶红茶,内源性和外源性酶共处理对速溶红茶的香气和化学物质转化起到协同作用[75]。添加外源酶可有效减轻红茶提取物的苦涩味,提高茶汤中茶黄素的含量,改善茶汤色泽、香气,提升速溶红茶的感官品质,而外源酶之间协同作用,内源酶与外源酶相互调控以及液态发酵与酶法结合等方式可以制备高质量速溶红茶,这为未来选择合适的技术措施生产速溶红茶提供了新的线索。
4.2.2 灌装液态茶饮料
茶饮料是以茶叶的水提取液或者浓缩液、速溶茶等为主要原料,通过加入水、食用香精、果汁、乳制品等经加工制成的液体饮料,是一种开瓶即饮的方便型茶叶深加工制品。目前茶浓缩液的得率、风味及稳定性一直是茶饮料向高品质纯茶饮料升级的难题。研究表明,单宁酶常用来澄清红茶饮料的初始茶汤,可以降低绿茶和红茶茶汤的浊度,同时还可提高茶汤亮度保持茶汤色泽稳定性,增加茶汤抗氧化能力,改善传统的加工工艺,为其在茶饮料行业中的应用提供基础[76−77]。杨军[78]筛选出复合破壁酶、蛋白酶、单宁酶等三种酶,可以提高茶叶浸提得率,减缓茶乳酪沉淀的问题,在一定程度上还起到增香的作用。即饮红茶是新型的饮茶方式,需要经过一个长时间的制作过程,Faustina等[79]利用外源酪氨酸酶和β-葡萄糖苷酶直接在工厂生产即饮红茶,缩短生产时间的同时也改善了红茶的冲泡色泽、增加令人愉悦的香气。廖凯[80]结合单宁酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶和超声的技术处理红茶饮料,所获的红茶饮料香气纯正,风味适中,稳定性较好,且滋味醇和。由此可见,酶技术可有效解决速溶茶得率低、冷溶性差、浑浊等问题,但外源酶之间的复合处理与物理化学技术相结合成为攻克红茶饮料一系列难题的新方法。
5. 总结与展望
目前茶叶加工中常用的外源酶主要有单宁酶、果胶酶、纤维素酶、多酚氧化酶、过氧化物酶等,研究者利用它们各自的功能特性改善茶叶品质是一种绿色科学的技术手段。酶在适宜条件下才会发挥理想作用,所以在茶叶加工过程中不仅需要考虑添加酶的种类,还需考虑温度、湿度、添加时间以及添加量等条件。外源酶在红茶深加工中的应用,主要用于茶黄素的提取制备、茶饮料的品质提升。尽管红茶的制作工艺已经研究得较为系统和全面,但仍有需要解决和突破的瓶颈问题。首先,外源酶在红茶加工中的作用机制比较复杂,如TFs和聚酯型儿茶素类(Theasinesins,TSs)的形成途径、茶叶内源酶与外源酶相互之间的作用机制,仍然是困扰研究人员的难题,阻碍了外源酶改善红茶滋味品质、理化性质等方面的深入研究。其次,在红茶制作工艺的同一工序中添加不同外源酶,可能带来不同的作用效果,外源酶相互作用之间的机理研究是相对薄弱的。添加外源酶酶促合成茶黄素成为工业化生产的关键途径,但找到优质酶源仍然是提高茶黄素含量需要深入探索的重要技术瓶颈。相信利用外源酶促进茶叶中品质与活性成分的有益转化,改善夏秋红茶及其深加工产品的品质,相关技术成果的应用前景将会日益广阔。
综上所述,外源酶在茶叶中的应用研究还存在很多的未知,随着现代酶工程技术的不断发展和制茶工艺技术水平的提升,未来在夏秋红茶加工过程中添加新型果蔬多酚氧化酶提升品质、增加天然果香,以及利用酶与物理技术协同作用、酶法包埋提高茶饮料品质等都非常值得关注。
-
[1] 林剑峰, 白建阳, 吴理文, 等. 外源酶对夏秋红茶主要品质成分影响研究[J]. 中国茶叶加工,2020,161(3):51−57. [LIN J F, BAI J Y, WU L W, et al. Effect of exogenous enzymes on main components of black tea in summer and autumn[J]. China Tea Processing,2020,161(3):51−57.] LIN J F, BAI J Y, WU L W, et al . Effect of exogenous enzymes on main components of black tea in summer and autumn[J]. China Tea Processing,2020 ,161 (3 ):51 −57 .[2] 袁国凤. 加大科研力度夏秋茶释放更多茶“动能”[N]. 中国食品报, 2021-12-02(7). [YUAN G F. Increase scientific research efforts to release more tea "kinetic energy" from summer and autumn tea[N]. China Food News, 2021-12-02 (7).] YUAN G F. Increase scientific research efforts to release more tea "kinetic energy" from summer and autumn tea[N]. China Food News, 2021-12-02 (7).
[3] LI Y C, HE C, YU X L, et al. Effects of red-light withering on the taste of black tea as revealed by non-targeted metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis[J]. LWT,2021,147:111620. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111620
[4] 夏秋茶的增值利用[J]. 农村新技术, 2010, 338(10):64−65. [Value added utilization of summer and autumn tea[J]. New Rural Technology, 2010, 338 (10):64−65.] Value added utilization of summer and autumn tea[J]. New Rural Technology, 2010, 338 (10): 64−65.
[5] 李永章, 熊飞. 充分利用夏秋茶深度开发茶资源[J]. 四川农业科技,2007,232(1):42. [LI Y Z, XIONG F. Fully utilizing summer and autumn tea to deeply develop tea resources[J]. Sichuan Agricultural Science and Technology,2007,232(1):42.] LI Y Z, XIONG F . Fully utilizing summer and autumn tea to deeply develop tea resources[J]. Sichuan Agricultural Science and Technology,2007 ,232 (1 ):42 .[6] 何小庆. 夏秋茶资源开发利用现状及发展对策[J]. 现代农业科技,2011,558(16):361−362. [HE X Q. Development and utilization status and countermeasures of summer-autumn tea[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2011,558(16):361−362.] HE X Q . Development and utilization status and countermeasures of summer-autumn tea[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2011 ,558 (16 ):361 −362 .[7] 冯花, 王飞权, 郭雅玲. 添加外源酶对夏季红茶品质的影响[J]. 商洛学院学报,2021,35(6):62−69. [FENG H, WANG F Q, GUO Y L. Effect of addition exogenous enzymes on quality of black tea in summer[J]. Journal of Shangluo University,2021,35(6):62−69.] FENG H, WANG F Q, GUO Y L . Effect of addition exogenous enzymes on quality of black tea in summer[J]. Journal of Shangluo University,2021 ,35 (6 ):62 −69 .[8] 李丽田, 黄煌政, 陈家伯, 等. 一种红茶浓缩液的制备方法:CN 201510591650[P]. CN 105076580 A [2023-06-24]. [LI L T, HUANG H Z, CHEN J B, et al. A method for preparing black tea concentrate:CN 201510591650[P]. CN 105076580 A [2023-06-24].] LI L T, HUANG H Z, CHEN J B, et al. A method for preparing black tea concentrate: CN 201510591650[P]. CN 105076580 A [2023-06-24].
[9] 杨洁茹, 陈晖, 张慧敏, 等. 酶法改良信阳夏秋茶抹茶风味的工艺探究[J]. 安徽农学通报,2023,29(4):123−127,186. [YANG J R, CHEN H, ZHANG H M, et al. Study on the technology of improving the flavor of Xinyang summer and autumn tea matcha by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Anhui Agricultural Bulletin,2023,29(4):123−127,186.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2023.04.031 YANG J R, CHEN H, ZHANG H M, et al . Study on the technology of improving the flavor of Xinyang summer and autumn tea matcha by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Anhui Agricultural Bulletin,2023 ,29 (4 ):123 −127,186 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2023.04.031[10] 汤凯, 陈尉怡, 占剑峰, 等. 佛手山药多酚氧化酶提取及酶促合成茶黄素研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2023,34(3):27−32. [TANG K, CHEN W Y, ZHAN J F, et al. Extraction of polyphenol oxidase from bergamot yam and enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins[J]. China Foods Limited Additives,2023,34(3):27−32.] TANG K, CHEN W Y, ZHAN J F, et al . Extraction of polyphenol oxidase from bergamot yam and enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins[J]. China Foods Limited Additives,2023 ,34 (3 ):27 −32 .[11] 谢李玲, 薛婉茹, 李丹阳, 等. 外源酶对陈年武夷岩茶香气品质的改善作用[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(5):155−164. [XIE L L, XUE W R, LI D Y, et al. Exogenous enzymes improve the aroma quality of Wuyi rock tea[J]. Food Studies and Development,2023,44(5):155−164.] XIE L L, XUE W R, LI D Y, et al . Exogenous enzymes improve the aroma quality of Wuyi rock tea[J]. Food Studies and Development,2023 ,44 (5 ):155 −164 .[12] BLANCA D, HECTOR R, JUAN A, et al. Bacterial tannases:Classification and biochemical properties[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2019,103(2):603−623. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9519-y
[13] MOSTAFA H S. Potato peels for tannase production from penicillium commune HS2, a high tannin-tolerant strain, and its optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery,2022,13(18):16765−16778.
[14] AHARWAR A, PARIHAR D K. Talaromyces verruculosus tannase immobilization, characterization, and application in tea infusion treatment[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery,2021,13(1):261−272.
[15] ANDRADE P M L, BAPTISTA L, BEZERRA C O, et al. Immobilization and characterization of tannase from Penicillium rolfsii CCMB 714 and its efficiency in apple juice clarification[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2021,15(2):1005−1013. doi: 10.1007/s11694-020-00705-9
[16] AMINLARI M. Plant-and animal-derived enzymes and their potential application in food processing and preservation[M/OL]. Singapore:Springer 2022:41−80.
[17] 李力群, 孙志康, 郝捷, 等. 果胶酶生产及工业应用进展[J]. 生物技术进展,2022,12(4):549−558. [LI L Q, SUN Z K, HAO J, et al. Progress on production and industrial application of pectinase[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2022,12(4):549−558.] LI L Q, SUN Z K, HAO J, et al . Progress on production and industrial application of pectinase[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2022 ,12 (4 ):549 −558 .[18] KHAN M, NAKKEERAN E, UMESH-KUMAR S. Potential application of pectinase in developing functional foods[J]. Annual Review of Food Science & Technology,2013,4(1):21−34.
[19] FAA B, HNB B, MB C. Recent advances in the production strategies of microbial pectinases-a review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,122:1017−1026. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.048
[20] EJAZ U, SOHAIL M, GHANEMI A. Cellulases:From bioactivity to a variety of industrial applications[J]. Biomimetics,2021,6(3):44. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics6030044
[21] KE L J, XU W, GAO J N, et al. Isolation and characterization of thermo-tolerant polyphenol oxidases in a black tea infusion[J]. Food Control,2021,119(1):107465.
[22] PANADARE D, RATHOD V K. Extraction and purification of polyphenol oxidase:A review[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology,2018,14:431−437. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2018.03.010
[23] SUSANA R C. Fungal laccase:A versatile enzyme for biotechnological applications:3rd ISNPS[M]. Avignon, France, 2019:429−457.
[24] MINUSSI R C, PASTORE G M, DURAN N. Potential applications of laccase in the food industry[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2002,13(6):205−216.
[25] 林婷婷. 真菌漆酶的生产及在催化氧化茶多酚中的应用基础研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学, 2011. [LIN T T. Production of fungi laccase and its application in oxidation of tea polyphenol[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University of Technology, 2011.] LIN T T. Production of fungi laccase and its application in oxidation of tea polyphenol[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2011.
[26] 谭和平, 周李华, 钱杉杉, 等. 茶叶发酵中的酶学研究进展[J]. 中国测试,2009,35(1):19−23. [TAN H P, ZHOU L H, QIAN S S, et al. Research progress of enzyme in tea fermentation[J]. China Testing,2009,35(1):19−23.] TAN H P, ZHOU L H, QIAN S S, et al . Research progress of enzyme in tea fermentation[J]. China Testing,2009 ,35 (1 ):19 −23 .[27] 李志慧. 一种含有多酚氧化酶和过氧化物酶的茶饮料制备方法:CN 201510550670.5[P]. CN 106472756 A [2023-06-28]. [LI Z H. A method for preparing tea beverage containing polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase:CN 201510550670.5[P]. CN 106472756 A [2023-06-28].] LI Z H. A method for preparing tea beverage containing polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase: CN 201510550670.5[P]. CN 106472756 A [2023-06-28].
[28] 焦天慧, 吕长鑫, 冯叙桥, 等. 单宁酶的分离纯化及其在软饮料工业中的应用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2016,42(11):262−269. [JIAO T H, LÜ C X, FENG X Q, et al. Extraction and purification of tannase and its application in soft drink industry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2016,42(11):262−269.] JIAO T H, LÜ C X, FENG X Q, et al . Extraction and purification of tannase and its application in soft drink industry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2016 ,42 (11 ):262 −269 .[29] 薄佳慧, 张杨玲, 宫连瑾, 等. 外源酶对改善茶叶品质作用的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(11):212−217. [BO J H, ZHANG Y L, GONG L J, et al. Research progress on exogenous enzymes effect on improving the quality of tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(11):212−217.] BO J H, ZHANG Y L, GONG L J, et al . Research progress on exogenous enzymes effect on improving the quality of tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2021 ,42 (11 ):212 −217 .[30] SUNNY D, GUNJAN M, KUMAR S A. Recent trends and advancements in microbial tannase-catalyzed biotransformation of tannins:A review[J]. International Microbiology,2018,21(4):175−195. doi: 10.1007/s10123-018-0027-9
[31] ZHANG Y, YIN J, CHEN J, et al. Improving the sweet aftertaste of green tea infusion with tannase[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,192:470−476. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.046
[32] THIYONILA B, KANNAN M, RENEETA N P, et al. Influence of tannase from Serratia marcescens strain IMBL5 on enhancing antioxidant properties of green tea[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology,2020,27:101675. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101675
[33] IIBUCHI S, MINODA Y, YAMADA K. Studies on tannin acyl hydrolase of microorganisms:Part II. A new method determining the enzyme activity using the change of ultra violet absorption[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry,1967,32(7):803−809.
[34] BISWAS I, MITRA D, PRADEEP K, et al. Structural and catalytic advancement of fungal tannase:A proteomic contribution in industrial applicability[J]. Bioresource Technology Reports,2022,19:2589−014X.
[35] 曹秋萍, 李扬帆, 杨林玲, 等. 论多酚氧化酶的开发及应用前景[J]. 北京农业,2015,619(14):17. [CAO Q P, LI Y F, YANG L L, et al. On the development and application prospects of polyphenol oxidase[J]. Beijing Agriculture,2015,619(14):17.] CAO Q P, LI Y F, YANG L L, et al . On the development and application prospects of polyphenol oxidase[J]. Beijing Agriculture,2015 ,619 (14 ):17 .[36] 薛金金, 尹鹏, 张建勇, 等. 工夫红茶品质化学成分及加工工艺研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(18):219−224. [XUE J J, YIN P, ZHANG J Y, et al. Research progress on quality-related chemical components and processing technology of Congou black tea[J]. Food Studies and Development,2020,41(18):219−224.] XUE J J, YIN P, ZHANG J Y, et al . Research progress on quality-related chemical components and processing technology of Congou black tea[J]. Food Studies and Development,2020 ,41 (18 ):219 −224 .[37] 张娅楠. 黄金茶1号夏秋红茶加工技术及香味品质形成机理研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2019. [ZHANG Y N. Study on the processing technology and forming mechanism of aroma and taste quality of black tea of Huangjing 1 tea mading in summer and autumn[D]. Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University, 2019.] ZHANG Y N. Study on the processing technology and forming mechanism of aroma and taste quality of black tea of Huangjing 1 tea mading in summer and autumn[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2019.
[38] CHEN L, WANG H J, YE Y, et al. Structural insight into polyphenol oxidation during black tea fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2023,17:2590−1575.
[39] TANAKA T, YASUMATSU M, HIROTANI M, et al. New degradation mechanism of black tea pigment theaflavin involving condensation with epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,370:131326.
[40] 徐斌, 薛金金, 江和源, 等. 茶叶中聚酯型儿茶素研究进展[J]. 茶叶科学,2014,34(4):315−323. [XU B, XUE J J, JIANG H Y, et al. Review on theasinensins in tea[J]. Tea Science,2014,34(4):315−323.] XU B, XUE J J, JIANG H Y, et al . Review on theasinensins in tea[J]. Tea Science,2014 ,34 (4 ):315 −323 .[41] LIU Y, CHEN Q, LIU D, et al. Multi-omics and enzyme activity analysis of flavour substances formation:Major metabolic pathways alteration during Congou black tea processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,403:134263.
[42] 陆安霞, 周心如, 闫敬娜, 等. 外源添加茶汁或梨汁对梅占工夫红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(2):51−59. [LU A X, ZHOU X R, YAN J N, et al. Effect of exogenous addition of tea or pear juice on the quality of Meizhan black tea[J]. Food Industry Technology,2023,44(2):51−59.] LU A X, ZHOU X R, YAN J N, et al . Effect of exogenous addition of tea or pear juice on the quality of Meizhan black tea[J]. Food Industry Technology,2023 ,44 (2 ):51 −59 .[43] 叶飞, 高士伟, 龚自明. 砂梨多酚氧化酶处理对夏秋红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(23):92−95. [YE F, GAO S W, GONG Z M. Effects of Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai polyphenol oxidase treatment on the quality of black tea in summer and autumn[J]. Food Science,2013,34(23):92−95.] YE F, GAO S W, GONG Z M . Effects of Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai polyphenol oxidase treatment on the quality of black tea in summer and autumn[J]. Food Science,2013 ,34 (23 ):92 −95 .[44] 邹纯, 许勇泉, 陈建新, 等. 利用水果多酚氧化酶改善夏秋红茶品质[J]. 浙江农业科学,2021,62(3):579−582. [ZOU C, XU Y Q, CHEN J X, et al. Study on improving quality of black tea summer and autumn by using polyphenol oxidase from fruit[J]. Agricultural Science,2021,62(3):579−582.] ZOU C, XU Y Q, CHEN J X, et al . Study on improving quality of black tea summer and autumn by using polyphenol oxidase from fruit[J]. Agricultural Science,2021 ,62 (3 ):579 −582 .[45] 付静, 江和源, 张建勇, 等. 外源多酚氧化酶催化合成儿茶素二聚体氧化产物的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(7):274−280. [FU J, JIANG H Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Recent progress in synthesis of oxidized dimeric catechin catalyzed by exogenous polyphenol oxidase[J]. Food Science,2019,40(7):274−280.] FU J, JIANG H Y, ZHANG J Y, et al . Recent progress in synthesis of oxidized dimeric catechin catalyzed by exogenous polyphenol oxidase[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (7 ):274 −280 .[46] 王丰园, 金海炎, 丁凌飞, 等. 纤维素酶及其活性提升研究进展[J]. 现代农村科技,2022,607(3):65−68. [WANG F Y, JIN H Y, DING L F, et al. Research progress on cellulase and its activity enhancement[J]. Modern Rural Science and Technology,2022,607(3):65−68.] WANG F Y, JIN H Y, DING L F, et al . Research progress on cellulase and its activity enhancement[J]. Modern Rural Science and Technology,2022 ,607 (3 ):65 −68 .[47] 缪凤, 王俊懿, 朱海燕. 外源纤维素酶对江华苦茶红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(17):38−46. [MIAO F, WANG J Y, ZHU H Y. Effects of exogenous cellulase on the quality of black tea of Jianghua-Kucha[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(17):38−46.] MIAO F, WANG J Y, ZHU H Y . Effects of exogenous cellulase on the quality of black tea of Jianghua-Kucha[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (17 ):38 −46 .[48] 汪珈慧, 李燕, 姚紫涵, 等. 利用固定化纤维素酶酶解夏季绿茶工艺的研究[J]. 茶叶科学,2012,32(1):37−43. [WANG J H, LI Y, YAO Z H, et al. Study on the influence of immobilized cellulase on the summer tea extract[J]. Tea Science,2012,32(1):37−43.] WANG J H, LI Y, YAO Z H, et al . Study on the influence of immobilized cellulase on the summer tea extract[J]. Tea Science,2012 ,32 (1 ):37 −43 .[49] GLIGOR O, MOCAN A, MOLDOVAN C, et al. Enzyme-assisted extractions of polyphenols-a comprehensive review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,88:302−315.
[50] SUPRIYADI S, NARESWARI A, FITRIANI A, et al. Enhancement of black tea aroma by adding the β-glucosidase enzyme during fermentation on black tea processing[J]. International Journal of Food Science,2021,2021:1−9.
[51] MÓL P C G, JÚNIOR J C Q, VERÍSSIMO L A A, et al. β-Glucosidase:An overview on immobilization and some aspects of structure, function, applications and cost[J]. Process Biochemistry,2023,130:26−39. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2023.03.035
[52] 程谦伟, 林颖凤, 杨菊, 等. 蛋白酶对茶汤中游离氨基酸含量的影响[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(11):100−102. [CHENG Q W, LIN Y F, YANG J, et al. Effect of protease on the content of free amino acids in tea[J]. Food Industry,2021,42(11):100−102.] CHENG Q W, LIN Y F, YANG J, et al . Effect of protease on the content of free amino acids in tea[J]. Food Industry,2021 ,42 (11 ):100 −102 .[53] 钟艳梅, 曾宪录, 郑清梅, 等. 利用木瓜蛋白酶和 α-淀粉酶澄清红茶茶汤的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(12):83−87. [ZHONG Y M, ZENG X L, ZHENG Q M, et al. Research on the clarification of black tea soup with papain and α-amylase[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(12):83−87.] ZHONG Y M, ZENG X L, ZHENG Q M, et al . Research on the clarification of black tea soup with papain and α-amylase[J]. Food Research and Development,2017 ,38 (12 ):83 −87 .[54] RABBANI G, AHMAD E, AHMAD A, et al. Structural features, temperature adaptation and industrial applications of microbial lipases from psychrophilic, mesophilic and thermophilic origins[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,225:822−839. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.146
[55] LI Y C, HE C, YU X L, et al. Study on improving aroma quality of summer-autumn black tea by red-light irradiation during withering[J]. LWT,2022,154:0023−6438.
[56] 罗晶晶, 王登良, 魏青. 外源酶对英红九号红茶品质的影响研究[J]. 广东农业科学,2015,42(4):9−13. [LUO J J, WANG D L, WEI Q. Effects of exogenous enzymes on quality of Yinghong No. 9 black tea[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Science,2015,42(4):9−13.] LUO J J, WANG D L, WEI Q . Effects of exogenous enzymes on quality of Yinghong No. 9 black tea[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Science,2015 ,42 (4 ):9 −13 .[57] CHIANG S H, YANG K M, WANG S Y, et al. Enzymatic treatment in black tea manufacturing processing:Impact on bioactive compounds, quality, and bioactivities of black tea[J]. LWT,2022,163:0023−6438.
[58] ANGAYARKANNI J, PALANISWAMY M, MURUGESAN S, et al. Improvement of tea leaves fermentation with aspergillus spp. pectinase[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2002,94(4):299−303. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80167-0
[59] 叶飞, 高士伟, 郑鹏程, 等. 利用砂梨多酚氧化酶减少夏秋红茶苦涩味研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2012,51(24):5685−5689,5699. [YE F, GAO S W, ZHENG P C, et al. Bitterness and astringency in summer and autumn black tea decreased by exogenous polyphenol oxidase[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science,2012,51(24):5685−5689,5699.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2012.24.038 YE F, GAO S W, ZHENG P C, et al . Bitterness and astringency in summer and autumn black tea decreased by exogenous polyphenol oxidase[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science,2012 ,51 (24 ):5685 −5689,5699 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2012.24.038[60] 叶飞, 高士伟, 龚自明, 等. 不同品种砂梨多酚氧化酶改善夏暑宜红茶的理化品质[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(5):231−237,251. [YE F, GAO S W, GONG Z M, et al. Improvement of Yihong black tea in summer by polyphenol oxidase from different Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020,36(5):231−237,251.] YE F, GAO S W, GONG Z M, et al . Improvement of Yihong black tea in summer by polyphenol oxidase from different Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020 ,36 (5 ):231 −237,251 .[61] 林世锋, 杜可兴, 邬开模. 利用葡萄糖苷酶促发酵制作葛叶红茶的工艺研究[J]. 农家致富顾问,2016,1(10):75. [LIN S F, DU K X, WU K M. Study on the technology of using glucoside enzymatic fermentation to produce Pueraria leaf black tea[J]. Rural Wealth Consultant,2016,1(10):75.] LIN S F, DU K X, WU K M . Study on the technology of using glucoside enzymatic fermentation to produce Pueraria leaf black tea[J]. Rural Wealth Consultant,2016 ,1 (10 ):75 .[62] 仝佳音, 杨毅坚, 杨方慧, 等. 添加多酚氧化酶和纤维素酶对大叶种红茶品质的影响[J]. 陕西农业科学,2020,66(5):50−53. [TONG J Y, YANG Y J, YANG F H, et al. The effect of adding polyphenol oxidase and cellulase on the quality of large leaf black tea[J]. Shaanxi Agricultural Science,2020,66(5):50−53.] TONG J Y, YANG Y J, YANG F H, et al . The effect of adding polyphenol oxidase and cellulase on the quality of large leaf black tea[J]. Shaanxi Agricultural Science,2020 ,66 (5 ):50 −53 .[63] 宛晓春. 茶叶生物化学[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2003. [WAN X C. Biochemistry of tea[M]. Beijing:China Agricultural Publishing House, 2003.] WAN X C. Biochemistry of tea[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2003.
[64] 薛金金, 尹鹏, 张建勇, 等. 植物源多酚氧化酶氧化儿茶素形成茶黄素和聚酯型儿茶素的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(20):76−81. [XUE J J, YIN P, ZHANG J Y, et al. Screening of plant-derived polyphenol oxidase for the formation of theaflavins and theasinensins from the oxidation of catechins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(20):76−81.] XUE J J, YIN P, ZHANG J Y, et al . Screening of plant-derived polyphenol oxidase for the formation of theaflavins and theasinensins from the oxidation of catechins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019 ,40 (20 ):76 −81 .[65] 王坤波, 刘仲华, 赵淑娟, 等. 梨多酚氧化酶同工酶组成及其对茶黄素合成的影响[J]. 湖南农业大学学报,2007,173(4):459−462. [WANG K B, LIU Z H, ZHAO S J, et al. The effect of PPO isoenzyme on the formation of theaflavin during in vitro oxidation[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University,2007,173(4):459−462.] WANG K B, LIU Z H, ZHAO S J, et al . The effect of PPO isoenzyme on the formation of theaflavin during in vitro oxidation[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University,2007 ,173 (4 ):459 −462 .[66] 徐洪梅. 梨多酚氧化酶生物催化合成茶黄素及其在茶叶深加工中的应用研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学, 2013. [XU H M. Study on the pear polyphenol oxidase biocatalytic synthesis of theaflavins and the application in the tea extraction[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University of Technology, 2013.] XU H M. Study on the pear polyphenol oxidase biocatalytic synthesis of theaflavins and the application in the tea extraction[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2013.
[67] XIA G, LIN C, LIU S. Tannase-mediated biotransformation assisted separation and purification of theaflavin and epigallocatechin by highspeed counter current chromatography and preparative high performance liquid chromatography:A comparative study[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique,2016,79(9):880−889. doi: 10.1002/jemt.22715
[68] 李洁媛, 李东, 童凯, 等. 马铃薯多酚氧化酶的分离纯化、酶学性质及酶促合成茶黄素性能研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(11):26−31. [LI J Y, LI D, TONG K, et al. Enzymatic properties of purified polyphenol oxidase from potato and its ability to enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(11):26−31.] LI J Y, LI D, TONG K, et al . Enzymatic properties of purified polyphenol oxidase from potato and its ability to enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021 ,47 (11 ):26 −31 .[69] YABUKI C, YAGI K, NANJO F. Highly efficient synthesis of theaflavins by tyrosinase from mushroom and its application to theaflavin related compounds[J]. Process Biochemistry,2017,55(4):61−69.
[70] LI D, DONG L, LI J, et al. Optimization of enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins from potato polyphenol oxidase[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering,2022,45:1047−1055. doi: 10.1007/s00449-022-02723-x
[71] KUMAR C S, SUBRAMANIAN R, RAO L J. Application of enzymes in the production of RTD black tea beverages:A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science & Nutrition,2013,53(2):180−197.
[72] CHANDINI S K, RAO L J, GOWTHAMAN M K, et al. Enzymatic treatment to improve the quality of black tea extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,127(3):1039−1045. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.078
[73] 刘政权. 多酚氧化酶体外氧化技术优化速溶红茶品质的工艺研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2012. [LIU Z Q. Studies on the technology to optimize the quality of instant black tea by in-vitro oxidation with polyphenol oxidase[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012.] LIU Z Q. Studies on the technology to optimize the quality of instant black tea by in-vitro oxidation with polyphenol oxidase[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012.
[74] 钟艳梅, 郑清梅, 曾宪录, 等. 外源过氧化氢酶对液态发酵红茶色素的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(3):256−260. [ZHONG Y M, ZHENG Q M, ZENG X L, et al. Effect of exogenous catalase on the pigment composition of fermented instant black tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(3):256−260.] ZHONG Y M, ZHENG Q M, ZENG X L, et al . Effect of exogenous catalase on the pigment composition of fermented instant black tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016 ,37 (3 ):256 −260 .[75] KONG J, YANG X, ZUO X, et al. High-quality instant black tea manufactured using fresh tea leaves by two-stage submerged enzymatic processing[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(3):676−685. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.025
[76] 饶建平. 固定化单宁酶澄清茶汤工艺条件的研究[J]. 茶叶学报,2018,59(1):53−56. [RAO J P. Study on the technology of tea infusion clarification using immobilizing tannase[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2018,59(1):53−56.] RAO J P . Study on the technology of tea infusion clarification using immobilizing tannase[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2018 ,59 (1 ):53 −56 .[77] 李梦迪. 黑曲霉单宁酶TahA在茶饮料品质提升中的作用[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2018. [LI M D. Quality improvement of tea beverages with tannase TahA from Aspergillus niger[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.] LI M D. Quality improvement of tea beverages with tannase TahA from Aspergillus niger[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[78] 杨军. 酶解技术改善绿茶浓缩液品质的研究[D]. 厦门:集美大学, 2018. [YANG J. Study of improving the quality of green tea concentrate by enzymatic technology[D]. Xiamen:Jimei University, 2018.] YANG J. Study of improving the quality of green tea concentrate by enzymatic technology[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2018.
[79] FAUSTINA D R, GUNADI R, FITRIANI A, et al. Alteration of phenolic and volatile compounds of tea leaf extract by tyrosinase and β-glucosidase during preparation of ready-to-drink tea on farm[J]. International Journal of Food Science,2022,2022:1977762.
[80] 廖凯. 超声-酶法对红茶饮料风味品质的影响[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017. [LIAO K. Effect of ultrasound-enzyme technology on the flavor of black tea beverages[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2017.] LIAO K. Effect of ultrasound-enzyme technology on the flavor of black tea beverages[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



