Development of a Multi-Dimensional Integrated Training System for First-Class Food Talents Construction and Implementation—Taking Food Science and Engineering Specialty of Chengdu University as an Example
-
摘要: 近年来,我国食品产业发展迅速加快,对食品人才的质量提出了更高的需求。本文立足于习近平新时代中国特色社会主义思想,论述了一流食品人才多维度融合培养体系构建的必要性;指出高校是人才培育的主载体,从德育与智育融合、学科与专业融合、科研与教学融合,探索“德育与智育、学科与专业、产业与专业”等多维度融合育人体系的构建方法和途径。通过党建引领课程思政,协同培育立德树人;学科专业齐头发展,教学科研共助学生培养;优化课程资源配置,助力学生多元发展,回答“培养什么人?”、“如何培养人?”,以期为食品产业的发展提供强有力的人才资源支撑。Abstract: China's food industry has witnessed rapid and accelerated development in recent years, which poses higher demands on the quality of food talents. Drawing on Xi Jinping's Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, this paper argues for the necessity of constructing a multi-dimensional integration cultivation system for first-class food talents. It also points out that universities, as the main carriers of talent cultivation, should explore the methods and approaches of constructing such a system by integrating moral and intellectual education, discipline and specialty, scientific research and teaching, and industry and specialty. To cultivate talents with moral integrity through party building and ideological and political education in curriculum, to foster students' professional growth through the coordinated development of discipline and specialty and the mutual assistance of teaching and scientific research, and to enhance students' diversified development through the optimization of curriculum resource allocation. By doing so, this paper addresses the questions of "what kind of people to cultivate?" and "how to cultivate?", aiming to provide a strong talent resource support for the development of food industry.
-
Keywords:
- food talent /
- multi-dimensional fusion /
- training system /
- industrial development
-
习近平总书记在全国教育大会上指出,“要提升教育服务经济社会发展能力”、“推进产学研协同创新,积极投身实施创新驱动发展战略,着重培养创新型、复合型、应用型人才”[1]。创新型、复合型、应用型人才的主要特点就是指在多个维度和领域都表现突出又相互融合,兼具领导型、创新型和专家型人才特性的人才,是企业和社会发展最需要的人才[2−5]。
食品产业是健康产业、民生产业;是国民经济支柱产业[6−7];是推动实施乡村振兴战略、提升产业竞争力、促进区域经济发展的重要抓手[8−9]。因此,新时代需要高质量发展食品产业,以满足人民日益增长的对美好生活的需求、保障粮食安全,以及“逐步形成以国内大循环为主体、国内国外双循环相互促进的新发展格局”的需要。人才是第一生产力,一流食品人才作为食品产业发展的动力引擎,是支撑食品制造、食品创造的重要力量[10−13],是联接技术创新与生产实践最核心、最基础的劳动要素[14−17]。高校作为育人的摇篮,肩负着“为党育人,为国育才”的使命,应与时俱进,创新人才培养模式,切实培养契合时代发展需要的人才。成都大学食品科学与工程专业以培养服务四川省万亿食品产业技术需求国内一流专业人才为培养目标,构建“德育与智育、学科与专业、产业与专业”多维度融合的人才培养体系,培养一流食品专业人才,以期为食品产业的发展提供强有力的人才资源支撑。
1. 一流食品人才多维度融合培养体系构建的必要性
1.1 食品产业高质量发展,亟需培养大量一流食品专业人才支撑产业发展
食品产业是国民经济和社会发展的基础性、民生性产业,也是四川重要的支柱优势产业[18−20]。2018年四川省“5+1”现代产业体系部署中,“食品饮料”产业成为5个万亿级支柱产业之一。同时,成都市“5+5+1”重点产业领域中“绿色食品”被列入5大重点产业中,2020年达到千亿级。2022年四川省食品生产经营主体达140万户,规模以上食品工业企业2410家,营业收入占四川工业的16.8%,产业规模居全国前列[21−24]。随着国家科技迅猛发展,食品产业的发展也呈现出多元化、综合性和国际化的发展特征,逐渐向着智能化、数字化、科技化的现代化方向发展[25−27]。食品产业的智能化、数字化、科技化高质量发展,必然亟需一流食品专业人才。
然而,受制于经济发展的限制,在食品领域人才培养和引进上,位于西部的四川省长期处于劣势。食品加工位列成都紧缺人才岗位中,高层次技术人才不到实际需求的20%,人才培养与产业发展呈现巨大反差,未来10年食品人才缺口预计高达10万人以上。同时,食品从业人员的职业素养偏低,30%员工团队合作能力低,自我中心意识严重,20%的员工缺乏吃苦耐劳的精神品质[28−30]。随着四川省乃至全国食品产业高速发展,食品产业相关领域应用型人才短缺问题将日益凸显。这就亟需高校创新食品专业人才培养模式,以培养一流的食品专业人才,从而为食品产业的良性、持续发展提供可靠、充足的优质人力资源保障[31−34]。
1.2 高校是人才培育的主载体,多维度融合育人体系是培养一流食品专业人才的有效途径之一
党的二十大报告指出,教育、科技、人才是全面建设社会主义现代化国家的基础性、战略性支撑[35−38]。教育是基础,科技是关键,人才是根本。高校作为原始创新的主渠道和创新人才培养的主阵地,必须想国家之所想、急国家之所急,在卓越人才培养和科技创新方面主动作为,肩负起助力地方产业发展的主体大任。据统计,四川省10余所高校,每年食品本科毕业生1500人左右、硕士毕业生500人左右,是我省食品人才主要的培育载体[39−41]。在国家统筹推进“世界一流大学”、“一流学科建设”、“一流专业建设”战略指导下,高校需发挥自身学科优势,促进特色专业建设,培养食品一流人才,促进和引领食品产业发展,在强国建设和乡村振兴战略中承担起国家和时代赋予的历史重任[42−45]。
产业是人才发展的基石,人才的厚度决定产业的高度。食品产业高质量发展需要的是综合素质优良、知识面广、具备多学科知识背景、能够适应市场多变局面的通用型、创新型一流食品人才[46−48]。面对食品产业对食品人才质量的新要求,高校人才育人模式将面临重大挑战。只有创新育人体系,加强德智、学科专业、科研教学等多维度融合以多层面、多角度、多方位、多形式地协同育人,才是培养德才兼备的一流食品专业人才的有效途径之一[49−54]。
2. 多维度融合育人体系构建方法与途径
成都大学食品科学与工程专业以培养具有社会责任感、良好的人文素养、扎实的专业基础、过硬的实践能力、突出的创新精神和创业能力“五位一体”的一流食品人才为目标,针对培养方案、课程设置、师资队伍建设、实践基地(平台)建设等环节存在的不足,融合学科优势,依托一流专业,一流师资领航,构建“德育与智育、学科与专业、产业与专业”多维度融合的人才培养体系,切实落实立德树人的人才培养根本任务,突出培养特色、提升培养内涵,实现科教互为促进协同发展,培养学生创新创业能力,解决专业设置与地方产业需求脱节、专业同质化、工程实践能力弱化等难题[6]。
2.1 德育与智育融合,立德树人,以本为本
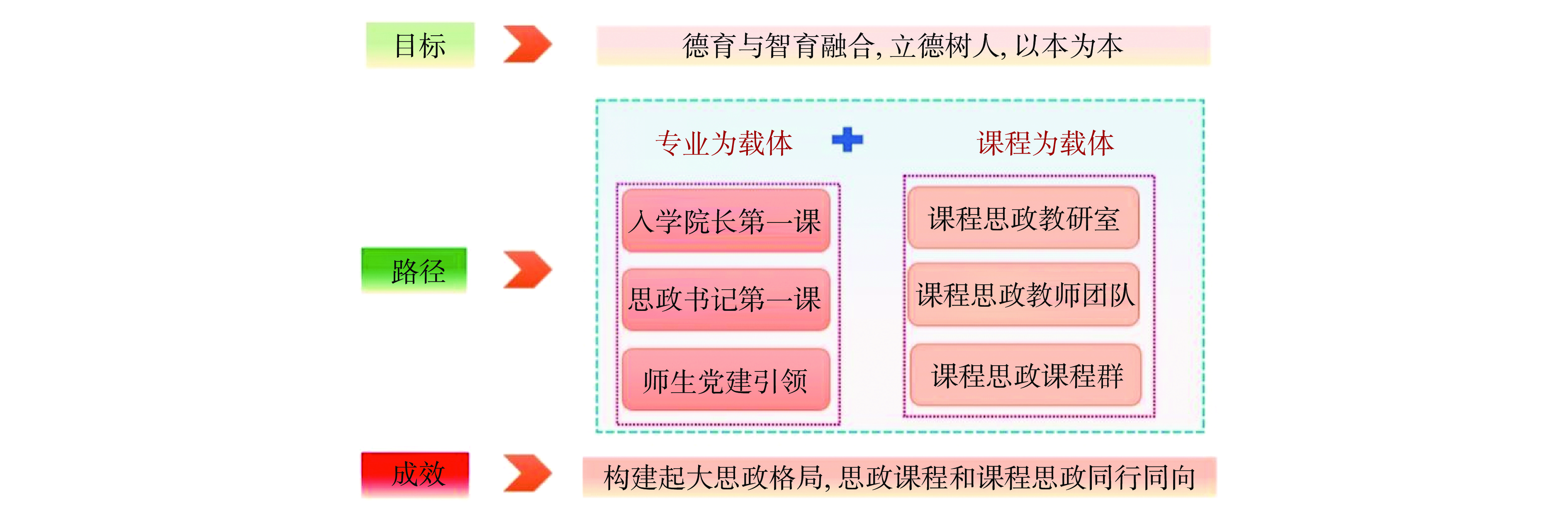
党的二十大报告指出:教育是国之大计、党之大计。培养什么人、怎样培养人、为谁培养人是教育的根本问题。育人的根本在于立德。立德树人是高校办学治校的根本任务[55−60]。成都大学食品科学与工程专业将思政教育贯穿人才培养全过程,全面落实到质量标准、课程教学、实践活动和文化育人中,形成“大思政”育人格局(图1)。一是以专业为载体,发掘专业特点和优势。开展入学第一课、思政第一课、教师党建、学生党建等主题活动,实现专业教育与思想政治教育一体化建设与发展。二是以课程为载体,寓德育于课程。专门成立“课程思政教研室”,建立“课程思政教学团队”,打造“课程思政群”,将思想价值融入知识体系,着力打造课程思政示范课,培养课程思政优秀教师。
2.2 学科与专业融合,突出培养特色,提升培养内涵
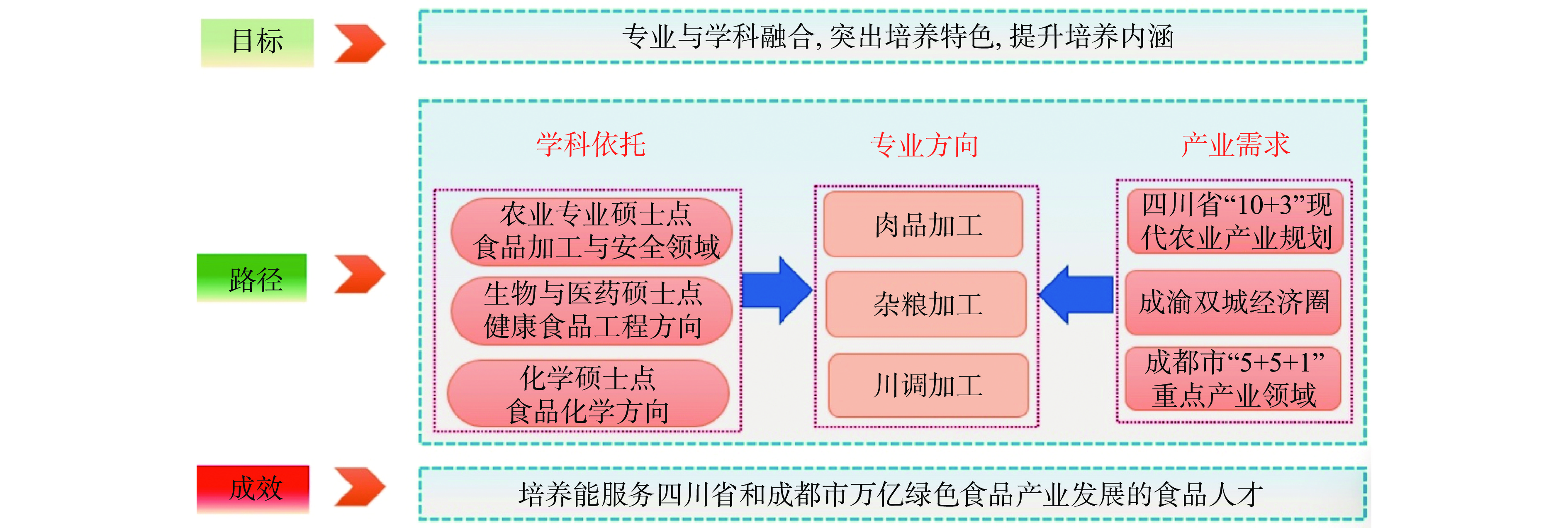
学科建设是专业持续发展的基础,专业则是学科建设的根本依托,更是检验人才培养水平的根本标准[61−63]。将学科与专业融合,学科和专业并重,两者平衡发展,相互促进、协同发展,在融合中形成学科品牌和优势,打造人才培养的优势与特色。成都大学食品科学与工程专业由化学一级学科、农业硕士专业食品质量安全领域、生物与医药专业硕士健康食品工程方向提供全面学科支撑。依托学科优势将专业建设与学科发展相融合,注重学科建设与专业发展之间的平衡(图2)。
一是专业办学强化学科支撑。主动适应食品学科新技术、新产业、新经济发展,紧扣省市食品产业发展需要,凝练人才培养目标和专业特色,以服务四川省和成都市万亿绿色食品产业高新技术创新需求为宗旨,逐渐形成肉品加工、川菜调味品和杂粮加工为特色的专业发展方向。二是以产业需求为引领,打造一流专业。以产业科技、人才需求,建设食品科学与工程国家一流本科专业,开展中国工程教育专业再认证。三是发挥学科优势,培养拔尖人才。本专业于2021年开设张澜学院拔尖人才-“食品基地班”,实施“准研究生”培养机制,为学院研究生人才培养提供优质生源和人才储备。四是依托学科优势,优化课程体系设置。优化各类课程比重结构,优化课程内容、更新教学大纲,更好地体现学科特点、学科发展方向和学科优势,凸显食品专业特色。
2.3 科研与教学融合,实现科教互为促进协同发展
人才培养和科学研究是高校的两大基本功能。在科研与教学的关系上,科研是源,教学是流。高校从单纯教学转向科教并重是历史的必然选择。科教融合,不仅是构筑新工学的飞跃进步,也是产业与教育合并的催化剂。科研与教学彼此融合,互为促进,协同发展,才能充分发挥培育“高素质、创造性”人才的主战场作用。强化科研与教学融合,以实现科教相互促进协同育人。一是用最优秀的人培养更优秀的人。要求教授100%给本科生授课,推动资深教授讲授专业基础课程和核心课程。二是科研成果及时转化为教学内容。开设反映学科发展前沿和新兴方向的课程,将学术训练融进专业培养方案和课程体系。新增设置课程《食品科学导论》,邀请相关教授专家,以最新的科学前沿成果作为课程教学内容主题,激发学生专业学习兴趣。三是科学研究方法转化为教学手段。以已建立的省级虚拟仿真实验教学中心为基础,开设《食品工厂设计》、《发酵工程》等虚拟仿真实践项目,激发学生科学探索兴趣。四是建立学生参与科研训练项目制度。实施本科生全程导师制,进入教师科研团队,不断提高毕业论文与综合训练的质量。
3. 多维度融合育人体系实践成效
3.1 党建引领课程思政,协同培育立德树人
以党建引领为抓手,将学生党员与学术导师教师党员组建成师生融合党支部。党员教师围绕“培养什么人、怎样培养人、为谁培养人”这一根本问题,以党建“反哺”育人,提升育人实效,让学生远方有灯、脚下有路、眼前有光。师生党支部紧密围绕在新时代打造更高水平的“天府粮仓”积极工作,积极发展绿色农业、生态农业和高效农业,牢固树立落实新发展理念,为推进成都大学农业学科的持续快速发展提供了坚强的政治保证。落实成都大学“扎根成都、面向世界、服务社会”的服务定位,秉持“党建+业务”的工作理念,创建了“党建+科技+人才”协同助力乡村振兴党建工作品牌。
食品科学与工程专业于2019年设立课程思政研究室。2020年组建起一支由21位专任教师组成的食品科学与工程课程思政教学团队,团队中国家农业产业体系四川创新团队岗位专家4人、省学术与技术带头人及后备人选3人、省教学名师1人,“双师型”教师占专任教师比达90%。2020年开始,教学团队着力打造特色专业课程思政群,将“大食品观”、“粮食安全”、“食品安全”、“抗疫精神”、“大国工匠精神”、“饮食文化自信”等思政元素融入《食品保藏原理》、《畜产品加工学》、《微生物学》等8门专业课程,取得显著成效。该教学团队于2022年入选四川省“食品科学与工程”课程思政示范教学团队,打造的课程思政群8门课程中,4门课程入选省级一流课程、2门入选校级一流课程,2门入选校级“课程思政”。课程思政研究室承担校级“课程思政”教改项目2项,荣获四川省教学成果奖二等奖1项。食品科学与工程专业已形成思政课程和课程思政同向同行的大思政格局,思政课程和课程思政同频共振。
3.2 学科专业齐头发展,教学科研共助学生培养
食品科学与工程专业根植农业硕士专业食品质量安全领域、生物与医药专业硕士健康食品工程方向和化学一级学科硕士点,不断凝练专业人才培养方向,学生科创训练、学科竞赛、生产实习主要集中在肉品、川味调味品、杂粮三个领域,逐渐形成以肉品加工、川味调味品开发、杂粮营养食品开发三个特色鲜明的人才培养方向,学生就业也主要集中在三个领域的企事业单位,人才培养特色凸显。
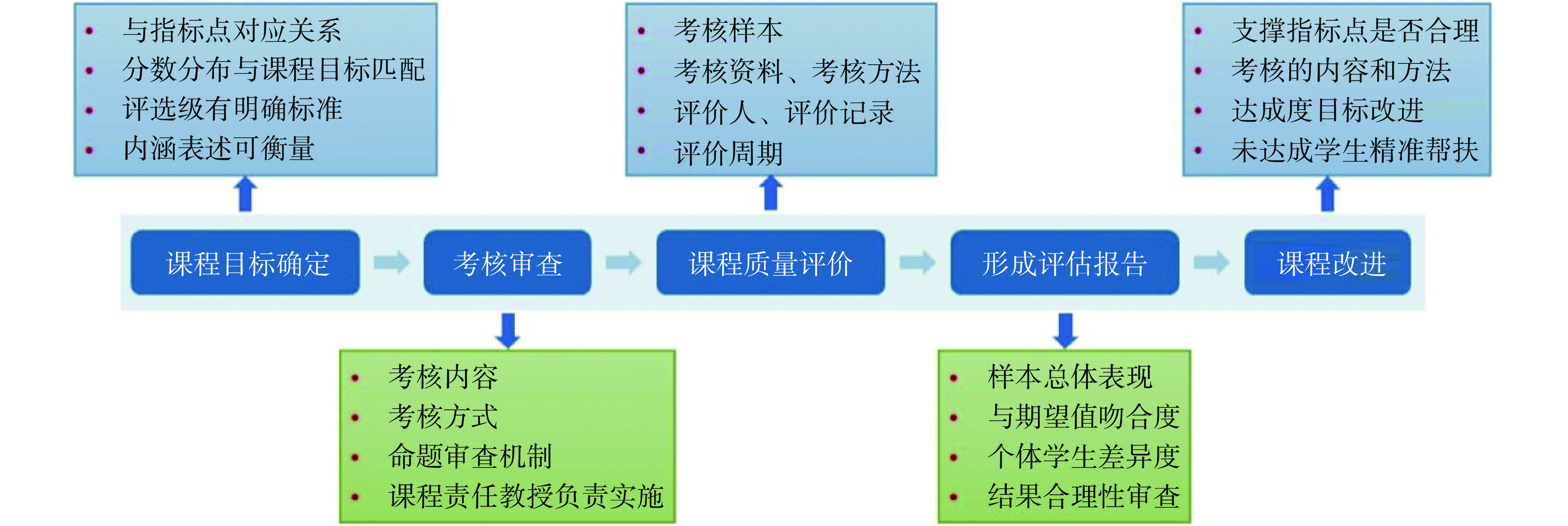
2016年率先在西南地区同类专业通过中国工程教育专业认证,并持续改进,先后制定(修订)《成都大学食品与生物工程学院基于产出导向的课程评价办法(修订版)》、《成都大学关于完善产出导向教学评价机制的实施办法》等课程目标达成评价办法。现已经构建起从培养方案、教学大纲、课程教学、实习实践、毕业设计、课程考核、教学督导、教学质量评价的全链条课程目标达成评价机制(图3),持续改进本专业课程目标达成评价机制。
学科优势反哺学生科学素养培养。通过实施专业导师制,在优秀导师的引领下,近5年,约250名学生参与科创活动,师生协作荣获省级科技进步奖一等奖3项、二等奖8项,承担国家自然科学基金35项(其中面上8项);学生发表高水平学术论文13篇,承担大学生科创项目国家级18项、省级42项,荣获学科竞赛国家级36项、省级108项。2022年本科生考取研究生率57.33%,就业率94.67%。
通过学科专业融合,学科专业并重,两者平衡发展,相互促进、协同发展,学科专业齐头发展。2021年食品科学与工程专业入选国家一流本科专业建设点,2023年本学科泰晤士学科评级B级,位列全国第16位,为西南各省同类学科唯一上榜学科。
3.3 优化课程资源配置,助力学生多元发展
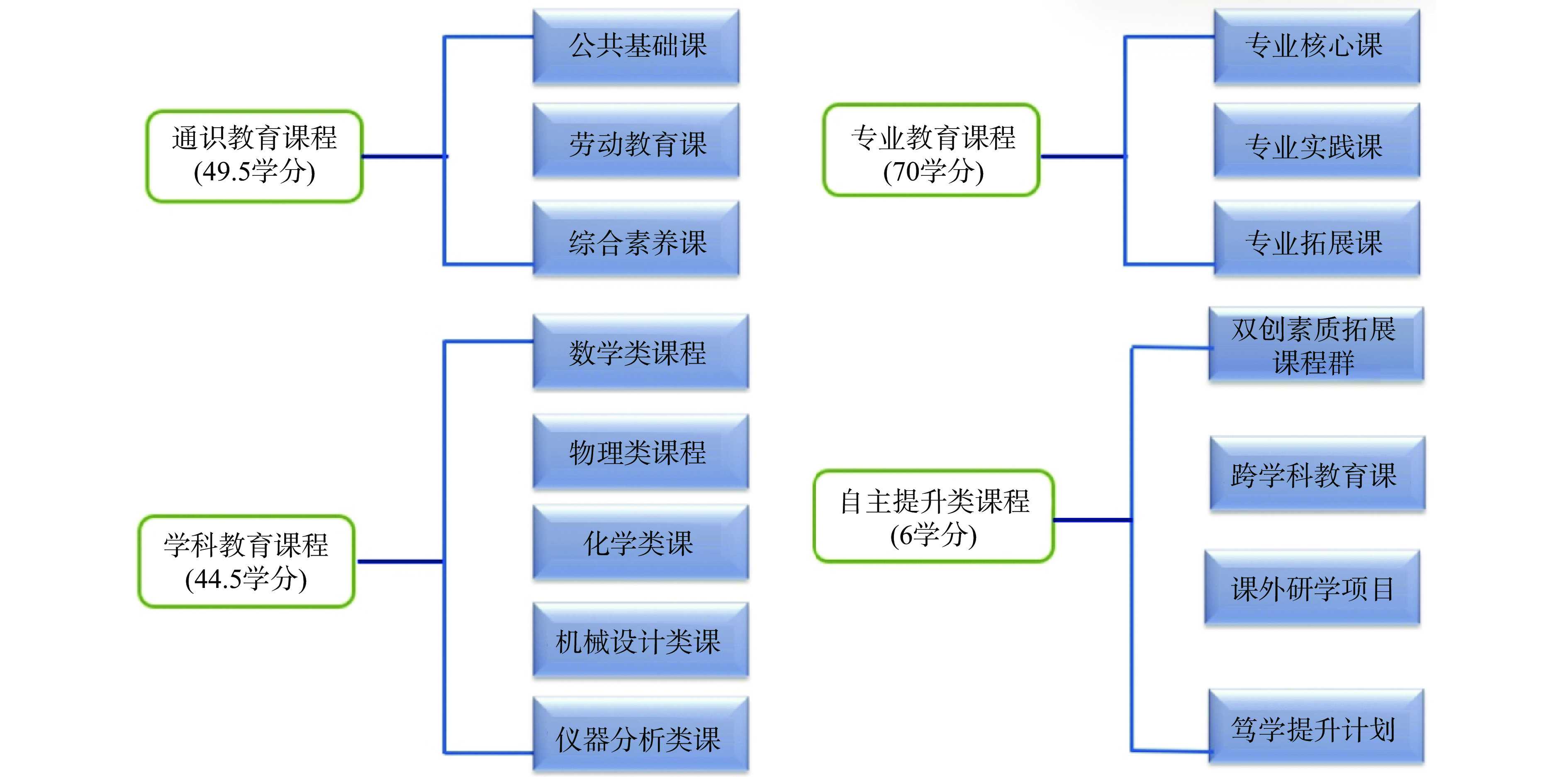
课堂教学是人才培养的主渠道、主阵地,课程体系是课堂教学的关键依托。按照通识、基础、核心、提升四大类,不断完善第一课堂的课程体系(图4)。数学与自然科学类课程学分占比19.1%,工程基础类课程、专业基础课程与专业类课程学分占比31.8%,工程实践与毕业设计学分占比31.8%,人文社会科学类通识教育课程学分占比19.1%。同时,着力补足体育、美育和劳动教育的课程设计,开设了劳动教育、创新创业课程、跨学科教育课、课外研学项目、笃学提升计划等自主发展类课程,五育并举提升学生综合素质素养。
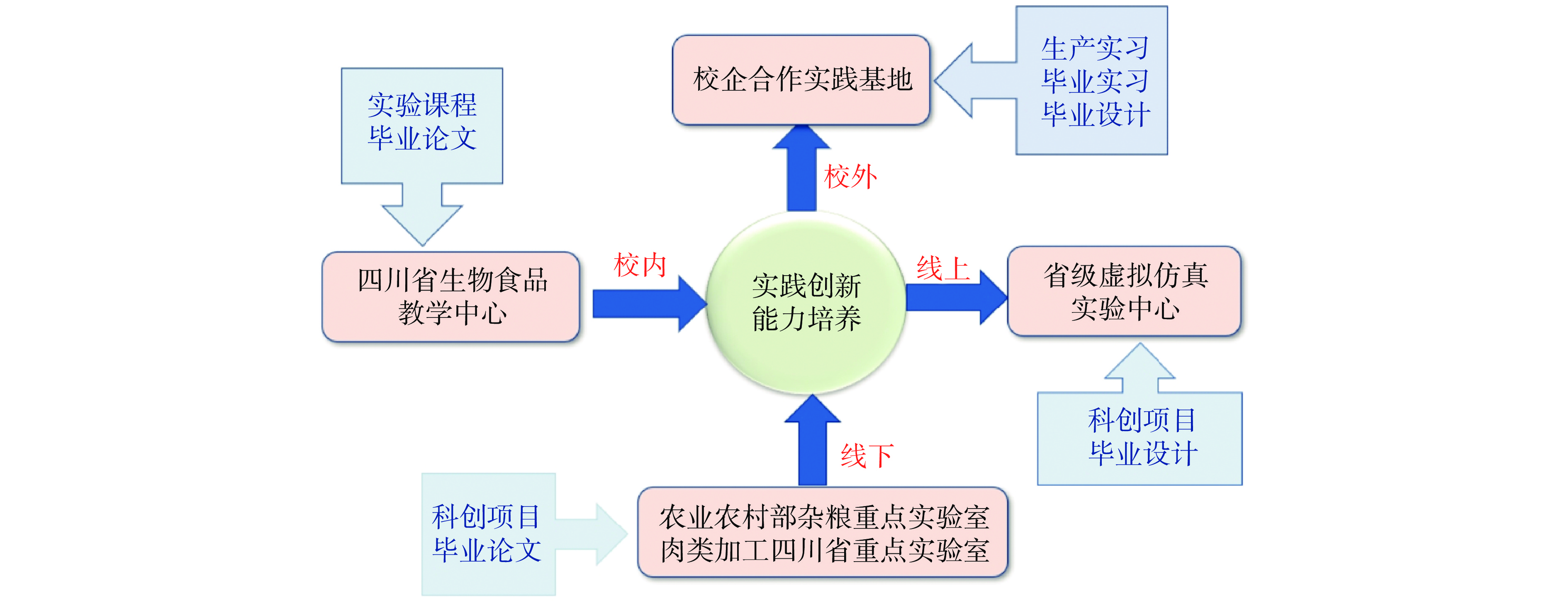
同时,不断优化整合科研和教学实验实训平台资源(图5),建立25个校外实践教学基地,其中肉品加工实践基地荣获2021年四川省大学生校外实践基地;建设37个虚拟仿真线上课程(项目),其中国家级虚拟仿真项目1项、省级虚拟仿真项目1项、省级虚拟仿真一流课程2门。通过校外校内,线上线下的科研和教学实验实训课程的优化配置,实践课程的科学性、完备性和竞争性显著增强。通过优化课程资源配置,在主抓专业核心能力培养时,同时兼顾学生多元化能力培养,学生考研深造专业、毕业就业领域也呈现出多样化。
4. 结论
建立有利于一流食品人才培养的教育体系,是一项系统建设工程。成都大学食品科学与工程专业致力于构建“德育与智育、学科与专业、产业与专业”等多维度融合的一流食品专业人才培养体系。经过8年的实践,本专业在专业内涵建设、人才培养、产业服务等方面取得显著成效:2021年获批国家一流本科专业建设点,尤其以肉品、杂粮和调味品加工为专业特色;专业点支撑的工程、农业、化学学科均进入全球ESI前1%。2023年泰晤士评级食品科学与工程学科B级,系西南各省唯一上榜学科,位列全国第16位;专业建有《食品保藏原理》等14门省级质量课程;拥有一支省级“食品科学与工程”课程思政示范教学团队;2023年荣获国家教学成果奖二等奖1项,2022年获四川省教学成果奖二等奖2项。2020~2022年专业学生考取研究生率连续三年50%以上,就业率95%以上,毕业生受到用人单位的高度认可。“德育与智育、学科与专业、产业与专业”等多维度融合的一流食品专业人才培养体系模式充分彰显了“德育为首,育人为本,育人成才”的育人理念,高度契合了食品产业的现代化发展,可为产业的发展提供强有力的人才资源支撑。
-
-
[1] 成尚荣. 新时代中国特色社会主义教育改革发展的纲领——学习习近平在全国教育大会上重要讲话的体会[J]. 中国教师,2019(4):5−10. [CHENG Shangrong. Program for the reform and development of socialist education with Chinese characteristics in the new era:Learning from Xi Jinping's important speech at the national education conference[J]. China Teachers,2019(4):5−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2051.2019.04.002 CHENG Shangrong . Program for the reform and development of socialist education with Chinese characteristics in the new era: Learning from Xi Jinping's important speech at the national education conference[J]. China Teachers,2019 (4 ):5 −10 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2051.2019.04.002[2] 郑纳. 道理、学理、哲理、原理:新时期高校人才培养供给侧改革的多重逻辑[J]. 教育理论与实践,2023,43(9):3−8. [ZHENG Na. Reason, theory, philosophy and principle:Multiple logic of supply-side reform of college talent training in the new era[J]. Education Theory & Practice,2023,43(9):3−8. ZHENG Na . Reason, theory, philosophy and principle: Multiple logic of supply-side reform of college talent training in the new era[J]. Education Theory & Practice,2023 ,43 (9 ):3 −8 .[3] 袁丰. 高校人才培养与企业需求有效对接探析[J]. 哈尔滨职业技术学院学报,2023(2):89−91. [YUAN Feng. Analysis on the effective connection between talent training and enterprise demand in colleges and universities[J]. Journal of Harbin Vocational and Technical College,2023(2):89−91. doi: 10.16145/j.cnki.cn23-1531/z.2023.02.027 YUAN Feng . Analysis on the effective connection between talent training and enterprise demand in colleges and universities[J]. Journal of Harbin Vocational and Technical College,2023 (2 ):89 −91 . doi: 10.16145/j.cnki.cn23-1531/z.2023.02.027[4] 杨佑琼, 杨科正. 应用型、创新型、复合型人才之辨及培养策略[J]. 教育探索,2022(6):34−37. [YANG Youqiong, YANG Kezheng. Identification and training strategies of application-oriented, innovative and composite talents[J]. Education Exploration,2022(6):34−37. YANG Youqiong, YANG Kezheng . Identification and training strategies of application-oriented, innovative and composite talents[J]. Education Exploration,2022 (6 ):34 −37 .[5] 杨洪英, 陈国宝, 刘承军, 等. “双一流”高校国际化人才培养的逻辑依归、问题表征与应然路向[J]. 现代教育管理,2023(3):47−57. [YANG Hongying, CHEN Guobao, LIU Chengjun, et al. The logical dependence, problem representation and proper direction international talent cultivation for "double first-class" universitie[J]. Modern Education Management,2023(3):47−57. doi: 10.16697/j.1674-5485.2023.03.006 YANG Hongying, CHEN Guobao, LIU Chengjun, et al . The logical dependence, problem representation and proper direction international talent cultivation for "double first-class" universitie[J]. Modern Education Management,2023 (3 ):47 −57 . doi: 10.16697/j.1674-5485.2023.03.006[6] 石谢新. 地方特色食品产业指导意见解读[J]. 中国食品工业,2023(7):19−21. [SHI Xiexin. Interpretation of guiding opinions on local specialty food industry[J]. China Food Industry,2023(7):19−21. SHI Xiexin . Interpretation of guiding opinions on local specialty food industry[J]. China Food Industry,2023 (7 ):19 −21 .[7] 孙宝国, 刘慧琳. 健康食品产业现状与食品工业转型发展[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2023,41(2):1−6. [SUN Baoguo, LIU Huilin. Current situation of healthy food industry and transformation and development of food industry[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2023,41(2):1−6. doi: 10.12301/spxb202300126 SUN Baoguo, LIU Huilin . Current situation of healthy food industry and transformation and development of food industry[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2023 ,41 (2 ):1 −6 . doi: 10.12301/spxb202300126[8] 郑博强, 麻少莹, 李绍波, 等. 乡村振兴背景下食品加工技术人才培养模式创新与实践[J]. 农业研究与应用,2022,35(6):71−76. [ZHENG Boqiang, MA Shaoying, LI Shaobo, et al. Innovation and practice of talent training mode of food processing technology based on transformation and upgrade of rural industries for rural vitalization[J]. Agricultural Research and Application,2022,35(6):71−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2022.06.011 ZHENG Boqiang, MA Shaoying, LI Shaobo, et al . Innovation and practice of talent training mode of food processing technology based on transformation and upgrade of rural industries for rural vitalization[J]. Agricultural Research and Application,2022 ,35 (6 ):71 −76 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0764.2022.06.011[9] 张明明. 壮大食品工业集群 助力乡村振兴[N]. 2021-11-4. [ZHANG Mingming. Expanding food industry clusters to help rural revitalization[N]. 2021-11-4. ZHANG Mingming. Expanding food industry clusters to help rural revitalization[N]. 2021-11-4.
[10] 高梦祥, 江洪波. 基于农业全产业链的食品类专业人才培养[J]. 食品工业,2023,44(1):255−258. [GAO Mengxiang, JIANG Hongbo. The cultivation of innovative talents in food science and engineering ba on the whole agricultural industry chain[J]. Food Industry,2023,44(1):255−258. GAO Mengxiang, JIANG Hongbo . The cultivation of innovative talents in food science and engineering ba on the whole agricultural industry chain[J]. Food Industry,2023 ,44 (1 ):255 −258 .[11] 陈碧, 韦巧艳, 周永升, 等. 四位一体培养食品类新工科复合型人才[J]. 食品工业,2023,44(2):190−193. [CHEN Bi, WEI Qiaoyan, ZHOU Yongsheng, et al. Compound talents cultivation mode of food science and engineering specialty based on the quaternity[J]. Food Industry,2023,44(2):190−193. CHEN Bi, WEI Qiaoyan, ZHOU Yongsheng, et al . Compound talents cultivation mode of food science and engineering specialty based on the quaternity[J]. Food Industry,2023 ,44 (2 ):190 −193 .[12] 周婧琦. 高职食品加工技术专业创新型人才培养研究[J]. 中国食品工业,2023(2):108−109,158. [ZHOU Jingqi. Research on the training of innovative talents in higher vocational food processing technology[J]. China Food Industry,2023(2):108−109,158. ZHOU Jingqi . Research on the training of innovative talents in higher vocational food processing technology[J]. China Food Industry,2023 (2 ):108 −109,158 .[13] 佘有缘. 基于应用型人才培养探索食品企业管理的创新举措——评《食品企业管理》[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(2):343−344. [SHE Youyuan. Exploring innovative measures of food enterprise management based on application-oriented talent training——commenting on food enterprise management[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2023,14(2):343−344. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2023.2.spaqzljcjs202302050 SHE Youyuan . Exploring innovative measures of food enterprise management based on application-oriented talent training——commenting on food enterprise management[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2023 ,14 (2 ):343 −344 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2023.2.spaqzljcjs202302050[14] 史振霞, 胡美仙, 闫训友, 等. 地方院校食品科学与工程专业创新型人才培养模式探索[J]. 廊坊师范学院学报(自然科学版),2023,23(1):114−117. [SHI Zhenxia, HU Meixian, YAN Xunyou, et al. Exploration of innovative talents training model for food science and engineering major in local colleges and universities[J]. Journal of Langfang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2023,23(1):114−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3229.2023.01.023 SHI Zhenxia, HU Meixian, YAN Xunyou, et al . Exploration of innovative talents training model for food science and engineering major in local colleges and universities[J]. Journal of Langfang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2023 ,23 (1 ):114 −117 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3229.2023.01.023[15] 沈晓溪, 解慧. 多学科融合食品科学与工程专业人才培养的研究[J]. 科技资讯,2022,20(11):248−250. [SHEN Xiaoxi, XIE Hui. Research on talent training of food science and engineering specialty w multi-disciplinary integration[J]. Science & Technology Information,2022,20(11):248−250. doi: 10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2201-5042-5061 SHEN Xiaoxi, XIE Hui . Research on talent training of food science and engineering specialty w multi-disciplinary integration[J]. Science & Technology Information,2022 ,20 (11 ):248 −250 . doi: 10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2201-5042-5061[16] 李慧芸. OBE背景下食品科学与工程一流专业人才培养模式研究[J]. 农产品加工,2022(20):100−101,105. [LI Huiyun. Research on cultivation mode of first-class professional talents in food science and engineering based on OBE concept[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022(20):100−101,105. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.10.054 LI Huiyun . Research on cultivation mode of first-class professional talents in food science and engineering based on OBE concept[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022 (20 ):100 −101,105 . doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.10.054[17] 黄海, 陈美花, 付满. 食品产业应用型创新人才协同育人平台构建探索与实践[J]. 中国校外教育,2017(18):15−16. [HUANG Hai, CHEN Meihua, FU Man. Exploration and practice of building a collaborative education platform for applied innovative talents in food industry[J]. China Extramural Education,2017(18):15−16. HUANG Hai, CHEN Meihua, FU Man . Exploration and practice of building a collaborative education platform for applied innovative talents in food industry[J]. China Extramural Education,2017 (18 ):15 −16 .[18] SARAIVA A, CARRASCOSA C, RAMOS F, et al. Brazzein and Monellin:Chemical analysis, food industry applications, safety and quality control, nutritional profile and health impacts[J]. Foods,2023,12(10):1943. doi: 10.3390/foods12101943
[19] NYCHAS G J, SIMS E, TSAKANIKAS P, et al. Data science in the food industry[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science,2021,4:341−367. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-020221-123602
[20] LENCUCHA R. Situating food industry influence:Governance norms and economic order comment on "'part of the solution':Food corporation strategies for regulatory capture and legitimacy"[J]. International Journal of Health Policy and Management,2022,11(11):2736−2739.
[21] 舒莉. 四川地区旅游食品产业发展影响因素及趋势分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(22):227−228. [SHU Li. Analysis of influencing factors and trends of tourism food industry development in Sichuan[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(22):227−228. SHU Li . Analysis of influencing factors and trends of tourism food industry development in Sichuan[J]. Food Research and Development,2022 ,43 (22 ):227 −228 .[22] 李杨. 新常态下基于SWOT模型的四川食品饮料工业发展对策探索[J]. 产业与科技论坛,2016,15(4):17−18. [LI Yang. Exploration of countermeasures for the development of Sichuan food and beverage industry based on SWOT model under the new normal[J]. Industry and Technology Forum,2016,15(4):17−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5641.2016.04.008 LI Yang . Exploration of countermeasures for the development of Sichuan food and beverage industry based on SWOT model under the new normal[J]. Industry and Technology Forum,2016 ,15 (4 ):17 −18 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5641.2016.04.008[23] 闫志农. 四川稳步推进绿色食品事业再上新台阶[J]. 农村工作通讯,2015(20):25−26. [YAN Zhinong. Sichuan steadily promotes green food to a new level[J]. Rural Work Newsletter,2015(20):25−26. YAN Zhinong . Sichuan steadily promotes green food to a new level[J]. Rural Work Newsletter,2015 (20 ):25 −26 .[24] 廖梦洁, 孙静, 勾丽明. 中国食品企业环境友好现状分析——以河南、四川与青海三省为例[J]. 再生资源与循环经济,2015,8(1):24−26. [LIAO Mengjie, SUN Jing, GOU Liming. Analysis of environmental friendliness of chinese food enterprises:A case study of Henan, Sichuan and Qinghai Provinces[J]. Renewable Resources and Circular Economy,2015,8(1):24−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0912.2015.01.008 LIAO Mengjie, SUN Jing, GOU Liming . Analysis of environmental friendliness of chinese food enterprises: A case study of Henan, Sichuan and Qinghai Provinces[J]. Renewable Resources and Circular Economy,2015 ,8 (1 ):24 −26 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0912.2015.01.008[25] 魏旭. 二维码防伪溯源的智能化食品包装设计[J]. 丝网印刷,2022(24):46−48. [WEI Xu. Intelligent food packaging design based on QR-code anti-counterfeiti traceability[J]. Screen Printing,2022(24):46−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4867.2022.24.013 WEI Xu . Intelligent food packaging design based on QR-code anti-counterfeiti traceability[J]. Screen Printing,2022 (24 ):46 −48 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4867.2022.24.013[26] 张朝正, 陈婷, 潘登, 等. 冬奥会食品供应链有害因子知识图谱和智能化快筛技术研究[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志,2022,34(5):884−888. [ZHANG Chaozheng, CHEN Ting, PAN Deng, et al. Knowledge map and intelligent rapid screening technology of harmfu factors in food supply chain of Winter Olympics[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2022,34(5):884−888. doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2022.05.004 ZHANG Chaozheng, CHEN Ting, PAN Deng, et al . Knowledge map and intelligent rapid screening technology of harmfu factors in food supply chain of Winter Olympics[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2022 ,34 (5 ):884 −888 . doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2022.05.004[27] 周强, 傅少川. 智能化冷链物流综合防控技术体系研究[J]. 科技管理研究,2020,40(13):196−201. [ZHOU Qiang, FU Shaochuan. Research on intelligent cold chain logistics integrated prevention an control technology system[J]. Science and Technology Management Research,2020,40(13):196−201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7695.2020.13.028 ZHOU Qiang, FU Shaochuan . Research on intelligent cold chain logistics integrated prevention an control technology system[J]. Science and Technology Management Research,2020 ,40 (13 ):196 −201 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7695.2020.13.028[28] 戴小枫, 张德权, 武桐, 等. 中国食品工业发展回顾与展望[J]. 农学学报,2018,8(1):133. [DAI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Dequan, WU Tong, et al. Historical review and future prospect of China's food industry development[J]. Journal of Agronomy,2018,8(1):133. DAI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Dequan, WU Tong, et al . Historical review and future prospect of China's food industry development[J]. Journal of Agronomy,2018 ,8 (1 ):133 .[29] 崔艳, 程鹏, 付荣霞, 等. 产学研合作模式下生物发酵人才培养的探索[J]. 创新教育研究,2022,10(1):11−15. [CUI Yan, CHENG Peng, FU Rongxia, et al. Exploration on the cultivation of biological fermentation talents under the mode of industry-university-research cooperation[J]. Creative Education Studies,2022,10(1):11−15. doi: 10.12677/CES.2022.101003 CUI Yan, CHENG Peng, FU Rongxia, et al . Exploration on the cultivation of biological fermentation talents under the mode of industry-university-research cooperation[J]. Creative Education Studies,2022 ,10 (1 ):11 −15 . doi: 10.12677/CES.2022.101003[30] 陈德, 王剑, 金伟, 等. 国内外餐饮行业从业人员食品安全健康教育研究进展[J]. 健康教育与健康促进,2016,11(6):442−444. [CHEN De, WANG Jian, JIN Wei, et al. Review of domestic and overseas studies of health education concern food safety among catering handles[J]. Health Education and Health Promotion,2016,11(6):442−444. doi: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.201606011 CHEN De, WANG Jian, JIN Wei, et al . Review of domestic and overseas studies of health education concern food safety among catering handles[J]. Health Education and Health Promotion,2016 ,11 (6 ):442 −444 . doi: 10.16117/j.cnki.31-1974/r.201606011[31] DREWNOWSKI A, AMANQUAH D, GAVIN-SMITH B. Perspective:How to develop nutrient profiling models intended for global use:A manual[J]. Advances in Nutrition,2021,12(3):609−620. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab018
[32] PAPADOPOULOS T, ALLENDE A, EGEA J A, et al. Training in tools to develop quantitative risk assessment of fresh produce using water reuse systems in Mediterranean production[J]. Efsa Journal,2022,20(Suppl 1):e200416.
[33] MOHAMMED A, POTDAR V, QUADDUS M. Exploring factors and impact of blockchain technology in the food supply chains:An exploratory study[J]. Foods,2023,12(10):2052. doi: 10.3390/foods12102052
[34] MOUSAVI KHANEGHAH A, NEMATOLLAHI A, ABDIMOGHADAM Z, et al. Research progress in the application of emerging technology for reducing food allergens as a global health concern:A systematic review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,26:1−16.
[35] 陈杰, 林洁, 顾容. 教师思政赋能课程思政的底层逻辑与实践理路——基于党的二十大“强化现代化建设人才支撑”的视角[J]. 浙江工业大学学报(社会科学版),2023,22(1):10−18. [CHEN Jie, LIN Jie, GU Rong. The logic and methods of ideological and political education empowered teachers' ideological and political education:from the perspective of "strengthening the support of talents for modernization construction" the 20th CPC National Congress[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology (Social Science Edition),2023,22(1):10−18. CHEN Jie, LIN Jie, GU Rong . The logic and methods of ideological and political education empowered teachers' ideological and political education: from the perspective of "strengthening the support of talents for modernization construction" the 20th CPC National Congress[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology (Social Science Edition),2023 ,22 (1 ):10 −18 .[36] 本刊编辑部. 深入学习贯彻党的二十大精神系列《聚焦》 为现代化产业发展提供人才支撑[J]. 中国人才,2023(1):8. [Editorial Department. In-depth study and implementation of the 20th national congress of the communist party of china spirit series "focus" to provide talent support for the development of modern industry[J]. Chinese Cai,2023(1):8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3521.2023.01.003 Editorial Department . In-depth study and implementation of the 20th national congress of the communist party of china spirit series "focus" to provide talent support for the development of modern industry[J]. Chinese Cai,2023 (1 ):8 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3521.2023.01.003[37] 隋宇飞. 深刻领会二十大精神 全面贯彻新时代人才工作新理念新战略新举措[J]. 农银学刊,2022(6):4−8. [SUI Yufei. Studying the resolutions from the 20th cpc national congress and implementing the strategic policy of fostering talents in the new era[J]. Agricultural Banking Journal,2022(6):4−8. SUI Yufei . Studying the resolutions from the 20th cpc national congress and implementing the strategic policy of fostering talents in the new era[J]. Agricultural Banking Journal,2022 (6 ):4 −8 .[38] 白静. 教育、科技、人才 协同支撑强国建设——深入学习贯彻党的二十大精神[J]. 中国科技产业,2022(11):9−11. [BAI Jing. Education, science and technology, and talent synergistically support the construction of a strong country:In-depth study and implementation of the spirit of the 20th National Congress of the communist party of China[J]. China Science and Technology Industry,2022(11):9−11. BAI Jing . Education, science and technology, and talent synergistically support the construction of a strong country: In-depth study and implementation of the spirit of the 20th National Congress of the communist party of China[J]. China Science and Technology Industry,2022 (11 ):9 −11 .[39] 谢凤英, 王辉, 吴瑕, 等. 工程认证与新工科背景下食品专业人才培养策略[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(2):219−222. [XIE Fengying, WANG Hui, WU Xia, et al. Strategies for cultivating food engineering professionals under enginee certification and new engineering background[J]. Food Industry,2022,43(2):219−222. XIE Fengying, WANG Hui, WU Xia, et al . Strategies for cultivating food engineering professionals under enginee certification and new engineering background[J]. Food Industry,2022 ,43 (2 ):219 −222 .[40] 潘磊庆, 宋菲, 辛志宏. 国内食品质量与安全本科专业人才培养方案比较分析[J]. 农产品加工,2022(3):95−98,100. [PAN Leiqing, SONG Fei, XIN Zhihong. Comparative analysis on training scheme for undergraduate major of food quality and safety in China[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022(3):95−98,100. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.02.025 PAN Leiqing, SONG Fei, XIN Zhihong . Comparative analysis on training scheme for undergraduate major of food quality and safety in China[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022 (3 ):95 −98,100 . doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.02.025[41] 李振珲, 周明珠, 王行, 等. 关于我国营养与食品相关专业技术人才培养及大众科普等教育体系的研究[C]//中国营养学会, 中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所, 农业农村部食物与营养发展研究所, 中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所, 华中科技大学公共卫生学院. 中国营养学会第十五届全国营养科学大会论文汇编, 2022:1. [LI Zhenhun, ZHOU Mingzhu, WANG Xing, et al. Research on the training of nutrition and food-related professional and technical personnel and popular science education system in China[C]// Chinese Society of Nutrition, National Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Institute of Food and Nutrition Development, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, School of Public Health, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Proceedings of the 15th National Conference of Nutrition Science of Chinese Nutrition Society, 2022:1. LI Zhenhun, ZHOU Mingzhu, WANG Xing, et al. Research on the training of nutrition and food-related professional and technical personnel and popular science education system in China[C]// Chinese Society of Nutrition, National Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Institute of Food and Nutrition Development, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, School of Public Health, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Proceedings of the 15th National Conference of Nutrition Science of Chinese Nutrition Society, 2022: 1.
[42] ZUTSHI A. How to develop well-informed and assured teams to embed food safety compliance in the UK catering and hospitality industry[J]. Perspect Public Health,2019,139(6):294−295. doi: 10.1177/1757913919872783
[43] MILLER K B, ECKBERG J O, DECKER E A, et al. Role of food industry in promoting healthy and sustainable diets[J]. Nutrients,2021,13(8):2740. doi: 10.3390/nu13082740
[44] SANTEN S A, VAN RITE E, HAMMOUD M, et al. Supporting medical education innovation:Evaluation of a grants initiative[J]. Academic Medicine,2023,98(10):1159−1163. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000005279
[45] STONE S N, RYDBERG L. Creating and confirming observable professional activities (OPAs):A brief report on the practical approach for OPA design for resident education[J]. Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine,2023,46(5):865−869. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2023.2191100
[46] ANDERKO L, OTTER A, CHALUPKA S, et al. Web-based environmental health education:Fish facts[J]. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing,2013,44(3):121−127. doi: 10.3928/00220124-20130115-29
[47] FETROW J, ROYSTER E, MORIN D, et al. Development and implementation of a national center of excellence in dairy production medicine education for veterinary students:Description of the effort and lessons learned[J]. Journal of Veterinary Medical Education,2020,47(3):250−262. doi: 10.3138/jvme.1117-161r
[48] GALGOTIA D, LAKSHMI N. Implementation of knowledge management in higher education:A comparative study of private and government universities in india and abroad[J]. Front Psychol,2022,13:944153. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.944153
[49] LEBLANC C, SONNENBERG L K, KING S, et al. Medical education leadership:From diversity to inclusivity[J]. GMS Journal for Medical Education,2020,37(2):Doc18.
[50] GUINOVART J J, ARIMON M. Scientists in education:A biomedical research institute's perspective[J]. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education,2020,48(6):559−562. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21344
[51] MA C W, CHENG P S, CHAN Y S, et al. Virtual reality:A technology to promote active learning of physiology for students across multiple disciplines[J]. Advances in Physiology Education, 2023.
[52] UZORKA A, NAMARA S, OLANIYAN A O. Modern technology adoption and professional development of lecturers[J]. Education and Information Technologies (Dordr),2023,47(3):594−603.
[53] STUMBRIENE D, JEVSIKOVA T, KONTVAINE V. Key factors influencing teachers' motivation to transfer technology-enabled educational innovation[J]. Education and Information Technologies (Dordr),2023,20:1−35.
[54] AL-SAID K, KRAPOTKINA I, GAZIZOVA F, et al. Distance learning:Studying the efficiency of implementing flipped classroom technology in the educational system[J]. Education and Information Technologies (Dordr),2023,31:1−24.
[55] 许门友, 马珂琦, 李峙谦. 把握高校思政课作为新时代立德树人“关键课程”的三个维度[J]. 山西高等学校社会科学学报,2023,35(5):22−26. [XU Menyou, MA Keqi, LI Zhiqian. Grasping the three dimensions of ideological and political theory courses in universities as the "key courses" for moral education an talent cultivation in the new era[J]. Journal of Social Sciences of Shanxi Universities,2023,35(5):22−26. doi: 10.16396/j.cnki.sxgxskxb.2023.05.004 XU Menyou, MA Keqi, LI Zhiqian . Grasping the three dimensions of ideological and political theory courses in universities as the "key courses" for moral education an talent cultivation in the new era[J]. Journal of Social Sciences of Shanxi Universities,2023 ,35 (5 ):22 −26 . doi: 10.16396/j.cnki.sxgxskxb.2023.05.004[56] 王家琴. 立德树人视域下高校思政课功能的定位及实现路径[J]. 西部素质教育,2023,9(7):70−73. [WANG Jiaqin. Positioning and implementation path of ideological and political course in colleges and universities from the perspective of virtue cultivation[J]. Western China Journal of Quality Education,2023,9(7):70−73. doi: 10.16681/j.cnki.wcqe.202307017 WANG Jiaqin . Positioning and implementation path of ideological and political course in colleges and universities from the perspective of virtue cultivation[J]. Western China Journal of Quality Education,2023 ,9 (7 ):70 −73 . doi: 10.16681/j.cnki.wcqe.202307017[57] 沈瑞芳. 新时代构建高校立德树人共同体的价值逻辑和实践逻辑[J]. 扬州大学学报(高教研究版),2023,27(1):21−28. [SHEN Ruifang. Value and practice logic of building a community of strengthenin moral education and cultivating people in universities in the new era[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Higher Education Research Edition),2023,27(1):21−28. SHEN Ruifang . Value and practice logic of building a community of strengthenin moral education and cultivating people in universities in the new era[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Higher Education Research Edition),2023 ,27 (1 ):21 −28 .[58] 杨崇泽. 立德树人背景下食品类专业人才培养模式的探索[J]. 中国食品,2023(6):41−43. [YANG Chongze. Exploration on the training model of food professionals under the background of cultivating virtue and cultivating talents[J]. China Food,2023(6):41−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1085.2023.06.009 YANG Chongze . Exploration on the training model of food professionals under the background of cultivating virtue and cultivating talents[J]. China Food,2023 (6 ):41 −43 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1085.2023.06.009[59] 李建宇. 聚焦立德树人根本任务 以高质量党建引领高校高质量发展[J]. 艺术教育,2023(1):15−17. [LI Jianyu. Focusing on the fundamental task of cultivating virtue and cultivating people, leading the high-quality development of colleges and universities with high-quality party building[J]. Art Education,2023(1):15−17. LI Jianyu . Focusing on the fundamental task of cultivating virtue and cultivating people, leading the high-quality development of colleges and universities with high-quality party building[J]. Art Education,2023 (1 ):15 −17 .[60] 曹娜, 田程程, 周彦波, 等. 高校科研团队立德树人育人机制与举措探究[J]. 教育教学论坛,2023(3):135−138. [CAO Na, TIAN Chengcheng, ZHOU Yanbo, et al. Research on the educational mechanism and measures of "morality education" of scientific research team in colleges and universities[J]. Education and Teaching Forum,2023(3):135−138. CAO Na, TIAN Chengcheng, ZHOU Yanbo, et al . Research on the educational mechanism and measures of "morality education" of scientific research team in colleges and universities[J]. Education and Teaching Forum,2023 (3 ):135 −138 .[61] 韩涛, 米兆荣, 周建, 等. 学科交叉融合与建设——以“园艺学专业”为例[J]. 现代园艺,2023,46(6):184−186. [HAN Tao, MI Zhaorong, ZHOU Jian, et al. Interdisciplinary integration and construction:A case study of "horticulture"[J]. Modern Horticulture,2023,46(6):184−186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2023.06.065 HAN Tao, MI Zhaorong, ZHOU Jian, et al . Interdisciplinary integration and construction: A case study of "horticulture"[J]. Modern Horticulture,2023 ,46 (6 ):184 −186 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2023.06.065[62] 葛显龙, 梁永宏. “双一流”背景下地方行业高校学科建设经验浅谈——以重庆交通大学为例[J]. 教育教学论坛,2023(11):125−128. [GE Xianlong, LIANG Yonghong. Discussion on the experience of discipline construction in local industry colleges and universities under the background of "double first-class" construction:Taking chongqing jiaotong university as an example[J]. Education and Teaching Forum,2023(11):125−128. GE Xianlong, LIANG Yonghong . Discussion on the experience of discipline construction in local industry colleges and universities under the background of "double first-class" construction: Taking chongqing jiaotong university as an example[J]. Education and Teaching Forum,2023 (11 ):125 −128 .[63] 王金龙, 吴雯娟, 杨伶. “双一流”与新农科背景下农林经济管理学科、专业及课程一体化建设研究[J]. 智慧农业导刊,2022,2(22):104−106,110. [WANG Jinlong, WU Wenjuan, YANG Ling. Research on the integrated construction of agricultural and forestry economic management discipline, specialty and curriculumunder the double first-class initiative and emerging agricuture[J]. Smart Agriculture Guide,2022,2(22):104−106,110. doi: 10.20028/j.zhnydk.2022.22.033 WANG Jinlong, WU Wenjuan, YANG Ling . Research on the integrated construction of agricultural and forestry economic management discipline, specialty and curriculumunder the double first-class initiative and emerging agricuture[J]. Smart Agriculture Guide,2022 ,2 (22 ):104 −106,110 . doi: 10.20028/j.zhnydk.2022.22.033 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘阳泰,董庆利,王翔,夏雪娟. 中国式现代化视域下的“食品工艺学”课程建设. 食品工业. 2024(01): 218-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 梁娟,严家凤,周安,解松子,孙念霞,智楠楠,邹容欣. 新工科背景下食品类专业课程思政建设中存在的问题及应对策略. 安徽开放大学学报. 2024(01): 67-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李晓东,刘璐,李嘉钰,张秀秀,郑冬梅,崔立雪,张宏伟. 《乳品工艺学》课程思政教育的改革与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(19): 376-382 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



