Effects of Asparagus Powder Addition on Dough and Noodles Properties
-
摘要: 为了实现芦笋及其副产物的全质化利用,将芦笋通过干燥制备成芦笋粉并用于面条的制备。系统地研究了芦笋粉添加量(0~10%)对混合粉溶剂保持力,面团的吸水率、形成时间、稳定时间、弱化度、回生值,面条蒸煮时间、吸水率、断条率、损失率、剪切力、拉伸强度,及蛋白质二级结构和淀粉消化特性的影响。研究发现随着芦笋粉添加量的增加混合粉的溶剂保持力增加,蒸馏水、蔗糖、碳酸钠和乳酸SRC在芦笋粉添加量为10%时分别为79.30%、111.92%、99.07%和94.34%;面团的弱化度C1-C2值随芦笋粉添加量的增加而增加,在添加量10%最大,为799.33 mN·m,而回生值C5-C4随芦笋粉添加量的增加而减小,在添加量10%最小,为1060.33 mN·m。随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面条的蒸煮断条率、吸水率和损失率之间无显著差异(P>0.05),而蒸煮时间、拉伸强度、拉伸距离和剪切力都呈下降的趋势。随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面条中巯基含量逐渐增加,二硫键逐渐降低,在添加量10%时分别为8.37和0.59 μmol/g。在芦笋粉添加量8%~10%时血糖生成指数显著降低(P<0.05),但还属于高GI食品。综合芦笋添加对面团特性,面条蒸煮特性、质构特性和淀粉消化特性的影响,芦笋粉添加量6%时挂面的品质可以接受。该研究将为芦笋副产物全质化利用提供重要的理论的依据,也为高纤、高活性物质营养面条的开发提供了思路。Abstract: In order to realize the comprehensive utilization of asparagus and its by-products, asparagus was dried to prepare asparagus powder and used for the preparation of noodles. The effects of asparagus powder addition (0~10%) on solvent retention capacity (SRC) of mixed powder, water absorption rate, formation time, stability time, weakening degree, retrogradation value of dough, cooking time, water absorption rate, breaking rate, loss rate after cooking, shear force, tensile strength, protein secondary structure and starch digestibility of noodles were systematically studied. It was found that as the amount of asparagus powder added increased, the SRC of the mixed powder increased. Distilled water, sucrose, sodium carbonate, and lactic acid SRC were 79.30%, 111.92%, 99.07%, and 94.34%, respectively, when the amount of asparagus powder added was 10%. The weakening degree C1-C2 value of the dough increased with the increase of asparagus powder addition, reaching a maximum of 799.33 mN·m at 10%, while the retrogradation value C5-C4 decreased with the increase of asparagus powder addition, reaching a minimum of 1060.33 mN·m at 10%. There was no significant difference (P>0.05) in the breaking rate, water absorption rate, and loss rate after cooking of noodles during cooking as the amount of asparagus powder added increased. However, cooking time, tensile strength, tensile distance, and shear force showed a decreasing trend. As the amount of asparagus powder added increased, the sulfhydryl content in noodles gradually increased, and the disulfide bond gradually decreased, reaching 8.37 and 0.59 μmol/g at a 10% addition, respectively. When adding 8%~10% asparagus powder, the glycemic index significantly decreased (P<0.05), but it still belonged to high GI foods. According to the effects of adding asparagus on dough properties, noodle cooking characteristics, texture characteristics and starch digestion characteristics, the quality of the noodles was acceptable when adding 6% asparagus powder. This study will provide important theoretical basis for the comprehensive utilization of asparagus by-products, and also provide ideas for the development of high fiber and high activity nutrient noodles.
-
Keywords:
- asparagus powder /
- noodles /
- cooking properties /
- texture properties /
- starch digestion
-
芦笋(Asparagus officinalis L.)是天门冬科天门冬属多年生草本植物[1],鲜芦笋中除了水分外富含碳水化合物,蛋白质,游离氨基酸,膳食纤维,矿物质,维生素和各种生物活性物质(主要是酚类和皂苷类化合物),其被认为是一种对人体有益的食物[2]。根据FAO数据,我国2021年芦笋种植面积为144万公顷,产量为734万吨,在全球芦笋产量中占比高达85.35%。由于绿芦笋采后生理代谢旺盛,呼吸作用强,且易受致病菌侵染引起变质,因此芦笋主要以鲜食为主[3]。为解决芦笋集中上市造成的原料积压,芦笋及其制品常出国外,出口方式主要以芦笋罐头为主,中国芦笋罐头的产量达到世界产量的75%[4]。此外,少量芦笋被用用于深加工,深加工产品有芦笋酒[5]、芦笋醋[6]、芦笋茶[7]、芦笋汁[8]等。
芦笋采后销售和加工过程中会产生大量的非商品笋和副产物,这些笋的营养成分与商品笋相当,但是一般都会被丢弃或用于畜禽饲料等。现阶段主要利用非商品笋和芦笋下脚料提取功能性成分、制备芦笋粉等。如从芦笋下脚料中提取膳食纤维、多糖、黄酮并研究其抗氧化性和各种生物活性[9−15],此外芦笋可用于面条的制备。白玉婷[16]将芦笋榨汁后用于面条的制备,研究发现芦笋汁的添加能够显著降低面条蒸煮时间,但是对于蒸煮损失率和断条率无显著性影响,此外芦笋汁的添加使得硬度、弹性显著性增加,粘聚性、咀嚼性和回复性均显著下降,但是芦笋汁在添加量30%时才显著提高面条总酚含量。周驰[17]通过烫漂、酶解、干燥等工艺将芦笋加工副产物制备成芦笋粉,可溶性膳食纤维含量为30 mg/g,将芦笋粉添加于面粉后显著提升面团的吸水率,在芦笋粉添加量3%时形成时间、稳定时间和粉质指数最大,3%的芦笋粉能改善面条的蒸煮、质构和感官特性;同时该方法制备的粉可提高面包色泽,保持面包的质构特性,提高面包的感官品质,增加面包的口感,但是添加量不超过3%。
为了实现非商品笋和副产物的全质化利用,前期将芦笋制备成为芦笋粉的研究中发现,制备的芦笋粉中可溶性膳食纤维含量约13%,不可溶性膳食纤维约63%,相比前人可溶性膳食纤维含量大大提升[18]。膳食纤维中可溶性部分主要以亲水性多糖的形式存在,其添加可以提高面团的持水性、耐揉混性及谷蛋白的膨胀特性,促进面筋网络的发展和淀粉的溶胀,并抑制淀粉回生,改善面条的品质[19−20]。而现阶段对高含量可溶性膳食纤维的芦笋粉添加对面条品质的影响还不明确,因此,本研究将芦笋粉添加于面粉中,研究其添加对于面团特性,面条蒸煮特性、质构特性和消化特性的影响,以期为芦笋副产物的综合利用提供重要支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
五得利高筋小麦粉 五得利面粉集团公司;鲜绿芦笋(品种:达宝丽,2022年7月采摘于麻城市) 由麻城市王集鸿发芦笋专业合作社提供;α-淀粉酶(30 U/mg)、淀粉葡糖苷酶(10万U/g)、胰蛋白酶(250 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;光谱纯溴化钾 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;碳酸钠、乳酸、蔗糖、Tris、盐酸、尿素、Ellman氏试剂、三氯乙酸、甘氨酸、盐酸胍、NaOH、HCl、葡萄糖、无水乙醇、磷酸盐缓冲、3, 5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
FC1-220型电动压面机 武汉丰创机械设备有限公司;TA-XTPlus质构仪 英国Stable Micro System;Mixolab 2混合试验仪 法国肖邦技术公司;UV-2800分光光度计 优尼科;CF-100 A醒发箱 中山卡士电器有限公司;CS 580 A色差计 杭州彩谱科技有限公司; IRPrestige-21傅里叶变换光谱仪 日本岛津公司;L3 5TB1热泵干燥机 广东威而信实业有限公司;ZG-LZ358和面机、ZG-HTY粉碎机 永康市红太阳机电有限公司;C22-RT22E01美的电磁炉 美的集团有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 芦笋粉的制备
将芦笋切成2~3 mm薄片,在温度50 ℃下通过热泵干燥,干燥终点控制含水量小于8%。干燥粉碎后过80目筛网,4 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 面条制备
面条的制备参考相关的文献并根据实际情况做适当的修改[21]。称取不同质量的芦笋粉与面粉混合,制成含有芦笋粉0%、2%、4%、6%、8%、10%的混合粉。基于混合粉质量加入31%的水,室温(25 ℃)和面8~10 min,熟化30 min,用压面机压成2 mm的薄片,用压面机切刀切成2 mm圆面条,晾干备用。
1.2.3 混合粉溶剂保持力(solvent retention capacity,SRC)
参照GB/T 35866-2018 粮油检验 小麦粉溶剂保持力的测定中的方法进行测定。
1.2.4 混合粉混合特性测定
参照GB/T 37511-2019 粮油检验 小麦粉面团流变学特性测试 混合试验仪法中的方法进行测定。
1.2.5 色差测定
参照方勇等的方法并做少许修改[22]。将面条干燥后粉碎过80目筛网,采用全自动色差仪对样品的色泽进行测定,记录L*,a*和b*值。以未添加芦笋粉的面条作为参比样(L*参,a*参和b*参),按照下式计算色差△E值。
ΔE=√(L*−L*参)2+(a*−a*参)2+(b*−b*参)2 (1) 1.2.6 面条蒸煮特性测定
面条蒸煮特性(最佳蒸煮时间、蒸煮断条率、蒸煮吸水率和蒸煮损失率)参照GB/T 40636-2021进行测定。蒸煮断条率、蒸煮吸水率和蒸煮损失率按照下式计算。
蒸煮断条率(%)=断条数煮制总根数×100 (2) 蒸煮吸水率(%)=W2−W1W1×100 (3) 蒸煮损失率(%)=W1−W3W1×100 (4) 式中:W1为样品干重(g),W2为干面条蒸煮后捞出沥水后重(g),W3为W2烘干后的质量(g)。
1.2.7 面条质构特性分析
面条在最佳蒸煮时间下蒸煮后,过凉水10 s,采用以下几种方式对面条质构进行分析[23]:
剪切力测定:探头型号:A/LKB-F。参数设定:模式:压缩;测试前运行速度:2 mm/s;测试速度:0.8 mm/s;测试结束返回速度:0.8 mm/s;压缩程度:90%;触发形式:Auto-3 g。每次将3根面条水平放置于载物台上,面条之间要有一定的间隔,用设备的刀具进行剪切,每个试样做至少6次平行实验。
拉伸强度测定:探头型号:Code A/SPR。参数设定:模式:拉伸;测试前速度:2 mm/s;测试速度:2 mm/s;测试结束返回速度:10 mm/s;触发距离:100 mm;触发形式:Auto-0.5 g。每次将1根面条缠绕固定在两个平行的摩擦轮之间(面条在被拉的过程中不能够松动),上面的轮子匀速的向上拉伸面条,直至面条断裂,每个试样做至少6次平行实验。
1.2.8 游离巯基和二硫键测定
参照Jia等[24]的方法进行测定并做少许修改。取75 mg干燥后的经过粉碎的面条用1 mL Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液混合均匀后加入4.7 g盐酸胍,用缓冲定容到10 mL。测定巯基时,取1 mL样品加4 mL脲-盐酸胍溶液和0.05 mL Ellman试剂,于412 nm处测量吸光度。测定二硫键时,取1 mL样品加0.05 mL巯基乙醇和4 mL脲-盐酸胍溶液,于25 ℃保温1 h,然后加入10 mL 12%三氯乙酸,继续25 ℃恒温1 h,5000×g离心10 min,用5 mL 12%三氯乙酸清洗沉淀两次,将沉淀溶解在10 mL 8 mol/L脲中,加0.04 mL Ellman试剂,于412 nm处测量吸光度。-SH和-S-S-按照下式计算。
-SH(µmol/g)=73.53A412DC (5) -S-S-(µmol/g)=N1−N22 (6) 式中:A412为样品412 nm处吸光值;D为巯基还原前后值,分别取5.02和10;C为样品浓度,mg/mL;N1、N2分别为还原前后巯基含量。
1.2.9 FTIR测定面条中蛋白质二级结构
将最后干燥的面粉继续研磨,过100目筛网。将样品与烘干的溴化钾按质量比1:100加入研钵混合研磨均匀,用红外压片机压成均匀透明薄片,在400~4000 cm−1范围红外扫描,扫描32次。使用Peak Fit软件(版本4.12)对酰胺I区(1600~1700 cm−1)进行基线校准,然后高斯去卷积,最后使用二阶导数拟合。 确定酰胺I区的吸收峰位置和面积。使用相应面积与酰胺I总条带面积之比计算各个二级结构的百分比[25]。
1.2.10 面条淀粉消化特性和血糖生成指数
取0.5 g煮熟的面条于50 mL离心管中,加入5 mL 0.01 mol/L NaOH溶液和15 mL 0.1 mol/L的磷酸盐标准缓冲液(pH6.8),然后加入41.8 mg α-淀粉酶,3 mg淀粉葡糖苷酶和72 mg胰蛋白酶,随后使样品在37 ℃下恒温水浴振荡3 h,在不同消化时间下取出0.1 mL消化液,采用DNS法测定消化液中葡萄糖含量并计算淀粉水解率,以吸光度为横坐标,葡萄糖浓度为纵坐标做标曲,标曲为y=1.8502x+0.0487(R2=0.9991)。
淀粉的体外消化水解曲线遵循一级反应方程式,通过对淀粉水解曲线下面积(AUC)的积分得到淀粉水解指数(HI),根据HI值预估挂面血糖生成指数(eGI)[26]。具体公式为:
HI=AUC样品AUC参考食品×100 (7) eGI=39.71+0.549HI (8) 1.3 数据处理
每组实验至少重复3次,结果用平均值±标准差表示,采用Excel 2016或Origin 2018对所得数据进行作图处理。用SPSS 20 通过一元方差分析(One-Way ANOVA)进行多个组间平均数的比较,如果组间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),则采用Duncan检验进行组间多重比较。
2. 结果与分析
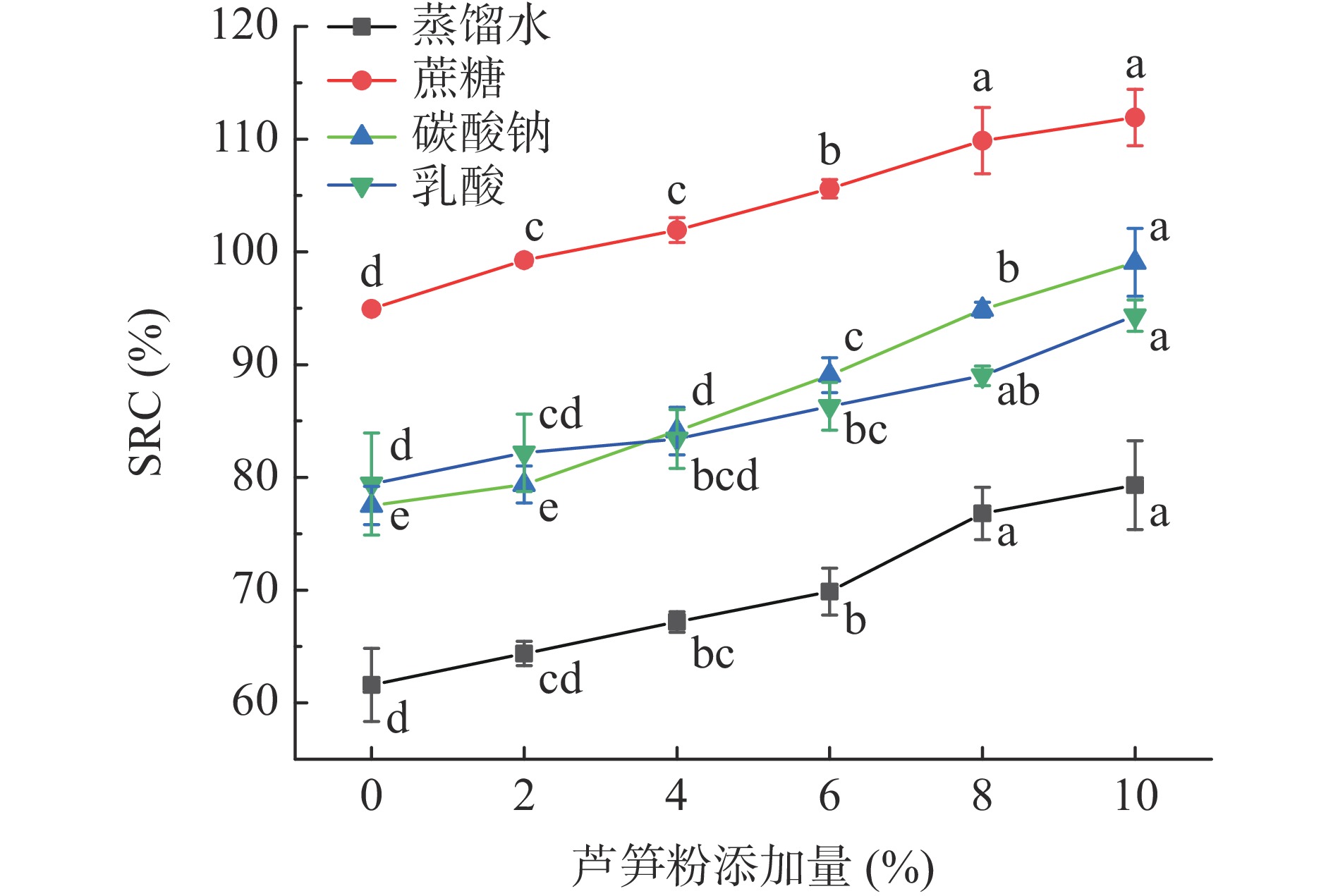
2.1 芦笋粉添加对混合粉溶剂保持力的影响
芦笋粉添加对混合粉溶剂保持力影响见图1。从图中可以看出未添加芦笋粉时小麦粉蒸馏水、蔗糖、碳酸钠和乳酸SRC分别为61.58%、94.94%、77.5%和79.41%,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加混合粉的溶剂保持力都呈增加的趋势,在芦笋粉添加量为10%时分别为79.30%、111.92%、99.07%和94.34%。混合粉的溶剂保持力反映了不同组分对于溶剂的作用能力,蔗糖SRC与混合粉中聚阿拉伯糖木糖相关;碳酸钠SRC与破碎淀粉含量相关;乳酸SRC与面团谷蛋白网络形成和谷蛋白网络强度有关;而蒸馏水SRC与面粉全部组成有关,反映了混合粉综合特性[27]。可溶性膳食纤维的多糖以聚阿拉伯木糖为主,其添加会增加蔗糖SRC;此外,可溶性膳食纤维有利于蛋白网络的形成进而提升乳酸SRC;芦笋粉中不溶性膳食纤维和可溶性膳食纤维含有更多的亲水基团,其对水的吸附能力较高,约为4 g/g[18],其添加会显著提升蒸馏水和碳酸钠SRC,这与Kong等[28]的结论一致。
2.2 芦笋粉添加对面团混合特性的影响
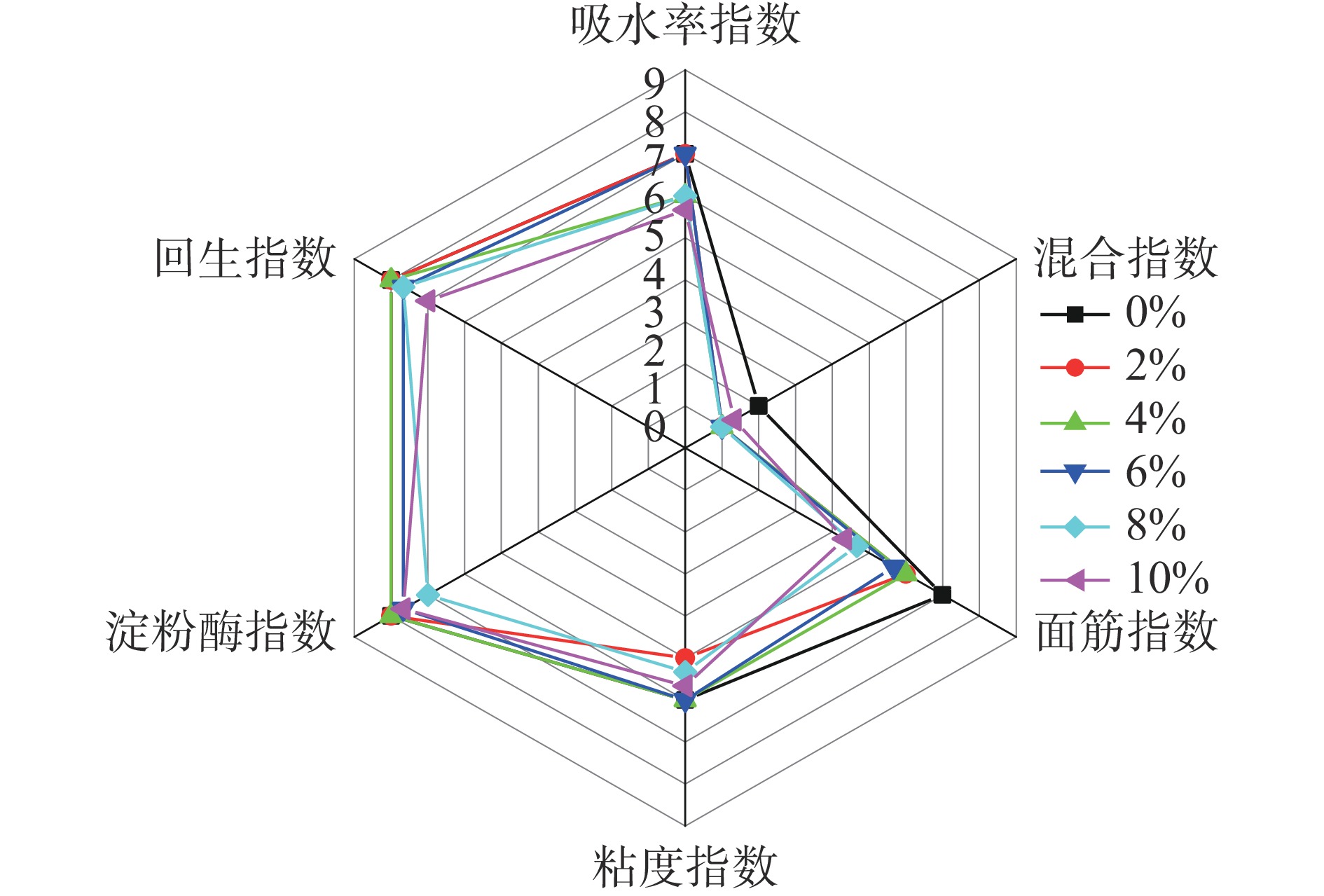
芦笋粉添加对面团混合特性影响见表1。从表中可以看出,吸水率在添加量为6%时最高为60.50%,但是其与添加量0%和2%时无显著差异(P>0.05),而在添加量为10%时最低为58.97%,相对于最高值相差仅1.53%。添加芦笋粉后面团的形成时间呈先降低后增加的趋势,在添加量为4%时最低,为3.65 min,总体而言加入芦笋粉后面团的形成时间显著降低(P<0.05);而面团的稳定时间在添加量0%最高,为3.61 min,在添加量2%~6%范围内显著降低(P<0.05),但是其之间无显著差异(P>0.05)。周驰[17]发现面团吸水率随着芦笋粉添加量的增加而增加,而形成时间、稳定时间呈先增加后减小的趋势。芦笋粉亲水性强,在和面过程中与面粉会形成致密的网络结构,提升吸面团的吸水率、形成时间和稳定时间;但过多添加虽然会增加面团的吸水性,但会稀释面筋蛋白,降低面团形成时间和稳定时间。Liu等[20]认为多纤维中的多羟基能够通过氢键促进水合作用进而提升吸水率,而通过常规制备的芦笋粉暴露的羟基含量少而造成其对面团吸水率无显著促进作用。蛋白的弱化度C1-C2值随着芦笋粉添加量的增加而增加,说明添加芦笋粉后面团对机械搅拌的承受能力降低,这主要是因为芦笋粉中高含量膳食纤维导致面筋蛋白含量降低造成的。芦笋粉在添加量4%时C3-C2值最大,为1380.67 mN·m,其余不同添加量之间无显著差异(P>0.05);在芦笋添加量4%~10%范围内也无显著差异(P>0.05)。C3-C4值为面团的热稳定性,负值说明其在加热过程中热稳定性增加,在芦笋添加量为2%和4%时,C3-C4值分别为−108.00、−106.50 mN·m,显著大于0%时的C3-C4值(P<0.05),说明适量的芦笋粉添加量能提升面团的热稳定性。面团的回生值C5-C4随着芦笋粉添加量的增加而减小,添加量为10%时最低,为1060.33 mN·m,这说明芦笋粉的添加能够抑制面团的回生[29]。
表 1 芦笋粉添加对面团混合特性的影响Table 1. Effect of asparagus powder addition on mixing properties of dough芦笋粉添加量(%) 吸水率(%) 形成时间(min) 稳定时间(min) C1-C2(mN·m) C3-C2(mN·m) C3-C4(mN·m) C5-C4(mN·m) 0 59.90±0.00ab 4.94±0.23a 3.61±0.08a 662.00±7.81d 1346.33±2.31b −58.00±9.9bc 1420.00±7.00a 2 60.10±0.35ab 3.76±0.18bc 3.08±0.23b 737.67±21.03c 1340.33±10.12b −108.00±4.24a 1326.33±22.01b 4 59.40±0.00bc 3.65±0.16c 3.17±0.06b 775.67±9.07b 1380.67±10.12a −106.5±10.61a 1295.00±70.19b 6 60.50±0.00a 3.67±0.09c 3.05±0.23b 770.67±16.2b 1351.67±4.93ab −76.50±9.19b 1150.33±46.52c 8 59.37±1.03bc 4.00±0.10b 3.50±0.15a 792.00±2.00ab 1357.00±32.92ab −49.00±0.00c 1130.67±24.11c 10 58.97±0.40c 3.98±0.12b 3.58±0.07a 799.33±9.29a 1362.33±11.68ab −64.00±4.24bc 1060.33±26.27d 注:表中同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著;表2、表3同。 添加芦笋粉对混合粉面团指数影响见图2。由图2可见,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加,面团的吸水率指数、面筋指数、混合指数、黏度指数、淀粉酶指数和回生指数下降都呈下降趋势,其中面筋指数下降趋势最为显著。这说明添加芦笋粉后面团蛋白质被稀释,面团吸水率、稳定性、黏度、酶活降低,而产品不易回生,货架期较长[30]。
2.3 芦笋粉添加对面条色差的影响
色泽是表征面条品质的重要指标之一,是消费者选择产品的重要依据。芦笋粉添加对面条色差的影响见表2。从表中能看出随着芦笋粉添加量的增加,L*和a*减小,b*值增加,说明添加芦笋后面条白度下降,绿色增加,且黄色也增加。面条的色泽受小麦颗粒天然色素、出粉率、蛋白质含量、多酚氧化酶活性、面团水分含量、灰分、外来添加物颜色等因素的影响。本研究中主要因为芦笋粉为绿色,颜色偏深,其加入使面条颜色变深,绿色值增加,黄蓝值向偏黄的方向变化[31]。以小麦粉作为参比计算△E值,在芦笋粉添加量2%时△E值为3.23,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加,△E值显著增加(P<0.05),添加量10%时最大为11.58,说明芦笋粉添加能显著改变面条的颜色,因此消费者可以根据面条的颜色估计芦笋粉的添加量。
表 2 芦笋粉添加对面条色差的影响Table 2. Effect of asparagus powder addition on noodles color芦笋粉
添加量(%)L* a* b* ΔE 0 89.68±1.69a 0.83±0.09a 7.24±0.30e − 2 89.87±0.15a −1.59±0.06b 12.39±0.5d 3.32±0.12e 4 86.04±0.68b −2.21±0.02c 14.37±0.63c 5.46±0.41d 6 82.48±0.69c −2.67±0.07d 15.33±0.74b 8.50±0.54c 8 81.64±1.22c −3.37±0.10e 18.15±0.50a 9.68±0.96b 10 79.55±1.42d −3.60±0.06f 18.65±1.00a 11.58±1.23a 2.4 芦笋粉添加对面条蒸煮特性的影响
芦笋粉添加对面条蒸煮特性的影响见表3。从表中能看出来,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面条的蒸煮断条率、吸水率和损失率范围分别为3.33%~4.17%,213.09%~229.29%,8.05%~9.41%,几个指标之间无显著差异(P>0.05),说明芦笋粉的添加对面条的蒸煮断条率、吸水率和损失率无显著影响(P>0.05),芦笋粉的添加量还在可接受的范围。芦笋粉中的可溶性膳食纤维具有较高的黏性,其与淀粉、蛋白可以形成较为紧密的网络结构,抵消因添加芦笋粉对面条蒸煮断条率、吸水率和损失率造成的影响[17]。而蒸煮时间随着芦笋添加量的增加呈降低趋势,在添加量为0~4%范围内无显著差异(P>0.05),在添加量为8%和10%时显著降低(P<0.05),分别为314.67和315.33 s。芦笋粉中不含面筋蛋白,芦笋粉的添加稀释了混合粉面筋蛋白,使淀粉不能完全被面筋网络包裹,面条结构变得松散,稳定性降低,水分更易侵入,降低了面条的蒸煮时间[32]。综合面团的混合特性和面条的蒸煮特性,芦笋粉添加量在添加量较高(10%)时还具有较高的品质。
表 3 芦笋粉添加对面条蒸煮特性的影响Table 3. Effect of asparagus powder addition on cooking properties of noodles芦笋粉
添加量(%)蒸煮时间(s) 蒸煮断条率
(%)蒸煮吸水率
(%)蒸煮损失率
(%)0 377.67±7.77a 4.17±0.72a 229.29±10.33a 9.37±0.88a 2 378.67±11.93a 3.33±0.72a 218.57±3.63a 8.26±0.61a 4 364.33±11.02ab 4.17±0.72a 213.09±1.52a 8.38±0.73a 6 356.00±7.55b 3.75±0.00a 214.98±9.79a 8.05±1.20a 8 314.67±7.57c 3.33±0.72a 215.68±11.65a 8.14±0.38a 10 315.33±5.51c 4.17±0.72a 215.1±13.04a 9.41±1.17a 2.5 芦笋粉添加对面条质构特性的影响
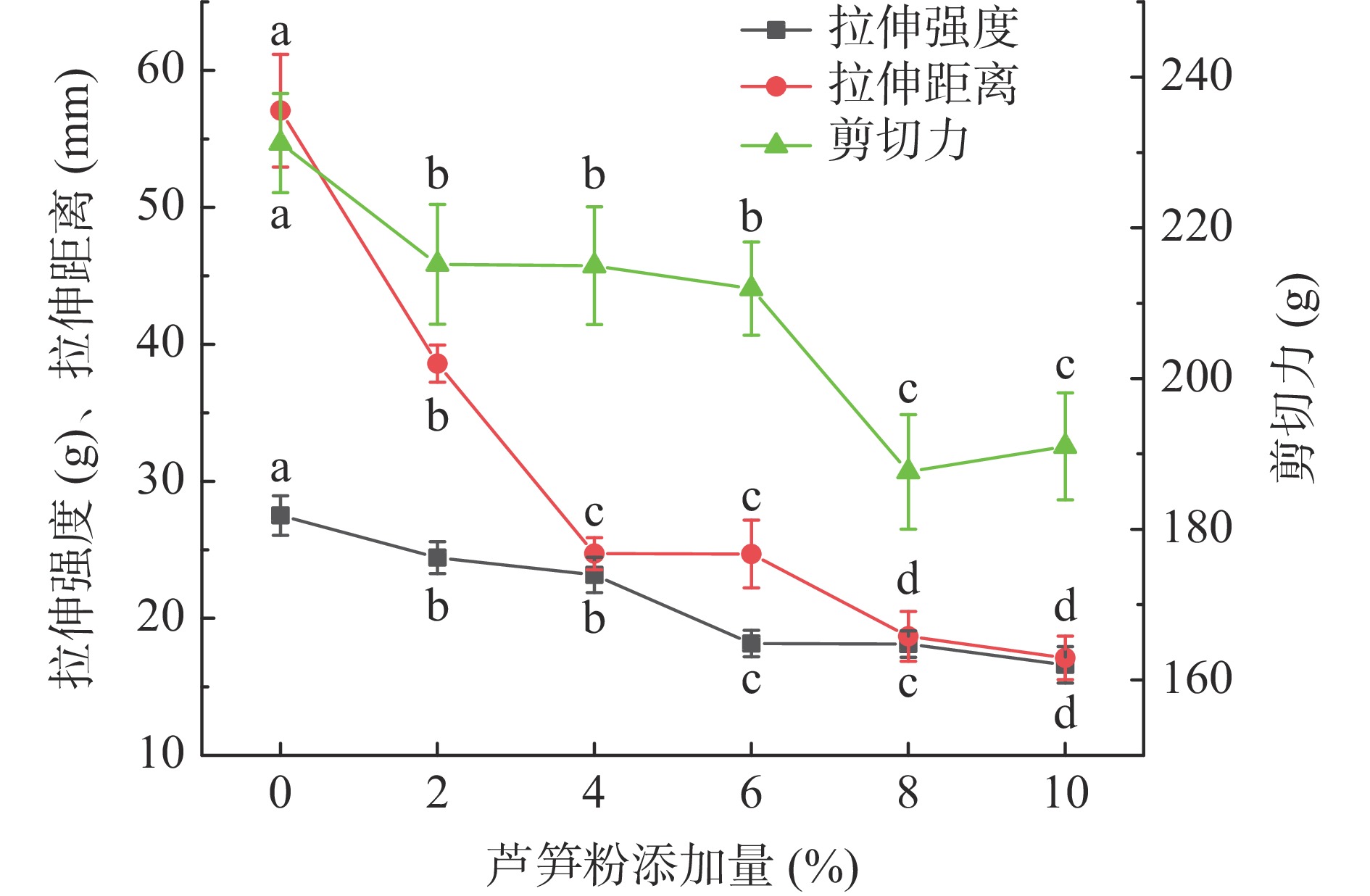
芦笋粉添加对面条质构特性的影响见图3。从图中能看出来,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面条拉伸强度、拉伸距离和剪切力都呈下降的趋势。在添加量0%时,面条拉伸强度、拉伸距离和剪切力分别为27.50 g、57.06 mm和231.24 g,而添加量为10%时其值分别下降了50.54%、70.01%和17.40%,这说明芦笋粉的添加对于面条的质构特性有极大影响。虽然芦笋粉的添加对面条的蒸煮特性影响不大,但是芦笋粉中膳食纤维主要以不可溶性为主,一方面其与蛋白竞争水分,阻碍面筋蛋白三维网络结构的形成,使面条结构变得松散;另一方面,直接粉碎的芦笋粉颗粒较大,能够阻断面条紧密网络结构的形成,使面条内容部出现空隙,降低面条的物理强度[33];此外,表1显示随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面团的弱化度C1-C2值增加,说明芦笋粉的添加也使面团蛋白网络结构遭到了破坏。
2.6 芦笋粉添加对面条游离巯基和二硫键含量的影响
面筋蛋白主要包括麦醇溶蛋白和麦谷蛋白,前者为单肽链,分子质量较小,通过分子内二硫键、氢键和疏水作用形成球状结构,赋予面团延展性、流动性和膨胀性;后者是非均质的大分子聚合体,分子中(链内和链间)含有大量的二硫键,容易发生聚集作用,构成面团网络的骨架作用,主要赋予面团弹性、黏合性和强度[34]。芦笋粉添加对面条游离巯基和二硫键含量的影响见图4。从图中能看出来随着芦笋粉添加量的增加巯基含量逐渐增加,二硫键含量逐渐降低。未添加芦笋粉时巯基和二硫键含量分别为4.67和3.95 μmol/g,在芦笋粉添加量10%时其分别为8.37和0.59 μmol/g。-S-S-含量的减少与-SH含量的增加说明芦笋粉的添加阻断了-S-S-的形成,使其转化为-SH,导致面筋网络形成变得疏松,面条强度变弱[35−36],这也从另一个方面解释了面条质构指标下降的原因。
2.7 芦笋粉添加对面条蛋白质二级结构的影响
蛋白质中酰胺在1600~1700 cm−1处的吸收可以用来指认蛋白质的二级结构,可以将蛋白质分为β-折叠、无规则卷曲、α-螺旋、β-转角四种[37]。芦笋粉添加对面条蛋白质二级结构的影响见表4。从表中能看出来,小麦粉中蛋白质主要以无规则卷曲、α-螺旋为主,占比分别为33.83%和31.18%;β-折叠和β-转角含量较少,分别为12.99%和21.99%。添加芦笋粉后蛋白质也是主要以无规则卷曲、α-螺旋为主,但是其含量大大提高,含量分别都在44%左右,β-折叠含量减低到8%左右,β-转角减低到5%左右。有研究认为,α-螺旋和β-折叠构象是一种较为稳定的结构,而β-转角和无规卷曲具有不稳定的特点,其含量的变化将会改变面条蛋白网络稳定性[38]。膳食纤维中的纤维素、多糖、阿魏酸对于蛋白二级结构有不同的影响[39],芦笋粉作为一种多组分其添加可以降低β-折叠构象的含量、增加α-螺旋构象的含量。
表 4 芦笋粉添加对面条蛋白质二级结构的影响Table 4. Effect of asparagus powder addition on secondary structure of protein in noodles芦笋粉添加量(%) β-折叠(%) 无规则卷曲(%) α-螺旋(%) β-转角(%) 0 12.99 33.83 31.18 21.99 2 7.87 43.07 44.19 4.88 4 7.91 43.35 43.97 4.77 6 8.12 43.04 43.82 5.02 8 8.08 43.24 43.79 4.89 10 7.94 43.24 44.18 4.64 2.8 芦笋粉添加对面条淀粉消化特性和血糖生成指数的影响
芦笋粉添加对面条淀粉水解和血糖生成指数的影响见图5。从图中能看出来,面条淀粉水解速率都低于白面包,芦笋粉添加量0~6%时,淀粉水解率80.97%~85.34%,添加量为8%~10%时,淀粉水解率为76.30%~74.51%。通过计算发现面条都属于高GI食品;芦笋粉添加量0~6%时eGI值之间没有显著差异(P>0.05),添加量8%~10%时,eGI值显著降低(P<0.05)。芦笋粉中含有大量的膳食纤维,可以与小麦粉形成一个完整的网状结构,降低了消化酶的敏感性,有效地延缓淀粉的消化[40];此外,芦笋粉中的黄酮类物质以及酚类物质的存在也会抑制淀粉酶的活性,降低淀粉的消化速率[41]。在膳食纤维和黄酮的作用下降低了淀粉的消化,但是本研究中制备的面条还属于高GI食品。
3. 结论
通过研究发现随着芦笋粉添加量的增加混合粉的溶剂保持力增加,面团的形成时间呈先降低后增加的趋势,蛋白的弱化度C1-C2值随着芦笋粉添加量的增加而增加,面团的回生值C5-C4随着芦笋粉添加量的增加而减小,随着芦笋粉添加量的增加面条的蒸煮断条率、吸水率和损失率之间无显著差异(P>0.05),而面条蒸煮时间、拉伸强度、拉伸距离和剪切力都呈下降的趋势。随着芦笋粉添加量的增加,面条中巯基含量逐渐增加,二硫键含量逐渐降低,在芦笋粉添加量8%~10%时面条的血糖生成指数显著降低(P<0.05)。综合芦笋添加对面团特性,面条蒸煮特性、质构特性和淀粉消化特性的影响,芦笋粉添加量6%时挂面的品质可以接受。本研究将为芦笋副产物全质化利用提供重要的理论依据,也为高纤、高活性物质营养面条的开发提供了思路;但是研究发现在芦笋粉添加量较高时面条还是属于高GI食品,因此在后续的研究当中将通过添加多糖形成凝胶高芦笋粉添加量,同时提升面条蒸煮品质和质构品质。
-
表 1 芦笋粉添加对面团混合特性的影响
Table 1 Effect of asparagus powder addition on mixing properties of dough
芦笋粉添加量(%) 吸水率(%) 形成时间(min) 稳定时间(min) C1-C2(mN·m) C3-C2(mN·m) C3-C4(mN·m) C5-C4(mN·m) 0 59.90±0.00ab 4.94±0.23a 3.61±0.08a 662.00±7.81d 1346.33±2.31b −58.00±9.9bc 1420.00±7.00a 2 60.10±0.35ab 3.76±0.18bc 3.08±0.23b 737.67±21.03c 1340.33±10.12b −108.00±4.24a 1326.33±22.01b 4 59.40±0.00bc 3.65±0.16c 3.17±0.06b 775.67±9.07b 1380.67±10.12a −106.5±10.61a 1295.00±70.19b 6 60.50±0.00a 3.67±0.09c 3.05±0.23b 770.67±16.2b 1351.67±4.93ab −76.50±9.19b 1150.33±46.52c 8 59.37±1.03bc 4.00±0.10b 3.50±0.15a 792.00±2.00ab 1357.00±32.92ab −49.00±0.00c 1130.67±24.11c 10 58.97±0.40c 3.98±0.12b 3.58±0.07a 799.33±9.29a 1362.33±11.68ab −64.00±4.24bc 1060.33±26.27d 注:表中同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著;表2、表3同。 表 2 芦笋粉添加对面条色差的影响
Table 2 Effect of asparagus powder addition on noodles color
芦笋粉
添加量(%)L* a* b* ΔE 0 89.68±1.69a 0.83±0.09a 7.24±0.30e − 2 89.87±0.15a −1.59±0.06b 12.39±0.5d 3.32±0.12e 4 86.04±0.68b −2.21±0.02c 14.37±0.63c 5.46±0.41d 6 82.48±0.69c −2.67±0.07d 15.33±0.74b 8.50±0.54c 8 81.64±1.22c −3.37±0.10e 18.15±0.50a 9.68±0.96b 10 79.55±1.42d −3.60±0.06f 18.65±1.00a 11.58±1.23a 表 3 芦笋粉添加对面条蒸煮特性的影响
Table 3 Effect of asparagus powder addition on cooking properties of noodles
芦笋粉
添加量(%)蒸煮时间(s) 蒸煮断条率
(%)蒸煮吸水率
(%)蒸煮损失率
(%)0 377.67±7.77a 4.17±0.72a 229.29±10.33a 9.37±0.88a 2 378.67±11.93a 3.33±0.72a 218.57±3.63a 8.26±0.61a 4 364.33±11.02ab 4.17±0.72a 213.09±1.52a 8.38±0.73a 6 356.00±7.55b 3.75±0.00a 214.98±9.79a 8.05±1.20a 8 314.67±7.57c 3.33±0.72a 215.68±11.65a 8.14±0.38a 10 315.33±5.51c 4.17±0.72a 215.1±13.04a 9.41±1.17a 表 4 芦笋粉添加对面条蛋白质二级结构的影响
Table 4 Effect of asparagus powder addition on secondary structure of protein in noodles
芦笋粉添加量(%) β-折叠(%) 无规则卷曲(%) α-螺旋(%) β-转角(%) 0 12.99 33.83 31.18 21.99 2 7.87 43.07 44.19 4.88 4 7.91 43.35 43.97 4.77 6 8.12 43.04 43.82 5.02 8 8.08 43.24 43.79 4.89 10 7.94 43.24 44.18 4.64 -
[1] CHITRAKAR B, ZHANG M, ADHIKARI B. Asparagus ( Asparagus officinalis):Processing effect on nutritional and phytochemical composition of spear and hard-stem byproducts[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,93:1−11.
[2] TRUONG T Q, NGUYEN T T, CHO J Y, et al. Effect of processing treatments on the phytochemical composition of asparagus ( Asparagus officinalis L.) juice[J]. LWT,2022,169:113948. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113948
[3] 陈贝莉. 绿芦笋保鲜及胆固醇护绿机理研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工商大学, 2015. [CHEN Beili. Study on preservation of postharvest green asparagus and green-maitaining mechanism of cholesterol treatment[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2015.] CHEN Beili. Study on preservation of postharvest green asparagus and green-maitaining mechanism of cholesterol treatment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2015.
[4] 杨晓春, 黎重阳, 张玲玲, 等. 响应面法优化绿芦笋罐头的生产工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(8):82−88. [YANG Xiaochun, LI Zhongyang, ZHANG Lingling, et al. Processing technology optimization of canned green asparagus by response surface method[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(8):82−88.] YANG Xiaochun, LI Zhongyang, ZHANG Lingling, et al . Processing technology optimization of canned green asparagus by response surface method[J]. Food Research and Development,2023 ,44 (8 ):82 −88 .[5] 丁立孝, 胡晓文, 丁振. 芦笋保健酒工艺研究与开发[J]. 食品研究与开发,2010,31(7):82−84. [DING Lixiao, HU Xiaowen, DING Zhen. Research and development of the asparagus health wine technology[J]. Food Research and Development,2010,31(7):82−84.] DING Lixiao, HU Xiaowen, DING Zhen . Research and development of the asparagus health wine technology[J]. Food Research and Development,2010 ,31 (7 ):82 −84 .[6] 马忠明. 芦笋醋饮料的研制及其降血脂实验研究[J]. 食品科技,2009,34(7):51−54. [MA Zhongming. Preparation of asparagus vinegar beverage and its reducing blood lipid function[J]. Food Science and Technology,2009,34(7):51−54.] MA Zhongming . Preparation of asparagus vinegar beverage and its reducing blood lipid function[J]. Food Science and Technology,2009 ,34 (7 ):51 −54 .[7] 蔡广霞, 陈季旺, 王元凤, 等. 芦笋叶速溶茶微波辅助浸提工艺研究[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(16):1−5. [CAI Guangxia, CHEN Jiwang, WANG Yuanfeng, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of Asparagus officinalis leaves to provide a flavonoids-enriched infusion for instant tea production[J]. Food Science,2010,31(16):1−5.] CAI Guangxia, CHEN Jiwang, WANG Yuanfeng, et al . Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of Asparagus officinalis leaves to provide a flavonoids-enriched infusion for instant tea production[J]. Food Science,2010 ,31 (16 ):1 −5 .[8] 陈学红, 秦卫东, 马利华, 等. 不同制汁工艺对绿芦笋汁理化成分和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(13):224−227. [CHEN Xuehong, QIN Weidong, MA Lihua, et al. Effect of different extracting juice technologies on physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activity of green asparagus juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(13):224−227.] CHEN Xuehong, QIN Weidong, MA Lihua, et al . Effect of different extracting juice technologies on physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activity of green asparagus juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012 ,33 (13 ):224 −227 .[9] 陈蓬凤, 梅新, 黄师荣, 等. 不同品种薯尖的总酚、总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(3):132−138. [CHEN Pengfeng, MEI Xin, HUANG Shirong, et al. Comparison of the total phenolics, total flavonoids and antioxidant activities in potato tips of different varieties[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(3):132−138.] CHEN Pengfeng, MEI Xin, HUANG Shirong, et al . Comparison of the total phenolics, total flavonoids and antioxidant activities in potato tips of different varieties[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021 ,37 (3 ):132 −138 .[10] 窦勇博. 白芦笋下脚料多糖提取、结构表征及其应用研究[D]. 济南:齐鲁工业大学, 2020. [DOU Yongbo. Study on extraction, structural characterization and application of polysaccharides from white asparagus processing waste[D]. Jinan:Qilu University of Technology, 2020.] DOU Yongbo. Study on extraction, structural characterization and application of polysaccharides from white asparagus processing waste[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2020.
[11] 王崇队, 张明, 马超, 等. 蒸汽爆破对绿芦笋废弃物膳食纤维改性的研究[J]. 中国果菜,2020,40(2):28−34. [WANG Chongdui, ZHANG Ming, MA Chao, et al. Study on modification of dietary fiber from green asparagus waste by steam blasting[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable,2020,40(2):28−34.] WANG Chongdui, ZHANG Ming, MA Chao, et al . Study on modification of dietary fiber from green asparagus waste by steam blasting[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable,2020 ,40 (2 ):28 −34 .[12] 彭买姣, 惠华英, 肖嫩群, 等. 芦笋对高脂饮食小鼠肠道内容物细菌多样性的影响[J]. 核农学报,2019,33(11):2229−2236. [PENG Maijiao, HUI Huaying, XIAO Nenqun, et al. Influence of asparagus on bacterial diversity of intestinal contents in high-fat diet mice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2019,33(11):2229−2236.] doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.11.2229 PENG Maijiao, HUI Huaying, XIAO Nenqun, et al . Influence of asparagus on bacterial diversity of intestinal contents in high-fat diet mice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2019 ,33 (11 ):2229 −2236 . doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.11.2229[13] 随子房. 芦笋汁改善记忆和调节肠道菌群的研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [SUI Zifang. A study on improving the memory and regulating intestinal flora by asparagus juice[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017.] SUI Zifang. A study on improving the memory and regulating intestinal flora by asparagus juice[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[14] 季宇彬, 汲晨锋. 芦笋多糖对肿瘤小鼠红细胞离子通道活性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(7):27−31. [JI Yubin, JI Chenfeng. Effect of asparagus polysaccharide on erythrocyte ion channel in tumor model mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014,14(7):27−31.] JI Yubin, JI Chenfeng . Effect of asparagus polysaccharide on erythrocyte ion channel in tumor model mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014 ,14 (7 ):27 −31 .[15] 钟慧球, 张丽, 黄云祥, 等. 速溶芦笋粉营养成分分析及改善人体睡眠作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(23):367−370. [ZHONG Huiqiu, ZHANG Li, HUANG Yunxiang, et al. Analysis of nutritional components in instant powder of asparagus and the effects on sleeping disorder[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(23):367−370.] ZHONG Huiqiu, ZHANG Li, HUANG Yunxiang, et al . Analysis of nutritional components in instant powder of asparagus and the effects on sleeping disorder[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012 ,33 (23 ):367 −370 .[16] 白玉婷. 添加芦笋和热处理的苦荞对面团及面条品质的影响[D]. 成都:成都大学, 2022. [BAI Yuting. Effects of asparagus and heat treated tartary buckwheat on the quality of dough and noodles[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University, 2022.] BAI Yuting. Effects of asparagus and heat treated tartary buckwheat on the quality of dough and noodles[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University, 2022.
[17] 周驰. 芦笋粉加工关键技术及应用研究[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2015. [ZHOU Chi. Key processing technology and application of asparagus powder[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2015.] ZHOU Chi. Key processing technology and application of asparagus powder[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2015.
[18] 赵时珊, 李少斌, 施建斌, 等. 不同护色方式对芦笋粉物化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(9):283−290. [ZHAO Shishan, LI Shaobin, SHI Jianbin, et al. Effects of different color protection methods on physicochemical properties of asparagus powder[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(9):283−290.] ZHAO Shishan, LI Shaobin, SHI Jianbin, et al . Effects of different color protection methods on physicochemical properties of asparagus powder[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023 ,49 (9 ):283 −290 .[19] 张明皓, 贾鑫, 闫文佳, 等. 小麦阿拉伯木聚糖对鲜湿面条品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(2):233−240. [ZHANG Minghao, JIA Xin, YAN Wenjia, et al. Effects of wheat bran arabinoxylan on the properties of fresh wet noodles[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(2):233−240.] ZHANG Minghao, JIA Xin, YAN Wenjia, et al . Effects of wheat bran arabinoxylan on the properties of fresh wet noodles[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022 ,22 (2 ):233 −240 .[20] LIU Y, LIU X, WAN L, et al. Study on the quality characteristics of hot-dry noodles by microbial polysaccharides[J]. Food Research International,2023,163:112200. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112200
[21] 施建斌, 隋勇, 蔡沙, 等. 荞麦面条配方优化及其体外消化特性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(10):153−161. [SHI Jianbin, SUI Yong, CAI Sha, et al. Optimization of buckwheat noodle formula and its starch digestibility in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(10):153−161.] SHI Jianbin, SUI Yong, CAI Sha, et al . Optimization of buckwheat noodle formula and its starch digestibility in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development,2023 ,44 (10 ):153 −161 .[22] 方勇, 王红盼, 杨文建, 等. 金针菇复配发芽糙米挤压膨化工艺及产品品质特性[J]. 中国农业科学,2016,49(4):727−738. [FANG Yong, WANG Hongpan, YANG Wenjian, et al. Extrusion process of germinated brown rice compounded of Flammulina velutipes and extrudant quality properties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2016,49(4):727−738.] FANG Yong, WANG Hongpan, YANG Wenjian, et al . Extrusion process of germinated brown rice compounded of Flammulina velutipes and extrudant quality properties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2016 ,49 (4 ):727 −738 .[23] 蔡茜茜, 陈旭, 陈选, 等. 超微绿茶粉对面条品质特性的影响及绿茶面条配方优化[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(9):179−185. [CAI Qianqian, CHEN Xu, CHEN Xuan, et al. Effects of ultra-fine green tea powder on noodle quality and optimization of green tea noodle formula[J]. Food & Machinery,2021,37(9):179−185.] CAI Qianqian, CHEN Xu, CHEN Xuan, et al . Effects of ultra-fine green tea powder on noodle quality and optimization of green tea noodle formula[J]. Food & Machinery,2021 ,37 (9 ):179 −185 .[24] JIA F, MA Z, WANG X, et al. Effect of kansui addition on dough rheology and quality characteristics of chickpea-wheat composite flour-based noodles and the underlying mechanism[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,298:125081.
[25] HAN C, MA M, ZHANG H, et al. Progressive study of the effect of superfine green tea, soluble tea, and tea polyphenols on the physico-chemical and structural properties of wheat gluten in noodle system[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,308:125676.
[26] BAE I Y, OH I K, JUNG D S, et al. Influence of arabic gum on in vitro starch digestibility and noodle-making quality of Segoami[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,125:668−673. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.027
[27] JEON S, BAIK B K, KWEON M. Solvent retention capacity application to assess soft wheat flour quality for making white-salted noodles[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2019,96(3):497−507. doi: 10.1002/cche.10150
[28] KONG F, LI Y, XUE D, et al. Physical properties, antioxidant capacity, and starch digestibility of cookies enriched with steam-exploded wheat bran[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:1068785.
[29] 李月, 张笑莹, 王永霞, 等. 沙棘黑全麦生鲜面的配方优化及品质评价[J]. 粮食与油脂,2022,35(1):96−101. [LI Yue, ZHANG Xiaoying, WANG Yongxia, et al. Formula optimization and quality evaluation of seabuckthorn black whole wheat fresh noodles[J]. Grain & Oil,2022,35(1):96−101.] LI Yue, ZHANG Xiaoying, WANG Yongxia, et al . Formula optimization and quality evaluation of seabuckthorn black whole wheat fresh noodles[J]. Grain & Oil,2022 ,35 (1 ):96 −101 .[30] 周小理, 马思佳, 朱思怡, 等. 苦荞-小麦混合粉面团特性及其鲜湿面条的研制[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(8):168−175. [ZHOU Xiaoli, MA Sijia, ZHU Siyi, et al. Characteristics of tartary buckwheat flour dough and development of fresh and wet noodles[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(8):168−175.] ZHOU Xiaoli, MA Sijia, ZHU Siyi, et al . Characteristics of tartary buckwheat flour dough and development of fresh and wet noodles[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021 ,37 (8 ):168 −175 .[31] 葛珍珍, 张圆圆, 李盈, 等. 魔芋葡甘聚糖对面条质构及微观结构的影响[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(9):67−72. [GE Zhenzhen, ZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Ying, et al. Effect of konjac glucomannan on the texture and microstructure of noodles[J]. Cereals & Oils,2021,34(9):67−72.] GE Zhenzhen, ZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Ying, et al . Effect of konjac glucomannan on the texture and microstructure of noodles[J]. Cereals & Oils,2021 ,34 (9 ):67 −72 .[32] 赵红倩, 马亚娟, 王文秀, 等. 紫色马铃薯粉及Na2CO3对小麦-紫色马铃薯熟面的品质改良[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(8):151−158. [ZHAO Hongqian, MA Yajuan, WANG Wenxiu, et al. Quality improvement of wheat-purple potato cooked noodles by purple potato powder and Na2CO3[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022,37(8):151−158.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.08.022 ZHAO Hongqian, MA Yajuan, WANG Wenxiu, et al . Quality improvement of wheat-purple potato cooked noodles by purple potato powder and Na2CO3[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022 ,37 (8 ):151 −158 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.08.022[33] 李玉栋, 李华, 刘鑫慧, 等. 麦麸不溶性膳食纤维对面团及面条品质的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,44(4):43−50. [LI Yudong, LI Hua, LIU Xinhui, et al. Effect of insoluble dietary fiber on the quality of dough and noodles[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,44(4):43−50.] LI Yudong, LI Hua, LIU Xinhui, et al . Effect of insoluble dietary fiber on the quality of dough and noodles[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023 ,44 (4 ):43 −50 .[34] 徐茹, 杨晓清, 刘晓波, 等. 超声波处理对马铃薯全粉面团网状结构的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(10):242−251. [XU Ru, YANG Xiaoqing, LIU Xiaobo, et al. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on protein enhanced network structure of potato flour dough[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(10):242−251.] XU Ru, YANG Xiaoqing, LIU Xiaobo, et al . Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on protein enhanced network structure of potato flour dough[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022 ,22 (10 ):242 −251 .[35] ZHANG L, GUAN E, YANG Y, et al. Impact of wheat globulin addition on dough rheological properties and quality of cooked noodles[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,362:130170. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130170
[36] LIU C, SONG M, HONG J, et al. Effects of salt and kansui on rheological, chemical and structural properties of noodle dough during repeated sheeting process[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,342:128365. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128365
[37] CHEN G, HU R, LI Y. Potassium bicarbonate improves dough and cookie characteristics through influencing physicochemical and conformation properties of wheat gluten[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2020,5:100075. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100075
[38] 郭金英, 贺亿杰, 韩四海, 等. 魔芋葡甘聚糖对冷冻小麦面团面筋蛋白结构和功能特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(24):33−39. [GUO Jinying, HE Yijie, HAN Sihai, et al. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the structural and functional properties of gluten in frozen wheat dough[J]. Food Science,2019,40(24):33−39.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6603-20181225-294 GUO Jinying, HE Yijie, HAN Sihai, et al . Effects of konjac glucomannan on the structural and functional properties of gluten in frozen wheat dough[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (24 ):33 −39 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6603-20181225-294[39] WANG M, ZHAO Z, NIU M, et al. Thermomechanical behaviors and protein polymerization in bread dough modified by bran components and transglutaminase[J]. LWT,2020,133:109894. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109894
[40] 王庆卫, 刘启玲. 藜麦粉对面条品质以及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(1):31−34. [WANG Qingwei, LIU Qiling. Effects of quinoa powder on noodle quality and in vitro digestion characteristics[J]. Cereals & Oils,2021,34(1):31−34.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2021.01.010 WANG Qingwei, LIU Qiling . Effects of quinoa powder on noodle quality and in vitro digestion characteristics[J]. Cereals & Oils,2021 ,34 (1 ):31 −34 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2021.01.010[41] BAE I Y, CHOI A S, LEE H G. Impact of buckwheat flavonoids on in vitro starch[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2016,93(3):299−305. doi: 10.1094/CCHEM-03-15-0047-R
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 胡烘陶,王晶,字成庭,孙培元. 天然化合物基于Notch通路抑制肿瘤的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(05): 138-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘馨颐,梁晓杰,马静阁,魏峰. 香菇多糖的生物活性及在鸡、猪养殖中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧杂志. 2024(04): 64-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李俊生,管丽,李嘉慧,夏至,谭冲,左金龙. 香菇多糖提取、结构特征及生物活性研究进展. 中国调味品. 2024(09): 208-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王大军,徐红伟,王亮,彭亚南. 增强CT对胰腺癌的周围血管侵犯的评估价值分析. 中国CT和MRI杂志. 2024(11): 106-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘俊杰,梁家,庞天舒,薛佳龙,刘德纯. 香菇多糖通过IL-6/STAT3通路对AOM/DSS诱导结肠炎相关结直肠癌的抑制作用及机制. 肿瘤防治研究. 2024(11): 908-912 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
