Storage Characteristics and Shelf-life Prediction of Probiotic Fermented Kiwifruit Juice
-
摘要: 本文探究了益生菌发酵猕猴桃果汁在4 ℃冷藏条件下的贮藏特性,即在14 d贮藏过程中乳酸菌的活菌数以及果汁的理化性质、感官品质、营养品质及功能特性的变化,并基于抗坏血酸在贮藏过程中的变化进行了初步货架期预测。结果表明,在整个贮藏过程中,发酵猕猴桃果汁均具有良好的益生菌活性,其活菌数始终高于8.7 lg CFU/mL;同时,果汁在贮藏过程中保持了稳定的理化性质以及色泽和气味特征。与未发酵果汁相比,益生菌发酵有助于保留和维持果汁在贮藏过程中的抗坏血酸、总酚和抗氧化活性。特别是,经贮藏后,未发酵果汁损失了67.98%的抗坏血酸,而发酵果汁仅损失了23.94%。此外,基于零级动力学模型可有效预测贮藏期间果汁中抗坏血酸的变化,预测结果表明,以是否可以有效补充抗坏血酸为标准,发酵果汁可在4 ℃贮藏50 d,而未发酵果汁仅能贮藏15 d,这说明发酵猕猴桃果汁在冷藏期间可以保持较长时间的高营养品质,进一步为发酵猕猴桃果汁的商业化提供了可能性。Abstract: This study investigated the storage characteristics of probiotic fermented kiwifruit juice under 4 ℃ refrigeration. The research focused on the changes in the viable lactic acid bacteria count physicochemical properties, sensory quality, nutritional quality and functional properties of the juice during 14 days storage period. Additionally, preliminary shelf-life prediction was made based on the changes in ascorbic acid during the storage. The results showed that the fermented kiwifruit juice maintained good probiotic activity throughout the entire storage process with a consistently higher viable bacterial count of over 8.7 lg CFU/mL. Meanwhile, the fermented juice maintained stable physicochemical properties and color and odor characteristics during storage. Compared to unfermented juice, probiotic fermentation contributed to retaining and maintaining ascorbic acid, total phenols and antioxidant activity of juice during storage. In particular, the unfermented juice experienced a 67.98% loss in ascorbic acid after storage, while fermented juice only lost 23.94%. Moreover, based on the zero-order kinetic model, the study effectively predicted the changes in ascorbic acid in kiwifruit juice during storage. The prediction results indicated that fermented juice could be stored at 4 ℃ for 50 d, while unfermented juice could only be stored for 15 d, based on whether ascorbic acid could be effectively supplemented. This showed that fermented kiwifruit juice could maintain high nutritional quality for an extended period during cold storage, further providing the possibility for the commercialization of fermented kiwifruit juice.
-
Keywords:
- kiwifruit /
- probiotic fermentation /
- storage characteristics /
- shelf-life /
- ascorbic acid
-
猕猴桃(Actinidia spp.)营养丰富、风味独特深受消费者青睐[1]。然而,猕猴桃作为一种呼吸跃变型浆果,后熟后不易长期贮存,极易腐烂变质,这导致果实采后和贮藏的损失率较大。因此,开发优质化、营养化、健康化的猕猴桃精深加工产品,不仅能够解决猕猴桃的贮藏问题,丰富猕猴桃精深加工产品的种类,还有助于提高产品的附加值,增加经济效益[2]。
益生菌发酵果蔬汁,作为一种新型的功能型产品,主要通过两个方面为消费者提供健康益处。一是活性益生菌,当食品基质中的活性益生菌超过6 lg CFU/g或mL时,其经消化道后可对宿主健康产生有利影响[3];二是果蔬汁中的多种生物活性物质,并且发酵有助于促进果蔬汁中生物活性物质的产生,从而改善其功能特性[4−5]。基于课题组先前的研究[6],采用植物乳杆菌和短乳杆菌以1:2的比例混合发酵获得的猕猴桃果汁具有良好的发酵特性、感官品质及功能特性。然而,在贮藏过程中,发酵引起的酸性环境、包括有机酸在内的抗菌成分、变质微生物的生长以及贮藏环境的温度和光线等均可能会影响发酵果蔬汁的益生菌活性、营养和感官品质[7−9]。因此,确保货架期范围内发酵果汁中益生菌的总存活数以及生物活性物质的浓度对于维持其保健功能至关重要。目前,已对部分发酵果蔬汁的贮藏特性进行了探究,如发酵樱桃汁[10]和发酵番茄汁[11],但对于发酵猕猴桃果汁的贮藏特性及货架期预测鲜有报道。
大量研究表明,4 ℃下冷藏可有效延长益生菌在果蔬汁基质中的存活时间,同时低温有助于抑制部分生物活性物质的降解以及抗氧化活性的损失[7,10−11]。基于此,本文对发酵猕猴桃果汁(fermented kiwifruit juice,FKJ)在4 ℃冷藏条件下进行了14 d的贮藏实验,以全面探究益生菌发酵猕猴桃果汁的贮藏特性,即其在贮藏过程中乳酸菌的生存能力以及果汁的理化性质、感官品质、营养品质及功能特性的变化,并基于抗坏血酸(ascorbic acid,AA)在贮藏过程中的变化进行货架期预测,从而明确益生菌发酵猕猴桃果汁的商业可行性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
植物乳杆菌CICC 20265(Lactobacillus plantarum CICC 20265)、短乳杆菌 CICC 20269(Lactobacillus brevis CICC 20269) 中国工业微生物菌种保藏管理中心;‘瑞玉’猕猴桃(Actinidia deliciosa cv. Ruiyu) 于2022年20月12日采自陕西佰瑞猕猴桃研究院有限公司;MRS(Man Rogosa Sharpe)肉汤培养基、MRS琼脂培养基等 青岛高科技工业园海博生物技术有限公司;硫酸铜、酒石酸钾钠、葡萄糖、盐酸、甲醇、碳酸钠、亚硝酸钠、无水氯化铝、六水合三氯化铁等 分析纯,西陇科学股份有限公司;2,6-二氯靛酚、福林酚、1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼自由基(2,2-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、2,4,6-三吡啶基三嗪(tripyridyltriazine,TPTZ)等 分析纯,上海源叶生物有限公司。
AH-BASIC高压均质机 安拓思纳米技术(苏州)有限公司;GL-10MD大容量冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪离心机有限公司;PAL-1便携式数显折光仪 日本ATAGO;PHS-3EpH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;5804 R高速台式离心机 德国Eppendorf Corporate;UV-2800A型紫外可见分光光度计 上海尤尼柯仪器有限公司;CS-820色度仪 杭州彩谱科技有限公司;PEN 3电子鼻 德国 AIRSENSE。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 发酵猕猴桃果汁的制备
1.2.1.1 猕猴桃果汁的制备
将新鲜猕猴桃在室温下存放至食用成熟期,此时果实硬度为5±1 N,可溶性固形物含量(soluble solids content,SSC)为19.2±0.1°Brix。将食用成熟期的果实进行清洗、去皮、榨汁,并在4 ℃条件下进行两次高压均质,压力分别为300 bar和500 bar。将均质后得到的果浆以7000 r/min的速度在4 ℃下离心20 min,将上清液置于沸水浴中杀菌1 min,并冷却至40 ℃左右,作为发酵原液备用。此时,猕猴桃果汁的SSC为17.2±0.1°Brix,pH为4±0.1且符合GB 7101-2022《食品安全国家标准 饮料》规定的微生物限量要求。
1.2.1.2 菌种活化
将在-80 ℃甘油管保藏的植物乳杆菌和短乳杆菌在室温下解冻后,在无菌条件下,将菌液转移至MRS肉汤中在37 ℃下活化12 h,并将活化后的菌液在4 ℃下,以4000 r/min的速度离心5 min,随后弃去上清液,并将菌株重新均匀悬浮至无菌生理盐水中,得到菌悬液,并通过OD600确定菌悬液的活菌数[6],备用。
1.2.1.3 猕猴桃果汁的发酵
将制得的植物乳杆菌和短乳杆菌菌悬液以1:2的比例接入发酵原液中,并基于菌悬液的活菌数调整接种量使得果汁初始活菌数约为7 lg CFU/mL,之后再次通过OD600明确果汁中的准确初始活菌数[6]。随后,在37 ℃下发酵36 h获得发酵猕猴桃果汁(fermented kiwifruit juice,FKJ)。将同条件下培养但未接种乳酸菌的猕猴桃果汁作为对照,即CK。
1.2.2 发酵猕猴桃果汁的贮藏特性分析
将FKJ和CK在4 ℃下贮藏14 d,分别在贮藏的第0、2、4、6、8、10、12和14 d取样,并进行指标测定。
1.2.2.1 微生物指标测定
参照GB 4789.35-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 乳酸菌检验》的平板计数法测定果汁样品中的乳酸菌活菌数;参照GB 4789.3-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 大肠菌群计数》中的第一法 大肠菌群MPN计数法测定果汁样品中大肠菌群的最大可能数;参照GB 4789.15-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 霉菌和酵母计数》第一法 霉菌和酵母平板计数法测定果汁样品中霉菌和酵母的数量。
1.2.2.2 可溶性固形物、pH、总糖及总酸测定
采用便携式数显折光仪和pH计分别测定果汁样品的SSC和pH;采用标准葡萄糖溶液滴定法测定果汁样品中的总糖含量(total sugar content,TSC)[11];参考《GB 12456-2021 食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定》中的第一法 酸碱指示剂滴定法测定果汁样品中的总酸含量(total acid content,TA)。
1.2.2.3 色泽测定
果汁的颜色特征通过CS-820色度仪在全透射观察模式下进行测定。记录L*、a*、b*、C*和h°,其中L*表示亮暗(+为偏亮,-为偏暗),a*表示红绿(+为偏红,-为偏绿),b*表示黄蓝(+为偏黄,-为偏蓝),C*表示色饱和度,h°表示色度角。同时,根据公式(1)计算总色差(ΔE)。
ΔE=√(L∗−L∗0)2+(a∗−a∗0)2+(b∗−b∗0)2 (1) 式中,L∗0、a∗0和b∗0为贮藏第0 d果汁的色差测定值。
1.2.2.4 电子鼻测定
采用PEN 3电子鼻并参照Lan等[6]的测定方法评估果汁样品的整体气味特征。具体操作如下:将3 mL果汁样品放入20 mL顶空瓶中,在25 ℃下平衡10 min后进行测试。电子鼻的检测参数为载气速度300 mL/min,检测时间60 s,清洗时间300 s。
1.2.2.5 抗坏血酸及总酚测定
参考GB 5009.86-2016 《食品安全国家标准 食品中抗坏血酸的测定》中第三法2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法测定果汁样品中的抗坏血酸含量(ascorbic acid content,AAC)。依据Zhang等[12]的方法对果汁样品中的酚类物质进行提取,并采用福林酚比色法测定果汁样品中的总酚含量(total polyphenols content,TPC),结果用mg 没食子酸当量/L(mg gallic acid equivalent/L,mg GAE/L)来表示。
1.2.2.6 抗氧化能力的测定
参考Ma等[13]的方法测定果汁样品的DPPH自由基清除能力(DPPH free radical scavenging activity,DPPH)和铁还原抗氧化能力(ferric reducing antioxidant power,FRAP)以评估其抗氧化能力。结果以μmol trolox equiv (TE)/mL表示。
1.2.3 货架期预测模型的建立及验证
零级动力学模型和一级动力学模型通常被用于反映食品品质的变化[14−15],分别如公式(2)和(3)所示。
A=A0+kt (2) lnA=lnA0+kt (3) 式中,A为贮藏第t d质量指标的值;A0为贮藏第0 d质量指标的值;k为质量变化的速率常数;t为贮藏时间。
采用Excel对选定质量指标进行拟合,得到零级和一级反应速率常数,并结合R2值确定动力学模型,进一步导出货架期预测模型。
如为零级动力学模型,其预测模型为:
SL=A−A0k (4) 如为一级动力学模型,其预测模型为:
SL=lnA−lnA0k (5) 式中,SL为货架期(shelf-life);A为货架期结束时质量指标的值;A0为贮藏第0 d质量指标的值;k为质量变化的速率常数。
基于相对误差(relative error,RE)对模型进行验证,当RE<10%时,认为该模型具有较好的预测精度[15]。RE计算公式如下:
RE(%)=x1−x0x0×100 (6) 式中,x1为实际测量值;x0为模型预测值。
1.3 数据处理
实验指标的测定最少重复三次。采用Excel 16.4 和GraphPad Prism9.3.1对数据进行系统整理、分析和可视化。SPSS 26.0用于单因素方差分析和Duncan’s多重范围检验(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
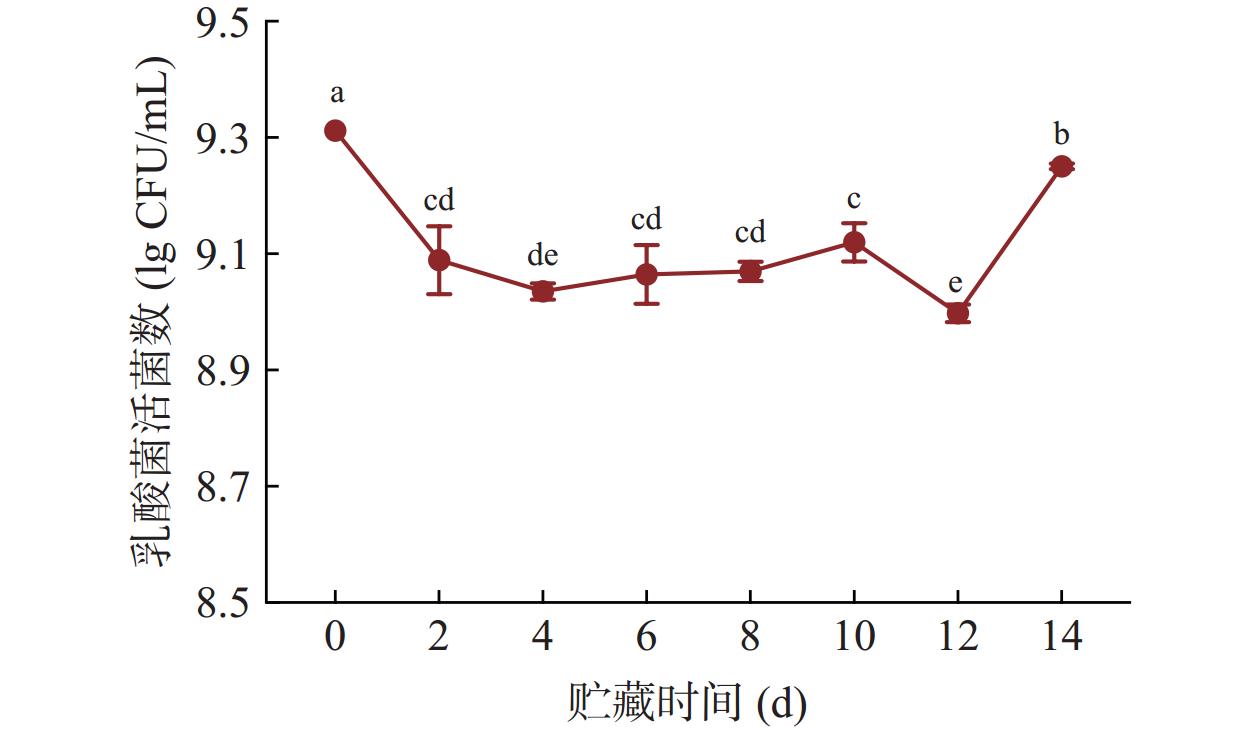
2.1 贮藏过程中发酵猕猴桃果汁乳酸菌活菌数的变化
为了确保贮藏过程中果汁的微生物安全,首先对果汁样品中可能会引起食品腐败的微生物进行了监测,结果表明,在贮藏期间,CK和FKJ均未监测到酵母、霉菌或大肠杆菌。进一步,对FKJ在冷藏过程中的乳酸菌活菌数进行监测(图1)。在整个冷藏过程中,FKJ中活菌数均保持在8.9 lg CFU/mL以上,这远高于益生菌可对人体产生健康益处的浓度和活性,因此,FKJ在此贮藏过程中均可被视为益生菌产品[16]。具体来说,在14 d的冷藏过程中,FKJ中的活菌数呈现出了先下降后上升的趋势,且在第14 d天时达到了与发酵结束后初始浓度(9.31 lg CFU/mL)接近的浓度,即9.25 lg CFU/mL。这表明本研究选用的混菌发酵菌株在不同环境下对猕猴桃果汁基质均具有良好的适应性。
本研究结果与先前的研究一致。Guedes等[17]探究了冷藏过程中干酪乳杆菌在百香果汁中的生存能力,结果表明,干酪乳杆菌在28 d的贮藏过程中表现出了二次生长曲线,其中在0~14 d表现出了与本文类似的先下降后上升的趋势。造成这一现象的原因可能是发酵果汁从37 ℃培养环境转移至4 ℃贮藏环境过程中部分乳酸菌无法及时适应突然产生的环境温度变化而失活,引起贮藏初期活菌数的降低;然而,随着贮藏时间的延长,乳酸菌通过对基质中碳水化合物的利用来适应低温环境从而再次进行生长繁殖,活菌数逐渐增加。此外,在发酵葡萄汁和石榴汁[18−19]中都观察到了类似的变化趋势。
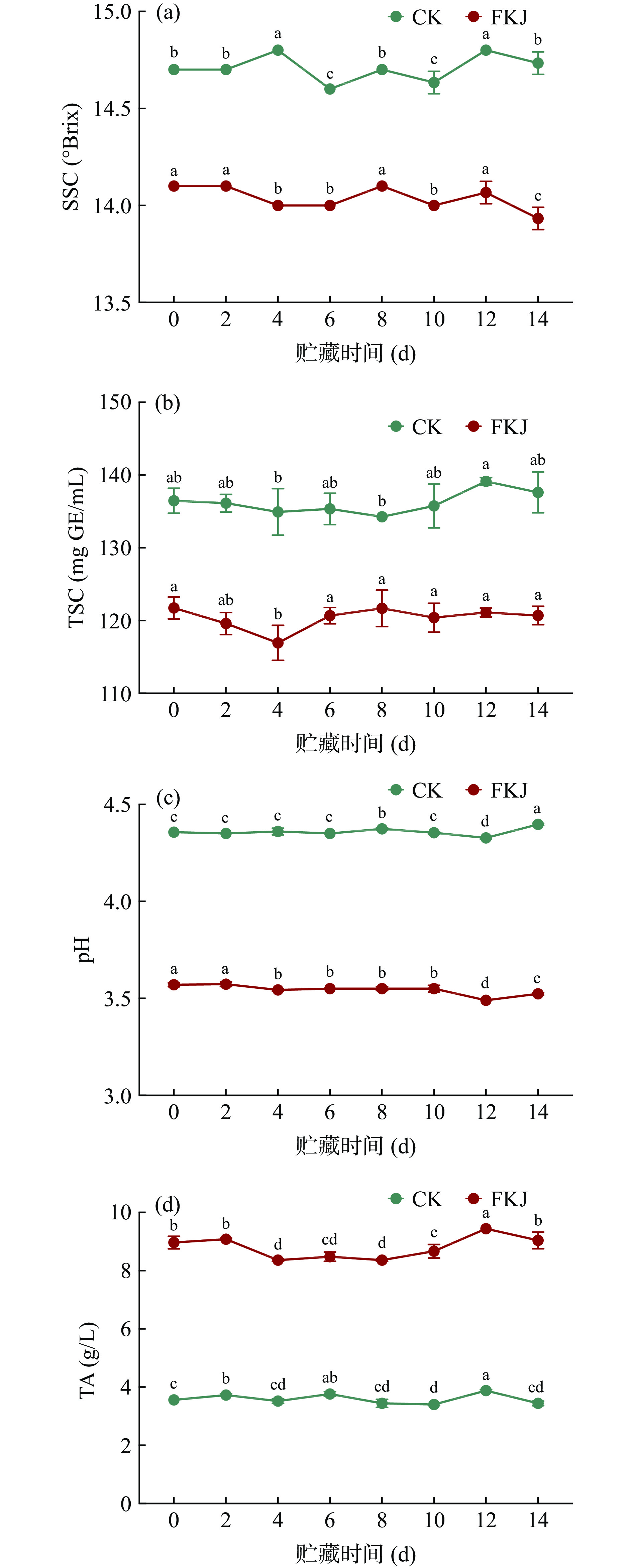
2.2 贮藏过程中发酵猕猴桃果汁理化性质的变化
果汁的理化指标是影响其货架期品质的内在因素[15]。图2显示了果汁样品在贮藏过程中理化性质的变化。在整个贮藏过程中,FKJ的SSC、TSC和pH均显著低于CK(P<0.05),而TA显著高于CK(P<0.05)。这主要是由于乳酸菌发酵利用了果汁基质中的碳水化合物并产生了大量的酸类物质,如有机酸和酚酸[20]。然而,两组猕猴桃果汁样品的SSC、TSC、pH和TA在14 d的冷藏过程中均在较小的范围内波动。对于CK而言,这可能由于果汁本身的高缓冲能力,如苹果酸及其钾盐形成缓冲体系使得其酸度变化较小[15]。然而,就FKJ而言,与贮藏第0 d相比,贮藏第14 d的pH和SSC均显著降低(P<0.05),而TSC和TA无显著差异(P>0.05)。这表明在贮藏过程中,乳酸菌可能利用了部分碳水化合物和有机酸为其正常生存和生长提供必要的能量,同时产生了部分酸类物质,并且通过水解酶作用于基质中的糖苷类物质产生游离糖,从而平衡乳酸菌对糖和酸的消耗[18,21]。总的来说,在贮藏过程中,猕猴桃果汁的理化性质并未发生剧烈变化,这可能取决于果汁本身的高缓冲能力以及低温抑制了乳酸菌的代谢。
2.3 贮藏过程中发酵猕猴桃果汁感官品质的变化
2.3.1 颜色特性
颜色特性是评价果汁品质的重要指标之一。如表1所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,CK和FKJ的a*显著增加(P<0.05),而b*、C*和h°显著降低(P<0.05)。这表明果汁在贮藏过程中有褐变的趋势。值得注意的是,L*在CK中显著降低(P<0.05),而在FKJ中贮藏14 d后并无显著变化(P>0.05)。这可能是由于相较于FKJ,CK具有显著较高的pH和较低的TA,使得在CK中更容易发生褐变。就ΔE而言,随着贮藏时间的延长,果汁与第0 d的样品之间的色差显著增大(P<0.05),但并没有形成肉眼可见的区别,即ΔE<2.0[18]。总的来说,在贮藏过程中,FKJ的颜色变化均处于稳定状态。
表 1 猕猴桃果汁在贮藏过程中的颜色指标Table 1. Color indicators of kiwifruit juice during storage组别 贮藏时间(d) L* a* b* C* h° ∆E CK 0 70.93±0.25a 2.04±0.06d 37.32±0.06c 37.37±0.06cd 86.87±0.09a 2 70.75±0.15ab 2.15±0.03c 37.40±0.03b 37.46±0.03b 86.72±0.06b 0.24±0.08b 4 70.60±0.12abc 2.19±0.02c 37.39±0.03b 37.46±0.04b 86.65±0.04b 0.39±0.24ab 6 70.69±0.26ab 2.21±0.06c 37.24±0.05d 37.30±0.04e 86.61±0.09bc 0.40±0.19ab 8 70.49±0.16bcd 2.30±0.04b 37.49±0.03a 37.56±0.03a 86.50±0.06cd 0.57±0.35ab 10 70.41±0.20bcd 2.35±0.04b 37.37±0.02bc 37.44±0.02bc 86.41±0.06d 0.63±0.39ab 12 70.32±0.15cd 2.43±0.03a 37.36±0.03bc 37.44±0.03bc 86.28±0.04e 0.74±0.28a 14 70.20±0.12d 2.48±0.05a 37.25±0.05d 37.33±0.05de 86.20±0.06e 0.86±0.12a FKJ 0 61.46±0.13ab 0.44±0.01f 33.09±0.05a 33.09±0.06a 89.25±0.01a 2 61.51±0.15ab 0.45±0.01ef 33.00±0.08ab 33.00±0.08ab 89.23±0.03a 0.11±0.01e 4 61.39±0.16ab 0.44±0.01f 32.91±0.08b 32.91±0.08b 89.25±0.01ab 0.31±0.07d 6 61.28±0.12b 0.46±0.01e 32.72±0.05cd 32.73±0.06cd 89.20±0.01bc 0.41±0.03cd 8 61.46±0.12ab 0.48±0.01b 32.77±0.05c 32.78±0.05c 89.17±0.02cd 0.38±0.06d 10 61.41±0.19ab 0.49±0.01c 32.61±0.09d 32.62±0.09d 89.14±0.01d 0.52±0.16c 12 61.38±0.15ab 0.53±0.01b 32.42±0.07e 32.42±0.07e 89.07±0.02e 0.68±0.03b 14 61.58±0.10a 0.56±0.02a 32.23±0.04f 32.23±0.03f 89.02±0.03f 0.90±0.04a 注:不同小写字母代表同一样品不同时间点存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.3.2 整体气味特征
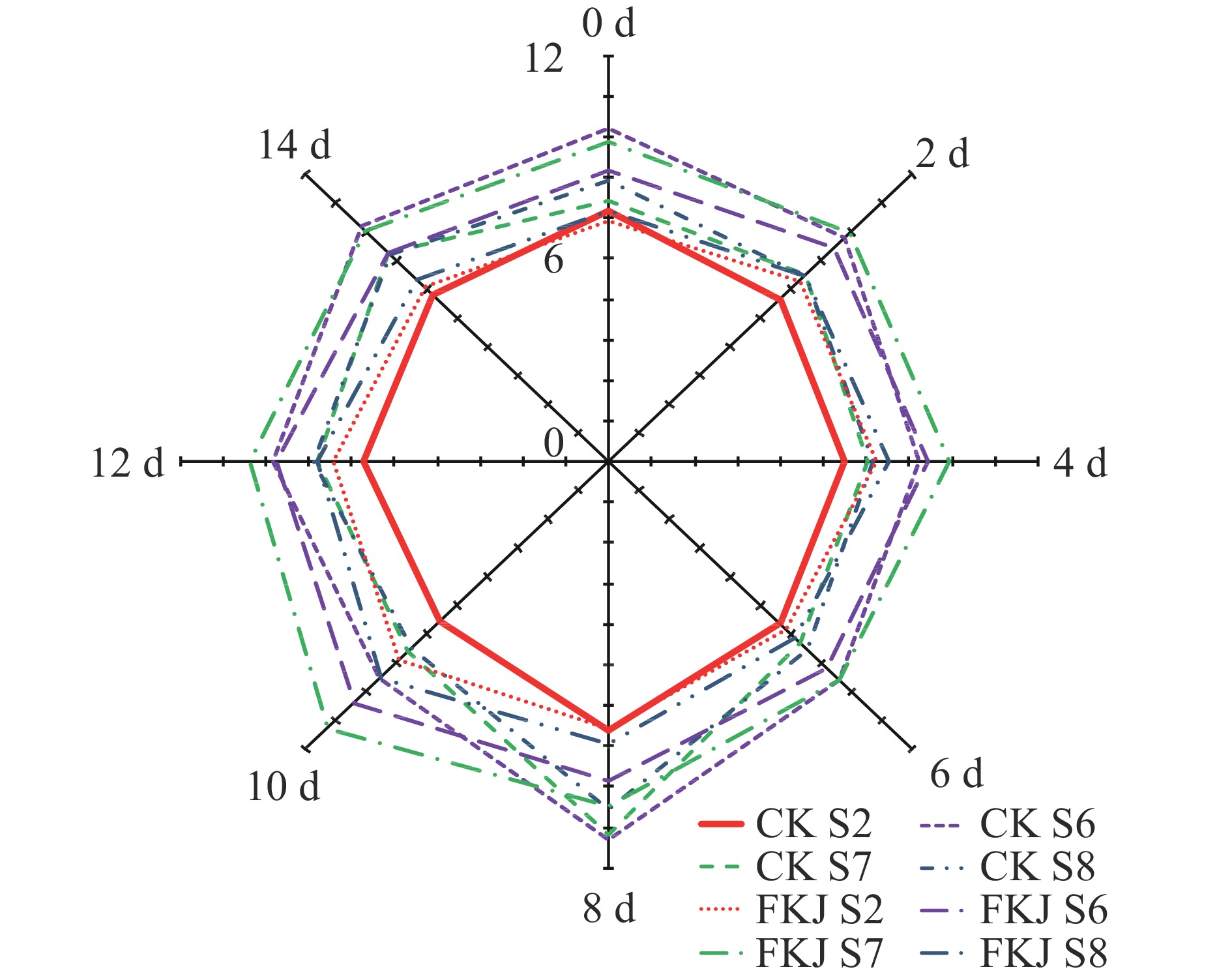
果汁产品风味劣变是其在贮藏过程中面临的主要问题之一,直接表现为特征香气减弱或产生异味等[22]。电子鼻作为一种模拟人体嗅觉的智能感官技术,被广泛应用于食品的品质检测、掺假鉴别以及货架期判断等多个方面[23]。本研究基于电子鼻对冷藏期间猕猴桃果汁的整体气味特征进行监测。在测定过程中,传感器S2(宽范围,非常敏感,对氮氧化物敏感)、S6(对甲烷敏感,宽范围)、S7(对许多萜烯和含硫有机化合物敏感)和S8(醇,对芳香化合物敏感,范围广泛,类似于S6)的响应较为突出,因此,基于以上四个传感器的数据进行后续的分析,并选取54~59 s的数据进行进一步统计分析,以确保数据的准确及稳定性。图3显示了猕猴桃果汁在贮藏过程中传感器S2、S6、S7和S8响应值的变化。在CK中,S6表现出了最高的响应值,其次是S7和S8,两者的响应值接近,而S2的响应值最低;而在FKJ中,S7表现出了最高的响应值,其次依次是S6、S8和S2。这表明CK与FKJ在香气特征上存在差异,并在整个贮藏过程中差异始终存在。此外,CK和FKJ的整体气味特征在贮藏前后并无明显差异,仅分别在贮藏第8 d和第10 d出现了一个较为显著的峰值。这表明,果汁在贮藏一段时间后,其气味特征可能更明显,这可能由于贮藏前期果汁中的部分酶仍具有较高的活性,持续作用于一些大分子物质并释放出更多香气物质。在代文清[22]对苹果梨黑果腺肋花揪果汁的贮藏研究中,同样发现了在贮藏的0~7 d香气物质种类和浓度的持续增加,而在贮藏后期(14~35 d)则观察到了部分香气物质的降解。总体而言,在4 ℃贮藏14 d的猕猴桃果汁,其颜色特征及整体气味特征均较为稳定,并未发生消费者可感知的感官劣变。
2.4 贮藏过程中发酵猕猴桃果汁营养与功能特性的变化
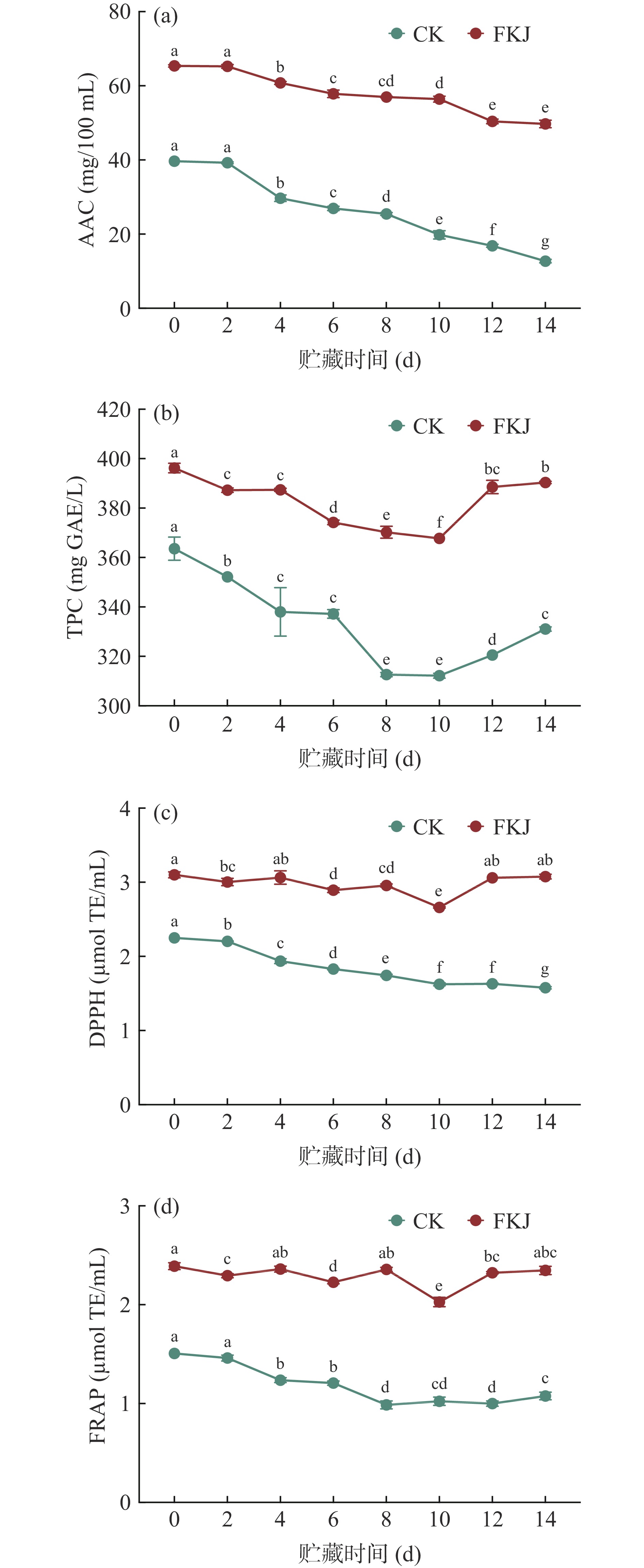
果汁中的生物活性物质对人体健康具有多种积极影响,如降低患癌风险、抗炎和抗氧化等,它们也是评价果汁营养品质和功能特性中的重要指标[24]。AAC是表征猕猴桃产品营养品质的关键参数,因其具有高度不稳定性,在贮藏过程中极易受到温度、光照、氧气、金属离子等因素的影响而氧化降解,从而对产品的营养品质产生负面影响[25]。如图4a所示,在贮藏过程中,CK与FKJ中的AAC均呈下降趋势,但FKJ的下降速度明显延缓,特别是在6~14 d。具体来说,CK在14 d内损失了67.98%的AA,而FKJ仅损失了23.94%。这可能由于乳酸菌发酵形成的低pH和低溶解氧环境以及低温贮藏环境均可以有效提升AA的稳定性[26−27]。
此外,大量研究表明,酚类物质的抗氧化活性为人体带来了显著的健康益处;同时,其对食品的颜色和感官特性均具有一定的积极影响[18,28]。如图4b所示,在整个贮藏期间,果汁中的TPC均呈现先下降后上升的趋势,且在贮藏14 d内,CK中的TPC降低了8.94%,而FKJ仅下降了1.48%。这可能是由于低温贮藏和乳酸发酵形成的低pH环境有助于酚类物质的低损耗,同时,在贮藏后期,随着乳酸菌对低温环境的逐步适应,乳酸菌产生的水解酶可能进一步将酚类聚合物或复杂酚类物质转换为更简单的形式,从而在贮藏过程中补充了因环境因素而降解的酚类物质[18]。
基于DPPH和FRAP评估了贮藏期间猕猴桃果汁的抗氧化能力(图4c、图4d)。结果表明,随着贮藏时间的延长,CK的DPPH和FRAP显著降低(P<0.05),与第0 d相比,贮藏14 d后,CK的DPPH和FRAP分别降低了29.93%和28.54%。而FKJ的DPPH和FRAP虽然在贮藏期间有所降低,但在贮藏结束时,与第0 d并无显著差异(P>0.05)。总的来说,与CK相比,FKJ在贮藏过程中保留了更多的营养物质,同时,具有更为稳定的抗氧化能力。
2.5 基于AAC预测猕猴桃果汁货架期
AA作为猕猴桃及其制品的标志性营养物质之一,常用来作为评价产品在营养品质上是否具有可食用性的标准[29]。因此,基于AAC对猕猴桃果汁进行货架期预测。首先,对CK和FKJ在冷藏期间的AAC进行零级和一级动力学模型拟合(表2)。结果表明,样品AAC下降的零级反应决定系数(R2)均大于0.95,且大于一级反应的R2,拟合度较高。因此,采用零级动力学模型对贮藏过程中AAC的变化进行拟合,并进一步获得果汁货架期预测模型。
表 2 CK和FKJ的AAC变化动力学模型参数Table 2. Parameters of Kinetic model of changes of AAC of CK and FKJ组别 零级动力学模型 一级动力学模型 k R2 k R2 CK −1.9301 0.9709 −0.3085 0.8783 FKJ −1.1061 0.953 −0.0817 0.8881 基于AAC的CK货架期预测模型为:
SL=A−39.66−1.9301 (7) 基于AAC的FKJ货架期预测模型为:
SL=A−65.36−1.1061 (8) 对上述预测模型进行验证(表3),数据显示实际测量值与模型预测值的相对误差均在0.28%~9.55%,均小于10%,这说明该预测模型具有较好的预测精度和可靠性。已有研究表明,当产品中的AAC<10 mg/100 mL时,食用该产品则不能有效地为人体补充AA[30]。因此,设置货架期结束时AAC含量为10 mg/100 mL计算果汁的货架期,结果表明,在4 ℃条件下,CK在贮藏15 d后,AAC低于10 mg/100 mL;而FKJ在贮藏50 d后,AAC才低于10 mg/100 mL。综上,FKJ在4 ℃冷藏期间可以保持较长时间的高营养品质。
表 3 货架期预测模型的验证Table 3. Evaluation of shelf life predictive model组别 贮藏时间(d) 实际测量值
(mg/100 mL)模型预测值
(mg/100 mL)RT(%) CK 0 39.66 39.66 2 39.22 35.80 9.55 4 29.68 31.94 −7.10 6 26.93 28.08 −4.12 8 25.44 24.22 5.02 10 19.80 20.36 −2.77 12 16.84 16.50 2.05 14 12.70 12.64 0.44 FKJ 0 65.36 65.36 2 65.23 63.14 3.30 4 60.76 60.93 −0.28 6 57.83 58.72 −1.52 8 56.95 56.51 0.78 10 56.40 54.29 3.88 12 50.39 52.08 −3.24 14 49.71 49.87 −0.31 3. 结论
在14 d的4 ℃冷藏过程中,FKJ保持了良好的益生菌活性,其乳酸菌活菌数始终高于8.7 lg CFU/mL,同时,果汁的理化性质和感官品质在整个贮藏过程中均表现出较为稳定的状态,特别是色泽和香气均未产生消费者可察觉的变化;就营养品质和功能特性而言,相较于未发酵果汁,益生菌发酵有助于保留和维持果汁中的AAC、TPC及抗氧化活性;此外,以是否可以有效补充AA为标准进行了货架期初步预测,结果表明,FKJ可在4 ℃贮藏50 d,而CK仅能贮藏15 d,这证明FKJ在贮藏期间可以保持较长时间的高营养品质,进一步为发酵猕猴桃果汁的商业化提供了可能性。
-
表 1 猕猴桃果汁在贮藏过程中的颜色指标
Table 1 Color indicators of kiwifruit juice during storage
组别 贮藏时间(d) L* a* b* C* h° ∆E CK 0 70.93±0.25a 2.04±0.06d 37.32±0.06c 37.37±0.06cd 86.87±0.09a 2 70.75±0.15ab 2.15±0.03c 37.40±0.03b 37.46±0.03b 86.72±0.06b 0.24±0.08b 4 70.60±0.12abc 2.19±0.02c 37.39±0.03b 37.46±0.04b 86.65±0.04b 0.39±0.24ab 6 70.69±0.26ab 2.21±0.06c 37.24±0.05d 37.30±0.04e 86.61±0.09bc 0.40±0.19ab 8 70.49±0.16bcd 2.30±0.04b 37.49±0.03a 37.56±0.03a 86.50±0.06cd 0.57±0.35ab 10 70.41±0.20bcd 2.35±0.04b 37.37±0.02bc 37.44±0.02bc 86.41±0.06d 0.63±0.39ab 12 70.32±0.15cd 2.43±0.03a 37.36±0.03bc 37.44±0.03bc 86.28±0.04e 0.74±0.28a 14 70.20±0.12d 2.48±0.05a 37.25±0.05d 37.33±0.05de 86.20±0.06e 0.86±0.12a FKJ 0 61.46±0.13ab 0.44±0.01f 33.09±0.05a 33.09±0.06a 89.25±0.01a 2 61.51±0.15ab 0.45±0.01ef 33.00±0.08ab 33.00±0.08ab 89.23±0.03a 0.11±0.01e 4 61.39±0.16ab 0.44±0.01f 32.91±0.08b 32.91±0.08b 89.25±0.01ab 0.31±0.07d 6 61.28±0.12b 0.46±0.01e 32.72±0.05cd 32.73±0.06cd 89.20±0.01bc 0.41±0.03cd 8 61.46±0.12ab 0.48±0.01b 32.77±0.05c 32.78±0.05c 89.17±0.02cd 0.38±0.06d 10 61.41±0.19ab 0.49±0.01c 32.61±0.09d 32.62±0.09d 89.14±0.01d 0.52±0.16c 12 61.38±0.15ab 0.53±0.01b 32.42±0.07e 32.42±0.07e 89.07±0.02e 0.68±0.03b 14 61.58±0.10a 0.56±0.02a 32.23±0.04f 32.23±0.03f 89.02±0.03f 0.90±0.04a 注:不同小写字母代表同一样品不同时间点存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 CK和FKJ的AAC变化动力学模型参数
Table 2 Parameters of Kinetic model of changes of AAC of CK and FKJ
组别 零级动力学模型 一级动力学模型 k R2 k R2 CK −1.9301 0.9709 −0.3085 0.8783 FKJ −1.1061 0.953 −0.0817 0.8881 表 3 货架期预测模型的验证
Table 3 Evaluation of shelf life predictive model
组别 贮藏时间(d) 实际测量值
(mg/100 mL)模型预测值
(mg/100 mL)RT(%) CK 0 39.66 39.66 2 39.22 35.80 9.55 4 29.68 31.94 −7.10 6 26.93 28.08 −4.12 8 25.44 24.22 5.02 10 19.80 20.36 −2.77 12 16.84 16.50 2.05 14 12.70 12.64 0.44 FKJ 0 65.36 65.36 2 65.23 63.14 3.30 4 60.76 60.93 −0.28 6 57.83 58.72 −1.52 8 56.95 56.51 0.78 10 56.40 54.29 3.88 12 50.39 52.08 −3.24 14 49.71 49.87 −0.31 -
[1] 任灏. 发酵型猕猴桃果汁饮料的研制[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2016. [REN H. Development of the fermented kiwifruit juice[D]. Yangling:Northwest A & F University, 2016.] REN H. Development of the fermented kiwifruit juice[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016.
[2] ZHAO N, ZHANG Y, LIU D, et al. Free and bound volatile compounds in ‘Hayward’ and ‘Hort16A’ kiwifruit and their wines[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2020,246:875−890. doi: 10.1007/s00217-020-03452-9
[3] SZUTOWSKA J. Functional properties of lactic acid bacteria in fermented fruit and vegetable juices:A systematic literature review[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2020,246:357−372. doi: 10.1007/s00217-019-03425-7
[4] WANG Z, FENG Y, YANG N, et al. Fermentation of kiwifruit juice from two cultivars by probiotic bacteria:Bioactive phenolics, antioxidant activities and flavor volatiles[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,373:131455.
[5] CELE N P, AKINOLA S A, MANHIVI V E, et al. Influence of lactic acid bacterium strains on changes in quality, functional compounds and volatile compounds of mango juice from different cultivars during fermentation[J]. Foods,2022,11:682. doi: 10.3390/foods11050682
[6] LAN T, LÜ X, ZHAO Q, et al. Optimization of strains for fermentation of kiwifruit juice and effects of mono- and mixed culture fermentation on its sensory and aroma profiles[J]. Food Chemistry: X,2023,17:100595. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100595
[7] PATEL A R. Probiotic fruit and vegetable juices- recent advances and future perspective[J]. International Food Research Journal,2017,24(5):1850−1857.
[8] MANDHA J, SHUMOY H, MATEMU A O, et al. Evaluation of the composition and quality of watermelon and mango juices fermented by Levilactobacillus brevis, Lacticaseibacillus casei and Pediococcus pentosaceus and subsequent simulated digestion and storage[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,57:5461−5471. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15878
[9] MA T, WANG J, WANG H, et al. Is overnight fresh juice drinkable? The shelf life prediction of non-industrial fresh watermelon juice based on the nutritional quality, microbial safety quality, and sensory quality[J]. Food & Nutrition Research 2020, 64:4237.
[10] BONTSIDIS C, MALLOUCHOS A, TERPOU A, et al. Microbiological and chemical properties of chokeberry juice fermented by novel lactic acid bacteria with potential probiotic properties during fermentation at 4 ℃ for 4 weeks[J]. Foods,2021,10:768. doi: 10.3390/foods10040768
[11] DZANDU B, CHOTIKO A, SATHIVEL S. Antioxidant activity and viability of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, Lacticaseibacillus casei, and co-culture in fermented tomato juice during refrigerated storage[J]. Food Bioscience,2022,50:102085. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.102085
[12] ZHANG H, ZHAO Q, LAN T, et al. Comparative analysis of physicochemical characteristics, nutritional and functional components and antioxidant capacity of fifteen kiwifruit ( Actinidia) cultivars—Comparative analysis of fifteen kiwifruit ( Actinidia) cultivars[J]. Foods,2020,9:1267. doi: 10.3390/foods9091267
[13] MA T, LAN T, JU Y, et al. Comparison of the nutritional properties and biological activities of kiwifruit ( Actinidia) and their different forms of products:Towards making kiwifruit more nutritious and functional[J]. Food & Function,2019,10:1317−1329.
[14] BAI X, HAN M, YUE T, et al. Control of post-acidification and shelf-life prediction of apple juice fermented by Lactobacillus[J]. Food Control,2022,139:109076. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109076
[15] 朱金艳, 赵雪梅, 王殿夫, 等. 超高压和热杀菌的蓝莓果汁饮料贮藏期品质的变化及货架期预测模型[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):320−327. [ZHU J Y, ZHAO X M, WANG D F, et al. Storage quality changes and shelf life predictive modeling of blueberry juice treated by ultra-high pressure and thermal sterilization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):320−327.] ZHU J Y, ZHAO X M, WANG D F, et al . Storage quality changes and shelf life predictive modeling of blueberry juice treated by ultra-high pressure and thermal sterilization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (20 ):320 −327 .[16] MIZUTA A G, DE-MENEZES J L, DA-SILVA L A, et al. High-intensity ultrasound reduces fermentation time and improves textural properties, antioxidant activity and probiotic survival in fermented probiotic strawberry drink[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2023,58:194−204. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.16187
[17] GUEDES C K R D, GUEDES A F L D, DA-SILVA J R, et al. Development of vegetal probiotic beverage of passion fruit ( Passiflora edulis Sims), yam ( Dioscorea cayenensis) and Lacticaseiba cillus casei[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,41(Suppl.2):619−626.
[18] GUMUS S, DEMIRCI A S. Survivability of probiotic strains, Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 and Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 20079 in grape juice and physico-chemical properties of the juice during refrigerated storage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,42:e08122. doi: 10.1590/fst.08122
[19] MANTZOURANI I, KAZAKOS S, TERPOU A, et al. Potential of the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14917 strain to produce functional fermented pomegranate juice[J]. Foods,2019,8:4.
[20] CHEN C, LU Y, YU H, et al. Influence of 4 lactic acid bacteria on the flavor profile of fermented apple juice[J]. Food Bioscience,2019,27:30−36. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2018.11.006
[21] ZHAO D, SHAH N P. Lactic acid bacterial fermentation modified phenolic composition in tea extracts and enhanced their antioxidant activity and cellular uptake of phenolic compounds following in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,20:182−194. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.10.033
[22] 代文清. 苹果梨黑果腺肋花揪汁贮藏品质变化及体外模拟胃肠消化[D]. 锦州:渤海大学, 2021. [DAI W Q. Quality changes of Pingguo pear and Aronia melanocarpa compound Juice during storage and gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[D]. Jinzhou:Bohai University, 2021.] DAI W Q. Quality changes of Pingguo pear and Aronia melanocarpa compound Juice during storage and gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[D]. Jinzhou: Bohai University, 2021.
[23] 胡海敏, 田佳乐, 孙思霖, 等. 固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱结合电子鼻技术分析发酵乳中挥发性风味物质[J]. 微生物学通报,2023,50(1):273−288. [HU H M, TIAN J L, SUN S L, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in fermented milk by solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose[J]. Microbiology China,2023,50(1):273−288.] HU H M, TIAN J L, SUN S L, et al . Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in fermented milk by solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose[J]. Microbiology China,2023 ,50 (1 ):273 −288 .[24] WANG S, QIU Y, ZHU F. Kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.):A review of chemical diversity and biological activities[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 350: 128469.
[25] LAN T, BAO S H, WANG J Q, et al. Shelf life of non-industrial fresh mango juice:Microbial safety, nutritional and sensory characteristics[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,42:101060. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101060
[26] CAI L Q, WANG W J, TONG J W, et al. Changes of bioactive substances in lactic acid bacteria and yeasts fermented kiwifruit extract during the fermentation[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,164:113629. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113629
[27] WANG J, XIE B, SUN Z. Quality parameters and bioactive compound bioaccessibility changes in probiotics fermented mango juice using ultraviolet-assisted ultrasonic pre-treatment during cold storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,137:110438. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110438
[28] LI T L, JIANG T, LIU N, et al. Biotransformation of phenolic profiles and improvement of antioxidant capacities in jujube juice by select lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 339:127859.
[29] 孙强, 张鑫, 高贵田. 海沃德猕猴桃货架期预测模型的建立[J]. [J]. 核农学报,2020,34(8):1729−1736. [SUN Q, ZHANG X, GAO G T. Establishment of prediction model of Hayward kiwifruit shelf-life[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(8):1729−1736.] doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.08.1729 SUN Q, ZHANG X, GAO G T . Establishment of prediction model of Hayward kiwifruit shelf-life[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020 ,34 (8 ):1729 −1736 . doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.08.1729[30] 陈登飘. 探究猕猴桃果汁饮料生产过程中的质量管理[J]. 现代食品,2018,12:161−163. [CHEN D P. Explore the quality management of kiwi fruit juice beverage[J]. Modern Food,2018,12:161−163.] CHEN D P . Explore the quality management of kiwi fruit juice beverage[J]. Modern Food,2018 ,12 :161 −163 . -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 罗康菁,文绍聪,张豆豆,狄建兵. 山药益生菌饮料的研制及其货架期预测. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2025(06): 199-207 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹晓倩,樊晓博,孙占育,党蓓蕾,侯清娥,彭浩,蒋宝. 猕猴桃酵素发酵工艺优化及关键技术分析. 陕西农业科学. 2024(06): 23-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李欣怡,孙翔宇,张文慧,张敏,彭雯,张春玲,马婷婷. 家庭贮藏条件下‘翠香’猕猴桃果实品质演变规律解析. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(22): 19-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



