Structural and Functional Characterization of Resistant Dextrins Prepared by Debranching and Recrystallization Methods
-
摘要: 为探究脱支和重结晶法制备抗性糊精的结构和功能特性。以蜡质玉米和普通玉米淀粉为原料,采用脱支和重结晶法制备抗性糊精,对其形貌特征、结晶结构、热力学特性、官能团、糖苷键等变化进行表征,并探究其抗消化特性。结果表明:与原淀粉相比,两种抗性糊精热稳定性和溶解度显著增加(P<0.05),具有良好的色泽。两种抗性糊精形貌粗糙、呈不规则形状的小碎片聚集体。蜡质玉米抗性糊精呈典型的A型结晶结构,普通玉米抗性糊精呈典型的B型结晶结构。由核磁共振波谱和红外结果可知,抗性糊精在制备过程中糖苷键断裂重新聚合形成新的抗消化糖苷键,无新的官能团产生。两种抗性糊精的抗消化性能力增加,且普通玉米淀粉制备的抗性糊精的慢消化和抗消化性能力最强。综上所述,脱支和重结晶法能提高抗性糊精的抗消化能力,将为抗性糊精的绿色制备工艺进而实现产业化生产提供新的思路和理论指导。Abstract: The purpose of this study was to investigate the structural and functional properties of resistant dextrins prepared by debranching and recrystallization. In this study, waxy maize and normal maize starches were used as raw materials to prepare resistant dextrins by debranching and recrystallization method. The morphological characteristics, crystalline structure, thermodynamic properties, functional groups and glycosidic bonds of the resistant dextrins were characterized, and their anti-digestive properties were explored. The results showed that compared with the native starch, the thermal stability and solubility of the two resistant dextrins were significantly increased (P<0.05), and had good color. The two resistant dextrins were rough in shape and showed small irregularly shaped fragmented aggregates. Waxy maize resistant dextrin showed a typical A-type crystalline structure and normal maize resistant dextrin showed a typical B-type crystalline structure. From the NMR spectra and infrared results, it could be seen that the glycosidic bonds of the resistant dextrins were broken and re-polymerized to form new anti-digestive glycosidic bonds during the preparation process, and there were no new functional groups generated. The anti-digestive ability of the two resistant dextrins increased, and the resistant dextrin prepared from normal maize starch had the strongest slowly digestible and anti-digestive ability. In conclusion, the debranching and recrystallization method can improve the anti-digestive ability of resistant dextrin, which will provide new ideas and theoretical guidance for the green preparation process of resistant dextrin and then realize the industrial production.
-
Keywords:
- resistant dextrin /
- debranching /
- recrystallization /
- structure /
- functional features /
- digestibility
-
膳食纤维是人体第七类营养素,具有控制体重,稳定胆固醇水平,改善消化系统功能和维持心血管健康等诸多功能[1−3]。近年来,通过强化食品加工过程中的膳食纤维含量,成为饮食干预常见慢性疾病的有效途径[4]。抗性糊精是短链葡萄糖聚合物,作为低分子量水溶性膳食纤维,具有缓解血糖骤升[5],降低血脂[6−7],调节肠道菌群[8−9],降低体重[10−11],增强微量元素的吸收[12−13]等诸多生理功效而备受关注。抗性糊精还被广泛应用于饮料、糖果、巧克力、乳制品、焙烤食品、营养能量棒和肉制品等产品中[14]。
目前,最早和最常用的抗性糊精的制备方法是酸热法,主要是通过在高温下用盐酸或其他酸浸泡淀粉,再经过液化、酶水解、脱色、过滤、浓缩、喷雾干燥等系列操作,最终得到抗性糊精产品[15]。研究表明,较高的酸浓度和较长的加热时间有利于增加抗性糊精中膳食纤维含量,而有机酸的浓度对抗性糊精的化学结构也有很大影响[16]。然而,酸热法制备的抗性糊精存在纯度低、产品颜色深、耗时耗力、环境污染等问题。近年来,有学者关注复合酶法制备抗性糊精的绿色工艺。Zhan等[17]采用分支酶和灰曲霉α-葡萄糖苷酶等酶作用于焦糊精,得到抗性含量为70.6%的抗性糊精。脱支和重结晶法复合酶解工艺主要是糊化后的淀粉在脱支酶的作用下使支链淀粉中的α-1,6糖苷键断裂,形成长短不一的直链分子链产物[18];然后在50 ℃或低温环境下高直链含量支链淀粉发生分子重排形成新的结晶体,得到抗性糊精。该方法对环境友好,产品色泽好,节省化学试剂,具有良好的工业应用前景。因此,本研究以蜡质玉米淀粉和普通玉米淀粉为原料,采用绿色环保的脱支和重结晶复合酶水解工艺制备抗性糊精,探究其结构特性和功能特性并构建关联,为抗性糊精的产业化生产和应用提供新的思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
普通玉米淀粉、蜡质玉米淀粉 东莞市东岳葡萄糖厂有限公司;普鲁兰酶(2 U/mg)、淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(0.3 U/mg) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;猪胰酶(8 U/mg)、猪胰α-淀粉酶(8 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;苯甲酸、醋酸、无水乙醇、氯化钙 分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂;葡萄糖氧化酶/过氧化物酶葡萄糖检测试剂盒(Glucose oxidase/peroxideenzymatic glucose assay kit,GOPOD) 爱尔兰Megazyme公司。
DSC-8000型差示扫描量热仪 美国Perkin-Elmer公司;D8-ADVANCE 型X射线衍射仪 德国BRUKER-AXS有限公司;TG20-WSI(I类B型)离心机 湘麓离心机仪器有限公司;TDL-60B离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;DZF-6096真空干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;Nicolet iN10显微红外光谱仪 美国Thermo Scientific;CM-5分光测色计 日本KONICA MINOLTA;SCIENTZ-18N冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;MR Hei-Tec磁力加热搅拌器 德国 Heigolph公司; 752N紫外分光光度计 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司; MA35水分测定仪 赛多利斯仪器系统有限公司; BRUKER AVANCE 400核磁共振波谱 德国布鲁克公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 抗性糊精的制备
参考Lee等[19]方法略作修改,分别称取50 g蜡质玉米淀粉(Waxy corn starch,WCS)和50 g普通玉米淀粉(Normal corn starch,NCS),分别加入醋酸钠缓冲溶液(0.01 mol/L、pH4.5)至浓度为0.2 g/mL,在沸水下加热搅拌糊化30 min。待淀粉溶液冷却至50 ℃后,加入普鲁兰酶(5%,w/w,基于淀粉干基质量),在50 ℃水浴锅中连续磁力搅拌7 d,使其完全脱支和重结晶,得到粗抗性糊精样品。随后,将粗抗性糊精样品沸水浴蒸煮10 min,然后冷却到60 ℃,使用氢氧化钠溶液(0.1 mol/L)调节溶液pH6.9,加入猪胰α-淀粉酶(5%,w/w,基于粗抗性糊精含量),在37 ℃下磁力搅拌12 h。经酶水解后的抗性糊精离心三次(10000×g,15 min),沉淀物进行冷冻干燥,粉碎,过100目筛密封保存备用。原淀粉对照样品分别标记为WCS和NCS,抗性糊精样品分别标记为WRD和NRD。
1.2.2 形貌特征观察
采用扫描电子显微镜对抗性糊精和原淀粉样品进行显微形貌观察。将抗性糊精和原淀粉样品均匀分散在贴有导电胶的样品台上,利用离溅射镀膜仪喷金,分别放大1000倍和2000倍观察样品的形貌特征。
1.2.3 热力学特性测定
利用差式扫描量热仪(DSC)测定抗性糊精和原淀粉样品的热力学特性。称取3 mg的干基样品,以3:7的比例加入蒸馏水溶解样品并密封在铝DSC锅中,然后在常温条件下放置过夜。在10 ℃/min的加热速率下,从25 ℃到120 ℃扫描样品,每个样品做三次平行,并使用空铝DSC盘作为参考。
1.2.4 结晶特性测定
将抗性糊精和原淀粉样品在鼓风干燥箱内烘干至恒重,采用X-射线衍射仪对其结晶结构进行测定。衍射条件为:电压30 kV,电流30 mA,铜靶,扫描区域2θ为5°~35°,辐射线为Cu Ka,扫描速度2°/min,步长间隔为0.02°[20]。采用MDI Jade 6软件对结晶区域和总面积区间分别进行积分计算,相对结晶度(Relative crystallinity,RC)按照公式(1)所示计算:
RC(%)=AcAc+Aa×100 (1) 式中:Ac—结晶区部分面积;Aa—非晶区部分面积;Ac+Aa—总面积区间。
1.2.5 显微红外光谱分析
利用显微红外光谱仪对样品的官能团进行测定。取少量的抗性糊精和原淀粉样品置于显微玻片中铺平后,放到红外显微镜下,在3500~750 cm−1范围进行红外光谱扫描,调至最佳光圈,寻找合适的样品特征,选取光谱图。
1.2.6 溶解度测定
称量0.5 g抗性糊精和原淀粉样品置于离心管中,加入25 mL去离子水配成质量分数2%的样品悬浮液,在室温(25 ℃)条件下磁力搅拌30 min防止样品沉淀,在3000×g下离心15 min,取上清液置于培养皿中,在105 ℃真空干燥箱中烘至恒重并称重。按照公式(2)计算溶解度:
溶解度(%)=AW×100 (2) 式中:A为上清液蒸干后质量(g);W为样品质量(g)。
1.2.7 白度
利用分光测色计测定抗性糊精和原淀粉样品的白度特征值。每个样品至少重复测定3次。按照公式(3)计算样品白度:
白度=√(100−L)2+a2+b2 (3) 式中:L为亮度;a为有色物质的红绿偏向;b为有色物质的黄蓝偏向。
1.2.8 核磁共振氢谱分析
分别将50 mg的抗性糊精样品及其原淀粉50 mg溶于0.55 mL D2O中,以此方法进行三次冷冻干燥处理使其与重水充分交换,复溶于D2O中 ,记录在25 ℃、400 MHz工作时的1H-NMR谱。该核磁共振波谱仪配备了一个5 mm低温探头和一个碳增强三共振反向探测器与一个脉冲场梯度探头,128次扫描,扫描宽度为16 (10-6),采样4 s,延迟时间为1 s,获得1H-NMR谱图,采用MestReNove进行数据处理和绘图。
1.2.9 体外消化性测定
参考Chen等[21]方法,分别称取600 mg的抗性糊精及其原淀粉样品于离心管中,加入20 mL乙酸钠缓冲液(pH5.2,0.1 mol/L),充分涡旋,沸水浴30 min,在水浴过程中要不断地振荡混匀使样品完全糊化。经冷却置于37 ℃水浴锅中磁力搅拌30 min。在离心管中加入5 mL由猪胰酶(3×103 U)和淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(40 U)组成的混合酶解液,振荡混匀,间隔20 min和120 min分别取出0.25 mL酶解液,置于10 mL 66%的乙醇中灭酶,涡旋混匀。酶解液在3500×g条件下离心10 min,采用GOPOD法测定葡萄糖含量。
通过公式(4)计算相应的样品中葡萄糖含量:
葡萄糖含量(%)=At×Vt×C×DAs×Wt×100 (4) 式中:At=测试溶液的吸光值;Vt=测试溶液的总体积(mL);C=标准葡萄糖的浓度(mg/mL);As=标准葡萄糖的吸光值;Wt=样品的重量(mg);D=稀释倍数40。
快速消化淀粉(Rapidly digestible starch,RDS)、慢消化淀粉(Slowly digestible starch,SDS)以及抗性淀粉(Resistant starch,RS)含量按照公式(5)~(7)计算:
RDS(%)=(G20−FG)×0.9 (5) SDS(%)=(G120−G20)×0.9 (6) RS(%)=[TS−(RDS+SDS)]=[TS−(G120×0.9)] (7) 式中:G20=淀粉水解20 min酶解液的葡萄糖含量(mg);FG=初始葡萄糖含量(mg);G120=淀粉水解120 min酶解液的葡萄糖含量(mg);TS=样品总淀粉含量(mg)。
1.3 数据处理
各组实验均至少重复测定3次,使用Excel 2019进行RDS、SDS、RS、溶解度和白度等数据计算和分析,利用SPSS 25软件进行标准偏差计算和单因素方差分析,使用Origin 2021进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
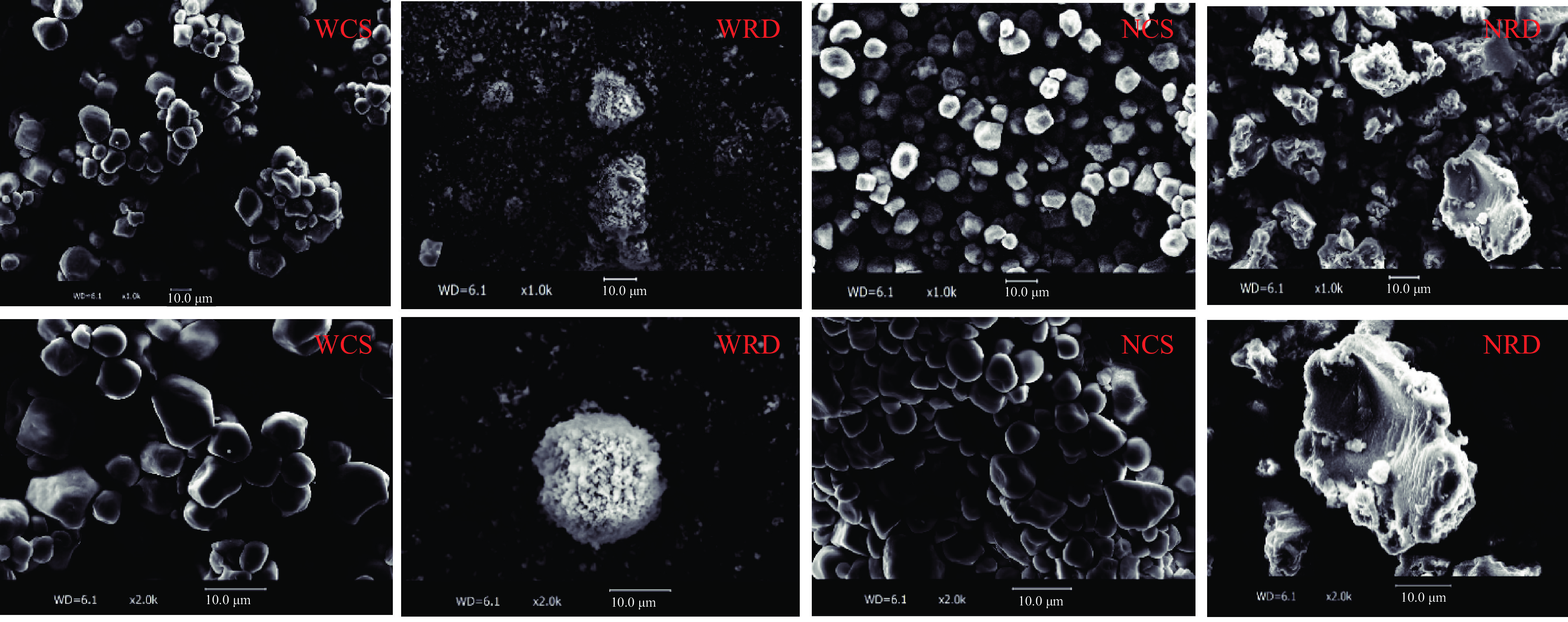
2.1 两种抗性糊精的微观结构分析
抗性糊精和原淀粉样品的扫描电子显微镜图如图1所示。NCS和WCS颗粒表面光滑,呈均匀圆球或多面体的典型A型淀粉结构特征[22]。抗性糊精样品由于在制备过程中颗粒结构遭到破坏,表面形态较为粗糙,主要归因于淀粉颗粒糊化后,淀粉中的大部分氢键断裂,双螺旋打开,支链和直链溶出,然后在脱支酶的作用下,使支链淀粉中的α-1,6糖苷键断裂,形成长短不一的直链分子链产物,通过分子重排结晶而形成不规则形状的小碎片聚集体。与NRD相比,WRD表面更为粗糙,碎片化程度更高,可能是WCS支链淀粉含量高(95%以上),在脱支和重结晶过程中脱支更完全,造成其含有的支链淀粉含量显著下降[23]。
2.2 两种抗性糊精的热力学特性分析
抗性糊精及其原淀粉样品的热力学特征值如表1所示。与天然淀粉相比,抗性糊精的糊化温度(起始温度To,峰值温度Tp和终止温度Tc)显著升高(P<0.05),表现出良好的热稳定性,主要归因于酶解脱支释放出的线形短直链淀粉分子经过重结晶形成了热稳定性更强的结构[22]。WCS和NCS的焓值(ΔH)分别为:17.13±0.63和21.41±0.89 J/g,而WRD和NRD的ΔH分别为9.79±1.15和2.28±0.18 J/g。与原淀粉相比,抗性糊精的ΔH显著降低(P<0.05),说明原淀粉在脱支和重结晶过程中,其支链淀粉中的双螺旋结构经酶解脱支作用,结晶结构遭到了破坏。WRD的焓值下降幅度低于NRD,这说明WRD容易脱支形成较多的线性直链分子,有利于在结晶过程中淀粉分子的重排形成更加致密的聚集体,这可能是WRD形貌更粗糙、碎片化程度更高的原因(图1)。
表 1 抗性糊精及其原淀粉的热力学特征值Table 1. Thermal transformation properties of resistant dextrins and their native starch样品 To (℃) Tp (℃) Tc (℃) Tc−To(℃) ΔH (J/g) WCS 63.43±0.15b 69.33±0.01b 75.41±0.15c 11.98±0.05c 17.13±0.63b WRD 97.41±1.00a 106.91±0.85a 114.27±0.38a 16.87±0.76bc 9.79±1.15c NCS 61.92±0.10b 69.63±0.24b 79.55±0.90b 17.62±0.91b 21.41±0.89a NRD 93.81±1.17a 104.12±0.29a 117.34±3.76a 23.52±2.60a 2.28±0.18d 注:同列字母不同代表数据之间有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.3 两种抗性糊精的结晶特性分析
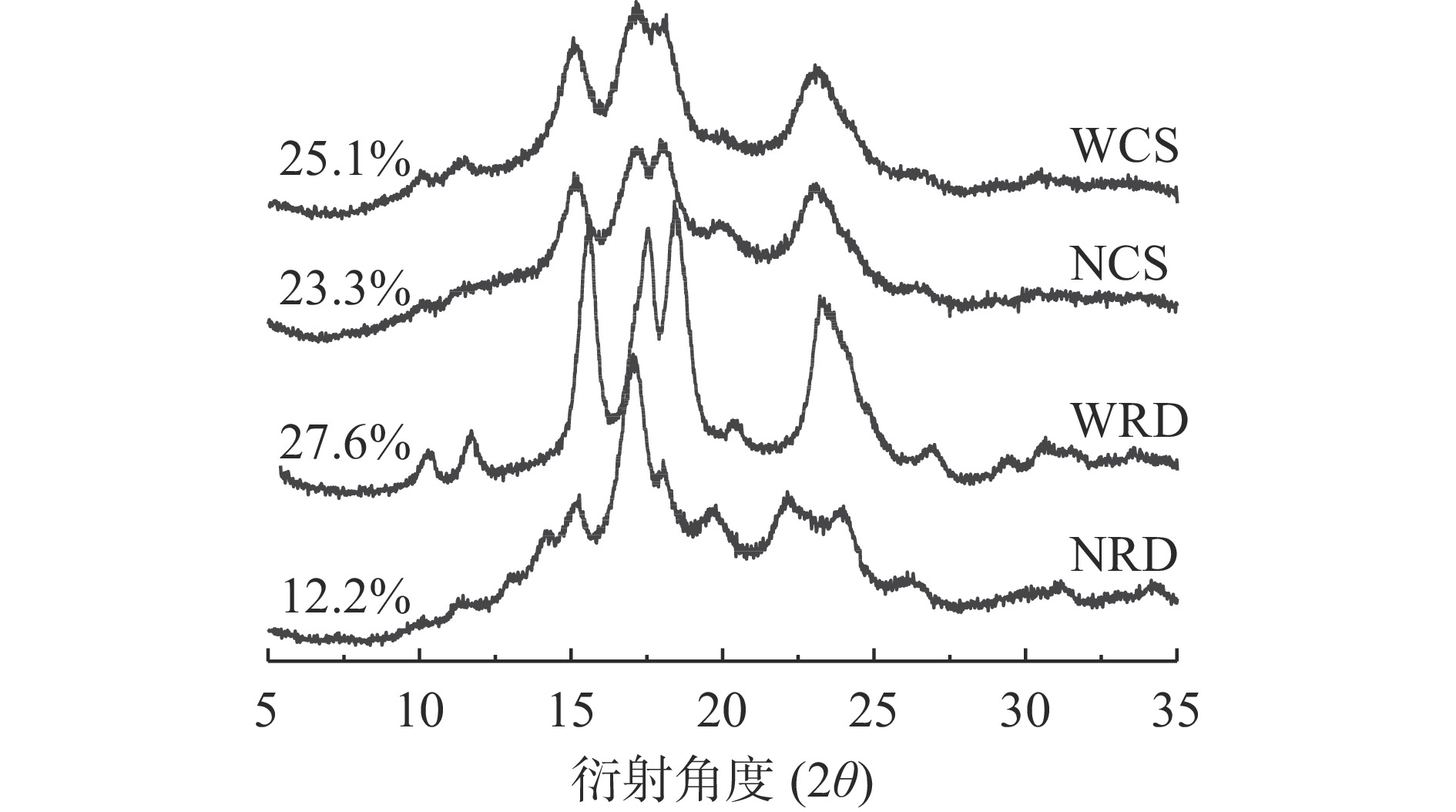
抗性糊精及其原淀粉的X-衍射图谱及结晶度如图2所示。NCS和WCS的结晶图谱在15°、17°、18°和23°有强衍射峰,且在17°和18°附近呈现双衍射峰,为典型的A型晶体结构[24]。与原淀粉相比,不同种类玉米淀粉制备的抗性糊精的结晶型和结晶度呈现出不同的变化趋势。与WCS相比,WRD的晶型未发生明显变化,结晶度呈现增加趋势,表明经普鲁兰酶酶解脱支后支链淀粉的线性链容易形成双螺旋[25]。与NCS相比,NRD的结晶图谱在15°和18°的衍射峰强度下降,由23°的强衍射峰转变为22°和24°的双衍射峰,呈现出典型的B型晶体结构,这是因为脱支的淀粉链在50 ℃下很容易结晶成B型排列,而快速链缔合结晶通常也会诱导形成完美度相对较低的B型晶体[19]。另一方面,WRD的结晶高于NRD,这可能是WRD在糊化和脱支过程中生成了更多的短直链分子链产物,脱支更完全,并在温和加热的条件下缓慢缔合形成了结晶度更高的A型晶体[26]。
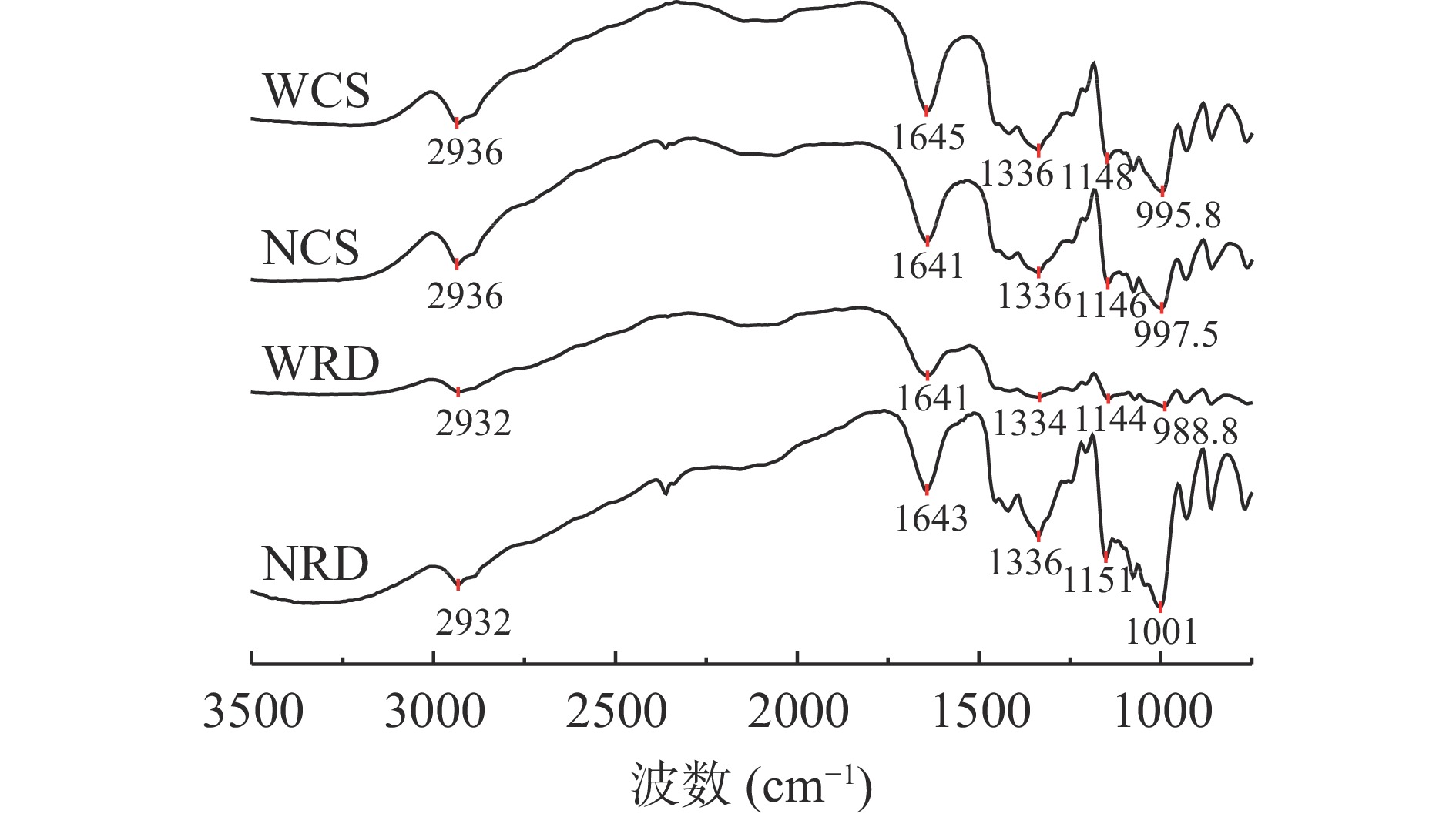
2.4 两种抗性糊精的显微红外光谱分析
抗性糊精及其原淀粉的红外光谱图如图3所示。由图3可知,原淀粉表现出在2920~2940 cm−1的C-H伸缩振动峰,1640~1150 cm−1的C=O伸缩振动峰,1000~990 cm−1处的吡喃糖环的特征吸收峰[27]。与原淀粉相比,抗性糊精的吸收峰位置未发生明显的变化,说明抗性糊精在形成的过程中未产生新的官能团,脱支和重结晶不会改变淀粉的结构,与张颖[28]和张婷等[29]的研究结果保持一致。但抗性糊精与原淀粉在吸收峰强度上存在差异,这可能归因于制备过程中发生的糖苷键断裂和聚合反应[30]。
2.5 两种抗性糊精的溶解度和白度分析
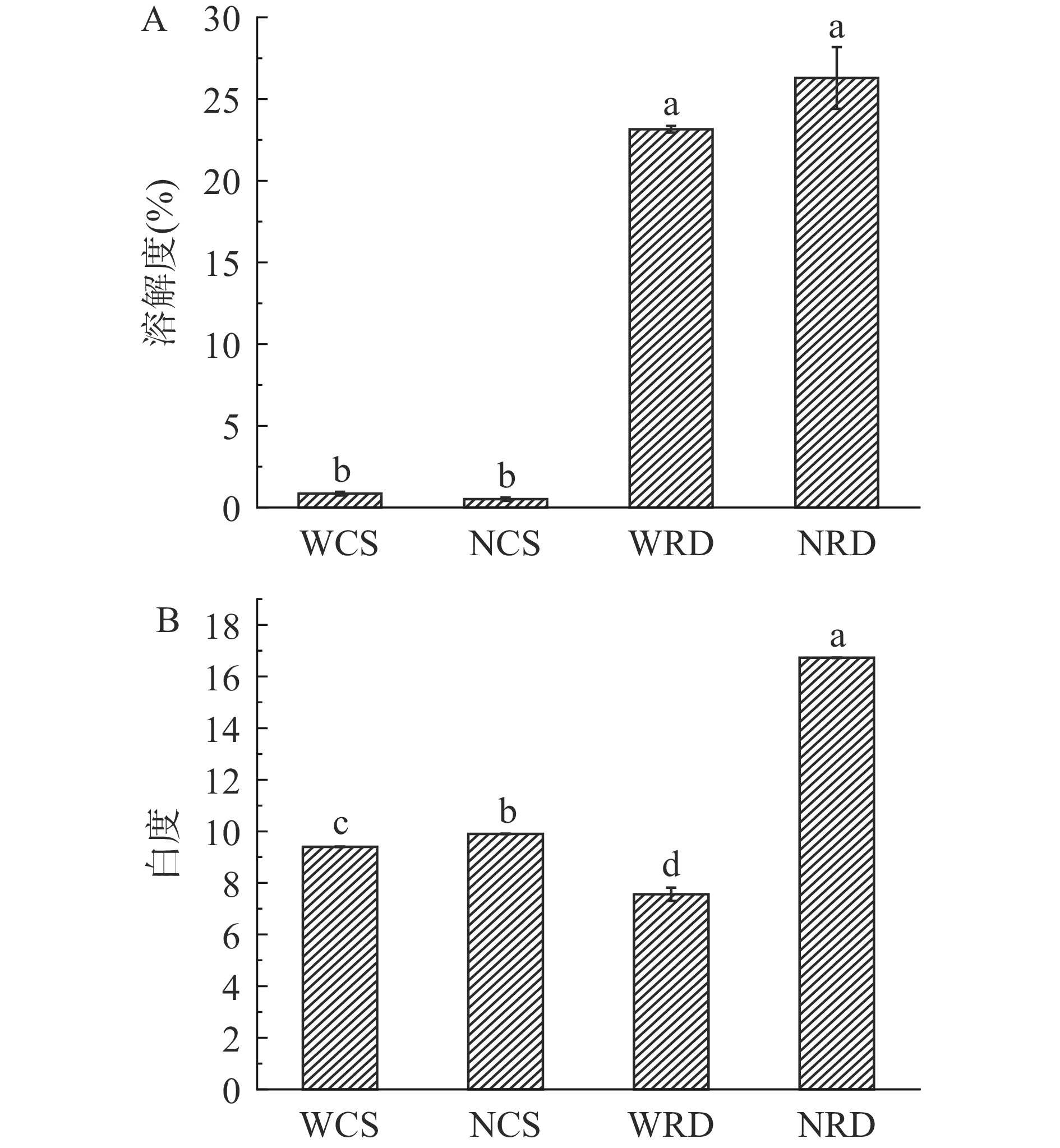
溶解度是评判抗性糊精在饮料等行业中应用的关键指标。抗性糊精及其原淀粉的溶解度和白度如图4所示。与原淀粉相比,抗性糊精的溶解度显著增加(P<0.05),这是因为在脱支酶的作用下,淀粉颗粒的无定形区、空间结构和结晶区被破坏,降解生成更多可溶性的小分子物质[31],随后再聚合生成可溶性更高的抗性糊精。如图4所示,NRD的白度显著增加(P<0.05),而WRD的白度略有下降,这说明经复合酶解工艺制备的抗性糊精具有优良的产品色泽。
![]() 图 4 抗性糊精及其原淀粉的溶解度(A)和白度(B)注:字母不同代表数据之间有显著性差异(P<0.05);图6同。Figure 4. Solubility (A) and whiteness (B) of resistant dextrins and their native starch
图 4 抗性糊精及其原淀粉的溶解度(A)和白度(B)注:字母不同代表数据之间有显著性差异(P<0.05);图6同。Figure 4. Solubility (A) and whiteness (B) of resistant dextrins and their native starch2.6 两种抗性糊精的核磁共振波谱分析
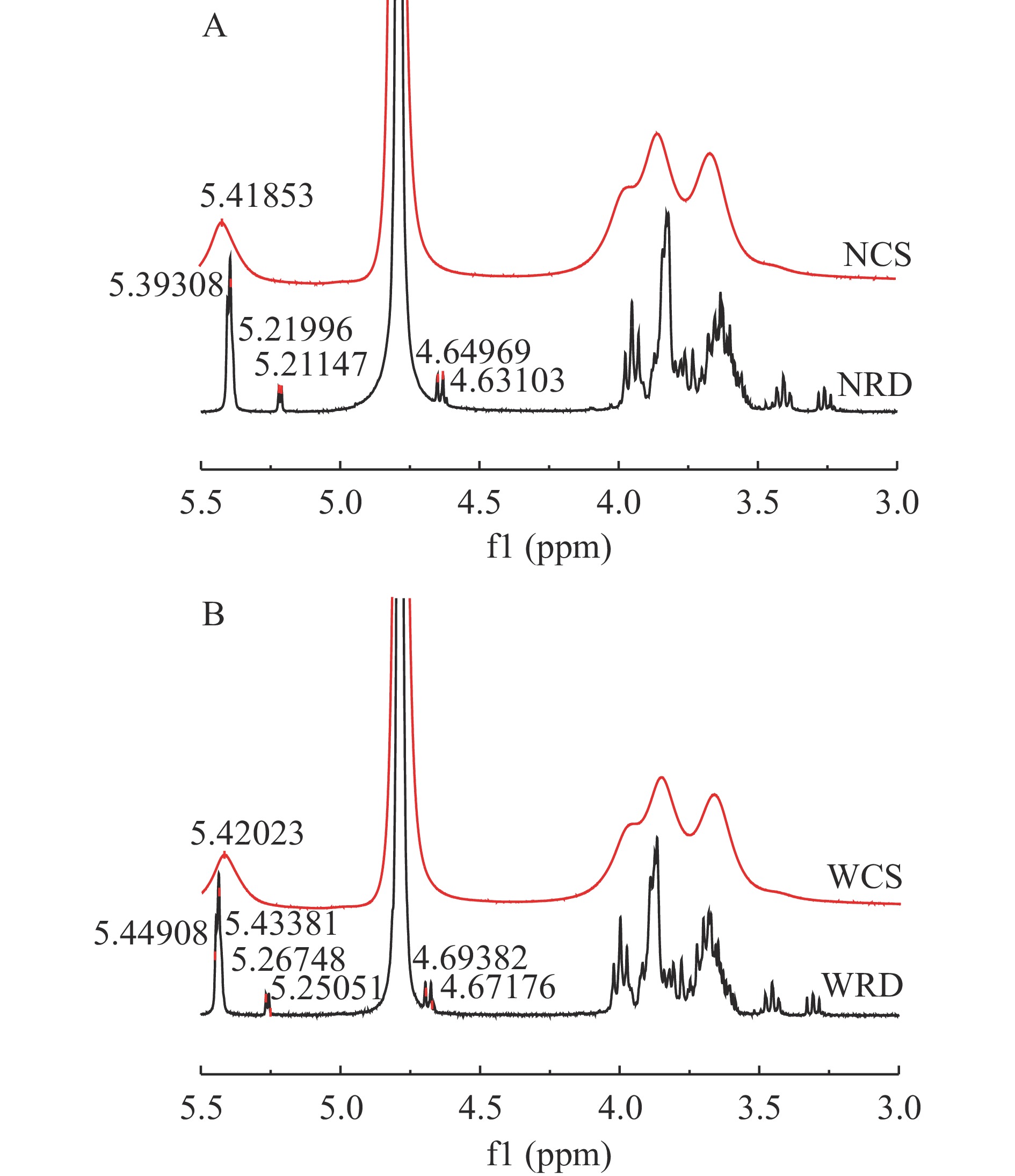
核磁共振波谱能分析抗性糊精样品的分子结构及糖苷键的类型,本研究采用1H-NMR分析抗性糊精及其原淀粉的糖苷键结构及其变化。抗性糊精及其原淀粉的一维氢谱如图5所示。由图5(A)可知,与NCS相比,NRD在δ 4.5~5.5×10−6区域内有5.39、5.21、4.63和4.64 ppm处出现了新的异头氢信号。由图5(B)可知,与WCS相比,WRD在δ 4.5~5.5×10−6区域内有5.44、5.43、5.26、5.25、4.69、4.67和4.69 ppm处出现了新的异头氢信号。其中,4.79 ppm为D2O质子峰,α型吡喃糖H-1质子的化学位移大于4.95 ppm,β型吡喃糖H-1质子的化学位移小于4.95 ppm[32]。与原淀粉相比,抗性糊精有β型吡喃糖和新的α型吡喃糖生成,表明原淀粉在糊化、脱支和重结晶过程中形成了新的糖苷键,进一步证实了抗性糊精在制备过程中发生了糖苷键的断裂和转糖苷化反应,而导致其糖环发生了振动[33],这与上述红外光谱的分析结果相一致。
2.7 两种抗性糊精的体外消化性分析
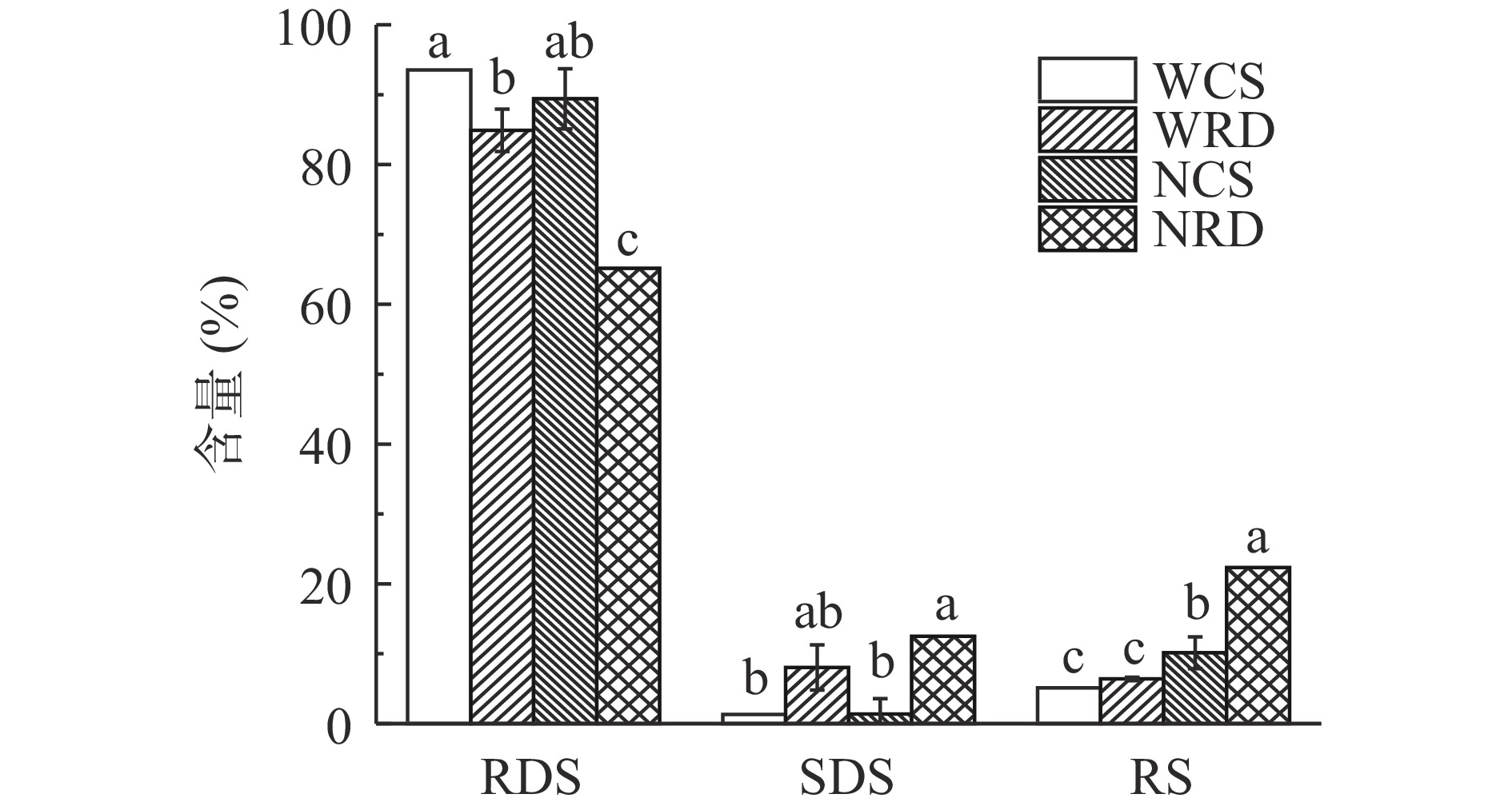
抗性糊精及其原淀粉的体外消化特性如图6所示。两种抗性糊精及其原淀粉的RDS含量排序依次是:WCS>NCS>WRD>NRD,SDS含量排序依次是:NRD>WRD>NCS>WCS,RS含量排序依次是:NRD>NCS>WRD>WCS。与原淀粉相比,两种抗性糊精的消化率明显下降,表现为RDS含量显著下降,SDS和RS含量显著升高(P<0.05)。两种抗性糊精相比之下,NRD的SDS和RS含量最高均高于WRD,具有更好的抗消化性。导致其抗消化性增加的原因有以下三点:a.本研究制备的抗性糊精具有较高的热稳定性,这有助于提高其对淀粉消化酶的抵抗力[34],是导致抗性糊精难消化的原因之一。经脱支得到的短直链线性分子通过去除淀粉中限制链结合的支链键而获得流动性,随着去分支的继续,淀粉分散度变薄,这促进了分子间的结合和双螺旋结构的形成[15],从而使抗性糊精的热稳定性提高、抗消化性提高。b.酶水解纯化提高了RD的结晶度,从而增加了抗性糊精对消化酶的抗性[35]。c.淀粉经糊化、脱支和重结晶过程发生了糖苷键的断裂和转糖苷化反应,经分子重排生成了一些抗消化的糖苷键例如β型吡喃糖和新的α型吡喃糖等,从而提高了抗性糊精对酶的抗消化性。
3. 结论
本研究以普通玉米淀粉和蜡质玉米淀粉为原料,采用绿色环保的脱支、重结晶结合酶水解工艺制备抗性糊精。通过脱支、重结晶和酶水解得到的两种抗性糊精表面粗糙,呈不规则形状的小碎片聚集体,热稳定性高,溶解度增加,具有优良的色泽。NRD呈典型的B型结晶结构,而WRD呈典型的A型结晶结构。在酶解脱支处理中,原有的糖苷键断裂,重新结晶聚合产生新的不易被淀粉酶消化的糖苷键,使抗性糊精的抗消化性增加,其中,NRD的慢消化和抗消化性最好。本研究将为进一步拓宽抗性糊精的绿色环保制备方法及其产业化生产和应用提供新的思路和理论指导。
-
图 4 抗性糊精及其原淀粉的溶解度(A)和白度(B)
注:字母不同代表数据之间有显著性差异(P<0.05);图6同。
Figure 4. Solubility (A) and whiteness (B) of resistant dextrins and their native starch
表 1 抗性糊精及其原淀粉的热力学特征值
Table 1 Thermal transformation properties of resistant dextrins and their native starch
样品 To (℃) Tp (℃) Tc (℃) Tc−To(℃) ΔH (J/g) WCS 63.43±0.15b 69.33±0.01b 75.41±0.15c 11.98±0.05c 17.13±0.63b WRD 97.41±1.00a 106.91±0.85a 114.27±0.38a 16.87±0.76bc 9.79±1.15c NCS 61.92±0.10b 69.63±0.24b 79.55±0.90b 17.62±0.91b 21.41±0.89a NRD 93.81±1.17a 104.12±0.29a 117.34±3.76a 23.52±2.60a 2.28±0.18d 注:同列字母不同代表数据之间有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] EDOARDO C. The behavior of dietary fiber in the gastrointestinal tract determines its physiological effect[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2017,57(16):3543−3564. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1180501
[2] WEN H, MA S, LI L, et al. Application and development prospects of dietary fibers in flour products[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2017,2017(1):1−8.
[3] DEVINDER D, MICHAEL M, RAJPUT H, et al. Dietary fibre in foods:A review[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2012,49(3):255−266. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0365-5
[4] OLIVIA-G S, KILPATRICK M, BRESLIN M, et al. Dietary fiber and its associations with depression and inflammation[J]. Nutrition Reviews,2020,78(5):394−411. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz072
[5] 胡帆, 钮忆欣, 屠晓芳, 等. 抗性糊精通过增强胰岛素信号转导改善db/db小鼠胰岛素抵抗[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版),2018,38(10):1157−1161. [HU F, NIU Y X, TU X F, et al. Resistant dextrin improves insulin resistance in db/db mice by enhancing insulin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Medical Science),2018,38(10):1157−1161.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2018.10.004 HU F, NIU Y X, TU X F, et al . Resistant dextrin improves insulin resistance in db/db mice by enhancing insulin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Medical Science),2018 ,38 (10 ):1157 −1161 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2018.10.004[6] YUKA K, OGA H, TAGAMI H, et al. Suppressive effect of resistant maltodextrin on postprandial blood triacylglycerol elevation[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2007,46(3):133−138. doi: 10.1007/s00394-007-0643-1
[7] YUKA K, YOSHIKAWA Y, MIYAZATO S, et al. Effect of resistant maltodextrin on digestion and absorption of lipids[J]. Journal of Health Science,2009,55(5):838−844. doi: 10.1248/jhs.55.838
[8] RENATA B, JOCHYM K, SLIZEWSKA K, et al. The effect of citric acid-modified enzyme-resistant dextrin on growth and metabolism of selected strains of probiotic and other intestinal bacteria[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2010,2(2):126−133. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2010.03.002
[9] LEFRANC-MILLOT C, GUERIN-DEREMAUX L, WILS D, et al. Impact of a resistant dextrin on intestinal ecology:How altering the digestive ecosystem with NUTRIOSE®, a soluble fibre with prebiotic properties, may be beneficial for health[J]. Journal of International Medical Research,2012,40(1):211−224. doi: 10.1177/147323001204000122
[10] MARK-R H, COMMANE D-M, GUERINUÉRIN-DEREMAUX L, et al. Impact of dietary supplementation with resistant dextrin (NUTRIOSE®) on satiety, glycaemia, and related endpoints, in healthy adults[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2021,60(8):4635−4643. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02618-9
[11] 傅金凤, 谭思敏, 涂师运, 等. 5种食品原料对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖大鼠肠道菌群和短链脂肪酸的影响(英文)[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(13):89−100. [FU J F, TAN S M, TU S Y, et al. Effects of five food materials on the abundance of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in high-fat diet-induced obese rats[J]. Food Science,2022,43(13):89−100.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210612-152 FU J F, TAN S M, TU S Y, et al . Effects of five food materials on the abundance of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in high-fat diet-induced obese rats[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (13 ):89 −100 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210612-152[12] SHOKO M, NAKAGAWA C, KISHIMOTO Y, et al. Promotive effects of resistant maltodextrin on apparent absorption of calcium, magnesium, iron and zinc in rats[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2010,49(3):165−171. doi: 10.1007/s00394-009-0062-6
[13] M-A F, DEHGHAN P, NAMAZI N. Prebiotic supplementation modulates advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), soluble receptor for AGEs (sRAGE), and cardiometabolic risk factors through improving metabolic endotoxemia:A randomized-controlled clinical trial[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2020,59(7):3009−3021. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-02140-z
[14] 李泽润, 朱坤福, 田延军, 等. 抗性糊精的生产方法及应用概述[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(6):196−199. [LI Z R, ZHU K F, TIAN Y J, et al. Production method and application overview of resistant dextrin[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(6):196−199.] LI Z R, ZHU K F, TIAN Y J, et al . Production method and application overview of resistant dextrin[J]. China Condiment,2022 ,47 (6 ):196 −199 .[15] KAMONRAT T, KRUSONG K, TANANUWONG K. In-depth study of the changes in properties and molecular structure of cassava starch during resistant dextrin preparation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297:124996. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124996
[16] KAMONRAT T, SHI Y-C, KRUSONG K, et al. Molecular structure and properties of cassava-based resistant maltodextrins[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,369:130876. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130876
[17] ZHAN Z L, LIU J, REN L Q, et al. Preparation of high-quality resistant dextrin through pyrodextrin by a multienzyme complex[J]. Food Bioscience,2022,47:101701. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101701
[18] 郭媚下. 支链淀粉不同条件脱支重结晶规律的研究[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2018. [GUO M X. Study on recrystallization orderlines of amylopctin under different debranching condtions[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.] GUO M X. Study on recrystallization orderlines of amylopctin under different debranching condtions[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[19] LEE D J , KIM J M , LIM S T. Characterization of resistant waxy maize dextrins prepared by simultaneous debranching and crystallization followed by acidic or enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,121:106942. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106942
[20] 徐美琪, 张昱格, 陈旭, 等. 冰湖野米粉及其淀粉的精细结构、理化和消化特性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(16):5279−5287. [XU M Q, ZHANG Y G, CHEN X, et al. Study on the fine structure, physicochemical and digestive characteristics of zizania palustris flour and its starch[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(16):5279−5287.] XU M Q, ZHANG Y G, CHEN X, et al . Study on the fine structure, physicochemical and digestive characteristics of zizania palustris flour and its starch[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022 ,13 (16 ):5279 −5287 .[21] CHEN X, ZHANG Y G, ZOU Y, et al. Heat-induced amorphous aggregates assembly of soy protein modulate in vitro digestibility of potato starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecule,2023,227:222−230. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.058
[22] 陈旭. 蛋白和脂质对淀粉消化特性的影响机理研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2017. [CHEN X. Mechanism for the digestion properties of starch influenced by lipid and protein[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2017.] CHEN X. Mechanism for the digestion properties of starch influenced by lipid and protein[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[23] DONG-JIN L, KIM J-M, LIM S-T. Characterization of resistant waxy maize dextrins prepared by simultaneous debranching and crystallization[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106315. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106315
[24] CHEN X, XIAO W H, XIONG F, et al. In vitro digestion and physicochemical properties of wheat starch/flour modified by heat-moisture treatment[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2015,63:109−115. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2015.03.003
[25] CHENG D C, GUO X, ZHOU Y, et al. A facile method for isolating long branch-chains of amylopectin from starch by preheating and pullulanase treatment[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2023,191:115987. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115987
[26] CAI L M, SHI Y-C, RONG L X, et al. Debranching and crystallization of waxy maize starch in relation to enzyme digestibility[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,81(2):385−393. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.036
[27] 徐佩琳. 酸热法和微波预处理—酶法制备山药抗性糊精及其特性研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2018. [XU P L. Preparation and characterization of yam resistant dextrin by acid heating method and microwave pretreatment-enzymolysis method[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2018.] XU P L. Preparation and characterization of yam resistant dextrin by acid heating method and microwave pretreatment-enzymolysis method[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2018.
[28] 张颖. 抗性糊精的纯化及应用特性研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2015. [ZHANG Y. Study on purification and application of resistant dextrin[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2015.] ZHANG Y. Study on purification and application of resistant dextrin[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[29] 张婷, 李佳瑶, 安双双, 等. 高粱抗性糊精的制备工艺优化及结构表征[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(4):232−237. [ZHANG T, LI J Y, AN S S, et al. Optimization of sorghum resistant dextrin preparation process and structure characterization[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(4):232−237.] ZHANG T, LI J Y, AN S S, et al . Optimization of sorghum resistant dextrin preparation process and structure characterization[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020 ,45 (4 ):232 −237 .[30] JOANNA L T, BLASZCAK W, SZWENGIEL A, et al. Molecular and supermolecular structure of commercial pyrodextrins[J]. J Food Sci,2016,81(9):C2135−C2142.
[31] 顾品品, 张燕萍. 不同处理方式对红香母芋抗性糊精性质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(15):30−35. [GU P P, ZHANG Y P. Effects of different treatment methods on the propertities of red taro resistant dextrin[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(15):30−35.] GU P P, ZHANG Y P . Effects of different treatment methods on the propertities of red taro resistant dextrin[J]. Food Research and Development,2020 ,41 (15 ):30 −35 .[32] 刘德志, 王维浩, 全志刚, 等. 绿豆抗性糊精的结构表征及抗消化特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):119−125. [LIU D Z, WANG W H, QUAN Z G, et al. Study on structure characterization and anti digestion properties of mung bean resistant dextrin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):119−125.] LIU D Z, WANG W H, QUAN Z G, et al . Study on structure characterization and anti digestion properties of mung bean resistant dextrin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (11 ):119 −125 .[33] YAN J B, SHI Y-C. Chemical structures in pyrodextrin determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,151:426−433. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.058
[34] 李泽润, 田延军, 黄艳红, 等. 超高压对抗性糊精制备过程的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2023,38(2):83−89. [LI Z R, TIAN Y J, HUANG Y H, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure on preparation of resistant dextrin[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2023,38(2):83−89.] LI Z R, TIAN Y J, HUANG Y H, et al . Effects of ultra-high pressure on preparation of resistant dextrin[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2023 ,38 (2 ):83 −89 .[35] YUAN H Z, ZHANG T, JIANG B, et al. Purification and characterization of resistant dextrin[J]. Foods,2021,10(1):185. doi: 10.3390/foods10010185





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



