Construction of Fourier Transform Near Infrared Spectroscopy Prediction Model for Main Components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr
-
摘要: 使用傅里叶变换近红外光谱(FT-NIR)结合化学计量学方法,开发了一种黑果枸杞干果和鲜果中主要成分(总糖、还原糖、总酸、氨态氮、花青素、原花青素、总酚、黄酮和多糖)含量的预测方法。首先比较了11种原始光谱的预处理方式,筛选出每种成分的最优预处理方法。然后比较了利用偏最小二乘(PLS)、区间偏最小二乘(iPLS)和联合区间偏最小二乘(siPLS)算法建立的模型,最终确定采用siPLS建模。结果表明:总酸、氨态氮、花青素、原花青素、总酚和黄酮的交叉验证相关系数(Rc)和预测集相关系数(RP)均大于0.9818,相对分析误差(RPD)均大于2.5,模型效果优异,总糖、还原糖和多糖的建模效果良好,建立的定标模型均可以用于实际检测。验证集样本实测值与预测值无显著性差异,预测误差在±0.1%,模型的预测结果可信度高。本研究建立的预测模型,可以实现黑果枸杞干果和鲜果中主要成分含量的无损、快速、准确检测。Abstract: A quantitative method of main components (total sugar, reducing sugar, total acid, ammonia nitrogen, anthocyanins, procyanidins, total phenols, flavonoids and polysaccharides) in Lycium ruthenicum Murr was developed using Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy (FT-NIR) combined with chemometric analysis. Firstly, 11 pretreatment methods were compared for the original spectra, and the optimal pretreatment method of each component was selected. Then, the model results established by partial least squares (PLS), interval partial least squares (iPLS) and synergistic interval partial least squares (siPLS) algorithms were compared, and finally siPLS was adopted for modeling. The results showed that the correlation coefficient of calibration (Rc) and prediction (RP) of total acids, ammonia nitrogen, anthocyanins, procyanidins, total phenols and flavonoids were all greater than 0.9818, and the relative analysis error (RPD) was more than 2.5, indicating an excellent model performance. The modeling effect of total sugar, reducing sugar, and polysaccharide was also good. The established calibration models could be used for actual detection. The predicted values of the verification samples did not significantly differ from the measured values, with a prediction error of only ±0.1%. Therefore, the prediction model had high reliability. The prediction model established in this study can enable nondestructive, rapid and accurate main components in dried and fresh fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murr.
-
黑果枸杞是我国传统具有补益功能的名贵中藏药材,是青海省重要的特色农产品,是花青素含量最高的浆果之一,有“花青素之王”的美誉[1],相应的研究表明,黑果枸杞具有抗氧化、抗疲劳、保护心脑血管、提高免疫力等方面的作用[2−3]。因其具有多种活性和营养成分,越来越受到消费者喜爱,所以对于黑果枸杞方面的研究日益增加。目前,有关黑果枸杞的研究多为开发利用、栽培技术、生理活性成分及保健药理作用研究[4−5];果实化学成分研究、有效成分含量测定与分析[6−7]等。上述的研究方式均采取传统理化方法进行枸杞中相关物质的测定,存在操作时间长、过程繁琐、污染环境等一系列问题,因此有必要开发一种黑果枸杞中快速、简便、无损检测的方法,促进黑果枸杞产业的纵深发展。
傅里叶变换近红外光谱(Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy,FT-NIR)分析技术因其快速、准确、便捷、无损的特点而备受人们关注,并且在农产品产地识别和品质定量检测方面应用广泛。其是利用有机质在近红外光谱区的振动吸收从而快速测定样品中多种化学成分含量的一种新型技术[8]。该方法可简便、直观地分析具有较大差异的非同种物质,但是在判别成分相近的食品时却无能为力,所以常需要结合化学计量学方法进行判别。近红外光谱技术的成熟与化学计量学方法的丰富使得两者相结合运用到物质的定性和定量分析成为一种趋势。目前已有傅里叶近红外光谱应用于黑果枸杞中的研究报道[9],该学者建立了干果粉末的花青素、胡萝卜素和总酸预测模型,性能优异,稳定性好,证明了近红外光谱技术在黑果枸杞果实的检测中具有良好的应用潜力。然而,仅建立干果模型无法预测鲜果中主要成分的含量。
本研究通过应用傅里叶变换近红外设备,对来自不同产地的黑果枸杞干果复水匀浆/鲜果打浆处理,混合干果和鲜果制备样本集,进行傅里叶近红外光谱扫描,得到近红外特征谱图,结合理化指标结果,对其所含有的总糖、还原糖、总酸、氨态氮、花青素、原花青素、总酚、黄酮和多糖共计9类指标通过偏最小二乘(partial least squares regression,PLS)、区间偏最小二乘(interval partial least squares regression,iPLS)和联合区间偏最小二乘(synergy interval partial least squares regression,siPLS)算法建立预测模型,并验证了模型的预测效果,以期为黑果枸杞检测技术的发展提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑果枸杞 北京同仁堂健康药业(青海)有限公司提供;氢氧化钠、冰醋酸、酒石酸钾钠、苯酚、亚硫酸钠、盐酸、无水乙醇、无水乙酸钠、冰醋酸、丙酮均为分析纯,没食子酸、芦丁、无水葡萄糖均为色谱纯 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;原花青素(色谱纯) 合肥博美生物科技有限责任公司;4-二甲氨基肉桂醛(DMAC)(色谱纯) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
UV-1800PC型紫外-可见光分光光度仪 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;MAX-190型酶标仪 美国分子仪器公司;Vortex-2型涡流器 美国科学仪器公司;Antaris MXFT-NIR型近红外光谱仪 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;BS-224S型分析天平 赛多利斯仪器设备制造有限公司;CF16XR-Ⅱ型离心机 日本日立公司;5B型自动滴定仪 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品的采集和制备
由北京同仁堂健康药业(青海)有限公司提供的从青海、甘肃、新疆、宁夏、内蒙古等不同地区收集的135份样本,其中包括45份干果样本和90份鲜果样本,干果浸泡打浆,鲜果直接打浆处理,以备用于指标测定或傅里叶近红外光谱采集。
黑果枸杞干果浆液:将黑果枸杞干果,去梗,1:2.5(g/mL)浸泡复水,打浆,5000 r/min 4 ℃条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,即得到料水比为1:2.5的黑果枸杞干果浆液。
黑果枸杞鲜果浆液:将黑果枸杞鲜果,打浆,5000 r/min 4 ℃条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,即得到鲜果浆液。
1.2.2 黑果枸杞中主要理化指标的测定
总糖与还原糖含量的测定参照中国食品安全农业标准NY/T 2742-2015《水果及制品可溶性糖的测定 3,5-二硝基水杨酸比色法》;总酸的测定参照中国食品安全国家标准GB 12456-2021《食品中总酸的测定》;氨基态氮采用自动滴定仪测定;花青素含量的测定采用pH示差法[10];原花青素含量的测定采用DMAC比色法[11]:以原花青素为标准品,建立标准曲线:y=0.0462x+0.0001,R2=0.9996;总酚含量的测定采用福林酚比色法[12]:以没食子酸为标准品,建立标准曲线:y=0.0146x+0.0026,R2=0.9979;总黄酮含量的测定采用芦丁比色法[13]:以芦丁为标准品,建立标准曲线:y=29.627x+0.0009,R2=0.9972;多糖测定采用苯酚-硫酸法[14]:以无水葡萄糖为标准品,建立标准曲线:y=13.595x+0.0432,R2=0.9982。
1.2.3 傅里叶变换近红外光谱采集
采用傅里叶变换近红外仪进行光谱采集,以卤钨灯为光源,InGaAs探测器,光谱范围为12000~4000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数为64次,实验过程中保持室内温湿度基本不变[15]。每个样品采集10张光谱,取平均值。
1.2.4 光谱预处理
采用11种不同的预处理方式[16−17],包括无光谱预处理(no spectrum pretreatment,NSDP)、消除常数偏移量(constant offsets eliminate,COE)、减去一条直线(straight line subtraction,SLS)、矢量归一化(standard normal variate,SNV)、最小-最大归一化(min max normalization,MMN)、多元散射校正(multiplicative scatte correction,MSC)、一阶导数(first derivative,1st Der)、二阶导数(second derivative,2nd Der)、一阶导数+减去一条直线(1st Der+SLS)、一阶导数+矢量归一化(1st Der+SNV)、一阶导数+多元散射校正(1st Der+MSC),消除光谱的背景噪声和干扰,确定不同检测指标的最佳处理方式。
1.2.5 预测模型建立与评估
通过偏最小二乘(partial least squares regression,PLS)、区间偏最小二乘(interval partial least squares regression,iPLS)和联合区间偏最小二乘(synergy interval partial least squares regression,siPLS)算法建立预测模型,模型的优劣通过交叉验证相关系数(correlation coefficient of calibration,Rc)、交叉验证均方根误差(root mean square error of calibration,RMSEC)、预测集相关系数(correlation coefficient of prediction,RP)、预测集均方根误差(root mean squared error of prediction,RMSEP)、相对分析误差(ratio prediction deviation,RPD)评估[18−19]。RPD用来验证模型的稳定性和预测能力,当RPD<1.5则模型预测性能较低,1.5≤RPD≤2.5则模型预测性能可满足快速检测的需要,RPD>2.5则模型具有较高的预测性能。
1.2.6 模型验证
将40份独立样本代入模型中,得到黑果枸杞中各成分含量的预测值,将样品实测值与预测值代入SPSS 22软件中进行T检验,根据T值与P值关系对预测结果进行评价。在T检验中若|T|<T(0.05,39)(由T分布表查表可知,T(0.05,39)=2.02),P>0.05,说明预测值和实测值没有显著性差异,即模型泛化能力好,反之则差异显著,说明模型不具有泛化能力。
1.3 数据处理
使用OPUS 7.2进行傅里叶近红外光谱采集,The Unscrambler X 10.4进行模型构建与分析,Origin 2022软件绘图,SPSS statistics 22.0软件进行T检验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 黑果枸杞中主要理化指标
黑果枸杞样品的9种主要成分的化学值如表1所示。样品的各成分总量范围:总糖130.48~870.05 mg/g,还原糖102.37~481.40 mg/g,总酸1.69~7.82 mg/g,氨态氮2.31~7.38 mg/g,花青素0.70~21.77 mg/g,原花青素0.69~7.83 mg/g,总酚14.85~37.93 mg/g,总黄酮4.05~41.21 mg/g,多糖14.77~43.50 mg/g。使用Kennard-Stone算法[15]对黑果枸杞样品集进行划分,用于校正集的样品95个,验证集40个。验证集化学值含量均位于校正集范围内,说明样本集划分合理。
表 1 黑果枸杞果实样品主要成分化学值Table 1. Chemical values of main components of Lycium ruthenicum Murr samples成分 数据集 含量(mg/g) 平均值(mg/g) 标准差 成分 数据集 含量(mg/g) 平均值(mg/g) 标准差 总糖 校正集 132.40~870.05 394.39 20.97 原花青素 校正集 0.69~7.83 3.83 0.27 验证集 130.48~818.32 386.94 20.66 验证集 0.69~5.83 3.30 0.27 还原糖 校正集 105.97~481.40 271.25 16.59 总酚 校正集 14.95~37.93 27.61 2.59 验证集 102.37~400.40 243.21 16.97 验证集 14.85~37.43 26.12 2.60 总酸 校正集 1.70~7.82 4.90 0.27 总黄酮 校正集 4.05~41.21 16.46 0.66 验证集 1.69~6.97 4.52 0.28 验证集 15.21~33.79 26.45 2.47 氨态氮 校正集 2.40~7.38 5.41 0.38 多糖 校正集 15.21~43.50 28.63 2.20 验证集 2.31~7.35 4.98 0.39 验证集 14.77~41.21 26.45 2.26 花青素 校正集 0.70~21.77 7.92 0.28 验证集 1.30~15.83 6.72 0.52 2.2 原始光谱数据分析
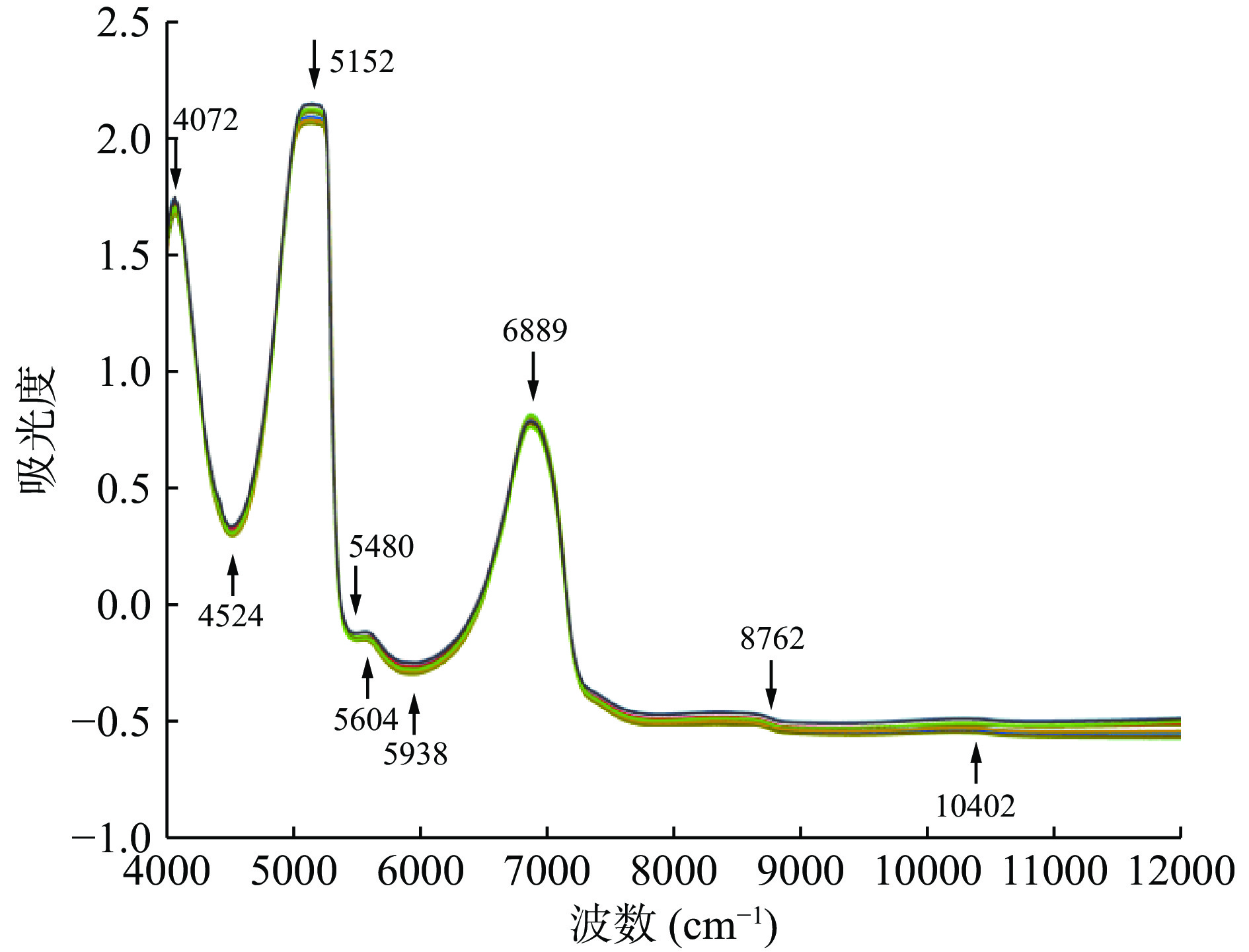
由图1可知,不同样品的光谱谱线区分较为明显,在10402、8762、6889、5938、5604、5480、5152、4524、4072 cm−1处有特征吸收(如图1箭头所示),吸收峰较窄,根据图谱反映信息来看,10402 cm−1为水O-H基团的二级倍频,同时也为其他化合物含OH基团的二级倍频;8696~8000 cm−1为C-H基团二级倍频。在放大谱图后发现,在8197 cm−1存在微弱吸收,可以确定为水O-H基团合频吸收(较弱);7502~5165 cm−1 为C=O基团三级倍频(相对该区域其他集团而言红外吸收较弱,且存在重合部分);6889 cm−1为其他化合物O-H基团一级倍频,同时也为水O-H基团一级倍频;5938 cm−1为化合物C-H基团一级倍频;5604~5480 cm−1之间为C=O基团二级倍频;5269~4996cm−1之间出现平峰,表明该区域出现饱和吸收,该区域为其他化合物O-H基团的合频(5000 cm−1),同时也为水的O-H基团合频吸收(水分子O-H基团在5155 cm−1红外吸收最强);4524 cm−1处为N-H基团的合频吸收(标准吸收峰应为4600 cm−1,由于受到饱和吸收的影响,谱线出峰位置后移);图谱放大后,发现在4416 cm−1处出现吸收峰(吸收较弱),在4072 cm−1处出现强吸收,经过分析后认为,这两处峰均为C-H基团的合频吸收峰(标准吸收位置为4545~4082 cm−1,由于受到饱和吸收的影响,出现后移)。不同黑果枸杞样品的光谱没有明显差异,在12820~3959 cm−1区域范围内光谱的吸光度之间差异较小,但是并非完全重合,说明采集的黑果枸杞样本整体保持一致,但不同样本之间存在一定差异,可以对黑果枸杞样品建立主要成分含量的预测模型。
2.3 近红外光谱预处理方式优化
图1所示的黑果枸杞原始近红外光谱混合了无关光谱信息、背景噪声和干扰,如果直接应用,可能会损害多变量校准模型的性能[20]。因此,采用数据预处理的方法去除噪声和异常值[21]。为了提高黑果枸杞各指标预测结果的准确性(Rc与Rp),降低模型RMSEC值和RMSEP值,在黑果枸杞全光谱(12000~4000 cm−1)范围内,进行各个指标光谱预处理方式的筛选,结果如表2所示。
表 2 不同光谱预处理方式对黑果枸杞果实中主要成分预测模型建立的影响Table 2. Effects of different spectral pretreatment methods on the establishment of prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr预处理方式 总糖 还原糖 总酸 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.8862 44.40 0.8752 46.00 4 0.8583 43.70 0.8300 41.30 6 0.8077 0.78 0.7530 0.89 COE 8 0.8859 46.00 0.8238 44.70 3 0.8534 44.40 0.8299 41.40 7 0.8295 0.74 0.8128 0.77 SLS 10 0.8509 52.70 0.786 54.00 4 0.9582 34.20 0.9590 35.00 5 0.8176 0.76 0.7833 0.78 SNV 7 0.8906 45.20 0.7878 49.30 4 0.8726 41.90 0.8236 42.40 5 0.8317 0.73 0.7802 0.80 MMN 5 0.8678 49.20 0.8125 47.50 5 0.8586 44.00 0.8162 43.30 5 0.8564 0.67 0.8294 0.71 MSC 7 0.8908 45.20 0.7864 49.50 4 0.8727 41.90 0.8224 42.40 5 0.8305 0.73 0.7688 0.82 1st Der 3 0.7314 67.90 0.8342 53.20 2 0.7789 53.30 0.8791 40.60 7 0.9259 1.21 0.9006 0.81 2nd Der 3 0.7698 88.00 0.7321 67.30 5 0.582 69.50 0.7214 53.00 10 0.5528 1.20 0.5616 1.10 1st+SLS 10 0.8257 58.60 0.8089 59.30 7 0.7759 53.60 0.8736 42.80 4 0.7405 0.91 0.759 0.84 1st+SNV 9 0.8129 63.80 0.8134 62.80 6 0.7825 53.50 0.8969 43.10 4 0.7432 0.90 0.7703 0.82 1st+MSC 9 0.8061 60.30 0.8003 63.60 6 0.7815 53.60 0.8899 43.80 5 0.7362 0.92 0.7658 0.83 预处理方式 氨态氮 花青素 原花青素 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.9397 0.50 0.9205 0.55 10 0.4402 3.33 0.6154 1.84 5 0.7524 0.89 0.6454 1.00 COE 6 0.9362 0.51 0.9366 0.50 8 0.5137 3.03 0.6463 1.89 7 0.7428 0.96 0.8378 0.76 SLS 5 0.9478 0.46 0.922 0.54 10 0.8727 2.85 0.8883 2.45 4 0.9393 0.95 0.9411 1.07 SNV 4 0.9457 0.47 0.9285 0.52 7 0.5792 2.84 0.5956 1.83 5 0.7643 1.07 0.7682 0.95 MMN 6 0.9444 0.47 0.9496 0.53 8 0.5385 2.99 0.6202 1.84 6 0.7453 0.94 0.7667 0.82 MSC 4 0.9449 0.47 0.928 0.52 7 0.5803 2.84 0.621 1.85 5 0.7639 1.07 0.766 0.97 1st Der 5 0.9471 0.47 0.9412 0.48 3 0.6219 2.56 0.4788 2.55 7 0.7165 1.15 0.7144 0.92 2nd Der 4 0.8993 0.63 0.8224 0.79 5 0.4831 3.00 0.4864 2.17 5 0.6959 1.17 0.6721 1.14 1st+SLS 10 0.9479 0.47 0.9338 0.50 3 0.6193 2.57 0.4804 2.54 7 0.7163 1.15 0.7031 0.93 1st+SNV 6 0.951 0.45 0.9333 0.50 10 0.5398 2.79 0.4644 2.84 9 0.7473 1.21 0.7252 0.89 1st+MSC 6 0.9476 0.47 0.9288 0.52 10 0.5409 2.79 0.4659 2.83 9 0.7337 1.23 0.6982 0.93 预处理方式 总酚 总黄酮 多糖 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.7996 5.61 0.8351 6.69 7 0.7589 5.21 0.7307 4.83 7 0.8808 5.21 0.8339 5.95 COE 3 0.8312 5.93 0.8434 5.74 3 0.8732 3.81 0.8375 3.93 7 0.8865 5.13 0.8747 5.24 SLS 9 0.9175 1.48 0.9136 1.70 4 0.9142 4.33 0.9038 5.72 6 0.8729 5.41 0.8806 5.00 SNV 4 0.8139 5.46 0.8483 6.11 3 0.7891 4.68 0.774 4.63 6 0.8625 5.64 0.8511 5.55 MMN 3 0.8166 5.92 0.8472 5.78 6 0.8162 3.98 0.8586 3.95 5 0.9348 3.73 0.9421 3.13 MSC 4 0.8138 5.46 0.8481 6.11 3 0.7589 4.68 0.7712 4.47 6 0.8602 5.69 0.8472 5.62 1st Der 3 0.7791 5.90 0.7900 6.26 9 0.8124 4.41 0.8142 4.20 6 0.8391 6.19 0.8711 5.28 2nd Der 4 0.7559 6.06 0.7466 6.54 7 0.8242 6.75 0.8358 6.30 4 0.7636 7.16 0.6321 8.10 1st+SLS 3 0.7773 5.92 0.7933 6.24 9 0.8039 4.40 0.8058 4.31 6 0.837 6.23 0.8756 5.35 1st+SNV 3 0.7658 6.01 0.7837 6.34 10 0.7483 6.69 0.7471 6.91 10 0.8496 5.93 0.8006 6.25 1st+MSC 3 0.7663 6.01 0.7824 6.35 10 0.8481 6.71 0.7392 5.98 10 0.8412 6.10 0.7973 6.30 最佳预处理方式选择的依据是最低的内部交叉验证均方根误差(RMSEC)和预测集均方根误差(RMSEP)及较高的内部交叉验证相关系数(Rc)和预测集相关系数(RP),优化的结果如表2加粗字体所示:总糖采用无光谱预处理(NSDP)的预处理方式,总酸和氨态氮采用一阶导数(1st Der)的预处理方式,还原糖、花青素、原花青素、总酚和总黄酮采用减去一条直线(SLS)的预处理方式,多糖采用最小-最大归一化(MMN)的预处理方式。
2.4 模型建立与评估
2.4.1 偏最小二乘模型
在得到不同样本最佳光谱预处理方式的基础上,建立针对黑果枸杞的全光谱(12000~4000 cm−1)PLS预测模型。结果如表3所示。
表 3 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的全光谱偏最小二乘预测模型Table 3. Full spectra PLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr种类 预处理方式 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 6 0.8862 44.40 0.8752 46.00 0.46 还原糖 SLS 4 0.9582 34.20 0.9590 35.00 0.76 总酸 1st Der 7 0.9259 1.21 0.9006 0.81 0.46 氨态氮 1st Der 5 0.9471 0.47 0.9412 0.48 0.77 花青素 SLS 10 0.8727 2.85 0.8883 2.45 0.23 原花青素 SLS 4 0.9393 0.95 0.9411 1.07 0.25 总酚 SLS 9 0.9175 1.48 0.9136 1.70 1.54 总黄酮 SLS 4 0.9142 4.33 0.9038 5.72 0.12 多糖 MMN 5 0.9348 3.73 0.9421 3.13 0.90 表3显示了黑果枸杞不同指标全波长PLS预测模型。由表3可知,样本全光谱PLS预测模型中氨态氮对应的RMSEP值最低,为0.48,表明建立的PLS模型对于样本中氨态氮含量的预测较为准确。总酸、花青素、原花青素、总酚、总黄酮和多糖的RMSEP值均在0.81~5.72之间,表明建模效果较好,然而,总糖与还原糖建模效果并不理想,RMSEP值分别为46.00和35.00,说明在模型准确度低,总糖全波长PLS预测模型,Rc和Rp分别为0.8862、0.8752小于0.90,表明该模型无论是从准确度方面,还是从预测与真值相关性方面,建模效果差于其他指标。基于PLS建立的全光谱预测模型,RPD ≤1.5,无法建立一个合适的、稳健的各指标含量与光谱数据之间的定量关系,可能是由于光谱中的一些区域可能包含非模型信息(噪声),因此应该从模型中排除这部分区域[22]。即,需要开发一个光谱区域选择的校准模型。
2.4.2 区间偏最小二乘模型
根据表4可知,除了总糖和还原糖iPLS预测模型外的大部分指标,在5~25个区间内有较低的RMESP值,iPLS模型中RMSEP值随着光谱区间细分而减小,可能是样本中水的存在导致了近红外光谱中出现过饱和吸收峰,产生基线漂移的同时也掩蔽了部分基团的红外吸收,从而使得有效信息在波段较宽时较少被提取到[23];而当波段较窄时,水的过饱和吸收对于实验结果的干扰降低,部分基团有效信息得以被更多提取,从而使模型预测准确度提高。
表 4 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的区间偏最小二乘预测模型Table 4. iPLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr种类 预处理方式 区间个数 光谱区域(cm−1) PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 5 8800~7200 8 0.9715 22.40 0.9821 22.50 0.93 10 8800~8000 9 0.9600 24.20 0.9672 19.60 1.07 20 8400~8000 8 0.9614 20.90 0.9816 14.70 1.43 25 8480~8160 8 0.9697 19.20 0.9817 18.70 1.12 50 8320~8160 9 0.9698 14.50 0.9768 13.90 1.51 还原糖 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9563 23.70 0.9501 24.30 1.09 10 8000~7200 9 0.9677 20.40 0.9605 22.70 1.17 20 8000~7600 8 0.9686 19.60 0.952 24.80 1.07 25 7840~7520 4 0.9472 25.90 0.9589 22.30 1.19 50 7680~7520 8 0.9447 25.80 0.9672 19.10 1.39 总酸 1st Der 5 12000~10400 8 0.9632 0.35 0.9698 0.39 0.96 10 11040~10720 5 0.9844 0.23 0.9845 0.29 1.29 20 8400~8000 6 0.9873 0.20 0.9864 0.20 1.87 25 7200~6880 8 0.9816 0.24 0.9875 0.21 1.78 50 6560~6400 9 0.9674 0.33 0.9839 0.59 0.63 氨态氮 1st Der 5 12000~10400 5 0.9479 0.45 0.9846 0.23 1.77 10 11200~10400 6 0.9400 0.48 0.9801 0.26 1.57 20 11600~11200 4 0.9322 0.52 0.9531 0.45 0.91 25 10400~10080 5 0.9791 0.36 0.959 0.35 1.17 50 10720~10560 6 0.9153 0.49 0.9276 0.45 0.91 花青素 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9638 0.69 0.9571 0.60 0.95 10 8000~7200 10 0.9681 0.85 0.9883 0.29 1.96 20 8000~7600 6 0.9771 0.74 0.9686 0.51 1.12 25 7840~7520 6 0.9611 0.91 0.9626 0.61 0.93 50 7680~7520 6 0.9776 0.70 0.9747 0.70 0.81 原花青素 SLS 5 10400~8800 7 0.9934 0.18 0.9885 0.20 1.36 10 9600~8800 8 0.9813 0.27 0.9877 0.21 1.29 20 9200~8800 7 0.9645 0.37 0.9718 0.3 0.90 25 9120~8800 8 0.9605 0.39 0.9603 0.26 1.04 50 8960~8800 6 0.8975 0.62 0.9534 0.4 0.68 总酚 SLS 5 8800~7200 7 0.9163 1.04 0.8709 1.71 1.53 10 9600~8800 7 0.9267 0.97 0.9531 0.99 2.65 20 8400~8000 5 0.9418 0.85 0.9478 0.85 3.08 25 8480~8160 4 0.9174 1.00 0.9341 0.99 2.65 50 8320~8160 7 0.9418 0.85 0.9169 0.87 3.01 总黄酮 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9621 1.76 0.9754 1.23 1.38 10 8000~7200 9 0.9766 1.40 0.9836 1.05 1.61 20 7600~7200 8 0.9755 1.43 0.9807 1.27 1.33 25 8800~8480 8 0.9843 1.18 0.9716 1.61 1.05 50 8800~8640 7 0.9737 1.51 0.9686 1.84 0.92 多糖 MMN 5 12000~10400 7 0.9682 2.71 0.9805 1.85 1.53 10 8800~8000 6 0.9636 2.88 0.9893 1.51 1.87 20 8000~7600 7 0.9668 3.89 0.9744 2.38 1.19 25 7840~7520 6 0.9859 1.78 0.9491 3.67 0.77 50 8000~7840 4 0.9803 2.10 0.9793 2.07 1.37 在进行光谱区间划分时,光谱区间较宽,能较为完全地提取到所需要的特征基团光谱,有利于建模,但是较宽的波段容易使得光谱噪声与提取到的无效信息增多,对模型实验结果造成干扰[24],如黑果枸杞中总黄酮的iPLS模型印证了这一观点。光谱选择区间较窄,虽然屏蔽掉部分光谱噪声和无效信息对实验结果的影响,但是光谱提取到的有效信息,如特征基团等的信息量较少,使得模型结果不准确。因此,选择合适的区间进行建模,有利于提高模型的准确性和稳定性,提高模型可信度,黑果枸杞样本中的花青素、原花青素以及总酚iPLS预测模型等均印证了这一观点。
2.4.3 联合区间偏最小二乘模型
由表5可知,除了总糖多糖指标以外,黑果枸杞鲜果样本大部分指标的siPLS预测模型RMSEP值表现出与先减小后增大的趋势。黑果枸杞总糖指标的siPLS预测模型在区间间隔数为5时,RMSEP值为14.10,而当区间间隔数为50时,为4.33,黑果枸杞多糖指标的siPLS预测模型在区间间隔为5时,RMSEP值为2.64,在区间间隔为50时,RMSEP值为1.47。由此可见,区间间隔数的增加大幅度提高了样本总糖和多糖的预测效果,这是因为随着区间间隔的增加,从光谱中提取的有效信息数量增加,同时噪声与其他无效信息减少,提高了模型预测精确度[25]。随着光谱区间的继续划分,虽然部分有效信息被过滤,导致可提取的信息量减少,但是由于屏蔽了大多数噪声的影响,因而与较小区间间隔相比,间隔数目较高指标的siPLS预测模型RMSEP值更低,准确度更高。对于黑果枸杞其他指标,光谱区间数的增加均使得模型预测准确度得到显著提高,并且最佳光谱区间间隔数目为10~25。造成这一结果的原因主要是由于增加的光谱区间间隔有效减少了水分的红外吸收对于实验结果的影响,同时使有效信息增多,无关信息减少,大幅度提高了黑果枸杞样本siPLS模型的预测效果。
表 5 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的联合区间偏最小二乘预测模型Table 5. siPLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr种类 预处理方式 区间个数 区间组合方式 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 5 1~3 8 0.9661 14.40 0.9866 14.10 1.49 10 6~10 9 0.9668 11.20 0.9852 10.40 2.02 20 11~17 9 0.9588 11.30 0.9816 10.80 1.94 25 19,20 9 0.9762 10.61 0.9835 9.66 2.17 50 37~40 6 0.9825 5.17 0.9887 4.33 4.84 还原糖 SLS 5 1,2 7 0.9794 16.80 0.9410 24.80 2.07 10 1~6,9,10 8 0.8643 40.60 0.9430 24.30 2.09 20 3,7,11 7 0.9882 20.60 0.9866 17.20 2.54 25 9,14 6 0.9749 18.20 0.9745 17.40 2.52 50 17,18,23~25,28 7 0.9743 17.50 0.9717 18.00 2.47 总酸 1st Der 5 1~3 8 0.9561 0.39 0.9715 0.30 2.24 10 2~4 8 0.9784 0.27 0.9767 0.27 2.38 20 10,12 8 0.9893 0.19 0.9848 0.20 2.87 25 9,10,16 7 0.9683 0.32 0.9303 0.44 1.85 50 30,32,34,35 9 0.9750 0.28 0.9581 0.38 1.98 氨态氮 1st Der 5 1,2 6 0.9809 0.28 0.9788 0.25 2.13 10 1,2,4,5 6 0.9818 0.27 0.9870 0.20 2.54 20 1,2,4,5,7,9,10 7 0.9824 0.27 0.9824 0.23 2.27 25 2,3,6,10 5 0.9838 0.25 0.9786 0.26 2.07 50 9,10,15 7 0.9816 0.27 0.9597 0.35 1.67 花青素 SLS 5 2,3 10 0.9405 0.64 0.9663 0.53 2.07 10 1,2,5~7 8 0.9890 0.53 0.9831 0.60 1.95 20 9~16 7 0.9804 0.46 0.9748 0.41 2.39 25 11,13~15 7 0.9880 0.74 0.9871 0.37 2.54 50 23,26,28 5 0.9857 0.60 0.9832 0.61 1.93 原花青素 SLS 5 1,2 8 0.9845 0.26 0.9742 0.33 0.82 10 3~5,8 8 0.9946 0.16 0.9942 0.14 1.94 20 4~6,8~12 7 0.9936 0.16 0.9971 0.11 2.56 25 5~10,14 6 0.9934 0.17 0.9939 0.15 1.81 50 17~20,24 6 0.9844 0.25 0.9756 0.28 0.97 总酚 SLS 5 1,3,4 7 0.9785 1.23 0.9631 1.70 1.54 10 2,4 6 0.9282 0.95 0.9287 0.73 3.59 20 4,7,8,10 5 0.9808 0.86 0.9854 0.64 4.10 25 8,12,14 4 0.9382 0.87 0.9239 0.86 3.05 50 24,25 4 0.9417 0.84 0.9405 0.85 3.08 总黄酮 SLS 5 1~3 6 0.9574 1.32 0.9479 1.65 2.03 10 1,3,6 7 0.9632 1.75 0.9821 1.22 2.39 20 9,12,16 8 0.9869 0.89 0.9906 0.90 2.69 25 10,11,13 9 0.9858 1.10 0.9911 1.16 2.46 50 21,22,26 8 0.9923 0.83 0.9870 1.31 2.29 多糖 MMN 5 1,2 8 0.9398 3.72 0.9606 2.64 2.07 10 1,4,5 9 0.9852 1.86 0.9870 1.83 2.55 20 7,11,14 8 0.9823 2.03 0.9890 2.11 2.34 25 9,14 7 0.9879 1.70 0.9891 1.71 2.66 50 25,26,28 7 0.9936 1.20 0.9884 1.47 2.93 2.4.4 模型比较
比较PLS、iPLS和siPLS模型的结果(表3~表5),siPLS模型显示出更好的预测能力。实验结果表明:PLS模型采用全光谱区域的所有变量来校正模型时,其中有许多变量是噪声光谱信息和非信息变量,这些变量不可避免地削弱了模型的性能;iPLS模型可以通过选择确定的光谱区间来降低噪声,但在校正模型时只选择了一个区间,可能会放弃一些有用的变量。由于在进行选择时没有考虑其它的相关信息,模型的整体性能不可避免的受到削弱。与iPLS相比,siPLS具有无可比拟的优势,siPLS不仅具有与iPLS相同的优点,而且克服了iPLS的缺点,将两个或三个区间结合起来,通过减少总变量(去除噪声谱信息)和更好的预测能力(不丢失信息)获得更好的模型。因此选择siPLS算法建立黑果枸杞中主要成分的定量检测模型。
2.5 模型验证
为了验证模型的可靠性和泛化能力,选取了40份未用于模型建立的样品,样品含量的真实值采用1.2.2的方法测定,预测值根据FT-NIR扫描的谱图,采用预测模型输出结果。采用配对样本T检验对黑果枸杞的真实值和预测值进行验证。由表6可知,|T|<T(0.05,39)(由T分布表查表可知,T(0.05,39)=2.02),P>0.05,差异无统计学意义,说明预测值与实测值基本一致,也表明通过近红外光谱法建立的预测模型能很好地预测黑果枸杞未知样本中总糖、还原糖、总酸、氨态氮、花青素、原花青素、总酚、总黄酮和多糖的含量。
表 6 黑果枸杞果实样本主要成分的实测值与预测值T检验结果Table 6. T-test results of measured and predicted values of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr samplesT检验 总糖 还原糖 总酸 氨态氮 花青素 原花青素 总酚 总黄酮 多糖 T 0.158 −1.369 −1.093 0.012 −0.045 1.114 1.308 −0.146 −0.854 P(双尾) 0.876 0.233 0.255 0.991 0.965 0.284 0.212 0.886 0.407 3. 结论
本研究采用不同的预处理和回归方法组合,建立黑果枸杞中主要成分的定量检测模型。对于不同指标对应的siPLS模型,在优化后的波段范围内均具有较为准确的预测结果,验证集样本实测值与预测值无显著性差异,相对分析误差均大于2.5,模型定标效果良好,重现性较好,建立的定标模型可以用于实际检测,黑果枸杞干果和鲜果均适用,模型应用范围广。与传统的实验室分析方法相比,该方法具有操作简单、成本低、速度快、污染小、无损、在线分析方便等优点。上述结果表明,傅里叶变换近红外光谱与化学计量学相结合是一种简单、快速、可靠的进行黑果枸杞中总糖、还原糖、总酸、氨态氮、花青素、原花青素、总酚、总黄酮和多糖含量预测的方法。
-
表 1 黑果枸杞果实样品主要成分化学值
Table 1 Chemical values of main components of Lycium ruthenicum Murr samples
成分 数据集 含量(mg/g) 平均值(mg/g) 标准差 成分 数据集 含量(mg/g) 平均值(mg/g) 标准差 总糖 校正集 132.40~870.05 394.39 20.97 原花青素 校正集 0.69~7.83 3.83 0.27 验证集 130.48~818.32 386.94 20.66 验证集 0.69~5.83 3.30 0.27 还原糖 校正集 105.97~481.40 271.25 16.59 总酚 校正集 14.95~37.93 27.61 2.59 验证集 102.37~400.40 243.21 16.97 验证集 14.85~37.43 26.12 2.60 总酸 校正集 1.70~7.82 4.90 0.27 总黄酮 校正集 4.05~41.21 16.46 0.66 验证集 1.69~6.97 4.52 0.28 验证集 15.21~33.79 26.45 2.47 氨态氮 校正集 2.40~7.38 5.41 0.38 多糖 校正集 15.21~43.50 28.63 2.20 验证集 2.31~7.35 4.98 0.39 验证集 14.77~41.21 26.45 2.26 花青素 校正集 0.70~21.77 7.92 0.28 验证集 1.30~15.83 6.72 0.52 表 2 不同光谱预处理方式对黑果枸杞果实中主要成分预测模型建立的影响
Table 2 Effects of different spectral pretreatment methods on the establishment of prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr
预处理方式 总糖 还原糖 总酸 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.8862 44.40 0.8752 46.00 4 0.8583 43.70 0.8300 41.30 6 0.8077 0.78 0.7530 0.89 COE 8 0.8859 46.00 0.8238 44.70 3 0.8534 44.40 0.8299 41.40 7 0.8295 0.74 0.8128 0.77 SLS 10 0.8509 52.70 0.786 54.00 4 0.9582 34.20 0.9590 35.00 5 0.8176 0.76 0.7833 0.78 SNV 7 0.8906 45.20 0.7878 49.30 4 0.8726 41.90 0.8236 42.40 5 0.8317 0.73 0.7802 0.80 MMN 5 0.8678 49.20 0.8125 47.50 5 0.8586 44.00 0.8162 43.30 5 0.8564 0.67 0.8294 0.71 MSC 7 0.8908 45.20 0.7864 49.50 4 0.8727 41.90 0.8224 42.40 5 0.8305 0.73 0.7688 0.82 1st Der 3 0.7314 67.90 0.8342 53.20 2 0.7789 53.30 0.8791 40.60 7 0.9259 1.21 0.9006 0.81 2nd Der 3 0.7698 88.00 0.7321 67.30 5 0.582 69.50 0.7214 53.00 10 0.5528 1.20 0.5616 1.10 1st+SLS 10 0.8257 58.60 0.8089 59.30 7 0.7759 53.60 0.8736 42.80 4 0.7405 0.91 0.759 0.84 1st+SNV 9 0.8129 63.80 0.8134 62.80 6 0.7825 53.50 0.8969 43.10 4 0.7432 0.90 0.7703 0.82 1st+MSC 9 0.8061 60.30 0.8003 63.60 6 0.7815 53.60 0.8899 43.80 5 0.7362 0.92 0.7658 0.83 预处理方式 氨态氮 花青素 原花青素 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.9397 0.50 0.9205 0.55 10 0.4402 3.33 0.6154 1.84 5 0.7524 0.89 0.6454 1.00 COE 6 0.9362 0.51 0.9366 0.50 8 0.5137 3.03 0.6463 1.89 7 0.7428 0.96 0.8378 0.76 SLS 5 0.9478 0.46 0.922 0.54 10 0.8727 2.85 0.8883 2.45 4 0.9393 0.95 0.9411 1.07 SNV 4 0.9457 0.47 0.9285 0.52 7 0.5792 2.84 0.5956 1.83 5 0.7643 1.07 0.7682 0.95 MMN 6 0.9444 0.47 0.9496 0.53 8 0.5385 2.99 0.6202 1.84 6 0.7453 0.94 0.7667 0.82 MSC 4 0.9449 0.47 0.928 0.52 7 0.5803 2.84 0.621 1.85 5 0.7639 1.07 0.766 0.97 1st Der 5 0.9471 0.47 0.9412 0.48 3 0.6219 2.56 0.4788 2.55 7 0.7165 1.15 0.7144 0.92 2nd Der 4 0.8993 0.63 0.8224 0.79 5 0.4831 3.00 0.4864 2.17 5 0.6959 1.17 0.6721 1.14 1st+SLS 10 0.9479 0.47 0.9338 0.50 3 0.6193 2.57 0.4804 2.54 7 0.7163 1.15 0.7031 0.93 1st+SNV 6 0.951 0.45 0.9333 0.50 10 0.5398 2.79 0.4644 2.84 9 0.7473 1.21 0.7252 0.89 1st+MSC 6 0.9476 0.47 0.9288 0.52 10 0.5409 2.79 0.4659 2.83 9 0.7337 1.23 0.6982 0.93 预处理方式 总酚 总黄酮 多糖 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP NSDP 6 0.7996 5.61 0.8351 6.69 7 0.7589 5.21 0.7307 4.83 7 0.8808 5.21 0.8339 5.95 COE 3 0.8312 5.93 0.8434 5.74 3 0.8732 3.81 0.8375 3.93 7 0.8865 5.13 0.8747 5.24 SLS 9 0.9175 1.48 0.9136 1.70 4 0.9142 4.33 0.9038 5.72 6 0.8729 5.41 0.8806 5.00 SNV 4 0.8139 5.46 0.8483 6.11 3 0.7891 4.68 0.774 4.63 6 0.8625 5.64 0.8511 5.55 MMN 3 0.8166 5.92 0.8472 5.78 6 0.8162 3.98 0.8586 3.95 5 0.9348 3.73 0.9421 3.13 MSC 4 0.8138 5.46 0.8481 6.11 3 0.7589 4.68 0.7712 4.47 6 0.8602 5.69 0.8472 5.62 1st Der 3 0.7791 5.90 0.7900 6.26 9 0.8124 4.41 0.8142 4.20 6 0.8391 6.19 0.8711 5.28 2nd Der 4 0.7559 6.06 0.7466 6.54 7 0.8242 6.75 0.8358 6.30 4 0.7636 7.16 0.6321 8.10 1st+SLS 3 0.7773 5.92 0.7933 6.24 9 0.8039 4.40 0.8058 4.31 6 0.837 6.23 0.8756 5.35 1st+SNV 3 0.7658 6.01 0.7837 6.34 10 0.7483 6.69 0.7471 6.91 10 0.8496 5.93 0.8006 6.25 1st+MSC 3 0.7663 6.01 0.7824 6.35 10 0.8481 6.71 0.7392 5.98 10 0.8412 6.10 0.7973 6.30 表 3 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的全光谱偏最小二乘预测模型
Table 3 Full spectra PLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr
种类 预处理方式 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 6 0.8862 44.40 0.8752 46.00 0.46 还原糖 SLS 4 0.9582 34.20 0.9590 35.00 0.76 总酸 1st Der 7 0.9259 1.21 0.9006 0.81 0.46 氨态氮 1st Der 5 0.9471 0.47 0.9412 0.48 0.77 花青素 SLS 10 0.8727 2.85 0.8883 2.45 0.23 原花青素 SLS 4 0.9393 0.95 0.9411 1.07 0.25 总酚 SLS 9 0.9175 1.48 0.9136 1.70 1.54 总黄酮 SLS 4 0.9142 4.33 0.9038 5.72 0.12 多糖 MMN 5 0.9348 3.73 0.9421 3.13 0.90 表 4 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的区间偏最小二乘预测模型
Table 4 iPLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr
种类 预处理方式 区间个数 光谱区域(cm−1) PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 5 8800~7200 8 0.9715 22.40 0.9821 22.50 0.93 10 8800~8000 9 0.9600 24.20 0.9672 19.60 1.07 20 8400~8000 8 0.9614 20.90 0.9816 14.70 1.43 25 8480~8160 8 0.9697 19.20 0.9817 18.70 1.12 50 8320~8160 9 0.9698 14.50 0.9768 13.90 1.51 还原糖 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9563 23.70 0.9501 24.30 1.09 10 8000~7200 9 0.9677 20.40 0.9605 22.70 1.17 20 8000~7600 8 0.9686 19.60 0.952 24.80 1.07 25 7840~7520 4 0.9472 25.90 0.9589 22.30 1.19 50 7680~7520 8 0.9447 25.80 0.9672 19.10 1.39 总酸 1st Der 5 12000~10400 8 0.9632 0.35 0.9698 0.39 0.96 10 11040~10720 5 0.9844 0.23 0.9845 0.29 1.29 20 8400~8000 6 0.9873 0.20 0.9864 0.20 1.87 25 7200~6880 8 0.9816 0.24 0.9875 0.21 1.78 50 6560~6400 9 0.9674 0.33 0.9839 0.59 0.63 氨态氮 1st Der 5 12000~10400 5 0.9479 0.45 0.9846 0.23 1.77 10 11200~10400 6 0.9400 0.48 0.9801 0.26 1.57 20 11600~11200 4 0.9322 0.52 0.9531 0.45 0.91 25 10400~10080 5 0.9791 0.36 0.959 0.35 1.17 50 10720~10560 6 0.9153 0.49 0.9276 0.45 0.91 花青素 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9638 0.69 0.9571 0.60 0.95 10 8000~7200 10 0.9681 0.85 0.9883 0.29 1.96 20 8000~7600 6 0.9771 0.74 0.9686 0.51 1.12 25 7840~7520 6 0.9611 0.91 0.9626 0.61 0.93 50 7680~7520 6 0.9776 0.70 0.9747 0.70 0.81 原花青素 SLS 5 10400~8800 7 0.9934 0.18 0.9885 0.20 1.36 10 9600~8800 8 0.9813 0.27 0.9877 0.21 1.29 20 9200~8800 7 0.9645 0.37 0.9718 0.3 0.90 25 9120~8800 8 0.9605 0.39 0.9603 0.26 1.04 50 8960~8800 6 0.8975 0.62 0.9534 0.4 0.68 总酚 SLS 5 8800~7200 7 0.9163 1.04 0.8709 1.71 1.53 10 9600~8800 7 0.9267 0.97 0.9531 0.99 2.65 20 8400~8000 5 0.9418 0.85 0.9478 0.85 3.08 25 8480~8160 4 0.9174 1.00 0.9341 0.99 2.65 50 8320~8160 7 0.9418 0.85 0.9169 0.87 3.01 总黄酮 SLS 5 8800~7200 6 0.9621 1.76 0.9754 1.23 1.38 10 8000~7200 9 0.9766 1.40 0.9836 1.05 1.61 20 7600~7200 8 0.9755 1.43 0.9807 1.27 1.33 25 8800~8480 8 0.9843 1.18 0.9716 1.61 1.05 50 8800~8640 7 0.9737 1.51 0.9686 1.84 0.92 多糖 MMN 5 12000~10400 7 0.9682 2.71 0.9805 1.85 1.53 10 8800~8000 6 0.9636 2.88 0.9893 1.51 1.87 20 8000~7600 7 0.9668 3.89 0.9744 2.38 1.19 25 7840~7520 6 0.9859 1.78 0.9491 3.67 0.77 50 8000~7840 4 0.9803 2.10 0.9793 2.07 1.37 表 5 黑果枸杞果实中主要成分的联合区间偏最小二乘预测模型
Table 5 siPLS prediction model of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr
种类 预处理方式 区间个数 区间组合方式 PCs Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP RPD 总糖 NSDP 5 1~3 8 0.9661 14.40 0.9866 14.10 1.49 10 6~10 9 0.9668 11.20 0.9852 10.40 2.02 20 11~17 9 0.9588 11.30 0.9816 10.80 1.94 25 19,20 9 0.9762 10.61 0.9835 9.66 2.17 50 37~40 6 0.9825 5.17 0.9887 4.33 4.84 还原糖 SLS 5 1,2 7 0.9794 16.80 0.9410 24.80 2.07 10 1~6,9,10 8 0.8643 40.60 0.9430 24.30 2.09 20 3,7,11 7 0.9882 20.60 0.9866 17.20 2.54 25 9,14 6 0.9749 18.20 0.9745 17.40 2.52 50 17,18,23~25,28 7 0.9743 17.50 0.9717 18.00 2.47 总酸 1st Der 5 1~3 8 0.9561 0.39 0.9715 0.30 2.24 10 2~4 8 0.9784 0.27 0.9767 0.27 2.38 20 10,12 8 0.9893 0.19 0.9848 0.20 2.87 25 9,10,16 7 0.9683 0.32 0.9303 0.44 1.85 50 30,32,34,35 9 0.9750 0.28 0.9581 0.38 1.98 氨态氮 1st Der 5 1,2 6 0.9809 0.28 0.9788 0.25 2.13 10 1,2,4,5 6 0.9818 0.27 0.9870 0.20 2.54 20 1,2,4,5,7,9,10 7 0.9824 0.27 0.9824 0.23 2.27 25 2,3,6,10 5 0.9838 0.25 0.9786 0.26 2.07 50 9,10,15 7 0.9816 0.27 0.9597 0.35 1.67 花青素 SLS 5 2,3 10 0.9405 0.64 0.9663 0.53 2.07 10 1,2,5~7 8 0.9890 0.53 0.9831 0.60 1.95 20 9~16 7 0.9804 0.46 0.9748 0.41 2.39 25 11,13~15 7 0.9880 0.74 0.9871 0.37 2.54 50 23,26,28 5 0.9857 0.60 0.9832 0.61 1.93 原花青素 SLS 5 1,2 8 0.9845 0.26 0.9742 0.33 0.82 10 3~5,8 8 0.9946 0.16 0.9942 0.14 1.94 20 4~6,8~12 7 0.9936 0.16 0.9971 0.11 2.56 25 5~10,14 6 0.9934 0.17 0.9939 0.15 1.81 50 17~20,24 6 0.9844 0.25 0.9756 0.28 0.97 总酚 SLS 5 1,3,4 7 0.9785 1.23 0.9631 1.70 1.54 10 2,4 6 0.9282 0.95 0.9287 0.73 3.59 20 4,7,8,10 5 0.9808 0.86 0.9854 0.64 4.10 25 8,12,14 4 0.9382 0.87 0.9239 0.86 3.05 50 24,25 4 0.9417 0.84 0.9405 0.85 3.08 总黄酮 SLS 5 1~3 6 0.9574 1.32 0.9479 1.65 2.03 10 1,3,6 7 0.9632 1.75 0.9821 1.22 2.39 20 9,12,16 8 0.9869 0.89 0.9906 0.90 2.69 25 10,11,13 9 0.9858 1.10 0.9911 1.16 2.46 50 21,22,26 8 0.9923 0.83 0.9870 1.31 2.29 多糖 MMN 5 1,2 8 0.9398 3.72 0.9606 2.64 2.07 10 1,4,5 9 0.9852 1.86 0.9870 1.83 2.55 20 7,11,14 8 0.9823 2.03 0.9890 2.11 2.34 25 9,14 7 0.9879 1.70 0.9891 1.71 2.66 50 25,26,28 7 0.9936 1.20 0.9884 1.47 2.93 表 6 黑果枸杞果实样本主要成分的实测值与预测值T检验结果
Table 6 T-test results of measured and predicted values of main components in Lycium ruthenicum Murr samples
T检验 总糖 还原糖 总酸 氨态氮 花青素 原花青素 总酚 总黄酮 多糖 T 0.158 −1.369 −1.093 0.012 −0.045 1.114 1.308 −0.146 −0.854 P(双尾) 0.876 0.233 0.255 0.991 0.965 0.284 0.212 0.886 0.407 -
[1] LIU Z G, LIU B L, WEN H X, et al. Phytochemical profiles, nutritional constituents and antioxidant activity of black wolfberry ( Lycium ruthenicum Murr.)[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,154(10):81−90.
[2] LU K K, WANG J, YU Y Y, et al. Lycium ruthenicum Murr. alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(6):2588−2597.
[3] XING X Y, KE Y. Nutritional value of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. and its relieving resistance to exercise-induced fatigue[J]. Progress in Nutrition,2019,21(4):876−881.
[4] 邓楷, 欧阳健, 胡娜, 等. 黑果枸杞花青素结构差异对其稳定性及细胞抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(2):213−219. [DENG K, OUYANG J, HU N, et al. Effects of structural difference on stability and cellular antioxidative activity of anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(2):213−219.] DENG K, OUYANG J, HU N, et al . Effects of structural difference on stability and cellular antioxidative activity of anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022 ,34 (2 ):213 −219 .[5] 张静, 米佳, 禄璐, 等. 黑果枸杞花色苷提取物对胰脂肪酶活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(5):8−14. [ZHANG J, MI J, LU L, et al. Effect of anthocyanins extract from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. fruit on pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Food Science,2020,41(5):8−14.] ZHANG J, MI J, LU L, et al . Effect of anthocyanins extract from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. fruit on pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (5 ):8 −14 .[6] 甘小娜, 王辉俊, 李廷钊, 等. 黑果枸杞化学成分的UPLC-Triple TOF/MS分析及其总花色苷类含量测定[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(18):185−190. [GAN X N, WANG H J, LI T Z, et al. Lycium ruthenicum Murray fruit:Chemical composition analysis by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple time of flight mass spectrometry and determination of total anthocyanins[J]. Food Science,2021,42(18):185−190.] GAN X N, WANG H J, LI T Z, et al . Lycium ruthenicum Murray fruit: Chemical composition analysis by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple time of flight mass spectrometry and determination of total anthocyanins[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (18 ):185 −190 .[7] 徐金楠, 刘玮, 刘春晶, 等. 不同枸杞中多糖含量与结构特征的对比研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(4):233−239. [XU J N, LIU W, LIU C J, et al. Comparative study of the content and structural features of polysaccharides from different Lycium[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15(4):233−239.] XU J N, LIU W, LIU C J, et al . Comparative study of the content and structural features of polysaccharides from different Lycium[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015 ,15 (4 ):233 −239 .[8] 王玥, 陈楠, 王博雨, 等. 基于激光驱动等离子体光源的近红外傅里叶变换光谱系统[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2022,42(6):1666−1673. [WNG Y, CHENG N, WANG B Y, et al. Near infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy system based on laser-driven plasma light source[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2022,42(6):1666−1673.] WNG Y, CHENG N, WANG B Y, et al . Near infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy system based on laser-driven plasma light source[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2022 ,42 (6 ):1666 −1673 .[9] ARSLAN M, XIAOBO Z, XUETAO H, et al. Near infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometric algorithms for predicting chemical components in black goji berries ( Lycium ruthenicum Murr.)[J]. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy,2018,26(5):275−286. doi: 10.1177/0967033518795597
[10] TAGHAVI T, PATEL H, RAFIE R. Comparing pH differential and methanol-based methods for anthocyanin assessments of strawberries[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2022,10(7):2123−2131.
[11] OSCAR V C, OSCAR N, CASSOU S H , et al. Assessment of experimental factors affecting the sensitivity and selectivity of the spectrophotometric estimation of proanthocyanidins in foods and nutraceuticals[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2021, 14(3):485−495.
[12] 张洋婷, 郗艳丽, 葛红娟, 等. 福林酚比色法测定酸浆宿萼中总多酚含量[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(23):138−141. [ZHANG Y T, XI Y L, GE H J, et al. Determination of total polyphenols in calyx physalis by Folin-ciocalteu method[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(23):138−141.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.23.032 ZHANG Y T, XI Y L, GE H J, et al . Determination of total polyphenols in calyx physalis by Folin-ciocalteu method[J]. Food Research and Development,2016 ,37 (23 ):138 −141 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.23.032[13] 冯琳. 发酵枸杞汁的制备及解酒护肝功能的评价[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2021. [FENG L. Liver-protectionjuice and its evaluation of anti-alcoholism and preparation of fermented Lycium barbarum[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2021.] FENG L. Liver-protectionjuice and its evaluation of anti-alcoholism and preparation of fermented Lycium barbarum[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[14] 张媛媛, 张彬. 苯酚-硫酸法与蒽酮-硫酸法测定绿茶茶多糖的比较研究[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(4):158−163. [ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG B. Comparison of phenol-sulfuric acid and anthrone-sulfuric methods for determination of polysaccharide in green tea[J]. Food Science,2016,37(4):158−163.] ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG B . Comparison of phenol-sulfuric acid and anthrone-sulfuric methods for determination of polysaccharide in green tea[J]. Food Science,2016 ,37 (4 ):158 −163 .[15] LIU J, SUN S, TAN Z, et al. Nondestructive detection of sunset yellow in cream based on near-infrared spectroscopy and interval random forest[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2020,242(1):12−17.
[16] 卢洁, 田婧, 梁振华, 等. 近红外光谱法快速测定香菇总糖含量[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(12):189−194. [LU J, TIAN J, LIANG Z H, et al. Application of near infrared spectroscopy in the rapid detection of total sugar content in Lentinula edodes[J]. Food Science,2021,42(12):189−194.] LU J, TIAN J, LIANG Z H, et al . Application of near infrared spectroscopy in the rapid detection of total sugar content in Lentinula edodes[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (12 ):189 −194 .[17] 白京, 李家鹏, 邹昊, 等. 近红外特征光谱定量检测羊肉卷中猪肉掺假比例[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(2):287−292. [BAI J, LI J P, ZOU H, et al. Quantitative detection of pork in adulterated mutton rolls based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Science,2019,40(2):287−292.] BAI J, LI J P, ZOU H, et al . Quantitative detection of pork in adulterated mutton rolls based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (2 ):287 −292 .[18] LI Y H, ZOU X B, SHEN T T, et al. Determination of geographical origin and anthocyanin content of black goji berry ( Lycium ruthenicum Murr.) using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2017,10(4):1034−1044. doi: 10.1007/s12161-016-0666-4
[19] 唐保山, 李坤, 张雯雯, 等. 近红外漫反射光谱结合偏最小二乘法对紫胶理化指标的快速测定[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(18):236−244. [TANG B S, LI K, ZHANG W W, et al. Rapid determination of physicochemical indexes in shellac using near infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy combined with PLS algorithm[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(18):236−244.] TANG B S, LI K, ZHANG W W, et al. Rapid determination of physicochemical indexes in shellac using near infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy combined with PLS algorithm[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(18): 236−244.
[20] GUO Z, BARIMAH A O, YIN L, et al. Intelligent evaluation of taste constituents and polyphenols-to-amino acids ratio in matcha tea powder using near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,353:129372.
[21] MISHRA P, BIANCOLILLO A, ROGER J M, et al. New data preprocessing trends based on ensemble of multiple preprocessing techniques[J]. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2020,132(9):28−33.
[22] 吕都, 唐健波, 姜太玲, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术快速检测稻谷水分含量[J]. 食品与机械,2022,38(2):51−56,63. [LÜ D, TANG J B, JIANG T L, et al. Research on rapid prediction model of rice moisture content based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food and Machinery,2022,38(2):51−56,63.] LÜ D, TANG J B, JIANG T L, et al . Research on rapid prediction model of rice moisture content based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food and Machinery,2022 ,38 (2 ):51 −56,63 .[23] HOSSEINI E, GHASEMI J B, DARAEI B , et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning-based classification and calibration methods in detection and measurement of anionic surfactant in milk[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2021, 104:104170.
[24] HUANG J, JIA X, ZHANG H , et al. Rapid determination of the total phosphorus and the nitrate nitrogen in denitrifying phosphorus removal with iPLS and near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2021, 30(4):3077−3084.
[25] ZAREEF M. 基于无损检测技术的红茶发酵过程快速监测研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2019. [ZAREEF M. Study on fast monitoring of the black tea fermentation using non-destructive techniques[D]. Zhenjiang:Jiangsu University, 2019.] ZAREEF M. Study on fast monitoring of the black tea fermentation using non-destructive techniques[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李文廷,叶沛,刘玲,陶蓉蓉,张瑞雨,师真,蒋孟圆. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定发酵乳制品中米酵菌酸和异米酵菌酸. 分析测试学报. 2025(02): 326-333 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑圣乐,李卓颖,王家浩,刘峻铭,方桂娇,韩鹿. 益生菌清除食品毒素的研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 129-134+139 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋娓娜,薛笛笛,路飞,李国德,肖志刚,史梦娜,张一凡. 食品中米酵菌酸的相关研究. 现代食品. 2023(11): 23-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宋娓娜,张嘉慧,赵秀红,路飞,肖志刚,张一凡. 植物乳杆菌对食品中常见毒素的抑制作用研究进展. 食品安全导刊. 2023(24): 174-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
