Characteristic Quality Evaluation of Nang from the Yili Region in Xinjiang Based on Principal Component and Cluster Analysis
-
摘要: 为研究新疆伊犁地区不同种类馕的品质特性,本文选取伊犁地区55个市售馕样品,对其进行了13项品质指标(重量、横径、高度、水分含量、水分活度、L*、a*、b*、硬度、内聚性、弹性、胶粘性、咀嚼性)的测定,采用主成分分析和聚类分析方法,筛选出馕品质评价的主要指标并对馕样品进行了分类,结合感官品质对不同种类馕进行了综合评价。结果表明,55份馕样品的13项品质指标间存在一定的相关性,其中高度与水分含量、水分活度、弹性、咀嚼性呈极显著相关(P<0.01),L*值与胶粘性呈显著相关(P<0.05);主成分分析法提取出3个主成分因子,累积方差贡献率达到76.856%,根据聚类分析结果得到,弹性、咀嚼性、胶粘性、硬度、L*值、b*值可作为评价馕品质的6项关键指标,基于以上结果,将55份馕划分为三大类,分别为大薄馕、窝窝馕、休闲馕;结合感官品质分析得出,三大类馕品质间存在显著差异(P<0.05),其中大薄馕色泽、风味、硬度评分最高,为14.85、13.52、14.37分,具有色泽金黄、香味浓郁的特点。窝窝馕弹性和咀嚼性评分最高,为14.82、14.54分,表明其富有弹性和咀嚼性。休闲馕酥脆性评分最高为14.47分,表明此类馕品尝时具有酥脆的口感。本研究明确了馕品质评价的关键指标并探明了新疆伊犁地区三大类馕的品质特性,提供了馕科学的分类方法,为新疆馕品质评价体系的构建奠定理论依据。Abstract: This study determined 13 quality indexes (weight, transverse diameter, height, moisture content, water activity, L*, a*, b*, hardness, cohesion, elasticity, adhesiveness, and chewability) in 55 different Nang samples from the Yili region in Xinjiang to examine their quality characteristics. The main indexes were selected for the Nang quality evaluation via principal component analysis, cluster analysis, and sensory quality assessment. The results showed an association between the 13 quality indexes of the 55 Nang samples. The height was highly significantly correlated with moisture content, water activity, elasticity, and chewiness (P<0.01), while the L* value and adhesiveness were substantially related (P<0.05). Three principal components were extracted via principal component analysis, with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 76.856%. Cluster analysis showed that six quality indexes, namely elasticity, chewability, adhesiveness, hardness, L* values, and b* values, were crucial for evaluating Nang quality. Then, the 55 Nang samples were classified into three categories: Large Nang, thick Nang, and snack Nang. The sensory quality analysis revealed significant differences between the quality of the three Nang categories (P<0.05). The color, flavor, and hardness scores of the large Nang were the highest at 14.85, 13.52, and 14.37, respectively, with a golden color and rich flavor. The elasticity and chewability scores of the thick Nang were the highest at 14.82 and 14.54, respectively, while the crisp score of the snack Nang was the highest at 14.47. These results revealed the key indexes for assessing the quality characteristics of three types of Nang from the Yili region in Xinjiang, providing a scientific classification method for constructing a Xinjiang Nang quality evaluation system.
-
馕在新疆历史悠久[1],是极具地域特色的传统主食[2−3],因其风味独特、食用方便、耐储便携等特点,深受新疆各族人民喜爱[4−5]。新疆馕制作方法多样,种类丰富,据不完全统计,目前至少有200多种[6],常见的有大薄馕、窝窝馕、干果馕、馅馕等[7]。“十四五”以来,馕产业被列为新疆重点发展的“十大产业”之一,在增加就业、促进经济社会发展等方面起到了关键作用[8−9]。但是,目前国内外有关馕的研究主要集中在加工工艺、饮食文化、贮藏保鲜和烘烤装置等方面[10−12],在馕科学分类以及质量评价体系方面的研究相对较少,使得馕标准化生产体系尚未形成,一定程度上制约了馕产业发展。
目前,食品品质评价研究中常用的数据统计分析方法有主成分分析、聚类分析、层次分析法等[13−15]。其中主成分分析和聚类分析已被广泛应用于面制食品品质关键指标筛选和质量综合评价研究,有学者利用主成分分析和聚类分析方法分别对饼干[16]、馒头[17]、面包[18−19]进行了品质评价。此外,还有学者研究了谷物粉[20]、全麦粉[21]、添加洋葱浆[22]、红枣粉[23]、马铃薯粉[24]等对馕品质的影响。张敏等[25]研究了发酵时间、烘烤工艺对黑木耳牛奶馕的品质影响,由此可见目前关于馕品质研究尚处于原辅料及加工工艺条件不同对馕产品品质的影响方面,对馕综合品质评价仍缺乏相关研究,因此,本文通过对新疆伊犁地区采集的55份馕样品的13项品质指标进行测定和分析,基于主成分分析和聚类分析的方法并结合感官品质对伊犁地区常见的三大类馕进行综合评价,揭示了伊犁地区不同种类馕品质间差异,为馕的科学分类提供了新的思路,也为构建精准有效的馕品质评价体系提供一定的参考依据和技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
55个馕样品 采集自新疆伊犁地区10余个县市,市售(选择当地具有代表性,且日常消费较多的馕购买,采样记录见表1)。
表 1 新疆伊犁地区馕样品采样信息Table 1. Sample collection of Nang in Yili area, Xinjiang序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 1 N001 伊宁市 15 N015 察布查尔县 29 N029 可克达拉市 43 N043 尼勒克县 2 N002 伊宁市 16 N016 察布查尔县 30 N030 可克达拉市 44 N044 尼勒克县 3 N003 伊宁市 17 N017 察布查尔县 31 N031 可克达拉市 45 N045 特克斯县 4 N004 伊宁市 18 N018 察布查尔县 32 N032 可克达拉市 46 N046 特克斯县 5 N005 伊宁市 19 N019 伊宁县 33 N033 可克达拉市 47 N047 特克斯县 6 N006 伊宁市 20 N020 伊宁县 34 N034 新源县 48 N048 特克斯县 7 N007 伊宁市 21 N021 伊宁县 35 N035 新源县 49 N049 巩留县 8 N008 伊宁市 22 N022 伊宁县 36 N036 新源县 50 N050 巩留县 9 N009 伊宁市 23 N023 伊宁县 37 N037 新源县 51 N051 巩留县 10 N010 伊宁市 24 N024 霍城县 38 N038 新源县 52 N052 巩留县 11 N011 伊宁市 25 N025 霍城县 39 N039 新源县 53 N053 昭苏县 12 N012 伊宁市 26 N026 霍城县 40 N040 尼勒克县 54 N054 昭苏县 13 N013 察布查尔县 27 N027 霍城县 41 N041 尼勒克县 55 N055 昭苏县 14 N014 察布查尔县 28 N028 霍城县 42 N042 尼勒克县 TA.XTPlus质构仪 英国Stable Micro System公司;CR-10 Plus色差仪 日本KonicaMinolta公司;LHS16-A水分测定仪 上海衡平仪器仪表厂;Aqualab Pawkit便携式水分活度仪 美国METER Group, Inc.公司;JA2603B电子天平 上海精科仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 外观特征检测
运用电子天平和游标卡尺分别测定馕的重量、高度、横径,每个样品做3次平行,取其均值。
1.2.2 水分和水分活度(Aw)的测定
将馕样品进行粉碎,称取2 g样品放入水分测定仪中进行测定,另取1 g样品放入水分活度仪中进行检测,每个样品做3次平行,取平均值。
1.2.3 色度值的测定
在每个馕的表皮选取6个不同位置,采用色差仪对其色差值(L*、a*、b*)进行测定,取6个测定值的平均值。
1.2.4 质构特性分析
参照邹淑萍等[24]方法,略有改动。取直径为30 mm的馕块置于质构仪的测试平板上,测定其硬度、内聚性、弹性、胶粘性和咀嚼性,每个馕样品设6个重复取平均值。质构仪参数测试条件如下:采用TMS 6 mm探头,预压速度 5.00 mm/s,下行速度 2.00 mm/s,穿刺后上行速度 2.00 mm/s,下压距离为 8.00 mm,触发力 0.1 N,压缩比40%,两次压缩时间间隔5 s。
1.2.5 感官品质评价
参照文献[24,26]的方法,稍有改动。将馕切成20 mm的小块,分装在餐盘中进行感官评价。选择10名对烘培类食品有品评经验的人员组成感官评价小组,成员为5名女性和5名男性,年龄在25~55岁。感官评价总分为100分,评价指标包括馕的7个特征:色泽、风味、组织结构、硬度、弹性、酥脆性和咀嚼性,根据消费者对馕品尝的喜好程度,将组织结构感官评价分值范围设置为1~10分,其它指标分值范围设置为1~15分,标准见表2。
表 2 馕感官品质评价标准Table 2. Criteria for sensory evaluation of Nang指标 评分标准 分值 色泽(15分) 从淡黄或焦黑到具有诱人的烘烤色泽,颜色焦黄,且表面光滑,带有光泽,颜色均匀 1~15 风味(15分) 从香味淡,咸度或甜度过高或过低到具有充足的烘烤食物和原辅料的香味,咸度或甜度适中 1~15 组织结构(10分) 从馕结构形态不规则,存在塌陷和变形到结构均匀,形态规则 1~10 硬度(15分) 从太软或太硬到硬度适宜 1~15 弹性(15分) 从无弹性或弹性差到弹性好 1~15 酥脆性(15分) 从无酥脆感到非常酥脆 1~15 咀嚼性(15分) 从每秒咀嚼一次的频率咀嚼至达吞咽粒度所需要的时间短到所需要的时间长 1~15 1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2016对测定数据进行整理和描述性统计,SPSS 26.0软件进行馕品质指标的主成分分析和聚类分析,Origin 9.0软件绘制馕样品的主成分析图和层次聚类分析图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 馕品质指标的主成分分析
2.1.1 馕品质指标的相关性分析
本研究对新疆伊犁地区55份馕样品的13项品质指标进行测定,利用SPSS 26.0对其测定值进行相关性分析,结果见表3。从表3可得,馕的外观特征、色度值和质构各指标间存在一定的相关性。其中,高度与水分含量、Aw、弹性、咀嚼性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与a*值呈显著正相关(P<0.05),说明馕外观越高,其水分含量、弹性和咀嚼性值越高,馕的色泽也更偏向于红色;弹性与咀嚼性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),说明质构测试中弹性高的馕其咀嚼性值也越高;L*值与a*值呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),这说明馕烤制后的颜色亮度越大,红度值也越高;此外,Aw与水分含量、内聚性、弹性和咀嚼性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),a*值与水分含量、Aw、弹性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。由各因子间相关性分析结果可得,各指标有一定程度上的信息重叠,因此通过应用主成分分析和聚类分析的方法,进行线性降维,用较少的新指标来综合反应原始指标[27],从而对馕品质特性进行综合评价。
表 3 馕13项品质指标之间的相关系数矩阵Table 3. Correlation coefficient matrix among 13 quality indexes of Nang指标 重量 横径 高度 L* a* b* 水分含量 Aw 硬度 内聚性 弹性 胶粘性 咀嚼性 重量 1.000 横径 0.524** 1.000 高度 0.111 −0.674 1.000 L* 0.302* 0.193 −0.082 1.000 a* 0.313* −0.060 0.303* 0.592** 1.000 b* −0.005 0.116 −0.044 0.150 0.063 1.000 水分含量 0.566** −0.068 0.545** 0.006 0.470** 0.047 1.000 Aw 0.611** 0.075 0.378** 0.135 0.421** 0.160 0.808** 1.000 硬度 −0.554 −0.542 0.245 −0.101 −0.142 −0.387 −0.450 −0.534 1.000 内聚性 0.539** 0.607** −0.413 0.262 −0.072 0.074 0.206 0.346** −0.694 1.000 弹性 0.172 −0.625 0.952** 0.002 0.363** −0.093 0.549** 0.409** 0.168 −0.325 1.000 胶粘性 0.230 0.268* −0.107 0.329* 0.062 0.298* −0.127 0.193 −0.125 0.254 −0.095 1.000 咀嚼性 0.145 −0.605 0.900** 0.052 0.261 −0.062 0.432** 0.416** 0.245 −0.276 0.925** 0.134 1.000 注:*在0.05水平(双侧)上相关性显著,P<0.05;**在0.01水平(双侧)上相关性极显著,P<0.01。 2.1.2 馕品质指标主成分分析结果
利用SPSS 26.0软件对55份样品的13项品质指标测定值进行了主成分分析,结果见表4和表5。由表4可知,第1主成分的贡献率为34.700%,第2主成分的贡献率为30.669%,第3主成分的贡献率为11.487%,前3个主成分的累积贡献率为76.856%,其值大于70%,包含了样品中的大多数信息,可以反应馕品质评价指标的整体信息,因此选择表4中的3个主成分进行分析。
表 4 主成分的特征值和贡献率Table 4. Eigenvalue and variance contribution rate主成分 初始特征值 提取载荷平方和 总计 方差的(%) 累积(%) 总计 方差的(%) 累积 (%) 1 4.511 34.700 34.700 4.511 34.700 34.700 2 3.987 30.669 65.369 3.987 30.669 65.369 3 1.493 11.487 76.856 1.493 11.487 76.856 4 1.143 8.794 85.650 5 0.661 5.085 90.735 6 0.374 2.877 93.612 7 0.239 1.840 95.452 8 0.207 1.589 97.042 9 0.139 1.071 98.113 10 0.102 0.785 98.898 11 0.081 0.627 99.524 12 0.038 0.293 99.818 13 0.024 0.182 100.000 表 5 主成分载荷矩阵Table 5. Component matrix指标 主成分 1 2 3 弹性 0.960 −0.087 −0.015 咀嚼性 0.955 −0.163 −0.040 胶粘性 0.908 −0.090 0.122 水分含量 0.672 0.544 −0.359 a* 0.483 0.372 0.444 硬度 0.131 −0.837 0.275 L* 0.217 0.817 −0.109 b* −0.320 0.764 −0.163 Aw 0.550 0.695 −0.169 横径 −0.622 0.649 −0.038 高度 0.046 0.420 0.758 重量 −0.074 0.363 0.586 内聚性 −0.063 0.295 0.296 主成分中的因子载荷能够反映各指标对主成分贡献率大小[28],从而反映出馕品质评价的主要指标。由表5可知,第1主成分特征值为4.511,弹性、咀嚼性、胶粘性具有较高的载荷值,其值分别为0.960、0.955、0.908,它们在第1主成分中起正向作用;第2主成分特征值为3.987,L*、b*的正向载荷权数较大,其值分别为0.817、0.764,硬度负向载荷权数较大,其值为−0.837,正向作用品质指标数多于负向作用品质指标数;第3主成分特征值为1.493,高度有较高的正向载荷值。由此可见,第1主成分反映了馕的质构品质,第2和第3主成分主要反映了馕的外观特征,均已涵盖了馕品质特性的所有信息。
2.2 馕品质的聚类分析
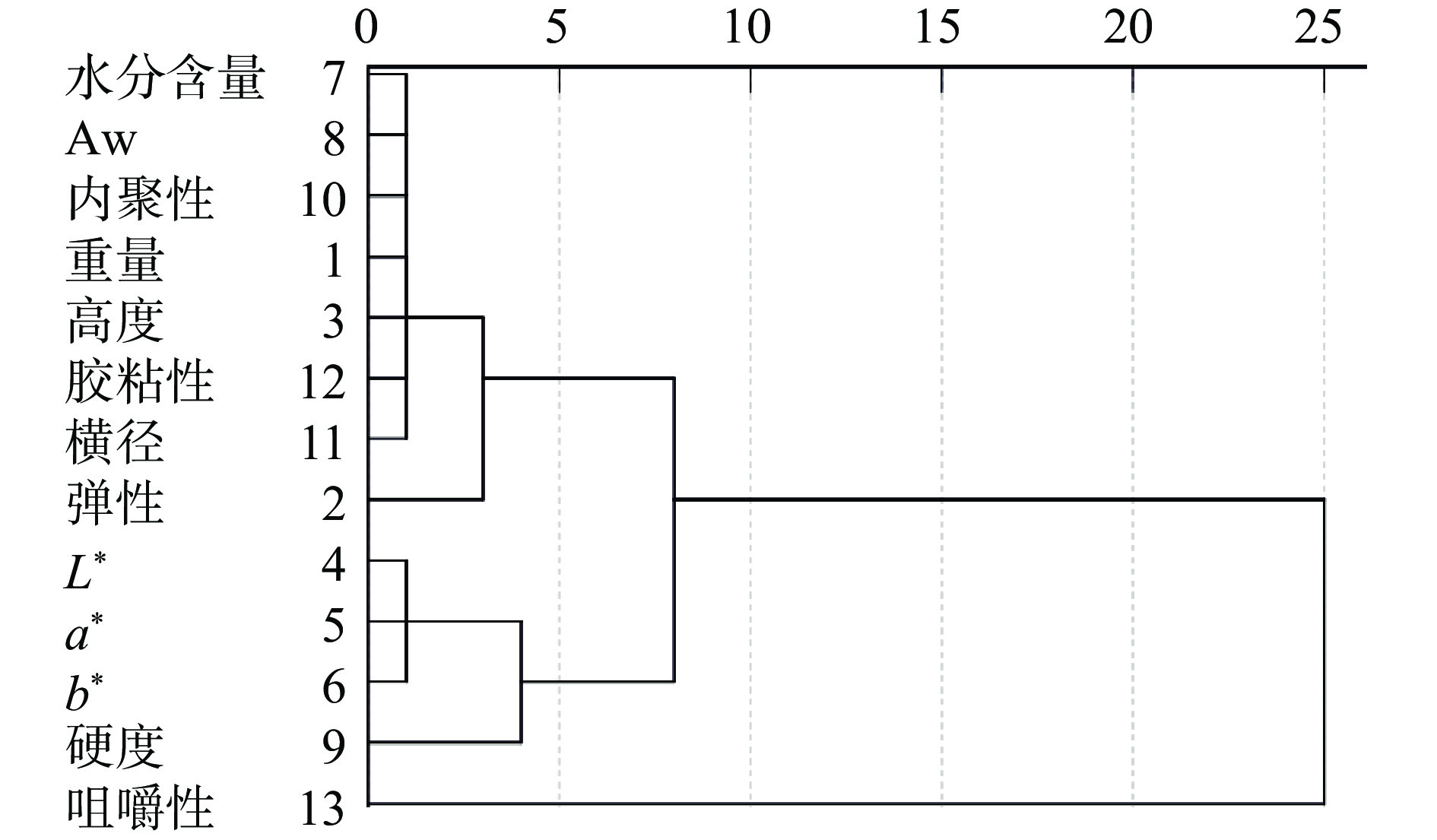
本研究在主成分分析的基础上,采用系统聚类分析方法对馕的13项品质指标进行R型聚类,聚类方法采用组间联接法,聚类区间为平方欧式距离,聚类结果见图1。由图1可得,当聚类距离为5时,可将馕品质指标分为3大类,第一类为水分含量、Aw、内聚性、重量、高度、胶粘性、横径、弹性;第2类为L*、a*、b*、硬度;第三类为咀嚼性。结合主成分载荷分析结果,最终选用弹性、硬度、胶粘性、咀嚼性、L*值和b*值为评价馕品质的关键性指标。此结果与李芳等[26]的研究结果存在一定的差异。本研究在李芳等[26]研究基础上,除对馕的质构品质进行分析外,又增加了水分含量、色差、重量、横径等指标,以期获得更加全面的馕品质评价指标。
2.3 馕样品的种类划分
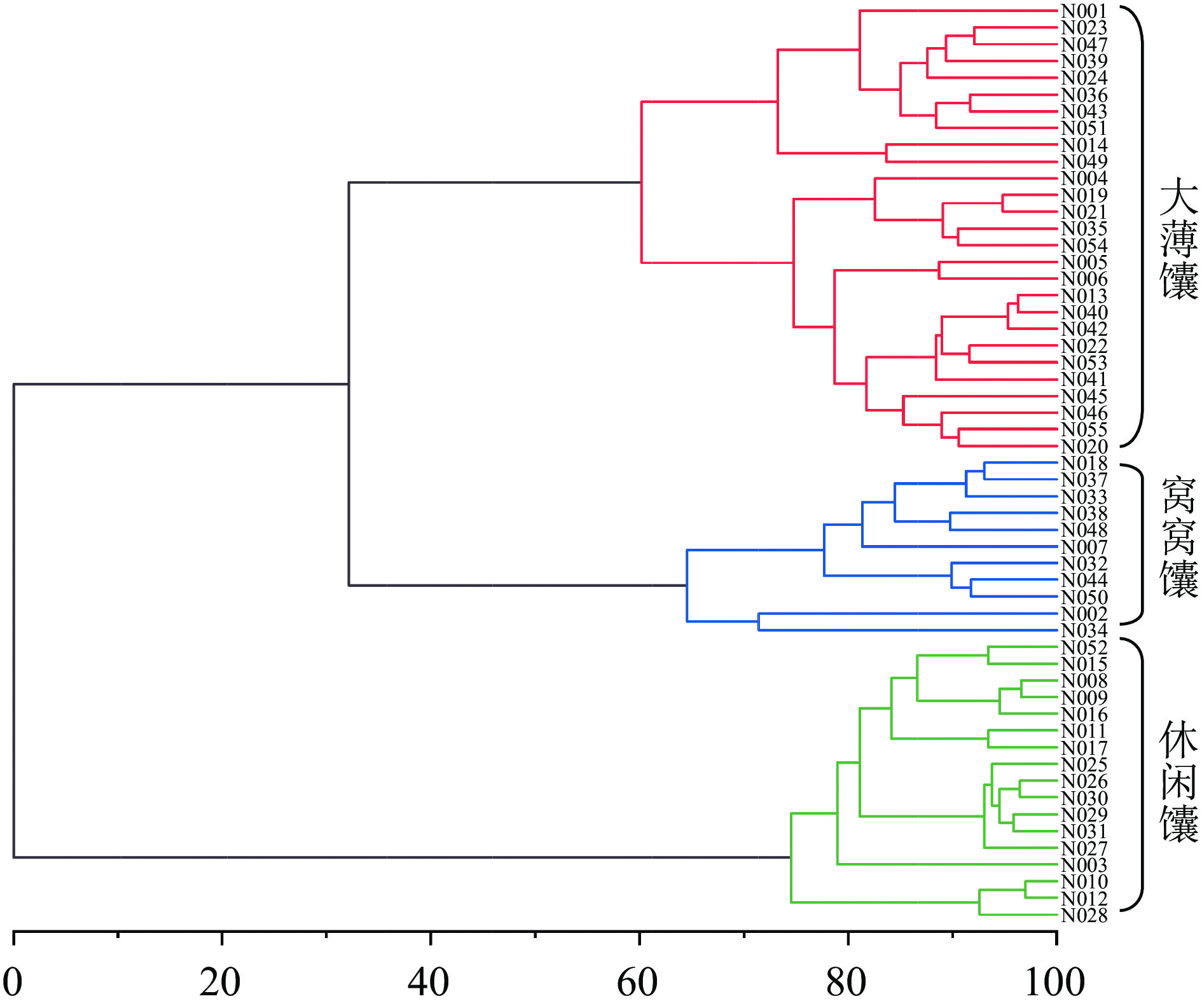
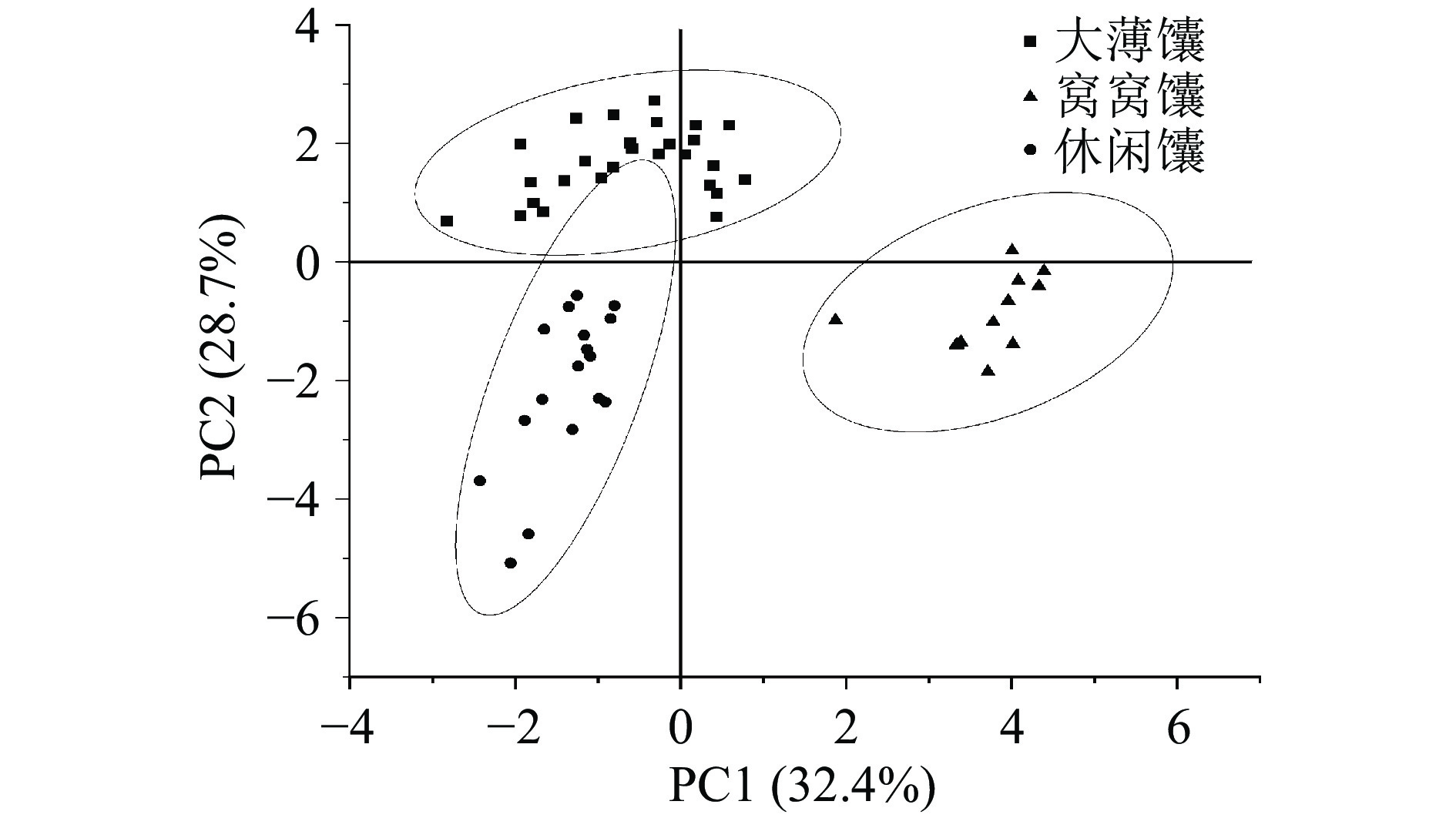
本研究基于以上分析结果,以影响馕品质的关键性指标为依据,利用Origin 9.0软件对采集的55份馕样品进行了层次聚类分析和主成分(PCA)分析,结果见图2和图3。由图2可知,在55%的相似度水平上,55份馕样品被划分为三大类,依据市场品类命名,分别为大薄馕、窝窝馕和休闲馕。从图3可以看出,三大类馕样品在组内呈现相互聚集的情况,不同种类馕品质间存在差异。以上结果验证了弹性、硬度、胶粘性、咀嚼性、L*值和b*值为评价馕品质的关键性指标,同时目前新疆馕主要依据其外观特征进行分类[2,29],人为主观性强,不具有科学性,本部分研究也为馕种类的划分提供了科学思路。
2.4 三大类馕品质指标分析及感官评价
在上述PCA分析结果基础上,为进一步明确三大类馕品质特性,本研究列示了三大类馕关键品质指标测定结果,见表6。由表6可知,大薄馕的L*值和b*值偏大,硬度值最小,其中大薄馕的L*值和硬度值与窝窝馕、休闲馕差异显著(P<0.05),b*值与窝窝馕差异显著(P<0.05),说明此类馕具有光泽、颜色金黄,硬度较小;窝窝馕弹性和咀嚼性值分别为22.49、138.69,远大于其它两类馕,且与其它两类馕差异显著(P<0.05),表明此类馕富有弹性和咀嚼性;休闲馕硬度最大,胶粘性值最小,均与大薄馕存在显著差异(P<0.05)。
表 6 三大类馕关键品质指标测定结果Table 6. Determination results of key quality indexs of 3 types of Nang馕种类 L* b* 硬度 弹性 咀嚼性 胶粘性 大薄馕 37.33±0.08a 41.28±0.05a 13.21±0.07b 5.25±0.12b 27.57±0.04b 9.71±0.14a 窝窝馕 34.13±0.11b 38.31±0.03b 39.83±0.01a 22.49±0.1a 138.69±0.16a 6.99±0.07b 休闲馕 31.90±0.01c 40.01±0.02ab 40.07±0.09a 3.32±0.05b 17.35±0.05c 5.04±0.16b 注:数据为同类馕测定值的平均值±标准误差;相同字母表示同列数据在0.05水平上差异不显著;表7同。 感官评价是食品品质评价的重要方法之一,可以从外观、风味、口感、质地等方面综合评价食品品质[30−31]。本研究对三大类55份馕样品进行感官评价,同一类馕得分取其均值,三大类馕感官得分结果见表7。由表7可得,三大类馕在感官品质上也存在较大差异,进一步验证了PCA分析结果。大薄馕色泽、风味、硬度得分最高,这与表6品质指标L*值、b*值、硬度测定结果相对应;窝窝馕弹性、咀嚼性得分最高,且与大薄馕、休闲馕差异显著(P<0.05),与品质指标弹性和咀嚼性值具有相关性;休闲馕酥脆性得分最高,与其它两类馕差异显著(P<0.05),与品质指标测定的硬度值大,胶粘性小相对应。
表 7 三大类馕感官评定结果Table 7. Sensory quality of 3 types of Nang馕种类 色泽 风味 组织结构 硬度 弹性 酥脆性 咀嚼性 大薄馕 14.85±0.79a 13.52±0.63a 8.26±1.56ab 14.37±0.82a 11.29±1.69b 12.39±0.93b 11.87±1.30b 窝窝馕 12.55±1.25b 11.03±1.14b 9.52±1.67a 11.64±1.43b 14.82±0.87a 9.05±0.84c 14.54±0.55a 休闲馕 9.41±1.53c 10.31±0.89b 7.35±0.77b 11.36±0.55b 9.19±1.00c 14.47±0.30a 9.04±0.89c 3. 结论
本研究采用主成分分析和聚类分析对新疆伊犁地区采集的55份馕样品的外观、色泽、质构等13项品质指标进行系统分析,最终得出弹性、硬度、胶粘性、咀嚼性、L*值和b*值为评价馕品质的关键性指标;以评价馕品质的6项关键指标为参数,采用层次聚类分析和主成分分析对55份馕样品进行种类划分,结合市场品类命名,将其分为三大类,分别为大薄馕、窝窝馕和休闲馕,继而结合感官评定结果,明确了三大类馕品质特性,大薄馕具有色泽金黄、原辅料烘烤香味浓郁、硬度适宜的特点;窝窝馕富有弹性和咀嚼性;休闲馕具有酥脆性好,弹性和咀嚼性差的特点。本研究为馕的分类提供了科学的方法,为馕品质评价体系的构建奠定了理论基础,同时也为消费者的选择提供参考依据。
-
表 1 新疆伊犁地区馕样品采样信息
Table 1 Sample collection of Nang in Yili area, Xinjiang
序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 序号 编号 采样地点 1 N001 伊宁市 15 N015 察布查尔县 29 N029 可克达拉市 43 N043 尼勒克县 2 N002 伊宁市 16 N016 察布查尔县 30 N030 可克达拉市 44 N044 尼勒克县 3 N003 伊宁市 17 N017 察布查尔县 31 N031 可克达拉市 45 N045 特克斯县 4 N004 伊宁市 18 N018 察布查尔县 32 N032 可克达拉市 46 N046 特克斯县 5 N005 伊宁市 19 N019 伊宁县 33 N033 可克达拉市 47 N047 特克斯县 6 N006 伊宁市 20 N020 伊宁县 34 N034 新源县 48 N048 特克斯县 7 N007 伊宁市 21 N021 伊宁县 35 N035 新源县 49 N049 巩留县 8 N008 伊宁市 22 N022 伊宁县 36 N036 新源县 50 N050 巩留县 9 N009 伊宁市 23 N023 伊宁县 37 N037 新源县 51 N051 巩留县 10 N010 伊宁市 24 N024 霍城县 38 N038 新源县 52 N052 巩留县 11 N011 伊宁市 25 N025 霍城县 39 N039 新源县 53 N053 昭苏县 12 N012 伊宁市 26 N026 霍城县 40 N040 尼勒克县 54 N054 昭苏县 13 N013 察布查尔县 27 N027 霍城县 41 N041 尼勒克县 55 N055 昭苏县 14 N014 察布查尔县 28 N028 霍城县 42 N042 尼勒克县 表 2 馕感官品质评价标准
Table 2 Criteria for sensory evaluation of Nang
指标 评分标准 分值 色泽(15分) 从淡黄或焦黑到具有诱人的烘烤色泽,颜色焦黄,且表面光滑,带有光泽,颜色均匀 1~15 风味(15分) 从香味淡,咸度或甜度过高或过低到具有充足的烘烤食物和原辅料的香味,咸度或甜度适中 1~15 组织结构(10分) 从馕结构形态不规则,存在塌陷和变形到结构均匀,形态规则 1~10 硬度(15分) 从太软或太硬到硬度适宜 1~15 弹性(15分) 从无弹性或弹性差到弹性好 1~15 酥脆性(15分) 从无酥脆感到非常酥脆 1~15 咀嚼性(15分) 从每秒咀嚼一次的频率咀嚼至达吞咽粒度所需要的时间短到所需要的时间长 1~15 表 3 馕13项品质指标之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 3 Correlation coefficient matrix among 13 quality indexes of Nang
指标 重量 横径 高度 L* a* b* 水分含量 Aw 硬度 内聚性 弹性 胶粘性 咀嚼性 重量 1.000 横径 0.524** 1.000 高度 0.111 −0.674 1.000 L* 0.302* 0.193 −0.082 1.000 a* 0.313* −0.060 0.303* 0.592** 1.000 b* −0.005 0.116 −0.044 0.150 0.063 1.000 水分含量 0.566** −0.068 0.545** 0.006 0.470** 0.047 1.000 Aw 0.611** 0.075 0.378** 0.135 0.421** 0.160 0.808** 1.000 硬度 −0.554 −0.542 0.245 −0.101 −0.142 −0.387 −0.450 −0.534 1.000 内聚性 0.539** 0.607** −0.413 0.262 −0.072 0.074 0.206 0.346** −0.694 1.000 弹性 0.172 −0.625 0.952** 0.002 0.363** −0.093 0.549** 0.409** 0.168 −0.325 1.000 胶粘性 0.230 0.268* −0.107 0.329* 0.062 0.298* −0.127 0.193 −0.125 0.254 −0.095 1.000 咀嚼性 0.145 −0.605 0.900** 0.052 0.261 −0.062 0.432** 0.416** 0.245 −0.276 0.925** 0.134 1.000 注:*在0.05水平(双侧)上相关性显著,P<0.05;**在0.01水平(双侧)上相关性极显著,P<0.01。 表 4 主成分的特征值和贡献率
Table 4 Eigenvalue and variance contribution rate
主成分 初始特征值 提取载荷平方和 总计 方差的(%) 累积(%) 总计 方差的(%) 累积 (%) 1 4.511 34.700 34.700 4.511 34.700 34.700 2 3.987 30.669 65.369 3.987 30.669 65.369 3 1.493 11.487 76.856 1.493 11.487 76.856 4 1.143 8.794 85.650 5 0.661 5.085 90.735 6 0.374 2.877 93.612 7 0.239 1.840 95.452 8 0.207 1.589 97.042 9 0.139 1.071 98.113 10 0.102 0.785 98.898 11 0.081 0.627 99.524 12 0.038 0.293 99.818 13 0.024 0.182 100.000 表 5 主成分载荷矩阵
Table 5 Component matrix
指标 主成分 1 2 3 弹性 0.960 −0.087 −0.015 咀嚼性 0.955 −0.163 −0.040 胶粘性 0.908 −0.090 0.122 水分含量 0.672 0.544 −0.359 a* 0.483 0.372 0.444 硬度 0.131 −0.837 0.275 L* 0.217 0.817 −0.109 b* −0.320 0.764 −0.163 Aw 0.550 0.695 −0.169 横径 −0.622 0.649 −0.038 高度 0.046 0.420 0.758 重量 −0.074 0.363 0.586 内聚性 −0.063 0.295 0.296 表 6 三大类馕关键品质指标测定结果
Table 6 Determination results of key quality indexs of 3 types of Nang
馕种类 L* b* 硬度 弹性 咀嚼性 胶粘性 大薄馕 37.33±0.08a 41.28±0.05a 13.21±0.07b 5.25±0.12b 27.57±0.04b 9.71±0.14a 窝窝馕 34.13±0.11b 38.31±0.03b 39.83±0.01a 22.49±0.1a 138.69±0.16a 6.99±0.07b 休闲馕 31.90±0.01c 40.01±0.02ab 40.07±0.09a 3.32±0.05b 17.35±0.05c 5.04±0.16b 注:数据为同类馕测定值的平均值±标准误差;相同字母表示同列数据在0.05水平上差异不显著;表7同。 表 7 三大类馕感官评定结果
Table 7 Sensory quality of 3 types of Nang
馕种类 色泽 风味 组织结构 硬度 弹性 酥脆性 咀嚼性 大薄馕 14.85±0.79a 13.52±0.63a 8.26±1.56ab 14.37±0.82a 11.29±1.69b 12.39±0.93b 11.87±1.30b 窝窝馕 12.55±1.25b 11.03±1.14b 9.52±1.67a 11.64±1.43b 14.82±0.87a 9.05±0.84c 14.54±0.55a 休闲馕 9.41±1.53c 10.31±0.89b 7.35±0.77b 11.36±0.55b 9.19±1.00c 14.47±0.30a 9.04±0.89c -
[1] 李正元. 馕的起源[J]. 中国边疆史地研究,2012,22(1):112−117. [LI Z Y. On the origin of Nang cake[J]. China’s Borderland History and Geography Studies,2012,22(1):112−117.] LI Z Y . On the origin of Nang cake[J]. China’s Borderland History and Geography Studies,2012 ,22 (1 ):112 −117 .[2] 孙含, 王晶, 赵晓燕, 等. 新疆特色面制品馕的研究进展[J]. 粮油食品科技,2018,26(6):19−24. [SUN H, WANG J, ZHAO X Y, et al. Research progress of Xinjiang characteristic flour product "nang"[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2018,26(6):19−24.] SUN H, WANG J, ZHAO X Y, et al . Research progress of Xinjiang characteristic flour product "nang"[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2018 ,26 (6 ):19 −24 .[3] 李芳, 张文, 达迪拉·买买提, 等. 影响新疆馕制品品质的因素[J]. 食品工业,2015,36(7):223−226. [LI F, ZHANG W, DADILA M, et al. The influencing factors on the quality of Xinjiang Nang products[J]. The Food Industry,2015,36(7):223−226.] LI F, ZHANG W, DADILA M, et al . The influencing factors on the quality of Xinjiang Nang products[J]. The Food Industry,2015 ,36 (7 ):223 −226 .[4] 曹俊梅, 张新忠, 芦静, 等. 馕专用小麦品种品质及食品品质评价标准[J]. 农村科技,2019(1):50−52. [CAO J M, ZHANG X Z, LU J, et al. Evaluation standard for quality of wheat varieties and food quality for Nang purposes[J]. Rural Science & Technology,2019(1):50−52.] CAO J M, ZHANG X Z, LU J, et al . Evaluation standard for quality of wheat varieties and food quality for Nang purposes[J]. Rural Science & Technology,2019 (1 ):50 −52 .[5] 安尼瓦尔·哈斯木. 馕·馕坑与馕文化漫谈[J]. 新疆地方志,2017(2):53−58. [ANIVAR H. Nang, Nang pit and Nang culture[J]. Xinjiang Local Records,2017(2):53−58.] ANIVAR H . Nang, Nang pit and Nang culture[J]. Xinjiang Local Records,2017 (2 ):53 −58 .[6] 罗华. 新疆馕文化[M]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆人民卫生出版社, 2012:19−25. [LUO H. The culture of Nang in Xinjiang[M]. Urumqi:Xinjiang People's Health Publishing House, 2012:19−25.] LUO H. The culture of Nang in Xinjiang[M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang People's Health Publishing House, 2012: 19−25.
[7] 王雪, 李季鹏, 王飞. 新疆少数民族食品(馕)企业品牌战略研究[J]. 经济论坛,2017(1):24−26. [WANG X, LI J P, WANG F. Research on brand strategy of Xinjiang minority food (Nang) enterprises[J]. Economy Forum,2017(1):24−26.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3580.2017.01.006 WANG X, LI J P, WANG F . Research on brand strategy of Xinjiang minority food (Nang) enterprises[J]. Economy Forum,2017 (1 ):24 −26 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3580.2017.01.006[8] 何婧云. 维吾尔族“馕”文化及其当代转型[J]. 农业考古,2006(4):256−259. [HE J Y. Nang, Uyghur "Nang" culture and its contemporary transformation[J]. Agricultural Archaeology,2006(4):256−259.] HE J Y . Nang, Uyghur "Nang" culture and its contemporary transformation[J]. Agricultural Archaeology,2006 (4 ):256 −259 .[9] 陈婷, 钱其龙. 新疆馕文化及产业发展现状[J]. 现代食品,2022,28(14):60−62. [CHEN T, QIAN Q L. The current situation of Xinjiang Naan culture and industry development[J]. Modern Food,2022,28(14):60−62.] CHEN T, QIAN Q L . The current situation of Xinjiang Naan culture and industry development[J]. Modern Food,2022 ,28 (14 ):60 −62 .[10] ZHAO X Y, SUN H, ZHU H T, et al. Effect of packaging methods and storage conditions on quality characteristics of flour product naan[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,56(12):5362−5373. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-04007-x
[11] 孙含. 新疆馕饼的加工新工艺及品质与保藏技术研究[D]. 济南:济南大学, 2019. [SUN H. Study on New Processing Technology, Quality and Preservation Technology of Xinjiang Naan [D]. Jinan:University of Jinan, 2019.] SUN H. Study on New Processing Technology, Quality and Preservation Technology of Xinjiang Naan [D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2019.
[12] 潘勇勇. 论文化交融视域下的馕文化[J]. 丝绸之路,2022(3):143−147. [PAN Y Y. On Naan culture in the context of cultural intermingling[J]. The Silk Road,2022(3):143−147.] PAN Y Y . On Naan culture in the context of cultural intermingling[J]. The Silk Road,2022 (3 ):143 −147 .[13] ADILOVA S S , QULMAMATOVA D E , BABOEV S K , et al. Multivariate cluster and principle component analyses of selected yield traits in uzbek bread wheat cultivars[J]. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2020, 11(6):903-912.
[14] LIU Y , LYON B G , WINDHAM W R , et al. Principal component analysis of physical, color, and sensory characteristics of chicken breasts deboned at two, four, six, and twenty-four hours postmortem. [J]. Poult, 2004, 83(1):101-108.
[15] 姜雪, 刘楠, 孙永, 等. 统计分析方法在食品品质评价中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2017,8(1):13−19. [JIANG X, LIU N, SUN Y, et al. Application of statistical analysis methods in food quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2017,8(1):13−19.] JIANG X, LIU N, SUN Y, et al . Application of statistical analysis methods in food quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2017 ,8 (1 ):13 −19 .[16] 王养平, 焦建军. 运动营养饼干品质指标的主成分分析及聚类分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(5):1405−1413. [WANG Y P, JIAO J J. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis of quality indexes of sports nutrition biscuits[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(5):1405−1413.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.5.spaqzljcjs202205007 WANG Y P, JIAO J J . Principal component analysis and cluster analysis of quality indexes of sports nutrition biscuits[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022 ,13 (5 ):1405 −1413 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.5.spaqzljcjs202205007[17] 闫博文, 管璐静, 赵建新, 等. 基于多元统计分析方法建立北方馒头品质评价体系[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(1):214−219. [YAN B W, GUAN L J, ZHAO J X, et al. Development of the quality evaluation system of chinese northern steamed bread by multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(1):214−219.] YAN B W, GUAN L J, ZHAO J X, et al . Development of the quality evaluation system of chinese northern steamed bread by multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019 ,40 (1 ):214 −219 .[18] 张怀予, 沈世爽, 张浩, 等. 枸杞面包复合改良剂优化及其品质的主成分分析法多指标评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(13):232−241. [ZHANG H Y, SHEN S S, ZHANG H, et al. Optimization of composite improver for Lycium barbarum bread and evaluation of its multiple quality variables[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(13):232−241.] ZHANG H Y, SHEN S S, ZHANG H, et al . Optimization of composite improver for Lycium barbarum bread and evaluation of its multiple quality variables[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019 ,45 (13 ):232 −241 .[19] 王兰静, 王菲, 钱淑君, 等. 无麸质大米面包品质评价方法的建立及原料品种适用性研究[J]. 美食研究,2022,39(2):72−78. [WANG L J, WANG F, QIAN S J, et al. Establishment of gluten-free rice bread quality evaluation model and study on rice varieties applicability[J]. Journal of Researches on Dietetic Science and Culture,2022,39(2):72−78.] doi: 10.19913/j.cnki.2095-8730msyj.2022.02.12 WANG L J, WANG F, QIAN S J, et al . Establishment of gluten-free rice bread quality evaluation model and study on rice varieties applicability[J]. Journal of Researches on Dietetic Science and Culture,2022 ,39 (2 ):72 −78 . doi: 10.19913/j.cnki.2095-8730msyj.2022.02.12[20] 王岸娜, 王艺洁, 吴立根. 谷物粉对馕品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2023,34(3):9−18. [WANG A N, WANG Y J, WU L G. Effects of different grain flour on Nang quality and antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2023,34(3):9−18.] WANG A N, WANG Y J, WU L G . Effects of different grain flour on Nang quality and antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2023 ,34 (3 ):9 −18 .[21] 丁帅杰. 全麦粉馕产品品质改良的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆大学, 2021. [DING S J. Study on quality improvement of whole wheat naan. [D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang University, 2021.] DING S J. Study on quality improvement of whole wheat naan. [D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2021.
[22] 古丽乃再尔·斯热依力, 阿衣古丽·阿力木, 付文欠, 等. 不同添加量洋葱浆对馕品质的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(3):195−202,210. [GULNAZAR S, AYGUL A, FU W Q, et al. Effects of different levels of onion pulp addition on the quality of Naan[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(3):195−202,210.] GULNAZAR S, AYGUL A, FU W Q, et al . Effects of different levels of onion pulp addition on the quality of Naan[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022 ,38 (3 ):195 −202,210 .[23] 王文静. 红枣粉对面团与馕品质特性的影响研究[D]. 郑州:郑州轻工业大学, 2019. [WANG W J. Effect of red jujube powder on quality characteristics of dough and Nang[D]. Zhengzhou:Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2019.] WANG W J. Effect of red jujube powder on quality characteristics of dough and Nang[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2019.
[24] 邹淑萍, 许铭强, 张春平, 等. 马铃薯粉添加量对新疆馕加工品质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(11):33−39. [ZHOU S P, XU M Q, ZHANG C P, et al. Effect of potato powder addition on the quality characteristics of Nang in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020,35(11):33−39.] ZHOU S P, XU M Q, ZHANG C P, et al . Effect of potato powder addition on the quality characteristics of Nang in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020 ,35 (11 ):33 −39 .[25] 张敏, 布海丽且姆·阿卜杜热合曼, 姜露熙, 等. 基于模糊数学评价法优化黑木耳牛奶馕的工艺研究[J]. 发酵科技通讯,2023,52(1):8−15. [ZHANG M, BUHAILIQIEMU A, JIANG L X, et al. Formula optimization of Auricularia auricula milk of Nang based on fuzzy mathematics evaluation[J]. Bulletin of Fermentation Science and Technology,2023,52(1):8−15.] ZHANG M, BUHAILIQIEMU A, JIANG L X, et al . Formula optimization of Auricularia auricula milk of Nang based on fuzzy mathematics evaluation[J]. Bulletin of Fermentation Science and Technology,2023 ,52 (1 ):8 −15 .[26] 李芳, 蒋小锋, 谢琼, 等. 新疆馕制品TPA指标与感官评价指标的相关性研究[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(3):205−208. [LI F, JIANG X F, XIE Q, et al. Study of correlation between TPA parameters and sensory evaluation index of Nang products[J]. The Food Industry,2016,37(3):205−208.] LI F, JIANG X F, XIE Q, et al . Study of correlation between TPA parameters and sensory evaluation index of Nang products[J]. The Food Industry,2016 ,37 (3 ):205 −208 .[27] D'AGOSTINO R B. Principal Components Analysis[M]. New York:Springer, 2010:373-378.
[28] GRANE A, JACH A . Applications of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) in food science and technology[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2014:286-293.
[29] 康峰, 刘艳祥, 刘娟, 等. 新疆传统特色食品馕的种类及其文化[J]. 现代食品,2021,12(12):43−48. [KANG F, LIU Y X, LIU J, et al. The types and culture of Xinjing traditional food Nang[J]. Modern Food,2021,12(12):43−48.] KANG F, LIU Y X, LIU J, et al . The types and culture of Xinjing traditional food Nang[J]. Modern Food,2021 ,12 (12 ):43 −48 .[30] MOLLAKHALILI-MEYBODI N, SHEIDAEI Z, KHORSHIDIAN N, et al. Sensory attributes of wheat bread:A review of influential factors[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2022,17(3):2172−2181.
[31] SARAH E. Application of sensory evaluation in food research[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2008,43(9):1507−1511.
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 曹雪丽,韩笑,李屿恺,王泽莹,董海钰,杨娟,郭晓. 响应面法优化泰山女儿茶总黄酮提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究. 广东化工. 2024(06): 7-10+60 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周志红,赵昕,胡勤,肖明明. 超声波处理与纤维素酶协同提取山楂总多酚的工艺优化研究. 当代化工研究. 2024(11): 152-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄月,向海芹,王双辉,龚意辉,陈致印. 穇子多酚的分离纯化及其抗氧化能力研究. 食品工业. 2023(01): 42-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾诗琴,梁强,李云成,赵玲,徐霞,熊伟,宣朴,姚英政. 浓香菜籽油SiO_2脱胶工艺优化及品质分析. 中国油脂. 2023(04): 21-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王媛媛,郝璟嵘,闫思颖,张甜甜,党玲,王晓婧. 沙棘冻干粉泡腾片的制备工艺优化及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(10): 235-241 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 杨春晖,王文平,续丹丹,崔宇倩,鞠岩,许春艳,吕小婷. 不同原料酿造酱油功能成分及抗氧化活性比较. 食品工业科技. 2023(14): 318-325 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 刘敏卓,张小月,张灵芝,曹孟君,叶素芳,吴泽华,张杰,曾志红. 竹茹总黄酮超声波处理与纤维素酶协同提取工艺优化及其体外抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(20): 221-229 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 张鑫,朱青永,徐慧敏,吴梦园,陈小娥,陈启和,刘政捷. 黄绿卷毛菇中原伊鲁烷型倍半萜芳基酯提取工艺优化及活性研究. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2023(06): 813-824 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 关玉婷,陈瑞瑞,蔡如玉,范蓓,孙晶,张瑞,张紫阳,常世敏. 超声辅助提取茄皮酚工艺优化及其降血糖功效研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



