Changes of Spoilage Bacteria on the Surface of Broiler Carcasses during the Efficient Slaughtering Process of Yellow Feather Chicken
-
摘要: 为了分析黄羽肉鸡屠宰加工环节的肉鸡胴体污染菌的菌群组成,本试验利用平板倾注法及Illumina MiSeq高通量测序高效地测定黄羽肉鸡屠宰过程中加工环境和胴体表面腐败菌的多样性。结果表明,净膛、预冷及分级是黄羽肉鸡菌落总数增长的主要污染来源工序,分级秤、分级车间工人手套、预冷槽及净膛工人手套为以上三个工序中污染来源接触面,且分级秤及分级车间工人手套所污染菌群是黄羽鸡胴体菌群的主要来源,使黄羽鸡胴体表面菌落总数及假单胞菌增长率高达24.13%、41.27%,经过分级秤及分级车间工人手后黄羽鸡菌落总数显著(P<0.05)增加至4.63 lg(CFU/g)。打毛后(DM)、净膛后(JH)、净膛消毒后(CH)黄羽鸡胴体优势菌主要为链球菌属(Streptococcus),大肠杆菌属(Escherichia)和气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)。黄羽鸡经预冷槽预冷后气单胞菌属丰度大幅增加,链球菌属次之。经过分级秤分级后黄羽鸡胴体菌群中不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)为主要优势菌,巨球菌属(Macrococcus)次之。添加次氯酸电解水减菌后,黄羽肉鸡胴体表明气单胞菌属和链球菌属丰度大幅下降,说明次氯酸电解水减菌效果较好。本研究结果通过对黄羽肉鸡屠宰过程中微生物分布情况的分析,可以为黄羽肉鸡屠宰车间的环境控制和产品品质维持、货架期延长提供数据支持和理论依据。Abstract: To analyze the changes of spoilage bacteria on the carcasses of broiler during the slaughtering of yellow feather broiler, the diversity of spoilage bacteria in the processing environment and on the carcass surface during the efficient slaughter of yellow feather broiler was determined by the plate pouring method and Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that the main contamination procedure for the growth of bacteria of yellow feather broilers was eviscerating, pre-cooling and grading procedure, and the grading scale, in which the grading scale, workers' gloves from grading workshop, pre-cooling tank and workers' gloves from eviscerating manual gloves were contamination sources in the three processes aforementioned. Moreover, grading scale and workers' gloves in the decomposition workshop were the main source of contaminated flora of yellow feather broilers carcasses. The growth rate of total viable counts (TVC) and Pseudomonas on the surface of yellow feather broilers carcasses was as high as 24.13% and 41.27%, respectively. The TVC of yellow feather broilers increased to 4.63 lg(CFU/g) after grading scale and grading workshop worker's hands (P<0.05). Streptococcus, Escherichia and Aeromonas were the main dominant bacteria in yellow feather broilers carcasses after plucking (DM), evisceration (JH) and disinfection (CH). The abundance of Aeromonas increased substantially in yellow feather broilers after pre-cooling, followed by Streptococcus. After the grading scale, Acinetobacter was the dominant bacterium in the yellow feather broilers carcasses, followed by Macrococcus. As the abundance of Aeromonas and Streptococcus decreased significantly on the carcasses of yellow feather broilers treated with slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW), it indicated that the disinfecting effect of SAEW was obvious. The results of the present investigation could provide data support and theoretical reference for environmental control, product quality maintenance and shelf-life extension in yellow feather broilers slaughterhouse by analyzing the microbial distribution during the slaughter of yellow feather broilers.
-
鸡肉具有低脂肪、高蛋白优点,鲜美细嫩的肉质使其受到消费者的青睐[1]。2021年我国鸡肉产量为1470万吨,位居世界第二[2]。在我国禽肉消费市场主要有两大品类,即白羽肉鸡及黄羽肉鸡。白羽肉鸡产业是中国畜禽养殖产业中规模化养殖程度最高的产业,经过多年产业发展与技术升级,白羽肉鸡屠宰可实现自动化流水线作业,每小时屠宰产能可达1万只以上,市场流通产品以冰鲜分割品及调理品为主。黄羽肉鸡又称国鸡主要以我国地方品种为主,市场流通主要以毛鸡为主,黄羽肉鸡体重较白羽肉鸡小且均匀度差,未能像白羽肉鸡一样实现自动化流水线屠宰作业,屠宰关键工序掏膛主要依赖人工,屠宰水平差异导致黄羽肉鸡屠宰加工产业在发展过程中会比白羽肉鸡产业存在更多痛点。目前,我国部分城市的主城区开始限制活禽交易,主张家禽“集中屠宰,冷鲜上市”[3]。在理想情况下,鸡的肌肉组织中不存在微生物,然而在屠宰过程中,会不可避免地从各种污染源(如皮肤、羽毛、粪便、刀具、台面、操作工人的手等)带入微生物到肉鸡胴体及其分割产品中[4−5]。集中屠宰过程中因屠宰量大,且部分屠宰场环境比较落后,很容易造成微生物的交叉污染[3]。冷鲜鸡肉加工过程温度相对较低,使得大部分微生物粘附于其胴体表面,易导致其腐败变质,缩短其货架期,甚至引发食品安全问题[6]。比起贮藏温度,生产过程中良好的操作和预冷方式对货架期的延长更具关健作用[7]。汤飞[8]从安徽省宣城地区所产鸡肉中分离出大肠菌群,假单胞菌,乳酸菌,金黄色葡萄球菌,沙门氏菌等。王光宇[9]发现鸡肉上的腐败菌主要有假单胞菌和气单胞菌。Laconi等[10]从鸡肉中分离出空肠弯曲杆菌和大肠弯曲杆菌。
关于鸡肉中菌种的分离鉴定主要有两种方法,传统培养基鉴定法和高通量测序鉴定法[11]。传统培养基鉴定法指的是将稀释后的菌液均匀涂布在各种特异性选择性培养基上,然后通过肉眼观察,挑选出单菌落并置于液体培养基中培养,然后纯化分离并提取DNA[12]。仅仅凭肉眼去观察和挑取菌落,主观性比较强,很容易遗漏部分菌株[12−13]。高通量测序技术指的是不需要通过培养细菌,就能准确的分析出样品中微生物的多样性。它可以在短时间内生成数千个序列,还能覆盖复杂的和低丰度的微生物,因此该技术可以发现一些传统培养基鉴定方法中无法检测出的微生物[14]。目前,高通量测序技术已被广泛应用于食品加工、土壤、水质和肠道菌群等相关样品的微生物多样性分析[15]。
前期的研究大多以白羽肉鸡为实验原料,因此,本试验以黄羽鸡为研究对象,利用平板倾注法及Illumina MiSeq高通量测序测定高效地确定黄羽肉鸡宰过程中加工环境和胴体表面腐败菌的多样性,研究了屠宰至加工的各个过程中鸡肉的表面,以及其可能接触到的各个台面的细菌。旨在分析黄羽肉鸡屠宰加工环节的肉鸡胴体菌群组成,将为黄羽肉鸡屠宰企业提高肉鸡屠宰卫生品质、延长贮藏期奠定坚实的理论基础,为黄羽肉鸡屠宰技术提升和产业发展提供研究数据和研究方向。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黄羽鸡 温氏食品集团股份有限公司;营养琼脂(Nutrient Agar) 北京路桥技术有限责任公司;氯化钠 国药集团化学试剂有限公司
NextSeq 500高通量测序仪 美国illumina公司;TG16-WS型台式高速离心机 湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;LRH-250-HS型恒温恒湿培养箱 沈阳亮衡天平仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品采集
为了分析黄羽鸡屠宰过程各工艺中胴体及所接触台面的菌群组成,选取屠宰加工过程的黄羽鸡为试验样品,并对所接触的台面进行擦拭以获得黄羽鸡接触台面的菌相。本文在屠宰工艺流程取样点(打毛后(DM);净膛后(JH);净膛消毒后(CH);预冷后(YH);次氯酸电解水处理后(DH);分级后成品(BZ);对照(CN))每个点随机选取三只去毛掏膛后的黄羽鸡进行微生物检测。在接触面(净膛工人手套(JS)、分级秤的表面(BC)、分级车间台面(BT)、分级车间工人手套(BS)、预冷池内表面(YB)、预冷池内角(YJ))取样进行微生物检测,测定在不同工艺点的胴体和接触面所取的样品的菌落总数及假单胞菌数。同时将洗菌后菌悬液离心获得菌泥并保存于−80 ℃,用于菌群多样性分析。
1.2.2 屠宰工艺流程点测试菌液制备
在屠宰工艺流程的不同取样点随机选取黄羽肉鸡3只。将称重后的每只黄羽肉鸡胴体与同质量无菌生理盐水加入到无菌取样袋,室温条件下200 r/min振荡10 min。然后吸取1 mL菌悬液加入9 mL灭菌生理盐水中进行十倍梯度稀释,制备测试菌液。
1.2.3 加工环境表面测试菌液制备
选择加工环境取样点与肉鸡胴体直接接触的暴露面为取样点,将棉签在5 cm×5 cm的取样器范围内擦拭,取样后置入装有225 mL无菌水的均质袋中,室温条件下200 r/min振荡10 min。重复取样三次。振荡混匀后,对菌悬液十倍稀释制备测试菌液。
1.2.4 菌落总数的测定
参照GB 4789.2-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》测定菌落总数,对30~300 CFU之间的平板进行计数[16−17]。
1.2.5 高通量测序
将上述不同屠宰工艺点及接触表面获得的菌液在4 ℃离心10 min(2000 r/min)进行第一次离心,然后吸取上清液于4 ℃、12000 r/min离心10 min进行第二次离心,将第二次获得菌泥并放入冰箱中,−80 ℃保存。选取引物338F(5’-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3’)和806R(5’-GGACTACNNGGG TATCTAAT-3’)对细菌的V3-V4区域进行扩增。利用Illumina Miseq高通量测序平台进行样品的测序。将相似性高于97%的测序样品中的物种进行分类单元操作(operational taxonomic units,OTU)[18]。然后,将所测得的OTU与Silva数据库里的信息进行比对,获得相应的物种多样性信息。并计算分析alpha多样性中的各个指数(Chao1、Observed_species、PD_whole_tree及Shannon)。利用UniFrac算法对系统进化的信息进行比较各个样品间微生物菌群的差异性,并进行Beta多样性分析。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据采用Excel进行统计,利用SPSS 19.0软件进行显著性分析,P<0.05为差异显著。使用Origin 2018C进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 屠宰过程中肉鸡胴体表面菌数变化
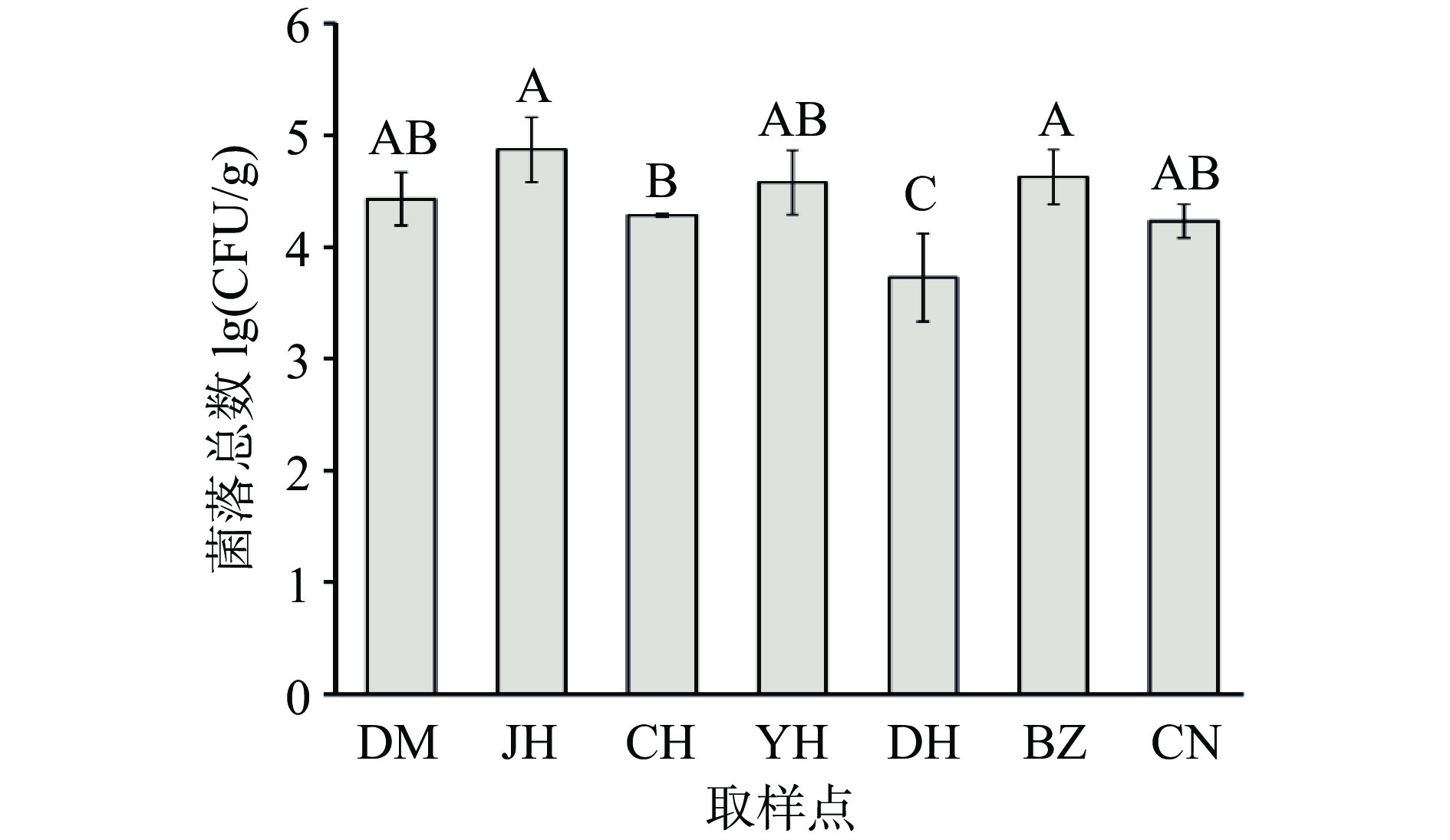
屠宰过程中各工艺点的黄羽鸡胴体总菌数变化如图1所示。由图1所示,在黄羽鸡屠宰流程中,经打毛后黄羽肉鸡胴体的菌落总数为4.43 lg(CFU/g),净膛后菌落总数为4.87 lg(CFU/g),这可能是因为净膛过程存在外源操作及肠道菌群污染的几率。净膛后胴体经过次氯酸钠溶液清洗后,菌落总数降为4.28 lg(CFU/g),经预冷后菌落总数回升至4.58 lg(CFU/g),说明预冷槽成为黄羽鸡胴体菌落总数增长的第二个污染点。经分级筛选后,胴体菌落总数再次上升至4.63 lg(CFU/g)。由图1可知,净膛、预冷及分级筛选是黄羽肉鸡菌数增长的主要污染源,在屠宰过程中需关注以上工序卫生操作及微生物控制。
2.2 加工环境表面菌数变化
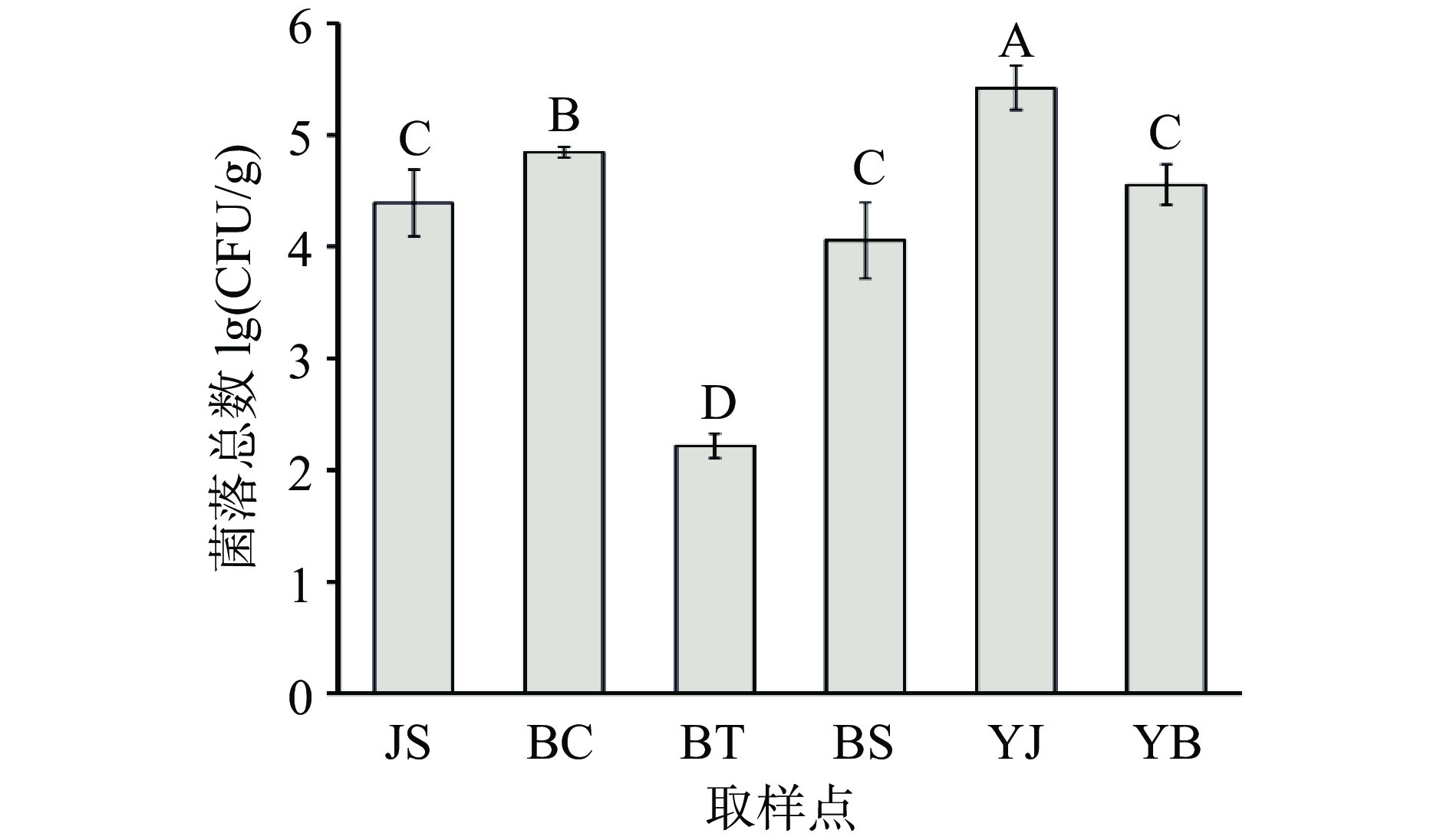
本试验选择净膛工人手套、预冷槽内表面和内角、分级车间台面及分级车间工人手套为取样对象,分析其总菌数分布情况,结果如图2。由图2可知,所有接触表面中预冷池内角总菌数最高,为5.42 lg(CFU/cm2);分级秤表面次之为4.85 lg(CFU/cm2);预冷槽内角、净膛工人手套、分级车间工人手套分别高达4.56、4.39、4.06 lg(CFU/cm2)。由此可知,净膛工人手套、预冷槽、分级秤及分级车间工人手套成为影响黄羽鸡总菌数变化在净膛、预冷及分级筛选后工艺点主要的污染源。
2.3 Alpha多样性指数分析结果
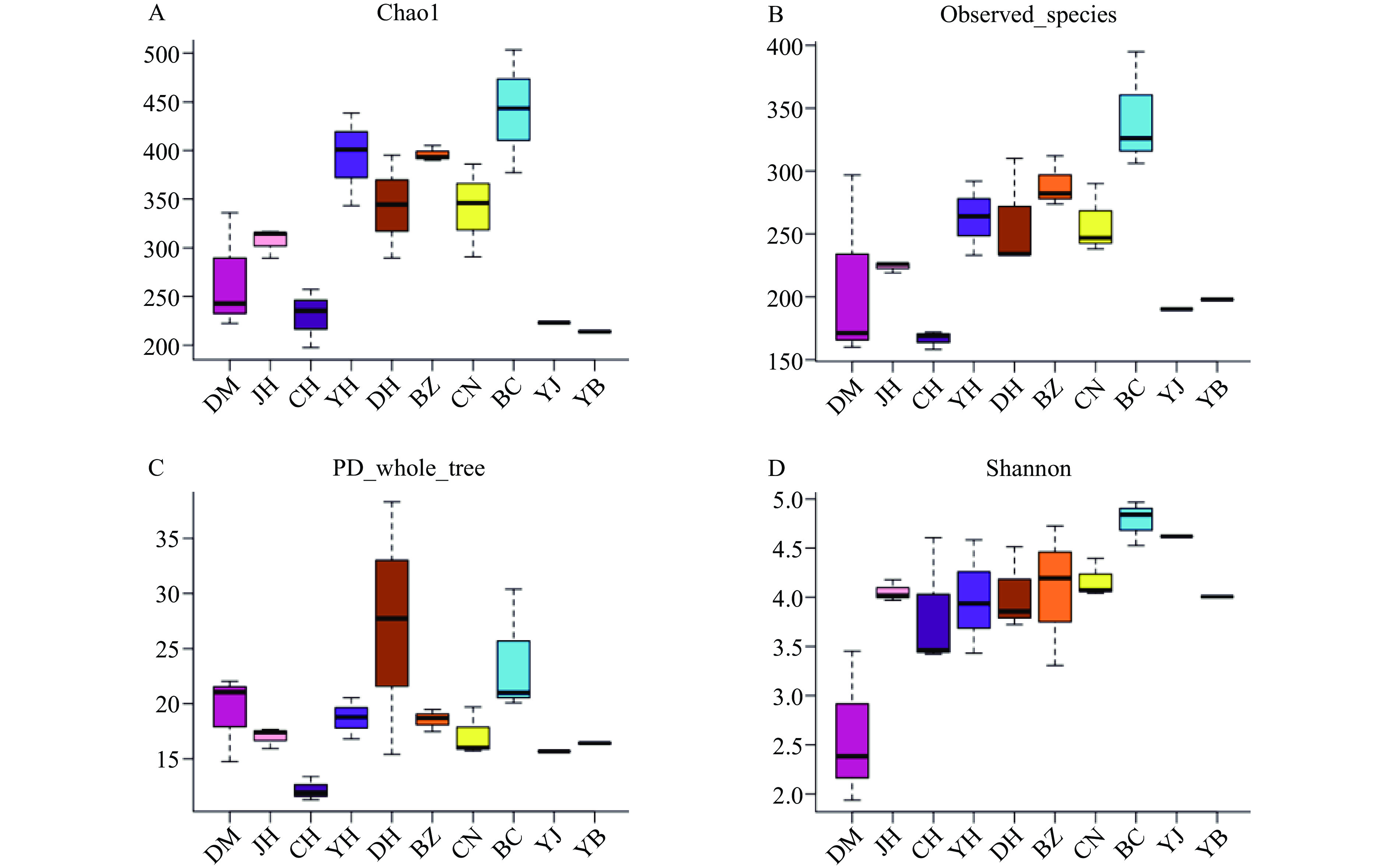
Alpha多样性指数是指特定环境内多样性,主要由Chao1、Observed_species、PD_whole_tree及Shannon反应物种丰度、均匀度以及测序深度[19−20]。由图3可知,分级秤的表面(BC)的Chao1、Shannon指数高于其他组,再次说明分级秤表面菌群丰度和多样性是各工艺点最高。这一结果与成品菌相丰度和多样性相一致。
2.4 菌群分布聚类分析
2.4.1 基于科分类水平的分析
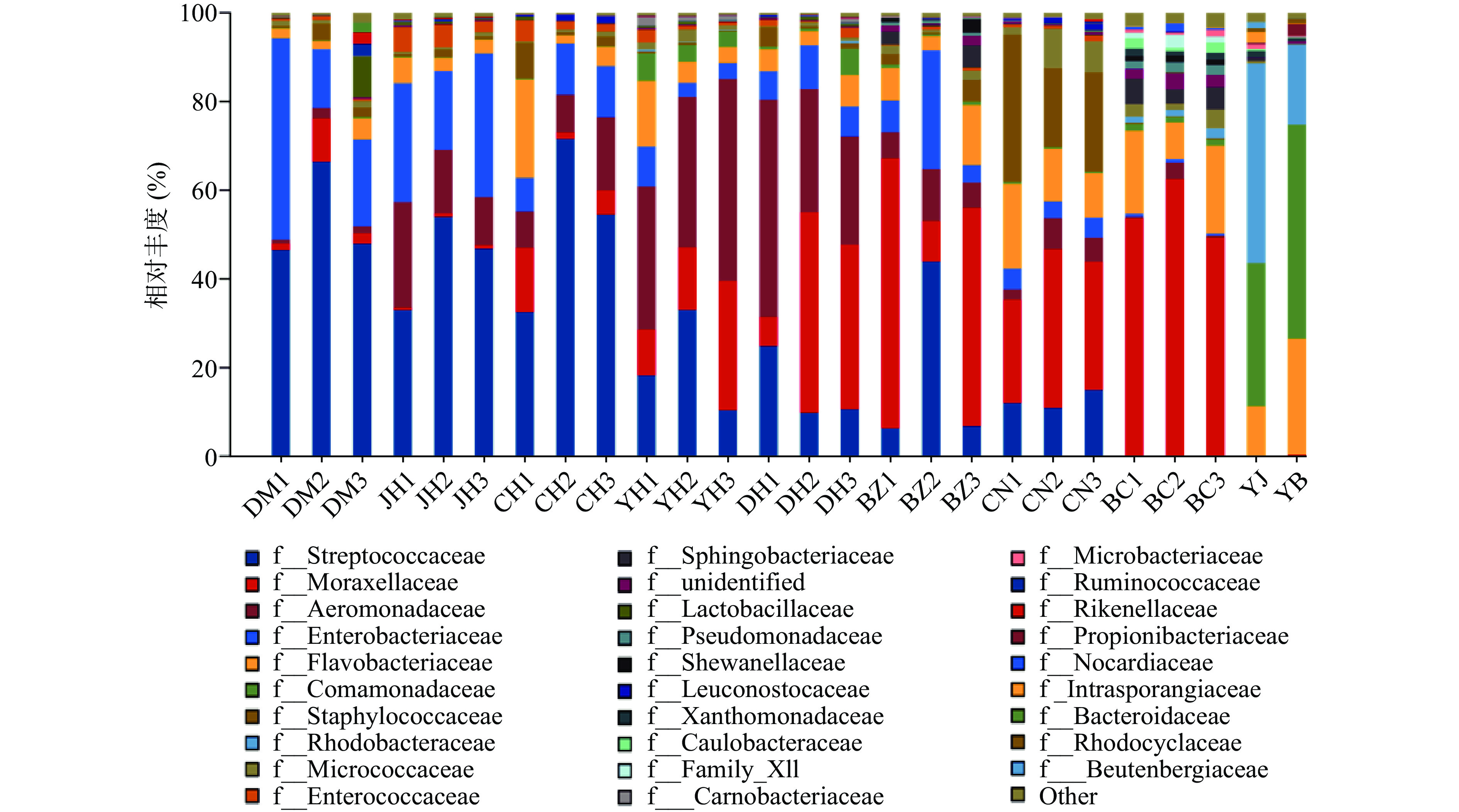
由图4可知,打毛后(DM)、净膛后(JH)、净膛消毒后(CH)黄羽鸡胴体优势菌主要为链球菌科(Streptococcaceae),肠杆菌科(Enterobacteriaceae)次之,气单胞菌科(Aeromonadaceae)仅次于肠杆菌科。净膛后经瞬时清洗消毒后肠杆菌科所占比例大幅下降。黄羽鸡经预冷槽预冷后气单胞菌科丰度大幅增加。说明预冷槽中环境温度及其他条件更适宜于气单胞菌科生长。进入电解水减菌槽后,气单胞菌科和链球菌科丰度大幅下降,说明次氯酸对这两类菌具有较好抑制作用。莫拉氏菌科(Moraxellaceae)成为黄羽鸡减菌后的优势菌群,气单胞菌科次之。经过分级秤分级后黄羽鸡胴体菌群中莫拉氏菌科丰度再次增加,说明分级秤表面污染优势菌群主要是莫拉氏菌科。并通过对分级秤表面菌群多样性的分析,也证实分级秤表面的优势菌主要为莫拉氏菌科。基于以上科属分析,屠宰过程微生物控制需关注不同科属菌类特性,控制屠宰条件定向消减微生物。
2.4.2 基于属分类水平的分析
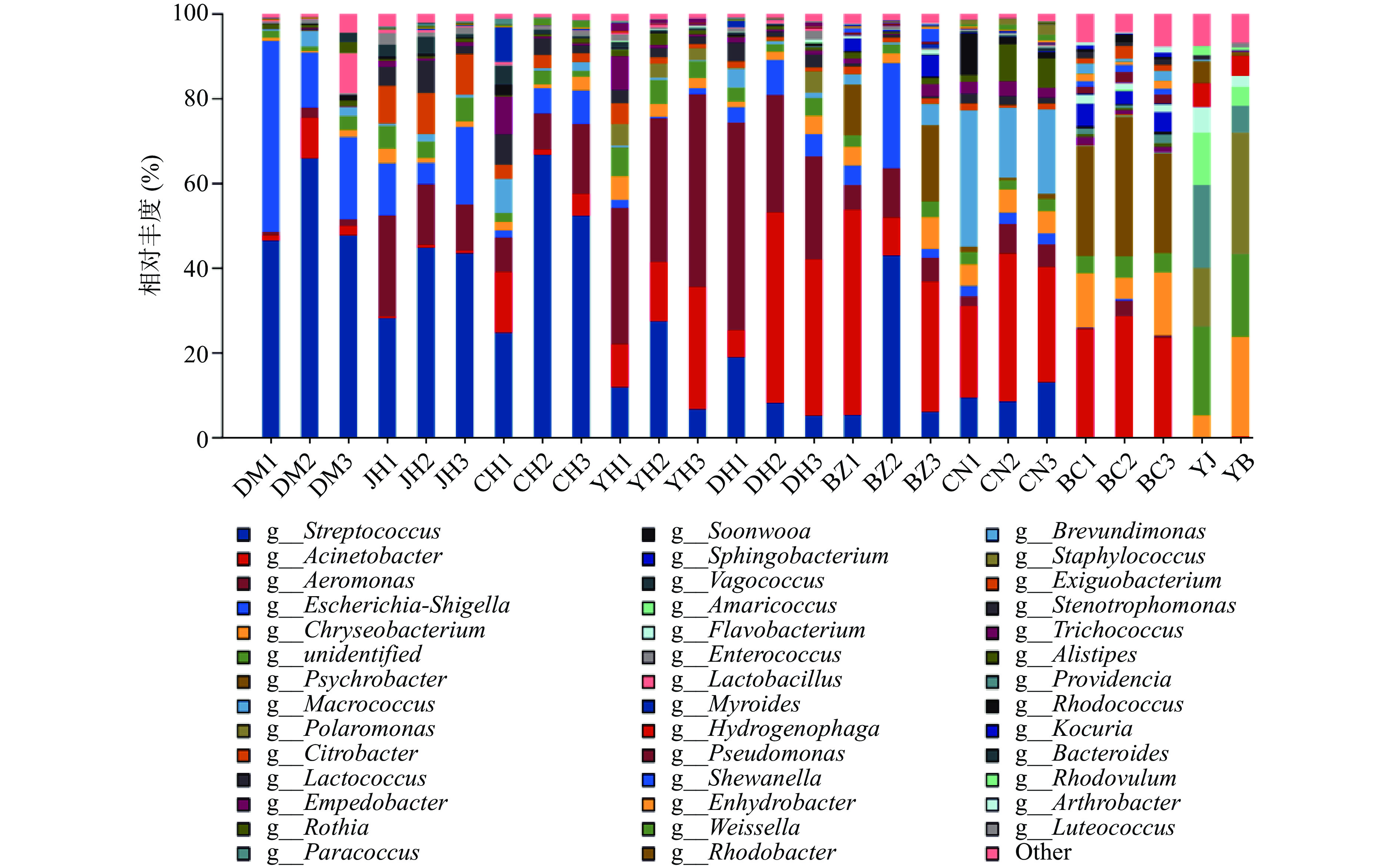
热图通过不同颜色深浅的变化来反映二维矩阵或表格中的原始数据信息[19],如图5所示,屠宰7个工艺点黄羽鸡胴体菌群多样性以及分级秤表面和预冷池内部菌群多样性结果。打毛后(DM)、净膛消毒后(CH)、预冷后(YH)、电解水处理后(DH)黄羽鸡胴体优势菌主要为链球菌属,大肠杆菌属、气单胞菌属。分级秤的表面(BC)、分级车间台面(BZ)优势菌主要为不动杆菌属、巨球菌属和嗜冷杆菌属。
由图6可知,打毛后(DM)、净膛后(JH)、净膛消毒后(CH)黄羽鸡胴体优势菌主要为链球菌属(Streptococcus),大肠杆菌属(Escherichia)和气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)次之。净膛后经瞬时清洗消毒对大肠杆菌科减菌效果显著。黄羽鸡经预冷槽预冷后气单胞菌属丰度大幅增加,链球菌属次之。经额外添加次氯酸电解水减菌后,气单胞菌属和链球菌属丰度大幅下降,说明次氯酸电解水减菌效果较好。经过分级秤分级后黄羽鸡胴体菌群中不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)成为主要优势菌,巨球菌属(Macrococcus)次之。并通过对分级秤表面菌群多样性的分析,也证实分级秤表面的优势菌主要为不动杆菌属、巨球菌属和嗜冷杆菌属(Psychrobacter)。以上检测数据表明,分级过程需针对性控制接触面微生物,目前黄羽肉鸡屠宰减菌技术主要依赖预冷环节次氯酸电解水进行减菌,需针对性研究附加减菌环节及屠宰分级过程接触面卫生控制方法。
3. 讨论
微生物是导致鸡肉腐败的主要因素。肉鸡在屠宰加工的过程中所接触的各个表面都将可能成为肉鸡胴体的污染源。因此,通过分析肉鸡胴体屠宰过程中所接触的各个表面的微生物菌群结构,从而为企业中鸡肉的保鲜防腐提供理论基础是非常必要的。肉鸡胴体、处理水和设备之间的交叉污染会增加肉鸡胴体的微生物污染水平[21]。本试验研究结果表明分级秤的表面(BC)的微生物的丰富度最高,这主要因为分级称会接触到不同的肉鸡胴体,这大大增加了鸡肉上微生物相互污染的机会;预冷池内表面(YB)和预冷池内角(YJ)的微生物生物的丰富度较低,这主要原因是屠宰预冷水中通常会加入一定含量的次氯酸电解水,这对微生物会有杀灭作用,可以有效地减少微生物的菌群数量,降低微生物的物种丰富度,抑制鸡肉胴体上腐败菌的生长[22],黄羽鸡经预冷槽预冷后气单胞菌科丰度大幅增加,说明预冷槽中环境温度及其他条件更适宜于气单胞菌科生长;净膛操作会增加微生物污染,这可能是因为净膛过程存在外源操作及肠道菌群污染的几率在净膛后经瞬时清洗消毒后肠杆菌科所占比例大幅下降。本试验测试了次氯酸电解水在屠宰后对黄羽肉鸡鸡胴体减菌效果,试验结果表明经额外添加次氯酸电解水减菌后,气单胞菌属和链球菌属丰度大幅下降,说明次氯酸电解水减菌效果较好。任晋东等[23]报道消毒剂可以显著地抑制鸡肉上腐败菌的生长,并不对鸡肉的感官品质产生不利的影响。韩千慧等[24]报道酸性电解水能有效地降低酱卤鸭制品在冷凉及贮藏过程中的微生物的数量。针对以上从属的水平上看,链球菌属(Streptococcus)、不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)等是肉鸡胴体在各个不同处理环节中都会存在的菌种。戴宝玲等[3]报道通过高通测序发现鸡肉屠宰场空气中含有不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、寡养单胞菌属(Stenotrophomonas)和埃希菌属(Escherichia)等菌属。桂国弘等[25]报道鸡肉的储藏过程中的优势菌属为乳酸杆菌属(Lactobacillus)、不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、嗜冷杆菌属(Psychrobacter)、肠球菌属(Enterococcus)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、大肠杆菌属(Escherichia),本研究结果与之相类似。
4. 结论
综合本试验研究结果,净膛、预冷及分级筛选工序是黄羽肉鸡菌数增长的主要污染来源工序,分级秤、分级车间工人手套、预冷槽及净膛工人手套为以上三个工序中污染来源接触面,且分级秤及分级车间工人手套所污染菌群是黄羽鸡胴体菌群的主要来源,促使黄羽鸡胴体表面总菌数增长率高达24.13%,经过分级秤及分级车间工人手后黄羽鸡菌落总数显著增加至4.63 lg(CFU/g)(P<0.05),黄羽肉鸡屠宰企业在屠宰过程中需关注以上三个工序卫生操作及接触面微生物控制,对分级秤、分级车间工人手套、预冷槽及净膛工人手套进行定期消毒将有助于黄羽鸡生鲜肉制品的保鲜和贮藏。打毛后(DM)、净膛后(JH)、净膛消毒后(CH)黄羽鸡胴体优势菌主要为链球菌属(Streptococcus),大肠杆菌属(Escherichia)和气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)次之。净膛后经瞬时清洗消毒对大肠杆菌科减菌效果显著。黄羽鸡经预冷槽预冷后气单胞菌属丰度大幅增加,链球菌属次之。经过分级秤分级后黄羽鸡胴体菌群中不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)为主要优势菌,巨球菌属(Macrococcus)次之。额外添加次氯酸电解水减菌后,黄羽肉鸡胴体表明气单胞菌属和链球菌属丰度大幅下降,说明次氯酸电解水减菌效果较好。本试验通过微生物分析发现了黄羽肉鸡屠宰过程中的主要污染源及不同环节微生物优势菌属,并证明次氯酸电解水有良好的杀菌效果,未针对性研究不同菌属减菌方法,也未能找到在分级挑选后集成流水线杀菌方法,后续相关研究工作者需关注屠宰工艺优化及关键污染环节杀菌集成方法,继续提升黄羽肉鸡屠宰水平。
-
-
[1] 樊艳凤, 唐修君, 葛庆联, 等. NaOH溶液处理对鸡肉品质的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2021,35(2):9−12. [FAN Y F, TANG X J, GE Q L, et al. Effect of aqueous NaOH treatment on chicken meat quality[J]. Meat Research,2021,35(2):9−12.] FAN Y F, TANG X J, GE Q L, et al . Effect of aqueous NaOH treatment on chicken meat quality[J]. Meat Research,2021 ,35 (2 ):9 −12 .[2] 辛翔飞, 郑麦青, 文杰, 等. 2021年我国肉鸡产业形势分析、未来展望与对策建议[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2022,58(3):222−226. [XIN X F, ZHENG M Q, WEN J, et al. 2021 China's broiler industry situation analysis, future prospects and suggestions for countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2022,58(3):222−226.] XIN X F, ZHENG M Q, WEN J, et al . 2021 China's broiler industry situation analysis, future prospects and suggestions for countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2022 ,58 (3 ):222 −226 .[3] 戴宝玲, 肖英平, 孙凤来, 等. 家禽定点屠宰场不同屠宰区域空气的微生物结构[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(21):219−223. [DAI B L, YIAO Y P, SUN F L, et al. Structure of airborne microbial communities in different slaughter areas of poultry slaughterhouse[J]. Food Science,2018,39(21):219−223.] DAI B L, YIAO Y P, SUN F L, et al . Structure of airborne microbial communities in different slaughter areas of poultry slaughterhouse[J]. Food Science,2018 ,39 (21 ):219 −223 .[4] JAMES C, VINCENT C. The primary chilling of poultry carcasses-A review[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2006,29:847−862. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2005.08.003
[5] KOTULA K L, PANDYA Y. Bacterial contamination of broiler chickens before scalding[J]. Journal of Food Protection,1995,58:1326−1329. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-58.12.1326
[6] 孙晋跃, 孙芝兰, 吴海虹, 等. 非热杀菌技术在低温鸡肉制品致病菌控制中的应用研究进展[J]. 肉类研究,2020,34(8):84−90. [SUN J Y, SUN Z L, WU H H, et al. Advances in application of non-thermal sterilization technologies to control pathogens in low temperature chicken products[J]. Meat Research,2020,34(8):84−90.] SUN J Y, SUN Z L, WU H H, et al . Advances in application of non-thermal sterilization technologies to control pathogens in low temperature chicken products[J]. Meat Research,2020 ,34 (8 ):84 −90 .[7] 管恩平, 于新春, 石明汉, 等. 出口冰鲜鸡肉保质期限的研究[J]. 肉类研究,2002(4):33−35. [GUAN E P, YU X C, SHI M H, et al. Study on the shelf life of exported iced fresh chicken[J]. Meat Research,2002(4):33−35.] GUAN E P, YU X C, SHI M H, et al . Study on the shelf life of exported iced fresh chicken[J]. Meat Research,2002 (4 ):33 −35 .[8] 汤飞. 冷鲜鸡肉生产过程中微生物污染分析及微冻保鲜技术研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2017:20. [TANG F. Analysis of microbial contamination in micro production of fresh chicken and study on micro freezing and fresh keeping technology[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2017:20.] TANG F. Analysis of microbial contamination in micro production of fresh chicken and study on micro freezing and fresh keeping technology[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2017: 20.
[9] 王光宇. 气调包装对冷鲜鸡肉中莓实假单胞菌致腐效应的抑制机制[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2018:29−30. [WANG G Y. Inhibition mechanisms of map against chilled chicken spoilage associated with pseudomonas fragi[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018:29−30.] WANG G Y. Inhibition mechanisms of map against chilled chicken spoilage associated with pseudomonas fragi[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018: 29−30.
[10] LACONI A, DRIGO I, PALMIERI N, et al. Genomic analysis of extra-intestinal Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from commercial chickens[J]. Veterinary Microbiology,2021,259:109161. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109161
[11] 汤纯, 诸永志, 吴海虹, 等. 基于传统培养和宏基因组测序分析泗洪小龙虾不同部位的菌群多样性[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(10):44−50. [TANG C, ZHU Y Z, WU H H, et al. Analysis of bacterial diversity in different parts of crayfifish from Sihong, east China’s Jiangsu province by traditional culture method and metagenomic analysis[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(10):44−50.] TANG C, ZHU Y Z, WU H H, et al . Analysis of bacterial diversity in different parts of crayfifish from Sihong, east China’s Jiangsu province by traditional culture method and metagenomic analysis[J]. Meat Research,2019 ,33 (10 ):44 −50 .[12] 江杨阳, 杨水兵, 余海霞, 等. 基于培养基法和高通量测序法分析冷藏小龙虾优势腐败菌[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(16):130−136. [JIANG Y Y, YANG S B, YU H X, et al. Analysis of specific spoilage organisms in chilled red swamp crayfish using culture-dependent method and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science,2019,40(16):130−136.] JIANG Y Y, YANG S B, YU H X, et al . Analysis of specific spoilage organisms in chilled red swamp crayfish using culture-dependent method and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (16 ):130 −136 .[13] 宋相宇, 李鸣, 王虎虎, 等. 高通量测序分析白切鸡菌群多样性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(17):246−252. [SONG X Y, LI M, WANG H H, et al. Analysis of bacterial community diversity of soft-boiled chicken by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science,2020,41(17):246−252.] SONG X Y, LI M, WANG H H, et al . Analysis of bacterial community diversity of soft-boiled chicken by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (17 ):246 −252 .[14] ZHANG Q Q, LI D, ZHANG W, et al. Comparative analysis of the bacterial diversity of Chinese fermented sausages using high-throughput sequencing[J]. LWT,2021,150:111975. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111975
[15] 刘亚文, 刘芳, 孙芝兰, 等. 基于传统培养和高通量测序方法分析羊肉加工过程中的菌群多样性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(9):95−101,107. [LIU Y W, LIU F, SUN Z L, et al. Analysis of microbial diversity in mutton processing based on traditional culture and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(9):95−101,107.] LIU Y W, LIU F, SUN Z L, et al . Analysis of microbial diversity in mutton processing based on traditional culture and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (9 ):95 −101,107 .[16] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 4789.2-2022 食品安全国家标准食品微生物学检测菌落总数测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2022. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2022 National standard for food safety:Determination of total colony counts in microbiological testing of food[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2022.] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2022 National standard for food safety: Determination of total colony counts in microbiological testing of food[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022.
[17] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. SN/T 4044-2014 出口肉及肉制品中假单胞菌属的计数方法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, SN/T 4044-2014 Enumeration method of Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products for export[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2014.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, SN/T 4044-2014 Enumeration method of Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products for export[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2014.
[18] 周涛, 吴晓营, 罗海波, 等. 贮藏温度对即食小龙虾品质及微生物菌群多样性的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(9):147−152. [ZHOU T, WU X Y, LUO H B, et al. Analysis of quality and colony diversity of products of crayfish under different storage temperatures[J]. Food and Machinery,2019,35(9):147−152.] ZHOU T, WU X Y, LUO H B, et al . Analysis of quality and colony diversity of products of crayfish under different storage temperatures[J]. Food and Machinery,2019 ,35 (9 ):147 −152 .[19] 吴海虹, 刘芳, 靳盼盼, 等. 3种植物源抗菌剂对青虾虾仁贮藏货架期及腐败菌多样性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(21):188−195. [WU H H, LIU F, JIN P P, et al. Effects of three plant-derived antimicrobial agents on shelf-life and bacterial diversity of freshwater swap shrimp meat ( Macrobrachium nipponense) during storage[J]. Food Science,2019,40(21):188−195.] WU H H, LIU F, JIN P P, et al . Effects of three plant-derived antimicrobial agents on shelf-life and bacterial diversity of freshwater swap shrimp meat (Macrobrachium nipponense) during storage[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (21 ):188 −195 .[20] 黄柳娟, 冯博, 刘海燕, 等. 冷鲜鸡肉表面及内部细菌菌群的多样性分析[J]. 上海农业学报,2021,37(1):104−109. [HUANG L J, FENG B, LIU H Y, et al. Diversity of bacterial flora in surface and internal tissue of cold fresh chicken[J]. Acta Agriculture Shanghai,2021,37(1):104−109.] HUANG L J, FENG B, LIU H Y, et al . Diversity of bacterial flora in surface and internal tissue of cold fresh chicken[J]. Acta Agriculture Shanghai,2021 ,37 (1 ):104 −109 .[21] THOMAS C J, MCEEKIN A. Contamination of broiler carcass skin during commercial processing procedures:an electron microscopic study[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1980,40:133−144. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.133-144.1980
[22] 王华伟, 王道营, 张牧焓, 等. 基于膜技术的预冷水微滤减菌工艺研究[J]. 天津农业科学,2015(10):126−128. [WANG H W, WANG D Y, ZHANG M H, et al. To filter the microbial in the pre-chilling water using membrane[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences,2015(10):126−128.] WANG H W, WANG D Y, ZHANG M H, et al . To filter the microbial in the pre-chilling water using membrane[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences,2015 (10 ):126 −128 .[23] 任晋东, 刘雅丽, 卢立志. 不同消毒剂处理对冷鲜鸡肉微生物的抑菌效果研究[J]. 畜牧与兽医,2019,51(9):104−108. [REN J D, LIU Y L, LU L Z, et al. Antibacterial effects of different disinfectants on microorganisms of cold chicken meat[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2019,51(9):104−108.] REN J D, LIU Y L, LU L Z, et al . Antibacterial effects of different disinfectants on microorganisms of cold chicken meat[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2019 ,51 (9 ):104 −108 .[24] 韩千慧, 欧阳何一, 朱玥, 等. 酸性氧化电解水对冷凉环节酱卤鸭制品微生物控制效果研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(2):98−102. [HAN Q H, OUYANG H Y, ZHU Y, et al. Study on microbial control effect of electrolyzed oxidizing water on braised duck in cold section[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(2):98−102.] HAN Q H, OUYANG H Y, ZHU Y, et al . Study on microbial control effect of electrolyzed oxidizing water on braised duck in cold section[J]. Food Research and Development,2019 ,40 (2 ):98 −102 .[25] 桂国弘, 杨华, 朱江群, 等. 冷鲜鸡冷藏保存过程中菌群结构变化分析[J]. 浙江农业学报,2019,31(1):47−55. [GUI G H, YANG H, ZHU J Q, et al. Study on microbial community structure in chilled chicken during cold storage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2019,31(1):47−55.] GUI G H, YANG H, ZHU J Q, et al . Study on microbial community structure in chilled chicken during cold storage[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2019 ,31 (1 ):47 −55 . -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 梅新成,徐幸莲,赵庭辉,王鹏,李令琦,黄天然,杨雨佳,王伟南,赵洋. 乳酸协同低温等离子体对黄羽肉鸡胴体的保鲜效果. 食品科学. 2024(17): 206-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶泽,季彬,彭轶楠,宋婕,赵廷伟,王治业. 变质浆水贮藏过程中理化指标及细菌菌群变化分析. 中国酿造. 2024(11): 113-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



