Determining the 59 Chemical Drugs Illegally Added in Herbal Tea by a Micro-QuEChERS-Based UPLC-MS/MS
-
摘要: 目的:建立一种微量QuEChERS(micro-QuEChERS)结合超高效液相色谱-串联质谱(UPLC-MS /MS)同时检测凉茶中59种非法添加药物的分析方法。方法:样品用乙腈超声提取5 min,提取液用NaCl及无水Na2SO4进行盐析分层,上清液用C18吸附剂进行净化后,经ACQUITY HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 μm)色谱柱分离,以0.01%甲酸水溶液(A)-乙腈:甲醇(8:2)(B)为流动相进行梯度洗脱,并采用电喷雾正负离子多反应监测模式检测,空白基质外标法定量。结果:59种化合物在其线性浓度范围内,线性关系良好,决定系数均大于0.999,检出限为5.0~10.0 μg/L,定量限为10.0~25.0 μg/L。在25.0、50.0、100.0 μg/L 3个添加水平下,平均回收率为60.3%~128.8%(n=6),相对标准偏差(RSD)1.0%~13.7%。结论:该方法操作简单,净化效果好,灵敏度高,可用于凉茶中59种非法添加化学药物的快速分析。
-
关键词:
- QuEChERS /
- 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法 /
- 凉茶 /
- 非法添加 /
- 化学药物
Abstract: Objective: An analysis method for simultaneous determination of 59 kinds of chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by micro-QuEChERS method combined with ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric (UPLC-MS/MS) was established. Method: The samples were extracted by ultrasonic extraction from acetonitrile solution for 5 min and salted out with sodium chloride (NaCl) and anhydrous sodium sulfate (Na2SO4). Supernatant was purified with C18 sorbent and separated on a ACQUITY HSS T3 column (100 mm×2.1mm, 1.8 μm) by gradient elution using a mixture of 0.01% formic acid and acetonitrile:methanol (8:2) as the mobile phase. Then the analytes were quantified by UHPLC-MS/MS in multiple reaction monitoring mode (MRM) via positive and negative electrospray ionization quantified by external standard method. Result: The coefficient of determination of the standard calibration curves for the 59 analytes were all above 0.9990. The limit of detection (LOD, S/N≥3) and the limit of quantitation (LOQ, S/N≥10) were 5.0~10.0 and 10.0~25 μg/L. At three spiked of 25.0, 50.0 and 100.0 μg/L, the average recoveries of 59 analytes were 60.3%~128.8% (n=6) with the relative standard deviations in the range of 1.0%~13.7%. Conclusion: The method developed was simple, sensitive, and had good purification effect. It could be applied for the rapid determination of 59 chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea.-
Keywords:
- QuEChERS /
- UPLC-MS/MS /
- herbal tea /
- illegal added /
- chemical drugs
-
凉茶是最独特的饮料之一,是岭南人民根据当地的气候和水土特性,由清热消暑、祛湿解毒的中草药熬制而成,含有黄酮、有机酸、多糖、生物碱等各种生物活性物质,具有抗菌、消炎、抗病毒和增强免疫力的药效[1−3]。发展至今,广东凉茶已经成为岭南中医药文化的一个重要分支,代表了一种中国独有的防病养生文化,2006年5月,经国务院批准,广东凉茶被列入第一批国家级非物质文化遗产。近年来,有些商家为提高凉茶疗效,吸引回头客、牟取暴利,非法往凉茶里添加化学药品,部分市区开展的食品安全专项行动中也有发现多家凉茶商铺存在非法添加西药的情况[4−6],消费者长期饮用含化学药品的凉茶,可能会出现重复或过量用药的情况,易发生严重的药品不良反应。
目前,针对凉茶非法添加药物的检测方法主要有免疫层析法[7−9]、高效液相色谱法[10−13]、液相色谱-串联质谱法[14−17],超高效液相色谱-高分辨质谱联用技术[18−20]等。免疫层析法假阳性率高、检测成分单一,而液相色谱法灵敏度、准确度较低。超高效液相色谱-高分辨质谱联用技术由于设备昂贵、维护成本高,不适合大规模推广应用。液相色谱-串联质谱法因具有高通量、高灵敏度、高准确度、抗干扰强的优点,是目前凉茶非法添加药物检测的主流手段。胡佳哲等[14]报道了HPLC-MS/MS同时测定凉茶中磺胺甲恶唑、马来酸氯苯那敏等19种非法添加药物的方法,结果表明,所建立的方法可以用于凉茶等植物型饮料中非法添加化学药物的快速测定。张科明等[21]建立了QuEChERS-UPLC-MS/MS方法,用于分析凉茶中非法添加的10种止咳平喘类化学药物,结果表明该方法操作简单、灵敏度高、可用于凉茶中10种非法添加的止咳平喘类化学药物的快速分析。
凉茶一般为一种或多种中草药的水溶液提取物,成分复杂,含有大量的亲水性多糖、有机酸、蛋白质以及生物碱等,针对复杂基质,目前处理方法主要有QuEChERS法[22−24]、固相萃取法[25−26]。QuEChERS(quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, safe)是一种高效的前处理技术。此技术在检测目标物具有灵敏度高、快速、回收率高且具有多残留检测的能力,被广泛应用于食品安全、环境检测及生物检测等领域[27−29],目前,QuEChERS技术在凉茶非法添加检测方面均采用常规QuEChERS,用5~10 mL的萃取溶剂,如乙腈去萃取5~10 mL的样品,取净化后5~20 μL的上清液进行仪器分析,而基于质谱的分析方法所使用的上样量很小,大部分的样品提取液被浪费,既不环保也不经济。微量QuEChERS(micro-QuEChERS)技术为小型化的QuEChERS方法,与传统QuEChERS相比,该方法产生使用较少的溶剂、样品、吸水剂和吸附剂量,节约了分析成本,其检测更快,并达到与QuEChERS相当的灵敏度[30−31],且产生的废液量小。本研究基于micro-QuEChERS前处理技术建立同时检测凉茶中59非法添加药物的UPLC-MS-MS方法,可实现目标物的准确定性和定量分析,满足市售实际样品的检测需求。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
20批次的凉茶样品 均为梅州本地市售凉茶;液体混标:大麻酚、大麻二酚、四氢大麻酚、甲基苯丙胺混标(4种)、磺胺类混标(18种)、喹诺酮类混标(10种)、四环素类混标(4种)、酰胺醇类混标(3种)、硝基咪唑类混标(2种)、罂粟碱类混标(5种) 纯度≥97%,浓度均为100 μg/mL,天津阿尔塔科技有限公司;固体单标:对乙酰氨基酚、美洛昔康、氯苯那敏、地塞米松、保泰松、特拉唑嗪、吡罗昔康、2-甲基-5硝基咪唑、氨基比林、地西泮、萘普生、双氯芬酸钠、布洛芬 纯度≥97%,中国药品生物制品检定所;甲醇、乙腈、甲酸、氨水 色谱纯,美国ACS恩科化学;氯化钠、无水硫酸钠、无水硫酸镁 分析纯,上海国药集团;活性炭、C18、PSA 天津博纳艾杰尔科技有限公司;Z-Sep+ 美国Supelco公司;多壁碳纳米管 南京先丰纳米科技公司。
AB Sciex 3500型三重四极杆液质联用仪 美国SCIEX公司;AUW220型电子分析天平 岛津企业管理有限公司;Thermo ST16R型高速冷冻离心机 美国Thermo Fisher公司;UC-7100S 型数控超声波清洗器 美瑞泰克科技有限公司;S25型旋涡混匀器 德国IKA公司;Milli Q型超纯水系统 美国Millipore公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 标准溶液的配制
1.2.1.1 13种混合标准储备液制备
分别精密称取对乙酰氨基酚、美洛昔康、氯苯那敏、地塞米松、保泰松、特拉唑嗪、吡罗昔康、2-甲基-5硝基咪唑、氨基比林、地西泮、萘普生、双氯芬酸钠、布洛芬固体标准品0.01 g用乙腈溶解并定容至100 mL,得到浓度为100 μg/mL的13种混合标准储备液,−18 ℃冰箱中避光保存。
1.2.1.2 混合标准工作液制备
分别吸取浓度为100 μg/mL大麻酚、大麻二酚、四氢大麻酚、甲基苯丙胺混标(4种)、磺胺类混标(18种)、喹诺酮类混标(10种)、四环素类混标(4种)、酰胺醇类混标(3种)、硝基咪唑类混标(2种)、罂粟碱类混标(5种)和13种混合标准储备液各1.0 mL,用乙腈定容至10 mL,配成浓度为10 μg/mL的59种混合标准工作液,−18 ℃冰箱中避光保存。
1.2.2 micro-QuEChERS前处理过程
准确量取1.0 mL的样品于10 mL离心管中,加入1.0 mL乙腈,混匀,超声提取5 min,随后加入盐包(含0.4 g无水Na2SO4及0.1 g NaCl),涡旋混匀1 min,4 ℃下10000 r/min离心5 min。准确取1.0 mL上清液至2 mL 净化管(含80 mg C18、150 mg无水Na2SO4),涡旋混合30 s,5000 r/min离心5 min,上清液经0.22 μm有机滤膜过滤后,待测。
1.2.3 液相色谱条件
色谱柱:ACQUITY HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 μm);流速0.2 mL/min;柱温40 ℃;流动相:A为乙腈:甲醇(8:2),B为0.01%甲酸水;梯度洗脱条件:0~0.5 min 95% A,0.5~2.0 min 95%~85% A,2.0~6.0 min 85%~68% A,6.0~7.5 min 68%~8% A,7.5~12.0 min 8%~3% A,12.0~14.0 min 3% A;14.0~14.1 min 3%~95%;14.0~16.0 min 95% A;进样量5 μL。
1.2.4 质谱条件
离子源:ESI源,正/负离子模式;离子源参数:IS电压:5500 V/−4500 V,气帘气CUR:30 psi,雾化气GS1:50 psi,辅助气GS2:60 psi,源温度TEM:550 ℃,碰撞气CAD:7 psi。
1.3 数据处理
采用AB Sciex Analyst软件完成数据的采集,AB Sciex OS软件完成数据处理。平行及精密度数据采用Microsoft Excel进行计算,采用Origin 8.0软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 仪器条件优化
2.1.1 质谱参数优化
质谱参数优化采用针泵连续进样的方式,分别将1 μg/mL的59种化合物标准溶液分别在正、负离子模式下对各待测化合物进行全扫描,确定合适的电离方式和准分子离子,再对相应的准分子离子进行二级质谱扫描,每种化合物选择信号高、干扰小的两个离子对作为定性与定量离子,通过优化去簇电压(DP)、碰撞能量(CE),使特征碎片离子信号达到最大,优化的质谱条件见表1。
表 1 59种化合物质谱参数Table 1. Mass spectrometric (MS) parameters for detection of 59 analytes化合物 离子化模式 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) DP(V) CE(V) 保留时间(min) 对乙酰氨基酚 ESI+ 152.1 110.0 65 23 5.78 152.1 92.9 65 31 5.78 美洛昔康 ESI+ 352.0 115.1 81 38 10.2 352.0 141.0 81 30 10.2 氯苯那敏 ESI+ 275.0 230.2 65 28 9.64 275.0 167.1 65 85 9.64 地塞米松 ESI+ 393.2 355.4 80 15 10.2 393.2 373.2 80 12 10.2 吗啡 ESI+ 285.9 181.2 150 46 1.65 285.9 165.2 150 58 1.65 可待因 ESI+ 299.9 215.2 158 37 6.31 299.9 165.0 158 55 6.31 蒂巴因 ESI+ 311.9 58.1 88 46 9.22 311.9 248.9 88 24 9.23 罂粟碱 ESI+ 340.0 201.9 154 38 9.6 340.0 171.0 154 52 9.6 那可丁 ESI+ 414.1 219.9 154 30 9.73 414.1 353.2 154 35 9.86 甲基苯丙胺 ESI+ 150.1 91.0 52 25 7.64 150.1 119.0 52 46 7.64 甲硝唑 ESI+ 172.0 128.2 58 20 6.25 172.0 82.2 58 35 6.25 保泰松 ESI+ 309.3 160.2 130 30 10.86 309.3 190.3 130 26 10.87 特拉唑嗪 ESI+ 388.2 247.3 145 42 9.17 388.2 290.3 145 39 9.17 吡罗昔康 ESI+ 331.9 121.2 103 42 10.28 331.9 164.1 103 23 10.28 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 ESI+ 128.1 82.1 87 23 6.25 128.1 56.1 87 19 6.24 氨基比林 ESI+ 232.1 113.2 95 18 8.19 232.1 187.1 95 15 8.18 四环素 ESI+ 445.1 410.2 80 24 8.93 445.1 427.1 80 19 8.93 金霉素 ESI+ 479.1 462.0 80 24 9.55 479.1 444.0 80 28 9.55 土霉素 ESI+ 461.2 426.2 80 25 8.67 461.2 443.2 80 17 8.65 多西环素 ESI+ 445.0 428.1 80 24 9.56 445.0 154.1 80 35 9.57 乙酰磺胺 ESI+ 214.9 156.0 26 21 5.42 214.9 108.1 26 30 5.42 磺胺吡啶 ESI+ 249.8 156.1 85 24 7.41 249.8 183.9 85 25 7.42 磺胺嘧啶 ESI+ 250.8 156.0 76 22 6.38 250.8 108.1 76 33 6.38 磺胺甲恶唑 ESI+ 254.0 156.2 80 23 9.47 254.0 108.0 80 34 9.47 磺胺噻唑 ESI+ 255.8 156.1 73 21 6.95 255.8 108.0 73 33 6.95 磺胺甲嘧啶 ESI+ 265.0 156.0 98 23 7.82 265.0 172.1 98 23 7.81 磺胺二甲异恶唑 ESI+ 267.9 155.9 90 23 8.40 267.9 113.1 90 23 8.40 磺胺甲噻二唑 ESI+ 270.8 156.0 75 21 8.62 270.8 108.2 75 36 8.61 苯甲酰磺胺 ESI+ 276.9 155.9 81 20 9.69 276.9 108.0 81 33 9.67 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 ESI+ 279.0 124.0 98 29 6.39 279.0 186.0 98 22 6.39 磺胺二甲嘧啶 ESI+ 279.0 185.9 88 25 8.87 279.0 155.9 88 25 8.87 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 280.8 156.0 96 23 8.62 280.8 108.0 70 37 8.61 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 ESI+ 280.8 156.0 70 24 8.89 280.8 108.0 70 38 8.89 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 280.8 156.1 70 26 9.30 280.8 108.1 70 38 9.30 磺胺氯哒嗪 ESI+ 284.8 156.0 82 21 9.34 284.8 108.0 82 38 9.34 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 310.8 156.0 92 27 9.52 310.8 108.0 92 40 9.52 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 310.8 156.1 80 27 9.77 310.8 108.1 80 36 9.77 磺胺苯吡唑 ESI+ 314.9 156.0 95 31 9.77 314.9 221.9 95 28 9.77 诺氟沙星 ESI+ 320.1 276.1 80 26 8.35 320.1 233.1 80 35 8.35 依诺沙星 ESI+ 321.0 303.0 80 24 8.15 321.0 234.0 80 30 8.15 环丙沙星 ESI+ 332.1 288.1 80 25 8.53 332.1 245.1 80 33 8.54 培氟沙星 ESI+ 334.1 316.1 80 27 8.44 334.1 290.2 80 25 8.44 洛美沙星 ESI+ 352.0 265.0 80 33 8.81 352.0 308.1 80 28 8.81 达氟沙星 ESI+ 358.1 340.1 77 30 8.77 358.1 314.1 77 24 8.77 恩诺沙星 ESI+ 360.0 316.1 80 25 8.95 360.0 245.1 80 35 8.95 氧氟沙星 ESI+ 362.2 318.1 80 26 8.32 362.2 261.1 80 38 8.32 沙拉沙星 ESI+ 386.0 342.3 80 25 9.26 386.0 299.0 80 38 9.26 二氟沙星 ESI+ 400.1 356.1 80 28 9.30 400.1 299.1 80 41 9.30 地西泮 ESI+ 285.1 154.0 80 36 10.76 285.1 193.0 80 40 10.76 地美硝唑 ESI+ 142.2 96.0 65 21 7.43 142.2 81.0 65 36 7.43 萘普生 ESI− 229.2 184.9 −45 −12 10.45 229.2 169.9 −45 −20 10.45 双氯芬酸钠 ESI− 295.9 251.9 −72 −16 10.83 295.9 213.8 −86 −29 10.83 布洛芬 ESI− 204.8 161.0 −43 −10 11.01 204.8 159.0 −49 −12 11.01 大麻二酚 ESI− 313.2 245.1 −120 −32 11.91 313.2 179.1 −120 −28 11.91 大麻酚 ESI− 309.1 279.1 −120 −45 12.69 309.1 222.1 −120 −61 12.69 四氢大麻酚 ESI− 313.2 245.1 −150 −38 13.25 313.2 191.1 −150 −40 13.25 氯霉素 ESI− 320.7 152.0 −68 −27 9.72 320.7 257.2 −68 −18 9.72 甲砜霉素 ESI− 354.0 185.1 −80 −29 8.33 354.0 289.9 −80 −19 8.33 氟苯尼考 ESI− 356.1 336.0 −68 −14 9.54 356.1 184.9 −68 −26 9.54 2.1.2 色谱条件优化
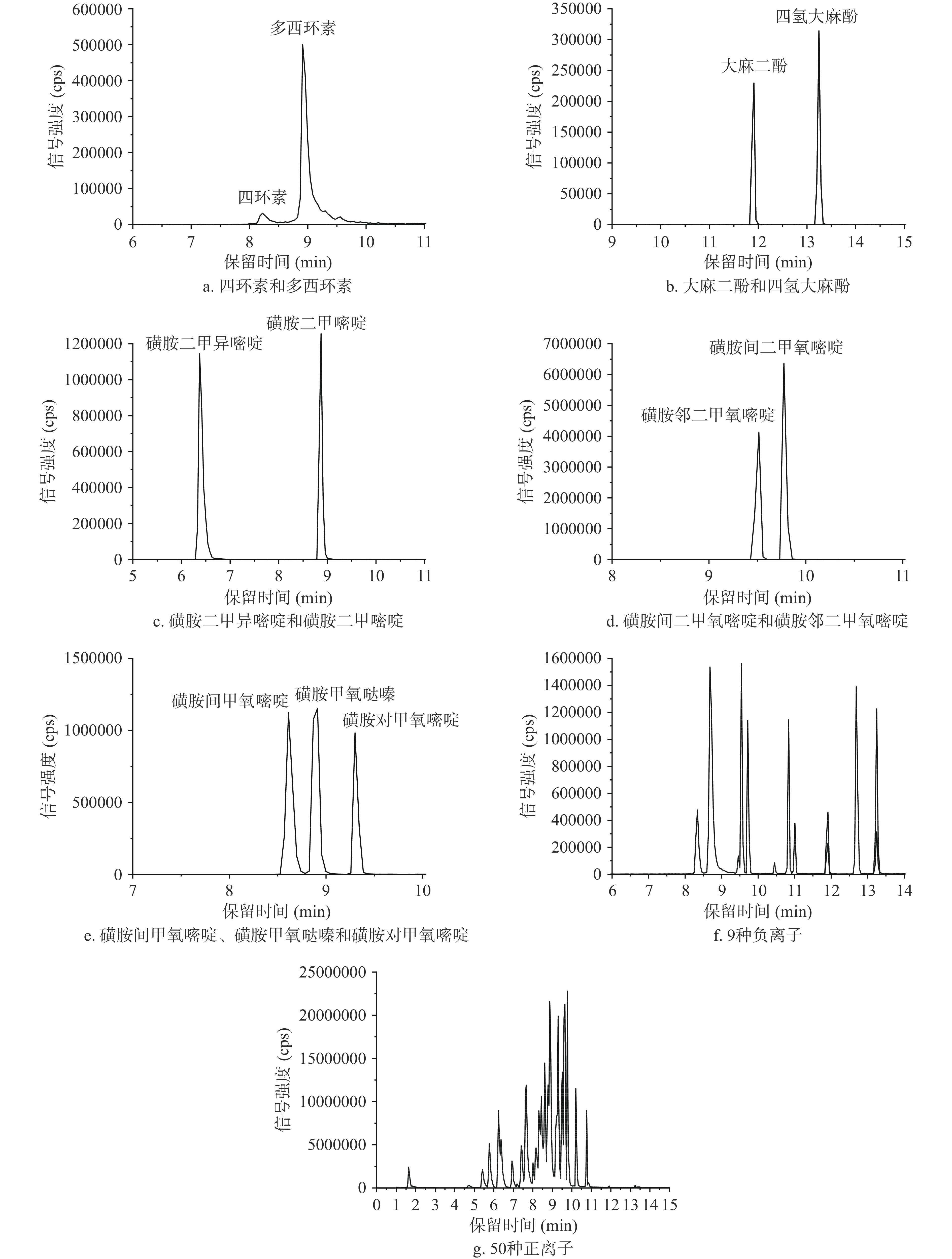
本实验检测对象有59种化合物,化学性质差异较大,同时含有5组11种化合物是同分异构体(磺胺二甲异嘧啶和磺胺二甲嘧啶、磺胺间甲氧嘧啶、磺胺甲氧哒嗪和磺胺对甲氧嘧啶、磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶和磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶、四环素和多西环素、大麻二酚和四氢大麻酚),同分异构体具有相同的母离子,色谱峰需要达到完全分离,才能进行准确定量。因此,实验针对色谱柱类型和流动相成分进行优化。
2.1.2.1 色谱柱优化
分别考察了EclipseXDB-C18(150 mm×2.1 mm,5 μm)、Kinetex F5(50 mm×3.0 mm,2.6 μm)、Shim-pack GIST-HP C18(100 mm×2.1 mm,3 μm)、ACQUITY HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 μm)4种型号的色谱柱对59种目标化合物的分离效果,结果发现使用ACQUITY HSS T3色谱柱时,各目标组分具有较好分离效果,特别是5对同分异构体能够完全分离、且峰形尖锐,结果见图1,最终选择采用ACQUITY HSS T3色谱柱进行分离。
2.1.2.2 流动相优化
考虑到本研究中磺胺类、喹诺酮类、四环素类化合物占比较多,参考国家标准GB 31658.17[32]方法选择乙腈:甲醇(8:2)作为优化条件之一,并与纯甲醇、纯乙腈有机流动相进行比较,通过比较发现,纯甲醇作为有机相时,甲硝唑、罂粟碱等化合物峰形毛刺多、分叉,出现前沿峰,且梯度运行时间长;纯乙腈作为有机相时,喹诺酮类、四环素类化合物峰形毛刺多、不对称,磺胺类同分异构体分离度较差,甲硝唑等硝基咪唑类保留差,有杂峰,灵敏度差;乙腈:甲醇(8:2)作为有机相时化合物峰型较窄、分离度好、灵敏度高、在16 min化合物能够完全分离。
电喷雾离子源正离子模式下,流动相中添加适量甲酸可增强目标分析物离子化效率,提高灵敏度,本实验大部分化合物均为正离子模式,但也有9种化合物采用负离子模式,因此对浓度为0、0.005%、0.01%、0.02%、0.05%、0.1%的甲酸水进行实验,实验发现甲酸浓度超过0.01%时,负离子模式的化合物色谱峰响应值下降明显,灵敏度不能满足检测需求;当浓度低于0.01%时,正离子模式的灵敏度较低,且峰形较差;甲酸浓度为0.01%时,大部分化合物峰形尖锐,灵敏度较高,能够满足检测需求,实验最终选择0.01%甲酸水-乙腈:甲醇(8:2)作为流动相,该条件下59种化学药物的分离效果好、各化合物灵敏度和和峰形均可满足检测要求。
2.2 Micro-QuEChERS条件优化
2.2.1 盐析试剂优化
QuEChERS前处理方法常用Na2SO4、MgSO4作为脱水剂、NaCl作为盐析剂,NaCl能够促进样品中水的析出,提高脱水剂效率,从而提高提取效率,实验分别对比了NaCl和Na2SO4、NaCl和MgSO4对目标化合物回收率的影响。取1 mL样品,按样品量:乙腈:NaCl:除水剂比率1.0:1.0:0.1:0.4(v/v/w/w),添加乙腈、NaCl、Na2SO4或MgSO4。当选用MgSO4作为脱水剂时,喹诺酮类和四环素类化合物的回收率明显降低,最高降低幅度达到80%。因为喹诺酮类和四环素类药物易与Mg2+形成螯合物导致溶解度降低[33]。当选用Na2SO4作为脱水剂时,喹诺酮、四环素回收率明显提高,其余化合物的回收率变化不大,因此本实验选用NaCl作为盐析剂、Na2SO4作为脱水剂。
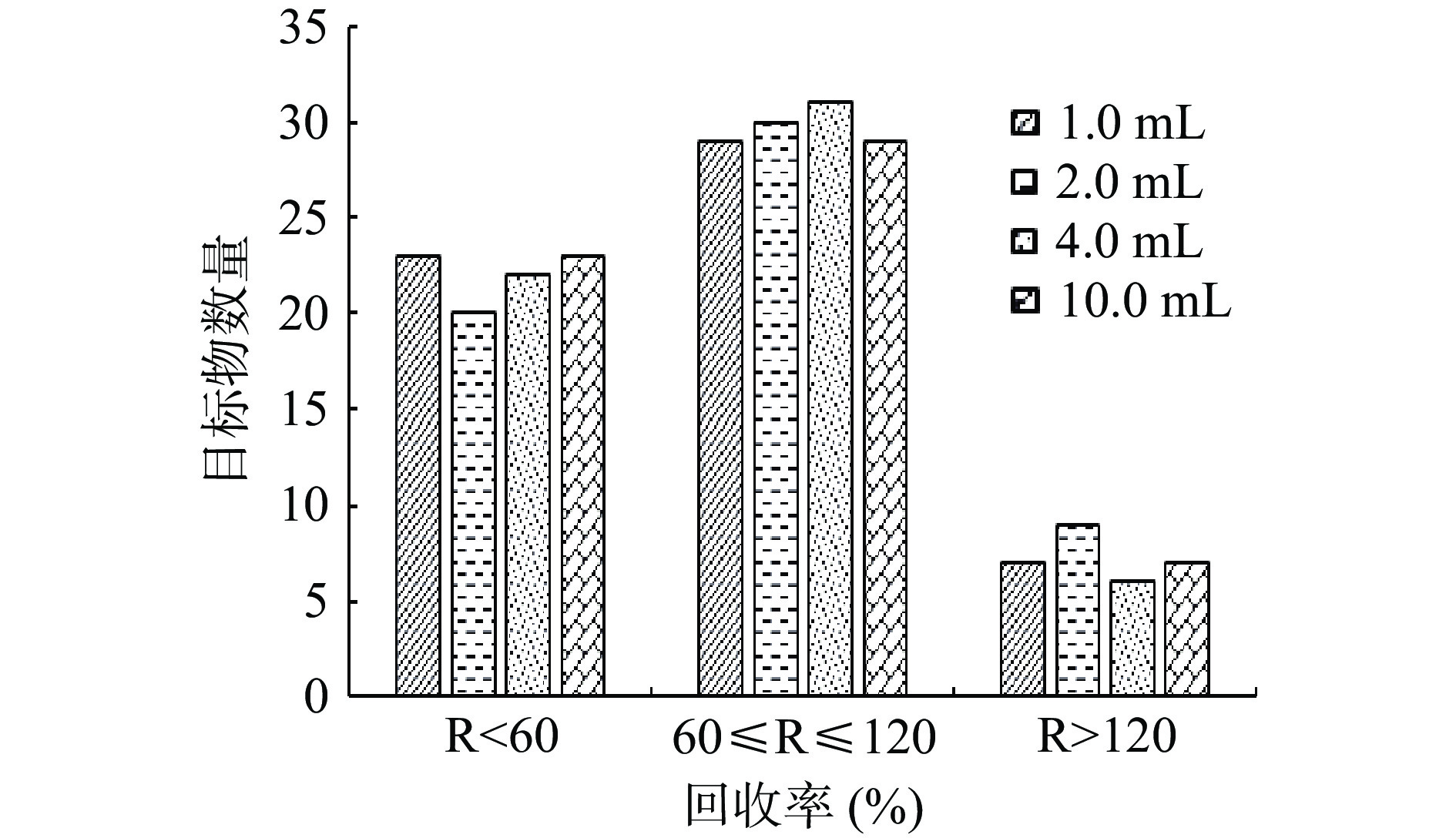
2.2.2 样品体积优化
传统QuEChERS方法中样品取样量通常为10 g或10 mL,为考察样品量对目标化合物提取效果影响,实验测试了1.0、2.0、4.0、10.0 mL取样量时目标化合物回收率。实验中按凉茶样品量:乙腈:NaCl:Na2SO4比率1.0:1.0:0.1:0.4(v/v/w/w),添加提取试剂、脱水剂、盐析剂,通过加标回收率进行评价。实验结果显示(图2)1.0、2.0、4.0、10.0 mL凉茶样品量的对应59种化合物回收率分别为47.7%~124.0%、48.5%~125.4%、44.9%~126.7%、41.0%~128.3%,RSD小于18.2%,实验结果表明样品量减少不会影响提取回收率,最终选择样品量为1 mL。
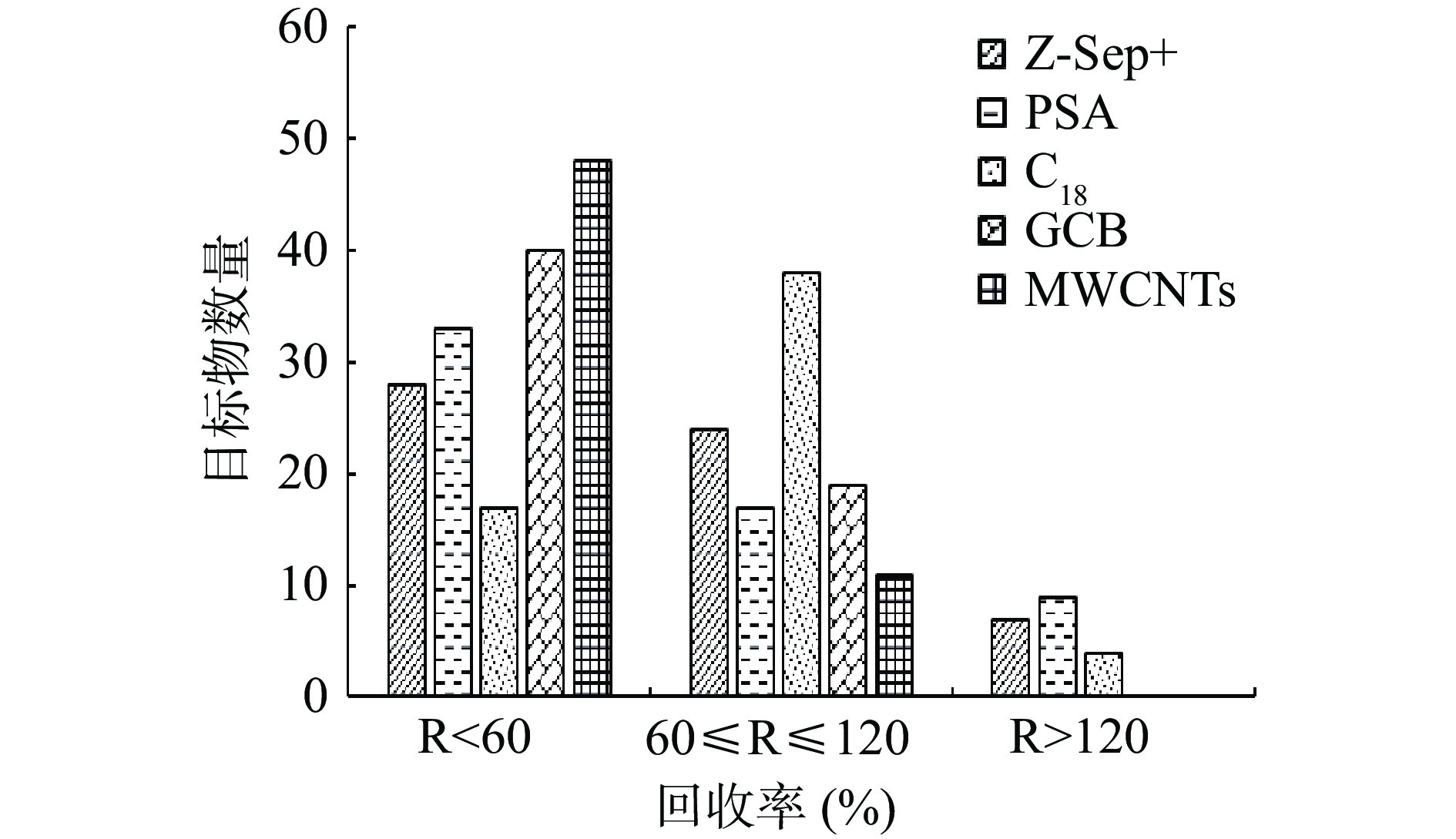
2.2.3 净化材料优化
根据凉茶基质的特点,实验首先考察了C18、PSA、Z-Sep+、GCB、MWCNTs吸附剂的净化效果,结果见图3。当各吸附剂用量为50 mg时,从回收率角度看,C18吸附剂效果最好,回收率在53%~126.0%,平均回收率为71.6%;Z-Sep+回收率在33.0%~131.9%,平均回收率为67.5%,其中回收率<60%有32种,特别是对萘普生、双氯芬酸钠、布洛芬等化合物有吸附作用,回收率较低;PSA对喹诺酮类、磺胺类、萘普生、布洛芬等带有羧基化合物具有较强吸附作用,回收率在24.1%~138.0%,平均回收率为56.3%;GCB、MWCNTs具有较强的吸附能力,能很好的去除凉茶中色素,但对喹诺酮类、磺胺类、大麻酚等吸附作用强,平均回收率均在50%以下。故最终选择C18作为净化吸附剂,并对净化吸附剂C18的用量进行优化,当其用量为80 mg时,59种化合物回收率最佳,回收率在60%~120%范围内的化合物个数占84.7%,最终确定C18用量为80 mg。
2.3 基质效应研究
基质效应(Matrix effect,ME)是指样品中除检测目标分析物之外的其他成分对分析过程造成的干扰和影响。基质效应可以通过基质标准曲线与纯溶剂标准曲线的斜率之比来评价。ME<0.8时,表示存在基质抑制效应;0.8≤ME≤1.2时,表示基质效应不明显;ME>1.2时,表示存在基质增强效应[34−35]。实验考察了59种化合物在凉茶中的基质效应,实验结果表明,17%化合物的ME<0.8,表现为基质抑制效应;64%化合物的ME为0.8~1.2,基质效应不明显;19%药物的ME>1.2,表现为基质增强效应。因此,本实验采用基质匹配标准曲线,可降低对目标药物基质效应的影响。
2.4 方法学评价
2.4.1 方法线性范围、检出限、定量限
按照1.2.2前处理方法制备得到空白基质溶液,用空白基质液配成系列混合标准工作溶液,以59种化合物基质匹配标准工作溶液的浓度为横坐标,定量离子峰面积为纵坐标绘制标准工作曲线,得到59种化合物线性范围、线性方程和决定系数(R2),结果显示,59种化合物在其线性范围内,线性关系良好,决定系数均大于0.999,实验结果见表2。
表 2 59种化合物基质效应、线性关系、检出限、定量限Table 2. Matrix effects, LOD and LOQ of 59 analytes项目 线性范围(ng/mL) 回归方程 决定系数(R2) 基质效应(%) LOD(μg/L) LOQ(μg/L) 对乙酰氨基酚 10~200 y=122029x+2689364 0.9994 0.85 5 10 美洛昔康 10~200 y=174261x+1548433 0.9991 1.02 5 10 氯苯那敏 10~200 y=213855x+3338602 0.9998 1.17 5 10 地塞米松 10~200 y=1468x+6819 0.9991 0.89 5 10 吗啡 25~500 y = 25478x+98863 0.999 0.83 10 25 可待因 25~500 y=49302x+243629 0.9994 1.73 10 25 蒂巴因 25~500 y=152035x+1148584 0.9992 1.15 5 10 罂粟碱 25~500 y=245436x+9496444 0.9994 1.53 5 10 那可丁 25~500 y=30836x+885753 0.9998 0.83 5 10 甲基苯丙胺 10~200 y=85430x+937224 0.9996 0.75 5 10 甲硝唑 10~200 y=157955x+2736008 0.999 1.35 5 10 保泰松 25~500 y=11052x+28925 0.9996 1.17 10 25 特拉唑嗪 10~200 y=61445x+1011146 0.9991 1.17 5 10 吡罗昔康 10~200 y=18731x+107583 0.9991 1.08 5 10 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 10~200 y=40388x+487332 0.9993 1.26 5 10 氨基比林 10~200 y=13271x+82261 0.999 0.91 5 10 四环素 25~500 y=37436x−238697 0.9996 1.14 10 25 金霉素 25~500 y=14665x−18961 0.9996 1.86 10 25 土霉素 25~500 y=41282x−177380 0.9996 1.02 10 25 多西环素 25~500 y=9187x−64238 0.9998 1.4 10 25 乙酰磺胺 10~200 y=4119x+80644 0.9997 0.66 5 10 磺胺吡啶 10~200 y=10577x+117358 0.9998 1.06 5 10 磺胺嘧啶 10~200 y=13291x+15372 0.9997 1.14 5 10 磺胺甲恶唑 10~200 y=2359x+37754 0.9995 1.00 5 10 磺胺噻唑 10~200 y=10271x+19676 0.9993 0.81 5 10 磺胺甲嘧啶 10~200 y=8606x+25786 0.9991 1.11 5 10 磺胺二甲异恶唑 10~200 y=3789x+18215 0.9995 1.38 5 10 磺胺甲噻二唑 10~200 y=6135x−18903 0.9993 1.00 5 10 苯甲酰磺胺 10~200 y=1693x+748 0.9995 0.58 5 10 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 10~200 y=4377x+75551 0.9995 0.65 5 10 磺胺二甲嘧啶 10~200 y=3082x+83327 0.9998 1.06 5 10 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=4664x−578.5886 0.9994 0.52 5 10 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 10~200 y=22643x+233406 0.9992 1.03 5 10 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=20336x+207113 0.9993 1.20 5 10 磺胺氯哒嗪 10~200 y=4532x−7225 0.9996 0.79 5 10 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=17667x−46137 0.9995 0.96 5 10 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=7168x+131929 0.9993 1.21 5 10 磺胺苯吡唑 10~200 y=2570x+14433 0.9993 0.61 5 10 诺氟沙星 10~200 y=4441x−17535 0.9991 0.85 5 10 依诺沙星 10~200 y=33471x−180451 0.9999 0.99 5 10 环丙沙星 10~200 y=7312x+10557 0.9994 1.15 5 10 培氟沙星 10~200 y=57859x+9947 0.9998 0.92 5 10 洛美沙星 10~200 y=11008x+22527 0.9996 1.07 5 10 达氟沙星 10~200 y=57401x−61967 0.9998 1.00 5 10 恩诺沙星 10~200 y=17537x+27100 0.9998 0.93 5 10 氧氟沙星 10~200 y =37238x−64982 0.9991 0.88 5 10 沙拉沙星 10~200 y=5610x+41835 0.9996 1.06 5 10 二氟沙星 10~200 y=10793x+8451 0.9996 0.74 5 10 地西泮 10~200 y=14880x+38696 0.9996 1.20 5 10 地美硝唑 10~200 y=7465x+5332 0.9999 0.94 5 10 萘普生 25~500 y=539x+2612 0.9999 2.37 10 25 双氯芬酸钠 25~500 y=15678x+144012 0.9997 0.96 10 25 布洛芬 25~500 y=4517x+12730 0.9991 1.44 10 25 大麻二酚 25~500 y=483x+3537 0.9996 0.99 10 25 大麻酚 25~500 y=3319x+1196 0.9992 1.55 10 25 四氢大麻酚 25~500 y=1149x−8920 0.9997 1.12 10 25 氯霉素 10~200 y=2730x+30243 0.9994 0.79 5 10 甲砜霉素 25~500 y=953x+1889 0.9994 0.94 10 25 氟苯尼考 25~500 y=2175x+7413 0.999 0.69 10 25 将混合标准工作液,逐级稀释后加入凉茶阴性样品中,按1.2.2前处理方法处理,上机测定,以目标峰信噪比(S/N)≥3时样品浓度确定为检出限(LOD),S/N≥10时样品浓度为定量限(LOQ),结果显示可知59种化合物的检出限在5.0~10.0 μg/L之间,定量限为10.0~25.0 μg/L在之间,结果详见表2,表明该方法具有较高的灵敏度。
2.4.2 回收率与精密度
取阴性凉茶样品为基质,添加25、50、100 μg/L低中高3个浓度水平标准溶液,每个添加水平平行测试6次,计算各化合物的平均回收率和相对标准偏差(RSD),由表3可知,结果表明,加标浓度为25 μg/L时,59种化合物回收率范围为60.3%~121.7%,RSD为2.0%~13.7%,加标浓度为50 μg/L时,59种化合物收率范围为70.2%~128.8%, RSD为1.2%~13.1%,加标浓度为100 μg/L时, 59 种化合物的平均回收率范围为66.3%~127.4%,RSD为1.0%~13.2%, 由此可见,回收率及精密度均能够满足定量分析的需求。
表 3 59种化合物平均回收率和精密度(n=3)Table 3. Recoveries and RSDs of 59 analytes spiked into blank matrix sample (n=3)化合物 25 μg/L 50 μg/L 100 μg/L 回收率(%) RSD(%) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 对乙酰氨基酚 87.4 2.8 81.5 1.6 77.5 6.2 美洛昔康 92.3 13.7 94.6 8.0 123.1 2.4 氯苯那敏 99.1 3.4 81.1 9.3 112.5 4.7 地塞米松 82.5 8.4 95.7 4.5 117.7 7.0 吗啡 81.8 2.8 87.3 12.9 81.2 1.3 可待因 96.4 9.4 113.1 12.7 93.6 2.9 蒂巴因 90.6 4.6 86.4 6.3 119.2 2.0 罂粟碱 116.4 8.9 102.1 9.8 112.3 5.6 那可丁 90.7 9.5 105.9 9.9 106.3 3.4 甲基苯丙胺 85.2 3.7 88.9 4.9 109.9 1.1 甲硝唑 93.2 4.7 87.8 2.9 101.1 7.1 保泰松 82.6 6.8 93.7 4.0 112.7 9.3 特拉唑嗪 97.8 10.3 80.1 12.5 97.0 1.9 吡罗昔康 93.6 12.4 115.6 2.7 115.0 1.0 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 85.3 4.6 103.4 5.5 111.8 9.6 氨基比林 84.8 7.9 123.9 13.1 123.0 4.9 四环素 85.9 4.4 76.9 7.4 80.4 1.5 金霉素 107.2 7.0 70.2 11.0 73.8 7.9 土霉素 85.7 2.7 95.2 2.9 82.8 6.3 多西环素 90.3 4.8 117.0 5.0 116.1 2.3 乙酰磺胺 86.9 2.9 124.1 7.6 110.9 2.1 磺胺吡啶 85.1 5.2 108.0 5.5 127.4 3.9 磺胺嘧啶 84.8 5.0 106.2 2.3 109.3 3.6 磺胺甲恶唑 70.3 4.8 128.6 2.3 120.8 1.4 磺胺噻唑 90.0 8.8 118.9 4.3 98.5 9.1 磺胺甲嘧啶 101.3 4.9 125.5 8.4 122.1 6.4 磺胺二甲异恶唑 88.1 3.5 122.8 1.8 124.1 2.2 磺胺甲噻二唑 94.9 4.4 108.0 8.6 111.0 3.3 苯甲酰磺胺 78.5 8.8 106.0 10.2 96.2 3.2 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 93.5 11.6 120.0 1.2 117.8 2.5 磺胺二甲嘧啶 93.5 5.6 102.2 2.1 86.6 7.1 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 89.4 7.1 111.4 5.0 105.1 4.5 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 100.7 5.8 128.8 4.5 116.3 12.7 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 91.0 4.0 103.9 3.6 111.4 3.6 磺胺氯哒嗪 67.4 9.9 104.1 9.9 126.5 1.5 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 112.4 8.0 123.3 3.1 121.1 13.2 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 84.8 3.2 113.9 9.7 123.1 3.7 磺胺苯吡唑 87.3 3.4 124.7 2.4 123.8 2.6 诺氟沙星 73.1 6.9 80.8 1.8 74.8 1.4 依诺沙星 84.0 2.0 79.3 11.8 80.9 1.1 环丙沙星 81.1 6.4 93.4 2.6 74.8 2.5 培氟沙星 85.5 11.9 85.9 9.6 83.4 1.7 洛美沙星 85.2 5.7 83.0 2.4 75.6 9.3 达氟沙星 99.9 5.3 78.5 1.8 70.9 5.8 恩诺沙星 83.8 5.0 83.4 7.8 88.7 6.5 氧氟沙星 91.6 9.7 98.3 5.2 66.3 3.7 沙拉沙星 86.2 7.7 119.4 2.1 98.1 4.9 二氟沙星 88.5 2.5 110.0 10.3 101.7 2.7 地西泮 87.3 10.0 118.1 1.8 108.3 4.6 地美硝唑 94.8 2.2 112.8 4.5 112.7 3.1 萘普生 98.9 13.5 91.0 10.7 100.0 7.0 双氯芬酸钠 121.7 2.5 94.6 7.8 120.0 1.9 布洛芬 78.0 11.4 110.5 6.5 102.3 9.8 大麻二酚 66.9 4.1 114.4 2.6 115.6 2.6 大麻酚 60.3 11.5 110.2 3.5 106.8 6.4 四氢大麻酚 60.9 3.6 82.0 2.8 107.8 7.8 氯霉素 88.1 3.0 113.7 12.7 114.1 4.5 甲砜霉素 90.5 8.3 123.8 3.9 109.6 2.7 氟苯尼考 108.2 5.2 115.0 5.5 114.1 6.8 2.5 方法学比较
与其他已有关于凉茶中非法添加化学药物检测方法及标准进行比较(表4),从表4中可看出,本方法在样品及提取溶剂使用量、检测药物数量、检测模式、仪器检测时间、检出限等方面具有优势,特别是在降低样品及试剂用量、提高检测效率、降低检测成本上优势明显。灵敏度方面与大部分研究相当,优于现有国家补充检验方法[36]。因此,所建方法灵敏、高效和可靠,可适用于凉茶中非法添加药物的快速、定量检测。
表 4 micro-QuEChERs/LC-MS/MS与其他已报道方法的比较Table 4. Comparison of micro-QuEChERs-LC-MS/MS with other reported methods检测方法 化学药物
种类检测
模式仪器检测时间(min) 样品量(mL/g) 提取溶剂
体积(mL)回收率(%) 检出限 文献 UPLC-Orbitrap HRMS 167 ESI+、ESI− 25 1 20 66.4~118.1 200 μg/kg [19] HPLC 28 / 30 5 25 88. 8~118. 6 1000~10000 μg/kg [13] HPLC-MS/MS 5 ESI+ 10 2 10 84.5~105.1 2~8 μg/kg [17] QuEChERS-HPLC-Q-TOF/MS 8 ESI+ 20 5 10 75.8~95.6 2~10 μg/kg [20] HPLC-MS/MS 20 ESI+ 16 10 50 88.13~114.6 1000~30000 μg/L [15] QuEChERS-UPLC-MS/MS 12 ESI+ 24 5 6 62.7~95.2 0.1~2.1 μg/L [23] BJS 201713 59 ESI+/ESI− 35 1 50 / 100~2500 μg/kg [36] 本方法 59 ESI+、ESI− 16 1 1 60.3~128.8 5~10 μg/L 2.6 实际样品分析
采用本研究建立的方法,随机对从梅州本地市场购买的感冒茶、咽喉茶、口腔茶、咽炎茶、清热解毒茶、祛湿茶等共20批次样品进行检测,结果显示20批凉茶样品均未检出以上59种化学药物。
3. 结论
本研究以凉茶为对象,采用micro-QuEChERS前处理方法,超高效液相色谱串联质谱法检测,建立了同时测定凉茶中59种非法添加药物的方法。该方法操作简便、检测效率高,药物覆盖面广,特别是大大减少了样品用量、试剂耗材用量,检测成本显著降低,与传统QuEChERS前处理方式相比,有着明显的优势。对方法的检出限、定量限、精密度及基质效应进行方法学评价,本方法检出限为5.0~10.0 μg/L、定量限为10.0~25.0 μg/L,平均回收率为60.3%~128.8%,相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.0%~13.7%,检出限优于国家补充检验方法BJS 201713,回收率、精密度等均满足要求,该方法可以广泛应用于凉茶中非法添加药物快速筛查和定量检测,为凉茶风险监测提供技术支持。
-
表 1 59种化合物质谱参数
Table 1 Mass spectrometric (MS) parameters for detection of 59 analytes
化合物 离子化模式 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) DP(V) CE(V) 保留时间(min) 对乙酰氨基酚 ESI+ 152.1 110.0 65 23 5.78 152.1 92.9 65 31 5.78 美洛昔康 ESI+ 352.0 115.1 81 38 10.2 352.0 141.0 81 30 10.2 氯苯那敏 ESI+ 275.0 230.2 65 28 9.64 275.0 167.1 65 85 9.64 地塞米松 ESI+ 393.2 355.4 80 15 10.2 393.2 373.2 80 12 10.2 吗啡 ESI+ 285.9 181.2 150 46 1.65 285.9 165.2 150 58 1.65 可待因 ESI+ 299.9 215.2 158 37 6.31 299.9 165.0 158 55 6.31 蒂巴因 ESI+ 311.9 58.1 88 46 9.22 311.9 248.9 88 24 9.23 罂粟碱 ESI+ 340.0 201.9 154 38 9.6 340.0 171.0 154 52 9.6 那可丁 ESI+ 414.1 219.9 154 30 9.73 414.1 353.2 154 35 9.86 甲基苯丙胺 ESI+ 150.1 91.0 52 25 7.64 150.1 119.0 52 46 7.64 甲硝唑 ESI+ 172.0 128.2 58 20 6.25 172.0 82.2 58 35 6.25 保泰松 ESI+ 309.3 160.2 130 30 10.86 309.3 190.3 130 26 10.87 特拉唑嗪 ESI+ 388.2 247.3 145 42 9.17 388.2 290.3 145 39 9.17 吡罗昔康 ESI+ 331.9 121.2 103 42 10.28 331.9 164.1 103 23 10.28 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 ESI+ 128.1 82.1 87 23 6.25 128.1 56.1 87 19 6.24 氨基比林 ESI+ 232.1 113.2 95 18 8.19 232.1 187.1 95 15 8.18 四环素 ESI+ 445.1 410.2 80 24 8.93 445.1 427.1 80 19 8.93 金霉素 ESI+ 479.1 462.0 80 24 9.55 479.1 444.0 80 28 9.55 土霉素 ESI+ 461.2 426.2 80 25 8.67 461.2 443.2 80 17 8.65 多西环素 ESI+ 445.0 428.1 80 24 9.56 445.0 154.1 80 35 9.57 乙酰磺胺 ESI+ 214.9 156.0 26 21 5.42 214.9 108.1 26 30 5.42 磺胺吡啶 ESI+ 249.8 156.1 85 24 7.41 249.8 183.9 85 25 7.42 磺胺嘧啶 ESI+ 250.8 156.0 76 22 6.38 250.8 108.1 76 33 6.38 磺胺甲恶唑 ESI+ 254.0 156.2 80 23 9.47 254.0 108.0 80 34 9.47 磺胺噻唑 ESI+ 255.8 156.1 73 21 6.95 255.8 108.0 73 33 6.95 磺胺甲嘧啶 ESI+ 265.0 156.0 98 23 7.82 265.0 172.1 98 23 7.81 磺胺二甲异恶唑 ESI+ 267.9 155.9 90 23 8.40 267.9 113.1 90 23 8.40 磺胺甲噻二唑 ESI+ 270.8 156.0 75 21 8.62 270.8 108.2 75 36 8.61 苯甲酰磺胺 ESI+ 276.9 155.9 81 20 9.69 276.9 108.0 81 33 9.67 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 ESI+ 279.0 124.0 98 29 6.39 279.0 186.0 98 22 6.39 磺胺二甲嘧啶 ESI+ 279.0 185.9 88 25 8.87 279.0 155.9 88 25 8.87 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 280.8 156.0 96 23 8.62 280.8 108.0 70 37 8.61 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 ESI+ 280.8 156.0 70 24 8.89 280.8 108.0 70 38 8.89 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 280.8 156.1 70 26 9.30 280.8 108.1 70 38 9.30 磺胺氯哒嗪 ESI+ 284.8 156.0 82 21 9.34 284.8 108.0 82 38 9.34 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 310.8 156.0 92 27 9.52 310.8 108.0 92 40 9.52 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 ESI+ 310.8 156.1 80 27 9.77 310.8 108.1 80 36 9.77 磺胺苯吡唑 ESI+ 314.9 156.0 95 31 9.77 314.9 221.9 95 28 9.77 诺氟沙星 ESI+ 320.1 276.1 80 26 8.35 320.1 233.1 80 35 8.35 依诺沙星 ESI+ 321.0 303.0 80 24 8.15 321.0 234.0 80 30 8.15 环丙沙星 ESI+ 332.1 288.1 80 25 8.53 332.1 245.1 80 33 8.54 培氟沙星 ESI+ 334.1 316.1 80 27 8.44 334.1 290.2 80 25 8.44 洛美沙星 ESI+ 352.0 265.0 80 33 8.81 352.0 308.1 80 28 8.81 达氟沙星 ESI+ 358.1 340.1 77 30 8.77 358.1 314.1 77 24 8.77 恩诺沙星 ESI+ 360.0 316.1 80 25 8.95 360.0 245.1 80 35 8.95 氧氟沙星 ESI+ 362.2 318.1 80 26 8.32 362.2 261.1 80 38 8.32 沙拉沙星 ESI+ 386.0 342.3 80 25 9.26 386.0 299.0 80 38 9.26 二氟沙星 ESI+ 400.1 356.1 80 28 9.30 400.1 299.1 80 41 9.30 地西泮 ESI+ 285.1 154.0 80 36 10.76 285.1 193.0 80 40 10.76 地美硝唑 ESI+ 142.2 96.0 65 21 7.43 142.2 81.0 65 36 7.43 萘普生 ESI− 229.2 184.9 −45 −12 10.45 229.2 169.9 −45 −20 10.45 双氯芬酸钠 ESI− 295.9 251.9 −72 −16 10.83 295.9 213.8 −86 −29 10.83 布洛芬 ESI− 204.8 161.0 −43 −10 11.01 204.8 159.0 −49 −12 11.01 大麻二酚 ESI− 313.2 245.1 −120 −32 11.91 313.2 179.1 −120 −28 11.91 大麻酚 ESI− 309.1 279.1 −120 −45 12.69 309.1 222.1 −120 −61 12.69 四氢大麻酚 ESI− 313.2 245.1 −150 −38 13.25 313.2 191.1 −150 −40 13.25 氯霉素 ESI− 320.7 152.0 −68 −27 9.72 320.7 257.2 −68 −18 9.72 甲砜霉素 ESI− 354.0 185.1 −80 −29 8.33 354.0 289.9 −80 −19 8.33 氟苯尼考 ESI− 356.1 336.0 −68 −14 9.54 356.1 184.9 −68 −26 9.54 表 2 59种化合物基质效应、线性关系、检出限、定量限
Table 2 Matrix effects, LOD and LOQ of 59 analytes
项目 线性范围(ng/mL) 回归方程 决定系数(R2) 基质效应(%) LOD(μg/L) LOQ(μg/L) 对乙酰氨基酚 10~200 y=122029x+2689364 0.9994 0.85 5 10 美洛昔康 10~200 y=174261x+1548433 0.9991 1.02 5 10 氯苯那敏 10~200 y=213855x+3338602 0.9998 1.17 5 10 地塞米松 10~200 y=1468x+6819 0.9991 0.89 5 10 吗啡 25~500 y = 25478x+98863 0.999 0.83 10 25 可待因 25~500 y=49302x+243629 0.9994 1.73 10 25 蒂巴因 25~500 y=152035x+1148584 0.9992 1.15 5 10 罂粟碱 25~500 y=245436x+9496444 0.9994 1.53 5 10 那可丁 25~500 y=30836x+885753 0.9998 0.83 5 10 甲基苯丙胺 10~200 y=85430x+937224 0.9996 0.75 5 10 甲硝唑 10~200 y=157955x+2736008 0.999 1.35 5 10 保泰松 25~500 y=11052x+28925 0.9996 1.17 10 25 特拉唑嗪 10~200 y=61445x+1011146 0.9991 1.17 5 10 吡罗昔康 10~200 y=18731x+107583 0.9991 1.08 5 10 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 10~200 y=40388x+487332 0.9993 1.26 5 10 氨基比林 10~200 y=13271x+82261 0.999 0.91 5 10 四环素 25~500 y=37436x−238697 0.9996 1.14 10 25 金霉素 25~500 y=14665x−18961 0.9996 1.86 10 25 土霉素 25~500 y=41282x−177380 0.9996 1.02 10 25 多西环素 25~500 y=9187x−64238 0.9998 1.4 10 25 乙酰磺胺 10~200 y=4119x+80644 0.9997 0.66 5 10 磺胺吡啶 10~200 y=10577x+117358 0.9998 1.06 5 10 磺胺嘧啶 10~200 y=13291x+15372 0.9997 1.14 5 10 磺胺甲恶唑 10~200 y=2359x+37754 0.9995 1.00 5 10 磺胺噻唑 10~200 y=10271x+19676 0.9993 0.81 5 10 磺胺甲嘧啶 10~200 y=8606x+25786 0.9991 1.11 5 10 磺胺二甲异恶唑 10~200 y=3789x+18215 0.9995 1.38 5 10 磺胺甲噻二唑 10~200 y=6135x−18903 0.9993 1.00 5 10 苯甲酰磺胺 10~200 y=1693x+748 0.9995 0.58 5 10 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 10~200 y=4377x+75551 0.9995 0.65 5 10 磺胺二甲嘧啶 10~200 y=3082x+83327 0.9998 1.06 5 10 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=4664x−578.5886 0.9994 0.52 5 10 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 10~200 y=22643x+233406 0.9992 1.03 5 10 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=20336x+207113 0.9993 1.20 5 10 磺胺氯哒嗪 10~200 y=4532x−7225 0.9996 0.79 5 10 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=17667x−46137 0.9995 0.96 5 10 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 10~200 y=7168x+131929 0.9993 1.21 5 10 磺胺苯吡唑 10~200 y=2570x+14433 0.9993 0.61 5 10 诺氟沙星 10~200 y=4441x−17535 0.9991 0.85 5 10 依诺沙星 10~200 y=33471x−180451 0.9999 0.99 5 10 环丙沙星 10~200 y=7312x+10557 0.9994 1.15 5 10 培氟沙星 10~200 y=57859x+9947 0.9998 0.92 5 10 洛美沙星 10~200 y=11008x+22527 0.9996 1.07 5 10 达氟沙星 10~200 y=57401x−61967 0.9998 1.00 5 10 恩诺沙星 10~200 y=17537x+27100 0.9998 0.93 5 10 氧氟沙星 10~200 y =37238x−64982 0.9991 0.88 5 10 沙拉沙星 10~200 y=5610x+41835 0.9996 1.06 5 10 二氟沙星 10~200 y=10793x+8451 0.9996 0.74 5 10 地西泮 10~200 y=14880x+38696 0.9996 1.20 5 10 地美硝唑 10~200 y=7465x+5332 0.9999 0.94 5 10 萘普生 25~500 y=539x+2612 0.9999 2.37 10 25 双氯芬酸钠 25~500 y=15678x+144012 0.9997 0.96 10 25 布洛芬 25~500 y=4517x+12730 0.9991 1.44 10 25 大麻二酚 25~500 y=483x+3537 0.9996 0.99 10 25 大麻酚 25~500 y=3319x+1196 0.9992 1.55 10 25 四氢大麻酚 25~500 y=1149x−8920 0.9997 1.12 10 25 氯霉素 10~200 y=2730x+30243 0.9994 0.79 5 10 甲砜霉素 25~500 y=953x+1889 0.9994 0.94 10 25 氟苯尼考 25~500 y=2175x+7413 0.999 0.69 10 25 表 3 59种化合物平均回收率和精密度(n=3)
Table 3 Recoveries and RSDs of 59 analytes spiked into blank matrix sample (n=3)
化合物 25 μg/L 50 μg/L 100 μg/L 回收率(%) RSD(%) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 对乙酰氨基酚 87.4 2.8 81.5 1.6 77.5 6.2 美洛昔康 92.3 13.7 94.6 8.0 123.1 2.4 氯苯那敏 99.1 3.4 81.1 9.3 112.5 4.7 地塞米松 82.5 8.4 95.7 4.5 117.7 7.0 吗啡 81.8 2.8 87.3 12.9 81.2 1.3 可待因 96.4 9.4 113.1 12.7 93.6 2.9 蒂巴因 90.6 4.6 86.4 6.3 119.2 2.0 罂粟碱 116.4 8.9 102.1 9.8 112.3 5.6 那可丁 90.7 9.5 105.9 9.9 106.3 3.4 甲基苯丙胺 85.2 3.7 88.9 4.9 109.9 1.1 甲硝唑 93.2 4.7 87.8 2.9 101.1 7.1 保泰松 82.6 6.8 93.7 4.0 112.7 9.3 特拉唑嗪 97.8 10.3 80.1 12.5 97.0 1.9 吡罗昔康 93.6 12.4 115.6 2.7 115.0 1.0 2-甲基-5硝基咪唑 85.3 4.6 103.4 5.5 111.8 9.6 氨基比林 84.8 7.9 123.9 13.1 123.0 4.9 四环素 85.9 4.4 76.9 7.4 80.4 1.5 金霉素 107.2 7.0 70.2 11.0 73.8 7.9 土霉素 85.7 2.7 95.2 2.9 82.8 6.3 多西环素 90.3 4.8 117.0 5.0 116.1 2.3 乙酰磺胺 86.9 2.9 124.1 7.6 110.9 2.1 磺胺吡啶 85.1 5.2 108.0 5.5 127.4 3.9 磺胺嘧啶 84.8 5.0 106.2 2.3 109.3 3.6 磺胺甲恶唑 70.3 4.8 128.6 2.3 120.8 1.4 磺胺噻唑 90.0 8.8 118.9 4.3 98.5 9.1 磺胺甲嘧啶 101.3 4.9 125.5 8.4 122.1 6.4 磺胺二甲异恶唑 88.1 3.5 122.8 1.8 124.1 2.2 磺胺甲噻二唑 94.9 4.4 108.0 8.6 111.0 3.3 苯甲酰磺胺 78.5 8.8 106.0 10.2 96.2 3.2 磺胺二甲异嘧啶 93.5 11.6 120.0 1.2 117.8 2.5 磺胺二甲嘧啶 93.5 5.6 102.2 2.1 86.6 7.1 磺胺间甲氧嘧啶 89.4 7.1 111.4 5.0 105.1 4.5 磺胺甲氧哒嗪 100.7 5.8 128.8 4.5 116.3 12.7 磺胺对甲氧嘧啶 91.0 4.0 103.9 3.6 111.4 3.6 磺胺氯哒嗪 67.4 9.9 104.1 9.9 126.5 1.5 磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶 112.4 8.0 123.3 3.1 121.1 13.2 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶 84.8 3.2 113.9 9.7 123.1 3.7 磺胺苯吡唑 87.3 3.4 124.7 2.4 123.8 2.6 诺氟沙星 73.1 6.9 80.8 1.8 74.8 1.4 依诺沙星 84.0 2.0 79.3 11.8 80.9 1.1 环丙沙星 81.1 6.4 93.4 2.6 74.8 2.5 培氟沙星 85.5 11.9 85.9 9.6 83.4 1.7 洛美沙星 85.2 5.7 83.0 2.4 75.6 9.3 达氟沙星 99.9 5.3 78.5 1.8 70.9 5.8 恩诺沙星 83.8 5.0 83.4 7.8 88.7 6.5 氧氟沙星 91.6 9.7 98.3 5.2 66.3 3.7 沙拉沙星 86.2 7.7 119.4 2.1 98.1 4.9 二氟沙星 88.5 2.5 110.0 10.3 101.7 2.7 地西泮 87.3 10.0 118.1 1.8 108.3 4.6 地美硝唑 94.8 2.2 112.8 4.5 112.7 3.1 萘普生 98.9 13.5 91.0 10.7 100.0 7.0 双氯芬酸钠 121.7 2.5 94.6 7.8 120.0 1.9 布洛芬 78.0 11.4 110.5 6.5 102.3 9.8 大麻二酚 66.9 4.1 114.4 2.6 115.6 2.6 大麻酚 60.3 11.5 110.2 3.5 106.8 6.4 四氢大麻酚 60.9 3.6 82.0 2.8 107.8 7.8 氯霉素 88.1 3.0 113.7 12.7 114.1 4.5 甲砜霉素 90.5 8.3 123.8 3.9 109.6 2.7 氟苯尼考 108.2 5.2 115.0 5.5 114.1 6.8 表 4 micro-QuEChERs/LC-MS/MS与其他已报道方法的比较
Table 4 Comparison of micro-QuEChERs-LC-MS/MS with other reported methods
检测方法 化学药物
种类检测
模式仪器检测时间(min) 样品量(mL/g) 提取溶剂
体积(mL)回收率(%) 检出限 文献 UPLC-Orbitrap HRMS 167 ESI+、ESI− 25 1 20 66.4~118.1 200 μg/kg [19] HPLC 28 / 30 5 25 88. 8~118. 6 1000~10000 μg/kg [13] HPLC-MS/MS 5 ESI+ 10 2 10 84.5~105.1 2~8 μg/kg [17] QuEChERS-HPLC-Q-TOF/MS 8 ESI+ 20 5 10 75.8~95.6 2~10 μg/kg [20] HPLC-MS/MS 20 ESI+ 16 10 50 88.13~114.6 1000~30000 μg/L [15] QuEChERS-UPLC-MS/MS 12 ESI+ 24 5 6 62.7~95.2 0.1~2.1 μg/L [23] BJS 201713 59 ESI+/ESI− 35 1 50 / 100~2500 μg/kg [36] 本方法 59 ESI+、ESI− 16 1 1 60.3~128.8 5~10 μg/L -
[1] JIN L, LI X B, TIAN D Q, et al. Antioxidant properties and color parameters of herbal teas in China[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2016,87:198−209. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.044
[2] 游飞祥, 韩彦琪, 龚苏晓, 等. HPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析植物凉茶中的化学成分[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(8):161−165. [YOU F X, HAN Y Q, GONG S X, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in herbal tea based on HPLC-Q-TOF-MS J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(8):161−165.]
[3] 邹玉婷, 赵晓娟, 吴俊铨. 广式凉茶的功效及其安全性研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2021(6):81−85. [ZOU Y T, ZHAO X J, WU J Q, et al. Research progress on efficacy and safety of cantonese herbal tea[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021(6):81−85.] ZOU Y T, ZHAO X J, WU J Q, et al . Research progress on efficacy and safety of cantonese herbal tea[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021 (6 ):81 −85 .[4] 霍婷婷, 高丽谊, 何珊丽, 等. 凉茶专项抽检情况分析与研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021(30):87−89,91. [HUO T T, GAO L Y, HE S L, et al. Special sampling analysis of illegal addition of herbal tea[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2021(30):87−89,91.] HUO T T, GAO L Y, HE S L, et al . Special sampling analysis of illegal addition of herbal tea[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2021 (30 ):87 −89,91 .[5] 王萍, 肖更生, 张友胜, 等. 广式凉茶研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2010,35(2):77−80. [WANG P, XIAO G S, ZHANG Y S, et al. Progress in study of Guangdong herbal tea[J]. Food Science and Technology,2010,35(2):77−80.] WANG P, XIAO G S, ZHANG Y S, et al . Progress in study of Guangdong herbal tea[J]. Food Science and Technology,2010 ,35 (2 ):77 −80 .[6] 尹佳, 黎星, 张涛, 等. 网购凉茶中非法添加抗风湿类药物状况分析及对策探讨[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(18):4964−4970. [YIN J, LI X, ZHANG T, et al. Status analysis and countermeasure discussion of illegal addition of anti-rheumatic drugs in the herbal teas purchased online[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2018,9(18):4964−4970.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.18.034 YIN J, LI X, ZHANG T, et al . Status analysis and countermeasure discussion of illegal addition of anti-rheumatic drugs in the herbal teas purchased online[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2018 ,9 (18 ):4964 −4970 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.18.034[7] FANG Y L, WANG Z, QUAN Q Q. et al. Developing an ultrasensitive immunochromatographic assay for authentication of an emergent fraud aminopyrine in herbal tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,406:135065. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135065
[8] WANG J, LAI W, LI Z D, et al. One-step ultra-sensitive immunochromatographic strip authenticating an emergent fraud acetophenetidin in herbal tea[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2022,165:113183. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113183
[9] LI S, GE W, SURYOPRABOWO S, et al. A paper-based sensor for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of ibuprofen in water and herbal tea[J]. Analyst,2021,146(22):6874−6882. doi: 10.1039/D1AN01533H
[10] 陈钰婷, 温颖婉, 封霖, 等. HPLC法同时测定凉茶中2种头孢类成分[J]. 海峡药学,2021,33(5):65−67. [CHEN Y T, WEN Y W, FENG L, et al. Determination of two cephalosporin components in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal,2021,33(5):65−67.] CHEN Y T, WEN Y W, FENG L, et al . Determination of two cephalosporin components in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal,2021 ,33 (5 ):65 −67 .[11] 江琦, 王邱, 罗丹. 高效液相色谱法同时测定凉茶中10种非法添加化学药物的含量[J]. 广东化工,2018,45(9):225−227. [JIANG Q, WANG Q, LUO D. Determination of ten chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2018,45(9):225−227.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.09.103 JIANG Q, WANG Q, LUO D . Determination of ten chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2018 ,45 (9 ):225 −227 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.09.103[12] 温家欣, 陈林, 赖宇红, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时快速测定凉茶中11种非法添加化学药物[J]. 分析测试学报,2016,35(3):285−291. [WEN J X, CHEN L, LAI Y H, et al. Rapid and simultaneous analysis of 11 adulterated drugs in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2016,35(3):285−291.] WEN J X, CHEN L, LAI Y H, et al . Rapid and simultaneous analysis of 11 adulterated drugs in herbal tea by HPLC[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2016 ,35 (3 ):285 −291 .[13] 何嘉雯, 温家欣, 赖宇红, 等. 高效液相色谱快速测定草本植物饮料中28种外源性药物和内源性成分[J]. 色谱,2018,36(8):758−765. [HE J W, WEN J X, LAI Y H, et al. Determination of 28 exogenous medicines and endogenous components in herbal drink using high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2018,36(8):758−765.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.02005 HE J W, WEN J X, LAI Y H, et al . Determination of 28 exogenous medicines and endogenous components in herbal drink using high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2018 ,36 (8 ):758 −765 . doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.02005[14] 胡佳哲, 赖宇红. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定凉茶中19种非法添加药物[J]. 分析试验室,2019,38(2):230−234. [HU J Z, LAI Y H. Detection of 19 illegally added drugs in herbal tea by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2019,38(2):230−234.] HU J Z, LAI Y H . Detection of 19 illegally added drugs in herbal tea by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2019 ,38 (2 ):230 −234 .[15] 罗伟, 杜俊威, 林秋凤, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定凉茶中20种非法添加化学药物[J]. 亚太传统医药,2020,16(6):43−47. [LUO W, DU J W, LIN Q F, et al. Determination of twenty chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine,2020,16(6):43−47.] LUO W, DU J W, LIN Q F, et al . Determination of twenty chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine,2020 ,16 (6 ):43 −47 .[16] 孙树周, 何燕莉, 陈泳恩, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法测定凉茶中非法添加的26种止咳平喘类化学药物[J]. 今日药学,2021,31(3):195−199. [SUN S Z, HE Y L, CHEN Y G, et al. Determination of 26 chemical drugs for the treatment of cough and asthma added illegally in herbal tea by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Pharmacy Today,2021,31(3):195−199.] SUN S Z, HE Y L, CHEN Y G, et al . Determination of 26 chemical drugs for the treatment of cough and asthma added illegally in herbal tea by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Pharmacy Today,2021 ,31 (3 ):195 −199 .[17] 刘敏敏, 谢小霞, 陈俏, 等. 液相色谱-质谱联用法(HPLC-MS/MS)快速测定凉茶中的5种罂粟壳类生物碱[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(23):266−272. [LIU M M, XIE X X, CHEN Q, et al. Rapid determination of five alkaloids in poppy shell in herbal tea by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(23):266−272.] LIU M M, XIE X X, CHEN Q, et al . Rapid determination of five alkaloids in poppy shell in herbal tea by HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (23 ):266 −272 .[18] 刘桂联, 陈茹, 罗小宝, 等. 超高效液相色谱-高分辨质谱快速筛查和确证凉茶中56种非法添加药物[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(10):336−341. [LIU G L, CHEN R, LUO X B, et al. Rapid screening and confirmation of 56 illegally added drugs in herbal tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2022,43(10):336−341.] LIU G L, CHEN R, LUO X B, et al . Rapid screening and confirmation of 56 illegally added drugs in herbal tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (10 ):336 −341 .[19] 何嘉雯, 温家欣, 刘亚雄, 等. 超高效液相色谱-静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱快速筛查和确证凉茶中167种非法添加药物[J]. 色谱,2022,40(3):253−265. [HE J W, WEN J X, LIU Y X, et al. Rapid screening and identification of 167 illegally added medicines in herbal tea by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2022,40(3):253−265.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.07006 HE J W, WEN J X, LIU Y X, et al . Rapid screening and identification of 167 illegally added medicines in herbal tea by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2022 ,40 (3 ):253 −265 . doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.07006[20] 曾广丰, 谢建军, 王志元, 等. QuEChERS前处理结合HPLC-Q-TOF/MS非靶向快速筛查凉茶中的非法添加物[J]. 分析测试学报,2019,38(4):429−434. [ZENG G F, XIE J J, WANG Z Y, et al. Non-target screening of illegal additive residues in herbal teas by high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry with QuEChERS purification[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2019,38(4):429−434.] ZENG G F, XIE J J, WANG Z Y, et al . Non-target screening of illegal additive residues in herbal teas by high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry with QuEChERS purification[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2019 ,38 (4 ):429 −434 .[21] 张科明, 许杨彪, 刘向红, 等. QuEChERS-液质联用法快速测定凉茶中非法添加的10种止咳平喘类化学药物[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(24):294−297. [ZHANG K M, XU Y B, LIU X H, et al. Rapid determination of ten chemical drugs for the treatment of cough and asthma added illegally in herbal tea by HPLC-MS/MS coupled with modified QuEChERS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(24):294−297.] ZHANG K M, XU Y B, LIU X H, et al . Rapid determination of ten chemical drugs for the treatment of cough and asthma added illegally in herbal tea by HPLC-MS/MS coupled with modified QuEChERS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (24 ):294 −297 .[22] 张宏峰, 彭荣飞, 罗晓燕, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定散装凉茶中非法添加的6种化学药物[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2017,27(16):2287−2290. [ZHANG H F, PENG R F, LUO X Y, et al. Determination of six chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by QuEChERS method coupled with ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,2017,27(16):2287−2290.] ZHANG H F, PENG R F, LUO X Y, et al . Determination of six chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by QuEChERS method coupled with ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,2017 ,27 (16 ):2287 −2290 .[23] 宋宁宁, 张科明, 刘向红, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法快速测定凉茶中非法添加的12种化学药物[J]. 色谱,2015,33(10):1026−1031. [SONG N N, ZHANG K M, LIU X H, et al. Determination of twelve chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with modified QuEChERS[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2015,33(10):1026−1031.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2015.05023 SONG N N, ZHANG K M, LIU X H, et al . Determination of twelve chemical drugs illegally added in herbal tea by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with modified QuEChERS[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2015 ,33 (10 ):1026 −1031 . doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2015.05023[24] 韩瑨烜, 宋敏, 罗芸, 等. 改良QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法快速测定减肥食品中19种违禁药物[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(13):4303−4309. [HAN J X, SONG M, LUO Y, et al. Rapid determination of 19 kinds of prohibit drugs in diet foods by improved QuEChERS-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(13):4303−4309.] HAN J X, SONG M, LUO Y, et al . Rapid determination of 19 kinds of prohibit drugs in diet foods by improved QuEChERS-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022 ,13 (13 ):4303 −4309 .[25] 韩婉清, 王斌, 吴楚森, 等. 固相萃取-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱测定凉茶中15种植物源性兴奋剂和外源性药物[J]. 分析化学,2016,44(10):1584−1592. [HAN W Q, WANG B, WU C S, et al. Determination of 15 kinds of plants originated stimulants and exogenous medicines using solid phase extraction combined with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2016,44(10):1584−1592.] HAN W Q, WANG B, WU C S, et al . Determination of 15 kinds of plants originated stimulants and exogenous medicines using solid phase extraction combined with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2016 ,44 (10 ):1584 −1592 .[26] ZHANG L, LI C H, XIAN Y P, et al. Investigation of 8 exogenous medicines illegally added into Guangdong herbal teas by solid phase extraction and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Microchemical Journal,2019,147:921−929. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.013
[27] 黄思琦, 郭珍玲, 牟仁祥, 等. QuEChERS-液相色谱-串联质谱法测定模拟稻田环境中水、土壤和水稻植株中二氯喹啉酸残留[J]. 农药学学报,2020,22(5):831−836. [HUANG S Q, GUO Z L, MOU R X, et al. Determination of quinclorac residue in paddy water, soil and rice plants in a simulated paddy environment based on QuEChERS-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science,2020,22(5):831−836.] HUANG S Q, GUO Z L, MOU R X, et al . Determination of quinclorac residue in paddy water, soil and rice plants in a simulated paddy environment based on QuEChERS-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science,2020 ,22 (5 ):831 −836 .[28] 刘洋, 何小维, 刘晓云, 等. QuEChERS结合UPLC-MS/MS检测血液中苯丙胺类及其相关9种物质[J]. 分析试验室,2020,39(1):101−106. [LIU Y, HE X W, LIU X Y, et al. Analysis of nine kinds of amphetamine-type compounds in blood by method of QuEChERS combined with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2020,39(1):101−106.] LIU Y, HE X W, LIU X Y, et al . Analysis of nine kinds of amphetamine-type compounds in blood by method of QuEChERS combined with UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2020 ,39 (1 ):101 −106 .[29] 马丽娜, 赵敏, 张静, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时测定鸡肉中7类42种兽药残留的研究[J]. 中国家禽,2021,43(8):68−74. [MA L N, ZHAO M, ZHANG J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 7 kinds of 42 veterinary drugs residues in chicken meat by QuEChERS-ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. China Poultry,2021,43(8):68−74.] MA L N, ZHAO M, ZHANG J, et al . Simultaneous determination of 7 kinds of 42 veterinary drugs residues in chicken meat by QuEChERS-ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. China Poultry,2021 ,43 (8 ):68 −74 .[30] 谭华东, 张汇杰, 武春媛. GC-MS结合微量QuEChERS法快速测定土壤中16种多环芳烃[J]. 中国测试,2020,46(1):64−70. [TAN H D, ZHANG H J, WU C Y, et al. Rapid determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with micro-QuEChERS[J]. China Measurement & Testing Technology,2020,46(1):64−70.] TAN H D, ZHANG H J, WU C Y, et al . Rapid determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with micro-QuEChERS[J]. China Measurement & Testing Technology,2020 ,46 (1 ):64 −70 .[31] CHEN H C, HUANG Y F, HSIEH C S, et al. Determining the trace-level photoinitiators in juices and milk from various types of packages in Taiwan by a micro-QuEChERS-based UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Food Chem,2022,388:132929. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132929
[32] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委. 国家市场监管总局. GB-31658.17-2021食品安全国家标准 动物性食品中四环素类、磺胺类和喹诺酮类药物残留量的测定 液相色谱-串联质谱法[S]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2022. [Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB-31658.17-2021 National food safety standards-Determination of tetracycline, sulfonamide, and quinolone residues in animal food-Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method[S]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2022.] Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB-31658.17-2021 National food safety standards-Determination of tetracycline, sulfonamide, and quinolone residues in animal food-Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2022.
[33] ZHAO L M, LUCAS D, LONG D, et al. Multi-class multi-residue analysis of veterinary drugs in meat using enhanced matrix removal lipid cleanup and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2018,1549:14−24. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.03.033
[34] 戴尽波, 沈洁, 何啸峰, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测禽源性食品中氟虫腈及其代谢物[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):325−332. [DAI J B, SHEN J, HE X F, et al. Optimized QuEChERS combined with UPLC-MS/MS for determination of fipronil and its metabolites in poultry-derived foods[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):325−332.] DAI J B, SHEN J, HE X F, et al . Optimized QuEChERS combined with UPLC-MS/MS for determination of fipronil and its metabolites in poultry-derived foods[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (2 ):325 −332 .[35] CHEN D, XU Q, LU Y P, et al. The QuEChERS method coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of diuretics in animal-derived foods[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2021,101:103965. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103965
[36] 国家市场监督管理总局. BJS 201713食品补充检验方法 饮料、茶叶及相关制品中对乙酰氨基酚等59种化合物的测定[Z]. 北京:2017. [State Administration for Market Regulation. BJS 201713 Food supplementary inspection method. Determination of 59 compounds including acetaminophen in beverages, tea and related products[Z]. Beijing:2017.] State Administration for Market Regulation. BJS 201713 Food supplementary inspection method. Determination of 59 compounds including acetaminophen in beverages, tea and related products[Z]. Beijing: 2017.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张黎梅,汪云飞,陈艳,董天秋,马文思,陈娴. HPLC-DAD法测定养生茶中的双氯芬酸钠. 食品与发酵科技. 2025(01): 169-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李肖斐. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定酵素梅中12种酚汀(酚丁)、酚酞及其酯类衍生物或类似物. 食品安全导刊. 2025(07): 105-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



