Effect of Ultra-high-pressure Sterilization on Flavor and Physicochemical Properties of Low-salt Sliced Bacon
-
摘要: 为探究不同压力的超高压杀菌对低盐切片腊肉品质的影响,样品在22 ℃下分别经200、400、600 MPa压力处理10 min,以未杀菌组为对照,于4 ℃储藏的第0、60、120、180 d测定理化指标、风味物质及菌落总数。结果表明,超高压处理后,低盐切片腊肉的水分含量、亚硝酸盐含量、硬度、a*值、b*值及菌落总数均降低,pH、POV值、L*值、弹性、回复力及内聚性均升高。储藏过程中,超高压增强了腊肉的持水性,减缓了脂肪氧化,有效抑制了微生物生长。第180 d时,超高压组的水分含量、L*值、a*值、弹性及内聚性均高于对照组,pH、亚硝酸盐含量、硬度及菌落总数均低于对照组。气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS)和电子鼻分析结果均显示,超高压组与对照组风味成分相似,含量占比差异较小,且超高压对腊肉风味的形成有促进和保护作用。但压力过高(600 MPa)会加剧脂肪氧化,影响腊肉的色泽和质构,进而影响其感官评分。综合分析可得,400 MPa为本研究的最佳处理压力。Abstract: The effect of ultra-high pressure (UHP) sterilization technology on the quality of low-salt sliced bacon was investigated by treating samples under 200, 400 and 600 MPa for 10 min at 22 ℃. The samples were stored at 4 ℃ and the unsterilized group was used as the control group. The physicochemical indexes, flavor substances and the total number of colonies of the samples were determined when the storage time was 0, 60, 120 and 180 days, respectively. The results indicated that the moisture content, nitrite content, hardness, a* value, b* value, and total bacterial counts of the low-salt sliced bacon decreased, while the pH value, POV value, L* value, elasticity, recovery, and cohesiveness increased after ultra-high pressure treatment. During the storage process, ultra-high pressure conditions enhanced the water-holding capacity of the bacon, slowed down lipid oxidation, and effectively inhibited the microbial growth. At 180 days, the moisture content, L* value, a* value, elasticity, and cohesiveness of the ultra-high pressure group were higher than those of the control group, while the pH value, nitrite content, hardness, and total bacterial counts were lower than those of the control group. The experimental results of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and electronic nose showed that the flavor components of ultra-high pressure group were similar to those of the control group, and then the difference of the content was small. Moreover, UHP treatment promoted and protected the flavor formation of bacon. However, excessive pressure (600 MPa) not only aggravated lipid oxidation, but also affected the color and texture of the bacon, thus affecting the sensory score of bacon. Overall, the optimal treatment pressure was determined to be 400 MPa in this study.
-
Keywords:
- low-salt /
- sliced bacon /
- ultra-high /
- physical and chemical properties /
- sensory quality
-
腊肉作为中国著名的传统腌腊肉制品,市场空间广阔,但传统工艺常通过添加大量食盐并降低含水量来延长保质期,导致腊肉盐含量较高、水分含量较低、口感柴硬,且不利于人体健康。此外,随着社会生产生活方式的转变,方便食品、预包装食品开始普及,传统腊肉需要做出创新与改变才能迎合现代消费市场。切片腊肉相较于传统整块腊肉更方便包装运输储藏以及烹饪食用,但切片过程增加了腊肉暴露在空气中的面积和时间,加速了脂肪氧化,增大了被微生物污染的概率,此时杀菌方式的选择就十分重要。目前,肉制品工业中常采用高温长时间杀菌的方式对微生物进行灭活,此法对肉制品的口感、色泽和营养物质造成的损失较大。因此,关于无热效应作用的冷杀菌工艺逐渐受到国内外食品行业的关注。
众多研究表明,高压可以有效减少肉及肉制品中的微生物数量,且适当的压力可以在杀菌的同时,较好地保持食品原有的色泽、味道及营养物质,同时还能产生一些正向、积极的影响[1]。如Garriga等[2]选择600 MPa压力处理包装好的切片火腿,发现对乳酸菌的杀灭效果显著,同时感官评价未发生改变。韩衍青等[3]发现400 MPa和600 MPa的超高压处理能够有效杀灭烟熏火腿中的大肠杆菌、热杀索丝菌、假单胞菌、霉菌和酵母,并且不会引起烟熏火腿脂肪的氧化酸败,能够较好地保持样品原有的脂肪酸含量。目前超高压技术在腌腊肉制品保鲜方面鲜有报道,且不同杀菌压力、时间及温度对腊肉品质有不同程度的影响,本文参考国内外研究成果,制作低盐、高水分的切片腊肉,真空包装超高压杀菌后,在4 ℃贮藏条件下,于第0、60、120、180 d时测定理化指标、风味物质及微生物情况,研究超高压压力大小对低盐切片腊肉品质的影响,探究最适合本实验腊肉产品的超高压杀菌参数。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜猪里脊肉 购于绵阳市青义镇家多乐超市;食盐 重庆合川盐化工业有限公司;烟熏柏木屑 购于河北省邢台市清河工业园区木林森木材商城;硼酸钠、亚铁氰化钾、亚硝酸钠、乙酸锌、对氨基苯磺酸、盐酸萘乙二胺、三氯乙酸、硫代巴比妥酸、无水硫酸钠、石油醚、三氯甲烷、冰乙酸、碘化钾、可溶性淀粉、硫代硫酸钠 均为分析纯,成都科龙试剂厂。
OPTO-LAB胴体肉质颜色测定仪 德国MATTHAUS;PEN3电子鼻 德国Airsence公司;GCMS-QP2020型GC-MS联用仪 日本岛津公司;75 µm碳分子筛/聚二甲基硅氧烷(carboxeml/polydimethylsiloxane,CARIPDMS)萃取头 美国Supelco公司;手动SPME进样器 上海安谱科学仪器有限公司;TA XTplus物性测试仪 英国SMS公司;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚容生化仪器厂;SW-CJ-2F超净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 低盐切片腊肉加工工艺
选用肥瘦比例在3:7~4:6之间的冷鲜猪里脊肉,修刮净皮层上的残毛及污垢,清洗干净,沿边修割整齐,分割为长15 cm、宽3 cm左右的长方形块状,于30 ℃温水中漂洗2 min,除去肉条表面的浮油、污物,取出后沥干水分;食盐添加量为肉重的2.5%,亚硝酸钠0.005%。于4 ℃冰箱中干腌48 h,每天翻动一次;腌制结束后于50 ℃(湿度为49%)预热1 h,60 ℃(湿度为62%)继续烘18 h,烘烤结束后用柏木屑烟熏8 h(烟熏温度为40~50 ℃),最终成品水分含量控制在40%左右;将制作得到的成品腊肉切成长为8 cm、宽为3 cm、厚为3 mm左右的肉片。
1.2.2 杀菌工艺
腊肉真空包装,设定压力为200、400、600 MPa,与未杀菌处理的样品做对比。升压速度约50 MPa/s,卸压速度约100 MPa/s,处理时间为10 min(不包括升压和卸压的时间)。传压介质为葵二酸二辛酯液压油,处理前油温22 ℃,处理时油温会上升,处理后油温降低至初始温度。超高压处理完成后用自来水清样品表面油质(水温10 ℃左右)[4]。
1.2.3 水分含量测定
按照GB 5009.3-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定》中直接干燥法进行测定。
1.2.4 pH测定
按照GB 5009.237-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定》进行测定。
1.2.5 质构特性测定
参考张云齐等[5]的方法。
1.2.6 色差测定
随机挑选3处测定,镜头紧贴肉样,记录L*、a*、b*值。
1.2.7 亚硝酸盐含量测定
按照GB 5009.33-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中亚硝酸盐与硝酸盐的测定》中分光光度法进行测定。
1.2.8 过氧化值(POV)测定
采用GB 5009.227-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中过氧化值的测定》中直接滴定法进行测定。
1.2.9 菌落总数测定
采用GB 47892-2022《食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》进行测定,结果用CFU/g表示。
1.2.10 风味物质种类及相对含量测定
取均匀的样品3.0 g于15 mL顶空瓶中,以聚四氟乙烯隔垫密封,采用微固相萃取,60 ℃水浴萃取40 min。解析条件为250 ℃,6 min。气相色谱与质谱参数参考刘芝君等[6]的方法设定,挥发性风味成分与自带数据库相匹配,选择匹配度≥80的结果,采用归一化法对峰面积进行定量。
1.2.11 电子鼻分析
在张云齐等[5]的方法基础上略作修改,分析采样时间设定为160 s,选取测定过程中140~142 s的数据用于后续分析。
1.2.12 感官评价
选定十名食品专业研究生作为感官评定人员并进行培训。将四组不同杀菌处理的低盐切片腊肉(真空包装)分别在100 ℃下蒸15 min。十名感官评定人员对腊肉色泽、组织结构、香味和口味四个方面进行感官评分并求平均值作为综合评分,具体评分标准参考宋忠祥等[7]的方法。采用雷达图法对评分结果进行分析[8]。
1.3 数据处理
实验取样完全随机,重复3次。采用Origin 7.0(OriginLab,USA)绘制柱状图、折线图及雷达图,相关性分析使用SPSS 25.0,采用Duncan法进行多样本间差异显著性分析,当P<0.05时被认为具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
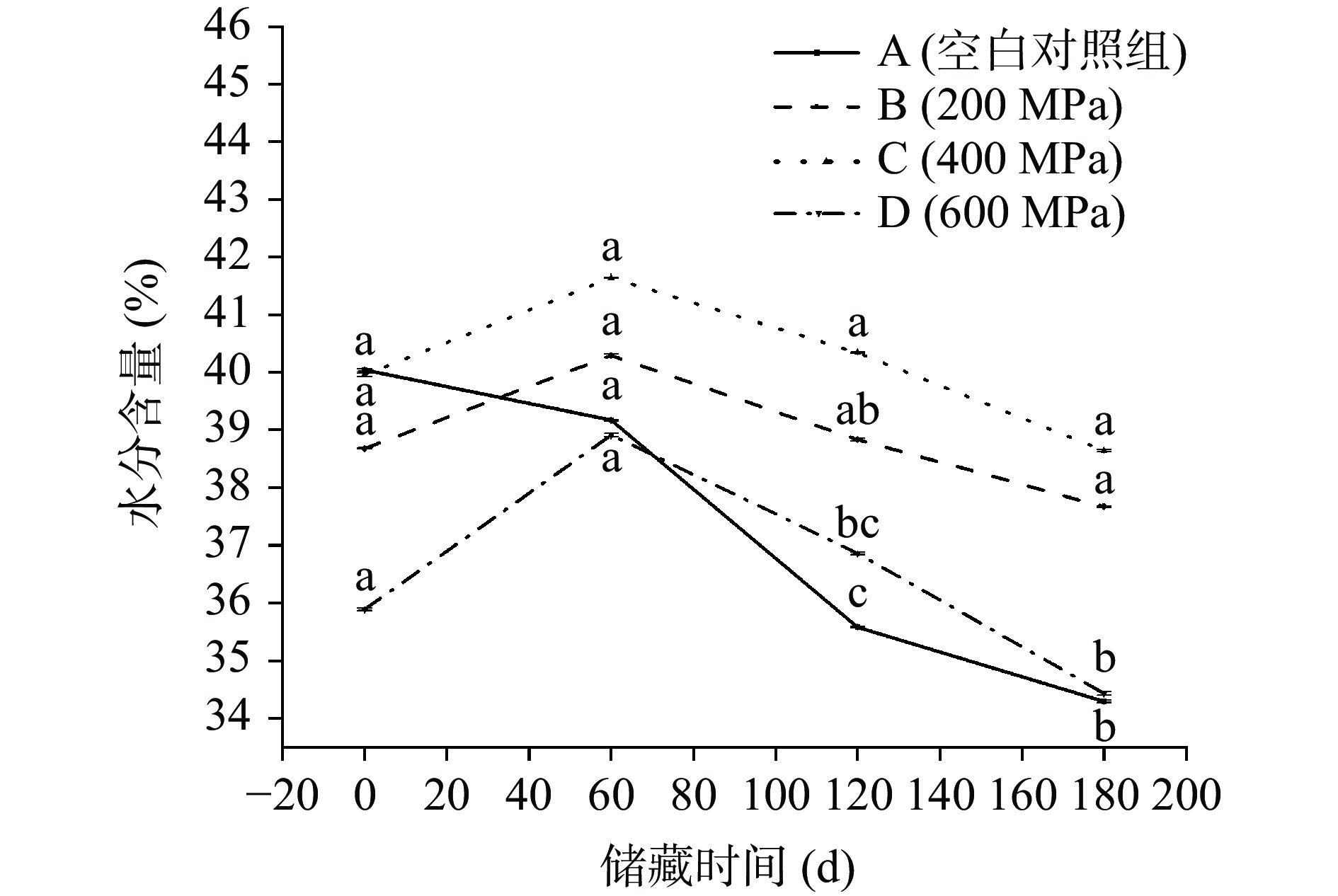
2.1 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉水分含量的影响
如图1所示,样品的水分含量随压力的升高而降低,因为超高压过程中的压缩及减压破坏了细胞结构,提高了细胞渗透性,促进了水分迁移,增加了渗透期间的水分损失[9]。储藏至60 d,对照组水分含量下降,各处理组水分含量均升高,这与超高压加工会引起食品中氢键、离子键和疏水键等非共价键的破坏或形成有关[10]。储藏至第180 d,四组样品的水分含量均有所下降,且随着压力的增大,水分下降速度呈先减小后增大的趋势,200~400 MPa时,样品的水分含量随压力的增大而增加,400~600 MPa时则反之,这与Marcos等[11]的研究结果相似。在其他条件相同的情况下,一定区间内随压力的增大,水分子间的氢氧原子距离逐渐缩短,氢键作用力逐渐增强,减缓了水分散失,提高了低盐切片腊肉的保水性[12]。同时高压可以通过改变肌原纤维的结构来增加盐溶性蛋白质的溶解度,以弥补低盐、低离子强度造成蛋白质溶解性降低的情况,进而提高腊肉的持水性[13]。综上所述,400 MPa压力处理后,腊肉的含水量为39.96%,储藏180 d后含水量为38.64%,水分含量较高,持水性较好。
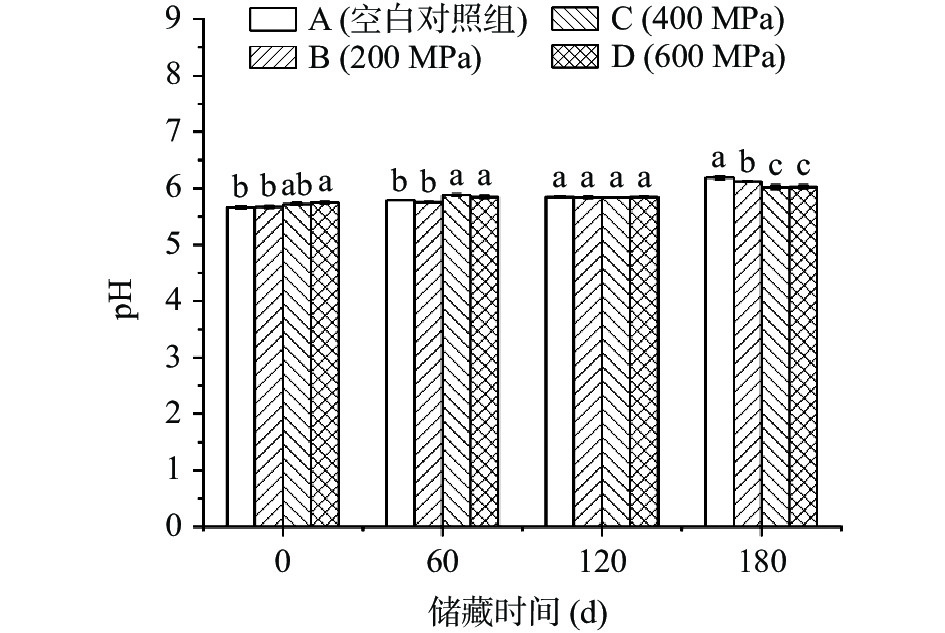
2.2 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉pH的影响
如图2所示,低盐切片腊肉的pH随压力的升高而增大,但B、C与对照组差异不显著(P>0.05)。周果等[14]的研究也出现类似的情况,这可能与超高压过程中某些蛋白质的变性有关,或是由于含氮物质(如自由氨基酸等)分解所引起的[15]。储藏期间,四组样品的pH总体都呈增长趋势,但超高压组的增长速度小于对照组。第180 d时,对照组的pH显著高于(P<0.05)各超高压组,这与贮藏期间微生物的生长繁殖有关,腊肉中的蛋白质在微生物或酶的作用下降解为胺及氨类等碱性物质,导致pH的升高。
2.3 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉色泽的影响
由表1可知,第0 d时,超高压组的L*值变大、a*、b*值变小,且随着压力的增加,变化量逐渐增大。这是因为干腌食品的颜色主要取决于亚硝基肌红蛋白和正铁肌红蛋白,前者较为稳定能耐受高压处理,后者易受高压影响而导致部分变性,从而增加反射光的量,这表现为腊肉表面颜色亮度的增加[16]。而红度的减少归因于肌红蛋白变性和血红素置换或释放[17]。储藏期间,各组的L*、a*、b*值均先升高后降低,且变化量都较小,这可能与水分含量的变化有关。储藏至180 d,超高压组的L*、a*值均高于对照组,b*值略低于对照组,这是因为超高压增加了低盐切片腊肉的持水性,储藏后水分含量较高,亮度值也较高;同时延缓了腊肉的脂肪氧化,减少了鲜红色的氧合肌红蛋白(Fe2+)氧化成棕色的高铁肌红蛋白(Fe3+),导致红度值高于对照组而黄度值略低。
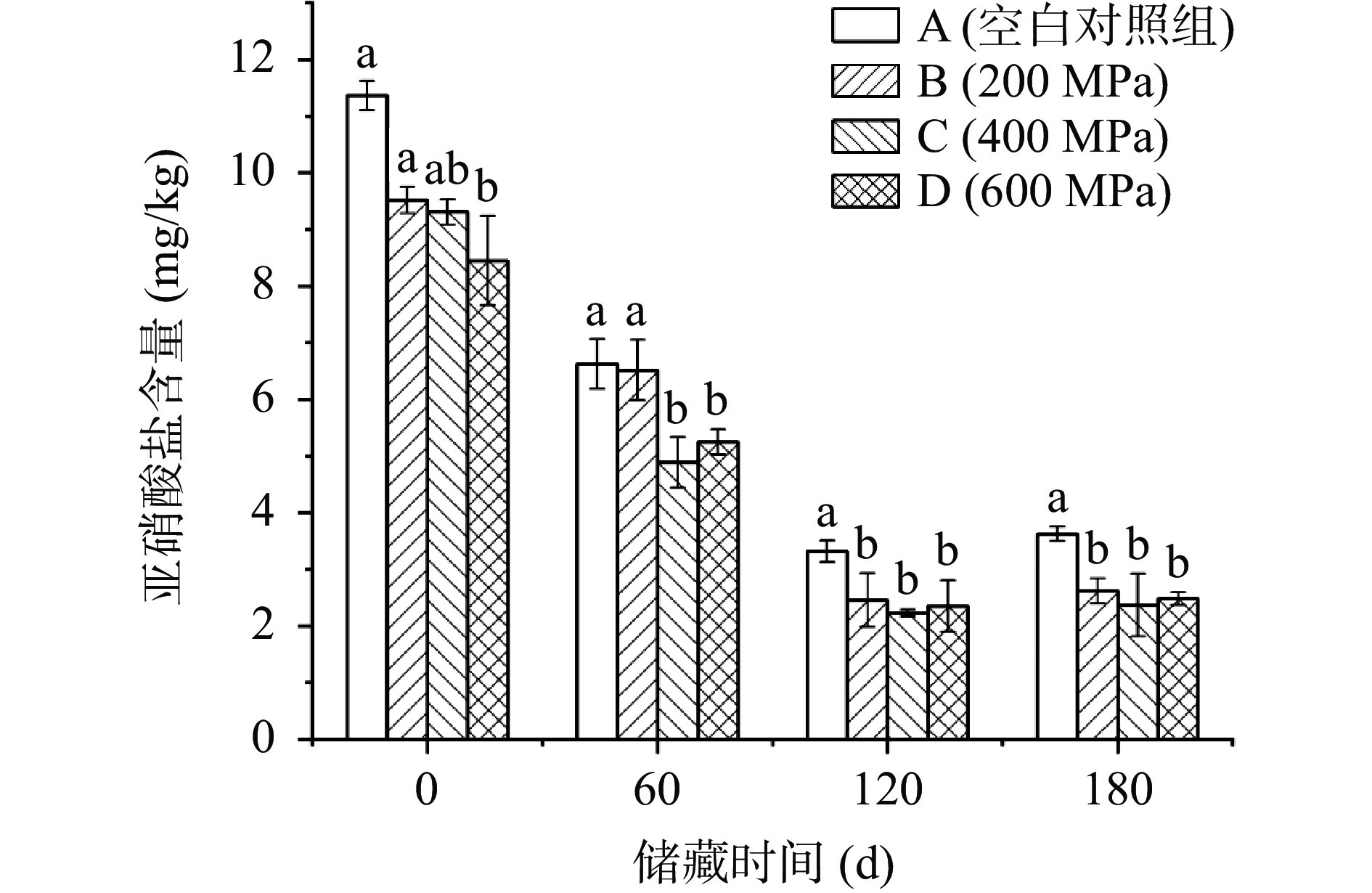
表 1 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的色泽变化Table 1. Color change of low-salt sliced bacon with different pressure treatments during the storage测定指标 储藏时间(d) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) L* 0 40.33±0.58b 40.67±0.58b 42.00±0.00a 42.67±0.58a 60 45.67±0.58a 43.33±1.53b 45.00±0.00ab 45.33±0.58a 120 42.00±0.00a 43.67±1.53a 43.33±0.58a 43.33±0.58a 180 38.67±0.58c 42.33±0.58ab 43.00±0.00a 42.00±0.00b a* 0 25.33±0.58a 25.00±0.00a 24.00±0.00b 23.00±0.00c 60 27.33±0.58a 25.33±0.58b 25.00±0.00b 25.00±0.00b 120 25.00±0.00b 26.67±0.58a 27.33±0.58a 24.33±0.58b 180 23.67±0.58b 25.67±0.58a 26.00±0.00a 24.00±0.00b b* 0 14.33±0.58a 13.00±0.00b 11.00±0.00c 11.33±0.58c 60 14.33±0.58a 13.00±0.00b 11.67±0.58c 12.67±0.58bc 120 14.00±0.00b 14.00±0.00b 14.33±0.58a 14.33±0.58a 180 14.00±0.00a 13.33±0.58a 13.33±0.58a 13.67±0.58a 注:相同储藏时间,不对实验组数据差异显著,P<0.05;表2同。 2.4 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉亚硝酸盐含量的影响
由图3可知,超高压显著降低了(P<0.05)低盐切片腊肉的亚硝酸盐含量,张鑫等[18]的研究也表明超高压会降低低盐牛肉乳化肠的亚硝酸盐含量,但各处理组之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。此外,四组样品的亚硝酸盐含量在储藏阶段呈先下降后上升的趋势,Wang等[19]也发现了类似规律,因为NO−2在肉类储藏过程中与各种组织成分如肌红蛋白、脂质、硫醇等发生反应,氧化为NO−3,导致亚硝酸盐含量的降低[20]。张隐等[21]的研究也同样表明,HPP处理抑制了微生物活性,从而导致亚硝酸盐含量下降。第180 d时,四组样品的亚硝酸盐含量均升高,这可能是由于某些有硝酸还原能力的微生物生长繁殖产生亚硝酸还原酶,导致亚硝酸盐含量增加。
2.5 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉质构的影响
由表2可知,第0 d时,随着压力的增大,低盐切片腊肉的硬度逐渐降低,对照组与B(200 MPa)差异不显著(P>0.05),与其余两组差异均显著(P<0.05);咀嚼性呈先降低后升高的趋势,D(600 MPa)与对照组差异显著(P<0.05)。咀嚼性是肌肉硬度、细胞间的凝聚力以及弹性等综合作用的结果,回复力和内聚性相关联且大致成正相关[22]。一方面,超高压处理使腊肉的肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白结合解离,肌肉的剪切力下降,肉质得到嫩化,硬度和咀嚼性都一定程度降低;另一方面压力使肌肉中的钙激活酶活性增加,加速了蛋白水解,导致肌肉成熟过程缩短[23]。而600 MPa时咀嚼性的大幅升高是因为此压力下腊肉弹性的显著增加。回复力、内聚性、弹性都随压力的增大而增大,因为蛋白质受压力的影响发生改变,变性后聚合形成凝胶结构,弹性和内聚性都得到提高[24−25];在更高压力时,二硫键的相互作用也可能是弹性增加的原因之一[26]。
表 2 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的质构变化Table 2. Texture changes of low-salt sliced bacon under different pressure during storage测定指标 储藏时间(d) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) 硬度(g) 0 4908.094±196.247a 4757.012±298.696a 3838.382±162.141b 3501.843±74.255b 60 5216.479±359.367a 4214.304±87.528b 5476.643±237.18a 5218.11±327.995a 120 5849.233±173.363a 4601.219±145.805b 5653.241±173.62a 4461.706±298.03b 180 5935.343±47.547a 5101.219±145.965b 5086.575±67.129b 5211.706±158.503b 咀嚼性 0 2877.558±157.222b 2779.559±87.55b 2328.924±152.461b 3697.234±170.504a 60 3583.955±220.446a 2886.862±220.147b 3473.017±277.379a 3374.731±231.841ab 120 4028.27±360.548a 2982.223±188.195b 3857.923±171.799a 3072.279±217.07b 180 3694.305±144.205a 3715.557±154.053a 3841.257±145.532a 3505.613±231.714a 弹性(%) 0 91.433±1.306b 91.573±2.122b 93.710±1.240b 98.943±5.747a 60 90.142±1.757a 90.742±2.712a 88.743±0.854a 91.413±1.947a 120 87.696±0.491b 93.907±2.779a 92.224±0.183a 92.286±0.291a 180 87.512±0.713b 91.028±4.038a 93.124±0.439a 91.952±0.362a 回复力 0 17.756±0.579c 17.879±0.722c 23.835±0.080b 31.455±1.732a 60 20.563±0.453c 21.973±0.578b 22.643±0.524b 26.755±0.345a 120 22.432±0.157b 21.109±0.749c 23.191±0.312b 28.914±0.427a 180 23.226±1.032ab 22.109±0.292c 23.722±0.656bc 25.022±0.314a 内聚性 0 0.657±0.002c 0.657±0.008c 0.699±0.009b 0.846±0.005a 60 0.693±0.004d 0.707±0.008c 0.721±0.001b 0.746±0.004a 120 0.700±0.010c 0.708±0.013bc 0.724±0.007b 0.809±0.002a 180 0.701±0.008c 0.713±0.008bc 0.727±0.007ab 0.738±0.020a 储藏期间,四组样品的硬度总体呈增长趋势,对照组的硬度始终高于各超高压组,这与腊肉水分含量的变化有关。除D(600 MPa)外,其余三组低盐切片腊肉样品的咀嚼性、回复力和内聚性在储藏期内大致都呈增长趋势,但变化量较小,这是因为过高压力会破坏细胞结构,降低持水性以及维持质构的能力。弹性是反映食品受外力作用变形后的恢复能力,与含水量、pH以及肌肉间的结合力大小有关[27]。对照组在储藏期间的弹性持续降低,超高压组无明显变化规律,但总体呈下降趋势。第180 d时,四组腊肉的弹性均小于初始值,B、C组变化量较小,这与水分含量的变化相关。
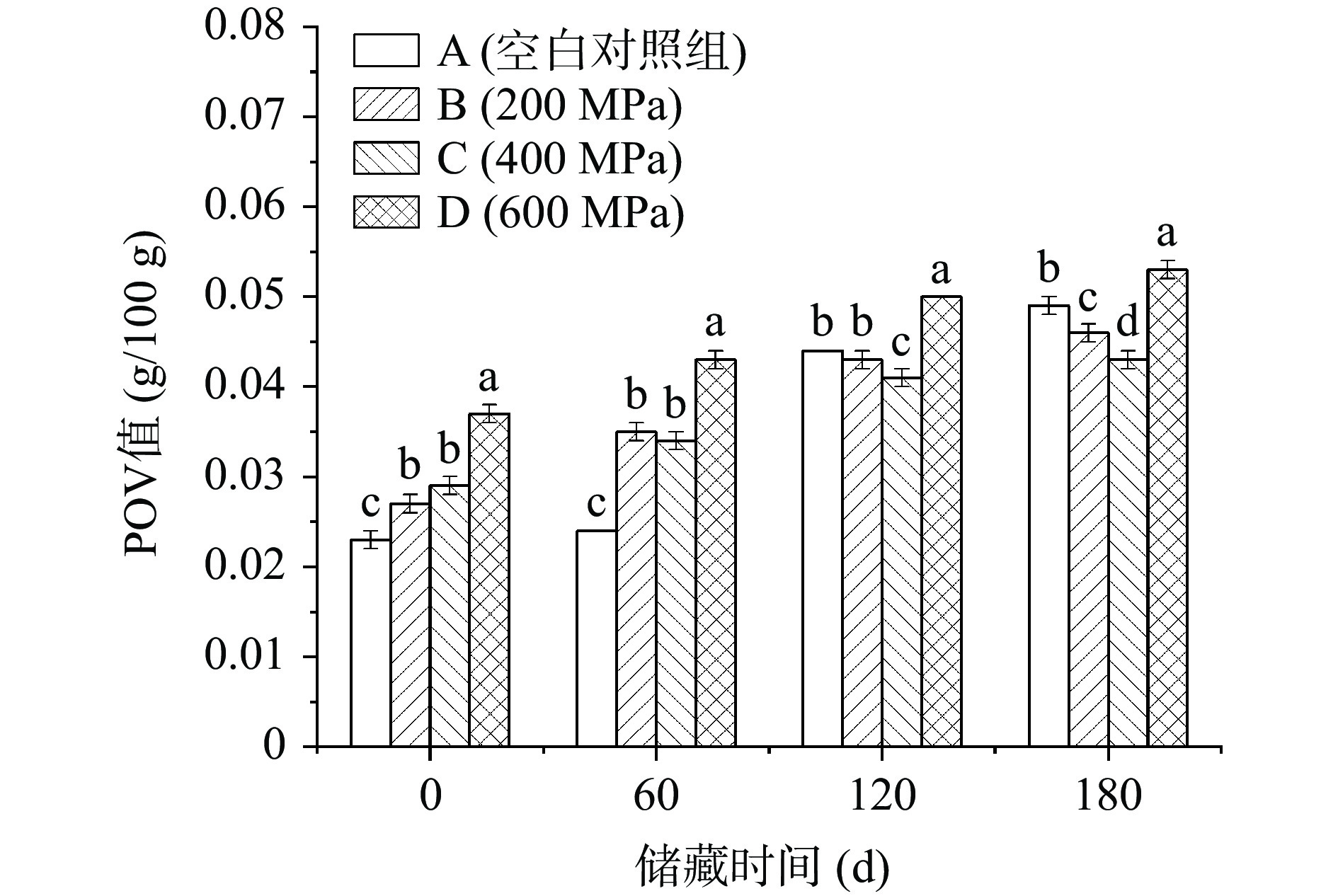
2.6 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉脂肪氧化的影响
图4显示,随压力的升高和储藏时间的增加,过氧化值呈上升趋势。第0 d时,超高压显著增加了(P<0.05)低盐切片腊肉的过氧化值,400 MPa前过氧化值增幅较小,高于此压力过氧化值迅速增大。研究表明[28],脂肪氧化是由色素蛋白构象发生改变所引起,导致具有催化作用的亚铁血红素基团暴露,或释放铁离子促进氧化过程;另一方面,压力还可能使铁蛋白中的铁离子游离出来,而高压又能促进Fe3+向氧化作用更强的Fe2+还原;更高压力处理时,氧化作用的加剧还可能与膜的破坏有关。储藏期间,四组低盐切片腊肉的POV值均呈上升趋势,但对照组的增长速率大于各超高压组。第180 d时,D组的POV值最大,其次是对照组。综上所述,超高压在杀菌过程中会加剧脂肪氧化,但由于抑制了微生物及酶活性[4],在储藏阶段则会延缓食品的氧化酸败。
2.7 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉菌落总数的影响
从表3可知,超高压对低盐切片腊肉的杀菌效果显著(P<0.05),其机理是高压破坏微生物的细胞壁、细胞膜及线粒体外膜,并且使蛋白质变性,生物酶失去活性,导致细菌的新陈代谢受阻[29]。储藏阶段,对照组的菌落总数及增长速率始终高于超高压组。第60 d前超高压组都未检出菌落。第180 d时,所有组的菌落总数均未超过国家标准,且超高压组的菌落总数维持在较低水平。综上所述,超高压可以有效抑制微生物的生长繁殖,且压力越高杀菌及抑菌效果越好。
表 3 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的菌落总数变化Table 3. Changes in the total number of colonies of low-salt sliced bacon with different pressure treatments during the storage储藏时间(d) 微生物总数(CFU/g) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) 0 2×102 0 0 0 60 3×102 0 0 0 120 7.5×103 8×102 1.5×102 1.2×102 180 8.75×104 1.35×103 6.75×102 3.5×102 2.8 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉风味物质的影响
如表4所示,第0 d时,A(空白对照组)、B(200 MPa)、C(400 MPa)、D(600 MPa)分别检出44、43、49、46种风味物质,其中醛类物质均占比最大,其次是酚类,烃类物质种数最多但含量占比较小;储藏至第180 d,分别检出52、56、56、63种风味物质,其中酚类物质均占比最大,其次是醛类,烃类物质依旧最多并且含量占比较初始时大幅增加。说明超高压杀菌对低盐切片腊肉的风味影响较小,储藏时间对腊肉风味的影响较大。
表 4 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的挥发性风味物质种类及相对含量Table 4. Types and relative contents of volatile flavor substances of low-salt sliced bacon at the storage stage with different pressure treatments化合物 挥发性物质种类 挥发性物质峰面积百分比(%) 0 d 180 d 0 d 180 d A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D 醛类 3 5 4 6 6 6 7 8 36.69 41.69 40.29 39.21 29.71 22.67 28.89 22.94 酚类 10 11 10 11 7 9 9 11 31.72 31.94 34.24 35.04 30.41 38.88 40.82 40.01 酮类 7 8 8 9 6 7 5 5 5.37 6.71 6.99 7.14 1.98 5.53 5.03 13.33 醇类 3 2 4 3 6 5 5 4 13.23 10.76 11.41 9.68 9.55 11.71 10.23 7.60 酯类 2 0 1 2 0 0 0 1 0.51 0 0.02 0.22 0 0 0 0.44 醚类 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 0.19 0.17 0.19 0.21 0.9 0.72 0.38 0.78 烃类 14 14 18 13 24 24 24 27 4.39 2.87 5.29 3.38 23.87 20.23 11.97 14.43 其他 4 2 3 1 1 3 5 5 7.90 5.87 1.57 5.12 3.59 0.27 2.68 0.47 合计 44 43 49 46 52 56 56 63 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 醛类大多来源于脂肪的氧化或降解,具有强烈的挥发性和脂肪香味,是腊肉风味的重要组成部分[30]。第0 d时,A、B、C、D分别检出醛类物质3、5、4、6种,分别占比36.69%、41.69%、40.29%、39.21%,超高压组略微升高但差异较小,其中含量占比最多的是糠醛,具有焦糖和烤面包香;其次是5-甲基呋喃醛;最末是壬醛,由油酸氧化产生,具有腊香、柑橘香、脂肪香及花香[31]。超高压组还检测出辛醛,赋予腊肉清香、叶香气味,癸醛使腊肉具有脂肪香气。在加工过程中产生的糠醛和5-甲基呋喃醛可能与苯丙氨酸的Strecker降解有关,Strecker降解一直被认为是风味产生的重要途经[32]。己醛是脂肪氧化的主要产物,但四组腊肉均未检出,说明超高压处理在一定程度上促进Strecker降解但无较强的促进脂肪氧化作用。储藏至第180 d,A、B、C、D分别检出醛类物质6、6、7、8种,分别占比29.71%、22.67%、28.89%、22.94%,较第0 d均大幅下降,其中下降最多的是糠醛,但A增加了3-糠醛;5-甲基呋喃醛、壬醛、辛醛、癸醛较第0 d均有所上升;均检测出己醛,标志着脂质氧化,在腊肉成熟阶段增添清香、木香及苹果香气,对腊肉整体风味有重要贡献[33]。
酚类物质是烟熏腊肉的重要风味成分,主要来源于烟熏材料的不完全燃烧,对腊肉风味的形成及抗氧化活性有重要贡献[34]。第0 d时,A、B、C、D分别检出酚类物质10、11、10、11种,分别占比31.72%、31.94%、34.24%、35.04%,超高压组略微升高但差异较小,其中含量最高的是愈创木酚,其次是2-甲氧基-5-甲基苯酚。四组样品均含有苯酚、2-甲基苯酚、2-甲氧基-5-甲基苯酚,赋予腊肉酚香味、烟熏气味;愈创木酚、4-乙基愈创木酚赋予腊肉药香、木香及烟熏味;丁香酚、反异丁香酚则增强腊肉的清甜香气。储藏至第180 d,除A组外,B、C、D所含的酚类物质较初始时均有所升高,分别占比30.41%、38.88%、40.82%、40.01%,并且成为低盐切片腊肉储藏后期的主要风味成分,赋予腊肉浓重的柏木烟熏味。其中含量最高的依然是愈创木酚,其次是2-甲氧基-5-甲基苯酚、苯酚、4-乙基愈创木酚,且超高压组的含量占比均大于对照组。综上所述,超高压对酚类物质的形成与降解影响较小,因而超高压组与对照组的烟熏风味接近。
酮类大多带有花果香和奶油香气,对烟熏腊肉的风味贡献小于醛类、酚类化合物,但对肉类风味的增强有一定的作用[35]。储藏前后超高压组的酮类物质含量占比均大于对照组。A、B、C在储藏期间的酮类物质含量均下降,但B、C变化量较小,D则显著上升,这与过高压力会促进脂肪的氧化有关。储藏前后所有组的主要醇类风味物质均为3-呋喃甲醇和柏木脑,超高压组和对照组风味相似,含量占比也较为接近。柏木脑天然存在于柏木油和桧叶油中,是柏木烟熏后的特征风味物质,其含量占比随压力的增大而增加,随储藏时间的延长而增加,表现为超高压后及储藏后烟熏风味突出。3-呋喃甲醇在储藏后所有组的含量占比均降低。超高压组在储藏后检测出4-乙基-1-辛炔-3-醇,赋予腊肉浓郁的脂香味。
烃类物质中的脂肪烃和芳香烃因阈值和沸点高而对腊肉整体风味贡献较小,烯烃类物质阈值较低,对香气有一定的影响[36]。储藏前后四组样品所含的主要烯烃为α-柏木烯、长叶烯、β-柏木烯、罗汉柏烯、花柏烯、花侧柏烯等,且储藏后均有所增加。这些物质主要来源于柏木油,超高压增强了腊肉的柏木烟熏味,储藏后风味更浓郁。呋喃类衍生物阈值低,是非常重要的呈味物质,主要来源于烟气和美拉德反应[37]。其中2-乙酰基呋喃占比最多,对腊肉风味有一定的影响。
综合分析可得,超高压组与对照组的风味成分相似,含量占比差异较小,储藏时间对风味物质的影响较大。腊肉的主要呈味物质—糠醛、5-甲基呋喃醛、愈创木酚、2-甲氧基-5-甲基苯酚等在超高压后都显著升高,储藏后超高压组的醛类物质占比降低,酚类物质占比升高,醇类变化较小;对照组的醛类、酚类、酮类和醇类占比均略微下降,说明超高压对腊肉风味的形成有促进和保护作用。各超高压组之间,除D储藏后所检出的酮类物质含量占比较高,与其余两组差异较大外,醛类、酚类、醇类等主要风味成分差异较小。
2.9 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉电子鼻分析的影响
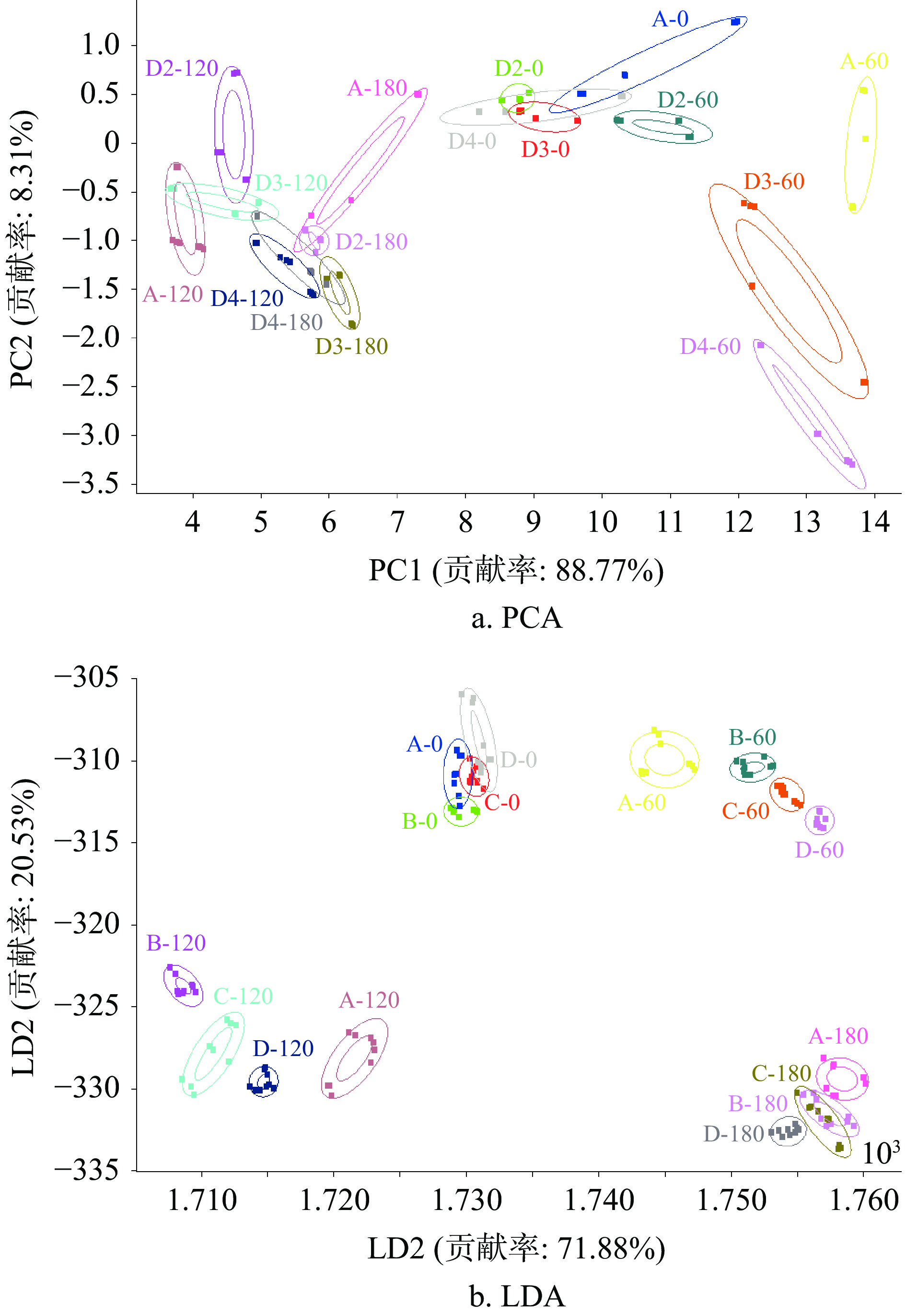
如图5所示,PCA分析中,PC1和PC2的方差贡献率分别为88.77%和8.31%,累计达97.08%,说明本PCA模型包含了大量反映样品整体的信息,且各样品间的差异主要体现在PC1。图中每个椭圆代表不同样品的数据采集点,可以看出第0 d的数据间均有重叠,说明PCA分析不能将样品区分开;第60 d的数据均分布于各自的独立区域,整体风味存在差异;第120 d与180 d的数据集中在一个区域,有部分重叠,但差异体现在PC1。这反映了超高压杀菌过程对腊肉风味影响较小,随着储藏时间的增加,腊肉整体风味差异先增大后减小。LDA分析图更加直观,LD1和LD2的贡献率分别为71.88%和20.53%,总计92.41%。与PCA分析相同,第0 d和第180 d时,四组数据均有部分重叠,说明LDA分析也不能将样品区分开;第60和120 d的数据各自独立分布,说明LDA分析能够有效区分此阶段的样品风味。综上所述,PCA和LDA均不能很好地将第0 d和第180 d的数据区分开,此阶段超高压组与对照组的挥发性风味成分相似,略有差异,与本实验GC-MS的分析相符。
2.10 不同压力对低盐切片腊肉感官评价的影响
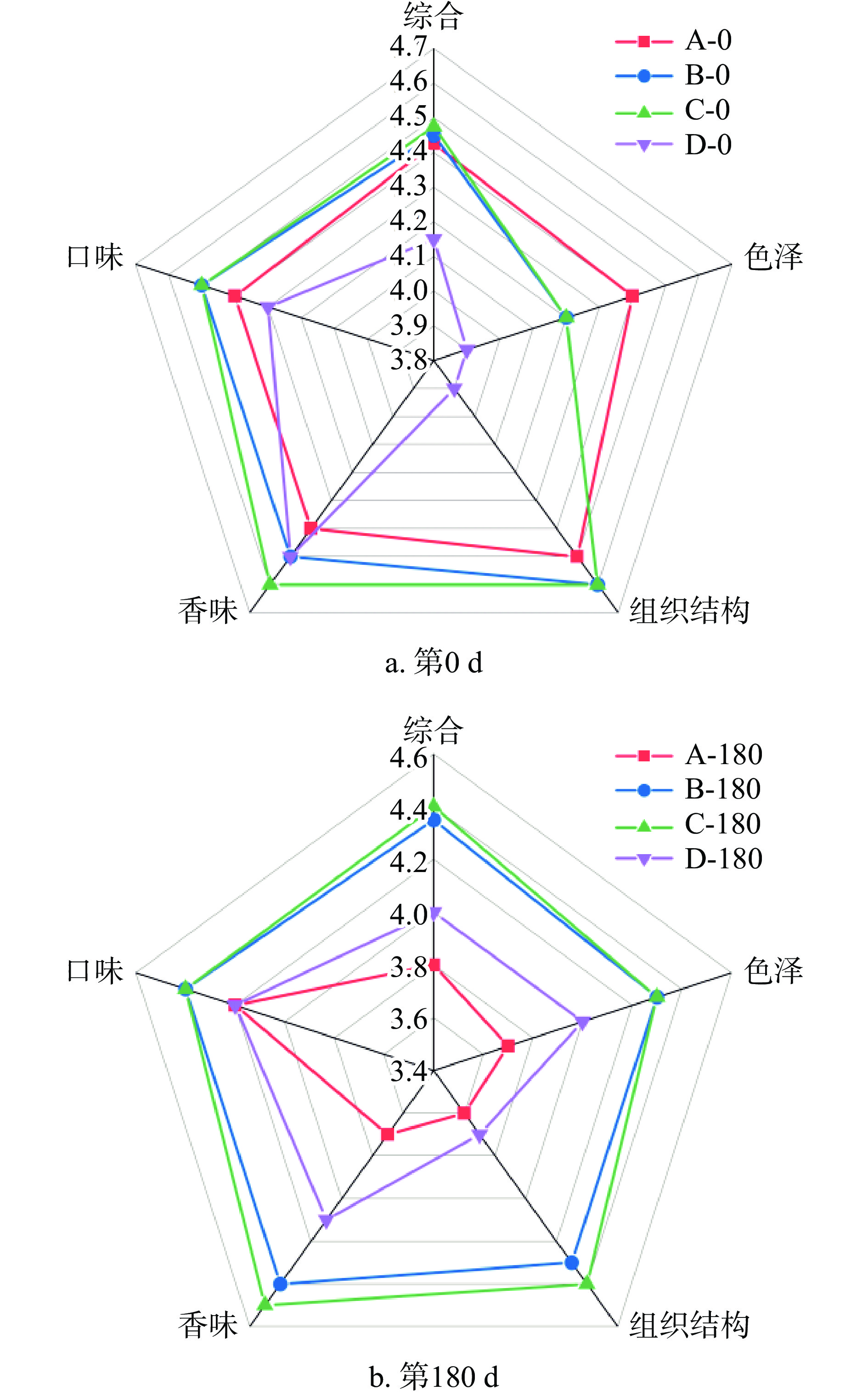
由于腊肉的保质期较长,且差异变化较小,故选择本实验储藏期的第0 d与最后一天对比分析,差异具有代表性(图6)。第0 d时,超高压组的肉色偏白,色泽评分低于对照组,D得分最低;组织结构方面,B、C肉质细嫩且富有弹性,评分较高,D过于软烂所以评分最低;四组腊肉香味方面差异较小,且超高压组的香味评分均高于对照组;口味方面所有组差异均较小。第180 d时,对照组的色泽、组织结构、香味评分大幅降低,超高压组的各指标评分变化较小。B、C的水分含量明显高于对照组,口感较好,组织结构评分较高;超高压组的肉色更加红亮且富有食欲,香气更加浓郁,所以色泽和香味评分均高于对照组。综合评分方面,第0 d时,D评分为4.2,A为4.4,B、C最高为4.5;第180 d时,A为3.8,D为4.0,B、C依旧评分最高为4.4。
3. 结论
超高压增强了低盐切片腊肉的持水性,减缓了储藏过程中的水分散失,但压力过高会破坏细胞结构导致保水性降低。加压过程导致腊肉蛋白质部分变性,L*升高、a*值降低,但储藏过程中超高压组的色泽保持较好,第180 d时,L*和a*值显著高于对照组。杀菌过程会促进脂肪氧化,导致POV值升高,但储藏过程中超高压组的脂肪氧化速度低于对照组,证实超高压可以延缓腊肉的脂肪氧化。高压还可以嫩化肉质,提高腊肉的弹性、内聚性及回复力,但压力过高会导致硬度过低,口感较差。杀菌方面,超高压对低盐切片腊肉的杀菌效果十分显著,后续的抑菌效果也较好,第180 d时菌落总数依旧处于较低水平。GC-MS和电子鼻分析均显示,超高压组与对照组风味差异较小,且超高压对腊肉风味的形成有促进和保护作用。综合分析,200、400 MPa组的样品在理化性质及风味方面优于600 MPa组,400 MPa组在风味及抑菌方面略优于200 MPa组,所以400 MPa为本研究的最佳超高压压力数值。
超高压杀菌对腊肉品质有着积极的影响,具有广阔的市场前景,为低盐高水分切片腊肉的研发及生产奠定了理论基础。但超高压技术应用于实际生产时,会面临许多现实问题,如装置的投入成本较高、批处理量少不便于流水线生产以及杀菌效果受原料特性、施压方式等因素影响,还需进一步深入探究。
-
表 1 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的色泽变化
Table 1 Color change of low-salt sliced bacon with different pressure treatments during the storage
测定指标 储藏时间(d) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) L* 0 40.33±0.58b 40.67±0.58b 42.00±0.00a 42.67±0.58a 60 45.67±0.58a 43.33±1.53b 45.00±0.00ab 45.33±0.58a 120 42.00±0.00a 43.67±1.53a 43.33±0.58a 43.33±0.58a 180 38.67±0.58c 42.33±0.58ab 43.00±0.00a 42.00±0.00b a* 0 25.33±0.58a 25.00±0.00a 24.00±0.00b 23.00±0.00c 60 27.33±0.58a 25.33±0.58b 25.00±0.00b 25.00±0.00b 120 25.00±0.00b 26.67±0.58a 27.33±0.58a 24.33±0.58b 180 23.67±0.58b 25.67±0.58a 26.00±0.00a 24.00±0.00b b* 0 14.33±0.58a 13.00±0.00b 11.00±0.00c 11.33±0.58c 60 14.33±0.58a 13.00±0.00b 11.67±0.58c 12.67±0.58bc 120 14.00±0.00b 14.00±0.00b 14.33±0.58a 14.33±0.58a 180 14.00±0.00a 13.33±0.58a 13.33±0.58a 13.67±0.58a 注:相同储藏时间,不对实验组数据差异显著,P<0.05;表2同。 表 2 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的质构变化
Table 2 Texture changes of low-salt sliced bacon under different pressure during storage
测定指标 储藏时间(d) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) 硬度(g) 0 4908.094±196.247a 4757.012±298.696a 3838.382±162.141b 3501.843±74.255b 60 5216.479±359.367a 4214.304±87.528b 5476.643±237.18a 5218.11±327.995a 120 5849.233±173.363a 4601.219±145.805b 5653.241±173.62a 4461.706±298.03b 180 5935.343±47.547a 5101.219±145.965b 5086.575±67.129b 5211.706±158.503b 咀嚼性 0 2877.558±157.222b 2779.559±87.55b 2328.924±152.461b 3697.234±170.504a 60 3583.955±220.446a 2886.862±220.147b 3473.017±277.379a 3374.731±231.841ab 120 4028.27±360.548a 2982.223±188.195b 3857.923±171.799a 3072.279±217.07b 180 3694.305±144.205a 3715.557±154.053a 3841.257±145.532a 3505.613±231.714a 弹性(%) 0 91.433±1.306b 91.573±2.122b 93.710±1.240b 98.943±5.747a 60 90.142±1.757a 90.742±2.712a 88.743±0.854a 91.413±1.947a 120 87.696±0.491b 93.907±2.779a 92.224±0.183a 92.286±0.291a 180 87.512±0.713b 91.028±4.038a 93.124±0.439a 91.952±0.362a 回复力 0 17.756±0.579c 17.879±0.722c 23.835±0.080b 31.455±1.732a 60 20.563±0.453c 21.973±0.578b 22.643±0.524b 26.755±0.345a 120 22.432±0.157b 21.109±0.749c 23.191±0.312b 28.914±0.427a 180 23.226±1.032ab 22.109±0.292c 23.722±0.656bc 25.022±0.314a 内聚性 0 0.657±0.002c 0.657±0.008c 0.699±0.009b 0.846±0.005a 60 0.693±0.004d 0.707±0.008c 0.721±0.001b 0.746±0.004a 120 0.700±0.010c 0.708±0.013bc 0.724±0.007b 0.809±0.002a 180 0.701±0.008c 0.713±0.008bc 0.727±0.007ab 0.738±0.020a 表 3 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的菌落总数变化
Table 3 Changes in the total number of colonies of low-salt sliced bacon with different pressure treatments during the storage
储藏时间(d) 微生物总数(CFU/g) A(空白对照组) B(200 MPa) C(400 MPa) D(600 MPa) 0 2×102 0 0 0 60 3×102 0 0 0 120 7.5×103 8×102 1.5×102 1.2×102 180 8.75×104 1.35×103 6.75×102 3.5×102 表 4 不同压力处理的低盐切片腊肉在储藏阶段的挥发性风味物质种类及相对含量
Table 4 Types and relative contents of volatile flavor substances of low-salt sliced bacon at the storage stage with different pressure treatments
化合物 挥发性物质种类 挥发性物质峰面积百分比(%) 0 d 180 d 0 d 180 d A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D 醛类 3 5 4 6 6 6 7 8 36.69 41.69 40.29 39.21 29.71 22.67 28.89 22.94 酚类 10 11 10 11 7 9 9 11 31.72 31.94 34.24 35.04 30.41 38.88 40.82 40.01 酮类 7 8 8 9 6 7 5 5 5.37 6.71 6.99 7.14 1.98 5.53 5.03 13.33 醇类 3 2 4 3 6 5 5 4 13.23 10.76 11.41 9.68 9.55 11.71 10.23 7.60 酯类 2 0 1 2 0 0 0 1 0.51 0 0.02 0.22 0 0 0 0.44 醚类 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 0.19 0.17 0.19 0.21 0.9 0.72 0.38 0.78 烃类 14 14 18 13 24 24 24 27 4.39 2.87 5.29 3.38 23.87 20.23 11.97 14.43 其他 4 2 3 1 1 3 5 5 7.90 5.87 1.57 5.12 3.59 0.27 2.68 0.47 合计 44 43 49 46 52 56 56 63 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 -
[1] SIMONIN H, DURANTON F, LAMBALLERIE M D. New insights into the high-pressure processing of meat and meat products[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science & Food Safety,2012,11(3):285−306.
[2] GARRIGA M , GRÈBOL N, AYMERICH M T, et al. Microbial inactivation after high-pressure processing at 600 MPa in commercial meat products over its shelf life[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2004, 5(4):451-457.
[3] 韩衍青, 张秋勤, 徐幸莲, 等. 超高压处理对烟熏切片火腿保质期的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(8):305−311. [HAN Y Q, ZHANG Q Q, XU X L, et al. Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on the shelf life of smoked sliced ham[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering,2009,25(8):305−311. HAN Y Q, ZHANG Q Q, XU X L, et al . Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on the shelf life of smoked sliced ham[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering,2009 ,25 (8 ):305 −311 .[4] 韩衍青, 孙新生, 刘登勇, 等. 应用超高压手段延长低温烟熏火腿的货架期[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(15):99−102. [HAN Y Q, SUN X S, LIU D Y, et al. Application of ultra-high pressure to extend the shelf life of low-temperature smoked ham[J]. Food Science,2011,32(15):99−102. HAN Y Q, SUN X S, LIU D Y, et al . Application of ultra-high pressure to extend the shelf life of low-temperature smoked ham[J]. Food Science,2011 ,32 (15 ):99 −102 .[5] 张云齐, 云周苗, 朱美淋, 等. 毛竹叶浸提浓缩液结合竹竿烟熏对腊肉风味品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(12):123−130. [ZHANG Y Q, YUN Z M, ZHU M L, et al. Effect of moso bamboo leaf extract concentrate combined with bamboo pole smoking on flavor quality of bacon[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(12):123−130. ZHANG Y Q, YUN Z M, ZHU M L, et al . Effect of moso bamboo leaf extract concentrate combined with bamboo pole smoking on flavor quality of bacon[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022 ,48 (12 ):123 −130 .[6] 刘芝君, 黄业传, 卿兰, 等. 茶多酚微胶囊对腊肉理化性质及挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(11):51−59. [LIU Z J, HUANG Y C, QING L, et al. Effect of tea polyphenol microcapsules on physicochemical properties and volatile flavor substances of bacon[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2020,41(11):51−59. LIU Z J, HUANG Y C, QING L, et al . Effect of tea polyphenol microcapsules on physicochemical properties and volatile flavor substances of bacon[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2020 ,41 (11 ):51 −59 .[7] 宋忠祥, 樊少飞, 付浩华, 等. 低盐液熏腊肉加工工艺优化及品质分析[J]. 肉类研究,2020,34(7):46−52. [SONG Z X, FAN S F, FU H H, et al. Optimization of low-salt liquid smoked bacon processing and quality analysis[J]. Meat Research,2020,34(7):46−52. SONG Z X, FAN S F, FU H H, et al . Optimization of low-salt liquid smoked bacon processing and quality analysis[J]. Meat Research,2020 ,34 (7 ):46 −52 .[8] 王洪伟, 索化夷, 张玉, 等. 感官评价和GC-MS结合偏最小二乘回归法分析酚类化合物对腊肉烟熏风味的贡献[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(21):244−249. [WANG H W, SUO H Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Sensory evaluation and GC-MS combined with partial least squares regression to analyze the contribution of phenolic compounds to the smoked flavor of bacon[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2019,45(21):244−249. WANG H W, SUO H Y, ZHANG Y, et al . Sensory evaluation and GC-MS combined with partial least squares regression to analyze the contribution of phenolic compounds to the smoked flavor of bacon[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2019 ,45 (21 ):244 −249 .[9] DASH K K, BALASUBRAMANIAM V M, KAMAT S. High pressure assisted osmotic dehydrated ginger slices[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2019,247(APR):19−29.
[10] 陈复生. 食品超高压加工技术[M]. 北京:化学业出版社, 2005. [CHEN F S. Food ultra-high pressure processing technology[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2005. CHEN F S. Food ultra-high pressure processing technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005.
[11] MARCOS B, MULLEN A M. High pressure induced changes in beef muscle proteome:Correlation with quality parameters[J]. Meat Science,2014,97(1):11−20. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.12.008
[12] GUÀRDIA E, MARTÍ J, PADRÓ J A, et al. Dynamics in hydrogen bonded liquids:Water and alcohols[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2002,96(none):3−17.
[13] 韩格, 秦泽宇, 张欢, 等. 超高压技术对低盐肉制品降盐机制及品质改良的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(13):312−319. [HAN G, QIN Z Y, ZHANG H, et al. Progress of research on salt reduction mechanism and quality improvement of low-salt meat products by ultra-high-pressure technology[J]. Food Sci,2019,40(13):312−319. HAN G, QIN Z Y, ZHANG H, et al . Progress of research on salt reduction mechanism and quality improvement of low-salt meat products by ultra-high-pressure technology[J]. Food Sci,2019 ,40 (13 ):312 −319 .[14] 周果, 杨文鸽, 崔燕, 等. 超高压处理对三疣梭子蟹感官及其肌原纤维蛋白生化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(23):269−274. [ZHOU G, YANG W G, CUI Y, et al. Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on sensory and biochemical properties of myogenic fibrin in Portunus trituberculatus[J]. Food Science,2017,38(23):269−274. ZHOU G, YANG W G, CUI Y, et al . Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on sensory and biochemical properties of myogenic fibrin in Portunus trituberculatus[J]. Food Science,2017 ,38 (23 ):269 −274 .[15] 王晓谦, 秦小明, 郑惠娜, 等. 超高压杀菌处理和热处理对香港牡蛎肉品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(11):93−100. [WANG X Q, QIN X M, ZHENG H N, et al. Effect of ultra-high-pressure sterilization treatment and heat treatment on the quality of Hong Kong oyster meat[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2015,41(11):93−100. WANG X Q, QIN X M, ZHENG H N, et al . Effect of ultra-high-pressure sterilization treatment and heat treatment on the quality of Hong Kong oyster meat[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2015 ,41 (11 ):93 −100 .[16] 张颖璐, 周敬阳, 徐倩倩, 等. 超高压对发酵兔肉干腌渍发色的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(7):120−125. [ZHANG Y L, ZHOU J Y, XU Q Q, et al. Study of ultra-high pressure on the color development of fermented rabbit dried meat marinade[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(7):120−125. ZHANG Y L, ZHOU J Y, XU Q Q, et al . Study of ultra-high pressure on the color development of fermented rabbit dried meat marinade[J]. Food Research and Development,2018 ,39 (7 ):120 −125 .[17] PERRETT S, ZHOU J M. Expanding the pressure technique:Insights into protein folding from combined use of pressure and chemical denaturants[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology,2002,1595(1-2):210−223. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(01)00345-4
[18] 张鑫, 闫玉雯, 朱迎春. 超高压处理对低盐牛肉乳化肠品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2021,35(10):2352−2360. [ZHANG X, YAN Y W, ZHU Y C. Effect of ultra-high pressure treatment on the quality of low-salt beef emulsified sausage[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2021,35(10):2352−2360. ZHANG X, YAN Y W, ZHU Y C . Effect of ultra-high pressure treatment on the quality of low-salt beef emulsified sausage[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2021 ,35 (10 ):2352 −2360 .[19] WANG Y L, LI F, ZHUANG H, et al. Effects of plant polyphenols and α-tocopherol on lipid oxidation, residual nitrites, biogenic amines, and N-nitrosamines formation during ripening and storage of dry-cured bacon[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,60(1):199−206. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.022
[20] MERLO T C, ANTONIO J C, SAVIAN T V, et al. Effect of the smoking using Brazilian reforestation woods on volatile organic compounds, lipid oxidation, microbiological and hedonic quality of bacons during shelf life[J]. Meat Science,2020,164:108110. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108110
[21] 张隐, 赵靓, 王永涛, 等. 超高压处理对泡椒凤爪微生物与品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(3):46−50. [ZHANG Y, ZHAO L, WANG Y T, et al. Effect of ultra-high-pressure treatment on microorganisms and quality of pickled pepper phoenix claws[J]. Food Sci,2015,36(3):46−50. ZHANG Y, ZHAO L, WANG Y T, et al . Effect of ultra-high-pressure treatment on microorganisms and quality of pickled pepper phoenix claws[J]. Food Sci,2015 ,36 (3 ):46 −50 .[22] DECKER E A, WELCH B. Role of ferritin as a lipid oxidation catalyst in muscle food[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,38(3):674−677.
[23] ANEMA S G. Effect of milk solids concentration on whey protein denaturation, particle size changes and solubilization of casein in high-pressure-treated skim milk[J]. International Dairy Journal,2008,18(3):228−235. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.08.009
[24] BAJOVIC B, BOLUMAR T, HEINZ V. Quality considerations with high pressure processing of fresh and value added meat products[J]. Meat Science,2012,92(3):280−289. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.04.024
[25] 卫永华, 刘永娟, 杨莉, 等. 超高压处理对乳清分离蛋白凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2018,44(8):203−210. [WEI Y H, LIU Y J, YANG L, et al. Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on the gel properties of whey isolate protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2018,44(8):203−210. WEI Y H, LIU Y J, YANG L, et al . Effect of ultrahigh-pressure treatment on the gel properties of whey isolate protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2018 ,44 (8 ):203 −210 .[26] SUN X D, RICHARD A H. High hydrostatic pressure effects on the texture of meat and meat products[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,75(1):17−23.
[27] 郝梦甄, 胡志和. 超高压和盐渍泡发处理海参的质构和功能成分比较研究[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(5):115−119. [HAO M Z, HU Z H. Comparative study on the textural and functional components of sea cucumbers treated with ultra-high pressure and salted soaking[J]. Food Science,2013,34(5):115−119. HAO M Z, HU Z H . Comparative study on the textural and functional components of sea cucumbers treated with ultra-high pressure and salted soaking[J]. Food Science,2013 ,34 (5 ):115 −119 .[28] 郭丽萍, 熊双丽, 黄业传, 等. 高压结合热处理对猪肉色泽及脂肪氧化的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(16):133−137. [GUO L P, XIONG S L, HUANG Y C, et al. Effect of high pressure combined with heat treatment on color and fat oxidation of pork[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2015,36(16):133−137. GUO L P, XIONG S L, HUANG Y C, et al . Effect of high pressure combined with heat treatment on color and fat oxidation of pork[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2015 ,36 (16 ):133 −137 .[29] 贾飞, 苗旺, 闫文杰, 等. 超高压处理对酱卤鸡腿品质及货架期的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2017,31(1):19−24. [JIA F, MIAO W, YAN W J, et al. Effect of ultra-high-pressure treatment on the quality and shelf life of soy-marinated chicken legs[J]. Meat Research,2017,31(1):19−24. JIA F, MIAO W, YAN W J, et al . Effect of ultra-high-pressure treatment on the quality and shelf life of soy-marinated chicken legs[J]. Meat Research,2017 ,31 (1 ):19 −24 .[30] MARUSIC N, VIDACEK S, JANCI T, et al. Determination of volatile compounds and quality parameters of traditional istrian dry-cured ham[J]. Meat Science,2014,96(4):1409−1416. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.12.003
[31] TANIMOTO S, KITABAYASHI K, FUKUSIMA C, et al. Effect of storage period before reheating on the volatile compound composition and lipid oxidation of steamed meat of yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata[J]. Fisheries Science,2015,81(6):1145−1155. doi: 10.1007/s12562-015-0921-4
[32] 张顺亮, 王守伟, 成晓瑜, 等. 湖南腊肉加工过程中挥发性风味成分的变化分析[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(16):215−219. [ZHANG S L, WANG S W, CHENG X Y, et al. Analysis of changes in volatile flavor components during the processing of Hunan bacon[J]. Food Science,2015,36(16):215−219. ZHANG S L, WANG S W, CHENG X Y, et al . Analysis of changes in volatile flavor components during the processing of Hunan bacon[J]. Food Science,2015 ,36 (16 ):215 −219 .[33] YU A N, SUN B G. Flavour substances of Chinese traditional smoke-cured bacon[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,89(2):227−233.
[34] YU A N, SUN B G, TIAN D T, et al. Analysis of volatile compounds in traditional smoke-cured bacon (CSCB) with different fiber coatings using SPME[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,110(1):233−238. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.040
[35] 周慧敏, 张顺亮, 郝艳芳, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS-O结合电子鼻对坨坨猪肉主体风味评价分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):218−226. [ZHOU H M, ZHANG S L, HAO Y F, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS-O combined with electron nose for flavor evaluation of Tuohuo pork main body[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):218−226. ZHOU H M, ZHANG S L, HAO Y F, et al . HS-SPME-GC-MS-O combined with electron nose for flavor evaluation of Tuohuo pork main body[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (2 ):218 −226 .[36] OLIVARES A, JOSÉ L N, MÓNICA F. Effect of fat content on aroma generation during processing of dry fermented sausages[J]. Meat Science,2011,87(3):264−273. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.10.021
[37] 唐静, 张迎阳, 吴海舟, 等. 传统腌腊肉制品挥发性风味物质的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(15):283−288. [TANG J, ZHANG Y Y, WU H Z, et al. Research progress of volatile flavor substances in traditional cured meat products[J]. Food Science,2014,35(15):283−288. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201415057 TANG J, ZHANG Y Y, WU H Z, et al . Research progress of volatile flavor substances in traditional cured meat products[J]. Food Science,2014 ,35 (15 ):283 −288 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201415057 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 武玫怡,焦文娟,赵甜甜,刘俊,周芳,刘伟峰,张业辉,南海军,陈晓瑛,黄利华. 高静水压与水煮处理对热带海参品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2025(01): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王素梅,孟少华,赵建生,赵琳,单吉祥,徐俊涛. 肉制品低钠策略及问题分析. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(07): 405-412 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵宇,丁甜,牛力源,沈默斐,孙宇豪,廖新浴. 自热食品品质提升与安全控制的研究进展. 包装工程. 2024(11): 118-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 周琪,张佳敏,王博,王卫,刘云鹤,钟正国. 肉制品风味形成机制及加工方式对风味影响的研究进展. 西华大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 74-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陶琦,钟飞,王志文,郑豪. 纳米材料在食品生产和保鲜中的应用. 包装学报. 2024(04): 89-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郭湘蕾,陈凌利,陈慧,于传龙,王文君. 预制菜生产过程关键加工技术研究进展. 食品科技. 2024(08): 64-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张顺君,王东亮,陈宏柱,汪雨晗,李新福. 超高压杀菌对酱卤肉制品贮藏期品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2023(12): 54-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



