Antioxidant Effects of Endogenous Components in Vegetable Oils
-
摘要: 本研究通过在复配植物油中添加不同的植物油内源性抗氧化物(生育酚、植物甾醇、多酚和角鲨烯),研究不同植物油内源性成分对植物油的抗氧化作用。采用Schaal烘箱加速实验,通过脂肪酸组成、酸价、过氧化值、茴香胺值、总氧化值等氧化稳定性指标的变化,评价内源性抗氧化物对复配油氧化稳定性的影响。结果表明,生育酚和多酚单独作用时抗氧化效果明显,且随浓度的增加而增强。生育酚和角鲨烯组合作用时,随着生育酚和角鲨烯浓度的升高,呈现先拮抗后协同效应,当生育酚含量大于480 mg/kg,角鲨烯的存在会显著提高生育酚的抗氧化能力(P<0.05)。从加速氧化的结果来看,未经预处理去除抗氧化成分的复配油脂肪酸组成只有微小的变化,经过预处理的复配油脂肪酸组成变化范围较大。经过预处理的复配油酸价和总氧化值在氧化前后的变化量也显著高于未经预处理的复配油(P<0.05),添加生育酚和多酚后,复配油的氧化稳定性得到提高,表明内源性抗氧化成分含量虽少,但对延缓植物油氧化过程起到了至关重要的作用。植物油中的主要内源性成分包括生育酚、植物甾醇、多酚和角鲨烯,其中生育酚和多酚起主要的抗氧化作用,同时内源性成分之间存在复杂的相互作用。该研究结果可为内源性抗氧化成分提高植物油氧化稳定性的应用提供参考依据。Abstract: Different endogenous components (tocopherols, phytosterols, polyphenols and squalene) of vegetable oils were added to compounded vegetable oils to investigate the antioxidant effects. Using a Schaal oven-accelerated experiment, the effects of endogenous antioxidants on the oxidative stability of compounded oils were examined by changes of fatty acid composition, acid value, peroxide value, anisidine value, and total oxidative value. The results demonstrated that the individual tocopherols and polyphenols showed a substantial antioxidant impact, and the antioxidant effect increased with concentration. As the concentrations of tocopherols and squalene increased, the combined of tocopherols and squalene showed antagonistic antioxidant effects and then synergistic effects, and the presence of squalene significantly increased the antioxidant capacity of tocopherols when the tocopherol content was greater than 480 mg/kg (P<0.05). The fatty acid composition of the compound oil without pretreatment to remove the antioxidant components changed only marginally as a result of accelerated oxidation, whereas the fatty acid content of the pretreated compound oil changed significantly. The degree of change in acid value and total oxidative value before and after oxidation was likewise much greater in pretreated compound oils than those in untreated compound oils (P<0.05). The addition of tocopherols and polyphenols increased the oxidative stability of the compound oils, demonstrating that the concentration of endogenous antioxidant components, while minor, played an important role in delaying the oxidation process of vegetable oils. Tocopherols, phytosterols, polyphenols, and squalene were the key endogenous components in vegetable oils, with tocopherols and polyphenols playing important antioxidant roles and complicated interactions between the endogenous components. The findings of this study can be used to guide the use of endogenous antioxidant components to increase the oxidative stability of vegetable oils.
-
Keywords:
- antioxidant /
- antioxidant interaction /
- vegetable oil /
- oxidative stability
-
食用植物油中的微量成分对植物油的营养价值和储存稳定性具有重要作用。生育酚是一种具有较高抗氧化活性的微量成分,Wen等[1]通过对多种植物油生育酚的种类和含量进行分析,发现植物油的种类对其生育酚的含量有很大影响。前期研究发现α-生育酚在高浓度时呈现出促氧化作用,但随着浓度的降低,变成了抗氧化作用,且在不同的油样中,存在着从促氧化作用到抗氧化作用的不同浓度拐点[2]。除生育酚外,多酚也具有很高的抗氧化活性,其中槲皮素和李子素是研究最广泛的多酚,槲皮素清除高活性自由基的能力可能与其潜在的有益健康作用有关[3]。Moudden等[4]使用多酚提取物作为天然抗氧化剂,明显延长了葵花油和菜籽油的贮藏期限。此外,植物油中含有丰富的β-谷甾醇、豆甾醇和角鲨烯,对脂质过氧化也有很强的抑制作用。Shi等[5]的研究显示玉米油和菜籽油的植物甾醇含量高于大豆油、葵花籽油和山茶油,其中山茶油的植物甾醇含量最低。在橄榄油的热诱导氧化过程中观察到角鲨烯的浓度依赖性抗氧化活性[6]。早期研究表明角鲨烯自由基氧化的主要产物为环状二氢过氧化物[7],近期研究显示其主要产物为醇和环氧化物[8]。
目前对于植物油内源性抗氧化成分的研究多集中在单一抗氧化成分的抗氧化作用或理想介质中的抗氧化相互作用。Cheng等[9]通过自由基清除能力和氧化稳定指标研究了多酚对亚麻籽油乳液氧化稳定性的影响,结果表明多酚可以提高亚麻籽油纳米乳液的稳定性。张莉莎等[10]研究发现α-生育酚和γ-谷维素在乙酸乙酯介质中存在拮抗作用。已有研究表明抗氧化成分在单纯溶剂介质和油脂介质中的抗氧化相互作用及机理不尽相同[11]。因此油脂中抗氧化成分的相互作用不能完全通过单纯溶剂介质的结果来反映,有必要进一步研究植物油介质中抗氧化成分的相互作用。
评估植物油的氧化程度的指标包括氧化稳定性指数、脂肪酸组成、酸价、过氧化值、茴香胺值、总氧化值等。通过Rancimat法测得的氧化稳定性指数被广泛用于研究油脂的氧化稳定性[12−13]。Li等[14]证明了大豆油的氧化稳定性指数与加热温度和时间无关。脂肪酸组成显著影响植物油的自动氧化,Multari等[15]发现油酸含量高的植物油比油酸含量低的大豆油在短期油炸过程中的氧化稳定性好。此外,根据过氧化值和茴香胺值计算的总氧化值也是表征油脂氧化程度的重要指标。朱雪梅等[16]使用Schaal烘箱氧化实验,加速氧化期间定期测定植物油总氧化值的变化来评估油脂的氧化程度。
本实验通过向预处理去除抗氧化成分的复配油样中添加不同浓度和比例的生育酚、植物甾醇、多酚和角鲨烯,以氧化稳定性指数和DPPH自由基清除能力为指标,并使用Bliss模型来研究主要内源性抗氧化成分在复配油脂介质中的单独抗氧化能力和相互作用类型,同时采用Schaal烘箱加速实验,通过脂肪酸组成、酸价、过氧化值、茴香胺值、总氧化值等氧化稳定性指标的变化,评价复配油的氧化稳定性,从而找出有效的抗氧化成分组合,为植物油精炼过程中适度保留内源性抗氧化成分提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
棕榈液油(天津聚龙)、玉米油(益海嘉里)、菜籽油(上海多力)、高油酸葵花籽油(上海日清)、芝麻油(河南三诚)、椰子油(海南冷榨) 江西南昌当地超市;标准脂肪酸甲酯(FAME,GLC-463) 美国NuChek-Prep公司;福林酚试剂、没食子酸、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、α-生育酚、γ-生育酚、菜油甾醇、豆甾醇、β-谷甾醇、角鲨烯、咖啡酸等标准品 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;甲醇、正己烷、乙腈和异丙醇 色谱纯,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;其他溶剂为分析纯。
OSI-24型油脂氧化稳定性测定仪 美国Omnion公司;6890N型气相色谱仪、Agilent 1100型高效液相色谱仪、Agilent 6890N气相色谱质谱联用仪 美国安捷伦公司;DSY-Ⅲ型氮吹仪 北京金科精华苑科技有限公司;AR1140电子分析天平 美国奥豪斯贸易公司;HH4型恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司;TDL-5-A 高速离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;RE52-4旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣玻璃仪器厂;DHG-9035A鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;EXL800 全自动酶标仪 美国 Biotek Instruments公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品预处理
使用棕榈液油、椰子油、高油酸葵花籽油、菜籽油、芝麻油、玉米油进行油脂的复配,以饱和脂肪酸和不饱和脂肪酸2:3的比例为条件,经MATLAB规划求解,得到脂肪酸组成类似但内源性抗氧化成分含量不同的复配油,用于研究抗氧化成分在复杂的油脂基质中的作用,复配油的配制比例如表1所示。按照Waraho等[17]的方法预处理复配油,采用柱层析法去除抗氧化成分。层析柱内径3 cm,高35 cm,填料使用硅胶和活性炭(共三层,最底层是22.5 g硅胶,中间层6 g活性炭,最上层22.5 g硅胶)。
表 1 复配油的配制比例Table 1. Confection proprotion of compound oil复配油 高油酸
葵花籽油(%)菜籽油
(%)芝麻油
(%)玉米油
(%)棕榈液油
(%)椰子油
(%)TH 3.91 37.22 1.97 19.14 2.79 34.95 TL 8.08 25.72 5.88 22.09 4.72 33.51 1.2.2 样品准备
参照Liu等[18]的方法,将生育酚(α-生育酚:γ−生育酚=1:1)、植物甾醇(菜油甾醇:豆甾醇:β-谷甾醇=1.6:1:1.6)、角鲨烯和咖啡酸标准品用乙酸乙酯制备成储备液,最终浓度分别为2000、10000、1000和200 mg/kg,按照表2和表3的组成和浓度回添进预处理去除抗氧化成分后的复配油中。
表 2 抗氧化成分回添到预处理油样中的浓度Table 2. Concentration of antioxidant components added back to the purified oil sample抗氧化成分 浓度(mg/kg) 生育酚(α-生育酚:γ-生育酚=1:1) T1 160 T2 320 T3 480 T4 640 T5 800 角鲨烯 S1 40 S2 80 S3 120 S4 160 S5 200 多酚(咖啡酸) P1 24 P2 48 P3 72 P4 96 P5 120 植物甾醇(菜油甾醇:豆甾醇:β-谷甾醇=
1.6:1:1.6)Ph1 1200 Ph2 2400 Ph3 3600 Ph4 4800 Ph5 6000 表 3 抗氧化成分以混合物形式回添到预处理油样中的组成Table 3. Composition of antioxidant components added back to the purified oil sample in the form of a mixture组合 混合物 浓度
(mg/kg)总浓度
(mg/kg)生育酚+角鲨烯 M1 T1+S1 160+40 200 M2 T1+S3 160+120 280 M3 T1+S5 160+200 360 M4 T3+S1 480+40 520 M5 T3+S3 480+120 600 M6 T3+S5 480+200 680 M7 T5+S1 800+40 840 M8 T5+S3 800+120 920 M9 T5+S5 800+200 1000 植物甾醇+多酚 M1 Ph1+P1 1200+24 1224 M2 Ph1+P3 1200+72 1272 M3 Ph1+P5 1200+120 1320 M4 Ph3+P1 3600+24 3624 M5 Ph3+P3 3600+72 3672 M6 Ph3+P5 3600+120 3720 M7 Ph5+P1 6000+24 6024 M8 Ph5+P3 6000+72 6072 M9 Ph5+P5 6000+120 6120 生育酚+植物甾醇 M1 T1+Ph1 160+1200 1360 M2 T1+Ph3 160+3600 3760 M3 T1+Ph5 160+6000 6160 M4 T3+Ph1 480+1200 1680 M5 T3+Ph3 480+3600 4080 M6 T3+Ph5 480+6000 6480 M7 T5+Ph1 800+1200 2000 M8 T5+Ph3 800+3600 4400 M9 T5+Ph5 800+6000 6800 多酚+角鲨烯 M1 P1+S1 24+40 64 M2 P1+S3 24+120 144 M3 P1+S5 24+200 224 M4 P3+S1 72+40 112 M5 P3+S3 72+120 192 M6 P3+S5 72+200 272 M7 P5+S1 120+40 160 M8 P5+S3 120+120 240 M9 P5+S5 120+200 320 生育酚+多酚 M1 T1+P1 160+24 184 M2 T1+P3 160+72 232 M3 T1+P5 160+120 280 M4 T3+P1 480+24 504 M5 T3+P3 480+72 552 M6 T3+P5 480+120 600 M7 T5+P1 800+24 824 M8 T5+P3 800+72 872 M9 T5+P5 800+120 920 植物甾醇+角鲨烯 M1 Ph1+S1 1200+40 1240 M2 Ph1+S3 1200+120 1320 M3 Ph1+S5 1200+200 1400 M4 Ph3+S1 3600+40 3640 M5 Ph3+S3 3600+120 3720 M6 Ph3+S5 3600+200 3800 M7 Ph5+S1 6000+40 6040 M8 Ph5+S3 6000+120 6120 M9 Ph5+S5 6000+200 6200 1.2.3 脂肪酸组成的测定
根据Zeng等[19]的方法对油样进行甲酯化,处理后的样品使用配备FID检测器、CP-Sil 88熔融石英毛细管柱(CP7489,100 m×0.25 mm×0.2 μm)的Agilent 6890N气相色谱分析,色谱条件与文献[19]方法一致。
1.2.4 生育酚含量的测定
根据曾俊鹏[20]的方法稍作修改。称取1.0 g左右的植物油样,正己烷定容到10 mL。通过0.22 μm的有机相滤膜后,用Agilent 1100高效液相色谱仪(带有VWD检测器)进行检测。HPLC测定条件:进样量10 μL,色谱柱Elite Hypersil ODS2(4.6 mm×150 mm×5 μm),流动相为甲醇/水(98:2,v/v),流速0.8 mL/min,柱温室温,检测波长为292 nm。
1.2.5 总酚含量的测定
对Ahmed等[21]的Folin-Ciocalteu方法稍作调整测定。称取2.0 g油样用1 mL正己烷和2 mL 80%的甲醇萃取三次,然后合并提取液。取1 mL的提取液转移到10 mL容量瓶中,然后加入2 mL去离子水和0.5 mL福林酚试剂。3 min后,向反应混合物中加入1.5 mL的1%(w/v)碳酸钠溶液。1 h后,与空白对照,在765 nm处测量吸光度。结果用mg GAE/kg表示。
1.2.6 植物甾醇含量的测定
根据Zhang等[22]和Shi等[23]的方法对油样进行预处理,取0.25 g油样进行皂化处理,提取不皂化物进行衍生化反应1 h。处理后的样品使用配备Agilent DB-5HT毛细管柱(30 m×320 mm×0.10 μm)的Agilent 6890N气相色谱分析,色谱条件参考曾俊鹏[20]的方法。
1.2.7 角鲨烯含量的测定
参照马力等[24]的方法,稍作修改。样品采用硅胶柱提纯处理,用Agilent 1100高效液相色谱仪(带有DAD检测器)进行检测。HPLC测定条件:进样量10 μL,色谱柱Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm×5 μm),流动相为乙腈/甲醇(40:60,v/v),流速1 mL/min,柱温40 ℃,检测波长为210 nm。
1.2.8 氧化稳定性指数(Rancimat法)测定
氧化稳定性指数的测定根据Becker等[25]和Liu等[18]的方法稍作修改。氧化诱导期IP是用美国OSI型油脂氧化稳定性测定仪在120 ℃和10 L/h的气流下进行测定。最终结果以额外诱导期aIP(h)表示:
aIP=IP(添加抗氧化剂)−IP(去除抗氧化剂) 根据对添加不同组合抗氧化剂的油样的测量,可以确定可能的相互作用。
若出现以下情况,则呈现协同作用:
aIP组合抗氧化剂(1+2) > aIP抗氧化剂(1)+aIP抗氧化剂(2) 当相等时,表示存在相加效应;当小于时,表示存在拮抗效应。上述评价方法中的理论值和实验值在数学上需要有统计上的差异。
1.2.9 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
1.2.9.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定
按照Liu等[18]的方法测定,稍作修改。用乙酸乙酯制备0.2 mmol/L DPPH·溶液,取0.10 g油样,加入4 mL乙酸乙酯制成样品溶液。取2 mL样品溶液与2 mL DPPH·溶液混合,放置暗处反应30 min后于517 nm处测定吸光度。实验清除能力(ESC)由以下公式计算:
ESC(%)=(1−Ai−AjA0)×100 其中,A0、Ai、Aj分别为2 mL乙酸乙酯+2 mL DPPH·溶液、2 mL样品溶液+2 mL DPPH·溶液以及2 mL样品溶液+2 mL乙酸乙酯的吸光度值。
1.2.9.2 抗氧化剂混合物的协同效应(SE)的计算
理论清除能力(TSC)被定义为混合物中每种等摩尔物质的单独清除能力之和[26],公式如下:
TSC混合物=ESCA+ESCB−ESCA×ESCB100 其中,ESCA和ESCB是混合物中各个化合物的ESC值。二元混合物的协同效应(SE)被定义为实验值除以理论值,它可以在数学上表示为:
SE=ESC混合物TSC混合物 如果SE>1,就意味着混合物呈现协同效应;如果SE<1,就是拮抗效应;而SE=1则显示为加成效应。根据实验清除值和理论清除值之间的显著差异(P<0.01),来确定协同、拮抗或加成效应。
1.2.10 植物油氧化指标的测定
复配油的酸价和过氧化值分别采用GB 5009.229-2016(热乙醇指示剂滴定法)和GB 5009.227-2016(滴定法)测定,茴香胺值采用GB/T 24304-2009的方法测定。
1.2.11 Schaal烘箱加速氧化实验
植物油置于带盖玻璃瓶中,稍加盖好,放入62±1 ℃恒温烘箱中连续加热氧化25 d,每12 h摇匀一次,并随即更换位置。每5 d取适量氧化油分析测定。
1.3 数据处理
样品平行测定三次,数值以均值±标准偏差(mean±SD)表示。统计学差异采用单因素ANOVA分析中的Duncan方法,P<0.05表示数据间有显著性差异,所有的数据通过SPSS 26.0软件进行分析比较,使用Origin 2019b作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 预处理对样品脂肪酸组成和内源性抗氧化成分的影响
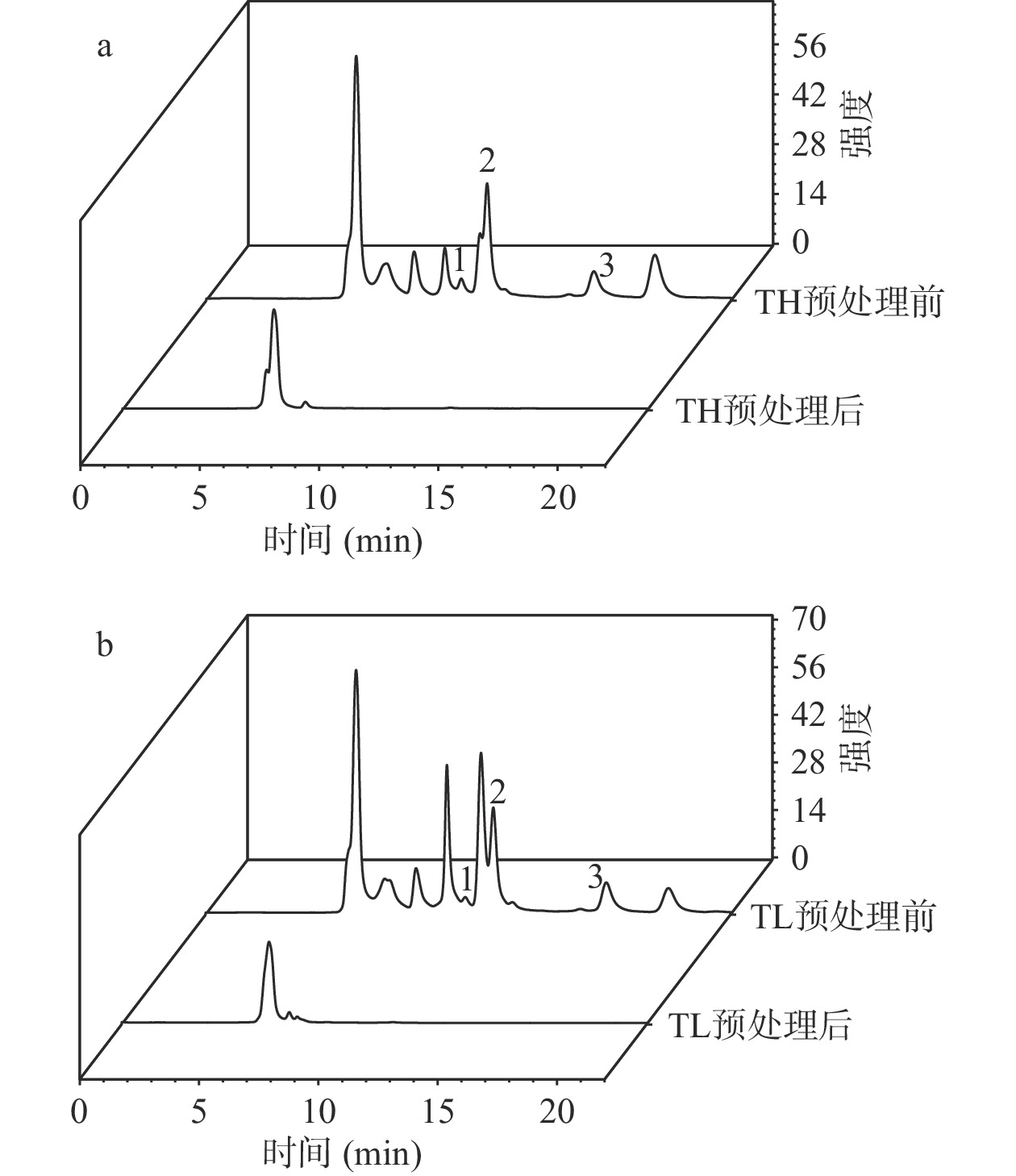
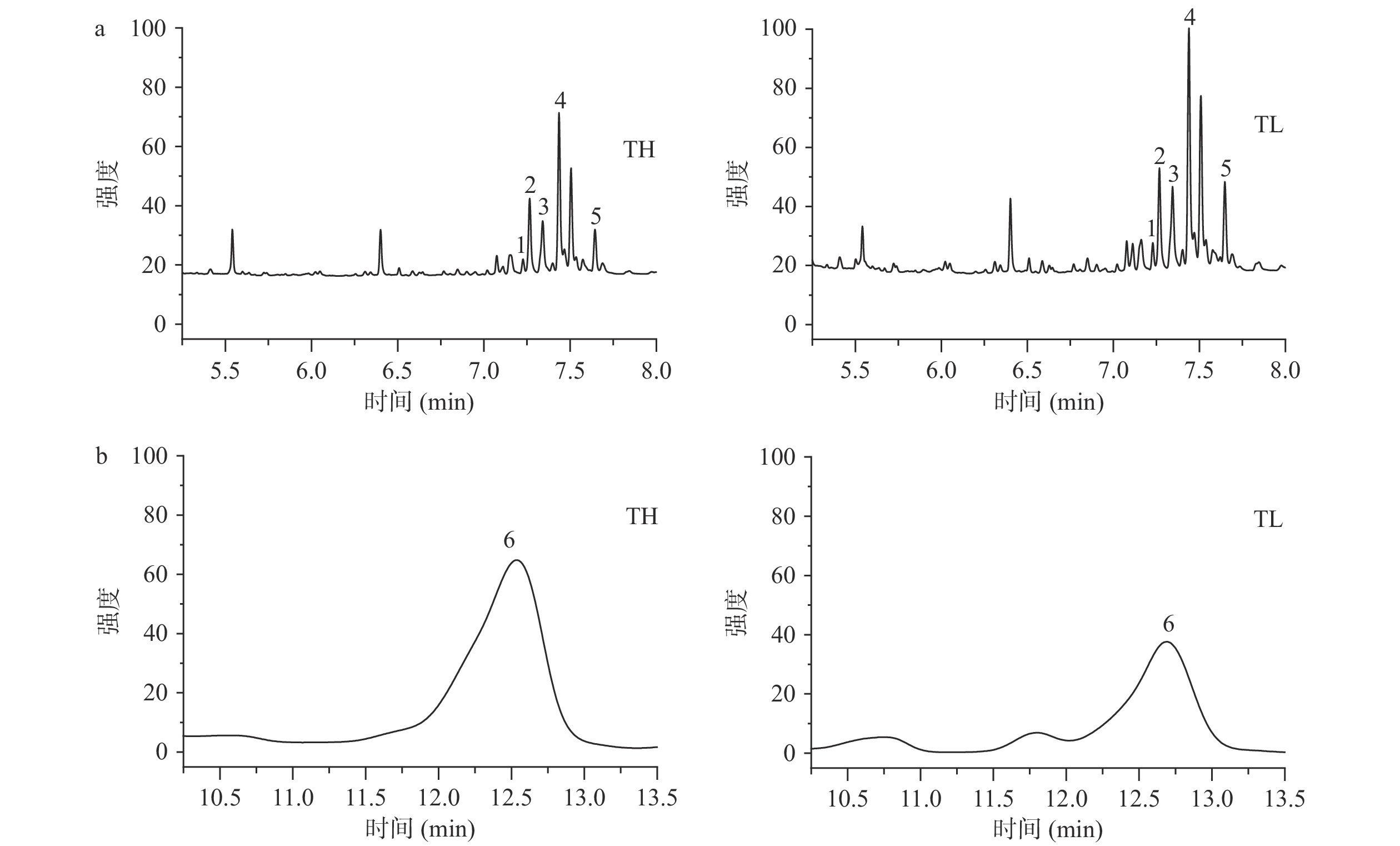
表4为预处理前后复配油的脂肪酸组成。从表4中可以看出,TH和TL的饱和脂肪酸(SFA)和单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA)含量之间无显著性差异(P>0.05),TH的n-6与n-3多不饱和脂肪酸的比值(n-6/n-3PUFA)显著低于TL(P<0.05),预处理前后复配油的脂肪酸组成无显著性差异(P>0.05)。图1和图2为样品中生育酚、植物甾醇和角鲨烯色谱图。表5为预处理前后复配油的主要内源性抗氧化成分含量。图1a和图1b显示预处理前复配油中含有一定含量的生育酚,预处理后复配油中则无法检测到相应的峰。从表5中可以看出,预处理前TH的α-生育酚、菜油甾醇、豆甾醇和总酚含量显著高于TL(P<0.05),γ-生育酚、β-谷甾醇和角鲨烯含量显著低于TL(P>0.05),预处理后α-生育酚、γ-生育酚和总酚含量均未检测出,植物甾醇和角鲨烯含量在预处理前后有显著性差异(P<0.05)。说明使用柱层析法对脂肪酸组成影响不大,且可以有效去除油中的内源性抗氧化成分。
表 4 预处理前后复配油的脂肪酸组成比较(总脂肪酸的百分比)Table 4. Comparison of fatty acid composition of compounded oils before and after the pretreatment (percentage of total fatty acids)脂肪酸(%) TH TL 预处理前 预处理后 预处理前 预处理后 C8:0 0.50±0.09 0.55±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.05±0.01 C10:0 1.52±0.15 1.66±0.02 1.00±0.13 1.06±0.11 C11:0 0.15±0.03 0.16±0.00 nd nd C12:0 16.45±0.21 16.31±0.05 16.50±0.52 16.50±0.78 C14:0 6.71±0.06 6.92±0.30 7.06±0.12 7.05±0.07 C16:0 8.57±0.01 8.66±0.13 10.99±0.19 10.88±0.24 C18:0 4.77±0.07 4.44±0.01 3.97±0.13 4.05±0.12 9c-C18:1 32.53±0.38 32.76±0.13 34.24±0.54 33.83±0.11 11c-C18:1 2.00±0.17 1.85±0.03 0.53±0.08 0.51±0.05 9c12c-C18:2n-6 21.53±0.33 21.18±0.23 22.65±1.02 23.04±1.17 C20:0 0.54±0.18 0.66±0.01 nd nd 8c-C20:1 0.06±0.01 0.06±0.00 nd nd 11c-C20:1 1.67±0.04 1.67±0.02 1.01±0.07 0.98±0.09 C18:3n-3 2.58±0.20 2.68±0.06 1.96±0.10 1.97±0.10 C22:0 0.23±0.00 0.23±0.00 nd nd C20:3n-6 nd nd nd nd C22:1n-9 0.07±0.00 0.11±0.01 0.07±0.01 0.07±0.02 C20:5n-3 nd nd nd nd C24:0 0.10±0.00 0.09±0.00 nd nd C22:3n-3 0.01±0.00 0.00±0.00 nd nd ∑SFA 39.55±0.66a 39.69±0.37a 40.00±0.76a 39.59±1.30a ∑MUFA 36.34±0.53a 36.45±0.08a 35.92±0.93a 35.40±0.23a ∑PUFA 24.11±0.13a 23.86±0.29a 24.08±0.17a 25.01±1.07a ∑n-3PUFA 2.58±0.20a 2.68±0.06a 2.01±0.01b 1.97±0.10b ∑n-6PUFA 21.53±0.33ab 21.18±0.23b 22.07±0.16ab 23.04±1.17a n-6/n-3PUFA 8.37±0.78b 7.90±0.08b 10.96±0.02a 11.74±1.21a 注:每个样品平行分析测定三次,数据以mean±SD的形式表达;不同小写字母表示不同复配油预处理前后的脂肪酸组成存在显著性差异(P<0.05);nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);SFA,饱和脂肪酸;MUFA,单不饱和脂肪酸;PUFA,多不饱和脂肪酸;n-3PUFA,n-3多不饱和脂肪酸;n-6PUFA,n-6多不饱和脂肪酸;n-6/n-3PUFA,n-6与n-3多不饱和脂肪酸的比值。 表 5 预处理前后复配油的抗氧化成分含量比较Table 5. Comparison of antioxidant content of compounded oils before and after the pretreatment抗氧化成分含量(mg/kg) TH TL 预处理前 预处理后 预处理前 预处理后 α-生育酚 270.68±2.98a nd 125.53±4.80b nd γ-生育酚 266.67±5.69b nd 307.48±4.92a nd 菜油甾醇 1694.34±23.13a 1090.36±12.19c 1457.68±9.36b 728.09±19.65d 豆甾醇 995.89±20.33a 474.99±6.23c 688.60±16.30b 282.32±25.21d β-谷甾醇 1613.65±28.36b 994.79±20.90c 1692.71±30.68a 695.79±12.68d 角鲨烯 544.21±3.41b 254.11±7.90d 566.93±18.69a 357.83±25.35c 总酚 61.21±1.39a nd 49.79±2.79b nd 注:nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);不同小写字母表示不同复配油预处理前后的抗氧化成分含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.2 样品中主要抗氧化成分的抗氧化能力
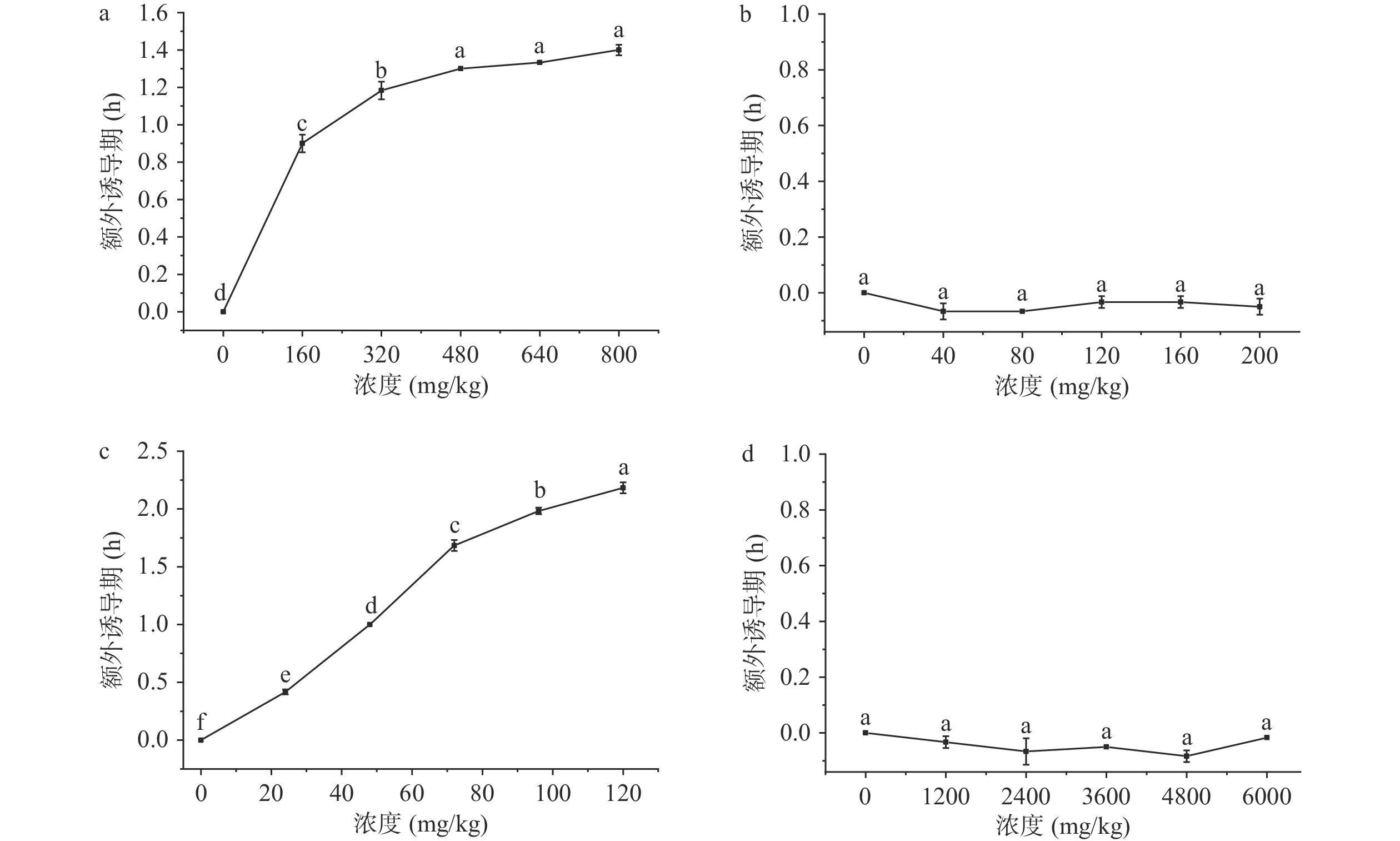
通过Rancimat试验和DPPH自由基清除率试验测定了内源性抗氧化成分的抗氧化能力。图3为通过Rancimat试验测定的单一抗氧化剂作用时的抗氧化效果,从图中可以看出,在160~800 mg/kg的浓度范围内,生育酚的最小氧化诱导期为4.43 h,最大氧化诱导期有4.93 h,预处理后复配油的氧化诱导期只有3.53 h。这说明生育酚在延长复配油的氧化稳定性方面起着积极作用。当生育酚浓度低于480 mg/kg时,增加生育酚浓度可以显著提高复配油的氧化诱导期,浓度在480~800 mg/kg的范围内时,继续增加生育酚浓度对氧化诱导期的延长没有起到显著作用。这与Liu等[18]研究α-生育酚在米糠油中的抗氧化性得到的结论一致。图3c表明,多酚在24~120 mg/kg的范围内可以显著提高复配油的氧化诱导期,且氧化诱导期随着浓度的增加而急剧增加,最大能达到5.72 h。潘东升等[27]研究表明多酚在植物油中的抗氧化效果随添加量的增加而增强,并呈现一定的剂量效应关系。图3d显示,植物甾醇在1200~6000 mg/kg的浓度范围内时,氧化诱导期没有得到显著的提升(P>0.05)。Liu等[18]发现植物甾醇在Rancimat试验条件下无明显抗氧化活性,反而起到了促氧化剂的作用。
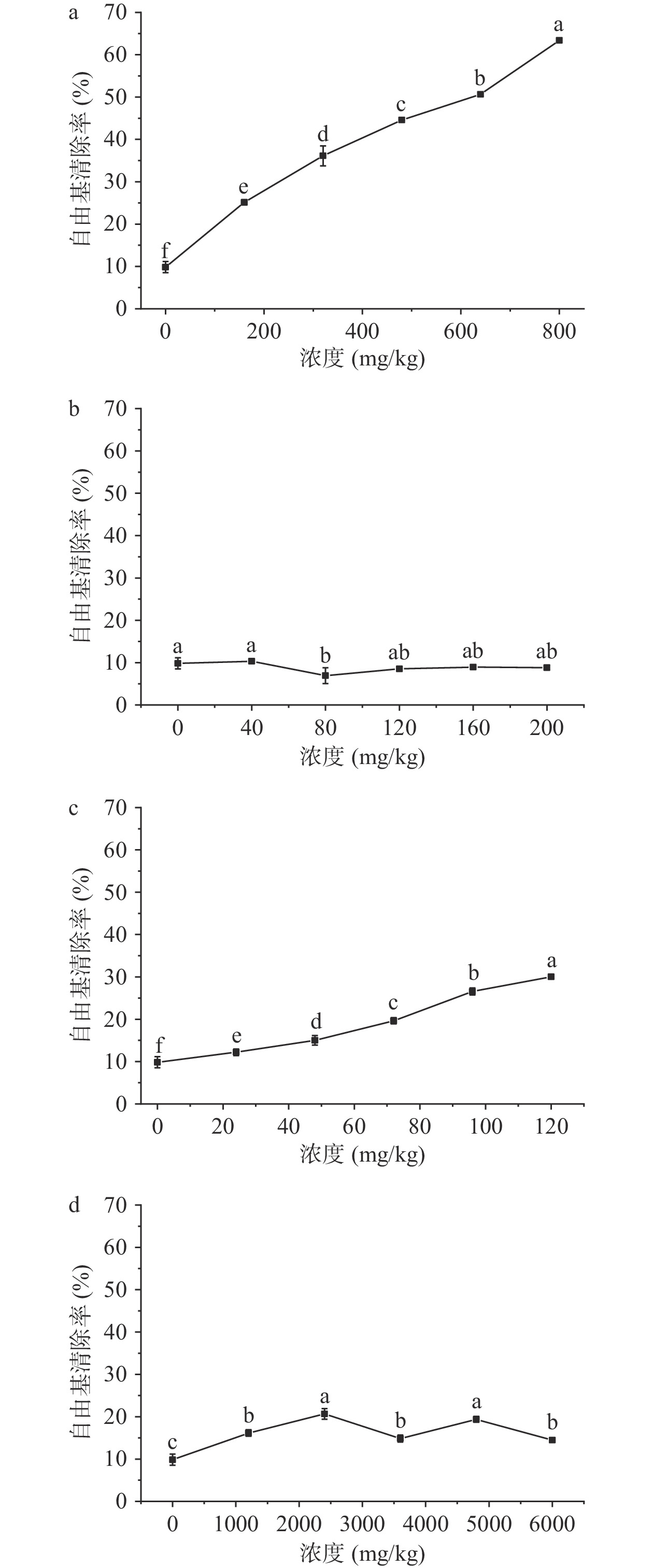
图4为通过DPPH自由基清除率实验测定的抗氧化效果,从图4a中可以看出,生育酚的DPPH自由基清除能力随浓度的增加而显著增加(P<0.05),当生育酚含量达到800 mg/kg时,DPPH自由基清除能力最强,达到63.39%。生育酚的DPPH自由基清除能力随着浓度的增加而急剧增加,这是由于生育酚含有酚羟基,它能为DPPH自由基贡献H原子,成为稳定的生育酚醌自由基[18]。如图4b所示,除角鲨烯为80 mg/kg时DPPH自由基清除能力显著降低(P<0.05),其余浓度下均没有显著差异(P>0.05)。这可能是由于在80 mg/kg的浓度下,角鲨烯的氧化速度快,氧化产物快速积累,已有研究发现角鲨烯的二次氧化产物对橄榄油表现出促氧化作用[8]。图4c显示,多酚的DPPH自由基清除能力也随浓度的增加而显著增加(P<0.05),最高可达到30.02%。图4d显示,植物甾醇在1200~6000 mg/kg的范围内时,DPPH自由基清除能力比不加抗氧化成分强(P<0.05),最高达到了20.65%,甾醇浓度与清除能力之间没有剂量效应关系。在早期的研究中,Sims等[28]发现只有结构中有亚乙基侧链的甾醇有抗氧化活性,没有亚乙基侧链的甾醇则没有明显的抗氧化效果。随后Gordon等[29]得到了相似的结果,并提出假设,认为具有亚乙基侧链的甾醇可能通过侧链上无阻碍的烯丙基质子与油脂中的自由基发生反应,生成相对更稳定的三级自由基而发挥抗氧化剂的作用。除此之外,内环双键的位置和数量也会影响甾醇的抗氧化活性。近期的研究中,Liu等[18]发现植物甾醇在Rancimat试验条件下无明显抗氧化活性,反而起到了促氧化剂的作用,在DPPH自由基清除试验条件下,植物甾醇抗氧化活性很低。已经有研究表明高温会促进植物甾醇的氧化,形成氧化产物,降低植物甾醇的抗氧化活性[30−31],且植物甾醇的醇羟基较低[32],因此显示出较差的抗氧化能力。
2.3 样品中主要抗氧化成分的抗氧化相互作用
2.3.1 通过Rancimat试验测定的相互作用
图5显示了不同组合的抗氧化成分的额外诱导期aIP以及相互作用。从图5a中可以看出,多酚与角鲨烯的组合下M1(多酚24 mg/kg+角鲨烯40 mg/kg)、M3(多酚24 mg/kg+角鲨烯200 mg/kg)、M5(多酚72 mg/kg+角鲨烯120 mg/kg)和M7(多酚120 mg/kg+角鲨烯40 mg/kg)有显著的拮抗作用,其余组表现为相加作用。这可能与多酚抑制角鲨烯自氧化有关[33]。
图5b表明,不同浓度和比例的生育酚(160~800 mg/kg)和多酚(24~120 mg/kg)在复配油样中呈现拮抗作用,多酚含量越高,拮抗作用越明显,生育酚含量升高,拮抗作用存在减弱的趋势。M7(生育酚800 mg/kg+多酚24 mg/kg)甚至呈现出相加作用。Becker等[25]研究发现α-生育酚和槲皮素在乳液中显示出强烈的协同作用,在脂质体中协同作用减弱,在100 ℃的葵花籽油中则有明显的拮抗作用,产生拮抗作用可能是由于两者形成的中间产物在高温油中容易被氧化。
图5c显示,生育酚和植物甾醇的组合呈现拮抗作用的趋势,当生育酚浓度达到480和800 mg/kg,植物甾醇浓度达到6000 mg/kg时出现了拮抗作用。已有研究[18]发现α-生育酚(50~500 mg/kg)和植物甾醇(2000~12000 mg/kg)在米糠油中呈现拮抗作用,且随着生育酚和甾醇浓度的升高,拮抗作用在逐渐减弱。
图5d表明植物甾醇与多酚有非常明显的拮抗作用,拮抗作用的程度与两者浓度没有明显相关性。可能是由于多酚抗氧化效果显著,会抑制植物甾醇发生氧化反应。
图5e中,当生育酚和角鲨烯组合作用时,二者均处于低浓度下呈现出了拮抗作用,提高生育酚或角鲨烯的浓度都能使拮抗作用减弱,M6组当生育酚浓度达到480 mg/kg、角鲨烯浓度达到200 mg/kg时,表现出较明显的协同作用,提高生育酚的浓度使协同作用增强。这说明角鲨烯单独作用时虽然没有明显抗氧化效果,但可以提高生育酚的抗氧化能力。植物甾醇与角鲨烯单独作用时aIP有负值出现,组合作用时也无明显抗氧化效果,所测aIP实验值与理论值之间无统计学差异(P>0.05)。
2.3.2 通过DPPH自由基清除试验测定的相互作用
图6a可以看出,当多酚和角鲨烯组合作用时,均比相同浓度的多酚单独作用时的ESC高,且随着多酚和角鲨烯浓度的上升,多酚与角鲨烯之间的拮抗作用逐渐减弱。M6组多酚浓度达到72 mg/kg、角鲨烯浓度达到120 mg/kg时拮抗作用消失,呈现相加效应。继续增加多酚和角鲨烯的浓度,仍然呈现相加效应。对于多酚与角鲨烯的组合,图5a和图6a显示的相互作用略有不同,但两种情况均表明,多酚浓度高的情况下拮抗作用会减弱甚至消失。
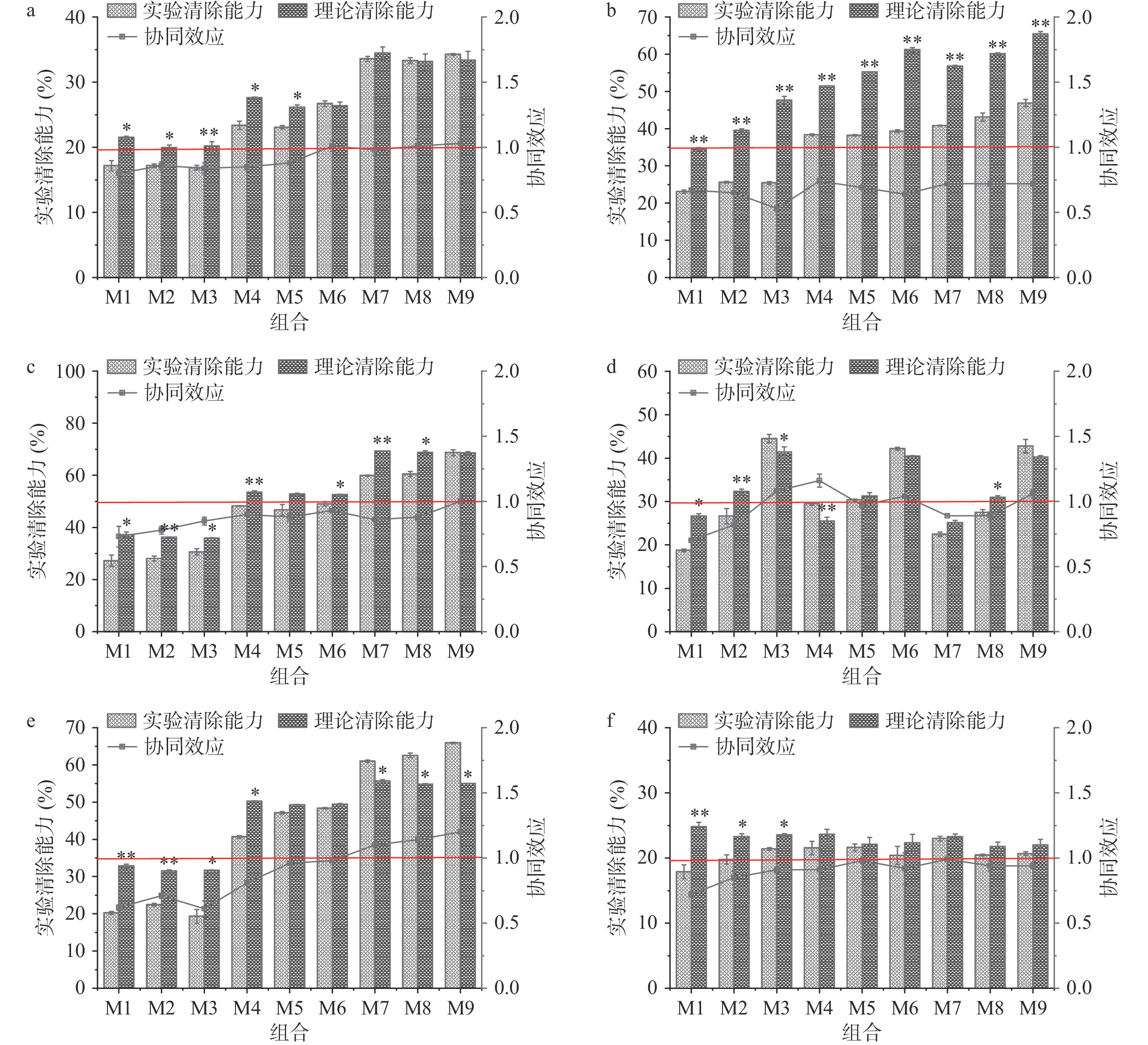
![]() 图 6 不同组合的DPPH自由基实验清除能力和理论清除能力及协同效应注:a. 多酚+角鲨烯;b. 生育酚+多酚;c. 生育酚+植物甾醇;d. 植物甾醇+多酚;e. 生育酚+角鲨烯;f. 植物甾醇+角鲨烯;*表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);**表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.01);不同组M1-M9回添的抗氧化成分组成和含量见表2。Figure 6. Experimental and theoretical scavenging capacities and synergistic effects of DPPH free radicals of different combinations
图 6 不同组合的DPPH自由基实验清除能力和理论清除能力及协同效应注:a. 多酚+角鲨烯;b. 生育酚+多酚;c. 生育酚+植物甾醇;d. 植物甾醇+多酚;e. 生育酚+角鲨烯;f. 植物甾醇+角鲨烯;*表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);**表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.01);不同组M1-M9回添的抗氧化成分组成和含量见表2。Figure 6. Experimental and theoretical scavenging capacities and synergistic effects of DPPH free radicals of different combinations图6b显示不同浓度和比例的生育酚和多酚在复配油样中均呈现拮抗作用,且同浓度的生育酚条件下,多酚含量越高,拮抗作用越明显。这与图5b的结果一致。
图6c显示生育酚与植物甾醇在不同组合下处于拮抗作用,生育酚浓度和植物甾醇浓度均达到最高时,呈现相加作用。这表明生育酚和植物甾醇之间拮抗作用的程度随植物甾醇浓度的增加而减弱。早期研究[34]表明植物甾醇对α-生育酚再生有抑制作用,最近的研究[18]也证明了α-生育酚与植物甾醇在植物油基质中呈现拮抗作用,这与本研究得到的结果一致。
图6d表明植物甾醇与多酚的组合M1(植物甾醇1200 mg/kg+多酚24 mg/kg)和M2(植物甾醇1200 mg/kg+多酚72 mg/kg)有明显的拮抗作用,M3(植物甾醇1200 mg/kg+多酚120 mg/kg)和M4(植物甾醇3600+多酚24 mg/kg)有协同效应,继续增加两者的浓度则显现出相加作用。这与图5d的结果有一定的区别,可能是由于温度对多酚的抗氧化活性产生影响[35],从而使两种方法测得的植物甾醇与多酚的相互作用类型存在差异。
图6e可以看出,当生育酚和角鲨烯组合作用时,随着生育酚和角鲨烯浓度的上升,生育酚与角鲨烯之间的拮抗作用逐渐减弱,生育酚浓度在达到800 mg/kg时拮抗作用消失,呈现协同效应。这和图5e的结果相同。目前关于角鲨烯和生育酚之间协同抗氧化作用的研究较少,机理尚不能明确。Psomiadou等[36]认为角鲨烯在光氧化研究中可以再生α-生育酚,这与Kohno等[37]的假说一致。图6f表明植物甾醇和角鲨烯组合M1(植物甾醇1200 mg/kg+角鲨烯40 mg/kg)和M2(植物甾醇1200 mg/kg+角鲨烯120 mg/kg)有较为明显的拮抗效应,其余各组则接近于相加效应。Finotti等[38]用克罗欣漂白法测定了α-生育酚、β-谷甾醇和角鲨烯之间的抗氧化相互作用,结果显示角鲨烯与α-生育酚和β-谷甾醇存在协同作用,这可能是由于角鲨烯可以作为一种竞争性的化合物在反应中发挥作用,从而降低氧化的速度。
2.4 通过Schaal法评价抗氧化成分不同的复配油氧化稳定性
表6为复配油初始抗氧化成分含量,如表所示,TH的α-生育酚和多酚含量显著高于TL,γ-生育酚含量显著低于TL(P<0.05)。TH0和TL0为TH和TL组去除抗氧化成分后的复配油,TH1和TL1是在TH和TL基础上调整了生育酚和多酚的含量,使得最终α-生育酚和γ-生育酚分别达到400 mg/kg左右,多酚含量达到120 mg/kg左右。刘慧敏[39]通过研究植物油储藏过程中微量成分和抗氧化能力的变化,分析了储藏过程中不同植物油微量成分含量与抗氧化能力之间的相关性,结果表明植物油中多酚的含量与极性部分的抗氧化能力呈显著相关性,植物油中的多酚和生育酚与植物油的抗氧化性能密切有关。Yao等[40]通过测定不同植物油的微量成分含量和自由基清除活性,建立了微量成分与其抗氧化能力之间的关系,结果表明多酚和α-生育酚是影响植物油抗氧化能力的主要因素。
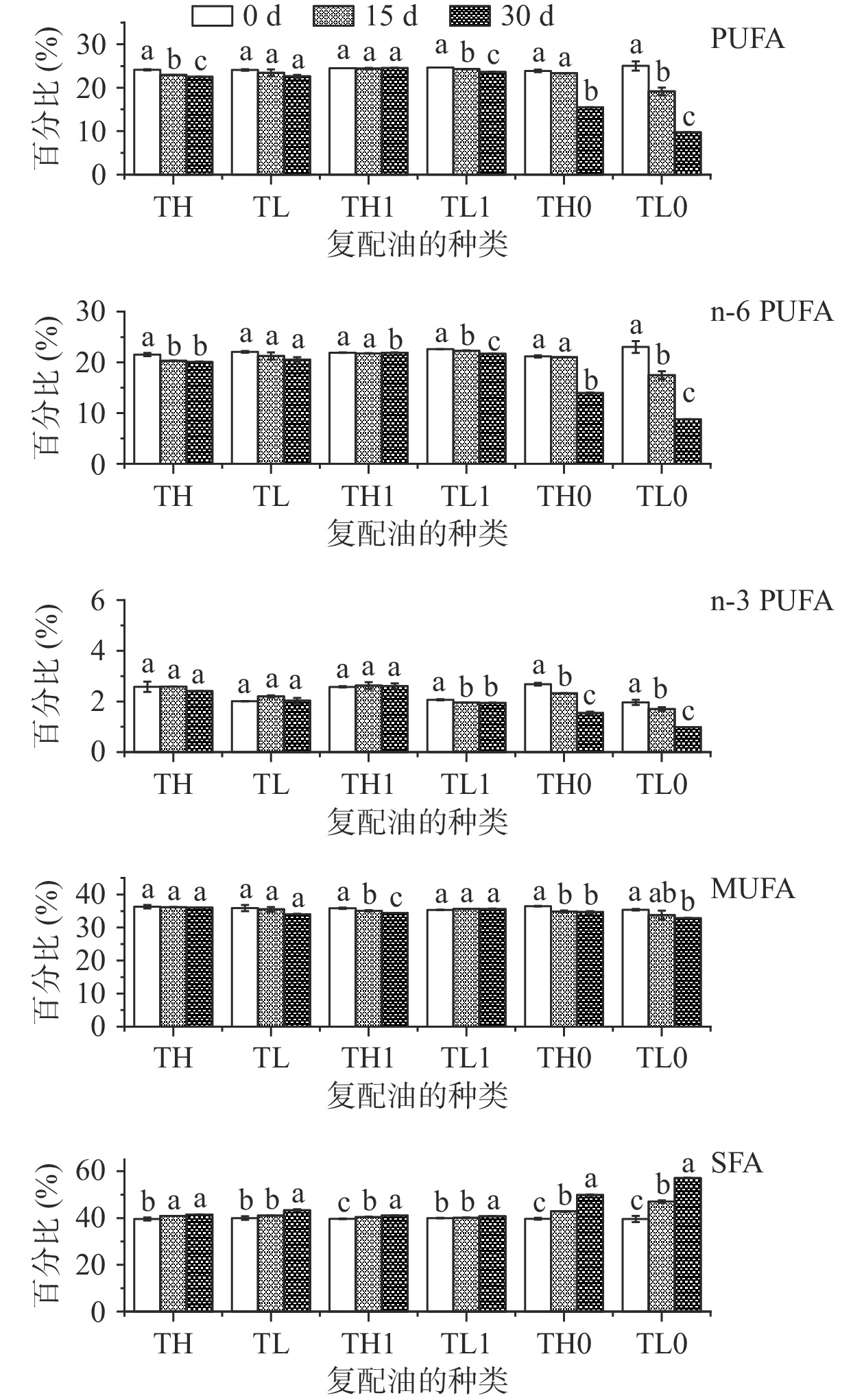
表 6 复配油初始抗氧化成分含量(mg/kg)Table 6. Initial antioxidant content of compounded oils (mg/kg)样品 α-生育酚 γ-生育酚 角鲨烯 多酚 TH 270.68±2.98b 266.67±5.69c 544.21±3.41a 61.21±1.39b TL 125.53±4.80c 307.48±4.92b 566.93±18.69a 49.32±2.14c TH1 400.88±11.90a 400.53±9.88a 553.68±17.91a 118.78±0.25a TL1 398.39±21.08a 406.62±5.25a 563.60±23.55a 118.56±0.49a TH0 nd nd 254.11±7.90c nd TL0 nd nd 357.83±25.35b nd 注:nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);TH1、TL1,为TH、TL经抗氧化成分调整后的复配油;TH0、TL0,为TH、TL预处理去除抗氧化成分的复配油;不同小写字母表示不同复配油抗氧化成分含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 图7为烘箱加速氧化下复配油脂肪酸组成的变化,从图中可以看出,复配油的PUFA 和MUFA随着氧化天数的增加而减少,SFA随着氧化天数的增加而增加。未经过预处理的组TH、TL、TH1和TL1脂肪酸组成只有微小的变化,经过预处理的组TH0和TL0脂肪酸组成变化范围较大。在未经过预处理的组中,SFA含量增加最多的是TL组,增加了3.33%。在经过预处理的组中,SFA含量增加最多的是TL0组,增加了17.51%。
如图8a所示,预处理后的复配油初始酸价极低,均在0.05 mg KOH/g以下。经过25 d的烘箱加速氧化,复配油的酸值都显著增加(P<0.05)。在氧化结束时,复配油酸价从高到低排列为TL0(1.45)、TH0(1.16)、TL1(0.61)、TH1(0.52)、TH(0.50)、TL(0.48)。TH0、TL0的酸价变化范围较大,且氧化第20 d到氧化结束期间,酸价增长最显著。图8b表明,复配油的POV随着烘箱内加速氧化时间的增加而增加,加速氧化结束时的POV顺序为TL0>TH0>TL>TL1>TH>TH1。TL0、TH0的初始POV值较低,均小于0.73 mmol/kg,但氧化第5天开始的POV值超过了初始POV较高的未预处理的组。图8c中复配油的p-茴香胺值随着氧化时间的增加而增加,其中TH1的初始p-茴香胺值最高,达到0.82。氧化结束时的p-茴香胺值的顺序是TL0>TH0>TH>TL>TH1>TL1。总氧化值为结合过氧化值和茴香胺值进行计算得到,图8d显示氧化结束时总氧化值的顺序是TL0>TH0>TL>TL1>TH>TH1。n-6/n-3PUFA值较低的TH的氧化稳定性比n-6/n-3PUFA较高的TL好,脂肪酸组成和抗氧化成分均类似的TH1和TL1相比,仍然是n-6/n-3PUFA较低的TH1氧化稳定性更好。这表明对于脂肪酸组成和抗氧化成分均类似但n-6/n-3PUFA不同的复配油来说,n-6/n-3PUFA值越低,氧化稳定性可能越好。曹君[41]通过对不同脂肪酸组成的调和油氧化稳定性进行分析,发现n-6PUFA较高的调和油过氧化值增长往往较明显,但并不是所有油样都适用,猜测可能因为较高含量的n-3PUFA会增加亚麻酸氢过氧化物的产生。
本研究结果显示,预处理去除抗氧化成分后,复配油的氧化稳定性指数显著降低,烘箱加速后的脂肪酸组成变化明显,酸价、过氧化值、茴香胺值等急剧增加。这表明内源性抗氧化成分含量虽少,但对延缓植物油氧化过程起到了至关重要的作用。
3. 结论
本实验以氧化稳定性指数和DPPH自由基清除能力为指标,研究了生育酚、多酚、甾醇、角鲨烯等主要抗氧化成分在复配油脂介质中的单独抗氧化能力和相互作用类型,并采用Schaal烘箱加速氧化试验评估复配油的氧化稳定性。结果表明,生育酚和多酚单独作用时抗氧化效果明显,植物甾醇和角鲨烯单独作用时则未显现出显著抗氧化效果。生育酚与多酚组合时呈现明显的拮抗作用,生育酚和角鲨烯组合作用时,随着生育酚和角鲨烯浓度的上升,呈现先拮抗后协同效应,当生育酚含量大于480 mg/kg,角鲨烯的存在会显著提高生育酚的抗氧化能力,其余组合低浓度下呈现拮抗作用,高浓度下多为相加作用。预处理去除抗氧化成分的复配油氧化稳定性非常差,在SFA、MUFA和PUFA比例和抗氧化成分含量都相似的情况下,n-6/n-3PUFA的值低的复配油氧化稳定性更好。
本研究结果为内源性抗氧化成分提高植物油氧化稳定性的应用提供参考依据,也为天然抗氧化剂的复配研究提供一定的科学指导。但由于植物油成分的复杂性,且内源性抗氧化成分的浓度和比例等都可能对相互作用的类型和程度产生影响,因此它们之间的多元相互作用还有待进一步研究。
-
图 6 不同组合的DPPH自由基实验清除能力和理论清除能力及协同效应
注:a. 多酚+角鲨烯;b. 生育酚+多酚;c. 生育酚+植物甾醇;d. 植物甾醇+多酚;e. 生育酚+角鲨烯;f. 植物甾醇+角鲨烯;*表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);**表示理论值与实验值之间存在显著性差异(P<0.01);不同组M1-M9回添的抗氧化成分组成和含量见表2。
Figure 6. Experimental and theoretical scavenging capacities and synergistic effects of DPPH free radicals of different combinations
表 1 复配油的配制比例
Table 1 Confection proprotion of compound oil
复配油 高油酸
葵花籽油(%)菜籽油
(%)芝麻油
(%)玉米油
(%)棕榈液油
(%)椰子油
(%)TH 3.91 37.22 1.97 19.14 2.79 34.95 TL 8.08 25.72 5.88 22.09 4.72 33.51 表 2 抗氧化成分回添到预处理油样中的浓度
Table 2 Concentration of antioxidant components added back to the purified oil sample
抗氧化成分 浓度(mg/kg) 生育酚(α-生育酚:γ-生育酚=1:1) T1 160 T2 320 T3 480 T4 640 T5 800 角鲨烯 S1 40 S2 80 S3 120 S4 160 S5 200 多酚(咖啡酸) P1 24 P2 48 P3 72 P4 96 P5 120 植物甾醇(菜油甾醇:豆甾醇:β-谷甾醇=
1.6:1:1.6)Ph1 1200 Ph2 2400 Ph3 3600 Ph4 4800 Ph5 6000 表 3 抗氧化成分以混合物形式回添到预处理油样中的组成
Table 3 Composition of antioxidant components added back to the purified oil sample in the form of a mixture
组合 混合物 浓度
(mg/kg)总浓度
(mg/kg)生育酚+角鲨烯 M1 T1+S1 160+40 200 M2 T1+S3 160+120 280 M3 T1+S5 160+200 360 M4 T3+S1 480+40 520 M5 T3+S3 480+120 600 M6 T3+S5 480+200 680 M7 T5+S1 800+40 840 M8 T5+S3 800+120 920 M9 T5+S5 800+200 1000 植物甾醇+多酚 M1 Ph1+P1 1200+24 1224 M2 Ph1+P3 1200+72 1272 M3 Ph1+P5 1200+120 1320 M4 Ph3+P1 3600+24 3624 M5 Ph3+P3 3600+72 3672 M6 Ph3+P5 3600+120 3720 M7 Ph5+P1 6000+24 6024 M8 Ph5+P3 6000+72 6072 M9 Ph5+P5 6000+120 6120 生育酚+植物甾醇 M1 T1+Ph1 160+1200 1360 M2 T1+Ph3 160+3600 3760 M3 T1+Ph5 160+6000 6160 M4 T3+Ph1 480+1200 1680 M5 T3+Ph3 480+3600 4080 M6 T3+Ph5 480+6000 6480 M7 T5+Ph1 800+1200 2000 M8 T5+Ph3 800+3600 4400 M9 T5+Ph5 800+6000 6800 多酚+角鲨烯 M1 P1+S1 24+40 64 M2 P1+S3 24+120 144 M3 P1+S5 24+200 224 M4 P3+S1 72+40 112 M5 P3+S3 72+120 192 M6 P3+S5 72+200 272 M7 P5+S1 120+40 160 M8 P5+S3 120+120 240 M9 P5+S5 120+200 320 生育酚+多酚 M1 T1+P1 160+24 184 M2 T1+P3 160+72 232 M3 T1+P5 160+120 280 M4 T3+P1 480+24 504 M5 T3+P3 480+72 552 M6 T3+P5 480+120 600 M7 T5+P1 800+24 824 M8 T5+P3 800+72 872 M9 T5+P5 800+120 920 植物甾醇+角鲨烯 M1 Ph1+S1 1200+40 1240 M2 Ph1+S3 1200+120 1320 M3 Ph1+S5 1200+200 1400 M4 Ph3+S1 3600+40 3640 M5 Ph3+S3 3600+120 3720 M6 Ph3+S5 3600+200 3800 M7 Ph5+S1 6000+40 6040 M8 Ph5+S3 6000+120 6120 M9 Ph5+S5 6000+200 6200 表 4 预处理前后复配油的脂肪酸组成比较(总脂肪酸的百分比)
Table 4 Comparison of fatty acid composition of compounded oils before and after the pretreatment (percentage of total fatty acids)
脂肪酸(%) TH TL 预处理前 预处理后 预处理前 预处理后 C8:0 0.50±0.09 0.55±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.05±0.01 C10:0 1.52±0.15 1.66±0.02 1.00±0.13 1.06±0.11 C11:0 0.15±0.03 0.16±0.00 nd nd C12:0 16.45±0.21 16.31±0.05 16.50±0.52 16.50±0.78 C14:0 6.71±0.06 6.92±0.30 7.06±0.12 7.05±0.07 C16:0 8.57±0.01 8.66±0.13 10.99±0.19 10.88±0.24 C18:0 4.77±0.07 4.44±0.01 3.97±0.13 4.05±0.12 9c-C18:1 32.53±0.38 32.76±0.13 34.24±0.54 33.83±0.11 11c-C18:1 2.00±0.17 1.85±0.03 0.53±0.08 0.51±0.05 9c12c-C18:2n-6 21.53±0.33 21.18±0.23 22.65±1.02 23.04±1.17 C20:0 0.54±0.18 0.66±0.01 nd nd 8c-C20:1 0.06±0.01 0.06±0.00 nd nd 11c-C20:1 1.67±0.04 1.67±0.02 1.01±0.07 0.98±0.09 C18:3n-3 2.58±0.20 2.68±0.06 1.96±0.10 1.97±0.10 C22:0 0.23±0.00 0.23±0.00 nd nd C20:3n-6 nd nd nd nd C22:1n-9 0.07±0.00 0.11±0.01 0.07±0.01 0.07±0.02 C20:5n-3 nd nd nd nd C24:0 0.10±0.00 0.09±0.00 nd nd C22:3n-3 0.01±0.00 0.00±0.00 nd nd ∑SFA 39.55±0.66a 39.69±0.37a 40.00±0.76a 39.59±1.30a ∑MUFA 36.34±0.53a 36.45±0.08a 35.92±0.93a 35.40±0.23a ∑PUFA 24.11±0.13a 23.86±0.29a 24.08±0.17a 25.01±1.07a ∑n-3PUFA 2.58±0.20a 2.68±0.06a 2.01±0.01b 1.97±0.10b ∑n-6PUFA 21.53±0.33ab 21.18±0.23b 22.07±0.16ab 23.04±1.17a n-6/n-3PUFA 8.37±0.78b 7.90±0.08b 10.96±0.02a 11.74±1.21a 注:每个样品平行分析测定三次,数据以mean±SD的形式表达;不同小写字母表示不同复配油预处理前后的脂肪酸组成存在显著性差异(P<0.05);nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);SFA,饱和脂肪酸;MUFA,单不饱和脂肪酸;PUFA,多不饱和脂肪酸;n-3PUFA,n-3多不饱和脂肪酸;n-6PUFA,n-6多不饱和脂肪酸;n-6/n-3PUFA,n-6与n-3多不饱和脂肪酸的比值。 表 5 预处理前后复配油的抗氧化成分含量比较
Table 5 Comparison of antioxidant content of compounded oils before and after the pretreatment
抗氧化成分含量(mg/kg) TH TL 预处理前 预处理后 预处理前 预处理后 α-生育酚 270.68±2.98a nd 125.53±4.80b nd γ-生育酚 266.67±5.69b nd 307.48±4.92a nd 菜油甾醇 1694.34±23.13a 1090.36±12.19c 1457.68±9.36b 728.09±19.65d 豆甾醇 995.89±20.33a 474.99±6.23c 688.60±16.30b 282.32±25.21d β-谷甾醇 1613.65±28.36b 994.79±20.90c 1692.71±30.68a 695.79±12.68d 角鲨烯 544.21±3.41b 254.11±7.90d 566.93±18.69a 357.83±25.35c 总酚 61.21±1.39a nd 49.79±2.79b nd 注:nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);不同小写字母表示不同复配油预处理前后的抗氧化成分含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 6 复配油初始抗氧化成分含量(mg/kg)
Table 6 Initial antioxidant content of compounded oils (mg/kg)
样品 α-生育酚 γ-生育酚 角鲨烯 多酚 TH 270.68±2.98b 266.67±5.69c 544.21±3.41a 61.21±1.39b TL 125.53±4.80c 307.48±4.92b 566.93±18.69a 49.32±2.14c TH1 400.88±11.90a 400.53±9.88a 553.68±17.91a 118.78±0.25a TL1 398.39±21.08a 406.62±5.25a 563.60±23.55a 118.56±0.49a TH0 nd nd 254.11±7.90c nd TL0 nd nd 357.83±25.35b nd 注:nd,未检测出其对应的峰或含量低于定量水平(<0.5 mg/kg);TH1、TL1,为TH、TL经抗氧化成分调整后的复配油;TH0、TL0,为TH、TL预处理去除抗氧化成分的复配油;不同小写字母表示不同复配油抗氧化成分含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] WEN Y Q, XU L L, XUE C H, et al. Assessing the impact of oil types and grades on tocopherol and tocotrienol contents in vegetable oils with chemometric methods[J]. Molecules,2020,25(21):5076. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215076
[2] CAO J, LI H Y, XIA X, et al. Effect of fatty acid and tocopherol on oxidative stability of vegetable oils with limited air[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2015,18(4):808−820. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2013.864674
[3] RATHER R A, BHAGAT M. Quercetin as an innovative therapeutic tool for cancer chemoprevention:Molecular mechanisms and implications in human health[J]. Cancer Medicine,2020,9(24):9181−9192. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1411
[4] MOUDDEN H E, IDRISSI Y E, BELMAGHRAOUI W, et al. Olive mill wastewater polyphenol‐based extract as a vegetable oil shelf life extending additive[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2020,44(12):e14990.
[5] SHI T, ZHU M T, ZHOU X Y, et al. H-1 NMR combined with PLS for the rapid determination of squalene and sterols in vegetable oils[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,287:46−54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.072
[6] PSOMIADOU E, TSIMIDOU M. On the role of squalene in olive oil stability[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1999,47(10):4025−4032. doi: 10.1021/jf990173b
[7] BOLLAND J L, HUGHES H. The primary thermal oxidation product of squalene[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society,1949,26:492−497.
[8] NAZIRI E, CONSONNI R, TSIMIDOU M Z. Squalene oxidation products:Monitoring the formation, characterisation and pro-oxidant activity[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2014,116(10):1400−1411. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201300506
[9] CHENG C, YU X, MCCLEMENTS D J, et al. Effect of flaxseed polyphenols on physical stability and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil-in-water nanoemulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125207
[10] 张莉莎, 倪菁潞, 刘睿杰, 等. α-生育酚、γ-谷维素及植物甾醇在乙酸乙酯介质中清除自由基相互作用研究[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(12):104−108,130. [ZHANG L S, NI J L, LIU R J, et al. Interaction on scavenging free radical of α-tocopherol, γ-oryzanol and phytosterol in ethyl acetate[J]. China Oils and Fats,2019,44(12):104−108,130.] ZHANG L S, NI J L, LIU R J, et al. Interaction on scavenging free radical of α-tocopherol, γ-oryzanol and phytosterol in ethyl acetate[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2019, 44(12): 104−108,130.
[11] 张莉莎. α-生育酚、植物甾醇和γ-谷维素清除DPPH自由基相互作用研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2019. [ZHANG L S. Effects of interaction between α-tocopherol, phytosterol and γ-oryzanol on the antiradical activity against DPPH radical[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2019.] ZHANG L S. Effects of interaction between α-tocopherol, phytosterol and γ-oryzanol on the antiradical activity against DPPH radical[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019.
[12] LAMA-MUÑOZ A, RUBIO-SENENT F, BERMÚDEZ-ORIA A, et al. Synergistic effect of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylglycol with hydroxytyrosol and α-tocopherol on the Rancimat oxidative stability of vegetable oils[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2019,51:100−106.
[13] ALMOSELHY R I M. Comparative study of vegetable oils oxidative stability using DSC and rancimat methods[J]. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry,2021,64(1):299−312.
[14] LI X, LI Y R, YANG F, et al. Oxidation degree of soybean oil at induction time point under Rancimat test condition:Theoretical derivation and experimental observation[J]. Food Research International,2019,120:756−762. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.11.036
[15] MULTARI S, MARSOL-VALL A, HEPONIEMI P, et al. Changes in the volatile profile, fatty acid composition and other markers of lipid oxidation of six different vegetable oils during short-term deep-frying[J]. Food Research International,2019,122:318−329. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.026
[16] 朱雪梅, 吴俊锋, 胡蒋宁, 等. α-生育酚在花生油、芝麻油和菜籽油中的抗氧化效能[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(10):85−90. [ZHU X M, WU J F, HU J N, et al. Antioxidative efficiency of α-tocopherol in peanut oil, sesame oil, and rapessed oil[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(10):85−90.] doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.10.013 ZHU X M, WU J F, HU J N, et al. Antioxidative efficiency of α-tocopherol in peanut oil, sesame oil, and rapessed oil[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2013, 39(10): 85−90. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.10.013
[17] WARAHO T, CARDENIA V, RODRIGUEZ-ESTRADA M T, et al. Prooxidant mechanisms of free fatty acids in stripped soybean oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(15):7112−7117. doi: 10.1021/jf901270m
[18] LIU R R, XU Y, CHANG M, et al. Antioxidant interaction of alpha-tocopherol, gamma-oryzanol and phytosterol in rice bran oil[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,343:128431. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128431
[19] ZENG J P, XIAO T, NI X G, et al. The comparative analysis of different oil extraction methods based on the quality of flaxseed oil[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,107:104373. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104373
[20] 曾俊鹏. 富含环肽的精炼冷榨亚麻籽油的制备及环肽的消化吸收[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2022. [ZENG J P. Preparation of refined cold-pressed flaxseed oil rich in cyclolinopeptides and in vitro digestion and absorption charactristics of cyclolinopeptides[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2022.] ZENG J P. Preparation of refined cold-pressed flaxseed oil rich in cyclolinopeptides and in vitro digestion and absorption charactristics of cyclolinopeptides[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2022.
[21] AHMED I A M, USLU N, OZCAN M M, et al. Effect of conventional oven roasting treatment on the physicochemical quality attributes of sesame seeds obtained from different locations[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,338:128109. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128109
[22] ZHANG T, WANG T, LIU R J, et al. Chemical characterization of fourteen kinds of novel edible oils:A comparative study using chemometrics[J]. LWT,2020,118:108725. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108725
[23] SHI T, WU G C, JIN Q Z, et al. Detection of camellia oil adulteration using chemometrics based on fatty acids GC fingerprints and phytosterols GC–MS fingerprints[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,352:129422. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129422
[24] 马力, 陈永忠, 钟海雁, 等. 油茶籽油中角鲨烯的高效液相色谱分析[J]. 江苏农业科学,2016,44(8):353−356. [MA L, CHEN Y Z, ZHONG H Y, et al. Determination of squalene in oil-tea camellia seed oil by HPLC[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2016,44(8):353−356.] MA L, CHEN Y Z, ZHONG H Y, et al. Determination of squalene in oil-tea camellia seed oil by HPLC[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(8): 353−356.
[25] BECKER E M, NTOUMA G, SKIBSTED L H. Synergism and antagonism between quercetin and other chain-breaking antioxidants in lipid systems of increasing structural organisation[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,103(4):1288−1296. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.034
[26] LUÍS Â, DUARTE A P, PEREIRA L, et al. Interactions between the major bioactive polyphenols of berries:Effects on antioxidant properties[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2018,244(1):175−185. doi: 10.1007/s00217-017-2948-5
[27] 潘东升, 谭祖顺, 郭燕华, 等. 石榴皮多酚对植物油的抗氧化作用[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(12):264−267. [PAN D S, TAN Z S, GUO Y H, et al. Antioxidant effect of pomegranate peel polyphenols on vegetable oil[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(12):264−267.] PAN D S, TAN Z S, GUO Y H, et al. Antioxidant effect of pomegranate peel polyphenols on vegetable oil[J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 42(12): 264−267.
[28] SIMS R J, FIORITI J A, KANUK M J. Sterol additives as polymerization inhibitors for frying oils[M]. Wiley Online Library, 1972, 49: 298–301.
[29] GORDON M H, MAGOS P. The effect of sterols on the oxidation of edible oils[J]. Food Chemistry,1983,10(2):141−147. doi: 10.1016/0308-8146(83)90030-4
[30] WINKLER J K, WARNER K. The effect of phytosterol concentration on oxidative stability and thermal polymerization of heated oils[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2008,110(5):455−464. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200700265
[31] CHEN J N, TANG G Y, ZHOU J F, et al. The characterization of soybean germ oil and the antioxidative activity of its phytosterols[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(68):40109−40117. doi: 10.1039/C9RA08771K
[32] FU Y Q, ZHANG Y, HU H Y, et al. Design and straightforward synthesis of novel galloyl phytosterols with excellent antioxidant activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,163:171−177. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.04.093
[33] GUO Y F, BASCHIERI A, AMORATI R, et al. Synergic antioxidant activity of γ-terpinene with phenols and polyphenols enabled by hydroperoxyl radicals[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,345:128468. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128468
[34] MORTENSEN A, SKIBSTED L H. Relative stability of carotenoid radical cations and homologue tocopheroxyl radicals. A real time kinetic study of antioxidant hierarchy[J]. FEBS Letters,1997,417(3):261−266. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01297-0
[35] 罗凡, 陈志吉, 蓝丽丽, 等. 加热对油茶籽油及饼粕总酚及其抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 林业科学,2020,56(2):61−68. [LUO F, CHEN Z J, LAN L L, et al. Effects of heating on total phenols and their antioxidant activities in camellia oleifera seed oil and the cake[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2020,56(2):61−68.] LUO F, CHEN Z J, LAN L L, et al. Effects of heating on total phenols and their antioxidant activities in camellia oleifera seed oil and the cake[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 56(2): 61−68.
[36] PSOMIADOU E, TSIMIDOU M. Stability of virgin olive oil. 1. Autoxidation studies[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(4):716−721. doi: 10.1021/jf0108462
[37] KOHNO Y, EGAWA Y, ITOH S, et al. Kinetic study of quenching reaction of singlet oxygen and scavenging reaction of free radical by squalene in n-butanol[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Lipids and Lipid Metabolism,1995,1256(1):52−56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(95)00005-W
[38] FINOTTI E, D'AMBROSIO M, PAOLETTI F, et al. Synergistic effects of α-tocopherol, β-sitosterol and squalene on antioxidant activity assayed by crocin bleaching method[J]. Nahrung (Weinheim),2000,44(5):373−374. doi: 10.1002/1521-3803(20001001)44:5<373::AID-FOOD373>3.0.CO;2-0
[39] 刘慧敏. 不同植物油微量成分与抗氧化能力的相关性研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2015. [LIU H M. Study on the minor components in different vegetable oils and their relation with antioxidant capacity[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2015.] LIU H M. Study on the minor components in different vegetable oils and their relation with antioxidant capacity[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[40] YAO Y P, LIU W T, ZHOU H, et al. The relations between minor components and antioxidant capacity of five fruits and vegetables seed oils in China[J]. Journal of Oleo Science,2019,68(7):625−635. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess19005
[41] 曹君. 不同脂肪酸结构食用油的氧化规律及其动力学研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2015. [CAO J. Oxidative patterns and kinetics of edible oils with different fatty acid compositions[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2015.] CAO J. Oxidative patterns and kinetics of edible oils with different fatty acid compositions[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2015.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈素艳,卢妍,吴光斌,陈发河. 黄秋葵酒渣纳米纤维素的制备工艺及表征分析. 食品研究与开发. 2024(17): 113-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗欣,周彦强,吴光斌,陈发河. 黄秋葵酒渣膳食纤维超微粉制备及特性研究. 食品与机械. 2021(08): 201-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



