Changes in Quality Characteristics of Abdomen and Cheliped Muscle of Swimming Crab (Portunus trituberculatus) during Chilled Storage
-
摘要: 目的:探究冷藏过程中三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉品质特性变化情况。方法:以三疣梭子蟹为对象,在4 ℃冷藏过程中,对蟹腹部和螯足肌肉进行定量描述分析,同时测定肌肉持水力、水分含量、水分活度、pH、挥发性盐基氮、三甲胺、TCA-可溶性肽、肌原纤维蛋白含量及其小片化指数等理化指标。结果:随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉特性出现相似的变化趋势,其中肌肉品质感官特性、持水力、水分含量和水分活度均呈下降趋势;肌肉pH呈先下降后上升趋势,腹部肌肉pH在冷藏第5 d时为7.7,而螯足肌肉pH在冷藏第4 d时已达7.99;挥发性盐基氮、三甲胺、TCA-可溶性肽含量和肌原纤维小片化指数则呈不断上升趋势;肌原纤维蛋白含量呈显著下降趋势(P<0.05),腹部和螯足肌肉在冷藏5 d后分别下降了38.11%和49.51%。在整个冷藏周期中,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉品质特性均显著优于螯足肌肉。结论:随着贮藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹肌肉品质逐渐发生劣变,其腹部肌肉品质特性相比螯足部分更加稳定。本研究为三疣梭子蟹冷藏品质劣变及调控技术提供理论参考。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the changes in the quality characteristics of abdomen and cheliped muscle of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) during chilled storage. Methods: The swimming crab was taken as the object. During chilled storage at 4 ℃, the abdomen and cheliped muscle of swimming crab was conducted quantitative descriptive analysis. At the same time, the physicochemical indicators of muscle such as water holding capacity, water content, water activity, pH, total volatile base nitrogen, trimethylamine, TCA-soluble peptide, myofibrillar protein content, and fragmentation index were measured. Results: With the extension of chilled storage time, the characteristics of the abdomen and cheliped muscle of swimming crab showed a similar trend of change, in which the quality sensory characteristics, water holding capacity, water content, and water activity of muscle showed a downward trend. The pH of muscle showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing. The pH of the abdomen muscle was 7.7 on the 5th day of chilled storage, while the pH of the cheliped muscle reached 7.99 on the 4th day of chilled storage. Total volatile base nitrogen, trimethylamine, TCA-soluble peptide, and myofibril fragmentation index showed an upward trend. The myofibrillar protein content showed a significant downward trend (P<0.05), their content in muscle of abdomen and cheliped reduced by 38.11% and 49.51%, respectively, after 5 d of chilled storage. During the entire refrigeration period, the quality characteristics of abdomen muscle of swimming crab were significantly better than those of the cheliped muscle. Conclusion: With the extension of storage time, the muscle quality of swimming crab gradually deteriorated, and the quality characteristics of abdomen muscle was more stable compared to the cheliped part. This study provides a theoretical reference for quality deterioration and control techniques of swimming crab during chilled storage.
-
Keywords:
- chilled storage /
- Portunus trituberculatus /
- abdomen /
- cheliped /
- quality characteristics
-
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus),属甲壳纲、十足目、梭子蟹科,俗称白蟹、梭子蟹,因其肉质细嫩、味道鲜美、营养丰富,而深受消费者喜爱,其也是我国沿海地区重要的经济海产品之一[1]。三疣梭子蟹捕获后极易发生死亡,其肌肉蛋白质在微生物和酶的作用下易分解成碱性含氮化合物,导致三疣梭子蟹可食用品质快速下降[2]。4 ℃冷藏是延长鲜活水产品货架期的有效地方式之一,能较好保持甲壳类水产品原有的风味[3]。目前,4 ℃冷藏也是三疣梭子蟹捕获进行后短期贮藏的首选方式。而随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹可食用品质依旧会发生不可逆的劣变,探究其冷藏过程中肌肉品质特性变化规律,对优化三疣梭子蟹贮藏方式及提高蟹类产品经济价值具有重要意义。
近年来,越来越多的学者关注于三疣梭子蟹在不同贮藏条件下的肌肉品质变化。宗腊梅等[4]通过对三疣梭子蟹进行感官评价和挥发性盐基氮含量、K值、pH及硫代巴比妥酸反应物等理化指标测定,确定三疣梭子蟹在0 ℃贮藏时货架期可接受上限为9 d。黄琳等[5]研究发现,−40 ℃冻藏比−20 ℃冻藏对三疣梭子蟹肌肉蛋白质的破坏程度更小。Yang等[6]研究镀冰衣处理对冻藏三疣梭子蟹品质的影响,发现镀冰衣处理可以改善冻藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉持水力和微观组织结构,同时可抑制肌肉脂质氧化和挥发性盐基氮含量的增加。目前,国内外对低温三疣梭子蟹肌肉品质变化研究仍处于起步阶段,并且对三疣梭子蟹不同部位肌肉品质特性变化情况,尚缺少系统性研究。因此,本研究以三疣梭子蟹为原料,测定肌肉pH、挥发性盐基氮和肌原纤维蛋白含量等理化指标,研究4 ℃冷藏对三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足两个部位肌肉品质特性的影响,旨在探究三疣梭子蟹冷藏过程中腹部和螯足肌肉品质变化规律,为三疣梭子蟹冷藏贮存货架期提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
活体三疣梭子蟹(250±50 g) 购于浙江舟山国际水产城,购买后立即充氧包装并放入装有碎冰的泡沫箱内,30 min内运回至实验室,并立即对其进行处理;氯化钠、氧化镁、硼酸、甲基红、溴甲酚绿、无水乙醇、三(羟甲基)氨基甲烷(Tris)、顺丁烯二酸、氯化钾、磷酸氢二钾、磷酸二氢钾、乙二醇双(2-氨基乙基醚)四乙酸(EGTA)、氯化镁等 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;0.1 mol/L盐酸标准溶液 深圳市博林达科技有限公司;三氯乙酸(TCA) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;三甲胺ELISA检测试剂盒 江苏晶美生物科技有限公司;蛋白质定量测试盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;快速Lowry法蛋白含量测定试剂盒 上海荔达生物科技有限公司。
H1750R高速台式冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;KDN-520全自动凯氏定氮仪 邦亿精密量仪(上海)有限公司;JC-HD型智能水分活度测量仪 青岛聚创环保集团有限公司;U-2800紫外可见分光光度计 日立(中国)有限公司;iMark酶标仪 美国BIO-RAD有限公司;UPR-I-5TNP优普系列超纯水机 四川优普超纯科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
鲜活三疣梭子蟹洗净后,用解剖针扎蟹心快速处死,自封袋单只分装后置于4 ℃冷藏。每24 h取蟹样品10~12只,分别取腹部和螯足肌肉检测相关指标,每个指标重复测定3次。
1.2.2 感官评定
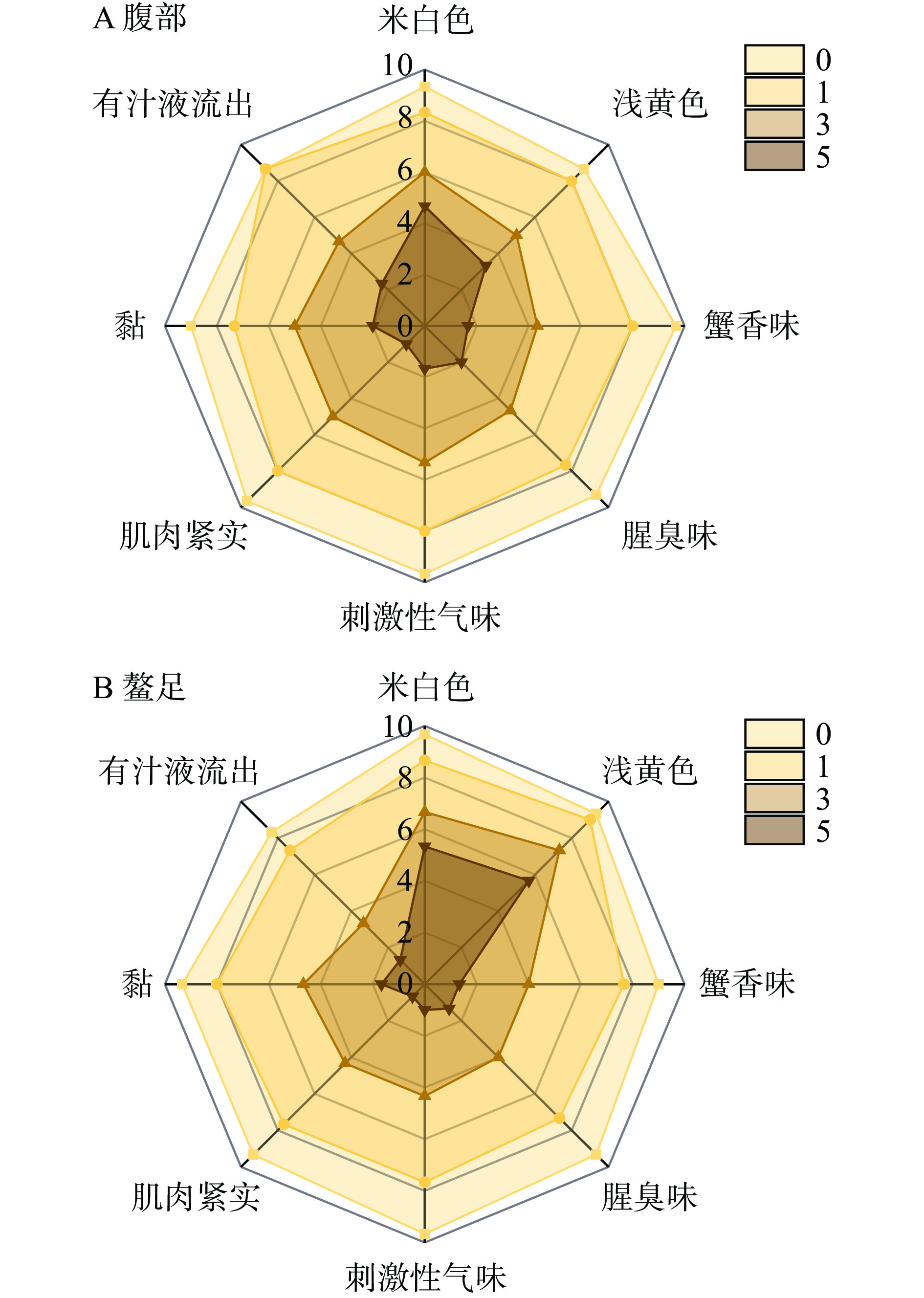
采用定量描述分析法(QDA),将三疣梭子蟹样品置于同一光源下,拍照记录蟹腹部、背部、腹腔内部三个部位感官变化情况。参考Yang等[7]报道方法,对三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉进行QDA法感官评定。参照GB/T 16291.1-2012《感官分析 选拔、培训与管理评价员一般导则 第1部分:优选评价员》[8]中的方法,经过多轮测试、培训和感官实验,最终选中8名优选评价员(3男5女)组成感官评价员小组。评价小组通过对样品感官特性进行综合评价,写出各自描述词,经过讨论,最终确定三疣梭子蟹8个感官描述词汇及定义。选取不同贮藏时间三疣梭子蟹肌肉组织样品,评价员根据表1中感官描述词汇及定义,利用0~10点标度法分别对每个感官特征进行评价。
表 1 三疣梭子蟹感官描述词汇及定义Table 1. Sensory description vocabulary and definition of swimming crab描述词汇 定义 米白色/粉白色 腹部肌肉为米白色,螯足肌肉为粉白色 浅黄色 肌肉变黄 蟹香味 具有三疣梭子蟹固有鲜香味 腥臭味 有腐败腥臭味 刺激性气味 有刺激氨臭味 肌肉紧实 肉质紧密有弹性 黏 肌肉具有黏附性 有汁液流出 肌肉自溶使得汁液流出 1.2.3 持水力(WHC)测定
取6×6 cm方形尼龙网(三层;重量记作m1),称取2.0 g块状腹部和螯足肌肉置于三层尼龙网上(重量记作m2),用尼龙网包裹好肌肉后,再用两层滤纸包裹置于底部放有棉花的离心管中,3000×g离心10 min后,再次称重(重量记作m3)。肌肉持水力计算公式如下所示。
WHC(%)=(1−m3−m1m3−m2)×100 (1) 1.2.4 水分含量和水分活度测定
参考GB 5009.3-2016中直接干燥法,测定蟹肌肉中水分含量[9];参考GB 5009.238-2016使用水分活度仪,测定蟹肌肉中水分活度[10]。
1.2.5 pH测定
称取2.0 g切碎肌肉样品,加入18 mL生理盐水,用匀浆机在15000×g条件下匀浆1 min,静置20 min后,3000×g下离心10 min(4 ℃),取上清液测定pH。
1.2.6 挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)和三甲胺(TMA)含量测定
参考GB 5009.228-2016中自动凯氏定氮仪法,测定蟹肌肉中TVB-N含量[11];使用三甲胺ELISA检测试剂盒,测定蟹肌肉中TMA含量,具体依据试剂盒操作说明进行。
1.2.7 TCA-可溶性肽含量测定
参考李学鹏[12]报道的方法,并稍作修改。准确称取2.0 g切碎肌肉样品,加入18 mL预冷的5% TCA溶液,15000×g条件下匀浆1 min。将匀浆液静置1 h,6800×g离心15 min,取上清液。采用快速Lowry法,测定上清液中TCA-可溶性肽含量,结果用mg/mL表示。
1.2.8 水溶性蛋白含量测定
准确称取2.0 g切碎肌肉样品,加入18 mL生理盐水,15000×g条件下匀浆1 min,静置20 min后,3000 ×g离心10 min(4 ℃),取上清液,用双缩脲法测定其中蛋白质含量。
1.2.9 肌原纤维蛋白含量及其小片化指数测定
肌原纤维蛋白含量:参考黄琳等[5]报道方法,并稍作修改。准确称取3.0 g切碎肌肉样品,加入27 mL 20 mmol/L Tris-maleate缓冲液(含50 mmol/L KCl,pH7.0),高速匀浆后置于8000×g离心10 min,弃去上清液。重复两次上述操作后,收集沉淀,加入27 mL 20 mmol/L Tris-maleate缓冲液(含0.6 mol/L KCl,pH7.0),高速匀浆后静置1.5 h,涡旋30 s后于10000×g条件下离心30 min,取上清液即为肌原纤维蛋白提取液,用双缩脲法测定蛋白质含量。肌原纤维小片化指数(MFI):参考Yang等[13]报道方法,并稍作修改。称取2.0 g切碎肌肉样品,加入30 mL MFI缓冲液(含100 mmol/L KCl,11.2 mmol/L K2HPO4,8.8 mmol/L KH2PO4,1 mmol/L EGTA和1 mmol/L MgCl2),高速匀浆后(15000×g,1 min,每30 s暂停10 s),5000×g离心10 min。收集沉淀,加入30 mL预冷的MFI缓冲液后,按上述匀浆离心条件重复操作一次。弃去上清液,用预冷的MFI缓冲液将所得沉淀制成蛋白质浓度为(0.50±0.05)mg/mL悬浊液,然后在540 nm处测定吸光度A540,A540×200即为肌原纤维小片化指数MFI。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2019、Origin 2021和SPSS 27对数据进行统计分析及作图,结果均以平均值±标准差表示,采用ANOVA方差分析法分析显著性差异水平,P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 冷藏三疣梭子蟹感官评价分析
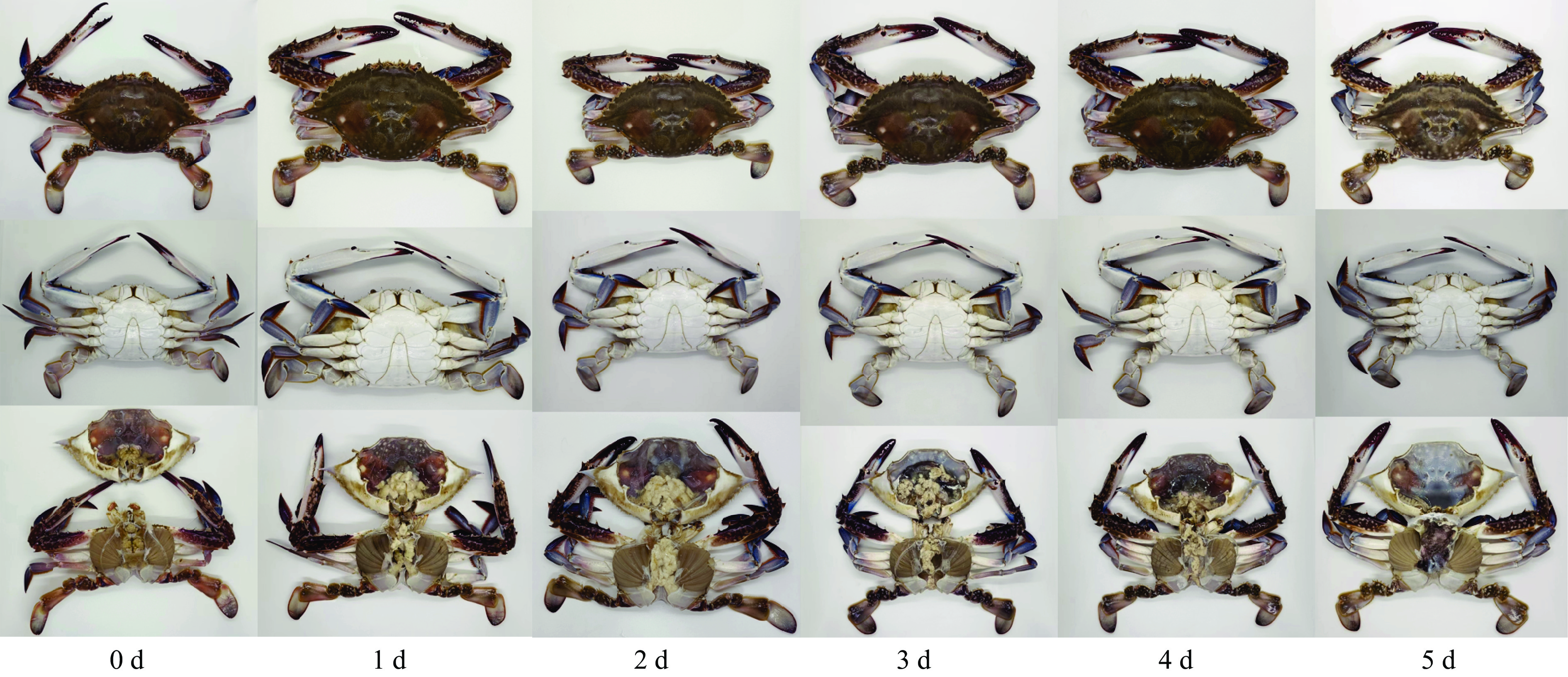
感官评价是评价水产品新鲜度和品质最直观的指标,在水产品品质评价方面被广泛应用[14]。由图1显示,新鲜三疣梭子蟹体表色泽鲜亮,背部呈青色,腹部呈白色,螯足与腹部连接紧实,肝胰腺轮廓分明。冷藏第5 d时,三疣梭子蟹体表暗沉,背部呈青灰色,腹部呈灰白色,肢体松散易脱落,肝胰腺糊化、呈水样状。根据表1中感官描述对三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉品质进行打分,结果如图2所示。随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉逐渐松散且由米白色逐渐转变成浅黄色,鲜香味逐渐被氨臭味和刺激性气味所替代,汁液流出量逐渐增多,肌肉黏性增强。与腹部肌肉相比,螯足肌肉随着贮藏时间延长肌肉松散程度下降更为明显、黏附性更强、汁液流出量更多、刺激性气味和氨臭味更强,可能是因为螯足肌肉中内源酶活性更强,造成螯足肌肉比腹部肌肉自溶作用更明显,进而导致螯足肌肉劣变速度比腹部肌肉更快;相反,腹部肌肉更易由米白色转变成浅黄色。宋雪[15]从外观、肉质和气味三方面对死后96 h内三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉品质进行综合打分,发现与腹部肌肉相比,螯足肌肉感官评分在死后24 h内更低,本研究结果与其相似。
2.2 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉持水力变化分析
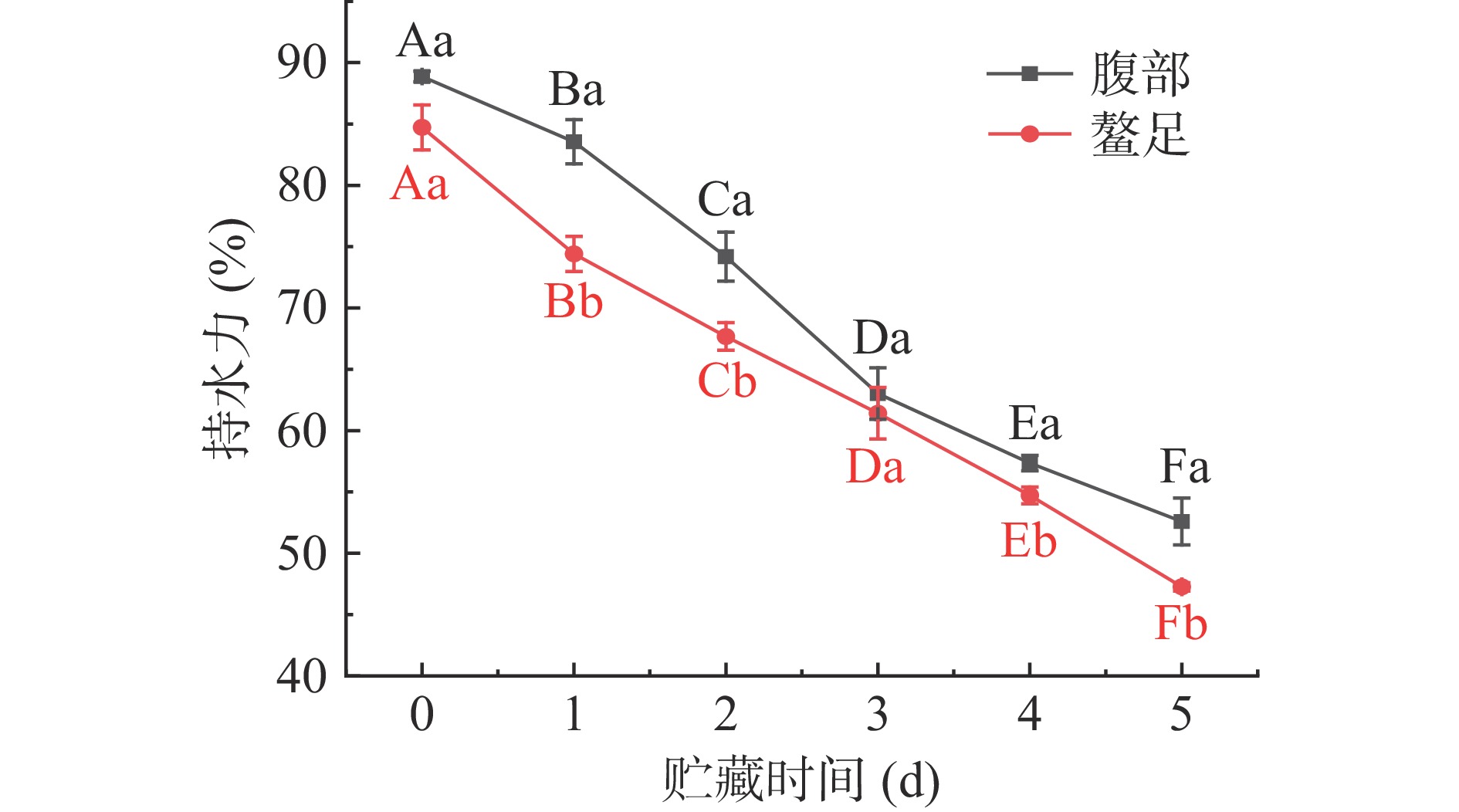
持水力表示肌肉组织阻碍其水分流失的能力,通常采用离心前后肌肉组织重量差表示持水力的大小[16]。由图3可知,新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉持水力分别为88.86%和84.72%,二者无显著性差异(P>0.05)。该结果与金超等测得的新鲜三疣梭子蟹蟹肉持水力结果相似[17]。随着贮藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉持水力均呈不断下降趋势,贮藏末期腹部和螯足肌肉分别下降了36.27%和37.46%。有研究表明,水产动物离水死后,肌肉中部分肌糖原经酵解产生乳酸,引起pH下降,致使肌肉组织松散、肌肉蛋白质束缚水分的能力减弱,同时肌肉收缩使得肌肉中水分流出,进而导致三疣梭子蟹肌肉持水力下降[18];此外,在贮藏过程中肌原纤维蛋白和结缔组织蛋白在内源性蛋白酶作用,使其发生降解,导致纤维间隙不断增大,保水能力不断下降[19]。在整个贮藏周期中,除贮藏第0和3 d外,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉持水力均显著高于螯足肌肉(P<0.05),这与感官评价结果相一致。
2.3 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉水分含量和水分活度变化分析
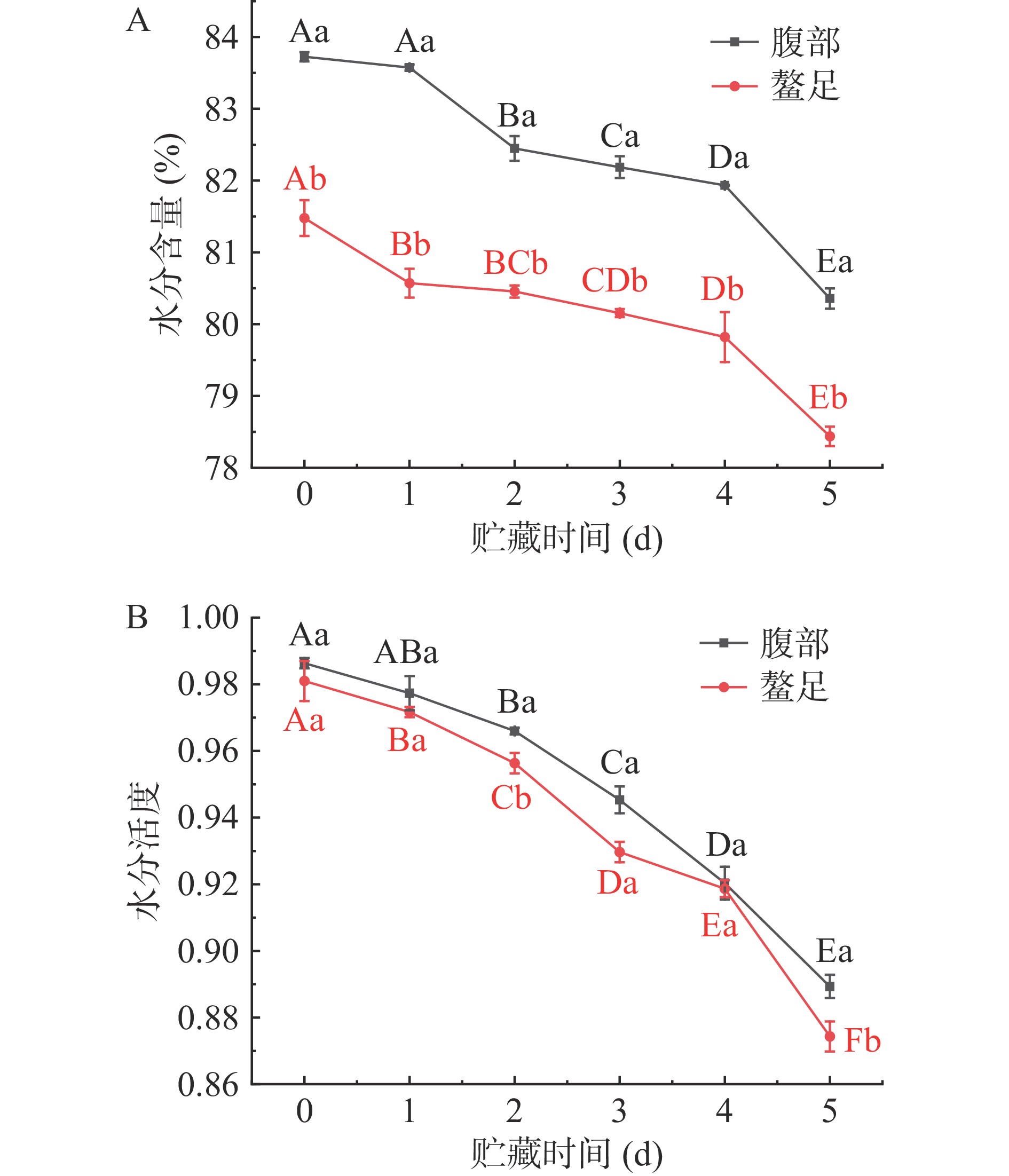
如图4A所示,随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水分含量均呈下降趋势,贮藏5 d后,腹部肌肉水分含量由新鲜时的83.73%下降到80.36%,螯足肌肉水分含量由新鲜时的81.48%下降到78.44%。原因可能是随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹肌肉组织结构破坏,导致肌肉组织中水分流失,进而导致肌肉水分含量下降[20]。在整个冷藏期间,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉水分含量均显著大于螯足肌肉(P<0.05)。张龙[21]在研究中华绒螯蟹肌肉品质特性时发现,中华绒螯蟹腹部肌肉水分含量比螯足肌肉水分含量高,本研究结果与之相似。
水分活度在水产品贮藏过程中起着关键作用,与微生物生长密切相关,是决定食品腐败变质和货架期的重要参数[22]。如图4B所示,新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水分活度分别为0.986和0.981,说明三疣梭子蟹肌肉新鲜度很高[23]。随着贮藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水分活度均呈不断下降趋势。可能是因为三疣梭子蟹肌肉处于高水分环境中,在贮藏过程中内源性蛋白酶发挥作用,水解肌肉蛋白质纤维,造成肌肉结构破坏,肌肉内游离水和部分结合水析出,进而造成水分活度下降[24]。这与三疣梭子蟹肌肉持水力和水分含量变化趋势相似。在贮藏过程中,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉水分活度均比螯足肌肉高,说明腹部肌肉新鲜度比螯足肌肉更优。
2.4 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉pH变化分析
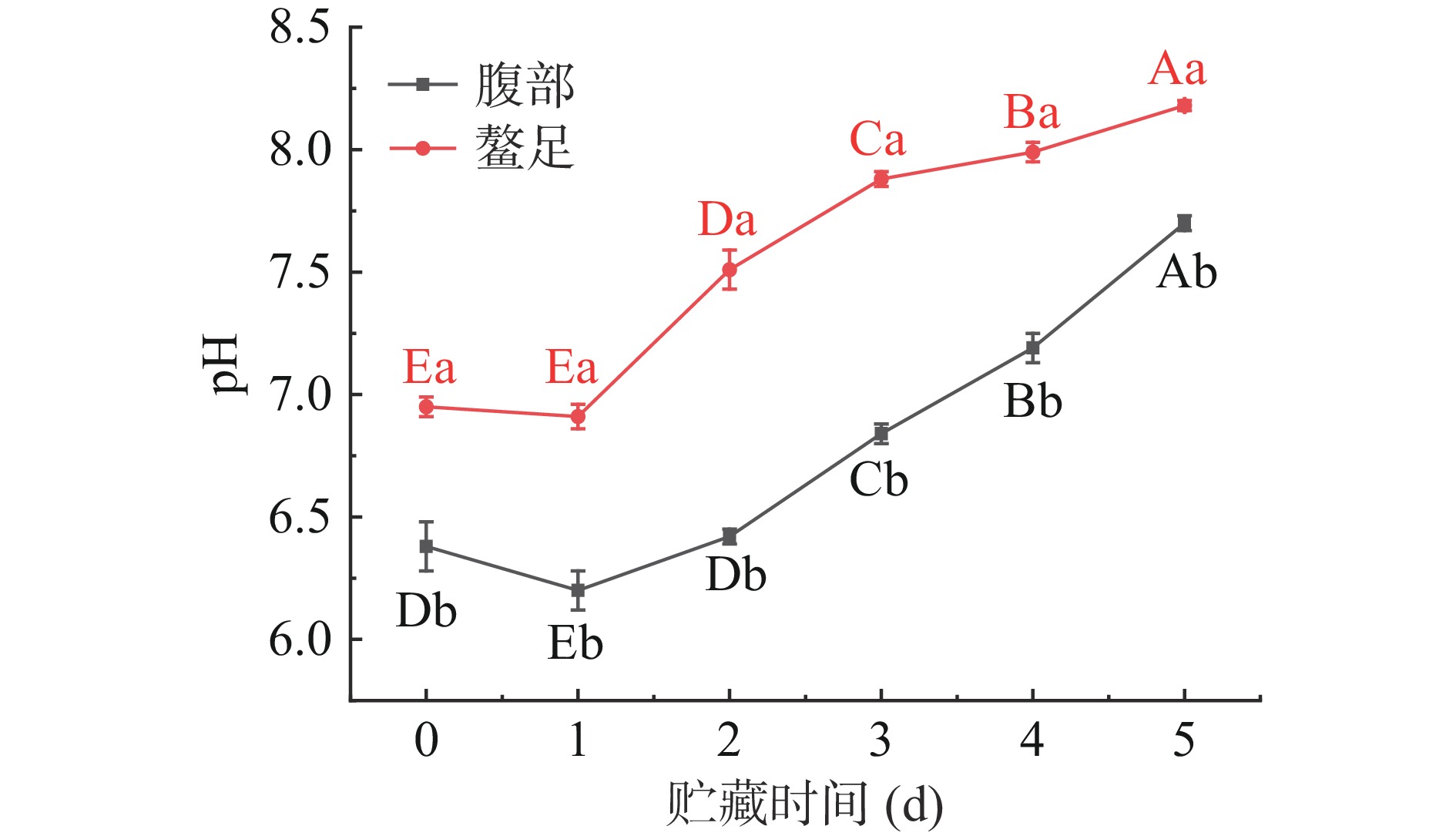
肌肉pH是评价水产品新鲜度的重要指标[25]。由图5可知,新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉pH分别为6.38和6.95,随着贮藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉pH均呈先下降后上升的趋势(P<0.05)。研究表明,水产动物在死亡后会逐渐停止呼吸,体内的存储糖易分解产生乳酸,使肌肉pH下降[26]。随后由于冷藏过程中肌肉蛋白质在微生物和酶的作用下分解产生氨、吲哚、三甲胺等碱性物质,使肌肉pH逐渐升高[27]。在整个贮藏周期,三疣梭子蟹螯足肌肉pH均显著大于腹部肌肉pH(P<0.05)。由于甲壳类动物的非蛋白含氮化合物含量高,pH总体偏高,建议pH可接受上限约为8.0[28]。腹部肌肉pH在贮藏第5 d时为7.7,未超过可接受上限;而螯足肌肉pH在贮藏第4 d时已达到7.99,趋近可接受上限。说明在贮藏过程中,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉冷藏保鲜效果比螯足肌肉更好。
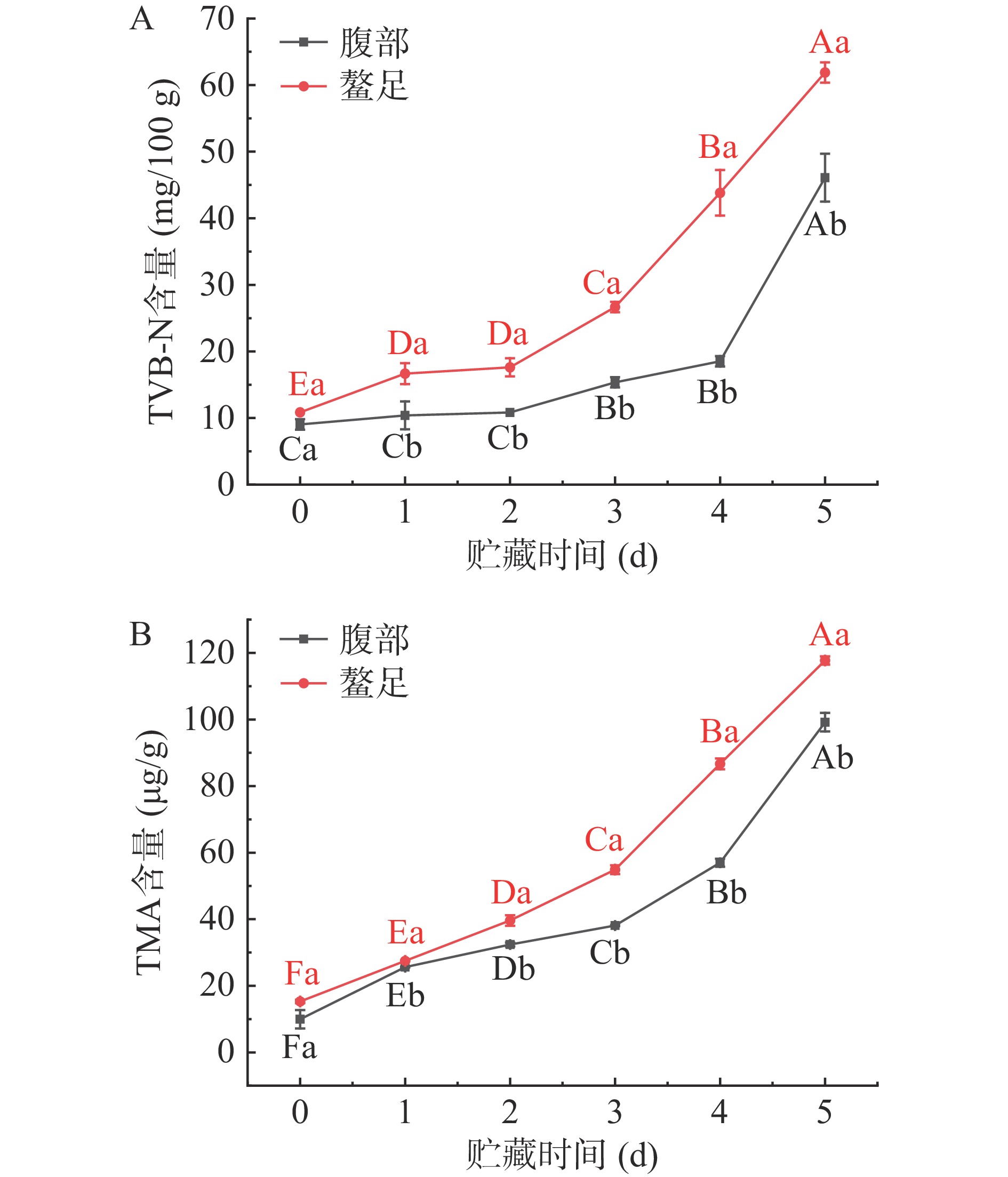
2.5 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉TVB-N含量和TMA含量变化分析
TVB-N含量能够反映水产品肌肉中含氮化合物降解情况,这类含氮化合物在内源酶及微生物作用下会降解产生具有挥发性的碱性物质,影响水产品新鲜度[29]。图6A显示冷藏期间三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TVB-N含量变化情况。新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TVB-N含量分别为9.04 mg/100 g和10.85 mg/100 g,两者无显著性差异(P>0.05)。随着贮藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TVB-N含量均呈不断上升趋势。腹部肌肉在贮藏第4~5 d时,螯足肌肉在贮藏第3~5 d时TVB-N含量快速增加,出现这种现象的原因可能是丝氨酸蛋白酶、组织蛋白酶的高活力以及微生物活动加强,分解大量氨基酸,脱氨基速度加快[30]。GB 2733-2015[31]中规定海蟹TVB-N含量超出25 mg/100 g,即认为不可食用。腹部肌肉TVB-N含量在第4 d时为18.52 mg/100 g仍低于国家标准,而螯足肌肉TVB-N含量在第3 d时达到26.66 mg/100 g,已超出国家标准,说明螯足肌肉微生物活动较腹部肌肉频繁。有研究表明[32],较低的pH能抑制肌肉微生物活性,与胺类物质的生长密切相关,致使腹部肌肉冷藏保鲜效果比螯足肌肉好,该研究结果与三疣梭子蟹肌肉pH结果相符。
TMA是造成鱼腥味的主要化合物,由氧化三甲胺在酶和微生物的作用下还原而来[33]。TMA含量越高,说明水产品鲜度值越低,腐败程度越严重。图6B为冷藏过程中三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TMA含量变化图。由图可知,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉初始TMA含量分别为9.96和15.29 μg/g,两者无显著性差异(P>0.05)。随着贮藏时间延长,腹部和螯足肌肉TMA含量均呈显著上升趋势,且在贮藏第3~5 d期间上升速度显著快于贮藏第0~3 d(P<0.05)。原因可能是贮藏后期肌肉组织中微生物生长旺盛,加快了氧化三甲胺还原成三甲胺的速度[34]。这与冷藏过程中三疣梭子蟹肌肉TVB-N含量变化结果相似。有研究表明,TMA含量超过35 μg/g鱼肉开始腐败变质,说明腹部肌肉第3 d时开始腐败,而螯足肌肉第2 d时就已开始腐败[35]。此外,由于甲壳类水产品肌肉中存在大量的游离氨基酸和含氮化合物,使得三疣梭子蟹肌肉极易被腐败微生物群快速降解,进而导致三疣梭子蟹肌肉TVB-N含量和TMA含量高于其他水产品[36]。
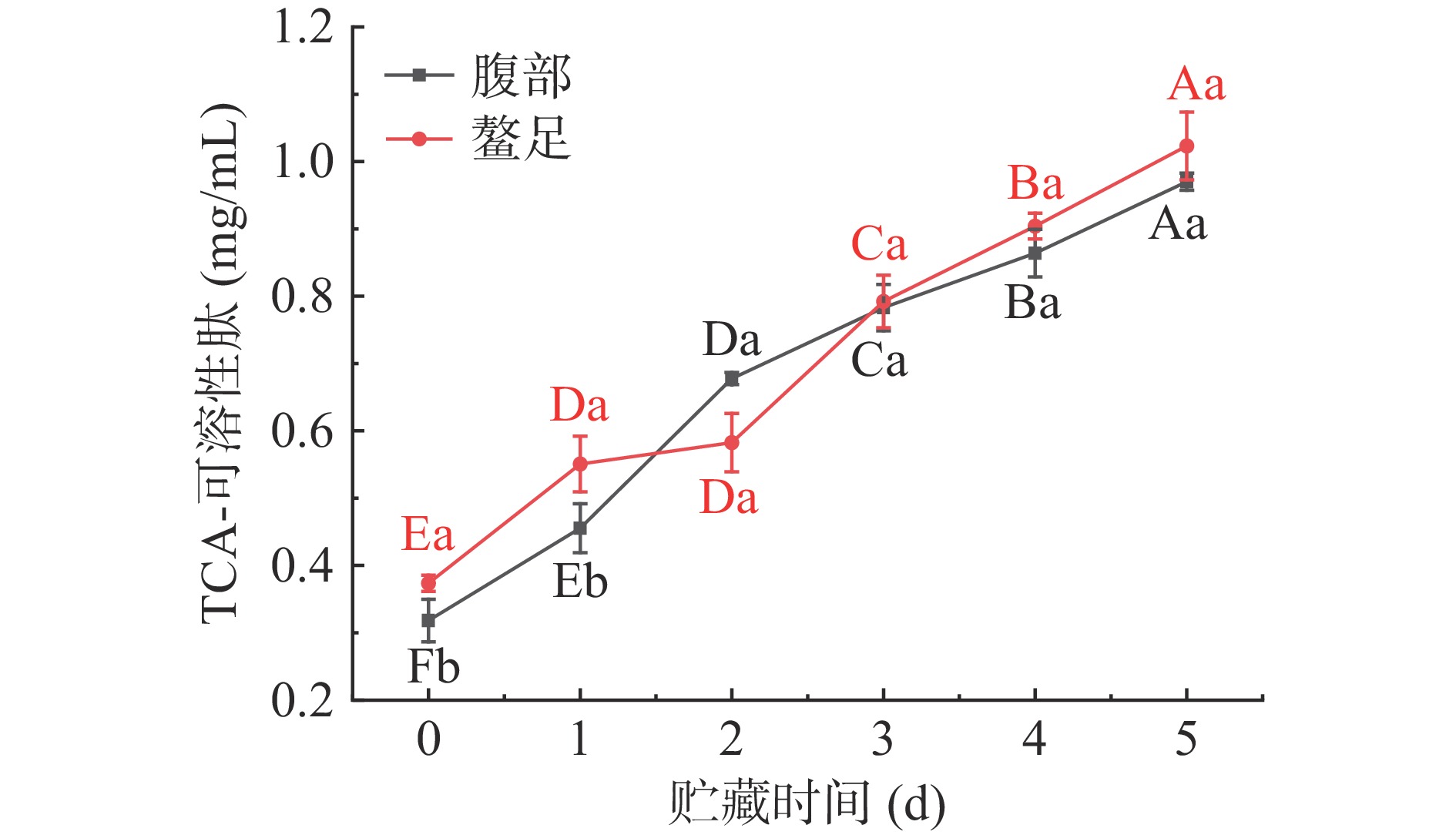
2.6 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量变化分析
TCA-可溶性肽含量通常用来反映蛋白质降解程度[37],含量越高,说明蛋白质降解程度越高。如图7所示,新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量分别为0.318和0.373 mg/mL。随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量呈显著上升趋势(P<0.05),表明在贮藏过程中,三疣梭子蟹肌肉蛋白质降解,生成小分子肽。TCA-可溶性肽含量前期上升可能是由于肌肉中内源性蛋白酶的降解作用,贮藏后期内源酶和微生物共同作用加速蛋白质降解[38]。这与Wang等[39]在研究大眼金枪鱼在0和4 ℃冷藏过程中TCA-可溶性肽含量变化结果相似。比较腹部和螯足两个部位肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量发现,贮藏第0~2 d时,腹部和螯足肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量差异性显著(P<0.05),第3~5 d时,腹部和螯足肌肉TCA-可溶性肽含量无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
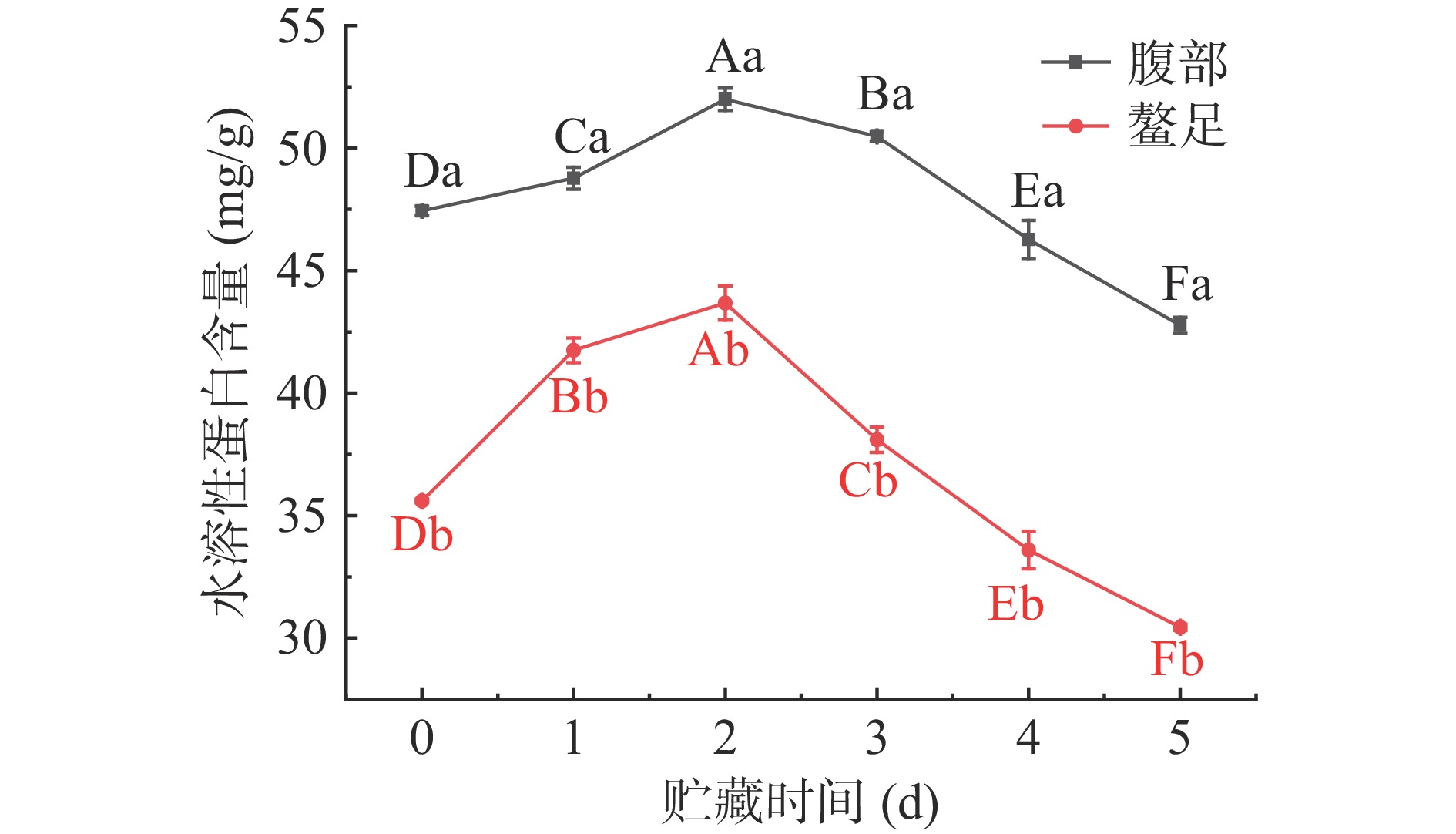
2.7 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉水溶性蛋白含量变化分析
水溶性蛋白主要成分为肌浆蛋白,包括与糖酵解相关的酶类,肌酸激酶以及肌红蛋白等水溶性物质[40]。如图8所示,0 d时三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水溶性蛋白含量分别为47.44和35.60 mg/g,第0~2 d时三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水溶性蛋白含量均呈显著上升趋势(P<0.05),可能是由于盐溶性蛋白降解成一些溶于水的小分子蛋白,使得水溶性蛋白含量上升;随着贮藏时间延长,第2~5 d时腹部和螯足肌肉水溶性蛋白含量均呈显著下降趋势(P<0.05),后期呈下降趋势是因为水溶性蛋白自身发生降解[41]。这与汪经邦等[42]在研究暗纹东方鲀低温贮藏期间水溶性蛋白的变化趋势相似。在整个贮藏过程中,腹部肌肉水溶蛋白含量均显著大于螯足肌肉(P<0.05),说明4 ℃冷藏过程中腹部肌肉蛋白质品质优于螯足肌肉,这与新鲜度指标结果基本吻合。
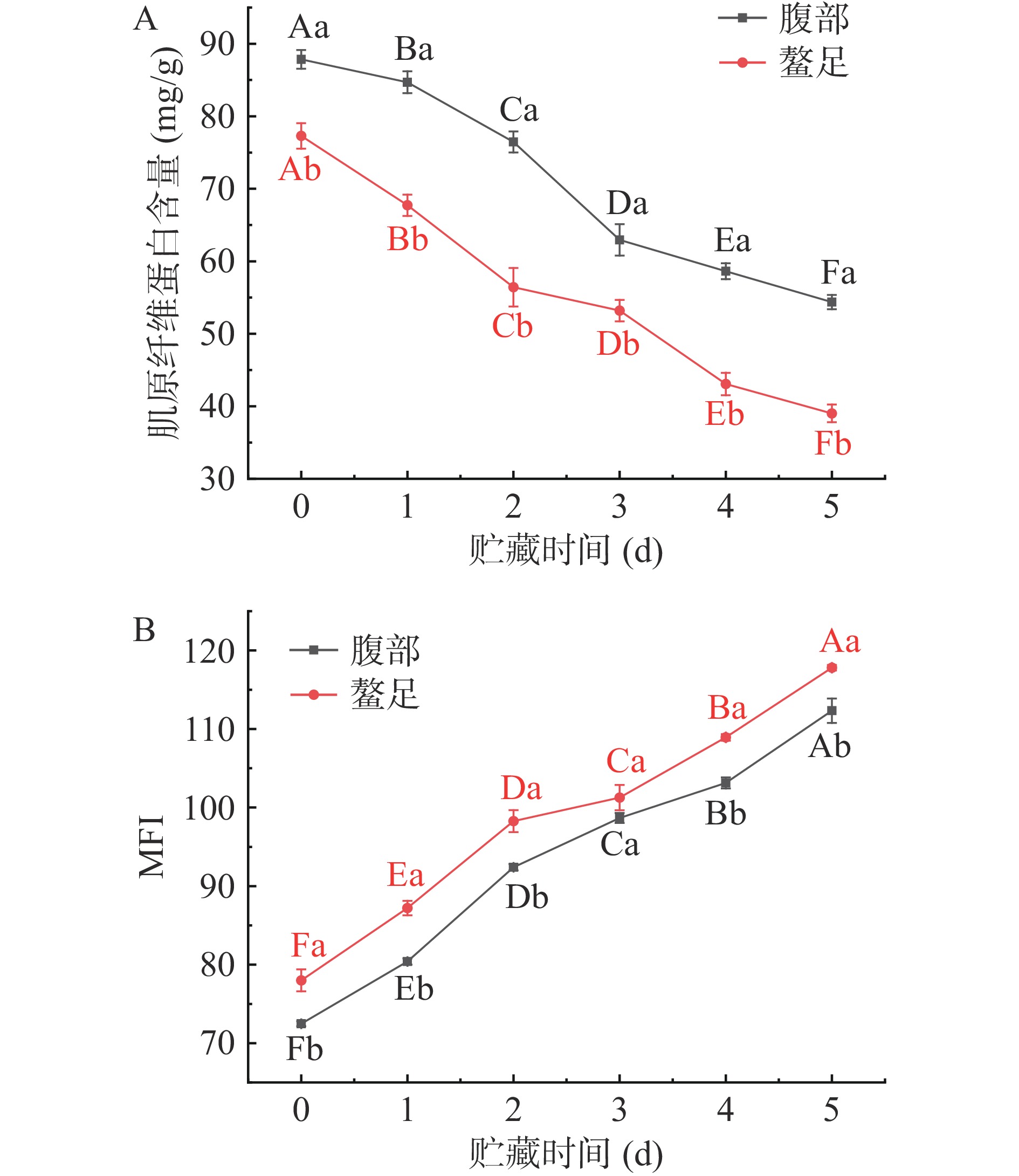
2.8 冷藏三疣梭子蟹肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量及其小片化指数变化分析
肌原纤维蛋白是一种重要的结构蛋白,是评价水产品肌肉质地软化,蛋白质降解的重要指标[43]。如图9A所示,随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量均呈显著下降趋势(P<0.05)。新鲜三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量分别为87.85 mg/g和77.29 mg/g;在冷藏第5 d时,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量分别下降了38.11%和49.51%,螯足肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量下降幅度较腹部肌肉更显著,且螯足肌肉肌原纤维蛋白含量显著小于腹部肌肉(P<0.05)。在整个贮藏期间,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉受微生物作用,肌原纤维蛋白降解。有研究表明,丝氨酸蛋白酶是导致三疣梭子蟹肌肉肌原纤维蛋白降解的原因之一[44]。在冷藏过程中,三疣梭子蟹肌肉蛋白质变性,使得细胞收缩间隙增大,进而导致腹部和螯足肌肉持水力和水分含量下降,影响三疣梭子蟹肌肉品质。这一结果与三疣梭子蟹肌肉冷藏过程中理化指标结果一致,进一步证明三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉品质劣变速度较螯足肌肉慢,三疣梭子蟹腹部贮藏时间较螯足长。
肌原纤维小片化指数(MFI)是表征肌原纤维蛋白降解程度的一个重要指标,反映了肌原纤维以及骨架蛋白的完整性[45]。由图9B可知,随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉MFI值均呈显著上升趋势(P<0.05),分别由最初的72.47和78上升至第5 d的112.33和117.8。这可能是因为随着冷藏时间延长,肌原纤维完整性受到破坏,三疣梭子蟹肌肉肌原纤维蛋白降解,小片化现象加剧。范铭良等[46]在研究冷藏过程中罗非鱼鱼肉肌原纤维变化情况时发现,贮藏时间越长,罗非鱼鱼肉肌原纤维碎片化现象越严重,MFI值越高,本实验结果与其研究结果一致。在整个贮藏周期,除贮藏第3 d外,其余时间点三疣梭子蟹螯足肌肉MFI值均显著大于腹部肌肉MFI值(P<0.05),说明在冷藏过程中三疣梭子蟹螯足肌肉蛋白质受到破坏的程度比腹部肌肉更严重。
3. 结论
本研究以三疣梭子蟹为研究对象,通过比较分析冷藏过程中腹部和螯足肌肉品质特性变化发现,三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉感官评价整体优于螯足肌肉。随着冷藏时间延长,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉水分含量、持水力、肌原纤维蛋白含量等均呈下降趋势;其三甲胺、TCA-可溶性肽含量和肌原纤维小片化指数均呈上升趋势。冷藏第4 d时,三疣梭子蟹螯足肌肉pH趋近8.0,TVB-N含量超过国家标准25 mg/100 g,肌肉品质已经腐败变质,超出可接受范围,而腹部肌肉品质整体优于螯足肌肉。由此可得,冷藏条件下三疣梭子蟹腹部肌肉保鲜效果比螯足肌肉更好。本研究为冷藏三疣梭子蟹品质劣变及调控技术提供理论参考,同时为后续研究冷藏过程中,三疣梭子蟹腹部和螯足肌肉间品质相互影响的作用机制提供思路。
-
表 1 三疣梭子蟹感官描述词汇及定义
Table 1 Sensory description vocabulary and definition of swimming crab
描述词汇 定义 米白色/粉白色 腹部肌肉为米白色,螯足肌肉为粉白色 浅黄色 肌肉变黄 蟹香味 具有三疣梭子蟹固有鲜香味 腥臭味 有腐败腥臭味 刺激性气味 有刺激氨臭味 肌肉紧实 肉质紧密有弹性 黏 肌肉具有黏附性 有汁液流出 肌肉自溶使得汁液流出 -
[1] 黄刚, 娄永江, 王春琳. 低温液体速冻对软壳三疣梭子蟹冻藏期间肌肉生化特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(11):328−331,358. [HUANG G, LOU Y J, WANG C L. Effect of cryogenic liquid quick-freezing on the biochemical properties of soft shell swimming crab ( Portunus trituberculatus) muscle during frozen storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(11):328−331,358. HUANG G, LOU Y J, WANG C L . Effect of cryogenic liquid quick-freezing on the biochemical properties of soft shell swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) muscle during frozen storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014 ,35 (11 ):328 −331,358 .[2] 周果, 崔燕, 杨文鸽, 等. 冰温贮藏对梭子蟹品质影响及其货架期模型的建立[J]. 核农学报,2017,31(4):719−727. [ZHOU G, CUI Y, YANG W G, et al. Impact of controlled freezing-point storage on the Portunus trituberculatus quality and model construction of its shelf-life[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2017,31(4):719−727. ZHOU G, CUI Y, YANG W G, et al . Impact of controlled freezing-point storage on the Portunus trituberculatus quality and model construction of its shelf-life[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2017 ,31 (4 ):719 −727 .[3] 王芳, 周国燕. 甲壳类水产品变质问题和低温保鲜及其辅助技术的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2021,57(4):106−112,121. [WANG F, ZHOU G Y. Advances in the research on the deterioration of crustacean aquatic products and the low temperature preservation and its auxiliary technologies[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology,2021,57(4):106−112,121. WANG F, ZHOU G Y . Advances in the research on the deterioration of crustacean aquatic products and the low temperature preservation and its auxiliary technologies[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology,2021 ,57 (4 ):106 −112,121 .[4] 宗腊梅, 李静竹, 谢嘉伟, 等. 三疣梭子蟹在0 ℃保存时品质变化评价指标研究[J]. 食品工业,2017,38(12):200−203. [ZONG L M, LI J Z, XIE J W, et al. Study on the quality changes and indicators of Portunus trituberculatus storing at 0 ℃ cold conditions[J]. The Food Industry,2017,38(12):200−203. ZONG L M, LI J Z, XIE J W, et al . Study on the quality changes and indicators of Portunus trituberculatus storing at 0 ℃ cold conditions[J]. The Food Industry,2017 ,38 (12 ):200 −203 .[5] 黄琳, 张莉, 武丹露. 三疣梭子蟹( Portunus trituberculatus)冻藏过程中肌肉蛋白质生化特性的变化[J]. 海洋科学,2017,41(6):41−47. [HUANG L, ZHANG L, WU D L. Changes in the biochemical properties of muscle protein of swimming crab ( Portunus trituberculatus) during frozen storage[J]. Marine Sciences,2017,41(6):41−47. HUANG L, ZHANG L, WU D L . Changes in the biochemical properties of muscle protein of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) during frozen storage[J]. Marine Sciences,2017 ,41 (6 ):41 −47 .[6] YANG S B, HU Y Q, TAKAKI K, et al. Effect of water ice-glazing on the quality of frozen swimming crab ( Portunus trituberculatus) by liquid nitrogen spray freezing during frozen storage[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2021,131:1010−1015. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2021.06.035
[7] YANG F, GUO H H, GAO P, et al. Comparison of methodological proposal in sensory evaluation for Chinese mitten crab ( Eriocheir sinensis) by data mining and sensory panel[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,356:129698. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129698
[8] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 16291.1-2012 感官分析 选拔、培训与管理评价员一般导则 第1部分:优选评价员[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2012. [Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 16291.1-2012 Sensory analysis, general guidance for the selection, training and monitoring of assessors, part 1:Selected assessors[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2012. Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 16291.1-2012 Sensory analysis, general guidance for the selection, training and monitoring of assessors, part 1: Selected assessors[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2012.
[9] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.3-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of water in food[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.3-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of water in food[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[10] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.238-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品水分活度的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.238-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of food water activity[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.238-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of food water activity[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[11] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.228-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.228-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of volatile basic nitrogen in foods[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.228-2016 National standard of food safety. Determination of volatile basic nitrogen in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[12] 李学鹏. 中国对虾冷藏过程中品质评价及新鲜度指示蛋白研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工商大学, 2012. [LI X P. Studies on quality assessment and protein indicators of freshness in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) during refrigerated storage[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2012. LI X P. Studies on quality assessment and protein indicators of freshness in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) during refrigerated storage[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2012.
[13] YANG F, JIA S N, LIU J X, et al. The relationship between degradation of myofibrillar structural proteins and texture of superchilled grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella) fillet[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125278. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125278
[14] DU Q, CHEN X N, JIANG H L, et al. Effect of stable chlorine dioxide and vacuum-packing treatments on the physicochemical and volatile flavor properties of pike eel ( Muraenesox cinereus) during chilled storage[J]. Foods,2022,11(17):2701. doi: 10.3390/foods11172701
[15] 宋雪. 冷藏条件下中华绒螯蟹与三疣梭子蟹ATP降解途径的探究及品质变化的评价[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2016. [SONG X. The exploration of ATP degradation pathways in Eriocheir sinensis and Portunus trituberculatus and its quality evaluation during chilled storage[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. SONG X. The exploration of ATP degradation pathways in Eriocheir sinensis and Portunus trituberculatus and its quality evaluation during chilled storage[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016.
[16] 李志鹏, 周晓娇, 水珊珊, 等. 低温贮藏中华管鞭虾肌肉品质及组织蛋白酶H活性变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(22):306−313. [LI Z P, ZHOU X J, SHUI S S, et al. Influence of cold storage on the quality of muscle and the activity of cathepsin H in red shrimp ( Solenocera crassicornis)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):306−313. LI Z P, ZHOU X J, SHUI S S, et al . Influence of cold storage on the quality of muscle and the activity of cathepsin H in red shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (22 ):306 −313 .[17] 金超, 赵艳. 三疣梭子蟹在4 ℃和0 ℃冷藏条件下的品质评价研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(9):317−320. [JIN C, ZHAO Y. Study on the quality changes and indicators of Trituberculatus storing at 4 ℃ and 0 ℃ cold conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(9):317−320. JIN C, ZHAO Y . Study on the quality changes and indicators of Trituberculatus storing at 4 ℃ and 0 ℃ cold conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010 ,31 (9 ):317 −320 .[18] 邹朝阳, 赵峰, 欧帅, 等. 冷藏和冰藏条件下大菱鲆品质变化与蛋白质氧化相关性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(22):213−219. [ZOU Z Y, ZHAO F, OU S, et al. Correlation between quality change and protein oxidation of turbot ( Scophthalmus maximus) during refrigerated and ice storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(22):213−219. ZOU Z Y, ZHAO F, OU S, et al . Correlation between quality change and protein oxidation of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) during refrigerated and ice storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019 ,45 (22 ):213 −219 .[19] 欧韦. 长牡蛎冷藏过程中闭壳肌品质变化的研究[D]. 厦门:集美大学, 2022. [OU W. Study on quality change of adductor muscle of Crassostrea gigas during cold storage[D]. Xiamen:Jimei University, 2022. OU W. Study on quality change of adductor muscle of Crassostrea gigas during cold storage[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2022.
[20] 陈晓楠. 海鳗鱼低温贮藏过程中肌肉品质特性变化及其发生规律[D]. 舟山:浙江海洋大学, 2022. [CHEN X N. Study on the quality characteristics and alternation mechanisms of pike eel (Muraenesox cinereus) muscle during cold storage[D]. Zhoushan:Zhejiang Ocean University, 2022. CHEN X N. Study on the quality characteristics and alternation mechanisms of pike eel (Muraenesox cinereus) muscle during cold storage[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2022.
[21] 张龙. 中华绒螯蟹蟹肉蛋白质性状变化及其对质地品质的影响[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2019. [ZHANG L. Effects of muscle protein changes on textural quality of Eriocheir sinensis[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2019. ZHANG L. Effects of muscle protein changes on textural quality of Eriocheir sinensis[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019.
[22] 蓝蔚青, 巩涛硕, 傅子昕, 等. 不同植物源提取液对冰藏鲳鱼水分迁移及蛋白质特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(8):179−188. [LAN W Q, GONG T S, FU Z X, et al. Effect of different plant-source extracts on water migration and protein characteristics in pomfret ( Pampus argenteus) during ice storage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(8):179−188. LAN W Q, GONG T S, FU Z X, et al . Effect of different plant-source extracts on water migration and protein characteristics in pomfret (Pampus argenteus) during ice storage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019 ,19 (8 ):179 −188 .[23] LAN W Q, YANG X, LIU J L, et al. Effects of phenolic acid grafted chitosan on moisture state and protein properties of vacuum packaged sea bass ( Lateolabrax japonicus) during refrigerated storage[J]. LWT,2022,159:113208. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113208
[24] 迟坤蕊, 姜竹茂, 华霄, 等. 冷藏即食虾仁保藏期间品质变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(9):283−289. [CHI K R, JIANG Z M, HUA X, et al. The change of quality during storage of shrimp in cold storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(9):283−289. CHI K R, JIANG Z M, HUA X, et al . The change of quality during storage of shrimp in cold storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (9 ):283 −289 .[25] 祁雪儿, 毛俊龙, 姚慧, 等. 蛋白质氧化对中华管鞭虾肌肉品质特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(18):15−21. [QI X E, MAO J L, YAO H, et al. Effect of protein oxidation on the quality attributes of Solenocera crassicornis muscle[J]. Food Science,2021,42(18):15−21. QI X E, MAO J L, YAO H, et al . Effect of protein oxidation on the quality attributes of Solenocera crassicornis muscle[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (18 ):15 −21 .[26] 刘小莉, 彭欢欢, 李莹, 等. 冻藏温度对斑点叉尾鮰鱼片蛋白质特性和感官品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(1):141−147. [LIU X L, PENG H H, LI Y, et al. Effect of storage temperature on protein characteristics and sensory quality of frozen catfish fillets[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(1):141−147. LIU X L, PENG H H, LI Y, et al . Effect of storage temperature on protein characteristics and sensory quality of frozen catfish fillets[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019 ,19 (1 ):141 −147 .[27] 杨冰, 王舒瀚, 许瑞红, 等. 鮰鱼肉冷藏过程中新鲜度变化[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(20):6474−6481. [YANG B, WANG S H, XU R H, et al. Study on the changes of freshness of Ictalurus punctatus meat during cold storage[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(20):6474−6481. YANG B, WANG S H, XU R H, et al . Study on the changes of freshness of Ictalurus punctatus meat during cold storage[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022 ,13 (20 ):6474 −6481 .[28] LALY S J, ANUPAMA T K, KUMAR K A, et al. Changes in biogenic amines, biochemical and microbial attributes of three spotted crab ( Portunus sanguinolentus) during iced and refrigerated storage[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,58(6):2197−2205. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04730-w
[29] 杨静. 暗纹东方鲀冷藏过程中质构劣化和蛋白降解变化研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [YANG J. Study on texture softening and protein deterioration change of puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus) during refrigerated storage[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017. YANG J. Study on texture softening and protein deterioration change of puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus) during refrigerated storage[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[30] 章骞, 陈宏, 阙华勇, 等. 长牡蛎( Crassostrea gigas)不同组织中蛋白酶的分布及冷藏过程中酶活力与鲜度变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2021,52(4):1039−1046. [ZHANG Q, CHEN H, QUE H Y, et al. Distribution of proteases in different tissues of Crassostrea gigas and changes of enzyme activity and freshness during cold storage[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,2021,52(4):1039−1046. ZHANG Q, CHEN H, QUE H Y, et al . Distribution of proteases in different tissues of Crassostrea gigas and changes of enzyme activity and freshness during cold storage[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,2021 ,52 (4 ):1039 −1046 .[31] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 2733-2015 食品安全国家标准 鲜、冻动物性水产品[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning. GB 2733-2015 National standard of food safety, fresh and frozen animal aquatic products[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning. GB 2733-2015 National standard of food safety, fresh and frozen animal aquatic products[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[32] HU Y J, XIA W S, LIU X Y. Changes in biogenic amines in fermented silver carp sausages inoculated with mixed starter cultures[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,104(1):188−195. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.11.023
[33] YU D W, JING D T, YANG F, et al. The factors influencing the flavor characteristics of frozen obscure pufferfish ( Takifugu Obscurus) during storage:Ice crystals, endogenous proteolysis and oxidation[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2021,122:147−155. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2020.10.028
[34] 霍霞飞, 张德权, 苏媛媛, 等. 三甲胺和二甲胺表征冷鲜羊肉新鲜度[J]. 肉类研究,2022,36(7):13−19. [HUO X F, ZHANG D Q, SU Y Y, et al. Potential of trimethylamine and dimethylamine to characterize the freshness of chilled mutton[J]. Meat Research,2022,36(7):13−19. HUO X F, ZHANG D Q, SU Y Y, et al . Potential of trimethylamine and dimethylamine to characterize the freshness of chilled mutton[J]. Meat Research,2022 ,36 (7 ):13 −19 .[35] 王亚会, 施文正, 王锡昌, 等. 中华绒螯蟹鲜活及死后品质评价[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(3):244−254. [WANG Y H, SHI W Z, WANG X C, et al. The quality evaluation of alive and dead chinese mitten crab ( Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(3):244−254. WANG Y H, SHI W Z, WANG X C, et al . The quality evaluation of alive and dead chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018 ,18 (3 ):244 −254 .[36] ANACLETO P, TEIXEIRA B, MARQUES P, et al. Shelf-life of cooked edible crab ( Cancer pagurus) stored under refrigerated conditions[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2011,44(6):1376−1382. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.01.010
[37] LI D Y, LIU Z Q, LIU B, et al. Effect of protein oxidation and degradation on texture deterioration of ready-to-eat shrimps during storage[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85(9):2673−2680. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15370
[38] 周婷, 水珊珊, 李志鹏, 等. 基于内源酶活性变化的冷藏哈氏仿对虾肌肉品质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(24):338−346. [ZHOU T, SHUI S S, LI Z P, et al. Study on muscle quality of sword prawn ( Parapenaeopsis hardwickii) during cold storage based on changes of endogenous enzyme activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(24):338−346. ZHOU T, SHUI S S, LI Z P, et al . Study on muscle quality of sword prawn (Parapenaeopsis hardwickii) during cold storage based on changes of endogenous enzyme activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (24 ):338 −346 .[39] WANG X Y, XIE J. Evaluation of water dynamics and protein changes in bigeye tuna ( Thunnus obesus) during cold storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,108:289−296. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.03.076
[40] 卢涵. 鳙鱼肉低温贮藏过程中蛋白氧化、组织蛋白酶活性与品质变化规律的研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2017. [LU H. Protein oxidation, cathepsins activity and the quality changes of bighead carp (Arisrichthys nobilis) during low-temperature storage[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2017. LU H. Protein oxidation, cathepsins activity and the quality changes of bighead carp (Arisrichthys nobilis) during low-temperature storage[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017.
[41] 李学鹏, 陈杨, 王金厢, 等. 冷藏大菱鲆新鲜度评价辅助蛋白指标和指示物[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(4):193−202. [LI X P, CHEN Y, WANG J X, et al. Studies on the auxiliary evaluation indexes and indicators of freshness for refrigerated turbot ( Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(4):193−202. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.026 LI X P, CHEN Y, WANG J X, et al . Studies on the auxiliary evaluation indexes and indicators of freshness for refrigerated turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018 ,18 (4 ):193 −202 . doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.026[42] 汪经邦, 谢晶, 刘大勇. 暗纹东方鲀低温贮藏期间水分、质地和蛋白质的变化规律[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(21):213−221. [WANG J B, XIE J, LIU D Y. Changes in water mobility, texture and protein structure in Takifugu obscurus during low temperature storage[J]. Food Science,2020,41(21):213−221. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191008-036 WANG J B, XIE J, LIU D Y . Changes in water mobility, texture and protein structure in Takifugu obscurus during low temperature storage[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (21 ):213 −221 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191008-036[43] LIU B, LIU Z Q, LI D Y, et al. Action of endogenous proteases on texture deterioration of the bay scallop ( Argopecten irra dians) adductor muscle during cold storage and its mechanism[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,323:126790. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126790
[44] SONG C H, SHI Y N, MENG X H, et al. Identification of a novel alkaline serine protease from gazami crab ( Portunus trituberculatus) hepatopancreas and its hydrolysis of myofibrillar protein[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,155:403−410. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.179
[45] XU J H, CAO H J, ZHANG B, et al. The mechanistic effect of bromelain and papain on tenderization in jumbo squid ( Dosidicus gigas) muscle[J]. Food Research International,2020,131:108991. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.108991
[46] 范铭良, 郝淑贤, 李来好, 等. 罗非鱼冷藏期间内源蛋白酶和热休克蛋白70对肌原纤维解离的影响[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业:1−10[2023-11-01]. [FAN M L, HAO S X, LI L H, et al. Effect of endogenous proteases and heat shock protein 70 on myofibril dissociation during refrigeration in tilapia[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries:1−10[2023-11-01]. FAN M L, HAO S X, LI L H, et al. Effect of endogenous proteases and heat shock protein 70 on myofibril dissociation during refrigeration in tilapia[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries: 1−10[2023-11-01].
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 彭思维,蒋沁芸,张睿涵,刘彦伟,陈应运,张宾,陈静. 低温等离子体预处理对贮藏期间蟹糊品质变化研究. 食品科技. 2024(10): 155-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



