Optimization of Inorganic Ceramic Membrane Filtration Process for Tea Enzymes
-
摘要: 为了提高茶叶酵素的澄清度,同时保证茶叶酵素在澄清过程中功能成分得到最大的保留,本试验以夏秋茶发酵所得茶叶酵素为原料,采用单因素实验和响应面试验考察无机陶瓷膜孔径、过膜功率、过膜压力、过膜温度对过膜后酵素液功能成分含量、膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量的影响,旨在优选出最佳的茶叶酵素陶瓷膜过滤条件。结果表明,茶叶酵素陶瓷膜过滤的最佳条件为:膜孔径400 nm、过膜功率47 Hz、过膜压力0.28±0.02 MPa,过膜温度15±2 ℃,在此条件下,茶叶酵素中茶多酚含量保留率为95.28%,茶氨酸含量保留率为82.91%,锌含量保留率为90.48%,硒含量保留率为91.67%,可溶性固形物含量保留率为84.46%,透光率为85.10%±0.12%,透光率与过膜前相比提高了2.5倍,膜通量为123.25±2.68 m3/(m2·h),该条件既能最大程度的保留茶叶酵素中功能成分的含量,又能使茶叶酵素透亮、均一。因此,采用该条件对茶叶酵素进行过滤澄清方法可行。Abstract: In order to enhance the clarity of tea enzymes while maximizing the preservation of their functional components during the clarification process, this experiment utilized tea enzymes derived from summer and autumn tea fermentation as the primary material. Through both single-factor and response surface experiments, the effects of inorganic ceramic membrane pore size, transmembrane power, transmembrane pressure, and transmembrane temperature on the content of functional components, membrane flux, transmittance, and soluble solids content of the enzyme solution after membrane filtration were examined. The objective was to determine the optimal conditions for ceramic membrane filtration of tea enzymes. The results showed that, the ideal conditions for ceramic membrane filtration of tea enzymes were as follows: Membrane pore size of 400 nm, transmembrane power of 47 Hz, transmembrane pressure of 0.28±0.02 MPa, and transmembrane temperature of 15±2 ℃. Under these conditions, the retention rates of tea polyphenols, theanine, zinc, selenium, and soluble solids content in tea enzymes were 95.28%, 82.91%, 90.48%, 91.67%, and 84.46% respectively. The transmittance reached 85.10%±0.12% with 2.5-fold improvement compared to before membrane filtration. Additionally, the membrane flux achieved 123.25±2.68 m3/(m2·h). These optimal conditions not only maximized the retention of functional components in tea enzymes, but also ensured their transparency and uniformity. Therefore, employing these conditions for the filtration and clarification of tea enzymes was a viable approach.
-
Keywords:
- tea enzyme /
- inorganic ceramic membrane /
- filtration /
- process optimization /
- tea polyphenols /
- theanine /
- retention rate
-
澄清对于保证酵素稳定性、延长贮藏期和提高酵素感官品质等方面具有重要作用。传统的澄清方法有加酶[1−2](果胶酶、复合酶)澄清法、加吸附剂[1−2](膨润土、硅藻土)澄清法、化学澄清法[3](冻融法、醇沉法、壳聚糖絮凝法)等,但这些澄清法在一定程度上会发生物理化学反应,导致酵素中功效成分发生变化,直接影响酵素的色、香、味,破坏其生物活性物质的含量。膜过滤技术[4−6]是天然或人工合成的高分子薄膜以压力差、浓度差、电位差和温度差等外界能量位差为推动力,对双组分或多组分的溶质和溶剂进行分离、分级、提纯和富集的方法。目前,膜分离所使用的材料大致可以分为无机膜和有机膜两大类,有机膜化学稳定性与机械强度较弱,寿命较短,较易堵塞;而无机陶瓷膜[7−9]化学稳定性好,耐酸、碱和有机溶剂的化学侵蚀;耐高温,抗微生物能力强,不与微生物发生作用;机械强度高,耐高压,有良好的耐磨、耐冲刷性能;孔径分布窄,分离性能好、渗透量大;可反复清洗、再生,弥补了高温浓缩法和有机膜分离法的不足,且采用膜分离技术可以滤除提取液中蛋白质、淀粉、果胶、鞣质等大分子物质以及微生物[10−11],对酸度、糖度无影响[12],且功效成分基本无截留[13−14],广泛应用于药品、食品的工业除杂领域。
目前,一些研究者应用陶瓷膜对乌龙茶水[15]、蔗汁[16]、红茶茶汤[17]、山茱萸水提液[18]、粗制茶多糖[19]等进行了研究,结果证明,应用陶瓷膜进行分离可达到澄清、除杂和功效成分富集的效果。但是目前以发酵的茶叶酵素为研究对象的还未有报道,且因发酵的原因,茶叶酵素的内含物质比茶水多,过膜时比茶水难,本课题组前期预实验发现无机陶瓷膜(20~400 nm)过滤后茶叶酵素感官品质(色泽、香气、滋味)基本无变化,透光率和保质期能得到较大的提高,同时该方法较易实现工业化成产。因此本文采用不同孔径的陶瓷膜对凤冈锌硒夏秋茶发酵后的茶叶酵素进行过滤澄清,对过滤后茶叶酵素的功能成分、透光率、膜通量、可溶性固形物含量进行测定,筛选出最佳的膜孔径和过膜条件,最终将其应用于工业生产,对贵州凤冈锌硒夏秋茶酵素工业化的可持续发展具有重要的推进意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
夏秋茶 2021年9月采摘于贵州省遵义市凤冈县田坝村,包括夏秋茶嫩叶、老叶及部分枝干;白砂糖 购买于德旺佳超市;红茶菌菌种 实验室自制引种;L-茶氨酸(DST211028-021)、茶多酚(DSTDC013001) 成都德思特生物技术有限公司;锌、硒标准溶液(1000 μg/mL) 国家有色金属及电子材料分析测试中心;硝酸、高氯酸 GR,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甲醇 GR,默克化工技术(上海)有限公司;三氟乙酸、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钾、硫酸亚铁、酒石酸钾钠 AR,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司。
Cary 60紫外可见分光光度计 美国安捷伦公司;Prodigy XP电感耦合等离子发射光谱仪 利曼科技有限公司;AFS-2100双道原子荧光光度计 北京海光仪器有限公司;BONA-GM-22陶瓷膜过滤实验机[CT-30-300无机陶瓷膜20 nm(膜编号:12200125)、50 nm(膜编号:05112073)、100 nm(膜编号:01081062)、200 nm(膜编号:07282049)、400 nm(膜编号:05272176)] 长度30 cm,过滤面积0.07 m2,通道19个,通道直径4 nm,山东博纳生物科技有限公司。
1.2 茶叶酵素发酵
红茶菌悬液培养:按凤冈锌硒夏秋茶:蔗糖:水=10:100:1000(m:m:V)的比例,先将水煮沸,加入夏秋茶浸泡于85~90 ℃水中保持20 min,滤去茶叶渣得茶汁,按比例加入溶化的糖水,混匀后分装到三角瓶中,每500 mL装入300 mL糖茶水,用牛皮纸包扎,进行巴氏消毒,冷却至室温,加入15%红茶菌菌种,于30 ℃恒温培养箱培养15 d,即得。
茶叶酵素制备:按茶水比3%,称取相应质量的夏秋茶,加入煮沸纯水,浸泡20 min,过滤,滤液加白砂糖10%(m/V),搅拌均匀并溶化,冷却至室温,装瓶40 L/50 L,接种15%红茶菌液,置于恒温发酵室内,发酵15 d,发酵温度30±2 ℃。
1.3 茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺
1.3.1 单因素实验
本文依次考察膜孔径、过膜功率、过膜压力、过膜温度对茶叶酵素过膜通量,过膜后酵素液透光率、固形物、功能成分含量的影响。
1.3.1.1 无机陶瓷膜孔径范围的确定
固定功率40 Hz,温度10~20 ℃,压力0.35 MPa,以膜孔径为单因素变量,分别考察膜孔径20、50、100、200、400 nm对茶叶酵素过膜通量,过膜后酵素液透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响。
1.3.1.2 过膜功率考察
固定膜孔径400 nm,过膜压力0.18 MPa,过膜温度10~20 ℃,以过膜功率为单因素变量,分别考察过膜功率30、35、40、45、50 Hz对茶叶酵素过膜通量,过膜后酵素液透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响。
1.3.1.3 过膜压力考察
固定膜孔径400 nm,过膜功率40 Hz,过膜温度10~20 ℃,以过膜压力为单因素变量,分别考察过膜压力0.15、0.20、0.25、0.30、0.35 MPa对茶叶酵素过膜通量,过膜后酵素液透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响。
1.3.1.4 过膜温度考察
固定膜孔径400 nm,过膜功率40 Hz,过膜压力0.25 MPa,以过膜温度为单因素变量,分别考察过膜温度10~20 ℃、20~30 ℃、30~40 ℃、40~50 ℃、50~60 ℃对茶叶酵素过膜通量,过膜后酵素液透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响。
1.3.2 响应面试验设计
通过对单因素的系统考察,固定400 nm孔径的陶瓷膜,以过膜功率(A)、过膜压力(B)、过膜温度(C)为自变量,因过膜的主要目的是在获得功能成分较高保留量的基础上获得最佳透光率。通过单因素实验的筛选,已经能够确保茶叶酵素中功能成分得到最大的保留,所以响应面试验设计以过膜后酵素液透光率为响应值,运用Design Expert V8.0.6软件进行三因素三水平[20−21]试验设计,茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺因素水平见表1。
表 1 茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺响应面优化试验因素水平设计Table 1. Level design of experimental factors for optimal response surface of tea enzyme membrane filtration process水平 因素 A过膜功率(Hz) B过膜压力(MPa) C过膜温度(℃) −1 40 0.25 10 0 45 0.30 20 1 50 0.35 30 1.4 理化指标测定方法
1.4.1 茶多酚、茶氨酸含量测定方法
用UV-VIS法测定,茶多酚含量测定参照GB/T 8313-2018茶叶中的茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测;茶氨酸含量测定参照GB/T 8314-2013茶 游离氨基酸总量的测定。
1.4.2 锌、硒含量测定方法
锌、硒含量测定方法:锌测定参照GB 5009.14-2017《食品安全国家标准 食品中锌的测定》第二法;硒测定参照GB 5009.93-2017《食品安全国家标准 食品中硒的测定》第一法。
1.4.3 膜通量测定方法
膜通量是指单位时间、单位膜面积透过组分的通过量,以J表示,本试验记录膜通量为发酵液过滤的平均膜通量[22]。
式中:J为膜渗透通量,m3/(m2·h);V为透过组分的体积,m3;A为膜有效面积,m2;t为操作时间,h。
1.4.4 透光率、可溶性固形物含量测定方法
透光率测定方法[23]:用紫外可见分光光度计在 625 nm处测量。
可溶性固形物含量测定方法[24]:取一定体积的茶叶酵素于蒸发皿中,放于烘箱中(105 ℃,5 h)进行烘干,烘干后固体物的重量即为可溶性固形物的含量。
1.5 数据处理
所有试验数据均为3次重复试验结果的平均值,采用SPSS Statistic 17进行单因素显著性分析,Design Expert V8.0.6软件进行响应面试验数据分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 无机陶瓷膜孔径对过滤效果的影响
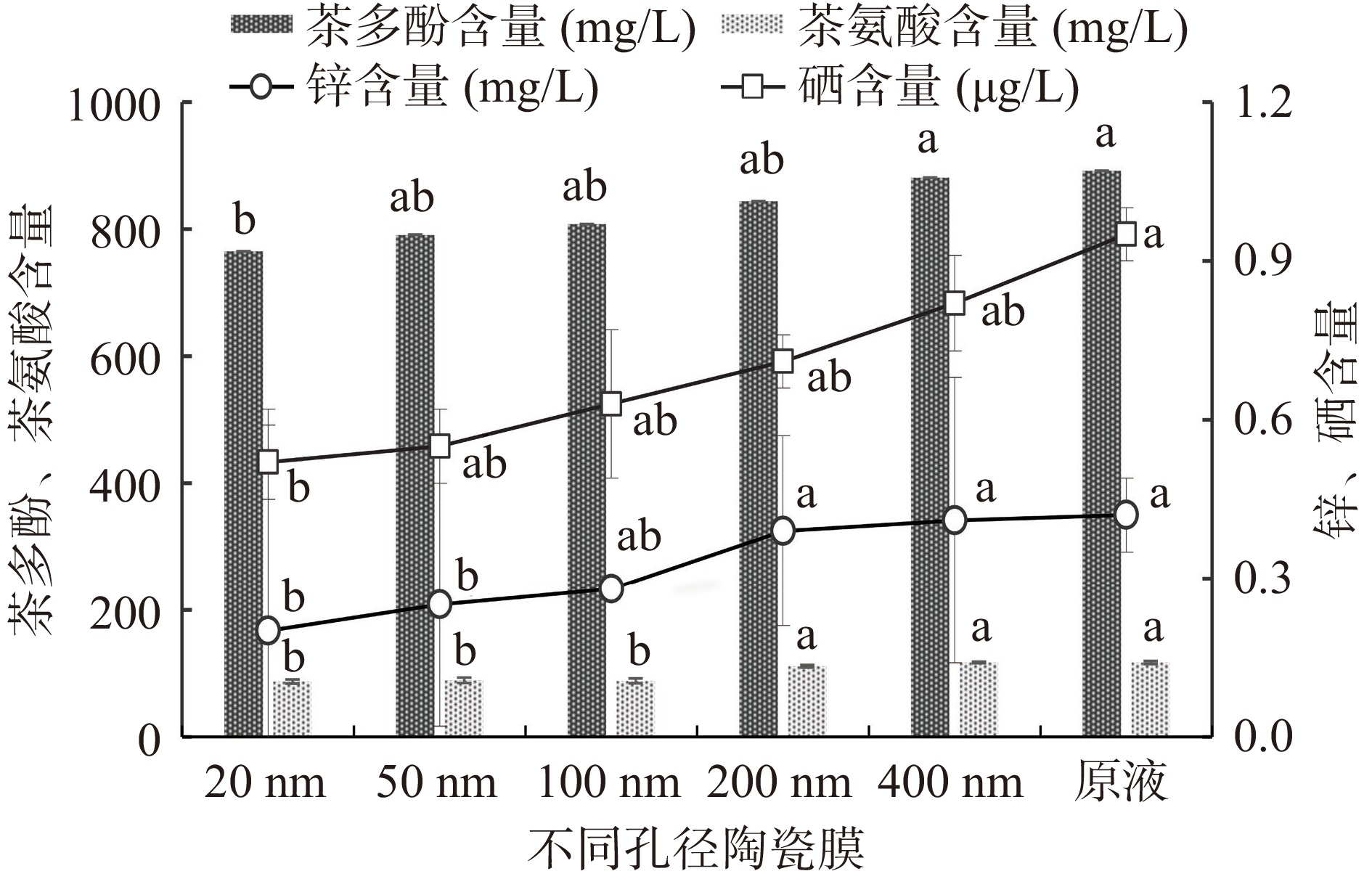
不同孔径无机陶瓷膜对茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响见图1和表2。
表 2 不同孔径陶瓷膜过滤后茶叶酵素的膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物(n=3)Table 2. Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids of tea enzymes filtered by ceramic membranes with different pore sizes (n=3)实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物(g/L) 原液 − 49.10±0.02d 95.67±0.48a 20 nm 32.66±3.73ed 94.94±0.99a 78.79±0.36e 50 nm 43.10±2.63cd 88.79±1.94b 83.45±0.20d 100 nm 49.88±2.33c 87.91±0.38b 82.96±0.48d 200 nm 88.16±2.07b 79.18±0.13c 84.81±1.12c 400 nm 142.86±1.80a 80.11±0.18c 88.42±0.21b 注:同列数据差异显著,P<0.05;表3~表5、表8同。 由图1可知,原液组中4种功能性成分的含量最高,其他组随着陶瓷膜孔径的增大,功能成分含量也随之增大。对于茶多酚含量,原液组与400 nm组含量最高,20 nm组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组与400 nm组;对于茶氨酸含量,原液组、400 nm组、200 nm组含量最高,20 nm组、50 nm组、100 nm组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组、400 nm组、200 nm组;对于锌含量,原液组、400 nm组、200 nm组含量最高,20 nm组、50 nm组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组、400 nm组、200 nm组;对于硒含量,原液组含量最高,20 nm组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组。因此,选择400 nm能尽可能多的保留功能成分的含量。由表2可知,随着陶瓷膜孔径的增大,膜通量逐渐增大、可溶性固形物含量也有增加趋势,酵素液的透光率呈降低趋势,各个陶瓷膜孔径过滤后酵素液透光率在79%以上,均为透亮澄清溶液,考虑到实际工业生产中生产量大,选择400 nm孔径过滤不仅膜通量大且不易堵塞。推测膜孔径增大,孔隙度也越大,孔径越均匀,允许通过的分子量也增多,因此功能成分含量、可溶性固形物含量增大;此外,增大的膜孔径会减小过膜阻力,功能成分的通行更顺畅,通过的物质增多,膜通量增大,透光率减小[25]。
2.1.2 过膜功率对过滤效果的影响
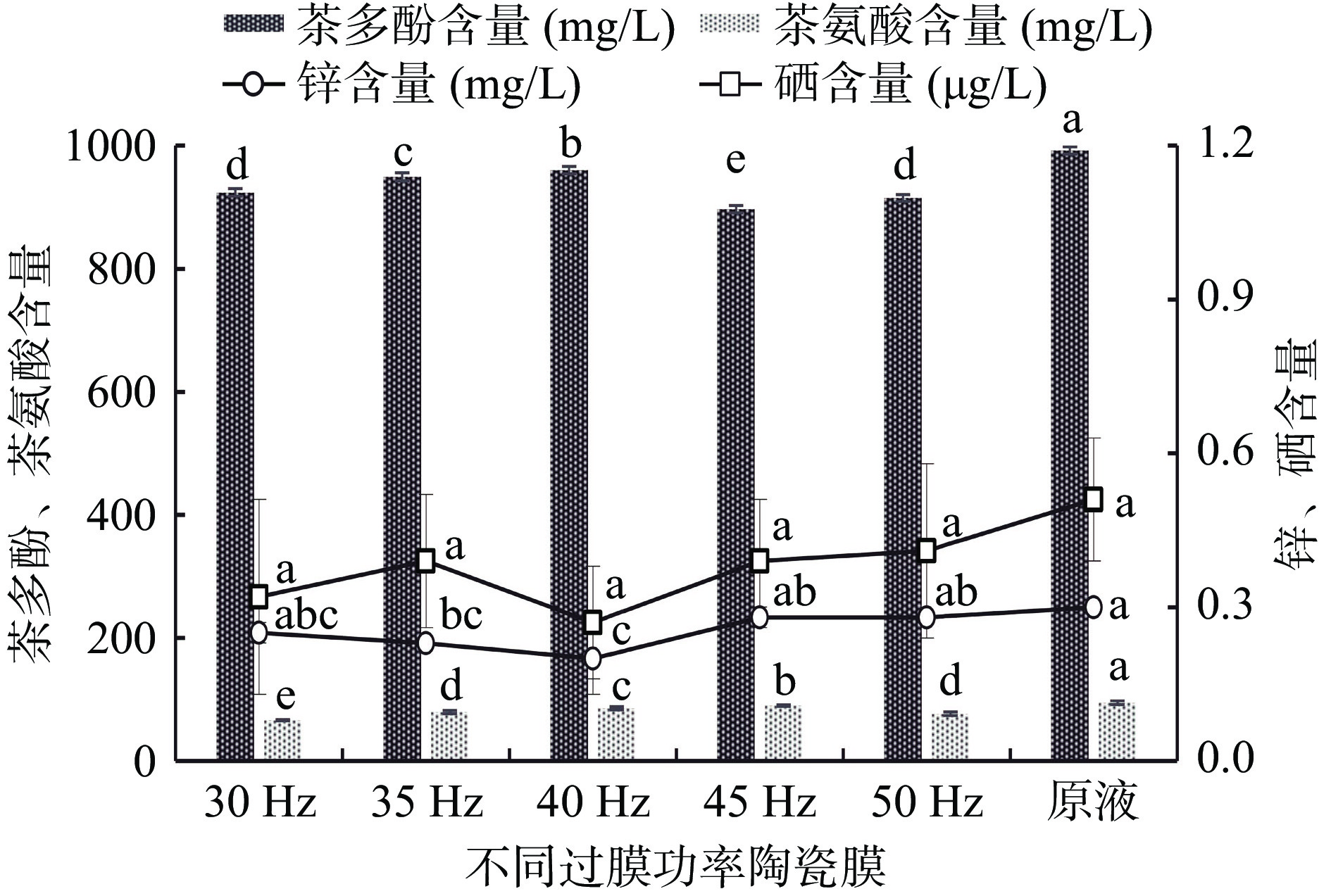
过膜功率对茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响见图2和表3。
表 3 不同功率过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)Table 3. Tea enzyme membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content after filtration with different powers (n=3)实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 50.73±0.08d 138.49±0.09a 30 Hz 98.18±3.62c 69.44±0.17c 127.23±0.65c 35 Hz 102.86±2.61c 75.95±0.24b 127.29±1.50c 40 Hz 115.71±1.81b 81.05±0.86a 129.11±2.61c 45 Hz 115.71±2.82b 80.30±0.88a 133.76±1.04b 50 Hz 137.14±4.84a 82.61±1.69a 132.46±1.97b 由图2可知,原液中4种功能成分的含量最高,随着过膜功率的变化,功能成分的含量也发生着变化。对于茶多酚含量,原液组含量最高,40 Hz组含量次高,45 Hz组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于其余各组;对于茶氨酸含量,原液组含量最高,45 Hz组含量次高,30 Hz组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于其余各组;对于锌含量,原液组含量最高,50 Hz组、45 Hz组含量次高,40 Hz组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组、50 Hz组、45 Hz组;对于硒含量,各组均差异不显著,说明过膜功率对其影响不大。因此,40 Hz时茶多酚含量保留率最高,45 Hz时茶氨酸含量保留率最高,45和50 Hz时锌含量保留率最高,从过膜后功能成分最大保留的条件出发,40、45、50 Hz对茶叶中功能成分有不同程度的保留作用。由表3可知,随着过膜功率的增大,膜通量逐渐增大,酵素液的透光率和可溶性固形物也呈增大趋势,40、45、50 Hz组酵素液透光率超80%,较为透亮澄清。因此,选用40、45、50 Hz作为过膜功率均可。综上,适当增大过膜功率有助于保留酵素液中的功能成分。推测设备功率增大,单位时间内工作效率变高,茶叶酵素中通过的功能成分增多,单位时间内的过膜速率增大,膜通量增大;此外,膜上的挤压力增大,膜孔径之间的缝隙变小,大分子物质不易透过,因此透光率增大。
2.1.3 过膜压力对过滤效果的影响
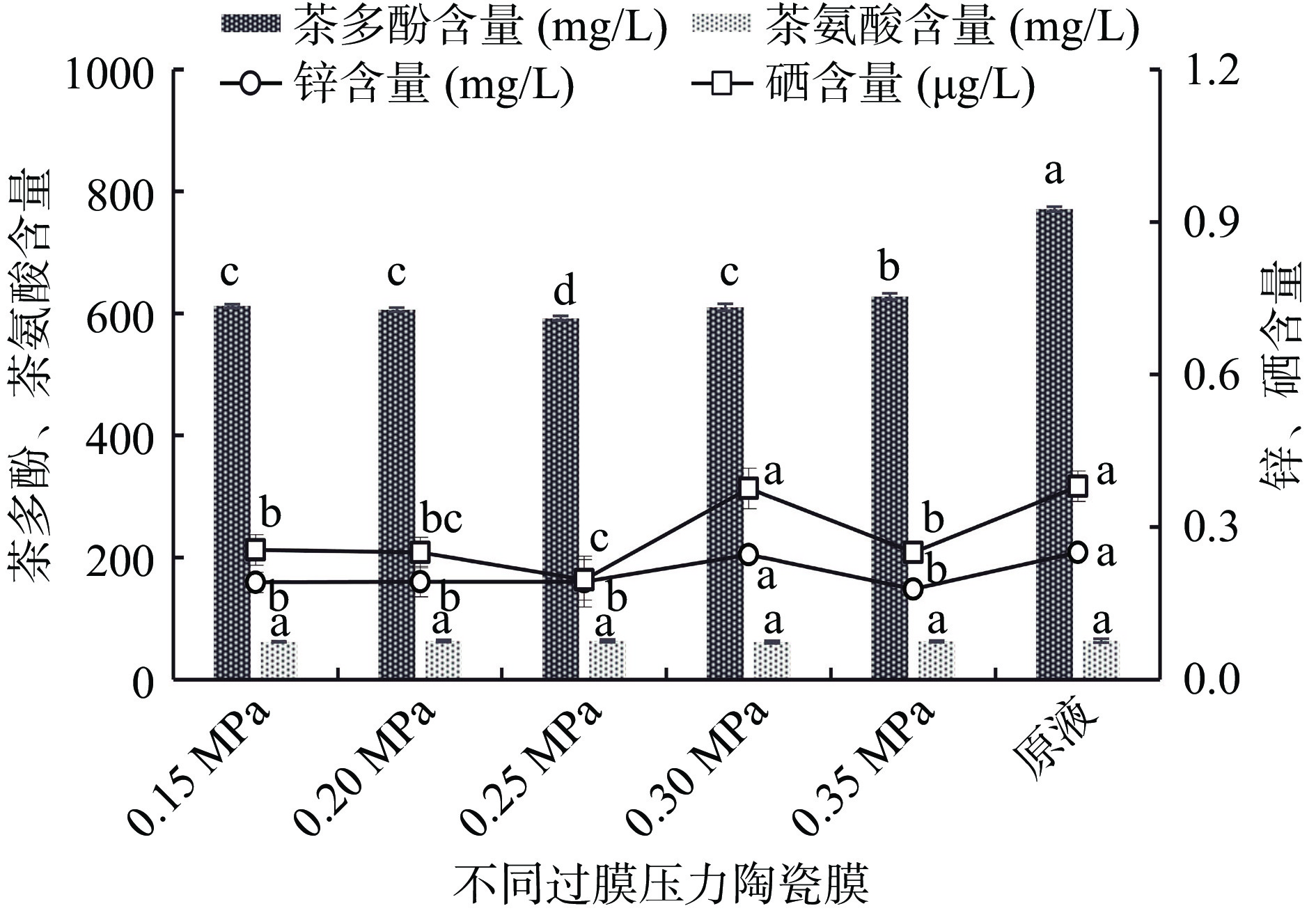
过膜压力对茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响见图3和表4。
表 4 不同压力过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)Table 4. Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content of tea fermentation under different pressure filtration (n=3)实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 31.02±0.09d 128.32±2.32a 0.15 MPa 72.73±4.23bc 65.80±2.12c 107.94±2.26c 0.20 MPa 70.59±3.26cd 72.11±1.32b 106.39±2.25c 0.25 MPa 72.73±4.16bc 79.29±0.98a 106.74±2.14c 0.30 MPa 75.00±2.65ab 79.89±1.02a 107.91±1.85c 0.35 MPa 77.42±3.62a 81.75±1.23a 110.46±1.65b 由图3可知,原液中4种功能成分的含量最高,随着过膜压力的变化,功能成分的含量也发生着变化。对于茶多酚含量,原液组含量最高,0.35 MPa组含量次高,0.25 MPa组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于其余各组;对于茶氨酸含量,各组均差异不显著,说明过膜压力对其影响不大;对于锌含量,原液组与0.30 MPa组含量最高,其余各组含量差异不显著;对于硒含量,原液组与0.30 MPa组含量最高,0.25 MPa组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组与0.30 MPa组。因此,0.35 MPa时茶多酚含量保留率最高,0.30 MPa时锌和硒含量保留率最高。由表4可知,随着过膜压力的增大,酵素液的透光率、可溶性固形物含量、膜通量呈增大趋势,0.25、0.30、0.35 MPa组酵素液透光率值较大且差异不显著,因此,选用0.25、0.30、0.35 MPa作为过膜压力均可。分析原因,在临界压力范围内[26],设备压力增大,过膜推动力增大,单位时间内的过膜速率增大,工作效率增高,膜上挤压力增大,膜孔径之间的缝隙变小,因此,增大设备压力,膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量有增大趋势。该结果与Loizzo等[27]研究结果部分一致,Loizzo MR使用膜分离对意大利Femminello comune果汁进行了分离,结果表明:在膜上施加越来越大的压力导致可溶性固形物含量略有减少,但不会导致总酚类活性化合物的损失。
2.1.4 过膜温度对过滤效果的影响
过膜温度对茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、固形物含量、功能成分含量的影响见图4和表5。
表 5 不同温度过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)Table 5. Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content of tea enzymes filtered at different temperatures (n=3)实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 49.84±0.08e 129.58±0.09a 10~20℃ 88.10±3.35e 86.79±0.31a 103.28±0.15d 20~30℃ 113.27±3.12d 80.73±0.64b 104.75±0.19c 30~40℃ 192.86±2.64c 74.33±1.68c 105.15±1.58c 40~50℃ 226.53±2.82b 67.65±1.65d 104.90±0.68c 50~60℃ 257.14±2.61a 66.73±2.52d 105.74±1.32b 由图4可知,原液中4种功能成分的含量最高,随着过膜温度的升高,功能成分的含量也呈增加趋势。对于茶多酚含量,原液组含量最高,30~40 ℃组含量次高,50~60 ℃组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组和30~40 ℃组;对于茶氨酸含量,原液组、50~60 ℃组含量最高,10~20 ℃组含量最低,显著(P<0.05)低于原液组和50~60 ℃组;对于锌含量,原液组、50~60 ℃组含量最高,显著(P<0.05)高于其余各组;对于硒含量,原液组、50~60 ℃、40~50 ℃组含量最高,其余各组含量差别不大。因此,50~60 ℃对茶叶酵素功能成分的保留效果最佳。由表5可知,随着过膜温度的增大,酵素液的膜通量、可溶性固形物呈增大趋势,但透光率呈降低趋势,10~20 ℃、20~30 ℃组酵素液透光率超80%,较为透亮澄清。因此,选用10~30 ℃作为最佳过膜温度。推测过膜温度升高,膜的渗透性升高,茶叶酵素的溶解度增加,粘度降低,浓差极化层变薄,从而降低了流阻,相应地提高了渗透率,过膜速率增快,过膜物质增多,因此酵素液功能成分含量增高,膜通量增大,可溶性固形物含量增大,透光率减小[28]。
2.2 响应面试验结果
根据孔径考察结果可知,孔径为400 nm时,茶叶酵素透光率超80%,且功能成分含量相对原液组最高;根据过膜功率考察结果可知,过膜功率为40、45、50 Hz时,茶叶酵素透光率超80%;根据过膜压力考察结果可知,过膜压力为0.25、0.30、0.35 MPa时,茶叶酵素透光率在80%左右;根据温度考察结果可知,温度为10~30 ℃时,茶叶酵素透光率超80%。因此,过膜功率、过膜压力、过膜温度对茶叶酵素透光率和功效成分有一定的影响,本文旨在提高茶叶酵素透光率的情况下尽可能多的保留酵素中的功效成分,因此在保证茶叶酵素透光率超80%的条件下,以合适的过膜功率(40~50 Hz)、过膜压力(0.25~0.35 MPa)、过膜温度(10~30 ℃)为自变量,过膜后酵素液透光率为响应值,应用响应面-星点设计法优化茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺的试验结果见表6和表7,其中表6为星点设计试验和结果;表7为茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺所建立的回归方程的方差分析。
表 6 响应面设计试验与结果(n=3)Table 6. Test and results of response surface design (n=3)实验号 A过膜功率(Hz) B过膜压力(MPa) C过膜温度(℃) 透光率(%) 1 40 0.35 20 80.95 2 45 0.35 10 82.20 3 40 0.25 20 80.35 4 45 0.3 20 84.42 5 50 0.35 20 82.54 6 45 0.25 10 82.41 7 45 0.3 20 83.14 8 40 0.3 10 83.05 9 45 0.25 30 78.27 10 40 0.3 30 74.74 11 50 0.3 30 78.68 12 45 0.35 30 79.29 13 50 0.25 20 83.48 14 45 0.3 20 81.87 15 50 0.3 10 83.42 表 7 回归方程方差分析Table 7. Variance analysis of regression equation方差来源 SS(平方和) Df(自由度) MS(均方差) F值 P值 显著性 模型 85.50 9 9.50 5.97 0.0317 * A-过膜功率 10.19 1 10.19 6.40 0.0525 B-过膜压力 0.028 1 0.028 0.02 0.9004 C-过膜温度 50.50 1 50.50 31.72 0.0024 * AB 0.59 1 0.59 0.37 0.5684 AC 3.19 1 3.19 2.00 0.2163 BC 0.38 1 0.38 0.24 0.6466 A2 3.27 1 3.27 2.06 0.2111 B2 0.51 1 0.51 0.32 0.5960 C2 18.35 1 18.35 11.52 0.0194 * 残差 7.96 5 1.59 失拟项 4.69 3 1.56 0.95 0.5483 不显著 纯误差 3.27 2 1.64 总变态 93.47 14 注:P<0.05,差异显著;P<0.01,差异极显著;R2=0.9148。 通过多元线性回归二项式拟合,在三重复的条件下以过滤液透光率(Y)为响应值,得回归方程为:Y=−21.9298+3.7202A+147.3350B−0.3474C−1.5400AB+0.0179AC+0.6150BC−0.0377A2−148.6000B2−0.0222C2,R2=0.9148,说明该模型与试验拟合良好,可用此模型进行分析和预测。由表7可知,方差模型P<0.0317,显著,说明建立的模型是有意义的;失拟项P(0.5483)>0.05,不显著,表明该模型能很好地预测过膜后酵素液的透光率;P值反映各因素对透光率的重要性,一次项C显著(P<0.05),二次项C2显著(P<0.05),说明对茶叶酵素过膜工艺的影响顺序为:过膜温度>过膜功率>过膜压力,过滤温度对茶叶酵素的影响较大。软件预测最佳过膜条件为:过膜功率47.17 Hz,过膜压力0.28 MPa,过膜温度14.99 ℃,在此过膜条件下,预测透过液的透光率为84.01%。
2.3 验证试验
基于响应面法优化的茶叶酵素最佳的过膜条件,结合实施的便利,将优化条件修正为过膜功率47 Hz,过膜压力0.28±0.02 MPa,过膜温度15±2 ℃,试验重复3组,得到过膜后茶叶酵素透光率平均值为85.10%±0.12%,接近于预测值;由表8可知,最佳过膜条件过滤后,茶多酚含量保留率为95.28%,茶氨酸含量保留率为82.91%,锌含量保留率为90.48%,硒含量保留率为91.67%,可溶性固形物含量保留率为84.46%,透光率与过膜前相比提高了2.5倍,膜通量为123.25 m3/(m2·h)。
表 8 原液组与验证组功能成分、膜通量、透光率,可溶性固形物含量变化(n=3)Table 8. Changes of functional components, membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solid content between the original solution group and the verification group (n=3)实验组 茶多酚含量(mg/mL) 茶氨酸含量(mg/mL) 锌含量(mg/mL) 硒含量
(μg/mL)膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率
(%)可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液组 1133.27±0.52 271.86±0.07 0.42±0.26 0.24±0.16 − 35.36±0.03 96.49±0.19 验证组 1079.75±2.41 225.41±1.35 0.38±0.08 0.22±0.06 123.25±2.68 85.16±0.12 81.50±0.08 3. 结论
本文应用无机陶瓷膜过滤技术对茶叶酵素进行过滤澄清,结果最佳的过膜条件为:膜孔径400 nm、过膜功率47 Hz、过膜压力0.28±0.02 MPa,过膜温度15±2 ℃,在此条件下,茶叶酵素功能成分含量保留率、可溶性固形物含量保留率>80%,透光率平均值为85.10%±0.12%。表明将无机陶瓷膜应用于茶叶酵素过滤澄清是可行的,其优点是在不改变茶叶酵素的色、香、味的前提下,能使茶叶酵素中功能成分损失少,过滤后滤液澄清度高,稳定性好,且工业生产中极易实现的操作,易于连续化、自动化、标准化成产,但工业生产中由于生产量大,易造成陶瓷膜的堵塞,因此陶瓷膜的定期清洗和保养是后期需要重点研究的方向。
-
表 1 茶叶酵素膜过滤工艺响应面优化试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Level design of experimental factors for optimal response surface of tea enzyme membrane filtration process
水平 因素 A过膜功率(Hz) B过膜压力(MPa) C过膜温度(℃) −1 40 0.25 10 0 45 0.30 20 1 50 0.35 30 表 2 不同孔径陶瓷膜过滤后茶叶酵素的膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物(n=3)
Table 2 Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids of tea enzymes filtered by ceramic membranes with different pore sizes (n=3)
实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物(g/L) 原液 − 49.10±0.02d 95.67±0.48a 20 nm 32.66±3.73ed 94.94±0.99a 78.79±0.36e 50 nm 43.10±2.63cd 88.79±1.94b 83.45±0.20d 100 nm 49.88±2.33c 87.91±0.38b 82.96±0.48d 200 nm 88.16±2.07b 79.18±0.13c 84.81±1.12c 400 nm 142.86±1.80a 80.11±0.18c 88.42±0.21b 注:同列数据差异显著,P<0.05;表3~表5、表8同。 表 3 不同功率过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)
Table 3 Tea enzyme membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content after filtration with different powers (n=3)
实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 50.73±0.08d 138.49±0.09a 30 Hz 98.18±3.62c 69.44±0.17c 127.23±0.65c 35 Hz 102.86±2.61c 75.95±0.24b 127.29±1.50c 40 Hz 115.71±1.81b 81.05±0.86a 129.11±2.61c 45 Hz 115.71±2.82b 80.30±0.88a 133.76±1.04b 50 Hz 137.14±4.84a 82.61±1.69a 132.46±1.97b 表 4 不同压力过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)
Table 4 Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content of tea fermentation under different pressure filtration (n=3)
实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 31.02±0.09d 128.32±2.32a 0.15 MPa 72.73±4.23bc 65.80±2.12c 107.94±2.26c 0.20 MPa 70.59±3.26cd 72.11±1.32b 106.39±2.25c 0.25 MPa 72.73±4.16bc 79.29±0.98a 106.74±2.14c 0.30 MPa 75.00±2.65ab 79.89±1.02a 107.91±1.85c 0.35 MPa 77.42±3.62a 81.75±1.23a 110.46±1.65b 表 5 不同温度过滤后茶叶酵素膜通量、透光率、可溶性固形物含量(n=3)
Table 5 Membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solids content of tea enzymes filtered at different temperatures (n=3)
实验组 膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率(%) 可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液 − 49.84±0.08e 129.58±0.09a 10~20℃ 88.10±3.35e 86.79±0.31a 103.28±0.15d 20~30℃ 113.27±3.12d 80.73±0.64b 104.75±0.19c 30~40℃ 192.86±2.64c 74.33±1.68c 105.15±1.58c 40~50℃ 226.53±2.82b 67.65±1.65d 104.90±0.68c 50~60℃ 257.14±2.61a 66.73±2.52d 105.74±1.32b 表 6 响应面设计试验与结果(n=3)
Table 6 Test and results of response surface design (n=3)
实验号 A过膜功率(Hz) B过膜压力(MPa) C过膜温度(℃) 透光率(%) 1 40 0.35 20 80.95 2 45 0.35 10 82.20 3 40 0.25 20 80.35 4 45 0.3 20 84.42 5 50 0.35 20 82.54 6 45 0.25 10 82.41 7 45 0.3 20 83.14 8 40 0.3 10 83.05 9 45 0.25 30 78.27 10 40 0.3 30 74.74 11 50 0.3 30 78.68 12 45 0.35 30 79.29 13 50 0.25 20 83.48 14 45 0.3 20 81.87 15 50 0.3 10 83.42 表 7 回归方程方差分析
Table 7 Variance analysis of regression equation
方差来源 SS(平方和) Df(自由度) MS(均方差) F值 P值 显著性 模型 85.50 9 9.50 5.97 0.0317 * A-过膜功率 10.19 1 10.19 6.40 0.0525 B-过膜压力 0.028 1 0.028 0.02 0.9004 C-过膜温度 50.50 1 50.50 31.72 0.0024 * AB 0.59 1 0.59 0.37 0.5684 AC 3.19 1 3.19 2.00 0.2163 BC 0.38 1 0.38 0.24 0.6466 A2 3.27 1 3.27 2.06 0.2111 B2 0.51 1 0.51 0.32 0.5960 C2 18.35 1 18.35 11.52 0.0194 * 残差 7.96 5 1.59 失拟项 4.69 3 1.56 0.95 0.5483 不显著 纯误差 3.27 2 1.64 总变态 93.47 14 注:P<0.05,差异显著;P<0.01,差异极显著;R2=0.9148。 表 8 原液组与验证组功能成分、膜通量、透光率,可溶性固形物含量变化(n=3)
Table 8 Changes of functional components, membrane flux, light transmittance and soluble solid content between the original solution group and the verification group (n=3)
实验组 茶多酚含量(mg/mL) 茶氨酸含量(mg/mL) 锌含量(mg/mL) 硒含量
(μg/mL)膜通量[m3/(m2·h)] 透光率
(%)可溶性固形物含量(g/L) 原液组 1133.27±0.52 271.86±0.07 0.42±0.26 0.24±0.16 − 35.36±0.03 96.49±0.19 验证组 1079.75±2.41 225.41±1.35 0.38±0.08 0.22±0.06 123.25±2.68 85.16±0.12 81.50±0.08 -
[1] 晏敏, 周宇, 贺肖寒, 等. 红柠檬果汁澄清工艺的优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2018,44(8):224−230. [YAN Min, ZHOU Yu, HE Xiao han, et al. Optimization of clarification process of red lemons juice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2018,44(8):224−230.] YAN Min, ZHOU Yu, HE Xiao han, et al . Optimization of clarification process of red lemons juice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2018 ,44 (8 ):224 −230 .[2] 李西腾, 魏楠, 郑楠, 等. 木瓜果汁澄清工艺的优化研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(14):100−105. [LI Xiteng, WEI Nan, ZHENG Nan, et al. Study on optimal clarification process of pawpaw fruit juice[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(14):100−105.] LI Xiteng, WEI Nan, ZHENG Nan, et al . Study on optimal clarification process of pawpaw fruit juice[J]. Food Research and Development,2017 ,38 (14 ):100 −105 .[3] 章国磊, 王静, 李珺铭, 等. 人参口服液澄清工艺的优化[J]. 中成药,2021,43(11):3121−3124. [ZHANG Guolei, WANG Jing, LI Junming, et al. Optimization of clarifying process of ginseng oral liquid[J]. Optimization of Clarifying Process of Ginseng Oral Liquid,2021,43(11):3121−3124.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.11.034 ZHANG Guolei, WANG Jing, LI Junming, et al . Optimization of clarifying process of ginseng oral liquid[J]. Optimization of Clarifying Process of Ginseng Oral Liquid,2021 ,43 (11 ):3121 −3124 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.11.034[4] 杨晓萍. 茶叶深加工与综合利用[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2021:1−8. [YANG Xiaoping. Tea intensive processing and comprehensive utilization[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2021:1−8.] YANG Xiaoping. Tea intensive processing and comprehensive utilization[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2021: 1−8.
[5] 王湛, 宋芃, 陈强, 等. 膜技术及其应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2022:1−5. [WANG Zhan, SONG Peng, CHEN Qiang, et al. Membrane technology and application[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2022:1−5.] WANG Zhan, SONG Peng, CHEN Qiang, et al. Membrane technology and application[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2022: 1−5.
[6] DIVAKAR S, PADAKI M, BALAKRISHNA R G. Review on liquid-liquid separation by membrane filtration[J]. ACS Omega,2022,7(49):44495−44506. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02885
[7] ABDULLAYEV A, BEKHEET M F, HANAOR D A H, et al. Materials and applications for low-cost ceramic membranes[J]. Membranes,2019,9(9):105. doi: 10.3390/membranes9090105
[8] SJLIN M, THUVANDER J, WALLBERG O, et al. Purification of sucrose in sugar beet molasses by utilizing ceramic nanofiltration and ultrafiltrati-on membranes[J]. Membranes,2020,10(1):2−17.
[9] HAKAMI M W, ALKHUDHIRI A, AL-BATTY S, et al. Ceramic microfiltration membranes in wastewater treatment:Filtration behavior, fouling and prevention[J]. Membranes,2020,10(9):248. doi: 10.3390/membranes10090248
[10] FIKSDAL L, LEIKNES T. The effect of coagulation with MF/UF membrane filtration for the removal of virus in drinking water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2006,279(1−2):364−371. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.023
[11] DORNIER M, BELLEVILLE M-P, VAILLANT F. Membrane technologies for fruit juice processing[J]. Fruit Preservation, 2018:211−248.
[12] COSIO M S, PELLICANO A, GARDANA C, et al. Debittering of grape juice by electrospun nylon nanofibrous membranes:Impact of filtration on physicochemical, functional, and sensory properties[J]. Polymers,2022,15(1):192. doi: 10.3390/polym15010192
[13] 王玉梅, 李洋, 罗佳沂, 等. 基于传统分离培养和高通量测序不同孔径陶瓷膜过滤前后泡菜汁中微生物变化的研究[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(5):60−68. [WANG Yumei, LI Yang, LUO Jiayi, et al. Study on the microbial changes in pickle juice before and after filtration with ceramic membranes of different pore size based on traditional isolation culture and high throughput sequencing[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(5):60−68.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2022.05.011 WANG Yumei, LI Yang, LUO Jiayi, et al . Study on the microbial changes in pickle juice before and after filtration with ceramic membranes of different pore size based on traditional isolation culture and high throughput sequencing[J]. China Condiment,2022 ,47 (5 ):60 −68 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2022.05.011[14] UROSEVIC T, POVRENOVIC D, VUKOSAVLJEVIC P, et al. Recent developments in microfiltration and ultrafiltration of fruit juices[J]. Food Bioprod Process,2017,106:147−161. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2017.09.009
[15] 林清霞, 杨军国, 王丽丽, 等. 乌龙茶水提物的膜分离制备及其体外抗氧化活性评价[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,2022,30(5):645−654. [LIN Qingxia, YANG Junguo, WANG Lili, et al. Preparation of oolong tea water extract by membrane separation and evaluation of antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2022,30(5):645−654.] LIN Qingxia, YANG Junguo, WANG Lili, et al . Preparation of oolong tea water extract by membrane separation and evaluation of antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2022 ,30 (5 ):645 −654 .[16] 李文, 谢彩锋, 彭文博, 等. 基于红糖生产的蔗汁陶瓷膜过滤工艺技术[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(1):61−69. [LI Wen, XIA Caifeng, PENG Wenbo, et al. Ceramic membrane filtration of cane juice for brown sugar production[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(1):61−69.] LI Wen, XIA Caifeng, PENG Wenbo, et al . Ceramic membrane filtration of cane juice for brown sugar production[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022 ,47 (1 ):61 −69 .[17] 周天山, 方世辉, 夏英英, 等. 陶瓷膜过滤及原料配比对速溶红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2006,32(9):140−143. [ZHOU Tianshan, FANG Shihui, XIA Yingying, et al. Effect of ceramic membrane filtration and raw material ratio on quality of instant black tea[J]. Food and Rmentation Industries,2006,32(9):140−143.] ZHOU Tianshan, FANG Shihui, XIA Yingying, et al . Effect of ceramic membrane filtration and raw material ratio on quality of instant black tea[J]. Food and Rmentation Industries,2006 ,32 (9 ):140 −143 .[18] 武婧, 唐志书, 古川, 等. 无机陶瓷膜微滤精制山茱萸水提液的工艺研究[J]. 中南药学,2015,13(9):943−946. [WU Jing, TANG Zhishu, GU Chuan, et al. Refinement of aqueous extract of Cornus offifi cinalis with inorganic ceramic membrane[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2015,13(9):943−946.] doi: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2015.09.013 WU Jing, TANG Zhishu, GU Chuan, et al . Refinement of aqueous extract of Cornus offifi cinalis with inorganic ceramic membrane[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2015 ,13 (9 ):943 −946 . doi: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2015.09.013[19] 张艳, 杜先锋. 膜技术分离纯化茶多糖的工艺研究[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2015,42(1):12−17. [ZHANG Yan, DU Xiangfeng. Separation and purification of tea polysaccharides with membrane technology[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2015,42(1):12−17.] ZHANG Yan, DU Xiangfeng . Separation and purification of tea polysaccharides with membrane technology[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2015 ,42 (1 ):12 −17 .[20] ECHAKOURI M, HENNI A, SALAMA A. High-frequency pulsatile parameterization study for the titania ceramic membrane fouling mitigation in oily wastewater systems using the box-behnken response surface methodology[J]. Membranes,2022,12(12):1198. doi: 10.3390/membranes12121198
[21] ONYEOGAZIRI F C, PAPANEOPHYTOU C. A general guide for the optimization of enzyme assay conditions using the design of experiments approach[J]. SLAS Discov,2019,24(5):587−596. doi: 10.1177/2472555219830084
[22] 赵亚辉, 胡志伟, 王一鸣, 等. 喷涂-浸涂结合法制备高渗透通量平板陶瓷超滤膜[J]. 膜科学与技术,2019,39(6):16−20. [ZHAO Yahui, HU Zhiwei, WANG Yiming, et al. High permeable flux plate ceramic ultrafiltration membrane was prepared by spraydip coating method[J]. Membr and Science and Technology,2019,39(6):16−20.] ZHAO Yahui, HU Zhiwei, WANG Yiming, et al . High permeable flux plate ceramic ultrafiltration membrane was prepared by spraydip coating method[J]. Membr and Science and Technology,2019 ,39 (6 ):16 −20 .[23] 范远景, 马凌云, 徐晓伟, 等. 膜技术分离金银花绿原酸提取液工艺研究[J]. 食品科学,2010(20):43−46. [FAN Yuanjing, MA Lingyun, XU Xiaowei, et al. Application of membrane separation for the purification of chlorogenic acid-rich extract from Lonicera japonica Thunb J]. Food Science,2010(20):43−46.]
[24] 朱苗, 田奇, 王锡念, 等. 天麻苦瓜绿茶复合饮料配方工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(4):112−116.142. [ZHU Miao, TIAN Qi, WANG Xinian, et al. Formulation process optimization of compound beverage with Gastrodia elata, Momordica charantia L. and green tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(4):112−116.142.] ZHU Miao, TIAN Qi, WANG Xinian, et al . Formulation process optimization of compound beverage with Gastrodia elata, Momordica charantia L. and green tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2021 ,42 (4 ):112 −116.142 .[25] CHRISTOPHER P, MORROW, AMY E, et al. Evidence, determination, and implications of membrane-independent limiting flux in forward osmosis systems[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2019,53:4380−4388. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b05925
[26] 杨文银, 赵士明, 章小同, 等. 小孔径陶瓷膜澄清甜叶菊提取液的工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(11):180−184. [YANG Wenyin, ZHAO Shiming, ZHANG Xiaotong, et al. Study on the clarification process of stevia extract by small-aperture ceramic film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(11):180−184.] YANG Wenyin, ZHAO Shiming, ZHANG Xiaotong, et al . Study on the clarification process of stevia extract by small-aperture ceramic film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (11 ):180 −184 .[27] LOIZZO MR, SICARI V, TUNDIS R, et al. The influence of ultrafiltration of Citrus limon L. Burm. cv femminello comune juice on its chemical composition and antioxidant and hypoglycemic properties[J]. Antioxidants,2019,8(1):23. doi: 10.3390/antiox8010023
[28] ALI M. B, HAMDI N, RODRIGUEZ M. A, et al. Preparation and characterization of new ceramic membranes for ultrafiltration[J]. Ceram Int,2018,44:2328−2335. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.199





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
