Optimization of Preparation Technology and Antioxidant Activity of Schisandrae chinensis Protein Peptides in Vitro by Response Surface Methodology
-
摘要: 目的:获取五味子蛋白肽的最适酶和最佳制备工艺并考察其体外抗氧化活性。方法:应用7种蛋白酶酶解,基于五味子蛋白不同酶解产物的水解度、自由基清除活性、多肽得率和含量结合SDS-PAGE中分子量多指标综合评价,筛选出最适蛋白酶。以DPPH自由基清除率为考察指标,通过单因素实验结合响应面分析法确定最佳酶解工艺。以五味子蛋白为参照,分析比较五味子蛋白肽对O2−·、·OH、DPPH·、ABTS+·的清除能力和Fe2+螯合能力及Fe3+还原能力。结果:制备五味子蛋白肽的最适酶为碱性蛋白酶,最佳酶解工艺参数为:底物浓度5%,酶底比1%,酶解时间3 h,酶解温度55 ℃,pH为9.0,在此条件下获得的多肽含量为88.61%,水解度为24.21%,DPPH·清除率为86.96%。五味子蛋白肽的自由基清除能力和还原能力均优于五味子蛋白。结论:本研究确定了五味子蛋白肽的最适酶和最佳水解工艺,同时指出,五味子蛋白肽具有更加优良的体外抗氧化活性,可作为一种天然的抗氧化剂。Abstract: Objective: To obtain the optimal enzyme and preparation process for Schisandra chinensis protein peptides and investigate its in vitro antioxidant activity. Methods: Seven proteases were used to hydrolyze Schisandra chinensis protein. Based on the degree of hydrolysis, free radical scavenging activity, polypeptide yield and content of different hydrolysates of Schisandra chinensis protein and the comprehensive evaluation of molecular weight in SDS-PAGE, the optimal protease was screened. The DPPH free radical scavenging rate was used as the index, and the optimal enzymatic hydrolysis process was determined by single factor test combined with response surface analysis. The scavenging ability of O2−·, ·OH, DPPH·, ABTS+·, Fe2+ chelating ability and Fe3+ reducing ability of Schisandrae chinensis protein peptides were analyzed and compared with Schisandra chinensis protein. Results: The optimum enzyme for the preparation of Schisandra chinensis protein peptides was alkaline protease. The optimum enzymatic hydrolysis parameters were as follows: substrate concentration 5%, enzyme-to-substrate ratio 1%, enzymatic hydrolysis time 3 h, enzymatic hydrolysis temperature 55 ℃, pH9.0. Under these conditions, the polypeptide content was 88.61%, the degree of hydrolysis was 24.21%, and the DPPH· scavenging rate was 86.96%. The free radical scavenging ability and reducing ability of Schisandrae chinensis protein peptides were better than those of Schisandrae chinensis protein. Conclusion: This study determined the optimum enzyme and hydrolysis process of Schisandrae chinensis protein peptides, and pointed out that Schisandrae chinensis protein peptides had better antioxidant activity in vitro and could be used as a natural antioxidant.
-
五味子是木兰科植物北五味子(Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill)干燥成熟的果实[1],为吉林省道地大宗药材。北五味子具有多样的生物活性和显著的临床疗效,在中医临床和保健食品及健康产品研究与开发中应用广泛[2−3]。项目组前期研究表明,北五味子中含有丰富的蛋白质资源,具备优良生物活性和食品加工特性[4−6]。但由于其分子量大导致机体难以快速消化吸收和利用,不能将其功能价值和生物活性快速发挥。如果将其制备成分子量较小的植物多肽,其生物活性和功能属性均可以得到明显的改善,柔性和生物相容性增加,消化吸收率会大幅度提高,能够更快地展开并在分子之间相互作用[7]。生物活性肽的分子量分布于蛋白质与氨基酸之间,具有毒性小、无副作用、分子量低、结构多样性、较好的生物相容性和易于被人体吸收利用等优点[7],具备抗氧化[8]、抗疲劳[9]、降血压[10]、增强免疫力[11]、抑制肿瘤[12]和抗菌[13]等多种生理功能,在制备功能性健康食品、生产保健食品中具有巨大的应用前景。研究表明,抗氧化肽能够对生物大分子的过氧化产生抑制作用,使体内过量的自由基被清除,在一定程度上可以消除生理障碍,从而降低各类疾病的发生率[8]。
生物蛋白酶酶解法因其安全性高、水解过程简便易控、反应条件相对温和、周期短、水解产物多肽得率及含量高和绿色环保等优势,在生物活性肽的制备中成为热点研究方法[14]。不同种类的蛋白酶作用于蛋白质中肽键的位点差异较大,因此本研究选用7种蛋白酶对五味子蛋白酶解,多指标综合评价并筛选出最适蛋白酶。通过单因素实验考查酶底比、酶解时间、酶解温度和pH对酶解效果的影响,并结合响应面分析法获取抗氧化活性优良、水解度高的五味子蛋白肽的最佳制备工艺参数。以维生素C和谷胱甘肽作为阳性对照,分析比较同等条件下五味子蛋白(Schisandrae chinensis protein,SCP)与五味子蛋白肽(Schisandrae chinensis protein peptides,SCAPH)体外抗氧化活性,为今后五味子蛋白肽在健康食品领域中开发与利用提供理论参考和科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
北五味子药材 购置于吉林省长春中医药大学附属医院,经药学院姜大成教授鉴定为木兰科五味子属植物北五味子Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Bail干燥成熟的果实;碱性蛋白酶(200 U/mg)、中性蛋白酶(100 U/mg)、木瓜蛋白酶(800 U/mg)、胃蛋白酶(1:30000)、胰蛋白酶(250 USPu/mg)、风味蛋白酶(≥20 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;复合蛋白酶(>120 U/mg) 上海楷洋生物技术有限公司;Folin-酚试剂、30%丙烯酰胺、β-巯基乙醇、标准蛋白Marker、三羟甲基胺基甲烷、过硫酸铵、邻二氮菲、1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼(DPPH)、2,2-联氮-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(ABTS)、维生素C(抗坏血酸)、谷胱甘肽(还原型) 分析纯,北京索莱宝生物科技有限公司。
ALB-224万分之一天平、AB265-S十万分之一天平、S220-K-CN标准型pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;SCIENTZ-50F真空冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝冻干设备股份有限公司;Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell蛋白电泳仪 美国Bio-rad公司;UV-2550紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津仪器有限公司;MiniSpin Plus 5920R高速离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;Multiskan MK3全自动酶标仪、LYNX6000 Sorvall LYNX高速离心机、Invitrogen iBright FL 1000凝胶成像仪 美国Thermo Fisher公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 五味子蛋白的提取
依据项目组前期制备方法[4],将五味子药材去除果肉,粉碎,石油醚脱脂后干燥,粉碎得五味子脱脂药粉。称取100 g北五味子干燥脱脂粉,按1:35料液比加去离子水匀浆,1 mol/L NaOH溶液将原液pH调至9.5,35 ℃水浴提取3 h,离心(3500 r/min,15 min),弃沉淀,1 mol/L HCl将上清液pH调至3.4,于4 ℃下静置2 h,离心,弃上清,用少量去离子水将沉淀溶解,pH调至中性后装入透析袋(Mw:8000~14000),4 ℃透析48 h,间隔2 h更换去离子水,透析袋中液体真空冷冻干燥,即得SCP。
1.2.2 最适蛋白酶筛选
去离子配制底物浓度为3%的SCP溶液,选择7种蛋白酶对SCP酶解,酶解条件依据于酶制剂公司提供的最适条件,详见表1。酶解结束后于100 ℃水浴中煮沸灭酶15 min,冷却至室温,调节pH至中性,离心(10000 r/min,10 min),冷冻干燥即得不同蛋白酶作用后的五味子蛋白酶解肽。以DPPH·和ABTS+·清除率作为评价指标,同时结合水解度、多肽得率与含量、SDS-PAGE电泳综合评价筛选出制备五味子蛋白肽的最适蛋白酶。
表 1 不同蛋白酶的最适酶解条件Table 1. Optimum enzymatic hydrolysis conditions of different proteases序号 蛋白酶种类 酶解温度(℃) 酶解pH 酶解时间(h) 酶底比(%) 1 木瓜蛋白酶 65 6.5 4 1 2 中性蛋白酶 50 7.0 4 1 3 碱性蛋白酶 55 8.5 4 1 4 复合蛋白酶 50 8.5 4 1 5 胃蛋白酶 37 2.0 4 1 6 胰蛋白酶 45 8.0 4 1 7 风味蛋白酶 50 6.5 4 1 1.2.3 评价指标测定
1.2.3.1 自由基清除能力比较
以国际目前最为公认的DPPH·和ABTS+·清除试验来评价五味子蛋白7种酶解产物清除自由基活性[15],方法与1.2.7.3和1.2.7.4一致。
1.2.3.2 水解度
水解样品中氨基氮的含量测定参考GB 5009.235-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸态氮的测定》项下甲醛值法;总氮含量参照GB5009.5-2.16《食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定》项下凯氏定氮法测定,水解度(DH)的结果利用公式(1)计算:
DH(%)=氨基氮含量样品中总氮含量×100 (1) 1.2.3.3 多肽得率和含量测定
酶解后所得酶解液的冻干粉质量与五味子蛋白质量比值作为多肽得率。以牛血清白蛋白作为标准溶液,采用Folin-酚法测定不同蛋白酶酶解后样品的多肽含量。按照Folin-酚法试剂盒说明操作后,以去离子水代替样品溶液,于500 nm处测定其吸光度值,绘制标准曲线后计算不同样品的多肽含量。
1.2.3.4 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(SDS-PAGE)电泳
SDS-PAGE参考VINAYASHREE等[16]的方法稍加修改。将不同蛋白酶酶解肽的样品溶液浓度配制为5 mg/mL,加入还原型蛋白上样缓冲液,沸水浴5 min后冷却,使用浓度为5%的浓缩胶和12%的分离胶进行SDS-PAGE电泳,上样量为10 µL。电泳结束后采用考马斯亮蓝R-250室温摇床染色1 h,脱色液脱色数次至背景透明、条带清晰后,使用凝胶成像仪扫描成像。
1.2.4 最佳底物浓度的确定
配制不同底物浓度(1%、2%、3%、4%、5%和6%)的SCP溶液,固定酶底比为1%,酶解温度为55 ℃,酶解pH为8.5,酶解时间为4 h,酶解结束后100 ℃沸水浴灭酶15 min,离心,上清液冷冻干燥,测定DH和DPPH·清除率,绘制不同底物浓度对酶解效果的影响曲线,结合不同底物浓度下的SDS-PAGE结果,确定最佳底物浓度。
1.2.5 单因素实验
在确定最适蛋白酶和最佳底物浓度的基础上进行单因素考察,以DH和DPPH·清除率为考察指标,依据表1中蛋白酶最适酶解条件,分别固定其他条件,考察酶底比(3%、2.5%、2%、1.5%、1%、0.5%)、酶解时间(6、5、4、3、2、1 h)、酶解温度(85、75、65、55、45、35 ℃)和酶解pH(12、11、10、9、8、7)各变量因素,绘制各变量因素对酶解效果的影响曲线,分析各变量因素对五味子蛋白酶解产物水解度和DPPH·清除率的影响。
1.2.6 响应面试验
1.2.6.1 响应面试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,响应值(Y)为DPPH·清除率,自变量为酶底比(A)、酶解时间(B)、酶解温度(C)和酶解pH(D)4个因素,利用Box-Behnken design(BBD)试验原理,设计四因素三水平的响应面试验,对SCAPH的酶解工艺条件进行优化。试验设计因素和水平见表2。
表 2 响应面试验因素水平编码表Table 2. Response surface test factor level coding table水平 因素 A酶底比(%) B酶解时间(h) C酶解温度(℃) D酶解pH −1 0.5 2 45 8 0 1.0 3 55 9 1 1.5 4 65 10 1.2.6.2 响应面试验分析
应用Design Expert 13.0软件对实验数据进行回归分析,得到DPPH·清除率对酶底比、酶解时间、酶解温度和酶解pH四个因素的回归模型,并对模型进行回归方差分析显著性检验,绘制不同影响因素的响应曲面图和等高线图,获取SCAPH的最佳酶解工艺参数,并进行实验验证。
1.2.7 自由基清除能力测定
1.2.7.1 超氧阴离子
以SCP为参照,采用邻苯三酚自氧化法测定SCAPH对O2−·清除的效果。取3 mL 0.1 mol/L Tris-HCl和0.1 mL质量浓度为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液加入试管,混合均匀,20 min后加入0.3 mL 7 mmol/L邻苯三酚溶液,反应4 min后加入1 mL 10 moL/L盐酸使反应终止;以等体积去离子水代替邻苯三酚溶液作为样品对照组;以等体积去离子水代替样品溶液作为空白对照组。以VC和谷胱甘肽(GSH)为阳性对照,去离子水做空白调零,于420 nm波长处测其吸光度。O2−·清除率按公式(2)计算:
O2−⋅清除率(%)=A0−A1+A2A0×100 (2) 式中:A0,空白对照组吸光度;A1,样品组吸光度;A2,样品对照组吸光度。
1.2.7.2 羟基自由基
通过邻二氮菲法测定SCP和SCAPH对·OH的清除作用。取0.75 mmol/L邻二氮菲溶液1 mL和0.2 mol/L PBS溶液2 mL加入试管,随后加入1 mL质量浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液,混匀,加入0.75 mmol/L FeSO4溶液1 mL,最后加入0.025% H2O2溶液1 mL,混匀,37 ℃水浴反应1 h,不同组别的吸光度于536 nm处进行测定。VC和GSH为阳性对照组,空白对照组以等体积去离子水代替样品溶液,样品对照组以等体积去离子水代替0.025% H2O2溶液,不同组别·OH清除率根据公式(3)计算:
⋅OH清除率(%)=A1−A0A2−A0×100 (3) 式中:A0,空白对照组吸光度;A1,样品组吸光度;A2,样品对照组吸光度。
1.2.7.3 DPPH自由基
将2 mL质量浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液和2 mL 0.04 mg/mL DPPH溶液充分混匀,室温避光反应30 min,吸光度于517 nm处测定,以2 mL甲醇代替DPPH溶液作为样品对照组,以2 mL去离子水代替样品溶液作为空白对照组,VC和GSH作为阳性对照组。通过公式(4)计算DPPH·清除率:
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=A0−A1+A2A0×100 (4) 式中:A0,空白对照组吸光度;A1,样品组吸光度;A2,样品对照组吸光度。
1.2.7.4 ABTS+自由基
将ABTS和过硫酸钾分别用去离子水配制,使其浓度分别为7.4 mmol/L和2.6 mmol/L,将2.5 mL ABTS储备液与44 μL过硫酸钾混匀作为工作液,4 ℃避光静置12~16 h,临用前用0.01 mol/L pH7.4 PBS溶液稀释至734 nm处吸光度值在0.7±0.2范围内,作为空白对照组吸光度。将10 μL质量浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液与200 μL工作液混匀,室温避光反应8 min,不同组别的吸光度于734 nm处测定。ABTS+·清除能力依据公式(5)计算:
ABTS+⋅清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 (5) 式中:A0,空白对照组吸光度;A1,样品组吸光度。
1.2.8 还原能力
1.2.8.1 Fe2+螯合能力
取96孔板,向100 μL质量浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液中加入50 μL 1.3 mmol/L FeCl2·4H2O,室温反应30 min,然后加入50 μL 0.1 mmol/L Ferrozine溶液。样品对照组以100 μL去离子水代替样品溶液,以VC和GSH为阳性对照,测定562 nm处的吸光度值。不用组别的Fe2+螯合能力依据公式(6)计算:
Fe2+螯合能力(%)=A0−A1A0×100 (6) 式中:A0,样品对照组吸光度;A1,样品组吸光度。
1.2.8.2 Fe3+还原能力
将1 mL质量浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 mg/mL的SCP和SCAPH样品水溶液与2.5 mL 0.2 mol/L pH6.6磷酸缓冲溶液和2.5 mL 1.0%铁氰化钾溶液混匀,于50 ℃水浴反应20 min,冷却至室温,加入2.5 mL 10%三氯乙酸,混匀后离心,取2.5 mL上清,加入2.5 mL去离子水和0.5 mL 0.1%三氯化铁,混匀,以去离子水做空白调零,吸光度值于700 nm处测定,以2.5 mL去离子水代替样品溶液作为样品对照组,以VC和GSH为阳性对照。通过公式(7)计算Fe3+还原能力:
Fe3+还原能力=A1−A2 (7) 式中:A1,样品组吸光度;A2,样品对照组吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均做3次平行,采用Origin 2019、Design-Expert 13和Microsoft office 2019处理和分析数据,结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 最适蛋白酶筛选
2.1.1 不同蛋白酶自由基清除能力和水解度对比
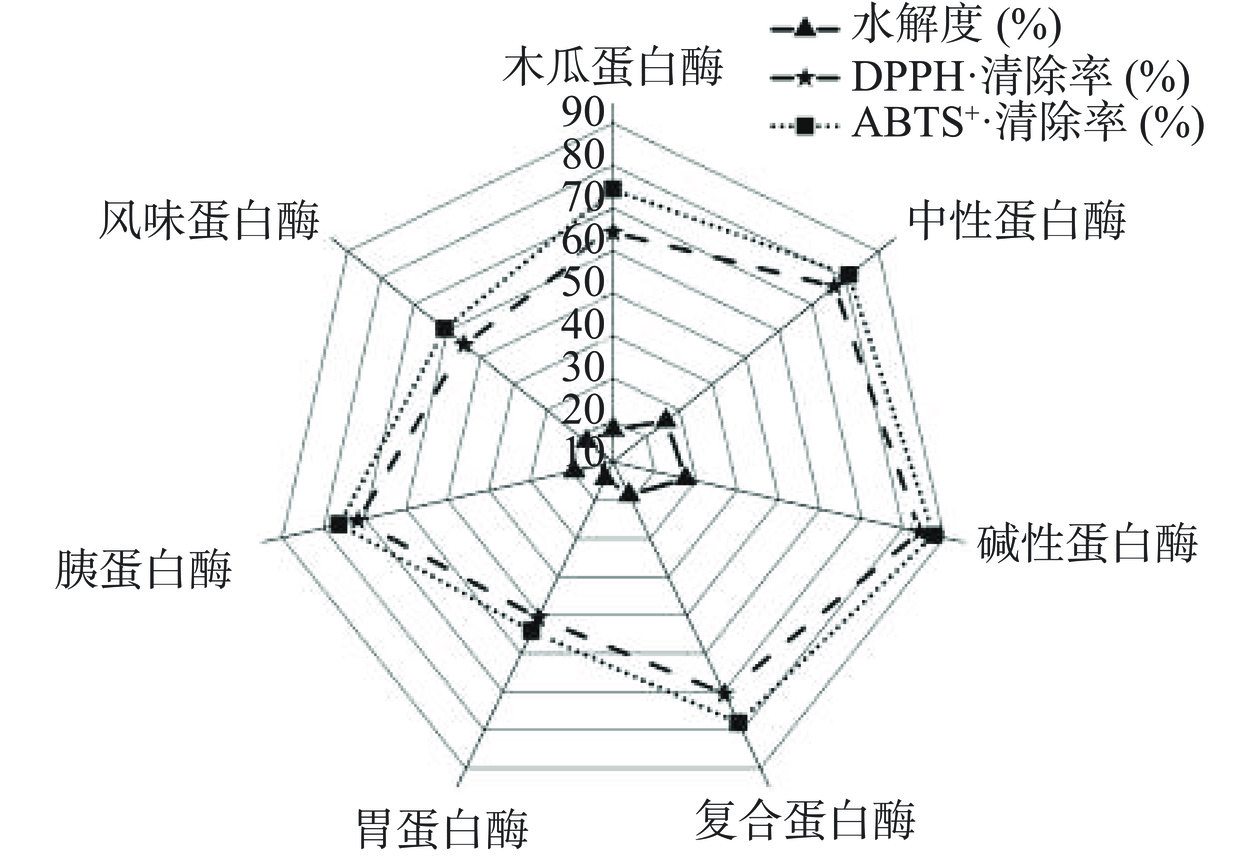
由图1可知,五味子蛋白经7种蛋白酶酶解后,均表现出一定的自由基清除能力。碱性蛋白酶酶解产物DPPH·和ABTS+·清除率与其他酶解产物相比较高,可能是碱性蛋白酶对SCP进行剪切时,能够对SCP中具有一定特异性的氨基酸序列进行识别,进而生成更多抗氧化活性高的小分子量多肽[17]。水解度效果最好的也是碱性蛋白酶,DH可达27.51%,其次是中性蛋白酶。DH越高表示蛋白质发生水解的程度越彻底,酶解产物中多肽的种类和功能越丰富。不同蛋白酶的DH不同,可能受到酶作用的酶切位点及其底物特性的影响[18]。因此,经碱性蛋白酶作用后的酶解产物抗氧化活性和水解度最高。
2.1.2 不同蛋白酶多肽得率和多肽含量对比
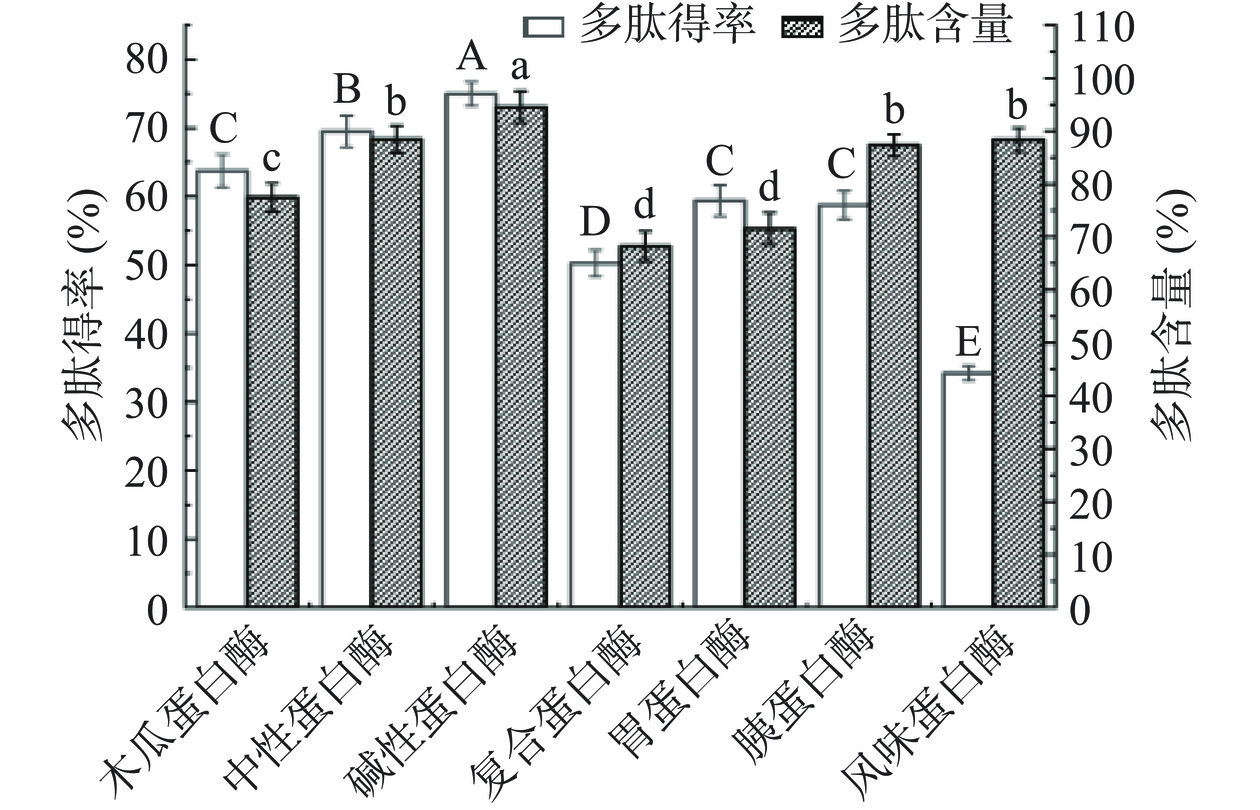
多肽含量线性回归方程为y=0.0006x−0.0022,相关系数R2为0.9995,说明多肽质量浓度在测定浓度范围内与吸光度呈现的线性关系良好。如图2所示,SCP经7种蛋白酶酶解后,碱性蛋白酶作用后多肽得率与含量均为最高,分别为74.52%和94.65%,且具有统计学显著差异(P<0.05),可能是由于碱性蛋白酶对五味子蛋白酶解相对彻底,水解度高,故生成的多肽含量较高。
2.1.3 不同蛋白酶及不同底物浓度下最适蛋白酶SDS-PAGE电泳对比
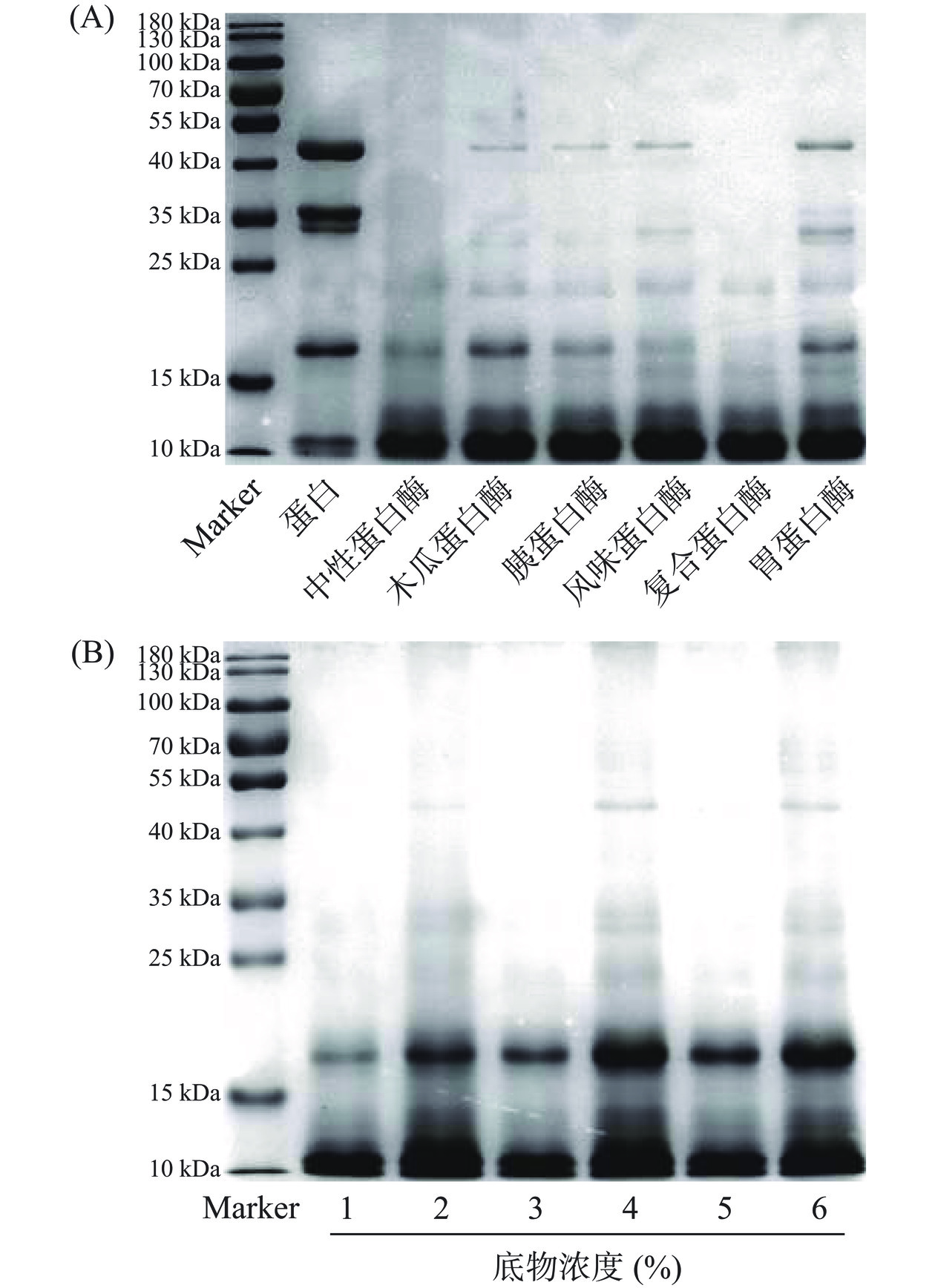
五味子蛋白在不同蛋白酶和不同底物浓度的碱性蛋白酶条件下测定的SDS-PAGE结果如图3(A)和(B)所示,五味子蛋白的亚基分子质量主要分布在12~45 kDa,为12、17、34、36、45 kDa。以SCP为对照,SCP经不同蛋白酶酶解后,处于高分子量区域内的亚基分子量呈现出不同程度的降低,其中碱性蛋白酶酶解效果优于其它6种蛋白酶,在底物浓度为2%、4%和6%时,亚基在40~55 kDa均有分布,当底物浓度为5%时达到最佳,亚基分子量分布明显低于其他情形。综合考虑其自由基清除能力、水解度、多肽含量和得率结合SDS-PAGE,制备五味子蛋白肽的最适酶为碱性蛋白酶,故选择其作为工艺优化的原料酶,进行后续研究。
2.2 最佳底物浓度筛选
由图4可知,随着底物浓度的增加,酶解产物DPPH·清除率和DH不断升高,当底物浓度超过5%时,两个指标均下降,这说明底物浓度过高会影响酶与底物的结合。底物浓度为5%时达到最高,且具有统计学显著差异(P<0.05)。当底物浓度低于5%时,随着底物浓度的升高,酶与底物的结合被促进,从而增加了酶解物中的抗氧化活性成分;当底物浓度超过5%时,反应体系浓度过高,使蛋白酶的分散性和酶解产物中活性物质的释放受到限制,进而使抗氧化活性成分含量降低。结合2.1.3项下不同底物浓度下的SDS-PAGE及DH和DPPH·清除效果,选择5%作为碱性蛋白酶作用下的最佳底物浓度。
2.3 单因素实验
2.3.1 酶底比对酶解效果的影响
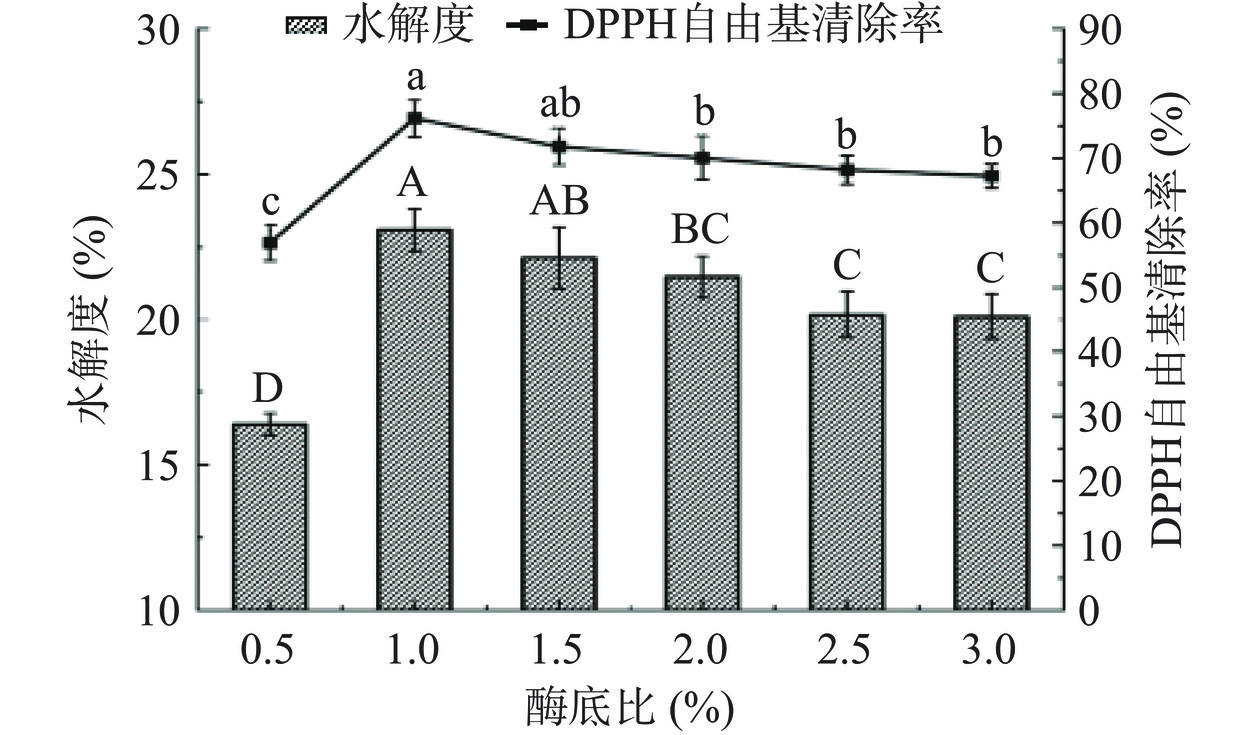
由图5可知,在酶底比为1%时,DPPH·清除能力和DH均达到最高值,分别为76.16%和23.08%,可能是在此酶底比浓度下,SCP与酶发生特异性结合的量达到最大。之后继续增加酶底比,DPPH·清除率和DH下降,随后趋于稳定,两个指标呈现出此现象的原因可能是碱性蛋白酶与SCP的特异性结合位点达到饱和,当继续增加酶底比,过量的酶将导致产物的反应变为逆反应,从而抑制了水解反应的进行,降低了水解速率。因此,即使继续加入蛋白酶达到饱和,水解度和清除率也会随着酶浓度的增加而下降,这是由于反应平衡受到了过量酶和产物的影响而发生的,由此呈现出平缓趋势,这与李晓叶等[19]研究的羊骨多肽加酶量结果相似。因此选择酶底比0.5%、1.0%、1.5%三个水平进行响应面分析。
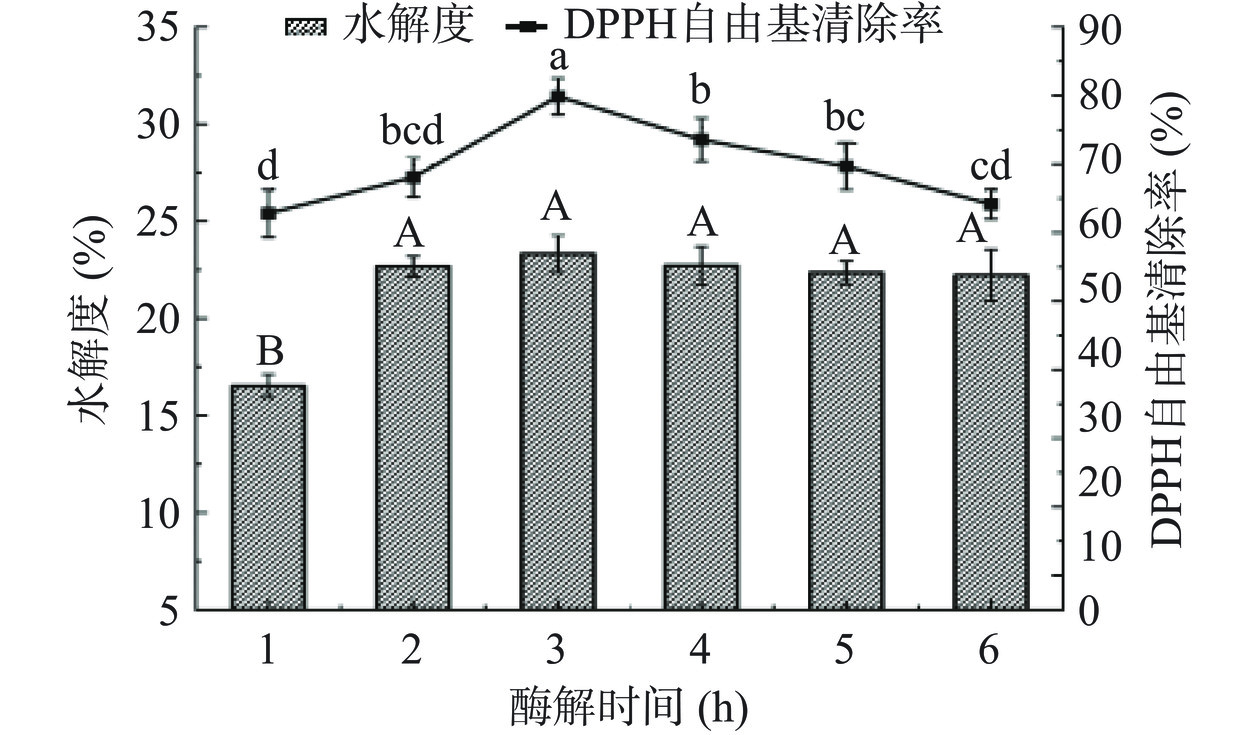
2.3.2 酶解时间对酶解效果的影响
如图6所示,SCP经酶解3 h后的DPPH·清除能力和DH最高,分别为79.87%和23.32%。可能是在最初加入碱性蛋白酶时,由于SCP充足,酶解速度较快,以剪切SCP为主,DPPH·清除能力和DH增加迅速,随着酶解时间继续增加,SCP浓度相对降低,导致分解速率降低,产物中多肽分解速率升高,蛋白酶对特异性的肽键结合接近于饱和状态,使蛋白酶的竞争性抑制趋向于平稳,DH基本达到峰值[20],使抗氧化活性较强的肽段可能被酶切为活性较弱的小肽,造成DPPH·清除率的下降,因此选择酶解时间为2、3、4 h三个水平进行响应面分析。
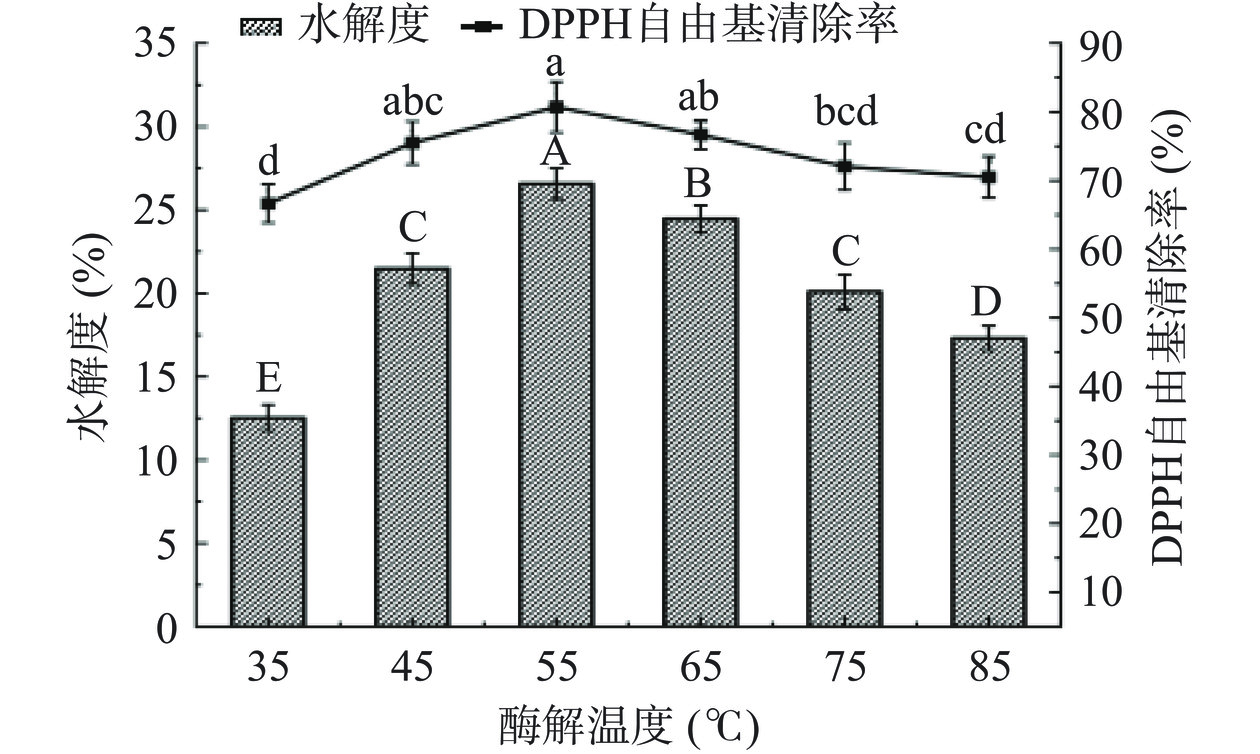
2.3.3 酶解温度对酶解效果的影响
酶解温度是影响酶促反应的重要因素之一,由图7可知,随着酶解温度的升高,五味子蛋白酶解物的DPPH·清除能力和DH呈现出先升高后降低的趋势。当体系中的温度较低时,酶的活性未得到充分发挥,当温度升高至55 ℃时,酶活性达到最佳,SCP暴露出更多与蛋白酶相互作用的位点,从而使DPPH·清除能力和水解度达到最佳。但随着温度继续升高,酶解效果反而降低,可能是温度过高导致酶的结构在一定程度上发生改变使活性降低,不利于水解反应的进行[21],因此酶解温度选择45、55和65 ℃三个水平进行响应面分析。
2.3.4 酶解pH对酶解效果的影响
如图8所示,随着酶解pH增加,五味子蛋白酶解物的DPPH·清除率和DH均呈现先上升后降低的趋势,主要是因为体系中pH过高或过低,酶和底物都会偏离等电点,蛋白酶的酶活降低,底物的空间结构发生改变,降低酶与SCP的结合效率,从而影响酶解效果[22],因此选择8、9和10三个水平进行响应面分析。
2.4 Box-Behnken响应面法优化试验
2.4.1 响应面试验设计及结果
依据Box-Behnken设计原理,在单因素实验结果的基础上,选取酶底比(A)、酶解时间(B)、酶解温度(C)、酶解pH(D)作为考察因素,以DPPH·清除率作为响应值,进行4因素3水平响应面试验优化设计,结果如表3所示。
表 3 响应面设计方案及结果Table 3. Design and results of response surface experiment试验号 A酶底比 B酶解时间 C酶解温度 D酶解pH DPPH自由基
清除率(%)1 −1 −1 0 0 60.92 2 0 0 0 0 87.13 3 0 1 1 0 75.29 4 1 0 1 0 83.59 5 0 0 0 0 87.65 6 0 −1 1 0 72.86 7 1 0 0 −1 79.35 8 0 0 0 0 84.76 9 −1 0 0 1 78.16 10 0 0 −1 1 77.87 11 0 −1 0 1 62.64 12 0 0 0 0 86.54 13 0 1 0 −1 61.93 14 1 0 0 1 84.80 15 0 1 −1 0 73.80 16 0 0 0 0 89.10 17 0 0 −1 −1 69.75 18 −1 1 0 0 68.81 19 −1 0 1 0 76.69 20 0 1 0 1 82.93 21 0 0 1 1 82.52 22 0 −1 0 −1 72.06 23 0 0 1 −1 74.04 24 1 −1 0 0 67.59 25 0 −1 −1 0 56.12 26 1 0 −1 0 77.12 27 −1 0 0 −1 67.96 28 1 1 0 0 82.12 29 −1 0 −1 0 68.04 2.4.2 回归模型建立与方差分析
为了寻求最佳酶解工艺,利用多元二次回归方程拟合各不同影响因素与响应值之间的函数关系,多变量问题应用回归方程进行分析解决[23]。运用Design-Expert 13软件对表3数据进行多元二次回归拟合,建立SCP酶解工艺参数回归模型。DPPH·清除率与各因素之间的二次多元回归方程式如下:
Y=87.04+4.5A+4.39B+3.52C+3.65D+1.66AB−0.545AC−1.19AD−3.81BC+7.61BD+0.09CD−4.83A2−12.09B2−5.76C2−4.97D2
对此二次多项回归模型进行方差分析,结果如表4所示,模型P<0.0001,F=43.88,且失拟项P=0.3532>0.05为不显著,说明模型高度显著,模型结果与实验结果拟合度较高。该模型决定系数R2=0.9777>0.9,说明理论值与实际值呈现出一定的相关性,模型调整系数R2Adj=0.9554,说明95.54%的响应值变化可以运用该模型进行解释,变异系数为2.49%,模型变异的可能性较小,进一步说明该模型具有优良拟合程度,整个实验结果可靠且过程稳定。一次项系数和二次项系数表现为极显著(P<0.01),说明对响应值影响极大。F值可以用来评价各因素对响应值的显著性,四个因素对五味子蛋白酶解物的DPPH·清除能力影响均极为显著,表4中F(A)>F(B)>F(D)>F(C),说明各因素对五味子蛋白酶解物的DPPH·清除能力影响顺序为酶底比>酶解时间>酶解pH>酶解温度。
表 4 响应面回归方程方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of response surface regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 2171.97 14 155.14 43.88 <0.0001 ** A 242.91 1 242.91 68.7 <0.0001 ** B 231.35 1 231.35 65.43 <0.0001 ** C 149.04 1 149.04 42.15 <0.0001 ** D 160.09 1 160.09 45.28 <0.0001 ** AB 11.02 1 11.02 3.12 0.0993 AC 1.19 1 1.19 0.336 0.5713 AD 5.64 1 5.64 1.6 0.2272 BC 58.14 1 58.14 16.44 0.0012 ** BD 231.34 1 231.34 65.43 <0.0001 ** CD 0.0324 1 0.0324 0.0092 0.9251 A² 151.38 1 151.38 42.81 <0.0001 ** B² 948.26 1 948.26 268.19 <0.0001 ** C² 215.46 1 215.46 60.94 <0.0001 ** D² 160.44 1 160.44 45.38 <0.0001 ** 残差 49.5 14 3.54 失拟项 39.43 10 3.94 1.57 0.3532 不显著 纯误差 10.07 4 2.52 总误差 2221.48 28 R2=0.9777,R2Adj=0.9554 注:*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.4.3 响应面各因素交互作用分析
响应面的坡度可以直观地展现出反应条件对响应值的敏感程度。图9直观反映了不同两因素之间的交互作用对DPPH·清除率的影响,响应曲面曲线走势越陡峭,等高线图形越呈现椭圆形,则两因素交互作用对DPPH·清除率的影响越显著[24]。由图9(d)和(e)可得,酶解时间分别与酶解温度和酶解pH交互作用对DPPH自由基清除率的影响具有显著性,图9(a)、(b)、(c)和(f)响应曲面相对平缓,等高线图接近圆形,说明以上两因素之间的交互作用对五味子蛋白酶解物DPPH·清除率的影响较小。
2.4.4 SCAPH制备最佳工艺参数及模型验证
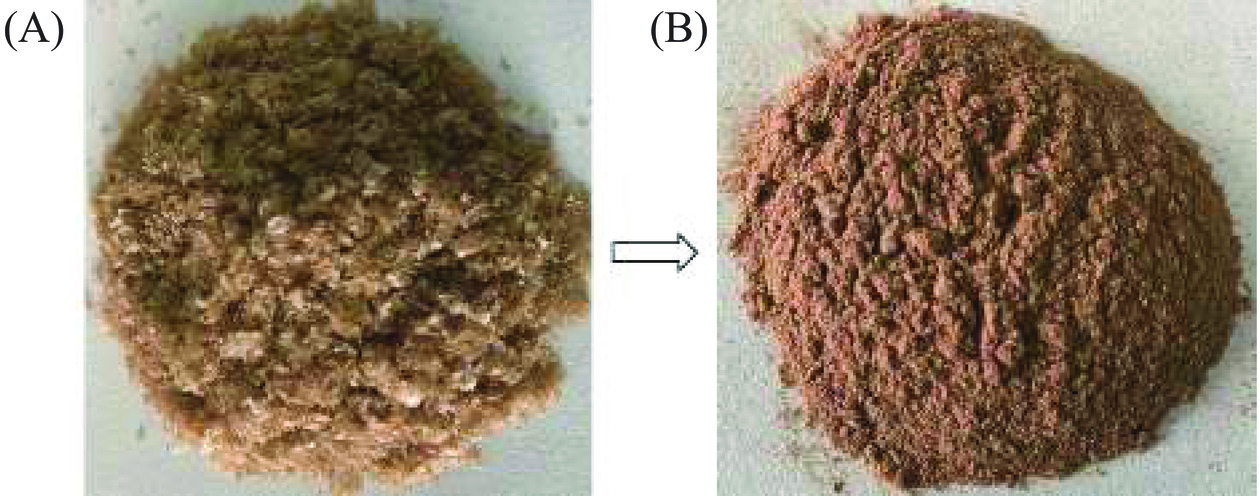
运用Design-Expert 13软件对模型进行解析,得到了一组碱性蛋白酶酶解SCP的最优条件为:酶底比1.21%,酶解时间3.19 h,酶解pH9.29,酶解温度55.99 ℃,在此条件下制备的SCAPH具有优良的DPPH·清除能力,其清除率为89.73%。根据实际操作条件,将五味子蛋白肽的最佳酶解条件修正为:酶底比为1%,酶解时间为3 h,酶解pH为9,酶解温度为55 ℃。如图10所示,在该条件下所得到的五味子蛋白肽为棕黄色粉末,水溶性极好,多肽含量为88.61%±2.19%,对DPPH·清除率为86.96%±2.08%,此时水解度为24.21%±0.76%,表明运用响应面法优化得到的回归模型和最佳工艺参数的可行性和准确度较高,与模型预测值相似,可用于指导实际的生产。
2.5 体外抗氧化实验结果
2.5.1 自由基清除实验
2.5.1.1 清除超氧阴离子自由基能力
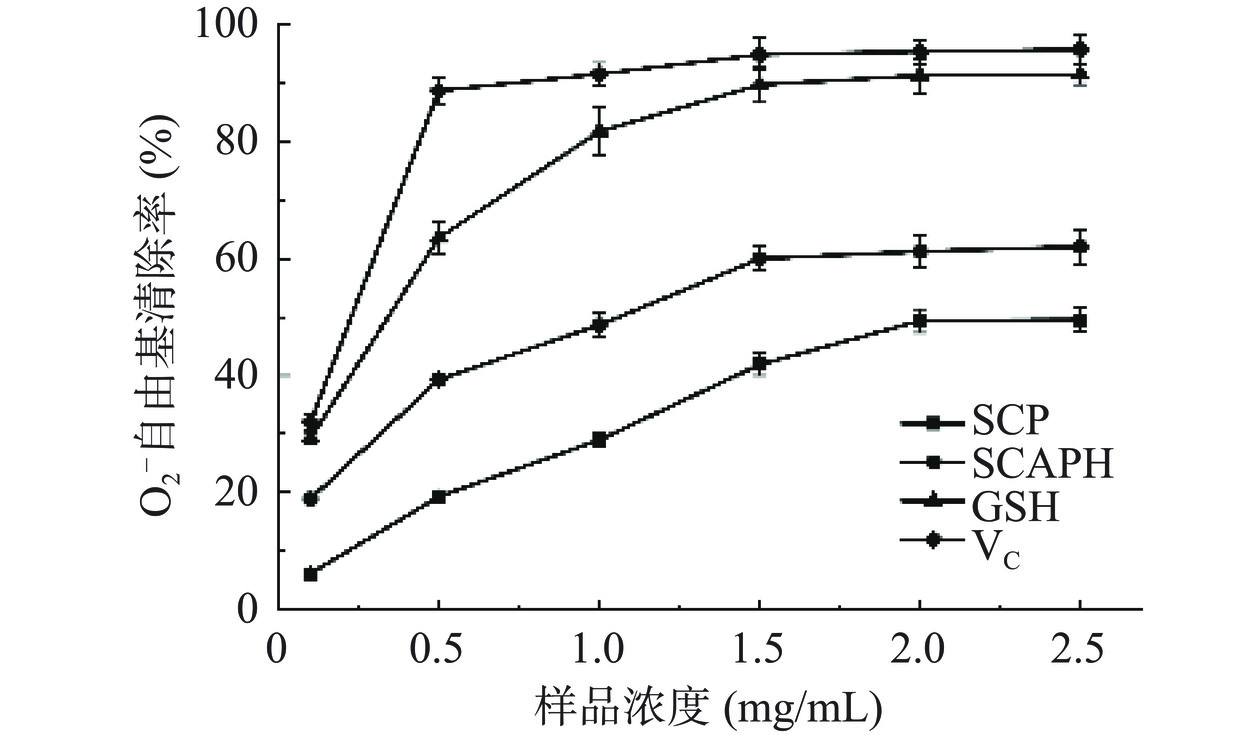
由图11可知,在测定的样品浓度范围内,SCP和SCAPH浓度与其清除率呈明显的正相关关系。其中,在0.1~2.5 mg/mL浓度范围内,SCAPH对超氧阴离子的清除作用强于SCP。IC50值越小,表明样品的抗氧化能力越强[25],分析SCP与SCAPH的 IC50 值可知,SCP的IC50值为2.91 mg/mL,SCAPH的IC50值为0.95 mg/mL。当样品浓度为1.5 mg/mL时,SCAPH清除率几乎达到最高,为59.96%,结果表明SCP经碱性蛋白酶酶解后提升了清除O2−·的能力。
2.5.1.2 清除羟基自由基能力
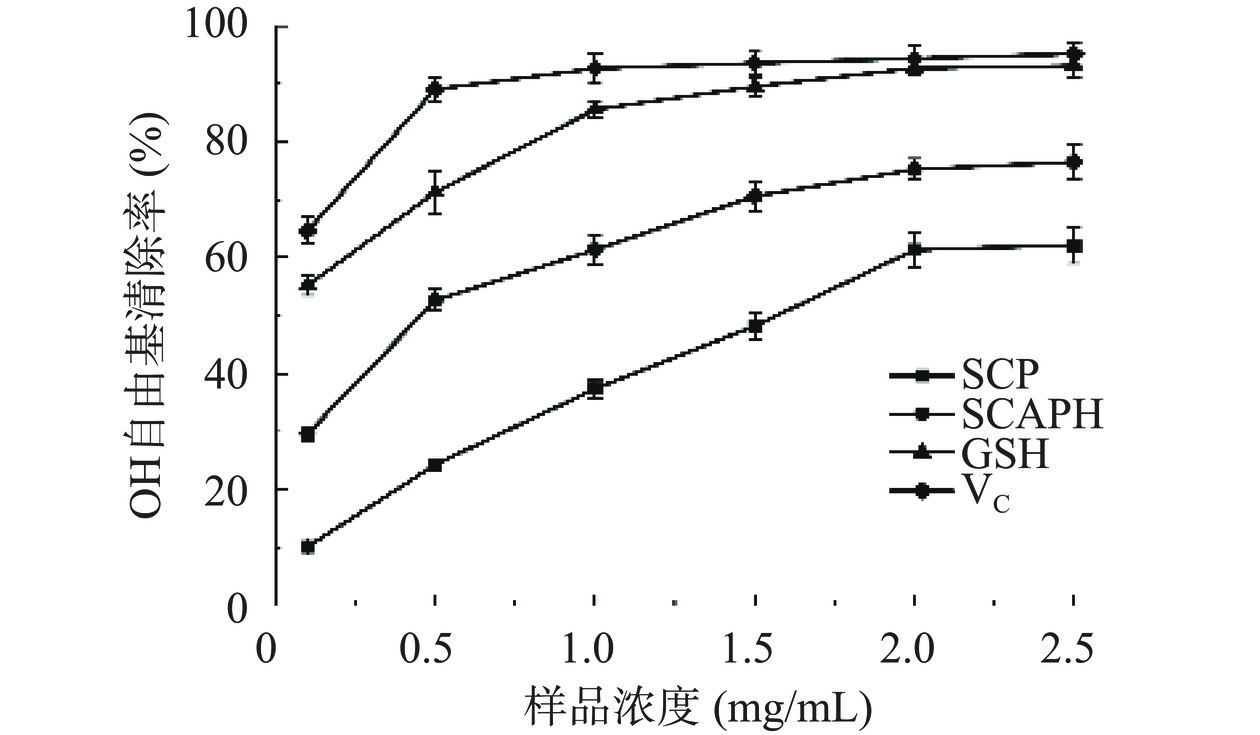
·OH是活性氧中最活泼、毒性最大的氧自由基,是造成生物体氧化损伤的主要因素[26]。图12结果表明,SCP与SCAPH对·OH的清除能力随着样品浓度的增加而增强。在0.1~2.5 mg/mL浓度范围内,SCAPH对·OH的清除能力高于SCP,在2.0 mg/mL时对·OH的清除能力趋向于平缓。由此表明,SCP与SCAPH均具有一定的·OH清除能力。SCP的IC50值为1.60 mg/mL,SCAPH的IC50值为0.43 mg/mL,因此SCAPH清除·OH能力优于SCP。
2.5.1.3 清除DPPH自由基能力
DPPH·清除能力越强表明抗氧化化合物提供电子或氢的能力越高,从而将自由基转化为更稳定的种类[27]。以VC和GSH作为阳性对照,SCP和SCAPH清除DPPH·的能力如图13所示,SCAPH清除能力高于SCP,在0.1~1.5 mg/mL浓度范围内,两者的清除能力呈现出随着样品浓度的增大而增强的趋势。当浓度为1.5 mg/mL时,SCP和SCAPH对DPPH·清除能力几乎达到最大值,分别为68.37%和86.96%,当浓度继续增大时,SCAPH的清除DPPH·能力与GSH相近。SCP与SCAPH都具有较好的DPPH·清除能力,SCP的IC50值为0.81 mg/mL,SCAPH的IC50值为0.41 mg/mL,结果表明,SCAPH清除DPPH·能力优于SCP,可作为一种优良的DPPH·清除剂。
2.5.1.4 清除ABTS+自由基能力
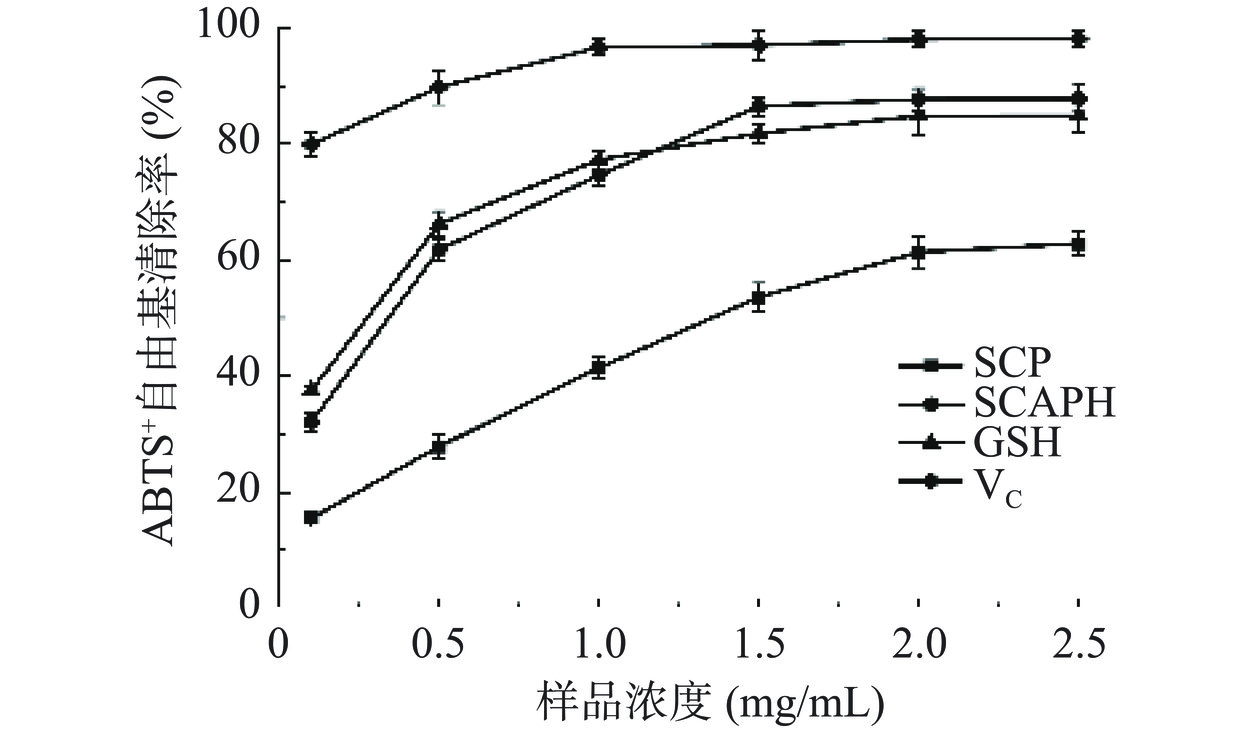
ABTS+·清除率可以反映抗氧化物质的总抗氧化能力[28]。由图14可知,在0.1~1.5 mg/mL浓度范围内,SCAPH对ABTS+·的清除能力随着样品浓度的增大而增强,且高于SCP,在1.5 mg/mL时趋向于平缓,此时清除能力超过阳性对照组GSH的清除能力,当浓度为2.5 mg/mL时达到最大值为87.81%。SCP的IC50值为1.11 mg/mL,SCAPH的IC50值为0.48 mg/mL,与SCP相比,SCAPH具有相对优良的自由基清除能力,可作为一种潜在的抗氧化剂。
2.5.2 还原能力实验
2.5.2.1 亚铁离子螯合能力
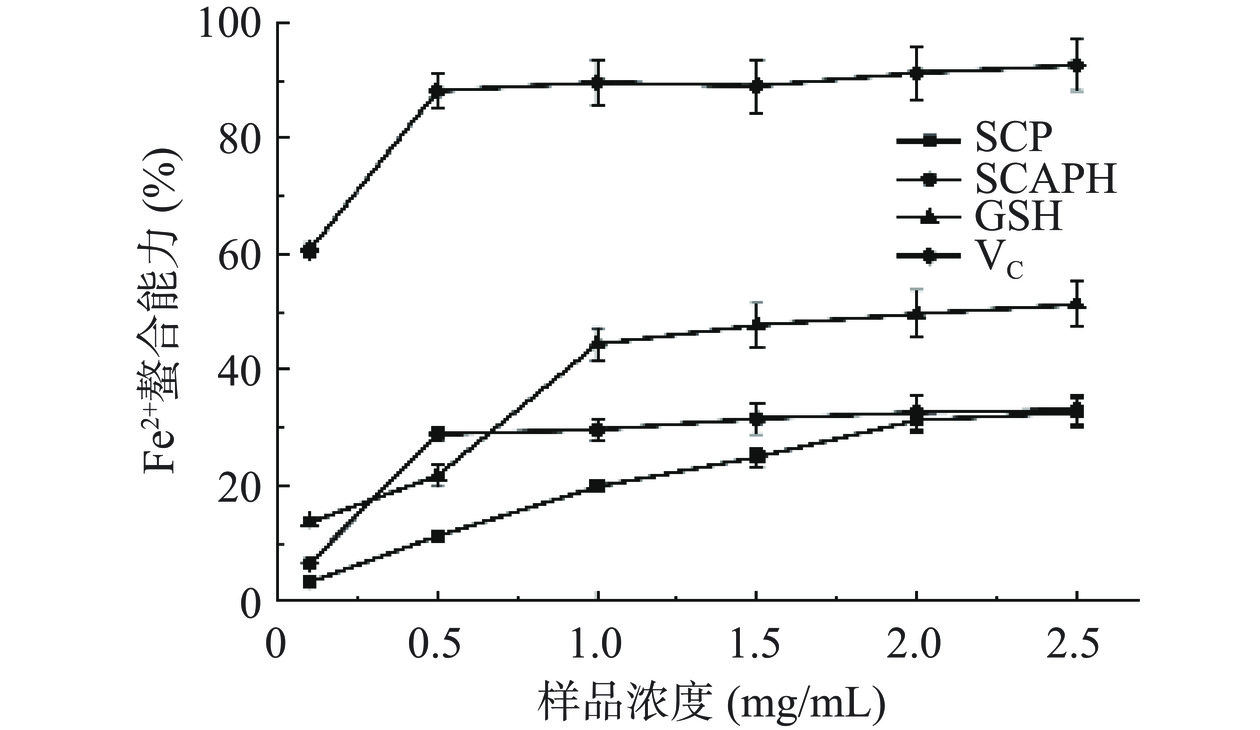
Fe2+作为过渡态金属离子中最为强大的助氧化剂,具有还原性质的样品可以与过渡态金属离子发生螯合,间接阻止·OH的形成,从而达到抗氧化的目的[29]。如图15所示,SCP和SCAPH对亚铁离子均具有一定的螯合能力,当样品浓度为0.5 mg/mL时,SCAPH螯合率趋向于平缓,为28.84%。五味子蛋白经酶解后,对Fe2+螯合能力增强,可能是酶解后肽键的断裂暴露出了更多的酸性和碱性氨基酸,使得侧链的羧基和氨基可以结合Fe2+。蛋白质的金属离子螯合能力大小与带电荷的氨基酸残基之间发生静电作用强弱有关,也可能在结构上通过俘获过渡态金属离子来完成,SCAPH这种作用优于SCP。因此SCAPH更适合作为一种相对优良的还原剂,通过螯合过渡态的金属离子,达到间接抗氧化的目的。
2.5.2.2 铁离子还原能力
抗氧化剂是通过自身的还原作用,给出电子与体内过量的自由基结合生成相对稳定的惰性物质,从而达到清除自由基的目的[30]。由图16所示,SCAPH的Fe3+还原能力优于SCP,可能由于其螯合过渡态的金属离子能力优于SCP。在0.1~1.5 mg/mL浓度范围内,SCP和SCAPH对Fe3+的还原能力随着样品浓度的增大而增强,在1.5 mg/mL时还原能力趋向于平缓,分别为0.91和1.79,SCAPH表现出更强的还原能力,是一种良好的还原剂,通过还原作用来间接达到抗氧化作用。
3. 结论
本研究以五味子蛋白为原料,运用碱性蛋白酶、中性蛋白酶、风味蛋白酶、复合蛋白酶、木瓜蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶7种蛋白酶对五味子蛋白酶解,以抗氧化活性、水解度、电泳结合多肽含量和多肽得率为考察指标,综合评价筛选出最适生物酶为碱性蛋白酶,最佳底物浓度为5%。运用单因素实验结合响应面试验确定了五味子蛋白肽的最佳酶解工艺参数,酶底比为1%,酶解时间为3 h,酶解温度为55 ℃,酶解pH为9.0。体外抗氧化活性结果表明,五味子蛋白肽的抗氧化活性优于五味子蛋白,其中五味子蛋白肽的O2−·、·OH、DPPH·、ABTS+·清除率最高分别为62.03%、76.51%、92.64%和87.81%,亚铁离子螯合能力为33.08%,铁离子还原能力为1.83。五味子蛋白肽不仅具有更加优良的自由基清除活性来直接发挥抗氧化活性,还具有优良的Fe2+螯合能力及Fe3+还原能力来间接发挥抗氧化作用。本研究结果为五味子蛋白制备抗氧化活性肽的工艺提供数据支持,为后续深入研究奠定基础。优良的抗氧化活性表明五味子蛋白水解产物来源的多肽在食品应用中可以作为一种有效的来源,为增加五味子蛋白肽的附加值并为其在健康产品研究与开发及保健食品中的应用提供理论依据和参考价值。
-
表 1 不同蛋白酶的最适酶解条件
Table 1 Optimum enzymatic hydrolysis conditions of different proteases
序号 蛋白酶种类 酶解温度(℃) 酶解pH 酶解时间(h) 酶底比(%) 1 木瓜蛋白酶 65 6.5 4 1 2 中性蛋白酶 50 7.0 4 1 3 碱性蛋白酶 55 8.5 4 1 4 复合蛋白酶 50 8.5 4 1 5 胃蛋白酶 37 2.0 4 1 6 胰蛋白酶 45 8.0 4 1 7 风味蛋白酶 50 6.5 4 1 表 2 响应面试验因素水平编码表
Table 2 Response surface test factor level coding table
水平 因素 A酶底比(%) B酶解时间(h) C酶解温度(℃) D酶解pH −1 0.5 2 45 8 0 1.0 3 55 9 1 1.5 4 65 10 表 3 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 3 Design and results of response surface experiment
试验号 A酶底比 B酶解时间 C酶解温度 D酶解pH DPPH自由基
清除率(%)1 −1 −1 0 0 60.92 2 0 0 0 0 87.13 3 0 1 1 0 75.29 4 1 0 1 0 83.59 5 0 0 0 0 87.65 6 0 −1 1 0 72.86 7 1 0 0 −1 79.35 8 0 0 0 0 84.76 9 −1 0 0 1 78.16 10 0 0 −1 1 77.87 11 0 −1 0 1 62.64 12 0 0 0 0 86.54 13 0 1 0 −1 61.93 14 1 0 0 1 84.80 15 0 1 −1 0 73.80 16 0 0 0 0 89.10 17 0 0 −1 −1 69.75 18 −1 1 0 0 68.81 19 −1 0 1 0 76.69 20 0 1 0 1 82.93 21 0 0 1 1 82.52 22 0 −1 0 −1 72.06 23 0 0 1 −1 74.04 24 1 −1 0 0 67.59 25 0 −1 −1 0 56.12 26 1 0 −1 0 77.12 27 −1 0 0 −1 67.96 28 1 1 0 0 82.12 29 −1 0 −1 0 68.04 表 4 响应面回归方程方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of response surface regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 2171.97 14 155.14 43.88 <0.0001 ** A 242.91 1 242.91 68.7 <0.0001 ** B 231.35 1 231.35 65.43 <0.0001 ** C 149.04 1 149.04 42.15 <0.0001 ** D 160.09 1 160.09 45.28 <0.0001 ** AB 11.02 1 11.02 3.12 0.0993 AC 1.19 1 1.19 0.336 0.5713 AD 5.64 1 5.64 1.6 0.2272 BC 58.14 1 58.14 16.44 0.0012 ** BD 231.34 1 231.34 65.43 <0.0001 ** CD 0.0324 1 0.0324 0.0092 0.9251 A² 151.38 1 151.38 42.81 <0.0001 ** B² 948.26 1 948.26 268.19 <0.0001 ** C² 215.46 1 215.46 60.94 <0.0001 ** D² 160.44 1 160.44 45.38 <0.0001 ** 残差 49.5 14 3.54 失拟项 39.43 10 3.94 1.57 0.3532 不显著 纯误差 10.07 4 2.52 总误差 2221.48 28 R2=0.9777,R2Adj=0.9554 注:*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典. 2020年版一部[M]. 北京:北京医药科技出版社, 2020:68. [National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 2020 edition[M]. Beijing:Beijing Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2020:68.] National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 2020 edition[M]. Beijing: Beijing Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 68.
[2] 许梦然, 王迦琦, 高婧雯, 等. 北五味子多糖提取工艺优化及其对LPS刺激巨噬细胞线粒体膜电位的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(20):33−40. [XU M R, WANG J Q, GAO J W, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide and its protective effect on LPS induced mitochondrial membrane potential in macrophages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(20):33−40.] XU M R, WANG J Q, GAO J W, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide and its protective effect on LPS induced mitochondrial membrane potential in macrophages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(20): 33−40.
[3] WANG J Y, ZHANG G L, YANG Y F, et al. Schisandra chinensis lignans exert antidepressant effects by promoting BV2 microglia polarization toward the M2 phenotype through the activation of the cannabinoid receptor type-2-signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 pathway[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(44):14157−14169. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04565
[4] SHAO S, WANG M X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Antifatigue activity of glycoprotein from Schisandra chinensis functions by reducing oxidative stress[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine:eCAM,2020:4231340.
[5] 王海东, 韩荣欣, 张红印, 等. Osborne法分级提取五味子蛋白及抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(23):59−65. [WANG H D, HAN R X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Extraction of Schisandra chinensis protein by Osborne method and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(23):59−65.] WANG H D, HAN R X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Extraction of Schisandra chinensis protein by Osborne method and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(23): 59−65.
[6] 王海东, 张红印, 曹珺, 等. 五味子四种组分蛋白结构、理化性质和功能特性比较[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(2):67−77. [WANG H D, ZHANG H Y, CAO J, et al. Comparison of protein structure, physicochemical properties, and functional properties of four components in Schisandra chinensis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(2):67−77.] WANG H D, ZHANG H Y, CAO J, et al. Comparison of protein structure, physicochemical properties, and functional properties of four components in Schisandra chinensis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(2): 67−77.
[7] 李双, 魏思雯, 吴凤凤. 植物活性肽的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(11):85−92. [LI S, WEI S W, WU F F. Research progress of plant active peptides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(11):85−92.] LI S, WEI S W, WU F F. Research progress of plant active peptides[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(11): 85−92.
[8] 郭浩彬, 张陆燕, 赵宇, 等. 藜麦水解蛋白肽制备及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(21):7073−7082. [GUO H B, ZHANG L Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Study on preparation and antioxidant activity of hydrolysate peptides derived from Chenopodium quinoa proteins[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(21):7073−7082.] GUO H B, ZHANG L Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Study on preparation and antioxidant activity of hydrolysate peptides derived from Chenopodium quinoa proteins[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(21): 7073−7082.
[9] 朱敬敬. 豆类多肽保健食品对羽毛球运动员体力的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(15):233−234. [ZHU J J. Effects of bean polypeptide health food on physical strength of badminton players[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(15):233−234.] ZHU J J. Effects of bean polypeptide health food on physical strength of badminton players[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(15): 233−234.
[10] 周佳琪, 马春燕, 李晓晖. 多肽类ACE抑制剂的设计合成及生物活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):26−34. [ZHOU J Q, MA C Y, LI X H. Design, synthesis and bioactivity of polypeptide ACE inhibitors[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):26−34.] ZHOU J Q, MA C Y, LI X H. Design, synthesis and bioactivity of polypeptide ACE inhibitors[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(23): 26−34.
[11] 何贵祥, 赵全民, 赵岩, 等. 鹿源生物活性肽的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(9):2916−2923. [HE G X, ZHAO Q M, ZHAO Y, et al. Research progress of deer-derived bioactive peptides[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(9):2916−2923.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.9.spaqzljcjs202209026 HE G X, ZHAO Q M, ZHAO Y, et al. Research progress of deer-derived bioactive peptides[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(9): 2916−2923. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.9.spaqzljcjs202209026
[12] ZHANG C Y, LI X, XING Z J, et al. Plasma metabolites-based design of long-acting peptides and their anticancer evaluation[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2023,631:122483−122483.
[13] HOU J, LI Y Q, WANG Z S, et al. Applicative effect of glycinin basic polypeptide in fresh wet noodles and antifungal characteristics[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,83:267−274.
[14] MA Y Z, YU H H, XING R, et al. Lipid-lowering activity and mechanism of peptides from jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2023,101:105421. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105421
[15] MIGUEL R H, JENNIFER K, NEAL A. B, et al. Peptide release, radical scavenging capacity, and antioxidant responses in intestinal cells are determined by soybean variety and gastrointestinal digestion under simulated conditions[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,405(PA):134929.
[16] VINAYASHREE S, VASU P. Biochemical, nutritional and functional properties of protein isolate and fractions from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata var. Kashi Harit) seeds[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,340:128177. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128177
[17] 张伟云, 张凤清. 鸡蛋壳膜多肽酶解工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(21):47−55. [ZHANG W Y, ZHANG F Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis and antioxidant activity of polypeptide from eggshell membrane[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(21):47−55.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.21.008 ZHANG W Y, ZHANG F Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis and antioxidant activity of polypeptide from eggshell membrane[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(21): 47−55. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.21.008
[18] 屈帅杰, 刘淑集, 苏永昌, 等. 响应面法优化菊黄东方鲀肌肉多肽制备工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(12):133−138. [QU S J, LIU S J, SU Y C, et al. Optimization of polypeptides extraction from Takifugu flavidus by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(12):133−138.] QU S J, LIU S J, SU Y C, et al. Optimization of polypeptides extraction from Takifugu flavidus by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(12): 133−138.
[19] 李晓叶, 张珍, 王琼, 等. 羊骨多肽酶法制备工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(10):130−135,142. [LI X Y, ZHANG Z, WANG Q, et al. Optimization enzymatic preparation process and antioxidant activity of sheep bone polypeptide[J]. Food & Machinery,2020,36(10):130−135,142.] LI X Y, ZHANG Z, WANG Q, et al. Optimization enzymatic preparation process and antioxidant activity of sheep bone polypeptide[J]. Food & Machinery, 2020, 36(10): 130−135,142.
[20] 陈江魁, 韩佳佳, 杨明建, 等. 文冠果多肽酶法制备及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(10):207−213. [CHEN J K, HAN J J, YANG M J, et al. Preparation and antioxidant activity of Xanthoceras sorbifolia polypeptide by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(10):207−213.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2021.10.spkj202110033 CHEN J K, HAN J J, YANG M J, et al. Preparation and antioxidant activity of Xanthoceras sorbifolia polypeptide by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(10): 207−213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2021.10.spkj202110033
[21] 付劢, 陈继兰, 王攀林, 等. 鸡胚蛋白的酶解工艺优化及抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(9):35−42. [FU M, CHEN J L, WANG P L, et al. Antioxidant and optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of chicken embryo protein[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(9):35−42.] FU M, CHEN J L, WANG P L, et al. Antioxidant and optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of chicken embryo protein[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(9): 35−42.
[22] 毕晓娟, 魏亮, 杨慧莹, 等. 响应面法优化元宝枫籽粕酶解工艺及多肽功能特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):204−214. [BI X J, WEI L, YANG H Y, et al. optimization of the enzymatic hydrolysis process of Acer truncatum seed meal by response surface methodology and the functional characteristics of the polypeptide obtained[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):204−214.] BI X J, WEI L, YANG H Y, et al. optimization of the enzymatic hydrolysis process of Acer truncatum seed meal by response surface methodology and the functional characteristics of the polypeptide obtained[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(14): 204−214.
[23] 杨大俏, 王锦旭, 李来好, 等. 响应面法优化褶牡蛎多糖多肽联产工艺[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(20):269−278. [YANG D Q, WANG J X, LI L H, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of Alectryonella plicatula Gmelin for simultaneous production of polysaccharides and polypeptides by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2019,40(20):269−278.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181009-070 YANG D Q, WANG J X, LI L H, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of Alectryonella plicatula Gmelin for simultaneous production of polysaccharides and polypeptides by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(20): 269−278. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181009-070
[24] 李伟民, 张莹丽, 刘可玉, 等. 苜蓿多肽制备工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(12):169−173. [LI W M, ZHANG Y L, LIU K Y, et al. Optimization of preparation technology and antioxidant activities of alfalfa polypeptide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(12):169−173.] LI W M, ZHANG Y L, LIU K Y, et al. Optimization of preparation technology and antioxidant activities of alfalfa polypeptide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(12): 169−173.
[25] SUJIN L, AN-HONG C, MISUNG K, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of various solvent extract from Sargassum serratifolium and its major antioxidant components[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,278:178−184.
[26] HU X J, MA X Y, TIAN J P, et al. Rapid and facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots with high antioxidant activity[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications,2020,122:108288. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108288
[27] QIU L Q, ZHANG M, MUJUMDAR A S, et al. Convenient use of near-infrared spectroscopy to indirectly predict the antioxidant activity of edible rose (Rose chinensis Jacq “Crimsin Glory” H. T.) petals during infrared drying[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,369:130951−130951. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130951
[28] 吕新河, 朱云龙. 泥鳅蛋白多肽的抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2022,41(1):22−27. [LÜ X H, ZHU Y L. Study on antioxidant activity of loach protein polypeptide[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2022,41(1):22−27.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.01.003 LÜ X H, ZHU Y L. Study on antioxidant activity of loach protein polypeptide[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2022, 41(1): 22−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.01.003
[29] KORCZEK, TKACZEWSKA, DUDA, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the antioxidant and antihypertensive activity as well as in vitro digestion stability of mackerel (Scomber scombrus) protein hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2020,29(1):73−89. doi: 10.1080/10498850.2019.1695033
[30] 王帅, 贺羽, 贺斌. 自然发酵泡菜中高体外抗氧化活性乳酸菌的筛选及其对模拟胃肠道环境的耐受性[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(22):93−97. [WANG S, HE Y, HE B. Screening of high antioxidant activity lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented pickles and its tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environments[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(22):93−97.] WANG S, HE Y, HE B. Screening of high antioxidant activity lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented pickles and its tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environments[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(22): 93−97.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 黄潇漪,贾利蓉,孙玉鼎,曹月刚,冉旭. 天然香辛料对烘炒花生仁货架期品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(12): 285-293 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 魏甜甜,魏勃,王承,李凯,谢彩锋,杭方学. 黄冰糖低温浸渍茉莉花制备风味糖浆工艺优化. 食品工业科技. 2022(12): 181-187 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 邹林武,姜福全,戚智胜. 白冰糖提取玫瑰花风味的工艺研究. 现代食品. 2022(15): 94-96+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宣晓婷,陈思媛,乐耀元,尚海涛,曾昊溟,凌建刚,张文媛. 高水分南美白对虾虾干货架期预测模型的构建. 农产品加工. 2022(19): 78-82+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
