Study on the Quality Difference of Yun Kang 10 Anaerobic Processed White Tea in Different Seasons
-
摘要: 本研究以春、夏、秋三个季节云抗10号一芽二、三叶鲜叶为原料,经过厌氧处理后采用相同工艺加工成白茶,对其进行感官审评、理化成分测定和UHPLC-MS/MS高通量技术检测氨基酸组分含量,以探究三个季节的原料经厌氧处理后制成的白茶品质差异。结果表明,三个季节的白茶品质差异明显,其中春季白茶干茶色泽翠绿,香气浓郁持久且高扬,并且有花蜜香、毫香、药香以及独特工艺香等多种香气类型,滋味浓鲜甜爽,汤色黄亮,叶底软嫩明亮,感官品质最好。春季白茶的氨基酸、可溶性糖、咖啡碱、水浸出物和黄酮类含量最高,夏季白茶的茶多酚含量最高。氨基酸成分中共检测到20种,其中显著性差异氨基酸有18种(P<0.05)。春季白茶γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)含量最高为1.22 mg/g,有8种氨基酸组分在春季白茶中含量最高;有3种在夏季白茶中含量最高;有6种在秋季白茶中含量最高。通过PCA主成分分析以及差异化合物筛选共得到15种区别三个季节白茶的差异化合物。综合感官审评结果、理化成分以及氨基酸组分来看,春季白茶与夏、秋两季白茶有明显差异,且春季白茶整体品质更优。
-
关键词:
- γ-氨基丁酸(GABA) /
- 云抗10号 /
- 品质差异 /
- 白茶 /
- 季节
Abstract: In this study, the fresh leaves of Yun kang 10 with one bud and two or three leaves in spring, summer and autumn were used as raw materials. After anaerobic treatment, white tea was processed by the same process. The quality differences of white tea made from raw materials in three seasons after anaerobic treatment were explored by sensory evaluation, physical and chemical composition determination and UHPLC-MS/MS high-throughput detection technology to detect the content of amino acid components. The results showed that there were significant differences in the quality of white tea in the three seasons. The dry tea of white tea in spring was bright green in color. The aroma was strong, lasting, high and intensive, and had a variety of aroma types such as flowery, honey, tip aroma, medicinal and the fragrance of unique process. The taste was strong, fresh, sweet and brisk. The color of tea soup was bright yellow. Infused leaf was soft and bright. The quality of sensory was the best. The contents of amino acids, soluble sugar, caffeine, water extract and flavonoids of white tea were the highest in spring, and the content of tea polyphenols white tea was the highest in summer. A total of twenty amino acids were detected, of which 18 amino acids were significantly different (P<0.05). The highest content of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) of white tea was 1.22 mg/g in spring. The content of 8 amino acid components was the highest in spring white tea. The content of three amino acid components was the highest in summer white tea. The content of six amino acid components was the highest in autumn white tea. Through PCA principal component analysis and differential compounds screening, a total of fifteen differential compounds were obtained to distinguish the three seasons of white tea. Based on the results of sensory evaluation, physical and chemical components and amino acid components, white tea in spring was significantly different from white tea in summer and autumn, and the overall quality of white tea in spring was better.-
Keywords:
- γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) /
- Yun kang 10 /
- quality difference /
- white tea /
- season
-
白茶主产于我国福建地区,按采摘标准和加工工艺不同可以分为白毫银针、白牡丹、贡眉、寿眉等。白茶的特点是不炒不揉,初加工工序只有萎凋和干燥[1]。白茶由于其独特的口感以及功效而受到消费者的青睐,各地的白茶产业发展迅速。其中,云南、浙江、福建等地通过茶树品种筛选与加工工艺改良,分别生产出一些具有地方特色的白茶产品,如云南白茶利用其大叶种原料的优势,有效提升了白茶滋味淡薄的缺点。段红星等[2]发现云南大叶种制作白茶具有独特的品种优势,大叶种的品质特征具有开发名优白茶的基础和条件。蒋宾等[3]通过对云南和福建白茶的差异性进行比较研究后制定了可参考的云南白茶标准化生产加工参数。而刘亚峰等[4]研究发现不同季节的白茶原料也对白茶的滋味具有一定的影响。季节性研究可以帮助改善夏秋茶品质,合理利用夏秋茶资源。
γ-氨基丁酸(γ-Aminobutyric,GABA)广泛地分布在动物、植物体内[5]。在食品领域,有关γ-氨基丁酸的研究越来越多。其中,日本津志田藤二郎于1987年首次发现经充氮除氧处理后的茶鲜叶能积累大量的GABA,而将GABA含量在1.5 mg/g以上的茶叶命名为γ-氨基丁酸茶[6]。研究表明,GABA茶风味独特且具有预防、辅助治疗高血压等心血管疾病[7],改善和治疗糖尿病[8−9],抗癌[10],抗疲劳[11],改善脑功能增强记忆力[12],镇痛作用[13],抗癫痫病等精神疾病[14−15],调节激素分泌及控制哮喘病等多种生理功能[16]。目前茶叶加工中主要使用厌氧技术使茶叶中GABA富集并改变整体氨基酸组分以影响茶叶风味,王芳等[17]发现厌氧温度对GABA的富集和成茶GABA含量均有显著影响。张金玉等[18]利用厌氧技术加工GABA红茶与绿茶,发现两种茶叶GABA含量随着厌氧时间的延长而增加,且氨基酸组分整体也呈现独特变化。李加凤等[19]研究发现经厌氧处理鲜叶后,用其制成的晒青毛茶与再制成的普洱生茶均符合GABA茶标准且氨基酸组分与品质有较大改善,证明使用厌氧技术可以有效改善茶叶品质。
目前,通过改变加工工艺来提升云南白茶品质的研究主要以萎凋、干燥等加工步骤为主[20−22],并未涉及到厌氧加工这项技术。本研究利用云抗10号春、夏、秋三个季节的鲜叶(一芽二、三叶)为原料厌氧处理后加工白茶,进行感官审评,理化成分检测并结合UHPLC-MS/MS高通量检测技术对白茶的氨基酸组分进行检测和分析,探究其生化成分和氨基酸组分差异,旨在为云南地区GABA白茶加工工艺优化、提质增效等方面提供理论指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
春、夏、秋云抗10号茶树品种一芽二、三叶鲜叶 采摘于云南省大理州云龙县宝丰乡大栗树茶厂的茶园,春、夏、秋季白茶鲜叶采摘时间依次为2021年4月、2021年6月、2021年8月;甲醇、95%乙醇、正丁醇、乙酸乙酯 分析纯,天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;三氯化铝、磷酸二氢钾、磷酸氢二钠、氯化亚锡、碳酸氢钠 分析纯,天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司;茚三酮、碳酸钠 分析纯,广东光华科技股份有限公司;草酸 分析纯,天津市光复科技发展有限公司;蒽酮、碱式乙酸铅 分析纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;浓硫酸、浓盐酸 分析纯,重庆市川东化工(集团)有限公司;福林酚 分析纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;香荚兰 分析纯,天津市光复精细化工研究所;甲醇、乙腈、甲酸 色谱纯,德国CNW Technologies公司。
AR1140电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;GT10-2高速台式离心机 北京时代北利离心机有限公司;BGZ-240电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博迅医疗生物仪器股份有限公司;UV-5100H紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;HWS-28电热恒温水浴锅 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;DSH-10A水分测定仪 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;SAGA-10TF实验室超纯水器 南京易普易达科技发展有限公司;SHZ-D(Ⅲ)循环水式真空泵 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;MDF-86V340E医用低温保存箱 安徽中科都菱商用电器股份有限公司;1290 Infinity II series UHPLC System超高效液相、6460 Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer质谱 美国Agilent公司;Heraeus Fresco17离心机 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;明澈D24 UV纯水仪 德国Merck Millipore公司;YM-080S超声仪 深圳市方奥微电子有限公司;JXFSTPRP-24研磨仪 上海净信科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 茶样制备
将刚采摘的鲜叶以厚度5 cm摊晾1 h、充N2厌氧6 h后,在温度20~25 ℃环境条件下萎凋60~72 h,摊叶厚度3 cm左右,之后60 ℃烘干机干燥至含水量<8.5%。春季、夏季、秋季白茶样品编号分别为SW、UW、AW。
1.2.2 感官审评方法
按照国家标准(GB/T 23776-2018)《茶叶感官审评方法》,干评茶叶外形的条索、色泽、整碎、净度,湿评茶叶内质的汤色、香气、滋味、叶底,根据品质特征给予相应评语,评分采用百分制,在茶学专用审评室由感官审评员(10人,5男5女)进行审评后打分,取其平均值为最后得分。
1.2.3 理化成分检测方法
水浸出物的检测参照国家标准(GB/T 8305-2013)《茶 水浸出物测定》、咖啡碱的检测参照国家标准(GB/T 8312-2013)《茶 咖啡碱测定》、游离氨基酸总量的检测参照国家标准(GB/T 8314-2013)《茶 游离氨基酸总量的测定》、茶多酚含量的检测参照国家标准(GB/T 8313-2018)《茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法》。黄酮总量的测定参照三氯化铝比色法[23],可溶性糖总量的测定参照蒽酮比色法[23],茶样制备采取三次平行重复原则。
1.2.4 氨基酸类物质检测方法
采用UHPLC-MS/MS高通量检测技术,检测厌氧白茶样本的20种氨基酸目标含量,实验方法如下:
目标提取:a. 称取20 mg样本于EP管中,加入1000 μL提取溶剂(体积比为乙腈:甲醇:水=2:2:1,含同位素标记内标混合物,−40 ℃预冷,涡旋30 s混匀;b. 40 Hz研磨处理4 min,冰水浴下超声5 min,重复三次;c. −40 ℃静置1 h;d. 4 ℃,12000 r/min(离心力13800×g,半径8.6 cm)离心15 min;e. 取100 μL上清液加900 μL提取溶剂,涡旋30 s混匀,在4 ℃,12000 r/min(离心力13800×g,半径8.6 cm)离心15 min;f. 取80 μL上清液至LC进样瓶中,用于UHPLC-MS/MS分析。
氨基酸标准溶液配制:准确称取相应量的标准品于10 mL容量瓶中,分别配制成10 mmol/L的标准品储备液。取相应量的标准品储备液于10 mL容量瓶中,配制成混合标准溶液。依次稀释该标准溶液得一系列校准溶液(含与样品中浓度一致的同位素标记内标混合物)。
上机检测:流动相条件:超高效液相色谱仪:Agilent 1290 Infinity II series(Agilent Technologies);液相色谱柱:Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide(100×2.1 mm,1.7 μm Waters);液相色谱A相:1%甲酸水溶液,B相:1%甲酸乙腈;其他:柱温为35 ℃,样品盘设为4 ℃,进样体积为1 μL。
质谱条件:使用装备AJS-ESI离子源的Agilent6460三重四极杆质谱仪。离子源参数如下:离子源电压为正离子模式4000 V,负离子模式−3500 V,喷嘴电压为正离子模式500 V,负离子模式−500 V,气体(氮气)温度为300 ℃,气体(氮气)流量为5 L/min,鞘气(氮气)温度为250 ℃,鞘气流量为11 L/min,喷雾器为45 psi。
氨基酸目标定量、定性方法:进行UHPLC-MS/MS分析之前,将目标化合物标准溶液引入质谱中。针对每个目标化合物,选取信号强度最高的数个母离子与子离子对,对其MRM参数进行优化,并选取其中响应最好的离子对用于定量分析,其它离子对用于目标化合物定性分析。
1.2.5 差异化合物筛选方法
利用统计学VIP值、P值进行差异化合物筛选,选取VIP>1且P<0.05的化合物为差异化合物。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据测定平行进行3次,计算平均值。数据处理及作图采用SPSS26.0、Simca14.0和WPS Office。使用Agilent MassHunter Work Station Software(B.08.00,Agilent Technologies)处理氨基酸目标质谱数据与氨基酸目标定量分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同季节云抗10号厌氧加工白茶的感官评价
根据1.2.2感官审评方法进行感官审评,结果如表1所示,不同季节厌氧处理后白茶感官品质特征和得分存在明显差异。SW芽叶连枝,干茶色泽翠绿,匀整,香气花蜜香、毫香带药香,汤色黄亮,滋味浓鲜甜爽,有回甘,叶底黄绿、软嫩明亮,综合得分为91.05。UW芽叶连枝,干茶色泽翠绿,尚匀整,香气花果香,汤色杏黄明亮,滋味鲜爽甜醇,叶底黄绿尚匀整,综合得分为89.6。AW芽叶连枝,干茶色泽青褐,匀整、亮,香气甜香馥郁带毫香,汤色杏黄明亮,滋味甜爽回甘,叶底黄褐、较软嫩明亮,芽叶成朵,匀整,综合得分为90.15。经过厌氧处理后,三个季节的白茶都展现了独特工艺香(富含γ-氨基丁酸所表现出的独特香气类型),可能由于季节性原因,SW本身内含成分更为丰富协调,所以从感官品质上来看,SW品质综合结果最优。
表 1 不同季节厌氧处理加工白茶感官审评记录Table 1. Sensory evaluation records of white tea processed by anaerobic treatment in different seasons样品
名称外形(25%) 香气(25%) 汤色(10%) 滋味(30%) 叶底(10%) 总分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 SW 芽叶连枝
翠绿匀整89 花蜜香,GABA香
带药香,毫香92 黄亮 89 浓鲜
甜爽回甘93 黄绿软亮 90 91.05 UW 芽叶连枝
翠绿,尚匀整86 GABA香
带花果香90 杏黄明亮 91 鲜爽甜醇 92 黄绿尚匀 89 89.6 AW 芽叶连枝
青褐匀整,亮87 甜香馥郁
带毫香,GABA香92 杏黄明亮 91 甜爽回甘 91 黄褐较软亮
芽叶成朵匀整90 90.15 2.2 不同季节云抗10号厌氧加工白茶的理化成分差异
由表2可知,SW可溶性糖、咖啡碱、水浸出物和黄酮的含量与其他两季白茶有着显著性差异(P<0.05)。游离氨基酸滋味多鲜甜,对于提高茶汤的鲜爽度、缓解苦涩味具有重要作用[24],三个季节中氨基酸总量最高的是SW,可以达到5.78%,因其呈味特点可作为茶汤鲜爽味的主要影响成分。可溶性糖是茶汤滋味和香气的来源之一,是构成茶汤甜味的主要成分[25],本研究中三个季节可溶性糖的含量范围在3.25%~4.23%,与刘东娜等[24]的研究一致,其中SW可溶性糖含量(4.23%)最高,是其具有甜味回甘特点的主要原因。咖啡碱是构成茶叶滋味的主要成分,是苦味的主要贡献者,既有刺激性又有提神作用[26]。SW咖啡碱含量(5.25%)高于UW与AW,三个季节白茶中咖啡碱的含量范围在4.16%~5.25%,对滋味协调性有着重要贡献作用,与和明珠等[27]的研究相一致。茶叶中水浸出物是指能被热水浸出的物质,同时也是茶汤的主要呈味物质,其含量高低反映了茶叶中可溶性物质的多少,标志着茶汤的厚薄和滋味的浓强程度,在一定程度上还反映了茶叶品质的优劣[28]。SW中水浸出物含量(53.97%)显著高于其他两季白茶,使其在感官上呈现滋味浓厚的特点。黄酮类物质及其氧化产物对白茶茶汤的色泽与滋味都有一定的影响[29]。本研究中SW中黄酮含量最高,可以达到0.86%,三个季节白茶中黄酮的含量范围在0.68%~0.86%。
表 2 不同季节白茶中主要理化成分(%)Table 2. Main physical and chemical compositions in white tea in different seasons (%)样品名称 氨基酸 可溶性糖 咖啡碱 水浸出物 茶多酚 黄酮 SW 5.78±
0.22a4.23±
0.06a5.25±
0.22a53.97±
0.75a19.98±
1.48b0.86±
0.03aUW 5.34±
0.13b3.25±
0.31c4.16±
0.26b42.22±
1.37c23.26±
1.72a0.70±
0.07bAW 5.63±
0.08ab3.64±
0.04b4.18±
0.05b49.52±
0.48b18.67±
0.04b0.68±
0.03b注:同一列不同小写字母表示显著差异(P<0.05)。 UW中茶多酚的含量显著高于SW和AW(P<0.05),可以达到23.26%。茶多酚对白茶的色、香、味的形成影响极大,是茶叶中最主要的保健作用功能性成分[30]。三个季节白茶中茶多酚的含量范围在18.67%~23.26%。由上可知,三个季节白茶中的主要生化成分差异显著,主要差异性应与季节性关联较大。夏季白茶茶多酚含量高于春季白茶和秋季白茶。结合感官审评结果,夏季白茶和秋季白茶虽然游离氨基酸含量和可溶性糖含量低于春季白茶,但是咖啡碱含量也低于春季白茶,可能是夏季白茶和秋季白茶依然呈现甜醇品质特征的原因。马原等[31]研究表明茶多酚在夏季白茶中含量最低,与本研究结果相反,可能是因为品种差异及加工环境条件不同,夏季鲜叶当中茶多酚含量最高[32],采用统一加工参数进行加工后,仍然是夏季白茶茶多酚含量最高。本研究中的白茶黄酮含量较低,可能是由于采用厌氧技术加工后,黄酮参与黄酮与类黄酮途径生成γ-氨基丁酸从而产生较大消耗[33]。
2.3 不同季节云抗10号厌氧加工白茶氨基酸组分差异
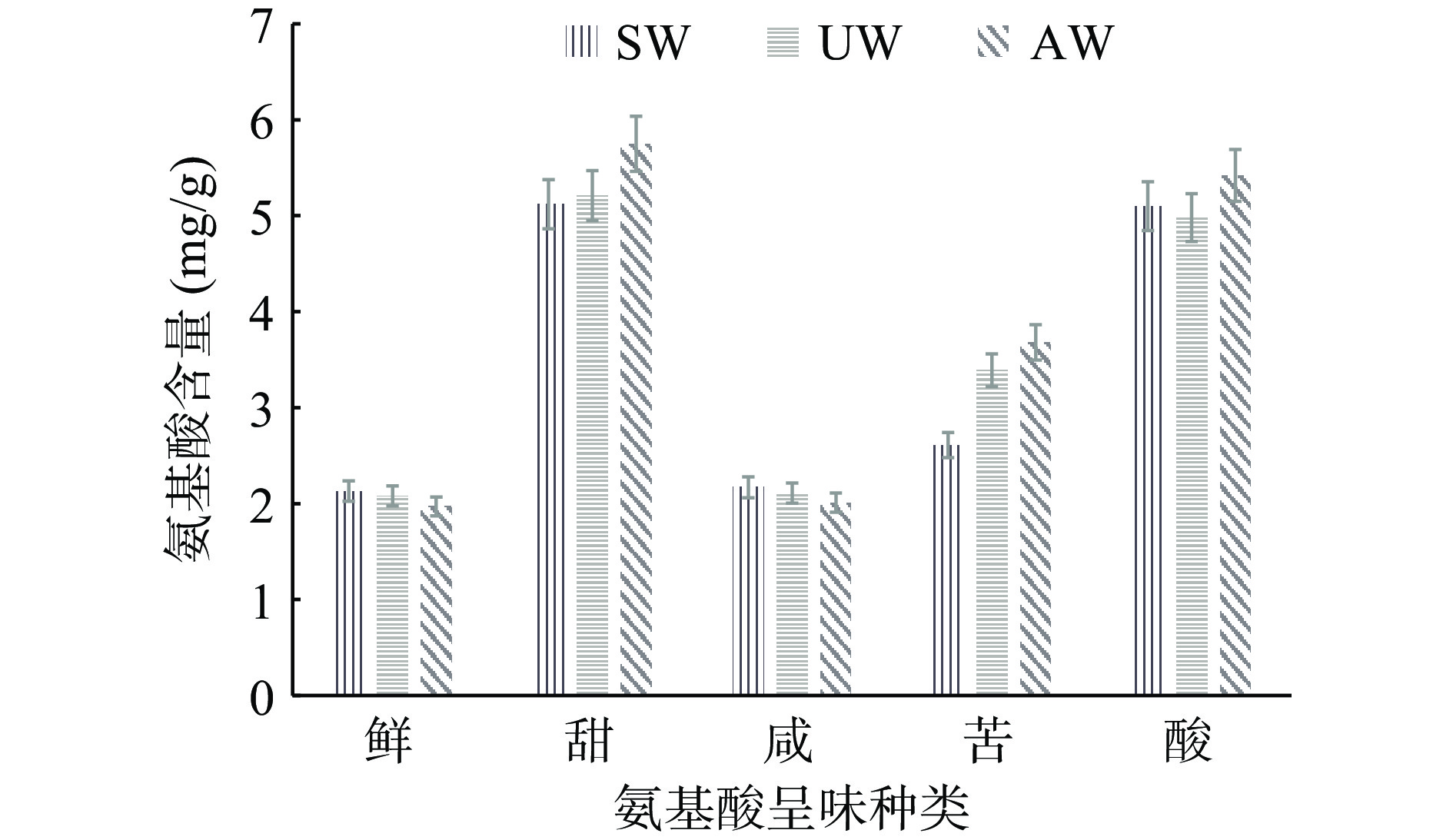
采用UHPLC-MS/MS高通量检测技术测定不同季节厌氧处理加工白茶样品中γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)、L-谷氨酸和L-天冬酰胺等20种氨基酸组分质量分数(表3)。由表3可知,SW中质量分数最高且与UW和AW有显著性差异(P<0.05)的氨基酸组分有γ-氨基丁酸(1.22 mg/g)、L-酪氨酸(0.58 mg/g)、L-丙氨酸(0.52 mg/g)、甘氨酸(0.02 mg/g)、L-谷氨酸(1.69 mg/g)、L-苏氨酸(0.53 mg/g)、L-谷氨酰胺(2.61 mg/g)、L-精氨酸(0.15 mg/g)。据图1以及结合相关氨基酸呈味研究[34]发现,L-丙氨酸、甘氨酸和L-苏氨酸可能是SW茶汤甜味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-谷氨酰胺可能是SW茶汤酸味和甜味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-酪氨酸和L-精氨酸可能是SW茶汤苦味的主要贡献氨基酸。γ-氨基丁酸可能是SW茶汤涩味的主要贡献氨基酸。β-丙氨酸和L-瓜氨酸可能是SW茶汤咸味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-谷氨酸(1.69 mg/g)可能是SW茶汤酸味、鲜味和咸味的主要贡献氨基酸。
表 3 不同季节白茶中主要氨基酸成分(mg/g)Table 3. Main amino acid compositions in white tea in different seasons (mg/g)化合物名称 缩写 SW UW AW 呈味 L-色氨酸 Trp 0.29±0.01c 0.38±0.01b 0.47±0.01a 苦 L-苯基丙氨酸 Phe 0.97±0.05b 1.58±0.11a 1.52±0.03a 苦 L-缬氨酸 Val 0.32±0.01c 0.61±0.03b 0.75±0.02a 苦 γ-氨基丁酸 GABA 1.22±0.03a 0.46±0.02b 0.48±0.01b 涩 L-酪氨酸 Tyr 0.58±0.03a 0.41±0.01c 0.49±0.02b 苦 β-丙氨酸 β-Ala 0.03±0.00a 0.02±0.00b 0.03±0.00a 咸 L-脯氨酸 Pro 0.43±0.01c 0.46±0.02b 0.59±0.01a 甜 L-丙氨酸 Ala 0.52±0.05a 0.45±0.02b 0.42±0.00b 甜 甘氨酸 Gly 0.02±0.00a 0.02±0.00a 0.02±0.00a 甜 L-谷氨酸 Glu 1.69±0.02a 1.38±0.05b 1.03±0.01c 酸、鲜、咸 L-苏氨酸 Thr 0.53±0.01a 0.45±0.02b 0.42±0.01b 甜 4-羟基脯氨酸 Hyp 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 甜 L-天冬氨酸 Asp 0.44±0.00c 0.70±0.03b 0.94±0.01a 酸、鲜、咸 L-谷氨酰胺 Gln 2.61±0.23a 1.10±0.04b 1.10±0.01b 酸、甜 L-丝氨酸 Ser 0.64±0.03c 0.92±0.06a 0.84±0.02b 甜 L-天冬酰胺 Asn 0.36±0.03c 1.80±0.12b 2.35±0.08a 酸、甜 L-瓜氨酸 Cit 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 咸 L-精氨酸 Arg 0.15±0.01a 0.09±0.01c 0.13±0.00b 苦 L-赖氨酸 Lys 0.15±0.01c 0.17±0.01a 0.16±0.00b 苦 L-组氨酸 His 0.15±0.02a 0.15±0.01a 0.16±0.00a 苦 注:同一行不同小写字母表示显著差异(P<0.05);“−”表示没有检测到。 UW中质量分数最高且与SW和AW有显著性差异(P<0.05)的氨基酸组分有L-丝氨酸(0.92 mg/g)、L-赖氨酸(0.17 mg/g)。L-丝氨酸可能是UW茶汤甜味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-苯基丙氨酸和L-赖氨酸可能是UW茶汤苦味的主要贡献氨基酸。
AW中质量分数最高且与SW和UW有显著性差异(P<0.05)的氨基酸组分有L-色氨酸(0.47 mg/g)、L-缬氨酸(0.75 mg/g)、L-脯氨酸(0.59 mg/g)、L-天冬氨酸(0.94 mg/g)、L-天冬酰胺(2.35 mg/g)。L-脯氨酸和4-羟基脯氨酸可能是AW茶汤甜味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-色氨酸和L-缬氨酸可能是AW茶汤酸味与苦味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-天冬氨酸可能是AW茶汤酸味、鲜味和咸味的主要贡献氨基酸。L-天冬酰胺可能是AW茶汤酸味和甜味的主要贡献氨基酸。
经过厌氧处理后,夏季白茶和秋季白茶γ-氨基丁酸含量仍然较低的原因可能是当季鲜叶本身氨基酸含量总量较低,因此缺少γ-氨基丁酸合成的前体物质谷氨酸。对于γ-氨基丁酸的富集,除了在萎凋前厌氧处理6 h这种方式以外,后续还可以通过改变萎凋方式[35],改变堆青次数[36]和选取成熟度更高的原料进行加工[37]等方式来进行提高白茶中γ-氨基丁酸含量的研究。
2.4 不同季节云抗10号厌氧加工白茶品质成分PCA和差异化合物筛选分析
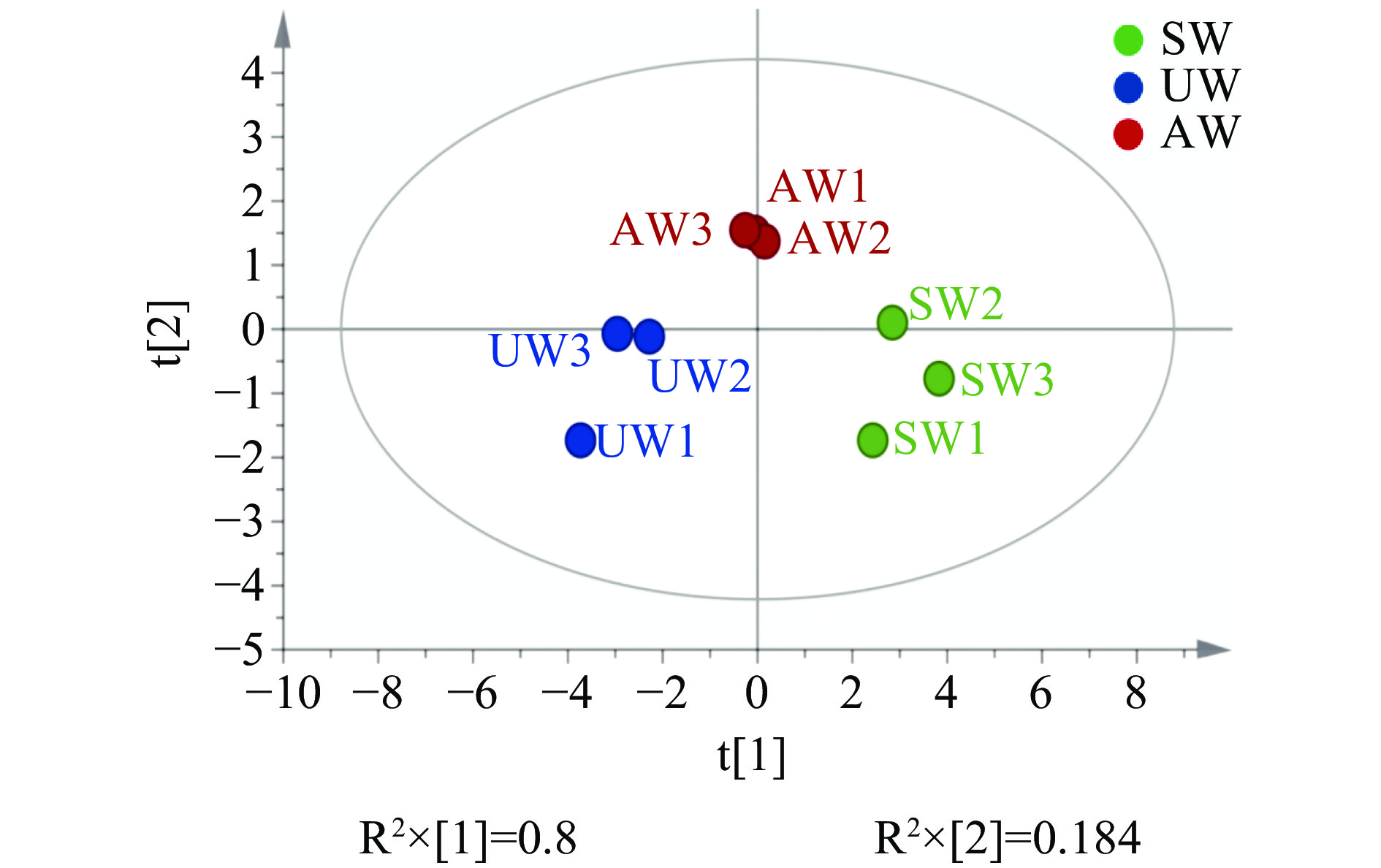
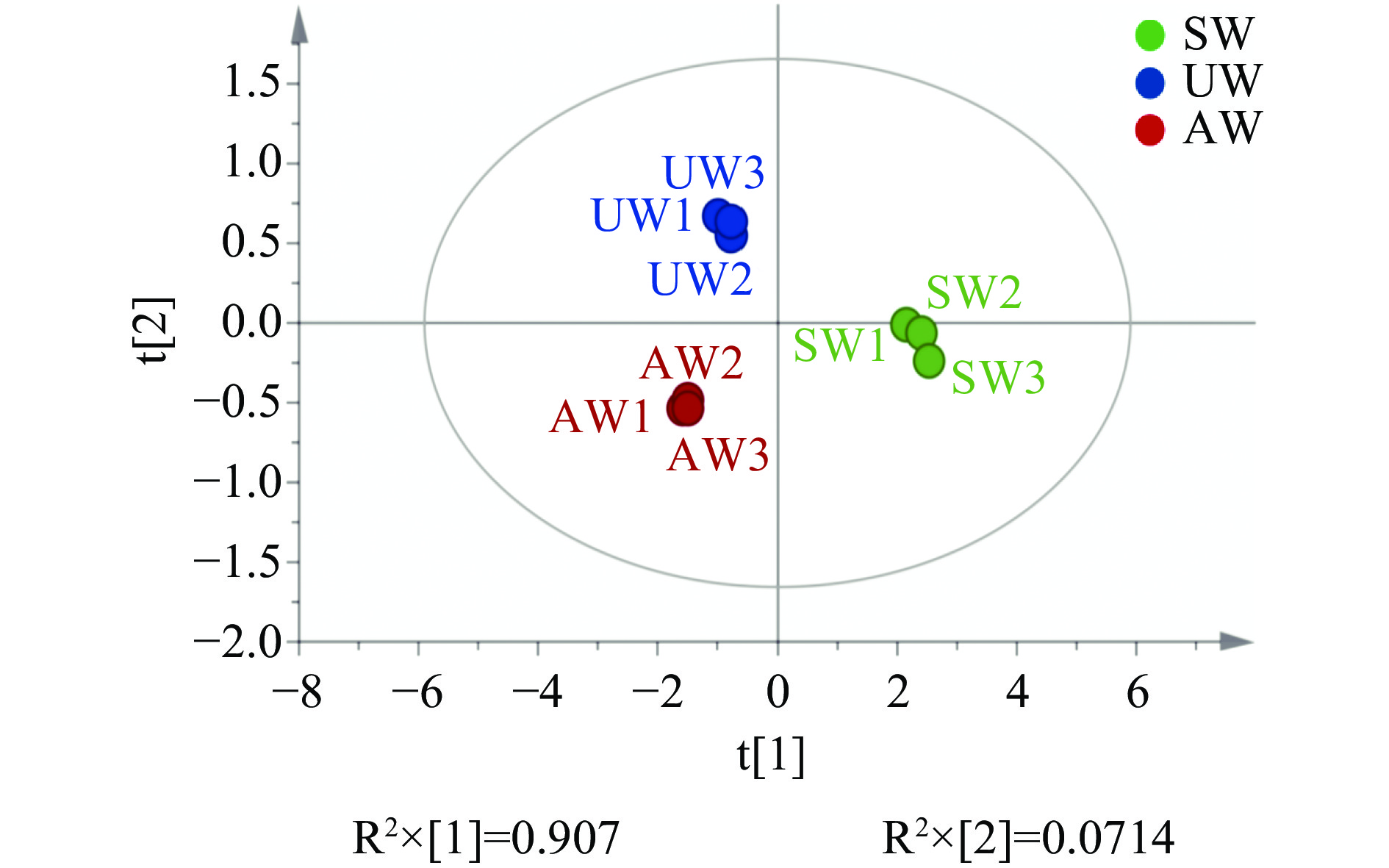
主成分分析图可反映样本中化合物丰度情况,样本之间位置越近则越相似,越远则反之[38]。以三个不同季节白茶的6种理化成分和20种氨基酸质量分数进行主成分提取,以第一主成分(PC1)和第二主成分(PC2)建模得到理化成分PCA得分图(图2)和氨基酸PCA得分图(图3)。理化成分主成分图结果显示,在模型中三个季节白茶各聚成3簇,差异明显且可以较好区分。图1中第一主成分PC1的解释率(R2X[1])和第二主成分PC2的解释率(R2X[2])建模可以解释98.4%的理化成分数据(原始数据详见表2),证明该模型结果较为稳定可靠。氨基酸主成分图如图2结果显示,在模型中三个季节白茶聚成3簇,差异明显且可以较好区分。且第一主成分PC1的解释率(R2X[1])和第二主成分PC2的解释率(R2X[2])建模可以解释97.84%的氨基酸成分数据(原始数据详见表3),证明该模型结果较为稳定可靠。
为进一步找出对结果分析起贡献作用和春、夏、秋三季白茶品质差异的特征理化成分和氨基酸组分,采用VIP筛选阈值(VIP>1)和t检验法(P<0.05)分析共得到15种差异化合物(表4)。咖啡碱、黄酮、L-色氨酸、L-苯基丙氨酸、L-缬氨酸、γ-氨基丁酸、L-脯氨酸、L-丙氨酸、甘氨酸、L-谷氨酸、L-苏氨酸、4-羟基脯氨酸、L-天冬氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺和L-天冬酰胺的含量差异有统计学意义,可作为区别三个季节的标志性差异化合物。
表 4 春、夏、秋白茶中VIP值>1且具有显著性差异的成分Table 4. Components with VIP value >1 in spring, summer and autumn white tea had significant differences化合物 VIP P 咖啡碱 1.102 0.001 黄酮 1.096 0.004 L-色氨酸 1.321 0.000 L-苯基丙氨酸 1.075 0.000 L-缬氨酸 1.278 0.000 γ-氨基丁酸 1.132 0.000 L-脯氨酸 1.267 0.000 L-丙氨酸 1.138 0.026 甘氨酸 1.192 0.008 L-谷氨酸 1.324 0.000 L-苏氨酸 1.242 0.000 4-羟基脯氨酸 1.139 0.009 L-天冬氨酸 1.319 0.000 L-谷氨酰胺 1.150 0.000 L-天冬酰胺 1.226 0.000 3. 结论
本文以春、夏、秋三个季节的云抗10号鲜叶为原料,经厌氧处理后采用统一参数加工白茶,运用感官审评、理化成分测定和UHPLC-MS/MS高通量检测技术检测氨基酸组分含量,探究三个季节白茶的品质差异。研究表明,春季白茶外形翠绿匀整,香气丰富,滋味浓鲜甜爽回甘,较夏秋两季白茶品质较好。三个季节白茶理化成分具有显著差异,氨基酸、可溶性糖、咖啡碱、水浸出物和黄酮在春季白茶中含量最高,茶多酚在夏季白茶中含量最高。三个季节白茶氨基酸组分具有显著差异,γ-氨基丁酸、L-酪氨酸、L-丙氨酸、L-谷氨酸、L-苏氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺、L-精氨酸在春季白茶中含量最高,L-苯基丙氨酸、L-丝氨酸、L-赖氨酸在夏季白茶中含量最高,L-色氨酸、L-缬氨酸、L-脯氨酸、4-羟基脯氨酸、L-天冬氨酸、L-天冬酰胺在秋季白茶中含量最高。经过厌氧处理后,虽然三个季节的白茶在感官审评中都呈现了GABA白茶的品质特征,如具有厌氧处理后的独特工艺香等。但只有春季白茶γ-氨基丁酸含量接近GABA茶标准(1.5 mg/g),因此春季云抗10号鲜叶(一芽二、三叶)更适制GABA白茶,后续可以通过检测挥发性物质成分来进一步探索不同季节厌氧后加工的白茶品质差异。本实验研究结果可为云南地区的白茶在GABA白茶加工工艺优化、提质增效等方面提供理论指导。
-
表 1 不同季节厌氧处理加工白茶感官审评记录
Table 1 Sensory evaluation records of white tea processed by anaerobic treatment in different seasons
样品
名称外形(25%) 香气(25%) 汤色(10%) 滋味(30%) 叶底(10%) 总分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 SW 芽叶连枝
翠绿匀整89 花蜜香,GABA香
带药香,毫香92 黄亮 89 浓鲜
甜爽回甘93 黄绿软亮 90 91.05 UW 芽叶连枝
翠绿,尚匀整86 GABA香
带花果香90 杏黄明亮 91 鲜爽甜醇 92 黄绿尚匀 89 89.6 AW 芽叶连枝
青褐匀整,亮87 甜香馥郁
带毫香,GABA香92 杏黄明亮 91 甜爽回甘 91 黄褐较软亮
芽叶成朵匀整90 90.15 表 2 不同季节白茶中主要理化成分(%)
Table 2 Main physical and chemical compositions in white tea in different seasons (%)
样品名称 氨基酸 可溶性糖 咖啡碱 水浸出物 茶多酚 黄酮 SW 5.78±
0.22a4.23±
0.06a5.25±
0.22a53.97±
0.75a19.98±
1.48b0.86±
0.03aUW 5.34±
0.13b3.25±
0.31c4.16±
0.26b42.22±
1.37c23.26±
1.72a0.70±
0.07bAW 5.63±
0.08ab3.64±
0.04b4.18±
0.05b49.52±
0.48b18.67±
0.04b0.68±
0.03b注:同一列不同小写字母表示显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同季节白茶中主要氨基酸成分(mg/g)
Table 3 Main amino acid compositions in white tea in different seasons (mg/g)
化合物名称 缩写 SW UW AW 呈味 L-色氨酸 Trp 0.29±0.01c 0.38±0.01b 0.47±0.01a 苦 L-苯基丙氨酸 Phe 0.97±0.05b 1.58±0.11a 1.52±0.03a 苦 L-缬氨酸 Val 0.32±0.01c 0.61±0.03b 0.75±0.02a 苦 γ-氨基丁酸 GABA 1.22±0.03a 0.46±0.02b 0.48±0.01b 涩 L-酪氨酸 Tyr 0.58±0.03a 0.41±0.01c 0.49±0.02b 苦 β-丙氨酸 β-Ala 0.03±0.00a 0.02±0.00b 0.03±0.00a 咸 L-脯氨酸 Pro 0.43±0.01c 0.46±0.02b 0.59±0.01a 甜 L-丙氨酸 Ala 0.52±0.05a 0.45±0.02b 0.42±0.00b 甜 甘氨酸 Gly 0.02±0.00a 0.02±0.00a 0.02±0.00a 甜 L-谷氨酸 Glu 1.69±0.02a 1.38±0.05b 1.03±0.01c 酸、鲜、咸 L-苏氨酸 Thr 0.53±0.01a 0.45±0.02b 0.42±0.01b 甜 4-羟基脯氨酸 Hyp 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 甜 L-天冬氨酸 Asp 0.44±0.00c 0.70±0.03b 0.94±0.01a 酸、鲜、咸 L-谷氨酰胺 Gln 2.61±0.23a 1.10±0.04b 1.10±0.01b 酸、甜 L-丝氨酸 Ser 0.64±0.03c 0.92±0.06a 0.84±0.02b 甜 L-天冬酰胺 Asn 0.36±0.03c 1.80±0.12b 2.35±0.08a 酸、甜 L-瓜氨酸 Cit 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 0.01±0.00a 咸 L-精氨酸 Arg 0.15±0.01a 0.09±0.01c 0.13±0.00b 苦 L-赖氨酸 Lys 0.15±0.01c 0.17±0.01a 0.16±0.00b 苦 L-组氨酸 His 0.15±0.02a 0.15±0.01a 0.16±0.00a 苦 注:同一行不同小写字母表示显著差异(P<0.05);“−”表示没有检测到。 表 4 春、夏、秋白茶中VIP值>1且具有显著性差异的成分
Table 4 Components with VIP value >1 in spring, summer and autumn white tea had significant differences
化合物 VIP P 咖啡碱 1.102 0.001 黄酮 1.096 0.004 L-色氨酸 1.321 0.000 L-苯基丙氨酸 1.075 0.000 L-缬氨酸 1.278 0.000 γ-氨基丁酸 1.132 0.000 L-脯氨酸 1.267 0.000 L-丙氨酸 1.138 0.026 甘氨酸 1.192 0.008 L-谷氨酸 1.324 0.000 L-苏氨酸 1.242 0.000 4-羟基脯氨酸 1.139 0.009 L-天冬氨酸 1.319 0.000 L-谷氨酰胺 1.150 0.000 L-天冬酰胺 1.226 0.000 -
[1] 梁月荣. 现代茶业全书[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2011:147−148. [LIANG Y R. Encyclopedia of modern tea industry[M]. Beijing:China Agricultural Publishing House, 2011:147−148. LIANG Y R. Encyclopedia of modern tea industry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2011: 147−148.
[2] 段红星, 孙围围. 福鼎白茶与景谷白茶内含成分与感官品质研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2016,31(6):1091−1096. [DUAN H X, SUN W W. Study on the components and sensory quality of Fuding white tea and Jinggu white tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2016,31(6):1091−1096. DUAN H X, SUN W W . Study on the components and sensory quality of Fuding white tea and Jinggu white tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2016 ,31 (6 ):1091 −1096 .[3] 蒋宾, 鄢远珍, 刘琨毅, 等. 云南和福建白茶差异比较研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,43(4):62−72. [JIANG B, YAN Y Z, LIU K Y, et al. Comparative study on the differences of white tea between Yunnan and Fujian[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2021,43(4):62−72. JIANG B, YAN Y Z, LIU K Y, et al . Comparative study on the differences of white tea between Yunnan and Fujian[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2021 ,43 (4 ):62 −72 .[4] 刘亚峰, 赵玉香, 金阳, 等. 浙江地区夏秋季白茶萎凋技术及品质研究[J]. 中国茶叶加工,2018(3):55−59. [LIU Y F, ZHAO Y X, JIN Y, et al. Withering technology and quality of white tea in summer and autumn in Zhejiang[J]. Tea Processing in China,2018(3):55−59. doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2018.03.016 LIU Y F, ZHAO Y X, JIN Y, et al . Withering technology and quality of white tea in summer and autumn in Zhejiang[J]. Tea Processing in China,2018 (3 ):55 −59 . doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2018.03.016[5] TSUSHIDA T, MURAI T, OMORI M, et al. Production of a new type tea containing a high level of γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Nippon Nõgeikagaku Kaishi, 1987, 61(7):817−822.
[6] OMORI M, YANO T, OKAMOTO J, et al. Effect of anaerobically treated tea (Gabaron tea) on blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Nippon Nõ geikagaku Kaishi,1987,61(11):1449−1451.
[7] PASANDI H, ABBASPOOR S, SHAFEI M. et al. GABA receptor in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus:Effects on cardiovascular system[J]. Pharmacological Reports,2018,70(5):1001−1009. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2018.03.010
[8] 郜秋艳, 尹杰, 张金玉, 等. 茶叶中 γ-氨基丁酸的研究进展[J]. 中国茶叶,2021,43(1):10−19. [GAO Q Y, YIN J, ZHANG J Y, et al. Research progress of γ-aminobutyric acid in tea[J]. Chinese tea,2021,43(1):10−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3150.2021.01.002 GAO Q Y, YIN J, ZHANG J Y, et al . Research progress of γ-aminobutyric acid in tea[J]. Chinese tea,2021 ,43 (1 ):10 −19 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3150.2021.01.002[9] CHERNG S, HUANG C, KUO W, et al. GABA tea prevents cardiac fibrosis by attenuating TNF−alpha and Fas/FasL−mediated apoptosis in streptozotocin−induced diabetic rats[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,65:90−96. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.12.022
[10] HUANG C, KUO W, WANG H, et al. GABA tea ameliorates cerebral cortex apoptosis and autophagy in streptozotocin−induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2014,6:534−544. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.11.020
[11] WANG H, CHUANG S, HSIAO C, et al. A synergistic effect of GABA tea and copper(II) on DNA breakage in human peripheral lymphocytes[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2011,49(4):955−962. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.12.020
[12] 杨帆, 金迪, 蔡东联, 等. γ-氨基丁酸茶对小鼠抗疲劳作用的研究[J]. 氨基酸和生物资源,2011,33(2):60−63. [YANG F, JIN D, CAI D L, et al. Studies on the anti-fatigue effect of γ-aminobutyric acid tea in mice[J]. Amino Acids and Biological Resources,2011,33(2):60−63. doi: 10.14188/j.ajsh.2011.02.014 YANG F, JIN D, CAI D L, et al . Studies on the anti-fatigue effect of γ-aminobutyric acid tea in mice[J]. Amino Acids and Biological Resources,2011 ,33 (2 ):60 −63 . doi: 10.14188/j.ajsh.2011.02.014[13] 张士善, 张力, 张丹参. 脑内Glu/GABA学习记忆调节系统[J]. 药学学报,1997(8):79−81. [ZHANG S S, ZHANG L, ZHANG D S. Brain Glu/GABA learning and memory regulation system[J]. Journal of Pharmacy,1997(8):79−81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-4870.1997.08.019 ZHANG S S, ZHANG L, ZHANG D S . Brain Glu/GABA learning and memory regulation system[J]. Journal of Pharmacy,1997 (8 ):79 −81 . doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-4870.1997.08.019[14] ABDALLAH K, MONCONDUIT L, ARTOLA A, et al. GABA(A) ergic inhibition or dopamine denervation of the all hypothalamic nucleus induces trigeminal analgesia[J]. Pain,2015,156(4):644−655. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000091
[15] PETIT-PRDROL M, ARMANGUE T, PENG X, et al. Encephalitis with refractory seizures, status epilepticus, and antibodies to the GABA(A) receptor:A case series, characterisation of the antigen, and analysis of the effects of antibodies[J]. Lancet Neurology,2014,13(3):276−286. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70299-0
[16] 冀林立, 孟和毕力格. γ-氨基丁酸的生理功能和研究进展[J]. 农产品加工(学刊),2007(12):11−14. [JI L L, MENG H B L G. Physiological function and research progress of γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products (Academic Journal),2007(12):11−14. JI L L, MENG H B L G . Physiological function and research progress of γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products (Academic Journal),2007 (12 ):11 −14 .[17] 王芳, 陈百文, 王飞权. 厌氧温度对白茶加工中GABA富集的影响[J]. 福建茶叶,2016,38(11):8−9. [WANG F, CHEN B W, WANG F Q. Effect of anaerobic temperature on GABA accumulation in white tea processing[J]. Fujian Teas,2016,38(11):8−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2291.2016.11.006 WANG F, CHEN B W, WANG F Q . Effect of anaerobic temperature on GABA accumulation in white tea processing[J]. Fujian Teas,2016 ,38 (11 ):8 −9 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2291.2016.11.006[18] 张金玉, 李美凤, 郜秋艳, 等. 不同厌氧时间对绿茶和红茶加工品质的影响[J]. 茶叶学报,2021,62(2):78−84. [ZHANG J Y, LI M F, GAO Q Y, et al. Effects of different anaerobic time on the processing quality of green tea and black tea[J]. Tea Journal,2021,62(2):78−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2021.02.007 ZHANG J Y, LI M F, GAO Q Y, et al . Effects of different anaerobic time on the processing quality of green tea and black tea[J]. Tea Journal,2021 ,62 (2 ):78 −84 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2021.02.007[19] 李加凤, 杨明容, 周红杰, 等. GABA普洱生茶加工工艺的研究[J]. 农业开发与装备,2013(3):45−46,69. [LI J F, YANG M R, ZHOU H J, et al. Study on the processing technology of GABA Pu'er raw tea[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment,2013(3):45−46,69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9205.2013.03.034 LI J F, YANG M R, ZHOU H J, et al . Study on the processing technology of GABA Pu'er raw tea[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment,2013 (3 ):45 −46,69 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9205.2013.03.034[20] 李双荣, 吴成远, 杨永泽, 等. 不同加工工艺对野生白茶感官品质的影响[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022,360(31):133−135. [LI S R, WU C Y, YANG Y Z, et al. Effects of different processing techniques on the sensory quality of wild white tea[J]. Food Safety Guide,2022,360(31):133−135. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2022.31.020 LI S R, WU C Y, YANG Y Z, et al . Effects of different processing techniques on the sensory quality of wild white tea[J]. Food Safety Guide,2022 ,360 (31 ):133 −135 . doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2022.31.020[21] 王燕, 邱岚. 云南白茶不同加工工艺比较[J]. 现代农业科技,2022,828(22):186−188, 193 [WANG Y, QIU L. Comparison of different processing techniques of Yunnan white tea[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2022,828(22):186−188, 193. WANG Y, QIU L . Comparison of different processing techniques of Yunnan white tea[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2022 ,828 (22 ):186 −188, 193 .[22] 黄刚骅, 李沅达, 邓秀娟, 等. 四种干燥方式云南白茶的香气组分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):283−292. [HUANG G H, LI Y D, DENG X J, et al. Analysis of aroma components of Yunnan white tea by four drying methods[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2022,43(18):283−292. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120080 HUANG G H, LI Y D, DENG X J, et al . Analysis of aroma components of Yunnan white tea by four drying methods[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2022 ,43 (18 ):283 −292 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120080[23] 李远华. 茶学综合实验[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2018.6. [LI Y H. Comprehensive experiment of tea science[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2018.6. LI Y H. Comprehensive experiment of tea science[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2018.6.
[24] 刘东娜, 罗凡, 李春华, 等. 白茶品质化学研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2018,20(4):79−91. [LIU D N, LUO F, LI C H, et al. Research progress on quality chemistry of white tea[J]. China Agricultural Science and Technology Review,2018,20(4):79−91. doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2017.0336 LIU D N, LUO F, LI C H, et al . Research progress on quality chemistry of white tea[J]. China Agricultural Science and Technology Review,2018 ,20 (4 ):79 −91 . doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2017.0336[25] 付赢萱. 不同类别普洱茶的特性及其渥堆发酵研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2016. [FU Y X. Study on the characteristics of different types of Pu-erh tea and its pile fermentation[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2016. FU Y X. Study on the characteristics of different types of Pu-erh tea and its pile fermentation[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016.
[26] 李子平, 赵云雄, 陈远权, 等. 黔茶1号白茶和福鼎大毫白茶品质差异分析[J]. 中国热带农业,2021(5):82−86. [LI Z P, ZHAO Y X, CHEN Y Q, et al. Quality difference analysis of Qiancha 1 white tea and Fuding Dahao white tea[J]. China Tropical Agriculture,2021(5):82−86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0658.2021.05.013 LI Z P, ZHAO Y X, CHEN Y Q, et al . Quality difference analysis of Qiancha 1 white tea and Fuding Dahao white tea[J]. China Tropical Agriculture,2021 (5 ):82 −86 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0658.2021.05.013[27] 和明珠, 李金秋, 万人源, 等. 云南白茶品质特征研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2022,38(17):82−89. [HE M Z, LI J Q, WAN R Y, et al. Study on the quality characteristics of Yunnan white tea[J]. China Agricultural Bulletin,2022,38(17):82−89. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0644 HE M Z, LI J Q, WAN R Y, et al . Study on the quality characteristics of Yunnan white tea[J]. China Agricultural Bulletin,2022 ,38 (17 ):82 −89 . doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0644[28] 赖兆祥, 黄国滋, 庞式, 等. 陈香茶适制品种筛选研究[J]. 广东农业科学,2009(10):54−55,74. [LAI Z X, HUANG G Z, PANG S, et al. Screening of suitable varieties of Chenxiang tea[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2009(10):54−55,74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2009.10.014 LAI Z X, HUANG G Z, PANG S, et al . Screening of suitable varieties of Chenxiang tea[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2009 (10 ):54 −55,74 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2009.10.014[29] 李金辉, 袁弟顺, 岳文杰, 等. 复式萎凋、加温萎凋对白茶品质的影响[C]//中国茶叶科技创新与产业发展学术研讨会论文集, 2009:356−365. [LI J H, YUAN D S, YUE W J, et al. Effects of double withering and heating withering on the quality of white tea[C]//Proceedings of the symposium on technological innovation and industrial development of Chinese Tea, 2009:356−365. LI J H, YUAN D S, YUE W J, et al. Effects of double withering and heating withering on the quality of white tea[C]//Proceedings of the symposium on technological innovation and industrial development of Chinese Tea, 2009: 356−365.
[30] 周琼琼, 孙威江, 叶艳, 等. 不同年份白茶的主要生化成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(9):351−354,359. [ZHOU Q Q, SUN W J, YE YAN, et al. Analysis of main biochemical components of white tea in different years[J]. Food Industry Technology,2014,35(9):351−354,359. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.09.068 ZHOU Q Q, SUN W J, YE YAN, et al . Analysis of main biochemical components of white tea in different years[J]. Food Industry Technology,2014 ,35 (9 ):351 −354,359 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.09.068[31] 马原, 任小盈, 马存强, 等. 不同采制季节信阳白茶品质成分的比较分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(7):217−224,315. [MA Y, REN X Y, MA C Q, et al. Comparative analysis of quality components of Xinyang white tea in different seasons[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(7):217−224,315. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2022.7.0898 MA Y, REN X Y, MA C Q, et al . Comparative analysis of quality components of Xinyang white tea in different seasons[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022 ,38 (7 ):217 −224,315 . doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2022.7.0898[32] 张亚敏. 基于代谢组解析厌氧处理促进茶鲜叶积累GABA的机理[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2018. [ZHANG Y M. Analyze the mechanism of anaerobic treatment promoting GABA accumulation in fresh tea leaves based on metabolomics[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2018. ZHANG Y M. Analyze the mechanism of anaerobic treatment promoting GABA accumulation in fresh tea leaves based on metabolomics[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018.
[33] 杨晨. 基于代谢组学的不同花色种类白茶滋味品质研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2018. [YANG C. Study on the taste quality of white tea with different flower colors based on metabolomics[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. YANG C. Study on the taste quality of white tea with different flower colors based on metabolomics[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018.
[34] 吴婷, 李沅达, 邓秀娟, 等. 萎凋方式对 γ-氨基丁酸白茶香气成分的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(13):4344−4351. [WU T, LI Y D, DENG X J, et al. Effects of withering methods on aroma components of γ-aminobutyric acid white tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2022,13(13):4344−4351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.13.spaqzljcjs202213035 WU T, LI Y D, DENG X J, et al . Effects of withering methods on aroma components of γ-aminobutyric acid white tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2022 ,13 (13 ):4344 −4351 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.13.spaqzljcjs202213035[35] 邬龄盛, 王秀萍, 章细英, 等. 高 γ-氨基丁酸白茶品质升级工艺探讨[J]. 茶叶科学技术,2012(4):13−15. [WU L S, WANG X P, ZHANG X Y, et al. Quality upgrading process of high γ-aminobutyric acid white tea[J]. Tea Science and Technology,2012(4):13−15. WU L S, WANG X P, ZHANG X Y, et al . Quality upgrading process of high γ-aminobutyric acid white tea[J]. Tea Science and Technology,2012 (4 ):13 −15 .[36] 杨高中, 彭群华, 张悦, 等. 厌氧处理对不同类型茶叶的氨基酸组成及生物活性的影响[J]. 茶叶科学,2022,42(2):222−232. [YANG G Z, PENG Q H, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of anaerobic treatment on amino acid composition and biological activity of different types of tea[J]. Tea Science,2022,42(2):222−232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.02.007 YANG G Z, PENG Q H, ZHANG Y, et al . Effects of anaerobic treatment on amino acid composition and biological activity of different types of tea[J]. Tea Science,2022 ,42 (2 ):222 −232 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.02.007[37] 李鑫磊, 俞晓敏, 林军, 等. 基于非靶向代谢组学的白茶与绿茶、乌龙茶和红茶代谢产物特征比较[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):197−203. [LI X L, YU X M, LIN J, et al. Comparison of metabolites between white tea and green tea, oolong tea and black tea based on non-targeted metabolomics[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):197−203. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190128-358 LI X L, YU X M, LIN J, et al . Comparison of metabolites between white tea and green tea, oolong tea and black tea based on non-targeted metabolomics[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (12 ):197 −203 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190128-358[38] CAO Q Q, ZOU C, ZHANG Y H, et al. Improving the taste of autumn green tea with tannase[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张红艳,林娟,黄守行. 低氘水生物技术对咖啡碱和茶多酚浸出率的作用. 西部林业科学. 2024(03): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈凌芝,孔亚帅,史猛,王晶晶,张向娜,陈义,孙慕芳,尹鹏. 冲泡方式对白牡丹茶汤品质成分及感官品质的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(09): 116-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 任志红,肖文敏,吴焕焕,张虹,王瀚悦,杨圣祥,孙海伟. 不同采摘时间谷雨茶的品质成分研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(18): 32-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张悦,邵晨阳,吕海鹏,林智,俞燎远,朱荫. 不同季节烘青绿茶中的挥发性成分与关键香气活性成分分析. 食品科学. 2024(21): 213-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



