Study on the Optimal Harvest Time of Stems and Leaves of Astragalus membranaceus Based on HPLC and Chemometrics
-
摘要: 目的:建立黄芪茎叶中7种黄酮类和3种皂苷类成分含量的HPLC同步检测方法,研究不同采收期黄芪茎叶中活性成分的动态变化规律,明确黄芪茎叶的最适采收期。方法:对色谱条件进行方法学考察,确定10种活性成分的HPLC同步检测方法,进而测定不同采收期黄芪茎叶中10种活性成分的含量,再结合聚类分析和主成分分析以及熵权TOPSIS法分析上述成分含量的动态变化与分布规律。结果:10种成分随不同采收期均呈显著变化(P<0.05),其中黄芪茎中黄酮总量在8月下旬~9月较高,皂苷总量在8月上旬达到最高;黄芪叶中黄酮总量在8月~9月上旬较高,皂苷总量变化趋势不明显。化学计量学分析结果显示,黄芪茎和叶中的化学成分含量在8月前后均有明显不同,进一步的熵权TOPSIS分析结果表明,8~9月的黄芪茎质量综合评价较高,8月的黄芪叶质量综合评价最高,建议黄芪茎叶适宜的采收期为8月下旬。结论:所建立的HPLC方法可用于黄芪茎叶中黄酮类和皂苷类活性成分的同步检测,所明确的黄芪茎叶最适采收期可为黄芪茎叶的质量控制和精深开发利用提供科学依据。Abstract: Objective: To establish the HPLC method for simultaneous content determination of seven flavonoids and three saponins ingredients in the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus, and to investigate its dynamic variation rules in different harvest time so as to determine the appropriate harvest time. Methods: After conducting the methodological investigation of chromatographic conditions, the HPLC detection method of ten active components was established. Then the method was used to determine the content of ten active components in the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus in different harvest time. Finally, the cluster analysis, principal component analysis and entropy weight TOPSIS method were used to analyze the dynamic variation and distribution of the above components. Results: There were significant differences in the contents of the ten ingredients in the aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus during different harvest periods (P<0.05). The total content of flavonoids in stems was higher from late August to September, and that of saponins was reached in early August. In contrast, the highest total amount of flavonoids in leaves was shown in the period of August to early September, and the amount of total saponins was not obviously changed. The results of chemometrics analysis showed that the contents of chemical components in the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus before August were significantly different with that after August. Further entropy weight TOPSIS analysis showed that the stems of Astragalus membranaceus from August to September shared better comprehensive quality than other periods, and the leaves of Astragalus membranaceus in August presented the best quality, suggesting that the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus should be harvested in late August. Conclusion: The HPLC method could be used for the simultaneous content detection of flavonoids and saponins ingredients in the aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus. The suggested harvest period of the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus could provide scientific basis for the quality control and further utilization of the stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus.
-
黄芪茎叶是豆科多年生草本植物蒙古黄芪Astragalus memeranaceus(Fisch.)Bge. Var. mongholicus(Bge.)Hsiao或膜荚黄芪Astragalus membranaceus(Fisch.)Bge.的地上部分。每年伴随黄芪入药根部的采挖,大量的地上茎叶被废弃,如何加强对黄芪茎叶的资源挖掘和精深开发利用逐渐成为研究者关注的重要现实问题[1]。现代科学研究表明,黄芪茎叶具有与其入药根部类似的多糖类、黄酮类、皂苷类等化学成分[2],其中黄酮类具有抗炎、抗氧化等活性[3],而皂苷类具有抗心力衰竭、抗心肌缺血等作用[4]。黄芪甲苷是黄芪皂苷类成分的代表,毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷是黄芪黄酮类成分的代表,这两种成分也是药典中所规定的黄芪质量控制的指标成分[5],说明黄酮类和皂苷类是植物黄芪的重要功效成分。
功效成分含量的高低会影响到黄芪茎叶资源的生理活性。分光光度法、高效液相色谱法、高效液相色谱-质谱联用法等可用于黄芪茎叶黄酮类和皂苷类功效成分的定量检测,其中高效液相色谱法仍然是多种单一成分精确定量分析的主流方法[6−7]。通过应用多波长、一测多评等方法,采用HPLC可实现仅单次色谱分离即可高通量同步测定多成分含量的目的,在植物资源质量控制、品质评价、代谢产物研究等方面有着广泛应用[8−11]。此外,功效成分含量的高低还会受到采收期的影响。相关研究表明膜荚黄芪中毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、芒柄花苷、芒柄花素和黄芪甲苷的含量随采收期呈动态变化趋势,其中毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、芒柄花苷和黄芪甲苷含量在10月份达到最高,而芒柄花素含量在该月达到最低[12];对蒙古黄芪的研究也表明黄酮和皂苷含量会受采收期的影响,8月上旬采收的黄芪中黄酮和皂苷含量最高[13]。类似地,对其他食药两用植物的研究也表明采收期会影响活性成分的含量,相关研究还证实了采收期会进一步影响植物资源的功效,如秋季采收的牛藤叶提取物抗炎活性最强[14],8月下旬采收的五味子果α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性最强[15]。
由此可见,采收期会影响黄芪茎叶功效成分的含量,从而影响到黄芪茎叶的活性,明确其活性成分随采收期的动态变化规律对于黄芪茎叶原料资源的质量控制具有重要意义。目前,黄芪茎叶的研究主要集中于活性成分解析和药效作用探索方面,其活性成分随采收期的动态变化规律尚不明确。基于此,本研究采用高效液相色谱法对黄芪茎叶中毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷等7种黄酮类成分和黄芪甲苷等3种皂苷类成分进行同步含量测定,并结合化学计量学方法分析活性成分随采收期的动态变化规律,以期明确黄芪茎叶的最适采收期,为黄芪茎叶的合理采集、按需采收和最大化利用提供一定科学依据,也为黄芪茎叶的质量控制和合理利用奠定理论基础,对植物黄芪的产业化开发和产业链延伸具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黄芪茎叶 采收于山西省浑源县黄花滩乡,经山西中医药大学中药资源与鉴定教研室刘计权教授鉴定为蒙古黄芪Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus的新鲜茎叶,样品采收后将茎、叶分离,自然阴干,干燥至恒重,粉碎,过4号筛后储存。样品信息见表1;芦丁、毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、黄芪皂苷Ⅱ HPLC≥98%,上海融合医药科技有限公司;金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、山奈酚、大豆皂苷Bb、黄芪甲苷 HPLC≥98%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;乙腈、甲醇 色谱纯,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;甲醇 分析纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;娃哈哈纯净水 杭州娃哈哈集团有限公司。
表 1 样品信息Table 1. Information of samples样品编号 采收日期 样品编号 采收日期 茎 叶 茎 叶 J1 Y1 2022.6.10 J6 Y6 2022.8.25 J2 Y2 2022.6.25 J7 Y7 2022.9.10 J3 Y3 2022.7.10 J8 Y8 2022.9.25 J4 Y4 2022.7.25 J9 2022.10.10 J5 Y5 2022.8.10 J10 2022.10.25 注:10月浑源县的黄芪叶已全部凋落,未采集到该月的黄芪叶。 HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 金坛市杰瑞尔电器有限公司;AR223CN电子天平 奥豪斯仪器(常州)有限公司;GZX-9030MBE电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博迅实业有限公司医疗设备厂;SB25-120超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;RIGOL L-3000系列高效液相色谱仪 北京普源精电科技有限公司;Agilent ZORBAX Extend C18色谱柱(4.5×250 mm,5 µm) 安捷伦科技公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 供试品溶液的制备
精密称取5 g干燥黄芪茎叶粉末,置于250 mL圆底烧瓶中,加入100 mL甲醇,50 ℃下超声提取1 h,室温下静置冷却,过滤。滤液旋蒸至含有少量流动液体后倒出,放入60 ℃烘箱中烘干。随即用色谱级甲醇溶解并定容至5 mL,稀释适当倍数后,摇匀得到供试品溶液。
1.2.2 混合对照品溶液的制备
取各待测成分对照品适量,精密称定,加色谱级甲醇制成芦丁、毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、大豆皂苷Bb、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、黄芪甲苷、山奈酚和黄芪皂苷Ⅱ质量浓度分别为41.00、35.01、39.90、40.42、101.00、11.65、13.50、510.00、41.00、486.00 µg/mL的混合对照品溶液。
1.2.3 色谱条件
采用Agilent ZORBAX Extend-C18(4.6×250 mm,5 µm)色谱柱,流动相为乙腈(A)-水(B),梯度洗脱(0~3 min,15%→19% A;3~6 min,19% A;6~13 min,19%→21% A;13~14 min,21%→32% A;14~16 min,32%→34% A;16~21 min,34%→37% A;21~23 min,37%→35% A;23~25 min,35% A;25~27 min,35%→40% A;27~30 min,40% A;30~35 min,40%→15% A);流速0.8 mL/min;检测波长203 nm(3种皂苷)和254 nm(7种黄酮);柱温25 ℃;进样量10 µL。
1.2.4 HPLC方法学考察
1.2.4.1 系统适应性考察
取“1.2.1”和“1.2.2”项下供试品溶液、混合对照品溶液适量,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样测定。
1.2.4.2 线性关系考察
精密吸取“1.2.2”项下混合对照品溶液4、8、12、16、20、24 μL[16−17],按“1.2.3”项下的色谱条件分别进样测定,记录10种成分吸收峰的峰面积,以各化合物的进样量(μg)为横坐标(X)、峰面积为纵坐标(Y)绘制标准曲线。
1.2.4.3 精密度考察
精密吸取混合对照品溶液10 µL,按“1.2.3”项下的色谱条件连续进样检测6次,记录10种成分吸收峰的峰面积。
1.2.4.4 稳定性考察
取同一批黄芪茎叶样品,按“1.2.1”项下方法制备供试品溶液,室温下于0、4、8、12、18、24 h,按照“1.2.3”项下的色谱条件分别进样检测,并记录10种成分吸收峰的峰面积。
1.2.4.5 重复性考察
取同批次黄芪茎叶样品6份,按“1.2.1”项下方法制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样检测,并记录10种成分吸收峰的峰面积。
1.2.4.6 加样回收率考察
精密称取已知含量的同批次黄芪茎叶样品粉末适量,按已知样品含量的50%、100%和150%分别加入混合对照品溶液[18],按“1.2.1”项下方法制备供试品溶液,然后再按照“1.2.3”项下的色谱条件进行测定,记录10种成分吸收峰的峰面积。
1.2.5 不同采收期样品的含量测定
分别取不同采收期的黄芪茎、叶样品粉末,按“1.2.1”项下方法制备供试品溶液,每个样品平行制备三份,然后按“1.2.3”项色谱条件下进样测定,将各成分峰面积代入相应回归方程求得成分检出量a(µg),然后按下式计算该成分的含量(mg/g)。
成分含量(mg/g)=a×n×V0.01×m×1000 (1) 式中,n为样品溶液稀释倍数;V为样品溶液体积,mL;0.01为检测时进样体积,mL;m为黄芪茎叶样品取样量,mg。
1.3 数据处理
各试验结果均重复3次取平均值并计算误差值,采用SPSS 26.0软件进行显著性差异分析和聚类分析,SIMCA 14.0软件进行主成分分析,SPSSPRO在线数据分析平台进行熵权TOPSIS法分析,采用Origin 2022软件绘制图表。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HPLC方法学考察
2.1.1 系统适应性考察
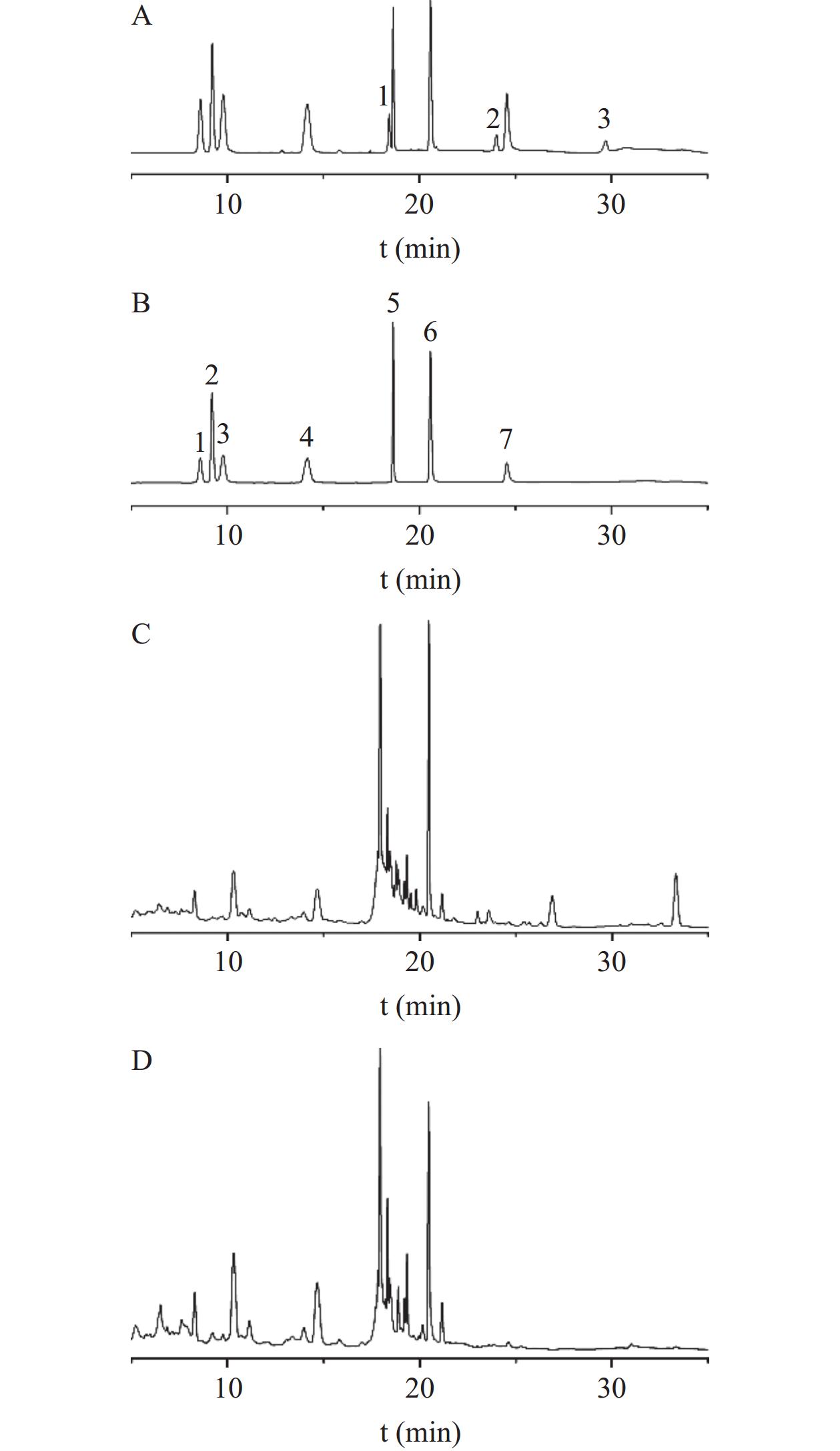
混合对照品和黄芪茎叶样品色谱图结果见图1。各成分理论塔板数均大于10000,分离度均大于1.5,说明柱效高,成分分离度良好,符合HPLC分析要求。
2.1.2 线性关系考察结果
计算出10种待测成分的回归方程和线性范围,结果见表2。10种成分相关系数均大于0.9990,线性关系良好。
表 2 10种成分的线性回归方程及其线性范围Table 2. Linear regression equation and linear range of 10 components序号 待测成分 回归方程 线性范围(μg) R2 1 芦丁 y=556.17x+41.695 0.164~0.984 0.9991 2 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 y=3111.3x+160.72 0.140~0.840 0.9992 3 金丝桃苷 y=735.03x+81.199 0.160~0.958 0.9996 4 槲皮苷 y=2437.9x–73.966 0.162~0.970 0.9997 5 芒柄花苷 y=8091.9x+80.36 0.047~0.280 0.9996 6 毛蕊异黄酮 y=6257.4x–37.298 0.054~0.324 0.9994 7 山奈酚 y=1058.8x–35.408 0.164~0.984 0.9995 8 大豆皂苷Bb y=176.97x+11.35 0.404~2.424 0.9993 9 黄芪甲苷 y=64.856x−18.937 2.040~12.240 0.9996 10 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ y=63.684x−18.125 1.944~11.664 0.9997 2.1.3 精密度考察结果
分别计算各成分峰面积的RSD值,结果显示芦丁、毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、山奈酚、大豆皂苷Bb、黄芪甲苷、黄芪皂苷Ⅱ的RSD值分别为1.19%、0.40%、1.54%、0.86%、0.30%、0.20%、1.30%、1.37%、0.41%、1.64%,均小于2%,表明仪器精密度良好。
2.1.4 稳定性考察结果
分别计算各成分峰面积的RSD值,结果显示芦丁、毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、山奈酚、大豆皂苷Bb、黄芪甲苷、黄芪皂苷Ⅱ的RSD值分别为0.39%、1.28%、0.41%、0.68%、0.23%、0.40%、1.21%、1.08%、0.84%、1.33%,均小于2%,表明供试品在24 h内稳定性良好。
2.1.5 重复性考察结果
分别计算各成分峰面积的RSD值,结果显示芦丁、毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、山奈酚、大豆皂苷Bb、黄芪甲苷、黄芪皂苷Ⅱ的RSD值分别为0.56%、1.63%、0.91%、0.82%、0.83%、1.33%、1.87%、1.95%、0.82%、1.03%,均小于2%,表明实验重复性良好。
2.1.6 加样回收率考察结果
计算其加样回收率和回收率的RSD值,结果见表3。平均加样回收率均在98%~101%之间;RSD值均小于2%,表明所建立的分析方法准确性良好。
表 3 加样回收率试验结果Table 3. Results of sample recovery rate test待测成分 加样回收率(%) 平均加样回收率(%) RSD(%) 芦丁 99.84~100.17 99.85 0.31 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 98.75~101.05 99.87 1.15 金丝桃苷 99.21~100.88 99.91 0.87 槲皮苷 99.36~101.58 100.32 1.14 芒柄花苷 99.96~100.28 100.13 0.16 毛蕊异黄酮 99.42~100.52 99.94 0.55 山奈酚 98.14~101.74 99.94 1.71 大豆皂苷Bb 98.14~100.12 99.38 1.09 黄芪甲苷 99.57~101.05 100.20 0.76 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 98.84~101.16 99.96 1.16 2.2 不同采收期黄芪茎叶样品活性成分的含量测定
2.2.1 不同采收期黄芪茎样品活性成分的含量测定
不同采收期黄芪茎中10种成分的含量结果见表4。由表4可以看出,10种成分的含量随不同采收期均有显著变化(P<0.05),且大部分成分含量呈先上升后下降的趋势,其中,芦丁和山奈酚的含量分别在9月25日和8月25日达到峰值;毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷和黄芪皂苷Ⅱ的含量在9月10日达到峰值;金丝桃苷、大豆皂苷Bb和黄芪甲苷的含量在8月10日达到峰值。其中山奈酚、金丝桃苷和槲皮苷是黄芪茎中含量较丰富的3种黄酮类成分,其次为芦丁和毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷,黄芪甲苷是含量最丰富的皂苷类成分其峰值为11.491±0.140 mg/g。
表 4 不同采收期黄芪茎中10种成分的含量(mg/g)Table 4. Relative contents of 10 components in stems of Astragalus membranaceus at different harvest time (mg/g)成分 不同采收期的黄芪茎样品 J1
(6.10)J2
(6.25)J3
(7.10)J4
(7.25)J5
(8.10)J6
(8.25)J7
(9.10)J8
(9.25)J9
(10.10)J10
(10.25)黄酮类 芦丁 0.130±0.014g 0.172±0.006gh 0.253±0.004de 0.208±0.029efg 0.242±0.033def 0.343±0.034c 0.481±0.047b 0.639±0.041a 0.317±0.007cd 0.155±0.009gh 毛蕊异黄酮
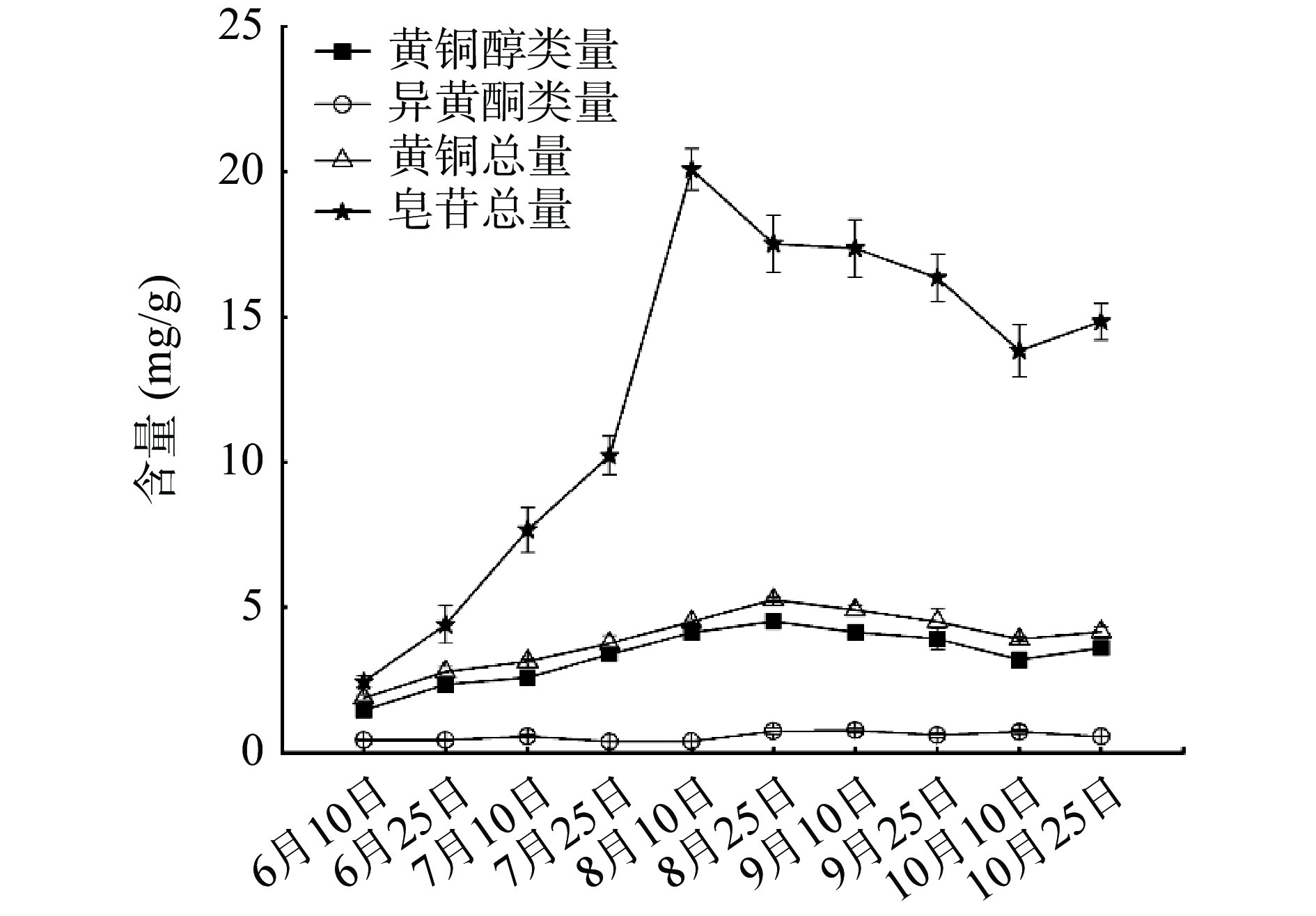
葡萄糖苷− 0.058±0.008c 0.156±0.003b 0.092±0.009bc 0.106±0.023abc 0.508±0.119abc 0.601±0.074abc 0.46±0.074abc 0.457±0.08abc 0.308±0.002a 金丝桃苷 0.204±0.007e 0.684±0.024cd 0.794±0.034cd 0.97±0.028ab 1.108±0.09a 0.884±0.059bc 0.702±0.087cd 0.728±0.071cd 0.783±0.027cd 0.800±0.081cd 槲皮苷 0.875±0.074cd 1.032±0.100ab 0.917±0.049bc 1.178±0.069a 0.956±0.05bc 0.724±0.039de 0.706±0.014e 0.700±0.006e 0.713±0.016e 0.957±0.036bc 芒柄花苷 0.241±0.025a 0.090±0.009d 0.105±0.019cd 0.106±0.015cd 0.148±0.023bc 0.088±0.015d 0.039±0.009e 0.039±0.021e 0.171±0.006b 0.145±0.002bc 毛蕊异黄酮 0.181±0.02b 0.286±0.021a 0.299±0.024a 0.177±0.009bc 0.133±0.008cd 0.143±0.012bcd 0.122±0.004de 0.103±0.024de 0.083±0.007e 0.097±0.013de 山奈酚 0.25±0.019f 0.460±0.073ef 0.619±0.086e 1.024±0.188d 1.815±0.029b 2.567±0.021a 2.257±0.026a 1.843±0.278b 1.374±0.128cd 1.699±0.079bc 皂苷类 大豆皂苷Bb 0.455±0.028e 0.262±0.027f 0.104±0.006g 0.353±0.044ef 3.354±0.036a 3.185±0.076b 1.201±0.076d 1.764±0.072c 1.096±0.042d 1.131±0.011d 黄芪甲苷 1.061±0.093h 1.092±0.088h 1.848±0.087g 3.962±0.366f 11.491±0.14a 9.334±0.148c 10.224±0.305b 9.65±0.295bc 6.993±0.332e 7.896±0.231d 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 0.929±0.247c 3.048±0.558bc 5.716±0.862a 5.903±0.688a 5.227±0.551ab 4.996±0.972ab 5.933±0.938a 4.924±0.897ab 5.745±0.891a 5.807±0.392a 黄酮醇类 1.46±0.076e 2.349±0.167de 2.583±0.082cd 3.381±0.237acde 4.122±0.082ab 4.518±0.077a 4.147±0.081bc 3.91±0.379abde 3.187±0.142bd 3.611±0.17abc 异黄酮类 0.422±0.041ab 0.433±0.02ab 0.56±0.039ab 0.375±0.016b 0.387±0.016b 0.739±0.11ab 0.762±0.086ab 0.602±0.077ab 0.711±0.071ab 0.55±0.013a 黄酮总量 1.882±0.114g 2.782±0.168efg 3.143±0.072df 3.756±0.253defg 4.508±0.075b 5.257±0.100a 4.908±0.165abc 4.513±0.455abcfg 3.898±0.077ce 4.161±0.166abcd 皂苷总量 2.444±0.18g 4.402±0.651g 7.668±0.779f 10.218±0.678e 20.073±0.713a 17.515±0.985b 17.358±0.991b 16.339±0.814bc 13.834±0.905d 14.835±0.634cd 注:“−”代表未检出;表中同一行不同上标字母代表具有显著性差异(P<0.05);括号内数字代表采收日期。 为了更直观的分析讨论上述成分的含量差异,将10种成分含量归纳为黄酮醇类(芦丁、金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、山奈酚)、异黄酮类(毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮)、黄酮总量(7种黄酮)和皂苷总量(3种皂苷)4大类,并分别作图,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,黄芪茎中皂苷总量在8月上旬达到最高,之后开始下降;黄酮醇类和黄酮总量在8月下旬达到最高,9月之后含量有所下降,黄酮醇类含量变化趋势和黄酮总量基本保持一致;异黄酮类含量变化波动不明显。此外,黄芪茎中皂苷总量始终高于黄酮总量,说明茎中含有较丰富的皂苷类成分。
2.2.2 不同采收期黄芪叶样品活性成分的含量
不同采收期黄芪叶中10种成分的含量结果见表5。黄芪叶中10种成分的含量随不同采收期也均呈显著变化(P<0.05),且大部分成分含量整体也呈先上升后下降的趋势,但达峰期明显不同于黄芪茎。其中,黄芪甲苷、山奈酚和芒柄花苷的含量分别在9月25日、9月10日和6月25日达到峰值;芦丁和黄芪皂苷Ⅱ的含量在8月10日达到峰值。芦丁、芒柄花苷和山奈酚是黄芪叶中的优势黄酮类成分,含量峰值分别为14.679±0.309、4.313±0.680和3.265±0.016 mg/g;黄芪皂苷Ⅱ是黄芪叶中的优势皂苷类成分,含量峰值分别为6.435±0.195 mg/g。
表 5 不同采收期黄芪叶中10种成分的含量(mg/g)Table 5. Relative content of 10 components in Astragalus membranaceus leaves at different harvest time (mg/g)成分 不同采收期的黄芪叶样品 Y1
(6.10)Y2
(6.25)Y3
(7.10)Y4
(7.25)Y5
(8.10)Y6
(8.25)Y7
(9.10)Y8
(9.25)黄酮类 芦丁 2.953±0.241e 8.997±0.848d 7.320±0.575e 10.386±0.044c 14.679±0.309a 13.236±0.685b 13.255±0.44b 11.686±0.045c 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 0.554±0.020b 0.296±0.007c 0.137±0.028d 0.851±0.037a 0.126±0.019d 0.349±0.029c 0.597±0.016b 0.565±0.007b 金丝桃苷 0.675±0.005a 0.144±0.004e 0.054±0.003f 0.056±0.003f 0.461±0.004d 0.552±0.011b 0.059±0.000f 0.514±0.006c 槲皮苷 0.585±0.195ab 0.765±0.198a 0.558±0.102ab 0.451±0.069ab 0.380±0.115b 0.352±0.081b 0.512±0.008ab 0.481±0.008ab 芒柄花苷 2.995±0.291b 4.313±0.680a 4.161±0.081a 3.357±0.205b 1.886±0.181c 1.801±0.024c 1.503±0.073c 1.357±0.036c 毛蕊异黄酮 0.516±0.052b 0.965±0.145a 1.032±0.008a 0.639±0.098b 0.283±0.027c 0.286±0.015c 0.243±0.031c 0.212±0.016c 山奈酚 0.324±0.001f 0.982±0.011e 1.172±0.011d 1.207±0.006d 1.253±0.011c 2.857±0.024b 3.265±0.016a 2.866±0.022b 皂苷类 大豆皂苷Bb 2.967±0.352c 6.339±0.742a 4.821±0.147b 4.377±0.365b 2.578±0.493cd 2.641±0.314c 1.455±0.264d 1.846±0.235cd 黄芪甲苷 0.619±0.117e 0.693±0.041de 0.754±0.086de 1.355±0.224cd 2.060±0.311c 2.788±0.297b 3.241±0.049b 5.925±0.499a 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 2.386±0.378e 4.590±0.646c 5.520±0.278ab 4.680±0.395bc 6.435±0.195a 5.634±0.036a 3.562±0.101d 2.688±0.065de 黄酮醇类 4.537±0.439e 10.889±0.854cd 9.104±0.505d 12.10±0.056bd 16.773±0.18ac 16.998±0.747ab 17.092±0.443ab 15.547±0.065ac 异黄酮类 4.065±0.337b 5.574±0.832a 5.330±0.056a 4.847±0.340ab 2.295±0.190c 2.436±0.067c 2.343±0.073c 2.134±0.049c 黄酮总量 8.601±0.776d 16.463±0.953abcd 14.434±0.505c 16.947±0.387bc 19.068±0.013abc 19.434±0.807ab 19.434±0.384a 17.682±0.114abcd 皂苷总量 5.972±0.389c 11.622±0.969abc 11.095±0.511ab 10.412±0.196ab 11.073±0.206a 11.062±0.647ab 8.258±0.339b 10.46±0.625ab 注:表中同一行不同上标字母代表具有显著性差异(P<0.05);括号内数字代表采收日期。 由图3可知,黄芪叶中的皂苷总量在6月下旬之后基本趋于平稳,而黄酮总量在7月之后保持增加的趋势,8月~9月上旬含量较高;黄酮醇类含量变化趋势和黄酮总量基本保持一致,而7月之后异黄酮类含量与黄酮醇类变化趋势正好相反,这说明黄芪叶中这两类黄酮类化合物的生物合成代谢过程中可能存在竞争作用。有文献表明苯丙烷代谢是黄酮类物质生物合成的主要途径,经柚皮素这一重要中间产物,再分别经黄酮醇支路和异黄酮支路合成异黄酮类和黄酮醇类化合物,其中异黄酮合酶(IFS)是合成异黄酮类的关键酶,黄酮醇合酶(FLS)是合成黄酮醇类的关键酶[19]。HU等[20]研究表明黄芪中IFS基因表达随着开花期的到来(6~7月)有所下降,而FLS的表达有所上升,这说明受关键酶活性变化的影响,开花期后黄酮醇支路的合成代谢将活跃于异黄酮支路,本研究所观察到的7月之后黄芪茎叶异黄酮类与黄酮醇类含量的相反变化趋势与其相一致。
2.2.3 黄芪茎和叶样品活性成分的含量比较
为了进一步比较黄芪不同部位活性成分的含量差异,将黄芪茎和黄芪叶的黄酮总量和皂苷总量作对比图,如图4所示。因10月黄芪叶枯萎凋落,未采集到10月的黄芪叶,故而主要对6月~9月的两个部位含量进行了对比。每个采收期黄芪叶中的黄酮总量均高于茎中,两个部位的黄酮总量均在8月~9月上旬同步达到较高水平;对于皂苷总量来说,7月下旬之前黄芪叶中的含量高于茎中,而进入8月之后茎中皂苷快速增加并显著高于叶中。这说明处于生长旺盛期的黄芪叶中黄酮类成分的积累更多,而黄芪茎中更利于积累皂苷类成分,提示两个部位的合用可同时兼顾这两类活性成分。
2.3 黄芪茎、叶的系统聚类分析(HCA)
为考察黄芪茎、叶中黄酮和皂苷类成分与采收期之间的相互关系,以10批不同采收时间的黄芪茎中10种成分含量和8批不同采收期的黄芪叶中10种成分含量为基准,采用系统聚类分析方法,通过组间连接法,以平方欧氏距离作为样品相似性的判定[14],分析结果见图5。以欧式距离10为临界点时,10个采收时间的黄芪茎聚集为2类,其中6~7月为一类、8~10月为第二类,说明6~7月黄芪茎中的成分与8月之后的明显不同。8个采收时间的黄芪叶聚集为3类,6月上旬为一类,6月下旬和7月为第二类,8、9月为第三类,说明8月前后黄芪叶中的成分有明显差异。
2.4 主成分分析(PCA)
为了更直观的比较不同采收期黄芪茎、叶成分的差异,将不同采收期黄芪茎、叶中10种成分的三次平行测定含量数据导入SIMCA 14.0进行主成分分析[21−23],结果表明黄芪茎前3个主成分的累积解释能力参数值R2X和预测能力参数值Q2分别为0.858和0.516,即可以用3个潜在综合指标来解释85.80%的总方差,基本能反映出不同采收期黄芪茎的主要特征;黄芪叶前3个主成分的累积解释能力参数值R2X和预测能力参数值Q2分别为0.843和0.525,即可以用3个潜在综合指标来解释84.30%的总方差,基本能反映出不同采收期黄芪叶的主要特征。从图6A所示的PCA得分图中可以看出,6、7月黄芪茎分布在纵轴左侧,8、9、10月分布在纵轴右侧,表明8月前后黄芪茎中成分含量差异较大。同时,因8月下旬和9月样本组间距离较近,表明采自于此阶段的黄芪茎中的活性成分含量差异较小。从图6B中可以看出,6、7月黄芪叶分布在纵轴左侧,8、9月分布在纵轴右侧,且6月下旬和7月样本分布较为集中,表明6月下旬和7月黄芪叶成分含量接近,8月和9月黄芪叶样本组间距离也较小,表明8~9月黄芪叶的成分组成接近。PCA分析结果与聚类分析基本一致。分析原因可能与7月是浑源的最热月(平均气温~22 ℃),而8月浑源平均气温(~20 ℃)开始下降有关,适宜的温度更利于黄芪这种喜凉植物的生长,使成分积累速度加快[24]。温度和水分是影响植物生长及其品质形成的两个重要因素,黄芪的最适生长季温度为15 ℃[25],而8月份浑源的平均气温为20 ℃,同时8月份也是降水高峰期,能有效促进化学成分的合成和积累。
2.5 熵权TOPSIS法分析
为进一步考察黄芪茎叶不同采收期样品的质量高低,采用SPSSPRO在线分析软件对不同采收期黄芪茎、叶进行TOPSIS法分析。10个成分指标均为极大型指标,进行正向化处理后,计算正理想解距离(D+)、负理想解距离(D-)和相对贴近度(C),其中相对贴近度值越接近1,表示综合评价越好[26],结果见表6。不同采收期黄芪茎质量的综合评价排序为J5>J6>J7>J8>J10>J4>J9>J3>J2>J1。不同采收期黄芪叶质量的综合评价排序为Y6>Y5>Y3>Y4>Y2>Y1>Y7>Y8。可见,黄芪茎在8~9月的质量较好,黄芪叶在整个8月的质量最高,综合考虑黄芪根的采挖时间(9~10月左右)并结合HCA和PCA分析结果,同时兼顾黄芪茎叶的生长规律和产量,建议黄芪茎单独部位的采收时间为9月,黄芪叶单独部位的采收时间为8月;若作为地上部分的整体利用,建议8月下旬采收黄芪茎叶较为合适,这样既可满足有效成分含量高峰期与产量高峰期一致的原则,同时也可尽量减少对黄芪根部生长的影响。
表 6 不同采收期黄芪茎叶熵权TOPSIS法分析结果Table 6. Analysis results of entropy weight TOPSIS method for stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus in different harvesting periods黄芪茎 黄芪叶 采收期 正理想解
距离(D+)负理想解
距离(D-)综合得分指数C 排序 采收期 正理想解
距离(D+)负理想解
距离(D-)综合得分指数C 排序 J1(6.10) 0.8354 0.3843 0.3150 10 Y1(6.10) 0.7426 0.5210 0.4122 6 J2(6.25) 0.7611 0.4528 0.3730 9 Y2(6.25) 0.7215 0.5165 0.4171 5 J3(7.10) 0.7123 0.4828 0.4040 8 Y3(7.10) 0.7169 0.5709 0.4433 3 J4(7.25) 0.6756 0.5174 0.4336 6 Y4(7.25) 0.6465 0.4906 0.4314 4 J5(8.10) 0.5294 0.6598 0.5548 1 Y5(8.10) 0.6311 0.6234 0.4969 2 J6(8.25) 0.5521 0.6557 0.5429 2 Y6(8.25) 0.6264 0.6739 0.5182 1 J7(9.10) 0.6368 0.6145 0.4910 3 Y7(9.10) 0.7590 0.4307 0.3620 8 J8(9.25) 0.6352 0.6107 0.4901 4 Y8(9.25) 0.7225 0.4377 0.3772 7 J9(10.10) 0.6628 0.4884 0.4242 7 J10(10.25) 0.6256 0.4929 0.4406 5 3. 结论
通过建立可用于黄芪茎叶中毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷等7种黄酮类和黄芪甲苷等3种皂苷类化合物的HPLC同步定量测定方法,揭示了这10种活性成分随采收期的动态变化规律,化学计量学和统计学方法分析结果表明黄芪茎在8~9月质量较高,叶在8月质量较高,因此结合黄芪根部的采挖时间(9~10月),对黄芪茎、叶单独部位以及茎叶合用部位的采收时间进行了合理建议。建议黄芪茎单独部位的采收时间为9月,黄芪叶单独部位的采收时间为8月;若作为地上部分的整体利用,建议8月下旬采收黄芪茎叶较为合适。后续研究可进一步探讨采收期对黄芪茎叶功效的影响,从而为黄芪茎叶的精准利用和有效开发提供理论基础和科学依据。
-
表 1 样品信息
Table 1 Information of samples
样品编号 采收日期 样品编号 采收日期 茎 叶 茎 叶 J1 Y1 2022.6.10 J6 Y6 2022.8.25 J2 Y2 2022.6.25 J7 Y7 2022.9.10 J3 Y3 2022.7.10 J8 Y8 2022.9.25 J4 Y4 2022.7.25 J9 2022.10.10 J5 Y5 2022.8.10 J10 2022.10.25 注:10月浑源县的黄芪叶已全部凋落,未采集到该月的黄芪叶。 表 2 10种成分的线性回归方程及其线性范围
Table 2 Linear regression equation and linear range of 10 components
序号 待测成分 回归方程 线性范围(μg) R2 1 芦丁 y=556.17x+41.695 0.164~0.984 0.9991 2 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 y=3111.3x+160.72 0.140~0.840 0.9992 3 金丝桃苷 y=735.03x+81.199 0.160~0.958 0.9996 4 槲皮苷 y=2437.9x–73.966 0.162~0.970 0.9997 5 芒柄花苷 y=8091.9x+80.36 0.047~0.280 0.9996 6 毛蕊异黄酮 y=6257.4x–37.298 0.054~0.324 0.9994 7 山奈酚 y=1058.8x–35.408 0.164~0.984 0.9995 8 大豆皂苷Bb y=176.97x+11.35 0.404~2.424 0.9993 9 黄芪甲苷 y=64.856x−18.937 2.040~12.240 0.9996 10 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ y=63.684x−18.125 1.944~11.664 0.9997 表 3 加样回收率试验结果
Table 3 Results of sample recovery rate test
待测成分 加样回收率(%) 平均加样回收率(%) RSD(%) 芦丁 99.84~100.17 99.85 0.31 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 98.75~101.05 99.87 1.15 金丝桃苷 99.21~100.88 99.91 0.87 槲皮苷 99.36~101.58 100.32 1.14 芒柄花苷 99.96~100.28 100.13 0.16 毛蕊异黄酮 99.42~100.52 99.94 0.55 山奈酚 98.14~101.74 99.94 1.71 大豆皂苷Bb 98.14~100.12 99.38 1.09 黄芪甲苷 99.57~101.05 100.20 0.76 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 98.84~101.16 99.96 1.16 表 4 不同采收期黄芪茎中10种成分的含量(mg/g)
Table 4 Relative contents of 10 components in stems of Astragalus membranaceus at different harvest time (mg/g)
成分 不同采收期的黄芪茎样品 J1
(6.10)J2
(6.25)J3
(7.10)J4
(7.25)J5
(8.10)J6
(8.25)J7
(9.10)J8
(9.25)J9
(10.10)J10
(10.25)黄酮类 芦丁 0.130±0.014g 0.172±0.006gh 0.253±0.004de 0.208±0.029efg 0.242±0.033def 0.343±0.034c 0.481±0.047b 0.639±0.041a 0.317±0.007cd 0.155±0.009gh 毛蕊异黄酮
葡萄糖苷− 0.058±0.008c 0.156±0.003b 0.092±0.009bc 0.106±0.023abc 0.508±0.119abc 0.601±0.074abc 0.46±0.074abc 0.457±0.08abc 0.308±0.002a 金丝桃苷 0.204±0.007e 0.684±0.024cd 0.794±0.034cd 0.97±0.028ab 1.108±0.09a 0.884±0.059bc 0.702±0.087cd 0.728±0.071cd 0.783±0.027cd 0.800±0.081cd 槲皮苷 0.875±0.074cd 1.032±0.100ab 0.917±0.049bc 1.178±0.069a 0.956±0.05bc 0.724±0.039de 0.706±0.014e 0.700±0.006e 0.713±0.016e 0.957±0.036bc 芒柄花苷 0.241±0.025a 0.090±0.009d 0.105±0.019cd 0.106±0.015cd 0.148±0.023bc 0.088±0.015d 0.039±0.009e 0.039±0.021e 0.171±0.006b 0.145±0.002bc 毛蕊异黄酮 0.181±0.02b 0.286±0.021a 0.299±0.024a 0.177±0.009bc 0.133±0.008cd 0.143±0.012bcd 0.122±0.004de 0.103±0.024de 0.083±0.007e 0.097±0.013de 山奈酚 0.25±0.019f 0.460±0.073ef 0.619±0.086e 1.024±0.188d 1.815±0.029b 2.567±0.021a 2.257±0.026a 1.843±0.278b 1.374±0.128cd 1.699±0.079bc 皂苷类 大豆皂苷Bb 0.455±0.028e 0.262±0.027f 0.104±0.006g 0.353±0.044ef 3.354±0.036a 3.185±0.076b 1.201±0.076d 1.764±0.072c 1.096±0.042d 1.131±0.011d 黄芪甲苷 1.061±0.093h 1.092±0.088h 1.848±0.087g 3.962±0.366f 11.491±0.14a 9.334±0.148c 10.224±0.305b 9.65±0.295bc 6.993±0.332e 7.896±0.231d 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 0.929±0.247c 3.048±0.558bc 5.716±0.862a 5.903±0.688a 5.227±0.551ab 4.996±0.972ab 5.933±0.938a 4.924±0.897ab 5.745±0.891a 5.807±0.392a 黄酮醇类 1.46±0.076e 2.349±0.167de 2.583±0.082cd 3.381±0.237acde 4.122±0.082ab 4.518±0.077a 4.147±0.081bc 3.91±0.379abde 3.187±0.142bd 3.611±0.17abc 异黄酮类 0.422±0.041ab 0.433±0.02ab 0.56±0.039ab 0.375±0.016b 0.387±0.016b 0.739±0.11ab 0.762±0.086ab 0.602±0.077ab 0.711±0.071ab 0.55±0.013a 黄酮总量 1.882±0.114g 2.782±0.168efg 3.143±0.072df 3.756±0.253defg 4.508±0.075b 5.257±0.100a 4.908±0.165abc 4.513±0.455abcfg 3.898±0.077ce 4.161±0.166abcd 皂苷总量 2.444±0.18g 4.402±0.651g 7.668±0.779f 10.218±0.678e 20.073±0.713a 17.515±0.985b 17.358±0.991b 16.339±0.814bc 13.834±0.905d 14.835±0.634cd 注:“−”代表未检出;表中同一行不同上标字母代表具有显著性差异(P<0.05);括号内数字代表采收日期。 表 5 不同采收期黄芪叶中10种成分的含量(mg/g)
Table 5 Relative content of 10 components in Astragalus membranaceus leaves at different harvest time (mg/g)
成分 不同采收期的黄芪叶样品 Y1
(6.10)Y2
(6.25)Y3
(7.10)Y4
(7.25)Y5
(8.10)Y6
(8.25)Y7
(9.10)Y8
(9.25)黄酮类 芦丁 2.953±0.241e 8.997±0.848d 7.320±0.575e 10.386±0.044c 14.679±0.309a 13.236±0.685b 13.255±0.44b 11.686±0.045c 毛蕊异黄酮葡萄糖苷 0.554±0.020b 0.296±0.007c 0.137±0.028d 0.851±0.037a 0.126±0.019d 0.349±0.029c 0.597±0.016b 0.565±0.007b 金丝桃苷 0.675±0.005a 0.144±0.004e 0.054±0.003f 0.056±0.003f 0.461±0.004d 0.552±0.011b 0.059±0.000f 0.514±0.006c 槲皮苷 0.585±0.195ab 0.765±0.198a 0.558±0.102ab 0.451±0.069ab 0.380±0.115b 0.352±0.081b 0.512±0.008ab 0.481±0.008ab 芒柄花苷 2.995±0.291b 4.313±0.680a 4.161±0.081a 3.357±0.205b 1.886±0.181c 1.801±0.024c 1.503±0.073c 1.357±0.036c 毛蕊异黄酮 0.516±0.052b 0.965±0.145a 1.032±0.008a 0.639±0.098b 0.283±0.027c 0.286±0.015c 0.243±0.031c 0.212±0.016c 山奈酚 0.324±0.001f 0.982±0.011e 1.172±0.011d 1.207±0.006d 1.253±0.011c 2.857±0.024b 3.265±0.016a 2.866±0.022b 皂苷类 大豆皂苷Bb 2.967±0.352c 6.339±0.742a 4.821±0.147b 4.377±0.365b 2.578±0.493cd 2.641±0.314c 1.455±0.264d 1.846±0.235cd 黄芪甲苷 0.619±0.117e 0.693±0.041de 0.754±0.086de 1.355±0.224cd 2.060±0.311c 2.788±0.297b 3.241±0.049b 5.925±0.499a 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ 2.386±0.378e 4.590±0.646c 5.520±0.278ab 4.680±0.395bc 6.435±0.195a 5.634±0.036a 3.562±0.101d 2.688±0.065de 黄酮醇类 4.537±0.439e 10.889±0.854cd 9.104±0.505d 12.10±0.056bd 16.773±0.18ac 16.998±0.747ab 17.092±0.443ab 15.547±0.065ac 异黄酮类 4.065±0.337b 5.574±0.832a 5.330±0.056a 4.847±0.340ab 2.295±0.190c 2.436±0.067c 2.343±0.073c 2.134±0.049c 黄酮总量 8.601±0.776d 16.463±0.953abcd 14.434±0.505c 16.947±0.387bc 19.068±0.013abc 19.434±0.807ab 19.434±0.384a 17.682±0.114abcd 皂苷总量 5.972±0.389c 11.622±0.969abc 11.095±0.511ab 10.412±0.196ab 11.073±0.206a 11.062±0.647ab 8.258±0.339b 10.46±0.625ab 注:表中同一行不同上标字母代表具有显著性差异(P<0.05);括号内数字代表采收日期。 表 6 不同采收期黄芪茎叶熵权TOPSIS法分析结果
Table 6 Analysis results of entropy weight TOPSIS method for stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus in different harvesting periods
黄芪茎 黄芪叶 采收期 正理想解
距离(D+)负理想解
距离(D-)综合得分指数C 排序 采收期 正理想解
距离(D+)负理想解
距离(D-)综合得分指数C 排序 J1(6.10) 0.8354 0.3843 0.3150 10 Y1(6.10) 0.7426 0.5210 0.4122 6 J2(6.25) 0.7611 0.4528 0.3730 9 Y2(6.25) 0.7215 0.5165 0.4171 5 J3(7.10) 0.7123 0.4828 0.4040 8 Y3(7.10) 0.7169 0.5709 0.4433 3 J4(7.25) 0.6756 0.5174 0.4336 6 Y4(7.25) 0.6465 0.4906 0.4314 4 J5(8.10) 0.5294 0.6598 0.5548 1 Y5(8.10) 0.6311 0.6234 0.4969 2 J6(8.25) 0.5521 0.6557 0.5429 2 Y6(8.25) 0.6264 0.6739 0.5182 1 J7(9.10) 0.6368 0.6145 0.4910 3 Y7(9.10) 0.7590 0.4307 0.3620 8 J8(9.25) 0.6352 0.6107 0.4901 4 Y8(9.25) 0.7225 0.4377 0.3772 7 J9(10.10) 0.6628 0.4884 0.4242 7 J10(10.25) 0.6256 0.4929 0.4406 5 -
[1] CUI Liyan, MA Zhennan, WANG Defu, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction, optimization, isolation, and antioxidant activity analysis of flavonoids from Astragalus membranaceus stems and leaves[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2022,90:106190. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106190
[2] 丛晶男, 张宇, 赵宏, 等. 黄芪茎叶质量标准研究[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2016,23(11):94−98. [CONG Jingnan, ZHANG Yu, ZHAO Hong, et al. Study on quality standards of stem and leaf of Astragali Radix[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,23(11):94−98.] CONG Jingnan, ZHANG Yu, ZHAO Hong, et al . Study on quality standards of stem and leaf of Astragali Radix[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016 ,23 (11 ):94 −98 .[3] 黄文静, 孙晓春, 张严磊. 基于PB-CCD设计的黄芪茎叶总黄酮提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2018(5):105−110. [HUANG Wenjing, SUN Xiaochun, ZHANG Yanlei. Optimization of extracting total flavonoids from stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus based on PB-CCD design and antioxidant activities evaluation[J]. China Food Additives,2018(5):105−110.] HUANG Wenjing, SUN Xiaochun, ZHANG Yanlei . Optimization of extracting total flavonoids from stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus based on PB-CCD design and antioxidant activities evaluation[J]. China Food Additives,2018 (5 ):105 −110 .[4] 陈长勋. 中药药理学[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2006:1129. [CHEN Changxun. Traditional Chinese pharmacology[M]. Shanghai:Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2006:1129.] CHEN Changxun. Traditional Chinese pharmacology[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2006: 1129.
[5] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing:China Medical Science Press, 2020.] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020.
[6] WANG Yi, MA Yan, TAO Li, et al. Recent advances in separation and analysis of saponins in aatural products[J]. Separations,2022,9(7):163. doi: 10.3390/separations9070163
[7] BIAN Yu, ZHANG Yuan, ZHOU Yu, et al. Progress in the pretreatment and analysis of flavonoids:An update since 2013[J]. Separation & Purification Reviews,2022,51(1):11−37.
[8] KHULUK R H, YUNITA A, ROHAETI E, et al. An HPLC-DAD method to quantify flavonoids in Sonchus arvensis and able to classify the plant parts and their geographical area through principal component analysis[J]. Separations,2021,8(2):12. doi: 10.3390/separations8020012
[9] ZHANG Yan, CAO Cuiling, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Simultaneous determination of 20 phenolic compounds in propolis by HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,115:104877. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104877
[10] ZHANG Ruiteng, QING Wangwang, YANG Lin, et al. Fingerprint combining with quantitative analysis of multi‐components by single marker for quality control of Chenxiang Huaqi tablets[J]. Phytochemical Analysis,2022,33(3):335−343. doi: 10.1002/pca.3090
[11] WU Linlin, ZHANG Shunnan, ZHOU Lihong, et al. Establishment and validation of the quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker for the quality control of Qishen Yiqi dripping pills by high-performance liquid chromatography with charged aerosol detection[J]. Phytochemical Analysis,2021,32(6):942−956. doi: 10.1002/pca.3037
[12] WANG Lingling, XIONG Feng, YANG Lucun, et al. A seasonal change of active ingredients and mineral elements in root of Astragalus membranaceus in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Biological Trace Element Research,2021,199:3950−3959. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02486-0
[13] 唐文文, 李国琴, 晋小军. 黄芪不同采收期有效成分含量比较[J]. 北方园艺, 2015(7):138-141. [TANG Wenwen, LI Guoqin, JIN Xiaojun. Comparison of active ingredient content of Astragalus in different harvest periods[J] Northern Horticulture, 2015(7):138-141.] TANG Wenwen, LI Guoqin, JIN Xiaojun. Comparison of active ingredient content of Astragalus in different harvest periods[J] Northern Horticulture, 2015(7): 138-141.
[14] DAN G, LE B V, CHONG W C, et al. Discrimination and quality evaluation of fifteen components in Stauntonia hexaphylla leaves from different harvest time by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS and ELSD coupled with multivariate statistical analysis and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation[J]. Applied Biological Chemistry,2020,63:1−11.
[15] LEE S, YEON S W, TURK A, et al. Variation of lignan content and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of Schisandra chinensis fruit at different maturation stages:Comparison with stem, leaf and seed[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2022,293:110679. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110679
[16] 张妍, 董琳, 雍婧姣, 等. HPLC 法同时测定黄芪药材中 10 种黄酮类成分的含量[J]. 中国药房,2017,28(21):2970−2973. [ZHANG Yan, DONG Lin, YONG Jingjiao et al. Simultaneous determination of 10 flavonoids in Astragalus membranaceus by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacy,2017,28(21):2970−2973.] ZHANG Yan, DONG Lin, YONG Jingjiao et al . Simultaneous determination of 10 flavonoids in Astragalus membranaceus by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacy,2017 ,28 (21 ):2970 −2973 .[17] 汪涛, 李良群, 严艳芳, 等. 刺梨中质量标记物的提取工艺优化及其含量同时测定[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):251−260. [WANG Tao, LI Liangqun, YAN Yanfang, et al. Optimization of extraction process and simultaneous content determination of quality marker in Rosa roxburghii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):251−260.] WANG Tao, LI Liangqun, YAN Yanfang, et al . Optimization of extraction process and simultaneous content determination of quality marker in Rosa roxburghii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (14 ):251 −260 .[18] 禹亚杰, 彭腾, 尚宁宁, 等. HPLC法测定不同产地黄芪中芒柄花苷的含量[J]. 中药与临床,2016,7(1):17−19. [YU Yajie, PENG Teng, SHANG Ningning, et al. Content determination of Ononin in Huangqi from different producing areas by HPLC[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2016,7(1):17−19.] YU Yajie, PENG Teng, SHANG Ningning, et al . Content determination of Ononin in Huangqi from different producing areas by HPLC[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2016 ,7 (1 ):17 −19 .[19] DONG NaiQian, LIN Hongxuan. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions[J]. Journal of integrative plant biology,2021,63(1):180−209. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13054
[20] HU Pengfei, Suriguga, ZHAO Ming, et al. Transcriptional regulation mechanism of flavonoids biosynthesis gene during fruit development in Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Frontiers in Genetics,2022,13:972900.
[21] 刘天亮, 杨林林, 董诚明, 等. 金银花不同采收期指纹图谱及成分变化情况研究[J]. 中药材,2021,44(10):2358−2362. [LIU Tianliang, YANG Linlin, DONG Chengming, et al. Study on the fingerprints and composition changes of Lonicerae japonicae Flos at different harvest periods[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2021,44(10):2358−2362.] LIU Tianliang, YANG Linlin, DONG Chengming, et al . Study on the fingerprints and composition changes of Lonicerae japonicae Flos at different harvest periods[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2021 ,44 (10 ):2358 −2362 .[22] WANG Yuanhui, ZHANG Yaru. Variations in compositions and antioxidant activities of essential oils from leaves of Luodian Blumea balsamifera from different harvest times in China[J]. PLoS One,2020,15(6):e0234661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234661
[23] ZHENG Wei, ZHOU Ming, CHAI Ruiping, et al. Quality analysis of hawthorn leaves (the leaves of Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var major N. E. Br) in different harvest time[J]. Phytochemical Analysis :PCA, 2022, 33(7):1147-1155.
[24] 李波, 赵倩, 关瑜, 等. 产地对黄芪主产区形成的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(1):186−188. [LI Bo, ZHAO Qian, GUAN Yu, et al. Effect of climatic conditions on the formation of Astragalus membranaceus production area[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2020,31(1):186−188.] LI Bo, ZHAO Qian, GUAN Yu, et al . Effect of climatic conditions on the formation of Astragalus membranaceus production area[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2020 ,31 (1 ):186 −188 .[25] 彭露茜, 郭彦龙. 中国黄芪地理分布和未来适生区预测[J]. 四川农业大学学报,2017,35(1):60−68. [PENG Luxi, GUO Yanlong. Geographical distribution of Astragali Radix and prediction of its suitable area in China[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University,2017,35(1):60−68.] PENG Luxi, GUO Yanlong . Geographical distribution of Astragali Radix and prediction of its suitable area in China[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University,2017 ,35 (1 ):60 −68 .[26] 高伟城, 王小平, 方瑞燕, 等. 不同采收期及气候因子对枇杷叶品质的影响研究[J]. 中药材,2022,45(8):1898−1903. [GAO Weicheng, WANG Xiaoping, FANG Ruiyan, et al. Effect study of quality of Eriobotryae folium with different harvesting period and climatic factors[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2022,45(8):1898−1903.] GAO Weicheng, WANG Xiaoping, FANG Ruiyan, et al . Effect study of quality of Eriobotryae folium with different harvesting period and climatic factors[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2022 ,45 (8 ):1898 −1903 . -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 伍蓉,贺灵芝,谭美玲,张华,阎睿. 重庆市蜂产品中31种农兽药残留检测方法开发及其膳食暴露风险评估. 中国酿造. 2025(02): 273-280 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋昆,余义冉,张雯雯,阮靖轩,石玉,陈雨,白红艳. 磺胺甲嗪(口恶)唑电化学检测方法的研究进展. 印染助剂. 2024(11): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



