Peanut Frostbite Detection Method Based on Near Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology
-
摘要: 花生在收获、运输、储存和加工过程中易受到温、湿度变化导致冻伤现象,从而影响花生及其制品的品质,为探索花生冻伤机理并提高冻伤花生检测效率,本文采用近红外高光谱技术研究花生冻伤无损检测可行性、基于特征变量筛选的判别模型优化方法以及花生冻伤机理。实验研究了变量标准化(Standard Normalized Variate,SNV)、多元散射校正(Multiplicative Scatter Correction,MSC)、Savitzky-Golag(SG)平滑以及SG平滑-SNV和SG平滑-MSC五种预处理方法对原始数据的影响,随后分别采用竞争自适应重加权法(competitive adapative reweighted sampling,CARS)、随机蛙跳(random frog,RF)、变量重要性投影(variable importance in projection,VIP)、连续投影算法(successive projections algorithm,SPA)、蒙特卡洛无信息变量消除(Monte Carlo uninformative variable elimination,MC-UVE)、迭代保留信息变量(Iteration retention information variable,IRIV)、变量组合种群分析-迭代保留信息变量(Variable combination population analysis-Iteration retention information variable,VCPA-IRIV)和变量组合种群分析-遗传算法(Variable combination population analysis-Genetic Algorithm,VCPA-GA)8种变量选择方法筛选得到与花生冻伤相关的特征波长,通过建立支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)选用达到判别准确率阈值为90%的特征波长作为花生冻伤特征波长。结果表明,基于近红外高光谱成像技术的花生冻伤检测总体可行,且精度较高,所有变量选择方法均能有效筛选与冻伤相关的特征波长,其中VCPA-GA算法选择了最少的7个特征波长,仅占数据集所有波长的3.125%,训练集和测试集准确率分别为91.60%和90.12%。经过筛选得出的冻伤特征波长体现了油酸和蛋白质的信息,验证了过低的温度会导致花生中油酸含量下降和蛋白质含量上升。本研究为花生冻伤快速无损检测提供了可参考的理论依据和技术支撑。Abstract: Peanuts were susceptible to frost damage during harvesting, transportation, storage, and processing due to temperature and humidity changes, which could affect the quality of peanuts and their products. In order to explore the mechanism of peanut frost damage and improve the detection efficiency of frost-damaged peanuts, this study used near-infrared hyperspectral technology to study the feasibility of non-destructive detection of peanut frost damage, optimization methods based on feature variable screening discriminant models, and the mechanism of peanut frost damage. The effects of five preprocessing methods, including standard normalized variate (SNV), multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), Savizkg-Golag (SG) smoothing, SG smoothing-SNV, and SG smoothing-MSC, on the original data were experimentally studied. Then, eight variable selection methods, including competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS), random frog (RF), variable importance in projection (VIP), successive projections algorithm (SPA), Monte Carlo uninformative variable elimination (MC-UVE), iteration retention information variable (IRIV), variable combination population analysis-iteration retention information variable (VCPA-IRIV), and variable combination population analysis-genetic algorithm (VCPA-GA), were used to screen the feature wavelengths related to peanut frost damage. Support vector machine (SVM) was used to select the feature wavelengths that reached the discrimination accuracy threshold of 90% as the feature wavelengths of peanut frost damage. The results showed that the detection of peanut frost damage based on near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology was generally feasible and had high accuracy. All variable selection methods can effectively screen the feature wavelengths related to frost damage. Among them, the VCPA-GA algorithm selected the least 7 feature wavelengths, accounting for only 3.125% of all wavelengths in the dataset. The accuracy of the training set and the test set were 91.60% and 90.12%, respectively. The selected frostbite characteristic wavelength reflects information about oleic acid and protein, verifying that excessively low temperatures can lead to a decrease in oleic acid content and an increase in protein content in peanuts. This study provides a theoretical basis and technical support for the rapid non-destructive detection of peanut frost damage.
-
花生是我国总产量及平均亩产最高、出口量最大的油料作物[1]。但是花生在收获、运输、储藏和加工过程中极易受环境温湿度变化出现冻伤现象,导致花生出油率和花生油品质明显下降。我国现行标准如花生GB 1532-2008、食用花生NY/T 1067-2006、油用花生NY/T 1068-2006等尚未规定花生冻伤判别的检测标准和方法。当前花生冻伤检测阶段还停留在人工判别阶段,通过对带有外皮的花生粒的外形、颜色、软硬程度观察实现人工判别,不仅效率低下、容易出现判别错误,而且受到检测者主观影响非常严重。因此,我国亟待大力发展便捷、绿色的花生品质检测技术以提高我国花生加工行业整体水平,满足我国在全球花生及花生制品进出口贸易中的发展需求[2−3]。
近红外高光谱成像技术集合了光谱技术和数字图像处理技术的优势,能够同时获得被测物的一维光谱信息和二维空间信息,相较于多光谱成像技术,高光谱成像技术能近乎连续地获取光谱信息,可以准确获取被测物质特征,增强检测和识别性能,并且在高光谱图像中可以估计出被测物质的状态参量,提升了成像分析质量。近年来在农产品品质[4−6]、食品安全[7−9]和食品品质[10−12]的快速无损检测技术领域日趋成为研究热点。但是近红外光谱本身吸收强度和灵敏度低、谱带宽且重叠严重,且采用全光谱方式建模还存在信息冗余度高、共线性强等问题导致模型预测性能较差。特征波长筛选可以有效简化模型,提升模型的运算效率并提高模型的可解释性,并消除可能影响模型预测性和稳定性的无关变量[13−14],因此特征波长筛选已然成为化学计量学和光谱分析、检测领域的研究热点[15]。王粒[16]采用GBDT、Light GBM、Cat Boost和XGBoost算法提取花生高光谱数据中的重要特征波段,对花生霉变情况进行检测,结果表明Light GBM是最优算法,其检测准确率为99.10%,并使用Optuna算法对其参数进行调优,减少了模型运行时间;刘良源[17]在基于近红外光谱的花生脂肪酸检测方法研究中利用SiPLS和BOSS算法联合提取花生的近红外光谱特征波长建立了SVM模型,有效减少了信息冗余,将脂肪酸模型的R2从0.8805提升到0.9446;孙建非[18]基于高光谱图像技术对花生霉变和水分含量进行研究,采用SPA算法对花生高光谱数据进行特征提取,结果表明SPA算法分别有效提取了与花生霉变和水分含量相关性最高的特征波长组,采用LDA模型的花生霉变识别准确率高达100%,采用MLR的花生水分含量模型预测集R2为0.9315,RMSEP为0.4895%。但是目前鲜有国内学者对花生冻伤的检测进行了研究。花生出现冻伤现象会导致花生品质严重恶化,蛋白质、亚油酸和蔗糖含量增加,油脂和油酸含量降低,油亚比(油酸/亚油酸)明显下降,严重影响经济效益,目前急需提升冻伤花生的检测效率。
针对当前花生冻伤缺乏快速无损检测技术的现状,本文重点探索基于近红外高光谱成像技术的花生冻伤快速判别方法的可行性,并研究采用竞争自适应重加权法[19−20](competitive adapative reweighted sampling,CARS)、随机蛙跳[21−22](random frog,RF)、变量重要性投影[23](variable importance in projection,VIP)、连续投影算法[24](successive projections algorithm,SPA)、蒙特卡洛无信息变量消除[25](Monte Carlo uninformative variable elimination,MC-UVE)、迭代保留信息变量[26](Iteration retention information variable,IRIV)、变量组合种群分析-迭代保留信息变量[27](Variable combination population analysis-Iteration retention information variable,VCPA-IRIV)和变量组合种群分析-遗传算法[27](Variable combination population analysis-Genetic Algorithm,VCPA-GA)8种变量选择方法初步筛选出与花生冻伤相关的特征波长,其中CARS、IRIV、VCPA-IRIV、VCPA-GA属于“组合寻优”类变量选择算法,RF、VIP、SPA和MC-UVE属于“变量重要性”类变量选择算法,为进一步探索花生冻伤机理,将“组合寻优”类方法筛选的特征波长采用VIP分析获得每个特征波长对冻伤检测的贡献度并排序,同“变量重要性”类变量选择算法筛选出的花生冻伤特征波长数据集通过建立支持向量机(Support vector machine,SVM)模型选用能达到判别准确率阈值为90%的最少波长变量组合作为花生冻伤特征波长变量,进一步对花生冻伤特征波长进行筛选,实现精选优选,并通过精选的特征波长进行花生冻伤机理分析,研究结果为花生冻伤检测技术提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
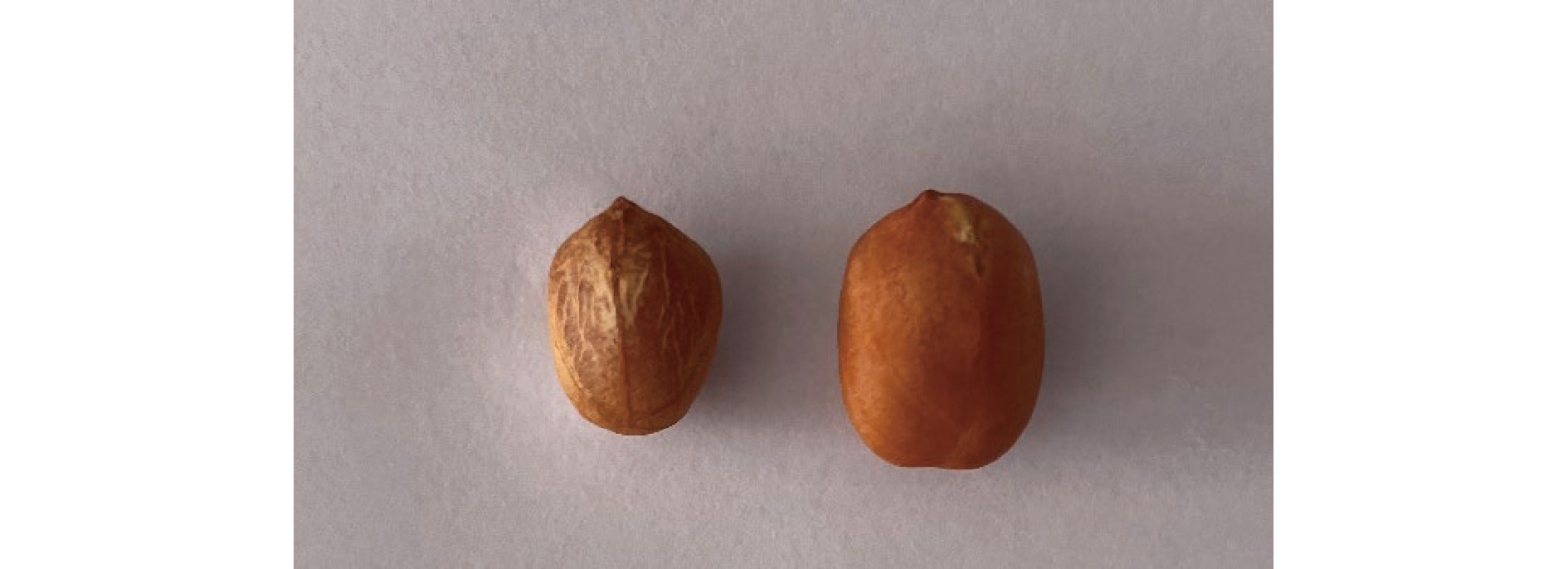
花生样本 共1623粒,来自某加工企业现场收集,包括787粒正常样本和836粒冻伤样本(由人工判断筛选)。单粒冻伤和正常花生如图1所示,冻伤花生与正常花生外观上有明显差异,相较于正常花生,冻伤花生整体干瘪,颜色较深,且表皮部分呈现透明状。
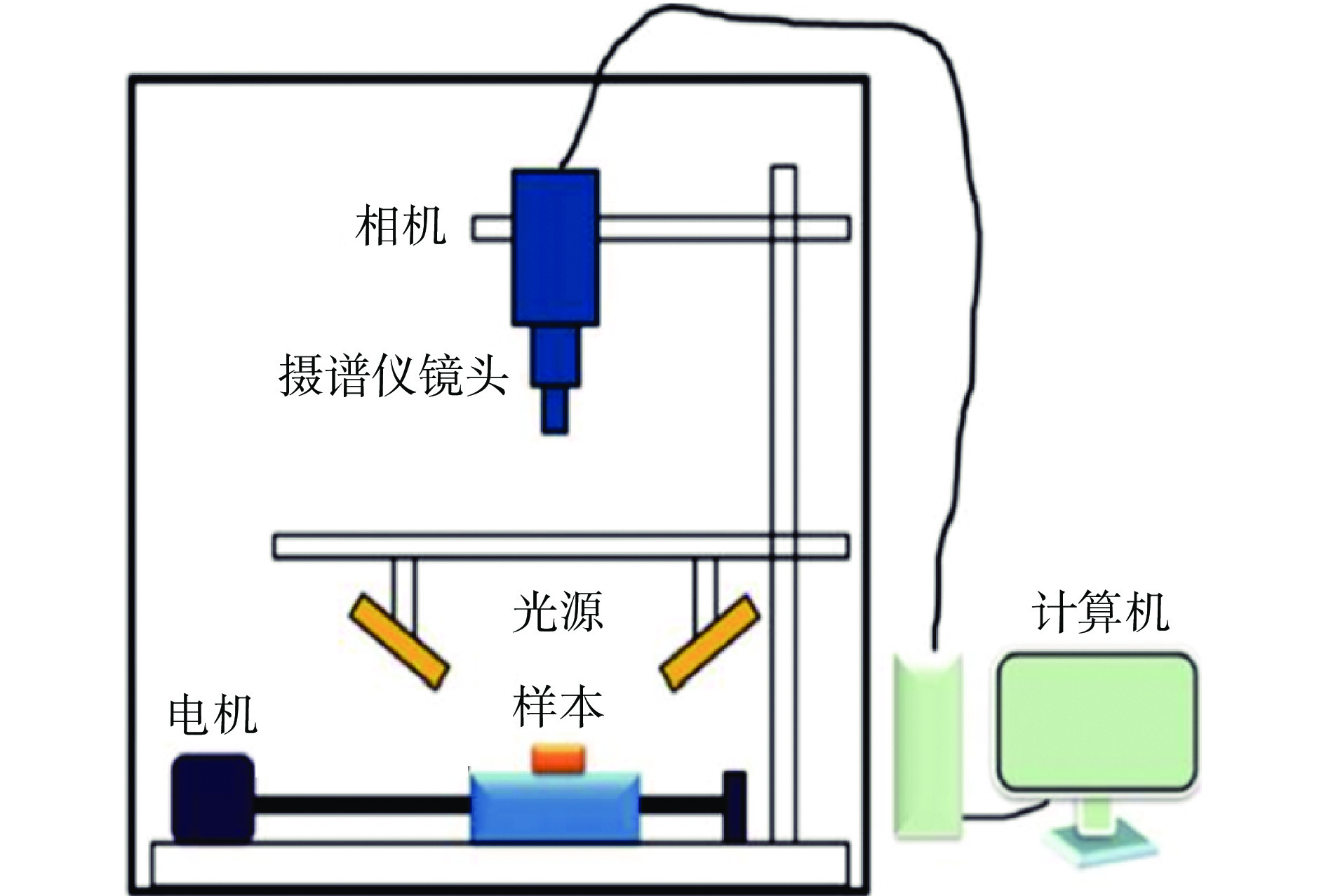
FX17高光谱相机(高光谱采集系统结构示意图2所示) 芬兰SPECIM公司。
1.2 数据采集
随机选取数据集中80%样品作为训练集,剩余20%样品为测试集。其中训练集630粒为正常花生,669粒为冻伤花生;测试集157粒为正常花生,167粒为冻伤花生。
设备参数设置:波长范围:935~1720 nm,FWHM谱宽:3.5 nm,波长变量:224个,帧率:50 Hz,曝光时间:2.0 μs,空间采样分辨率:640 px/line。在上述设备参数设置下采集花生高光谱图像,采样时将花生样本随机散放在置物台上以模拟流水线传送带,采取正常组和冻伤组每组交替采样以降低因高光谱相机随采集时间的增加而产生的影响。
1.3 数据处理方法
在高光谱采集过程中,除目标样品外,背景信息同样被采集,为后续花生籽粒数据进一步处理分析,首先需要将花生籽粒与背景分离。本研究采用主成分分析法(PCA)进行背景剔除,以实现花生高光谱图像中样品与背景分割的目的。
由于外界环境和仪器等影响因素,近红外光谱信号容易受到噪声的干扰,为了排除干扰,实验采用包括标准归一化变量SNV、多元散射校正MSC、Savitzky-Golag(SG)卷积平滑以及SG平滑-SNV和SG平滑-MSC组合预处理在内的五种预处理方法消除由环境或传感器的不确定干扰等引起的噪声,增强数据稳定性,提高频谱信噪比,并通过建立支持向量机模型验证预处理效果。
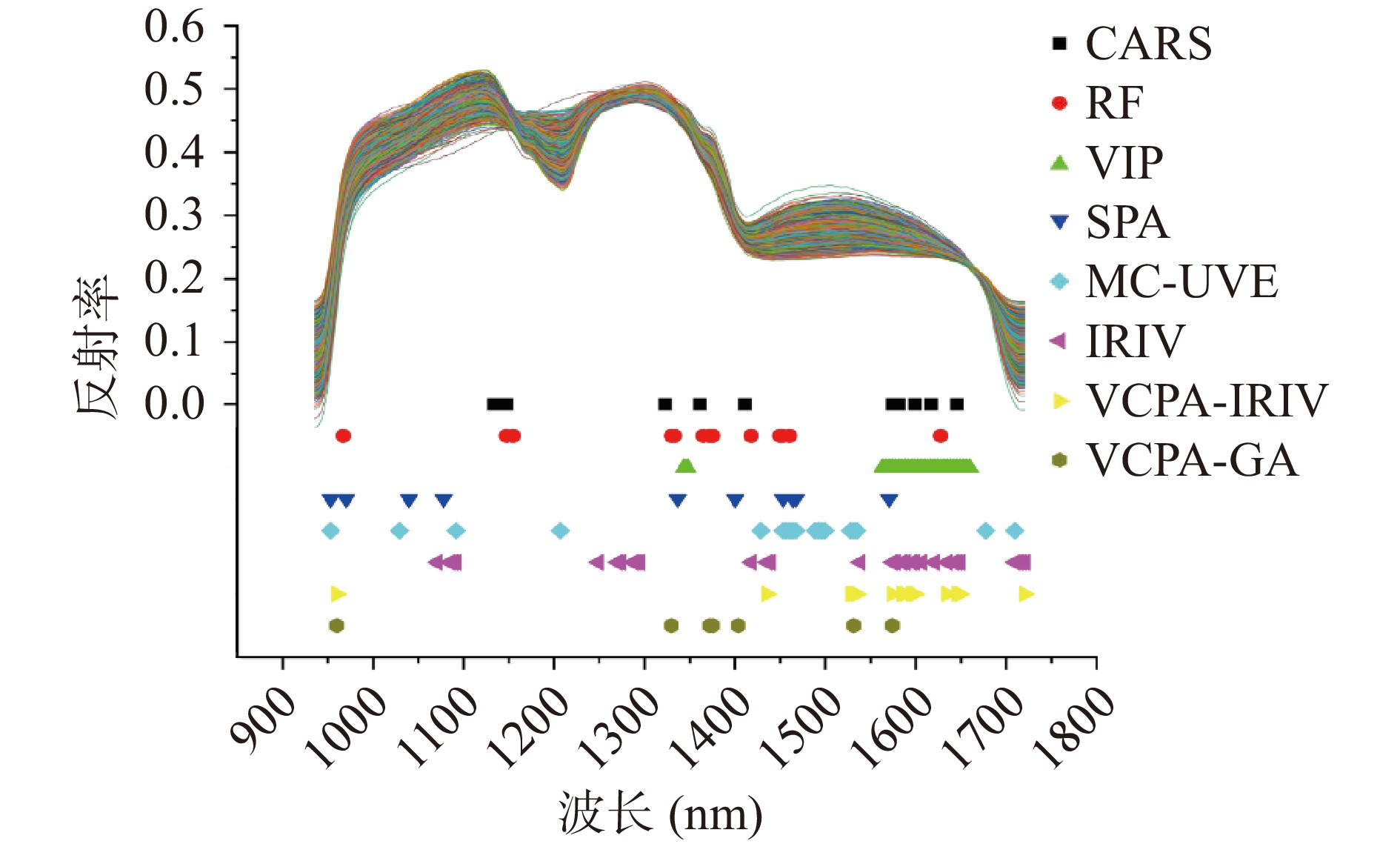
建立花生种子冻伤判别模型时,若使用花生种子的全谱近红外光谱数据作为输入变量,由于花生复杂的特性以及过多的全谱变量数,使得模型复杂程度高,导致模型性能下降,限制了实际生产的使用;而特征波长筛选方法可以实现模型的简化,提高预测结果的稳定性,消除共线性的原始数据。此外,由于国内外在花生冻伤领域研究较少,花生出现冻伤的内在特点也不够明确,因此,采用八种光谱波长点筛选(Wavelength point selection,WPS)算法:CARS、RF、VIP、SPA、MC-UVE、IRIV、VCPA-IRIV和VCPA-GA结合化学计量学方法对花生冻伤特征波长进行筛选,并对筛选出的特征波长进行分析。
文中选择的八种变量选择算法可分为两类—“组合寻优”类和“变量重要性”类,其中“组合寻优”类包括CARS、IRIV、VCPA-IRIV、VCPA-GA,“变量重要性”类包括RF、VIP、SPA、MC-UVE。“组合寻优”类变量选择算法研究有限范围内多变量非线性函数全局最优解的性质,以及寻找全局最优解计算方法的构造,组合寻优可以在合理的时间内逼近问题的最优解;“变量重要性”类变量选择算法通过某种规则建立数据集中每个变量的重要性并按变量重要性进行排序,RF、VIP、SPA和MC-UVE分别将每个变量的稳定性、VIP值、COSS值和RI值进行排序;分别采用上述两类变量选择算法对花生光谱数据进行特征波长筛选,建立支持向量机模型验证所选特征波长,为进一步筛选与花生冻伤相关性更高的特征波长,将“组合寻优”类方法结合VIP算法,将筛选的特征波长按变量重要性进行排序,选取变量重要性排名靠前的变量组合,“变量重要性”类方法同理将特征波长按变量重要性排列选取,建立支持向量机模型选用达到判别准确率阈值为90%的特征波长作为与花生冻伤相关性最高的特征波长并进行针对这些特征波长进行分析。
1.4 模型评价标准与分析软件
为了评估模型的性能,训练集和测试集的预测准确率作为模型性能评估的关键表征。训练集和测试集的预测准确率为正确分类的样本数与样本集总数的比值,本文以测试集预测准确率作为模型性能评价指标,预测准确率越高,说明被正确识别的样本数量越多,模型的性能越优秀。
实验采用MATLAB R2020a、Evince 2.7.15、The Unscrambler X 10.4和Origin 2022进行数据处理,其中高光谱图像的背景剔除和原始光谱数据提取在Evince 2.7.15中进行,原始光谱的预处理在The Unscrambler X 10.4软件中进行,训练集和测试集的划分、特征波长筛选、建立支持向量机判别模型在MATLAB R2020a软件中进行,图表的绘制在Origin 2022软件中进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 高光谱图像背景剔除与分析
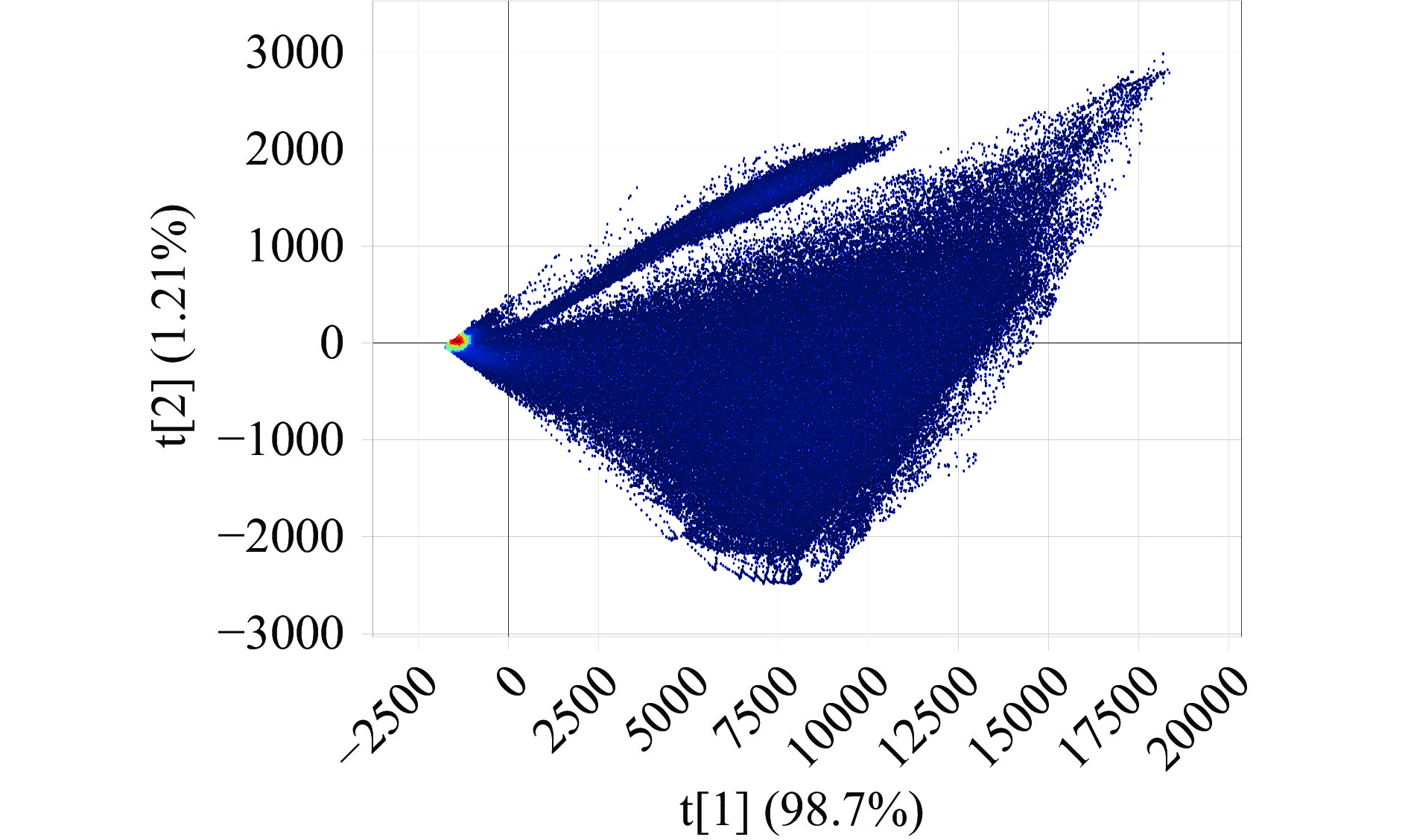
本研究采用Evince2.7.15软件对高光谱图像进行PCA分析,图3所示为原始高光谱图像的PCA分布图,采用PCA分析法可以有效去除背景,实现高光谱背景分割。
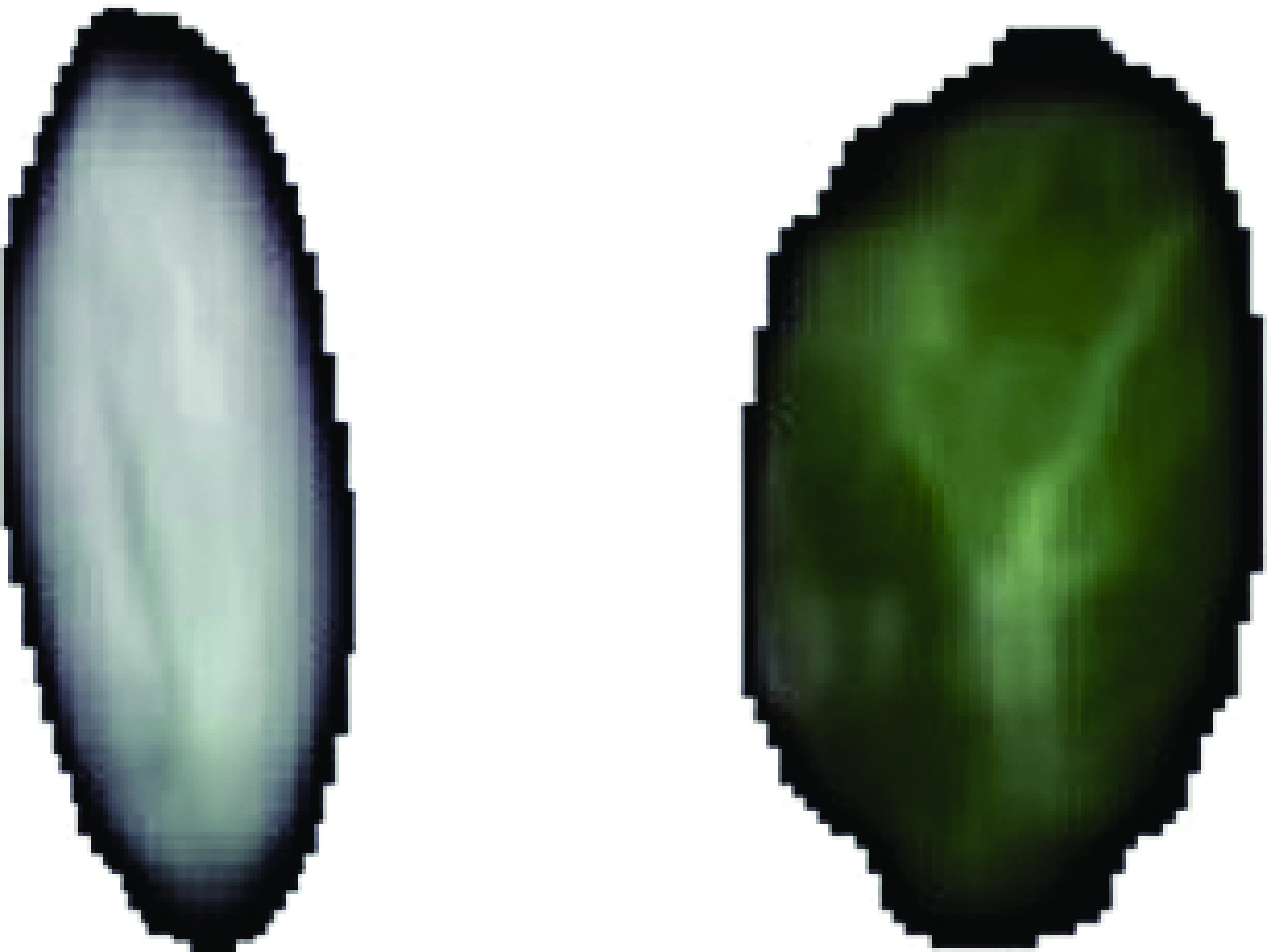
为方便观察,花生高光谱图像采用伪彩色可视化渲染,对比单粒冻伤与正常花生去除背景后的高光谱图像,如图4所示。通过观察对比,单粒正常花生高光谱呈现浅色;冻伤花生整体颜色较深,且花生冻伤情况越严重深色面积越大。通过单粒高光谱图像对比可以清晰观察到正常与冻伤花生的区别,初步证明采用高光谱成像技术和近红外光谱技术对花生冻伤进行检测是可行的。
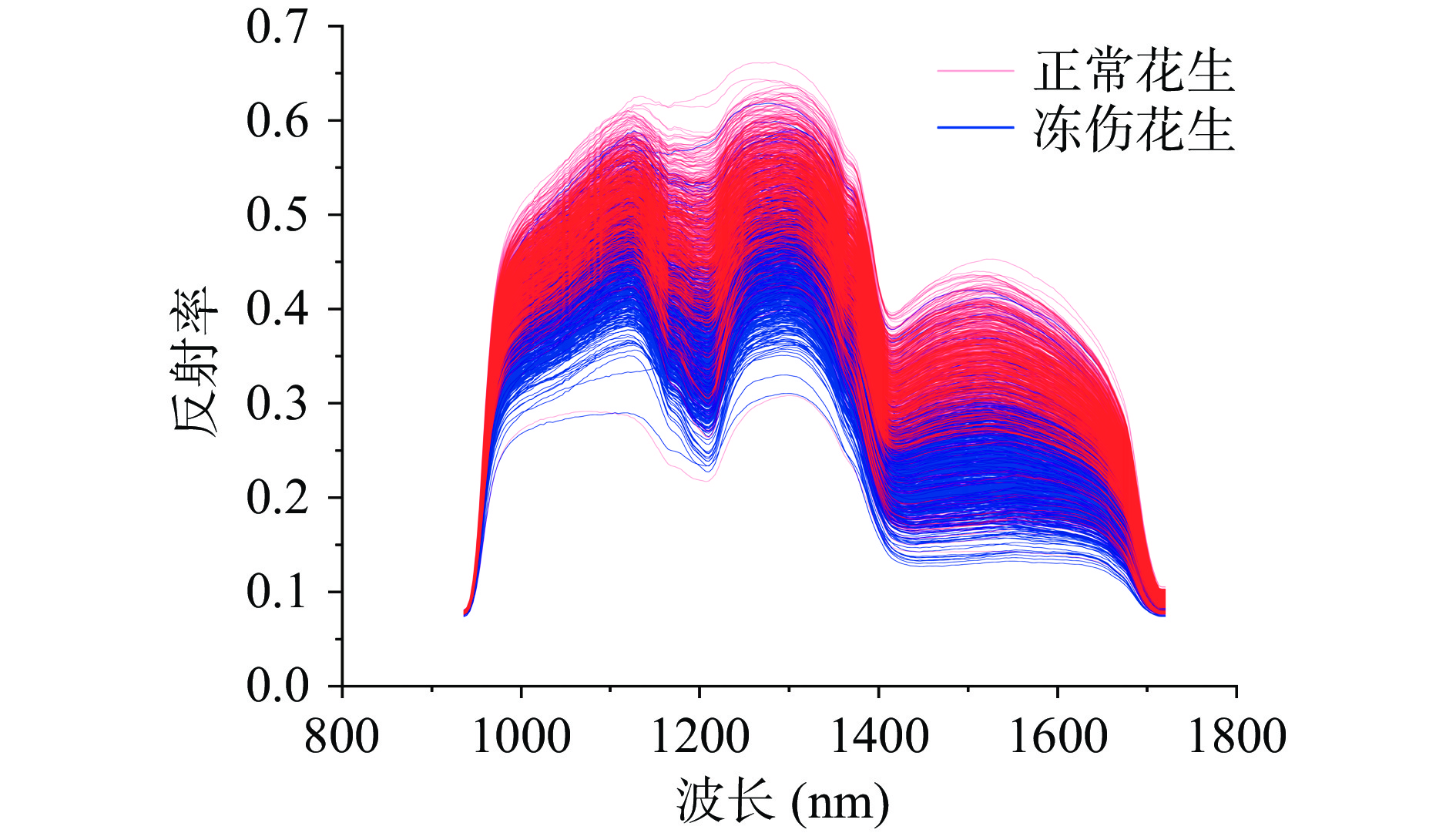
提取背景剔除后每粒花生的所有像素点,单粒花生的光谱数据采用该花生所有像素点光谱的平均值表示,从而获取1623粒花生的原始光谱数据集,如图5所示。
2.2 预处理结果
采用SVM作为建模方法对数据处理进行验证,由于其可解决高维问题,且较强的泛化能力[28],非常适合建立花生是否冻伤的模型。表1展示了原始数据、各种光谱预处理算法(SNV、MSC、SGSM、SGSM-SNV、SGSM-MSC)的花生冻伤SVM预测结果。本文通过测试集准确率来评估预处理后数据在建模性能上是否优于原始数据。建模选用RBF核函数,采用网格寻优法和五折交叉验证在给定范围内对SVM的c(惩罚系数)和核函数参数g(gamma)进行寻优,采用最优的c和g对数据集建立SVM模型进训练和预测。在表1中,基于不同数据(例如原始数据、SNV、MSC、SGSM、SGSM-SNV、SGSM-MSC)的模型在测试集中的准确率分别为:93.21%、93.83%、94.13%、93.52%、91.36%和93.83%。MSC预处理后的模型具有最高的测试集准确率,因此采用MSC预处理后的光谱作为变量选择算法的输入。
表 1 不同光谱预处理方法的SVM模型预测结果Table 1. SVM model prediction results of different spectral pretreatment methods预处理 参数 训练集 测试集 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) − 1247/1299 95.99 302/324 93.21 SNV 1245/1299 95.84 304/324 93.83 MSC 1273/1299 97.99 305/324 94.13 SGSM 1248/1299 96.07 303/324 93.52 SGSM-SNV 1215/1299 93.53 296/324 91.36 SGSM-MSC 1246/1299 95.92 304/324 93.83 注:SNV:标准归一化变量;MSC:多元散射校正;SGSM:Savizkg-Golag卷积平滑。 2.3 特征波长筛选结果
2.3.1 变量选择
对经过MSC预处理后的花生光谱数据采用八种不同变量选择方法进行特征波长筛选,图6和表2分别展示了经过MSC预处理后的花生光谱数据经过八种不同变量选择算法后筛选出的特征波长变量和采用它们作为输入分别建立SVM的建模结果。将224个波长变量按照1~224号进行标号,由于RF、VIP、SPA和MC-UVE方法筛选的特征波长变量按变量重要性进行排序,为保证筛选的特征波长变量组在包含充足信息且尽可能少包含无关变量和干扰变量,故本实验中“变量重要性”类方法筛选的特征波长只取重要性前50的波长变量。
表 2 不同光谱预处理方法的SVM模型预测结果Table 2. Prediction results of SVM model with different spectral preprocessing methods处理方法 变量数 训练集 测试集 建模时间(s) 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) MSC 224 1273/1299 97.99 305/324 94.13 590.97 MSC-CARS 49 1245/1299 95.843 306/324 94.44 237.22 MSC-RF 50 1240/1299 95.46 305/324 94.14 228.35 MSC-VIP 50 1224/1299 94.23 295/324 91.05 341.81 MSC-SPA 50 1237/1299 95.23 305/324 94.14 274.74 MSC-MCUVE 50 1231/1299 94.77 302/324 93.21 285.60 MSC-IRIV 68 1242/1299 95.61 302/324 93.21 249.59 MSC-VCPAIRIV 47 1249/1299 96.15 305/324 94.14 299.07 MSC-VCPAGA 66 1254/1299 96.54 306/324 94.44 219.21 注:MSC:多元散射校正;CARS: 竞争自适应重加权法;RF:随机蛙跳;随机蛙跳;VIP:变量重要性投影;SPA:连续投影算法;MCUVE:蒙特卡洛无信息变量消除;IRIV:迭代保留信息变量;VCPAIRIV:变量组合种群分析-迭代保留信息变量;VCPA-GA:变量组合种群分析-遗传算法。 由表2可以得出结论:8种变量选择算法经SVM建模达到可观的识别准确率,且对比全谱数据建模时间大幅缩短,说明8种变量选择方法均能有效对冻伤花生进行特征提取,并且降低了模型复杂程度。虽然花生数据集通过8种变量选择方法剔除部分无用或干扰变量,减少了冗余信息,但选出的特征波长仍较多,且分布在全谱范围,不利于花生冻伤的机理分析。
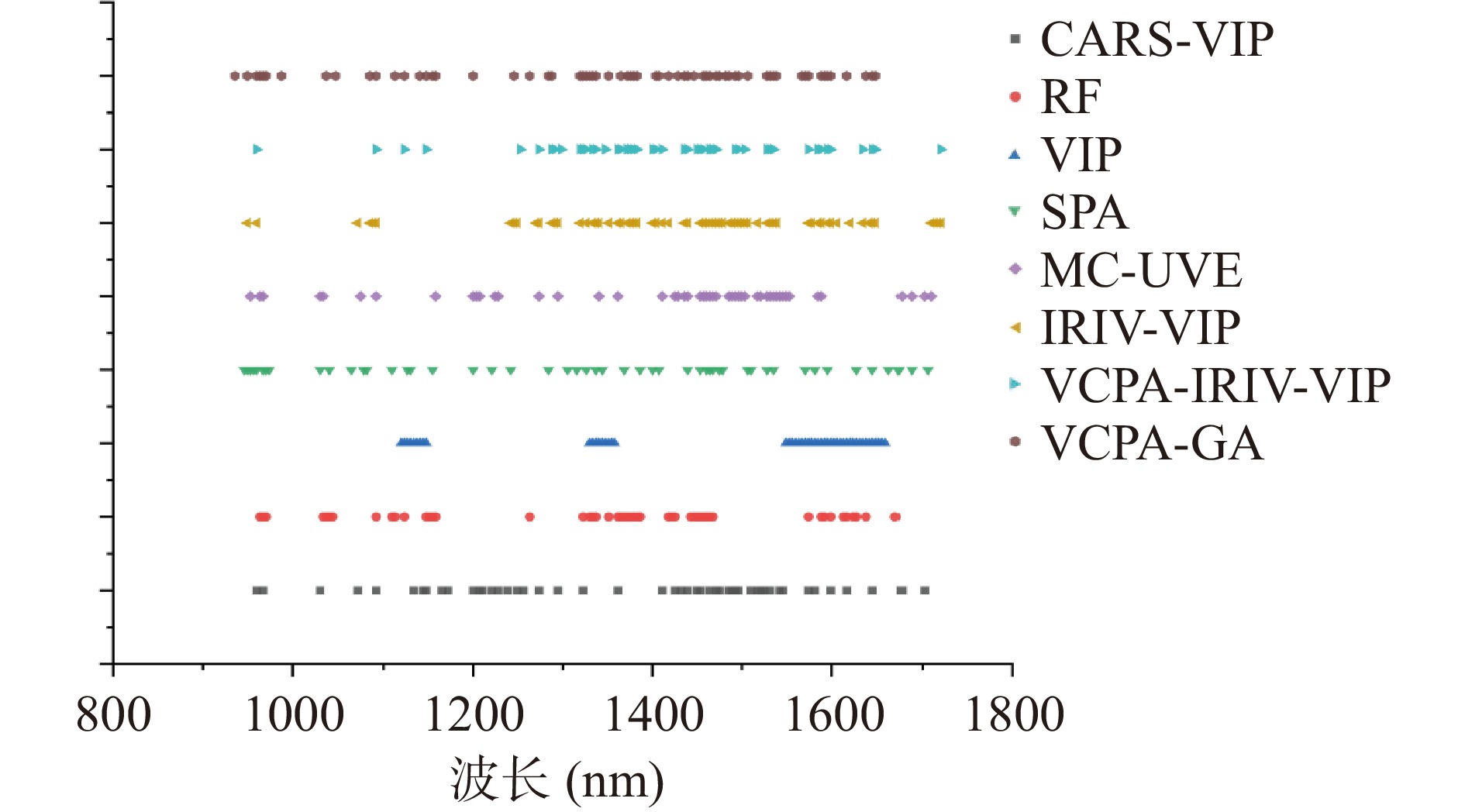
将“组合寻优”类变量选择算法选择的特征波长变量进行VIP分析,将特征波长变量按变量重要性进行排序,随后同“变量重要性”类建立SVM模型验证,选择达到判别准确率阈值为90%的最少特征波长变量作为与花生冻伤相关性最高的特征波长。表3展示了变量选择建立SVM模型验证的结果。图7展示了经MSC预处理后的所有花生样本光谱数据以及八种不同变量选择再筛选后的特征波长的位置。由表和图可以看出VCPA-GA能达到较高的准确率的情况下筛选出最少的特征波长,通过VCPA-GA方法筛选的7个特征波长分别为:959.81、1329.70、1371.97、1375.50、1403.73、1531.21和1573.87 nm,另外七种变量选择算法筛选出的特征波长除了IRIV,与通过VCPA-GA选择出的特征波长多数基本重叠,可以得出对于花生冻伤实验,VCPA-GA是针对花生冻伤特征分析性能相对优秀的变量选择算法,这主要是因为VCPA算法采用EDF对变量进行连续收缩,在EDF运行时会消除对结果贡献较小的波长变量,同时,BMS和MPA分别提供相同的采样能力,用于使用不同的变量组合构建子模型,并提取子模型中包含的最佳变量组合,通过每个子模型的判别准确率来保留子系统中一定比例的具有最高频率的变量。同时结合遗传算法(GA)进一步优化,充分结合遗传算法扩展性好、可搜索潜在并行性和鲁棒性强等优点,因此VCPA-GA的综合变量筛选策略在花生冻伤上优于其他方法。
表 3 花生冻伤特征波长精选验证结果Table 3. Validation results of peanut frostbite characteristic wavelength selection变量选择方法 变量数 SVM参数 训练集 测试集 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) CARS 11 1192/1299 91.1470 294/324 90.7407 RF 13 1211/1299 93.2256 294/324 90.7407 VIP 30 1193/1299 91.8399 297/324 91.6667 SPA 10 1214/1299 93.4565 294/324 90.7407 MC-UVE 19 1202/1299 92.5327 293/324 90.4321 IRIV 30 1222/1299 94.0724 303/324 93.5185 VCPA-IRIV 14 1184/1299 91.1470 294/324 90.7407 VCPA-GA 7 1190/1299 91.6089 292/324 90.1235 2.3.2 花生冻伤机理分析
近红外光谱主要是由分子振动的非谐振性使分子震动从基态向高能级跃迁时产生的[29−30]。在近红外光谱中分子中包含了单个化学键的基频振动的倍频和合频信息,它常常受含氢基团X-H(X=C、N、O)的倍频和合频重叠主导,近红外光谱能准确地表现出物质的结构信息[31],非常适合结合特征波长对目标物质进行物化分析。
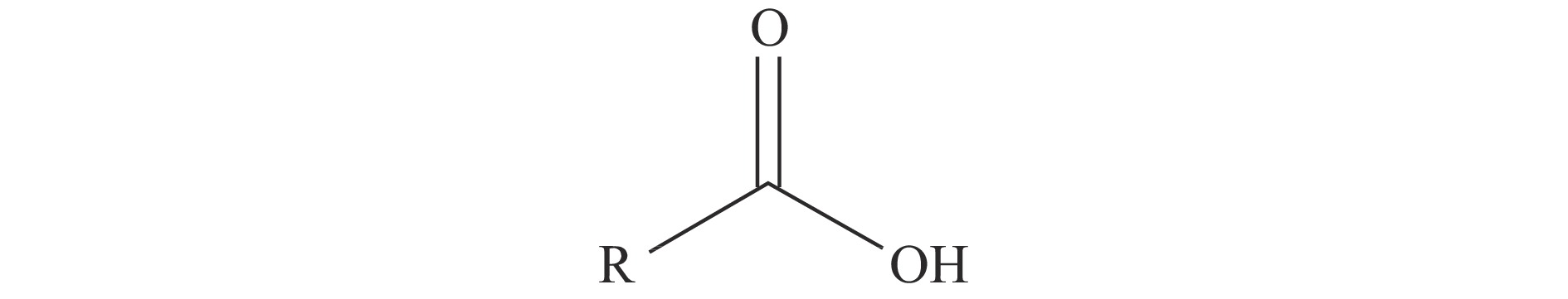
花生的主要营养物质为脂肪、蛋白质、糖类和其他微量元素,此外,花生中还含有7~8种人体所需的氨基酸及不饱和脂肪酸。花生出现冻伤现象会导致花生蛋白质、亚油酸和蔗糖含量增加,油脂和油酸含量降低,油亚比(油酸/亚油酸)明显下降[32]。花生中的不饱和脂肪酸主要为油酸,油酸属于羧酸类物质,其官能团为羧基,由一个碳原子、两个氧原子和一个氢原子组合而成,包含一个碳氧双键(C=O)、碳氧-氧键(O=C-O)以及氢氧键(O-H),其化学式为R-COOH,羧基的空间结构式如图8所示[33−34]。
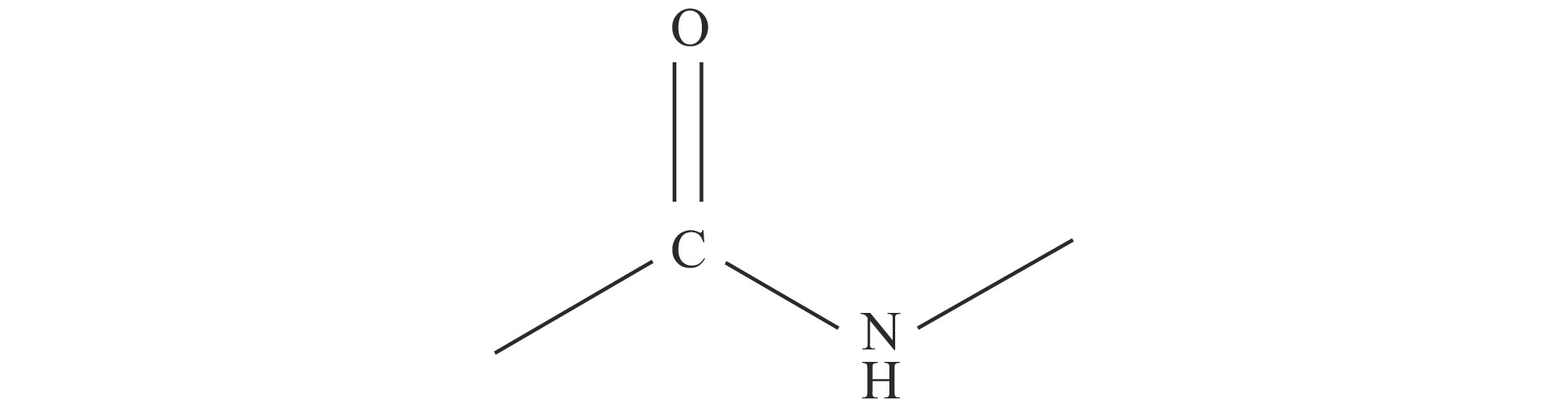
此外,花生主要营养物质中含量占比仅次于脂肪的成分为蛋白质,其主官能团为酰胺键,包含一个碳氧双键(C=O)、氮氢键(N-H),其化学式为R-CO-NH-R,酰胺键的空间结构式如图9所示[34]。
由花生冻伤特征波长筛选实验,对花生冻伤检测贡献最大的波长在959.81、1329.70、1371.97、1375.50、1403.73、1531.21和1573.87 nm处。在1350 nm附近,主要为O-H键伸缩振动和OCO弯曲振动一级倍频的组合频吸收,已测定蛋白质的特征谱带为1500~1530 nm附近的N-H伸缩振动一级倍频[35]。换言之由特征波长筛选出的特征波长体现了油酸和蛋白质的信息,由此可以推测油酸和蛋白质受到冻伤的负面影响,过低的温度会使花生呼吸作用受到抑制,使油酸发生氧化作用分解,导致油酸含量下降,同时使花生内部蛋白质代谢紊乱,导致蛋白质含量增加。最终导致花生的品质下降。
3. 结论与展望
针对在运输、存储的过程中受到低温影响产生冻伤的花生,本文探索了一种基于近红外高光谱成像技术的高效鉴别花生是否冻伤的方法,采用八种变量选择方法对经过MSC预处理后的花生光谱数据进行特征波长初步筛选,采用VIP算法对八种变量选择方法初步筛选出的特征波长按照变量重要性进行排序并组合,验证了“组合寻优”类与“变量重要性”类变量选择方法结合的可行性,采用SVM建立冻伤检测模型,筛选出达到判别准确率阈值为90%的特征波长作为与花生冻伤相关性最高的特征波长,其中采用VCPA-GA-VIP方法筛选出的前7个波长:959.81、1329.70、1371.97、1375.50、1403.73、1531.21和1573.87 nm满足条件,训练集和测试集判别准确率分别达到了91.6089%和90.1235%,可作为花生冻伤特征变量,为全谱波长数的3.125%。通过近红外光谱的吸收带对特征波长进行分析,验证了花生冻伤后内部油酸含量下降且蛋白质含量增加。实验结果表明高光谱成像技术、近红外光谱技术在花生冻伤检测上是可行的,基于近红外光谱的变量筛选方法的研究可为其他作物病害判别模型的建立以及特征波长筛选提供研究思路,且经本研究筛选出的花生冻伤特征波长可为研发专用型花生冻伤检测滤光片提供理论基础。但本研究仅能判断正常和冻伤花生内部物质的差异,无法确定物质含量的变化,且采用一个品种的花生进行冻伤检测分析,后续可以针对多品种花生冻伤检测进行研究,并建立相关分析数据库,将有利于完善我国花生冻伤检测行业标准,提升花生质量和经济收益。
-
表 1 不同光谱预处理方法的SVM模型预测结果
Table 1 SVM model prediction results of different spectral pretreatment methods
预处理 参数 训练集 测试集 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) − 1247/1299 95.99 302/324 93.21 SNV 1245/1299 95.84 304/324 93.83 MSC 1273/1299 97.99 305/324 94.13 SGSM 1248/1299 96.07 303/324 93.52 SGSM-SNV 1215/1299 93.53 296/324 91.36 SGSM-MSC 1246/1299 95.92 304/324 93.83 注:SNV:标准归一化变量;MSC:多元散射校正;SGSM:Savizkg-Golag卷积平滑。 表 2 不同光谱预处理方法的SVM模型预测结果
Table 2 Prediction results of SVM model with different spectral preprocessing methods
处理方法 变量数 训练集 测试集 建模时间(s) 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) MSC 224 1273/1299 97.99 305/324 94.13 590.97 MSC-CARS 49 1245/1299 95.843 306/324 94.44 237.22 MSC-RF 50 1240/1299 95.46 305/324 94.14 228.35 MSC-VIP 50 1224/1299 94.23 295/324 91.05 341.81 MSC-SPA 50 1237/1299 95.23 305/324 94.14 274.74 MSC-MCUVE 50 1231/1299 94.77 302/324 93.21 285.60 MSC-IRIV 68 1242/1299 95.61 302/324 93.21 249.59 MSC-VCPAIRIV 47 1249/1299 96.15 305/324 94.14 299.07 MSC-VCPAGA 66 1254/1299 96.54 306/324 94.44 219.21 注:MSC:多元散射校正;CARS: 竞争自适应重加权法;RF:随机蛙跳;随机蛙跳;VIP:变量重要性投影;SPA:连续投影算法;MCUVE:蒙特卡洛无信息变量消除;IRIV:迭代保留信息变量;VCPAIRIV:变量组合种群分析-迭代保留信息变量;VCPA-GA:变量组合种群分析-遗传算法。 表 3 花生冻伤特征波长精选验证结果
Table 3 Validation results of peanut frostbite characteristic wavelength selection
变量选择方法 变量数 SVM参数 训练集 测试集 准确比例 准确率(%) 准确比例 准确率(%) CARS 11 1192/1299 91.1470 294/324 90.7407 RF 13 1211/1299 93.2256 294/324 90.7407 VIP 30 1193/1299 91.8399 297/324 91.6667 SPA 10 1214/1299 93.4565 294/324 90.7407 MC-UVE 19 1202/1299 92.5327 293/324 90.4321 IRIV 30 1222/1299 94.0724 303/324 93.5185 VCPA-IRIV 14 1184/1299 91.1470 294/324 90.7407 VCPA-GA 7 1190/1299 91.6089 292/324 90.1235 -
[1] 廖伯寿. 我国花生生产发展现状与潜力分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2020,42(2):161−166. [LIAO Boshou. A review on progress and prospects of peanut industry in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences,2020,42(2):161−166.] LIAO Boshou . A review on progress and prospects of peanut industry in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences,2020 ,42 (2 ):161 −166 .[2] 张立伟, 王辽卫. 我国花生产业发展状况、存在问题及政策建议[J]. 中国油脂,2020,45(11):116−122. [ZHANG Liwei, WANG Liaowei. Development status, existing problems and policy recommendations of peanut industry in China[J]. China Oils and Fats,2020,45(11):116−122.] ZHANG Liwei, WANG Liaowei . Development status, existing problems and policy recommendations of peanut industry in China[J]. China Oils and Fats,2020 ,45 (11 ):116 −122 .[3] 孙玉鼎. 花生产品出口贸易发展及其管理研究[J]. 商讯,2020(30):9−10,13. [SUN Yuding. Research on the development and management of peanut product export trade[J]. Corporate Finance,2020(30):9−10,13.] SUN Yuding . Research on the development and management of peanut product export trade[J]. Corporate Finance,2020 (30 ):9 −10,13 .[4] 高彤, 吴静珠, 毛文华等. 单粒玉米种子成熟度快速判别方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(S1):399−403. [GAO Tong, WU Jingzhu, et al. Method for quickly determining maturity of single corn seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2019,50(S1):399−403.] GAO Tong, WU Jingzhu, et al . Method for quickly determining maturity of single corn seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2019 ,50 (S1 ):399 −403 .[5] 熊春晖, 佘永新, 焦逊, 等. 高光谱成像技术在农产品无损检测中的应用[J]. 粮油食品科技,2023,31(1):109−122. [XIONG Chunhui, SHE Yongxin, JIAO Xun, et al. Application of hyperspectral imaging technology in nondestructive testing of agricultural products[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2023,31(1):109−122.] XIONG Chunhui, SHE Yongxin, JIAO Xun, et al . Application of hyperspectral imaging technology in nondestructive testing of agricultural products[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2023 ,31 (1 ):109 −122 .[6] 王雷, 乔晓艳, 董有尔, 等. 高光谱图像技术在农产品检测中的应用进展[J]. 应用光学,2009,30(4):639−645. [WANG Lei, QIAO Xiaoyan, DONG Youer, et al. Application of hyper-spectral image technology in detecting agricultural product[J]. Journal of Applied Optics,2009,30(4):639−645.] WANG Lei, QIAO Xiaoyan, DONG Youer, et al . Application of hyper-spectral image technology in detecting agricultural product[J]. Journal of Applied Optics,2009 ,30 (4 ):639 −645 .[7] 王建伟, 陶飞, 郭双欢, 等. 近红外光谱技术在食品安全检测中的应用进展[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(12):461−464. [WANG Jianwei, TAO Fei, GUO Shuanghuan, et al. Progress in application of near infrared spectroscopy in food safety detection[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(12):461−464.] WANG Jianwei, TAO Fei, GUO Shuanghuan, et al . Progress in application of near infrared spectroscopy in food safety detection[J]. The Food Industry,2021 ,42 (12 ):461 −464 .[8] 陈岩. 基于高光谱快速检测面粉中添加剂及非法添加物含量[D]. 新乡:河南科技学院, 2022. [CHEN Yan. Rapid detection of additives and illegal additives in wheat flour based on hyperspectral technology[D]. Xinxiang:Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2022.] CHEN Yan. Rapid detection of additives and illegal additives in wheat flour based on hyperspectral technology[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2022.
[9] 洪旭东, 王超, 张德钧, 等. 光谱检测技术在食品安全检测中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(11):2684−2689. [HONG Xudong, WANG Chao, ZHANG Dejun, et al. Applications of spectral detection technology in food safety inspection[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2018,9(11):2684−2689.] HONG Xudong, WANG Chao, ZHANG Dejun, et al . Applications of spectral detection technology in food safety inspection[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2018 ,9 (11 ):2684 −2689 .[10] 陈泽珊. 高光谱成像技术在食品品质无损检测中的应用探究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022(26):149−151. [CHEN Zeshan. Application of hyperspectral imaging technology in nondestructive testing of food quality[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2022(26):149−151.] CHEN Zeshan . Application of hyperspectral imaging technology in nondestructive testing of food quality[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2022 (26 ):149 −151 .[11] 王冬, 吴静珠, 韩平等. 光谱关键变量筛选在农产品及食品品质无损检测中的应用进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(5):1593−1601. [WANG Dong, WU Jingzhu, HAN Ping, et al. Application of spectral key variable selection in non-destructive detection of the qualities of agricultural products and food[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021,41(5):1593−1601.] WANG Dong, WU Jingzhu, HAN Ping, et al . Application of spectral key variable selection in non-destructive detection of the qualities of agricultural products and food[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021 ,41 (5 ):1593 −1601 .[12] 雷裕, 胡新军, 蒋茂林, 等. 高光谱成像技术应用于畜禽肉品品质研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(21):8404−8411 [LEI Yu, HU Xinjun, JIANG Maolin, et al. Research progress on application of hyperspectral imaging technology in meat quality of livestock and poultry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(21):8404−8411.] LEI Yu, HU Xinjun, JIANG Maolin, et al . Research progress on application of hyperspectral imaging technology in meat quality of livestock and poultry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021 ,12 (21 ):8404 −8411 .[13] 宋相中, 唐果, 张录达等. 近红外光谱分析中的变量选择算法研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(4):1048−1052. [SONG Xiangzhong, TANG Guo, ZHANG Luda, et al. Research advance of variable selection algorithms in near infrared spectroscopy analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2017,37(4):1048−1052.] SONG Xiangzhong, TANG Guo, ZHANG Luda, et al . Research advance of variable selection algorithms in near infrared spectroscopy analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2017 ,37 (4 ):1048 −1052 .[14] 张进, 胡芸, 周罗雄等. 近红外光谱分析中的化学计量学算法研究新进展[J]. 分析测试学报,2020,39(10):1196−1203. [ZHANG Jin, HU Yun, ZHOU Luoxiong, et al. Progress of chemometric algorithms in near-infrared spectroscopic analysis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2020,39(10):1196−1203.] ZHANG Jin, HU Yun, ZHOU Luoxiong, et al . Progress of chemometric algorithms in near-infrared spectroscopic analysis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2020 ,39 (10 ):1196 −1203 .[15] YUN Y H, LI H D, DENG B C, et al. An overview of variable selection methods in multivariate analysis of near-infrared spectra[J]. TRAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019,113:102−115.
[16] 王粒. 基于高光谱图像的花生品种分类、霉变检测及蛋白质含量预测[D]. 雅安:四川农业大学, 2022. [WANG Li. Peanuts variety classification, mildew detection and protein content predication based on hyperspectral image[D]. Ya'an:Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022.] WANG Li. Peanuts variety classification, mildew detection and protein content predication based on hyperspectral image[D]. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022.
[17] 刘良源. 花生品质安全的近红外光谱检测方法研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2022. [LIU Liangyuan. Research on near infrared spectroscopy detection methods for quality and safety of peanut[D]. Zhenjiang:Jiangsu University, 2022.] LIU Liangyuan. Research on near infrared spectroscopy detection methods for quality and safety of peanut[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2022.
[18] 孙建非. 基于高光谱成像技术的花生多项品质参数无损检测方法的研究[D]. 淄博:山东理工大学, 2020. [SUN Jianfei. nondestructive detection methods of some peanut quality parameters based on hyperspectral imaging technology[D]. Zibo:Shandong University of Technology, 2020.] SUN Jianfei. nondestructive detection methods of some peanut quality parameters based on hyperspectral imaging technology[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2020.
[19] LI Hongdong, LIANG Yizeng, XU Qingsong, et al. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2009,648(1):77−84. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.06.046
[20] 张华秀, 李晓宁, 范伟, 等. 近红外光谱结合CARS变量筛选方法用于液态奶中蛋白质与脂肪含量的测定[J]. 分析测试学报,2010,29(5):430−434. [ZHANG Huaxiu, LI Xiaoning, FAN Wei, et al. Determination of protein and fat in liquid milk by nir combined with CARS variables screening method[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2010,29(5):430−434.] ZHANG Huaxiu, LI Xiaoning, FAN Wei, et al . Determination of protein and fat in liquid milk by nir combined with CARS variables screening method[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2010 ,29 (5 ):430 −434 .[21] YUN Y H, LI H D, WOOD LR, et al. An efficient method of wavelength interval selection based on random frog for multivariate spectral calibration[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc,2013(111):31−36.
[22] ZHAO Y R, YU K Q, HE Y. Hyperspectral imaging coupled with random frog and calibration models for assessment of total soluble solids in mulberries[J]. J Anal Methods Chem, 2015:343782.
[23] CHONG I G, JUN C H. Performance of some variable selection methods when multicollinearity is present[J]. Chemometrics & Intelligent Laboratory Systems,2005,78(1-2):103−112.
[24] 莫欣欣, 孙通, 刘津, 等. 近红外光谱结合变量选择方法定性检测食用油中高效氟吡甲禾灵残留[J]. 分析试验室,2018,37(2):125−130. [MO Xinxin, SUN Tong, LIU Jin, et al. Qualitative detection of haloxyfop-P-methyl residue in edible oil by near infrared spectroscopy combined with variable selection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2018,37(2):125−130.] MO Xinxin, SUN Tong, LIU Jin, et al . Qualitative detection of haloxyfop-P-methyl residue in edible oil by near infrared spectroscopy combined with variable selection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2018 ,37 (2 ):125 −130 .[25] NIU X, ZHAO Z, JIA K, et al. A feasibility study on quantitative analysis of glucose and fructose in lotus root powder by FT-NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,133(2):592−597. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.064
[26] YUN Y H, WANG W T, TAN M L, et al. A strategy that iteratively retains informative variables for selecting optimal variable subset in multivariate calibration[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2014,807:36−43. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.11.032
[27] YUN Y H, JUN B, LIU D L, et al. A hybrid variable selection strategy based on continuous shrinkage of variable space in multivariate calibration[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019,1058:58−69.
[28] KHODASEVICH M A, LYAKHNOVICH A V, ERIKLIOGLU H. Chocolate sample classification by principal component analysis of preprocessed terahertz transmission spectra[J]. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy,2022,89(2):251−255. doi: 10.1007/s10812-022-01351-3
[29] 赵燕东, 刘宇琦, 孙哲, 等. 土壤硝态氮含量原位检测系统设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(15):115−123. [ZHAO Yandong, LIU Yuqi, SUN Zhe, et al. Design of the detection system for the in-situ measurement of soil nitrate-nitrogen contents[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2022,38(15):115−123.] ZHAO Yandong, LIU Yuqi, SUN Zhe, et al . Design of the detection system for the in-situ measurement of soil nitrate-nitrogen contents[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2022 ,38 (15 ):115 −123 .[30] 陈鑫. 基于智能算法的近红外光谱分析预测模型建立方法研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2013. [CHEN Xin. Research of near infrared spectroscopy analysis prediction model based on intelligent method[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2013.] CHEN Xin. Research of near infrared spectroscopy analysis prediction model based on intelligent method[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2013.
[31] 艾立, 梁琼麟, 罗国安, 等. 近红外光谱在药学中的应用[J]. 亚太传统医药,2008,34(6):52−54. [AI Li, LIANG Qionglin, LUO Guoan, et al. Application of near infrared spectroscopy in pharmacy[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine,2008,34(6):52−54.] AI Li, LIANG Qionglin, LUO Guoan, et al . Application of near infrared spectroscopy in pharmacy[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine,2008 ,34 (6 ):52 −54 .[32] 陈娜, 程果, 潘丽娟, 等. 东北地区收获期低温对花生品质影响及耐低温品种筛选[J]. 植物生理学报,2020,56(11):2417−2427. [CHEN Na. CHENG Guo, PAN Lijuan, et al. Effect of low temperature on peanut quality and screening of low temperature tolerant varieties in Northeast China[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2020,56(11):2417−2427.] CHEN Na . CHENG Guo, PAN Lijuan, et al. Effect of low temperature on peanut quality and screening of low temperature tolerant varieties in Northeast China[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2020 ,56 (11 ):2417 −2427 .[33] 苏俏, 杨永庆, 李玉荣, 等. 高油酸花生籽仁发育过程中脂肪酸动态变化分析[J]. 河北农业大学学报,2023,46(4):1−7. [SU Qiao, YANG Yongqing, LI Yurong, et al. Analysis of fatty acid dynamic changes during kernel development in high oleic acid peanut[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University,2023,46(4):1−7.] SU Qiao, YANG Yongqing, LI Yurong, et al . Analysis of fatty acid dynamic changes during kernel development in high oleic acid peanut[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University,2023 ,46 (4 ):1 −7 .[34] 李先翠, 李保国, 姜元荣, 等. 花生萌发方法及营养物质变化研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2020,56(4):55−59,125. [LI Xiancui, LI Baoguo, JIANG Yuanrong, et al. Advances in the research of germination methods and nutrient composition changes of peanuts[J]. Food and Fermentation Science & Technology,2020,56(4):55−59,125.] LI Xiancui, LI Baoguo, JIANG Yuanrong, et al . Advances in the research of germination methods and nutrient composition changes of peanuts[J]. Food and Fermentation Science & Technology,2020 ,56 (4 ):55 −59,125 .[35] 王阿美, 涂宗财, 王辉, 等. 红外和CD光谱的HSA糖基化反应产物结构和反应进程分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(10):3090−3095. [WANG Amei. TU Zongcai, WANG Hui, et al. Rsearch in glycated progress and products of human serum albumin by infrared and CD spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2018,38(10):3090−3095.] WANG Amei . TU Zongcai, WANG Hui, et al. Rsearch in glycated progress and products of human serum albumin by infrared and CD spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2018 ,38 (10 ):3090 −3095 . -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王喜庆,李成凤,郭丽,赵洪波,马雪,李杨,苏适,郭齐. 创新创业背景下“食品营养学”课程思政教学改革与实践. 食品与发酵科技. 2025(01): 188-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 隋晓楠,张妍,黄国,付昳丹,梁香玉,赵尚清,王思琦,杨爱峥,霍俊伟,江连洲. 省一流专业引领下“粮油加工副产物综合利用”课程创新创业元素的设计与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(13): 308-314 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李晓东,刘璐,李嘉钰,张秀秀,郑冬梅,崔立雪,张宏伟. 《乳品工艺学》课程思政教育的改革与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(19): 376-382 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 罗港. 高职院校思政元素融入Premiere课程的研究与探索. 辽宁师专学报(社会科学版). 2023(02): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 桂亚,马栎,李逸鹤,田林双. 高职院校粮食工程专业劳动教育的实践探究. 现代面粉工业. 2023(05): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 贺光祖,叶惠慧,李逢振,王治昕,魏莎,李静. 食品类专业实践教学体系化微课的创新路径. 现代畜牧科技. 2023(11): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
1. 杨攀平,李惠侠,胡亚美. 盐池滩羊肉品质特性及其潜在调控机理探讨. 草业学报. 2025(04): 223-232 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕玲燕,胡湘云,刘明君,顾国才,汪燕玲,韦明松,刘庆友,王献伟. 茉莉花渣对隆林黑山羊养分表观消化率、生长性能、屠宰性能、肉品质及血清生化指标的影响. 饲料研究. 2025(03): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘嘉东,韩晓娟,张桂杰,黄帅. 柠条青贮替代全株玉米青贮对滩羊生长性能、脂肪沉积和肉品质的影响. 动物营养学报. 2023(09): 5827-5836 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



